-
大气气溶胶是均匀分散在大气中直径约0.001—100 μm的固体或液体微粒,可以散射和吸收太阳辐射,对气候变化有重要影响. 气溶胶来源分天然源(如森林火灾、火山爆发、沙尘暴等)和人为源(工业排放、机动车尾气、生物质燃烧等)[1]. 气溶胶化学组成主要包括有机碳(OC)、元素碳(EC)、硝酸盐、硫酸盐、铵盐等[2-3]. EC表现出强烈的吸光性又被称为黑碳(BC). BC可吸收红外和可见光波段的太阳辐射,使周围大气增温,表现为变暖作用.
近年来,国内外关于BC分布的研究如火如荼. Bahadar等[4]讨论了巴基斯坦北部4个高海拔地区2016—2017年BC的日、月分布及其对气候的影响. Wyche等[5]对4个欧洲城市的BC进行研究,发现BC在PM2.5中占比大,特别是交通发达区域和出行高峰期,最高时eBC/PM2.5达45%. eBC与其他大气污染物(O3、NOx、PM2.5、PM10)间呈正相关,反映机动车尾气对BC浓度的重要影响. Liu等[6]研究东南亚BC分布,结果表明,马来西亚某地大气中BC主要受生物质和化石燃料燃烧的源贡献,两种燃烧源对BC贡献相当;东南亚地区春季干旱季节生物质燃烧的贡献甚至更高,可能来自森林、灌木和农业火灾. 周变红等[7]研究发现,宝鸡高新区eBC变化范围为0.01—5.62 μg·m−3,eBC日变化呈“双峰双谷”型,峰值出现在09:00和19:00,谷值出现在05:00和16:00;eBC占PM2.5的0.84%,其吸收作用占大气消光的2.14%. 孙天林等[8]研究发现东莞站点eBC年均为3.98 μg·m−3. eBC湿季相对较低,干季相对较高. 盛涛[9]研究结果表明,2016、2017、2018年上海市路边大气中eBC年均分别为2.91、2.96、2.82 μg·m−3,eBC/PM2.5分别为9.30%、9.20%、9.50%. 关亚楠等[10]研究发现,石家庄eBC平均浓度为4.35 μg·m−3;不同季节eBC浓度分布为:冬>秋>春>夏;以化石燃料为能源的工业源和交通源对BC的贡献占主导地位. 以上国内外相关研究为本研究提供对比参考依据.
近年来,南昌随着工业和城市的快速发展,能源消耗增加,化石燃料燃烧和机动车数量不断增加,在污染物达标排放情况下,大气污染控制的形势依然严峻. 我们课题组对南昌地区PM2.5及其化学组分的分布开展一些前期研究,然而南昌城区在逐年扩大,尤其是红谷滩城区得到快速发展,区域内BC的分布特征与光学特性的深入细化研究对于区域环境空气质量的评估和大气污染的防控意义重大.
本文对南昌市红谷滩区前湖区域大气中BC的分布特征与光学特性进行研究;探究气态污染物和PM2.5对eBC浓度的影响程度;对比研究黑碳仪测定PM2.5中eBC与滤膜采样PM2.5中EC浓度之间的差异,为区域碳气溶胶的污染防控及其辐射强迫的科学评估提供参考依据和数据支撑.
-
采样点位于南昌市红谷滩区学府大道南昌大学前湖校区环境楼的六楼楼顶(高度约为25 m,经纬度E115°47′33″,N28°39′47″),附近无典型工业污染源,500 m范围内无高于采样点的自然或人工物体,是1个混合受体点,受道路交通源、生活排放源、建筑扬尘和城市其他源的混合影响.
-
2020年12月至2021年12月,采用AE-42型黑碳仪监测PM2.5中eBC质量浓度(由黑碳仪测定的黑碳质量浓度简称为eBC[11]),包括七波段([350 nm]紫外、[470 nm]蓝色、[520 nm]绿色、[590 nm]黄色、[660 nm]红色、[880 nm]红外1(标准黑碳)、[950 nm]红外)的eBC质量浓度. 黑碳仪每5 min记录一次eBC浓度. 对所记录得到的数据进行小时平均计算;剔除数据中显著异常的eBC浓度值,确保每小时eBC浓度数据的正常量在所有数据量的60%以上[12].
-
基于黑碳仪所测eBC质量浓度,采用经验公式[1]计算BC的吸光系数,见式1:
式中,MBC是AE-42黑碳仪880 nm波长测量的eBC浓度(μg·m−3);A532 nm是BC在532 nm波长的吸光系数(Mm−1).
根据世界气象组织推荐,能见度与大气消光系数的转换采用式2[13]:
式中,bext是大气消光系数(Mm−1);VR是大气能见度(km).
本文观测数据为2020年12月至2021年12月由AE-42型黑碳仪所监测得到的eBC质量浓度. 根据式1,通过eBC质量浓度计算得到BC在532 nm波长处的吸光系数(A532nm);大气能见度(VR)来自OTT激光雨滴谱监测数据;根据式2计算得到大气消光系数(bext). 根据经验公式(式1、式2)计算BC吸光系数和大气消光系数具有一定的不确定性.
-
本研究中CO、NO2、SO2、O3质量浓度数据来源于南昌市生态环境局空气质量实时发布平台(http://115.149.145.50:9080/). 气象观测资料来自便携式气象站. 降雨量、降雨强度、大气能见度来自OTT激光雨滴谱监测数据.
-
本研究同时还进行了PM2.5的滤膜采样,每个季节定期利用大气mini采样器进行PM2.5样品的采集. PM2.5的质量浓度采用称重法,对PM2.5的采样滤膜采用DRI-2015碳分析仪进行热光碳分析得到EC浓度[14],获得PM2.5中EC的质量浓度.
-
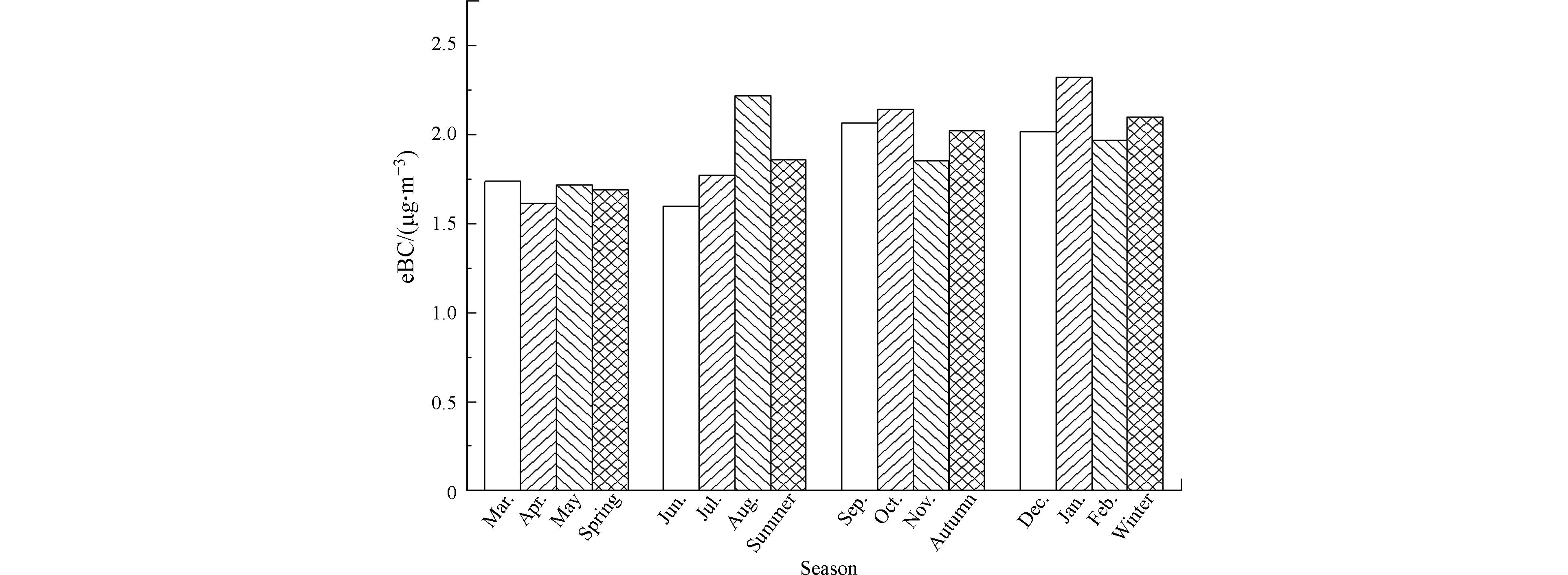
PM2.5中eBC质量浓度的季节分布见图1. 南昌前湖区域春、夏、秋、冬四个季节的eBC浓度分别为(1.69±1.14)、(1.86±1.37)、(2.02±1.05)、(2.10±1.28)μg·m−3.
冬、秋季高,夏、春季低. 不同季节eBC浓度分布差异的原因可能是BC的排放源类型与强度的差异,同时与温度、风速、湿度等气象条件也有密切关系. 夏季eBC浓度较低的原因是夏季长时间的日照、强烈的大气湍流利于BC的扩散,并且夏季具有较多的降水量,雨水冲刷清除BC的程度高[15],而冬季eBC浓度高的原因是冬季化石燃料燃烧量较多,源排放强度高,并且冬季日照时间短、大气稳定性较高不利于污染物的扩散,高浓度的eBC又会进一步增强大气边界层的稳定性,形成恶性循环,导致冬季浓度高[16].
-
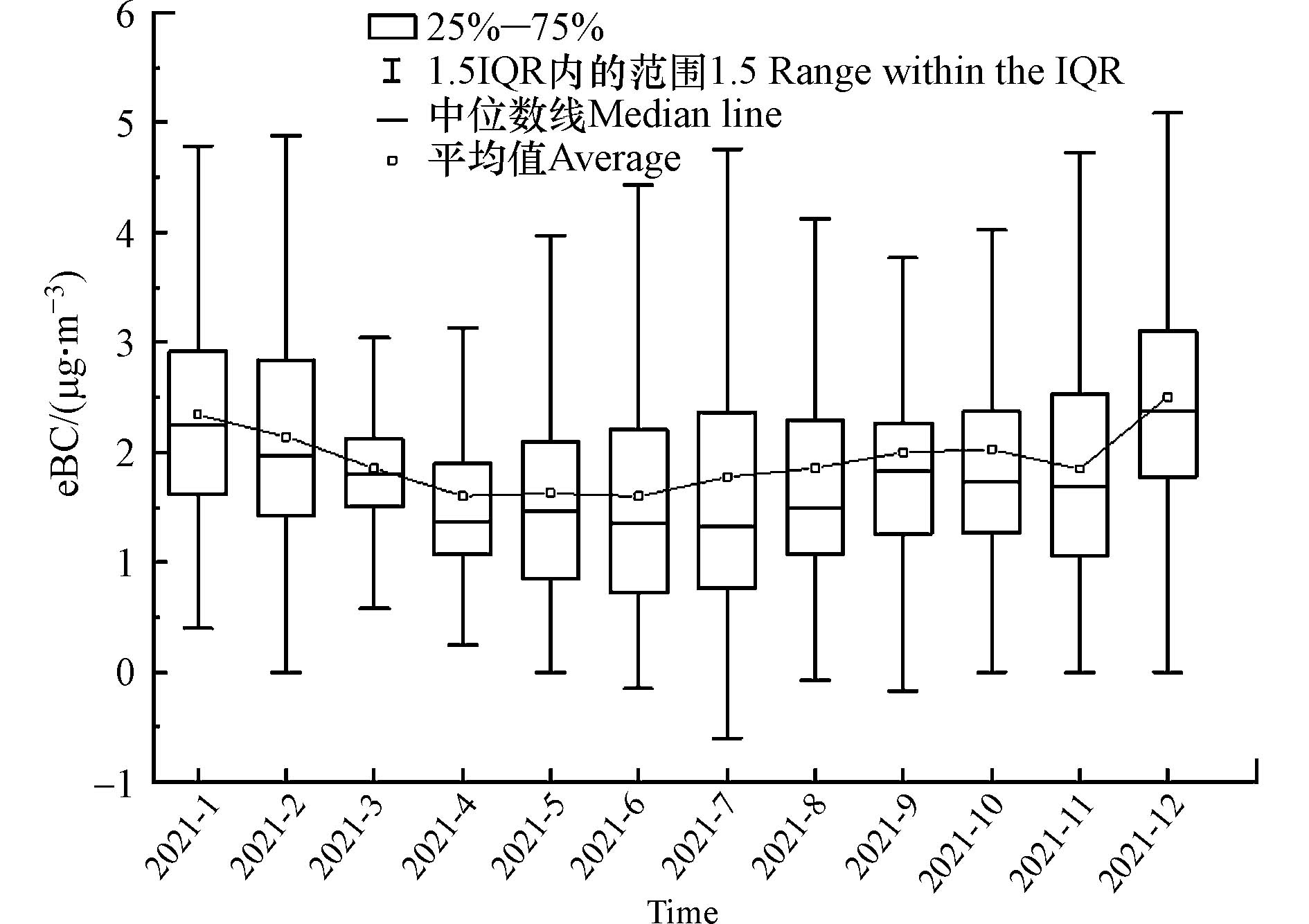
PM2.5中eBC质量浓度的月分布见图2. 南昌前湖区域2021年1月至2021年12月的eBC质量浓度均值为(1.93±1.13) μg·m−3, 1月最高(2.32±1.22)μg·m−3,6月最低(1.60±1.40)μg·m−3. 表1列出文献中中国地区和国外地区的eBC质量浓度,以对比南昌与国内外其它城市大气中eBC浓度水平的差异和分布特点.
根据表1,相比国内其它区域或城市,南昌前湖区域的eBC质量浓度低于上海[17]、南京、深圳[18]、石家庄[10]、北京[20]、平顶山[21]、沈阳[22]、贵阳[24]等城市站点的BC水平,与上海城郊站点[17]和大连[23]、新疆[25]等城市站点的eBC浓度接近,高于深圳城市站[18]、邢台城市站[19]、北京城郊站[20]的eBC浓度. 相比国外城市区域来说,南昌前湖区域的eBC质量浓度要低于印度[26]和但巴德[27]等城市站点的BC水平,高于德克萨斯洲[28]城市站的BC值. 因此,南昌前湖区域BC的分布需引起关注.
-
研究期间,南昌前湖区域eBC浓度的日分布见图3. 整体来说,各季节的eBC日变化趋势都存在明显的峰值和谷值,分布特征为双峰型,峰值分别出现在07:00—09:00和22:00—23:00,而最低谷则出现在下午13:00—16:00,次谷值出现在凌晨03:00—05:00左右. 这与我国安徽[17]、上海[17]、苏州[29]、广州[30]等地区eBC质量浓度日变化特征相似. 而对于不同季节来说,日变化规律是存在一定差异的. 南昌2021年春、夏、秋、冬四个季节中早晨的eBC浓度峰值分别为2.31、2.97、1.99、2.96 μg·m−3. 而夜晚的eBC浓度峰值分别为2.43、2.55、2.32、2.66 μg·m−3.
07:00—09:00峰值出现的原因为日出后人为活动增多,机动车辆增多,此时段为交通高峰时段,因此机动车尾气排放量增加导致eBC浓度明显上升. 同时早晨,由夜间产生稳定的边界层结构尚未破坏,不利于大气污染物的扩散,这也是BC出现早高峰的原因之一[16]. 而后因为随着上班早高峰的过去,浓度值逐渐下降,并且eBC浓度的降低还与近地面大气湍流及对流存在关系[31]. 上午10:00后随着太阳辐射的增强,近地面大气湍流及对流活动的增强,使得污染物不断地进行扩散,从而导致eBC浓度也在不断地下降,在下午13:00—16:00达到最低值. 傍晚前后随着太阳辐射的减小,大气湍流对流活动减弱,天黑后地面迅速降温,近地面大气湍流及对流活动停止,大气层结趋于稳定,扩散能力变差,使得污染物堆积并且在17:00后,此段时刻为下班晚高峰,人类活动增多,因此eBC浓度会不断上升,并在22:00—23:00达到峰值. 晚高峰后eBC浓度又会逐渐地降低,这可能与人类活动减少和机动车活动减少导致机动车尾气排放减少有关[32].
-
目前对于气溶胶中碳组分的测量可用直接测量法和间接测量法,直接测量法中最常用的则是基于OC、EC组分热稳定性差异的热光法,间接测量法主要利用碳气溶胶组分的吸光性差异,通过直接测量或间接反映光吸收信号,并结合转化系数(经验值)将吸收信号转化为吸光碳的浓度值,典型的测量仪器是黑碳仪[33]. 而DRI-2015碳分析仪是基于对OC和EC在不同的温度和环境下进行氧化分析. 分析时,选取约0.495 cm2面积的滤膜,根据程序温度进行升温到900 °C. OC组分在无氧环境下,升温到580 °C时逸散出来;EC在2%的含氧环境中逐步升温到840 °C时逸散出来. 逸散出的碳被加热氧化为CO2(催化剂为MnO2),可通过NDIR检测器进行定量检测. 仪器利用其多波长光学系统可以给出从405 nm到980 nm七个波段的焦化碳订正值,包括激光反射信号焦化碳订正值(OPR)和激光透射信号焦化碳订正值(OPT). 本研究使用的是IMPROVE分析方法,所以最终对EC进行焦化碳订正时使用的是OPR值. 图4(a)为研究区域内黑碳仪测定的eBC与滤膜采样热光碳分析仪测定的EC的分布对比图,分析两种不同方法测定BC的差异. 从图4(a)可知,碳分析仪热光法和黑碳仪光学法测出的eBC浓度是存在差异的,但变化趋势大致相同,夏、秋季eBC浓度稍高于EC浓度,而冬、春季EC浓度稍高于eBC浓度,存在差异的原因可能是因为仪器本身的测量原理不同,还可能是因为不同季节BC气溶胶的来源和混合状态的差异导致仪器识别测定结果的差异[34]. 图4(b)为滤膜样品DRI碳分析仪测定的EC浓度与黑碳仪测定的eBC浓度的相关性散点图,由图可知两种方法对黑碳的测定结果具有一定的相关性(R2=0.4868).
-
图5为研究区域内eBC与PM2.5的散点分布与相关性图. eBC与PM2.5的相关系数为0.7216,经检验,两者相关性显著(P<0.05*),说明PM2.5中eBC与PM2.5的来源总体相同. 本研究△BC/△PM2.5(回归斜率[35])比值为0.05,低于杭州的0.076[32],高于南京北郊的0.022[36],在不同地区研究获得△BC/△PM2.5的差异可能与不同地区的污染源和气象条件不同有关.
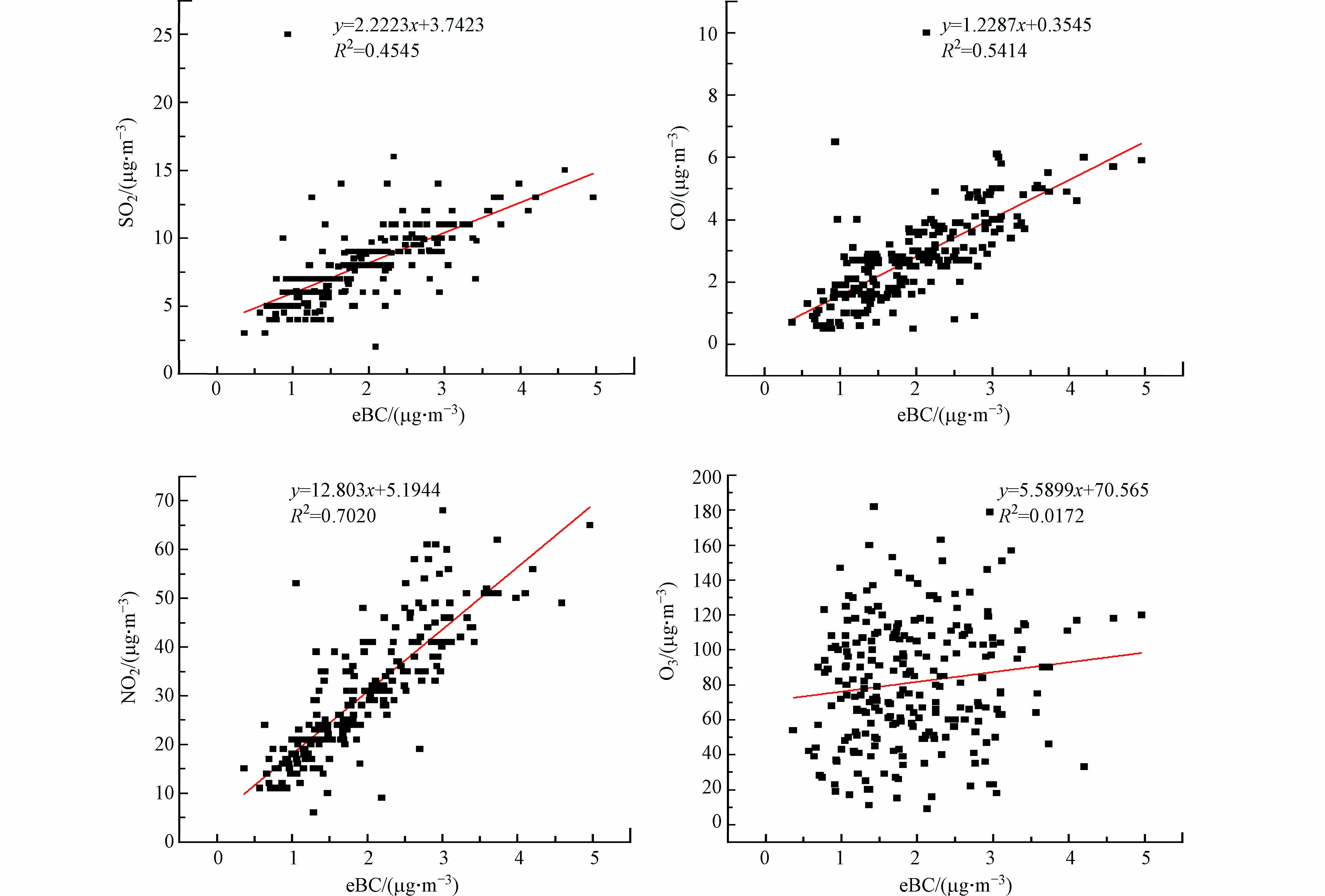
大气中的BC主要来源于化石和生物燃料的不完全燃烧[37]. 燃烧过程中产生BC的同时,也会释放出其他气体污染物,如CO、NO2和SO2等,因此eBC与CO、NO2、SO2等污染物的相关性具有一定的源示踪性. 另外eBC与CO、NO2、SO2等的相关性也会受到大气传输的影响. 研究指出,CO和BC主要源于含碳物质的不完全燃烧,SO2主要源于煤的燃烧,而NO2主要源于交通源的排放[10]. 图6为eBC与气态污染物(CO、NO2、SO2和O3)的散点分布与相关性,显示eBC与NO2有较强的相关性(R2=0.7020),表明两者来源相似. 这与本研究监测点直线距离100米远处有一条机动车通行繁忙的高速公路,受汽车尾气排放的影响,采样点NO2浓度较高的情况相符. eBC与SO2、CO的相关系数平方分别为0.4545和0.5414,具有良好的相关性,表明SO2、CO与eBC有部分贡献来源相同. O3与eBC的相关系数平方为0.0172, O3与eBC无相关性,说明两者来源差异大. 综上,eBC与NO2的相关性强于eBC与SO2、CO、O3的相关性,反映南昌前湖区域的BC受机动车尾气影响显著. 孔祥晨等[38]等研究发现,鄂尔多斯市夏秋季节eBC与PM2. 5、NO2的相关性最高,为0.6. eBC与NO2相关性高,说明BC主要受到交通源的影响;而eBC与SO2的相关系数仅为0.3,这说明工业源对鄂尔多斯市BC的影响较小. 张玲等[39]研究华北平原南部农村的黑碳气溶胶发现,eBC和 PM2. 5呈显著正相关,且相关性最高,其次为CO、NO2、SO2. 大气中的CO主要来源于燃烧过程. 该点位冬季eBC /CO为(0.0070 ± 0.0094),远高于夏季( 0.0012 ± 0.0007),表明冬季由生物质燃烧排放eBC的比例高于夏季. 与其他研究对比发现,eBC与气态污染物(PM2. 5、NO2、SO2、CO)的相关性分析结果具有地域性特点,相关性大小与当地污染源有关,但eBC与PM2.5的相关性均是最高的.
-
eBC在大气中极少因化学反应生成或消除,而是通过大气干、湿沉降清除[40],因此可根据气象因子(温度、相对湿度、风速)与eBC浓度的相关性,讨论分析温度、相对湿度、大气能见度对eBC浓度的影响[41]. 表2为采样期间南昌前湖区域的气象因子(温度、相对湿度、风速)数据.
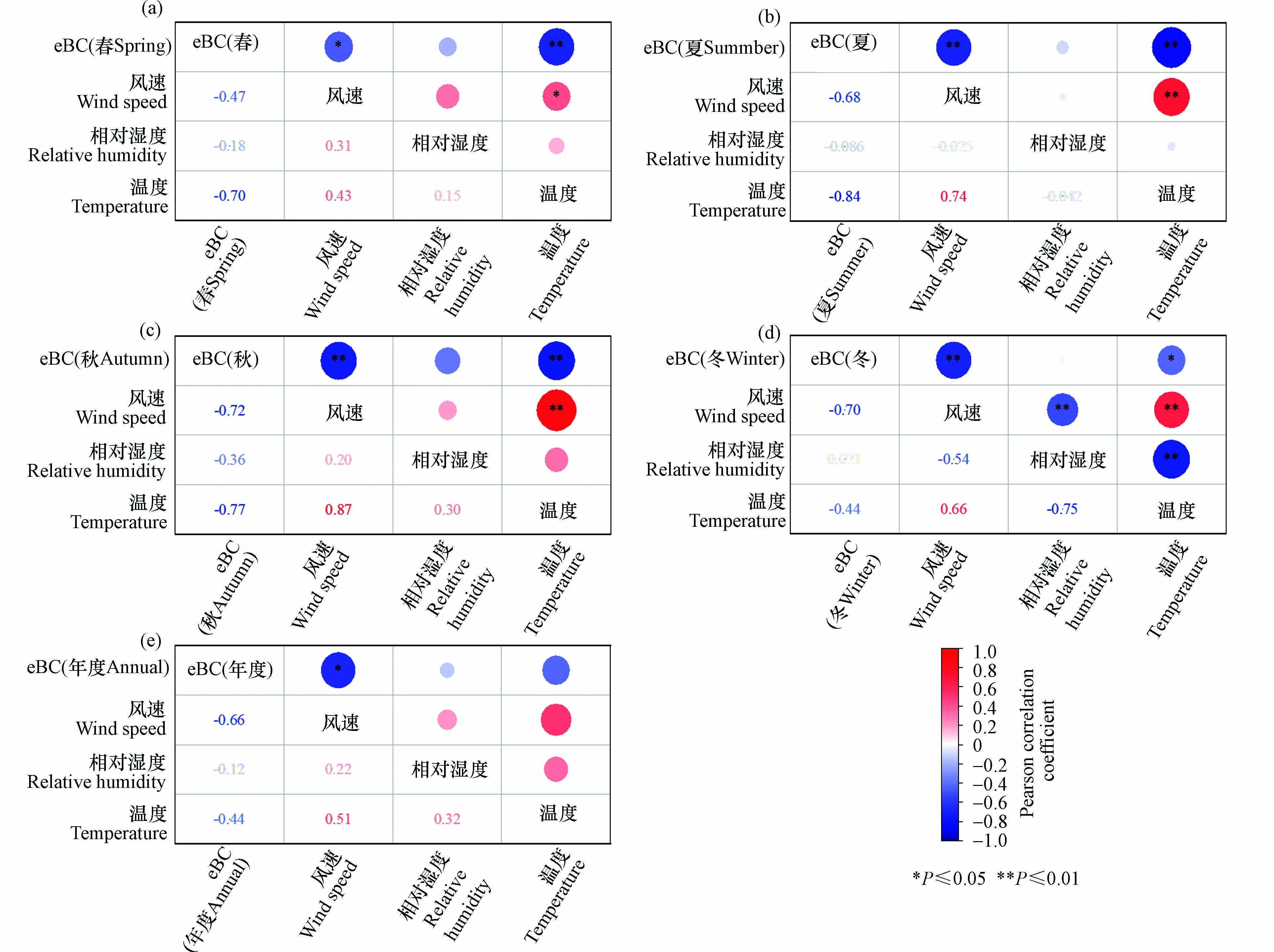
由图7可知,从全年分析,eBC与风速、温度和相对湿度等气象因子呈负相关,相关性按从大到小顺序为风速>温度>相对湿度. eBC与风速之间的负相关性显著,较大的风速更利于BC的扩散稀释[42],秋季的相关性最强,相关系数为−0.72;春季的相关性最弱,相关系数为−0.47. 温度会影响BC气溶胶表面的化学性质,从而影响黑碳气溶胶的存在形式和浓度值[43]. eBC浓度与温度呈负相关,最强负相关出现在夏季,相关系数为−0.84. eBC浓度也与相对湿度呈负相关,相对湿度大有利于BC的清除[44],但与温度和风速相比,其相关性最弱.
-
表3汇总了2021年度均值与四季均值的大气能见度、eBC质量浓度、BC吸收系数、大气消光系数及吸收系数占大气消光系数的贡献率,其中,大气能见度年均值为21.77 km,在春季略高于其他季节;eBC质量浓度在冬季达到最大值(2.10±1.28)μg·m−3. 吸收系数年均值为18.42 Mm−1、大气消光系数年均值为137.67 Mm−1,均冬季出现最大值,这可能是由于冬季大气稳定性较高不利于污染物的扩散,造成局部累积,污染加重. 此时吸收系数对大气消光系数的贡献率也达到最高. 与其他城市相比较,本研究吸收系数(18.42 Mm−1)高于河北廊坊市(16.05 Mm−1)[45]、香港(8.3 Mm−1)[46],低于南京(29.6 Mm−1)[47]、杭州(44.8 Mm−1)[32].
-
(1)南昌前湖区域eBC浓度年度均值为(1.93±1.13)μg·m−3,eBC浓度有明显的季节变化,冬季最高(2.10±1.28)μg·m−3,春季最低(1.69±1.14)μg·m−3. 各季节的eBC日变化趋势表现为明显的双峰特征,峰值分别出现在07:00—09:00和22:00—23:00.
(2)碳分析仪热光法和黑碳仪光学法测出的黑碳浓度是存在差异的,仪器测量原理不同,此外不同季节BC的来源和混合状态的差异也会导致仪器测定结果的差异.
(3)BC的吸收系数、大气消光系数年均值为18.42、137.67 Mm−1,且均在冬季出现最大值,这可能是由于冬季大气稳定性较高不利于污染物的扩散,造成局部累积,污染加重. 此时吸收系数对大气消光系数的贡献率也达到最高.
(4)eBC与PM2.5的相关系数为0.7216,说明eBC与PM2.5的来源总体相同;eBC与NO2的相关性强于eBC与SO2、CO、O3的相关性,反映南昌前湖区域的eBC浓度受机动车尾气影响显著. eBC与风速、温度和相对湿度等气象因子呈负相关,相关性按从大到小顺序为风速>温度>相对湿度,较大的风速更利于BC的扩散稀释.
南昌前湖区域黑碳的分布特征与光学特性
Distribution and optical properties of black carbon in Qianhu Area of Nanchang
-
摘要: 2020年12月—2021年12月,对南昌市前湖区域大气中黑碳(BC)进行连续观测,研究BC的分布特征与光学特性. 结果显示,南昌前湖区域eBC浓度2021年均值为(1.93±1.13)μg·m−3,有明显的季节变化,冬季最高(2.10±1.28)μg·m−3,春季最低(1.69±1.14)μg·m−3;eBC浓度日分布表现为明显的双峰特征,峰值出现在07:00—09:00和22:00—23:00. BC吸收系数、大气消光系数年均值为18.42、137.67 Mm−1. eBC与NO2的相关性强于eBC与SO2、CO、O3的相关性,反映区域内BC受机动车尾气影响显著. eBC与风速呈负显著性相关(*P<0.05),eBC与气象因子相关性按从大到小顺序为风速>温度>相对湿度,较大的风速更利于BC的扩散稀释. 本文研究结果可为区域碳气溶胶的污染防控及其辐射强迫的科学评估提供参考依据和数据支撑.Abstract: This paper carried out continuous observations of atmospheric black carbon (BC) in the Qianhu region of Nanchang to study the distribution characteristics and optical properties of BC from December 2020 to December 2021. The results of this paper showed that the average concentrations of eBC in the Qianhu region of Nanchang in 2021 was (1.93±1.13) μg·m−3. There was a seasonal variation in eBC. The highest in winter was (2.10±1.28) μg·m−3 and the lowest in spring is (1.69±1.14) μg·m−3. The daily distribution of eBC concentration showed obvious bimodal characteristics, with peaks at 07:00—09:00 and 22:00—23:00. The annual average values of absorption coefficient and atmospheric extinction coefficient for BC were 18.42 and 137.67 Mm−1. The correlation between eBC and NO2 was stronger than the correlation between eBC and SO2, CO, O3, which reflects the significant influence of motor vehicle emissions on BC. eBC was negatively correlated with wind speed (*P<0.05). The correlation between eBC and meteorological factors was wind speed > temperature > relative humidity. Higher wind speeds are more conducive to BC diffusion dilution. The results of the paper can provide reference basis and data support for the scientific assessment of carbonaerosol pollution prevention and control in this region.
-
近年来,我国城市近地面大气臭氧(ozone,O3)污染形势严峻,尤其是在夏季,臭氧已成为导致部分城市空气质量超标的首要污染因子。挥发性有机物(volatile organic compounds,VOCs)和氮氧化物(nitrogen oxides,NOx)的光化学反应是对流层臭氧的主要来源[1-2]。NOx主要来自于发电厂、燃煤锅炉、机动车等排放过程,经过严格治理,近年来全国的NOx 污染状况明显转好,据2015—2019年《中国生态环境状况公报》报道,全国337个城市NO2超标天数比例从2015的1.6%降至2019年的0.6%,但是臭氧污染问题仍然突出,2019年全国337个城市O3-8 h年均浓度为148 μg·m−3,较2015年上升10.45%[3]。VOCs作为臭氧和二次有机气溶胶(secondary organic aerosol,SOA)生成的重要前体物被广泛关注。VOCs来源十分广泛,主要分为天然源和人为源两大类。天然源主要有植物排放,人为源主要有燃料燃烧、溶剂使用、机动车尾气排放、汽油等液体燃料挥发、工业排放等[4]。VOCs成分复杂,包含数百种组分,每种组分具有不同的光化学反应活性,因此,研究挥发性有机物污染特征及其光化学反应特性对臭氧和雾霾污染治理具有十分重要的指导意义。
目前,挥发性有机物的研究主要集中在珠三角、长三角、京津冀等经济高速发展的地区,而西部地区的相关研究相对较少。宁夏回族自治区因其具有丰富的煤炭等资源,成为西部大开发中的重要发展对象,西部大开发以来,宁夏的工业化进程不断加快,能源、新型煤化工、新材料等产业发展迅速,与此同时,光化学污染问题在宁夏日益突出,2015—2019年《宁夏生态环境公报》显示,2019年全区五地市PM10、PM2.5年均浓度较2015年分别下降了24.53%、31.91%,而2019年O3-8 h年均浓度较2015年上升了5.19%(142 μg·m−3),可见,O3正成为宁夏的主要大气污染物之一[5]。为建立协同联动的发展机制,宁夏回族自治区预计2022年前打造完成以银川为核心、辐射带动石嘴山、吴忠、宁东基地协同发展的银川都市圈,银川都市圈的臭氧污染成为大气污染治理的重要对象。
本研究在银川都市圈内6个典型站点开展了挥发性有机物的观测,分析了采样期间挥发性有机物的污染特征、臭氧生成潜势、二次有机气溶胶生成潜势及VOCs潜在来源等,以期为银川都市圈臭氧和雾霾污染治理提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 样品采集
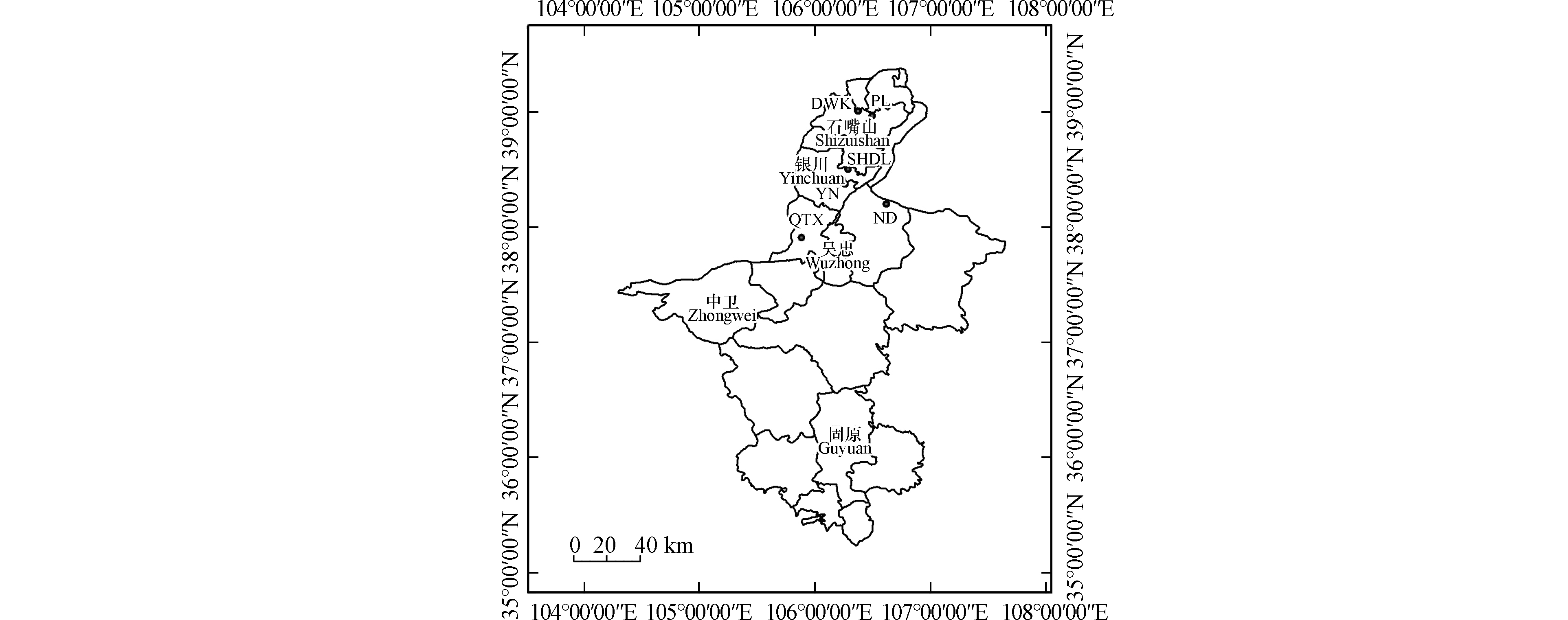
本研究于2019年6月12日—17日、8月4日—9日在银川都市圈内对环境空气中挥发性有机物进行了观测。采样点分别位于银川都市圈内的灵武市、永宁县、银川市、大武口区、平罗县和青铜峡市(图1),涉及工业区、商业/交通/居民混合区和工业/交通混合区(表1)。宁东和永宁采样点位于工业区,大气污染源复杂。宁东采样点位于宁东煤化工基地的某烯烃公司内,周围分布有煤制油、煤制烯烃、煤制乙二醇及精细化加工等化工企业。永宁采样点位于望远镇工业园的某药业公司内,周围集聚有家具厂、彩钢厂等工厂。上海东路和大武口采样点位于商业/交通/居民混合区,两个采样点周边都集中有居民区和商场,人口密度及交通流量较大。平罗和青铜峡采样点位于工业/交通混合区,二者周围均分布有高速公路及少数工厂,平罗采样点位于某精细化工有限公司内,青铜峡采样点位于新材料基地内。样品采集按照美国国家环境保护局(USEPA)推荐的标准方法(TO-14A[6]和 TO-15[7]),利用苏玛罐采集环境空气样品。采样前用自动清罐仪(Entech 3100;Entech Instrument Inc,California, USA)对苏玛罐进行清洗,采样频率为全天24 h,采样高度距地面1.5 m左右。表2给出了观测期间2019年6、8月份各采样点温度、湿度和主导风向的统计结果,6、8月份的平均温度分别为26.6℃、28.8℃,平均湿度分别为37.9%、40.7%,各采样点6月份主导风向以东南风、西北风和西北转北风为主,8月份以西北风为主。除少数几天有阵雨外,观测期间各采样点多为晴朗或多云天气。
表 1 采样点信息汇总Table 1. Summary of sampling information功能区Functional area 采样点Sampling points 经纬度Latitude and longitude 样本量Sample size 工业区Industrial areas 宁东 106.62 °E,38.20 °N 12 永宁 106.26 °E,38.37 °N 12 商业/交通/居民混合区Commercial, traffic, and residential mixed areas 上海东路 106.29 °E,38.50 °N 12 大武口 106.38 °E,39.01 °N 12 工业/交通混合区Industrial and traffic mixed areas 平罗 106.50 °E,38.96 °N 12 青铜峡 105.89 °E,37.91 °N 12 表 2 观测期间各采样点气象条件Table 2. Meteorological conditions at each sampling point during the observation period采样点Sampling points 项目Project 2019年6月 2019年8月 最小值Minimum value 最大值Maximum value 平均值Average value 最小值Minimum value 最大值Maximum value 平均值Average value 宁东Ningdong 温度/℃ 19 31 26.5 19 32 27.17 相对湿度/% 24 70 40 33 67 44.5 主导风向 东南风 西北风 永宁Yongning 温度/℃ 19 33 27.67 — — — 相对湿度/% 26 81 44.33 — — — 主导风向 东南风 西北风 上海东路Shanghai East Road 温度/℃ 26 32 28.67 25 34 29.5 相对湿度/% 16 42 30.83 18 59 34 主导风向 东南风 西北风 大武口Dawukou 温度/℃ 20 25 22.33 — — — 相对湿度/% 17 33 25.5 — — — 主导风向 西北风 西北风 平罗Pingluo 温度/℃ 18 31 26.83 23 31 28.83 相对湿度/% 28 80 44.33 31 69 46.83 主导风向 西北转北风 西北风 青铜峡Qingtongxia 温度/℃ 22 32 27 21 33 29.5 相对湿度/% 32 62 42.67 21 64 37.5 主导风向 西北转北风 西北风 注:“—”代表数据缺失.means data is missing. 1.2 分析方法
本研究使用搭载微板流控技术(Dean-Switch)的GC-MS/FID分析样品[8]。环境空气样品通过预浓缩仪(Entech7200;Entech Instrument Inc, California, USA)进行富集浓缩。样品依次进入三级冷阱的M1、M2、M3模块,目标化合物在此过程中被富集浓缩,同时,水和二氧化碳也被去除[9]。浓缩后的样品被载气带入气相色谱系统(Trace 1300; Thermo fisher, USA)进行分离和检测。气相色谱内选用 TG-1MS 和 TG-BOND Alumina(Na2SO4)色谱柱分别对高碳(C6—C12)VOCs和低碳的(C2—C6)VOCs进行一级和二级分离,随后低碳组分(乙烷、乙烯、丙烷、丙烯和乙炔)载入FID检测并用外标法定量,高碳组分(碳数较高的烷烃、烯烃和芳香烃)载入MS检测并用内标法定量。本研究选取在光化学反应中活性较高的56种挥发性有机物(PAMS组分)为目标化合物。
1.3 质量控制与质量保证
本研究使用PAMS标准气体购自美国Linde Electronics and Specialty Gases公司。本方法按照5个浓度水平的混合标准气体(不含0点)建立标准曲线,标准曲线线性回归的决定系数R2均大于99.99%,所有目标化合物具有良好的重现性(相对标准偏差均小于10%)。利用信噪比 S/N=10为方法检出限,目标化合物的检出限范围为7
× × 2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
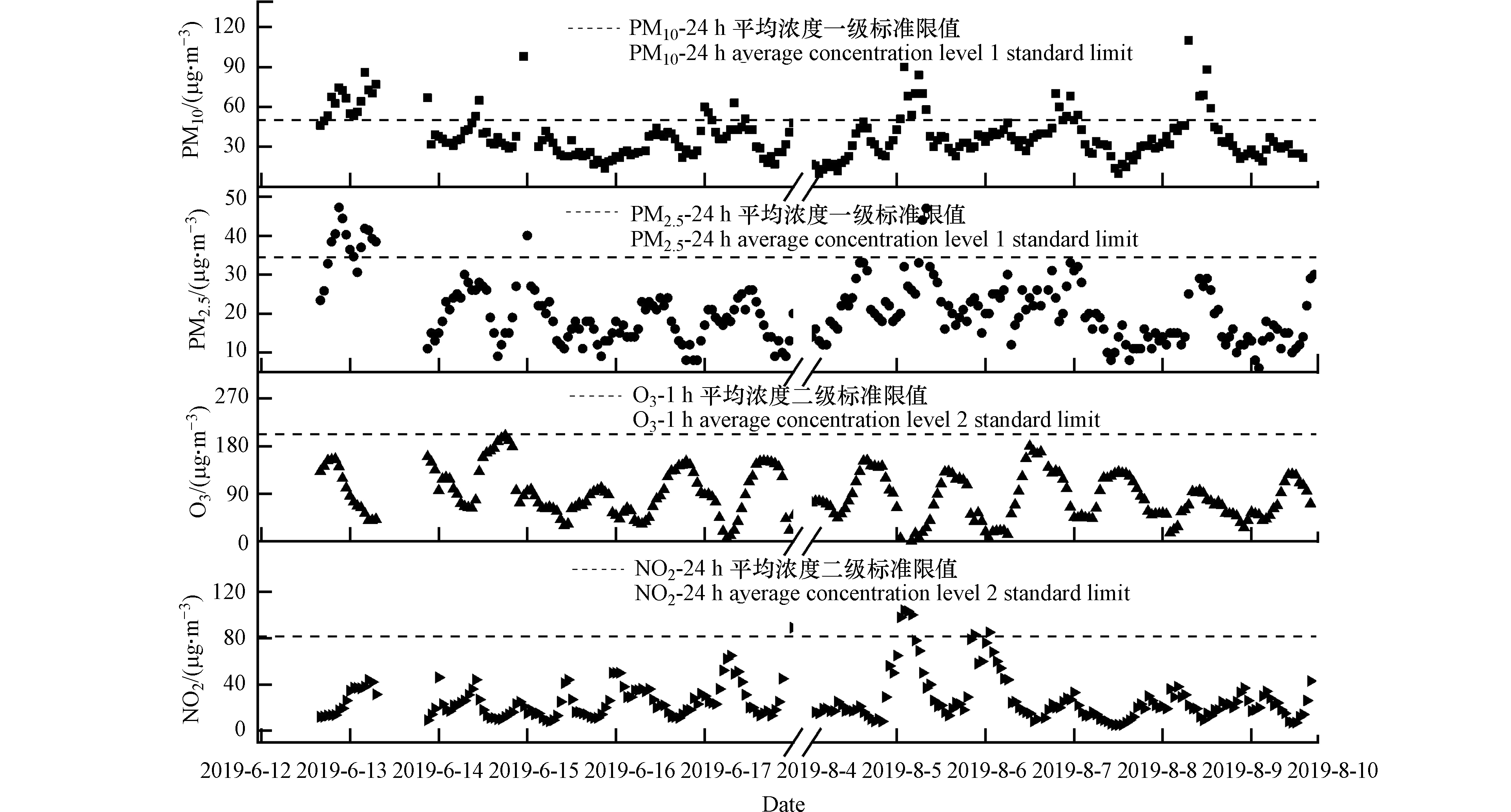
2.1 观测期间PM10、PM2.5 、O3、NO2浓度水平
观测期间银川上海东路环境空气中PM10、PM2.5、O3、NO2浓度水平见图2。O3和NO2的浓度分别为(5.0—200.0)μg·m−3和(5.0—123.0)μg·m−3,O3的浓度呈现出昼高夜低的日变化特征,其峰值出现在15:00—18:00;而NO2在日间浓度较低,呈现出与O3相反的日变化趋势,这可能是随着日出后光照强度的增加,前夜积累在对流层的NO2发生光解,O3浓度开始升高,并在后续的光化学过程发展中达到峰值,随着光照强度减弱,由NO2光解生成O3的速率逐渐降低,O3与NO的反应导致O3浓度逐渐下降,NO2浓度在前半夜的升高。此外,夜间NO2浓度还可能与较低的混合层高度有关,NO2在低层大气中积累,随着日出后边界层的抬升,NO2等人为排放污染物的浓度得到稀释。观测期间,PM10和PM2.5的浓度分别为(10.0—110.0)μg·m−3和(6.0—47.2)μg·m−3,根据环保部《环境空气质量标准》(GB3095—2012),PM10和PM2.5的浓度均未超过污染物浓度限值二级标准。在8月8日的12:00左右PM10和PM2.5出现浓度峰值时,O3浓度峰值较其他天数略有降低,这可能是因为颗粒物浓度较高时,大气中光化学反应速率降低,不利于O3生成。
2.2 浓度水平与组成特征
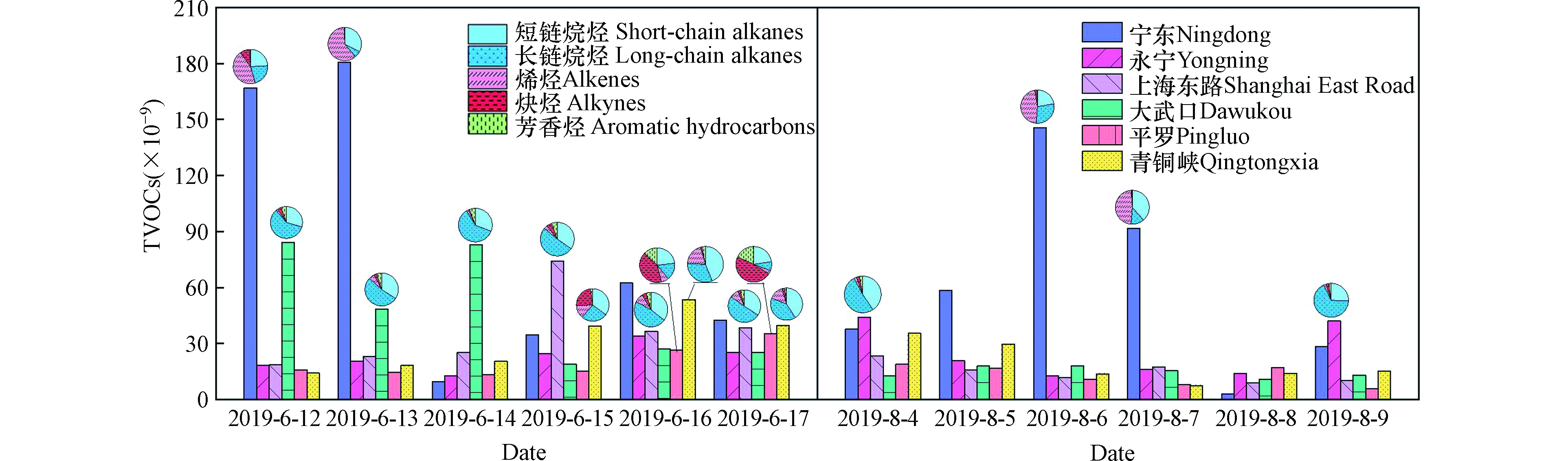
本研究根据VOCs各组分的分子结构及其与OH自由基(·OH)的反应活性,将测得的56种VOCs组分分成5个亚组,分别为短链烷烃(C ≤ 4)、长链烷烃(C > 4)、烯烃、炔烃和芳香烃。其中,短链烷烃、炔烃是低反应性烃,长链烷烃、烯烃和芳香烃(苯除外)是活性烃[10]。图3为观测期间各采样点环境空气中56种挥发性有机物总浓度水平(total volatile organic compounds,TVOCs),以及各采样点TVOCs浓度超过整个观测期间平均浓度水平时挥发性有机物的分类组成情况。各采样点TVOCs平均浓度分别为:宁东采样点(89.14
× × × × × × × × × × 而同为工业区的永宁采样点,其VOCs总浓度水平不高,表明不同类型工厂排放VOCs的强度存在一定差异。位于商业/交通/居民混合区的上海东路和大武口采样点的VOCs整体浓度水平相当,两个采样点TVOCs浓度在个别天内存在高值(例如6月12日—14日的大武口采样点和6月15日的上海东路采样点),其中,长链烷烃和短链烷烃的贡献最为明显,这可能是与某些非固定源异常排放有关,如机动车尾气排放等。位于工业/交通混合区的平罗和青铜峡采样点的TVOCs浓度之间存在一定差异,平罗采样点TVOCs浓度处于较低水平,而青铜峡采样点TVOCs浓度相对较高,且浓度较高时不同亚组VOCs的浓度占比差异明显,如6月15日炔烃的占比明显增大,这表明青铜峡采样点周围可能存在多个不同的VOCs排放源。
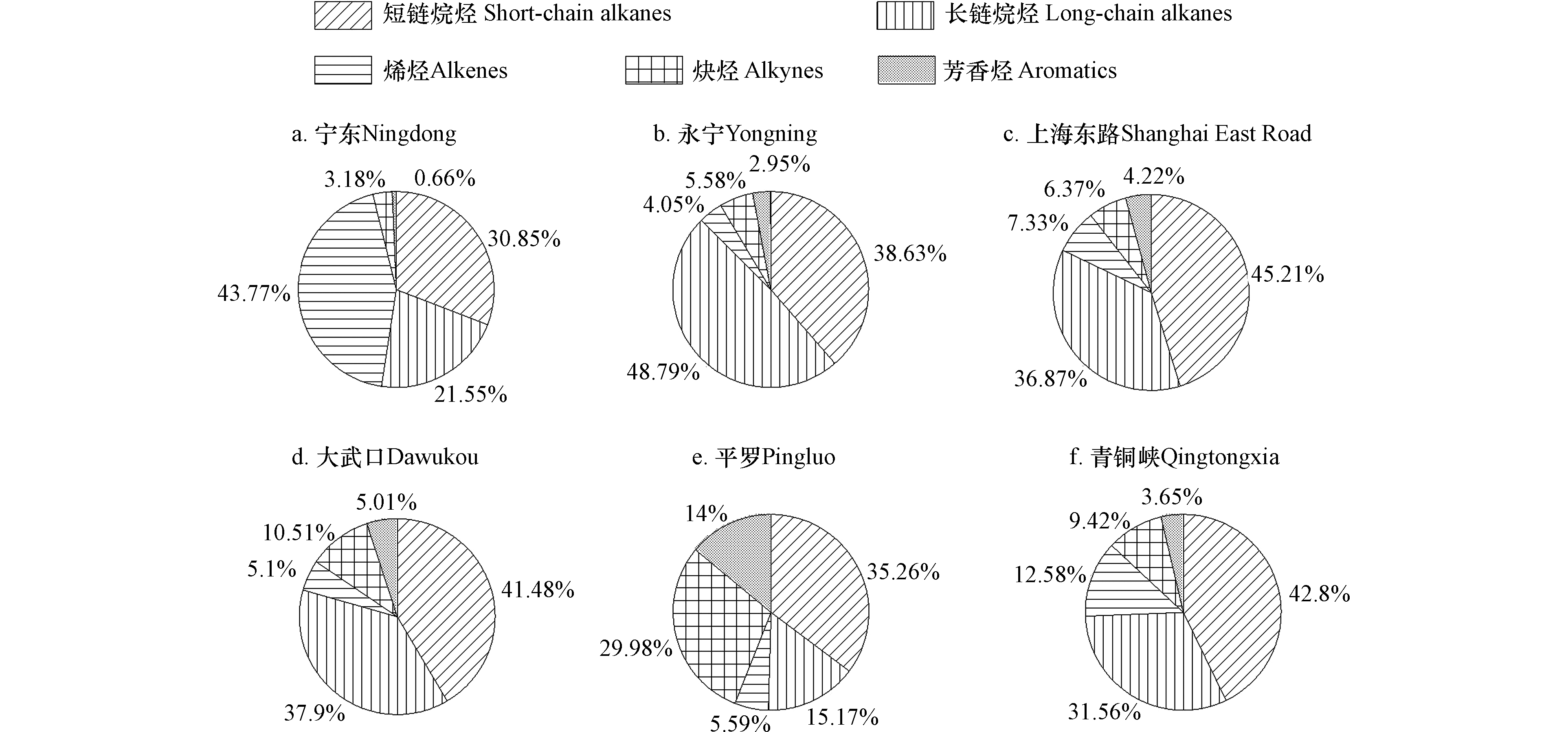
观测期间各采样点挥发性有机物分类组成如图4所示。短链烷烃、长链烷烃在6个采样点环境空气中均有较高占比,分别占TVOCs浓度的30.85%—45.21%、15.17%—48.79%;烯烃在宁东采样点的浓度占比最高,为43.77%;炔烃、芳香烃在平罗采样点的浓度占比最高,分别为29.98%和14.00%;其他采样点的炔烃和芳香烃的浓度占比均不高。
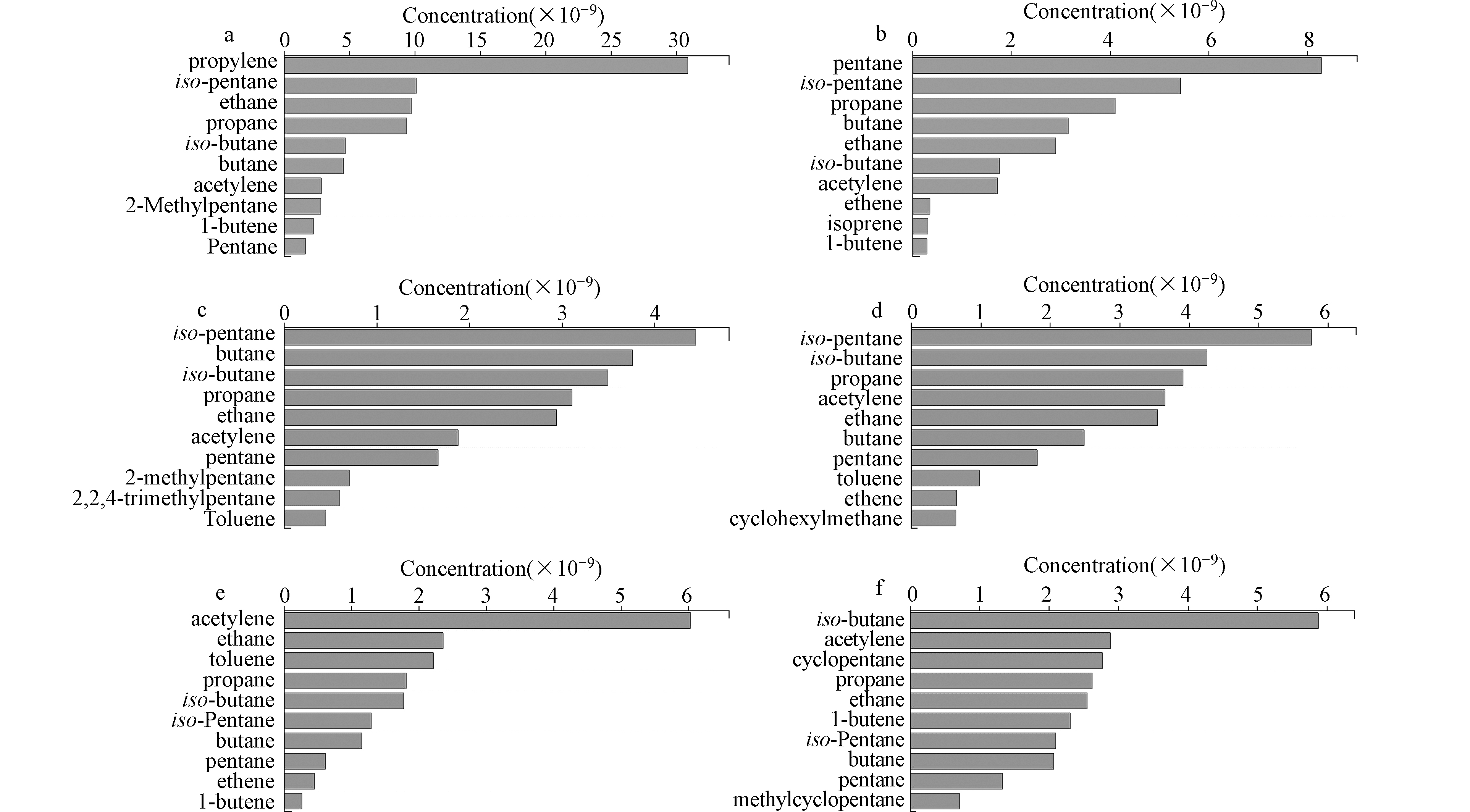
不同种类VOCs组成反映了各采样点VOCs来源具有差异,本研究通过各采样点浓度最大的前十位VOCs组分的对比(图5),进一步分析了各采样点VOCs可能来源及来源间差异。在6个采样点中,烷烃(包括短链烷烃和长链烷烃)总占比最大(50.43%—87.42%),其中,乙烷、丙烷、丁烷、异丁烷以及异戊烷在6个采样点均处于高浓度水平,乙烷、丙烷、丁烷和异丁烷是液化石油气(liquefied petroleum gas,LPG)助动车、汽油车和柴油车的主要排放物[11-12],异戊烷是汽油挥发的标志物[13],这反映出各采样点环境空气中的VOCs可能均受到来自机动车尾气排放的影响。宁东采样点烯烃占TVOCs的比例最大(43.77%),其中,丙烯浓度最为突出,平均浓度可以达到30.87
× 2.3 特征比值
不同采样点的污染源不同,并且不同污染源排放的VOCs特征组分间有一定差异,因此VOCs特征组分间的比值可初步判断VOCs的潜在来源。有研究发现,苯/甲苯(benzene/toluene, B/T)的比值在0.5左右时,机动车尾气排放为环境空气中VOCs主要来源[15];当B/T比值大于1时,煤或者生物质燃烧为主要贡献源[16];当B/T比值小于0.3时,工业排放的贡献较大[17]。本研究各采样点环境空气中苯/甲苯比值的箱线图如图6所示,可见永宁、上海东路和大武口采样点B/T比值的平均值都在0.5左右,表明这3个采样点环境空气中VOCs受机动车尾气排放的影响较大;平罗和青铜峡采样点的平均B/T比值分别为0.124、0.248,则这两个采样点VOCs主要受周围工业源排放的影响;宁东采样点平均B/T比值在1.5左右,表明宁东采样点环境空气中VOCs受到多种源的影响,其中煤或生物质燃烧的贡献较大,这可能与宁东采样点所处的煤化工基地有关。
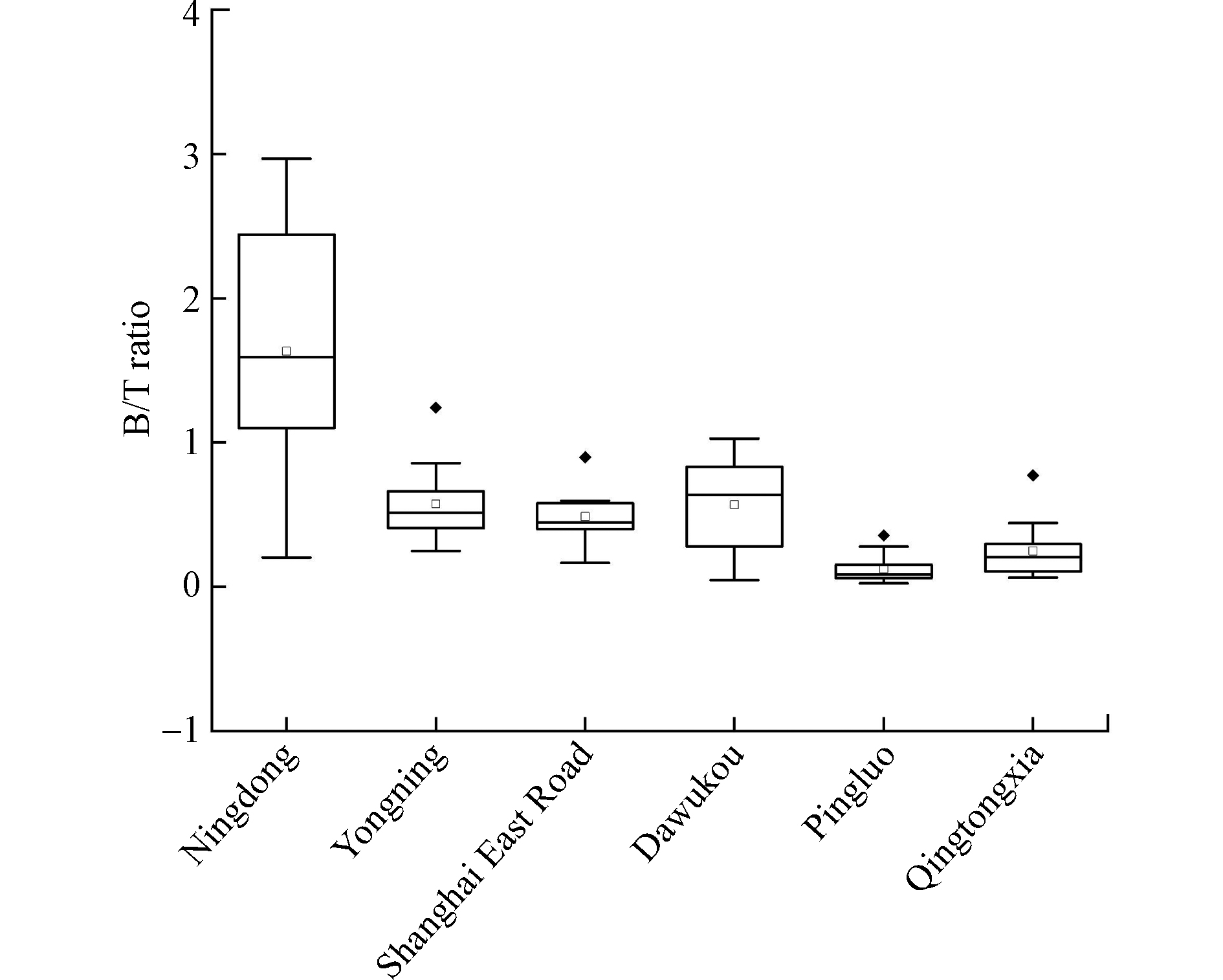 图 6 各采样点苯/甲苯比值箱线图Figure 6. Box and whisker plots of benzene/toluene ratio at each sampling site.框中实线代表中值浓度,框底部和顶部描绘了第25个(第一个四分位数)和第75个(第三个四分位数)百分位,空心点表示平均值,实心点表示异常值,晶须的末端分别对应在Q1和Q3的IQR的1.5倍之内的最低和最高数据The solid line in the box represents the median concentration. The bottom and top of the box depict the 25th (the first four Quantile) and the 75th (third quartile) percentile. The hollow dots represent the average value, and the solid dots represent the outliers. The ends of the whiskers correspond to the lowest and highest data still within 1.5 times the IQR of Q1 and Q3, respectively.
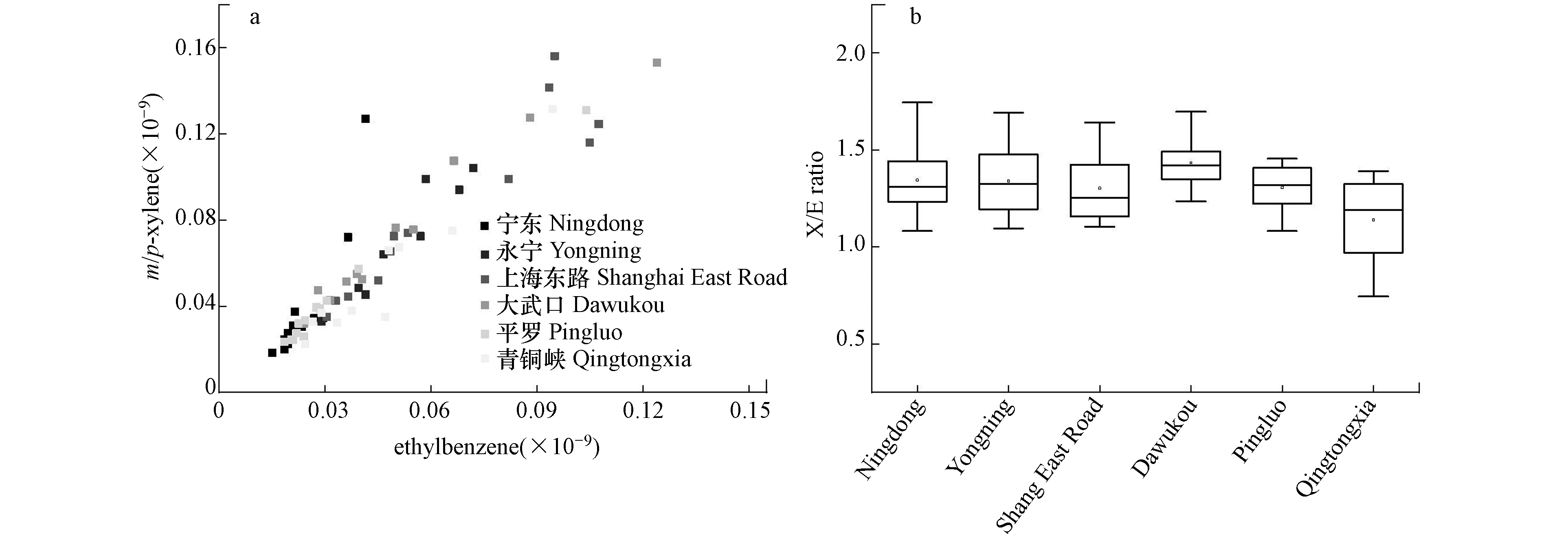
图 6 各采样点苯/甲苯比值箱线图Figure 6. Box and whisker plots of benzene/toluene ratio at each sampling site.框中实线代表中值浓度,框底部和顶部描绘了第25个(第一个四分位数)和第75个(第三个四分位数)百分位,空心点表示平均值,实心点表示异常值,晶须的末端分别对应在Q1和Q3的IQR的1.5倍之内的最低和最高数据The solid line in the box represents the median concentration. The bottom and top of the box depict the 25th (the first four Quantile) and the 75th (third quartile) percentile. The hollow dots represent the average value, and the solid dots represent the outliers. The ends of the whiskers correspond to the lowest and highest data still within 1.5 times the IQR of Q1 and Q3, respectively.一些VOCs组分虽然来源相似,但其光化学反应活性相差很大,因此,这些组分间的比值可用来反映光化学老化程度。图7为间/对-二甲苯/乙苯的散点图,结果表明,不同时间、不同采样点环境空气中间/对-二甲苯和乙苯对应浓度之间呈显著相关,说明观测期间这两种组分具有相似的来源[18-19]。间/对-二甲苯和乙苯可被·OH和·NO3氧化(白天主要与·OH反应,晚上主要与·NO3反应)[20-21]。间/对-二甲苯与·OH的反应速率大约是乙苯的3倍(间/对-二甲苯和乙苯与·OH的反应速率分别为18.90 × 10−12 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1、7.00 × 10−12 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1)[22-23],随着间/对-二甲苯与·OH的反应速率的增大,间/对-二甲苯和乙苯间的比值(m/p-Xylene/ Ethylbenzene,X/E)逐渐减小,X/E的值越小,·OH暴露量越大,大气中光化学反应越活跃,空气质量老化的程度就越高[24-25]。从各采样点的间/对-二甲苯/乙苯比值的箱线图来看,青铜峡采样点的平均X/E比值最小(在1.10左右),其他5个采样点平均X/E比值相当,表明青铜峡采样点的挥发性有机物与·OH自由基光的光化学反应活性相对较强烈,该采样点空气的老化程度最大,更易受老化气团控制。
2.4 臭氧生成潜势
臭氧生成潜势(ozone formation potential,OFP)常被用来衡量VOCs组分生成臭氧的能力。本研究通过最大增量反应活性法(maximum incremental reactivity,MIR)来计算VOCs组分的臭氧生成潜势,并分析VOCs各组成成分对臭氧生成的贡献[26],臭氧生成潜势的计算公式:
OFPi=VOCsi×MIRi 式中,OFPi为VOCs组分i的臭氧生成潜势,
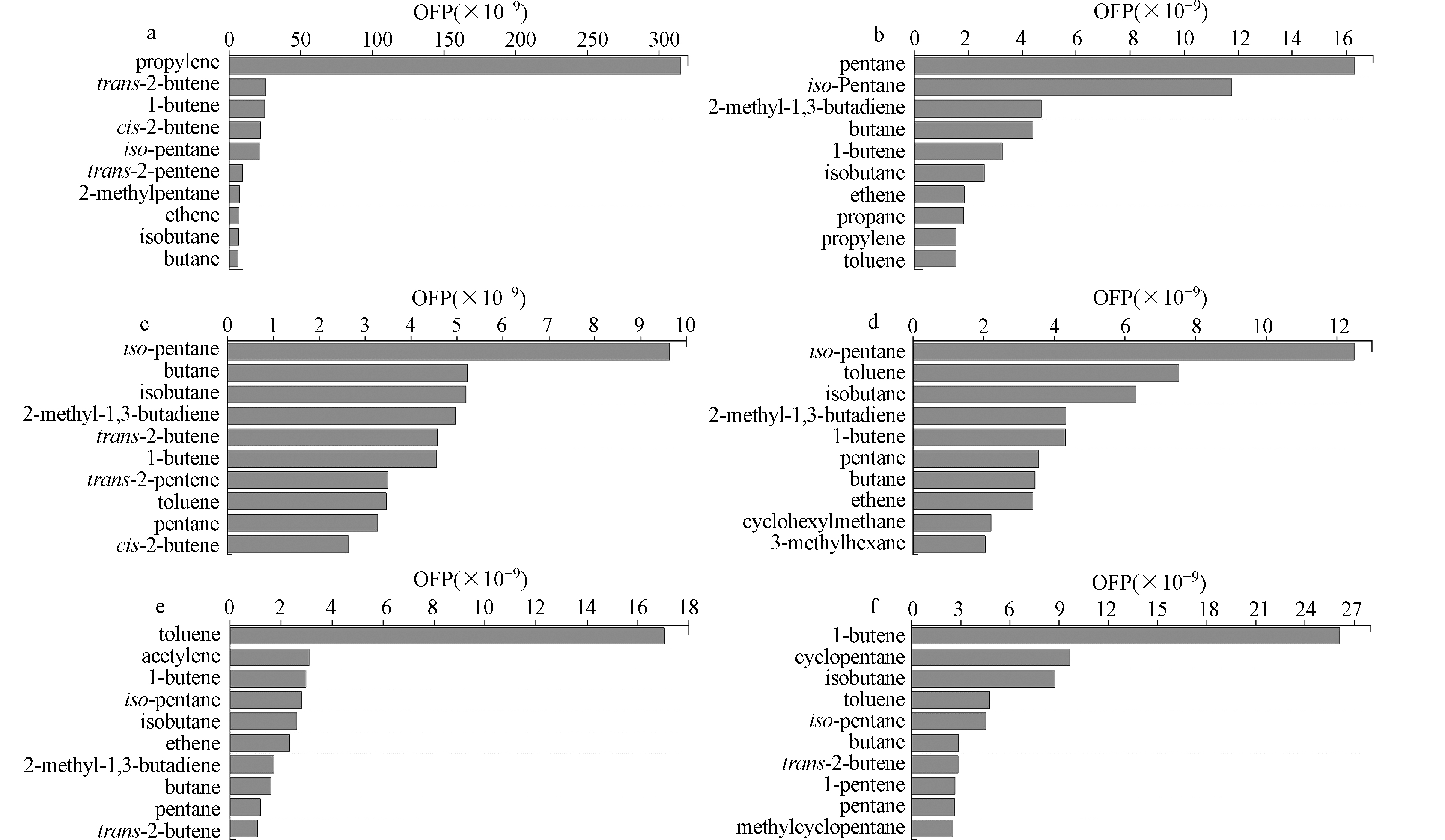
× × 图8显示了各采样点在观测期间不同类别挥发性有机物对臭氧生成潜势的贡献,结果表明,在6个采样点中烯烃对臭氧生成潜势都有较大贡献(23.20%—85.26%),其中,宁东采样点中烯烃对OFP的贡献率是6个采样点中最大,高达85.26%,这是由该采样点烯烃的高浓度及烯烃的高光化学反应活性共同导致的。与VOCs组成分析结果对比可知,不同VOCs组成的浓度占比与其对应的OFP贡献率之间存在一定关系。烯烃是主要的活性烃,在光照条件下能够产生大量自由基,从而对O3的生成产生重要贡献,从本研究结果看,烯烃对臭氧生成潜势的贡献情况与其浓度占比情况不一致,永宁、上海东路、大武口、平罗和青铜峡采样点中烯烃虽浓度占比不高,但其臭氧生成潜势贡献却十分明显,这主要与烯烃的高光化学反应活性有关。此外,在6个采样点中,短链烷烃的浓度占比高于长链烷烃,但短链烷烃对OFP的贡献率却低于长链烷烃,这与长链烷烃是活性烃,短链烷烃是低反应性烃有关。这些结果均表明VOCs组分的光化学反应活性在臭氧生成过程中起重要作用。
本研究中OFP贡献前10位的VOCs组分主要是烯烃和烷烃(图9),进一步与各采样点浓度最大的前10位VOCs组分(图5)比对可知,浓度较低的1-丁烯、顺式-2-丁烯、反式-2-丁烯等烯烃组分的对OFP的贡献反而较大,但不同采样点之间存在一定差异。
同处于工业区的宁东和永宁采样点,由于工业排放源种类以及污染物排放强度不同,对OFP贡献的主要VOCs组分也有所不同,宁东采样点中主要OFP贡献组分是丙烯(3.15
× × × × × × × × × × × × × × × × × 2.5 二次有机气溶胶生成潜势
为进一步了解环境空气中VOCs对银川都市圈地区二次有机气溶胶生成的影响,本研究采用气溶胶生成系数法(FAC法)估算观测期间各采样点的二次有机气溶胶生成潜势(SOAP),公式如下:
SOAP=VOCsi×FACi1−FVOCsi 式中,SOAP指SOA的生成潜势(μg·m−3);VOCsi指VOCs中i组分的浓度(μg·m−3);FACi指i组分的SOA的生成系数(%),FVOCsi为i组分参与氧化反应的份额(%)[27-28]。
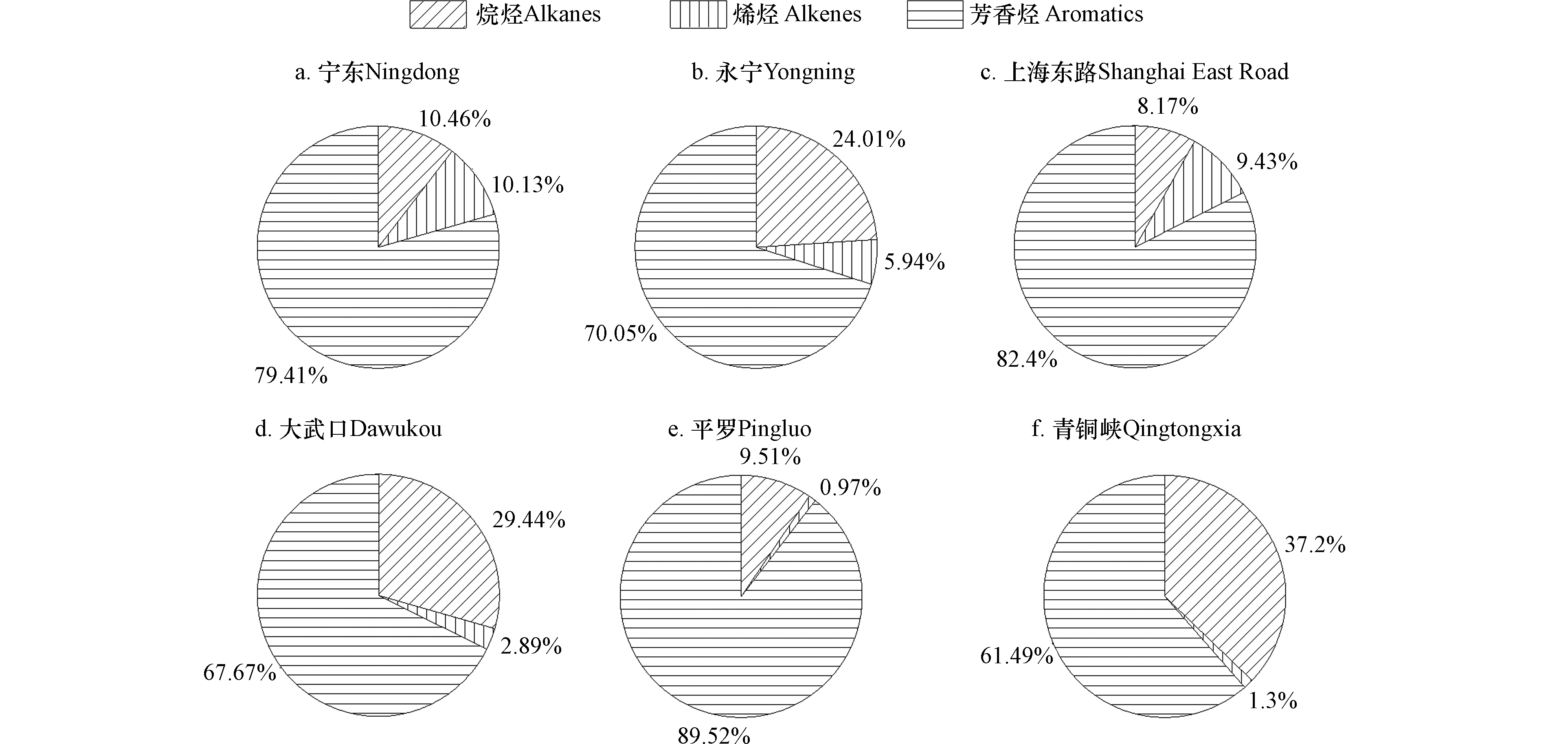
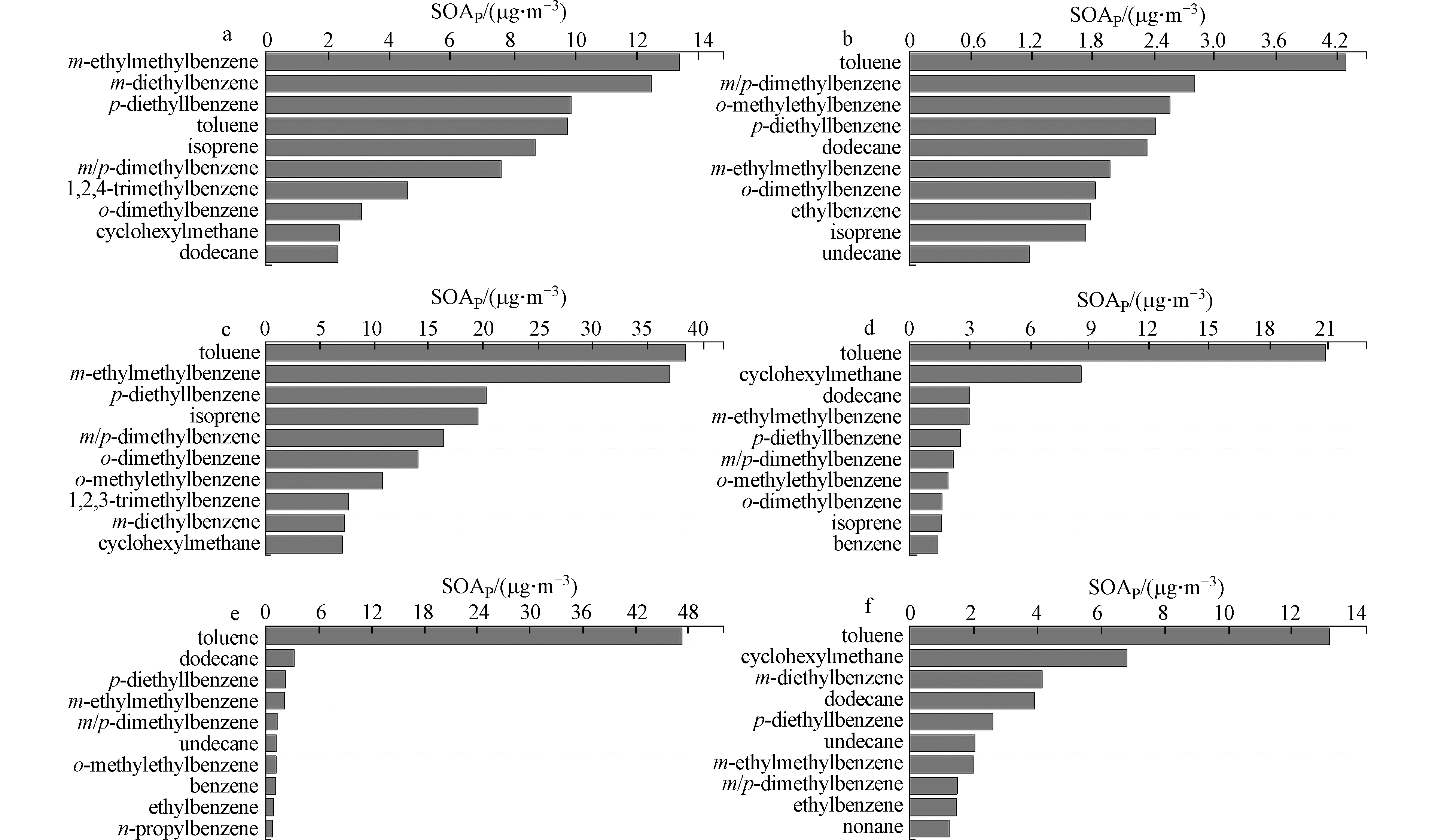
宁东、永宁、上海东路、大武口、平罗、青铜峡采样点SOAP均值分别为86.02、29.25、206.43、55.27、59.45、46.33 μg·m−3。6个采样点SOAP组成相似(图10),其中,芳香烃浓度占比最大(宁东79.41%、永宁70.05%、上海东路82.40%、大武口67.67%、平罗89.52%、青铜峡61.49%),而烷烃和烯烃的贡献相对较小。图11展示了各采样点对SOAP贡献前10的VOCs组分,结果表明,各采样点VOCs中对SOAP贡献较大的组分十分相似,均以芳香烃类居多,间/对-二甲苯、甲苯、间-乙基甲苯、对-二乙基苯对各采样点的SOAP中均有较大贡献,尤其在上海东路采样点中甲苯(3.85
× × × 3. 结论(Conclusion)
在银川都市圈工业区、商业/交通/居民混合区和工业/交通混合区中,尽管各采样点环境空气中VOCs的组分浓度及反应活性有所差异,但都以烯烃和长链烷烃组分为主;短链烷烃和长链烷烃在各点位都有较高的浓度占比,分别为30.85%—45.21%、15.17%—48.79%,这可能与机动车尾气排放有关。烯烃在宁东煤化工区采样点的浓度占比(43.77%)最为显著,炔烃、芳香烃在平罗采样点的浓度占比最高,分别为29.98%和14.00%,这可能与这些采样点的VOCs来源差异有关。宁东煤化工区采样点的VOCs总浓度水平高于其他5个采样点。尽管烯烃的浓度占比不高,但其生成臭氧的潜力较大,烯烃对臭氧生成潜势的贡献在23.2%—85.26%。6个采样点中各VOCs组成对SOAP的贡献相似,其中,芳香烃的贡献最大,贡献率在61.49%—89.52%。因此,O3污染和雾霾污染问题的改善需同时考虑VOCs组分浓度及其光化学反应活性。
-
表 1 南昌前湖区域与国内、外不同城市eBC浓度的对比
Table 1. Comparison of eBC concentrations in the Qianhu region of Nanchang with those in different cities/regions in China and abroad
地点Location 站点类型Site types 时间Time eBC/(μg·m−3) 参考文献References 南昌 城市 2021.1—2021.12 1.93 本研究 上海 城市 2016.1—2016.12 2.41 [17] 城郊 1.83 深圳 城市 2014—2015 2.58 [18] 城郊 1.12 石家庄 城市 2018.9—2019.8 4.79 [10] 城郊 2018.9—2019.8 4.35 邢台 城市 2019.1—2019.12 0. 85 [19] 北京 城市 2019.1—2019.12 2.27 [20] 城郊 1.58 平顶山 农村 2018.2—2018.3 6.78 [21] 沈阳 城市 2008.3—2009.2 6.14 [22] 大连 城市 2014.1—2014.12 1.64 [23] 贵阳 城市 2016.5—2017.4 5.19 [24] 新疆 城市 2019.6—2020.5 1.95 [25] 印度 城市 2017.12—2018.11 6.60 [26] 但巴德 城市 2012.1—2012.12 6.30 [27] 德克萨斯洲 城市 2008.1—2008.12 1.24 [28] 表 2 研究期间南昌前湖区域不同季节气象因子的统计
Table 2. Statistics on meteorological factors for different seasons in the Qianhu region of Nanchang during the study period
类别Categories 春季Spring 夏季Summer 秋季Autumn 冬季Winter 温度/°C 8.6—30.18 24.5—34.8 9.9—33.25 0.5—19.66 相对湿度/% 53.6—98.3 55.2—93.3 56.0—99.8 39.5—97.2 风速/(m·s−1) 2.7—13.1 4.3—14.7 2.3—17.1 2.7—13.1 表 3 2021年南昌前湖区域吸收系数、大气消光系数等相关汇总
Table 3. Summary of absorption coefficients, atmospheric extinction coefficients and other correlations for the Nanchang Qianhu region in 2021
季节Seasons 大气能见度/kmAtmospheric visibility eBC质量浓度/(μg·m−3)eBC mass concentration 吸收系数/Mm−1Absorption coefficient 大气消光系数/Mm−1Atmospheric extinction coefficient 贡献率/%Contribution rate 春季 22.23 1.69±1.14 16.23 134.76 12.04% 夏季 21.7 1.86±1.37 17.66 138.09 12.79% 秋季 21.88 2.02±1.05 18.96 137.00 13.84% 冬季 21.56 2.10±1.28 19.63 139.05 14.12% 年度均值 21.77 1.93±1.13 18.42 137.67 13.38% -
[1] 吴兑, 毛节泰, 邓雪娇, 等. 珠江三角洲黑碳气溶胶及其辐射特性的观测研究 [J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2009, 39(11): 1542-1553. WU D, MAO J T, DENG X J, et al. Observational study of black carbon aerosols and their radiative properties in the Pearl River Delta [J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2009, 39(11): 1542-1553(in Chinese).
[2] 李杏茹, 王英锋, 郭雪清, 等. 2008年奥运期间北京不同粒径大气颗粒物中元素碳和有机碳的变化特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(2): 313-318. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.02.020 LI X R, WANG Y F, GUO X Q, et al. Characteristics of elemental and organic carbon changes in atmospheric particulate matter of different particle sizes in Beijing during the 2008 Olympic Games [J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(2): 313-318(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2011.02.020
[3] NIU Z, ZHANG F, KONG X, et al. One-year measurement of organic and elemental carbon in size-segregated atmospheric aerosol at a coastal and suburban site in Southeast China [J]. J Environ Monit, 2012, 14(11): 2961-2967. doi: 10.1039/c2em30337j [4] ZEB B, ALAM K, NASIR J, et al. Black carbon aerosol characteristics and radiative forcing over the high altitude glacier region of Himalaya-Karakorum-Hindukush [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2020, 238(10):117711. [5] WYCHE K P, CORDELL R L, SIMITH L M, et al. The spatio-temporal evolution of black carbon in the North-West European 'air pollution hotspot[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2020, 243(15):117874. [6] LIU J, ANDERSSON A, ZHONG G, et al. Isotope constraints of the strong influence of biomass burning to climate-forcing Black Carbon aerosols over Southeast Asia [J]. Sci Total Environ, 2020, 744:140359. [7] 周变红, 曹夏, 张容端, 等. 宝鸡高新区春节前后大气中黑碳浓度特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(7): 1754-1762. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019113001 ZHOU B H, CAO X, ZHANG R R, et al. Characterization of black carbon concentration in the atmosphere before and after the Spring Festival in Baoji High-tech Zone and analysis of its sources [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(7): 1754-1762(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019113001
[8] 孙天林, 吴兑, 吴晟, 等. 东莞市黑碳气溶胶污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 地球化学, 2020, 49(3): 287-297. doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.2019.05.011 SUN T L, WU D, WU S, et al. Analysis of black carbon aerosol pollution characteristics and sources in Dongguan [J]. Geochimica, 2020, 49(3): 287-297(in Chinese). doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.2019.05.011
[9] 盛涛. 上海市路边环境空气黑碳气溶胶污染特征及影响因素研究 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2020, 36(2): 116-125. doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2020.02.14 SHENG T. Study on the characteristics and influencing factors of black carbon aerosol pollution in roadside ambient air in Shanghai [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2020, 36(2): 116-125(in Chinese). doi: 10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2020.02.14
[10] 关亚楠, 卢晶晶, 张毅森, 等. 石家庄南郊黑碳气溶胶污染特征与来源分析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(9): 3146-3154. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0129 GUAN Y N, LU J J, ZHANG Y S, et al. Characterization and source analysis of black carbon aerosol pollution in the southern suburbs of Shijiazhuang [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(9): 3146-3154(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0129
[11] 先久坤, 崔世杰, 张运江, 等. 亚洲地区黑碳气溶胶外场在线观测研究进展 [J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2022, 17(1): 104-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2022.01.007 XIAN J K, CUI J S, ZHANG Y J, et al. Advances in outfield online observation of black carbon aerosol in Asia [J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2022, 17(1): 104-124(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2022.01.007
[12] 徐义邦, 张吴, 秦文姜, 等. 南昌市冬季一次大气重污染过程的特征分析 [J]. 中国环境管理干部学院学报, 2018, 28(5): 85-89. doi: 10.13358/j.issn.1008-813x.2018.0423.01 XU Y B, ZHANG W, QIN W J, et al. Characterization of a heavy air pollution process in winter in Nanchang [J]. Journal of Hebei University of Environmental Engineering, 2018, 28(5): 85-89(in Chinese). doi: 10.13358/j.issn.1008-813x.2018.0423.01
[13] 姚婷婷, 黄晓锋, 何凌燕, 等. 深圳市冬季大气消光性质与细粒子化学组成的高时间分辨率观测和统计关系研究 [J]. 中国科学:化学, 2010, 40(8): 1163-1171. YAO T T, HUANG X F, HE L Y, et al. High temporal resolution observations and statistical relationships between atmospheric extinction properties and the chemical composition of fine particles in winter in Shenzhen [J]. Scientia Sinica(Chimica), 2010, 40(8): 1163-1171(in Chinese).
[14] 黄虹, 圣莉, 贺冰洁. 打印阶段PM2.5一次排放、碳组分谱与二次生成 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(7): 59-65. HUANG H, SHENG L, HE B J. Print phase PM2.5 primary emissions, carbon fraction profiles and secondary production [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(7): 59-65(in Chinese).
[15] SAFAIP D, DEVARA P C S, RAJU M P, et al. Relationship between black carbon and associated optical, physical and radiative properties of aerosols over two contrasting environments [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2014, 149: 292-299. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.07.006 [16] 杨晓旻, 施双双, 张晨, 等. 南京市黑碳气溶胶时间演变特征及其主要影响因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(2): 620-629. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201905245 YANG X W, SHI S S, ZHANG C, et al. Characteristics of the temporal evolution of black carbon aerosols in Nanjing and their main influencing factors [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(2): 620-629(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201905245
[17] 井安康, 朱彬, 丁德平, 等. 中国长江三角洲地区黑碳特征和来源分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(9): 3585-3594. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.09.001 JING A K, ZHU B, DING D P, et al. Characterization and source analysis of black carbon in the Yangtze River Delta region of China [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(9): 3585-3594(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.09.001
[18] 程丁, 吴晟, 吴兑, 等. 深圳市城区和郊区黑碳气溶胶对比研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(5): 1653-1662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.05.006 CHENG D, WU S, WU D, et al. Comparative study on black carbon aerosol in urban and suburban areas of Shenzhen [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(5): 1653-1662(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.05.006
[19] 郝巨飞, 杨允凌, 李二杰, 等. 邢台市城区黑碳气溶胶浓度与气象因子变化关系分析 [J]. 高原气象, 2021, 40(3): 671-679. doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2020.00049 HAO J F, YANG Y L, LI E J, et al. Analysis of the relationship between black carbon aerosol concentrations and changes in meteorological factors in the urban area of Xingtai City [J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2021, 40(3): 671-679(in Chinese). doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2020.00049
[20] 曹阳, 安欣欣, 刘保献, 等. 北京市黑碳气溶胶浓度特征及其主要影响因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(12): 5633-5643. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202103049 CAO Y, AN X X, LIU B X, et al. Characteristics of black carbon aerosol concentrations in Beijing and their main influencing factors [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(12): 5633-5643(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202103049
[21] 刘玺, 孔少飞, 郑淑睿, 等. 春节前后华北平原农村地区黑碳浓度及来源 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(8): 3169-3177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.08.005 LIU X, KONG S F, ZHENG S R, et al. Black carbon concentrations and sources in rural areas of the North China Plain around the Spring Festival [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(8): 3169-3177(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.08.005
[22] 王扬锋, 马雁军, 陆忠艳, 等. 辽宁地区大气黑碳气溶胶质量浓度在线连续观测 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2011, 24(10): 1088-1096. doi: 10.13198/j.res.2011.10.10.wangyf.013 WANG Y F, MA Y J, LU Z Y, et al. Continuous online observation of atmospheric black carbon aerosol mass concentration in Liaoning region [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 24(10): 1088-1096(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.res.2011.10.10.wangyf.013
[23] 徐洁. 大连市黑碳气溶胶观测研究及来源分析 [J]. 河北环境工程学院学报, 2020, 30(3): 51-55. XU J. Observational study and source analysis of black carbon aerosols in Dalian [J]. Journal of Hebei University of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 30(3): 51-55(in Chinese).
[24] 周瑞国, 梁隆超, 肖德安, 等. 西南典型高原山地城市大气黑碳气溶胶污染特征及来源解析 [J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(4): 375-380. doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2021.49.028 ZHOU R G, LIANG L C, XIAO D A, et al. Characterization and source analysis of atmospheric black carbon aerosol pollution in a typical southwestern highland mountain city [J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(4): 375-380(in Chinese). doi: 10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2021.49.028
[25] 范圣虎. 乌鲁木齐黑碳气溶胶浓度时间变化特征及影响因素分析 [J]. 新疆环境保护, 2021, 43(1): 28-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2301.2021.01.005 FAN S H. Analysis on the temporal variation characteristics and influencing factors of black carbon aerosol concentration in Urumqi [J]. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang, 2021, 43(1): 28-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2301.2021.01.005
[26] AMBADE B, SANKAR T K, PANICKER A S, et al. Characterization, seasonal variation, source apportionment and health risk assessment of black carbon over an urban region of East India [J]. Urban Climate, 2021, 38:100896. [27] SINGH S, TIWARI S, GOND D P, et al. Intra-seasonal variability of black carbon aerosols over a coal field area at Dhanbad, India [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2015, 161-162: 25-35. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.03.015 [28] RAYSONI A U, SAMAT J A, SSRNAT S E, et al. Binational school-based monitoring of traffic-related air pollutants in El Paso, Texas (USA) and Ciudad Juarez, Chihuahua (Mexico) [J]. Environ Pollut, 2011, 159(10): 2476-2486. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.06.024 [29] 丁铭, 邹强, 葛顺, 等. 苏州市黑碳气溶胶的污染特征分析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2014, 30(6): 67-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2014.06.011 DING M, ZOU Q, GE S, et al. Analysis of pollution characteristics of black carbon aerosol in Suzhou City [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2014, 30(6): 67-71(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2014.06.011
[30] 程丁, 吴晟, 吴兑, 等. 广州市城区干湿季黑碳气溶胶污染特征及来源分析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(6): 2223-2232. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0010 CHENG D, WU S, WU D, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of black carbon aerosol in Urban Area of Guangzhou during dry and wet seasons [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(6): 2223-2232(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0010
[31] 兰剑, 闫莹, 乔利平. 大城市城区黑碳气溶胶来源及其污染特性试验 [J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2020, 52(11): 53-62. doi: 10.11918/201905053 LAN J, YAN Y, QIAO L P. Experiment on sources and pollution characteristics of black carbon aerosol in Metropolitan Area [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020, 52(11): 53-62(in Chinese). doi: 10.11918/201905053
[32] 徐昶, 沈建东, 叶辉, 等. 杭州黑碳气溶胶污染特性及来源研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(12): 3026-3033. XU C, SHEN J D, YE H, et al. Pollution characteristics and sources of black carbon aerosol in Hangzhou [J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(12): 3026-3033(in Chinese).
[33] CHOW J C, WATSON J G, DORAISWAMY P, et al. Aerosol light absorption, black carbon, and elemental carbon at the Fresno Supersite, California [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2009, 93(4): 847-887. [34] 张娅蕴, 支国瑞, 田崇国, 等. 北京秋冬季有机碳和元素碳(黑碳)测试结果的细节研究 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2017, 30(8): 1184-1192. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2017.02.56 ZHANG Y Y, ZHI G R, TIAN Z G, et al. Details of measurement results of organic carbon and elemental carbon ( black carbon ) in autumn and winter in Beijing [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 30(8): 1184-1192(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2017.02.56
[35] WANG T. Emission characteristics of CO, NOx, SO2 and indications of biomass burning observed at a rural site in eastern China [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107. [36] 肖思晗, 于兴娜, 朱彬, 等. 南京北郊黑碳气溶胶污染特征及影响因素分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(9): 3280-3289:. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.09.005 XIAO S H, YU X N, ZHU B, et al. Analysis of black carbon aerosol pollution characteristics and influencing factors in the northern suburbs of Nanjing [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(9): 3280-3289:(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.09.005
[37] DAVID G, STREETS S G, STEPHANIE T. Black carbon emissions in China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2001, 35(25):4281-4296. [38] 孔祥晨, 张连霞, 张彩云, 等. 鄂尔多斯市夏秋季黑碳气溶胶时间演变特征及其来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(7): 3439-3450. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202110073 KONG X C, ZHANG L X, ZHANG C Y, et al. Temporal evolution characteristics and source analysis of black carbon aerosol in summer and autumn in Ordos City [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(7): 3439-3450(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202110073
[39] 张玲, 孔少飞, 郑煌, 等. 华北平原南部农村地区黑碳气溶胶浓度及来源 [J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(5): 2363-2372. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108052 ZHANG L, KONG S F, ZHENG H, et al. Black carbon aerosol concentrations and sources in rural areas of the southern North China Plain [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(5): 2363-2372(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108052
[40] 许黎, 王亚强, 陈振林, 等. 黑碳气溶胶研究进展Ⅰ: 排放、清除和浓度 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2006(4): 352-3603. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.04.004 XU L, WANG Y Q, CHEN Z L, et al. Advances in black carbon aerosol research I: Emissions, removals and concentrations [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006(4): 352-3603(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.04.004
[41] WHITEAKER J R, SUESS D T, PRATHER K A. Effects of meteorological conditions on aerosol composition and mixing state in Bakersfield, CA. [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36(11): 2345-2353. [42] TIWARI S, SRIVASTAVA A K, BISHT D S, et al. Diurnal and seasonal variations of black carbon and PM2.5 over New Delhi, India: Influence of meteorology [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2013, 25: 50-62. [43] 孙欢欢, 倪长健, 崔蕾. 成都市黑碳气溶胶污染特征及与气象因子的关系 [J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(06): 119-124, 129. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201606025 SUN H H, NI C J, CUI L. Characteristics of black carbon aerosol pollution in Chengdu and its relationship with meteorological factors [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(06): 119-124, 129(in Chinese). doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201606025
[44] TYAGI S, TIWARI S, MISHRA A, et al. Characteristics of absorbing aerosols during winter foggy period over the National Capital Region of Delhi: Impact of planetary boundary layer dynamics and solar radiation flux [J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017, 188(15): 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2017.01.001 [45] 李倩, 吴琳, 张进生, 等. 廊坊市夏季大气气溶胶消光特性及其来源 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(6): 2249-2257. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.06.002 LI Q, WU L, ZHANG J S, et al. Extinction characteristics and sources of atmospheric aerosol in summer in Langfang [J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(6): 2249-2257(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.06.002
[46] WANG J, VIRKKULA A, GAO Y, et al. Observations of aerosol optical properties at a coastal site in Hong Kong, South China [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2017, 17(4): 2653-2671. doi: 10.5194/acp-17-2653-2017 [47] ZHUANG B, WANG T, LIU J, et al. The surface aerosol optical properties in the urban area of Nanjing, west Yangtze River Delta, China [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2017, 17(2): 1143-1160. doi: 10.5194/acp-17-1143-2017 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 盛雪莹,刘景富,赖余建,于素娟,陈钰杭,周庆祥. 黑碳在环境中的赋存、时空分布及迁移转化特征. 环境化学. 2024(06): 1980-1995 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)
-






 下载:
下载: