-
随着我国城镇化步伐的加快,大量池塘受到污染或被填埋。这些池塘通过合理规划和利用不仅可以作为可观赏的景观塘,还可以兼用于污水的生化处理。本实验将景观设计和水体修复相结合,通过组合型生态浮岛原位修复技术改善水质,美化环境。
生态浮岛技术出现于20世纪50年代,直到20世纪80年代以后,生态浮岛技术在社会科技大发展的前提下才得以深入研究。DESTEFANI等[1]采用生态浮床净化某自然公园里的受污染的水体,浮岛植物选用香蒲、香根草、灯芯草,实验结果表明,浮床对水体中COD、TN、TP的去除率分别达到了66%、65%、13%。KANSIIME等[2]采用纸莎草浮床研究其对水体中N、P污染物的去除效果,实验结果表明,该浮床对TN、TP的去除率分别为80%~90%、70%~80%。李欲如等[3]在冬季采用生态浮床研究了多花黑麦草、大蒜、水芽对富营养化水体的处理效果,实验结果表明,3种植物对水体中COD去除率为49.2%~55.1%、总氮去除率为29.1%~58.9%、氨氮的去除率为39.7%~65.6%、总磷去除率为33.3%~54.9%。何成达[4]采用美人蕉浮床处理生活污水,实验结果表明,COD去除率达到90%以上,TN、TP去除率均达到80%以上。王郑等[5]通过将球形填料与美人蕉构建的组合型生态浮床处理农家乐废水,实验结果表明,该组合型生态浮床对COD、
NH+4 -N、TN、TP的去除率分别为79.71%、88.67%、73.88%、85.61%。研究[6-7]表明,单一的生态浮岛由于浮岛植物本身的性质,对环境和水质都有一定的要求并对污染物的吸收效率各不相同,因此,需要对特定物理情况和环境因素制定相匹配的浮床和浮岛植物。本研究将浮岛植物黄花鸢尾与改良型火山石填料相结合,通过改良型火山石的强化作用,为黄花鸢尾提供一个较好的环境,从而达到治理重污染水体的效果。
-
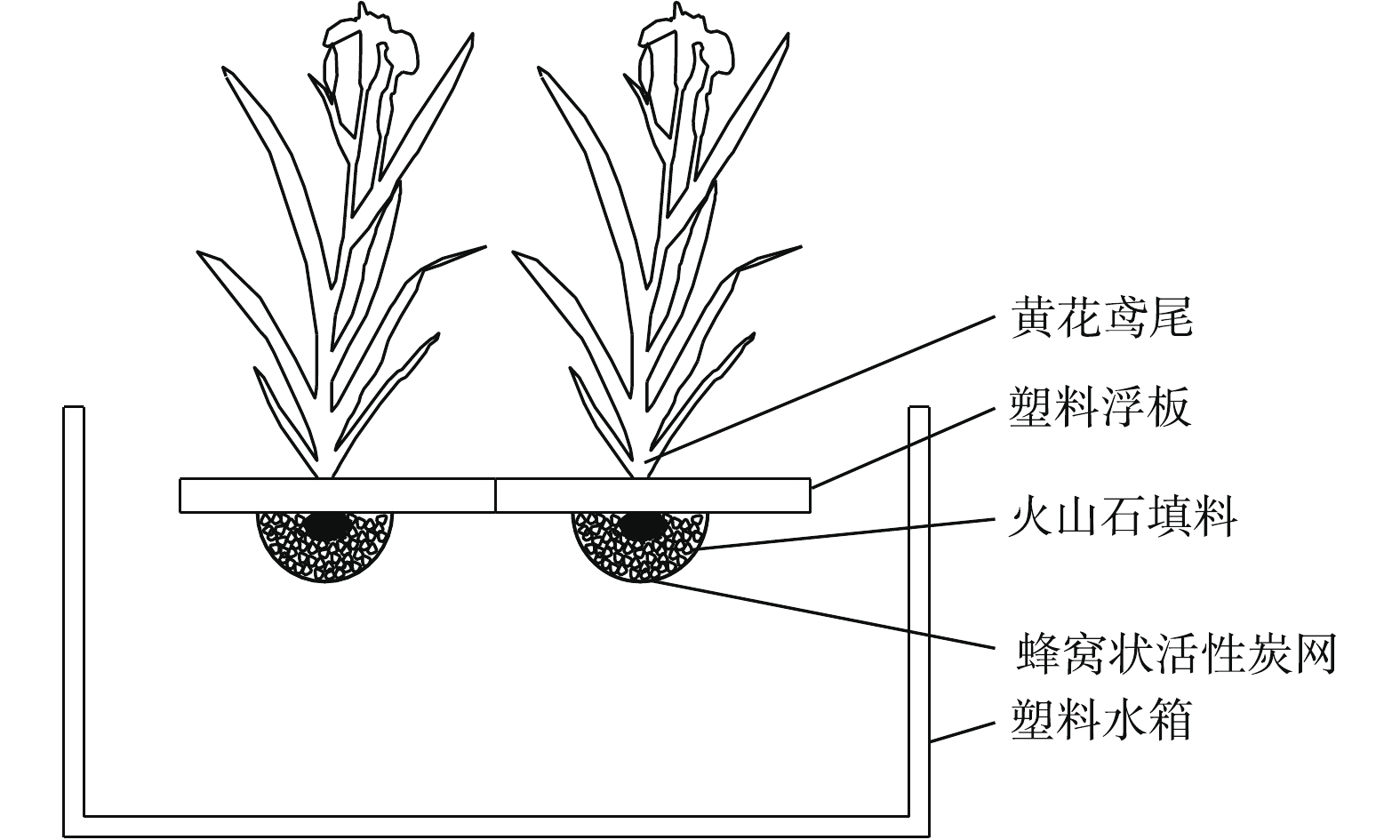
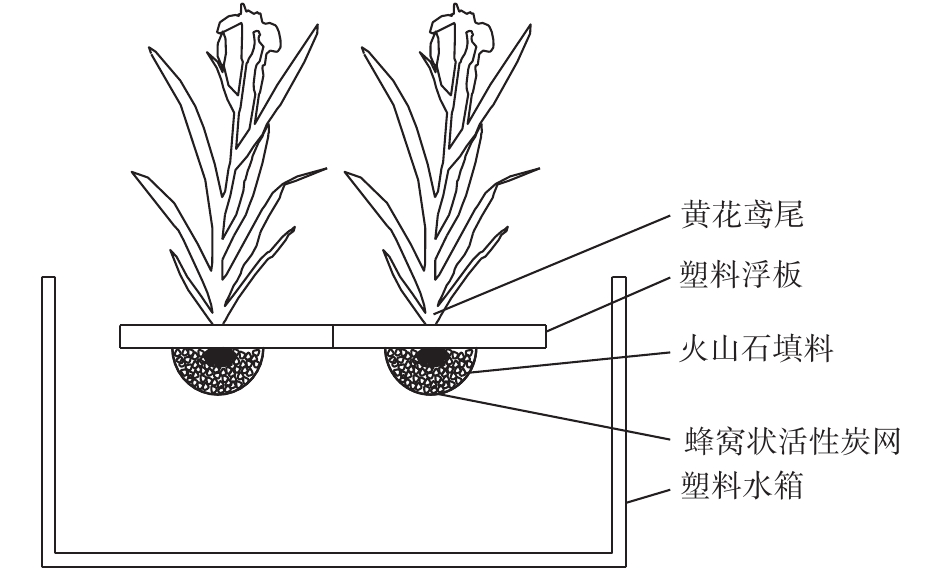
该组合型生态浮岛由浮岛植物黄花鸢尾、塑料浮板、改良型火山石填料、活性炭网组成(如图1所示)。将花黄鸢尾固定安放在中心镂空的塑料浮板上,每块浮板上种植1株黄花鸢尾,通过浮板的浮力使其漂浮在水面上,黄花鸢尾根部和改良型火山石填料用活性炭网包裹,所使用的改良型火山石直径略大于活性炭网网格孔径,每块浮板下改良型火山石填料用量控制在1.2~1.5 kg。各实验组在100 cm(长)×100 cm(宽)×80 cm(高)塑料水箱中进行,塑料水箱中水深控制在70 cm。
-
实验前,先将购买的黄花鸢尾幼苗放入实验水体中进行适应性培养1周,选取长势较好、株高基本一致的植株为实验所用,并将其根部做适当修剪,以保证实验植株的可对比性。将改良型火山石填料在实验室内用实验水体进行人工挂膜(水温控制在25 ℃左右),每隔6 h,通过曝气风机向水中曝气1次(水中溶解氧控制在2 mg·L−1),每隔3 d换1次水样,直至完全挂膜为止(开始挂膜时间约27 h;挂膜完全15 d)。实验共分为4组:空白对照组(0#)、黄花鸢尾处理组(1#)、火山石填料处理组(2#)、组合型生态浮岛处理组(3#)。实验从2018年4月25日开始,至2018年5月22日结束,实验期间平均气温在16 ℃左右。各组均放置在有阳光照射的池塘边,并做好防雨措施。每3 d取1次样,测定水体各指标,结束后测定植株高度和根部长度。本次实验水体取自某人工池塘,水体水质基本指标COD、TN、TP、
NH+4 -N、NO−3 -N、DO分别为80.6~107.3、9.16~11.97、0.86~1.14、7.58~8.44、3.11~3.23、1.4~2.3 mg·L−1。 -
各水质指标的测定方法参照文献中的方法[8]。COD采用重铬酸钾法测定,TN采用碱性过硫酸钾氧化法测定,TP采用钼锑抗分光光度法测定,
NH+4 -N采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定,DO采用电极测量法测定,植物株高及根长采用标准卷尺测定。 -
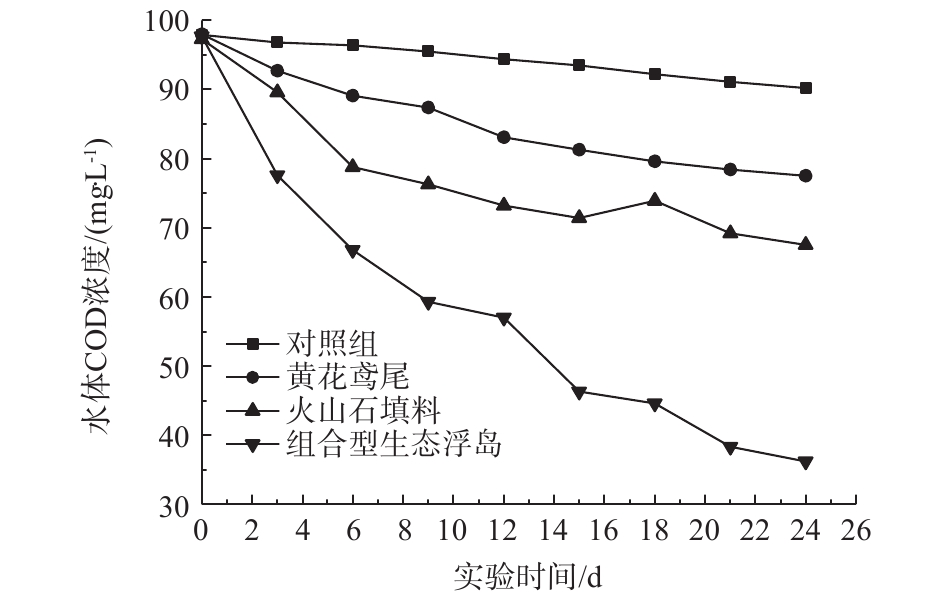
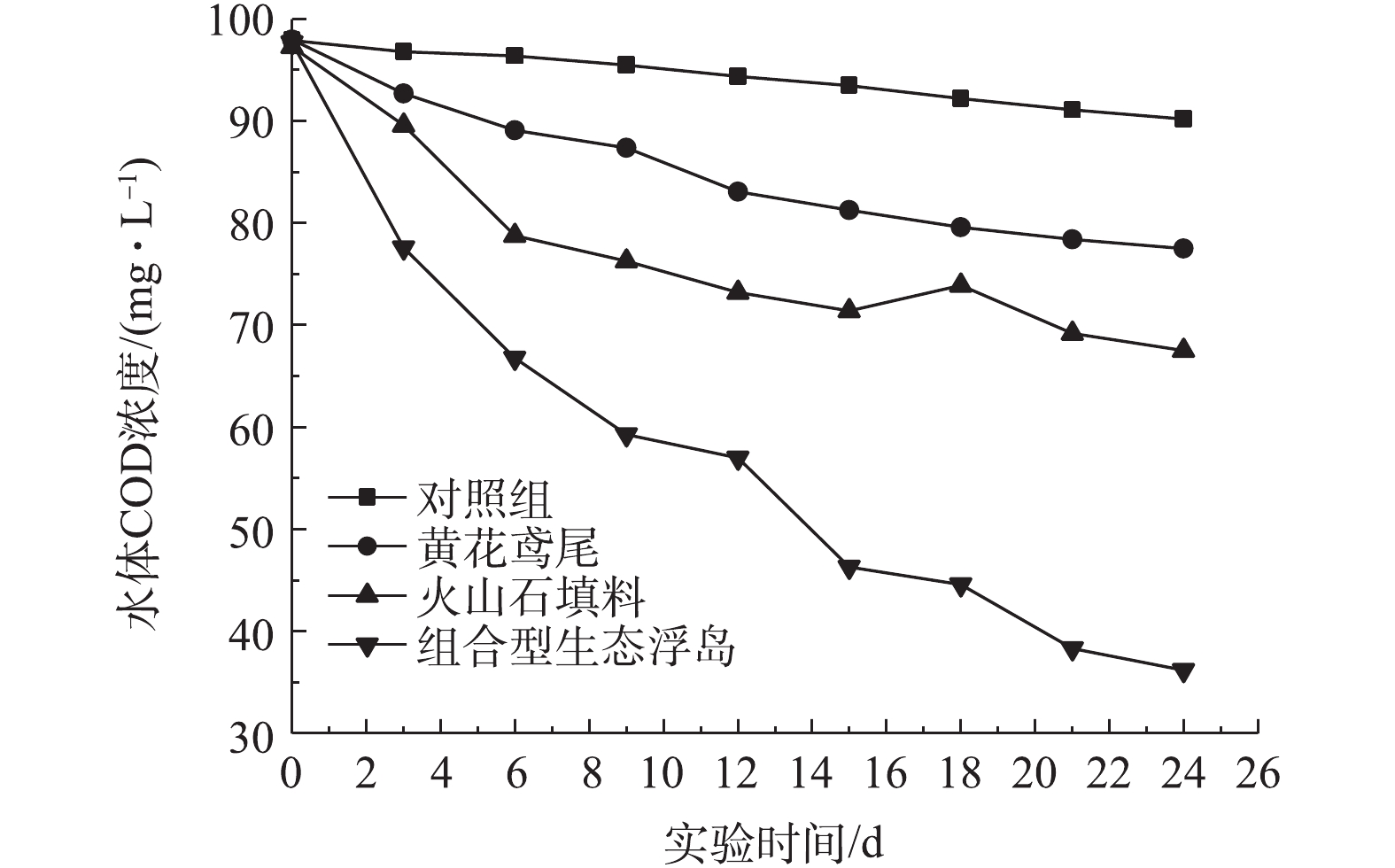
各处理组对水体COD的影响如图2所示。实验经过24 d后,0#、1#、2#、3#处理组对COD的去除率分别为7.86%、20.84%、30.63%、62.95%。由此可见,组合型生态浮岛对COD的去除率最高,且较单一的植物和填料处理组中COD去除效果明显,这与大量组合型生态浮岛处理污水的研究结果[9-11]一致。组合型生态浮岛对COD的去除率较高的原因主要包括3个方面。其一,浮岛下部的填料为改良型火山石。火山石自身具有对水流阻力小、不易堵塞、布水布气均匀、表面粗糙、挂膜速度快、反冲洗时微生物膜不易脱落、多孔性等物理特性。而且火山岩可以使水中的离子活跃(主要是增加了氧离子的含量)[12],从而促进了好氧微生物的生长,而好氧微生物生长过程需要消耗大量有机物。改良型火山石进一步扩大了其表面积,为微生物的生长提供了更大的空间,增加了微生物的数量。其二,黄花鸢尾为人工筛选后种植,其根系相对较为发达,为微生物繁殖提供了场所,且根系的泌氧作用为好氧微生物提供了有利的生存环境,增加了水体中有机物的消耗。其三,有研究[13]表明,活性炭网对水体和底泥中芳香族有机物有较好的去除效果。水体中的有机物一部分被活性炭网吸附,提高了有机物的去除率,并加速了水体中COD的去除。由图2也可以看出,前6 d内,2#、3#中COD降解速度较快。2#相较于1#处理组,处理效率高,这表明改良型火山石填料在COD的去除过程中起主要的作用。
-
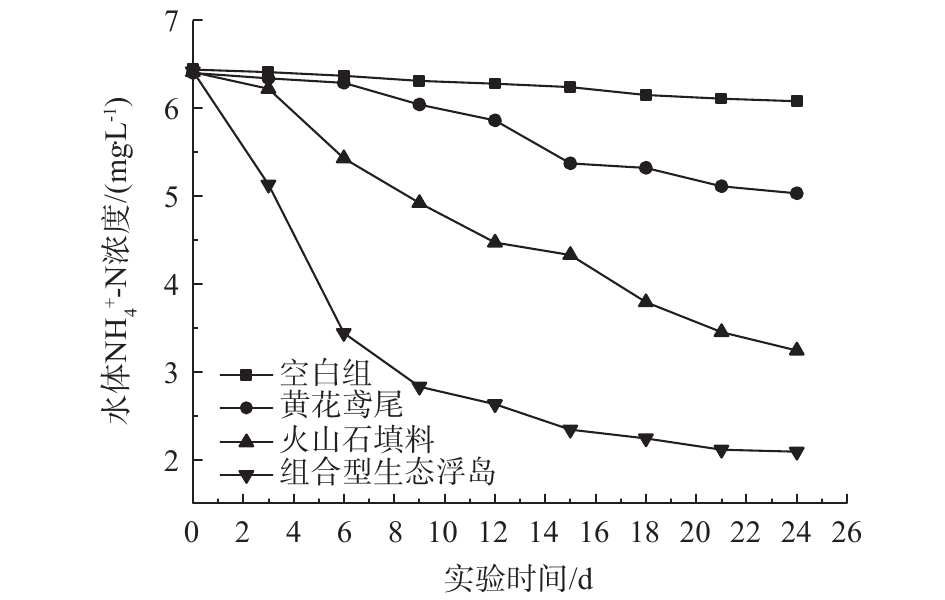
各处理组对水体
NH+4 -N的影响如图3所示。可以看出,在实验期内,各组NH+4 -N的含量都呈下降的趋势,其中组合型生态浮岛(3#)对NH+4 -N的去除率最高,达到67.45%。其余3个处理组0#、1#、2#去除率分别为5.59%、21.41%、49.45%。水体中NH+4 -N的去除主要通过植物吸收、微生物的硝化作用及NH3自然挥发[14]。可以看出,改良型火山石填料组(2#)对NH+4 -N的去除率相对于黄花鸢尾组(1#)较高,这说明对NH+4 -N的去除,微生物的硝化作用高于黄花鸢尾的吸收作用。改良型火山石对NH+4 -N的去除率较高的原因是由于它的多孔性产生的高表面积同样也是培养水中硝化细菌的良好温床,并且其表面带正电荷有利于微生物固着生长,亲水性强,把水中各种原因产生的NO−2 -N和NH+4 -N转化成毒性相对小的NO−3 ,从而降低了水体中NH+4 -N的含量。组合型生态浮岛通过改良型火山石填料中丰富的微生物及植物根系的泌氧作用,为硝化细菌提供了一个良好的生长繁殖条件,从而大幅度提高了NH+4 -N的去除率。 -
水体中的硝酸盐氮主要来源于受污染水体中自身含有的
NO−3 -N和由硝化作用产生的NO−3 -N,它的主要去除形式有反硝化作用和植物吸收等[15]。各处理组对水体
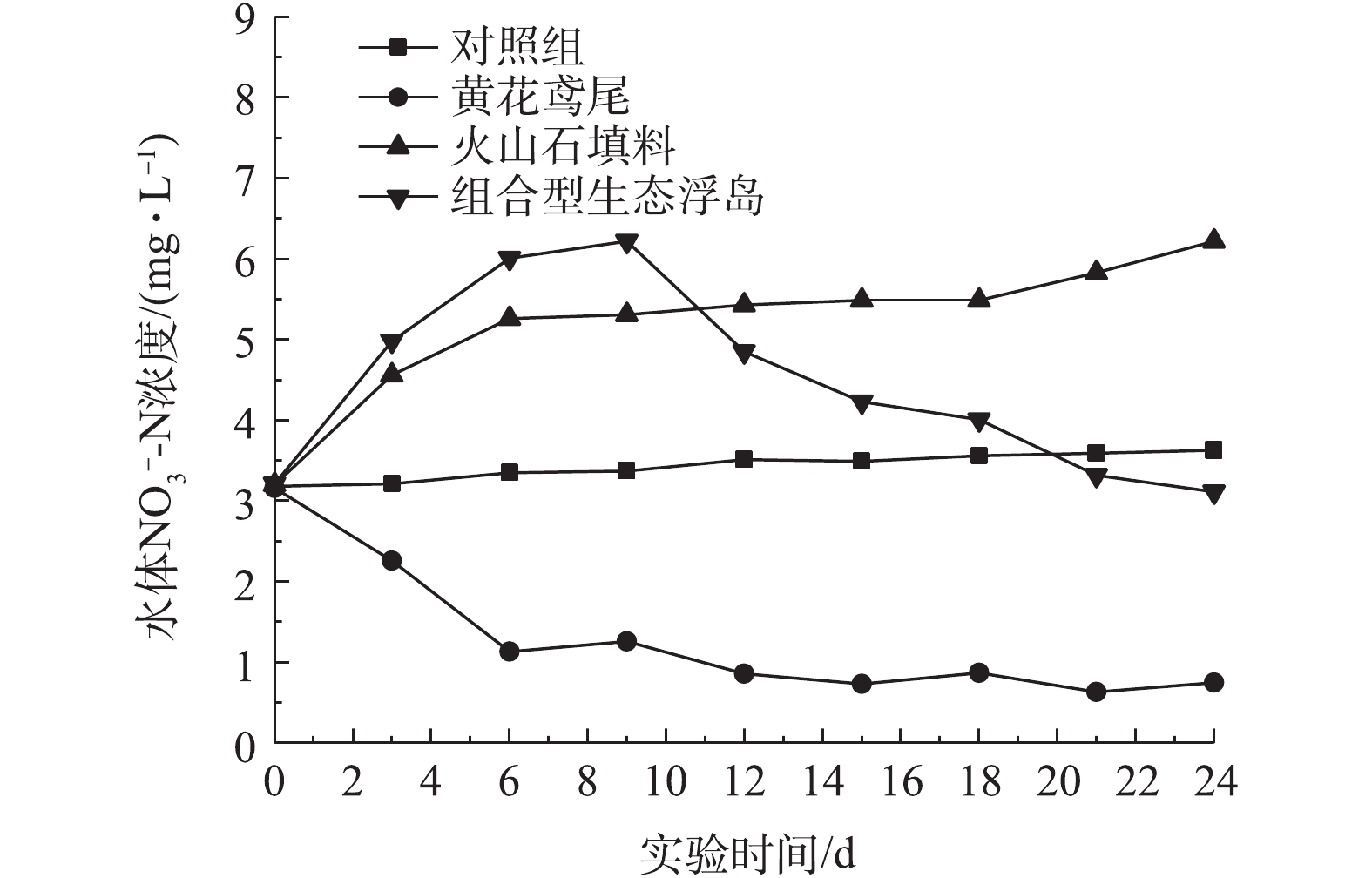
NO−3 -N的影响如图4所示。可以看出,空白对照组(0#)、改良型火山石填料处理组(2#)呈上升的趋势,组合型生态浮岛组(3#)呈先升后降的趋势,而黄花鸢尾处理组(1#)则呈下降趋势。由此推断出,黄花鸢尾对NO−3 -N的吸收作用高于水体中微生物的硝化作用。改良型火山石填料处理组水体中NO−3 -N大幅度升高,主要是由于其表面大量的硝化细菌将水体中的NH+4 -N转化成了NO−3 -N,这从NH+4 -N的去除曲线中也能明显地看出。组合型生态浮岛处理组在9 d前NO−3 -N处于上升阶段,这是由于整个水体中的硝化作用大于黄花鸢尾的吸收和反硝化作用。9 d后,NO−3 -N呈下降趋势,这是由于水体中溶解氧减少,硝化作用减弱,植物的吸收能力和反硝化作用占主导地位。21 d后,水体中NO−3 -N趋于平衡,这可能一方面由于植物的吸收达到饱和,另一方面从COD的变化曲线中可以推断,由于水体中碳源数量减少从而使反硝化作用降低。从图4中还可以看出,组合型生态浮岛处理组前期NO−3 -N含量的上升速度高于改良型火山石填料组,这是由于改良型火山石和植物根系两者的协同作用使水体中的氧离子高于单纯的改良性火山石填料组。 -
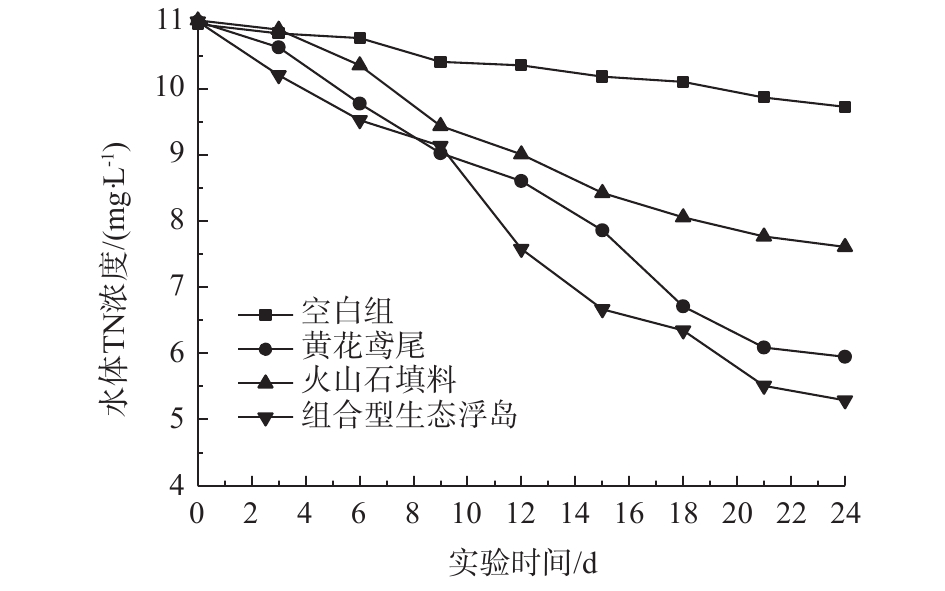
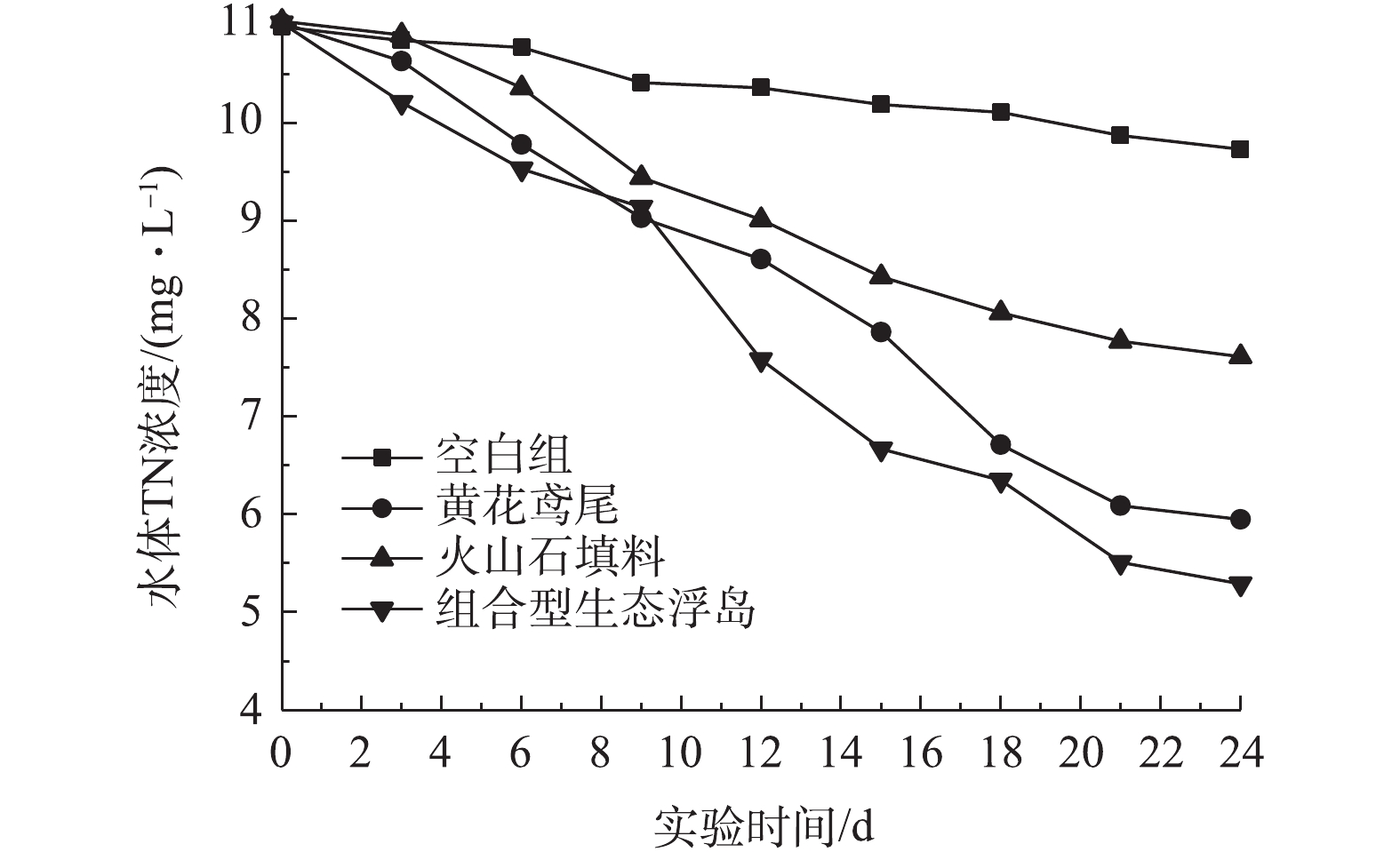
各处理组对水体TN的影响如图5所示。可以看出,4个处理组TN都呈下降趋势,0#、1#、2#、3#对TN的去除率分别为11.38%、46.01%、31.07%、51.99%,组合型生态浮岛(3#)处理效率高于其他实验组。组合型生态浮岛对水体中TN有较高的去除效果,这主要是由于改良型火山石填料为黄花鸢尾提供了一个较佳的生长环境。经过一段时间后,黄花鸢尾的根系植入改良型火山石填料内,有利于根系的保护,从而提高了黄花鸢尾根系对氮元素的吸收。同样,改良型火山石填料与植物根系的结合也为硝化及反硝化细菌提供了好氧与厌氧的生存环境,进一步加强了脱氮的效果。图5显示,黄花鸢尾处理组对TN的去除率高于填料处理组,而从空白组中可以看出,水体中分散的微生物对TN的自然去除率并不高,这表明黄花鸢尾处理组主要是靠植物的吸收作用和其根系微生物的硝化及反硝化作用达到去除目的。具体是由黄花鸢尾植物本身的吸收作用还是根系微生物的分解消耗起主导作用需要进一步研究。而改良型火山石填料处理组中TN去除则主要依靠微生物的作用。该组合型生态浮岛中微生物的脱氮作用应占主导地位,但其与花黄鸢尾吸收作用之间的差异还须做进一步研究。
-
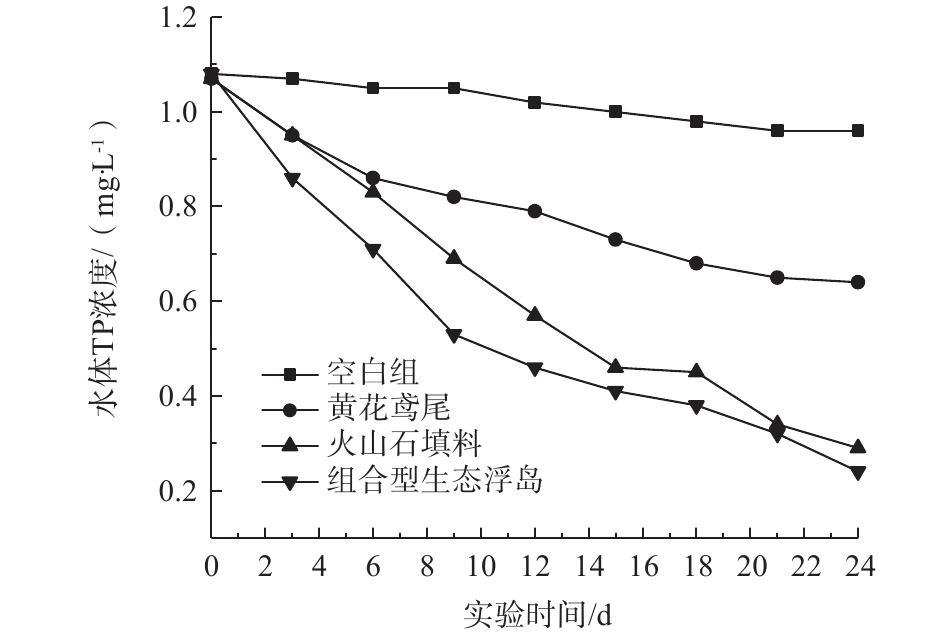
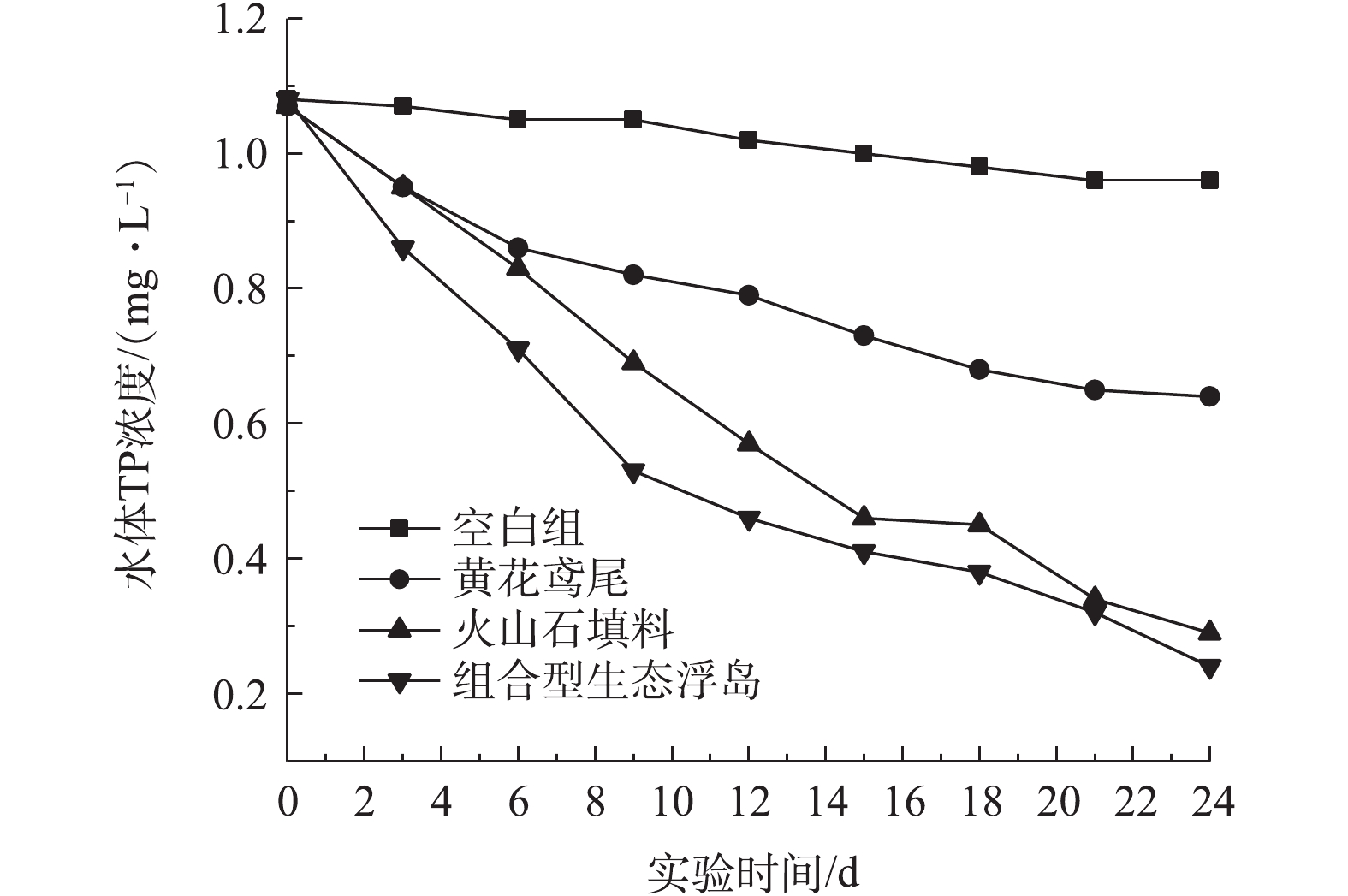
水体中的磷大体可分为颗粒型和溶解型2种形态。对TP的去除主要是靠植物吸收、微生物固定以及填料的吸附等[16]。各处理组对水体TP的影响如图6所示。可以看出,4个处理组TP都呈下降趋势,0#、1#、2#、3#对TP的去除率分别为11.11%、40.19%、72.90%、77.78%。可见组合型生态浮床对TP的去除效果较高,原因如下:1)黄花鸢尾根系对TP的吸收利用;2)改良型火山石填料中的聚磷菌在好氧条件下将部分TP作为自身生长繁殖所需的元素进行吸收并同化;3)通过填料自身的吸附作用将水体中颗粒型磷吸附到填料表面,从而降低水体中TP的含量。改良型火山石填料组对TP的去除速度及效率均高于黄花鸢尾处理组,这表明组合型生态浮岛中微生物的吸收同化及填料吸附作用是TP去除的主要机制。
-
黄花鸢尾实验开始与结束的生长状况如表1所示。可以看出,组合型生态浮岛中黄花鸢尾的株高及根长均大于黄花鸢尾组,由此看来,改良型火山石填料中的微生物促进了黄花鸢尾的生长。研究[17-18]表明,植物的氮磷吸收及固定的量与植物生物量呈显著相关,植物生物量越大,对氮磷吸收越多,对水体净化能力越强,这与本研究结果一致。
-
1)该组合型生态浮岛对COD、
NH+4 -N、TN、TP的去除率分别为62.95%、67.45%、51.99%、77.78%,且植物生物量高于单纯的植物处理组,填料中的微生物促进了植物的生长,从而提高了水质净化效果。2)黄花鸢尾与改良型火山石、表面微生物具有很好的协同作用,共同促进了水体中COD、
NH+4 -N、TN、TP等污染物的去除。3)针对不同的水质污染状况,合理搭配浮岛的组合方式可实现污染物的快速降解,达到净化水质的目的,适用于城镇水体尤其是居住区的静态水体的景观治理。
组合型生态浮岛原位修复重污染水体
Combined ecological floating island for in-situ remediation of heavily polluted water
-
摘要: 为解决某人工池塘水体环境污染的问题,采用组合型生态浮岛技术研究了其对该水体的治理效果。结果表明,组合型生态浮岛对此类水体有较好的处理效果,其中化学需氧量(COD)、氨氮(
NH+4 -N)、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)的去除率分别为62.95%、67.45%、51.99%、77.78%,均高于对照组及单一系统处理组。可见在该组合型生态浮岛中,黄花鸢尾的植物吸收、改良型火山石与微生物的协同作用对污染物的去除明显优于单一处理组。合理的植物-填料组合方式可提高污染物的降解效果,且投资小,环境效益好,又可达到一定的景观效果,适用于城镇水体尤其是居住区静态水体的景观治理。Abstract: In order to solve the problem of water environmental pollution in an artificial pond, the combined ecological floating island was used to study the control effect of the water body. Results showed that the combined ecological floating island had a good treatment performance on the waterbody, the removal efficiencies of chemical oxygen demand (COD), ammonia nitrogen (NH+4 -N), total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) were 62.95%, 67.45%, 51.99% and 87.96%, respectively, which were significantly higher than those of the contrast group and the single system treatment groups. The results also showed that in this combined ecological floating island, the plant absorption of iris pseudoacorus, and the synergistic effect between improved volcanic rocks and microorganisms on the removal of pollutants were significantly better than each single system treatment group. Reasonable combination of plant and filler can improve the degradation effect of pollutants, with small investment, good environmental benefits, and can also achieve a certain landscape effect. It is suitable for landscape control of urban water bodies, especially static water bodies in residential areas. -
随着我国城镇化步伐的加快,大量池塘受到污染或被填埋。这些池塘通过合理规划和利用不仅可以作为可观赏的景观塘,还可以兼用于污水的生化处理。本实验将景观设计和水体修复相结合,通过组合型生态浮岛原位修复技术改善水质,美化环境。
生态浮岛技术出现于20世纪50年代,直到20世纪80年代以后,生态浮岛技术在社会科技大发展的前提下才得以深入研究。DESTEFANI等[1]采用生态浮床净化某自然公园里的受污染的水体,浮岛植物选用香蒲、香根草、灯芯草,实验结果表明,浮床对水体中COD、TN、TP的去除率分别达到了66%、65%、13%。KANSIIME等[2]采用纸莎草浮床研究其对水体中N、P污染物的去除效果,实验结果表明,该浮床对TN、TP的去除率分别为80%~90%、70%~80%。李欲如等[3]在冬季采用生态浮床研究了多花黑麦草、大蒜、水芽对富营养化水体的处理效果,实验结果表明,3种植物对水体中COD去除率为49.2%~55.1%、总氮去除率为29.1%~58.9%、氨氮的去除率为39.7%~65.6%、总磷去除率为33.3%~54.9%。何成达[4]采用美人蕉浮床处理生活污水,实验结果表明,COD去除率达到90%以上,TN、TP去除率均达到80%以上。王郑等[5]通过将球形填料与美人蕉构建的组合型生态浮床处理农家乐废水,实验结果表明,该组合型生态浮床对COD、NH4+-N、TN、TP的去除率分别为79.71%、88.67%、73.88%、85.61%。
研究[6-7]表明,单一的生态浮岛由于浮岛植物本身的性质,对环境和水质都有一定的要求并对污染物的吸收效率各不相同,因此,需要对特定物理情况和环境因素制定相匹配的浮床和浮岛植物。本研究将浮岛植物黄花鸢尾与改良型火山石填料相结合,通过改良型火山石的强化作用,为黄花鸢尾提供一个较好的环境,从而达到治理重污染水体的效果。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置
该组合型生态浮岛由浮岛植物黄花鸢尾、塑料浮板、改良型火山石填料、活性炭网组成(如图1所示)。将花黄鸢尾固定安放在中心镂空的塑料浮板上,每块浮板上种植1株黄花鸢尾,通过浮板的浮力使其漂浮在水面上,黄花鸢尾根部和改良型火山石填料用活性炭网包裹,所使用的改良型火山石直径略大于活性炭网网格孔径,每块浮板下改良型火山石填料用量控制在1.2~1.5 kg。各实验组在100 cm(长)×100 cm(宽)×80 cm(高)塑料水箱中进行,塑料水箱中水深控制在70 cm。
1.2 实验方案
实验前,先将购买的黄花鸢尾幼苗放入实验水体中进行适应性培养1周,选取长势较好、株高基本一致的植株为实验所用,并将其根部做适当修剪,以保证实验植株的可对比性。将改良型火山石填料在实验室内用实验水体进行人工挂膜(水温控制在25 ℃左右),每隔6 h,通过曝气风机向水中曝气1次(水中溶解氧控制在2 mg·L−1),每隔3 d换1次水样,直至完全挂膜为止(开始挂膜时间约27 h;挂膜完全15 d)。实验共分为4组:空白对照组(0#)、黄花鸢尾处理组(1#)、火山石填料处理组(2#)、组合型生态浮岛处理组(3#)。实验从2018年4月25日开始,至2018年5月22日结束,实验期间平均气温在16 ℃左右。各组均放置在有阳光照射的池塘边,并做好防雨措施。每3 d取1次样,测定水体各指标,结束后测定植株高度和根部长度。本次实验水体取自某人工池塘,水体水质基本指标COD、TN、TP、NH4+-N、NO3−-N、DO分别为80.6~107.3、9.16~11.97、0.86~1.14、7.58~8.44、3.11~3.23、1.4~2.3 mg·L−1。
1.3 测试方法
各水质指标的测定方法参照文献中的方法[8]。COD采用重铬酸钾法测定,TN采用碱性过硫酸钾氧化法测定,TP采用钼锑抗分光光度法测定,NH4+-N采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定,DO采用电极测量法测定,植物株高及根长采用标准卷尺测定。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 水体COD的变化
各处理组对水体COD的影响如图2所示。实验经过24 d后,0#、1#、2#、3#处理组对COD的去除率分别为7.86%、20.84%、30.63%、62.95%。由此可见,组合型生态浮岛对COD的去除率最高,且较单一的植物和填料处理组中COD去除效果明显,这与大量组合型生态浮岛处理污水的研究结果[9-11]一致。组合型生态浮岛对COD的去除率较高的原因主要包括3个方面。其一,浮岛下部的填料为改良型火山石。火山石自身具有对水流阻力小、不易堵塞、布水布气均匀、表面粗糙、挂膜速度快、反冲洗时微生物膜不易脱落、多孔性等物理特性。而且火山岩可以使水中的离子活跃(主要是增加了氧离子的含量)[12],从而促进了好氧微生物的生长,而好氧微生物生长过程需要消耗大量有机物。改良型火山石进一步扩大了其表面积,为微生物的生长提供了更大的空间,增加了微生物的数量。其二,黄花鸢尾为人工筛选后种植,其根系相对较为发达,为微生物繁殖提供了场所,且根系的泌氧作用为好氧微生物提供了有利的生存环境,增加了水体中有机物的消耗。其三,有研究[13]表明,活性炭网对水体和底泥中芳香族有机物有较好的去除效果。水体中的有机物一部分被活性炭网吸附,提高了有机物的去除率,并加速了水体中COD的去除。由图2也可以看出,前6 d内,2#、3#中COD降解速度较快。2#相较于1#处理组,处理效率高,这表明改良型火山石填料在COD的去除过程中起主要的作用。
2.2 水体NH4+-N的变化
各处理组对水体NH4+-N的影响如图3所示。可以看出,在实验期内,各组NH4+-N的含量都呈下降的趋势,其中组合型生态浮岛(3#)对NH4+-N的去除率最高,达到67.45%。其余3个处理组0#、1#、2#去除率分别为5.59%、21.41%、49.45%。水体中NH4+-N的去除主要通过植物吸收、微生物的硝化作用及NH3自然挥发[14]。可以看出,改良型火山石填料组(2#)对NH4+-N的去除率相对于黄花鸢尾组(1#)较高,这说明对NH4+-N的去除,微生物的硝化作用高于黄花鸢尾的吸收作用。改良型火山石对NH4+-N的去除率较高的原因是由于它的多孔性产生的高表面积同样也是培养水中硝化细菌的良好温床,并且其表面带正电荷有利于微生物固着生长,亲水性强,把水中各种原因产生的NO2−-N和NH4+-N转化成毒性相对小的NO3−-N,从而降低了水体中NH4+-N的含量。组合型生态浮岛通过改良型火山石填料中丰富的微生物及植物根系的泌氧作用,为硝化细菌提供了一个良好的生长繁殖条件,从而大幅度提高了NH4+-N的去除率。
2.3 水体NO3−-N的变化
水体中的硝酸盐氮主要来源于受污染水体中自身含有的NO3−-N和由硝化作用产生的NO3−-N,它的主要去除形式有反硝化作用和植物吸收等[15]。
各处理组对水体NO3−-N的影响如图4所示。可以看出,空白对照组(0#)、改良型火山石填料处理组(2#)呈上升的趋势,组合型生态浮岛组(3#)呈先升后降的趋势,而黄花鸢尾处理组(1#)则呈下降趋势。由此推断出,黄花鸢尾对NO3−-N的吸收作用高于水体中微生物的硝化作用。改良型火山石填料处理组水体中NO3−-N大幅度升高,主要是由于其表面大量的硝化细菌将水体中的NH4+-N转化成了NO3−-N,这从NH4+-N的去除曲线中也能明显地看出。组合型生态浮岛处理组在9 d前NO3−-N处于上升阶段,这是由于整个水体中的硝化作用大于黄花鸢尾的吸收和反硝化作用。9 d后,NO3−-N呈下降趋势,这是由于水体中溶解氧减少,硝化作用减弱,植物的吸收能力和反硝化作用占主导地位。21 d后,水体中NO3−-N趋于平衡,这可能一方面由于植物的吸收达到饱和,另一方面从COD的变化曲线中可以推断,由于水体中碳源数量减少从而使反硝化作用降低。从图4中还可以看出,组合型生态浮岛处理组前期NO3−-N含量的上升速度高于改良型火山石填料组,这是由于改良型火山石和植物根系两者的协同作用使水体中的氧离子高于单纯的改良性火山石填料组。
2.4 水体TN的变化
各处理组对水体TN的影响如图5所示。可以看出,4个处理组TN都呈下降趋势,0#、1#、2#、3#对TN的去除率分别为11.38%、46.01%、31.07%、51.99%,组合型生态浮岛(3#)处理效率高于其他实验组。组合型生态浮岛对水体中TN有较高的去除效果,这主要是由于改良型火山石填料为黄花鸢尾提供了一个较佳的生长环境。经过一段时间后,黄花鸢尾的根系植入改良型火山石填料内,有利于根系的保护,从而提高了黄花鸢尾根系对氮元素的吸收。同样,改良型火山石填料与植物根系的结合也为硝化及反硝化细菌提供了好氧与厌氧的生存环境,进一步加强了脱氮的效果。图5显示,黄花鸢尾处理组对TN的去除率高于填料处理组,而从空白组中可以看出,水体中分散的微生物对TN的自然去除率并不高,这表明黄花鸢尾处理组主要是靠植物的吸收作用和其根系微生物的硝化及反硝化作用达到去除目的。具体是由黄花鸢尾植物本身的吸收作用还是根系微生物的分解消耗起主导作用需要进一步研究。而改良型火山石填料处理组中TN去除则主要依靠微生物的作用。该组合型生态浮岛中微生物的脱氮作用应占主导地位,但其与花黄鸢尾吸收作用之间的差异还须做进一步研究。
2.5 水体TP的变化
水体中的磷大体可分为颗粒型和溶解型2种形态。对TP的去除主要是靠植物吸收、微生物固定以及填料的吸附等[16]。各处理组对水体TP的影响如图6所示。可以看出,4个处理组TP都呈下降趋势,0#、1#、2#、3#对TP的去除率分别为11.11%、40.19%、72.90%、77.78%。可见组合型生态浮床对TP的去除效果较高,原因如下:1)黄花鸢尾根系对TP的吸收利用;2)改良型火山石填料中的聚磷菌在好氧条件下将部分TP作为自身生长繁殖所需的元素进行吸收并同化;3)通过填料自身的吸附作用将水体中颗粒型磷吸附到填料表面,从而降低水体中TP的含量。改良型火山石填料组对TP的去除速度及效率均高于黄花鸢尾处理组,这表明组合型生态浮岛中微生物的吸收同化及填料吸附作用是TP去除的主要机制。
2.6 黄花鸢尾生长状况
黄花鸢尾实验开始与结束的生长状况如表1所示。可以看出,组合型生态浮岛中黄花鸢尾的株高及根长均大于黄花鸢尾组,由此看来,改良型火山石填料中的微生物促进了黄花鸢尾的生长。研究[17-18]表明,植物的氮磷吸收及固定的量与植物生物量呈显著相关,植物生物量越大,对氮磷吸收越多,对水体净化能力越强,这与本研究结果一致。
表 1 黄花鸢尾生长状况Table 1. Growth status of Iris pseudoacorus组别 开始 结束 株高/cm 根长/cm 株高/cm 根长/cm 黄花鸢尾组 24.3 3.7 41.2 18.9 组合型生态浮岛组 24.1 3.6 55.7 32.6 3. 结论
1)该组合型生态浮岛对COD、NH4+-N、TN、TP的去除率分别为62.95%、67.45%、51.99%、77.78%,且植物生物量高于单纯的植物处理组,填料中的微生物促进了植物的生长,从而提高了水质净化效果。
2)黄花鸢尾与改良型火山石、表面微生物具有很好的协同作用,共同促进了水体中COD、NH4+-N、TN、TP等污染物的去除。
3)针对不同的水质污染状况,合理搭配浮岛的组合方式可实现污染物的快速降解,达到净化水质的目的,适用于城镇水体尤其是居住区的静态水体的景观治理。
-
表 1 黄花鸢尾生长状况
Table 1. Growth status of Iris pseudoacorus
cm 组别 开始 结束 株高 根长 株高 根长 黄花鸢尾组 24.3 3.7 41.2 18.9 组合型生态浮岛组 24.1 3.6 55.7 32.6 -
[1] DESTEFANI G, TOCCHETTO D, SALVATO M, et al. Performance of a floating treatment wetland for in-stream water amelioration in NE Italy[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2011, 674(3): 157-167. [2] KANSIIME F, ORYEM-ORIGA H, RUKWAGO S. Comparative assessment of the value of papyrus and cocoyams for the restoration of the Nakivubo wetland in Kampala, Uganda[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2005, 30: 698-705. doi: 10.1016/j.pce.2005.08.010 [3] 李欲如, 操家顺. 冬季低温条件下浮床植物对富营养化水体的净化效果[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2005, 27(7): 505-508. [4] 何成达. 循环水流-浮床种植法处理生活污水的实验研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2004, 27(6): 12-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2004.06.005 [5] 王郑, 崔康平, 许为义, 等. 组合型生态浮床处理农家乐污水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(1): 455-460. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20160175 [6] 王金丽, 颜秀勤, 宁冰, 等. 浮岛植物净化水质效果研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2011, 34(10): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2011.10.004 [7] 许世龙, 苏维词. 流域水环境治理新技术与新材料研究进展[J]. 贵州科学, 2014, 32(5): 48-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2014.05.006 [8] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [9] 铁柏清, 李希, 李杰峰, 等. 3种植物人工浮岛对生活污水水质动态净化特性的比较[J]. 环境工程学报, 2010, 4(7): 1566-1570. [10] 李先宁, 宋海亮, 朱光灿, 等. 组合型浮床生态系统的构建及其改善湖泊水源地水质的效果[J]. 湖泊科学, 2007, 29(4): 367-372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.04.003 [11] 许国晶, 段登选, 杜兴华, 等. 组合生态浮床净化养殖水体效果研究[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2015, 24(1): 94-101. [12] GABRIELLA N, LILLA M, ÁKOS T. Adsorption and chemical precipitation of lead and zinc from contaminated solutions in porous rocks: Possible application in environmental protection[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2016, 122(8): 98-106. [13] 韩梅. 活性炭纤维对底泥中芳香族有机污染物的吸附性能研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2017. [14] HU G, ZHOU M, HOU H, et al. An ecological floating made from dredged lake sludge for purification of eutrophic water[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2010, 36(10): 1448-1458. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.06.026 [15] 徐秀玲, 陆欣欣, 雷先德, 等. 不同水生植物对富营养化水体中氮磷去除效果的比较[J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2012, 30(1): 8-14. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1671-9964.2012.01.002 [16] 段金程, 张毅敏, 高月香, 等. 复合强化净化生态浮床对污水中N、P的去除效果[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2013, 29(4): 422-427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2013.04.003 [17] 成水平, 夏宜琤. 香蒲、灯心草人工湿地的研究: Ⅲ. 净化污水的机理[J]. 湖泊科学, 1998, 10(2): 66-71. doi: 10.18307/1998.0211 [18] ZHU B, FITZGERALD D. Alterration of ecosystem function by zebra mussels in Oneida Lake: Impacts on submerged macrophytes[J]. Ecosystems, 2006, 9(6): 1017-1028. doi: 10.1007/s10021-005-0049-y -






 下载:
下载: