-
新污染物(emerging contaminants, ECs)是指新近发现或被关注,对生态环境或人体健康存在风险,尚未纳入管理或者现有管理措施不足以有效防控其风险的污染物[1]. 主要包括但不限于药物及个人护理品、抗生素抗性基因、内分泌干扰物、消毒副产物、纳米材料以及包括多氯联苯、有机氯农药、多环芳烃和全氟化合物在内的持久性有机污染物. 这类化学物质稳定性高、亲水性强,它们可以在地下水、饮用水、地表水,甚至是污水处理厂的废水中检测到,其中大部分物质最终会进入并滞留在沿海水域,影响水产品的质量和安全,因其对水质环境的长期不良影响而受到科学界和公众的广泛关注[2 − 3]. 因此,迫切需要研究ECs在水生环境中的迁移转化过程机制. 为了调查和探究ECs在沿海水域的迁移转化并评估其生态环境风险,有必要提高对其降解过程的认识.
研究表明光化学降解是水体中有机污染物的主要转化途径[4 − 6],ECs的光化学降解包括直接、间接和自敏化光解3种方式[7]. 在直接光降解过程中,目标化合物对光子的吸收导致键断裂或重排以形成新的稳定产物;在自敏化光降解过程中,ECs吸收光子跃迁至激发态,同时将能量转移给基态3O2或H2O,产生活性氧自由基,进而引发自身降解;在间接光降解中,具有光活性的化合物吸收阳光,产生活性反应中间体(reactive intermediates,RIs),这些物质在ECs的光降解过程中起着重要作用[8 − 9]. 溶解有机物(dissolved organic matter, DOM)是一种具有优异光化学活性的天然光敏剂,在ECs的间接光解过程中发挥着重要作用:一方面DOM可以通过屏蔽阳光、清除RIs和淬灭目标污染物的激发态来减弱有机污染物的光降解;另一方面主要通过产生RIs促进光降解[10]. DOM在特定有机污染物光降解中的具体作用主要取决于DOM的类型、来源和组成[11 − 12]. 另外,环境因素如pH、光照强度等也会影响DOM的微观形态和光化学性质. 不同DOM的分子结构和特征性质存在内在差异,进而对ECs光降解表现出不同的作用.
然而,不同ECs在自然水体中的光降解行为并不一致,环境条件的动态变化也在影响该行为. 因此,研究DOM组分及环境因素对ECs在自然水体中的间接光降解作用,对预测其光化学命运至关重要,也将有助于更好地了解其他ECs的环境命运. 本文介绍了DOM诱导ECs间接光降解的降解途径和作用,讨论了DOM来源、类型、组分和其他环境条件对光降解效率的影响,以全面了解该行为机制.
-
DOM是一类由多种活性有机物(如多糖、蛋白质和木质素)组成的复杂且不均匀的混合物[13]. 它由各种官能团组成,包括醛、氨基、羧基、酯、羟基、酮、苯酚和其他官能团. DOM中的芳香酮类结构具有较强的得电子能力;酚类结构具有较强的给电子能力. 这两种结构可使DOM作为电子传递体,通过电子转移与水体中的其他物质发生氧化还原反应[14]. 研究表明,芳香酮和酚类结构在DOM中的比例对其光敏化过程起决定作用[15]. 按荧光结构划分,DOM分为类腐殖质和类蛋白质[16]. 在水生环境中主要存在两种腐殖酸组分:腐殖酸和富里酸. 腐殖酸和富里酸在分子量、化学成分、化学性质、芳香性和光学性质方面各有差异[17]. 由于有机物种的多样性和丰富的化学结构,DOM被认为是地球上最具有化学活性的有机物质之一[18].
DOM中能够吸收光的基团称为生色团,在DOM的光化学活性中起主导作用. 由于这部分结构的光吸收随着可见光(VIS)和紫外(UV)光谱中波长的降低而呈指数增长,其光吸收在UV区域最高,在光谱的红色区域下降到接近零的水平[19]. DOM在受到光辐照后通常会发生两个过程,即光漂白和光矿化. 光漂白是指DOM吸收光后发色基团吸光能力及芳香性降低的现象;而光矿化则是指随着光化学反应的发生,DOM中连接到芳香结构上的羧基发生脱羧,分解为简单矿物质后形成无机小分子化合物(如CO和CO2)的过程[20]. 由于DOM具有特殊的荧光特性,在受到光激发时会发射出荧光,通常采用三维荧光光谱与平行因子相结合的方式来分析其组成、来源和性质[21].
水体环境中的DOM可通过两个主要来源引入:内源或外源[22]. 内源主要是指水生生物,包括藻类、浮游生物和大型植物[23]. 在海洋中,浮游植物是DOM的主要来源[22];而在淡水湖泊中,植物凋谢物的分解被视为水生DOM的重要来源. 外源是指从外部水体环境中引入的外来DOM,引入途径主要包括土壤、雨水径流、大气(如雨水、沙尘暴)、地下水和人类活动等[24]. 由于营养状况、周围环境和水力特性等因素的不确定性,水体环境中DOM的来源及其比例变化很大,从而导致了其复杂性和异质性[25 − 26].
鉴于DOM在水生环境中的整体作用,深入了解其性质、反应性和环境影响在环境和生态化学领域具有重要意义.
-
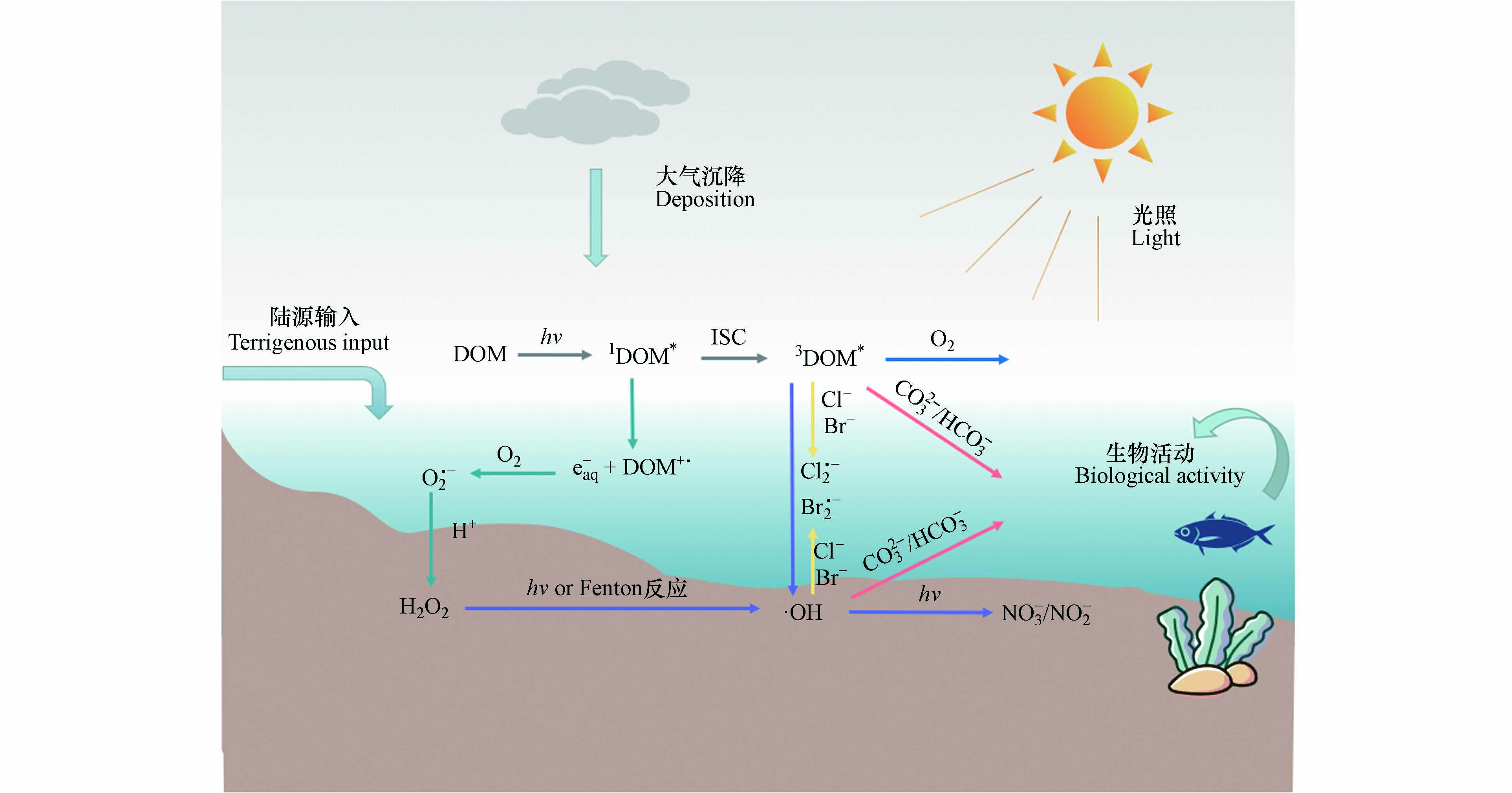
DOM是连接生命形态碳和无机碳的关键纽带,参与各种生物地球化学循环过程[27]. 尤其是DOM中的高分子量成分作为“太阳屏障”,对水生生态环境非常重要[18]. 吸光反应是DOM在水体中的重要光化学过程[28]. 由于DOM分子具有很强的光反应性,尤其是含有苯环、羧基、羟基等发色团,使其能够在水生环境中吸收光后诱导形成RIs,如羟基自由基(·OH)、单线态氧(1O2)、DOM的激发三重态(3DOM*)、过氧化氢(H2O2)等[29]. 这些光生反应物种由于其高度不稳定性和化学反应性而具有瞬态性质,可以对ECs的光降解产生不同程度的影响. 其主要反应途径如图1所示.
DOM通过辐射吸收,从电子基态(S0)光化学激发到激发单线态(1DOM*),通过荧光发射和无辐射跃迁释放能量回到基态,或在有利条件下通过系统间交叉(ISC,Intersystem Crossing)进化到三线态,从而形成3DOM*[30]. 3DOM*是水体中重要的过渡物种,可以通过能量、电子或氢转移与ECs反应,在后两种情况下,三重态通常表现为氧化剂. 在含氧水环境中,3DOM*可以将能量转移到基态分子氧以产生1O2[31]. 1O2在有机微污染物的转化中起着重要作用[32]. 3DOM*还能够通过水的氧化产生羟基化物种·OH[33]. 另外,1DOM*存在时间非常短,它会向水中释放电子形成水合电子(e-),从而在含氧水环境中产生超氧自由基(O2·-),与H+结合后转化为H2O2[34]. H2O2作为·OH的前驱体,通过直接光解或与过渡金属离子发生芬顿反应(Fenton)生成·OH[35]. ·OH还可以通过水体中NO3-/NO2-的光解产生,这也是·OH的重要来源[36]. ·OH是地表水中能产生的反应性最强的瞬态物种,它们对许多持久污染物都有很高的二阶动力学常数,因此涉及·OH的反应速率往往受到传质(扩散)现象的限制,但是它们通常可以与许多难降解的污染物反应[35]. 水体中的卤素离子也是有机污染物进行光化学转化的重要参与者. 3DOM*可以氧化卤素离子(如Cl-、Br-),从而生成卤素自由基(Cl·-、Br·-). 有研究表明,卤素自由基在富含卤化物的河口和沿海水域对污染物的光化学降解具有重要影响[37].
-
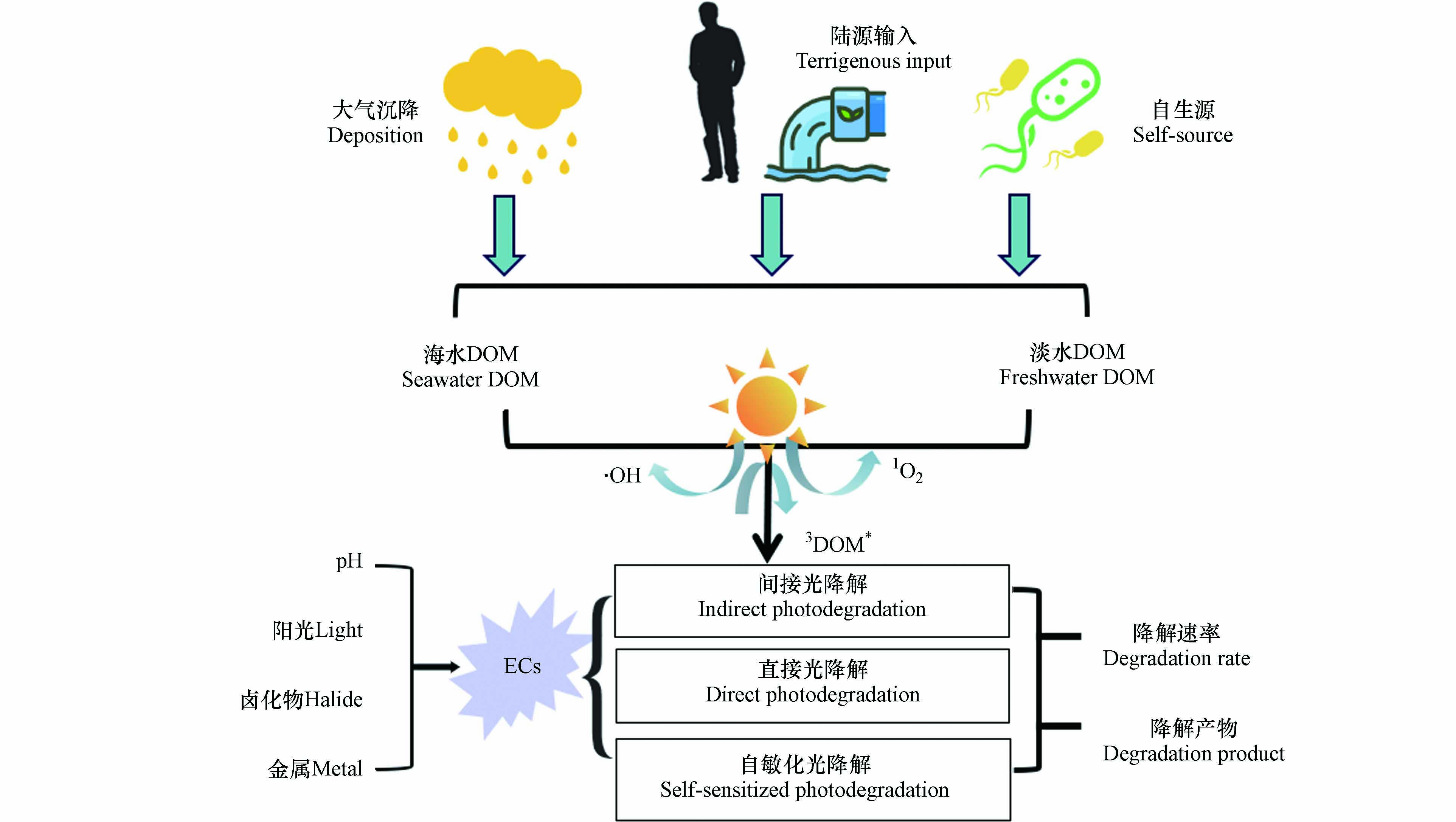
ECs通常水溶性较低,易被有机物质吸附,在水体中主要涉及一系列生物、物理和化学过程,包括吸附、生物降解和光化学降解[38 − 40]. 其中光化学降解是天然水环境中ECs的主要转化过程之一,尤其是在表层水体中[41]. 光化学降解一般分为直接光降解、间接光降解和自敏化光降解. 大多数ECs对光高度敏感,会对光子进行吸收,当光子具有足够的能量时ECs分子断裂进行直接分解;间接光降解是由水中的光敏剂产生RIs引发的;自敏化光降解是指ECs在吸收光子活化至激发态的同时,将能量转移给基态3O2或H2O,导致活性氧自由基的产生,进而引发自身降解[27,42 − 43]. ECs在水体中的光降解途径及影响因素如图2所示.
直接光降解和间接光降解的区别主要在于吸收光子的对象不同. 直接光降解是由ECs自身吸收光子引发的,而在间接光降解中吸收光子的对象则是光敏剂. 当ECs吸光能力较强时,DOM对其光降解的影响较弱. 例如,Zeng等[44]研究发现,相对于直接光降解速率,光敏剂的存在对氟乐灵的光降解速率没有影响. Carena等[45]研究发现,即使将苯达松溶解在含有光敏剂的天然水样中,苯达松的光降解速率与在纯水中相比并无显著差异. 该类物质在太阳光谱中具有很强的吸收作用,因此直接光降解是其在环境相关条件下的主要光降解途径. 对于这类物质来说,光敏剂如DOM的存在可能不会改变其光降解速率.
ECs的光降解过程与其化学结构密切相关. 在间接光降解过程中,光敏剂诱导ECs的光降解效率会受到ECs自身结构的影响. 先前研究发现敌草隆直接光降解速率非常缓慢,当加入DOM时光降解速率变快[46]. 由于敌草隆芳环上存在吸电子取代基,光敏剂DOM在阳光诱导下产生·OH,带有亲电性和非选择性,导致其与富电子的芳香族有机化合物的反应性最强[44]. Bertoldi等[47]研究发现与短波长辐射相比,在长波长辐射下腐殖酸对双酚A的光降解作用更弱. 由于双酚A分子结构中含有不饱和苯环,而不饱和烃、芳烃及其类似化合物对短波紫外光有很强的吸收,对波长大于290 nm的UVA和UVB几乎没有吸收作用[48]. 因此,双酚A在短波长辐射下光降解作用显著,而在长波长辐射下的光降解作用并不明显. Bertoldi等[47]还发现雌三醇(E3)比17β-雌二醇(E2)更易受到腐殖酸的诱导作用. 与E2相比,E3具有更多数量的羟基自由基,而腐殖酸结构中含有大量的羧基,它是由两个平行p轨道的横向重叠形成,有利于π-π相互作用[49]. 由此可见,ECs的自身结构会决定化学性质,从而影响间接光降解行为.
在自然水体中,DOM是有效的光敏剂,可以在辐照下生成RIs从而诱导ECs进行间接光降解[39,50]. 例如Ozaki等[51]将DOM浓度设置为与自然水体相似的浓度,发现TCS的光降解比在纯水中显著增强;Carena等[52]研究发现在DOM存在下,除草剂丙腈的间接光降解速率显著提高;任文华等[53]研究发现不同的DOM对丁吡吗啉降解存在不同程度的促进作用. 光降解效率增强的一个可能原因是在间接光降解过程中,DOM吸收光进行光解反应生成RIs,然后与化合物进行反应一起消耗,提高ECs降解效率并缩短残留ECs的半衰期. 相反,郑晓东等[54]研究三氯生光降解行为时发现DOM的存在降低其光降解速率;刘师宇等[55]向阿特拉津溶液中加入不同浓度的DOM后发现,DOM的存在对阿特拉津的光降解起到抑制作用,且浓度越高,抑制作用越显著. 这归因于DOM的抑制作用:DOM与ECs竞争光吸收进行自身光降解从而对其具有光屏蔽作用,另外DOM可以与RIs直接反应清除部分RIs,这也是抑制ECs光降解的一个重要原因[56]. 上述研究表明光敏化过程是由DOM诱导的. 因此,可以合理假设水体中的DOM是诱导ECs间接光降解的主要驱动因素.
-
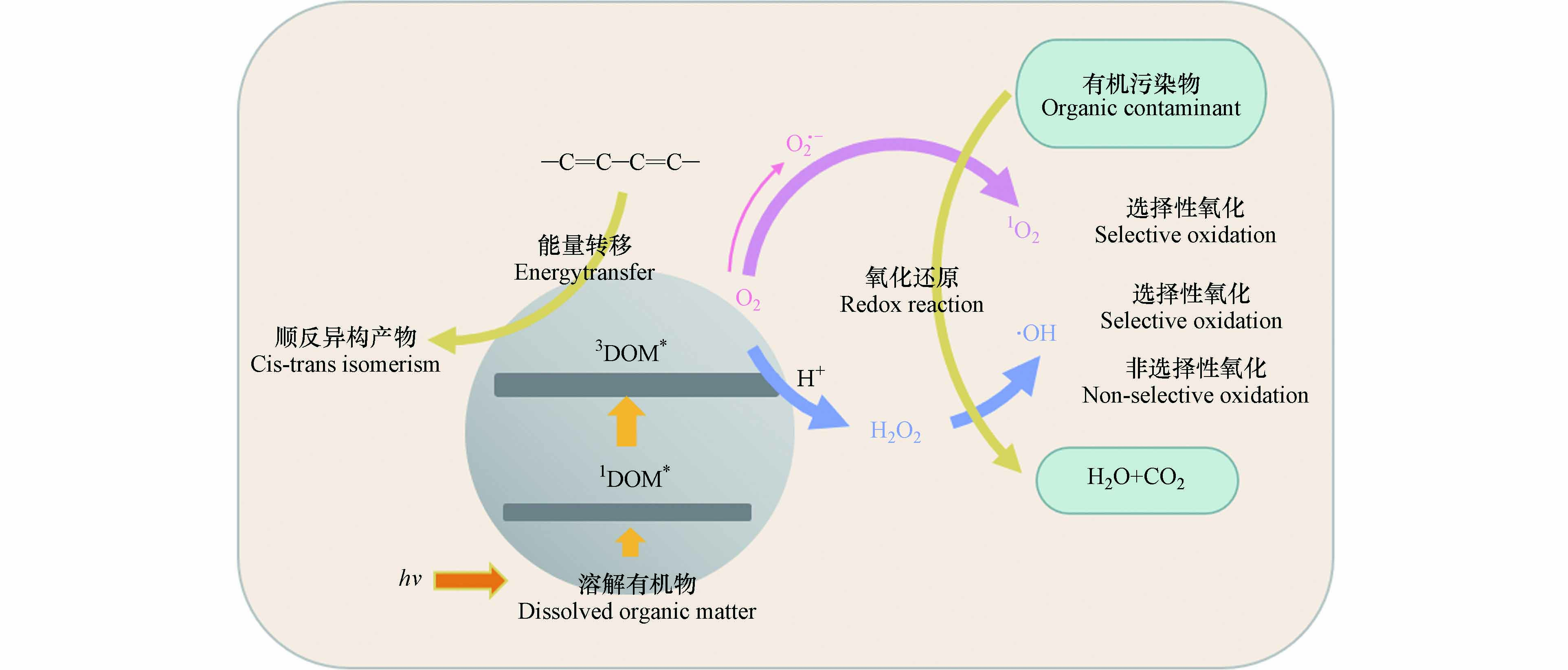
DOM诱导的ECs光降解是一种间接光降解,而间接光降解主要取决于氧化剂种类. 例如,DOM在光照下产生的·OH、1O2、H2O2、和3DOM*等[29,57]. DOM通常对ECs光降解过程产生两种影响:促进或抑制作用. DOM的促进作用主要表现在DOM吸光后产生RIs与ECs反应并促进其光降解;抑制作用主要包括两种机制:①DOM吸收阳光进行光降解,从而与有机污染物发生竞争作用;②清除RIs和淬灭目标污染物的激发态减弱有机污染物的光降解. 除影响ECs光降解速率外,DOM还可以改变其光降解产物,如Mansour等[58]研究发现二甲戊灵在没有DOM存在的情况下发生脱烷基化,在DOM存在的情况下发生硝基还原. DOM产生的·OH、1O2及3DOM*均可以作为氧化剂与供电子体发生氧化还原反应. 其中·OH为非选择性氧化剂;1O2为选择性氧化剂,易与烯烃、硫化物及富电子酚类物质发生氧化还原反应. 3DOM*在遇到共轭二烯结构时会发生能量转移,使含有该结构的ECs生成自身顺反异构产物;在遇到芳香胺、富电子酚类等富电子物质时发生氧化还原反应[27]. ECs在DOM水体中降解的大致路径如图3所示. 同时,DOM对ECs光降解的影响机制具有很强的特异性,这种特异性的产生可能有4个原因,即DOM类型不同,来源不同,组分不同,且DOM的性质及功能还会受到环境因素的影响. DOM对不同ECs光降解的影响如表1所示.
-
一般来说,DOM主要分为腐殖酸和富里酸[64]. 腐殖酸(humic acid,HA)又称胡敏酸,是一种天然有机高分子化合物,也是腐殖质的主要组成部分. 富里酸(fulvic acid,FA)又称黄腐酸,既溶于酸也溶于碱,是土壤腐殖质的组成成分之一[65]. HA和FA都是腐殖质中易溶于水的部分,主要由碳、氢、氧、氮、硫等元素构成[66]. 与HA相比,FA碳氢比值较低,分子结构方面芳香核的聚合度较小,官能团中酚羟基和甲氧基的数目比较多,含有更多含氧官能团和脂肪结构,且腐殖化程度更深[67]. 此外,FA的酸性官能团(—COOH)含量也高于HA,因此其在水溶液中具有较强的酸性[68]. HA和FA分子结构和特征性质的内在差异往往导致其对ECs的间接光降解作用表现不一致.
研究表明,DOM结构对光活性有重要影响[69 − 70]. 任东等[57]在研究E2光降解时发现,与HA相比FA的促进作用更强. 这主要与HA和FA的含氧官能团含量和分子极性大小有关. 含氧官能团如酚、醌、酮等组分结构与·OH、1O2等活性氧物种的产生密切相关. 杜超等[71]研究发现,含氧官能团含量会影响3DOM*的电子转移和能量传递过程,且含量高的组分在光照下产生RIs的能力更高. Fang等[72]研究发现,醌类结构在DOM生成·OH和1O2过程中起主要作用. 含氧官能团的含量制约着腐殖酸的可溶性、亲疏水性等,是光诱导DOM生成RIs的重要影响因素. 大分子作为较小组分的超分子聚集体,其特点是电荷转移相互作用有利于内部转化,而牺牲了光物理(例如荧光)和光化学过程[73 − 74]. 腐殖质的低分子量组分具有更高的形成三重态的能力[75 − 76]. 从这个角度来看,与HA相比,FA具有更高的生成3DOM*的能力. Ren等[60]研究发现,与HA相比,FA表现出较弱的光吸收,但在促进17α-乙炔基雌二醇(EE2)光降解方面,FA的促进作用比HA更强. 其猝灭实验表明·OH是HA溶液中EE2光降解的主要贡献者,而3DOM*在FA溶液中主导EE2的降解. 这种机制差异主要归因于以下两个原因:①FA中酮羰基和羟基的数量高于HA;②HA中的分子内相互作用可以强烈抑制3DOM*的形成[77 − 79]. 由于HA生成的3DOM*产率受到抑制,导致·OH在ECs光降解过程中起主导作用. 综上来看,与HA相比,FA具有更强的光敏能力、更低的反应物种猝灭效应和较弱的光衰减. 因此FA在ECs光降解中的促进作用强于HA.
-
目前研究的淡水DOM主要购自腐殖酸协会,如SRHA、SRFA、SRNOM及JKHA等[43,46],而海水DOM主要取自海水水域,通过电渗析/反渗透、固相萃取等方式获得[61,80]. 由于水域不同,海水DOM与淡水DOM在参与ECs间接光降解过程中通常会表现出不同的作用.
Wang等[61]在研究沿海海水DOM和淡水河流DOM对二苯甲酮-1(BP-1)光降解影响时发现,BP-1的光降解在不同DOM水体中出现了不同结果. 研究发现与沿海海水DOM相比,淡水DOM的光吸收率较高,导致吸光后产生的RIs稳态浓度较高,DOM光致产生活性中间体的稳态浓度决定了DOM对有机污染物的反应性[81]. 而且淡水DOM通常具有更高的发色团和荧光团含量,这与稳定状态下的挥发性有机物浓度有关[82]. Li等[4]研究也发现二苯甲酮-3在海水中的光降解速率相对低于在淡水中的光降解速率. 不同的是,在海水中的间接光降解主要归因于3DOM*,而在淡水中,3DOM*和·OH是其间接光降解的主要原因. 对于不同来源的DOM,组成成分不同,相应的3DOM*也具有不同的激发态还原电势[82]. 说明沿海海水和淡水DOM的光反应性对污染物的光降解具有内在差异,且淡水DOM对ECs的光降解促进作用更明显.
由于人为排放,例如海水养殖活动的影响,来自养殖海域的DOM与来自原始海水的DOM对ECs光降解表现出不同程度的行为. 人为投放的营养饵料和高强度动物活动是海水养殖的特定DOM来源[83]. 之前有研究表明,海水DOM对磺胺类抗生素的光降解具有显著的促进作用,且受海水养殖影响较大DOM的促进作用强于其他海域DOM[84 − 85]. Chen等[12]研究也发现,与来自原始海水DOM相比,受海水养殖活动影响较大的DOM表现出更高的吸光度,且对2-(2-羟基-5-苯甲基)苯并三唑的光降解促进作用更显著. 这表明养殖活动会增强DOM的光敏化降解能力. 光漂白是从天然水中去除DOM的主要过程,可以降低海洋中DOM的紫外线吸收率和分子量[86 − 87]. 与来自沿海水域的DOM相比,受海水养殖影响较大海域的DOM光漂白较少,类腐殖质物质比例较高,芳香结构和羰基结构比例较高,通常具有较高的光吸收率、3DOM*的形成量子产率和3DOM*稳态浓度,从而会对ECs的光降解产生更高的光敏效应[84]. 说明养殖区海水DOM具有更强的光敏化降解能力,并且主要是通过3DOM*加速光降解过程.
综上,光漂白过程弱、富含发色团和芳香结构的DOM光敏化降解能力更强. 由于来源不同,DOM经历的光漂白过程及所含的发色团和芳香结构含量不同,其产生RIs的能力不同,从而导致来自淡水、海水及特殊海水水域的DOM在诱导ECs间接光降解过程中表现出不同的作用.
-
激发发射矩阵光谱(EEM)与平行因子分析(PARAFAC)相结合是表征DOM的常用分析技术[88 − 89]. 该方法可以根据不同的光源、特性以及迁移和转换方式,将DOM划分为具有特殊光学性质的不同组分[90]:首先利用PARAFAC得到荧光组分图,根据最大激发发射波长得到荧光峰的位置,通过与前人所研究的荧光峰位置对比及荧光参数分析,从而得到DOM组分性质及来源的相关信息[91]. DOM组分一般分为类色氨酸、类络氨酸、类腐殖质等荧光组分[92]. 由于DOM组分千差万别,ECs与不同组分的DOM发生相互作用时,效果也不一致.
白莹等[62]研究发现,布洛芬主要进行间接光降解且光降解速率与DOM的组成成分密切相关. Bai等[63]在研究DOM各组分对对乙酰氨基酚光降解影响时发现,对乙酰氨基酚与所有组分的间接光降解速率常数均呈显著正相关,且外源DOM的相关性强于自源DOM. 为进一步分析探究,Bai等[3]在研究DOM组分对磺胺类抗生素光降解影响时,将DOM分为4个组分C1、C2、C3和C4,通过与前人研究结果对照发现C1、C2、C3为外源DOM,C4为自源DOM,且各组分的分子量和芳香度顺序为C3>C1>C2>C4,与组分荧光强度的衰减和光降解速率的相关系数一致. 说明这4种组分在光降解过程中起重要作用,且外源性荧光组分起主要作用. 与源自微生物合成的自源DOM相比,外源DOM可能具有更多芳香环和电供体基团,因此往往具有更高的芳香性[93 − 95]. DOM中含羰基和芳香结构的部分为主要发色团,RIs的稳态浓度与DOM的芳香性呈显著正相关[96]. 这是由于高分子量DOM的量子产率下降,而DOM的高芳香性超过了其量子产率,能够产生RIs或表现出较低的猝灭速率[97]. 与上述研究相符,Batista等[96]报道了芳香性与·OH稳态浓度及·OH生成速率之间的密切关系. Timko等[11]观察到芳香性与1O2和3DOM*的形成速率呈正相关. Zhou等[98]的研究表明,DOM(E2/E3)的吸光度比与1O2的表观量子产率之间存在正相关,并且DOM的芳香结构是产生3DOM*和1O2的主要部分. RIs的稳态浓度随DOM的分子量、光学性质和组成而变化. 由于DOM组分不同,其产生的RIs活性效率不同. 芳香度更高的组分对RIs的生成贡献更大,从而对ECs间接光降解过程促进作用更明显. 因此,我们应该了解DOM组分的变化,以评估DOM对ECs间接光降解的影响.
-
除了DOM的类型、来源及组分差异外,DOM诱导的ECs光降解还受到环境因素的影响,例如pH大小、光照强度、离子强度及金属元素等.
-
吸光是光化学反应的前提条件,DOM中的发色团可以吸收290—500 nm的太阳光,且光吸收强度随着波长增长呈现近似指数的下降趋势[81,99]. 当光源强度不同,产生的光子能量自然不同,从而会影响DOM对ECs的光降解效率. Peng等[100]研究发现,在UV-vis辐照下(λ>200 nm),DOM抑制了普萘洛尔的光降解,然而在模拟太阳辐照下(λ>290 nm),DOM促进其光降解. 研究表明在不同光源照射下,DOM对普萘洛尔光降解的双重作用十分典型. 一方面由于DOM具有很强的光敏性,能进行光解产生大量的RIs;另一方面当DOM自身发生光解时,会与污染物竞争光吸收从而产生光屏蔽作用. 在波长较小的UV-vis辐照下,DOM吸光强度变大,此时可能以竞争光吸收的抑制作用为主. 另外,光源强度还会影响DOM产生活性物种的能力. 如刘砚弘等[101]研究发现,汞灯照射下DOM产生活性物种的能力显著高于氙灯照射条件下,说明光源强度越大,DOM产生的活性物种越多.
-
上述研究中提到DOM可以产生RIs,其中3DOM*能够氧化卤化物离子(如Cl-,Br-),从而生成卤素自由基(Reactive halogen species,RHs),如Cl·、Br·、Cl·-、Br·-等. 这些自由基可以促进海水中许多ECs的光解. 例如,Zhao等[102]研究发现,磺胺嘧啶的光解随着上游至下游河口水域卤化物浓度的增加而增强. Pinto等[103]研究表明,在低浓度的DOM溶液和盐水中,毒死蜱主要进行直接光降解;而在高浓度的DOM溶液和盐水中,其主要进行间接光降解. 由于3DOM*的寿命变化和3DOM*与其他卤化物离子生成RHs,从而增强ECs的间接光降解速率.
但是,3DOM*与卤化物离子反应产生的RHs也可能导致3DOM*的猝灭. Hou等[104]研究发现,向DOM溶液中添加卤化物,卡马西平光解速率明显降低. 因此,即使在RHs主导的河口水域中有些污染物出现了光降解增强的现象,可能也会有部分污染物光降解受到抑制. 3DOM*诱导产生的RHS反应无法补偿3DOM*因猝灭效应对降解产生抑制,这可能会减缓ECs在卤化物浓度相对较高的河口水域中的光降解. 此外,卤化物离子的离子强度效应也会影响3DOM*衰变,从而影响3DOM*的稳态浓度[105].
-
pH值的变化会严重影响ECs的电离形式并改变其光化学反应性[69],pH值在污染物的光降解中起着重要作用. 例如Bai等[63]研究发现,在碱性条件下APAP的光降解速率显著增强. 在pH为碱性时,APAP中的羟基转变为酚阴离子,由于酚阴离子在芳香环上的电子密度较高,因此其与3DOM*的反应比酚羟基更容易[106]. Jin等[107]研究发现,氧四环素直接光解速率常数随pH的增加而增加. Ge等[69]研究发现,沙拉沙星和加替沙星的光解速率常数随着pH值的增加先增大后减小. pH决定了ECs的离子存在形式. 可电离污染物最佳离子形式占主导地位,光吸收率也随之增加;而当污染物以最稳定形式存在时,光化学活性降低. 因此,ECs的不同解离状态具有不同的光化学反应性,光降解速率随pH的变化与其在给定pH值下的解离状态密切相关.
另外,pH还会改变DOM的性质和微观形态,从而影响DOM产生RIs的浓度[108]. 于莉莉等[109]研究发现,DOM吸光系数随pH值的增大而增大. 由于在碱性条件下DOM结构发生膨胀,导致显色基团暴露增多,从而其吸光系数变大[110]. Zhang等[111]研究发现,氧四环素的光解速率常数与含DOM水溶液的酸碱度呈正相关. DOM中含有较多的含氧官能团和芳香官能团,活性氧在光照下介导形成苯氧自由基,含氧官能团和芳香物质与四环素络合. 在碱性条件下,四环素更容易受到活性氧的攻击,提高DOM与四环素在光照下的反应效率从而加速四环素的光降解[112]. Gao等[113]研究发现,随着离子强度的增加,DOM吸光度始终在较高pH下增加更明显. 离子强度可以影响DOM的光化学特性,增强DOM诱导的间接光降解作用,而这种增强效应主要依赖于酸碱度[111,113].
-
在水环境中,DOM能够与痕量金属(如Cu2+、Fe3+、Mn2+和Zn2+)结合后产生不同络合强度的稳定配合物[114 − 115]. 据研究称,光激发的金属DOM络合物可以进行配体到金属的电荷转移,从而产生·HO2和O2·-,进一步反应生成·OH[116 − 117]. 这一过程可能会显著影响金属离子和DOM共存体系ECs的间接光降解. Wang等[118]研究发现,Fe3+和丙酮酸形成的络合物是·OH的来源. Liu等[119]研究发现,Fe(Ⅲ)黄腐酸络合物通过在盐水中产生更多·OH,促进了双酚A的光氯化. 庄晓虹等[120]研究发现与只含有DOM的体系相比,DOM和铁(Ⅲ)的络合体系对壬基酚的光降解表现出更显著的促进作用. 在辐照下Fe(Ⅲ)产生自由基时更具有光活性[121]. Fe(Ⅲ)-DOM络合物很容易被光解,引入的氧气促进了这一过程. Fe3+首先被还原为Fe2+,同时生成H2O2,这两种产物进行类芬顿反应,从而生成·OH促进有机物的光降解[122 − 123].
除生成·OH外,向DOM溶液中添加金属离子还会导致DOM的荧光猝灭[115,124]. Wan等[125]研究发现,金属离子和DOM的络合能力与3DOM*的猝灭呈正相关. Liu等[126]研究发现,对于具有较强给电子基团的ECs,Cu(Ⅱ)-DOM络合物显著抑制了3DOM*诱导的有机污染物光降解. 这可能因为Cu2+的络合作用降低了3DOM*形成速率,导致3DOM*稳态浓度的降低. 通过金属离子的静态猝灭效应,1DOM*的形成受到抑制,从而形成3DOM*以及水生环境中其他RIs的进一步减少. 同时,金属离子还可以通过形成偶合络合物直接淬灭ECs的激发三重态,然后进行电子转移和能量转移或无辐射跃迁到基态,产生动态猝灭[127]. 因此,共存的金属离子对DOM诱导的ECs光降解有明显的影响. 研究这一因素对于系统地了解金属离子配位在DOM中如何影响ECs光降解的机制是必要的.
综上,DOM的光敏化降解能力会受到光源、卤化物、pH及金属离子等因素的影响:(1)光源会影响DOM诱导ECS的间接光降解过程. 在短波长辐射下,DOM的光吸收强度更强,在ECs光降解过程中产生的光屏蔽作用更明显. 在强光源辐射下,DOM产生的光活性物种更多,从而对ECs光降解的促进作用更明显. (2)卤化物离子通常在DOM诱导ECs间接光降解过程中表现出双重作用. 3DOM*可以诱导卤素离子产生卤素自由基促进ECs的光降解,但在该过程中3DOM*也可能发生猝灭从而抑制ECs光降解. (3)pH可以改变DOM的性质和微观形态,影响DOM产生的RIs浓度,从而影响DOM诱导ECs的间接光降解过程. (4)金属离子能够与DOM络合,在电荷转移过程中,DOM能够产生·HO2和O2·-,同时又会发生荧光猝灭,对诱导ECs的间接光降解过程起到双重作用.
-
DOM介导的光化学过程对水生系统的生物地球化学有着深远的影响. 目前对ECs在DOM水体中的光转化行为研究常在实验室开展,且选取的DOM溶液大多为实验室配制. 虽然研究的目标物质化学性质各有不同,但大多研究的结论也不尽相同. 另外,许多环境因素包括盐度、pH、离子强度、硝酸盐和碳酸氢盐等也被列入研究范围. 随着分析技术和手段不断进步,对ECs在水环境中光解动力学和机理的研究也逐渐深入.
目前的研究多集中于DOM对单种ECs光降解过程的影响,但是水体环境所含成分较为复杂,且DOM成分复杂、功能多样,同时自然水体中往往是多种DOM与多种ECs共存的情况;另外,部分ECs的代谢物比母体化合物具有更高的活性. 基于此,今后可重点关注以下几个方面:
(1)探究DOM的化学成分与ECs相互作用的机制. 注意与实际相结合,对多种DOM-ECs混合体系中的相互作用规律进行探究,明晰其作用过程和机理,建立相应数据库.
(2)探究ECs在间接光降解后可能形成的降解产物及产物转化途径. 应特别关注母体化合物及其代谢物的环境归宿,分析DOM作用后ECs性质的变化及毒性,为预测ECs的环境行为及评估其生态环境风险作出理论支持.
(3)探究水质因素和环境因素等可变因素综合作用对ECs光降解过程的影响. 河口是受海洋和陆地共同影响的动态系统,在环境条件(如pH、离子强度和卤化物浓度)是动态的河口地区,阐明ECs的光化学转化行为具有重要意义.
新污染物在含溶解有机物水体中光降解行为研究进展
Research progress on photodegradation behavior of emerging pollutants in water containing dissolved organic matter
-
摘要: 新污染物(emerging contaminants,ECs)是一类稳定性高、亲水性强的环境污染物,其中大部分物质最终会进入并滞留在自然水域,因其对生态和人类健康的危害而受到广泛关注. 光化学降解是ECs在水体中的主要转化过程之一,包括直接光解、间接光解和自敏化光解. 溶解有机物(dissolved organic matter,DOM)作为水体中具有优异光化学性质的光敏剂,吸光后产生·OH、1O2、3DOM*等活性反应中间体,对ECs的间接光降解过程有着重要影响. 为探究ECs在水体中的迁移转化并评估其生态环境风险,有必要提高对其降解过程的认识. 鉴于此,文章在论述DOM环境光化学特性和过程的基础上,重点阐述了DOM类型、来源、荧光组分及环境因素对ECs光降解过程的影响. DOM对ECs间接光降解过程的影响主要包括促进作用和抑制作用. 促进作用主要表现在DOM产生的活性反应中间体与ECs反应,抑制作用主要包括光屏蔽作用和猝灭效应. DOM的作用效果与其类型、来源、组分及环境因素密切相关. 同时,文章就DOM对ECs光降解影响的研究工作进行展望,这将有助于更全面地了解ECs的光化学行为,对于评估ECs在自然水体中的环境归趋和生态风险具有重要意义.Abstract: Emerging contaminants (ECs) are a class of environmental pollutants with high stability and hydrophilicity, most of which eventually enter and remain in natural waters. They have received increasing attention for its harm to ecological and human health. Photochemical degradation is one of the main transformation processes of ECs in water, including direct photodegradation, indirect photodegradation and self-sensitized photodegradation. As a photosensitizer with excellent photochemical properties, dissolved organic matter (DOM) produces active reaction intermediates such as ·OH, 1O2, and 3DOM* after light absorption, which has an important influence on the indirect photodegradation process of ECs. In order to explore the migration and transformation of ECs in water and assess their ecological risks, it is necessary to improve the understanding of their degradation process. In view of this, on the basis of discussing the environmental photochemical characteristics and processes of DOM, this paper focused on the effects of types, sources, fluorescent components of DOM and environmental factors on the photodegradation process of ECs. Influence of DOM on the photodegradation process of ECs mainly includes promoting effect and inhibiting effect. The promoting effect is mainly manifested in the reaction of active reaction intermediates generated by DOM with ECs. However, the inhibition effect mainly includes light shielding effect and quenching effect. The effect of DOM on the photodegradation of ECs was closely related to type, source, composition and environmental factors of DOM. Meanwhile, the future research work on the effect of DOM on the photodegradation of ECs was prospected. This will contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the photochemical behaviour of ECs, which is of importance for assessing the environmental fate and ecological risk of ECs in natural waters.
-
新污染物(emerging contaminants, ECs)是指新近发现或被关注,对生态环境或人体健康存在风险,尚未纳入管理或者现有管理措施不足以有效防控其风险的污染物[1]. 主要包括但不限于药物及个人护理品、抗生素抗性基因、内分泌干扰物、消毒副产物、纳米材料以及包括多氯联苯、有机氯农药、多环芳烃和全氟化合物在内的持久性有机污染物. 这类化学物质稳定性高、亲水性强,它们可以在地下水、饮用水、地表水,甚至是污水处理厂的废水中检测到,其中大部分物质最终会进入并滞留在沿海水域,影响水产品的质量和安全,因其对水质环境的长期不良影响而受到科学界和公众的广泛关注[2 − 3]. 因此,迫切需要研究ECs在水生环境中的迁移转化过程机制. 为了调查和探究ECs在沿海水域的迁移转化并评估其生态环境风险,有必要提高对其降解过程的认识.
研究表明光化学降解是水体中有机污染物的主要转化途径[4 − 6],ECs的光化学降解包括直接、间接和自敏化光解3种方式[7]. 在直接光降解过程中,目标化合物对光子的吸收导致键断裂或重排以形成新的稳定产物;在自敏化光降解过程中,ECs吸收光子跃迁至激发态,同时将能量转移给基态3O2或H2O,产生活性氧自由基,进而引发自身降解;在间接光降解中,具有光活性的化合物吸收阳光,产生活性反应中间体(reactive intermediates,RIs),这些物质在ECs的光降解过程中起着重要作用[8 − 9]. 溶解有机物(dissolved organic matter, DOM)是一种具有优异光化学活性的天然光敏剂,在ECs的间接光解过程中发挥着重要作用:一方面DOM可以通过屏蔽阳光、清除RIs和淬灭目标污染物的激发态来减弱有机污染物的光降解;另一方面主要通过产生RIs促进光降解[10]. DOM在特定有机污染物光降解中的具体作用主要取决于DOM的类型、来源和组成[11 − 12]. 另外,环境因素如pH、光照强度等也会影响DOM的微观形态和光化学性质. 不同DOM的分子结构和特征性质存在内在差异,进而对ECs光降解表现出不同的作用.
然而,不同ECs在自然水体中的光降解行为并不一致,环境条件的动态变化也在影响该行为. 因此,研究DOM组分及环境因素对ECs在自然水体中的间接光降解作用,对预测其光化学命运至关重要,也将有助于更好地了解其他ECs的环境命运. 本文介绍了DOM诱导ECs间接光降解的降解途径和作用,讨论了DOM来源、类型、组分和其他环境条件对光降解效率的影响,以全面了解该行为机制.
1. DOM的性质和来源及光化学过程(Properties, sources and photochemical processes of DOM)
1.1 DOM的性质和来源
DOM是一类由多种活性有机物(如多糖、蛋白质和木质素)组成的复杂且不均匀的混合物[13]. 它由各种官能团组成,包括醛、氨基、羧基、酯、羟基、酮、苯酚和其他官能团. DOM中的芳香酮类结构具有较强的得电子能力;酚类结构具有较强的给电子能力. 这两种结构可使DOM作为电子传递体,通过电子转移与水体中的其他物质发生氧化还原反应[14]. 研究表明,芳香酮和酚类结构在DOM中的比例对其光敏化过程起决定作用[15]. 按荧光结构划分,DOM分为类腐殖质和类蛋白质[16]. 在水生环境中主要存在两种腐殖酸组分:腐殖酸和富里酸. 腐殖酸和富里酸在分子量、化学成分、化学性质、芳香性和光学性质方面各有差异[17]. 由于有机物种的多样性和丰富的化学结构,DOM被认为是地球上最具有化学活性的有机物质之一[18].
DOM中能够吸收光的基团称为生色团,在DOM的光化学活性中起主导作用. 由于这部分结构的光吸收随着可见光(VIS)和紫外(UV)光谱中波长的降低而呈指数增长,其光吸收在UV区域最高,在光谱的红色区域下降到接近零的水平[19]. DOM在受到光辐照后通常会发生两个过程,即光漂白和光矿化. 光漂白是指DOM吸收光后发色基团吸光能力及芳香性降低的现象;而光矿化则是指随着光化学反应的发生,DOM中连接到芳香结构上的羧基发生脱羧,分解为简单矿物质后形成无机小分子化合物(如CO和CO2)的过程[20]. 由于DOM具有特殊的荧光特性,在受到光激发时会发射出荧光,通常采用三维荧光光谱与平行因子相结合的方式来分析其组成、来源和性质[21].
水体环境中的DOM可通过两个主要来源引入:内源或外源[22]. 内源主要是指水生生物,包括藻类、浮游生物和大型植物[23]. 在海洋中,浮游植物是DOM的主要来源[22];而在淡水湖泊中,植物凋谢物的分解被视为水生DOM的重要来源. 外源是指从外部水体环境中引入的外来DOM,引入途径主要包括土壤、雨水径流、大气(如雨水、沙尘暴)、地下水和人类活动等[24]. 由于营养状况、周围环境和水力特性等因素的不确定性,水体环境中DOM的来源及其比例变化很大,从而导致了其复杂性和异质性[25 − 26].
鉴于DOM在水生环境中的整体作用,深入了解其性质、反应性和环境影响在环境和生态化学领域具有重要意义.
1.2 DOM光致生成自由基的过程
DOM是连接生命形态碳和无机碳的关键纽带,参与各种生物地球化学循环过程[27]. 尤其是DOM中的高分子量成分作为“太阳屏障”,对水生生态环境非常重要[18]. 吸光反应是DOM在水体中的重要光化学过程[28]. 由于DOM分子具有很强的光反应性,尤其是含有苯环、羧基、羟基等发色团,使其能够在水生环境中吸收光后诱导形成RIs,如羟基自由基(·OH)、单线态氧(1O2)、DOM的激发三重态(3DOM*)、过氧化氢(H2O2)等[29]. 这些光生反应物种由于其高度不稳定性和化学反应性而具有瞬态性质,可以对ECs的光降解产生不同程度的影响. 其主要反应途径如图1所示.
DOM通过辐射吸收,从电子基态(S0)光化学激发到激发单线态(1DOM*),通过荧光发射和无辐射跃迁释放能量回到基态,或在有利条件下通过系统间交叉(ISC,Intersystem Crossing)进化到三线态,从而形成3DOM*[30]. 3DOM*是水体中重要的过渡物种,可以通过能量、电子或氢转移与ECs反应,在后两种情况下,三重态通常表现为氧化剂. 在含氧水环境中,3DOM*可以将能量转移到基态分子氧以产生1O2[31]. 1O2在有机微污染物的转化中起着重要作用[32]. 3DOM*还能够通过水的氧化产生羟基化物种·OH[33]. 另外,1DOM*存在时间非常短,它会向水中释放电子形成水合电子(e-),从而在含氧水环境中产生超氧自由基(O2·-),与H+结合后转化为H2O2[34]. H2O2作为·OH的前驱体,通过直接光解或与过渡金属离子发生芬顿反应(Fenton)生成·OH[35]. ·OH还可以通过水体中NO3-/NO2-的光解产生,这也是·OH的重要来源[36]. ·OH是地表水中能产生的反应性最强的瞬态物种,它们对许多持久污染物都有很高的二阶动力学常数,因此涉及·OH的反应速率往往受到传质(扩散)现象的限制,但是它们通常可以与许多难降解的污染物反应[35]. 水体中的卤素离子也是有机污染物进行光化学转化的重要参与者. 3DOM*可以氧化卤素离子(如Cl-、Br-),从而生成卤素自由基(Cl·-、Br·-). 有研究表明,卤素自由基在富含卤化物的河口和沿海水域对污染物的光化学降解具有重要影响[37].
2. 水体中ECs的光降解过程(Photodegradation process of ECs in water)
ECs通常水溶性较低,易被有机物质吸附,在水体中主要涉及一系列生物、物理和化学过程,包括吸附、生物降解和光化学降解[38 − 40]. 其中光化学降解是天然水环境中ECs的主要转化过程之一,尤其是在表层水体中[41]. 光化学降解一般分为直接光降解、间接光降解和自敏化光降解. 大多数ECs对光高度敏感,会对光子进行吸收,当光子具有足够的能量时ECs分子断裂进行直接分解;间接光降解是由水中的光敏剂产生RIs引发的;自敏化光降解是指ECs在吸收光子活化至激发态的同时,将能量转移给基态3O2或H2O,导致活性氧自由基的产生,进而引发自身降解[27,42 − 43]. ECs在水体中的光降解途径及影响因素如图2所示.
直接光降解和间接光降解的区别主要在于吸收光子的对象不同. 直接光降解是由ECs自身吸收光子引发的,而在间接光降解中吸收光子的对象则是光敏剂. 当ECs吸光能力较强时,DOM对其光降解的影响较弱. 例如,Zeng等[44]研究发现,相对于直接光降解速率,光敏剂的存在对氟乐灵的光降解速率没有影响. Carena等[45]研究发现,即使将苯达松溶解在含有光敏剂的天然水样中,苯达松的光降解速率与在纯水中相比并无显著差异. 该类物质在太阳光谱中具有很强的吸收作用,因此直接光降解是其在环境相关条件下的主要光降解途径. 对于这类物质来说,光敏剂如DOM的存在可能不会改变其光降解速率.
ECs的光降解过程与其化学结构密切相关. 在间接光降解过程中,光敏剂诱导ECs的光降解效率会受到ECs自身结构的影响. 先前研究发现敌草隆直接光降解速率非常缓慢,当加入DOM时光降解速率变快[46]. 由于敌草隆芳环上存在吸电子取代基,光敏剂DOM在阳光诱导下产生·OH,带有亲电性和非选择性,导致其与富电子的芳香族有机化合物的反应性最强[44]. Bertoldi等[47]研究发现与短波长辐射相比,在长波长辐射下腐殖酸对双酚A的光降解作用更弱. 由于双酚A分子结构中含有不饱和苯环,而不饱和烃、芳烃及其类似化合物对短波紫外光有很强的吸收,对波长大于290 nm的UVA和UVB几乎没有吸收作用[48]. 因此,双酚A在短波长辐射下光降解作用显著,而在长波长辐射下的光降解作用并不明显. Bertoldi等[47]还发现雌三醇(E3)比17β-雌二醇(E2)更易受到腐殖酸的诱导作用. 与E2相比,E3具有更多数量的羟基自由基,而腐殖酸结构中含有大量的羧基,它是由两个平行p轨道的横向重叠形成,有利于π-π相互作用[49]. 由此可见,ECs的自身结构会决定化学性质,从而影响间接光降解行为.
在自然水体中,DOM是有效的光敏剂,可以在辐照下生成RIs从而诱导ECs进行间接光降解[39,50]. 例如Ozaki等[51]将DOM浓度设置为与自然水体相似的浓度,发现TCS的光降解比在纯水中显著增强;Carena等[52]研究发现在DOM存在下,除草剂丙腈的间接光降解速率显著提高;任文华等[53]研究发现不同的DOM对丁吡吗啉降解存在不同程度的促进作用. 光降解效率增强的一个可能原因是在间接光降解过程中,DOM吸收光进行光解反应生成RIs,然后与化合物进行反应一起消耗,提高ECs降解效率并缩短残留ECs的半衰期. 相反,郑晓东等[54]研究三氯生光降解行为时发现DOM的存在降低其光降解速率;刘师宇等[55]向阿特拉津溶液中加入不同浓度的DOM后发现,DOM的存在对阿特拉津的光降解起到抑制作用,且浓度越高,抑制作用越显著. 这归因于DOM的抑制作用:DOM与ECs竞争光吸收进行自身光降解从而对其具有光屏蔽作用,另外DOM可以与RIs直接反应清除部分RIs,这也是抑制ECs光降解的一个重要原因[56]. 上述研究表明光敏化过程是由DOM诱导的. 因此,可以合理假设水体中的DOM是诱导ECs间接光降解的主要驱动因素.
3. DOM诱导ECs间接光降解机制(Indirect photodegradation mechanism of ECs induced by DOM)
DOM诱导的ECs光降解是一种间接光降解,而间接光降解主要取决于氧化剂种类. 例如,DOM在光照下产生的·OH、1O2、H2O2、和3DOM*等[29,57]. DOM通常对ECs光降解过程产生两种影响:促进或抑制作用. DOM的促进作用主要表现在DOM吸光后产生RIs与ECs反应并促进其光降解;抑制作用主要包括两种机制:①DOM吸收阳光进行光降解,从而与有机污染物发生竞争作用;②清除RIs和淬灭目标污染物的激发态减弱有机污染物的光降解. 除影响ECs光降解速率外,DOM还可以改变其光降解产物,如Mansour等[58]研究发现二甲戊灵在没有DOM存在的情况下发生脱烷基化,在DOM存在的情况下发生硝基还原. DOM产生的·OH、1O2及3DOM*均可以作为氧化剂与供电子体发生氧化还原反应. 其中·OH为非选择性氧化剂;1O2为选择性氧化剂,易与烯烃、硫化物及富电子酚类物质发生氧化还原反应. 3DOM*在遇到共轭二烯结构时会发生能量转移,使含有该结构的ECs生成自身顺反异构产物;在遇到芳香胺、富电子酚类等富电子物质时发生氧化还原反应[27]. ECs在DOM水体中降解的大致路径如图3所示. 同时,DOM对ECs光降解的影响机制具有很强的特异性,这种特异性的产生可能有4个原因,即DOM类型不同,来源不同,组分不同,且DOM的性质及功能还会受到环境因素的影响. DOM对不同ECs光降解的影响如表1所示.
表 1 DOM对不同污染物光降解的影响Table 1. Effects of DOM on photodegradation of different pollutants污染物Pollutants CAS号CAS number 主要光降解途径Main photodegradation pathways DOM来源DOM source 促进/抑制作用Promotion/inhibition DOM主要作用机制Main mechanism of DOM 参考文献Reference 氟乐灵 1582-09-8 直接光降解 SRHA/SRFA/SRNOM — — [44] 苯达松 25057-89-0 直接 湖水/稻田 — — [45] 二甲戊灵 40487-42-1 直接 湖水 — — [58] 敌草隆 330-54-1 间接 SRFA 促进 光致产生·OH [46] 雌三醇 50-27-1 间接 SRFA/SRNOM 促进 π-π相互作用 [47] 17-β雌二醇 50-28-2 间接 滇池底泥 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [59] 三氯生 3380-34-5 间接 腐殖酸(购自日本) 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [51] NLHA/NLFA 抑制 光屏蔽;动态猝灭 [54] 丙腈 107-12-0 间接 蒽醌-2-磺酸钠 促进 光致产生3DOM* [52] 丁吡吗啉 868390-90-3 间接 腐殖酸(购自中国天津) 促进 氢键、离子交换等作用力 [53] 阿特拉津 1912-24-9 间接 腐殖酸(购自中国上海) 抑制 竞争光吸收 [55] 17α-乙炔基雌二醇 57-63-6 间接 河水腐殖酸 促进 光致产生·OH [60] 河水富里酸 促进 光致产生3DOM* [60] 二苯甲酮-1 131-56-6 间接 海水DOM/SRFA/SRNOM 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [61] 二苯甲酮-3 131-57-7 间接 淡水DOM/海水DOM 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [4] 2-(2-羟基-5-苯甲基)苯并三唑 2440-22-4 间接 海水DOM 促进 光致产生3DOM* [12] 磺胺嘧啶 68-35-9 间接 SRHA/SRFA/SRNOM/JKHA 促进 光致产生3DOM* [3] 布洛芬 15687-27-1 间接 SRHA/SRFA/SRNOM/JKHA 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2 [62] 对乙酰氨基酚 103-90-2 间接 SRHA/SRFA/SRNOM/JKHA 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [63] 注:蒽醌-2-磺酸钠为DOM替代物,SRHA为苏万尼河腐殖酸,SRFA为苏万尼河富里酸,SRNOM为苏万尼河天然有机物,NLHA为Nordic湖腐植酸,NLFA为Nordic湖富里酸,JKHA为J&K科技有限公司腐殖酸,上述均为商品化DOM. Note:anthraquinone-2-sulfonate is a DOM substitute, SRHA is Suwannee River humic acid, SRFA is Suwannee River fulvic acid, SRNOM is Suwannee River natural organic matter, NLHA is Nordic Lake humic acid, NLFA is Nordic Lake fulvic acid, JKHA is humic acid from J&K Scientific Ltd. All of the above are commercial DOM. 3.1 不同类型DOM对光降解的影响
一般来说,DOM主要分为腐殖酸和富里酸[64]. 腐殖酸(humic acid,HA)又称胡敏酸,是一种天然有机高分子化合物,也是腐殖质的主要组成部分. 富里酸(fulvic acid,FA)又称黄腐酸,既溶于酸也溶于碱,是土壤腐殖质的组成成分之一[65]. HA和FA都是腐殖质中易溶于水的部分,主要由碳、氢、氧、氮、硫等元素构成[66]. 与HA相比,FA碳氢比值较低,分子结构方面芳香核的聚合度较小,官能团中酚羟基和甲氧基的数目比较多,含有更多含氧官能团和脂肪结构,且腐殖化程度更深[67]. 此外,FA的酸性官能团(—COOH)含量也高于HA,因此其在水溶液中具有较强的酸性[68]. HA和FA分子结构和特征性质的内在差异往往导致其对ECs的间接光降解作用表现不一致.
研究表明,DOM结构对光活性有重要影响[69 − 70]. 任东等[57]在研究E2光降解时发现,与HA相比FA的促进作用更强. 这主要与HA和FA的含氧官能团含量和分子极性大小有关. 含氧官能团如酚、醌、酮等组分结构与·OH、1O2等活性氧物种的产生密切相关. 杜超等[71]研究发现,含氧官能团含量会影响3DOM*的电子转移和能量传递过程,且含量高的组分在光照下产生RIs的能力更高. Fang等[72]研究发现,醌类结构在DOM生成·OH和1O2过程中起主要作用. 含氧官能团的含量制约着腐殖酸的可溶性、亲疏水性等,是光诱导DOM生成RIs的重要影响因素. 大分子作为较小组分的超分子聚集体,其特点是电荷转移相互作用有利于内部转化,而牺牲了光物理(例如荧光)和光化学过程[73 − 74]. 腐殖质的低分子量组分具有更高的形成三重态的能力[75 − 76]. 从这个角度来看,与HA相比,FA具有更高的生成3DOM*的能力. Ren等[60]研究发现,与HA相比,FA表现出较弱的光吸收,但在促进17α-乙炔基雌二醇(EE2)光降解方面,FA的促进作用比HA更强. 其猝灭实验表明·OH是HA溶液中EE2光降解的主要贡献者,而3DOM*在FA溶液中主导EE2的降解. 这种机制差异主要归因于以下两个原因:①FA中酮羰基和羟基的数量高于HA;②HA中的分子内相互作用可以强烈抑制3DOM*的形成[77 − 79]. 由于HA生成的3DOM*产率受到抑制,导致·OH在ECs光降解过程中起主导作用. 综上来看,与HA相比,FA具有更强的光敏能力、更低的反应物种猝灭效应和较弱的光衰减. 因此FA在ECs光降解中的促进作用强于HA.
3.2 海水和淡水DOM对光降解的影响
目前研究的淡水DOM主要购自腐殖酸协会,如SRHA、SRFA、SRNOM及JKHA等[43,46],而海水DOM主要取自海水水域,通过电渗析/反渗透、固相萃取等方式获得[61,80]. 由于水域不同,海水DOM与淡水DOM在参与ECs间接光降解过程中通常会表现出不同的作用.
Wang等[61]在研究沿海海水DOM和淡水河流DOM对二苯甲酮-1(BP-1)光降解影响时发现,BP-1的光降解在不同DOM水体中出现了不同结果. 研究发现与沿海海水DOM相比,淡水DOM的光吸收率较高,导致吸光后产生的RIs稳态浓度较高,DOM光致产生活性中间体的稳态浓度决定了DOM对有机污染物的反应性[81]. 而且淡水DOM通常具有更高的发色团和荧光团含量,这与稳定状态下的挥发性有机物浓度有关[82]. Li等[4]研究也发现二苯甲酮-3在海水中的光降解速率相对低于在淡水中的光降解速率. 不同的是,在海水中的间接光降解主要归因于3DOM*,而在淡水中,3DOM*和·OH是其间接光降解的主要原因. 对于不同来源的DOM,组成成分不同,相应的3DOM*也具有不同的激发态还原电势[82]. 说明沿海海水和淡水DOM的光反应性对污染物的光降解具有内在差异,且淡水DOM对ECs的光降解促进作用更明显.
由于人为排放,例如海水养殖活动的影响,来自养殖海域的DOM与来自原始海水的DOM对ECs光降解表现出不同程度的行为. 人为投放的营养饵料和高强度动物活动是海水养殖的特定DOM来源[83]. 之前有研究表明,海水DOM对磺胺类抗生素的光降解具有显著的促进作用,且受海水养殖影响较大DOM的促进作用强于其他海域DOM[84 − 85]. Chen等[12]研究也发现,与来自原始海水DOM相比,受海水养殖活动影响较大的DOM表现出更高的吸光度,且对2-(2-羟基-5-苯甲基)苯并三唑的光降解促进作用更显著. 这表明养殖活动会增强DOM的光敏化降解能力. 光漂白是从天然水中去除DOM的主要过程,可以降低海洋中DOM的紫外线吸收率和分子量[86 − 87]. 与来自沿海水域的DOM相比,受海水养殖影响较大海域的DOM光漂白较少,类腐殖质物质比例较高,芳香结构和羰基结构比例较高,通常具有较高的光吸收率、3DOM*的形成量子产率和3DOM*稳态浓度,从而会对ECs的光降解产生更高的光敏效应[84]. 说明养殖区海水DOM具有更强的光敏化降解能力,并且主要是通过3DOM*加速光降解过程.
综上,光漂白过程弱、富含发色团和芳香结构的DOM光敏化降解能力更强. 由于来源不同,DOM经历的光漂白过程及所含的发色团和芳香结构含量不同,其产生RIs的能力不同,从而导致来自淡水、海水及特殊海水水域的DOM在诱导ECs间接光降解过程中表现出不同的作用.
3.3 不同荧光组分DOM对光降解的影响
激发发射矩阵光谱(EEM)与平行因子分析(PARAFAC)相结合是表征DOM的常用分析技术[88 − 89]. 该方法可以根据不同的光源、特性以及迁移和转换方式,将DOM划分为具有特殊光学性质的不同组分[90]:首先利用PARAFAC得到荧光组分图,根据最大激发发射波长得到荧光峰的位置,通过与前人所研究的荧光峰位置对比及荧光参数分析,从而得到DOM组分性质及来源的相关信息[91]. DOM组分一般分为类色氨酸、类络氨酸、类腐殖质等荧光组分[92]. 由于DOM组分千差万别,ECs与不同组分的DOM发生相互作用时,效果也不一致.
白莹等[62]研究发现,布洛芬主要进行间接光降解且光降解速率与DOM的组成成分密切相关. Bai等[63]在研究DOM各组分对对乙酰氨基酚光降解影响时发现,对乙酰氨基酚与所有组分的间接光降解速率常数均呈显著正相关,且外源DOM的相关性强于自源DOM. 为进一步分析探究,Bai等[3]在研究DOM组分对磺胺类抗生素光降解影响时,将DOM分为4个组分C1、C2、C3和C4,通过与前人研究结果对照发现C1、C2、C3为外源DOM,C4为自源DOM,且各组分的分子量和芳香度顺序为C3>C1>C2>C4,与组分荧光强度的衰减和光降解速率的相关系数一致. 说明这4种组分在光降解过程中起重要作用,且外源性荧光组分起主要作用. 与源自微生物合成的自源DOM相比,外源DOM可能具有更多芳香环和电供体基团,因此往往具有更高的芳香性[93 − 95]. DOM中含羰基和芳香结构的部分为主要发色团,RIs的稳态浓度与DOM的芳香性呈显著正相关[96]. 这是由于高分子量DOM的量子产率下降,而DOM的高芳香性超过了其量子产率,能够产生RIs或表现出较低的猝灭速率[97]. 与上述研究相符,Batista等[96]报道了芳香性与·OH稳态浓度及·OH生成速率之间的密切关系. Timko等[11]观察到芳香性与1O2和3DOM*的形成速率呈正相关. Zhou等[98]的研究表明,DOM(E2/E3)的吸光度比与1O2的表观量子产率之间存在正相关,并且DOM的芳香结构是产生3DOM*和1O2的主要部分. RIs的稳态浓度随DOM的分子量、光学性质和组成而变化. 由于DOM组分不同,其产生的RIs活性效率不同. 芳香度更高的组分对RIs的生成贡献更大,从而对ECs间接光降解过程促进作用更明显. 因此,我们应该了解DOM组分的变化,以评估DOM对ECs间接光降解的影响.
3.4 环境因素的影响
除了DOM的类型、来源及组分差异外,DOM诱导的ECs光降解还受到环境因素的影响,例如pH大小、光照强度、离子强度及金属元素等.
3.4.1 光源及光照强度
吸光是光化学反应的前提条件,DOM中的发色团可以吸收290—500 nm的太阳光,且光吸收强度随着波长增长呈现近似指数的下降趋势[81,99]. 当光源强度不同,产生的光子能量自然不同,从而会影响DOM对ECs的光降解效率. Peng等[100]研究发现,在UV-vis辐照下(λ>200 nm),DOM抑制了普萘洛尔的光降解,然而在模拟太阳辐照下(λ>290 nm),DOM促进其光降解. 研究表明在不同光源照射下,DOM对普萘洛尔光降解的双重作用十分典型. 一方面由于DOM具有很强的光敏性,能进行光解产生大量的RIs;另一方面当DOM自身发生光解时,会与污染物竞争光吸收从而产生光屏蔽作用. 在波长较小的UV-vis辐照下,DOM吸光强度变大,此时可能以竞争光吸收的抑制作用为主. 另外,光源强度还会影响DOM产生活性物种的能力. 如刘砚弘等[101]研究发现,汞灯照射下DOM产生活性物种的能力显著高于氙灯照射条件下,说明光源强度越大,DOM产生的活性物种越多.
3.4.2 卤化物浓度
上述研究中提到DOM可以产生RIs,其中3DOM*能够氧化卤化物离子(如Cl-,Br-),从而生成卤素自由基(Reactive halogen species,RHs),如Cl·、Br·、Cl·-、Br·-等. 这些自由基可以促进海水中许多ECs的光解. 例如,Zhao等[102]研究发现,磺胺嘧啶的光解随着上游至下游河口水域卤化物浓度的增加而增强. Pinto等[103]研究表明,在低浓度的DOM溶液和盐水中,毒死蜱主要进行直接光降解;而在高浓度的DOM溶液和盐水中,其主要进行间接光降解. 由于3DOM*的寿命变化和3DOM*与其他卤化物离子生成RHs,从而增强ECs的间接光降解速率.
但是,3DOM*与卤化物离子反应产生的RHs也可能导致3DOM*的猝灭. Hou等[104]研究发现,向DOM溶液中添加卤化物,卡马西平光解速率明显降低. 因此,即使在RHs主导的河口水域中有些污染物出现了光降解增强的现象,可能也会有部分污染物光降解受到抑制. 3DOM*诱导产生的RHS反应无法补偿3DOM*因猝灭效应对降解产生抑制,这可能会减缓ECs在卤化物浓度相对较高的河口水域中的光降解. 此外,卤化物离子的离子强度效应也会影响3DOM*衰变,从而影响3DOM*的稳态浓度[105].
3.4.3 pH
pH值的变化会严重影响ECs的电离形式并改变其光化学反应性[69],pH值在污染物的光降解中起着重要作用. 例如Bai等[63]研究发现,在碱性条件下APAP的光降解速率显著增强. 在pH为碱性时,APAP中的羟基转变为酚阴离子,由于酚阴离子在芳香环上的电子密度较高,因此其与3DOM*的反应比酚羟基更容易[106]. Jin等[107]研究发现,氧四环素直接光解速率常数随pH的增加而增加. Ge等[69]研究发现,沙拉沙星和加替沙星的光解速率常数随着pH值的增加先增大后减小. pH决定了ECs的离子存在形式. 可电离污染物最佳离子形式占主导地位,光吸收率也随之增加;而当污染物以最稳定形式存在时,光化学活性降低. 因此,ECs的不同解离状态具有不同的光化学反应性,光降解速率随pH的变化与其在给定pH值下的解离状态密切相关.
另外,pH还会改变DOM的性质和微观形态,从而影响DOM产生RIs的浓度[108]. 于莉莉等[109]研究发现,DOM吸光系数随pH值的增大而增大. 由于在碱性条件下DOM结构发生膨胀,导致显色基团暴露增多,从而其吸光系数变大[110]. Zhang等[111]研究发现,氧四环素的光解速率常数与含DOM水溶液的酸碱度呈正相关. DOM中含有较多的含氧官能团和芳香官能团,活性氧在光照下介导形成苯氧自由基,含氧官能团和芳香物质与四环素络合. 在碱性条件下,四环素更容易受到活性氧的攻击,提高DOM与四环素在光照下的反应效率从而加速四环素的光降解[112]. Gao等[113]研究发现,随着离子强度的增加,DOM吸光度始终在较高pH下增加更明显. 离子强度可以影响DOM的光化学特性,增强DOM诱导的间接光降解作用,而这种增强效应主要依赖于酸碱度[111,113].
3.4.4 金属离子
在水环境中,DOM能够与痕量金属(如Cu2+、Fe3+、Mn2+和Zn2+)结合后产生不同络合强度的稳定配合物[114 − 115]. 据研究称,光激发的金属DOM络合物可以进行配体到金属的电荷转移,从而产生·HO2和O2·-,进一步反应生成·OH[116 − 117]. 这一过程可能会显著影响金属离子和DOM共存体系ECs的间接光降解. Wang等[118]研究发现,Fe3+和丙酮酸形成的络合物是·OH的来源. Liu等[119]研究发现,Fe(Ⅲ)黄腐酸络合物通过在盐水中产生更多·OH,促进了双酚A的光氯化. 庄晓虹等[120]研究发现与只含有DOM的体系相比,DOM和铁(Ⅲ)的络合体系对壬基酚的光降解表现出更显著的促进作用. 在辐照下Fe(Ⅲ)产生自由基时更具有光活性[121]. Fe(Ⅲ)-DOM络合物很容易被光解,引入的氧气促进了这一过程. Fe3+首先被还原为Fe2+,同时生成H2O2,这两种产物进行类芬顿反应,从而生成·OH促进有机物的光降解[122 − 123].
除生成·OH外,向DOM溶液中添加金属离子还会导致DOM的荧光猝灭[115,124]. Wan等[125]研究发现,金属离子和DOM的络合能力与3DOM*的猝灭呈正相关. Liu等[126]研究发现,对于具有较强给电子基团的ECs,Cu(Ⅱ)-DOM络合物显著抑制了3DOM*诱导的有机污染物光降解. 这可能因为Cu2+的络合作用降低了3DOM*形成速率,导致3DOM*稳态浓度的降低. 通过金属离子的静态猝灭效应,1DOM*的形成受到抑制,从而形成3DOM*以及水生环境中其他RIs的进一步减少. 同时,金属离子还可以通过形成偶合络合物直接淬灭ECs的激发三重态,然后进行电子转移和能量转移或无辐射跃迁到基态,产生动态猝灭[127]. 因此,共存的金属离子对DOM诱导的ECs光降解有明显的影响. 研究这一因素对于系统地了解金属离子配位在DOM中如何影响ECs光降解的机制是必要的.
综上,DOM的光敏化降解能力会受到光源、卤化物、pH及金属离子等因素的影响:(1)光源会影响DOM诱导ECS的间接光降解过程. 在短波长辐射下,DOM的光吸收强度更强,在ECs光降解过程中产生的光屏蔽作用更明显. 在强光源辐射下,DOM产生的光活性物种更多,从而对ECs光降解的促进作用更明显. (2)卤化物离子通常在DOM诱导ECs间接光降解过程中表现出双重作用. 3DOM*可以诱导卤素离子产生卤素自由基促进ECs的光降解,但在该过程中3DOM*也可能发生猝灭从而抑制ECs光降解. (3)pH可以改变DOM的性质和微观形态,影响DOM产生的RIs浓度,从而影响DOM诱导ECs的间接光降解过程. (4)金属离子能够与DOM络合,在电荷转移过程中,DOM能够产生·HO2和O2·-,同时又会发生荧光猝灭,对诱导ECs的间接光降解过程起到双重作用.
4. 结论与展望(Conclusion and prospects)
DOM介导的光化学过程对水生系统的生物地球化学有着深远的影响. 目前对ECs在DOM水体中的光转化行为研究常在实验室开展,且选取的DOM溶液大多为实验室配制. 虽然研究的目标物质化学性质各有不同,但大多研究的结论也不尽相同. 另外,许多环境因素包括盐度、pH、离子强度、硝酸盐和碳酸氢盐等也被列入研究范围. 随着分析技术和手段不断进步,对ECs在水环境中光解动力学和机理的研究也逐渐深入.
目前的研究多集中于DOM对单种ECs光降解过程的影响,但是水体环境所含成分较为复杂,且DOM成分复杂、功能多样,同时自然水体中往往是多种DOM与多种ECs共存的情况;另外,部分ECs的代谢物比母体化合物具有更高的活性. 基于此,今后可重点关注以下几个方面:
(1)探究DOM的化学成分与ECs相互作用的机制. 注意与实际相结合,对多种DOM-ECs混合体系中的相互作用规律进行探究,明晰其作用过程和机理,建立相应数据库.
(2)探究ECs在间接光降解后可能形成的降解产物及产物转化途径. 应特别关注母体化合物及其代谢物的环境归宿,分析DOM作用后ECs性质的变化及毒性,为预测ECs的环境行为及评估其生态环境风险作出理论支持.
(3)探究水质因素和环境因素等可变因素综合作用对ECs光降解过程的影响. 河口是受海洋和陆地共同影响的动态系统,在环境条件(如pH、离子强度和卤化物浓度)是动态的河口地区,阐明ECs的光化学转化行为具有重要意义.
-
表 1 DOM对不同污染物光降解的影响
Table 1. Effects of DOM on photodegradation of different pollutants
污染物Pollutants CAS号CAS number 主要光降解途径Main photodegradation pathways DOM来源DOM source 促进/抑制作用Promotion/inhibition DOM主要作用机制Main mechanism of DOM 参考文献Reference 氟乐灵 1582-09-8 直接光降解 SRHA/SRFA/SRNOM — — [44] 苯达松 25057-89-0 直接 湖水/稻田 — — [45] 二甲戊灵 40487-42-1 直接 湖水 — — [58] 敌草隆 330-54-1 间接 SRFA 促进 光致产生·OH [46] 雌三醇 50-27-1 间接 SRFA/SRNOM 促进 π-π相互作用 [47] 17-β雌二醇 50-28-2 间接 滇池底泥 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [59] 三氯生 3380-34-5 间接 腐殖酸(购自日本) 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [51] NLHA/NLFA 抑制 光屏蔽;动态猝灭 [54] 丙腈 107-12-0 间接 蒽醌-2-磺酸钠 促进 光致产生3DOM* [52] 丁吡吗啉 868390-90-3 间接 腐殖酸(购自中国天津) 促进 氢键、离子交换等作用力 [53] 阿特拉津 1912-24-9 间接 腐殖酸(购自中国上海) 抑制 竞争光吸收 [55] 17α-乙炔基雌二醇 57-63-6 间接 河水腐殖酸 促进 光致产生·OH [60] 河水富里酸 促进 光致产生3DOM* [60] 二苯甲酮-1 131-56-6 间接 海水DOM/SRFA/SRNOM 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [61] 二苯甲酮-3 131-57-7 间接 淡水DOM/海水DOM 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [4] 2-(2-羟基-5-苯甲基)苯并三唑 2440-22-4 间接 海水DOM 促进 光致产生3DOM* [12] 磺胺嘧啶 68-35-9 间接 SRHA/SRFA/SRNOM/JKHA 促进 光致产生3DOM* [3] 布洛芬 15687-27-1 间接 SRHA/SRFA/SRNOM/JKHA 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2 [62] 对乙酰氨基酚 103-90-2 间接 SRHA/SRFA/SRNOM/JKHA 促进 光致产生·OH,1O2,3DOM* [63] 注:蒽醌-2-磺酸钠为DOM替代物,SRHA为苏万尼河腐殖酸,SRFA为苏万尼河富里酸,SRNOM为苏万尼河天然有机物,NLHA为Nordic湖腐植酸,NLFA为Nordic湖富里酸,JKHA为J&K科技有限公司腐殖酸,上述均为商品化DOM. Note:anthraquinone-2-sulfonate is a DOM substitute, SRHA is Suwannee River humic acid, SRFA is Suwannee River fulvic acid, SRNOM is Suwannee River natural organic matter, NLHA is Nordic Lake humic acid, NLFA is Nordic Lake fulvic acid, JKHA is humic acid from J&K Scientific Ltd. All of the above are commercial DOM. -
[1] 周林军, 梁梦园, 范德玲, 等. 新污染物环境监测国际实践及启示[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(12): 1532-1539. doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2021.0293 ZHOU L J, LIANG M Y, FAN D L, et al. International practices and enlightenment for environment monitoring of emerging pollutants[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2021, 37(12): 1532-1539(in Chinese). doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2021.0293
[2] SOLÁ-GUTIÉRREZ C, SCHRÖDER S, SAN-ROMÁN M F, et al. Critical review on the mechanistic photolytic and photocatalytic degradation of triclosan[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 260: 110101. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110101 [3] BAI Y, ZHOU Y L, CHE X W, et al. Indirect photodegradation of sulfadiazine in the presence of DOM: Effects of DOM components and main seawater constituents[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 268: 115689. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115689 [4] LI Y J, QIAO X L, ZHOU C Z, et al. Photochemical transformation of sunscreen agent benzophenone-3 and its metabolite in surface freshwater and seawater[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 153: 494-499. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.080 [5] BAO Y P, NIU J F. Photochemical transformation of tetrabromobisphenol A under simulated sunlight irradiation: Kinetics, mechanism and influencing factors[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 134: 550-556. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.12.016 [6] de LAURENTIIS E, MINELLA M, SARAKHA M, et al. Photochemical processes involving the UV absorber benzophenone-4 (2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone-5-sulphonic acid) in aqueous solution: Reaction pathways and implications for surface waters[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(15): 5943-5953. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.07.017 [7] 葛林科, 张思玉, 谢晴, 等. 抗生素在水环境中的光化学行为[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2010, 40(2): 124-135. doi: 10.1360/zb2010-40-2-124 GE L K, ZHANG S Y, XIE Q, et al. Progress in studies on aqueous environmental photochemical behavior of antibiotics[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica), 2010, 40(2): 124-135(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/zb2010-40-2-124
[8] GE L K, ZHANG P, HALSALL C, et al. The importance of reactive oxygen species on the aqueous phototransformation of sulfonamide antibiotics: Kinetics, pathways, and comparisons with direct photolysis[J]. Water Research, 2019, 149: 243-250. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.009 [9] AL HOUSARI F, VIONE D, CHIRON S, et al. Reactive photoinduced species in estuarine waters. Characterization of hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen and dissolved organic matter triplet state in natural oxidation processes[J]. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 2010, 9(1): 78-86. [10] WENK J, von GUNTEN U, CANONICA S. Effect of dissolved organic matter on the transformation of contaminants induced by excited triplet states and the hydroxyl radical[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(4): 1334-1340. [11] TIMKO S A, ROMERA-CASTILLO C, JAFFÉ R, et al. Photo-reactivity of natural dissolved organic matter from fresh to marine waters in the Florida Everglades, USA[J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2014, 16(4): 866-878. [12] CHEN X, WANG J Q, CHEN J W, et al. Photodegradation of 2-(2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)benzotriazole (UV-P) in coastal seawaters: Important role of DOM[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2019, 85: 129-137. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.017 [13] AIKEN G R, GILMOUR C C, KRABBENHOFT D P, et al. Dissolved organic matter in the Florida Everglades: Implications for ecosystem restoration[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 41(sup1): 217-248. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2010.530934 [14] 刘雪石, 乔显亮, 刘远. DOM的光化学活性及其对污染物光解的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(1): 85-94. LIU X S, QIAO X L, LIU Y. Photoreactivity of DOM and its effect on the photo-transformation of pollutants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(1): 85-94(in Chinese).
[15] 杜超. 不同来源腐殖酸及其组分光致产生活性氧物种能力的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2019. DU C. The ability of photo-induced reactive oxygen species from different sources of humic acid and its components[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2019(in Chinese).
[16] COBLE P G, GREEN S A, BLOUGH N V, et al. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in the Black Sea by fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Nature, 1990, 348(6300): 432-435. doi: 10.1038/348432a0 [17] KOWALCZUK P, DURAKO M J, YOUNG H, et al. Characterization of dissolved organic matter fluorescence in the South Atlantic Bight with use of PARAFAC model: Interannual variability[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2009, 113(3/4): 182-196. [18] ZHANG H F, ZHENG Y C, WANG X C, et al. Characterization and biogeochemical implications of dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 294: 113041. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113041 [19] STEDMON C A, MARKAGER S. Behaviour of the optical properties of coloured dissolved organic matter under conservative mixing[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2003, 57(5/6): 973-979. [20] 任东, 陈芳, 蒲红玉, 等. 溶解有机质的光化学行为及其环境效应[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019, 35(5): 563-572. doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.0319 REN D, CHEN F, PU H Y, et al. Photochemical behaviors and environmental effects of dissolved organic matter[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2019, 35(5): 563-572(in Chinese). doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.0319
[21] ISHII S K L, BOYER T H. Behavior of reoccurring PARAFAC components in fluorescent dissolved organic matter in natural and engineered systems: A critical review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(4): 2006-2017. [22] MENG F G, HUANG G C, YANG X, et al. Identifying the sources and fate of anthropogenically impacted dissolved organic matter (DOM) in urbanized rivers[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(14): 5027-5039. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.05.043 [23] DERRIEN M, BROGI S R, GONÇALVES-ARAUJO R. Characterization of aquatic organic matter: Assessment, perspectives and research priorities[J]. Water Research, 2019, 163: 114908. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.114908 [24] ARTIFON V, ZANARDI-LAMARDO E, FILLMANN G. Aquatic organic matter: Classification and interaction with organic microcontaminants[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 649: 1620-1635. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.385 [25] CONNOLLY C T, CARDENAS M B, BURKART G A, et al. Groundwater as a major source of dissolved organic matter to Arctic coastal waters[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1479. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15250-8 [26] HOSEN J D, ARMSTRONG A W, PALMER M A. Dissolved organic matter variations in coastal plain wetland watersheds: The integrated role of hydrological connectivity, land use, and seasonality[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2018, 32(11): 1664-1681. doi: 10.1002/hyp.11519 [27] MELENDEZ-PEREZ J J, MARTÍNEZ-MEJÍA M J, AWAN A T, et al. Characterization and comparison of riverine, lacustrine, marine and estuarine dissolved organic matter by ultra-high resolution and accuracy Fourier transform mass spectrometry[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2016, 101: 99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2016.08.005 [28] SONG N, JIANG H L. Coordinated photodegradation and biodegradation of organic matter from macrophyte litter in shallow lake water: Dual role of solar irradiation[J]. Water Research, 2020, 172: 115516. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115516 [29] 郭忠禹, 陈景文, 张思玉, 等. 天然水中溶解性有机质对有机微污染物光化学转化的影响[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(26): 2786-2803. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0791 GUO Z Y, CHEN J W, ZHANG S Y, et al. Effects of dissolved organic matter on photochemical transformation of organic micropollutants in natural waters[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(26): 2786-2803(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0791
[30] ZHANG D N, YAN S W, SONG W H. Photochemically induced formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) from effluent organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(21): 12645-12653. [31] CANONICA S, FREIBURGHAUS M. Electron-rich phenols for probing the photochemical reactivity of freshwaters[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(4): 690-695. [32] BODHIPAKSHA L C, SHARPLESS C M, CHIN Y P, et al. Role of effluent organic matter in the photochemical degradation of compounds of wastewater origin[J]. Water Research, 2017, 110: 170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.12.016 [33] ZHOU C Z, CHEN J W, XIE Q, et al. Photolysis of three antiviral drugs acyclovir, zidovudine and lamivudine in surface freshwater and seawater[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 138: 792-797. [34] 邰超, 李雁宾, 阴永光, 等. 天然水体中可溶性有机质的自由基光化学行为[J]. 化学进展, 2012, 24(7): 1388-1397. TAI C, LI Y B, YIN Y G, et al. Free radical photochemistry of dissolved organic matter in natural water[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2012, 24(7): 1388-1397(in Chinese).
[35] VIONE D, MINELLA M, MAURINO V, et al. Indirect photochemistry in sunlit surface waters: Photoinduced production of reactive transient species[J]. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2014, 20(34): 10590-10606. doi: 10.1002/chem.201400413 [36] JI Y F, ZENG C, FERRONATO C, et al. Nitrate-induced photodegradation of atenolol in aqueous solution: Kinetics, toxicity and degradation pathways[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 88(5): 644-649. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.050 [37] ZHANG K, PARKER K M. Halogen radical oxidants in natural and engineered aquatic systems[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(17): 9579-9594. [38] ZHANG H Q, XIE H B, CHEN J W, et al. Prediction of hydrolysis pathways and kinetics for antibiotics under environmental pH conditions: A quantum chemical study on cephradine[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(3): 1552-1558. [39] LEAL J F, ESTEVES V I, SANTOS E B H. BDE-209: Kinetic studies and effect of humic substances on photodegradation in water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(24): 14010-14017. [40] REMUCAL C K. The role of indirect photochemical degradation in the environmental fate of pesticides: A review[J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2014, 16(4): 628-653. [41] DABIĆ D, BABIĆ S, ŠKORIĆ I. The role of photodegradation in the environmental fate of hydroxychloroquine[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 230: 268-277. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.032 [42] GARCÍA P E, QUEIMALIÑOS C, DIÉGUEZ M C. Natural levels and photo-production rates of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in Andean Patagonian aquatic systems: Influence of the dissolved organic matter pool[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 217: 550-557. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.179 [43] CHIWA M, HIGASHI N, OTSUKI K, et al. Sources of hydroxyl radical in headwater streams from nitrogen-saturated forest[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 119: 1386-1390. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.046 [44] ZENG T, ARNOLD W A. Pesticide photolysis in prairie potholes: Probing photosensitized processes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(13): 6735-6745. [45] CARENA L, FABBRI D, PASSANANTI M, et al. The role of direct photolysis in the photodegradation of the herbicide bentazone in natural surface waters[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 246: 125705. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125705 [46] GERECKE A C, CANONICA S, MÜLLER S R, et al. Quantification of dissolved natural organic matter (DOM) mediated phototransformation of phenylurea herbicides in lakes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(19): 3915-3923. [47] BERTOLDI C, RODRIGUES A G, FERNANDES A N. Removal of endocrine disrupters in water under artificial light: The effect of organic matter[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2019, 27: 126-133. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2018.11.016 [48] JIA C Z, WANG Y X, ZHANG C X, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A in aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide[J]. Environmental Engineering Science, 2012, 29(7): 630-637. doi: 10.1089/ees.2011.0132 [49] LEE J H, ZHOU J L, LEE Y, et al. Changes in the sorption and rate of 17β-estradiol biodegradation by dissolved organic matter collected from different water sources[J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring: JEM, 2012, 14(2): 543-551. doi: 10.1039/C1EM10690B [50] XUE S, SUN J J, LIU Y, et al. Effect of dissolved organic matter fractions on photodegradation of phenanthrene in ice[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 361: 30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.072 [51] OZAKI N, TANAKA T, KINDAICHI T, et al. Photodegradation of fragrance materials and triclosan in water: Direct photolysis and photosensitized degradation[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 23: 101766. [52] CARENA L, MINELLA M, BARSOTTI F, et al. Phototransformation of the herbicide propanil in paddy field water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(5): 2695-2704. [53] 任文华, 肖玉梅, 黄金莉, 等. 丁吡吗啉在腐殖酸存在下的光降解[J]. 农药, 2020, 59(3): 193-196, 208. REN W H, XIAO Y M, HUANG J L, et al. The photolysis of pyrimorph on the effect of humic acid[J]. Agrochemicals, 2020, 59(3): 193-196, 208(in Chinese).
[54] 郑晓冬, 乔显亮, 肖杰, 等. 水中溶解性有机质对三氯生光解的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2013, 36(10): 182-185. ZHENG X D, QIAO X L, XIAO J, et al. Photolysis of TCS by DOM in water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 36(10): 182-185(in Chinese).
[55] 刘师宇, 向武, 黄碧捷, 等. 腐殖酸和β-环糊精对阿特拉津光降解的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(7): 93-96. LIU S Y, XIANG W, HUANG B J, et al. Effects of humic acids and β-cyclodextrins on photodegradation of atrazine[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(7): 93-96(in Chinese).
[56] DIMOU A D, SAKKAS V A, ALBANIS T A. Trifluralin photolysis in natural waters and under the presence of isolated organic matter and nitrate ions: Kinetics and photoproduct analysis[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2004, 163(3): 473-480. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2004.02.001 [57] TIAN Y J, ZOU J R, FENG L, et al. Chlorella vulgaris enhance the photodegradation of chlortetracycline in aqueous solution via extracellular organic matters (EOMs): Role of triplet state EOMs[J]. Water Research, 2019, 149: 35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.076 [58] MANSOUR M, FEICHT E A, BEHECHTI A, et al. Experimental approaches to studying the photostability of selected pesticides in water and soil[J]. Chemosphere, 1997, 35(1/2): 39-50. [59] 任东, 杨小霞, 马晓冬, 等. DOM结构特征及其对17β-雌二醇光降解的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(5): 1375-1383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.05.012 REN D, YANG X X, MA X D, et al. Structural characteristics of DOM and its effects on the photodegradation of 17β-estradiol[J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(5): 1375-1383(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.05.012
[60] REN D, CHEN F, REN Z G, et al. Different response of 17α-ethinylestradiol photodegradation induced by aquatic humic and fulvic acids to typical water matrixes[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 121: 367-373. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2018.11.018 [61] WANG J Q, CHEN J W, QIAO X L, et al. Disparate effects of DOM extracted from coastal seawaters and freshwaters on photodegradation of 2, 4-Dihydroxybenzophenone[J]. Water Research, 2019, 151: 280-287. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.045 [62] 白莹, 崔正国, 苏荣国, 等. 水体中布洛芬的间接光降解作用机理研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(7): 2831-2837. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.07.017 BAI Y, CUI Z G, SU R G, et al. The indirect photodegradation mechanism of ibuprofen in simulated seawater[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(7): 2831-2837(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.07.017
[63] BAI Y, CUI Z G, SU R G, et al. Influence of DOM components, salinity, pH, nitrate, and bicarbonate on the indirect photodegradation of acetaminophen in simulated coastal waters[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 205: 108-117. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.087 [64] POWELL H K J, FENTON E. Size fractionation of humic substances: Effect on protonation and metal binding properties[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1996, 334(1/2): 27-38. [65] KOIVULA N, HÄNNINEN K. Concentrations of monosaccharides in humic substances in the early stages of humification[J]. Chemosphere, 2001, 44(2): 271-279. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00167-3 [66] 傅平青, 刘丛强, 吴丰昌. 水环境中腐殖质金属离子键合作用研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2004, 23(6): 143-148. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.2004.0217 FU P Q, LIU C Q, WU F C. Binding of metal-ions with humic substances in aquatic environments: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2004, 23(6): 143-148(in Chinese). doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.2004.0217
[67] 李会杰. 腐殖酸和富里酸的提取与表征研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2012. LI H J. Study on extraction and characterization of HA and FA[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [68] 郝港利, 邓文博, 刘文娟. 芦芽山阔叶林土壤中腐殖酸和富里酸的提取与表征研究[J].山西大学学报(自然科学版),2023(4):961-968. HAO G L, DENG W B, LIU W J. Study on isolation and characterization of soil humic acid and fulvic acid in broadleaf forest from Luya mountain[J]. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition), 2023(4):961-968.
[69] GE L K, CHEN J W, WEI X X, et al. Aquatic photochemistry of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Kinetics, pathways, and multivariate effects of main water constituents[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(7): 2400-2405. [70] THESE A, WINKLER M, THOMAS C, et al. Determination of molecular formulas and structural regularities of low molecular weight fulvic acids by size-exclusion chromatography with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2004, 18(16): 1777-1786. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1550 [71] 杜超, 程德义, 代静玉, 等. 不同来源溶解性有机质在光辐射下产生活性氧基团能力的差异[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(7): 2279-2287. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0094 DU C, CHENG D Y, DAI J Y, et al. Differences in the ability of dissolved organic matter from different sources to produce reactive oxygen species under light irradiation[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(7): 2279-2287(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0094
[72] FANG G D, ZHU C Y, DIONYSIOU D D, et al. Mechanism of hydroxyl radical generation from biochar suspensions: Implications to diethyl phthalate degradation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 176: 210-217. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.032 [73] del VECCHIO R, BLOUGH N V. On the origin of the optical properties of humic substances[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2004, 38(14): 3885-3891. [74] NEBBIOSO A, PICCOLO A. Advances in humeomics: Enhanced structural identification of humic molecules after size fractionation of a soil humic acid[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2012, 720: 77-90. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2012.01.027 [75] MINELLA M, ROMEO F, VIONE D, et al. Low to negligible photoactivity of lake-water matter in the size range from 0.1 to 5 μm[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 83(11): 1480-1485. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.093 [76] MINELLA M, MERLO M P, MAURINO V, et al. Transformation of 2, 4, 6-trimethylphenol and furfuryl alcohol, photosensitised by Aldrich humic acids subject to different filtration procedures[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 90(2): 306-311. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.07.013 [77] YUAN C Y, CHAKRABORTY M, CANONICA S, et al. Isoproturon reappearance after photosensitized degradation in the presence of triplet ketones or fulvic acids[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(22): 12250-12257. [78] JANSSEN E M L, ERICKSON P R, MCNEILL K. Dual roles of dissolved organic matter as sensitizer and quencher in the photooxidation of tryptophan[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(9): 4916-4924. [79] WENK J, AESCHBACHER M, SANDER M, et al. Photosensitizing and inhibitory effects of ozonated dissolved organic matter on triplet-induced contaminant transformation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(14): 8541-8549. [80] 郑国航, 邢明飞, 郝智能, 等. 固相萃取法分离富集环境水体中溶解性有机质的研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(8): 2288-2298. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021022403 ZHENG G H, XING M F, HAO Z N, et al. Isolation and concentration of dissolved organic matter by using solid phase extraction method in environmental waters[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(8): 2288-2298(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021022403
[81] 王杰琼. 近岸海水中溶解性有机质对有机微污染物光降解行为的影响[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019. WANG J Q. Effects of dissolved organic matter extracted from coastal seawaters on photodegradation behavior of organic micropollutants[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[82] MCNEILL K, CANONICA S. Triplet state dissolved organic matter in aquatic photochemistry: Reaction mechanisms, substrate scope, and photophysical properties[J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2016, 18(11): 1381-1399. [83] HERBECK L S, UNGER D, WU Y, et al. Effluent, nutrient and organic matter export from shrimp and fish ponds causing eutrophication in coastal and back-reef waters of NE Hainan, tropical China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2013, 57: 92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.05.006 [84] WANG J Q, CHEN J W, QIAO X L, et al. DOM from mariculture ponds exhibits higher reactivity on photodegradation of sulfonamide antibiotics than from offshore seawaters[J]. Water Research, 2018, 144: 365-372. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.043 [85] 郭忠禹. 海水溶解性有机质对磺胺氯哒嗪光降解的影响[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2020. GUO Z Y. Photodegradation of sulfachloropyridazine in presence of seawater dissolved organic matter[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2020(in Chinese).
[86] HELMS J R, STUBBINS A, PERDUE E M, et al. Photochemical bleaching of oceanic dissolved organic matter and its effect on absorption spectral slope and fluorescence[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2013, 155: 81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2013.05.015 [87] del VECCHIO R, BLOUGH N V. Photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in natural waters: Kinetics and modeling[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2002, 78(4): 231-253. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(02)00036-1 [88] SINGH S, D'SA E J, SWENSON E M. Chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) variability in Barataria Basin using excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence and parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(16): 3211-3222. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.03.044 [89] YANG L, ZHANG J, YANG G P. Mixing behavior, biological and photolytic degradation of dissolved organic matter in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 762: 143164. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143164 [90] BAI Y, SU R G, YAO Q Z, et al. Characterization of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy (EEMs) and parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC)[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 2017, 40(5): 1325-1345. doi: 10.1007/s12237-017-0221-6 [91] 纪美辰, 李思佳, 常明, 等. 二龙湖表层水体有色溶解有机物的光学特性及来源[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(8): 1821-1829. JI M C, LI S J, CHANG M, et al. Photometric characteristics and sources of colored dissolved organic matter in surface water from erlong lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(8): 1821-1829(in Chinese).
[92] COBLE P G. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1996, 51(4): 325-346. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(95)00062-3 [93] NIU X Z, LIU C, GUTIERREZ L, et al. Photobleaching-induced changes in photosensitizing properties of dissolved organic matter[J]. Water Research, 2014, 66: 140-148. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.08.017 [94] BARSOTTI F, GHIGO G, VIONE D. Computational assessment of the fluorescence emission of phenol oligomers: A possible insight into the fluorescence properties of humic-like substances (HULIS)[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2016, 315: 87-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2015.09.012 [95] PENG N, WANG K F, LIU G G, et al. Quantifying interactions between propranolol and dissolved organic matter (DOM) from different sources using fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2014, 21(7): 5217-5226. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-2436-9 [96] BATISTA A P S, TEIXEIRA A C S C, COOPER W J, et al. Correlating the chemical and spectroscopic characteristics of natural organic matter with the photodegradation of sulfamerazine[J]. Water Research, 2016, 93: 20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.036 [97] CAVANI L, HALLADJA S, TER HALLE A, et al. Relationship between photosensitizing and emission properties of peat humic acid fractions obtained by tangential ultrafiltration[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(12): 4348-4354. [98] ZHOU H X, LIAN L S, YAN S W, et al. Insights into the photo-induced formation of reactive intermediates from effluent organic matter: The role of chemical constituents[J]. Water Research, 2017, 112: 120-128. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.048 [99] LIU Y Z, SUN H W, ZHANG L Q, et al. Photodegradation behaviors of 17β-estradiol in different water matrixes[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2017, 112: 335-341. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2017.08.044 [100] PENG N, WANG K F, LIAO P P, et al. Dual roles of fulvic acid on the photodegradation of propranolol under different light-source irradiation[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2018, 199: 052050. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/199/5/052050 [101] 刘砚弘, 李威, 韩建刚. Fe(Ⅲ)对不同来源溶解性有机质的光化学活性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(11): 2563-2572. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0411 LIU Y H, LI W, HAN J G. Effect of Fe(Ⅲ)on the photochemical activity of dissolved organic matter from different sources[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(11): 2563-2572(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0411
[102] ZHAO Q, FANG Q, LIU H Y, et al. Halide-specific enhancement of photodegradation for sulfadiazine in estuarine waters: Roles of halogen radicals and main water constituents[J]. Water Research, 2019, 160: 209-216. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.061 [103] PINTO M I, SALGADO R, COTTRELL B A, et al. Influence of dissolved organic matter on the photodegradation and volatilization kinetics of chlorpyrifos in coastal waters[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2015, 310: 189-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2015.05.024 [104] HOU Z C, FANG Q, LIU H Y, et al. Photolytic kinetics of pharmaceutically active compounds from upper to lower estuarine waters: Roles of triplet-excited dissolved organic matter and halogen radicals[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 276: 116692. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116692 [105] LI Y J, QIAO X L, ZHANG Y N, et al. Effects of halide ions on photodegradation of sulfonamide antibiotics: Formation of halogenated intermediates[J]. Water Research, 2016, 102: 405-412. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.054 [106] ZHANG X, WU F, WU X W, et al. Photodegradation of acetaminophen in TiO2 suspended solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 157(2/3): 300-307. [107] JIN X, XU H Z, QIU S S, et al. Direct photolysis of oxytetracycline: Influence of initial concentration, pH and temperature[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2017, 332: 224-231. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.08.032 [108] BAENA-NOGUERAS R M, GONZÁLEZ-MAZO E, LARA-MARTÍN P A. Degradation kinetics of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in surface waters: Photolysis vs biodegradation[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 590/591: 643-654. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.015 [109] 于莉莉, 钟晔, 孙福红, 等. pH值对滇池水体溶解性有机质(DOM)光降解作用的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(8): 2533-2539. YU L L, ZHONG Y, SUN F H, et al. Effects of pH values on the photo-degradation of dissolved organic matter (DOM) from Dianchi Lake[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(8): 2533-2539(in Chinese).
[110] PACE M L, RECHE I, COLE J J, et al. pH change induces shifts in the size and light absorption of dissolved organic matter[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2012, 108(1/2/3): 109-118. [111] ZHANG Y N, ZHAO J C, ZHOU Y J, et al. Combined effects of dissolved organic matter, pH, ionic strength and halides on photodegradation of oxytetracycline in simulated estuarine waters[J]. Environmental Science. Processes & Impacts, 2019, 21(1): 155-162. [112] CHU C J, SHAO M Y, WANG X. Dissolved biochar promoted photodegradation of tetracycline in aqueous environment[J]. E3S Web of Conferences, 2021, 251: 02055. [113] GAO Y, YAN M Q, KORSHIN G V. Effects of ionic strength on the chromophores of dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(10): 5905-5912. [114] PAN Y H, GARG S, WAITE T D, et al. Copper inhibition of triplet-induced reactions involving natural organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(5): 2742-2750. [115] PAN Y H, RUAN X X, GARG S, et al. Copper inhibition of triplet-sensitized phototransformation of phenolic and amine contaminants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(16): 9980-9989. [116] RORABACHER D B. Electron transfer by copper centers[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(2): 651-698. doi: 10.1021/cr020630e [117] CIEŚLA P, KOCOT P, MYTYCH P, et al. Homogeneous photocatalysis by transition metal complexes in the environment[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2004, 224(1/2): 17-33. [118] WANG L, ZHANG C B, WU F, et al. Determination of hydroxyl radicals from photolysis of Fe(III)-pyruvate complexes in homogeneous aqueous solution[J]. Reaction Kinetics and Catalysis Letters, 2006, 89(1): 183-192. doi: 10.1007/s11144-006-0101-8 [119] LIU H, ZHAO H M, QUAN X, et al. Formation of chlorinated intermediate from bisphenol A in surface saline water under simulated solar light irradiation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(20): 7712-7717. [120] 庄晓虹, 喻婷, 胡桂娟, 等. 铁离子、铜离子及腐殖酸对壬基酚光降解的影响[J]. 辽宁大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 44(1): 75-80. doi: 10.16197/j.cnki.lnunse.2017.01.015 ZHUANG X H, YU T, HU G J, et al. Effect of iron ions, copper ions and humic acid on nonylphenol's photodegradation[J]. Journal of Liaoning University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2017, 44(1): 75-80(in Chinese). doi: 10.16197/j.cnki.lnunse.2017.01.015
[121] WANG L, ZHANG C, MESTANKOVA H, et al. Photoinduced degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol in water: Influence of various Fe(Ⅲ) carboxylates[J]. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 2009, 8(7): 1059-1065. [122] 王丽苹. Fe0/H2O2类芬顿法对污泥脱水性能的改善及机理分析[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018. WANG L P. Improvement of waste activated sludge dewaterability by Fe~0/H2O2 Fenton-like process and its mechanism analysis[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese).
[123] 丁世敏, 涂建峰, 崔小平, 等. 类-Fenton体系对水中17β-雌二醇的光降解[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2005(7): 29-32. DING S M, TU J F, CUI X P, et al. Light induced degradation of 17β-estradiol in Fenton-like system[J]. Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control, 2005(7): 29-32(in Chinese).
[124] 石陶然, 张远, 于涛, 等. 滇池沉积物不同分子量溶解性有机质分布及其与Cu和Pb的相互作用[J]. 环境科学研究, 2013, 26(2): 137-144. SHI T R, ZHANG Y, YU T, et al. Distribution of different molecular weight fractions of dissolved organic matters and their complexation with Cu and Pb in the sediment from Dianchi Lake, China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 26(2): 137-144(in Chinese).
[125] WAN D, SHARMA V K, LIU L, et al. Mechanistic insight into the effect of metal ions on photogeneration of reactive species from dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(10): 5778-5786. [126] LIU H Y, ZHANG Z Y, TU Y N, et al. Dual roles of Cu2+ complexation with dissolved organic matter on the photodegradation of trace organic pollutants: Triplet- and OH-induced reactions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 815: 152934. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.152934 [127] OGAWA K, GUO F Q, SCHANZE K S. Phosphorescence quenching of a platinum acetylide polymer by transition metal ions[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2009, 207(1): 79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2009.04.013 -




 下载:
下载: