-
重金属具有蓄积性、持久性以及高毒性等特点,且拥有广泛的来源,主要有河流径流、城镇污水、工业废水以及近海养殖等[1 − 4],现已成为海洋环境中备受关注的重要污染物之一[5]. 作为各种污染物主要的汇[6 − 8],沉积物富集了大量的重金属,并且受海水环境变化的影响,重金属会从沉积物中释放至海水中,不仅影响海水水质,而且易于在水生生物体内富集,通过食物链转移至捕食者或者人体,对人体健康和海洋生态系统造成长期的影响[9 − 10]. 海湾是链接陆地和海洋的重要界面,受到人类活动影响剧烈,是研究重金属污染物发生沉降、输运、转化和埋藏等生物地球化学过程的重要环境. 因此,对海湾沉积物重金属开展研究,分析海洋重金属的污染程度,对海湾环境生态风险评价具有重要的意义[11].
位于惠州市南部的大亚湾,由于海产资源丰富,已成为是中国南方重要的海湾之一[12]. 位于广东省南部的红海湾,凭借丰富的海洋渔业资源,使得海水养殖业发展迅速,已被列为汕尾市经济开发区,同时也是南海半封闭型海湾规模化养殖试验区[13]. 然而,近几十年来,随着这两大海湾区域经济的发展,海洋生态环境状况已遭受人类活动所带来的不同程度的危害[14 − 15],城镇生活污水排放、工业企业污染排放、近海养殖等带来的重金属污染成为该区域面临的主要环境问题[16 − 18]. 例如,杨文超等[18 − 19]对2010—2018年期间大亚湾内表层沉积物中的5类重金属进行研究,发现重金属高值区均集中在石化区一带,推测重金属的主要来源可能是沿岸水产养殖和工业企业排放. 唐得昊等[17]对大亚湾2015年采集的23个表层沉积物种5类重金属分析结果显示,重金属总体污染程度达到了中等污染水平,汞(Hg)是潜在风险最高的. 孙钦帮等[15]2015年对红海湾近岸表层沉积物中7类重金属的分析,发现海域沉积物重金属 Cu、Pb、Zn、Cr和As的主要来源为工业废水与城市污水. 尽管前人对该区域重金属开展了不少研究,但是一方面随着经济发展和人口增加会加剧海洋沉积物污染程度,另外一方面,随着国民海洋环保理念不断增强和国家层面海洋环保政策不断完善,使得已有的报道不能充分反映大亚湾和红海湾沉积物中重金属的生态风险状况.
本研究以大亚湾和红海湾为研究靶区域,采集表层沉积物并分析其中7种重金属含量,分别为砷(As)、锌(Zn)、镉(Cd)、铜(Cu)、铬(Cr)、汞(Hg)和铅(Pb),研究了重金属的空间分布,并推断其潜在来源. 此外,结合潜在生态风险评价法,对沉积物中重金属的污染程度进行评价,以期为改善大亚湾和红海湾海洋环境质量、建立美丽海湾建设提供科学理论依据.
-
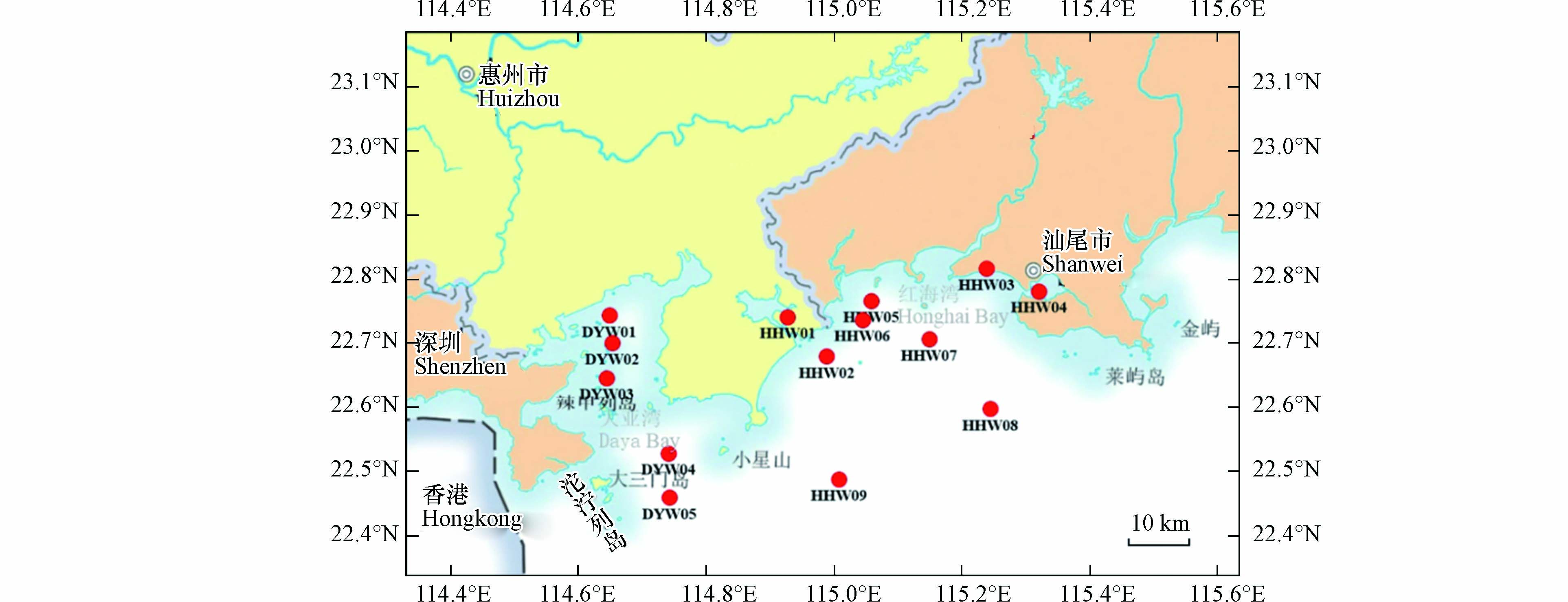
研究区域位于大亚湾和红海湾近岸(图1),大亚湾和红海湾均属于半封闭海湾,水动力条件整体偏弱. 相对于大亚湾,红海湾更开阔,与近海水体交换面积更大,使得红海湾湾内污染物相对难保存,人类活动产生的污染物相对更容易被运移.
2021年9月,利用抓斗采泥器,分别在大亚湾(DYW01—DYW05)和红海湾海域(HHW01—HHW09)采集了14个表层沉积物,详细站位见图1. 将各站位沉积物表层未扰动的0—2 cm沉积物分别放入洁净聚乙烯瓶中,贴上提前打印好的标签,之后将样品运回实验室−20 ℃冻存. 严格按照《海洋监测规范》(GB17378—2007) 要求,采集、保存和运输沉积物样品.
-
本研究严格按照《海洋监测规范第 5 部分:沉积物分析》(GB 17378.5-2007)开展实验,对沉积物样品进行前处理及分析检测. 前处理步骤如下:取一部分沉积物样品置于洁净的环境,在室温下自然干燥,筛除沉积物中的杂质(如石头等大颗粒物),用研钵研碎沉积物,过100目网筛,待测重金属含量;另一部分沉积物样品进行冷冻干燥,待测总有机碳.
重金属测定方法:取一定量的前处理好的沉积物样品,加入到HCl-HNO3-HF-HClO4中,用石墨消解仪进行消解、定容. 样品中Hg和As采用原子荧光光谱法(原子荧光光度计BAF-2000),Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(电感耦合等离子体质谱仪ICP-MS). Hg、As、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb的检测限分别为0.002、0.01、0.4 g、0.3、0.6、0.03 、2.0 mg·kg−1.
总有机碳测定方法:按照海洋监测规范第5部分沉积物分析(有机碳重铬酸钾氧化-还原容量法)(GB 17378.5-2007),有机碳含量的分析采用的是重铬酸钾氧化硫酸亚铁滴定法,检出限为0.01%.
-
按照《海洋沉积质量标准》(GB 18668-2002),将沉积物分为三类,分别是第一类、第二类和第三类沉积物(表1),对砷、锌、镉、铜、铬、汞和铅开展单因子污染评价分析[3],计算如式(1)。
其中,重金属i的污染指数用Cim表示;实测浓度(mg·kg−1)用Ci表示,Cin是沉积物重金属评价标准值. 当沉积物判定为污染程度低时,Cim是≤1,其含量满足第一类标准;当沉积物重金属含量超过第一类标准评价时,Cim>1;当沉积物重金属为中等污染程度时,1<Cim≤3;当沉积物重金属为重污染程度时,3<Cim≤6;当沉积物重金属为严重污染程度时,Cim>6.
-
根据瑞典科学家 Hakanson 提出的潜在生态风险指数法,本研究对沉积物开展重金属污染研究,并推断其潜在生态风险评价[20]. 结合不同地域环境背景重金属差异,Hakanson法依据沉积物中重金属浓度及毒性响应特征和污染物类型,不仅能够实现对某一特定环境下单一重金属对环境的影响的评估,而且能实现对多种重金属对环境影响的综合效应的评价,从而实现对重金属的潜在生态风险程度划分的定量分析. 因此,该方法在海洋沉积物重金属风险评价中广泛应用[3, 17, 19]. 具体公示如(2)和(3):
其中,Cim代表某种重金属i的污染指数;Cf代表某种重金属的综合污染系数;Pi代表沉积物重金属总体污染指数;Eir表示某一重金属i的潜在生态风险指数;RI是潜在生态风险指数;Cin为沉积物中重金属i的参考值(mg·kg−1). 重金属背景值往往具有较强区域特征,受多种因子影响,一方面受生物因子干扰(如生物活动),另一方面受非生物过程影响(如水文地质)等多种外在因素的影响. 本研究采用广东省沿海沉积物含量为背景值,As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Pb 和 Zn含量分别为13、0.14、106、15.5、0.122、30、63.3 mg·kg−1 [21 − 22];沉积物中某种重金属i的毒性系数使用Tir来表示,代表该重金属毒性水平及生物对该重金属污染的敏感度,本研究标准化重金属的毒性系数是采用Hakanson制定,汞、铅、砷、镉、铬、铜和锌毒性系数分别为40、5、10、30、2、5和5(表2).
-
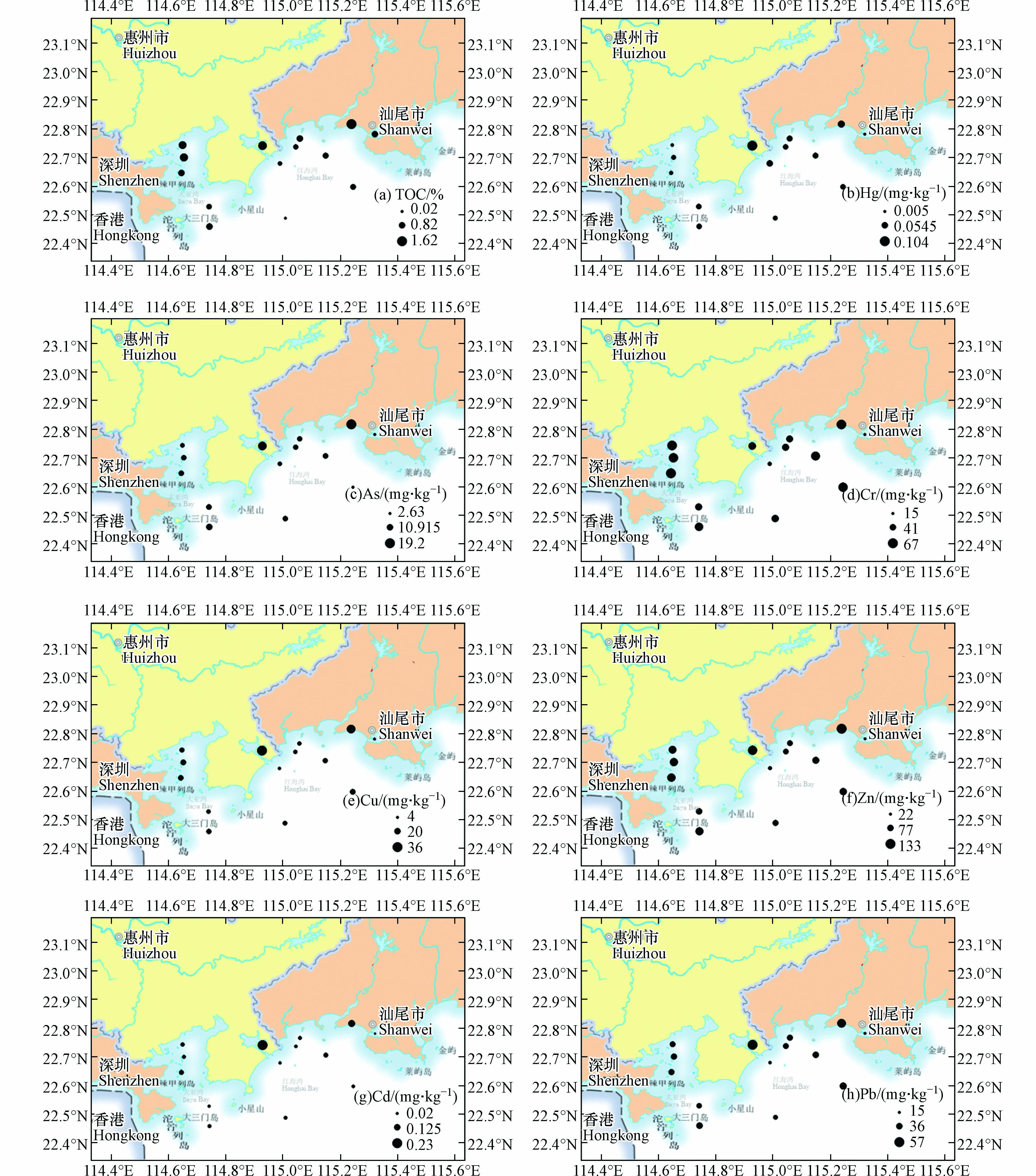
大亚湾和红海湾7种重金属含量及分布特征见图2和表3. 大亚湾Hg、As、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd 和 Pb含量分别为0.01—0.04、6.59—10.9、45.9—67.4、10.9—16.6、78.1—109.0、0.03—0.08和30.2—36.6 mg·kg−1, 平均值分别为0.03、8.71、59.78、14.2、99.4、0.05、33.4 mg·kg−1, 这与杨文超等[18 − 19]和唐得昊等[17]研究者的结果基本相当. 大亚湾Hg、As含量从近岸到远岸略有增加,Cr、Cu和Zn含量从近岸到远岸呈降低趋势,Cd和Pb在空间分布上没有差异. 在大亚湾内,这7 种重金属含量在空间上不同的分布规律,说明不同重金属含量在地域上存在差异,这可能是由于受沉积物的来源和输运过程等影响. 与文献中2015年和2018年沉积物结果对比[18-19],发现近年来Hg、Cr和Cu含量明显降低,这可能与“十三五”期间国家层面推动实施一系列海洋环境保护政策有关,改善了海洋环境质量,而As和Zn含量略有波动增大,Pb没有明显变化,这3种重金属含量均满足第I类沉积物标准 (表3),表明表层沉积物污染程度低,属于正常波动.
红海湾Hg、As、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd 和 Pb含量分别为0.005—0.104、2.63—19.2、14.4—65.2、3.4—36.1、21.7—133.0、0—0.23、14.5—57 mg·kg−1,平均值分别为0.049、9.03、46.29、15.4、77.7、0.07、34.1 mg·kg−1, 与孙钦帮等[15]的结果基本相当. 除重金属Cr之外,其他重金属含量分布特征为远岸明显低于近岸,近岸的HHW01和HHW03站位重金属含量较高,可能受人类活动影响显著,远岸站位可能与南海水体交换频繁,重金属较难保存,且外海陆源污染较少. 与文献中2015年沉积物结果对比,发现本研究红海湾重金属含量明显增大(表3),表明近年来,红海湾重金属呈现一定程度富集.
整体而言,红海湾重金属Hg、As、Cu、Cd和Pb含量明显高于大亚湾的,而红海湾的Cr和Zn含量低于大亚湾的,可能由于沉积物重金属具有不同来源和不同输运过程,造成了这种空间分布差异. 对比其他区域的研究(表3),本研究中两个湾区沉积物中的重金属含量明显低于深圳湾、大鹏湾和珠江口,也低于广东省近岸沉积物重金属含量,然而却高于北部湾的重金属含量. 不同海湾重金属含量的差异,与海湾的经济发展有密切关系,经济发达的海湾重金属含量相对高,经济落后的湾区重金属含量相对较低,这与张起源等[27]研究结果一致.
-
由于TOC对重金属具有极强的富集和络合作用,研究者常利用TOC含量与重金属含量之间的相关性分析,对重金属的来源进行初步判断[3, 17-18]. 本研究,大亚湾沉积物中TOC含量为0.63%—1.21%(均值为0.93%),红海湾沉积物中的为0.39%—1.62%(均值为0.87%),将大亚湾和红海湾沉积物中7种重金属含量与沉积物TOC含量进行了相关性分析,具体结果如下所示(表4).
沉积物中TOC含量与As、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb含量分别具有显著正相关关系,表明沉积物中TOC的含量会影响这些重金属元素的富集;然而Hg和Cr与TOC没有显著相关关系,表明这两种重金属在沉积物富集受TOC影响较小,可能受人为输入以及其自身的赋存状态影响大. 由此可见,TOC含量影响了部分重金属的分布. 其中,Cu与TOC的相关系数最大,这表明了Cu更易与TOC形成络合物,富集在沉积物中.
此外,除了Cr分别与Hg、As、Cd没有显著相关性外,其他重金属两两之间均具有显著相关性,推测沉积物中不同重金属之间可能具有同源性,也可能代表了重金属之间具有类似的沉积物输运过程以及相似的空间分布规律;而Cr的来源和自身赋存状态可能与其他重金属有所不同. 相比其他金属,Cr元素来源可能受人为输入的影响较大. 此外,与其他重金属相比,在沉积物中Cr元素主要以残渣态形式存在,主要分布在原生和次生硅酸盐矿物晶格中, 性质稳定, 难以迁移和被生物利用.
-
对大亚湾和红海湾中沉积物重金属含量进行单因子分析,发现大亚湾内所有沉积物的重金属污染因子均<1,表明污染程度低,满足第I类沉积物标准;然而红海湾内,仅有HHW01站位Cu的污染因子超过1,属于中度污染程度,其余站位重金属污染因子均小于1,污染程度低,满足第I类沉积物标准. 大亚湾表层沉积物重金属单因子污染指数在0.06—0.84之间,平均值为0.44±0.23;红海湾的为0.00—1.03之间,平均值为0.42±0.26. 综合大亚湾和红海湾的结果,重金属污染指数平均值大小为Cr>Zn>Pb>As>Cu>Pb>Cd,推测Cr、Zn和Pb是湾区沉积物中主要的环境污染因子. 大亚湾的综合污染指数(Cf)平均值为3.07±0.26,而红海湾Cf平均值为2.95±1.33,其中红海湾近岸的HHW01和HHW03站位的Cf值较高. 除了HHW01站位Cf高于5,属于中等污染水平外,其余站位均低于5,污染较低.
-
评价本研究中两个湾区重金属潜在生态风险,获得了2项生态风险指标(表5),分别是单个重金属潜在生态风险指数和综合生态风险指数.
大亚湾Hg、As、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd 和 Pb的潜在风险系数平均值为6.70、11.6、1.13、4.59、20.2、5.56和1.57,表明重金属潜在生态风险水平较低,相对而言,Hg潜在风险程度最高,其次是Cd和As.
红海湾Hg、As、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd 和 Pb的潜在风险系数平均值为6.95、15.7、0.87、4.97、31.9、5.69和1.23,表明重金属潜在生态风险水平较低,与大亚湾重金属的风险水平相同. 其中,红海湾HHW01站位Cd和Hg的潜在风险系数分别为49.3和68.2,属于中等危害程度.
通过对红海湾和大亚湾的重金属综合潜在生态风险指数计算,发现两个湾区的指数均<150,属于低等潜在风险水平. 以上研究表明,随着我国不断加强海洋生态环境治理,已经取得较为理想的成效,近年来沉积物污染程度有降低的趋势. 但是,随着大亚湾和红海湾经济区工业化和城市化的不断发展,以及人口的不断聚集,该区域污染程度和潜在生态风险程度未来可能还会增大,仍需要继续加强监管.
-
1)大亚湾Hg、As含量近岸低于远岸,Cr、Cu和Zn含量近岸高于远岸,Cd和Pb近岸和远岸相差不大. 除重金属Cr之外,红海湾其他重金属含量近岸明显高于远岸. 这表明大亚湾重金属来源可能较为复杂,而红海湾重金属来源较为一致,主要来自于陆源输入.
2)红海湾重金属Hg、As、Cu、Cd和Pb含量明显高于大亚湾的,而红海湾的Cr和Zn含量低于大亚湾的. 与历史数据相比,大亚湾近年来Hg、Cr和Cu含量明显降低,而As和Zn含量有增大的趋势,Pb没有明显变化,而红海湾重金属有明显富集. 与其他区域相比,大亚湾和红海湾沉积物中重金属含量处于较低水平.
3)大亚湾和红海湾沉积物中TOC与As、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb呈良好的线性正相关关系,揭示了TOC含量影响了这些重金属元素在沉积物中的富集;然而Hg和Cr与TOC没有显著相关关系,表明这两种重金属在沉积物富集受TOC影响较小,这可能与该2种元素自身的赋存状态有关.
4)红海湾和大亚湾重金属综合潜在生态风险分析显示,该区域低等潜在风险水平. 但是红海湾局部近岸站位Cd和Hg的潜在风险系数较高,属于中等危害程度.
广东省大亚湾和红海湾表层沉积物重金属分布特征及风险评价
Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal sediments in Daya Bay and Honghai Bay of Guangdong Province
-
摘要: 2021年夏季采集了大亚湾和红海湾表层沉积物样品,分析了沉积物中铜(Cu)、砷(As)、铬(Cr)、镉(Cd)、汞(Hg)、铅(Pb)和锌(Zn)含量,探讨了重金属分布及污染特征,重金属之间及与总有机碳(TOC)的相关关系,并评价了重金属的总体污染状况和潜在生态风险. 结果显示,大亚湾Hg、As、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd 和 Pb含量平均值分别为0.03、8.71、59.8、14.2、99.4、0.05、33.4 mg·kg−1,红海湾Hg、As、Cr、Cu、Zn、Cd 和 Pb含量平均值分别为0.05、9.03、46.3、15.4、77.7、0.07、34.1 mg·kg−1. 大亚湾Hg、As含量近岸低于远岸,Cr、Cu和Zn含量近岸高于远岸,Cd和Pb近岸和远岸相差不大. 除重金属Cr之外,红海湾其他重金属含量近岸明显高于远岸. 除Hg和Cr与TOC无显著相关性,沉积物中As、Cu、Zn、Cd和Pb与TOC呈显著正相关性. 大亚湾和红海湾沉积物重金属,单因子污染影响程度依次为Cr>Zn>Pb>As>Cu>Pb>Cd,总体污染程度很低. 基于总金属综合潜在风险评价,大亚湾和红海湾沉积物的风险较低,生态危害影响依次为,Hg>Cd>As>Pb>Cu>Zn>Cr.Abstract: In the summer of 2021, surface sediment samples were collected from Daya Bay and Honghai Bay. The concentrations of Cu, As, Cr, Cd, Hg, Pb and Zn in the sediments were analyzed to investigate the distribution and pollution characteristics of heavy metals. The relationships between the heavy metals and total organic carbon (TOC) were also examined, and an assessment of the overall pollution status and potential ecological hazards of the heavy metals was conducted. The results showed that the average concentrations of Hg, As, Cr, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in Daya Bay sediments were 0.03, 8.71, 59.78, 14.2, 99.4, 0.05, and 33.4 mg·kg−1, respectively. In Honghai Bay sediments, the average concentrations of Hg, As, Cr, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb were 0.05, 9.03, 46.29, 15.4, 77.7, 0.07, and 34.1 mg·kg−1, respectively. The concentrations of Hg and As were lower near the coast than offshore in Daya Bay, while the concentrations of Cr, Cu, and Zn were higher near the coast than offshore. The difference in Cd and Pb concentrations between nearshore and offshore areas was not significant. In Honghai Bay, except for Cr, the concentrations of other heavy metals were significantly higher near the coast than offshore. Except for Hg and Cr, there was a significantly positive correlation between the concentrations of As, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, and TOC in the sediments. The single factor pollution degree of heavy metals in Daya Bay and Honghai Bay sediment was ranked as Cr>Zn>Pb>As>Cu>Pb>Cd, indicating a low pollution status. Based on the comprehensive potential risk assessment of total metals, the risks associated with the sediments in Daya Bay and Honghai Bay were low, with the ecological hazards ranked as Hg>Cd>As>Pb>Cu>Zn>Cr.
-
Key words:
- the Daya Bay and Honghai Bay /
- sediment /
- heavy metals /
- ecological risk assessment.
-
表 1 我国海洋沉积物中重金属含量的标准值
Table 1. The standard values of heavy metals in marine sediments of China
指标Index 海洋沉积物质量标准值/( mg·kg−1)Standard value of marine sediment As Cd Cr Cu Hg Pb Zn 第Ⅰ类 Class Ⅰ 20 0.5 80 35 0.2 60 150 第Ⅱ类 Class Ⅱ 65 1.5 150 100 0.5 130 350 第Ⅲ类 Class Ⅲ 93 5 270 200 1 250 600 表 2 沉积物中重金属污染程度及潜在生态危害程度分类
Table 2. Contaminant grades and potential ecological hazard levels of heavy metals in sediment
Eir 单个重金属潜在生态危害程度Potential ecological hazard of single metal RI 重金属总体潜在生态危害程度Overall potential ecological hazard of metals ≤50 低等 ≤150 低等 40—80 中等 150—300 中等 80—160 较重 300—600 较重 160—320 重度 600—1200 重度 >320 极严重 >1200 极严重 表 3 大亚湾和红海湾沉积物中重金属含量及其他区域对比(mg·kg−1)
Table 3. Comparison of heavy metals in surface sediments of Daya Bay, Honghai Bay and other bays(mg·kg−1)
区域Zone 数据统计Data statistics 汞(Hg) 砷(As) 铬(Cr) 铜(Cu) 锌(Zn) 镉(Cd) 铅(Pb) 采样时间 Sampling time 参考文献Reference 大亚湾Daya Bay 最小值 0.01 6.59 45.9 10.9 78.1 0.03 30.2 2021.09 本研究 最大值 0.04 10.9 67.4 16.6 109 0.08 36.6 平均值 0.03 8.71 59.78 14.2 99.4 0.05 33.4 标准偏差 0.01 1.38 7.91 2.0 11.1 0.02 2.10 I 类沉积物数量 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 红海湾Honghai Bay 最小值 0.005 2.63 14.4 3.4 21.7 0.00 14.5 最大值 0.104 19.2 65.2 36.1 133 0.23 57.0 平均值 0.049 9.03 46.3 15.4 77.7 0.07 34.1 标准偏差 0.025 5.19 16.2 10.3 33.8 0.07 13.1 1类沉积物数量 9 9 9 8 9 9 9 大亚湾 Daya Bay 平均值 0.04 7.35 — 18.9 83.1 — 33.2 2018.12 [18 − 19] 大亚湾 Daya Bay 平均值 0.12 6.78 — 22.8 81.9 — 31.7 2015.01 [18 − 19] 大亚湾 Daya Bay 平均值 0.10 43.1 23.6 88.6 — 33.2 2015.10 [17] 红海湾 Honghai Bay 平均值 0.07 7.97 15.32 6.29 57.9 0.03 25.4 2015.05 [15] 深圳湾 Shenzhen Bay 平均值 — 23.2 — 79.3 307 2.26 74.5 2012.11 [23] 大鹏湾 Dapeng Bay 平均值 0.05 — 63.6 15.7 87.1 — 35.9 1998—2006 [24] 珠江口 Pearl River Estuary 平均值 — — — 348 383 1.72 103 2007.07 [25] 广东省近岸Coast of Guangdong Province 平均值 0.13 20.8 — 43.8 140 0.38 44.3 2008.01 [26] 北部湾Beibu Gulf 平均值 0.03 3.73 — 11.2 27.8 0.06 18.9 2018.08 [3] “—”:没有数据. “—”: No data. 表 4 大亚湾和红海湾沉积物重金属之间及与TOC之间的相关分析
Table 4. Correlation between heavy metals and TOC in sediments of Daya Bay and Honghai Bay
TOC 汞 砷 铬 铜 锌 镉 铅 TOC 1 汞 0.31 1 砷 0.588* 0.71** 1 铬 0.41 0.09 0.37 1 铜 0.68* 0.74** 0.82** 0.54* 1 锌 0.66* 0.44 0.71** 0.87** 0.85** 1 镉 0.60* 0.80** 0.81** 0.38 0.94** 0.71** 1 铅 0.65* 0.72** 0.75** 0.66* 0.94** 0.88** 0.86** 1 *在0.05水平上显著相关;**在0.01水平上显著相关. *Significantly correlated at the 0.05 level; **Significantly correlated at the 0.01 level. 表 5 大亚湾和红海湾表层沉积物重金属单因子污染指数、综合污染指数、潜在单个重金属生态风险系数和总体生态风险指数
Table 5. Single factor pollution index (Cim), comprehensive pollution index (Cf), potential ecological hazard coefficients (Eir), and risk indices (RI) of heavy metals in surface sediments of Daya Bay and Honghai Bay
站位Station Cim Cf Eir RI As Cd Cr Cu Hg Pb Zn As Cd Cr Cu Hg Pb Zn DYW01 0.33 0.12 0.82 0.39 0.07 0.54 0.67 2.93 5.07 12.9 1.24 4.35 9.18 5.38 1.58 39.7 DYW02 0.42 0.10 0.79 0.47 0.17 0.57 0.71 3.23 6.42 10.7 1.20 5.35 21.6 5.70 1.67 52.7 DYW03 0.44 0.16 0.84 0.45 0.12 0.56 0.73 3.29 6.7 17.1 1.27 5.03 15.1 5.60 1.72 52.6 DYW04 0.45 0.06 0.57 0.31 0.21 0.50 0.52 2.63 6.95 6.43 0.87 3.52 27.5 5.03 1.23 51.6 DYW05 0.55 0.10 0.70 0.41 0.21 0.61 0.69 3.28 8.38 10.7 1.06 4.68 27.5 6.10 1.64 60.1 HHW01 0.81 0.46 0.63 1.03 0.52 0.95 0.82 5.22 12.5 49.3 0.95 11.6 68.2 9.5 1.94 154 HHW02 0.32 0.06 0.31 0.17 0.28 0.29 0.27 1.69 4.92 6.43 0.46 1.87 36.1 2.92 0.63 53.3 HHW03 0.96 0.28 0.82 0.87 0.32 0.84 0.89 4.97 14.8 30.0 1.23 9.81 42 8.35 2.1 108.2 HHW04 0.13 0.00 0.18 0.10 0.03 0.24 0.14 0.82 2.02 0.00 0.27 1.1 3.3 2.42 0.34 9.4 HHW05 0.41 0.10 0.56 0.29 0.24 0.56 0.45 2.61 6.36 10.7 0.84 3.23 31.5 5.63 1.07 59.3 HHW06 0.41 0.08 0.57 0.29 0.21 0.54 0.44 2.53 6.36 8.57 0.86 3.23 26.9 5.38 1.03 52.3 HHW07 0.45 0.16 0.75 0.41 0.23 0.60 0.58 3.18 6.88 17.1 1.14 4.61 30.2 6.00 1.36 67.3 HHW08 0.14 0.08 0.79 0.47 0.21 0.66 0.61 2.97 2.17 8.57 1.2 5.35 26.9 6.63 1.45 52.3 HHW09 0.43 0.10 0.60 0.35 0.17 0.44 0.47 2.56 6.58 10.7 0.91 3.94 22.3 4.38 1.12 49.9 均值 average 0.45 0.13 0.64 0.43 0.21 0.56 0.57 — 6.86 14.23 0.96 4.83 27.73 5.64 1.35 — “—”:没有数据. “—”: No data. -
[1] CHEN L, ZHOU S L, WU S H, et al. Concentration, fluxes, risks, and sources of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in the Lihe River watershed, Taihu region, Eastern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 255: 113301. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113301 [2] ISLAM M S, AHMED M K, RAKNUZZAMAN M, et al. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2015, 48: 282-291. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.016 [3] 陈海南, 张春华, 刘国强, 等. 广西北部湾沉积物重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(9): 2872-2879. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021051505 CHEN H N, ZHANG C H, LIU G Q, et al. Evaluation on sediment pollution and potential ecological risks in Guangxi Beibu Gulf[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(9): 2872-2879(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021051505
[4] 王萧, 张文思, 迟光希, 等. 辽东湾及其附近海域重金属污染研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(10): 2317-2326. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112606 WANG X, ZHANG W S, CHI G X, et al. The heavy metals contamination in Liaodong Bay and its adjacent waters[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(10): 2317-2326(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112606
[5] BIRCH G F. Determination of sediment metal background concentrations and enrichment in marine environments - A critical review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 580: 813-831. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.028 [6] ARIKIBE J E, PRASAD S. Determination and comparison of selected heavy metal concentrations in seawater and sediment samples in the coastal area of Suva, Fiji[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 157: 111157. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111157 [7] 曾维特, 杨永鹏, 张东强, 等. 海南岛北部海湾沉积物重金属来源、分布主控因素及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(3): 1085-1094. ZENG W T, YANG Y P, ZHANG D Q, et al. Sources, distribution of main controlling factors, and potential ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in the surface sediment of Hainan Island north bay, south China[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(3): 1085-1094(in Chinese).
[8] 吴斌, 宋金明, 李学刚. 黄河口表层沉积物中重金属的环境地球化学特征[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(4): 1324-1332. WU B, SONG J M, LI X G. Environmental characteristics of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Huanghe Estuary[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(4): 1324-1332(in Chinese).
[9] LIU J J, WANG P F, WANG , et al. Heavy metal pollution status and ecological risks of sediments under the influence of water transfers in Taihu Lake, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(3): 2653-2666. [10] ROBERTS D A. Causes and ecological effects of resuspended contaminated sediments (RCS) in marine environments[J]. Environment International, 2012, 40: 230-243. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.11.013 [11] 陈思杨, 宋琍琍, 刘希真, 等. 浙江典型海湾潮间带沉积物污染及生态风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(4): 1771-1781. CHEN S, SONG L L, LIU X, et al. Evaluation on sediment pollution and potential ecological risks in the intertidal zone of typical bays in Zhejiang Province[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(4): 1771-1781(in Chinese).
[12] WANG Y S, LOU Z P, SUN C C, et al. Multivariate statistical analysis of water quality and phytoplankton characteristics in Daya Bay, China, from 1999 to 2002[J]. Oceanologia, 2006, 48(2): 193-211. [13] 甘居利, 林钦, 贾晓平, 等. 红海湾底质重金属分布与背景值探讨[J]. 热带海洋学报, 1999, 18(2): 64-71. GAN J L, LIN Q, JIA X P, et al. Distribution and background values of heavy metals in surficial sediments of Honghai Bay[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1999, 18(2): 64-71 (in Chinese).
[14] YANG W F, ZHAO X F, ZHANG F, et al. Identification of the earlier human-induced sedimentation change in Daya Bay, northern South China Sea using 210Pb and 137Cs[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 126: 334-337. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.11.025 [15] 孙钦帮, 张冲, 乌立国, 等. 广东红海湾表层沉积物重金属含量的空间分布特征与污染状况评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(5): 843-849. SUN Q, ZHANG C, WU L, et al. Concentration distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in Honghai Bay[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(5): 843-849(in Chinese).
[16] 甘居利, 贾晓平, 林钦, 等. 近岸海域底质重金属生态风险评价初步研究[J]. 水产学报, 2000, 24(6): 533-538. GAN J L, JIA X P, LIN Q, et al. A primary study on ecological risk caused by the heavy metals in coastal sediments[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2000, 24(6): 533-538(in Chinese).
[17] 唐得昊, 刘兴健. 大亚湾表层沉积物中重金属污染与潜在生态风险评价[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2018, 13(4): 1-7. TANG D H, LIU X J. Heavy metals pollution and potential ecological risk assessment in surface sediments from Daya bay[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2018, 13(4): 1-7(in Chinese).
[18] 杨文超, 黄道建, 陈继鑫, 等. 大亚湾海域2009—2018年重金属时空分布及污染评价[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 52(5): 65-75. YANG W C, HUANG D J, CHEN J X, et al. Pollution assessment and temporal-spatial distribution of heavy metals in seawater of Daya bay during 2009-2018[J]. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 52(5): 65-75(in Chinese).
[19] 杨文超, 黄道建, 陈继鑫, 等. 大亚湾近十年沉积物中汞、砷分布及污染评价[J]. 水产科学, 2020, 39(6): 915-921. YANG W C, HUANG D J, CHEN J X, et al. Distribution and pollution assessment of Hg and As contents in surface sediments of Daya bay in the past ten years[J]. Fisheries Science, 2020, 39(6): 915-921(in Chinese).
[20] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [21] 郑江鹏, 矫新明, 方南娟, 等. 江苏近岸海域沉积物重金属来源及风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(4): 1514-1522. ZHENG J P, JIAO X M, FANG N J, et al. Sources and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments in Jiangsu coastal areas[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(4): 1514-1522(in Chinese).
[22] 何悦强, 温伟英. 广东沿海底质某些重金属含量及其分布规律的探讨[J]. 热带海洋, 1982, 1(1): 58-71. HE Y Q, WEN W Y. Distribution and concentrations of some heavy metals in the offshore bottom sediments, Guangdong Province[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1982, 1(1): 58-71(in Chinese).
[23] 唐得昊, 刘兴健, 邹欣庆. 海湾表层沉积物重金属污染与潜在生态危害评价: 以深圳湾为例[J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(8): 1294-1300. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.08.002 TANG D H, LIU X J, ZOU X Q. Heavy metals pollution and their potential ecological risk assessment in the surface sediment from Shenzhen Bay[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(8): 1294-1300(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.08.002
[24] 周凯, 李绪录, 夏华永, 等. 大鹏湾中表层沉积物的有害要素及其环境质量[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2011, 30(2): 172-176. ZHOU K, LI X, XIA H, et al. Harmful parameters and environmental quality in surface sediment of Mirs Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2011, 30(2): 172-176(in Chinese).
[25] NIU H Y, DENG W J, WU Q H, et al. Potential toxic risk of heavy metals from sediment of the Pearl River in South China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(8): 1053-1058. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62381-5 [26] ZHAO G M, LU Q Y, YE S Y, et al. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of the West Guangdong coastal region, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 108(1/2): 268-274. [27] 张起源, 刘谞承, 赵建刚, 等. 广东沿海沉积物重金属含量及风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(12): 4653-4660. ZHANG Q Y, LIU X C, ZHAO J G, et al. Contents and risk assessment of heavy metal sediments in Guangdong coastal areas[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(12): 4653-4660(in Chinese).
-




 下载:
下载: