-
湿地享有“地球之肾”的美名,被人类视为地球上最重要的自然生存环境之一[1]. 由于地势低洼,湿地易在水动力作用下持续汇集人类活动产生的重金属,而成为重金属的重要汇源地之一[2-4]. 因此,湿地土壤重金属已成为众多学者关注的对象之一. 本世纪以来,广大学者在重金属富集[5]、空间分布[6]、赋存形态[7]、生态风险评价[8]等方面对湿地表层土壤开展一系列的研究,结果表明当前世界各地湿地土壤均存在不同程度的重金属累积,并呈现稳步增长的态势. 对湿地表层土壤中重金属的研究不足以解释自然和人为双重作用下的重金属分布特征,更难以阐明重金属在剖面土壤中的垂向迁移特征及其对生态环境的潜在污染风险等问题.
重金属在进入土壤后受耕种、淋滤和翻耕等因素综合影响会向土壤的不同方向发生迁移转化,从而导致不同土层受到污染[9],这不仅阻碍农作物健康生长,而且会对地下水的安全构成严重威胁. 同时,重金属在不同深度土壤中的垂向迁移特征是展现重金属迁移能力和土壤污染状况最直观的指标之一[10-11]. 据研究报道,国内外对剖面土壤重金属研究多集中在工矿业场地[12]、城市土壤[13]、农田土壤[14]以及喀斯特地区[15]. 但是,目前对于湿地土壤剖面重金属分布特征及其迁移规律的研究报道较少. 此外,湿地周边不同类型土壤所处环境不同,其性质差异较大,以本研究的草滩和泥滩为例,二者在植被类型、土壤质地及水位变化条件等方面都存在较大差异,其重金属含量特征及迁移规律也必然有所不同. 因此,开展湿地土壤重金属的垂向分布特征及其影响因素研究,对揭示重金属在湿地土壤中的分布特征及迁移规律是十分必要的.
菜子湖作为长江中下游典型的沿江湿地,其生态环境质量对长江生态环境保护至关重要. 菜子湖湿地是国家工程“引江济淮”线路中重要节点之一,该工程完工后主要用以保障城乡供水和农业灌溉用水、促进航运发展、改善水生态环境,对沿途地区社会经济的发展至关重要[16-17]. 前人研究表明,菜子湖湿地周边土壤已累积了部分重金属,并存在不同程度的生态风险[2,18]. 基于此,本研究以菜子湖湿地为案例地,以湿地周边不同类型垂直剖面土壤为研究对象,阐明湿地土壤重金属在垂直方向上的分布特征及其迁移规律,以期为沿江湿地生态环境保护提供基础数据和科学依据.
-
菜子湖,隶属于长江中下游支流水体(116°07′—117°44′ E,29°50—30°58′ N)(图1),为典型的北亚热带湿润季风气候,湖面由3个主要湖泊(白兔湖、嬉子湖、菜子湖)共同组成. 菜子湖流域境内自然物种丰富,据不完全统计,湿地范围内仅维管植物就多达一百多种,不同类型植物群落(芦苇、水浊等)广泛分布,更有大量湖泊的优势种随处可见(菹草、黑藻、苦草、菰等). 同时,湿地周边土壤受不同水位变化条件的影响,草滩和泥滩分布广泛,两种类型土壤在理化性质和植被类型等方面存在差异.
-
于2022年1月初,选择湿地暴露明显的6个典型样地(祠堂、大坟墓、许咀、王家大圩、河脚庄、湿地公园),每个样地分别采集草滩与泥滩两种类型湿地土壤,每种类型土壤均挖取3个剖面,剖面采集深度均为100 cm,并按照(0—10 cm、 10—20 cm、20—40 cm、 40—60 cm、 60—80 cm、80—100 cm)分层取样,然后将采集的剖面土壤样品装入封口袋后带回实验室,在室温条件下自然风干,再去除细小石块、植物残根等多余杂质. 将自然风干的土壤按实验要求分别研磨过10目、60目和100目筛,过10目和60目的样品用于测定土壤理化性质,过100目的样品用于测定土壤重金属元素.
本研究中土壤有机质采用高温外热重铬酸钾氧化-容量法测定;全磷采用酸溶-钼锑抗比色法测定;pH采用电位法(水土比2.5∶1),pH计测定[19]. 粒度和全氮数据分别采用贝克曼COULTER LS230型激光粒度分析仪与德国Elementar公司生产的Vario MACRO CHNS元素分析仪测定,并根据美国农业部(USAD)制定的标准,将土壤粒级一共分为6个等级:粗砂粒(500—1000 μm)、中砂粒(250—500 μm)、细砂粒(100—250 μm)、极细砂粒(50—100 μm)、粉粒(2—50 μm)和黏粒(<2 μm)[20]. 土壤重金属元素As、Co、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、V、Zn采用HF-HClO4-HNO3三酸消解,电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(Perkin Elmer ICP-OES Optima 7000)测定[21]. 实验过程进行严格质量控制,平行样测定的相对标准偏差(RSD)总体控制在5%以下,标准物质(GSS-1)的整体回收率范围在84%—121%.
-
为计算菜子湖湿地剖面土壤重金属的迁移系数,因Al元素在土壤自然成土过程中比较稳定,不易受外源输入影响而发生变化,且本研究区内土壤中Al元素含量未超过安庆市土壤背景值,变异程度也较低,说明Al元素在土壤中稳定性高且受人为影响较小,故选择Al作为参比元素[22]. 迁移系数计算公式如下:
式中,Tj表示湿地土壤剖面中j元素的迁移系数,Cj,s表示土壤样品中j元素的含量,Cj,b表示土壤中j元素的背景值,CAl,s表示土壤样品中Al的含量,CAl,b表示研究区土壤中Al的背景值. 当Tj=0时,说明j元素相对于Al元素来说不存在富集或者部分流失,Tj=−1时,说明j元素在湿地土壤剖面中完全流失,Tj>0时,说明j元素出现明显富集,Tj<0 时,说明j元素流失.
-
研究区所采集的剖面土壤pH值变化范围为4.45—7.96,均值为5.83(表1),整体呈弱酸性,且土壤pH值随着土层深度的增加表现出明显的上升趋势. 土壤SOM、TN和TP含量范围分别为1.16—61.94、0.39—5.37、0.02—0.32 g·kg−1,平均值分别为16.41、1.51、0.11 g·kg−1. 此外,研究区土壤组成总体以粉粒为主(77.87%),黏粒次之(20.55%),砂粒占比最小(1.58%),平均粒径为6.77 μm. 通过对比发现,各级土壤粒度的变化特征不尽相同,其中砂粒和粉粒均表现为底层大于表层的垂向分布特征,而黏粒则呈现出相反的变化趋势. 总体来看,平均粒径呈现出随土壤深度增加而波动增大的变化趋势,这主要是受当地植被类型及覆盖程度、成土母质及人为扰动等众多因素的综合影响.
除Cr、Cu和Pb外,其余元素均超过安庆市土壤背景值(表2). As、Co、Ni、V和Zn的含量分别是当地土壤背景值的3.06、1.35、1.52、1.19、1.04倍,说明As、Co、Ni、V和Zn等元素在菜子湖湿地土壤中已经出现累积现象,尤以As和Ni较严重. As富集主要受菜子湖周边农业活动的影响,农田中的化肥农药会通过地表径流进入湖边草滩及泥滩土壤中;Ni富集是因为菜子湖流域内分布着铁矿、铜铁矿以及铁锰矿等金属矿产资源,且安庆市作为重要的化工基地,其石油化工企业较多,人为开采矿产资源以及石油化工企业排放的“三废”等都会向周边土壤缓慢释放重金属[23],从而促使湿地土壤中Ni的累积. 各重金属元素变异系数均在0.1—1之间,属于中等变异,这说明人类活动已对该地土壤中重金属含量造成了显著影响.
-
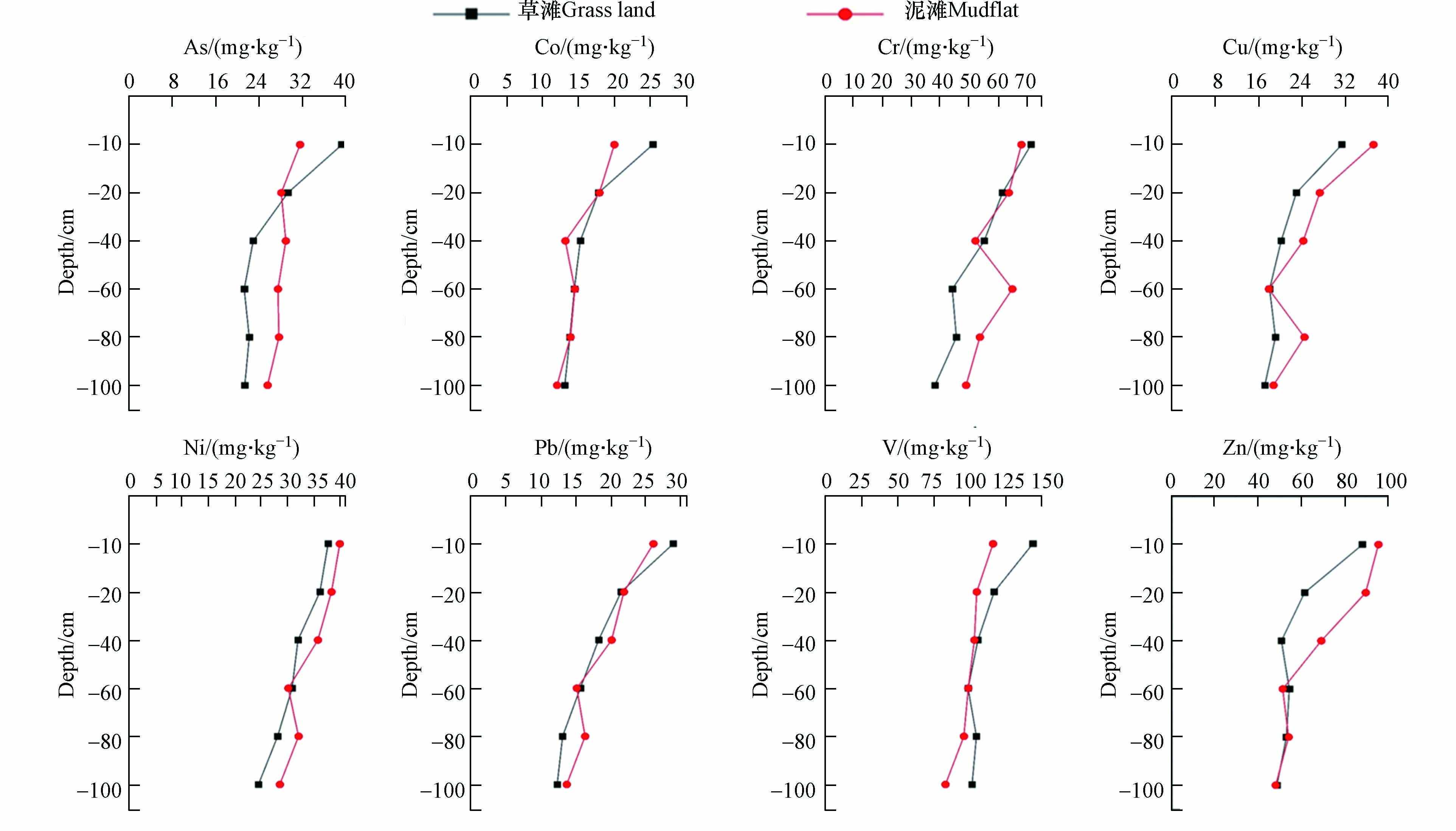
整体上,菜子湖湿地土壤剖面中各重金属含量随土层深度变化虽有波动,但主体趋势表现为随土层深度的增加而逐渐减少(图2),主要是由于湿地土壤表层汇聚着大量有机质,而有机质主要以腐殖质为主,其中胡敏酸(HA)与富里酸(FA)带有大量的负电荷以及各种官能团,对重金属产生强烈的吸附能力,致使湿地土壤表层相比底层更易聚集重金属[24];并且也有学者指出,土壤环境中大多数重金属元素受母质影响较大,迁移能力较差,故主要在土壤0—20 cm表层积累[25].
As、Co、Cr、Pb、V等元素含量在土壤表层均呈现出草滩>泥滩的规律(图3),这主要由3个原因造成,一是跟泥滩相比,菜子湖湿地草滩距离当地居民的农耕区更近,容易受到农民耕作及放牧等活动的外源影响,大量农药、化肥不合理施用以及禽畜排便等都会导致土壤中重金属的逐渐累积;二是因为草滩能够为候鸟提供更优的生存环境,菜子湖湿地作为东亚-澳大利西亚候鸟迁徙途中的必经之地,大量候鸟迁徙至此并在草滩进行觅食、栖息等活动,而鸟类会通过一系列自身行为来释放所富集的重金属[26],加之生物体可以对重金属产生富集与放大作用,都会进一步促使土壤中重金属的富集;三是因为草滩土壤表层植被类型丰富,土壤内部植物根系发达,易于吸附土壤中的重金属,从而成为重金属在土壤表层的主要富集载体[27]. 而在底层土壤,除Co和V之外,其它重金属元素含量又表现为泥滩>草滩的规律,一是因为泥滩靠近湖边浅水区,土壤含水率较大(泥滩55.92%>草滩33.85%,P<0.05),水的向下淋溶作用会导致部分移动性较强的重金属元素向深层土壤转移[24,28];二是因为泥滩底层土壤有机质含量高于草滩(6.10 g·kg−1>4.90 g·kg−1,P<0.05),有机质带有大量负电荷以及各种官能团能够对重金属产生强烈的吸附能力,进而导致泥滩底层土壤相比于草滩底层更容易积累重金属.
不同类型土壤剖面的物质来源及其理化性质都不相同,因而重金属元素的垂直分布特征既有相似或共同之处,又存在差异. 与泥滩相比,草滩不同土层深度的重金属含量垂向变化规律更为明显(图3),主要表现为随土层深度增加而线性降低的变化趋势,表明重金属元素在草滩土壤的垂直剖面演化过程中未受明显人为扰动;此外,本研究发现,草滩土壤表层黏粒含量大于底层(21.84%>19.89%,P<0.05),草滩土壤重金属变化趋势与土壤的黏粒和淤泥含量随土层深度增加而下降有关,有研究报道,重金属在不同土层深度富集与土壤颗粒大小存在显著相关[29]. 泥滩土壤中As、Co和Zn含量的变化特征基本一致,整体表现为随土层深度增加而波动下降的趋势. Cr、Cu、Ni和Pb含量分别在60—80 cm深度土壤中出现一个峰值,一方面与不同时期Cr、Cu、Ni和Pb的输入、不同地理位置湿地沉积速度及湿地水文条件变化有关;另一方面,根据采样观察发现,中层土壤结构较为疏松且拥有良好的通透性,而深层土壤的紧实度和保水性能较好,在降水作用下重金属会由中层向深层富集[30],本研究中泥滩的深层土壤黏粒含量要略高于中层,这也一定程度上解释了部分重金属元素含量在底层土壤中出现峰值的原因.
-
通常情况下,在相同或相似的地质条件下,化学性质相似的元素会呈现相互聚集共生的现象[31]. 菜子湖湿地土壤剖面各理化性质与重金属含量的相关系数如图4所示. 除As外,土壤黏粒、SOM与各重金属均呈显著正相关,平均粒径与各重金属呈显著负相关,这是因为细小颗粒土壤具有较大的比表面积和较高的表面活性,更利于重金属的吸附[32-33];而SOM具有较高的阳离子交换量, 并具有大量不同的官能团,它们可以通过表面沉淀、络合和离子交换吸附金属元素. 除V外,土壤pH与各重金属元素呈显著负相关,这是因为土壤pH越低,H+越多,重金属被解吸的越多,其活动性就越强[34],故重金属不易富集. TP与各重金属无显著相关性,可知TP对湿地土壤重金属含量富集影响十分微弱,而TN与各重金属呈显著正相关,土壤中的TN主要以有机氮为主,本研究中TN与SOM呈极显著正相关,这也进一步验证了前文的解释.
人类活动和土壤母质都会对土壤中重金属的来源和含量累积产生重要影响,一般来说,相似的外源输入会使不同的重金属元素呈现出相近的特点,因此,不同重金属元素间的同源性判断可采用相关性分析,进而为重金属来源解析提供合理参考[35]. 由图4可知,研究区8种重金属之间基本都具有显著正相关性,这说明菜子湖湿地土壤重金属可能具有相同的来源[36].
-
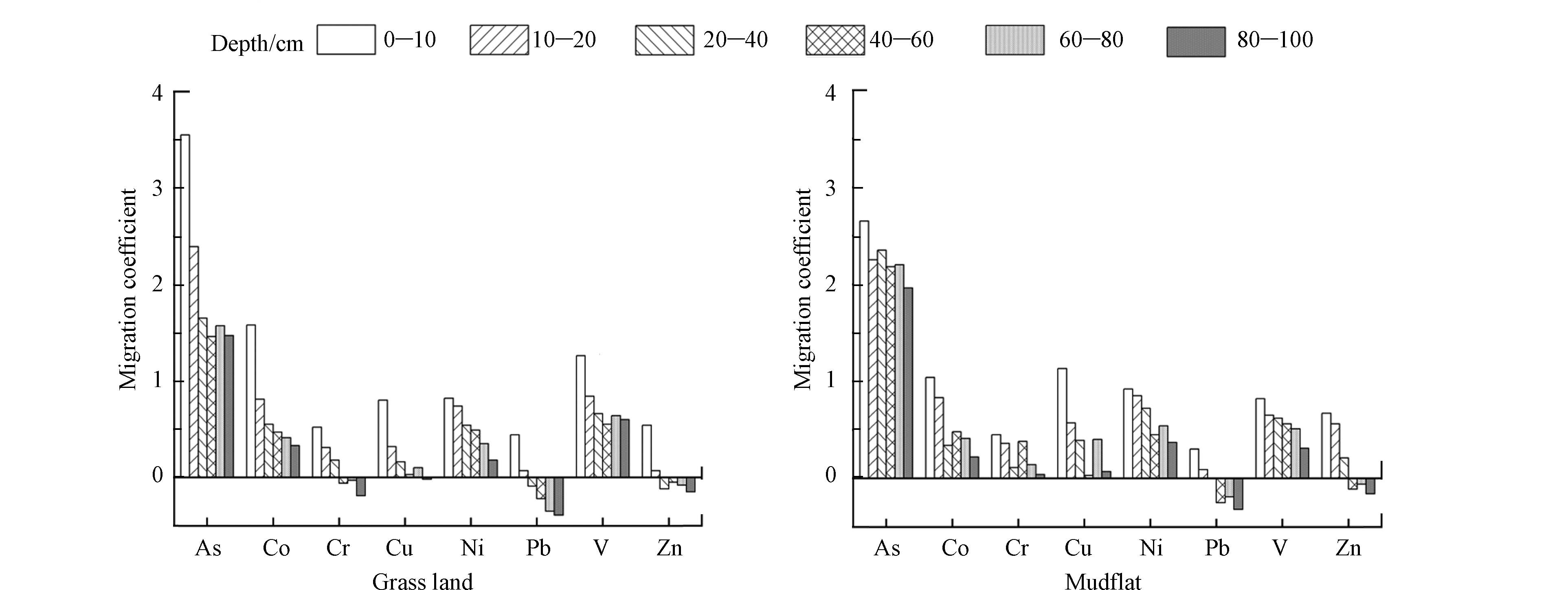
从垂直剖面迁移系数(图5)来看,菜子湖湿地两种类型土壤中As、Co、Ni和V这4种元素的迁移系数在整个剖面中均大于0,且As的迁移系数远高于其它元素,而Cu也仅是在80—100 cm的草滩中为负,其余深度均为正,说明这些元素已在菜子湖湿地土壤中出现富集,并且已经开始向深层土壤缓慢迁移,尤以As最为严重. 重金属迁移与土壤pH值有关,pH值会对土壤中重金属的溶解度产生显著影响,从而对其形态和迁移能力产生决定性作用[37]. 研究区土壤整体呈弱酸性(pH=5.83),在酸性条件下土壤重金属易向下迁移[38],这是上述几种重金属由表层土壤向深层迁移的原因之一.
Cr在草滩40—100 cm的迁移系数为负,其余土层深度均为正,主要原因为:一方面,草滩土壤周边存在小范围的农业活动以及渔业养殖,农耕机器的运作以及渔船燃料的消耗,都会导致Cr的外源输入[39];另一方面,安庆市区拥有大量的石油化工企业以及金属冶炼厂,而菜子湖正处于安庆市区夏季风的下风向,工业活动排放的大量废气会随盛行风向外扩散,进一步加剧Cr在菜子湖周边表层土壤中的累积[40],且Cr相比其它重金属元素的水溶性较高,在土壤剖面中可随降水一直向下渗漏迁移[30],故Cr容易在含水率较高的泥滩中底层土壤中富集. Pb和Zn在湿地剖面土壤中的迁移特征较为相似,其迁移系数均是在草滩0—20 cm土壤中为正,草滩20—100 cm为负,在泥滩0—40 cm土壤中为正,泥滩40—100 cm为负,这是因为土壤中Pb主要以Pb(OH)2、PbCO3和PbSO4等固体形式存在,土壤溶液中可溶性Pb含量很低,Pb2+也可以置换黏土矿物上吸附的Ca2+,因此Pb在土壤中基本很少移动[41];土壤胶体表面的Zn以配位吸附形态为主,pH越接近中性,有机胶体对Zn的配位吸附固定能力越强,故移动性就越弱[42],而菜子湖湿地整体剖面土壤接近中性,且pH值随土层深度增加而上升,因此中底层土壤中的Zn不易出现富集;同时Zn含量实测值与背景值相差不大,推测也一定程度受母质影响.
-
(1) 研究区As、Co、Ni、V和Zn的含量分别是当地土壤背景值的3.06、1.35、1.52、1.19、1.04倍,说明存在不同程度的重金属累积现象;各重金属元素变异系数均在0.1—1之间,属于中等变异.
(2) 湿地不同类型土壤重金属含量整体呈现出随土壤深度的增加而逐渐减少的趋势,但存在一定波动. 草滩土壤重金属垂直分布规律较为明显,表现为随土壤深度增加而线性降低的趋势,而泥滩变化特征则稍显复杂.
(3) 除As外,SOM、土壤黏粒与各重金属均呈显著正相关,而平均粒径与各重金属呈显著负相关;除V外,土壤pH值与各重金属元素呈显著负相关,TP与各重金属元素无显著相关性,而TN与各重金属元素均呈显著正相关;同时,研究区各重金属元素之间基本都呈显著正相关性,推测菜子湖湿地周边土壤重金属可能具有相同来源.
(4) As、Co、Ni和V在草滩和泥滩整个剖面土壤中的迁移系数均大于0,表明这几种元素均存在明显富集现象,尤以As较为严重;Cu和Cr在两种类型土壤剖面中以富集为主,仅在草滩中底层土壤中出现流失;Pb和Zn均是在草滩0—20 cm和泥滩0—40 cm土壤中出现不同程度富集,在草滩20—100 cm和泥滩40—100 cm土壤中集体流失.
菜子湖湿地不同类型土壤重金属的垂直分布特征及迁移规律
Vertical distribution and migration of heavy metals in different types of soils in Caizi Lake wetland
-
摘要: 湿地是全球三大生态系统之一,而重金属污染已经成为桎梏湿地生态功能的重要环境问题. 本文以菜子湖湿地草滩和泥滩两种不同类型0—100 cm垂直剖面土壤为研究对象,通过对比实验方法,分析菜子湖湿地土壤剖面8种重金属元素(As、Co、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、V、Zn)的垂向分布特征及迁移规律. 结果表明,从整体剖面来看,除Cr、Cu和Pb外,其余重金属元素均不同程度超过安庆市土壤背景值,尤以表层土壤较为严重,说明当地存在重金属累积现象;根据土壤垂直分布来看,草滩和泥滩土壤重金属含量垂向变化较一致,总体表现出随土层深度的增加而逐渐减少的趋势,其中,草滩变化规律较为明显,而泥滩变化规律则稍显复杂;As、Co、Ni和V在草滩和泥滩整个剖面中的迁移系数均大于0,表明存在不同程度的富集,尤以As较为严重;Cu和Cr在两种类型土壤剖面中以富集为主,部分土层深度流失;Pb和Zn在垂直剖面土壤中的迁移特征较相似,均表现为在土壤表层富集,在中底层流失. 研究结果可为沿江湿地环境保护提供理论支撑和科学依据.Abstract: Wetland is one of the three major ecosystems in the world, and heavy metal pollution has become an important environmental problem restricting wetland ecological function. In this study, two different types of vertical profile soil (0—100 cm) from Caizi Lake wetland grassland and mudflat were collected and the vertical distribution characteristics and migration rules of eight heavy metals (As, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, V, Zn) in the profile soil were analyzed by comparative experimental methods. The results showed that :(1) Except for Cr, Cu and Pb, all the other heavy metals in the profile soils exceeded the background values of the soil in Anqing city to varying degrees, especially in the surface soil, indicating that there was heavy metal accumulation in the local area. (2) According to the vertical distribution of soil, the vertical variation of heavy metal content in soil of grass flat and mud flat was consistent, and it gradually decreased with the increase of soil depth. The variation pattern of grass flat was more obvious, while that of mud flat was slightly more complex. (3) The migration coefficients of As, Co, Ni and V in the whole section of grass and mud flats were all greater than 0, indicating that they were enriched in varing degrees , especially in As. Cu and Cr were mainly enriched in the two types of soil profiles, and part of the soil depth was lost. The migration characteristics of Pb and Zn in vertical profile soil were similar, both of which were enriched in the surface layer and lost in the middle and bottom layer. The results can provide theoretical support and scientific basis for the environmental protection of wetland along the Yangtze River.
-
Key words:
- wetland soil /
- heavy metals /
- vertical distribution /
- migration law /
- Caizi Lake
-
湿地享有“地球之肾”的美名,被人类视为地球上最重要的自然生存环境之一[1]. 由于地势低洼,湿地易在水动力作用下持续汇集人类活动产生的重金属,而成为重金属的重要汇源地之一[2-4]. 因此,湿地土壤重金属已成为众多学者关注的对象之一. 本世纪以来,广大学者在重金属富集[5]、空间分布[6]、赋存形态[7]、生态风险评价[8]等方面对湿地表层土壤开展一系列的研究,结果表明当前世界各地湿地土壤均存在不同程度的重金属累积,并呈现稳步增长的态势. 对湿地表层土壤中重金属的研究不足以解释自然和人为双重作用下的重金属分布特征,更难以阐明重金属在剖面土壤中的垂向迁移特征及其对生态环境的潜在污染风险等问题.
重金属在进入土壤后受耕种、淋滤和翻耕等因素综合影响会向土壤的不同方向发生迁移转化,从而导致不同土层受到污染[9],这不仅阻碍农作物健康生长,而且会对地下水的安全构成严重威胁. 同时,重金属在不同深度土壤中的垂向迁移特征是展现重金属迁移能力和土壤污染状况最直观的指标之一[10-11]. 据研究报道,国内外对剖面土壤重金属研究多集中在工矿业场地[12]、城市土壤[13]、农田土壤[14]以及喀斯特地区[15]. 但是,目前对于湿地土壤剖面重金属分布特征及其迁移规律的研究报道较少. 此外,湿地周边不同类型土壤所处环境不同,其性质差异较大,以本研究的草滩和泥滩为例,二者在植被类型、土壤质地及水位变化条件等方面都存在较大差异,其重金属含量特征及迁移规律也必然有所不同. 因此,开展湿地土壤重金属的垂向分布特征及其影响因素研究,对揭示重金属在湿地土壤中的分布特征及迁移规律是十分必要的.
菜子湖作为长江中下游典型的沿江湿地,其生态环境质量对长江生态环境保护至关重要. 菜子湖湿地是国家工程“引江济淮”线路中重要节点之一,该工程完工后主要用以保障城乡供水和农业灌溉用水、促进航运发展、改善水生态环境,对沿途地区社会经济的发展至关重要[16-17]. 前人研究表明,菜子湖湿地周边土壤已累积了部分重金属,并存在不同程度的生态风险[2,18]. 基于此,本研究以菜子湖湿地为案例地,以湿地周边不同类型垂直剖面土壤为研究对象,阐明湿地土壤重金属在垂直方向上的分布特征及其迁移规律,以期为沿江湿地生态环境保护提供基础数据和科学依据.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区概况
菜子湖,隶属于长江中下游支流水体(116°07′—117°44′ E,29°50—30°58′ N)(图1),为典型的北亚热带湿润季风气候,湖面由3个主要湖泊(白兔湖、嬉子湖、菜子湖)共同组成. 菜子湖流域境内自然物种丰富,据不完全统计,湿地范围内仅维管植物就多达一百多种,不同类型植物群落(芦苇、水浊等)广泛分布,更有大量湖泊的优势种随处可见(菹草、黑藻、苦草、菰等). 同时,湿地周边土壤受不同水位变化条件的影响,草滩和泥滩分布广泛,两种类型土壤在理化性质和植被类型等方面存在差异.
1.2 样品采集与处理
于2022年1月初,选择湿地暴露明显的6个典型样地(祠堂、大坟墓、许咀、王家大圩、河脚庄、湿地公园),每个样地分别采集草滩与泥滩两种类型湿地土壤,每种类型土壤均挖取3个剖面,剖面采集深度均为100 cm,并按照(0—10 cm、 10—20 cm、20—40 cm、 40—60 cm、 60—80 cm、80—100 cm)分层取样,然后将采集的剖面土壤样品装入封口袋后带回实验室,在室温条件下自然风干,再去除细小石块、植物残根等多余杂质. 将自然风干的土壤按实验要求分别研磨过10目、60目和100目筛,过10目和60目的样品用于测定土壤理化性质,过100目的样品用于测定土壤重金属元素.
本研究中土壤有机质采用高温外热重铬酸钾氧化-容量法测定;全磷采用酸溶-钼锑抗比色法测定;pH采用电位法(水土比2.5∶1),pH计测定[19]. 粒度和全氮数据分别采用贝克曼COULTER LS230型激光粒度分析仪与德国Elementar公司生产的Vario MACRO CHNS元素分析仪测定,并根据美国农业部(USAD)制定的标准,将土壤粒级一共分为6个等级:粗砂粒(500—1000 μm)、中砂粒(250—500 μm)、细砂粒(100—250 μm)、极细砂粒(50—100 μm)、粉粒(2—50 μm)和黏粒(<2 μm)[20]. 土壤重金属元素As、Co、Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、V、Zn采用HF-HClO4-HNO3三酸消解,电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(Perkin Elmer ICP-OES Optima 7000)测定[21]. 实验过程进行严格质量控制,平行样测定的相对标准偏差(RSD)总体控制在5%以下,标准物质(GSS-1)的整体回收率范围在84%—121%.
1.3 迁移系数
为计算菜子湖湿地剖面土壤重金属的迁移系数,因Al元素在土壤自然成土过程中比较稳定,不易受外源输入影响而发生变化,且本研究区内土壤中Al元素含量未超过安庆市土壤背景值,变异程度也较低,说明Al元素在土壤中稳定性高且受人为影响较小,故选择Al作为参比元素[22]. 迁移系数计算公式如下:
Tj=(Cj,s/Cj,b)(CAl,s/CAl,b)−1 (1) 式中,Tj表示湿地土壤剖面中j元素的迁移系数,Cj,s表示土壤样品中j元素的含量,Cj,b表示土壤中j元素的背景值,CAl,s表示土壤样品中Al的含量,CAl,b表示研究区土壤中Al的背景值. 当Tj=0时,说明j元素相对于Al元素来说不存在富集或者部分流失,Tj=−1时,说明j元素在湿地土壤剖面中完全流失,Tj>0时,说明j元素出现明显富集,Tj<0 时,说明j元素流失.
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 湿地土壤剖面理化性质及重金属总量特征
研究区所采集的剖面土壤pH值变化范围为4.45—7.96,均值为5.83(表1),整体呈弱酸性,且土壤pH值随着土层深度的增加表现出明显的上升趋势. 土壤SOM、TN和TP含量范围分别为1.16—61.94、0.39—5.37、0.02—0.32 g·kg−1,平均值分别为16.41、1.51、0.11 g·kg−1. 此外,研究区土壤组成总体以粉粒为主(77.87%),黏粒次之(20.55%),砂粒占比最小(1.58%),平均粒径为6.77 μm. 通过对比发现,各级土壤粒度的变化特征不尽相同,其中砂粒和粉粒均表现为底层大于表层的垂向分布特征,而黏粒则呈现出相反的变化趋势. 总体来看,平均粒径呈现出随土壤深度增加而波动增大的变化趋势,这主要是受当地植被类型及覆盖程度、成土母质及人为扰动等众多因素的综合影响.
表 1 湿地土壤剖面理化性质总体特征 (n=170)Table 1. Overall characteristics of physical and chemical properties of soil in wetland profile (n=170)项目Item pH SOM/(g·kg−1) TN/(g·kg−1) TP/(g·kg−1) 砂粒/%Sand 粉粒/%Silt 黏粒/%Clay 平均粒径/μmAverage grain diameter 最大值 7.96 61.94 5.37 0.32 9.75 86.18 30.72 10.40 最小值 4.45 1.16 0.39 0.02 0.04 59.11 12.00 4.07 平均值 5.83 16.41 1.51 0.11 1.58 77.87 20.55 6.77 标准差 0.70 14.77 1.05 0.05 1.49 3.54 3.29 1.33 变异系数 0.12 0.90 0.70 0.45 0.94 0.05 0.16 0.20 除Cr、Cu和Pb外,其余元素均超过安庆市土壤背景值(表2). As、Co、Ni、V和Zn的含量分别是当地土壤背景值的3.06、1.35、1.52、1.19、1.04倍,说明As、Co、Ni、V和Zn等元素在菜子湖湿地土壤中已经出现累积现象,尤以As和Ni较严重. As富集主要受菜子湖周边农业活动的影响,农田中的化肥农药会通过地表径流进入湖边草滩及泥滩土壤中;Ni富集是因为菜子湖流域内分布着铁矿、铜铁矿以及铁锰矿等金属矿产资源,且安庆市作为重要的化工基地,其石油化工企业较多,人为开采矿产资源以及石油化工企业排放的“三废”等都会向周边土壤缓慢释放重金属[23],从而促使湿地土壤中Ni的累积. 各重金属元素变异系数均在0.1—1之间,属于中等变异,这说明人类活动已对该地土壤中重金属含量造成了显著影响.
表 2 湿地土壤剖面重金属总量特征(mg·kg−1,n=170)Table 2. Characteristics of Total heavy metals in soil of wetland profile项目Item As Co Cr Cu Ni Pb V Zn 最小值 2.74 0.62 17.44 2.44 4.65 0.08 38.18 19.14 最大值 70.33 48.09 125.36 101.29 81.36 61.73 216.32 301.28 平均值 28.81 16.65 59.42 24.21 36.19 19.35 111.59 77.22 标准差 11.55 8.30 22.27 11.64 14.96 10.63 30.91 41.58 变异系数 0.40 0.50 0.37 0.48 0.41 0.55 0.28 0.54 土壤背景值 9.41 12.35 63.38 30.30 23.75 26.92 93.79 74.41 注:土壤背景值参考依据来源于安徽省环境监测中心-1992. Note: The reference basis of soil background value is from Anhui Environmental Monitoring Center-1992. 2.2 湿地不同类型土壤重金属垂向分布特征及影响因素分析
整体上,菜子湖湿地土壤剖面中各重金属含量随土层深度变化虽有波动,但主体趋势表现为随土层深度的增加而逐渐减少(图2),主要是由于湿地土壤表层汇聚着大量有机质,而有机质主要以腐殖质为主,其中胡敏酸(HA)与富里酸(FA)带有大量的负电荷以及各种官能团,对重金属产生强烈的吸附能力,致使湿地土壤表层相比底层更易聚集重金属[24];并且也有学者指出,土壤环境中大多数重金属元素受母质影响较大,迁移能力较差,故主要在土壤0—20 cm表层积累[25].
As、Co、Cr、Pb、V等元素含量在土壤表层均呈现出草滩>泥滩的规律(图3),这主要由3个原因造成,一是跟泥滩相比,菜子湖湿地草滩距离当地居民的农耕区更近,容易受到农民耕作及放牧等活动的外源影响,大量农药、化肥不合理施用以及禽畜排便等都会导致土壤中重金属的逐渐累积;二是因为草滩能够为候鸟提供更优的生存环境,菜子湖湿地作为东亚-澳大利西亚候鸟迁徙途中的必经之地,大量候鸟迁徙至此并在草滩进行觅食、栖息等活动,而鸟类会通过一系列自身行为来释放所富集的重金属[26],加之生物体可以对重金属产生富集与放大作用,都会进一步促使土壤中重金属的富集;三是因为草滩土壤表层植被类型丰富,土壤内部植物根系发达,易于吸附土壤中的重金属,从而成为重金属在土壤表层的主要富集载体[27]. 而在底层土壤,除Co和V之外,其它重金属元素含量又表现为泥滩>草滩的规律,一是因为泥滩靠近湖边浅水区,土壤含水率较大(泥滩55.92%>草滩33.85%,P<0.05),水的向下淋溶作用会导致部分移动性较强的重金属元素向深层土壤转移[24,28];二是因为泥滩底层土壤有机质含量高于草滩(6.10 g·kg−1>4.90 g·kg−1,P<0.05),有机质带有大量负电荷以及各种官能团能够对重金属产生强烈的吸附能力,进而导致泥滩底层土壤相比于草滩底层更容易积累重金属.
不同类型土壤剖面的物质来源及其理化性质都不相同,因而重金属元素的垂直分布特征既有相似或共同之处,又存在差异. 与泥滩相比,草滩不同土层深度的重金属含量垂向变化规律更为明显(图3),主要表现为随土层深度增加而线性降低的变化趋势,表明重金属元素在草滩土壤的垂直剖面演化过程中未受明显人为扰动;此外,本研究发现,草滩土壤表层黏粒含量大于底层(21.84%>19.89%,P<0.05),草滩土壤重金属变化趋势与土壤的黏粒和淤泥含量随土层深度增加而下降有关,有研究报道,重金属在不同土层深度富集与土壤颗粒大小存在显著相关[29]. 泥滩土壤中As、Co和Zn含量的变化特征基本一致,整体表现为随土层深度增加而波动下降的趋势. Cr、Cu、Ni和Pb含量分别在60—80 cm深度土壤中出现一个峰值,一方面与不同时期Cr、Cu、Ni和Pb的输入、不同地理位置湿地沉积速度及湿地水文条件变化有关;另一方面,根据采样观察发现,中层土壤结构较为疏松且拥有良好的通透性,而深层土壤的紧实度和保水性能较好,在降水作用下重金属会由中层向深层富集[30],本研究中泥滩的深层土壤黏粒含量要略高于中层,这也一定程度上解释了部分重金属元素含量在底层土壤中出现峰值的原因.
2.3 重金属相关性分析
通常情况下,在相同或相似的地质条件下,化学性质相似的元素会呈现相互聚集共生的现象[31]. 菜子湖湿地土壤剖面各理化性质与重金属含量的相关系数如图4所示. 除As外,土壤黏粒、SOM与各重金属均呈显著正相关,平均粒径与各重金属呈显著负相关,这是因为细小颗粒土壤具有较大的比表面积和较高的表面活性,更利于重金属的吸附[32-33];而SOM具有较高的阳离子交换量, 并具有大量不同的官能团,它们可以通过表面沉淀、络合和离子交换吸附金属元素. 除V外,土壤pH与各重金属元素呈显著负相关,这是因为土壤pH越低,H+越多,重金属被解吸的越多,其活动性就越强[34],故重金属不易富集. TP与各重金属无显著相关性,可知TP对湿地土壤重金属含量富集影响十分微弱,而TN与各重金属呈显著正相关,土壤中的TN主要以有机氮为主,本研究中TN与SOM呈极显著正相关,这也进一步验证了前文的解释.
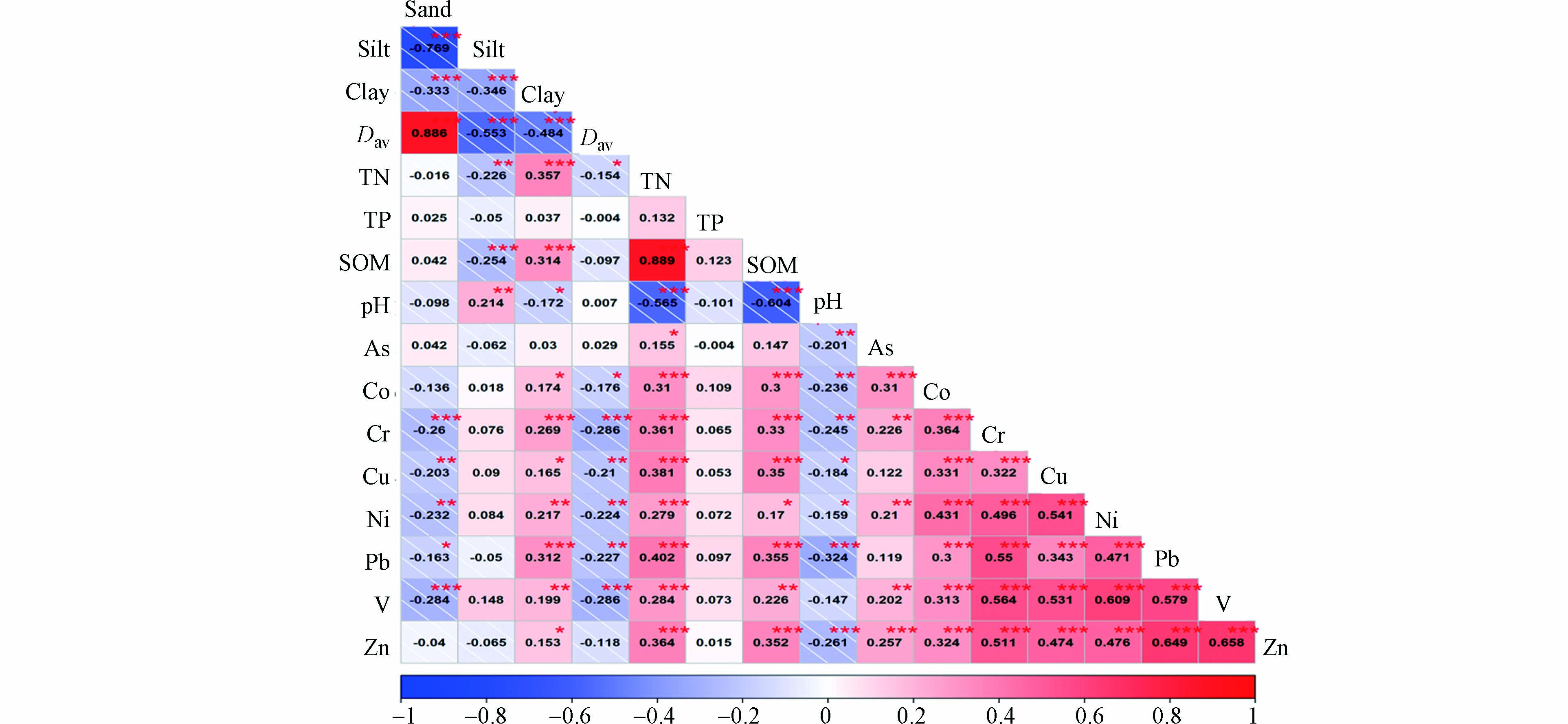 图 4 不同理化性质与各重金属元素相关系数 (n=170)Figure 4. Correlation coefficients between different physicochemical properties and heavy metal elements (n=170)注:***、**、*表示相关性(P<0.001)、相关性(P<0.01) 、相关性(P<0.05); Dav表示平均粒径.Note: ***, ** and * indicate correlation (P<0.001), correlation (P<0.01) and correlation (P<0.05);Dav stands for average grain diameter.
图 4 不同理化性质与各重金属元素相关系数 (n=170)Figure 4. Correlation coefficients between different physicochemical properties and heavy metal elements (n=170)注:***、**、*表示相关性(P<0.001)、相关性(P<0.01) 、相关性(P<0.05); Dav表示平均粒径.Note: ***, ** and * indicate correlation (P<0.001), correlation (P<0.01) and correlation (P<0.05);Dav stands for average grain diameter.人类活动和土壤母质都会对土壤中重金属的来源和含量累积产生重要影响,一般来说,相似的外源输入会使不同的重金属元素呈现出相近的特点,因此,不同重金属元素间的同源性判断可采用相关性分析,进而为重金属来源解析提供合理参考[35]. 由图4可知,研究区8种重金属之间基本都具有显著正相关性,这说明菜子湖湿地土壤重金属可能具有相同的来源[36].
2.4 湿地土壤重金属垂向迁移特征及影响因素分析
从垂直剖面迁移系数(图5)来看,菜子湖湿地两种类型土壤中As、Co、Ni和V这4种元素的迁移系数在整个剖面中均大于0,且As的迁移系数远高于其它元素,而Cu也仅是在80—100 cm的草滩中为负,其余深度均为正,说明这些元素已在菜子湖湿地土壤中出现富集,并且已经开始向深层土壤缓慢迁移,尤以As最为严重. 重金属迁移与土壤pH值有关,pH值会对土壤中重金属的溶解度产生显著影响,从而对其形态和迁移能力产生决定性作用[37]. 研究区土壤整体呈弱酸性(pH=5.83),在酸性条件下土壤重金属易向下迁移[38],这是上述几种重金属由表层土壤向深层迁移的原因之一.
Cr在草滩40—100 cm的迁移系数为负,其余土层深度均为正,主要原因为:一方面,草滩土壤周边存在小范围的农业活动以及渔业养殖,农耕机器的运作以及渔船燃料的消耗,都会导致Cr的外源输入[39];另一方面,安庆市区拥有大量的石油化工企业以及金属冶炼厂,而菜子湖正处于安庆市区夏季风的下风向,工业活动排放的大量废气会随盛行风向外扩散,进一步加剧Cr在菜子湖周边表层土壤中的累积[40],且Cr相比其它重金属元素的水溶性较高,在土壤剖面中可随降水一直向下渗漏迁移[30],故Cr容易在含水率较高的泥滩中底层土壤中富集. Pb和Zn在湿地剖面土壤中的迁移特征较为相似,其迁移系数均是在草滩0—20 cm土壤中为正,草滩20—100 cm为负,在泥滩0—40 cm土壤中为正,泥滩40—100 cm为负,这是因为土壤中Pb主要以Pb(OH)2、PbCO3和PbSO4等固体形式存在,土壤溶液中可溶性Pb含量很低,Pb2+也可以置换黏土矿物上吸附的Ca2+,因此Pb在土壤中基本很少移动[41];土壤胶体表面的Zn以配位吸附形态为主,pH越接近中性,有机胶体对Zn的配位吸附固定能力越强,故移动性就越弱[42],而菜子湖湿地整体剖面土壤接近中性,且pH值随土层深度增加而上升,因此中底层土壤中的Zn不易出现富集;同时Zn含量实测值与背景值相差不大,推测也一定程度受母质影响.
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1) 研究区As、Co、Ni、V和Zn的含量分别是当地土壤背景值的3.06、1.35、1.52、1.19、1.04倍,说明存在不同程度的重金属累积现象;各重金属元素变异系数均在0.1—1之间,属于中等变异.
(2) 湿地不同类型土壤重金属含量整体呈现出随土壤深度的增加而逐渐减少的趋势,但存在一定波动. 草滩土壤重金属垂直分布规律较为明显,表现为随土壤深度增加而线性降低的趋势,而泥滩变化特征则稍显复杂.
(3) 除As外,SOM、土壤黏粒与各重金属均呈显著正相关,而平均粒径与各重金属呈显著负相关;除V外,土壤pH值与各重金属元素呈显著负相关,TP与各重金属元素无显著相关性,而TN与各重金属元素均呈显著正相关;同时,研究区各重金属元素之间基本都呈显著正相关性,推测菜子湖湿地周边土壤重金属可能具有相同来源.
(4) As、Co、Ni和V在草滩和泥滩整个剖面土壤中的迁移系数均大于0,表明这几种元素均存在明显富集现象,尤以As较为严重;Cu和Cr在两种类型土壤剖面中以富集为主,仅在草滩中底层土壤中出现流失;Pb和Zn均是在草滩0—20 cm和泥滩0—40 cm土壤中出现不同程度富集,在草滩20—100 cm和泥滩40—100 cm土壤中集体流失.
-
表 1 湿地土壤剖面理化性质总体特征 (n=170)
Table 1. Overall characteristics of physical and chemical properties of soil in wetland profile (n=170)
项目Item pH SOM/(g·kg−1) TN/(g·kg−1) TP/(g·kg−1) 砂粒/%Sand 粉粒/%Silt 黏粒/%Clay 平均粒径/μmAverage grain diameter 最大值 7.96 61.94 5.37 0.32 9.75 86.18 30.72 10.40 最小值 4.45 1.16 0.39 0.02 0.04 59.11 12.00 4.07 平均值 5.83 16.41 1.51 0.11 1.58 77.87 20.55 6.77 标准差 0.70 14.77 1.05 0.05 1.49 3.54 3.29 1.33 变异系数 0.12 0.90 0.70 0.45 0.94 0.05 0.16 0.20 表 2 湿地土壤剖面重金属总量特征(mg·kg−1,n=170)
Table 2. Characteristics of Total heavy metals in soil of wetland profile
项目Item As Co Cr Cu Ni Pb V Zn 最小值 2.74 0.62 17.44 2.44 4.65 0.08 38.18 19.14 最大值 70.33 48.09 125.36 101.29 81.36 61.73 216.32 301.28 平均值 28.81 16.65 59.42 24.21 36.19 19.35 111.59 77.22 标准差 11.55 8.30 22.27 11.64 14.96 10.63 30.91 41.58 变异系数 0.40 0.50 0.37 0.48 0.41 0.55 0.28 0.54 土壤背景值 9.41 12.35 63.38 30.30 23.75 26.92 93.79 74.41 注:土壤背景值参考依据来源于安徽省环境监测中心-1992. Note: The reference basis of soil background value is from Anhui Environmental Monitoring Center-1992. -
[1] SHAN V, SINGH S K, HARITASH A K. Evaluation of water quality and potential metal contamination in ecologically important Bhindawas bird sanctuary, India [J]. Applied Water Science, 2021, 11(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1007/s13201-020-01330-z [2] 徐明露, 方凤满, 林跃胜. 安庆菜子湖退耕湿地土壤中的重金属含量及其污染评价 [J]. 湿地科学, 2015, 13(4): 437-443. XU M L, FANG F M, LIN Y S. Contents and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in soils of wetlands after returning farmland to lake in Caizi lake in Anqing City [J]. Wetland Science, 2015, 13(4): 437-443(in Chinese).
[3] 李亚瑾, 孙志高, 李晓, 等. 闽江大樟溪下游沿线湿地沉积物中重金属分布特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(2): 331-339. LI Y J, SUN Z G, LI X, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of wetland along the lower reach of the Dazhang stream(Min River) [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(2): 331-339(in Chinese).
[4] 李伟, 布多, 孙晶, 等. 拉萨巴嘎雪湿地土壤重金属分布及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(1): 195-203. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019092006 LI W, BU D, SUN J, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal elements in the surface sediments of Bagaxue wetlands in Lhasa [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(1): 195-203(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019092006
[5] RAMOS-MIRAS J J, ROCA-PEREZ L, GUZMÁN-PALOMINO M, et al. Background levels and baseline values of available heavy metals in Mediterranean greenhouse soils (Spain) [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 110(2): 186-192. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.05.009 [6] HARIKUMAR P S, NASIR U P, RAHMAN M P M. Distribution of heavy metals in the core sediments of a tropical wetland system [J]. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 6(2): 225-232. [7] HOQUE R R, GOSWAMI K G, KUSRE B C, et al. Distribution and solid-phase speciation of toxic heavy metals of bed sediments of Bharali tributary of Brahmaputra River [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2011, 177(1/2/3/4): 457-466. [8] CUI J, ZANG S Y, ZHAI D L, et al. Potential ecological risk of heavy metals and metalloid in the sediments of Wuyuer River Basin, Heilongjiang Province, China [J]. Ecotoxicology (London, England), 2014, 23(4): 589-600. doi: 10.1007/s10646-014-1182-1 [9] 何梦媛, 董同喜, 茹淑华, 等. 畜禽粪便有机肥中重金属在土壤剖面中积累迁移特征及生物有效性差异 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(4): 1576-1586. HE M Y, DONG T X, RU S H, et al. Accumulation and migration characteristics in soil profiles and bioavailability of heavy metals from livestock manure [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(4): 1576-1586(in Chinese).
[10] STERCKEMAN T, DOUAY F, PROIX N, et al. Vertical distribution of Cd, Pb and Zn in soils near smelters in the North of France [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2000, 107(3): 377-389. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00165-7 [11] 刘洪莲, 李恋卿, 潘根兴. 苏南某些水稻土中Cu Pb Hg As的剖面分布及其影响因素 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2006, 25(5): 1221-1227. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2006.05.026 LIU H L, LI L Q, PAN G X. Profile distribution of total Cu, Pb, Hg, as in some paddy soils from the southern Jiangsu, China and the influencing factors [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2006, 25(5): 1221-1227(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2006.05.026
[12] YOUNG G, CHEN Y Q, YANG M. Concentrations, distribution, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the iron tailings of Yeshan National Mine Park in Nanjing, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 271: 129546. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129546 [13] 姜玉玲, 阮心玲, 杨玲, 等. 开封市城市土壤剖面Hg、As和Sb分布特征分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(5): 1036-1046. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.05.2016112903 JIANG Y L, RUAN X L, YANG L, et al. Distribution of Hg, As and Sb concentrations in urban soil profiles of Kaifeng City, Henan Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(5): 1036-1046(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.05.2016112903
[14] 窦韦强, 安毅, 秦莉, 等. 农田土壤重金属垂直分布迁移特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(2): 166-172. DOU W Q, AN Y, QIN L, et al. Characteristics of vertical distribution and migration of heavy metals in farmland soils and ecological risk assessment [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(2): 166-172(in Chinese).
[15] 孙子媛, 文雪峰, 吴攀, 等. 喀斯特地区典型风化剖面重金属超标程度及元素迁移特征研究 [J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(1): 50-56. SUN Z Y, WEN X F, WU P, et al. Excessive degrees and migration characteristics of heavy metals in typical weathering profiles in Karst areas [J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47(1): 50-56(in Chinese).
[16] 王钟, 范中亚, 杨忠勇, 等. “引江济淮”工程对安徽菜子湖水龄分布的影响 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(6): 1576-1586. doi: 10.18307/2018.0609 WANG Z, FAN Z Y, YANG Z Y, et al. Effects of Water Diversion Project from the Yangtze River to Huaihe River on the water age distribution of Lake Caizi, Anhui Province [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(6): 1576-1586(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2018.0609
[17] LI C, DING S M, YANG L Y, et al. Diffusive gradients in thin films: Devices, materials and applications [J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2019, 17(2): 801-831. doi: 10.1007/s10311-018-00839-9 [18] JIANG Z G, XU N, LIU B X, et al. Metal concentrations and risk assessment in water, sediment and economic fish species with various habitat preferences and trophic guilds from Lake Caizi, Southeast China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 157: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.078 [19] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000: 13-14, 107-108. LU R K. Analysis method of soil agrochemistry[M]. China Agriculture Scientech Press, 2000: 13-14, 107-108(in Chinese).
[20] 董智今, 展秀丽, 丁小花. 毛乌素沙地西南缘不同土地利用类型土壤颗粒分形特征 [J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(3): 43-48,56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2022.3.stbcyj202203007 DONG Z J, ZHAN X L, DING X H. Fractal features of soil particles under different land uses in the southwestern edge of the Mu Us sandy land [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 29(3): 43-48,56(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2022.3.stbcyj202203007
[21] 方凤满, 武慧君, 姚有如, 等. 鸟粪对同里湿地公园土壤重金属及其形态的影响 [J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(8): 2925-2933. FANG F M, WU H J, YAO Y R, et al. Heavy metal concentrations and speciation of soil affected by bird droppings in Tongli Wetland Park, East China [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(8): 2925-2933(in Chinese).
[22] ZHANG H H, CHEN J J, ZHU L, et al. Anthropogenic mercury enrichment factors and contributions in soils of Guangdong Province, South China [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 144: 312-319. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.01.031 [23] GUAN Q Y, WANG F F, XU C Q, et al. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 193: 189-197. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.151 [24] 赵津, 刘汝海, 金嘉欣, 等. 子牙新河下游湿地土壤重金属垂直分布及形态特征 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(10): 2044-2050. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.10.2016022001 ZHAO J, LIU R H, JIN J X, et al. Vertical distribution and speciation characteristics of heavy metals in wetlands soils of Ziyaxin River downstream [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(10): 2044-2050(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.10.2016022001
[25] 郑国璋. 关中娄土剖面中重金属元素的垂直分布规律研究 [J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(1): 109-115. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.01.014 ZHENG G Z. The vertical distribution regularity of heavy metal elements in Guanzhong tier soil profile [J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2008, 29(1): 109-115(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.01.014
[26] WARNKEN J, OHLSSON R, WELSH D T, et al. Antimony and arsenic exhibit contrasting spatial distributions in the sediment and vegetation of a contaminated wetland [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 180: 388-395. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.142 [27] 张国伟, 张永波, 吴艾静, 等. 湿地植物对煤矿老窑水污染土壤中重金属的富集能力研究 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2021, 43(10): 1244-1248. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2021.10.005 ZHANG G W, ZHANG Y B, WU A J, et al. Study on the accumulation ability of wetland plants to heavy metals in the soil polluted by acid mine drainage [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2021, 43(10): 1244-1248(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2021.10.005
[28] 唐世琪, 刘秀金, 杨柯, 等. 典型碳酸盐岩区耕地土壤剖面重金属形态迁移转化特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(8): 3913-3923. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202101066 TANG S Q, LIU X J, YANG K, et al. Migration, transformation characteristics, and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metal fractions in cultivated soil profiles in a typical carbonate-covered area [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(8): 3913-3923(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202101066
[29] KOSTASCHUK R, CHEN Z Y, SAITO Y, et al. Sedimentation rates and heavy metals in a macrotidal salt marsh: Bay of Fundy, Canada [J]. Environmental Geology, 2008, 55(6): 1291-1298. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-1077-z [30] 史锐, 岳荣, 张红. 有色金属采选冶基地周边土壤中重金属纵向分层研究 [J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(1): 186-191. doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2016.01.029 SHI R, YUE R, ZHANG H. Research on vertical distribution of heavy metal in soil around non-ferrous metal industry area [J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(1): 186-191(in Chinese). doi: 10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2016.01.029
[31] 张响荣, 罗红, 祝安安, 等. 武汉市某旱地自然土壤剖面中重金属迁移规律研究 [J]. 资源环境与工程, 2022, 36(3): 274-279. doi: 10.16536/j.cnki.issn.1671-1211.2022.03.002 ZHANG X R, LUO H, ZHU A N, et al. Study on the migration of heavy metals in natural soil profile of a dryland in Wuhan City [J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2022, 36(3): 274-279(in Chinese). doi: 10.16536/j.cnki.issn.1671-1211.2022.03.002
[32] 赵玉庭, 孙珊, 由丽萍, 等. 莱州湾沉积物粒度与重金属分布特征 [J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(3): 43-50. ZHAO Y T, SUN S, YOU L P, et al. Distribution characteristics of grain size and heavy metals of sediments in Laizhou Bay [J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(3): 43-50(in Chinese).
[33] ZHOU W X, HAN G, LIU M, et al. Vertical distribution and controlling factors exploration of Sc, V, Co, Ni, Mo and Ba in six soil profiles of the Mun River Basin, Northeast Thailand [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(5): 1745-1759. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051745 [34] 胡青青, 沈强, 陈飞, 等. 重构土壤垂直剖面重金属Cd赋存形态及影响因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6): 2878-2888. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201911023 HU Q Q, SHEN Q, CHEN F, et al. Reconstructed soil vertical profile heavy metal Cd occurrence and its influencing factors [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6): 2878-2888(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201911023
[35] 李晋昌, 张红, 石伟. 汾河水库周边土壤重金属含量与空间分布 [J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(1): 116-120. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.01.027 LI J C, ZHANG H, SHI W. Concentrations of soil heavy metals and their spatial distribution in the surrounding area of Fenhe reservoir [J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(1): 116-120(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.01.027
[36] BAI J H, XIAO R, CUI B S, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from the young and old reclaimed regions in the Pearl River Estuary, South China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(3): 817-824. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.11.004 [37] 李俊莉, 宋华明. 土壤理化性质对重金属行为的影响分析 [J]. 环境科学动态, 2003, 28(1): 24-26. LI J L, SONG H M. Effects of soil physicochemical properties on heavy metal behavior [J]. Environmental Science Trends, 2003, 28(1): 24-26(in Chinese).
[38] ZHANG P Y, QIN C Z, HONG X, et al. Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches ofYellow River irrigation in China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633: 1136-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.228 [39] 王国梁, 周生路, 赵其国, 等. 菜地土壤剖面上重金属元素含量随时间的变化规律研究 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2006, 22(1): 79-84. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2006.01.017 WANG G L, ZHOU S L, ZHAO Q G, et al. Spatial and temporal changes of soil heavy metal concentrations in vegetable cultivation land [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2006, 22(1): 79-84(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2006.01.017
[40] 石东平, 刘秋荣. 工业园道路两侧土壤及行道树的叶片Cr富集与污染评价 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2019, 19(5): 1803-1809. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2019.05.043 SHI D P, LIU Q R. Chromium(Cr) enrichment and pollution assessment in soil and leaves of street-by trees on both sides of industrial park roads [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2019, 19(5): 1803-1809(in Chinese). doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2019.05.043
[41] 戴树桂. 环境化学[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006: 283-284. DAI S G. Environmental chemistry [M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006: 283-284(in Chinese).
[42] 王敬国. 生物地球化学: 物质循环与土壤过程[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2017: 369-370. WANG J G. Biogeochemistry-material cycle and soil process[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2017: 369-370(in Chinese).
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 梁学超,郭朝晖,黄驰岳,高梓伦,杨锦波. 铅锌矿区冶炼地块土壤渗透性对重金属垂向分布的影响. 中南大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 44-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 林跃胜,王飞,郭尔洛,李鹤冉,方凤满. 菜子湖湿地土壤-植物体系重金属富集、转运及影响因素分析. 环境科学学报. 2025(03): 373-383 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 乌达木,高琪,朱荟. 重金属在矿山不同土壤类型中的特征与分布规律研究. 世界有色金属. 2024(16): 109-111 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李卫娜,蔡虹明,袁玮,郑旺,陈玖斌. 土柱实验在土壤重金属污染研究中的应用进展与展望. 地球与环境. 2024(05): 652-661 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载: