-
我国北方大部分区域属于干旱半干旱区,地表水较少,而地下水由于分布广泛、变化稳定、水质优良的特点,已成为当地工、农业生活生产的主要用水[1]. 但随着农药、化肥的广泛使用、污水的大量排放,地表水与地下水水质不断恶化,城市经济发展和生态良性循环受到严重制约[2-3]. 开展流域水化学特征及水质评价研究,对明确水质现状、揭示水循演化规律、健全水污染防治与水资源管理制度具有重要意义[4-5].
针对流域水化学特征及水质评价,国内外学者已开展了大量研究工作. 丁启振等[6]通过对新疆博尔塔拉河上游河谷地区不同水体进行取样分析,揭示了该区水化学的控制作用,明确了水化学组分的主要来源及水质现状. 夏璐等[7]运用多种水化学方法,对胶东半岛沿海地区的地下水进行分析,明确了区域水化学特征,并揭示了地下水污染主要是由人类活动引起的. Srilert等[8]通过对泰国碧差汶府与披集府交界处的地下水进行取样分析,明确了研究区不同时期的水化学类型,并基于主成分分析揭示了自然因素和人类活动对水化学的影响. Bouselsal等[9]基于多种水化学分析方法,揭示了阿尔及利亚地区地下水的水化学成因规律及主要离子反应,并使用电导率(EC)、钠吸附比(SAR)等不同参数,对饮用水源和灌溉水源分别进行了水质评价.
在以往的研究中,众学者主要集中于泉域地下水水化学特征沿流向的演化规律研究,或不同水体的水化学特征及成因机制研究,很少涉及对流域水化学在垂向的分布特征及成因规律研究. 而在该地区,也主要集中于对三姑泉域岩溶地下水的水化学特征研究,缺乏对丹河流域水化学特征及其成因规律的针对性探究. 因此,本文以丹河流域泽州段的地表水、浅层地下水、深层地下水及泉水等4种水体类型为研究对象,基于采样实测数据,结合流域水文地质条件,旨在查明流域水化学的垂向分布特征及成因规律,明确不同水体的水质现状,为丹河流域的水源保护及生态管理提供科学依据.
-
丹河是沁河的最大支流[10],流经山西、河南两省,并在河南省沁阳县汇入沁河. 丹河全长162 km,平均坡降7.6‰,流域面积为3220 km2. 丹河干流上建成的两座中型水库是任庄水库和东焦河水库;支流主要有白洋泉河、巴公河、北石店河及东大河. 河道常年有水,据任庄水库观测资料,多年平均流量为1.6 m3·s−1. 由于受晋城—高平断裂构造的影响,河水在中上游任庄水库段补给地下水,地下水在泽州县小会以下河段以泉的形式补给河水. 流域内岩溶裂隙发育,地下水储量丰富,是我国岩溶水系统的代表区域.
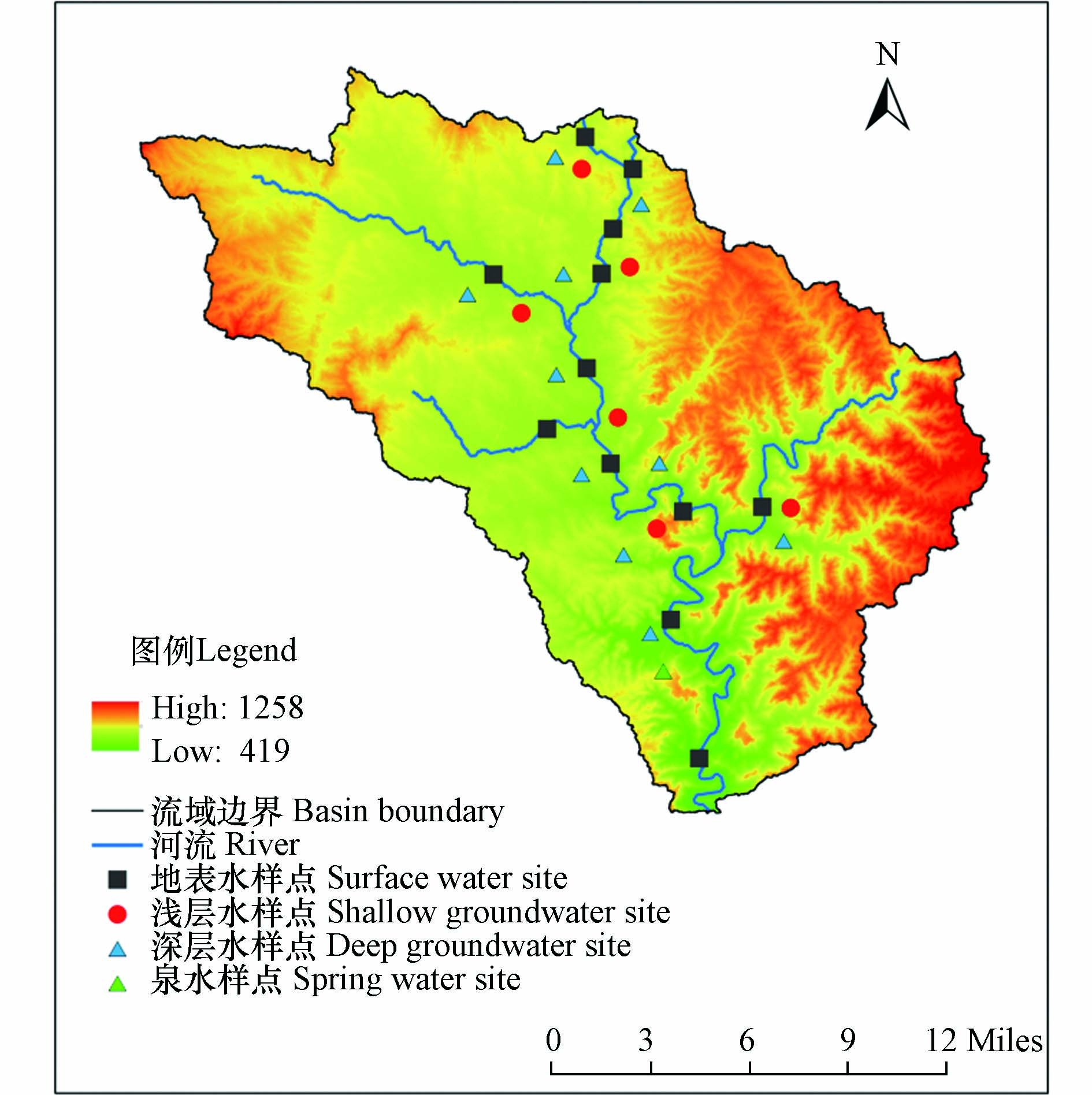
本文以丹河流域泽州段为研究区(图1),属暖温带大陆性半干旱气候区,四季分明;自南向北气温逐渐递减,年平均气温为10—11 ℃. 区内多年平均降雨量625.2 mm,汛期6—9月的降雨量占全年降雨量的68%,7—8月雨量比较集中,多以强暴雨的形式出现. 区内多年平均蒸发量为1693 mm,其中最大蒸发量为398.3 mm,集中在6月;最小蒸发量为15.6 mm,一般在12月.
-
2022年6月在研究区共采集了29组水样(河水12组、浅层地下水6组、深层地下水10组、泉水1组),采样点分布见图1. 取样完成后放置于棕色水样瓶加冰保存,并于48 h内送至实验室检测. pH、温度、TDS、溶解氧和电导率由哈纳(HANNA)HI9829笔式测定仪现场测定;HCO3−采用盐酸滴定法检测;K+、Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+、F−、Cl−、SO42−采用离子色谱法检测.
-
利用SPSS Statistics软件分析水化学各检测指标的最大值(Max)、中值(Me)、最小值(Min)、均值(Mean)、方差(SD)及变异系数(CV),采用相关性分析、Piper三线图、Gibbs图、氯碱指数及主要阴阳离子比值等水化学方法,研究水体水化学特征及成因规律.
-
根据水质级别的确定原则,水质评价方法可分为确定性评价方法和不确定性评价方法,确定性评价方法包括单因子法、综合指数法、分级评价法等;不确定性评价方法包括模糊评价法、主成分分析法等[11]. 但由于水质类别的一个区间范围,归属同一水质类别的不同水体,其污染状况也不全相同,尤其当指标浓度值靠近类别值的上限和下限时,确定性评价方法的评价结果会严重失真[12],因此,在实际应用过程中,不确定性评价方法的评价结果往往更加接近实际情况[13]. 而模糊评价法基于隶属度理论能有效的解决模糊不清和量化困难的问题,适合将问题的定性描述转化为定量分析,相较主成分分析法更能体现不同评价因子对水质的综合影响[14-15].
使用模糊评价法进行水质评价的过程中,关键问题是如何确定权重,这直接影响水质评价的结果[16]. 污染加权法、专家评判法、层次分析法等都是较为常用的确定权重方法. 但污染加权法难以准确描述多个评价指标的相互联系,容易造成评价结果出现均化、失真;专家评判法和层次分析法过分依赖个人的意见,使结果受人为影响较大. 而熵权法是基于客观数学计算的一种赋权方法,既可以有效避免人为赋权的主观性,又可以考虑到不同指标的相对重要性[17],因此本文选用基于熵权法的模糊评价法,可以准确评价目标水体的水质状况.
(1)建立隶属函数和关系矩阵
水体的水质一般被分为5个等级,分别计算各项评价因子在不同水质等级的隶属度,再基于计算结果构建评价指标的模糊关系矩阵R[18].
式中,
xi1 、xi2 、xi3 、xi4 、xi5 为某一指标对应不同水质等级的隶属度;n为指标实测值;c1 、c2 、c3 、c4 、c5 该指标水质分类标准值.(2)熵权法计算权重系
①构造判断矩阵
T=(tij)m∗n(i=1,2,…,n;j=1,2,…,m) . 其中m为评价对象个数,n为评价指标个数.②对判断矩阵进行归一化处理,得到矩阵
B=(bij)m∗n(i=1,2…n;j=1,2,…m) . 其中,数值越小水质越好的指标,其计算公式为:数值越大水质越好的指标,其计算公式为:
式中,
tij 为第m个评价对象的第n项指标检测值.③指标熵(
Hi )的计算,公式如下:式中,
fij 为第m个评价对象的第n项指标检测值在所有评价对象中所占的比例.fij=bij/∑mn=1bij ;k=1/lnm ;当fij=0 时,令fijlnfij=0 ④指标熵权值(
wi )的计算公式如下,且满足∑nn=1wi=1 .(3)确定评价等级
式中,P为评价水体对应不同水质等级的隶属度,W为权重所构成的权重矩阵,R为模糊关系矩阵,基于计算结果,采用最大值原则进行水质等级评价.
-
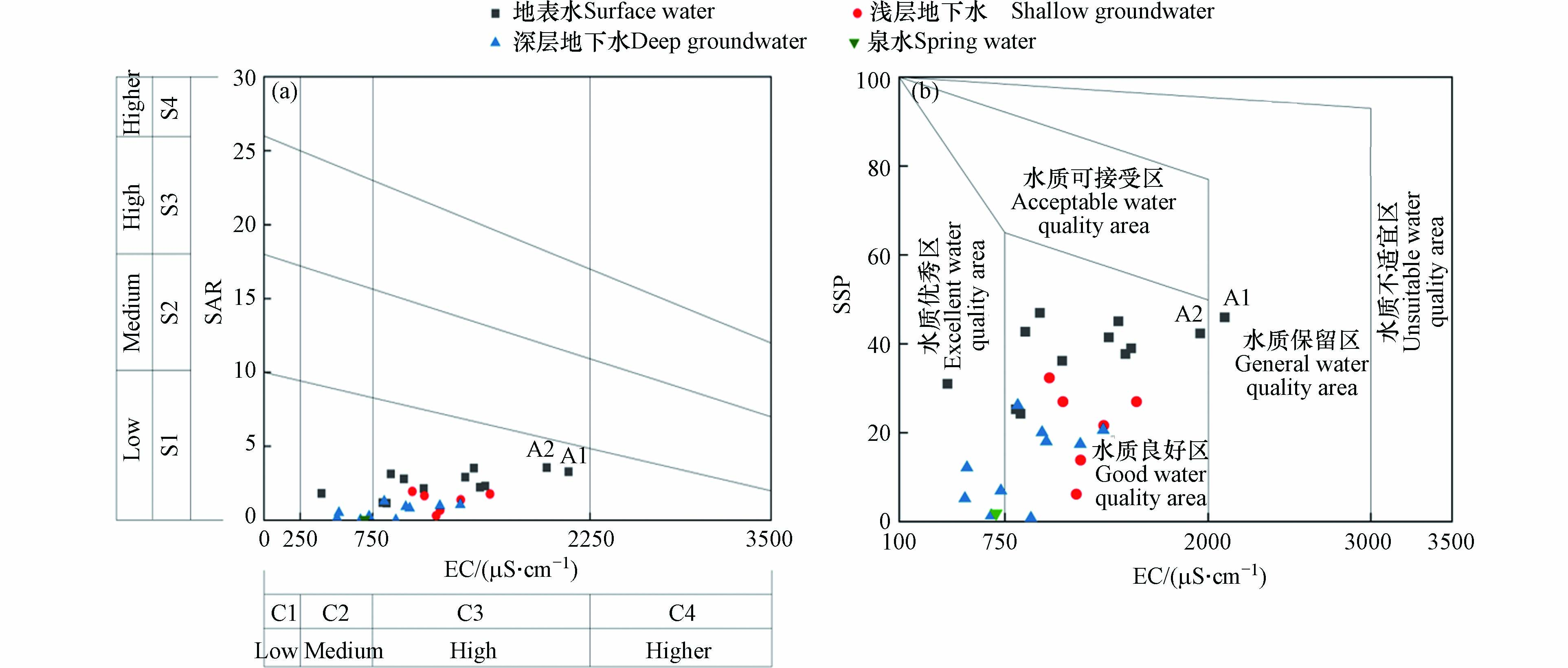
研究区内第一产业以农业为主,除居民生活用水外,区内水资源主要用于农田灌溉,而灌溉水质是影响土壤肥力的主要因素,当灌溉水中可溶性盐含量较高时,容易造成土壤盐碱化. 研究区内水体阴阳离子含量丰富,由TDS检测结果可知,部分水体已经属于微咸水,有造成土壤盐碱化的风险,而钠吸附比(SAR)和钠百分比(SSP)是我国北方碱性灌溉水质的重要参数,当土壤中钠离子含量过多就会改变土壤碱化性质、破坏团粒结构,导致土壤板结、透水性及透气性变差,最终影响作物正常生长发育[19]. 因此本文基于SAR和SSP两个重要指标,对研究区内灌溉水源进行水质评价,用以描述水体中的钠含量,衡量水体对土壤盐碱化的影响程度[20].
式中,
[Na+] 、[Ca2+] 、[Mg2+] 、[K+] 均为以meq·L−1为单位的离子浓度. -
计算研究区水化学特征参数如表1所示,不同水体pH介于7.32—8.69之间,均值为7.96,标准差介于0.19—0.21之间,说明研究区水体呈弱碱性,不同采样点之间pH差异较小,变化稳定,且不同水体pH大小表现为地表水>深层水>浅层水. 区内水体TDS介于193—1051 mg·L−1之间,按照水体矿化度的分类标准,地下水、泉水及多数地表水属于淡水,但地表水仍存在少量微咸水. TDS和F−浓度在垂向上呈现由上至下逐渐减小的趋势.
通过对阳离子的检测发现,Ca2+含量表现为浅层水>深层水>地表水,Na+、Mg2+和K+含量表现为地表水>浅层水>深层水,且水体中的Na+含量在垂向下降最为严重. 其含量关系表现为,地表水:Na+>Ca2+>Mg2+>K+;浅层水和深层水:Ca2+>Na+>Mg2+>K+. 阴离子中,HCO3−表现为浅层水>深层水>地表水,SO42−和Cl−含量表现为地表水>浅层水>深层水;其含量关系表现为,地表水与浅层水:SO42−>HCO3−>Cl−;深层水:HCO3−>SO42−>Cl−.
-
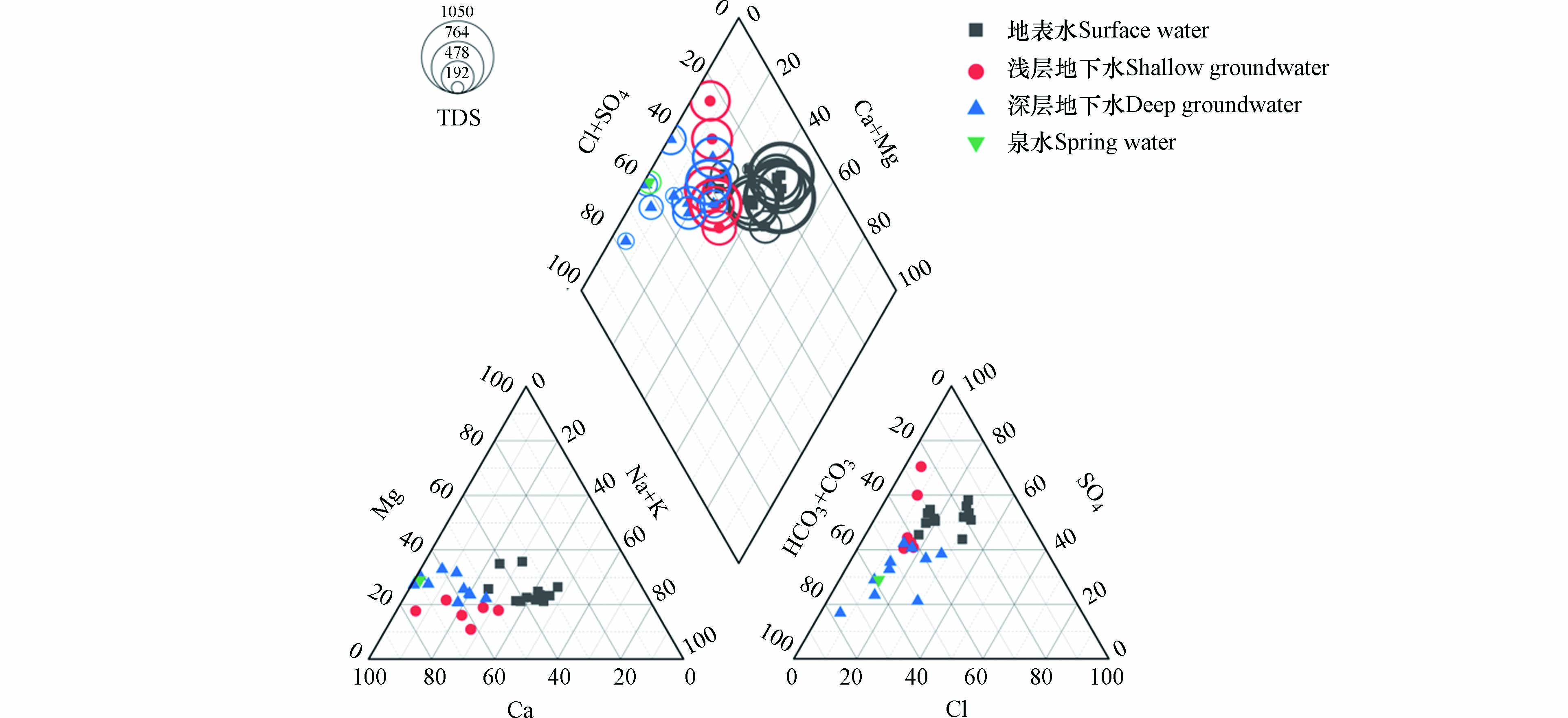
Piper三线图是最为广泛应用于的水化学分析方法之一[21],根据对研究区不同水体水化学组分的检测结果,绘制Piper三线图如图2所示. 由阳离子分析可知,地表水及部分浅层水主要以Ca-Na型水为主;深层水、泉水及部分浅层水主要以Ca型水为主;由阴离子分析可知,地表水和浅层水主要以重碳酸盐和硫酸盐型水为主;深层水主要以重碳酸盐型水为主. 泉水的水化学组分与深层水高度一致,说明泉水来源于深层地下水.
按照舒卡夫分类法,地表水水化学类型为SO4-Ca·Na和SO4·HCO3-Ca·Na;浅层水为HCO3·SO4-Ca·Na和SO4·HCO3-Ca;深层水和泉水为HCO3-Ca和HCO3·SO4-Ca;整体而言,在地表水下渗的过程中,阳离子倾向于由Ca-Na型向Ca型转变,阴离子倾向于由SO4型向HCO3型转变.
-
本文基于相关性分析来描述水化学组分之间相关程度[22],当相关性系数越接近1时,表示两组元素间相关性越大[23]. 不同水体水化学组分的相关性分析如表2所示,水体中TDS与除F−和pH外的其他7种离子具有正相关关系,其中与Ca2+、Na+、SO42−及Cl−相关性较高,说明这几种离子对TDS影响较大. 地表水和深层水中SO42−与Ca2+、Na+、Mg2+等3种离子均具有较高的相关性,说明其具有相同的离子来源,可能来源于石膏、硫酸盐岩的溶解. 地表水和浅层水中K+与Na+具有高度相关性,其相关系数大于0.9,说明其主要来源于蒸发盐岩溶解.
-
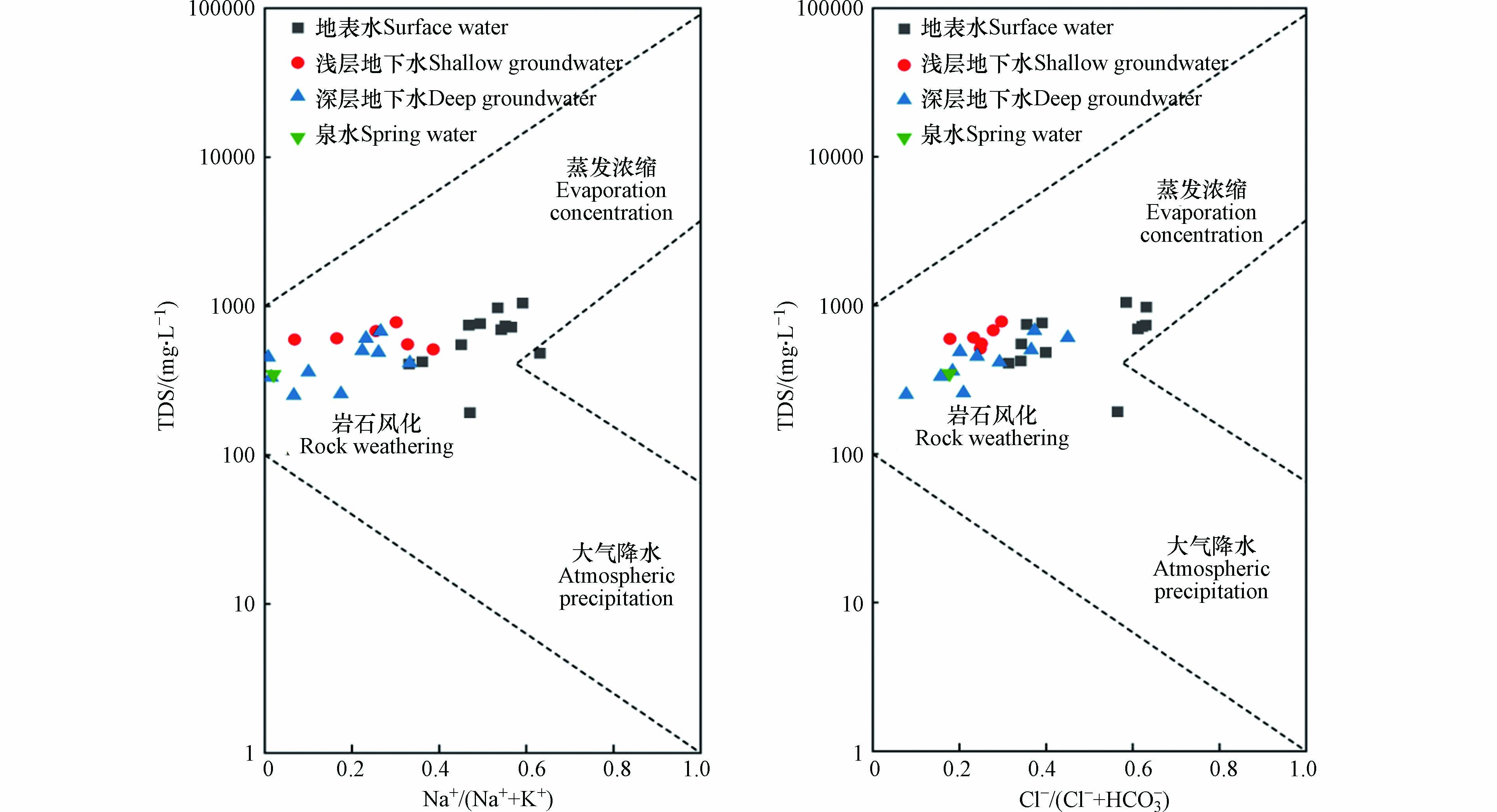
Gibbs图通过TDS与Na+/(Na++Ca2+)、Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−)的比值关系,判断水化学特征主要控制作用是岩石风化、大气降水还是蒸发浓缩[24]. 如图3所示,不同水体的TDS与Na+/(Na++Ca2+)、Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−)的比值主要分布于岩石风化作用控制的区域内,并远离大气降水作用控制的区域. 说明该区水化学特征主要受岩石风化用控制,区域气候干、降雨少,雨水所携带的可溶性离子极少可忽略不计[25]. 地表水取样点分布向蒸发浓缩作用控制区域靠近,说明地表水还受到蒸发浓缩作用的影响.
-
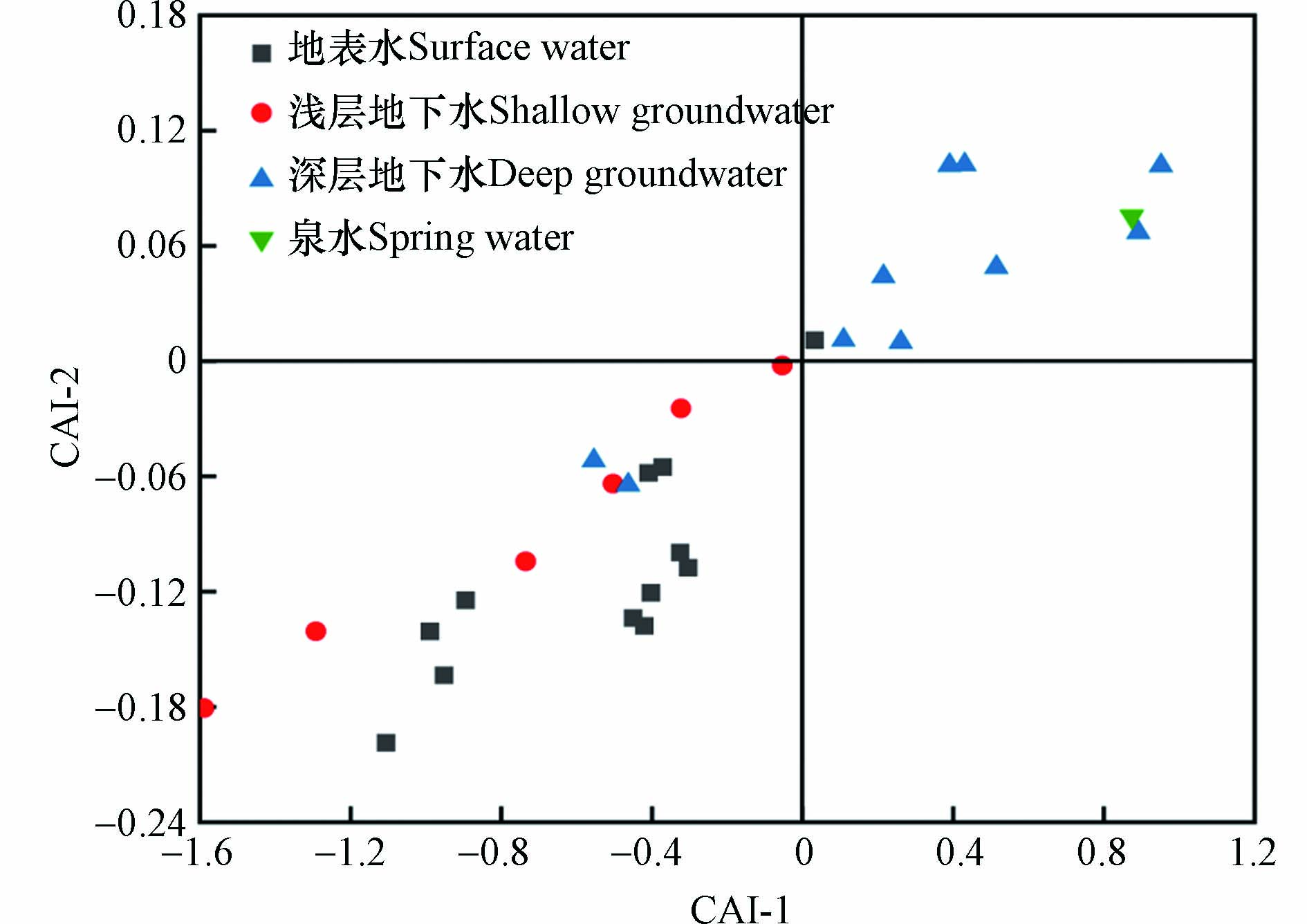
氯碱指数一般用于判断研究区内水体是否存在阳离子交换作用[26],且当CAI-1和CAI-2的绝对值越大时,证明水体中的阳离子交换作用就越强[27]. 如图4所示,地表水和浅层水的取样点主要位于坐标系中第三象限,说明该两类水发生正向阳离子交换作用,水体中的Ca2+和Mg2+将含水介质中的Na+和K+置换出来[27];而深层水和泉水的取样点主要位于第一象限,说明该两类水发生反向阳离子交换作用,水体中的Na+和K+将含水介质中的Ca2+和Mg2+置换出来[27],导致在地表水下渗过程中,Na+含量减少,Ca2+含量增加. 且水体阳离子交换作用强度表现为:浅层水和地表水>泉水和深层水.
-
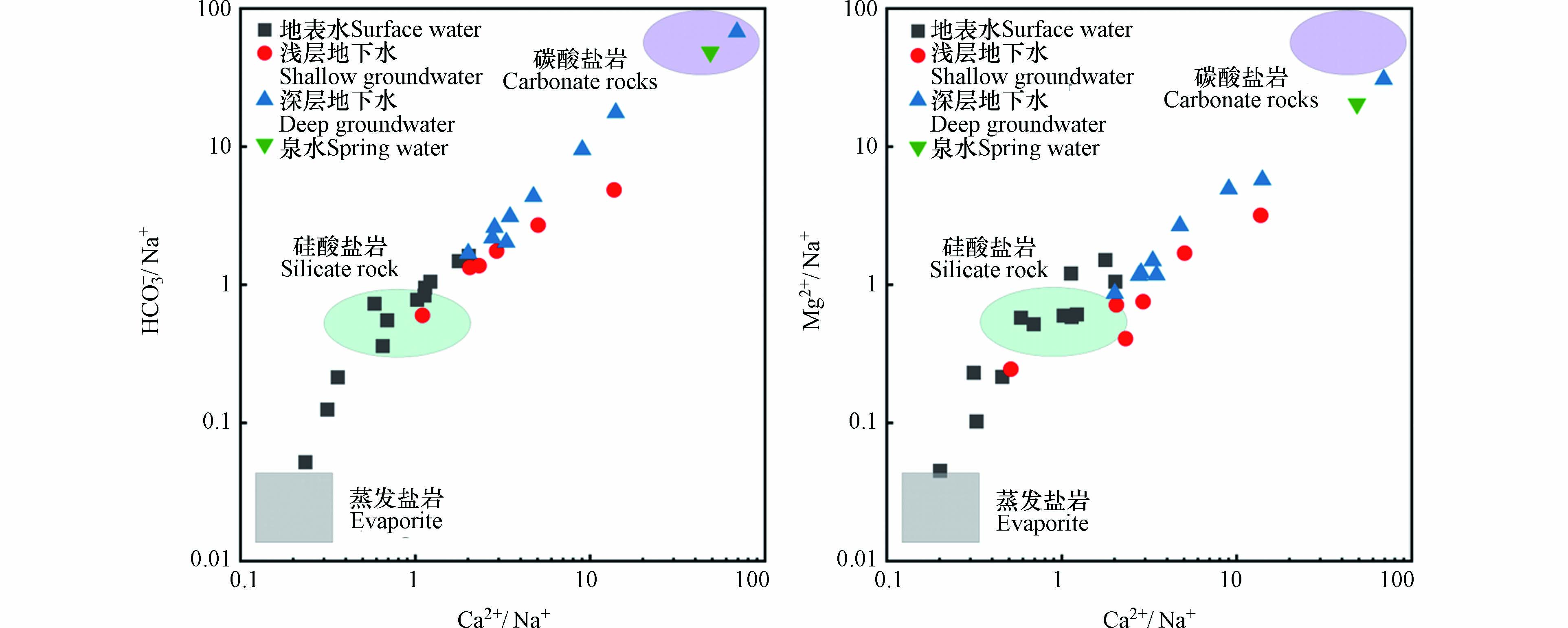
为进一步了解水化学组分的来源,可对水体的主要阴阳离子比值进行分析. 如图5绘制离子比值端元图,可以看出,硅酸盐岩区域附近取样点分布较为集中,说明研究区水化学组分主要来源为硅酸盐岩风化溶解[28];而地表水取样点分布靠近蒸发盐岩端元,泉水及深层水取样点分布靠近碳酸盐岩端元,说明地表水的水化学组分还来源于蒸发盐岩风化溶解,深层水及泉水的水化学组分还来源于碳酸盐岩风化溶解.
当水体中Na+含量与Cl−含量的比值接近于1时,表示水化学组分受到蒸发盐岩溶解的影响[29]. 如图6(a)所示,地表水及浅层水的取样点主要分布在y=x直线上方,说明Na+含量大于Cl−含量,蒸发盐岩的溶解不是水体中的Na+的唯一来源,Na+还来源于硅酸盐矿物的溶解,如钠长石. 此外,阳离子交换作用也会导致Na+含量增多. 深层水及泉水的取样点主要分布于y=x直线的下方,其原因主要是深层水发生反向阳离子交换作用,使得Na+含量小于Cl−含量.
当水体中(Ca2++Mg2+)含量与(HCO3−+SO42−)含量的比值大于1时,表示水化学组分主要受钙镁硅酸盐岩和蒸发盐岩溶解的影响,反之则为碳酸盐岩[7]. 如图6(b)所示,不同水体的取样点主要分布在y=x直线上方,说明研究区水化学组分主要受到钙镁硅酸盐岩和蒸发盐岩溶解的影响.
当水体中(SO42−+Cl−)含量与HCO3−含量的比值小于1时,表示水化学组分主要受碳酸盐岩溶解的影响,反之则主要受蒸发盐岩溶解影响[30]. 图6(c)显示,研究区内地表水、浅层水及部分深层水的取样点均分布于y=x直线上方,说明其水化学组分主要来源于蒸发盐岩溶解. 而泉水及多数深层水的取样点分布于y=x直线下方,说明其水化学组分主要受到碳酸盐岩溶解的影响.
利用Ca2+与Mg2+关系图可以判断出水体中钙、镁离子是否来源于白云石和方解石的溶解[31]. 图6(d)显示,地表水取样点主要分布于y=x和y=2x直线之间,说明,水体中Ca2+与Mg2+同时来自于方解石和白云石的溶解. 浅层水、深层水及泉水的取样点主要位于y=2x直线上方,表明其Ca2+除了来源于方解石和白云石溶解外,还来来源于反向阳离子交换作用.
-
由于研究区内,居民生活饮用以地下水为主,地表水主要用于灌溉,因此本文选择对浅层水、深层水及泉水进行饮用水质评价. 根据对水体的18项水质指标的检测结果可知,氨氮和硫酸盐超标最为严重,选取超标风险较高的pH、NH3-N、NO3-N、NO2-N、F−、SO42−、TDS作为评价指标进行水质评价. 首先分别计算以上7项指标在5个水质等级的隶属度,并构建模糊关系矩阵;然后使用SPSSPRO软件计算各水质指标的权重,构造权重矩阵;最后将两矩阵相乘得到评价水体对应不同水质等级的隶属度,并按照最大隶属度的原则进行水质等级判定,结果如表3所示. 浅层水中适宜人体饮用(Ⅰ、Ⅱ类)的水样有4个,占比66.7%;不适宜人体饮用(Ⅳ、Ⅴ类)的水样有2个,占比33.3%. 深层水中适宜人体饮用(Ⅰ、Ⅱ类)的水样有9个,占比90%;基本适宜人体饮用的水样(Ⅲ类)有1个,占比10%;不存在不适宜人体饮用的水样. 总的来说,研究区水质类别以Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类为主,水质较好.
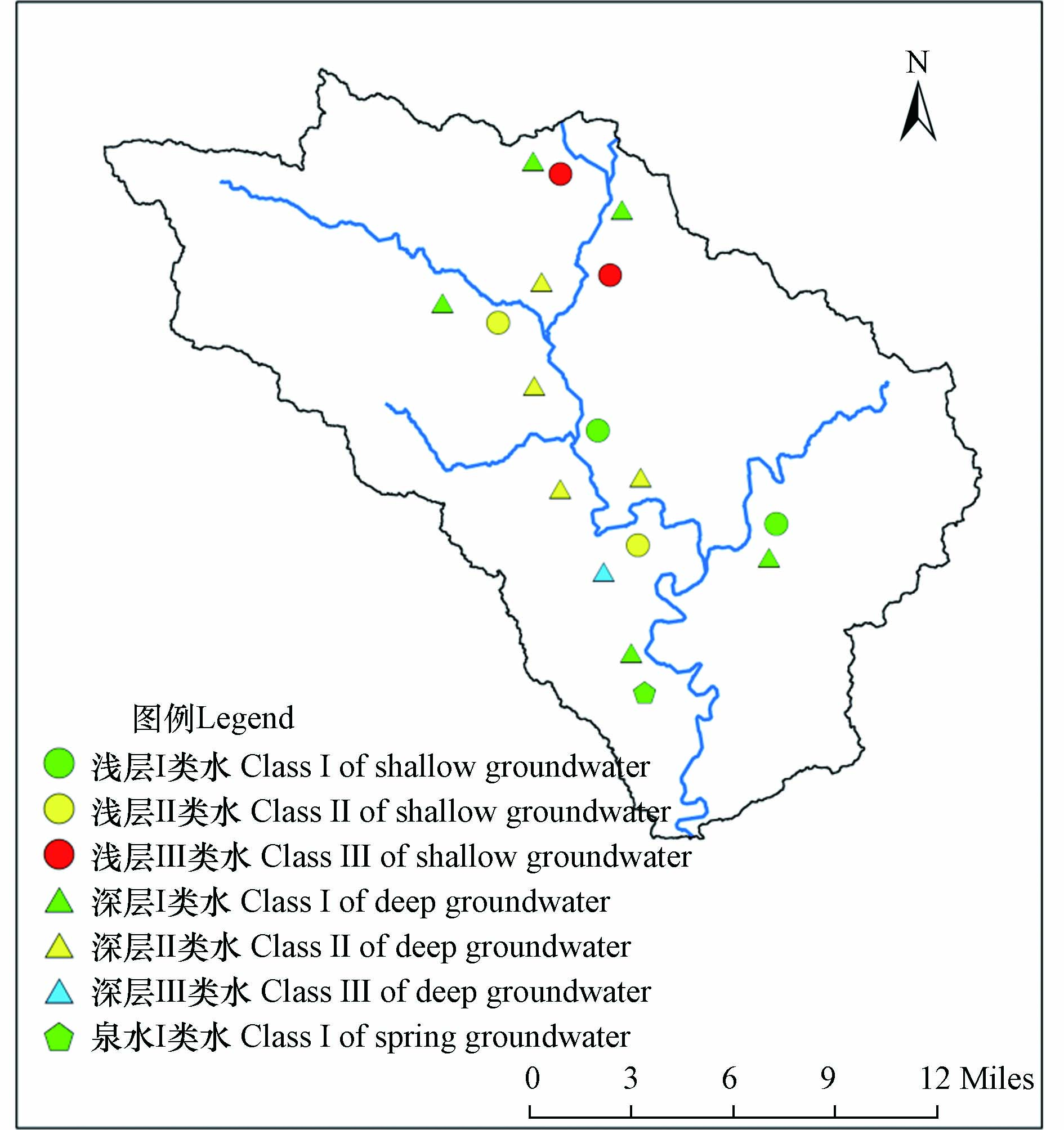
绘制研究区饮用水源水质分布图,如图7所示,丹河下游水质整体好于上游,其原因主要为流域上游为平原丘陵区,人类活动明显,且村庄多沿河道分布,生活污水和农业污染对水质影响较重;而流域下游为高山区,河道从峡谷穿过,无污染源输入,因而水质较好. 在丹河上游,浅层水主要为Ⅳ类水,而深层水主要为Ⅰ类水,说明上游深层水与浅层水之间没有水力联系,深层水主要来源于侧向补给,水质不受上层污染影响;而在丹河中游,浅层水与深层水水质具有一致性,说明两水存在补给关系.
-
研究区内的地表水、浅层水、深层水及泉水均用于农业灌溉,因此对区内4种类型的水体采用基于SAR-SSP的灌溉水质评价法,评估其用于灌溉引起的土壤盐碱危害. 如图8,USSL图[32]的全区被划分为16个子区域,左下角水质最好,右上角水质最差[7];Wilcox图[32]的全区被划分为5个区域,分别为水质优秀区、良好区、可接受区、保留区及不适宜区[33].
以水体EC值(盐害)为横坐标,SAR值(碱害)为纵坐标,绘制灌溉水质分类USSL图,如图8(a)所示,1个地表水、4个深层水和1个泉水取样点位于C2-S1区域,其余取样点均位于C3-S1区域,表明研究区内水样碱度危害很低,但盐度危害以中、高为主,且地表水和浅层水的盐度危害风险明显高于深层水和泉水,其中盐度危害最严重的分别为A1和A2水样点,长期用于农业灌溉可能会有土壤盐害风险[34]. 根据马贵仁等[35]的研究发现,适当施加有机肥和生物肥可降低土壤盐害. 以水体EC值(盐害)为横坐标,SSP(碱害)为纵坐标,绘制灌溉水质分类Wilcox图,如图8(b)所示,1个地表水、4个深层水和1个泉水取样点位于水质优秀区,10个地表水、6个浅层水和6个深层水取样点位于水质良好区,只有1个地表水取样点位于水质保留区,表明研究区内绝大多数水体水质较好,可直接用于灌溉. Wilcox图中A1和A2水样点相对其他水样点水质最差,与USSL图分析结果一致,说明研究区上游的地表水不符合灌溉用水需求,应当优先采用地下水进行农田灌溉.
-
通过对丹河流域泽州段地表水、地下水及泉水的水化学特征及水质研究,得出以下结论:
(1)研究区不同水体pH均呈弱碱性,且大小关系为地表水>深层水>浅层水. 水体TDS介于192—1051 mg·L−1之间,绝大多数属于淡水,但地表水仍存在少量微咸水. TDS和F−浓度在垂向上呈现由上至下逐渐减小的趋势.
(2)地表水主要阳离子含量关系为Na+>Ca2+>Mg2+>K+;浅层水和深层水为Ca2+>Na+>Mg2+>K+. 地表水与浅层水阴离子含量关系为SO42−>HCO3−>Cl−;深层水为HCO3−>SO42−>Cl−. 地表水和浅层水的水化学类型主要为HCO3·SO4-Ca·Na;深层水和泉水主要为HCO3·SO4-Ca;整体而言,在地表水下渗的过程中,阳离子倾向于由Ca-Na型向Ca型转变,阴离子倾向于由SO4型向HCO3型转变.
(3)研究区水化学特征的主控作用为岩石风化,且地表水还受到蒸发浓缩作用的影响. 水化学组分主要来源于硅酸盐岩溶解;且还存在蒸发盐岩溶解、碳酸盐岩溶解及阳离子交换作用.
(4)研究区水质主要受到氨氮和硫酸盐超标的影响,饮用水水质评价结果显示,66.7%的浅层水、100%的深层水和泉水符合Ⅲ类水标准,适合人体饮用. 灌溉水水质评价结果显示,研究区内绝大多数地表水的水质较好,可直接用于灌溉;少量地表水的盐害风险较高,可适当施加有机肥和生物肥.
丹河流域(泽州段)不同水体水化学特征及水质评价
Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of different water bodies in Zezhou section of Danhe River Basin
-
摘要: 为研究丹河流域不同水体水化学特征及水质现状,采用相关性分析、Piper三线图、氯碱指数及主要阴阳离子比值等多种水化学方法,对地表水、浅层水、深层水及泉水的水化学特征进行分析,并基于熵权-模糊综合评价法和Wilcox、USSL图解法进行水质评价,结果表明:(1)区内水体均呈弱碱性;TDS和F−浓度由上至下逐渐减小. (2)地表水和浅层水的水化学类型主要为HCO3 SO4-Ca·Na;深层水和泉水主要为HCO3·SO4-Ca;在地表水下渗过程中,阳离子倾向于由Ca-Na型向Ca型转变,阴离子倾向于由SO4型向HCO3型转变. (3)研究区水化学特征主要受岩石风化作用控制;水化学组分主要来源于硅酸盐岩溶解,且还存在蒸发盐岩溶解、碳酸盐岩溶解及阳离子交换作用. (4)水质评价结果显示,66.7%的浅层水、100%的深层水和泉水适合人体饮用;部分地表水的灌溉盐害风险较高. 该研究明确了区内不同水体水化学特征及水质现状,结果可为水资源开发及保护提供有效依据.
-
关键词:
- 水化学特征 /
- 水质评价 /
- 熵权-模糊综合评价法 /
- 丹河.
Abstract: In order to study the hydrochemical characteristics and water quality status of different water bodies in Danhe River Basin, the hydrochemical characteristics of surface water, shallow groundwater, deep groundwater and spring water were analyzed by using various hydrochemical methods such as correlation analysis, Piter trilinear, chlor alkali index and the ratio of main cation and anion. The water quality was evaluated based on entropy weight fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method and Wilcox and USSL graphical methods. The results showed that: (1) The water bodies in the area were weakly alkaline; The concentrations of TDS and F−decreased gradually from top to bottom. (2) The hydrochemical types of surface water and shallow groundwater are mainly HCO3·SO4-Ca; The deep groundwater and spring water are mainly HCO3·SO4-Ca; In the process of surface water infiltration, cations tend to change from Ca-Na type to Ca type, and anions tend to change from SO4 type to HCO3 type. (3) The hydrochemical characteristics of the study area are mainly controlled by rock weathering; The hydrochemical components mainly come from the dissolution of silicate rocks, and there are also evaporation salt rock dissolution, carbonate rock dissolution and cation exchange. (4) The results of water quality evaluation show that 66.7% of shallow groundwater, 100% of deep groundwater and spring water are suitable for human consumption; Some surface water has high risk of salt damage. The study clarified the hydrochemical characteristics and water quality status of different water bodies in the area, and the results can provide an effective basis for water resources development and protection. -
挺水植物(emergent macrophytes),作为水生植物的重要类型以及淡水水域重要的初级生产力之一,对淡水生态系统具有重要作用. 挺水植物地上组织(茎和叶)挺出水面,而地下组织(根或根茎)一般生长于水陆交界处浅水区域沉积物中[1 − 2]. 挺水植物主要从沉积物中获取生长所需营养物质[3 − 5],其庞大根系所在区域(根区)微生物数量和种类远高于非根区沉积物,形成明显的根际效应[6 − 8]. 因此,挺水植物根区是沉积物-根系-微生物三者紧密结合相互影响的关键场所,其影响可归纳为以下方面:一方面,挺水植物通过其根系向沉积物输送氧气,促进了好氧条件下营养元素的物质循环[9]. 如成水平等[10]发现植物根系泌氧将增强硝化过程提高沉积物硝态氮(NO3−-N)含量. 王文林等[9]则报道菖蒲成株根系的氧扩散能力显著高于幼苗阶段,这可能与植物叶面积以及根系生物量、根表面积的大小等有密切关系. 可见,挺水植物的氧气扩散能力受物种以及生长阶段的强烈影响;另一方面,挺水植物的根系能释放超过200种的分泌物,如糖、氨基酸、有机酸等,这些分泌物不仅影响根区沉积物的微生境,还为沉积物微生物提供了碳源和营养物质[11],使根际微生物的数量及代谢活性远高于非根际沉积物[12]. 因此,吴林坤等[13]等认为,根系分泌物对根际微生物具有选择塑造作用,其群落结构的独特性与代表性将受植物物种差异以及生长阶段的影响. 可见,物种及其生长阶段将是影响挺水植物根区微生物的关键因子.
菖蒲(Acorus calamus),天南星科菖蒲属,典型的多年生挺水植物,广泛分布于河流、沼泽以及湖泊岸边等浅水水域. 菖蒲根系发达,对氮、磷等营养盐有很强的吸收能力[2,9,14],加之其形态美观,常被用于人工湿地或园林景观中[7]. 近年来,关于菖蒲根区沉积物微生物已有一些研究报告. 如顾诗云等[2]研究了淹水胁迫对菖蒲生理特性及其根际细菌群落特征的影响. 寄博华[15]发现斗南湿地菖蒲植物群丛沉积物细菌群落的丰富度和多样性均最大,高于芦苇和美人蕉植物群从. 赵良元等[16]通过90 d的培养发现,菖蒲的生长可大大提高沉积物中微生物的活性及多样性. 但现有研究均仅为短期内针对菖蒲的培养实验所获得的结果,对不同生长阶段菖蒲根区沉积物微生物的变化特征的认识仍十分不足.
本研究通过为期 175 d的培养时间,基于16S-rRNA高通量测序技术并结合FAPOTAX功能预测,探究菖蒲根区沉积物细菌群落结构和功能特征在三个生长阶段(生长期、成熟期、衰亡期)的差异,以期进一步阐明挺水植物的生长对其根区细菌群落结构及其功能组成的影响.
1. 材料与方法 (Materials and methods)
1.1 植物和沉积物准备
本研究所用菖蒲和沉积物采自江苏大学校内湖泊(119°30′23'' E,32°11′58'' N),所采植物株高约60 cm,块状茎保持完整. 采样完成后,将植物样品迅速带回实验室后,用自来水冲洗根系以及植物表面泥土等供后续实验所用;表层沉积物(0—20 cm)样品带回实验室后用不锈钢网(20目)先过滤掉大颗粒以及各种杂质,然后使用混合器彻底将所采沉积物样品混合均匀,以确保各实验系统沉积物初始状态一致.
1.2 实验系统构建及样品采集
采用直径40 cm,深度60 cm的圆形桶作为实验容器. 首先在各实验桶中铺设预先混匀的30 cm厚沉积物,将所采植物种植于各实验桶(CA),随后沿桶壁注入自来水,注水深度为桶壁45 cm处;另设一组不种植植物的系统作为对照(CK,仅包含沉积物和水体). 实验组和对照组分别设置3组重复. 实验过程中,定期补充各实验桶中自来水,以确保上覆水始终在同一深度. 实验于2022年5月—11月在室外培养(培养环境可以避免降雨的影响),共培养175 d.
实验第35、105和175 天时分别采集各实验桶内沉积物样品,按照菖蒲生长习性,这3次采样时间可代表菖蒲的旺盛生长期、成熟期和衰亡期. 采集的沉积物随机分成两部分,一部分经干燥、研碎、混匀、过100目筛,自封袋封装,于4 ℃保存,供沉积物理化指标测定,另一部分于 −25 ℃条件下保存用于沉积物NO3−-N和微生物测定.
1.3 沉积物理化指标测定
沉积物pH值(固水比为2.5:1)采用pH计测定(雷磁PHSJ-3F,INESA,上海);沉积物全碳(TC)和总氮(TN)采用元素分析仪(Vario EL cube,德国)测定;沉积物硝态氮(NO3−-N)和氨态氮(NH4+-N)用 2 mol·L−1 氯化钾(KCL)浸提后用紫外可见分光光度计(N4)测定;有机物质(O.M)采用水合热重铬酸钾氧化-比色法(《土壤农化分析》)进行测定;总磷(TP)采用高氯酸-浓硫酸(HClO4-H2SO4)消煮后用钼锑抗比色法测定.
1.4 沉积物细菌测定
沉积物样品通过FastDNAchen® Spin Kit for Soil试剂盒提取总DNA,每个样本3个重复. 通过1%的琼脂凝胶电泳检测DNA提取质量,使用NanoDrop 2000测定DNA浓度和纯度. 采用细菌通用引物338F (5'- ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3') 和 806R (5'-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3') 对细菌16S rRNA 基因 V3-V4 区进行 PCR 扩增. PCR体系为 20 μL,含有 5×FastPfu Buffer 缓冲液 4 μL,2.5 mmol.L−1 d NTPs 2 μL,正向引物0.8 μL,反向引物0.8 μL,FastPfu 聚合酶 0.4 μL,BSA 0.2 μL,模板DNA 10 ng,最终ddH2O至 20 μL. PCR扩增程序为:95 ℃ 初始变性3 min,随后95 ℃ 变性30 s,55 ℃ 退火30 s,72 ℃ 延伸45 s共27个循环,最后72 ℃ 延伸10 min,10 ℃ 结束. PCR扩增产物通过2% 琼脂糖凝胶胶电泳检测,后委托上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司(Illumina Miseq PE300平台,美国)完成高通量测序.
1.5 数据的分析与处理
原始序列经质控、过滤、拼接后利用UPARSE 软件(http://drive5.com/uparse/)进行聚类,得到97% 相似水平下的操作分类单元(OTU). 本研究中按最小样本序列数将各样品抽平处理后共得到13835个OTUs. 基于所获OTUs,经RDP classifier(https://sourceforge.net/projects/rdp-classifier/,RDP:http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/)获得各样品细菌物种分类信息(分类置信度:0.7);通过Mothur软件计算各实验组沉积物样品细菌Alpha多样性指数(Shannon、Simpson、Sobs、ACE和Chao);采用非度量多维尺度分析(non-metric multidimensional scaling,NMDS)解析菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物细菌群落Beta多样性;基于韦恩图(Venn)和柱形图研究沉积物细菌物种组成和相对丰度的变化;采用冗余分析(RDA)、相关热图分析(Correlation heatmap diagram)、排序回归分析(Sorting regression analysis)和 Mantel Test等方法评价细菌群落与沉积物理化参数之间的关系. 使用FAPROTAX(functional annotation of prokaryotic taxa)对微生物群落进行功能预测. 通过Wilcoxon秩和检验(对照组CK与菖蒲组CA)和 Kruskal-Wallis H检验(3个培养时间)对细菌群落Alpha多样性指数和优势门显著性差异进行检验;通过相似性分析(Analysis of similarities,ANOSIM)以及置换多元方差分析(Permutational Multivariate Analysis Of Variance,PERMANOVA)对群落结构差异进行统计学分析. 以上与微生物相关的分析均在美吉生物云平台在线完成 (http://cloud.majorbio.com). 其他数据(平均值±标准差)采用 Microsoft Excel和 SPSS 软件进行计算与分析. P<0.05和P<0.01分别为差异显著和差异极显著.
2. 结果与讨论 (Result and discussion)
2.1 沉积物的理化参数的变化
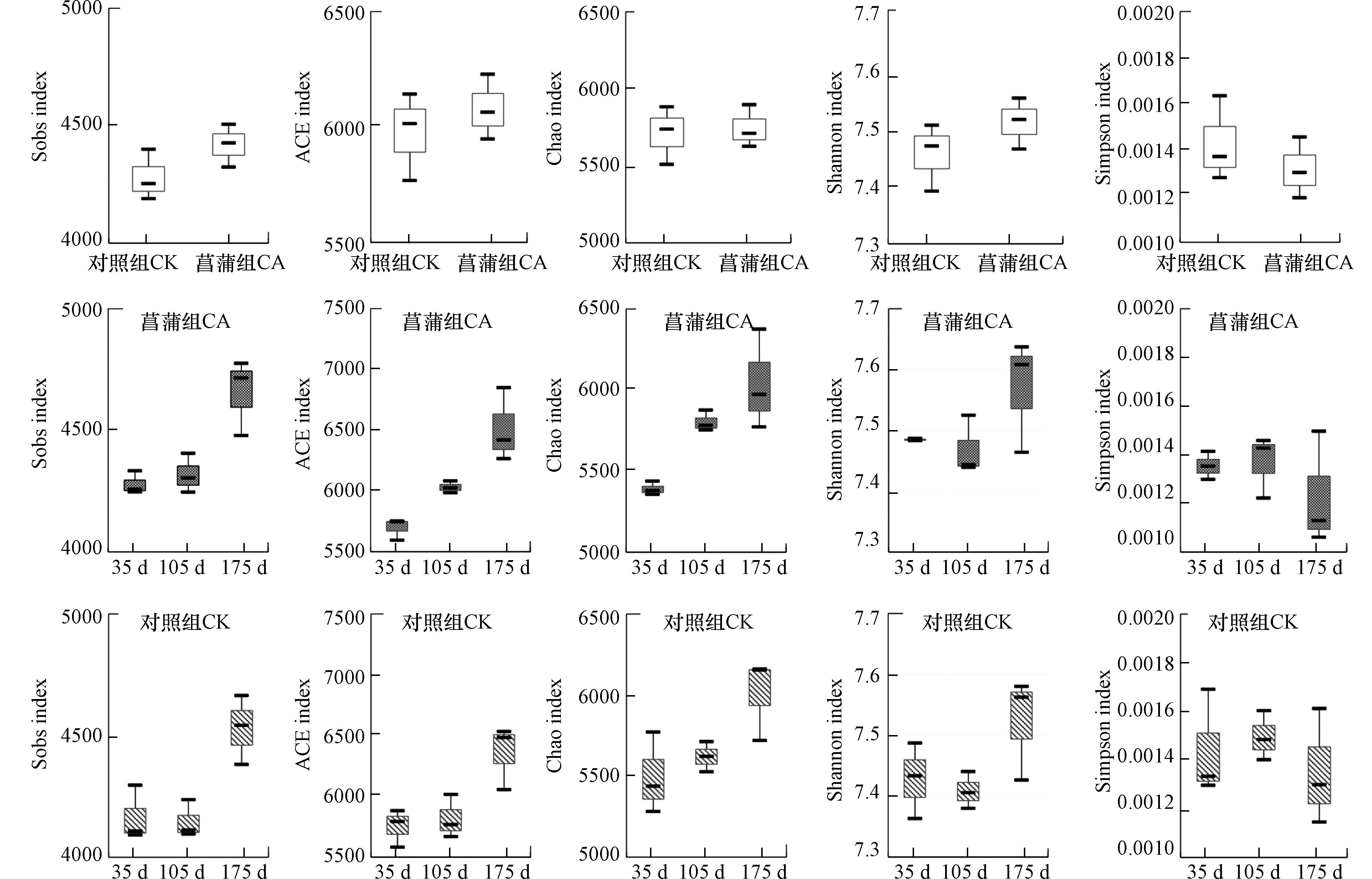
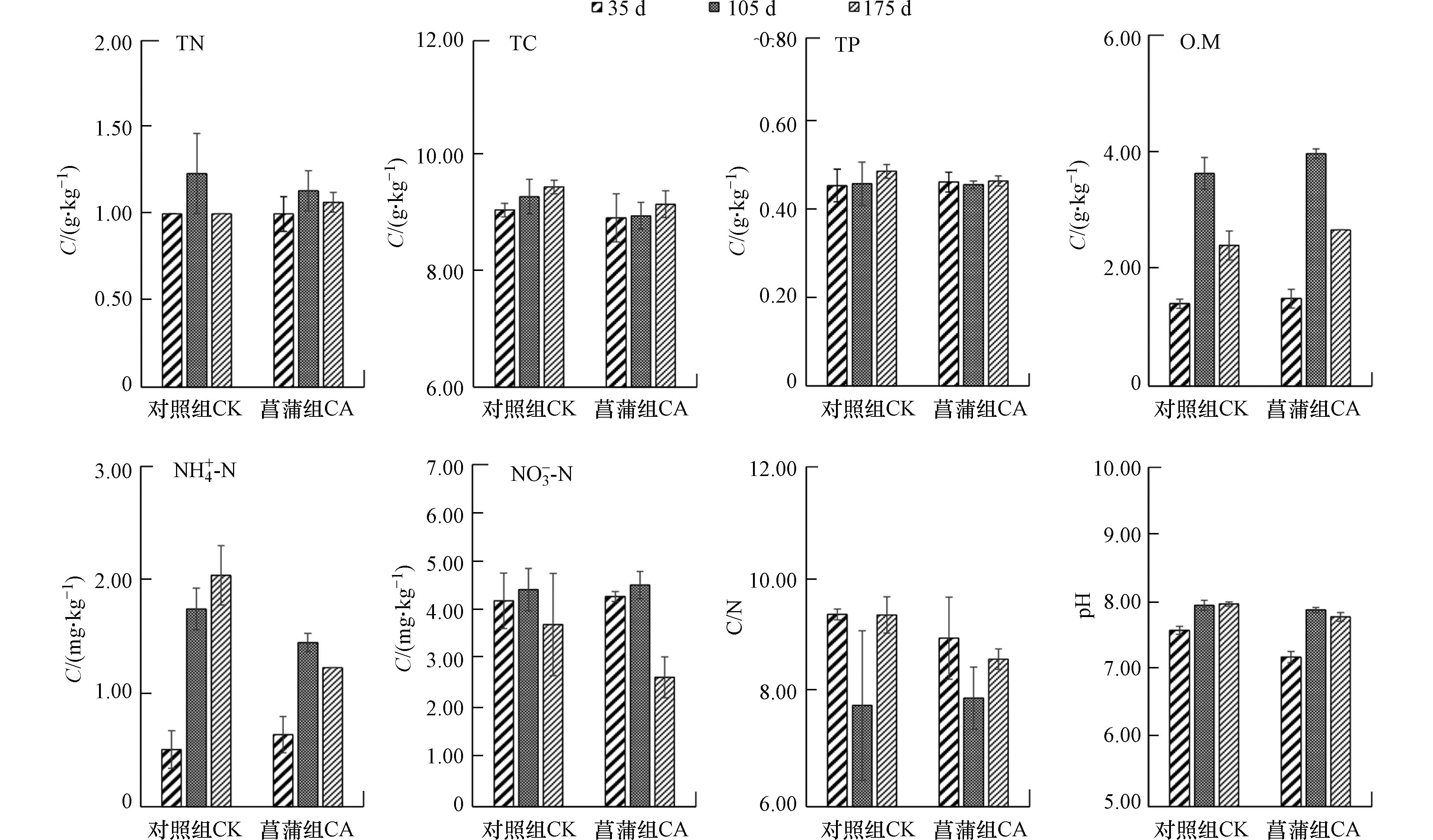
实验期间,菖蒲根区和对照系统中沉积物pH值分别介于7.15—7.91以及之间7.60—8.03,呈弱碱性(图1). 实验过程中菖蒲组沉积物pH值始终低于对照组,这与菖蒲根系活动及其根系分泌物有密切关系,其影响途径表现在:植物根系呼吸所释放的二氧化碳以及分泌的有机酸类等物质,在一定程度上降低了沉积物pH值[17];此外,植物根际微生物的活动所产生的酸性物质也可降低根际土壤pH值[13]. 张金萍[18]针对挺水植物香蒲的研究证实了同样的规律.
菖蒲根区沉积物TN、NH4+-N、NO3−-N的平均含量分别为1.07 g·kg−1、1.10 mg·kg−1和3.83 mg·kg−1,稍低于对照组氮素含量,其值分别为1.08 g·kg−1、1.43 mg·kg−1以及4.13 mg·kg−1(图1). 菖蒲根区沉积物和对照系统沉积物TC含量分别介于8.60—9.40 g·kg−1以及9.00—9.60 g·kg−1之间(图1),表现为对照>菖蒲. 菖蒲庞大的根系组织将吸收沉积物中碳氮磷等营养元素以供植物良好的生长发育,在这一过程中植物根区沉积物元素含量有所下降. 这与余居华等[4]研究的结果一致. 陈登等[19]同样证实水生植物水蕴草(Egeria densa)、狐尾藻(Myriophyllum verticillatum)和苦草(Vallisneria natans)能显著降低了沉积物铵态氮含量,除了植物根系的直接吸收外,根区沉积物氮循环菌所驱动的硝化-反硝化以及厌氧氨氧化等作用也是铵态氮含量降低的原因之一. 此外,生长过程中挺水植物往往通过根系释放氧气和氧化性物质[20],从而在植物根系表面形成铁锰氧化物胶膜等具有胶体性质的物质,可进一步促进植物根系对磷的吸收,降低根际沉积物磷元素的含量[18]. 对于O.M来说,植物根区及对照系统沉积物中含量分别为1.39—4.05 g·kg−1和1.33—3.93 g·kg−1(图1),表现为对照<菖蒲. 以上结果证实了菖蒲的生长对沉积物理化参数将产生一定的影响.
进一步分析了沉积物理化参数随采样时间的变化规律. 结果发现(图1),菖蒲根区沉积物TN、NH4+-N、O.M以及pH值大小顺序为105 d>175 d>35 d;TP表现为:175 d>35 d>105 d;TC含量表现为175 d>105 d>35 d,沉积物C/N则表现为35 d>175 d>105 d,表明植物根区沉积物理化参数随植物生长发育而波动变化. 对于菖蒲而言,从快速生长期到成熟期,植物快速生长,根系活力增强,植物需从沉积物中获取大量氮素用于自身生长发育,对周围环境的影响也较大;如王文林等[9]利用溶氧微电极发现,菖蒲幼苗、成株根系的不同部位均存在从根表面至沉积物氧饱和度由高到低的氧扩散层,证实了不同生长阶段菖蒲根系氧扩散能力的差异. 加之本研究在该时间段环境温度较高(平均温度29.8 ℃),加剧了沉积物中微生物的生长代谢过程. 当植物进入衰亡阶段,植物生理活动减缓,且逐渐开始衰亡,部分植物残体及根系脱落物等进入沉积物并开始腐烂,在短时间内可增加沉积物元素含量. 对于对照系统沉积物而言,沉积物TN、NO3−-N以及O.M值最高值出现在实验第105 d,NH4+-N、TC、TP以及pH值峰值则出现在实验第175 d;沉积物C/N在实验第35 d最高,其次为175 d,最低值出现在实验第105 d. 由此可见,实验过程中,无植物的对照系统以及菖蒲根区沉积物理化因子均随培养时间呈现不同变化趋势的波动.
2.2 菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物细菌群落特征分析
对3个采样时间所采菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物样品进行高通量测序及数据分析,共得到13835个OTUs,分属64门、201纲、477目、768科、1430属和3256种. 其中,菖蒲根区沉积物样品中共检测到OTUs共计11659个(细菌63门196纲455目733科1339属2991种),对照组沉积物共获得OTUs数量为10337个(细菌62门196纲450目709科1290属2863种). 基于OTUs,对沉积物中细菌群落Alpha多样性、Beta多样性以及物种组成特征等进行分析.
2.2.1 菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物细菌群落Alpha多样性差异分析
细菌群落的多样性对于维持沉积物的稳定性和功能具有重要的生态意义[21 − 22]. Shannon和Simpson指数指示了物种的多样性,Shannon指数与物种多样性成正比,该指数越大,群落多样性就越高[15],而Simpson指数则与物种多样性成反比[23];Sobs、ACE和Chao指数表示了物种的丰富度,指数越大意味着群落丰富度越高[15]. 本研究对菖蒲根区及对照沉积物细菌群落Alpha多样性指数(Shannon、Simpson、Sobs、ACE和Chao)的统计结果见图2所示. 沉积物细菌群落Shannon、Sobs、ACE和Chao指数平均值表现为CA>CK,而Simpson指数平均值则切好相反,表明菖蒲的生长在一定程度上提高了沉积物细菌的丰富度以及多样性(图2). 马玉等[20]利用菖蒲湿地处理含油废水时同样发现菖蒲根区功能性微生物种类和数量多于对照区域,这与植物庞大的根系为微生物附着提供的更大的表面积和附着点[24]以及植物根系分泌物为附着微生物提供碳源和营养物质等有密切关系[19,25]. 此外,植物根系可以通过一系列行为,如改变水流速度、沉降特性和水里传导率等[26],为细菌的粘附和生长提供有力的条件,从而提高沉积物中的微生物的多样性.
进一步,对三个采样时间沉积物样品Alpha多样性指数进行分析(图2). 由图2可知,CA组沉积物Sobs、ACE和Chao指数随实验时间的增加呈增加趋势,表现为35 d<105 d<175 d. 基于Kruskal-Wallis秩和检验,ACE、Chao和Sobs指数在第35和第175 天之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),ACE、Sobs指数在第105 天与第175 天亦有显著差异(P<0.05). ACE、Chao和Sobs指数的变化证实了菖蒲的不同生长阶段对其根区沉积物细菌群落丰富度将产生不同的影响. CA组沉积物Shannon指数最高值分别出现在实验第175 d,最低值出现在105 d,Simpson指数变化趋势与Shannon值恰好相反,即105 d>35 d>175 d. 线性回归模型显示,ACE、Sobs和Chao指数与培养时间成显著正相关(ACE指数:y=5.058x+5495.908,P<0.01;Sobs指数:y=2.644x+4071.042,P<0.01;Chao指数:y=4.153x+5290.131,P<0.01).
2.2.2 菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物细菌群落Beta多样性
细菌群落Beta多样性主要聚焦于不同生境间微生物群落结构多样性的比较[23,27],群落结构特征的差异是微生物与所处生境相互响应的结果[23]. 基于Bray-Curtis距离算法(OTUs水平)通过NMDS对各实验组沉积物细菌群落结构进化了可视化分析(图3). 由图3可知,CK和CA实验组沉积物细菌群落结构可分成重叠的两个区域,PERMANOVA结果证实了两个系统沉积物细菌群落结构无显著差异(F=0.950;R2=0.056;P>0.01). 尽管CK和CA实验组沉积物细菌群落结构呈现重叠,但图3显示,无植物的对照系统各样点间距离较近,意味着对照系统各样点沉积物细菌群落结构波动较小,而菖蒲根区沉积物各样品间更为离散,表明菖蒲系统中沉积物细菌群落结构变化较大,这可能是菖蒲在生长过程对沉积物的影响所致. 由图3可知,同一时间所采样品集聚起来,3个采样时间菖蒲根区沉积物细菌群落则明显区分成3个区域,尤其是第35 天所采样品与第105和175 天时区分明显(ANOSIM,P<0.01). PERMANOVA进一步验证了3个采样时间菖蒲根区沉积物细菌群落结构差异显著(F=1.64;R2=0.353;P<0.01). 张丁予等[28]等同样发现,植物根区沉积物微生物群落结构随着生长周期变化而变化,而且时间越长差异越显著,这与植物不同生长阶段根系活力以及根系分泌物的变化有密切关系. 植物生长过程中,其根系可分泌包括糖、氨基酸、有机酸、生物酶等多达200种以上的物质,这些物质敏感地响应植物的不同生长状态,并因此为微生物的生存创造良好的条件[1, 29].
2.2.3 菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物细菌群落组成
基于OTUs绘制韦恩图对菖蒲根区及对照系统各样品中共有和独有细菌进行分析(图4). 由图4a可知,整个实验过程中,菖蒲根区及对照系统中共有的细菌OTUs为8161,占OTUs总数的58.99%,意味着超50% 的细菌同时存在于菖蒲根区以及无植物的对照系统沉积物中. 进一步分析后发现,菖蒲根区沉积物和对照组沉积物样品中独有的OTUs数量分别为3498和2176,分别占总OTUs的25.28% 以及15.73%,独有的OTUs反映了不同来源样本中细菌群落组成的差异性. 相比于对照组而言,菖蒲根区独有的OTUs数量略高,意味着植物生长可能会丰富根区沉积物细菌的物种组成,在植物根区沉积物中细菌群落的多样性更好,物种组成更为丰富,这与菖蒲根区沉积物细菌Alpha多样性的结果一致.
门水平(Phylum)上(图4b),菖蒲根区和无对照系统沉积物细菌群落相对丰度前10的门主要为变形菌门(Proteobacteria,21.21% 和19.34%),绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi,17.29% 和17.42%)、酸杆菌门(Acidobacteriota,13.05% 和14.30%)、放线菌门(Actinobacteriota,10.60% 和11.69%)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes,4.539% 和5.474%)、脱硫菌门(Desulfobacterota,5.192% 和4.613%)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota,4.258% 和4.358%)、粘菌门(Myxococcota,3.871% 和3.524%)、硝化螺旋门(Nitrospirota,2.569% 和2.384%)和芽单胞菌门(Gemmatimonadota,1.648% 和1.734%),这10类约占总测序序列的84.22%—84.83%. 以上优势菌群在淡水沉积物中已被广泛检出[10,28]. 顾诗云等[2]发现菖蒲根际细菌优势门类为变形菌门、拟杆菌门、绿弯菌门、酸杆菌门和厚壁菌门;秦玉春等[24]发现5种湿地植物根系沉积物优势菌门均为变形菌门、放线菌门和拟杆菌;寄博华等[15]同样发现变形菌门、绿弯菌、放线菌门以及酸杆菌门为滇池湖滨湿地3种优势挺水植物(菖蒲、芦苇、美人蕉)根区沉积物的优势细菌门. 这些优势细菌群落中,变形菌门在生物脱氮除磷和降解污染物等方面均发挥重要作用[11,17,24]. 绿弯菌门为光能自养菌,该类群可通过光合作用产生能量,在湿地中广泛存在,且与沉积物碳循环有关,具有发酵、固定二氧化碳(CO2)和乙酸化作用[23,30]. 绿弯菌门是本研究中相对丰度仅次于变形菌门的第二大优势细菌,现有研究证实菖蒲根际对绿弯菌门具有选择性,且随着菖蒲的生长其选择性不同[31]. 绿弯菌门可从环境中吸收和同化多种生物和非生物来源的有机物,菖蒲根区大量存在的绿弯菌门为其改善沉积物环境提供了有力条件. 放线菌门和酸杆菌门则被认为是重要的根际细菌[15,25],尤其是放线菌门,大部分固氮细菌以及部分硝化、反硝化细菌等菌属于该门类,在氮循环中占有重要地位[32]. 本文研究发现,随菖蒲的生长其根区沉积物芽单胞菌门以及甲基菌门(Methylomirabilota)等细菌类群相对丰度差异显著(Kruskal-wallis秩和检验,P<0.05),具体表现为:根区沉积物细菌芽单胞菌门、甲基菌门相对丰度随着菖蒲的生长而逐渐减少,其原因可能在于同一生境中,优势菌的丰度较高会对其它非优势菌群的生存产生压迫[31],从而导致其相对丰度的下降.
在纲水平(Class)上,相对丰度前10位的优势纲占据菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物细菌群落的57.21% 和57.11%. γ‐变形菌纲(Gammaproteobacteria)、厌氧蝇菌纲(Anaerolineae)、α-变形菌纲(Alphaproteobacteria)、Vicinamibacteria和拟杆菌纲(Bacteroidia)为菖蒲根区沉积物细菌群落相对丰度前5的纲. 其中,α-变形菌纲和γ-变形菌纲属于变形菌门中2个亚类,该门还包括δ-变形菌纲(Deltaproteobacteria)和ε-变形菌纲(Epsilonproteobacteria)2个亚类. 拟杆菌纲是拟杆菌门中的优势类群,厌氧蝇菌纲则为绿弯菌门中主要亚类. 此外,共有6个纲在植物及对照系统中存在显著差异(Wilcoxon rank-sum test,P<0.05),且相对丰度均小于1%. 研究表明,α-变形菌纲、β-变形菌纲(Betaproteobacteria)和γ-变形菌纲含有许多反硝化细菌,可促使自养或异养反硝化过程[15,26]. 此外,刘忠航等[33]发现,α-变形菌纲中的部分菌群可以利用有机磷,加速有机磷的矿化,在沉积物磷元素循环中亦发挥重要作用.
而在目水平(Order)上,菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物各样品共有13个目相对丰度小于1%的物种存在显著差异(Wilcoxon rank-sum test,P<0.05). 属水平(Genus),CA和CK组沉积物分别有15个和16个优势物种相对丰度大于1%,分别占26.87% 和29.44%;两组沉积物中细菌群落组成属水平上相对丰度小于 0.5% 的菌属分别占了51.29% 和48.26%. 统计分析后发现共有36个相对丰度低于 0.5% 的属在菖蒲根区以及对照沉积物二者间存在显著性差异(Wilcoxon rank-sum test,P<0.05). 综合纲、目、属水平的分析结果可知,菖蒲的生长可能对沉积物细菌群落中占比较小的物种产生更显著的影响.
植物不同生长阶段,其优势菌群的变化,可能与植物生长不同阶段所分泌的不同根系分泌物对微生物产生促进或抑制作用有关[11,34],也可能受根系泌氧的因素所致. 研究表明,植物根系在促使微生物富集等方面发挥着至关重要的作用[15]. 受植物物种以及所处生长阶段差异等因素的影响,植物根系形态、根系分泌物、根系泌氧量等呈现明显差异,这些因素将驱动植物根区微生物群落的影响变化[15]. 如张丁予[28]报道,根系发达的植物其分泌的营养物质可以有效地提高根际微生物的数量. 菖蒲是典型的挺水植物,其根系非常发达,属于毛发状须根,可扎入沉积物中并从多方面对沉积物产生影响. 一方面:本文研究证实了植物生长对根区沉积物理化参数的影响. 研究发现3次采样所获菖蒲根区沉积物pH值均小于无植物生长的沉积物,其原因在于植物根系呼吸释放二氧化碳以及分泌有机酸类物质,在一定程度上降低了沉积物pH值[20]. 此外,前人研究表明,菖蒲等挺水植物可通过径向泌氧(ROL)补充水体溶解氧[15,31],并因此对水-沉积物界面好氧微生物的生存提供条件. 本文研究证实了这一点,相对于无植物的对照沉积物,菖蒲根区沉积物存在更多的硝化螺旋菌属(Nitrospira)和亚硝酸菌属(Nitrosomonas),这与张丁予等[28]和Cordovez等[35]的研究一致,其发现根系越发达的植物其分泌的营养物质可以更有效地提高根际微生物的数量.
2.3 菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物细菌功能预测分析
细菌是介导沉积物物质循环的主要微生物类群,在营养元素的生物地球化学循环中发挥着重要作用[36]. 沉积物细菌群落结构及物种组成的差异将在一定程度上影响其在物质循环中的潜力. 本文通过FAPROTAX对菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物细菌代谢及生态功能进行注释,共得到67种细菌群落功能类型,相对丰度最高的为化能异养(chemoheterotrophy)(21.36% 和21.83%),其次为需氧化能异养(aerobic chemoheterotrophy)(14.35% 和14.84%),发酵(fermentation)、固氮作用(nitrogen fixation)、光能自养作用(Photoautotrophy)、硝酸盐还原功能(nitrate reduction)等功能类群的相对丰度介于1%—10% 之间(图5). 有6个功能类型在菖蒲根区及对照系统沉积物样品中表现出显著差异(P<0.05),分别为氮呼吸(nitrogen respiration)、硝酸盐呼吸(nitrate respiration)、无氧光自氧硫氧化(anoxygenic photoautotrophy S oxidizing)、厌氧自养性(anoxygenic photoautotrophy)、动物寄生虫或共生体(animal parasites or symbionts)以及human pathogens all,这些差异性的功能类群涉及到沉积物氮和硫的循环过程.
氮代谢是生物地球化学循环的关键过程. 研究表明,氮代谢一般包括同化、氨化、固氮、硝化、反硝化和厌氧氨氧化过程[36 − 37]. 本研究中发现,硝酸盐呼吸所占丰度最高,其次为尿素分解功能(ureolysis)和亚硝酸盐呼吸(nitrite respiration). 反硝化作用(denitrification)、硝酸盐氨化(nitrate ammoniation)、亚硝酸盐氨化(nitrite ammoniation)、氧化亚氮脱氮(nitrous oxide denitrification)、硝酸盐反硝化(nitrate denitrification)、硝化作用(nitrification)以及氮呼吸等相对丰度在菖蒲根区及对照系统发生变化,相对丰度均表现为CA>CK,例如对功能预测相对丰度前20的菌群进行分析后发现菖蒲根区沉积物细菌群落硝酸盐还原以及氮呼吸作用功能相对丰度分别为无植物的对照系统的1.17倍以及1.31倍,证实菖蒲的存在对沉积物氮循环过程产生一定的影响,这种影响将随菖蒲的不同生长阶段而有所变化.
在硫循环中,菖蒲根区沉积物显著增加了暗硫化物氧化作用(dark sulfide oxidation)(与CK相比相对丰度增加了5.36%). 菖蒲的存在降低了沉积物无氧光自氧硫氧化的相对丰度(仅为对照系统的0.43)(P<0.05).
2.4 沉积物细菌群落影响因子分析
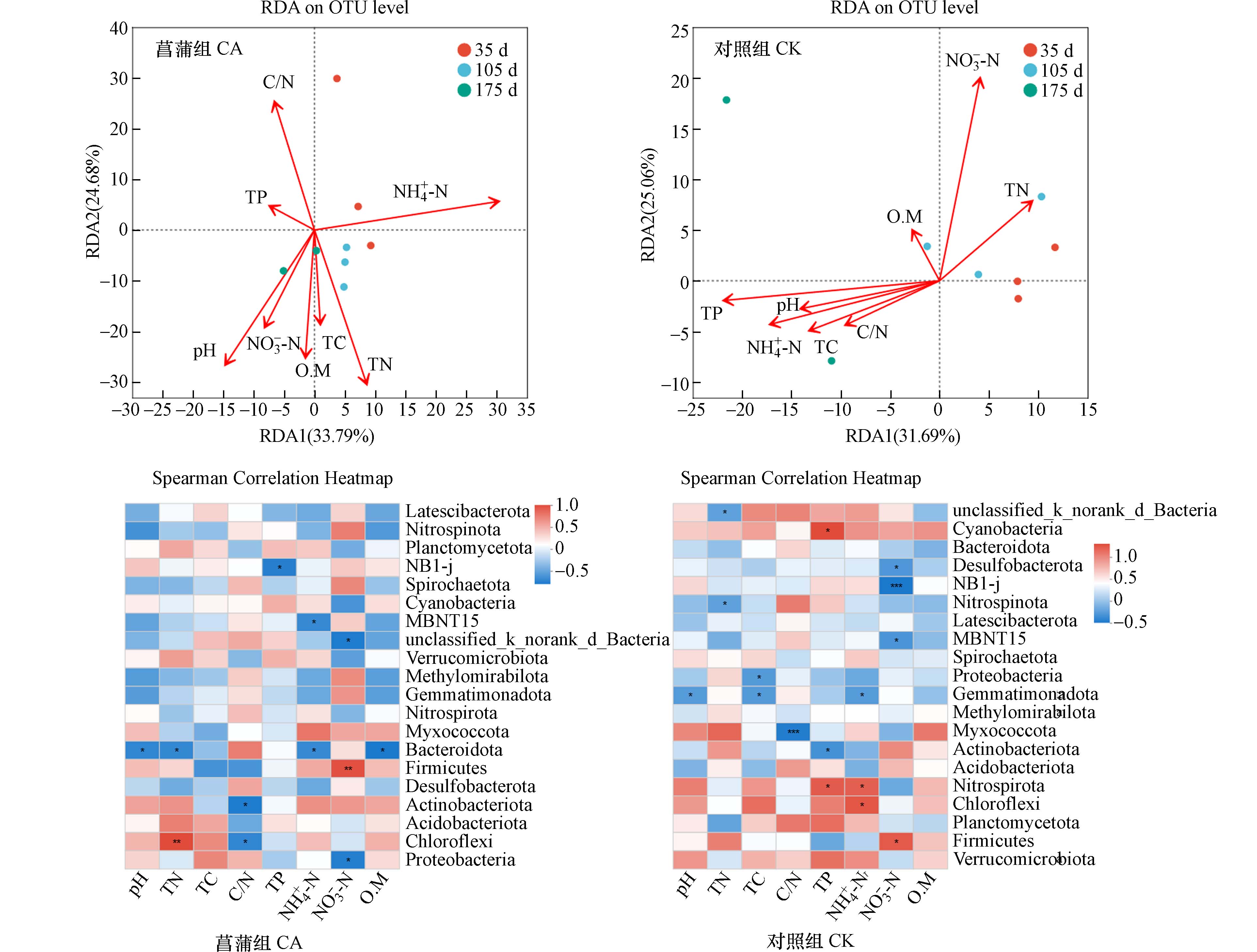
对沉积物理化参数与细菌群落Alpha多样性、Beta多样性以及群落物种组成以及功能特征间的作用关系进行分析. 结果发现,沉积物NO3−-N含量与Chao、Shannon和Sobs指数间呈显著相关关系(P<0.05),这与曹洋等[23]的研究相一致,其认为沉积物中细菌群落多样性随营养盐水平升高而下降.
基于Mantel分析(OTUs水平上)结果,菖蒲根区沉积物(Mantel r statistic:0.4046,P<0.05)和无植物对照系统沉积物(Mantel r statistic:0.4461,P<0.05)理化参数与细菌群落结构间存在显著相关关系(P<0.05). RDA分析(OTUs水平上)结果发现菖蒲根区以及对照沉积物理化特征对细菌群落结构变异的累计解释率分别为58.47% 和56.75%,菖蒲根区细菌群落受TN影响较多,而对照组则更受沉积物TP含量的影响. 这与马率等[17]的研究结果一致,其认为O.M和TN对沉积物微生物群落有明显的驱动作用.
除此之外,沉积物理化因子参数对细菌物种组成具有显著影响(图6). 如,对于菖蒲组而言,优势门变形菌门受沉积物NO3−-N的影响(P<0.05);绿弯菌门受到沉积物TN和C/N的影响(P<0.05);拟杆菌门则与沉积物pH、TN、NH4+-N以及O.M值之间存在显著相关关系(P<0.05);而对照组变形菌门受沉积物TC的显著影响(P<0.05).
3. 结论 (Conclusion)
挺水植物菖蒲的生长将提高植物根区沉积物细菌Alpha多样性并丰富细菌的物种组成,改变细菌群落的结构特征,这种影响随菖蒲生长发育的不同阶段而呈现显著差异. 基于FAPROTAX的功能预测证实了菖蒲的存在将对氮呼吸、硝酸盐呼吸、无氧光自氧S氧化以及无氧光自氧等涉及到沉积物氮和硫的循环过程的功能类群产生显著影响. 总之,本研究证实了菖蒲根区改变了沉积物原有细菌群落结构将引起沉积物细菌代谢及生态功能的变化,研究结果将对进一步揭示水生植物与微生物间的互作关系提供一定的依据.
-
表 1 水化学特征参数统计
Table 1. Statistics of hydrochemical characteristic parameters
水体类型Water type 统计量Wtatistics pH TDS Ca2+ Mg2+ Na+ K+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− F− 地表水Surface water(n=12) Max 8.69 1051.00 155.80 56.60 205.21 9.90 224.60 667.74 270.44 2.66 Me 8.23 709.50 94.29 40.47 102.71 7.33 116.24 369.21 215.36 0.40 Min 7.81 193.00 53.47 28.34 50.99 3.59 58.73 211.02 178.80 0.21 Mean 8.25 645.83 98.64 40.33 119.13 6.91 129.45 378.42 216.26 0.70 SD 0.20 234.42 23.69 9.60 46.21 1.74 58.70 124.83 23.98 0.67 CV 0.02 0.36 0.24 0.24 0.39 0.25 0.45 0.33 0.11 0.96 浅层地下水Shallow groundwater(n=6) Max 7.88 780.00 231.52 32.70 99.56 5.04 89.23 570.97 375.49 0.90 Me 7.54 601.50 180.17 31.92 84.18 3.43 59.16 292.09 306.05 0.32 Min 7.32 512.00 130.27 21.12 19.41 1.24 31.56 215.04 250.33 0.15 Mean 7.58 621.17 180.56 29.64 69.66 3.33 61.50 338.50 310.11 0.44 SD 0.21 87.55 34.54 4.11 30.50 1.44 20.12 118.22 46.77 0.27 CV 0.03 0.14 0.19 0.14 0.44 0.43 0.33 0.35 0.15 0.62 深层地下水Deep groundwater(n=10) Max 8.34 677.00 158.74 42.82 55.40 1.74 141.54 266.20 330.79 0.57 Me 7.81 435.00 99.50 28.49 29.79 1.07 50.37 140.42 297.26 0.33 Min 7.67 252.00 77.80 19.13 1.32 0.75 14.43 51.40 248.09 0.21 Mean 7.86 435.00 110.49 28.98 28.18 1.17 63.12 155.17 291.01 0.33 SD 0.19 133.01 24.73 6.44 20.83 0.30 37.17 68.09 21.21 0.11 CV 0.02 0.31 0.22 0.22 0.74 0.25 0.59 0.44 0.07 0.32 表 2 水体主要水化学组分相关性
Table 2. Correlation of main hydrochemical components of water body
水体类型Water type Ca2+ Mg2+ Na+ K+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− TDS F− pH 水体类型Water type 地表水Surface water Ca2+ 1 −0.04 −0.42 −0.62 0.03 0.68 0.11 0.72 −0.77 0.12 浅层地下水Shallow groundwater Mg2+ 0.55 1 −0.57 0.47 −0.61 0.39 −0.49 0.23 0.22 0.35 Na+ 0.73 0.58 1 0.91 0.81 −0.94 0.79 0.72 0.33 −0.31 K+ 0.74 0.71 0.94 1 −0.76 0.14 −0.80 0.53 0.49 0.38 地表水Surface water Cl− 0.71 0.81 0.92 0.88 1 −0.69 0.98 0.88 −0.23 −0.52 浅层地下水Shallow groundwater SO42− 0.86 0.67 0.95 0.90 0.85 1 −0.64 0.71 −0.48 0.34 HCO3− 0.14 −0.50 −0.14 −0.11 −0.33 0.04 1 0.62 −0.24 −0.38 TDS 0.63 0.09 0.73 0.59 0.64 0.76 0.16 1 −0.74 −0.58 F− 0.72 0.57 0.67 0.60 0.65 0.79 −0.01 0.64 1 0.09 pH −0.59 −0.13 −0.37 −0.32 −0.37 −0.42 −0.02 −0.48 −0.29 1 深层地下水Deep groundwater Ca2+ 1 Mg2+ 0.80 1 Na+ 0.24 0.21 1 K+ 0.19 −0.05 0.73 1 Cl− 0.76 0.59 0.68 0.56 1 SO42− 0.88 0.75 0.66 0.45 0.67 1 HCO3− 0.48 0.25 −0.59 −0.54 0.11 0.09 1 TDS 0.67 0.42 0.68 0.60 0.84 0.69 0.12 1 F− −0.15 0.24 −0.18 −0.29 −0.34 0.02 −0.19 −0.28 1 pH 0.12 0.11 0.42 0.50 0.09 0.41 −0.55 −0.04 0.14 1 表 3 水质综合评价结果表
Table 3. Comprehensive evaluation results of water quality
水体类型Water type 取样点Water sample Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ 水质Water quality 浅层地下水Shallow ground water B1 0.032 0.138 0.277 0.37 0.183 Ⅳ B2 0.047 0.105 0.253 0.406 0.189 Ⅳ B3 0.257 0.389 0.337 0.017 0 Ⅱ B4 0.437 0.262 0.294 0.007 0 Ⅰ B5 0.208 0.394 0.283 0.105 0.009 Ⅱ B6 0.252 0.285 0.321 0.125 0.017 Ⅰ 深层地下水Deep ground water C1 0.497 0.323 0.179 0 0 Ⅰ C2 0.638 0.253 0.109 0 0 Ⅰ C3 0.246 0.536 0.218 0 0 Ⅱ C4 0.528 0.347 0.126 0 0 Ⅰ C5 0.269 0.423 0.309 0 0 Ⅱ C6 0.351 0.38 0.243 0.027 0 Ⅱ C7 0.343 0.491 0.166 0 0 Ⅱ C8 0.793 0.138 0.069 0 0 Ⅰ C9 0.275 0.352 0.372 0 0 Ⅲ C10 0.449 0.432 0.119 0 0 Ⅰ 泉水Spring water S 0.47 0.32 0.178 0.032 0 Ⅰ -
[1] 李国秀. 吉林省西部地区地下水水质演化研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017. LI G X. Research on evolution of groundwater quality in the western Jilin Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017 (in Chinese).
[2] 石立明. 邯郸黑龙港平原地下水水文地球化学特征及水质评价研究[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2020. SHI L M. Research on hydrogeochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of groundwater in heilonggang basin of Handan city[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2020 (in Chinese).
[3] 高燕燕. 关中平原地下水化学成分时空演化规律及人体健康风险评价[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020. GAO Y Y. Spatio-temporal evolution of hydrochemical components and human health risk assessment of groundwater in Guanzhong plain[D]. Xi'an: Chang’an University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[4] 杨锐, 周金龙, 魏兴, 等. 新疆和田东部平原区地下水化学特征及演化规律 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(4): 1367-1379. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020120202 YANG R, ZHOU J L, WEI X, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the eastern plain of Hotian Prefecture, Xinjiang [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(4): 1367-1379(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020120202
[5] 高磊, 陈建耀, 王江, 等. 东莞石马河流域水化学特征时空差异及来源辨析 [J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(5): 1573-1581. GAO L, CHEN J Y, WANG J, et al. Temporal-spatial variation and source identification of hydro-chemical characteristics in Shima River catchment, Dongguan city [J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(5): 1573-1581(in Chinese).
[6] 丁启振, 雷米, 周金龙, 等. 博尔塔拉河上游河谷地区水化学特征及水质评价 [J]. 干旱区研究, 2022, 39(3): 829-840. DING Q Z, LEI M, ZHOU J L, et al. An assessment of groundwater, surface water, and hydrochemical characteristics in the upper valley of the Bortala River [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2022, 39(3): 829-840(in Chinese).
[7] 夏璐, 游海池, 刘久潭, 等. 胶东半岛沿海地区地下水水化学特征及水质评价 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(10): 1-10. XIA L, YOU H C, LIU J T, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of groundwater in coastal area of Jiaodong peninsula [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(10): 1-10(in Chinese).
[8] CHOTPANTARAT S, THAMRONGSRISAKUL J. Natural and anthropogenic factors influencing hydrochemical characteristics and heavy metals in groundwater surrounding a gold mine, Thailand [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021, 211: 104692. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104692 [9] BOUSELSAL B, SAIBI H. Evaluation of groundwater quality and hydrochemical characteristics in the shallow aquifer of El-Oued region (Algerian Sahara) [J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2022, 17: 100747. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2022.100747 [10] 安静, 徐明德, 孙凯迪, 等. 三级生态保护体系区划研究: 以山西省高平市为例 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(10): 226-232. AN J, XU M D, SUN K D, et al. Research on delineation of three-level ecological conservation system: A case study in Gaoping city, Shanxi provice [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(10): 226-232(in Chinese).
[11] 赵兴华, 李泽利, 贾冰莹, 等. 不同评价方法在地下水源水质评价中的应用: 以天津市为例 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2021, 38(4): 686-692. ZHAO X H, LI Z L, JIA B Y, et al. Application of different methods for quality evaluation of groundwater drinking water sources: A case study of Tianjin [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2021, 38(4): 686-692(in Chinese).
[12] 丁冉, 肖伟华, 于福亮, 等. 水资源质量评价方法的比较与改进 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2011, 27(3): 63-68. DING R, XIAO W H, YU F L, et al. Evaluation method for water quality: A review and further investigation for improvement [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2011, 27(3): 63-68(in Chinese).
[13] 唐宁. 无锡梁溪河水质模型及其不确定性分析[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2017. TANG N. Water quality model of Liangxi River in Wuxi and its uncertainty analysis[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2017 (in Chinese).
[14] 侯玉婷, 周忠发, 王历, 等. 基于改进模糊综合评价法的喀斯特山区水质评价研究 [J]. 水利水电技术, 2018, 49(7): 129-135. HOU Y T, ZHOU Z F, WANG L, et al. Improved fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method-based study on water quality evaluation in Karst Mountain area [J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2018, 49(7): 129-135(in Chinese).
[15] ZHOU Z Y, ZHANG X J, DONG W Y. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation for safety guarantee system of reclaimed water quality [J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2013, 18: 227-235. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2013.04.029 [16] WANG X J, ZOU Z H, ZOU H. Water quality evaluation of Haihe River with fuzzy similarity measure methods [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 25(10): 2041-2046. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60260-5 [17] ZOU Z H, YUN Y, SUN J N. Entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 18(5): 1020-1023. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(06)60032-6 [18] 陈朋, 王家鼎, 袁亮, 等. 修正内梅罗指数法和模糊综合评判法在凤凰镇地下水水质评价中的应用 [J]. 水土保持通报, 2017, 37(2): 165-170. CHEN P, WANG J D, YUAN L, et al. Application of modified nemerow index and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method on groundwater quality evaluation in Fenghuang town [J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 37(2): 165-170(in Chinese).
[19] 岳自慧, 许兴, 毛桂莲. 燃煤脱硫废弃物中的钙对提高作物抗盐碱胁迫的可能机理及进展 [J]. 农业科学研究, 2009, 30(2): 48-52. YUE Z H, XU X, MAO G L. Effects of calcium of desulphurized coal-burning residue on stress-resistant ability under saline-alkali stress of plant [J]. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 30(2): 48-52(in Chinese).
[20] KHONG L X, ISMAIL S, SAAD N A, et al. Evaluation on groundwater quality of limestone aquifer in Kinta Valley, Perak for the use as irrigation water [J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2022, 66: 3040-3043. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2022.07.334 [21] MORÁN-RAMÍREZ J, RAMOS-LEAL J A, FUENTES-RIVAS R M, et al. Hydrogeochemical processes in aquifers of volcano-sedimentary origin using inverse modeling [J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2022, 117: 103888. doi: 10.1016/j.jsames.2022.103888 [22] WANG J H, LI C, XU Y P, et al. Identifying major contributors to algal blooms in Lake Dianchi by analyzing river-lake water quality correlations in the watershed [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 315: 128144. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128144 [23] 杨巧凤, 王瑞久, 徐素宁, 等. 莱州湾南岸卤水的稳定同位素与地球化学特征 [J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(2): 343-352. YANG Q F, WANG R J, XU S N, et al. Hydrogeochemical and stable isotopic characteristics of brine in Laizhou Bay [J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(2): 343-352(in Chinese).
[24] 张景涛, 史浙明, 王广才, 等. 柴达木盆地大柴旦地区地下水水化学特征及演化规律 [J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(4): 194-205. ZHANG J T, SHI Z M, WANG G C, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Dachaidan area, Qaidam Basin [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(4): 194-205(in Chinese).
[25] 曾邯斌, 苏春利, 谢先军, 等. 河套灌区西部浅层地下水咸化机制 [J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(6): 2267-2277. ZENG H B, SU C L, XIE X J, et al. Mechanism of salinization of shallow groundwater in western Hetao irrigation area [J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(6): 2267-2277(in Chinese).
[26] WANG H, JIANG X W, WAN L, et al. Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater flow systems in the discharge area of a river basin [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 527: 433-441. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.04.063 [27] 孙厚云, 王晨昇, 卫晓锋, 等. 大兴安岭南段巴音高勒流域水化学特征及驱动因子 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(9): 2507-2519. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020032102 SUN H Y, WANG C S, WEI X F, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and driving factors in the water of the Bayingaole Basin, Southern Great Xing’an Range [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(9): 2507-2519(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020032102
[28] PENG H, YANG W, NADINE FERRER A S, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and health risk assessment of groundwater in Karst areas of southwest China: A case study of Bama, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 341: 130872. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130872 [29] 曾小仙, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 等. 石河子市浅层地下水化学特征及其成因分析 [J]. 干旱区研究, 2021, 38(1): 68-75. doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.01.08 ZENG X X, ZENG Y Y, ZHOU J L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and cause analysis of the shallow groundwater in Shihezi City [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2021, 38(1): 68-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2021.01.08
[30] SHARMA M K, KUMAR P, PRAJAPATI P, et al. Study of hydrochemical and geochemical characteristics and solute fluxes in upper Ganga basin, India [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences:X, 2022, 8: 100108. doi: 10.1016/j.jaesx.2022.100108 [31] 林云, 曹飞龙, 武亚遵, 等. 北方典型岩溶泉域地下水水文地球化学特征分析: 以鹤壁许家沟泉域为例 [J]. 地球与环境, 2020, 48(3): 294-306. LIN Y, CAO F L, WU Y Z, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in typical Karst spring areas of North China-a case study in the Xujiagou Spring area, Hebi [J]. Earth and Environment, 2020, 48(3): 294-306(in Chinese).
[32] SANGADI P, KUPPAN C, RAVINATHAN P. Effect of hydro-geochemical processes and saltwater intrusion on groundwater quality and irrigational suitability assessed by geo-statistical techniques in coastal region of eastern Andhra Pradesh, India [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2022, 175: 113390. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113390 [33] GEETHA S A, SIVAKUMAR C Appraisement of phreatic water characteristic using water quality Index modeling and GIS in industrialized region[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 43: 1568-1581. [34] 周永学, 李美琪, 黄志杰, 等. 长期咸水滴灌对灰漠土理化性质及棉花生长的影响 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2021, 39(4): 12-20. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2021.04.02 ZHOU Y X, LI M Q, HUANG Z J, et al. Effects of long-term saline water drip irrigation on physicochemical properties and cotton growth in grey desert soil [J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2021, 39(4): 12-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2021.04.02
[35] 马贵仁, 王丽萍, 屈忠义, 等. 构建河套灌区大规模盐碱地改良效果评估指标体系 [J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2020, 39(8): 72-84. MA G R, WANG L P, QU Z Y, et al. Constructing an index-based system to evaluate the efficacy of large-scale remediation of saline-alkali soil for Hetao irrigated district [J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2020, 39(8): 72-84(in Chinese).
-






 下载:
下载: