-
地下水是自然循环过程中重要组成部分,也是生态环境系统的活跃因子[1 − 2]. 赋存于岩石中的地下水长期与周围环境进行物质、能量的交换,其化学成分特征可以反映地下水环境的历史演变规律,提供环境变化信息[3 − 6]. 众多学者对不同地区地下水水化学特征及成因开展了研究,形成以水文地球化学模拟、Piper三线图、Gibbs模型、离子比值分析等方法为主要组成部分的研究体系. 陈晨等[7]通过现场调查,运用离子比值分析方法对山东省泰莱盆地地下水类型分布特征及其控制因素进行分析,发现以牟汶河为中轴线,由边缘基岩裸露区向盆地内部离子呈上升趋势,离子主要来源于盆地南部碳酸盐岩和石膏等硫酸盐岩的共同溶解作用. 冯建国等[8]综合运用数理统计、相关性分析、Piper三线图以及离子比等方法,对山东省新泰市地下水进行了分析,发现新泰市地下水离子主要来源于硅酸盐岩和碳酸盐岩的风化溶解,同时受到人类生活、工业生产及农药化肥过量使用的影响. 通过开展地下水水化学组分特征分析,可以有效的分析地下水来源及成因,为地下水资源评价与合理保护提供重要的支持[9 − 10].
泉水是地下水的天然露头,也是不可多得的地下水资源. 泉水不仅代表着一个地区的地下水径流条件,也构成了大自然中一道靓丽的人文景观. 莱芜地区泉水众多,前人并未对莱芜地区泉水开展过系统研究,对泉水水化学特征及泉水成因研究较少. 莱芜撤市划区并入济南市后,首次对莱芜地区泉水开展了系统的泉水调查研究工作. 本文基于本次调查及泉水取样结果,运用地下水水化学特征研究分析方法,结合莱芜盆地水文地质条件,对泉水水化学特征及成因进行了分析,揭示了泉水水化学成分控制因素,从而为泉水资源开发利用及合理保护提供科学管理依据.
-
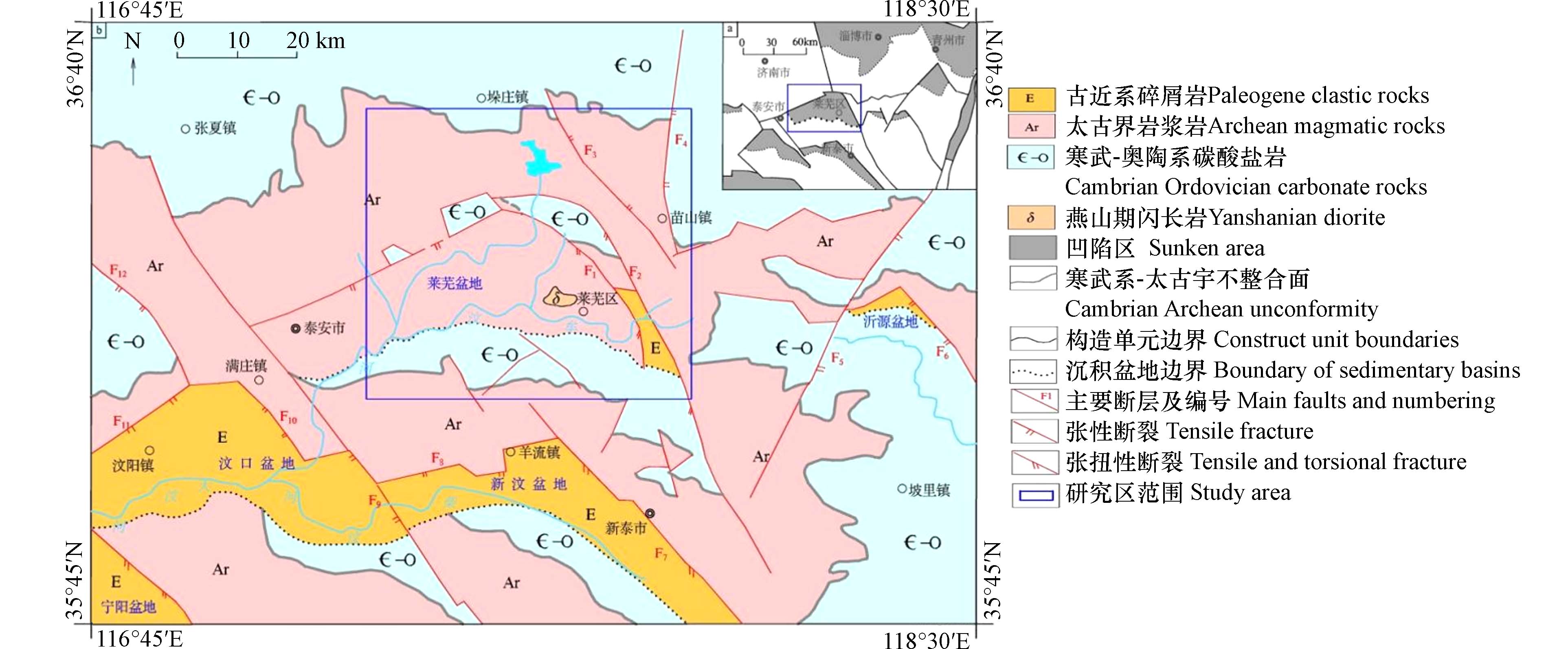
研究区位于山东省中部低山丘陵区,受地质构造影响形成莱芜盆地. 地理坐标为东经117º19′—117º58′,北纬36º02′—36º33′,南北长61 km,东西宽58 km,总面积2246.21 km2. 属温带大陆性半湿润气候,四季分明,春凉秋爽,冬冷夏热,年平均降雨量699.7 mm[11]. 区内地表水系较为发育,主要为大汶河水系. 盆地内发育牟汶河、赢汶河等汶河支流,总体由东向西南方向径流. 水库主要有雪野水库、乔店水库及大冶水库等,受降水及蒸发影响明显,水量变化量大.
盆地北、东、南三面环山,西部开阔,地势总体由东向西倾斜,呈簸箕状. 盆地北部为香山、大山等泰山余脉,南部分布莲花山、新甫山等,皆为山势陡峻、沟谷发育、切割强烈的中低山;东部分布万福山等低山丘陵[12 − 14]. 整体外形为南缓北陡,向北突出的半圆形盆地. 区内地层出露较为齐全,盆地外围出露大面积太古宇变质花岗岩类,盆地内部是由寒武—奥陶系(∈-O)碳酸盐岩地层呈单斜状产出,上部覆盖厚层古近系(E)、新近系(N)砂岩、页岩地层,地表覆盖第四系(Q)粉砂、黏土等(图1)[15 − 16].
-
莱芜盆地含水岩组类型齐全,主要包括盆地边缘新太古代岩浆岩变质岩类裂隙含水岩组,覆盖在侵入岩体上近东西向的碳酸盐岩类裂隙岩溶岩组,盆地内广泛沉积的中新生代碎屑岩类孔隙裂隙含水岩组及地表覆盖的松散岩类孔隙含水岩组(图2)[17].
在盆地北部,水文地质结构单一,地下水主要以浅层风化裂隙水为主,沿地势起伏方向由北向南径流,富水性差. 受北部盆缘深大断裂泰安-口镇断裂、大王庄-铜冶店断裂影响,碳酸盐岩含水岩组呈“断块状”分布在断裂影响带内,裂隙岩溶发育,接受北部裂隙水、地表水补给后形成富水块段[18],主要有大鱼池水源地. 在盆地南部,地层结构整体呈单斜式向北倾斜.
地下水主要运移驱动力为重力势差,初始来源为大气降水. 岩溶水接受大气降水及南部裂隙水补给,地下水径流方向与地层倾向相一致,经裸露的寒武系地层及奥陶系地层后向盆地腹部排泄[19 − 20]. 局部地段受断裂构造、侵入岩体阻水影响,可形成富水块段或出露成泉,分布吴家岭水源地、叶马曹水源地等. 地下水整体往盆地内部呈“向心状”径流,受内部古近系、新近系地层阻水后转向西北、西南方向径流排泄. 泉水主要出露在盆地南北两侧边缘地带,盆地内部受煤矿开采等人类活动影响,造成地下水水位下降、地层结构破坏,泉水已干涸灭失.
-
研究区共有泉水223处,其中102处泉水入选《济南市名泉名录》,主要包括北泉、普惠泉、圣水泉等;依据行政区划分,莱芜区167处、钢城区56处. 泉水依据成因类型划分为上升泉、下降泉和泉井3类;依据含水岩组类型可分为岩溶泉水和裂隙泉水两类. 岩溶泉水主要分布在盆地南侧单斜状碳酸盐岩地区及北部、东部边缘一带,岩溶水接受补给后沿地层倾向或地势由高到低方向径流,在排泄区或地层阻水处出露成泉,具有规律性、循环性和持续性;裂隙泉水主要分布于铜冶店—孙祖断裂外围大面积古元古代岩浆岩分布区,泉水接受补给后沿浅层风化裂隙或构造裂隙向地势低洼处径流,在河流沟谷、断裂构造处成泉,具有季节性、局部循环等特征.
-
2021年9月份对研究区102处名泉泉水开展水样采集,共采集样品100件(2处泉水干涸). 其中岩溶泉水67件,裂隙泉水33件. 采样点位置见图1. 样品采集前,对取样瓶采用蒸馏水进行冲洗,采样时用泉水冲洗至少3次,取水前让泉水流动10 min以上,保证取得的泉水可以准确反映泉水的真实状况. 现场采用快检设备对pH、水温、溶解氧等参数进行现场测定,采用GPS测定泉水经纬度与高程.
样品测试由具有检测资质的山东省地矿工程勘察院实验室完成,检测项目包括K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、HCO3−、CO32−、Cl−、SO42−、TDS等. SO42−、Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪测定,CO32−、HCO3−采用酸碱指示剂滴定法测定,Cl−采用硝酸银滴定法测定.溶解性总固体通过计算求得. K+检测限为0.05 mg·L-1,Na+检测限为0.01 mg·L-1,Ca2+、Mg2+和Cl-检测限为1.0 mg·L-1,SO42-检测限为5.0 mg·L-1.
-
数理统计分析的结果可以反映研究区地下水化学成分的基本状况. 因此,对泉水水样的pH值、常规离子SO42−等水化学参数进行统计特征值分析(表1).
pH值是反映水文地球化学平衡信息的重要因子[21]. 从表1可以看出,区内泉水pH值范围在6.6—8.27之间,平均值为7.69,且变异系数为0.04,表明区内泉水pH值空间差异不大,呈弱碱性.
TDS是指水中以悬浮形式存在的全部有机和无机溶质的总量,其数值越高,表明泉水中的溶解物质越多. 研究区泉水TDS范围在152.75—982.64 mg·L−1之间,平均值为423.15 mg·L−1,低于饮用水标准限值(1000 mg·L−1),说明区内泉水都属于低矿化度水,且变异系数为0.32,表明空间分布相对均匀.
泉水阳离子浓度排序为Ca2+>Mg2+>Na+>K+,表明Ca2+、Mg2+为泉水中占主导地位的阳离子,其中Ca2+平均值为117.33 mg·L−1,且变异系数最小,表明Ca2+在研究区内分布相对均匀;阴离子浓度排序为HCO3−>SO42−>NO3−>Cl−,表明HCO3−、SO42−为泉水中占主导地位的阴离子,其中HCO3−平均值为294.17 mg·L−1,为泉水中主要阴离子.
SO42−、Cl−、NO3−变异系数相对较大,表明空间差异变化较大,其主要分布在颜庄镇西、柳桥峪等人类活动较为密集区域. 该地区工矿企业分布、人类活动密集,地下水不同程度的污染造成了单点泉水SO42−、Cl−、NO3−等离子含量的超标.
-
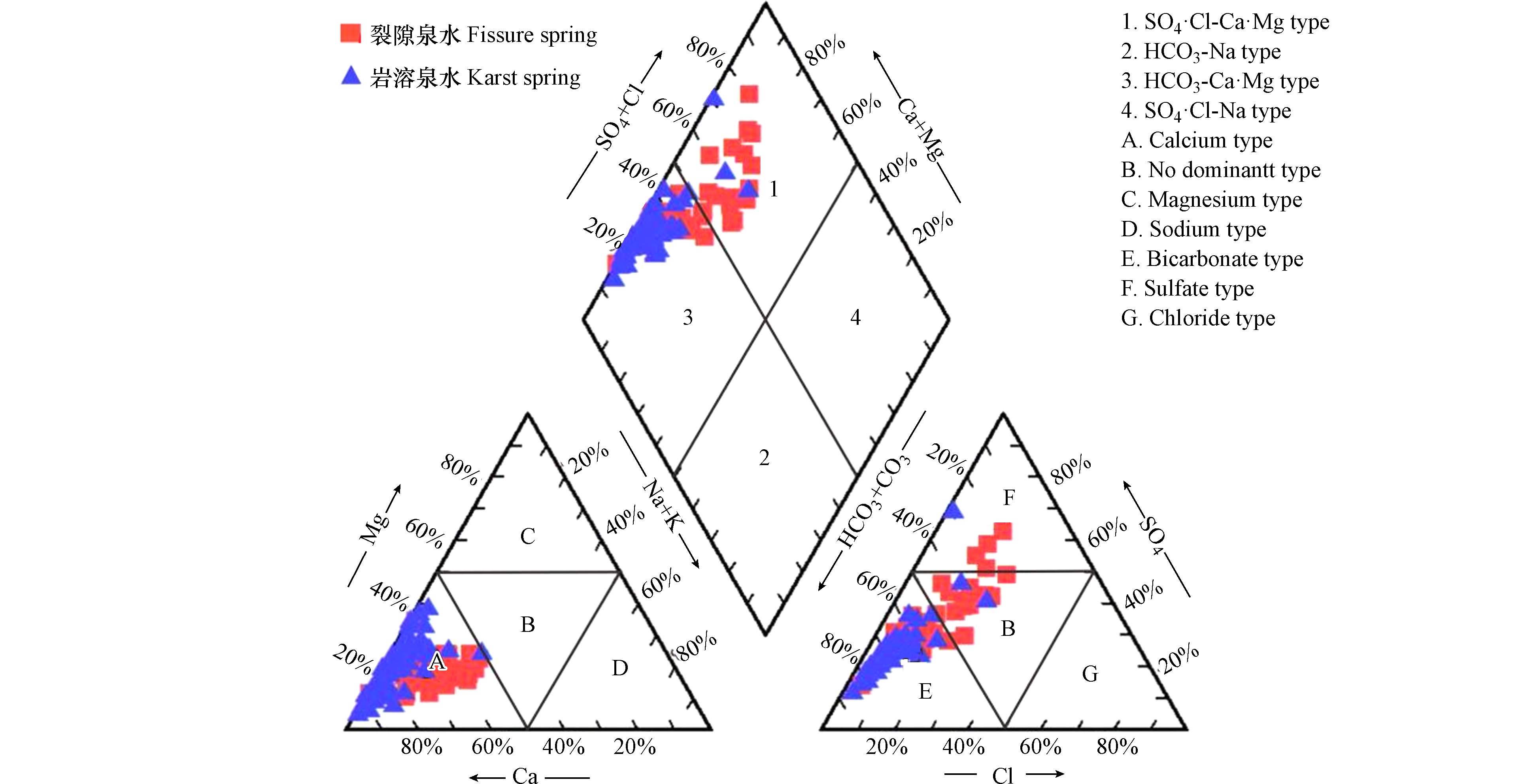
Piper三线图是一种常用的水化学分类图示方法,可以表现水体总的水化学性质和主要例子组成变化特征[22 − 23]. 如图3所示,区内泉水阴离子类型可划分为HCO3型、HCO3·SO4型、SO4型和Cl·SO4型4种类型;阳离子类型可划分为Ca型、Ca·Mg型、Ca·Na型3种类型.
不同类型泉水受含水岩组、地形地貌、人类活动等因素影响,水化学类型略有差异. 岩溶泉水主要分布在阳离子三角区左下角,表明其阳离子以Ca2+为主,其次为Mg2+、Na+;裂隙泉水主要分布在阳离子三角区中下部,表明其主要阳离子以Ca2、Na+为主,其次为Mg2+. 岩溶泉水、裂隙泉水阴离子均集中分布在左侧,说明两类泉水中主要阴离子为HCO3−、SO42+. 总体来看,区内各泉水水化学特征差异不大,水化学类型以HCO3-Ca型、HCO3·SO4-Ca型、HCO3-Ca·Mg型为主;表现出受区内物理性质和人类活动作用影响特征,呈现出局部点状的差异性.
-
控制地下水中离子组分含量的因素多样,对离子组分相关性分析可以有效的揭示地下水中溶解物质的来源[24 − 25]. 因此,相关系分析方法在地下水水化学研究过程中得到了广泛应用. 本次运用SPSS软件对莱芜地区泉水的常规化学指标进行了相关性分析,结果如表2所示.
研究区泉水TDS与Ca2+、Mg2+、Na+、Cl−、SO42−、NO3−之间的相关性较为显著,表明这些组分对TDS的贡献较大,特别是Ca2+、SO42−相关系数均超过了0.80;Na+与Cl−、NO3−之间显著相关,表明它们之间存在相同的来源;SO42−与Ca2+、Mg2+存在正相关关系,说明三者有共同的来源,可能与岩盐、石膏等硫酸盐岩的风化溶解有关. 另外,NO3−与Cl−之间存在明显的相关关系,表明两种离子具有明显的同源性,其主要来源可能为人类活动.
-
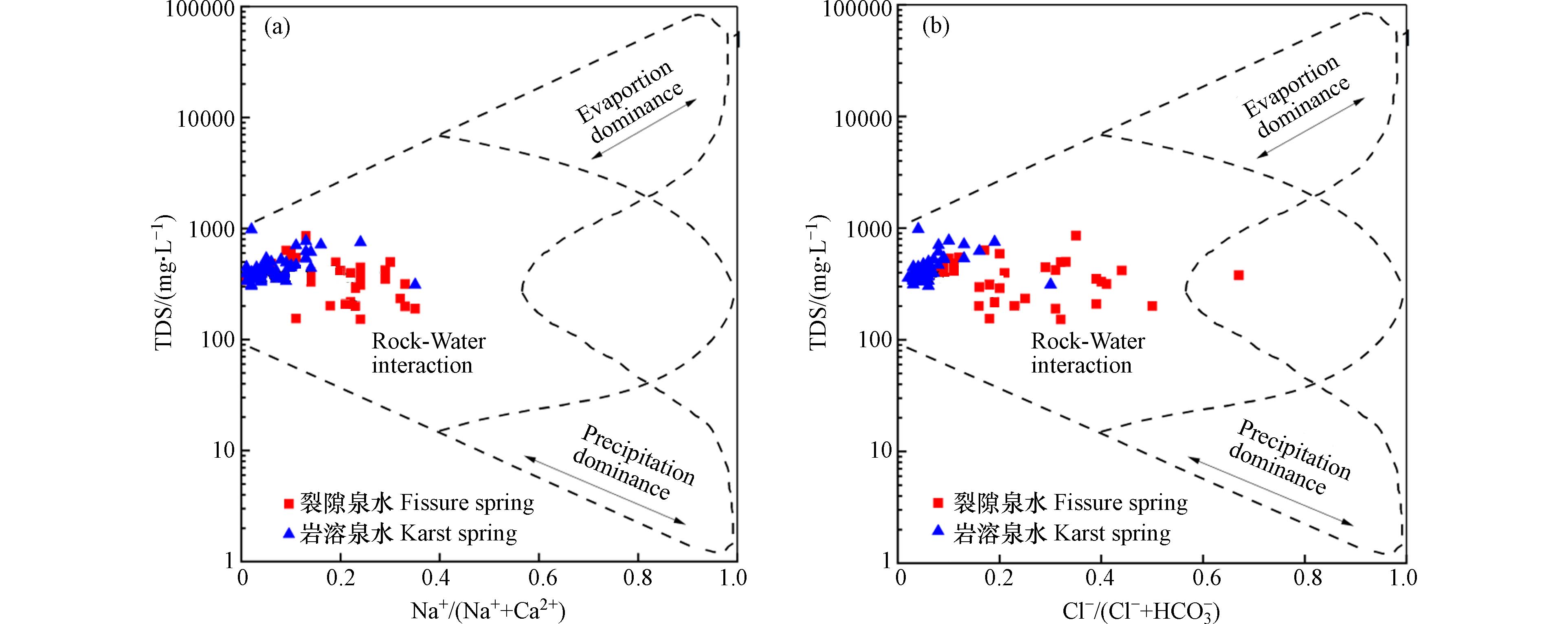
运用Gibbs图可以将天然水体的化学形成机制划分为蒸发结晶、岩石风化和大气降水三类[26 − 27]. 通过图4可以看出,区域内的泉水取样点主要分布在岩石风化区域,且大部分都落于Na+/(Na++Ca2+)值和Cl-/(Cl-+HCO3-)值小于0.5的区域,表明泉水的主要离子成分来源于水与岩土的相互作用,是区域泉水化学组分形成的主要控制因素. TDS介于152.75—982.64 mg·L-1之间,平均值为423.15 mg·L-1,Cl-/(Cl-+HCO3-)范围在0.02—0.71之间,平均值为0.21,Na+ /(Na+ +Ca2+)范围在0.01—0.41之间,均值为0.18.
区域地层中发育较多的碳酸盐岩矿物主要为方解石、白云石等,可知岩溶泉水中的Ca2+、Mg2+和HCO3-主要来源于碳酸盐岩的溶解和风化作用,个别岩溶泉水呈现向右偏移趋势,表明部门岩溶水体化学组分受离子交换作用影响. 裂隙泉水分布更为集中,受水岩相互作用明显,化学离子成分主要来源于岩石风化作用.
-
利用水体中各种离子比值关系可以进一步推断水中各离子来源,分析水化学成因,反映不同岩石风化对化学来源的影响程度[28 − 29].
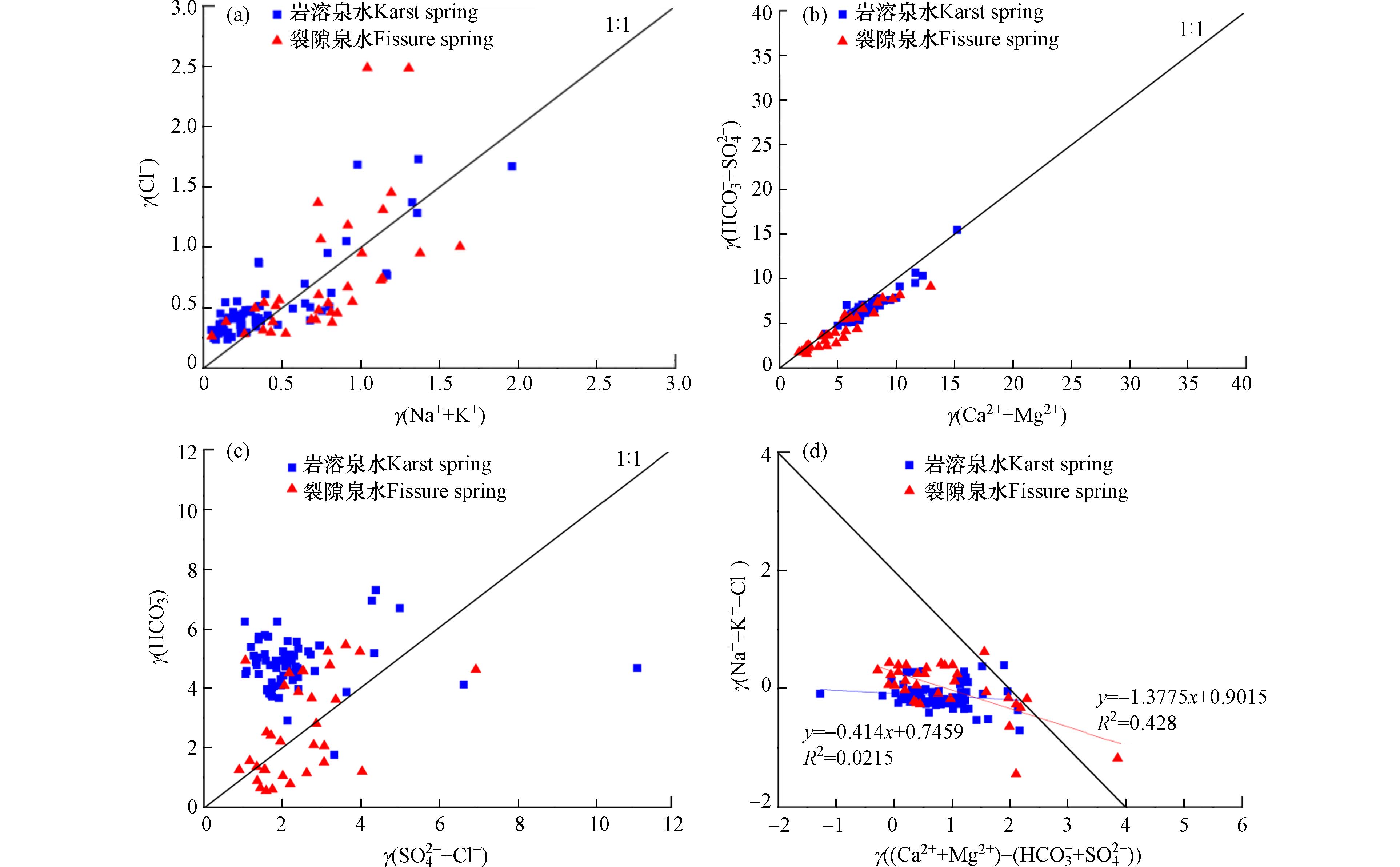
当γ(Na++K+)/γCl-值接近于1时,表明Na+、K+离子主要来源于岩盐的风化溶解[30]. 由图5a可以看出,泉水中Na+、K+离子主要分布在1:1线的两侧,说明泉水中Na+、K+离子主要来源于岩盐的溶解作用,部分裂隙泉水点分布在1:1线之下,说明Na+、K+离子当量浓度大于Cl-,说明裂隙泉水中Na+、K+离子来源除了岩盐溶解外,还可能有硅酸盐矿物或阳离子交替吸附作用[31].
利用γ(Ca2++Mg2+)/γ(HCO3-+SO42-)的比值关系,可以分析泉水中Ca2+、Mg2+的主要来源. 若γ(Ca2++Mg2+)/γ(HCO3-+SO42-)比值大于1,说明Ca2+、Mg2+主要来源于碳酸盐岩的溶解,若γ(Ca2++Mg2+)/γ(HCO3-+SO42-)比值小于1,说明Ca2+、Mg2+主要来源于硅酸盐岩或硫酸盐矿物的风化溶解[32]. 由图5b可以看出,泉水取样点主要坐落于1:1线的下方,说明泉水中Ca2+、Mg2+离子主要来源于碳酸盐岩的溶解作用.
计算γ(SO42-+Cl-)与γHCO3-的比值,可以判断地下水中离子来源. 当γ(SO42-+Cl-)/γHCO3-大于1时,地下水中化学成分主要是来自蒸发岩的溶解;当小于1时,则说明主要来自碳酸盐的溶解[33]. 由图5c可以看出,岩溶泉水取样点大部分位于1:1线上侧,说明岩溶泉水中HCO3-主要来源于碳酸盐岩矿物溶解;裂隙泉水取样点分布在1:1线两侧,说明裂隙泉水中HCO3-与蒸发盐岩溶解和碳酸盐岩溶解均存在一定关系.
阳离子交换反映可以通过γ(Na++K+-Cl-)与γ(Ca2++Mg2+)-γ(SO42-+HCO3-)的比值来反映[34 − 35]. 由图5d可以看出,岩溶泉水水样分布在斜率为-0.414的直线周围,R2=0.0215,斜率远离-1,说明岩溶泉水阳离子交换作用相对较弱;裂隙泉水水样分布在斜率为-1.3775的直线附近,R2=0.428,斜率接近-1,说明裂隙泉水中阳离子交换作用相对较强.
-
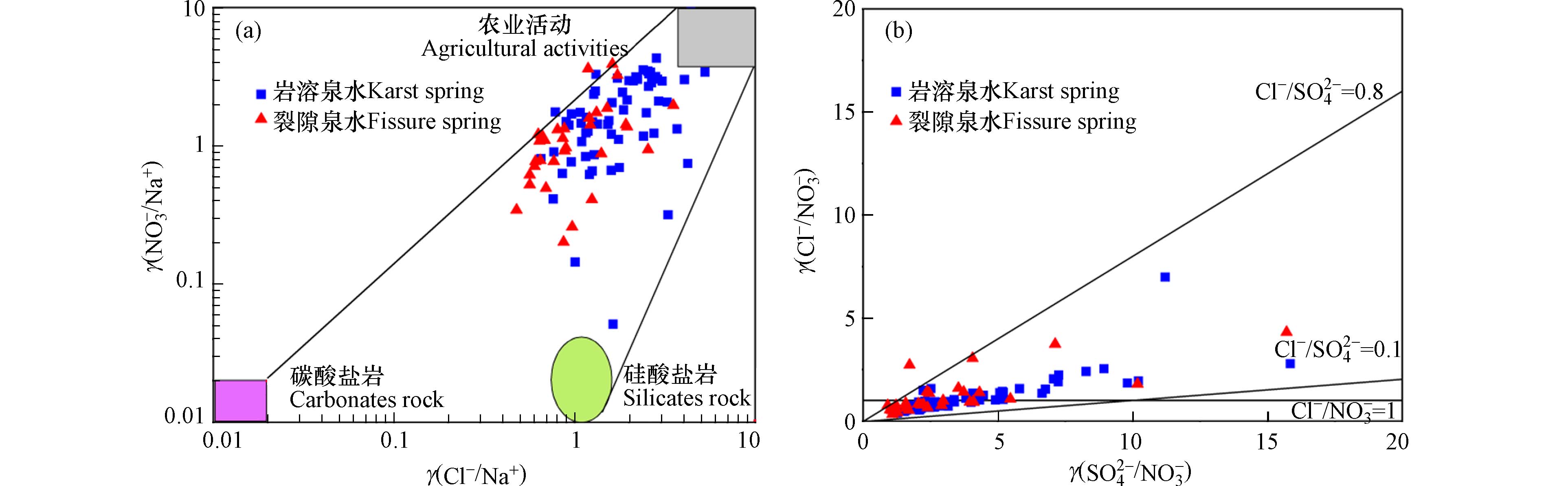
莱芜盆地周边低山丘陵区农业种植分布广泛,盆地内部工矿企业、煤炭、铁矿等较为集中,农业、工业活动对泉水质量造成了一定程度的影响. 在人类活动较为密集的区域,往往Cl−、SO42−、NO3−离子浓度较高. 受人为输入影响,泉水中Cl−/Na+和NO3−/Na+比值通常会较高[36]. 如图6(a)所示,在研究区内泉水水样点主要靠近农业活动区域,仅个别岩溶泉水点靠近硅酸盐岩区域,表明在区内泉水受人类活动影响较强,泉水中的NO3−主要来自人类活动影响,盆地周边农业种植发达,污染物可随大气降水、地表水一起渗入地下水进行迁移,进而影响泉水水化学特征. 利用离子比值趋势图(图6(b))可以看出,泉水采样点在Cl−/NO3−=1线两侧分布均匀,表明大多数泉水受到了人类生活污染的影响. Cl−/SO42−的值均较小,说明泉水也受到了工业活动的影响. 另外,SO42−/NO3−的值较小,说明区内泉水还受到了农业污染的影响,与图6(a)相对应.
-
(1)研究区内泉水pH值在6.6—8.27之间,呈弱碱性. 泉水中阳离子以Ca2+为主,其次为Mg2+、Na+;阴离子以HCO3−为主,其次为SO42−、NO3−、Cl−. Ca2+、HCO3−变异系数相对较小,含量比较稳定,SO42−、Cl−、NO3−变异系数较大,表明空间差异变化较大,受其他因素影响明显.
(2)泉水水化学类型差异较小,岩溶泉水主要以HCO3-Ca型、HCO3-Ca·Mg型为主,裂隙泉水主要以HCO3·SO4-Ca型、HCO3·SO4-Ca·Na型为主. 表现出受区内物理性质和人类活动作用影响特征,呈现出局部点状的差异性.
(3)区内泉水化学组分形成的主要控制因素是水与岩土的相互作用,主要包括碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩的风化溶解. 岩溶泉水阳离子交换作用相对较弱,裂隙泉水阳离子交换作用相对强烈. 此外,人类活动也对泉水化学组分产生了明显的影响,主要有农业活动、工业活动等. 下一步应建立健全区内名泉水量、水质监测体系;深入研究岩溶水采、补均衡关系,解决供水与保泉矛盾关系,确保泉水持续喷涌.
山东莱芜地区泉水水化学特征及形成机制
Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of spring water in Laiwu, Shandong Province
-
摘要: 基于山东莱芜地区2021年9月泉水普查取样水化学数据,运用数理统计、相关性分析、Piper三线图、Gibbs图及离子比值分析等方法,总结了泉水水化学特征,对其形成机制进行分析. 结果表明,泉水整体呈弱碱性,阳离子以Ca2+为主,阴离子以HCO3−为主,TDS在152.75—982.64 mg·L−1之间,平均值为423.15 mg·L−1,为低矿化度水;区内泉水水化学类型以HCO3-Ca型、HCO3·SO4-Ca型、HCO3-Ca·Mg型为主,局部呈点状差异分布;泉水中离子主要来源于水岩相互作用,碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩矿物溶解是主要离子来源. 同时,区内泉水受人类活动影响明显,NO3−主要来自于农业活动. 本研究可为莱芜地区泉水保护与合理规划利用提供依据.Abstract: Hydrochemical characteristics of spring are summarized and analyzed its formation mechanism using mathematical statistics, correlation analysis, Piper trigram, Gibbs chart and ion ratio analysis according to hydrochemistry results of spring water survey project that is conducted in study area in September 2021. The results show that spring is weakly alkaline, which dominant cation and dominant anion is Ca2+, HCO3− respectively. TDS of spring ranges from 152.75 mg·L−1to 982.64 mg·L−1 with average of 423.15 mg·L−1. Hydrochemical types of spring are mainly HCO3-Ca, HCO3·SO4-Ca, HCO3-Ca·Mg while other type distributes locally. Ion sources of spring is water-rock interaction primarily including dissolution of carbonates and silicates. In addition, spring is also affected by anthropogenic activities, especially nitrates from agricultural activities. This research results can provide scientific and technical guidance for spring protection and rational planning and utilization in Laiwu area.
-
Key words:
- spring /
- hydrochemical characteristics /
- formation mechanism /
- Laiwu area.
-
易挥发的剧毒氯代烃有机物1,2-二氯乙烷(1,2-dichloroethane,简称1,2-DCA)具有致癌、致畸、致突变效应,是土壤和地下水环境中常见有机污染物之一[1]。因其溶解性高、性质稳定,导致其在土壤和地下水中环境的降解难度大。因此,研究和探讨1,2-二氯乙烷在地下水中的降解具有重要意义。
地下水有机污染的主要修复方法包括抽出处理[2-3]、气相抽提[4]、可渗透反应墙[5]以及生物修复[6]等,但这些方法在处理成本、去除率及运行周期等方面尚存在不足之处。原位化学氧化技术虽然在污染地下水修复方面还处于研究发展阶段,但已表现出良好的处理效果[7-8]。碱活化过硫酸盐原位修复地下水是其中一种被广泛应用的技术。有研究[9]表明,过硫酸盐氧化体系中存在硫酸盐自由基(
SO−⋅4 SO−⋅4 增大修复药剂在地下水含水层中的有效影响半径是地下水原位修复技术工程化应用的关键之一。修复药剂在含水层的运移受含水层自身水文地质条件和地下水渗流场影响较大。水动力控制法是利用井群系统,通过抽水或向含水层注水,人为地改变地下水的水力梯度,进而影响含水层的地下水渗流特征。在进行原位化学氧化修复时,通过水动力调控可以影响修复药剂的扩散和运移,从而间接影响地下水中污染物降解效果。
目前,针对氯代烃污染地下水原位化学修复的研究主要是室内氧化批实验以及土柱或砂箱模拟实验,因其存在尺度效应而影响了该技术的推广应用。本研究中,以某有机污染场地污染含水层为实验对象,采用水动力控制法强化原位化学氧化技术修复受1,2-二氯乙烷污染含水层,分析了碱活化过硫酸盐降解目标污染物的效果,探讨实验过程中目标污染物及地下水参数的变化规律,以期为该技术修复污染地下水的工程化应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验区概况
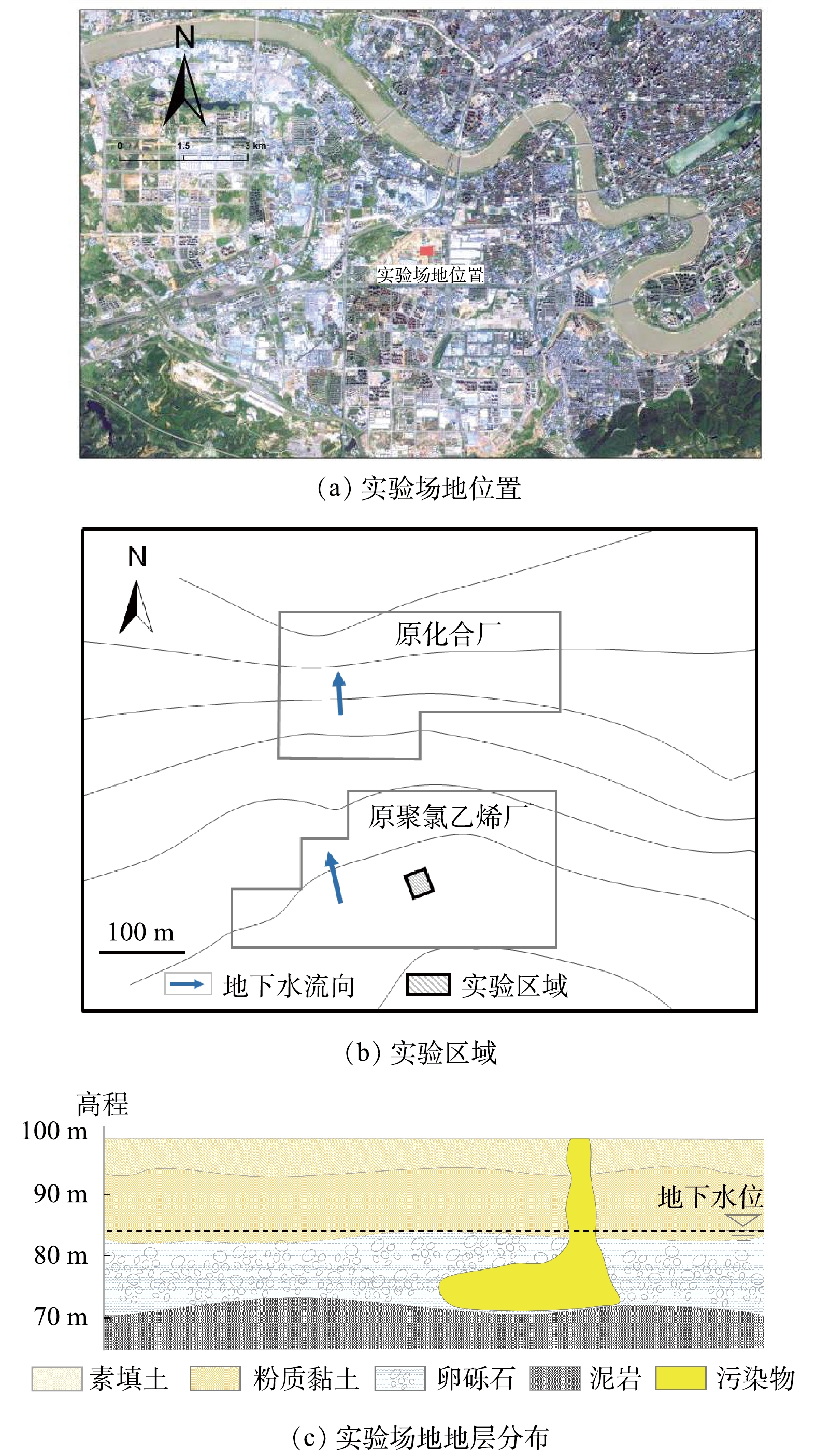
本研究中,以某化工厂停产搬迁后的遗留有机污染场地含水层为实验对象,场地位置如图1(a)所示,实验区域如图1(b)所示。场地地层结构主要由素填土、粉质黏土、圆砾和泥岩组成(图1(c)),各层厚度分别为0~6.00、7.00~15.00、10.00~29.50 m,泥岩层未穿透,地下水位埋深11.48~17.00 m。实验区域位于污染区域内,地下水主要赋存于卵砾石潜水含水层中,实验中修复的目标含水层位于地下15.00~29.00 m,含水层中的主要污染物为1,2-二氯乙烷。
1.2 实验方法
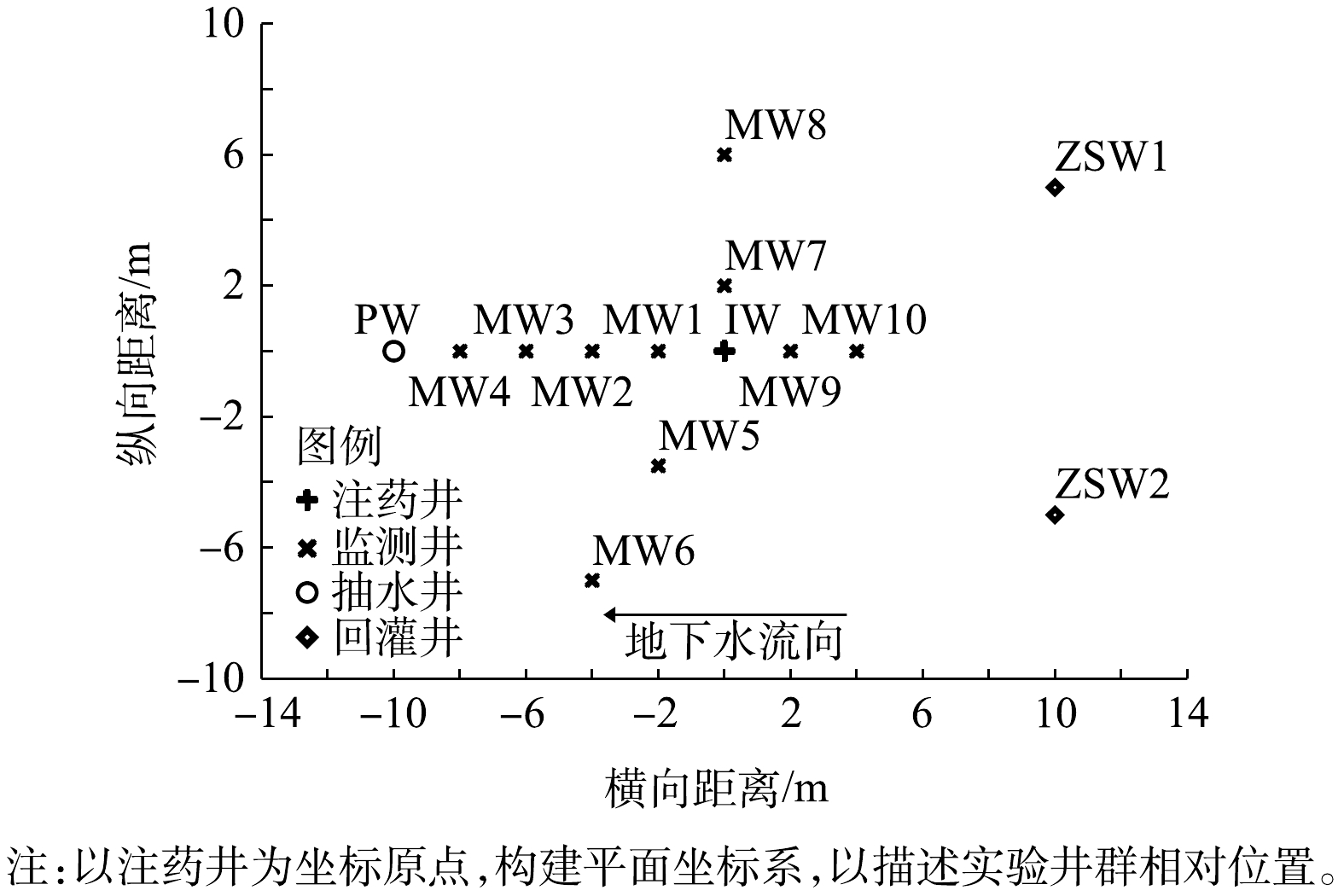
实验分为3个阶段进行:第1阶段为水文地质调查阶段,在实验区内开展抽水实验和示踪实验获取水文地质参数,并在实验区周围完善实验井群(图2)布置;第2阶段为修复实验阶段,开展地下水水动力控制、监控修复前地下水监测井中污染物浓度,将过硫酸钠和氢氧化钠注入目标含水层;第3阶段为采样监测阶段,在注药完成后,采集实验区域内地下水样品,检测和分析目标污染物含量及相应的理化参数。
1)水文地质实验。水文地质实验分为抽水实验和示踪实验。抽水实验为单孔完整井稳定流抽水实验[13],实验过程中使用秒表、电磁流量计记录抽水过程中的时间间隔和流量值。实验现场无其他观测井,将抽水井PW直接作为观测井处理,使用水位仪记录抽水井水位变化。实验过程持续9 h,抽水稳定流量为7 m3·h−1,最大降深为2.30 m。
示踪实验采用配制的饱和NaCl溶液作为示踪剂,实验前开启抽水泵抽水,待观测井的水位降深达到稳定后开始进行实验。实验过程中,抽水井PW定流量抽水,抽水流量为7 m3·h−1。示踪剂投放前,先对示踪剂投源井IW和观测井MW1处于稳定水位时的地下水Cl−浓度进行测定。经测定,实验区地下水Cl−背景浓度为104~110 mg·L−1。实验所用示踪剂溶液由质量为250 kg NaCl配制而成,一次性持续注入,并将示踪剂投放时间作为弥散实验开始的时间。投放示踪剂后,平均每隔1 h在示踪剂投源井IW和观测井MW1取样监测Cl−浓度。现场实验的延续时间,主要是根据水样中Cl−质量浓度随时间变化曲线而决定的。当所取水样中的示踪剂离子质量浓度从背景值达到峰值并逐渐降低到起始背景质量浓度值,然后再稳定一段时后终止实验。本次实验中示踪剂注入时间为抽水实验进行9 h后,共持续48 h。
2)原位化学氧化修复。实验中采用的氧化剂为工业过硫酸钠(含量99%),活化剂为氢氧化钠(液碱,含量30%)。在注入地下水含水层前需将过硫酸钠配制成浓度适合的流体状药剂。根据以往应用经验、实验室小试数据及场地的实际污染程度,确定本次实验期间过硫酸钠溶液注入浓度为300 kg·m−3,实验期间共注入过硫酸钠15 t和氢氧化钠12 m3。
注药前24 h,开启抽水井PW进行抽水,并回灌至注水井ZSW1和ZSW2,抽、注水流量为7 m3·h−1,通过抽水和注水控制实验区域内地下水水力梯度。注药时,开启注药泵,向注药井IW内注入过硫酸钠溶液和液碱。过硫酸钠溶液为持续性恒流量注入,注入流量为2 m3·h−1;液碱为间歇性注入,注入流量为0.5 m3·h−1,注入时间和间歇时间均为20 min。注药结束后,停止抽水和回灌,水动力控制结束。
3)修复效果监测。药剂注入工作完成后,从监测井中采集地下水样品进行分析测试。地下水监测项目主要包括1,2-二氯乙烷含量和地下水的理化性质。采用便携气囊式低流量采样泵(QED MP50,美国)慢速洗井和采样,在监测井水位下2、8和14 m处取样,取平均值作为监测井中样品浓度(Mean ± SEM)。有机样品使用40 mL棕色玻璃瓶在4 ℃保存,无机样品使用250 mL塑料瓶保存。
地下水pH、溶解氧、氧化还原电位、电导率采用HACH Q300HD便捷式水质分析仪现场测定。地下水样品中Cl−含量采用硝酸银滴定法测定。地下水样品中硫酸盐含量采用离子色谱法检测,检测仪器为离子色谱仪(Aquion,美国),具有电导检测器和抑制器,电导检测器进样体积200 μL,使用阴离子分离柱,流速1.2 mL·min−1,柱温25 ℃,碳酸盐淋洗液Na2CO3为0.6 mmol·L−1,NaHCO3为0.6 mmol·L−1。地下水样品中1,2-二氯乙烷含量采用吹扫捕集/气相色谱-质谱法检测,检测仪器为气相色谱-质谱联用仪(Agilent,美国),配备DB-624极性石英毛细管色谱柱,AQUATek 100吹扫捕集进样器(Agilent,美国);进样口温度260 ℃,分流比10∶1,柱流量1 mL·min−1,传输线温度230 ℃;色谱柱升温程序:初始柱温40 ℃,保持3 min,以20 ℃·min−1升至200 ℃,再以10 ℃·min−1升至250 ℃,保持3 min,载气为高纯氦气(99.999%);电离能量69.9 eV,离子源温度230 ℃,四级杆温度150 ℃,采集模式为SIM模式,溶剂延迟3 min;定量方法采用峰面积外标法。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 实验区的水文地质参数
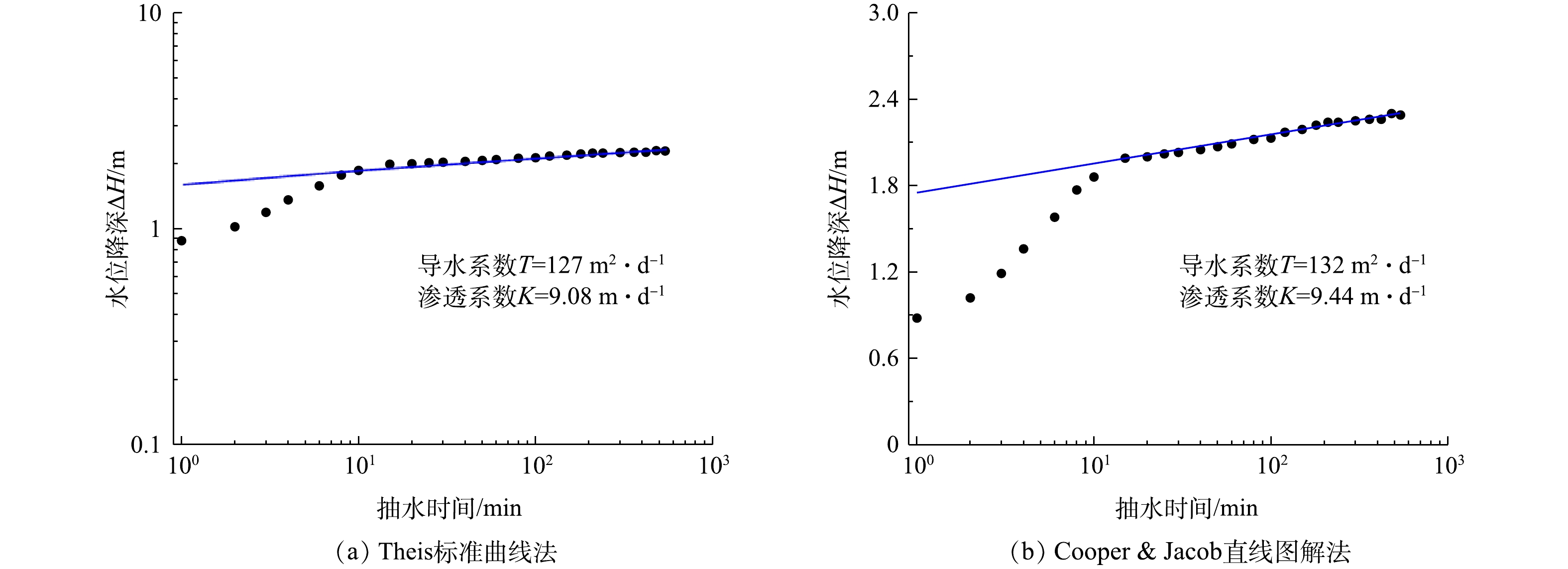
1)抽水实验结果与分析。抽水实验是野外求取含水层参数的重要方法,NEUMAN等利用抽水实验求取重力释水滞后条件下含水层参数[14]。本次抽水实验中无观测井,以抽水井实验数据为基础求解含水层参数,因此,在数据处理过程中需要对抽水井井储[15]及表皮效应[16]的影响进行修正。由于抽水前期数据受井损和水泵扬程等影响流量变化较快,故需对前期变化较快数据进行筛选,利用 Aquifer Test中Theis模型求解其对抽水井PW井抽水数据处理,运用Theis曲线拟合及Cooper & Jacob线性拟合分别求解含水层参数,拟合结果如图3所示。
Dupuit公式法是水文地质调查过程中常用的求取含水层参数(式(1)~式(3))的方法,薛禹群[17]对以稳定流为基础的Dupuit公式和影响半径问题有详细的阐述。
K=0.732Q(2H−s)slgRr (1) R=2s√HK (2) T=KH (3) 式中:K为渗透系数,m·d−1;Q为抽水井涌水量,m3·d−1;s为抽水井稳定时水位降深值,m;R为影响半径,m;r为抽水井半径,m;H为潜水含水层的厚度,m;T为导水系数,m2·d−1。
本研究中采用试算法求解。在求解过程中,由于Dupuit所利用的是最终达到“稳定”阶段的水位数据,因此,抽水流量采用最终稳定流量计算。抽水井井径为0.13 m,稳定抽水流量为168 m3·d−1,含水层厚度为14 m,最大降深为2.30 m,经试算法求解得到抽水影响半径为39.08 m,含水层渗透系数为5.15 m·d−1,导水系数为72 m2·d−1。
对于Aquifer Test中Theis标准曲线拟合法求解,可有效利用所有数据,但在求解过程中随意性较大。对于Dupuit公式法求解,方法较为成熟,其要求抽水实验时间长,但在求解过程中需关注最终稳定流量和水位降深,前期数据利用效率低。综合运用不同的含水层参数求解方法,得到实验区域含水层参数(平均值),结果表明,渗透系数为7.89 m·d−1,导水系数为101 m2·d−1。
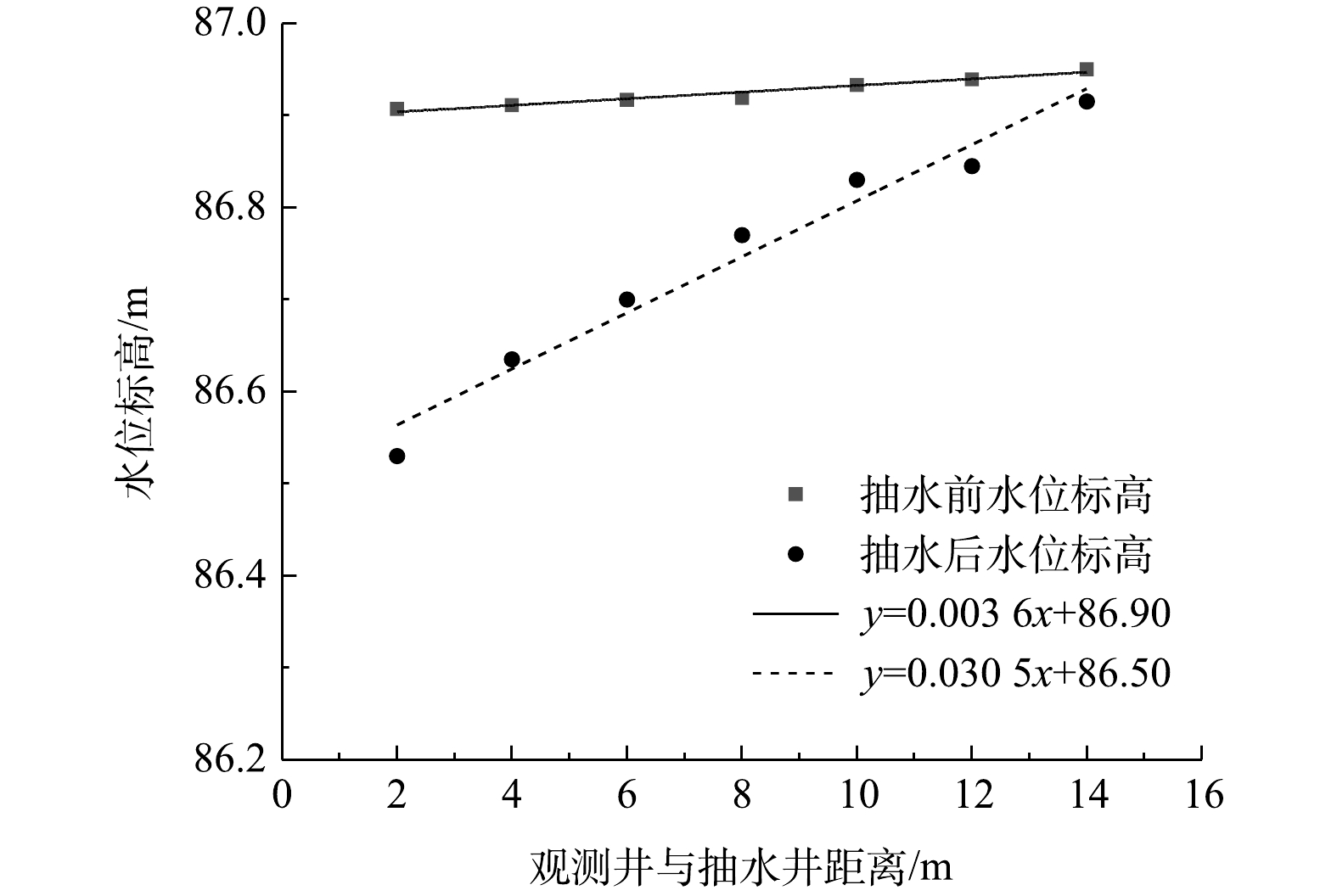
2)场地水动力弥散特征。抽水实验前后实验区域观测井水位标高如图4所示,自然流场下地下水流向由南向北,水力坡度为0.36%,持续抽水9 h后,地下水流场趋于稳定,场地水力坡度为3.05%,通过稳定流抽水可有效调控实验区域地下水渗流场。
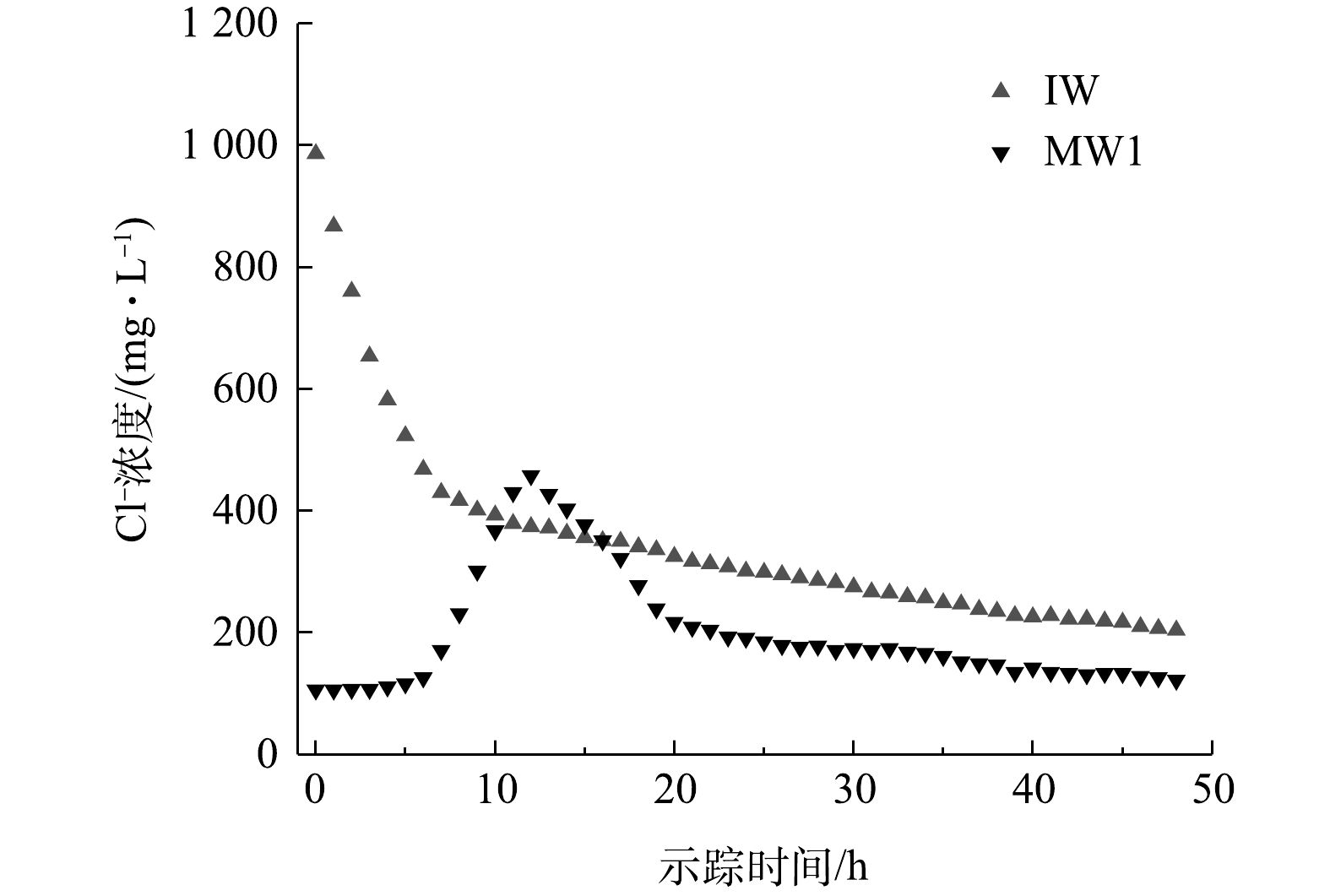
实验区域潜水含水层示踪弥散实验开始于抽水井PW抽水9 h后,示踪实验历时48 h,Cl−浓度随时间变化过程见图5。观测井MW1中Cl−浓度在实验开始后4 h开始升高,在12 h后达到峰值458 mg·L−1,之后逐渐下降。
以示踪剂投源井IW为坐标原点,地下水流速主方向为x轴正方向,垂直于地下水流速方向为y轴正方向,观测井位于x轴上。向IW井中注入示踪剂NaCl,Cl−在含水层中的运移过程主要受机械弥散作用,分子扩散作用的影响可忽略不计,其运移过程可简化为一维稳定流场中的二维弥散问题,位于坐标为(x,y)点处观测井中的Cl−浓度随时间变化过程的解析式如式(4)所示。
C(x,y,t)=M4πnut√αTαL⋅exp(−(x−ut)24αLut−y24αTut) (4) 式中:C(x, y, t)为t时刻区域任意点处示踪剂的浓度,mg·L−1;M为单位含水层厚度上目标离子瞬时投放质量,kg;n为含水层有效孔隙率,u为地下水流速,m·d−1;αL、αT为含水层纵、横向弥散度,m。
由图5所示的示踪剂投源井IW和观测井MW1中Cl−浓度与时间的关系,以式(4)对观测井MW1中Cl−浓度进行拟合,可得αL=0.89 m、u=3.85 m·d−1。根据前人的研究结果及经验判断,场地的横向弥散度αT大致为纵向弥散度αL的1/10[18],可得横向弥散度αT的经验推断值为0.089 m。
2.2 1,2-二氯乙烷降解规律及动力学分析
在注入过硫酸钠和氢氧化钠后,不同监测井中1,2-二氯乙烷降解规律存在明显距离-速率效应。注药后,距离注药井较近区域(4 m内)地下水中的污染物浓度呈快速下降趋势,距离注药井较远区域(6~8 m)地下水中的污染物浓度呈缓慢下降趋势。距离注药井2 m处监测井(MW1、MW7和MW9)和距离注药井4 m处监测井(MW2、MW5和MW10)中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度的变化情况如图6所示。MW1、MW7和MW9中1,2-二氯乙烷初始浓度分别为2.31、3.18和3.32 mg·L−1,在注药后地下水中1,2-二氯乙烷快速下降,注药后28 d,3个监测井中的1,2-二氯乙烷均被完全降解(低于检出限1.4 μg·L−1);注药后58 d,3个监测井中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度开始回升,到实验结束时,3个监测井中的1,2-二氯乙烷浓度分别为1.91、3.18和1.22 mg·L−1。MW2、MW5和MW10中1,2-二氯乙烷初始浓度为4.17、3.13和3.67 mg·L−1,在注药后地下水中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度快速下降;注药后28 d,3个监测井中的1,2-二氯乙烷浓度分别为0.28、0.44和0.35 mg·L−1,与初始浓度相比,分别降低了94.00%、85.86%和86.70%。与2 m处监测井相似,MW2、MW5和MW10中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度均在实验期间出现下降后回升,到实验结束时,3个监测井中的1,2-二氯乙烷浓度分别为3.46、4.43和1.10 mg·L−1。
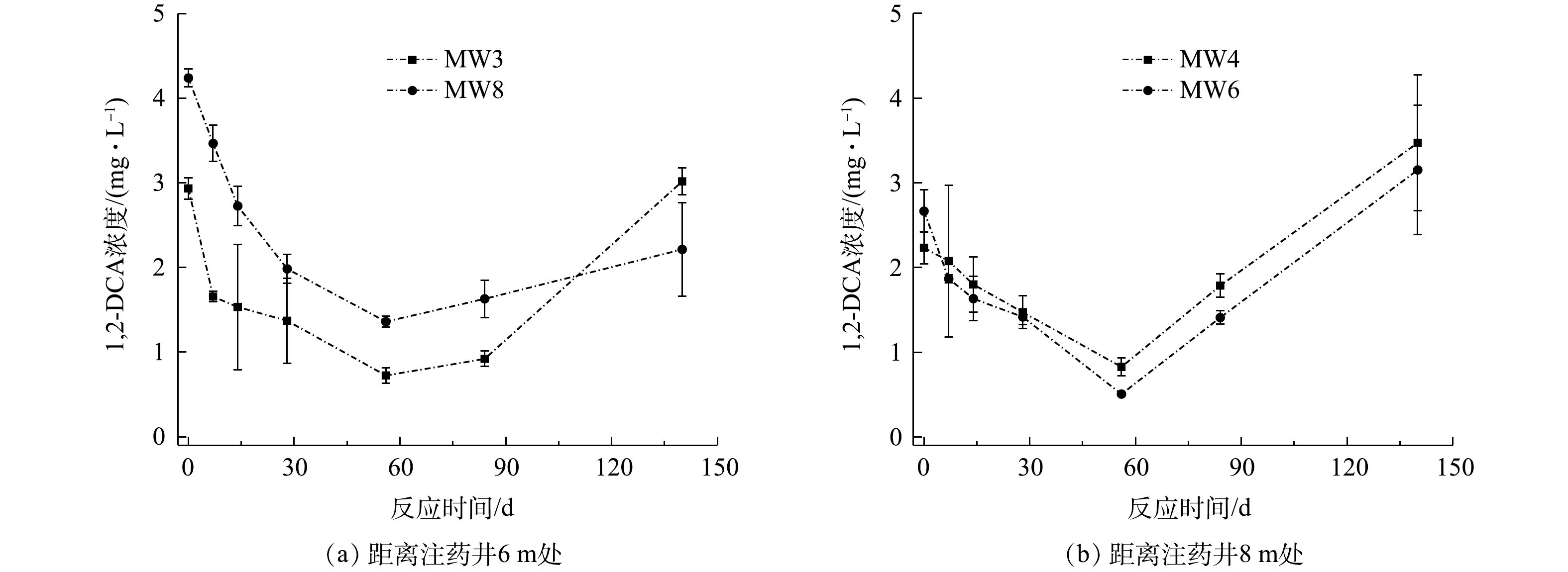
距离注药井6 m处监测井(MW3和MW8)和距离注药井8 m处监测井(MW4和MW6)中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度变化情况如图7所示。MW3、MW8、MW4和MW6中1,2-二氯乙烷初始浓度为2.93、4.24、2.23和2.67 mg·L−1,在注药后56 d内,监测井中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度稳定下降,在第56天,4个监测井中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度下降至最低值,分别为0.72、1.36、0.83和0.51 mg·L−1,与初始浓度相比,分别下降了53.34%、53.22%、33.98%和46.83%。注药84 d后,监测井中观测到1,2-二氯乙烷浓度开始回升,到实验结束时,MW3、MW8、MW4和MW6中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度分别为3.02、2.21、3.47和3.15 mg·L−1。
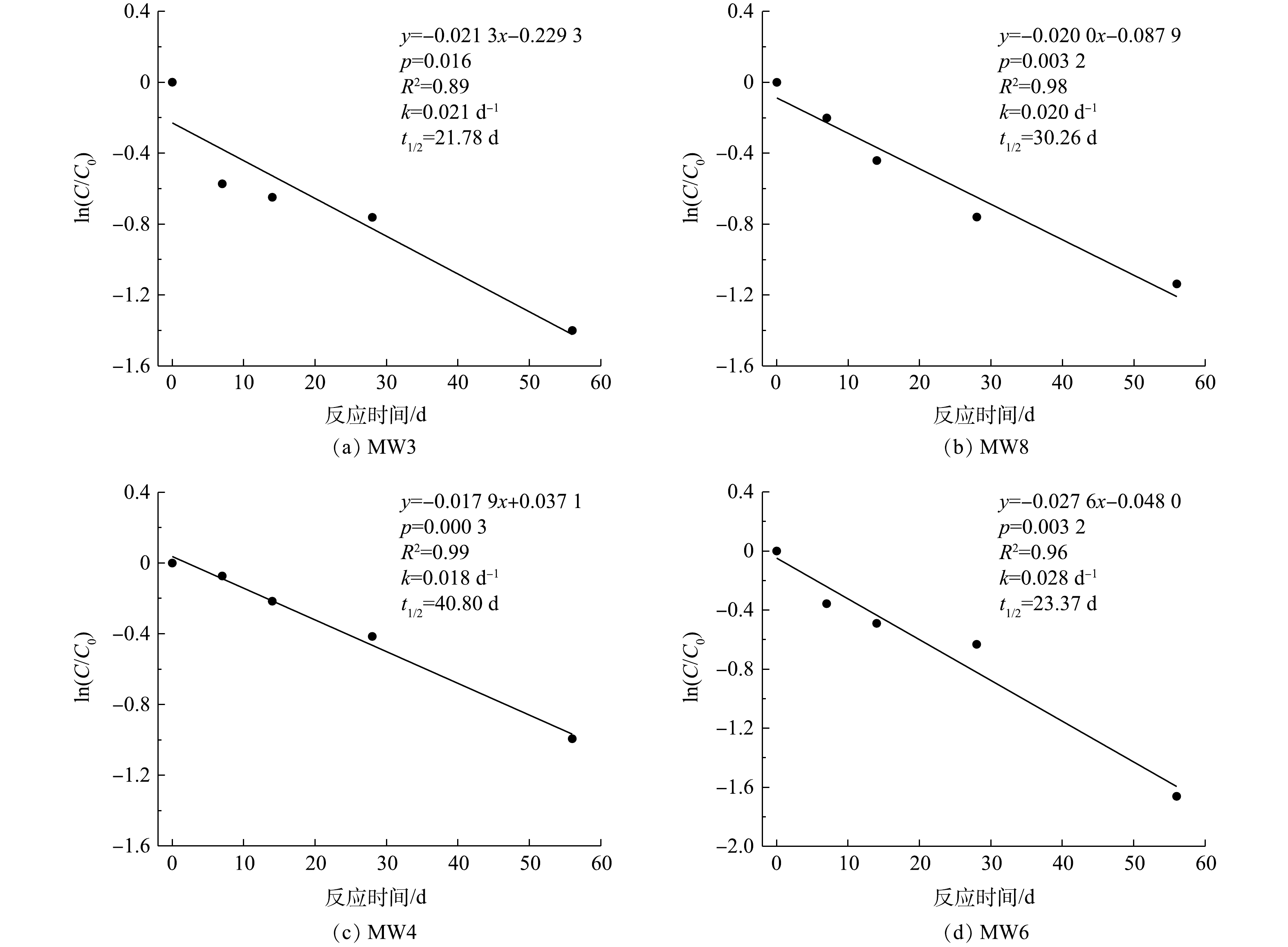
在注药后56 d内,对MW3、MW8、MW4和MW6中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度与其初始浓度比值的自然对数值-时间进行拟合,由图8可知,ln(C/C0)-t呈线性关系,地下水中1,2-二氯乙烷降解过程遵循准一级动力学方程(式(5))。
ln(C/C0)=−kt (5) 式中,k为反应速率常数,d−1;C为t时刻的反应物浓度,mg·L−1;C0为反应物初始浓度,mg·L−1;t为反应时间,d;t1/2为半衰期,d。
分析实验期间1,2-二氯乙烷浓度随时间变化规律,求解得到各监测井中1,2-二氯乙烷的反应速率常数和半衰期(平均值),碱活化过硫酸盐降解1,2-二氯乙烷反应速率常数为0.022 d−1,半衰期为29 d。
2.3 地下水修复效果
注入修复药剂后,实验区域含水层中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度分布变化情况如图9所示。注药后第7天,仅MW1、MW9和注药井修复达标(浓度低于场地修复目标值0.15 mg·L−1即为达标);第14天,MW1、MW2、MW5、MW9和注药井修复达标。注药后0~28 d,实验区域内地下水1,2-二氯乙烷污染物浓度总体呈下降趋势,实验区域内1,2-二氯乙烷浓度修复达标区域面积逐渐增大,这表明碱活化过硫酸盐对受1,2-二氯乙烷污染含水层有较好的修复效果。实验28 d后,实验区域地下水中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度开始回升,达标区域开始减小。其原因在于,实验区间注入修复药剂有限,当氧化药剂被完全消耗后,周边含水层未降解的污染物由于分子扩散作用向达标区补给,使修复达标区域的含水层重新被污染。
修复药剂在含水层中的迁移和扩散受含水层自身的非均质性和地下水的渗流特征控制,抽取地下水时也会对地下水流场产生严重干扰,从而间接影响修复药剂迁移[19]。本实验区域含水层为卵砾石层,渗透系数为7.89 m·d−1,透水性较好,修复药剂注入期间,受抽水的机械弥散作用影响,修复药剂随地下水渗流方向运移,污染物修复达标区域逐渐变为以注药点为中心,长轴方向与地下水渗流方向一致的近似椭圆形。但污染物修复达标范围有限,这是由于地下水水力坡度(0.36%~3.05%)较小以及修复药剂总量相对较少造成的[20]。
2.4 地下水中硫酸盐浓度和pH的变化
在注入氧化剂和活化剂后,地下水中硫酸盐浓度变化情况如图10(a)所示(图中列举了地下水主流向上监测井中硫酸盐浓度的变化)。在实验前,实验区域硫酸盐浓度为30.30~47.70 mg·L−1。MW1和MW2在注药后前28 d内,硫酸盐浓度持续上升,最高分别达到425 mg·L−1和408 mg·L−1;第28天后,硫酸盐浓度持续稳定下降,实验结束时,恢复至原浓度水平。MW3和MW4在注药后的第7天,硫酸盐浓度出现明显增长,分别达到102 mg·L−1和75.70 mg·L−1,与MW1和MW2中硫酸盐浓度峰值相比较小,之后呈下降趋势。过硫酸盐氧化过程中会产生了大量的硫酸盐,硫酸盐在过硫酸盐被完全消耗前会持续增加,在过硫酸盐被完全消耗之后,硫酸盐浓度呈下降趋势,这也反映了化学氧化作用的剧烈程度。这与吴圣华等[21]在采用过硫酸盐氧化处理汽油BTEX污染地下水时所得的结果类似。
碱活化过硫酸盐体系会引起地下水pH的变化。图10(b)所示是实验过程中地下水pH的变化情况。在注入氧化剂和活化剂前,实验区域地下水pH为4.93~5.57。MW1和MW2在注药后第7天,pH分别上升至10.90和12.08,为碱活化过硫酸盐创造较适宜的pH环境,之后总体呈下降趋势。MW3和MW4在注药后的28 d内pH有小幅度下降。这可能是由于实验期间注入过硫酸盐总量大于氢氧化钠总量,在水动力控制条件下,过硫酸盐自然扩散和随水力控制运移范围大于氢氧化钠,造成距离注药井相对较远的MW3和MW4中pH有一定程度下降。有研究[22]表明,过硫酸钠投加可对地下水环境造成一定的酸化效应。随着过硫酸盐消耗及周边地下水侧向补给,在实验结束时,监测井中pH恢复至原水平。LIANG等[23]认为,过硫酸盐的氧化作用较缓慢且温和,虽然反应过程中土壤pH会下降至2~4,但随着过硫酸盐的继续消耗,pH会逐渐回升,二次污染可控,故使用过硫酸盐原位修复有机污染土壤和地下水具有独特的优势和较好的应用前景。
过硫酸钠的化学氧化机理是:其溶解后形成的过硫酸盐
S2O82− SO−⋅4 SO2−4 3. 结论
1)实验区含水层渗透系数为7.89 m·d−1,导水系数为101 m2·d−1,在一维稳定流场中二维弥散条件下,含水层纵、横向弥散度αL和αT分别为0.89 m和0.089 m,地下水流速为3.85 m·d−1,水动力条件明显优于自然状态,通过水动力控制法干扰地下水流场可有效控制修复药剂在含水层中的扩散速度和影响范围。
2)注药后实验区污染物浓度整体呈下降趋势,在第14天,注药井4 m以内1,2-二氯乙烷浓度低于检出限,药剂效果在含水层中可保持28 d。碱活化过硫酸盐降解1,2-二氯乙烷反应速率常数为0.022 d−1,半衰期为29 d。在实验后期,因周边未修复区污染物向修复区扩散、补给,导致实验区地下水中1,2-二氯乙烷浓度出现回升。
3)实验过程中,实验区地下水中硫酸盐浓度先升高后下降,在140 d内恢复至原浓度水平,对实验场地二次污染影响较小。碱活化过硫酸盐在氯代烃类污染场地修复中具有广阔的应用前景。
-
表 1 泉水水化学特征
Table 1. Chemical characteristics of spring
泉水类型Spring type 特征值Eigenvalue 水化学/(mg·L−1)Hydrochemisty pH TDS/(mg·L−1) H2SiO3/(mg·L−1) Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− NO3− 岩溶泉水(n=67) 最大值 44.9 13.6 204 60.5 61.48 517 444.52 107 8.27 982.64 36.89 最小值 0.667 0.079 53.7 3.55 8.39 37.4 107.3 0.5 7.1 303.72 1.08 平均值 8.47 1.55 117.33 18.72 18.85 86.77 294.17 35.33 7.79 446.45 15.70 标准差 8.32 2.51 24.19 10.64 12.10 62.40 52.97 23.45 0.27 120.65 5.91 变异系数 0.98 1.62 0.21 0.57 0.64 0.72 0.18 0.66 0.03 0.27 0.38 裂隙泉水(n=33) 最大值 36.8 7.72 196 38.1 88.3 216 332.53 120 8.1 857.54 51.49 最小值 0.952 0.24 26.9 3.22 9.4 29.8 33.72 4.49 6.6 152.75 11.83 平均值 16.43 1.98 80.94 14.57 26.88 81.27 163.32 50.60 7.49 375.84 27.54 标准差 8.25 1.93 43.06 8.41 19.78 36.02 101.17 33.52 0.36 156.55 10.43 变异系数 0.50 0.97 0.53 0.58 0.74 0.44 0.62 0.66 0.05 0.42 0.38 全部泉水(n=100) 最大值 44.9 13.6 204 60.5 88.3 517 444.52 120 8.27 982.64 51.49 最小值 0.667 0.079 26.9 3.22 8.39 29.8 33.72 0.5 6.6 152.75 1.08 平均值 11.10 1.69 105.32 17.35 21.50 84.95 250.99 40.37 7.69 423.15 19.61 标准差 9.07 2.33 35.85 10.11 15.44 54.97 94.88 27.96 0.33 136.89 9.47 变异系数 0.82 1.38 0.34 0.58 0.72 0.65 0.38 0.69 0.04 0.32 0.48 表 2 泉水主要化学组分相关关系矩阵
Table 2. Correlation coefficients between major ionsin spring
岩溶泉水Karst spring TDS Ca2+ Mg2+ K+ Na+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− NO3− TDS 1 Ca2+ 0.849** 1 Mg2+ 0.764** 0.398** 1 K+ 0.200 0.069 0.117 1 Na+ 0.606** 0.308* 0.483** 0.390** 1 Cl− 0.650** 0.458** 0.463** 0.213 0.879** 1 SO42− 0.837** 0.644** 0.675** 0.055 0.373** 0.367** 1 HCO3− 0.426** 0.521** 0.422** −0.033 0.063 0.151 0.053 1 NO3− 0.566** 0.467** 0.310* 0.432** 0.619** 0.647** 0.204 0.099 1 裂隙泉水Fissure spring TDS Ca2+ Mg2+ K+ Na+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− NO3− TDS 1 Ca2+ 0.952** 1 Mg2+ 0.875** 0.818** 1 K+ 0.097 0.060 0.004 1 Na+ 0.426* 0.183 0.233 0.120 1 Cl− 0.654** 0.501** 0.589** −0.019 0.624** 1 SO42− 0.911** 0.842** 0.821** 0.014 0.422 0.613** 1 HCO3− 0.757** 0.879** 0.719** 0.118 −0.072 0.190 0.600** 1 NO3− 0.605** 0.421 0.460** 0.122 0.595** 0.546** 0.502** 0.054 1 *表示在0.05水平上显著相关;**表示在0.01水平上显著相关. *Indicates a significant correlation at the 0.05 level.**Indicates a significant correlation at the 0.01 level. -
[1] 张应华, 仵彦卿, 温小虎, 等. 环境同位素在水循环研究中的应用[J]. 水科学进展, 2006, 17(5): 738-747. ZHANG Y H, WU Y Q, WEN X H, et al. Application of environmental isotopes in water cycle[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2006, 17(5): 738-747 (in Chinese).
[2] 胡玥, 刘传琨, 卢粤晗, 等. 环境同位素在黑河流域水循环研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(10): 1158-1166. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.10.1158 HU Y, LIU C K, LU Y H, et al. Application of environmental isotopes in understanding hydrological processes of the Heihe River Basin[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(10): 1158-1166 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.10.1158
[3] 高宗军, 田红, 张春荣. 水环境评价概述[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 26(1): 20-22,48. GAO Z J, TIAN H, ZHANG C R. Outline of water environment evaluation[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2007, 26(1): 20-22,48 (in Chinese).
[4] 孙英, 周金龙, 魏兴, 等. 巴楚县平原区地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(11): 2601-2609. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018121002 SUN Y, ZHOU J L, WEI X, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and cause analysis of groundwater in the plain area of Bachu County[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(11): 2601-2609 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018121002
[5] 袁利, 蒋少杰, 汪定圣, 等. 宿州市城区地下水化学特征及成因机制研究[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(4): 1555-1566. YUAN L, JIANG S J, WANG D S, et al. Study on hydrochemical characteristics and formation of groundwater in urban district of Suzhou[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(4): 1555-1566 (in Chinese).
[6] 韩朝辉, 王郅睿, 田辉, 等. 汉中盆地地下水水化学特征及其成因研究[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 263-273. HAN C H, WANG Z R, TIAN H, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of groundwater in the Hanzhong Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 263-273 (in Chinese).
[7] 陈晨, 高宗军, 李伟, 等. 泰莱盆地地下水化学特征及其控制因素[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(6): 1339-1347. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018090504 CHEN C, GAO Z J, LI W, et al. Characteristics and possible factors of hydrochemistry in the groundwater in Tailai Basin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(6): 1339-1347 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018090504
[8] 冯建国, 鲁统民, 高宗军, 等. 新泰市地下水水化学特征及成因探讨[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 39(1): 11-20. FENG J G, LU T M, GAO Z J, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and causes of groundwater in Xintai city[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 39(1): 11-20 (in Chinese).
[9] 杨楠, 苏春利, 曾邯斌, 等. 基于水化学和氢氧同位素的兴隆县地下水演化过程研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(6): 154-162. YANG N, SU C L, ZENG H B, et al. Evolutional processes of groundwater in Xinglong County based on hydrochemistry and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(6): 154-162 (in Chinese).
[10] 童辉, 高宗军, 高法生, 等. 沂河流域地下水水化学特征及水质评价[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(11): 3443-3454. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020122802 TONG H, GAO Z J, GAO F S, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of groundwater in the west of Yi River Basin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(11): 3443-3454 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020122802
[11] 高峰, 王振涛, 靳丰山, 等. 山东省莱芜盆地岩溶塌陷风险性评价[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2016, 26(增刊2): 359-362. GAO F, WANG Z T, JIN F S, et al. Risk assessment of karst collapse in the Laiwu of Shandong Province[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2016, 26(Sup 2): 359-362 (in Chinese).
[12] 李波, 王金晓, 吴璇, 等. 山东莱芜盆地东部水文地质条件及富水块段特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(5): 637-649. doi: 10.11932/karst2020y34 LI B, WANG J X, WU X, et al. Hydrogeological conditions and characteristics of water-rich sections in the eastern Laiwu Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(5): 637-649 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11932/karst2020y34
[13] 段壮, 高明波, 高继雷, 等. 山东莱芜张家洼铁矿床金云母40Ar/39Ar定年及其对成矿构造背景的启示[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(4): 1279-1296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.04.010 DUAN Z, GAO M B, GAO J L, et al. Phlogopite 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Zhangjiawa iron deposit, Laiwu district, Shandong Province: Implications for regional iron skarn mineralization of North China Craton[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(4): 1279-1296 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.04.010
[14] 王超, 张立川, 王应强, 等. 莱芜地区地下水污染研究[J]. 地下水, 2021, 43(6): 21-24,229. WANG C, ZHANG L C, WANG Y Q, et al. Study on groundwater pollution in Laiwu Region[J]. Ground Water, 2021, 43(6): 21-24,229 (in Chinese).
[15] 马明, 高继雷, 高明波, 等. 鲁西莱芜地区地球物理特征及富铁矿床勘查模型建立[J]. 华北地震科学, 2020, 38(2): 13-20. MA M, GAO J L, GAO M B, et al. Geophysical characteristics of Laiwu Area in western Shandong Province and establishment of exploration model for iron rich deposits[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 2020, 38(2): 13-20 (in Chinese).
[16] 刘书锋. 山东莱芜地区中生代侵入杂岩特征与成矿关系[J]. 地质学刊, 2020, 44(增刊1): 34-47. LIU S F. Characteristics of the Mesozoic intrusive complexes and their relation to metallogeny in Laiwu Area, Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Geology, 2020, 44(Sup 1): 34-47 (in Chinese).
[17] 李波, 王金晓, 赵无忌, 等. 莱芜盆地牟汶河流域水体同位素特征与分析[J]. 山东国土资源, 2019, 35(7): 58-63. doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2019.07.009 LI B, WANG J X, ZHAO W J, et al. Analysis on isotopic characteristics of water body of Muwen river basin in Laiwu Basin[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2019, 35(7): 58-63 (in Chinese). doi: 10.12128/j.issn.1672-6979.2019.07.009
[18] 刘元晴, 周乐, 李伟, 等. 山东莱芜盆地西北缘古近系半固结含水岩组的特征及其成因[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(6): 737-748. LIU Y Q, ZHOU L, LI W, et al. The characteristics and genetic analysis of the Paleogene semi-consolidated water-bearing formation on the northwestern margin of Laiwu Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(6): 737-748 (in Chinese).
[19] 马振民, 刘立才, 陈鸿汉, 等. 山东泰安岩溶水系统地下水化学环境演化[J]. 现代地质, 2002, 16(4): 423-428. MA Z M, LIU L C, CHEN H H, et al. Hydrochemical environmental evolution of Karst water system in Tai’an, Shandong Province[J]. Geoscience, 2002, 16(4): 423-428 (in Chinese).
[20] 孙逊, 王克红, 孙启堂, 等. 鲁中南山区岩溶裂隙水富水带类型及分布特征[J]. 工程勘察, 2010, 38(2): 52-56. SUN X, WANG K H, SUN Q T, et al. Types and distribution of Karst fissure water in central and southern Shangdong Province[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2010, 38(2): 52-56 (in Chinese).
[21] 聂振龙, 陈宗宇, 程旭学, 等. 黑河干流浅层地下水与地表水相互转化的水化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2005, 35(1): 48-53. NIE Z L, CHEN Z Y, CHENG X X, et al. The chemical information of the interaction of unconfined groundwater and surface water along the Heihe River, northwestern China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2005, 35(1): 48-53 (in Chinese).
[22] 汪敬忠, 吴敬禄, 曾海鳌, 等. 内蒙古河套平原水体同位素及水化学特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2013, 35(4): 104-112. WANG J Z, WU J L, ZENG H A, et al. Characteristics of water isotope and hydrochemistry in Hetao Plain of Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2013, 35(4): 104-112 (in Chinese).
[23] 田原, 余成群, 雒昆利, 等. 西藏地区天然水的水化学性质和元素特征[J]. 地理学报, 2014, 69(7): 969-982. TIAN Y, YU C Q, LUO K L, et al. Water chemical properties and the element characteristics of natural water in Tibet, China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2014, 69(7): 969-982 (in Chinese).
[24] REN C B, ZHANG Q Q. Groundwater chemical characteristics and controlling factors in a region of Northern China with intensive human activity[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(23): 9126. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17239126 [25] ZHOU P P, WANG Z M, ZHANG J Y, et al. Study on the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater along the Taklimakan Desert Highway[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(20): 1378. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6204-2 [26] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. LIANG X, ZHANG J W, LAN K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33 (in Chinese).
[27] 李贵恒, 冯建国, 鲁统民, 等. 泰莱盆地地下水水化学特征及水质评价[J]. 水电能源科学, 2019, 37(4): 52-55,121. LI G H, FENG J G, LU T M, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of groundwater in Tailai Basin[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2019, 37(4): 52-55,121 (in Chinese).
[28] 董维红, 孟莹, 王雨山, 等. 三江平原富锦地区浅层地下水水化学特征及其形成作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(2): 542-553. DONG W H, MENG Y, WANG Y S, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation of the shallow groundwater in Fujin, Sanjiang Plain[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(2): 542-553 (in Chinese).
[29] 高建飞, 丁悌平, 罗续荣, 等. 黄河水氢、氧同位素组成的空间变化特征及其环境意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(4): 596-602. GAO J F, DING T P, LUO X R, et al. δD and δ18O variations of water in the Yellow River and its environmental significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(4): 596-602 (in Chinese).
[30] 高宗军, 万志澎, 贺可强, 等. 大汶河流域中上游地区岩溶地下水水化学特征及其控制因素分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022(5): 264-272. GAO Z J, WAN Z P, HE K Q, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of Karst groundwater in middle and upper reaches of Dawen River Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022(5): 264-272 (in Chinese).
[31] 王攀, 靳孟贵, 路东臣. 河南省永城市浅层地下水化学特征及形成机制[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(6): 2232-2244. WANG P, JIN M G, LU D C. Hydrogeochemistry characteristics and formation mechanismof shallow groundwater in Yongcheng city, Henan province[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(6): 2232-2244 (in Chinese).
[32] 朱秉启, 杨小平. 塔克拉玛干沙漠天然水体的化学特征及其成因[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(13): 1561-1566. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.13.013 ZHU B Q, YANG X P. Chemical characteristics and causes of natural water bodies in Taklimakan Desert[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(13): 1561-1566 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.13.013
[33] 吴璇, 宋一心, 王金晓, 等. 山东省柴汶河上游地区地下水化学特征分析[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(7): 2125-2134. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020022701 WU X, SONG Y X, WANG J X, et al. Groundwater hydrogeochemical characteristics in the up reaches of Chaiwen River, Shandong Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(7): 2125-2134 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020022701
[34] ZHU G F, SU Y H, HUANG C L, et al. Hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Heihe River Basin, Northwest China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010, 60(1): 139-153. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0175-5 [35] 李舒, 杨佳雪, 李小倩, 等. 地下水化学组成的时空聚类分析与多级嵌套水流系统识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 309-318. LI S, YANG J X, LI X Q, et al. Lumped cluster analysis for understanding spatial and temporal patterns of groundwater geochemistry and hierarchically nested flow systems[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 309-318 (in Chinese).
[36] FAN B L, ZHAO Z Q, TAO F X, et al. Characteristics of carbonate, evaporite and silicate weathering in Huanghe River Basin: A comparison among the upstream, midstream and downstream[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 96: 17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.005 -






 下载:
下载: