-
土壤是生态系统的主要媒介,也是人类赖以为生的重要基础,土壤污染问题一直受到高度关注[1]. 随着经济的不断发展,土壤污染问题日益加剧[2],其中有色金属开采及加工是主要的污染来源之一[3-5]. 土壤重金属污染具有显著的潜伏性、不可逆性、持久性等典型特征[6-7],通过各种途径进入土壤中并随之积累,最终随着食物链进入人体和生物体内,对人体健康和生态安全形成威胁. 因此,精确、全面、高效地评价土壤重金属的污染情况、查明污染源,对于矿区及其周围土壤污染防治具有重要意义[8-10].
目前,相关研究主要针对重金属污染评价、空间分布规律、污染源分析和修复治理等方面[10-17]. 重金属污染来源分析包括源识别及源解析两类,主要包括因子分析法(FA)、主成分分析法(PCA)、化学质量平衡模型法(CMB)、主成分多元线性回归法(APCS-MLR)、正定矩形因子分解法(PMF)、主成分/绝对主成分分数法(PCA/APCS)和UNMIX模型法等[18-19]. 其中PMF模型[20-21]由于无需构建污染源成分谱,且能对因子分解矩阵进行非负约束,近年来已被广泛用于土壤污染源解析. 张扣扣等[22]采用IDW插值、空间统计分析及PMF模型对某矿区周边土壤重金属污染分析表明:重金属污染区域主要集中在采矿区、选矿区和种植区,主要污染来源为矿业活动和农业活动. 陈航等[23]对铜山矿区周边农田土壤污染分析表明土壤重金属主要来自于矿业开发排放、农业活动、自然母质和化石燃烧释放. 有色金属开采及其相关工业活动对周围土壤重金属含量影响较大,通常存在多种重金属复合污染情况,对区域生态环境造成不良影响. 因此,针对重点区域开展土壤重金属污染调查、来源解析及土壤修复治理相关研究是十分有必要的.
本文以云南某铜选冶厂周边农田土壤为研究对象,将污染评价、空间分析及PMF模型相结合,综合分析研究区土壤重金属分布特征及来源,评估土壤重金属的污染程度及所存在的环境风险,以对类似农田土壤重金属污染研究及后续治理修复提供参考.
-
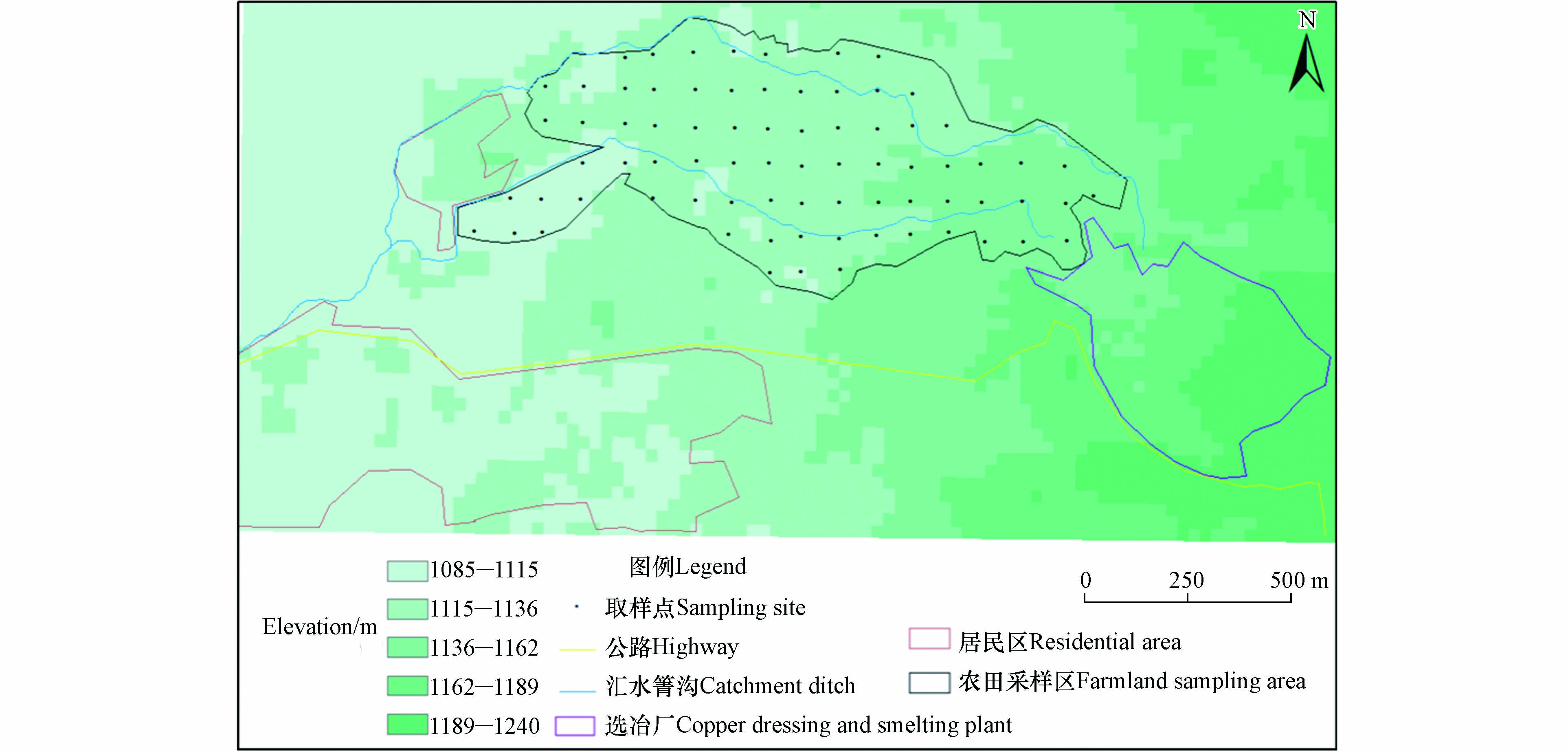
研究区地处山间河谷盆地边缘,区内山脉走向多为近南北向,地势东高西低,海拔760—2220.6 m. 研究区属亚热带高原型湿润季风气候,四季不分明,但干、雨季节区分较为明显. 年气温变化在2.1—36.7 ℃之间,年平均气温为17.2—20.1 ℃,每年5—10月为雨季,降雨量占全年的84.7%,相对湿度75%,全年多为西南风. 根据现场调查,研究区土壤类型以红壤土和赤红壤为主,土壤偏酸、缺磷且氮钾较低,土壤肥力较好,同时具有良好的抗蚀性.
选冶厂占地面积约252330 m2,生产工艺是以铜矿石为原料,采用“堆浸-萃取-电积”工艺生产电积铜产品,生产规模为年产电积铜4000 t·a−1. 选冶厂于2005年正式运营,2013年随着资源枯竭而停产,从建厂到停产期间,生产工艺未发生改变. 位于选冶厂西、西偏北分布少量农田,主要种植玉米、水稻和茶叶,其余均为林地.
-
土壤点位布设按照100m×100m的网格布点,共布设76个土壤采样点位,每个点位分别采取表层(0—20 cm)及(30—50 cm)的土壤样品,共152个土壤样品,采样位置见图1. 土壤样品经自然风干、去除植物根系和砂石杂质后碾碎研磨过100目筛,利用HNO3-HF-HClO4法消解,其中As、Hg经王水消解,采用火焰原子吸收分光光度法(Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni元素)、石墨炉原子吸收分光光度法(Pb、Cd元素)、原子荧光法(As、Hg元素)测定. 在测试过程中使用国家土壤一级标准物质(GSS-8、GSS-5)进行质量控制,Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni、Pb和Cd样品回收率为89%—110%,As和Hg样品回收率为92%—98%.
-
污染负荷指数法[6]能反映出不同重金属污染污染程度及整体污染状况贡献度. 污染负荷指数评价分级见表1,公式如(1—3)所示.
式中,Pi为重金属i的单因子污染指数,Ci为重金属i的实际浓度,C0i为重金属i的背景值(本文采用云南省土壤背景值[10]),PLI为采样点的污染负荷指数,n为重金属种类数,PLIzone为研究区污染负荷指数,N为采样点个数.
-
地累积指数法[8,10]是德国学者Muller提出,该方法综合分析了人为活动和自然地质过程对于重金属污染的影响,地累积指数评价分级见表2,公式如式(4):
式中:Igeo为地累积污染指数;Ci为重金属i的实测值;Bi为重金属i的背景值(本文采用云南省土壤背景值[10]);K为常数,一般取1.5.
-
潜在生态危害指数法[8,15]最早是由Hakanson(瑞典学者)提出,该方法除了分析土壤重金属的含量,还考虑了重金属毒性的影响,潜在生态风险指数的评价分级详见表3,公式如(5):
式中:Ci为土壤重金属浓度实测值;Si为该元素的评价标准(本文采用云南省土壤环境背景值[10]);Ti为金属元素i的毒性响应系数(参考相关文献取值[24]);Ei为重金属i的单项生态风险指数,RI为某一点位的综合生态风险指数.
-
正定矩阵因子分解模型(PMF)[24-26]是利用样本组成对污染源进行定量解析的数学方法. 该方法假设矩阵X为试验测定的样品数据,矩阵X可以分解为载荷矩阵F和分数矩阵G,残差矩阵E表示矩阵Xij和模型矩阵Yij之间的差值. 其基本方程如下:
式中,Xij为第i个样品中的第j个重金属浓度,Eij为残差矩阵;Gik为源分数矩阵;Fkj为源载荷矩阵. PMF模型将实验实测数据分为系数的贡献(G)和因子数(F)两个矩阵,利用每个取样点污染物含量和不确定度数据,对各个点进行加权,得到最小目标函数Q,见公式(7):
式中,uij为各样品污染物种类的不确定性,计算方法如式(8):
式中,RSD为重金属浓度的相对标准偏差,LMDL为方法检出限,xij为重金属样品浓度.
-
运用Excel2010进行土壤重金属含量统计分析,SPSS19.0进行土壤重金属相关性,空间插值在Arcgis10.8中完成,PMF模型分析在EPA PMF5.0中完成.
-
研究区152件土壤样品中8种金属元素含量统计见表4,土壤pH值范围为4.10—6.50,平均值为5.1. 从重金属含量来看,Cd、Hg、As、Pb、Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn 的平均值分别为1.55、0.261、12.2、46.2、115、74、59、113 mg·kg−1,除As元素外,其他7种元素的平均值均未超过《土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB 15618—2018)限定的筛选值. 浅层土壤样品及深层土壤样品中As、Hg、Cr、Pb元素含量平均值分别是云南省土壤背景值的3.04、1.58、1.21、1.08倍和3.41、1.62、1.29、1.12倍,深层土壤样品中重金属含量范围分布相对较小. 浅层土壤中Cd元素属于强变异,其余重金属元素均属于中等变异,表明Cd元素的离散程度较高,该元素在研究区内分布不均匀,受研究区人类活动影响大.
-
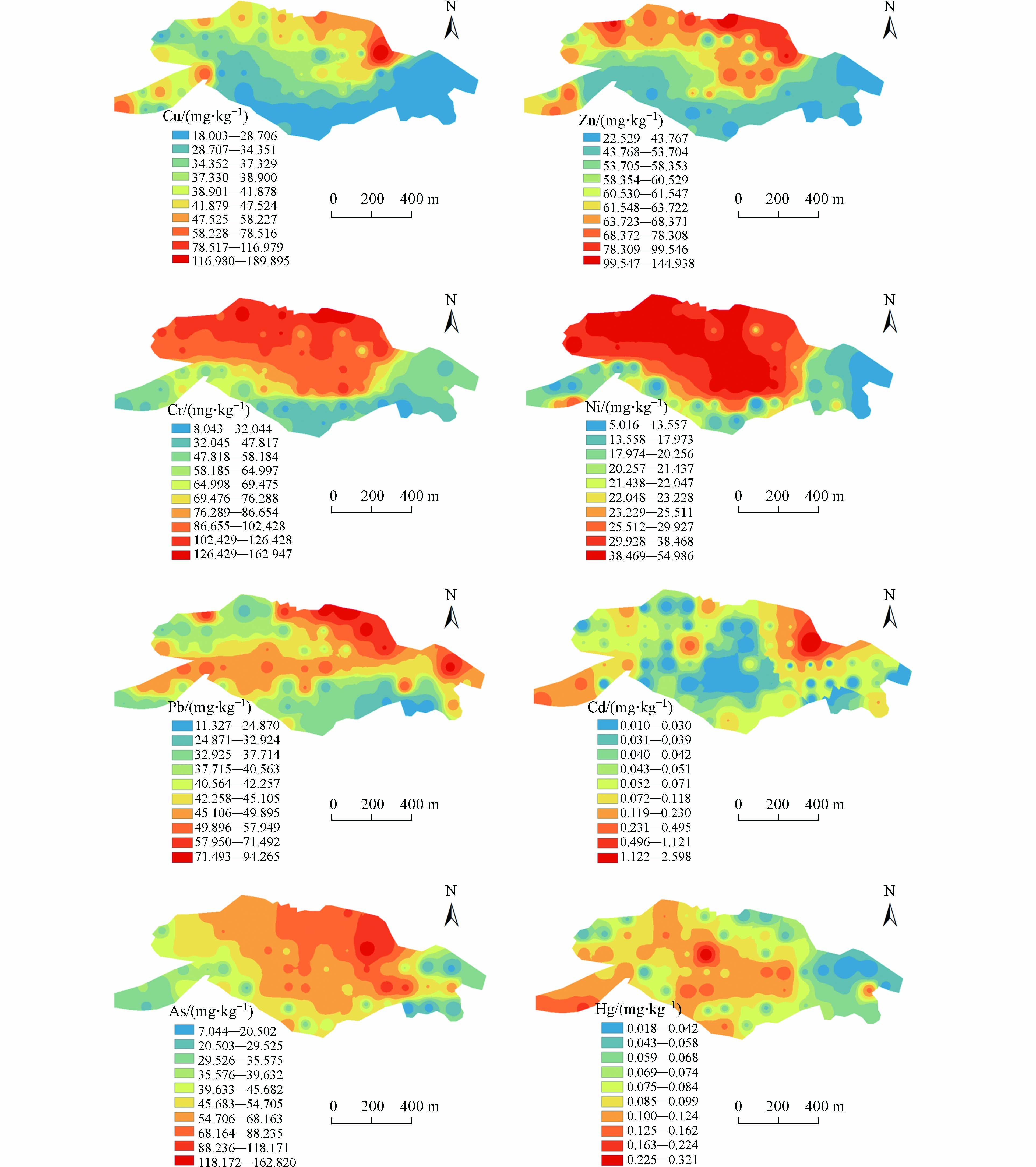
采用反距离权重法(IDW)对研究区表层土壤样品(0—20 cm)中的重金属含量进行空间插值,结果见图2. 空间分析表明:Cu、Zn元素空间分布较为一致,集中分布于研究区北侧及西南角,南部及东部区域含量相对较低;Cr、Ni元素分布规律类似,相对高值点主要集中在研究区中部及北部区域;Pb元素除局部高值点位于研究区东北部外,中部区域呈东西向的条状分布;Cd元素高值点位于研究区东北侧,其余多呈现零星分布;As元素整体含量相对较高,其空间上呈东北向西南带状分布;Hg元素相对高值点位于研究区西南部及中部. 重金属含量较高区域主要沿着研究区两条汇水箐沟存在累积现象,并向沟两侧农田延伸,重金属通过大气降尘、废水等途径进入汇水箐沟内并逐步累积,两侧可能是污水灌溉导致重金属累积.
-
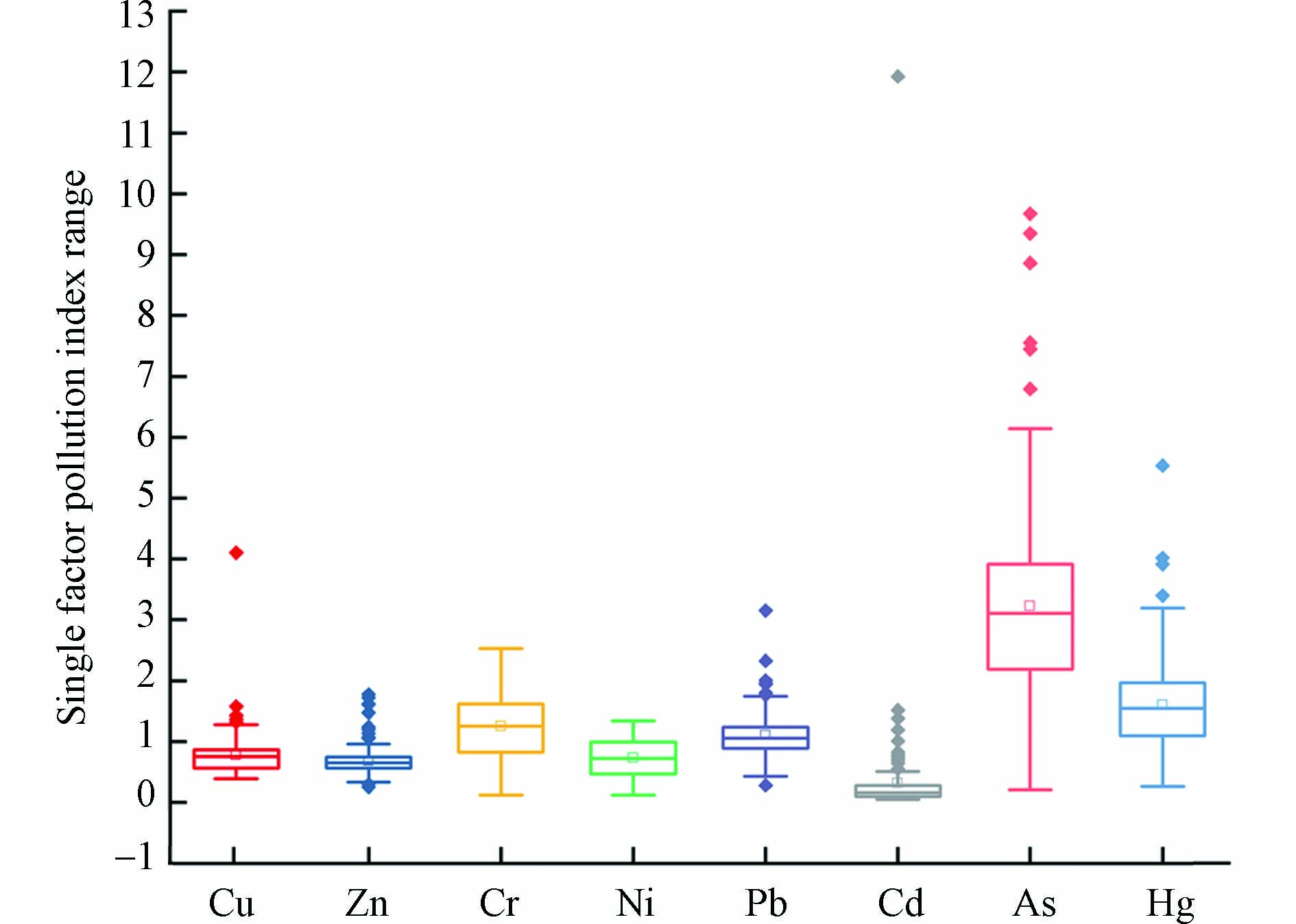
研究区的土壤重金属单因子污染指数的评价结果如图3所示. 各重金属元素单因子污染指数平均值由大到小排序为:As(3.22)>Hg(1.60)>Cr(1.25)>Pb(1.10)>Cu(0.78)>Ni(0.73)>Zn(0.68)>Cd(0.68),其中Cu、Zn、Ni、Cd元素属于无污染—轻微污染水平,Cr、Pb、Hg元素属于轻度污染水平,As元素为重度污染水平. 研究区土壤污染负荷指数属于轻微污染. 土壤样品重金属元素污染程度分布不同,其中Cd元素中93.42%的样品属于无污染水平. Cu、Zn、Ni元素中分别有86.18%、93.42%、76.32%的样品处于无污染—轻微污染水平,少部分样品为轻度污染. Cr、Pb元素中低于50%的样品处于无污染—轻微污染,大部分属于轻度污染. As、Hg元素中占比分别为4.60%、19.08%的样品为无污染—轻微污染,大部分样品的Hg元素为轻度污染,而As元素大部分样品为重度污染. 研究区整体为无污染—轻微污染水平,尽管污染水平不高,但其中As、Hg元素多为轻度污染以上,其危害不容忽视.
-
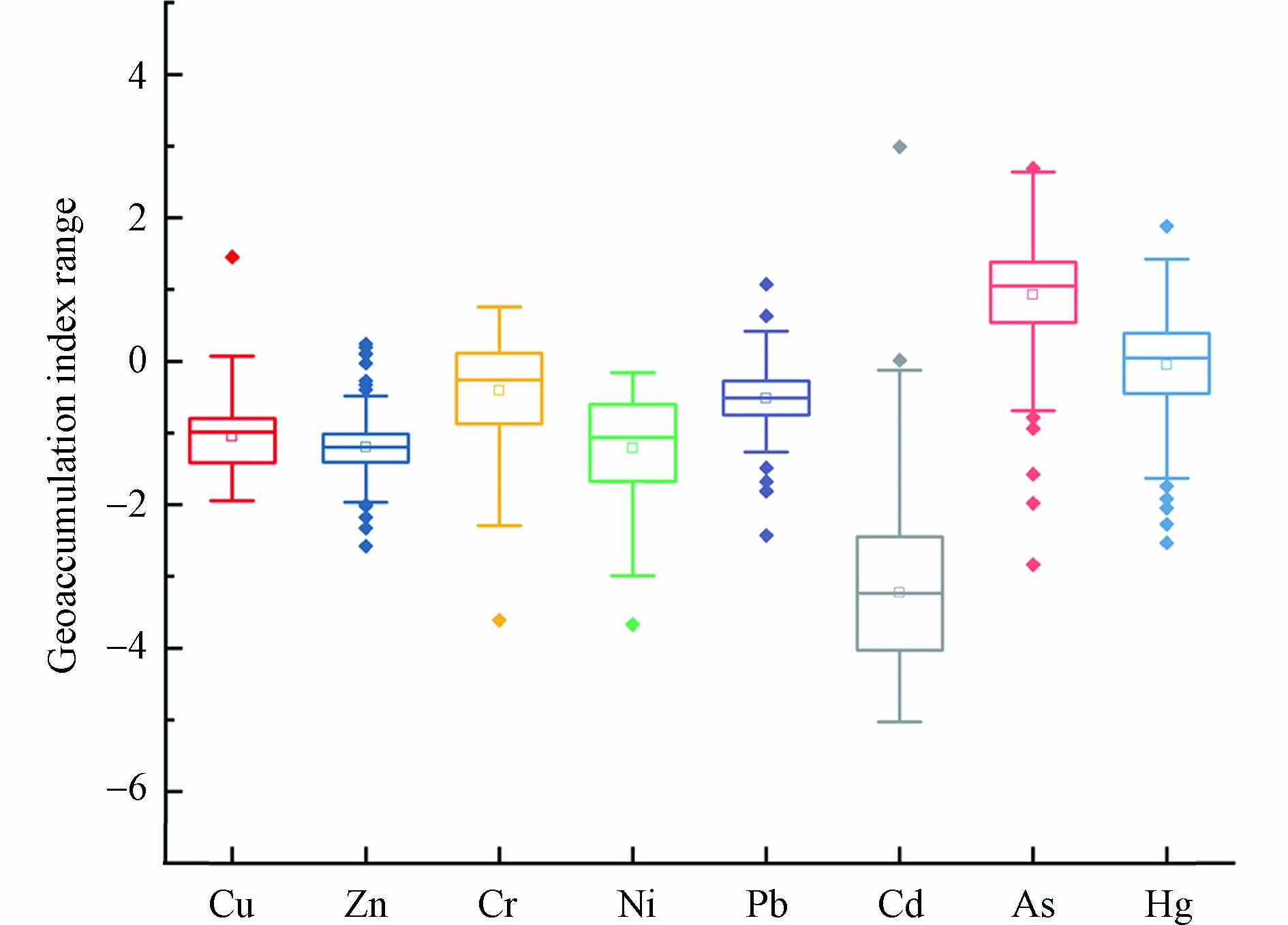
研究区土壤重金属地累积指数评价结果见图4. 本次研究测定的8种重金属元素地累积指数平均值由大到小排序依次为:As(0.92)>Hg(−0.05)>Cr(−0.41)>Pb(−0.52)>Cu(−1.05)>Zn(−1.20)>Ni(−1.21)>Cd(−3.23),其中,As属于轻度累积,其余重金属均属于无累积. 从重金属累积程度的分布来看,8种重金属地累积指数等级最高为4级(中度累积),其中,As元素在偏中度累积(3级)和中度累积(4级)的比例为53.94%,也进一步说明As元素受污染较严重,其余重金属元素基本属于无累积(1级)—轻度累积(2级)之间.
-
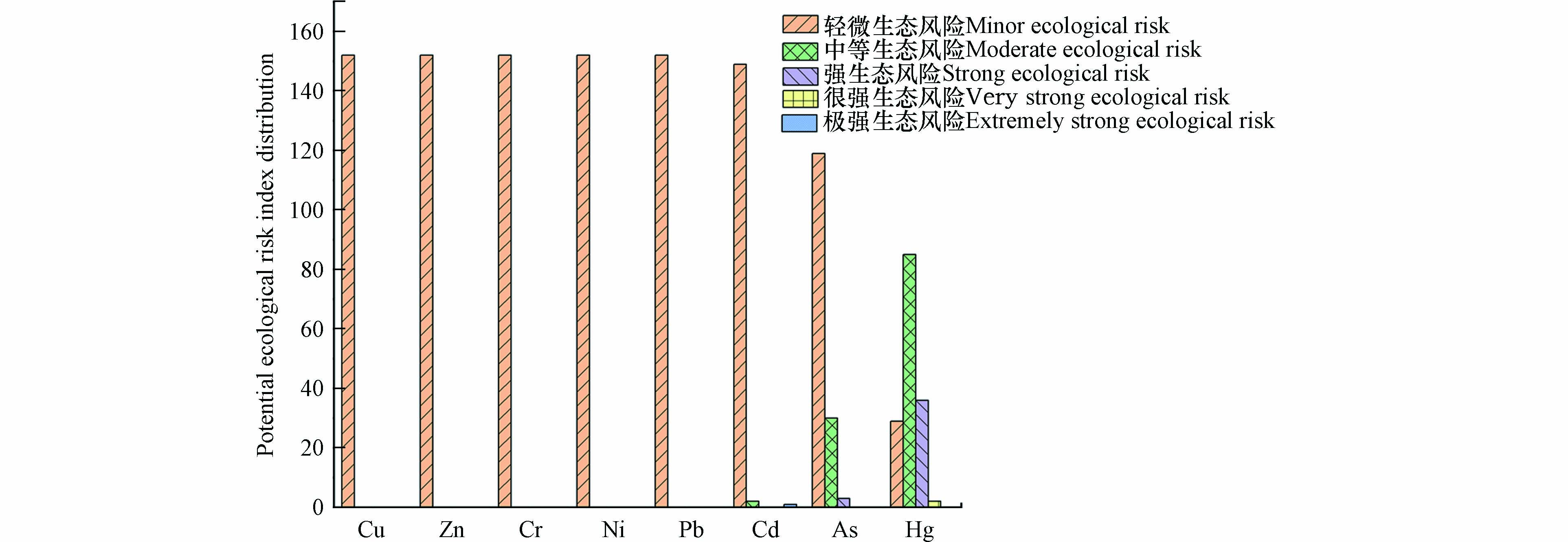
研究区土壤重金属潜在生态危害指数的统计结果详见图5. 各重金属元素的单项生态风险指数平均值由大到小分别为:Hg(64.17)>As(32.23)>Cd(9.50)>Pb(5.49)>Cu(3.88)>Ni(3.63)>Cr(2.50)>Zn(0.68). 其中Hg元素处于中等生态风险水平,其余7种元素均处于轻微生态风险水平,研究区土壤重金属综合生态风险指数处于轻微生态风险水平. 其中Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni、Pb 的5种元素所有样品均为轻微生态风险,Cd、As、Hg元素中的轻微生态风险占比分别是98.03%、78.29%、19.08%,中等生态风险占比分别是1.32%、19.74%、55.92%,强生态风险占比分别是0%、1.97%、23.68%. Hg和As的贡献值相对高,Hg的贡献率达52.56%,As次之,贡献为26.4%,而其余6种重金属的贡献率相对较低. 潜在生态风险指数结果不仅受重金属含量的影响,很大程度上也与重金属毒性相关.
-
对研究区土壤样品重金属进行Spearman相关性分析(见表5),分析结果表明,Cd、Hg元素与其他元素之间无明显相关性,且Cd与Hg也无相关性,说明两元素可能为独立来源. 在Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni、Pb和As元素中,除铅元素外,其余重金属元素之间为显著正相关,几种重金属元素之间相关性反映了重金属可能存在共同源.
-
采用PMF模型对研究区土壤重金属进行来源解析. 将重金属浓度、不确定度数据导入EPAPMF5.0分析软件,8种重金属均被归类为“Strong”(S/N>3),本研究设置3—6个因子,最终运算确定了因子数为5,18次迭代运算时的Q(Robust)与Q(True)相接近,表明真实含量值与模型预测值之间达到最佳拟合效果,大部分残差处于−3—3之间,分析结果见表6. 8种重金属元素的拟合曲线R2均大于0.7,表明PMF模型解析结果可靠.
PMF模型计算得到5个因子,贡献率分别为14.8%、16.1%、15.3%、26.6%和27.2%. 因子1对As元素的贡献较高,贡献率为62.9%,同时对Hg元素的贡献率为20.3%. 方红夏[27]研究表明,硫化物矿物暴露在空气中易被氧化,释放As和其他有毒元素,造成As元素进入土壤. 农田上游为铜选冶厂,场地内堆有大量堆浸渣,铜矿石中伴生有一定的As元素,同时在铜矿石生产过程中的浸出、电解和萃取等一系列工序,会导致As等重金属元素从铜矿石中释放,以三废的形式进入周边环境中[28-29]. 因此,因子1为工业源.
因子2对Pb元素贡献率较高,贡献率为62.0%,同时对Zn元素的贡献率为26.2%. 研究表明,Pb元素的主要来源很可能是汽油和柴油燃烧产生的,同时Zn元素可能来源于轮胎和制动器磨损、润滑剂燃烧和车辆部件腐蚀[30-31]. 空间分析发现Pb元素存在东西向带状分布,且高值区域与研究区中部田间小路及南侧道路分布一致,说明研究区Pb元素有可能来自交通污染. 因此,因子2可以被认为是交通源.
因子3对Cd元素的贡献率较高,为94.3%,相关研究表明农业土壤中重金属Cd元素主要来自肥料、农药和杀虫剂等农业用品[32],Cd元素一般被作为农业活动的标志元素[25]. 研究区中Cd元素属于强变异,受人为影响较大,相关性分析中其具有独立来源,研究区农田主要种植有水稻、玉米,肥料及相关农业产品的使用可能造成Cd元素的累积. 所以,因子3为农业源.
因子4对Ni、Cr、Cu、Zn元素的贡献率较高,贡献率分别为62%、55.1%、38.6%、30.3%,Cr、Ni元素一般被认为受土壤背景控制,但也有研究表明Ni元素受工业活动的影响[28],在研究区中几种元素含量都低于或接近土壤背景值含量,且相互呈显著正相关性,推测几种元素可能与成土母质有关. 因此,因子4为自然源.
因子5对Hg元素污染的贡献较高,贡献率为78.8%,同时对Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni元素的贡献率分别为27.7%、27.2%、25.4%、33.8%. 研究表明Hg元素是通过大气沉降到土壤中,主要是来源于煤燃烧和有色金属冶炼[13, 33-34],同时研究指出石油及大部分煤中也含有Ni、Cu元素,会在燃烧过程释放出来[4],在空间分布中Hg元素高值点主要位于研究区西南部及中部靠近居民聚集区,居民生产生活中煤及化石燃料的消耗会导致几种元素的累积. 所以,因子5为化石燃料源.
-
1)研究区土壤中Cr、As、Pb、Hg等4种元素的平均含量超过云南省的土壤背景值,深层土壤样品重金属含量范围分布相对较小,从平均值来看,两个深度土壤中的重金属含量相接近. 空间上土壤重金属元素高值点呈岛状及带状分布,位于研究区北侧、中部及西南角局部区域重金属含量较高,南部及东部区域含量相对较低.
2)研究区土壤中8种重金属污染负荷指数结果表明整体处于轻微污染. 地累积指数结果表明As元素属于轻度累积,其余重金属均为无累积. 除Hg元素的潜在生态风险单项指数达到中等,其余的7种重金属元素潜在生态风险单项指数为轻微,整体处于轻微生态风险状态. 评价表明研究区As、Hg元素的风险较高,尤其是As元素最为突出.
3)重金属来源分析中PMF模型共解析5个因子,贡献率分别为14.75%、16.11%、15.34%、26.6%和27.2%. 分析结果表明研究区土壤中As元素主要为工业源,Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni元素主要为土壤成土母质源、Cd元素主要为农业活动源、Pb元素主要为交通源及Hg元素主要为化石燃料源.
铜选冶厂周边农田土壤重金属污染特征及来源解析
Analysis of heavy metal contamination characteristics and sources in farmland soil around copper dressing and smelting plant
-
摘要: 为分析云南某铜选冶厂周边农田土壤重金属污染特征及来源,通过测定农田土壤中重金属(Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni、Pb、Cd、As、Hg)的含量,采用污染负荷指数、地累积指数及潜在生态危害指数法评价农田土壤重金属污染特征,并结合相关性分析和PMF模型对土壤重金属来源进行分析. 结果表明:研究区土壤中Cr、As、Pb、Hg 4种重金属元素的平均含量均高于云南省土壤背景值;污染负荷指数处于轻微污染;地累积指数中As(0.92)>Hg(−0.05)>Cr(−0.41)>Pb(−0.52)>Cu(−1.05)>Zn(−1.20)>Ni(−1.21)>Cd(−3.23),As元素属于轻度累积,其余重金属均为无累积;潜在生态风险单项指数中除Hg元素达到中等生态风险,其余7种重金属元素均为轻微生态风险,研究区整体处于轻微生态风险. 土壤重金属来源分析中PMF模型解析5个因子,贡献率分别为14.8%、16.1%、15.3%、26.6%和27.2%. 其中As元素主要为工业活动源,Cu、Zn、Cr、Ni元素主要为土壤成土母质源、Cd元素主要为农业活动源、Pb元素主要为交通源、Hg元素主要为化石燃料源.Abstract: To analyze the characteristics and sources of heavy metal pollution in farmland soils around a copper dressing and smelting plant in Yunnan, the content of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cr, Ni, Pb, Cd, As, Hg) in farmland soils was measured, and the pollution load index, ground accumulation index and potential ecological hazard index methods were used to evaluate the characteristics of heavy metal pollution in farmland soils, and the sources of soil heavy metals were analyzed by combining correlation analysis and PMF model.The results show that the average contents of Cr, As, Pb and Hg in the soils of the study area are higher than the background values of soils in Yunnan Province; the pollution load index is slightly polluted; the geoaccumulation index is As (0.92) > Hg (−0.05) > Cr (−0.41) > Pb (−0.52) > Cu (−1.05) > Zn (−1.20) > Ni (−1.21)>Cd (−3.23), the element As belongs to light accumulation, and the rest of heavy metals are non-accumulative; among the potential ecological risk single index, except for the element Hg, which reaches medium ecological risk, the other seven heavy metals are all at slight ecological risk, and the study area as a whole is at slight ecological risk. The PMF model analyzed five factors in the analysis of soil heavy metal sources, with contributions of 14.8%, 16.1%, 15.3%, 26.6% and 27.2%, respectively. Among them, element As is mainly the source of industrial activities, Cu, Zn, Cr and Ni are mainly the sources of soil-forming parent material, Cd is mainly the source of agricultural activities, Pb is mainly the source of traffic, and Hg is mainly the source of fossil fuels.
-
Key words:
- copper dressing and smelting plant /
- farmland /
- heavy metals /
- pollution assessment /
- PMF model
-
表 1 污染负荷指数分级
Table 1. Pollution load index classification
Pi 等级Grade PLI 等级Grade Pi<0.7 无污染 PLI<0.7 无污染 0.7≤Pi <1 轻微污染 0.7≤PLI<1 轻微污染 1≤Pi <2 轻度污染 1≤PLI<2 轻度污染 2≤Pi <3 中度污染 2≤PLI<3 中度污染 Pi≥3 重度污染 PLI≥3 重度污染 表 2 地累积指数分级
Table 2. Classification of the geoaccumulation index
Igeo Igeo<0 0≤Igeo<1 1≤Igeo<2 2≤Igeo<3 3≤Igeo<4 4≤Igeo<5 Igeo≥5 等级 无累积 轻度累积 偏中度累积 中度累积 偏重度累积 重度累积 严重累积 表 3 单项潜在生态风险指数(Ei)和综合潜在生态风险指数(RI)分级
Table 3. Classification of individual potential ecological risk index (Ei) and comprehensive potential ecological risk index (RI)
Ei 风险等级Risk level RI 风险等级Risk level Ei<40 轻微 RI<150 轻微 40≤Ei<80 中等 150≤RI<300 中等 80≤Ei<160 强 300≤RI<600 强 160≤Ei<320 很强 RI≥600 很强 Ei≥320 极强 表 4 重金属含量统计表
Table 4. Statistical table of heavy metal content (mg·kg−1)
采样深度Sampling depth 元素Element 均值Mean value 最小值Minimum value 最大值Maximum value 标准差Standard deviation 变异系数Coefficient of variation 偏度Skewness 峰度Kurtosis 背景值Background value 筛选值Filter value 0—0.2 m Cu 37.03 18.00 190.00 21.10 0.57 5.28 37.09 46.30 50.00 Zn 59.02 23.00 145.00 17.87 0.30 1.82 6.94 89.70 200.00 Cr 78.91 8.00 163.00 33.71 0.43 0.13 −0.57 65.20 150.00 Ni 29.63 5.00 55.00 13.01 0.44 −0.02 −1.15 42.50 60.00 Pb 43.80 11.30 94.30 13.83 0.32 1.18 2.82 40.60 70.00 Cd 0.09 0.01 2.60 0.30 3.18 8.08 68.33 0.22 0.30 As 55.86 6.99 163.00 24.34 0.44 1.18 3.95 18.40 40.00 Hg 0.09 0.02 0.32 0.04 0.46 2.13 9.96 0.06 1.30 0.3—0.5 m Cu 34.88 18.00 63.00 10.93 0.31 0.56 −0.07 46.30 50.00 Zn 63.41 30.00 159.00 23.48 0.37 2.56 7.61 89.70 200.00 Cr 84.03 21.00 165.00 33.73 0.40 0.30 −0.44 65.20 150.00 Ni 32.08 9.00 57.00 13.47 0.42 −0.04 −1.21 42.50 60.00 Pb 45.38 17.30 128.00 14.94 0.33 2.44 11.70 40.60 70.00 Cd 0.04 0.01 0.18 0.04 0.93 1.47 1.51 0.22 0.30 As 62.74 3.86 178.00 32.15 0.51 1.32 3.01 18.40 40.00 Hg 0.09 0.02 0.23 0.04 0.45 0.93 1.84 0.06 1.30 表 5 重金属元素相关性系数矩阵
Table 5. Correlation coefficient matrix of heavy metal elements
Cu Zn Cr Ni Pb Cd As Hg Cu 1.00 Zn 0.72** 1.00 Cr 0.72** 0.75** 1.00 Ni 0.66** 0.72** 0.85** 1.00 Pb 0.30* 0.22 0.15 -0.10 1.00 Cd 0.19 0.12 -0.03 -0.13 0.26 1.00 As 0.43** 0.51** 0.47** 0.48** 0.29 -0.15 1.00 Hg 0.32* 0.30* 0.15 0.30* -0.22 -0.02 0.09 1.00 **在0.01(双侧),相关性极显著;*在0.05(双侧),相关性显著. **At 0.01 (bilateral), the correlation is extremely significant; * At 0.05 (bilateral), the correlation is significant. 表 6 土壤重金属污染PMF模型源解析结果
Table 6. Source analysis results of PMF model of soil heavy metal pollution
F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 R2 Cu 4.1 16.9 12.7 38.6 27.7 0.92 Zn 12.2 26.2 4.1 30.3 27.2 0.72 Cr — 17.0 2.5 55.1 25.4 0.86 Ni 3.4 — 0.8 62.0 33.8 0.83 Pb 15.1 62.0 4.0 — 19.0 0.99 Cd — — 94.3 — 5.7 0.99 As 62.9 5.9 4.3 26.8 — 1.00 Hg 20.3 0.9 — — 78.8 0.99 -
[1] 成晓梦, 孙彬彬, 吴超, 等. 浙中典型硫铁矿区农田土壤重金属含量特征及健康风险 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 442-453. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202102161 CHENG X M, SUN B B, WU C, et al. Heavy metal concentration characteristics and health risks of farmland soils in typical pyrite mining area of the central Zhejiang Province, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 442-453(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202102161
[2] 李志涛, 王夏晖, 何俊, 等. 四川省江安县某硫铁矿区周边农田土壤重金属来源解析及污染评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(6): 1272-1279. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-1076 LI Z T, WANG X H, HE J, et al. Source identification and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around a pyrite mining area in Jiang’an County, Sichuan Province, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(6): 1272-1279(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-1076
[3] 秦旭芝, 罗志祥, 季文兵, 等. 桂西北地质高背景区有色金属冶炼对周边土壤重金属污染与生态风险评价 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8): 2324-2333. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202108.012 QIN X Z, LUO Z X, JI W B, et al. Pollution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surrounding soil by nonferrous metal smelting with high geological background in Northwest Guangxi [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(8): 2324-2333(in Chinese). doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.202108.012
[4] 汪峰, 黄言欢, 李如忠, 等. 有色金属矿业城市典型村镇土壤重金属污染评价及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(9): 4800-4809. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202112016 WANG F, HUANG Y H, LI R Z, et al. Contamination assessment and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in typical villages and towns in a nonferrous metal mining city [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(9): 4800-4809(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202112016
[5] 王越, 莫莉, 余新晓, 等. 粤北典型工矿区土壤重金属富集特征、来源解析及风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(3): 1636-1645. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202204271 WANG Y, MO L, YU X X, et al. Enrichment characteristics, source apportionment, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the industrial and mining area of northern Guangdong Province [J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(3): 1636-1645(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202204271
[6] 王锐, 邓海, 贾中民, 等. 汞矿区周边土壤重金属空间分布特征、污染与生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(6): 3018-3027. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202010140 WANG R, DENG H, JIA Z M, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics, pollution, and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals around mercury mining areas [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(6): 3018-3027(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202010140
[7] 程睿. 铜矿弃渣场下游农田土壤重金属污染特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2020, 10(2): 280-287. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190095 CHENG R. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil downstream of a copper mine slag dumps [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2020, 10(2): 280-287(in Chinese). doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20190095
[8] 余嘉衍, 李冰玉, 周一敏, 等. 湖南省某矿遗址周围农业土壤重金属污染及风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 1024-1030. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019040201 YU J Y, LI B Y, ZHOU Y M, et al. Pollution and risk assessment of heavy metal in agricultural soil around an abandon mine site in Hunan Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 1024-1030(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019040201
[9] 邬光海, 王晨昇, 陈鸿汉. 内蒙古废弃钨钼矿区周围土壤重金属污染生态环境评价及成因分析 [J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1838-1852. doi: 10.12029/gc20200619 WU G H, WANG C S, CHEN H H. Eco-environmental assessment and genetic analysis of heavy metal pollution in the soil around the abandoned tungsten-molybdenum mine area in Inner Mongolia [J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1838-1852(in Chinese). doi: 10.12029/gc20200619
[10] 陈盟, 潘泳兴, 黄奕翔, 等. 阳朔典型铅锌矿区流域土壤重金属空间分布特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(10): 4545-4555. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201127 CHEN M, PAN Y X, HUANG Y X, et al. Spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in soil of a typical lead-zinc mining area, Yangshuo [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(10): 4545-4555(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201127
[11] 他维媛, 康桢, 孟昭君, 等. 秦岭典型停产关闭锌冶炼企业场地土壤重金属污染特征研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1513-1521. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.07.020 TA W Y, KANG Z, MENG Z J, et al. Research of pollution characteristics of heavy metals in soil of typical closed zinc smelting enterprises in Qinling Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(7): 1513-1521(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.07.020
[12] 张恬雨, 胡恭任, 于瑞莲, 等. 基于PMF模型的垃圾焚烧厂周边农田土壤重金属源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(12): 5718-5727. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202202116 ZHANG T Y, HU G R, YU R L, et al. Source analysis of heavy metals in farmland soil around a waste incineration plant based on PMF model [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(12): 5718-5727(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202202116
[13] YANG J Z, SUN Y L, WANG Z L, et al. Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of a typical volcanic area: Risk assessment and source appointment [J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 304: 135340. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135340 [14] MEN C, LIU R M, WANG Q R, et al. Spatial-temporal characteristics, source-specific variation and uncertainty analysis of health risks associated with heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 278: 116866. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116866 [15] 王海洋, 韩玲, 谢丹妮, 等. 矿区周边农田土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(4): 2104-2114. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202106218 WANG H Y, HAN L, XIE D N, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in farmland soils around mining areas and pollution assessment [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(4): 2104-2114(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202106218
[16] 周艳, 陈樯, 邓绍坡, 等. 西南某铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属空间主成分分析及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201707125 ZHOU Y, CHEN Q, DENG S P, et al. Principal component analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around a Pb-Zn Mine in southwestern China [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201707125
[17] 王乔林, 宋云涛, 王成文, 等. 滇西地区土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(8): 3693-3703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.08.026 WANG Q L, SONG Y T, WANG C W, et al. Source identification and spatial distribution of soil heavy metals in Western Yunnan [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(8): 3693-3703(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.08.026
[18] 张博伦, 刘玲玲, 黄占斌, 等. 基于UNMIX模型的地质高背景地区土壤重金属源解析 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2023, 36(2): 393-402. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.10.15 ZHANG B L, LIU L L, HUANG Z B, et al. Source apportionment of soil heavy metal(loid)s in high geochemical background area based on the UNMIX model [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2023, 36(2): 393-402(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2022.10.15
[19] 陈雅丽, 翁莉萍, 马杰, 等. 近十年中国土壤重金属污染源解析研究进展 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(10): 2219-2238. CHEN Y L, WENG L P, MA J, et al. Review on the last ten years of research on source identification of heavy metal pollution in soils [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(10): 2219-2238(in Chinese).
[20] 马杰, 沈智杰, 张萍萍, 等. 基于APCS-MLR和PMF模型的煤矸山周边耕地土壤重金属污染特征及源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(4): 2192-2203. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202206045 MA J, SHEN Z J, ZHANG P P, et al. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soils around the gangue heap of coal mine based on APCS-MLR and PMF receptor model [J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(4): 2192-2203(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202206045
[21] 魏迎辉, 李国琛, 王颜红, 等. PMF模型的影响因素考察: 以某铅锌矿周边农田土壤重金属源解析为例 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(11): 2549-2559. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0492 WEI Y H, LI G C, WANG Y H, et al. Investigating factors influencing the PMF model: A case study of source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soils near a lead-zinc ore [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(11): 2549-2559(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0492
[22] 张扣扣, 贺婧, 钟艳霞, 等. 基于GIS对宁夏某铜银矿区周边土壤重金属来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(11): 5192-5204. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201113 ZHANG K K, HE J, ZHONG Y X, et al. Identification of soil heavy metal sources around a copper-silver mining area in Ningxia based on GIS [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(11): 5192-5204(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201113
[23] 陈航, 王颖, 王澍. 铜山矿区周边农田土壤重金属来源解析及污染评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(5): 2719-2731. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108281 CHEN H, WANG Y, WANG S. Source analysis and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil around Tongshan mining area [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(5): 2719-2731(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108281
[24] 俞诗颖. 区域土壤重金属污染源解析和污染风险情景模拟[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021. YU S Y. Source apportionment and risk scenario simulation of heavy metal pollution in regional soil[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2021 (in Chinese).
[25] 沈宸宇, 闫钰, 于瑞莲, 等. APCS-MLR结合PMF模型解析厦门杏林湾近郊流域沉积物金属来源 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(5): 2476-2488. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108337 SHEN C Y, YAN Y, YU R L, et al. APCS-MLR combined with PMF model to analyze the source of metals in sediment of xinglin bay suburban watershed, Xiamen [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(5): 2476-2488(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108337
[26] 夏子书, 白一茹, 王幼奇, 等. 基于PMF模型的宁南山区小流域土壤重金属空间分布及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 432-441. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202105128 XIA Z S, BAI Y R, WANG Y Q, et al. Spatial distribution and source analysis of soil heavy metals in a small watershed in the mountainous area of southern Ningxia based on PMF model [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 432-441(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202105128
[27] 方红夏. 宿东矿区废弃地土壤质量评价[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2021. FANG H X. Soil quality evaluation of wasteland in sudong mining area[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science & Technology, 2021 (in Chinese).
[28] 陈丹丹, 谭璐, 聂紫萌, 等. 湖南典型金属冶炼与采选行业企业周边土壤重金属污染评价及源解析 [J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(9): 2667-2679. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021010901 CHEN D D, TAN L, NIE Z M, et al. Evaluation and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in the soil around typical metal smelting and mining enterprises in Hunan Province [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(9): 2667-2679(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021010901
[29] 彭驰, 刘旭, 周子若, 等. 铜冶炼场地周边土壤重金属污染特征与风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(1): 367-375. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201040 PENG C, LIU X, ZHOU Z R, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil around copper smelting sites [J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(1): 367-375(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202201040
[30] 骆逸飞. 白云鄂博矿区土壤重金属污染特征与风险评价[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2020. LUO Y F. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil of Bayan obo mining area[D]. Baotou: Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, 2020 (in Chinese).
[31] 张素荣, 王昌宇, 刘继红, 等. 雄安新区西南部土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(4): 238-249. ZHANG S R, WANG C Y, LIU J H, et al. Assessments of heavy metal pollution in soils of the southwestern Xiongan District and its ecological risk [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(4): 238-249(in Chinese).
[32] 台凌宇. 垃圾焚烧厂周围土壤重金属污染源解析及人体健康风险评价[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018. TAI L Y. Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around waste to energy plant[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2018 (in Chinese).
[33] 余洪慧. 北京市顺义区表层土壤重金属地球化学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019. YU H H. Geochemical characteristics of heavy metals in topsoil of Shunyi district in Beijing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2019 (in Chinese).
[34] 张富贵, 彭敏, 王惠艳, 等. 基于乡镇尺度的西南重金属高背景区土壤重金属生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9): 4197-4209. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201912241 ZHANG F G, PENG M, WANG H Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals at township scale in the high background of heavy metals, southwestern, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(9): 4197-4209(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201912241
-




 下载:
下载: