-
重金属具有持久、易累积及不可降解等特性,在低浓度下仍有着强烈的毒性,可以由多种途径进入生态系统,造成资源浪费、环境污染,同时严重损害人体健康[1-2]. 湖泊是物质的“汇”,流域物质随大气沉降、降水直接进入水体,或是通过径流作用间接汇集至湖泊中,入湖后流速减缓,物质发生沉淀,形成湖泊沉积物,其中,重金属是最重要的成分之一. 沉积物重金属是湖泊流域众多污染源中对生态环境造成危害最大和影响最持久的污染源[3]. 在湖泊系统中沉积物既是重金属的“汇”,也可能是重金属的“源”:重金属可在沉积物中积累,而在水动力等外力作用下,沉积物会释放出重金属,造成二次污染[4]. 因此探究湖泊沉积物中重金属分布,评估湖泊重金属污染状况至关重要.
目前已有大量学者针对湖泊沉积物重金属污染问题开展了相关研究. 研究内容主要集中在沉积物重金属的时空分布特征[5-7]、定年与沉积速率[8-12]、来源分析[13-15]等方面. 研究结果表明,沉积柱重金属含量分布受到自然沉积的影响,也可能与不同时期的人类活动显著相关. 上游的人类活动主要通过工业活动[16-18]、燃料燃烧[17]、采矿冶炼[17,19]、生活污水[16]、农业生产、交通运输等途径影响沉积物重金属的来源与含量. 因此,根据湖泊沉积柱中重金属不同时期的沉积特征来反演其污染历史,对于目前湖泊重金属污染治理具有指导作用,但是仅通过沉积年代与重金属的垂向分布来大致推测重金属的来源与影响机制具有一定的不确定性,仍需结合上游活动等进一步验证. 因此,不同沉积年代的重金属特征与上游活动的关联关系仍需进一步研究.
洞庭湖具有重要的生态地位,但由于上游存在历时长、范围广的工业活动,湖泊生态安全受到严重威胁. 现有洞庭湖重金属研究集中于表层重金属含量、污染程度演化及来源解析[20-22];关于沉积柱定年研究主要集中在“四水”入湖沉积物系[23]. 对于湖中沉积柱重金属在不同区域环境、不同历史时期的分布和流域污染源仍具有不确定性.
为探究湖中沉积柱重金属含量与流域人类活动的关系,本次研究选取洞庭湖泥沙频繁交换的关键区域——东洞庭湖区作为研究对象,选取3种人类活动类型区域(码头、旅游区、自然保护区),采用同位素定年法,分析东洞庭湖沉积速率及分层依据,探究其典型重金属的垂向分布特征;运用相关性、主成分分析,确定各类重金属污染物的来源;结合湖泊沉积背景与流域内人为活动,验证并总结不同阶段东洞庭湖沉积物污染情况,以期为东洞庭湖沉积物重金属污染防治提供历史依据.
-
东洞庭湖(28°28'—29°35′N,112°19′—113°05′E)位于长江中下游荆江段南侧,是洞庭湖湖系中最大的湖泊,其水系构成较为复杂,南侧湘江、南洞庭湖来水与汨罗江自岳阳县境内注入,东西两侧分别有新墙河及华容河、藕池河注入. 最终来自四水和西洞庭、南洞庭的水沙经东洞庭由城陵矶汇入长江. 因此,东洞庭湖对保障长江流域及环湖地区的水安全起着关键作用[24]. 湖区总面积约1328平方公里,其中湿地面积广阔,具有调节气候以及保护生物多样性的生态功能. 作为长江中游的重要节点,东洞庭湖地处湘鄂两省交界处,联通长江经济带,内河航运发达,人类活动显著. 境内自然与人文资源兼备,旅游业发展水平高. 自改革开放以来,社会经济迅速发展,湖泊上游流域矿产资源丰富,持续采矿活动使得大量重金属流入东洞庭湖,与此同时沿岸排放的工农业废水和生活污水造成的重金属污染问题已经引起学者的重视.
-
东洞庭湖沉积物采样于2020年12月进行,此时湖泊处于枯水期,入湖河流输沙量达到峰值,输沙过程趋于稳定. 据研究区主要人类活动种类,于码头、旅游区、自然保护区的3种类型中,分别在鹿角(LJ)、君山岛(JSD)和东洞庭湖主湖体(DDTH)采集沉积柱样品. 采样点均使用GPS定位,样点基本情况见图1和表1. 采样时使用美国犀牛S1土壤钻采集2 m的沉积柱样. 随后样品按5 cm进行分层,将每层沉积物样品分别装入聚乙烯袋中,密封编号、避光保存,送至实验室. 将取回后的样品放在阴凉通风口处自然风干,除去明显异物(石砾、根系等). 用玛瑙研钵磨碎,分别过10目、100目筛,混匀,保存备用.
-
样品采用HF-HNO3-HClO4-HCl酸溶解法进行消解[20]. 称0.2 g过100目筛的沉积物样品放入50 mL的聚四氟乙烯消解管. 在30 ℃条件下,各管内依次加入硝酸5 mL、盐酸5 mL、氢氟酸5 mL、高氯酸5 mL后,振荡摇匀1 min. 连接石墨消解仪,设置参数,消煮至内容物呈白色粘稠状. 降至室温后,用超纯水定容到100 mL容量瓶中,并摇匀静置,通过0.45 µm水系滤头过滤后转移至离心管中待测. 选择东洞庭湖沉积物中典型的7种重金属As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Mn、Pb、Zn,使用电感耦合原子子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES)测定含量. 利用空白样和标样对样品检测指标进行质量控制,计算加标回收率进行校正.
使用高纯锗γ能谱仪(型号Model GR 4021)检测湖泊沉积物样品210Pb的放射性活度,检测方法为γ能谱法:称取80 g过10目筛的沉积物样品置入10 mL聚乙烯离心管中,在暗室中蜡封20 d,使210Pb处于永久衰变平衡体. 随后将预处理好的样品放入仪器中进行210Pb含量的测定,每个样品的测量时间在40000 S以上,以保证数据的精确性. 210Pb和226Ra的比活度(Bq·kg−1)分别根据46.5 keV和661.6 keV的γ射线谱峰面积得到[21]. 用 210Pb和226Ra 的差值 计算 210Pbex 的比活度(Bq·kg−1).
210Pbex 测定沉积物年代的方法包括恒定初始浓度模型(Constant Initial Concentration, CIC)、恒定供给速率模型(Constant Rate of Supply model, CRS)、周期通量模型(Periodic Flux model, PF)和恒定沉降通量与沉积速率模型(Constant Flux Constant Sedimentation 86 model, CFCS). 其中CRS模型可用于210Pb输入通量恒定时,沉积速率可能会发生变化的情况. 因此,本研究采用CRS模型对东洞庭湖沉积物进行定年测定.
CRS模式计算公式为:
其中,t(i)为i层所对于的的年代,t(0)为采样年份,λ为210Pb的衰变系数(0.03114), A(0)为整个沉积柱210Pbex累积量(Bq·cm−2), A(i)为i层以下210Pbex累积量(Bq·cm−2), Cx为x质量深度的210Pbex活度(Bq·kg−1 ),ρx 为x 质量深度的样品容重(g·cm−2).
-
研究采用主成分分析、相关性分析的统计学方法,来辨别重金属的来源. 通过7种重金属元素含量的相关性分析,来判定各元素是否具备同源性. 主成分分析是判定重金属来源最常用的多元统计方法,一般借助于一个正交变换,对多维变量系统进行降维处理,同时保留原始数据之间的联系[22]. 因此,研究分别对3个点位的沉积柱中7种重金属含量进行主成分分析. 除此之外,从岳阳市志、湖南省统计年鉴中,收集1979—2020年岳阳市农田面积、汽车数量数据,以用于近期沉积物重金属来源的分析.
-
采用Microsoft Excel 2019和SPSS软件进行重金属含量统计以及斯皮尔曼相关分析、主成分分析(PCA),以说明沉积柱重金属的关联性与同源性. 其中PCA分析采用KMO值与巴特利特球形检验进行验证,仅LJ和JSD的中层以及DDTH的上层数据通过检验. 采用Arcgis10.8绘制样点分布图,其他数据制图使用Origin 2019b软件完成.
-
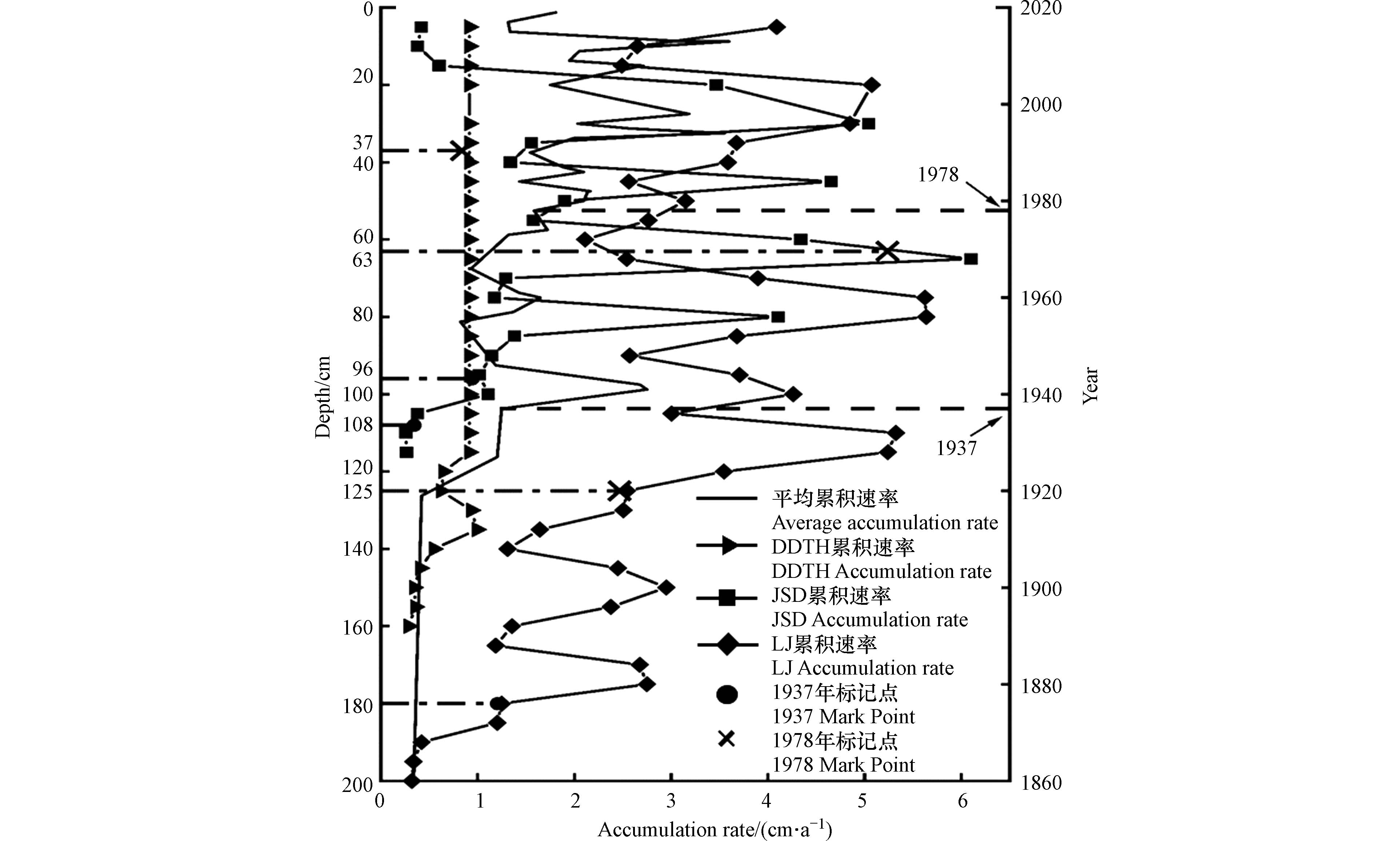
放射性同位素210Pb的结果表明,LJ、JSD、DDTH的210Pbex比活度范围分别为:1.36—58.95 Bq·kg−1、0.13—74.44 Bq·kg−1、0.02—39.3 Bq·kg−1,平均值为18.49、11.91、7.82 Bq·kg−1. 在沉积柱范围内,210Pbex比活度随深度增加大致呈指数衰减,表明沉积环境相对稳定. 根据CRS模型得到LJ、JSD、DDTH沉积柱的平均沉积速率分别为2.52、1.94、1.18 cm·a−1,分别代表3个点位1858—2020年、1894—2020年、1854—2020年的沉积物. 其中LJ平均速率远高于其他两点沉积柱,可能是由于LJ受上游湘江与南洞庭湖来水的影响,以及大坝的修建,蓄水泄洪工程开展,使得LJ附近水动力条件增强[23],泥沙沉积量显著增加. 相较于DDTH,JSD点位毗邻长江,其沉积过程受长江来水影响较大,自上游长江三峡大坝修建以来,泥沙量的减少更为明显[24],沉积速率显著下降 . 而DDTH远离河口,泥沙沉积率较河口处较少,其沉积速率在这3点中最小.
沉积柱210Pb累积速率随深度变化如图2,结合同位素定年结果,3个采样点的210Pb累积速率在沉积柱中呈现明显分层情况。其中,LJ沉积物的210Pb累积速率在1937年前较为稳定,近似自然沉积,1937—1978年间累积速率在1—3 cm·a−1之间波动,而1978年后速率变化程度达到新的水平,于2—6 cm·a−1间波动;JSD点位的累积速率在1937—1978年变异程度极高,在其他时段接近自然沉积速率,扰动程度小;DDTH点位除在1937年之前存在小幅波动外,其后累积速率一直稳定. 由此,将沉积柱划分为3个时期:第一阶段为1937年前,此阶段为人类活动程度较低,对沉积环境的扰动较轻,沉积环境较为稳定,结合史料,累积速率的波动可能与山体滑坡、洪水决堤等自然现象有关;第二阶段所覆盖时期为1937—1979年,流域内大面积的围湖造田、修坝建闸,使得泥沙淤积速率加快,湖泊面积骤减,人类活动对沉积过程的影响进一步增加[25];第三阶段所包含年份为1979—2020年,在1982年后,由于东洞庭湖自然保护区的建立,人类扰动沉积过程的情况得以缓解,此时沉积物累积速率也有所下降.
-
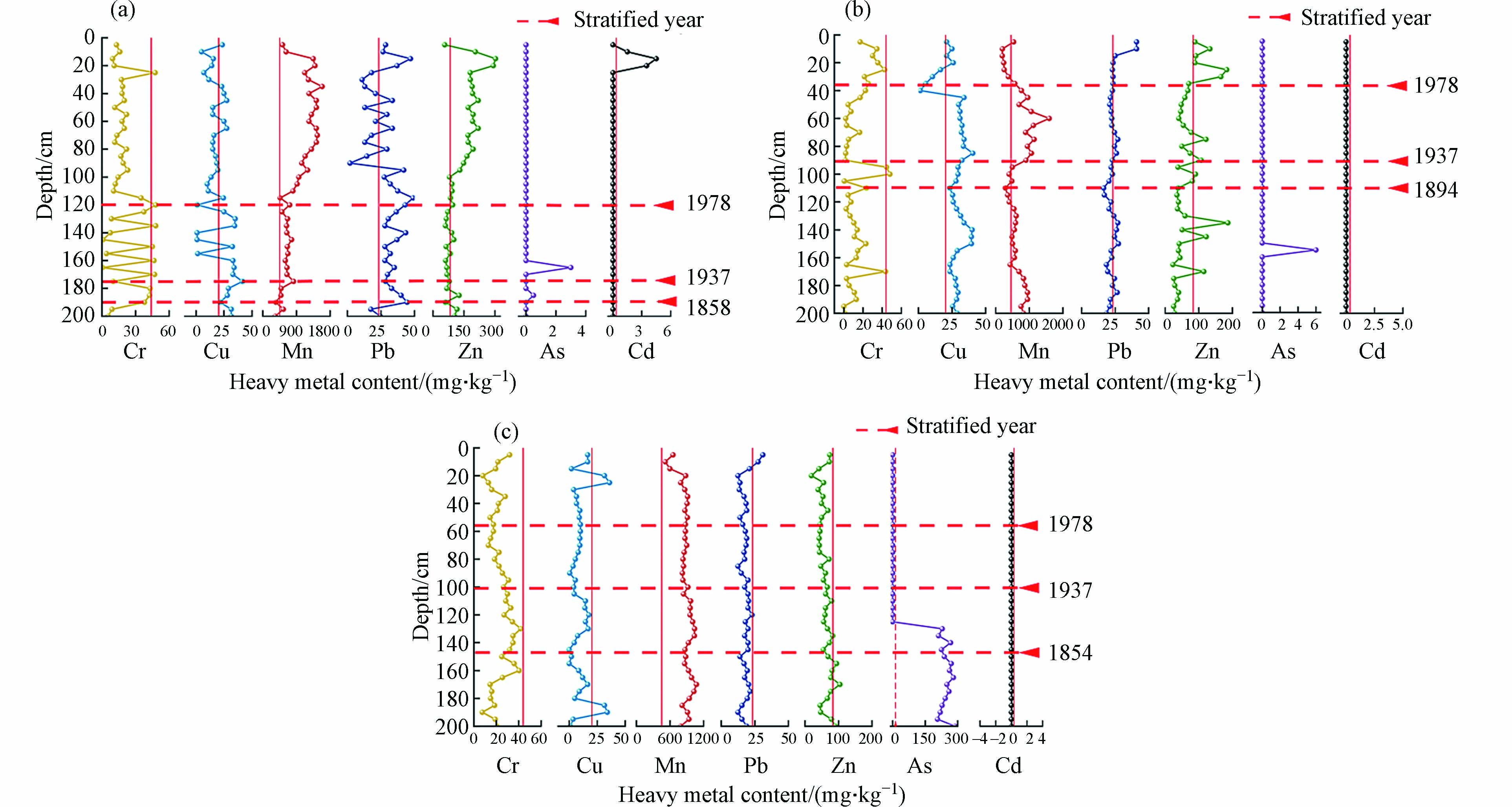
如表2所示,As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Zn在各点位不同层间均值差异较大,其中As变异程度最为显著,各类重金属在垂向上的含量变幅较剧烈;除LJ的Mn、Zn,JSD的Cr、Pb、Zn,DDTH的Cu、Pb以外,沉积柱中重金属平均含量均为中下层高于上层,可能与洞庭湖流域内及其上游污染治理计划的实施有关[27-29]. 除As以外,鹿角各层的重金属元素平均值高于君山岛和东洞庭湖保护区,说明鹿角受到上游湘江流域污染的影响[30].
如表3所示,与全国不同区域典型湖泊中沉积物重金属含量比较发现,1937年时,长江中下游的典型湖泊沉积柱中,东洞庭湖3个沉积柱中Pb、Zn含量较高,但Cu、Cr、As显著低于其余湖泊沉积柱;同时Mn含量是鄱阳湖的1.14—1.25倍;1978年总体重金属含量特征类似,仅有LJ沉积柱中Pb含量、DDTH中Zn含量较其他湖泊偏低;2020年表层中重金属中3个样品中Pb、Zn均低于其他湖泊. 这说明东洞庭湖的重金属含量与不同时期人为活动类型有着密切联系[38].
根据沉积物随深度的分层,LJ、JSD、DDTH重金属垂向分布如图3所示. 从图3可以看出Cd、As随深度变化不明显,且多数样点Cd的含量低于检测限,仅于2015年在LJ点位出现波动,含量达4.5 mg·kg−1,显著高于背景值,说明湘江入湖处受到较为严重的镉污染,其污染程度的骤增与2005、2006、2009年的大型镉污染事件有关,在李利强等的研究中发现类似结果[39];As大部分时刻含量偏低,但1916年前,DDTH沉积柱中其含量均在在200 mg·kg−1以上,显著超过背景值,反映近代以来长时期的上游雄黄矿采冶活动,致使该点位出现污染.
重金属元素Cu、Pb、Mn的含量总体表现为随深度增加而小幅增加,其中Cu和Pb的平均含量呈现LJ>JSD>DDTH,而Mn表现为LJ>DDTH>JSD,反映三者沉积过程中可能受到水动力条件、工业活动等因素的影响[34]. LJ中层的Cu含量在背景值附近具有显著的波动,在1940年处出现峰值,这与抗日战争后新中国工业的迅速发展有着一定的联系,而Pb元素在LJ整个沉积柱的变异程度高,峰值位于1981年,可能与各时期铅锌矿采冶活动有关,Mn中下层含量较为稳定,自1979年开始元素值随深度减小而增加,在2010年有高值;而在JSD上层,1972—1983年间Cu的含量出现显著下降,之后在27 mg·kg−1附近波动,Pb元素则是在2000—2012年迅速增加至417 mg·kg−1,Mn含量在中层波动较大,上下层随深度变化不大,说明在中层Mn元素的沉积环境最不稳定,且于1963年出现峰值,达1592 mg·kg−1;此外,Mn、Cu、Pb分别在DDTH的170、25、5 cm出现峰值,达1074、36、31 mg·kg−1.
元素Cr和Zn的含量呈现围绕定值波动的垂向分布特征,平均含量为:LJ>JSD>DDTH,说明这两种重金属低于背景值的历史时期较长,污染程度较轻. 在LJ上层Cr于2013年处出现高含量,而该层Zn含量随深度减小逐渐增加,在2015年处高达303 mg·kg−1后骤减,可能与近代环保力度的加大有关;在鹿角的中层Cr值存在显著波动,在1966年、1978年出现峰值,此时Zn元素值稳定分布于83.3 mg·kg−1附近;在JSD两种重金属均在中层较为稳定,而在上下层变幅较大,体现早期与近代的工业活动对重金属含量分布有显著影响,分别于1929年、1981年达到峰值;DDTH点位的两种元素含量均低于其背景值,说明在该处未出现污染.
-
为了明确东洞庭湖沉积物中重金属来源,研究采用主成分分析结合斯皮尔曼相关性分析来进行重金属源分析. 本研究中7种重金属的潜在来源可能来自以下四个方面:采矿源(矿物采冶活动)、工业源(造纸业、印染业、纺织业等工业)、农业源(化肥农药施用等)、交通源(燃油尾气、轮胎磨损等). 从垂直分布情况可以看出,7种重金属含量元素有3个显著变化的阶段,其变化与湖南省早期工业活动一致,并且与流域内的人类活动有较强的相关性.
1937年前:JSD的Zn和Cr、Cu、Pb显著相关,Cu和Pb极显著相关(表4),因此Zn、Cr、Cu、Pb等4种金属可能具有相同的来源;DDTH的 Mn和Cu显著相关. 大量研究表明,矿物冶炼是重金属污染的重要来源. 结合铜冶炼烟气富含Cu、As、Pb等元素,戴翌晗由主成分分析得出Cu、Pb属冶炼源[40]. 孟婉等采用多元统计分析,发现长江中游湖泊的Zn与锌矿产的开采有关[13],且锌矿石中含有Cd、Co、Ni、Cu等重金属元素,这些元素都会给周边环境带来污染[41]. 郭旻欣总结了土壤重金属污染的来源,可以看出Cr主要来自于矿产开采、冶炼和加工排放的三废[42]. 建国前采矿冶金业占据湖南省工业的主体地位,据省志记载[43],20世纪以来,湖南省境内官办商办矿厂数目渐长,由于采冶技术落后且均以土法开采,造成了早期的重金属污染[44],在降水、径流的作用下汇入湖泊造成污染并富集于沉积物中[45]. 因此造成早期重金属污染的主要是“采矿源”.
1937—1978年:由主成分分析结果可知[图4(a)],LJ沉积柱的中层主成分1(PC1)上载荷较重的元素有Zn(0.962)和Pb(0.790),其中Mn(0.567)也有较高的载荷. 且由相关性分析可知(表5),Zn、Pb极显著相关,因此这3种金属具有相同的来源. Pb、Zn主要来源于矿山开采和工业活动,是工业活动的主要标志[46],而李欢娟等通过对曲江池重金属进行聚类分析,得出Mn、Pb主要源于工业活动[45]. 抗日战争以来,众多工厂内迁湖南,加之1949年后本省大规模的经济建设的开展,湖南省的工厂数目到达高峰期[43],沿江沿湖工业“三废”的肆意排放也造成了严重的环境污染问题. 因此,造成LJ在这一时段的重金属污染主要是源于造纸、化工、冶炼、纺织等工业活动的“工业源”.
而在JSD点位[图4(b)]的中层主成分1(PC1)上载荷较重的元素有Cu(0.887)和Mn(0.774). Cu是动物饲料的重要成分[47],也可以作为使用农业活动的标志元素[48]. Mn也是制备化肥农药的原材料[49]. 经调查,作为洞庭湖区的重要农业活动中心,岳阳市农业种植中开始使用肥料和农药的时期较早,且面源影响较广,收集1996年以来的岳阳市志数据[50],与重金属浓度的空间分布情况对应,推测第一主成分为“农业源”. 在该点位主成分2的主要载荷变量为Pb和Zn,分别达到0.835、0.911,且由相关性分析可知,Zn、Pb显著相关,因此这两种金属来源相同. 张爱国等的研究表明,Pb、Zn的来源与交通运输业的影响有着显著关联[51],因此第二主成分为“交通源”. 随着流域内经济水平迅速提高,工业化、城市化进程迅速,在该阶段东洞庭湖受到“工业源”、“农业源”及“交通源”的共同影响,且由于土地利用类型的分化,各区域的污染源种类有显著差异.
1978—2020年,在LJ点位的上层,由相关性分析(表6)可知,Zn、Mn、Cd极显著相关,因此这三种金属可能具有相同的来源,张转玲等研究草海沉积物得出Zn、Pb的主要来源于矿产开采[52],Cd也常作为农业生产的指示元素,且浓度的高值与上游大型化工污染事件有显著对应关系[53—55],在本阶段该点位主要的污染源为工、农业共同控制形成的“混合源”;在DDTH点位上层,结合岳阳市志中汽车量、农田面积[56-57],运用主成分分析法[图4(c)],发现在第一主成分:Pb、Cr、Zn有较高载荷,分别为0.99、0.86、0.75,且汽车数量(0.91)、农田面积(0.60)也有较高的载荷,1986年JSD点位附近新建旅游车道,开始通车;据数据统计[57],自1980年—2012年,岳阳市汽车拥有量由684辆增至197855辆. 故Pb、Zn、Cr受到农业及交通运输业的综合作用,因此第一主成分为“混合源”. 第二主成分的主要载荷变量为Cu,因此Cu主要为“农业源”. 结合湖南省发展历史,该阶段工业发展水平速度最快,污染与治理并行,也使得这一时期的污染情况最为复杂.
-
本文以东洞庭湖流域为研究对象,分析了东洞庭湖沉积物中As、Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn、Cr和Mn共7种重金属含量的时空分布特征、污染来源以及影响机制,得到以下结论:
(1)210Pb定年结果表明东洞庭湖沉积物的平均沉积速率为1.88 cm·a−1,覆盖了近100年的沉积历史. 不同沉积点之间沉积速率差异显著,呈现出码头(LJ)>旅游区(JSD)>自然保护区(DDTH). 此外,洞庭湖沉积物的沉积过程大体可分为三个阶段:早期(1937年前)近似自然沉积;中期(1937—1978年)人为活动的影响显著提高;近期(1978年至今)的沉积环境变异程度较大,扰动性进一步加强.
(2)沉积柱的重金属含量表明,东洞庭湖沉积物的As、Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn污染较为严重. Cd、As随深度变化不明显;Cr和Zn的空间分布相似,表现为:码头(LJ)>旅游区(JSD)>自然保护区(DDTH),Cu、Pb、Mn的含量总体表现相似,均随深度增加含量小幅增加,Cu、Pb垂向上的平均含量呈现码头(LJ)>旅游区(JSD)>自然保护区(DDTH),而Mn表现为码头(LJ)>自然保护区(DDTH)>旅游区(JSD).
(3)主成分分析结果表明,东洞庭湖重金属主要有4个来源,分别为采矿源、工业源、农业源以及交通源. 其中,早期重金属主要来源于早期采冶活动带来的采矿源;中期东洞庭湖受到工业、农业和交通运输业的共同影响,而1978年以来,伴随工业化和城镇化水平的快速发展,污染来源多样且复杂.
基于多元统计方法的东洞庭湖沉积物重金属时空分布特征与来源变化
Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and source changes of heavy metals in sediments of East Dongting Lake based on multivariate statistical methods
-
摘要: 流域上游矿山开采和重金属冶炼等人类活动的影响使得洞庭湖水域重金属污染问题严重,制约了该区域社会经济的可持续发展. 针对近100年来洞庭湖重金属污染不明的现状,本研究以东洞庭湖为研究对象,结合放射性核素210Pb定年技术,分析沉积物中7种重金属(As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Mn、Pb、Zn)的时空分布特征,并采用主成分分析方法,解析重金属污染物的来源. 研究结果表明,近100年来东洞庭湖存在As、Cd、Pb、Cu、Zn污染情况. 其中As的平均含量较高,在东洞庭湖自然保护区(DDTH)下层均值达184.05 mg·kg−1;除鹿角(LJ)下层,Mn元素平均含量均高于洞庭湖背景值,对其需引起重视. 重金属含量在垂向上变幅较大,且沉积过程大体可分为3个阶段(1937年前;1937—1978年;1978—2020年). 源解析结果表明,早期的东洞庭湖沉积物重金属污染主要来自“采矿源”;中期主要受到“工业源”、“农业源”及“交通源”的共同影响;而近期为多种污染源共同支配形成的“混合源”. 本研究结果进一步明确了湖泊沉积物重金属的空间分布特征以及污染历史的演化过程,为湖泊环境管理提供理论支撑.Abstract: The heavy metal pollution in Dongting Lake is serious due to the intensive human activities such as mining and heavy metal smelting in the upper reaches, which restricts the sustainable development of the region’s society and economy. For the uncertain situation of the heavy metal pollution in Dongting Lakre over the past century, this study selected East Dongting Lake as the research object. The spatial and temporal distributions of seven heavy metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Mn, Pb, and Zn) in sediments were analyzed with the help of 210Pb dating technique, and their source was identified by principal component analysis. The results showed that the East Dongting Lake was contaminated by As, Cd, Pb, Cu and Zn in the past 100 years. In DDTH (the nature reserve), the average content of As was relatively high with the value in the lower layer reaching 184.05 mg·kg−1. Except for the lower layer LJ (wharf), the average content of Mn in all the sites exceeded the background value, which needs more attention. The content of heavy metals showed obvious variation along the vertical direction, and the deposition process can be divided into three stages: before 1937,1937—1978, and 1978—2020. The source identification results showed that heavy metal pollution of sediments in East Dongting Lake was mainly from “mining sources” in the early period. In the middle period, it was mainly affected by the “industrial source”, “agricultural source” and “transportation source”. In recent years, the “mixed source” formed the combined domination of the pollution sources. Our findings clarified the spatial distributions of heavy metals in lake sediments and their evolutionary processes of pollution history, and further provided theoretical support for lake environmental management.
-
Key words:
- heavy metals /
- East Dongting Lake /
- sediments /
- pollution history /
- sources.
-
四环素(TC)常被用作饲料添加剂应用于畜牧业及水产养殖业[1-2],因在动物体内吸收率较低,常以原药和代谢产物的形式随粪尿排出体外,造成水体及土壤环境污染[3]. 目前,常规的处理工艺无法有效去除废水中抗生素,因此导致TC能够在不同的水源甚至饮用水中被检测到[4-5]. TC在地表水中的浓度可达μg∙L−1级别[6],尽管浓度较低,但同样能增强细菌耐药性,从而对生态环境和人类健康造成潜在威胁[7-8].
地表水中的可溶性有机物可通过光化学反应产生H2O2[9],而水体中H2O2与有机污染物的氧化还原反应有密切关系,能够影响化学物质的降解转化和生态效应[10]. 水中的Cu2+、Fe2+等过渡金属离子可催化H2O2分解为∙OH(E0=2.80 V)[11],而自然水体的沉淀物中广泛存在过渡金属氧化物,能够缓慢的释放出金属离子催化H2O2产生活性物质形成类Fenton反应降解水中有机物[12]. 水合氧化铁(HFO)广泛分布于沉积物和土壤中[13],具有很强的亲水性、较高的表面羟基密度和电子传输[14] 等特性. 现有关于HFO对水中污染物的去除研究多集中于吸附作用方面[15-16],鲜有关于水合氧化铁在水环境中催化H2O2降解抗生素污染物方面的报道.
本研究以HFO为材料,模拟其催化H2O2降解TC反应过程,优化反应条件并探索HFO/H2O2体系的潜在氧化机制,同时采用超高效液相色谱串联质谱(LC-TOF-MS/MS)的分析结果,鉴定TC代谢转化产物并提出了TC可能的降解途径. 研究结果可为探讨自然水体中HFO催化降解TC提供理论参考,也可为含TC废水处理提供技术支撑.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 试剂与材料
盐酸四环素纯度>98%,购自于上海源叶生物科技有限公司;六水合氯化铁(FeCl3∙6H2O),分析纯,购自于天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;过氧化氢(H2O2),质量分数30%,购自于上海沃凯生物技术有限公司;乙腈和甲醇,色谱级,购自于美国Merck公司;氢氧化钠、盐酸、苯醌、硫代硫酸钠、叔丁醇等均为分析纯,购自于西陇化工股份有限公司;实验用水均为超纯水.
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 催化剂的制备
水合氧化铁(HFO)的制备方法参考文献 [17] 并做修改,在磁力搅拌下,将10.0 g的FeCl3∙6H2O溶解在100 mL超纯水中,然后用1 mol∙L−1的NaOH溶液将FeCl3∙6H2O溶液的pH值调至7.0. 形成的悬浮液连续搅拌1 h,并在室温下陈化24 h,然后通过离心(4500 r·min−1,5 min)法收集沉淀的水合氧化铁颗粒,然后用超纯水洗涤3次,去除残留离子. 最后,将水合氧化铁冷冻干燥,在玛瑙研钵中研磨,并通过200目筛,收集并存储在棕色玻璃瓶中备用.
1.2.2 催化剂的表征
ESCALAB 250Xi 型X-射线衍射仪测试样品的X射线衍射(XRD)谱图; Tristar II 3020M全自动比表面积和孔隙分析仪测定样品的比表面积和孔径; JES-FA200电子顺磁共振波谱仪(EPR)测试反应体系中产生的自由基种类; Nicolette iS50傅立叶红外-拉曼光谱仪测试样品红外光谱(FTIR); Cary Eclipse荧光分光光度计测试样品的三维荧光光谱(3D EMM).
1.2.3 TC催化降解及影响因素实验
配制50 mL初始pH6.5的四环素溶液(40 mg∙L−1),分别加入HFO、H2O2和HFO/H2O2(其中HFO为20 mg,H2O2为5 mmol∙L−1),在25 ℃的水浴温度下以150 r∙min−1速率震荡,反应一定时间后取样,样品用0.2 mol∙L−1的硫代硫酸钠溶液(甲醇:水 体积比为 1:1)稀释1倍,终止反应,样品经10000 r∙min−1离心10 min后取上清液过0.22 μm水相滤膜过滤后用UPLC测定.
探讨H2O2浓度的影响,将实验中H2O2浓度分别设置为0、0.5、1、2、5、10 mmol∙L−1;探讨初始pH影响时用0.1 mol∙L−1的NaOH或HCl调节溶液pH值分别为2、3、5、6.5、9、10;比较共存离子的影响时在HFO/H2O2反应体系中分别添加25 mmol∙L−1和50 mmol∙L−1的不同离子(Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、
NO−3 HCO−3 SO2−4 1.2.4 自由基淬灭实验
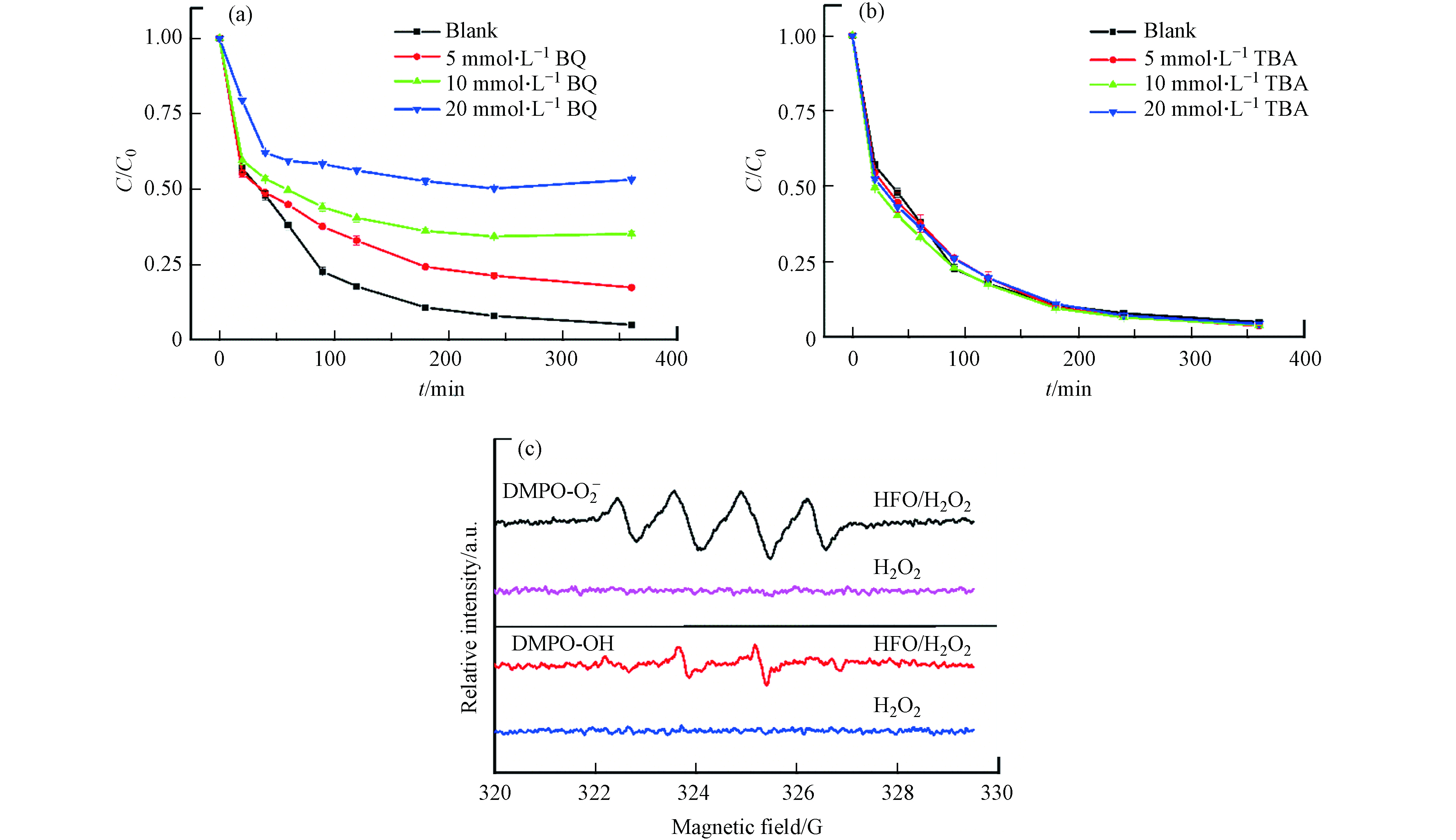
为研究催化反应体系中的活性氧种类,分别使用叔丁醇(TBA)和苯醌(BQ)作为羟基自由基(∙OH)和超氧自由基(∙O2-)的抑制剂,采用电子自旋共振谱(EPR)验证体系中∙OH和∙O2-,∙OH和∙O2-自由基的捕获剂是100 mmol∙L−1 DMPO.
1.2.5 四环素的测定
使用Waters UPLC-VWD型超高效液相色谱检测溶液中TC. 色谱柱为ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18反相柱(100 mm × 2.1 mm i.d.,1.7 μm),检测波长为254 nm,进样量为10 μL,柱温40 ℃,流动相A为1‰甲酸,流动相B为乙腈. 梯度设置:95.0% A(0 min)、5.0% A(2.5 min)、95.0% A(3.51 min)、95.0% A(5 min),流速为0.30 mL∙min−1.
1.3 数据处理与分析
剩余率:η=1−T=Ct/C0 (1) 一级速率常数计算式为:ln(Ct/C0)=kt (2) 式中,C0和Ct分别代表四环素的起始质量浓度和t时刻的质量浓度,单位mg∙L−1.
所有数据均以3次重复的平均值±标准偏差表示,并使用Origin 8.5绘制数据. 使用SPSS 21.0软件对数据进行统计分析.
2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 HFO的表征
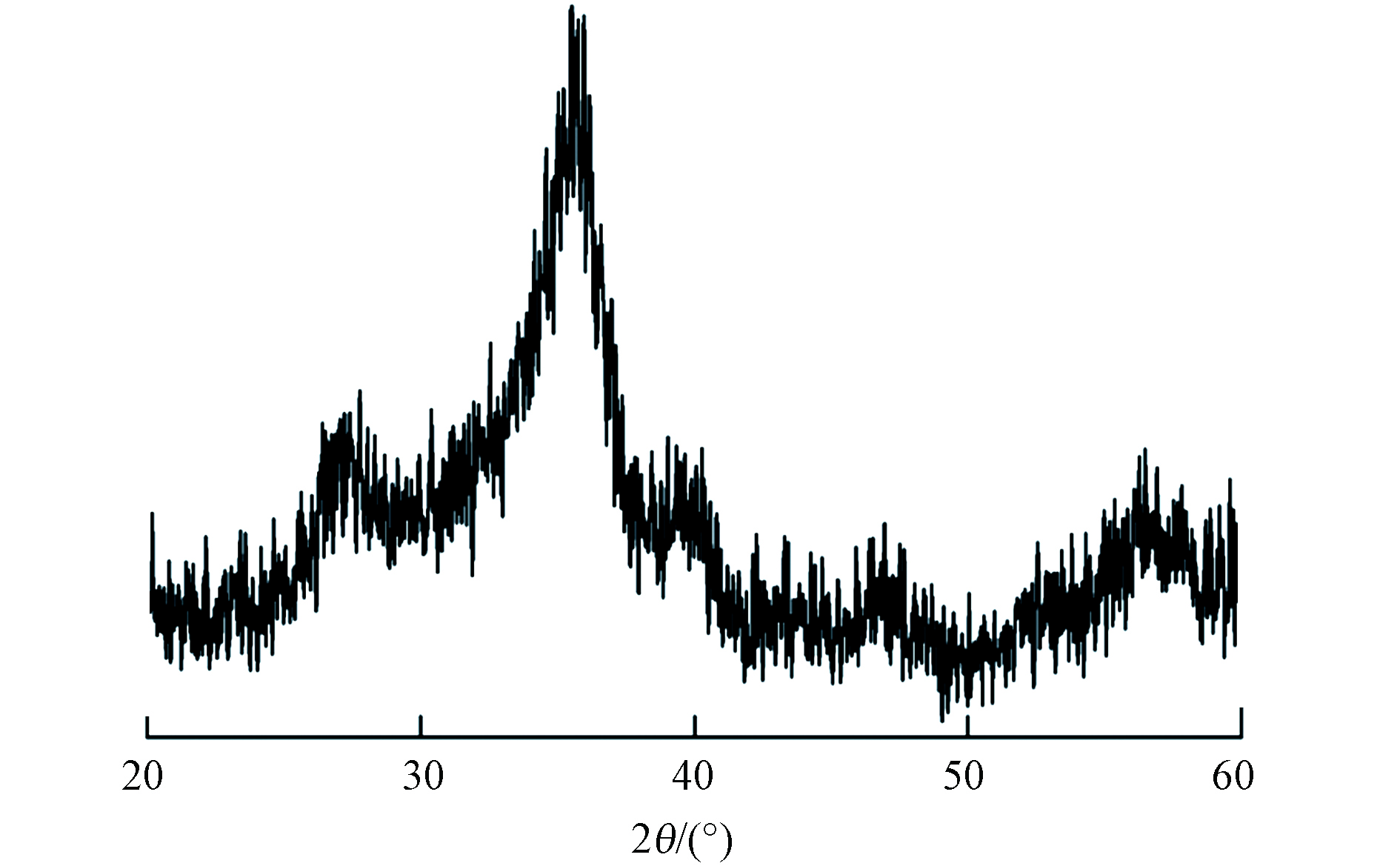
HFO的XRD图谱如图1所示. 图1中未出现较强的衍射特征峰,这表明水合氧化铁不具有晶体结构. 水合氧化铁在36.4º处出现1个宽峰,出峰位置与水铁矿相似 (JCPDS No. 29-0712)[18] ,表明合成的水合氧化铁为无定形铁氧化物.
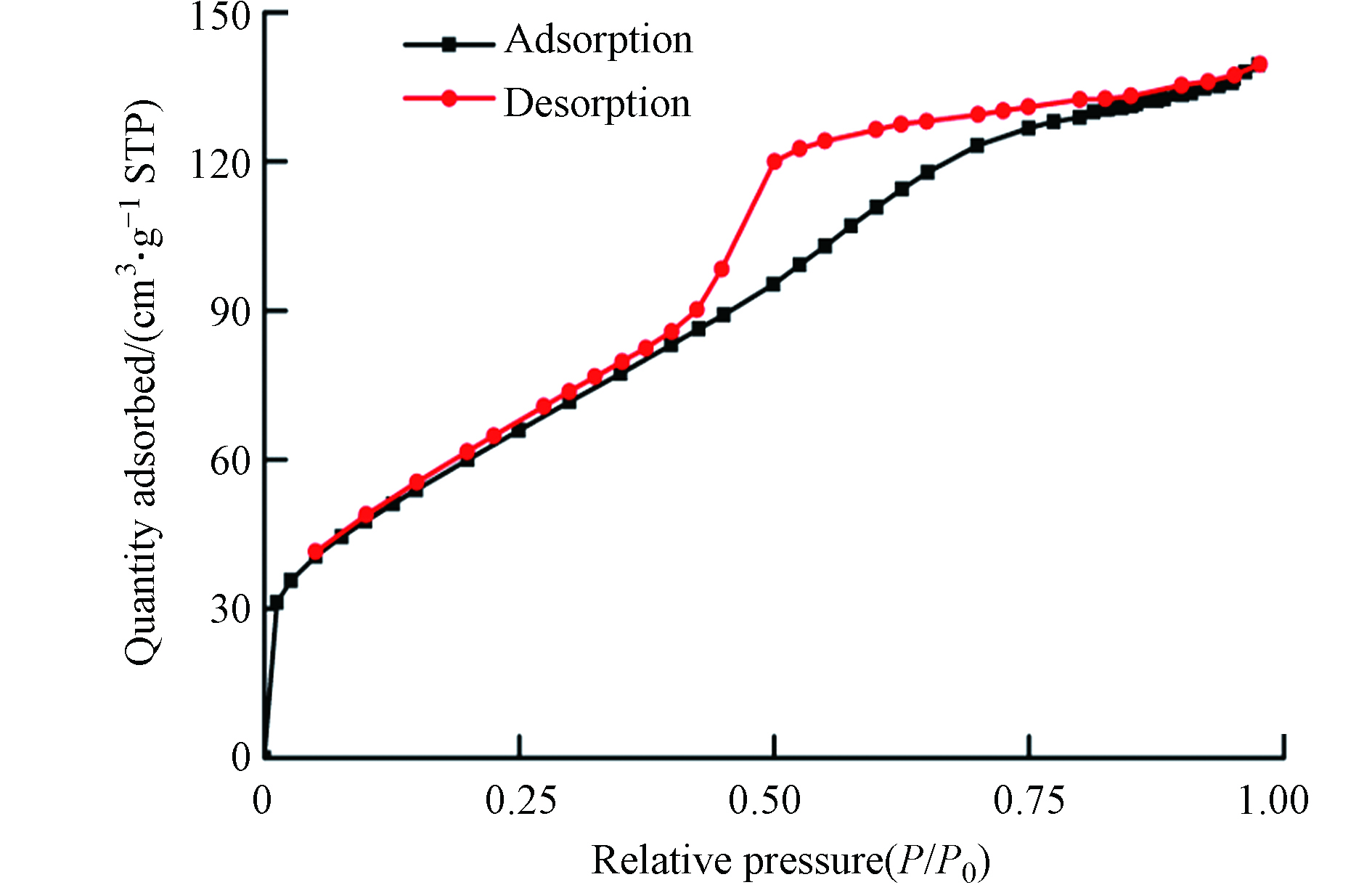
HFO的氮气吸附解吸曲线如图2所示. HFO的N2吸附-脱附曲线属于V型等温线并具有H4型滞后回环,表明合成的样品中主要存在的是介孔结构[19]. 水合氧化铁的比表面积,孔体积和孔径分别为226.796 m2∙g−1、0.167 cm3∙g−1和3.495 nm. 由上述数据可知,水合氧化铁的孔隙结构较为发达,拥有较高的比表面积,可提供更多的Fe活性位点,有利于催化H2O2降解污染物.
2.2 不同反应体系下TC的降解速率
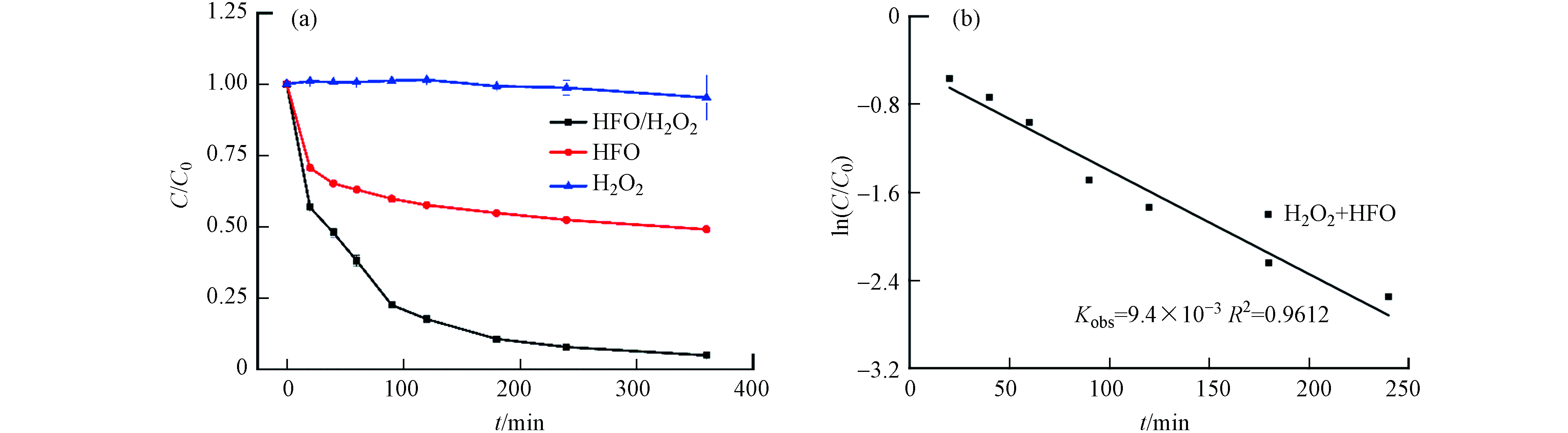
不同反应体系(H2O2、HFO和H2O2/HFO)下TC的降解动态如图3(a)所示. 当H2O2单独存在时,0—6 h内TC浓度几乎不变,这表明仅仅使用H2O2难以直接降解TC. 单独加入HFO时,四环素去除率为54%. 这可能是因为催化剂和TC发生了吸附反应. 在H2O2/HFO体系下,TC的去除率可达97%,这表明HFO可有效地催化H2O2氧化降解TC. 在实验中采用拟一级动力学拟合HFO/H2O2体系的降解数据,如图3(b)所示,与该模型相对吻合(R2>0.9),相对应的表观速率常数为9.4×10−3 min−1,这表明HFO可以有效催化激活H2O2生成自由基,促进TC的降解.
2.3 H2O2浓度对TC降解的影响
H2O2浓度会直接影响自由基的生成,进而影响TC的降解效率[20]. 不同H2O2浓度对TC降解的影响见图4.
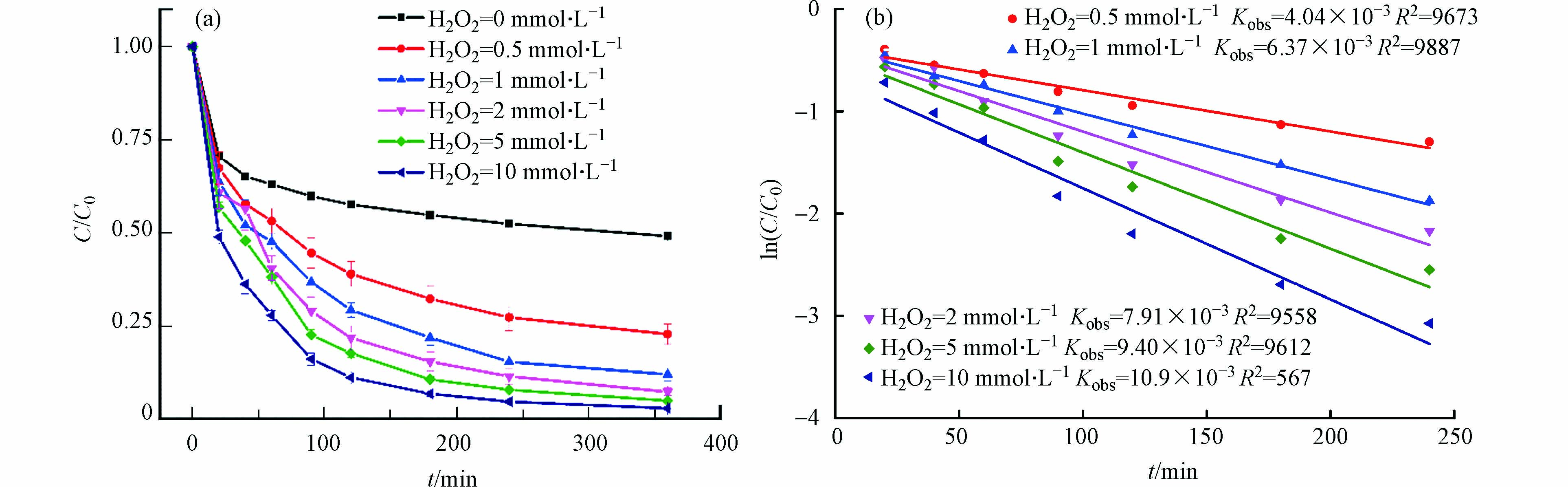
H2O2的浓度从0 mmol∙L−1增加到10 mmol∙L−1时,TC的去除率从54%增加到98%. 采用拟一级动力学模型拟合HFO催化不同浓度H2O2降解四环素的过程,结果见图4(b). 当H2O2的浓度从0.5 mmol∙L−1增加到10 mmol∙L−1时,其相对应的表观速率常数从4.04×10−3 min−1增加到10.9×10−3 min−1,这表明随着H2O2浓度增加促进了TC的降解速率. 这主要是由于随着H2O2浓度的增加,HFO能够催化H2O2产生更多的自由基降解TC.
2.4 溶液初始pH值对TC降解的影响
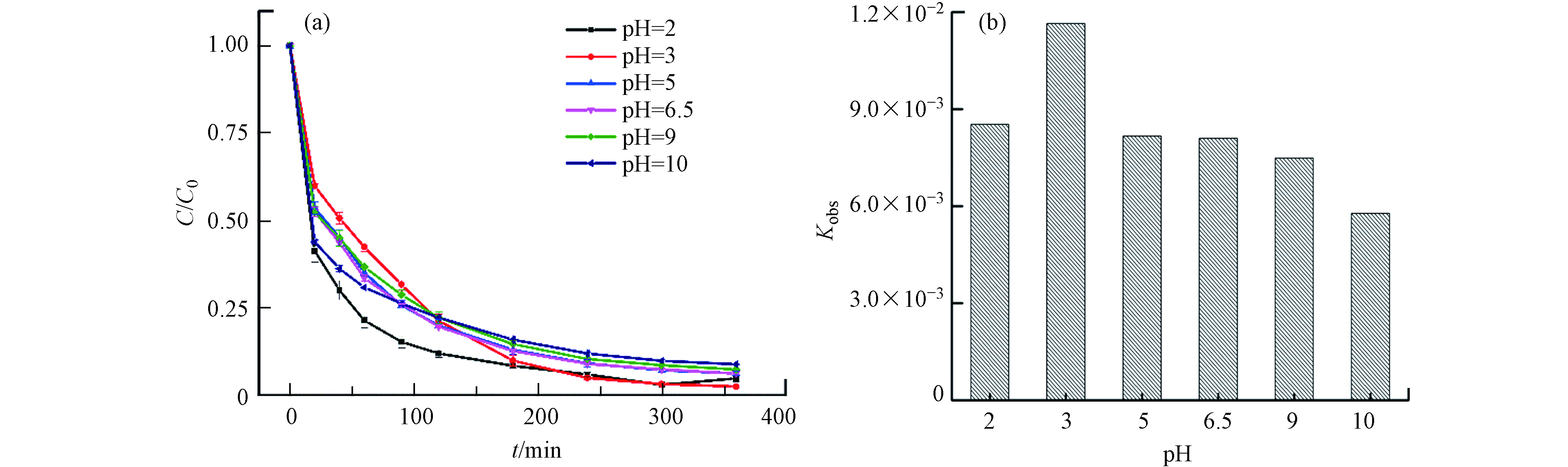
溶液初始pH值对TC降解速率的影响如图5所示,在酸性条件下,TC具有更高的降解速率和去除率. 这可以归因于,在酸性条件下,HFO催化剂表面更容易溶解出Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)催化H2O2生成自由基降解TC. 由图5(a)可知,初始pH值在2—10之间时催化剂对TC都具有良好的降解效果,降解效率都在90%之上. 可见HFO催化H2O2对TC的降解有着较好的pH适应性.
2.5 共存离子对TC降解的影响
由于在实际水体中含有大量的阴离子和阳离子,因此在实验中研究了共存Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+、
NO−3 HCO−3 SO2−4 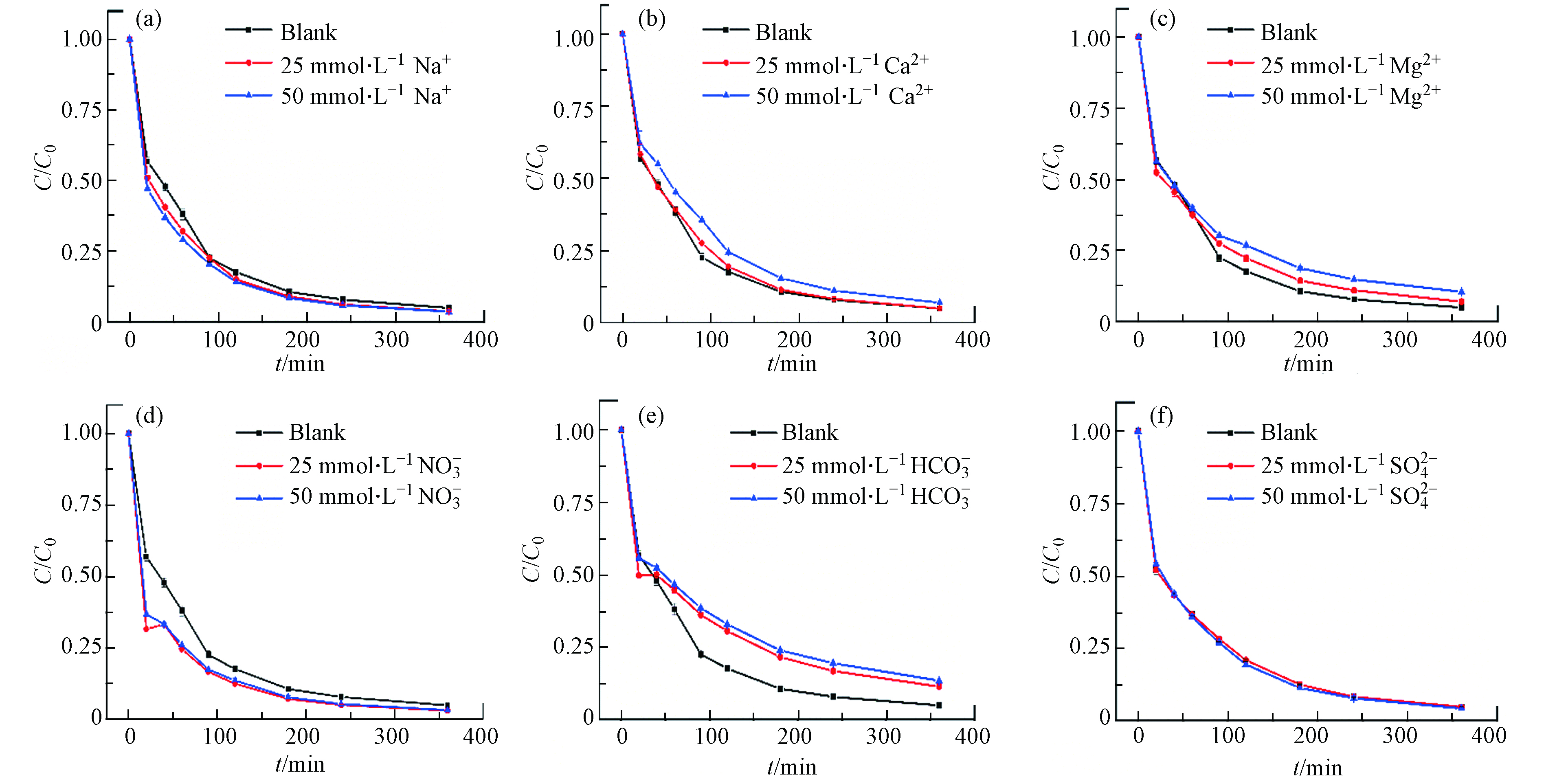 图 6 无机盐离子(a) Na+,(b) Ca2+,(c) Mg2+,(d) NO3-,(e) HCO3-,(f) SO42-对HFO催化H2O2降解四环素的影响Figure 6. Effect of inorganic salt ions on HFO catalytic degradation of tetracycline by H2O2.(实验条件:催化剂投加量 为 0.4 g∙L−1;pH = 6.5;[TC]= 40 mg∙L−1;[H2O2]= 5 mmol∙L−1)(Dosage 0.4 g∙L−1; pH = 6.5; [TC] = 40 mg∙L−1;[H2O2] = 5 mmol∙L−1)
图 6 无机盐离子(a) Na+,(b) Ca2+,(c) Mg2+,(d) NO3-,(e) HCO3-,(f) SO42-对HFO催化H2O2降解四环素的影响Figure 6. Effect of inorganic salt ions on HFO catalytic degradation of tetracycline by H2O2.(实验条件:催化剂投加量 为 0.4 g∙L−1;pH = 6.5;[TC]= 40 mg∙L−1;[H2O2]= 5 mmol∙L−1)(Dosage 0.4 g∙L−1; pH = 6.5; [TC] = 40 mg∙L−1;[H2O2] = 5 mmol∙L−1)Na+、Ca2+、
NO−3 SO2−4 HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 CO−3 2.6 三维荧光光谱分析
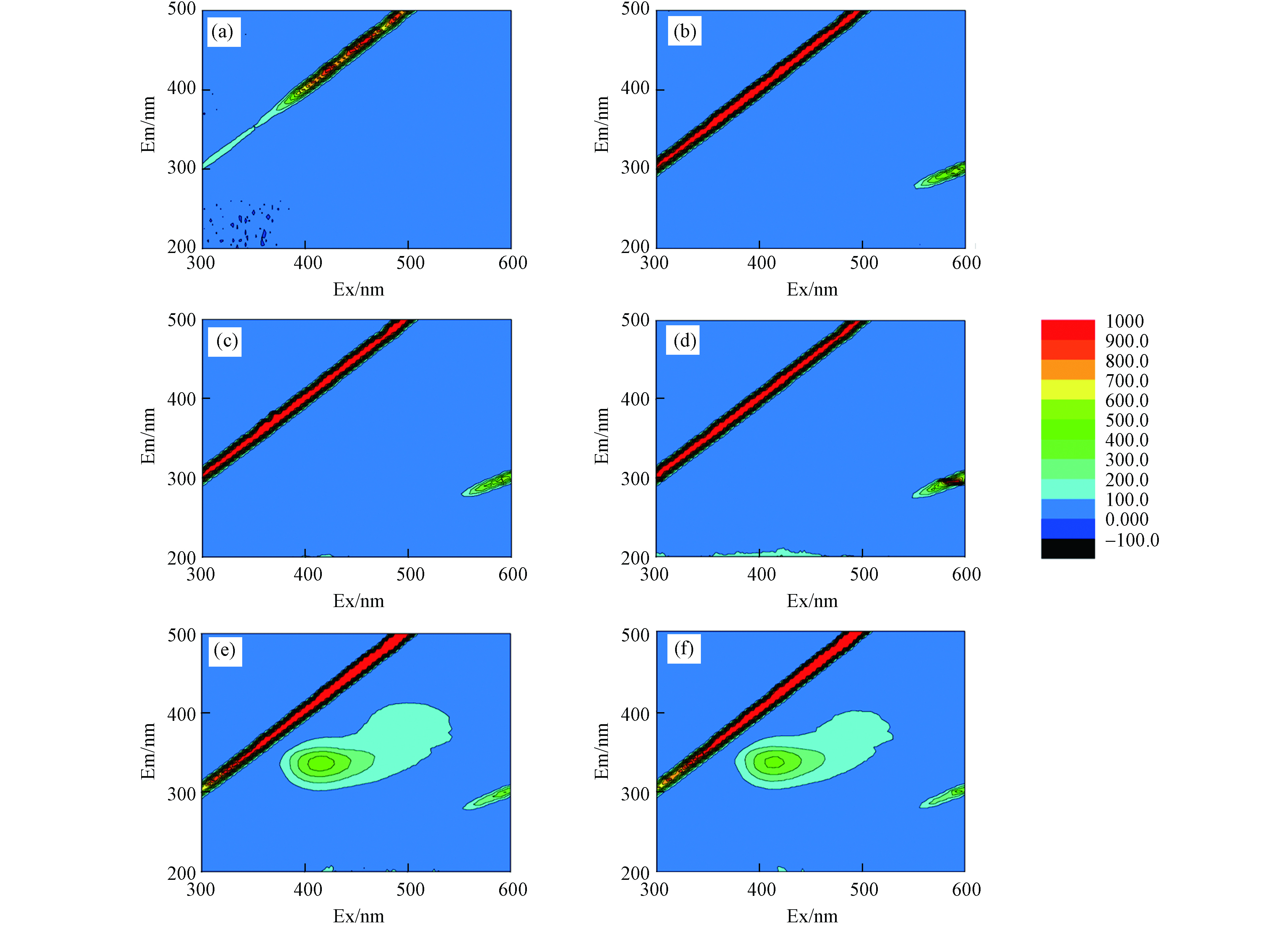
采用荧光光谱技术检测分析了四环素在不同体系(TC、H2O2/TC、HFO/TC和H2O2/HFO/TC)反应后的三维荧光特征及其指纹特征. 在实验中收集了6个样品(M1-M6),M1:初始TC溶液的三维荧光光谱、M2:HFO/TC体系在黑暗中振荡6 h后,离心取上清液测定的三维荧光光谱、M3:H2O2/TC体系在黑暗中震荡4 h后,离心取上清液测定的三维荧光光谱、M4:H2O2/TC体系在黑暗中振荡6 h后,离心取上清液测定的三维荧光光谱、M5:HFO/H2O2/TC体系在黑暗中震荡4 h后,离心取上清液测定的三维荧光光谱、M6:HFO/H2O2/TC体系在黑暗中振荡6 h后,离心取上清液测定的三维荧光光谱. M1-M6的三维荧光如图7所示.
Shi等 [22] 研究表明在三维荧光中,TC的存在会起到荧光淬灭作用. 如图7(a)、(b)、(c)和(d)所示,在TC、HFO/TC和H2O2/TC体系中均未检测到荧光信号,这表明在TC、HFO/TC和H2O2/TC体系中TC分子均没有被完全去除. 由图7(e)和(f)可知,在HFO/H2O2体系中,出现了一个对应于类腐殖酸区域的荧光峰(λEX/λEM=(305—330 nm)/(430—450 nm) )[23],且峰强度随着反应的进行而减弱,表明TC及其降解产物在HFO/H2O2体系中不断被降解.
2.7 催化降解后HFO的FTIR分析
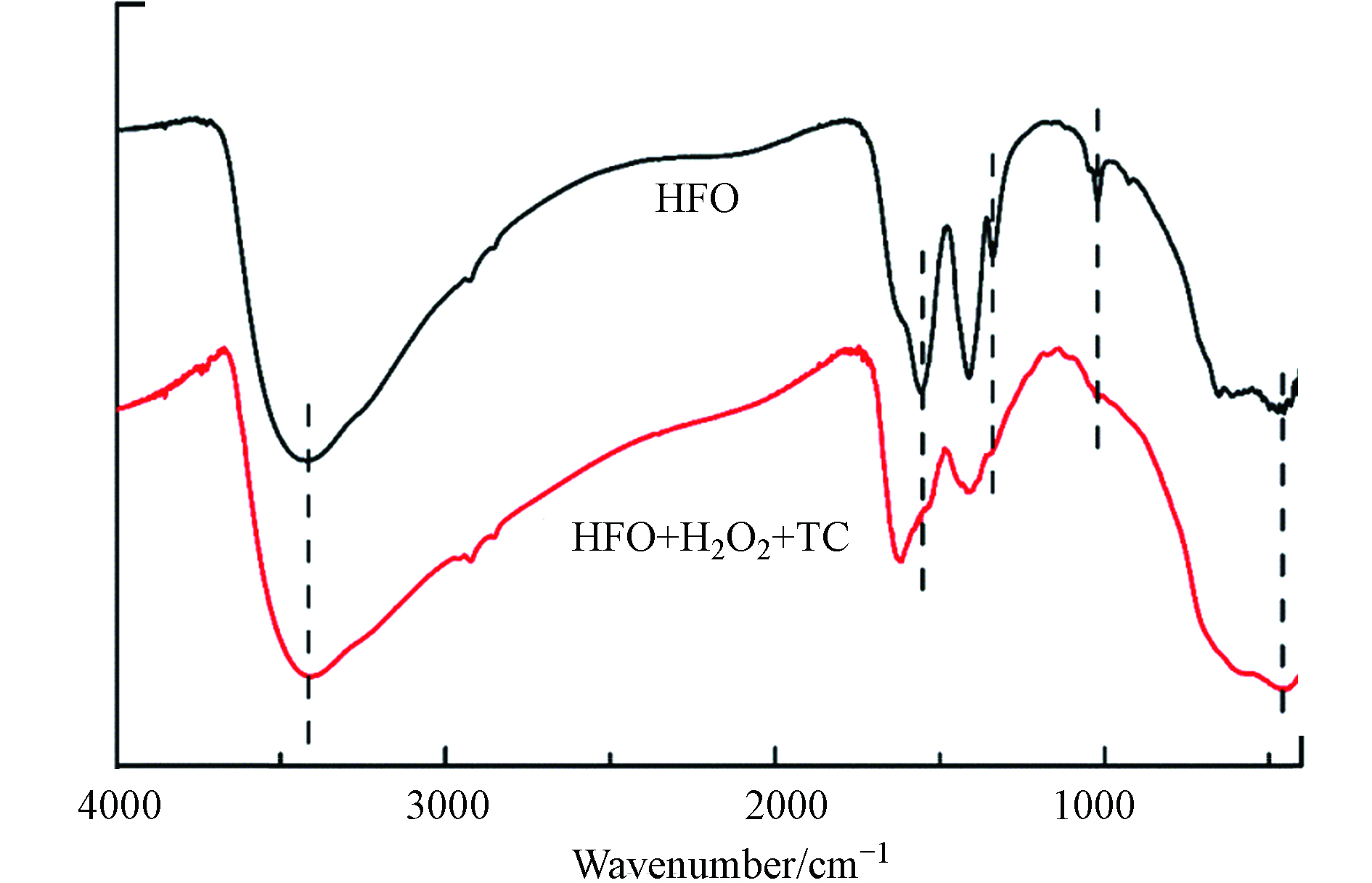
图8为HFO在催化反应前后的FTIR图谱. 由图8可知,HFO的红外光谱中出现了—OH(3405 cm−1、1629 cm−1)这表明了羟基的存在. 444 cm−1处为Fe—O键伸缩振动峰,1023 cm−1处为Fe—OH键伸缩振动峰[24]. HFO在催化过程中,Fe—O的出峰位置从444 cm−1迁移到463 cm−1,Fe—OH的吸收峰消失,这表明Fe—O和Fe—OH官能团参与了催化作用. 在3405 cm−1处的羟基伸缩振动峰移至3416 cm−1,这表明在催化反应过程中羟基参与了反应.
2.8 催化反应前后HFO的XPS分析
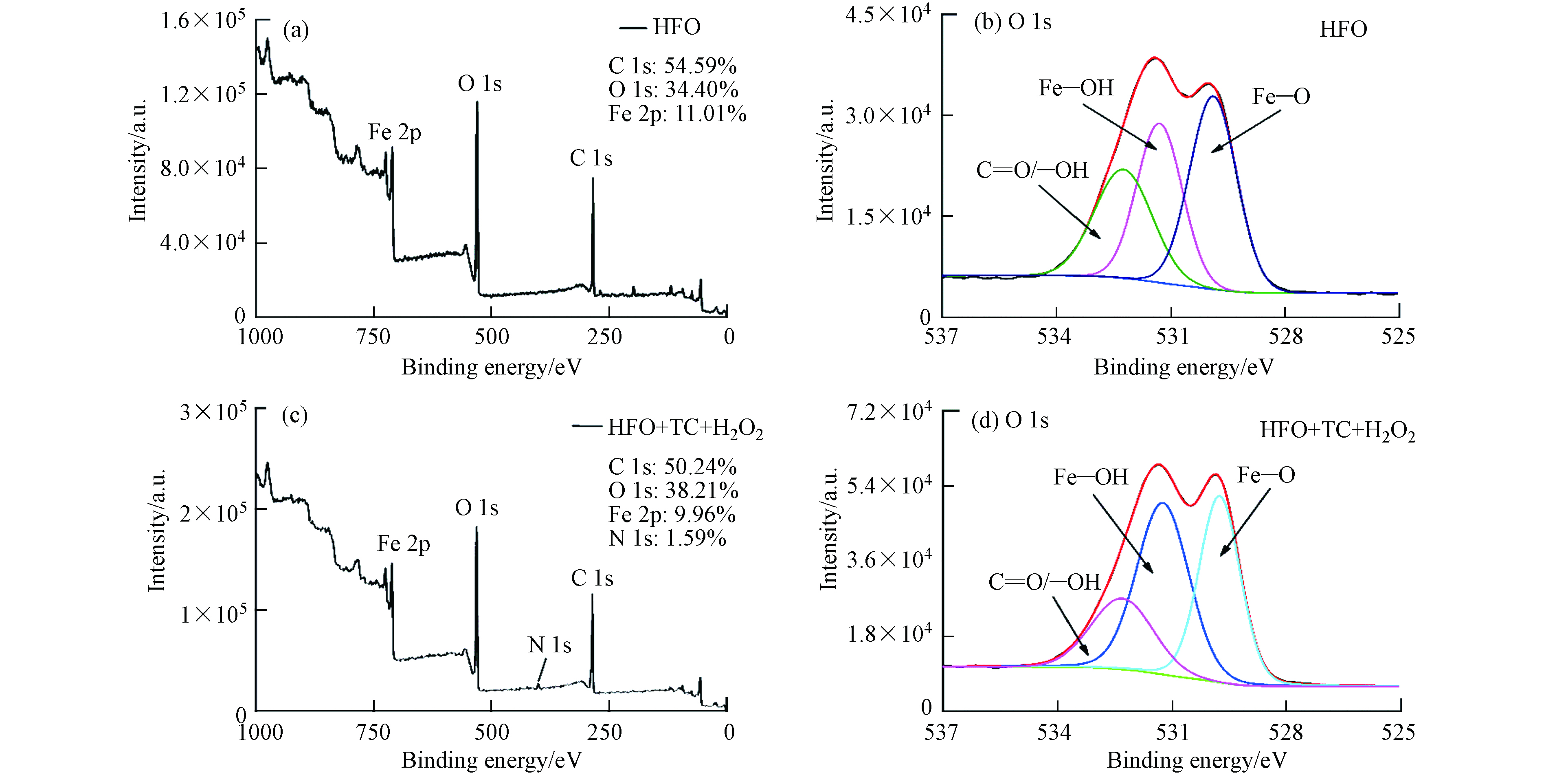
图9为HFO催化反应前后的XPS分析结果. 由图9(a)和(c)可知,HFO的全扫描能谱中出现了C 1s、O 1s和Fe 2p的3个能区,而HFO催化后的全扫描能谱中出现了C 1s、O 1s、Fe 2p和N1s的4个能区,这表明HFO在催化过程中吸附了一定量的TC及其降解产物. 图9(b)和(d)为HFO催化前后O 1s的高分辨扫描能谱,其中530 eV、531 eV和532 eV处的3个主峰分别对应Fe—O、Fe—OH和C=O/OH的结合能[25]. 其中催化后Fe—OH峰面积从32%增加值43%,Fe—O的峰面积从40%降低到37%,这表明HFO在催化过程中部分Fe—O官能团转变成Fe—OH官能团,铁主要分布在HFO的表面.
2.9 循环次数对HFO降解TC效果的影响
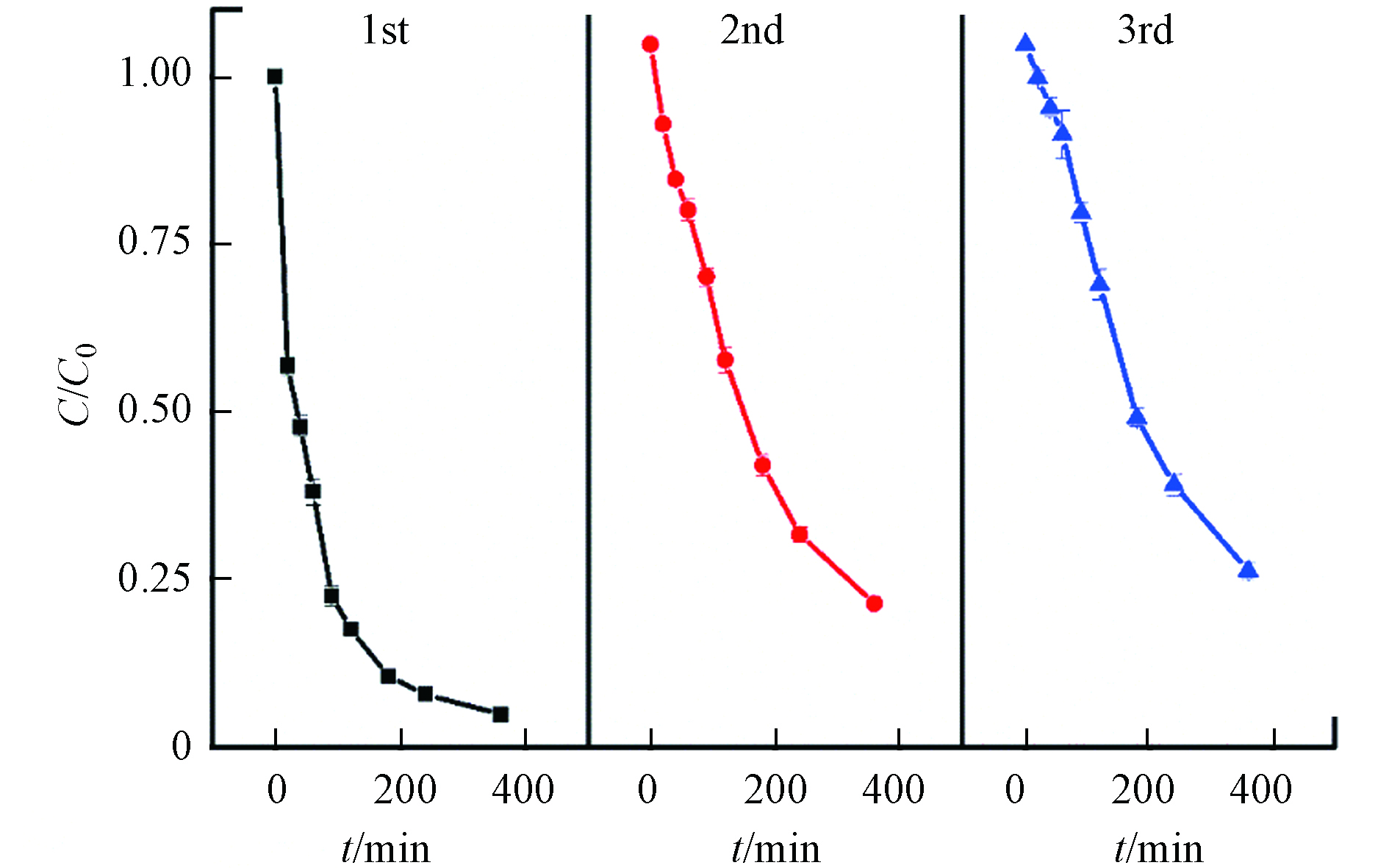
催化剂的稳定性和可重复利用性对其在实际应用中至关重要. 通过连续反应3次循环实验评估HFO在黑暗处催化H2O2降解TC的效率,以验证HFO的可重复利用性,结果如图10所示. 经过3次循环实验后,在360 min内对TC的降解速率逐渐降低,表明HFO上的某些催化活性位点可能会随Fe的浸出而损失[26]. HFO经历3次循环后,TC在360 min内的去除率分别为95%、80%和75%. 因此,在HFO/H2O2具有可重复应用的潜力.
2.10 活性氧化物质的鉴定
通过自由基淬灭实验和电子自旋共振波谱仪测定反应体系中的主要自由基. 在淬灭实验中分别使用苯醌(BQ)和叔丁醇(TBA)对类Fenton反应过程中产生的∙O2-和∙OH进行淬灭[27]. 如图11(a)所示,当反应溶液中分别添加5、10、20 mmol∙L−1的苯醌时,在360 min内,TC的降解率从95%分别下降到82%、64%和46%. 但是当添加5、10、20 mmol∙L−1的叔丁醇时,在360 min内,TC的降解率几乎没有下降,说明HFO/H2O2反应体系中产生的主要活性物质是∙O2-[28].
为了进一步确认反应机理,通过EPR检测反应体系中的活性物质,采用DMPO作为∙OH和∙
O−2 O−2 O−2 O−2 2.11 TC降解途径
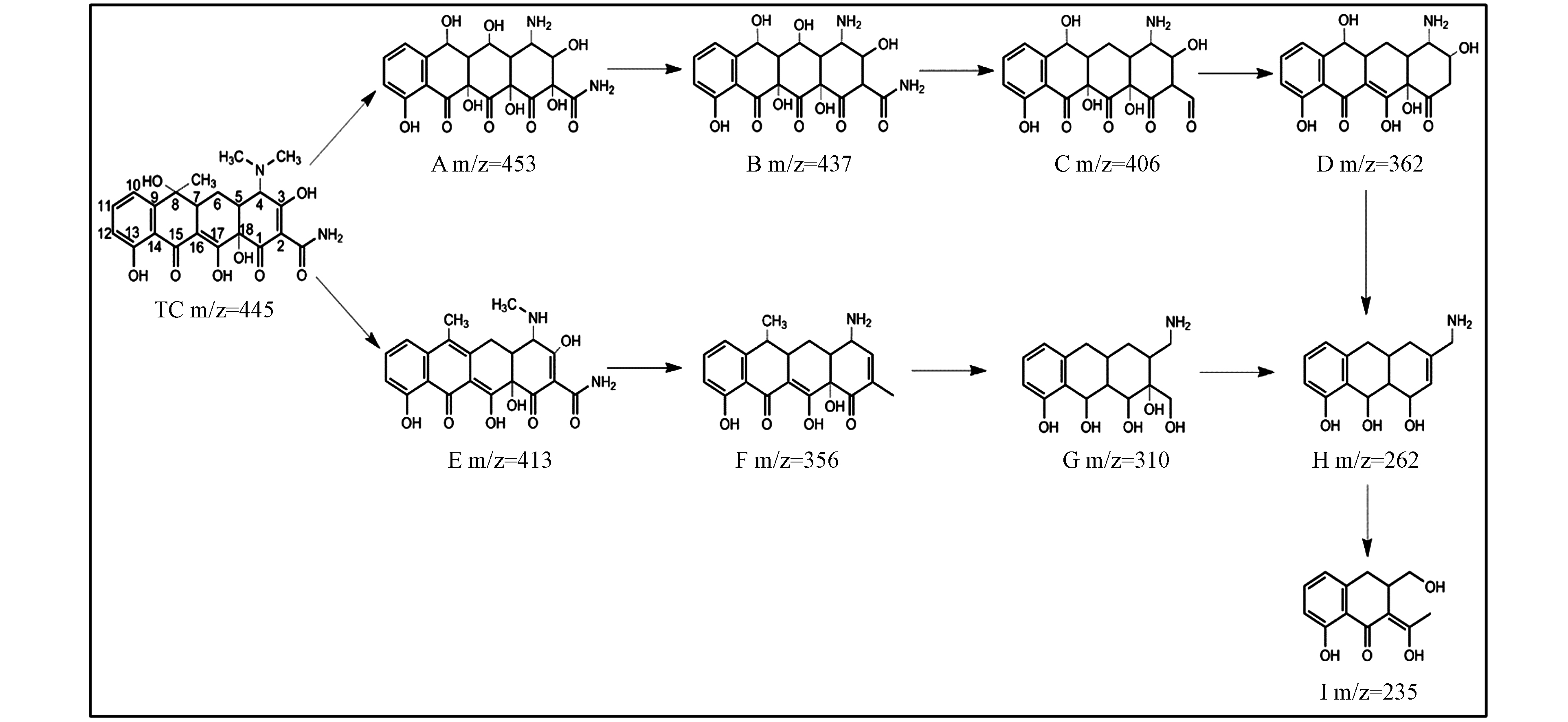
利用LC-TOF-MS共检测到9种TC的中间降解产物,质荷比(m/z)分别为:A(m/z=453)、B(m/z=437)、C(m/z=406)、D(m/z=362)、E(m/z=413)、F(m/z=356)、G(m/z=310)、H(m/z=262)和I(m/z=235). 根据分子量、理论分子量和文献报道,推测HFO/H2O2降解TC中间产物的结构和反应路径如图12所示.
TC降解途径Ⅰ,TC上碳碳双键羟基化,生成产物A(m/z=453)[30],通过A脱羟基形成产物B(m/z=437),通过C—N键断裂和脱羟基形成产物C(m/z=406),通过去甲基化作用将产物 C 进一步转化为产物 D(m/z =362)[31],通过开环、去甲基化和去羟基将产物D转化为产物H(m/z=262),然后产物H通过开环和加羟基化为产物I(m/z=235)[32],最后产物I被转化为小分子物质并进一步氧化为H2O和CO2. 降解途径Ⅱ,TC去甲基和羟基生成产物E(m/z=413)[33],通过E去甲基、脱羟基和NH2形成产物F(m/z =356),F通过开环和C=C双键的氢加成变成产物G(m/z=310),G通过脱C18上的羧基(—C—OH)和羟基生产H(m/z=262),最后再进一步通过开环和加羟基化为产物I(m/z=235)[32],最后产物I被转化为小分子物质并进一步氧化为H2O和CO2.
3. 结论 (Conclusion)
HFO/H2O2体系在H2O2的浓度为5 mmol∙L−1,催化剂为0.4 mg∙L−1,pH=3,温度25 ℃的反应条件下可在180 min内去除水中90%的TC. 在pH为2—10的范围内和共存离子存在时,HFO都可有效的催化H2O2降解水体中的TC,HFO/H2O2体系降解TC的主要活性物质是∙O2-. TC降解过程中出现了9种中间产物,说明TC主要是通过羟基化、去甲基、去酰胺基和开环等途径被降解成小分子化合物. 本研究揭示了HFO对TC催化降解作用,说明自然界存在的HFO在TC降解和代谢过程中起到重要作用.
-
表 1 样品点基本信息
Table 1. Basic information of sample points
采样点Sampling site 地理位置Location 代表意义Meanings LJ 112°59' 24.09" E,29°7' 42.90" N 鹿角;湘江入湖口、港口、航运中心 JSD 113°0' 25.88" E,29°22' 6.82" N 君山岛;旅游景区沿线公路附近 DDTH 112°47' 33.87" E,29°27' 49.66" N 东洞庭自然保护区;位于湿地保护区核心,远离人类活动 表 2 东洞庭湖沉积柱重金属含量(mg·kg−1)
Table 2. Contents of heavy metals in sedimentary columns of East Dongting Lake (mg·kg−1)
东洞庭湖分区East Dongting Lake Subdivision As Cd Cr Cu Mn Pb Zn DDTH 上层 ND ND 19.36 13.45 798.55 18.55 51.91 中层 ND ND 21.33 6.22 861.39 17.22 53.11 下层 184.05 ND 26.75 10.85 939.58 18.55 71.5 JSD 上层 ND ND 30.17 20.00 298.33 29.5 124.92 中层 ND ND 9.17 28.17 974.25 23.42 67.80 下层 0.27 ND 13.80 29.32 596.16 22.19 55.55 LJ 上层 ND 0.40 19.52 16.50 1139.78 26.69 167.38 中层 0.27 ND 23.23 24.73 661.41 32.45 73.77 下层 0.10 ND 27.60 28.30 441.00 31.90 132.58 洞庭湖重金属背景值[26] 12.90 0.33 44.00 20.20 450.00 23.30 83.30 “ND”,未检测出数据. ”ND”, No data is detected. 表 3 大型湖泊沉积物重金属含量(mg·kg−1)
Table 3. Heavy metal content in large lake sediments (mg·kg−1)
年份Years Cd Cr Cu Mn Pb Zn 2020年 太湖[31] 0.07 93.69 31.32 — 34.16 101.93 洪泽湖[32] 0.23±0.07 66.78±12.33 25.35±6.23 27.28±6.31 74.77±18.19 鄱阳湖[33] 0.79 70.2 39.8 — 43.0 119.4 洞庭湖[34] 1.91 93.47 37.98 — 36.35 147.19 1978年 太湖北部[35] — 6082 20—30 — 8—14 40—75 洪泽湖[36] — 27—70 38—47 0.4—0.9 9.5—16 45—78 鄱阳湖[37] — 120 320 900 5 500 1937年 太湖北部 — 60—69 20—25 — 7—12 40—64 鄱阳湖 — 62 175 720 2 260 “—”,数据缺失. “—”, missing data. 表 4 沉积物下层重金属含量相关性分析结果
Table 4. Correlation analysis results of heavy metal content in lower layer of sediment
Cr Cu Mn Pb Zn As LJ Cr 1.00 Cu 0.00 1.00 Mn 0.00 1.00** 1.00 Pb 0.00 −1.00** −1.00** 1.00 Zn −0.10 0.400 0.40 −0.40 1.00 As 0.00 −0.35 −0.35 0.35 0.71 1.00 JSD Cr 1.00 Cu 0.26 1.00 Mn −0.20 0.17 1.00 Pb 0.25 0.76** 0.32 1.00 Zn 0.50* 0.50* −0.17 0.46* 1.00 As 0.19 0.07 0.05 −0.02 0.00 1.00 DDTH Cr 1.00 Cu −0.23 1.00 Mn 0.08 0.46* 1.00 Pb 0.12 0.17 0.41 1.00 Zn 0.14 −0.38 0.22 0.08 1.00 As −0.05 −0.36 −0.16 −0.16 0.51* 1.00 *. P<0.05,相关性显著;**. P<0.01,相关性极显著. *. P < 0.05, significant correlation; **. P < 0.01, the correlation was extremely significant. 表 5 沉积物中层重金属含量相关性分析结果
Table 5. correlation analysis results of heavy metal content in the middle layer of sediment
Cr Cu Mn Pb Zn As LJ Cr 1.00 Cu 0.16 1.00 Mn −0.22 −0.37 1.00 Pb −0.41 −0.72* 0.29 1.00 Zn −0.37 −0.85** 0.56 0.89** 1.00 As −0.50 0.30 −0.10 0.10 −0.10 1.00 JSD Cr 1.00 Cu −0.44 1.00 Mn −0.52 0.57 1.00 Pb −0.08 0.40 0.13 1.00 Zn 0.07 0.36 −0.14 0.69* 1.00 — DDTH Cr 1.00 Cu −0.71* 1.00 Mn −0.43 0.53 1.00 Pb −0.22 0.64 0.23 1.00 Zn 0.64 −0.67* −0.37 −0.34 1.00 — *. P<0.05,相关性显著;**. P<0.01,相关性极显著. *. P < 0.05, significant correlation; **. P < 0.01, the correlation was extremely significant. 表 6 沉积物上层重金属含量相关性分析结果
Table 6. correlation analysis results of heavy metal content in the upper layer of sediment
Cr Cu Pb Mn Zn Cd LJ Cr 1.00 Cu 0.34 1.00 Pb 0.03 0.12 1.00 Mn −0.09 0.27 −0.24 1.00 Zn 0.05 0.10 0.11 0.56** 1.00 Cd −0.44* −0.29 0.33 0.02 0.55** 1.00 JSD Cr 1.00 Cu 0.18 1.00 Pb 0.73** 0.05 1.00 Mn −0.76** −0.28 −0.76** 1.00 Zn 0.90** −0.05 0.83** −0.78** 1.00 — DDTH Cr 1.00 Cu −0.46 1.00 Pb 0.67** −0.46 1.00 Mn −0.44 0.23 −0.82** 1.00 Zn 0.82** −0.24 0.49* −0.28 1.00 — *. P<0.05,相关性显著;**. P<0.01,相关性极显著. *. P < 0.05, significant correlation; **. P < 0.01, the correlation was extremely significant. -
[1] GAFUR N, SAKAKIBARA M, SANO S, et al. A case study of heavy metal pollution in water of bone river by artisanal small-scale gold mine activities in eastern part of gorontalo, Indonesia [J]. Water, 2018, 10(11): 1507. doi: 10.3390/w10111507 [2] ZHANG S C, CHEN B, DU J R, et al. Distribution, assessment, and source of heavy metals in sediments of the Qinjiang River, China [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(15): 9140. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159140 [3] 王永平, 洪大林, 申霞, 等. 骆马湖沉积物重金属及营养盐污染研究 [J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2013, 11(6): 45-48,143. WANG Y P, HONG D L, SHEN X, et al. Heavy metals and nutrients pollution in sediments of Luoma Lake [J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2013, 11(6): 45-48,143(in Chinese).
[4] DAI L J, WANG L Q, LI L F, et al. Multivariate geostatistical analysis and source identification of heavy metals in the sediment of Poyang Lake in China [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 621: 1433-1444. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.085 [5] ENGDAW F, HEIN T, BENEBERU G. Heavy metal distribution in surface water and sediment of megech river, a tributary of lake Tana, ethiopia [J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(5): 2791. doi: 10.3390/su14052791 [6] KÜKRER S, ÇAKıR Ç, KAYA H K, et al. Historical record of metals in Lake Küçükçekmece and Lake Terkos (Istanbul, Turkey) based on anthropogenic impacts and ecological risk assessment [J]. Environmental Forensics, 2019, 20(4): 385-401. doi: 10.1080/15275922.2019.1657985 [7] 赵晓亮, 李响, 卢洪斌,等. 东江湖表层沉积物重金属污染特征与潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(6): 3048-3057. ZHAO X L, LI X, LU H B, et al. Analysis of heavy metal pollution characteristics and potential ecological risks of surface sediments in Dongjiang Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(6): 3048-3057(in Chinese).
[8] BAUD A, AULARD C, GHANBARI H, et al. A framework for 210 Pb model selection and its application to 37 cores from Eastern Canada to identify the dynamics and drivers of lake sedimentation rates [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2022, 47(10): 2518-2530. doi: 10.1002/esp.5391 [9] ZANKO L M, REAVIE E D, POST S P, et al. Inhalable, Elongate mineral particles from lake sediment records trace mining activities in northern Minnesota [J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2022, 68(2): 215-230. doi: 10.1007/s10933-022-00243-y [10] STRAKHOVENKO V D, BELKINA N A, EFREMENKO N A, et al. The first data on the mineralogy and geochemistry of the suspension of lake onego [J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2022, 63(1): 55-71. doi: 10.2113/RGG20204280 [11] 李忠武, 王磊, 冉凤维, 等. 基于APCS-MLR模型的西洞庭湖沉积物重金属来源解析 [J]. 长沙理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 19(2): 1-14. LI Z W, WANG L, RAN F W, et al. Source analysis of heavy metals in sediments of West Dongting Lake based on APCS-MLR model [J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science & Technology (Natural Science), 2022, 19(2): 1-14(in Chinese).
[12] DU Y, CAI S M, ZHANG X Y, et al. Interpretation of the environmental change of Dongting Lake, middle reach of Yangtze River, China, by 210Pb measurement and satellite image analysis [J]. Geomorphology, 2001, 41(2/3): 171-181. [13] MENG W, LIU Y, ZHU S J, et al. Distribution and ecological risk of heavy metals in sediment across the Dongting Lake Basin [J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2021, 19(4): 739-749,767. [14] MAYANGLAMBAM B, NEELAM S S. Geochemistry and pollution status of surface sediments of Loktak Lake, Manipur, India [J]. SN Applied Sciences, 2020, 2(12): 2097. doi: 10.1007/s42452-020-03903-8 [15] CÉCILE G, MARC D, ZHANG M X, et al. Trace Element Contamination in One of the Yangtze Tributaries (Hunan, China)—Source Review and Potential Release from Sediments [J]. Water, 2021, 13(3): 1-24. [16] WANG J, LIU G, LU L, et al. Geochemical normalization and assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, and Ni) in sediments from the Huaihe River, Anhui, China [J]. Catena, 2015, 129: 30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2015.02.008 [17] LI J, MICHALSKI G, OLSON E J, et al. Geochemical characterization and heavy metal sources in PM10 in Arequipa, Peru [J]. Atmosphere, 2021, 12(5): 641. doi: 10.3390/atmos12050641 [18] FEBRIANSYAH M R, SEPTIANA L M, SUPRIATIN S, et al. The patterns of lead and copper levels in the vicinity of heavy metal sources in Lampung, the southern part of Sumatra, Indonesia [J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 739(1): 012001. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/739/1/012001 [19] EL OUATY O, EL M'RINI A, NACHITE D, et al. Assessment of the heavy metal sources and concentrations in the Nador Lagoon sediment, Northeast-Morocco [J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2022, 216: 105900. [20] XU Y F, WU Y, HAN J G, et al. The current status of heavy metal in lake sediments from China: Pollution and ecological risk assessment [J]. Ecology and Evolution, 2017, 7(14): 5454-5466. doi: 10.1002/ece3.3124 [21] RAN F W, NIE X D, LI Z W, et al. Chronological records of sediment organic carbon at an entrance of Dongting Lake: Response to historical meteorological events [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 794: 148801. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148801 [22] ZENG J, HAN G L, WU Q X, et al. Geochemical characteristics of dissolved heavy metals in Zhujiang River, Southwest China: spatial-temporal distribution, source, export flux estimation, and a water quality assessment [J]. PeerJ, 2019, 7: e6578. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6578 [23] 隆院男, 唐蓉, 蒋昌波, 等. 近60年湘江流域水沙特性及其对人类活动的响应 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(24): 132-143. LONG Y N, TANG R, JIANG C B, et al. Variability characteristics of runoff-sediment discharge and their response to human activities in Xiang River Basin in recent 60 years [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(24): 132-143(in Chinese).
[24] 李从先, 杨守业, 范代读, 赵娟. 三峡大坝建成后长江输沙量的减少及其对长江三角洲的影响 [J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(5): 495-500. LI C X, YANG S Y, FAN D D, et al. The change in Changjiang suspended load and its impact on the delta after completion of Three Gorges Dam [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(5): 495-500(in Chinese).
[25] 吴道喜. 长江中游洪灾成因及防治策略研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2005. WU D X. Flood disaster in the middle Yangtze River: The reason and its management[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2005 (in Chinese).
[26] 李健, 曾北危, 姚岳云, 张立成, 丘昌强, 钱杏珍. 洞庭湖水系水体环境背景值调查研究 [J]. 环境科学, 1986, 7(4): 62-68,104. LI J, ZENG B W, YAO Y Y, et al. Studies on environmental background levels in waters of Dongting Lake system [J]. Environmental Science, 1986, 7(4): 62-68,104(in Chinese).
[27] 李超显, 黄健柏. 流域重金属污染治理政策工具选择的政策网络分析: 以湘江流域为例 [J]. 湘潭大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2017, 41(6): 21-27. LI C X, HUANG J B. The policy network analysis of policy instrument selection of heavy metal pollution governance in river basin: A case study of Xiangjiang river basin [J]. Journal of Xiangtan University(Philosophy and Social Sciences), 2017, 41(6): 21-27(in Chinese).
[28] 杨梦昕, 付湘晋, 李忠海, 等. 湘江流域重金属污染情况及其对食物链的影响 [J]. 食品与机械, 2014, 30(5): 103-106. YANG M X, FU X J, LI Z H, et al. Heavy metal pollution status in Xiangjiang river and its effect on food chain [J]. Food & Machinery, 2014, 30(5): 103-106(in Chinese).
[29] 彭海波. 两型社会建设中湘江污染治理的法制建设研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2013. PENG H B. Study on legal construction for the goverance of Xiangjiang River pollution in the two-oriented society construction [D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2013 (in Chinese).
[30] 谢意南, 欧阳美凤, 黄代中, 等. 洞庭湖及其入湖口沉积物中重金属的污染特征、来源与生态风险 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(10): 2253-2264. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017020303 XIE Y N, OUYANG M F, HUANG D Z, et al. Pollution characteristics, sources and ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments from Dongting Lake and its lake inlets [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(10): 2253-2264(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017020303
[31] 邓延慧, 王正文, 丁润楠, 等. 太湖湖体沉积物营养盐和重金属污染特征研究 [J]. 环境生态学, 2020(12): 67-72. DENG Y H, WANG Z W, DING R N, et al. Study on pollution characteristics of nutrient salts and heavy metals in sediment of Taihu Lake [J]. Environmental Ecology, 2020(12): 67-72(in Chinese).
[32] 訾鑫源, 张鸣, 谷孝鸿, 等. 洪泽湖围栏养殖对表层沉积物重金属含量影响与生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(11): 5355-5363. ZI X Y, ZHANG M, GU X H, et al. Impact of enclosure culture on heavy metal content in surface sediments of Hongze Lake and ecological risk assessment [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(11): 5355-5363(in Chinese).
[33] 刘佳伟, 杨明生. 鄱阳湖流域重金属污染评价与分析 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2022, 44(1): 99-103. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2022.01.017 LIU J W, YANG M S. Assessment and analysis of heavy metal pollution in Poyang Lake Basin [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2022, 44(1): 99-103(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2022.01.017
[34] 尹宇莹, 彭高卓, 谢意南, 等. 洞庭湖表层沉积物中营养元素、重金属的污染特征与评价分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2399-2409. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020042401 YIN Y Y, PENG G Z, XIE Y N, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of nutrients and heavy metals pollution in sediments of Dongting Lake [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2399-2409(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020042401
[35] 张伯镇. 太湖北部湖湾沉积物毒害污染物分布特征及风险评价: 以重金属和多环芳烃为例[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2015. ZHANG B Z. Pollution characteristics and risk of persistent toxic substances in the sediments from northern Taihu Lake—a case study for heavy metal and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiatong University, 2015 (in Chinese).
[36] 张文斌. 洪泽湖沉积物中营养盐和重金属分布特征、评价及其演化规律研究[D]. 长春: 吉林建筑工程学院, 2010. ZHANG W B. Study on the distribution, evaluation and evolution of nutrients and heavy metals in Hongze Lake sediments[D]. Changchun: Jilin Jianzhu University, 2010 (in Chinese).
[37] 刘小真. 鄱阳湖流域底质重金属及杀虫剂类POPs垂直污染分布特征[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2008. LIU X Z. Perpendicularity pollution and distributing character of both heavy metal and OCPs of sediment in Poyang Lake drainage basin[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2008 (in Chinese).
[38] 蔡长卿, 金昌盛, 陈佳, 等. 东洞庭湖沉积物重金属污染及生态-健康风险 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(6): 1337-1347. CAI C Q, JIN C S, CHEN J, et al. Sediment heavy metal pollution and its ecological and health risk assessment in the East Dongting Lake, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2022, 41(6): 1337-1347(in Chinese).
[39] 李利强, 王丑明, 张屹, 等. 洞庭湖大型底栖动物与表层沉积物重金属研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(2): 286-291. LI L Q, WANG C M, ZHANG Y, et al. Study of macrozoobenthos and heavy metals of surface sediment in Dongting Lake [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(2): 286-291(in Chinese).
[40] 戴翌晗. 典型矿冶城市农田土壤重金属污染来源解析 [J]. 环境生态学, 2022, 4(5): 25-31. DAI Y H. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil of a typical mining and metallurgy city [J]. Environmental Ecology, 2022, 4(5): 25-31(in Chinese).
[41] 解瑞峰. 中国北方典型湖泊重金属沉积特征、污染来源与趋势预测[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2021. XIE R F. Deposition characteristic, source analysis and trend prediction of heavy metals in typical lakes in Northern China[D]. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[42] 郭旻欣. 基于GIS的淮南矿区土壤Cu、Ni、As、Zn和Cr元素空间分布特征及来源分析[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016. GUO M X. Research on spatial distribution and contamination sources of heavy metal Cu, Ni, As, Zn, Cr in Huainan mining area based on GIS[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2016 (in Chinese).
[43] 湖南省志编纂委会. 湖南省志[M]. 长沙: 湖南人民出版社, 1982. Hunan Provincial Chronicles Compilation Committee. Hunan Provincial chronicles[M]. Changsha: Hunan People's Publishing House, 1982 (in Chinese).
[44] 余燕飞. 近代湘鄂赣山区煤铁开发及其影响 [J]. 江汉论坛, 2020(4): 103-110. YU Y F. Coal and steel mining development in Hunan, Hubei and Jiangxi Mountains in modern China and its influence [J]. Jianghan Tribune, 2020(4): 103-110(in Chinese).
[45] 李欢娟, 李会霞, 史兴民. 西安市主要湖泊表层沉积物重金属污染及生态风险评估 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(2): 122-126. LI H J, LI H X, SHI X M. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals and ecological risk assessment for the surface sediments of the lakes in Xi'an [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(2): 122-126(in Chinese).
[46] 周艳, 陈樯, 邓绍坡, 等. 西南某铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属空间主成分分析及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. ZHOU Y, CHEN Q, DENG S P, et al. Principal component analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around a Pb-Zn mine in southwestern China [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892(in Chinese).
[47] 王宏. 东洞庭湖湿地土壤重金属的分布特征及风险评价[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2012. WANG H. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in Eastern Dongting Lake wetland[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2012 (in Chinese).
[48] 朱陈名, 朱咏莉, 韩建刚, 等. 洪泽湖重金属污染现状与防控技术 [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(3): 175-181. ZHU C M, ZHU Y L, HAN J G, et al. The heavy metal pollution situation and control in Hongze Lake [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2017, 41(3): 175-181(in Chinese).
[49] 杜吉净, 毛龙江, 谭志海, 等. 海州湾岩芯沉积物重金属污染评价和来源分析 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2016(6): 814-821. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2016.06.028 DU J J, MAO L J, TAN Z H, et al. Pollution evaluation and source identification of heavy metals in sediments from core in Haizhou Bay [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2016(6): 814-821(in Chinese). doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2016.06.028
[50] 李湘岳. 岳阳市志[M]. 北京: 中央文献出版社, 2005. LI X Y. Yueyang annals[M]. Beijing: Central Literature Publishing House, 2005 (in Chinese).
[51] 张爱国, 魏兴萍. 西南典型岩溶槽谷土壤重金属污染与来源解析 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(12): 166-176. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.12.023 ZHANG A G, WEI X P. Pollution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils of typical Karst troughs in southwestern China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(12): 166-176(in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.12.023
[52] 张转玲, 谭红, 何锦林, 等. 贵州草海表层沉积物重金属污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(12): 2314-2320. ZHANG Z L, TAN H, HE J L, et al. Distribution characteristics and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of Caohai Lake in Guizhou [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(12): 2314-2320(in Chinese).
[53] 金恺. 两种蔊菜属植物对重金属镉的耐性研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2019. JIN K. Studies of two species of Rorippa on resistance to cadmium[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019 (in Chinese).
[54] 雷津宁, 蒋兰香. 生态环境损害法律责任追究实证研究: 以湖南十大案件为素材 [J]. 时代法学, 2017, 15(2): 56-63. LEI J N, JIANG L X. On empirical research for law accountability of eco-environmental —as for the material of top 10 cases in Hunan [J]. Presentday Law Science, 2017, 15(2): 56-63(in Chinese).
[55] 赵思颖. 稻田镉污染高光谱响应及其关系研究[D]. 南昌: 江西师范大学, 2016. ZHAO S Y. Research on response and its relationship of Cd pollution in paddy field and hyperspectral[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University, 2016 (in Chinese).
[56] 何培金, 朱培高. 岳阳市情要览[M]. 长沙: 湖南人民出版社, 1988. HE P J, ZHU P G. Overview of Yueyang City[M]. Changsha: Hunan People's Publishing House, 1988 (in Chinese).
[57] 岳阳市农村区划委员会. 湖南省岳阳地区农业区划报告集[M]. 岳阳: 岳阳地区印刷厂, 1985. Yueyang Rural Zoning Committee. Report Collection of Agricultural Zoning in Yueyang, Hunan Province[M]. Yueyang: Yueyang printing house, 1985 (in Chinese).
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 曾洪,刘芮,杨思培,朱式业,吴志斌,梁运姗. 荧光光谱结合分子对接探究Cu~(2+)、Pb~(2+)与Cry1Ac毒素的相互作用. 环境化学. 2025(02): 690-699 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 周亚磊,陈志远,程晋静,笪春年. 淮河(淮南至蚌埠段)沉积物柱芯中多溴联苯醚的污染特征及生态风险评价. 蚌埠学院学报. 2024(02): 35-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 欧阳美凤,尹宇莹,张金谌,刘清霖,谢意南,方平. 洞庭湖典型水域重金属含量的空间分布与来源解析. 生态环境学报. 2024(08): 1269-1278 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-








 下载:
下载: