-
我国产业结构的优化升级和城市化进程的加速,促使传统工业企业转型,纷纷由城市中心搬迁至工业园区[1]. 然而原有企业在运营期间,环保意识淡薄、管理不当,使原址场地中的土壤和地下水受到不同程度的污染,不仅给周边环境和居民健康带来威胁和风险,也使遗留场地的再次开发利用受到限制. 企业生产工艺的多元化与生产活动的长期性,导致了大多遗留场地属于污染物种类复杂、风险程度高且累积性强的复合污染场地[2-3].
重金属与多环芳烃复合污染是典型的无机-有机型复合污染,不仅来源广泛、危害性大,且物化性质稳定,会长期滞留在土壤和地下水中,难以去除,因此受到国内外诸多学者的关注. 王耀锋等[4]对我国焦化场地中PAHs和重金属进行污染评价,发现山西与河北地区的焦化场地危害程度最高;刘颖等[5]研究重复合污染场地中重金属与PAHs的空间分布特征和健康风险评估,以此提出各类污染物的风险管控值;杨悦锁等[6]提出,目前针对重金属与PAHs复合污染场地的修复方法主要有淋洗修复、生物修复和联合修复,但行之有效的方法较少;Wong等[7]认为石油与焦化行业的废水排放是土壤复合污染的重要原因. 重金属与PAHs在土壤环境中,经过迁移至某一区域后,相互作用相互影响,从而形成复合污染,会对人体健康和土壤环境产生更大的危害[8-9],因此研究重金属与PAHs的污染特征及风险评价能够为复合污染场地提供理论科学依据,具有重要的理论与实际意义[10].
本文以湖南某焦化厂遗留的重金属-多环芳烃复合污染场地为研究对象,通过场地环境调查和地质勘探,明确了该场地的地层结构和地下水特征;通过对场地不同功能区的不同深度土壤样品中重金属及多环芳烃含量测试,分析了场地主要污染物的含量与空间分布特征;通过对重金属与多环芳烃的相关性分析,阐述了其共存特征与来源;通过内梅罗综合污染指数法、质量基准法分别对重金属、多环芳烃进行生态风险评价,以期为该焦化场地的土壤污染治理和修复提供科学依据.
-
本文研究的焦化场地属于丘岗地形,地表起伏较大,地势北高南低,属构造侵蚀红岩丘陵地带,场地内地层由上而下分别为:人工填土(Q4ml)、粉质粘土(Q4al)、强风化泥质粉砂岩(Kdld). 地下水主要有上层滞水和碎屑岩类孔隙裂隙水,地下水流向受单斜构造影响,整体呈北东流向南西,径流条件复杂,水位水量季节性变化明显,区域蓄水保水性能差,属于地下水贫乏区.
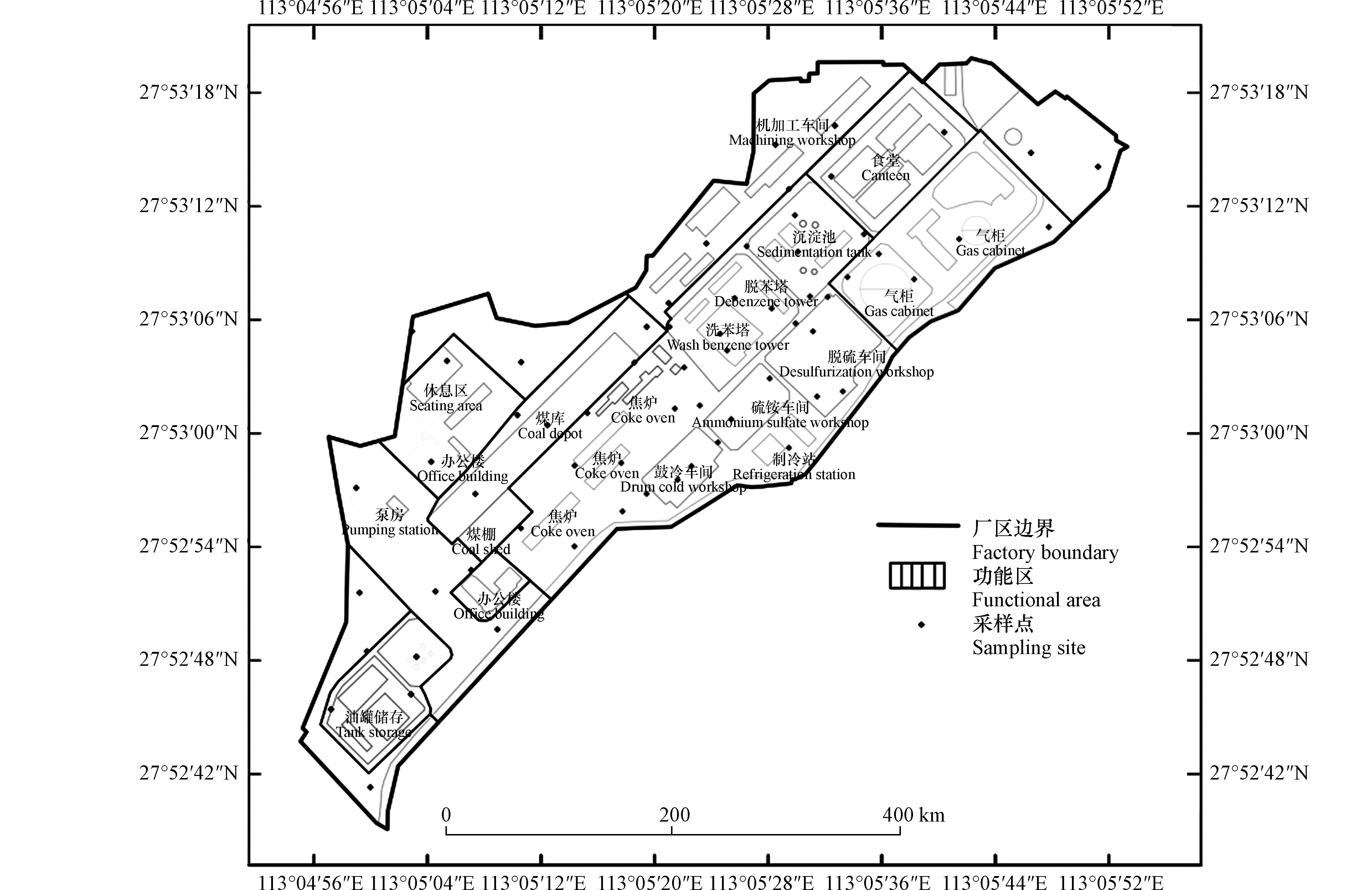
该焦化厂于1988年开始生产,2008年9月份停产,生产原料包括主焦煤、瘦煤、气煤、燃料煤、硫酸、轻柴油、纯碱和水等. 焦炉生产的荒煤气,经过鼓冷-脱硫-冼氨-洗苯脱苯等工艺,产生包括煤气、焦炭、焦油、硫铵、粗苯和硫磺等产品,原场地功能区布置如图1所示. 由于原工厂环境管理措施不当,存在废水乱排、废渣乱堆乱放等现象,造成场地污染. 目前,场地建(构)筑物拆除清理完毕,场地主要规划为住宅区,按照《土壤环境质量标准》(GB36600-2018),划分为第一类用地.
-
采样点布设参照《建设用地污染状况调查技术导则》(HJ25.1-2019),采用判断布点法,调查区域平均土壤布点密度为40 m×40 m,污染严重区域以20 m×20 m网格布点控制,共布设64个采样点位,采集463份土壤样品,样品深度范围0—5 m,每个采样点深度依污染源情况而定. 0—3 m 深度每隔0.5 m采集1个样品,深度超过3 m 时根据地层特性和光离子化检测仪(PID)快速检测数据,决定土壤样品的采集深度. 采样过程中,通过手持式GPS进行定位,SH-30型钻机钻取土壤样品,土壤样品从钻具中取出后,撇去植物根系与石块等杂物,装入250 mL棕色顶空瓶,加入保护剂,将样品瓶放入冷藏保温箱中低温避光保存(温度不超过4 ℃),当天送往实验室进行检测.
-
依据《土壤和沉积物 12种金属元素的测定 王水提取-电感耦合等离子体质谱法》(HJ803-2016)测定土壤样品的重金属含量. 土壤研磨充分,过100目尼龙筛后,取0.1 g土样于消解罐中,加入6 mL王水(由1.19 g·mL−1的HCL溶液和1.42 g·mL−1的HNO3溶液按照体积比3 : 1混合配制而成),放入微波消解仪进行消解. 冷却后,将提取液收集于50 mL容量瓶,加蒸馏水定容,使用820—MS 型ICP—MS 质谱仪对重金属含量进行测定[11].
-
参照《土壤和沉积物 多环芳烃的测定 气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ805-2016) 测定土壤中多环芳烃的含量.
(1)样品前处理
土壤样品中加入适量无水硫酸钠,进行脱水研磨成细粒状(约1 mm);取20 g土样于离心管,加入适量体积比为1:1的丙酮-正己烷混合溶液(ρ=500 µg·mL−1)进行加压流体萃取;将提取液转移至浓缩器皿中,浓缩至2.0 mL,并经硅酸镁净化小柱净化后,用丙酮-正己烷混合溶剂定容至1.0 mL,混匀后转入2 mL样品瓶中,待测[12].
(2)仪器分析与质量控制
土壤样品中的PAHs采用色谱-质谱仪(GC-MC)检测,色谱条件为:进样口温度为280 ℃,流量为1 mL·min−1,进样量1.0 μL,氦气为载气,不分流进样. 升温程序:柱起始温度80 ℃,保持2 min,然后以20 ℃·min−1速率上升至180 ℃,保持5 min,再以10 ℃·min−1的速率上升至290 ℃,保持5 min. 质谱条件:离子轰击电离源(EI源),电子能力70 eV,传输线温度为280 ℃,离子源温度为250 ℃,扫描范围(m/z)45—450 amu,全扫描模式.
-
为评价污染物生态风险,对土壤中重金属采用内梅罗综合污染指数法评价,对多环芳烃污染物采用质量基准法评价.
-
内梅罗综合污染指数法是当前国内外进行综合污染指数计算的最常用方法之一[13-14],该方法能够突出污染物最大含量对环境质量的影响和作用,综合反映多种重金属的联合污染水平. 计算公式如下:
式中,Ci、C0、Pi分别为土壤样品中污染物的实测值、《土壤环境质量 建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB366000-2018)中第一类用地筛选值(下文称筛选值)以及单因子污染指数;P、Pmax、Pave分别是内梅罗综合污染指数、单因子指数的最大值和平均值,依据《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T 166-2004),其分级标准见表1.
-
采用国内外常用的质量基准法对场地不同功能区的多环芳烃生态风险进行评价[4, 15],公式如下:
式中,QME为平均效应区间中值商;Ci为土壤中多环芳烃的实测值,mg·kg−1;Ei为多环芳烃的效应区间中值,mg·kg−1,见表2;n为多环芳烃的种类,此处为16;质量基准法风险等级划分见表3.
-
采用SPSS 22.0和Excel 2019对土壤中重金属和多环芳烃含量数据进行统计分析,结合origin 2018制图;采用反距离插值法(IDW)[16]对场地的重金属和多环芳烃空间分布特征进行分析,并采用surfer 15绘制场地污染物空间分布图.
-
场地中0—3 m土壤样品中的污染物含量如表4所示. 与筛选值相比,重金属中仅有Pb和As两种超过筛选值,最大检测值分别为1190 mg·kg−1和956 mg·kg−1,最大超标倍数分别为1.98、22.9,样品超标率分别为17%、8.33%;与湖南省土壤元素背景值[17](Pb=29.7 mg·kg−1、As=14 mg·kg−1)相比,最高含量分别是背景值的40.07倍和68.3倍. 多环芳烃中Nap、Phe、BaA及BaP超过筛选值,最大检测值分别为255、266、8.5、8.5 mg·kg−1,最大超标倍数分别为9.2、52.2、0.55及14.5,样品超标率分别为8.3%、14.3%、13.3%和15%,且场地内0—3 m土壤中的低环PAHs(2—3环)含量明显高于土壤高环PAHs(4环及以上)含量.
变异系数的大小能够反映污染物在土层间的平均变异程度以及污染物受外界因素的影响程度[18]. 如表4所示,场地表层、中层和下层的污染物变异系数范围分别为0.83—2.92、0.77—2.32、0.72—2.0,均属于高度变异,表明场地内污染物含量受焦化厂生产活动的影响很大,在土层间均具有波动幅度较大、连续性变化差的特点. 研究区整体偏弱碱性,0—1 m、1—2 m、2—3 m深度的土壤pH值范围分别为5.86—7.62、6.43—7.84、6.72—8.87,平均值分别为6.83、7.35和7.94.
-
运用反距离插值法(IDW)分析获取了厂区土壤重金属的污染羽分布图(图2). 重金属Pb和As的污染主要集中在煤库/煤棚、焦炉、鼓冷车间等区域. Pb集中分布在B2点位(焦炉)、B13点位(鼓冷车间)、B15点位(煤库)及B26点位(气柜),以B2点位和B13点位的0.5 m污染物浓度最高,为1190 mg·kg−1,超标倍数为2.96倍,污染超标最大深度为2 m;As的污染范围较广,浓度最高值在煤棚附近S15点位的0.5 m,浓度为956 mg·kg−1,超标倍数为22.9倍,最大污染超标深度为4 m;另外,As在气柜、脱硫车间及食堂等区域零星分布,超标较轻,污染超标深度不超过2 m. 经调查分析可知,在本场地中,Pb和As集中分布在土壤表层,浓度随深度增大而逐渐减小,中层和下层的重金属浓度远小于表层,尤其在煤棚附近区域更加明显.
场地内土壤污染物的空间分布特征与土壤理化性质及污染物本身物化性质息息相关. Pb、As集中分布的土壤浅层,垂向上浓度随深度增大而减小,这可能与土壤质地有关,场地浅层(0—3 m)土壤以杂填土为主,渗透系数K较小,在一定程度上限制污染物的运移;而场地内表层土壤(0—1 m)的pH值在5.86—7.62之间,基本呈现弱酸性,较中层和下层的土壤pH小,有利于重金属在表层迁移[19];重金属污染深度一定程度上能够反映其在土壤中的迁移能力,Pb和As的最大污染深度分别为2 m和4 m, 即砷的迁移能力强于铅,这与Zheng关于郴州某大型有色冶炼厂重金属空间分布的研究一致[20-21].
-
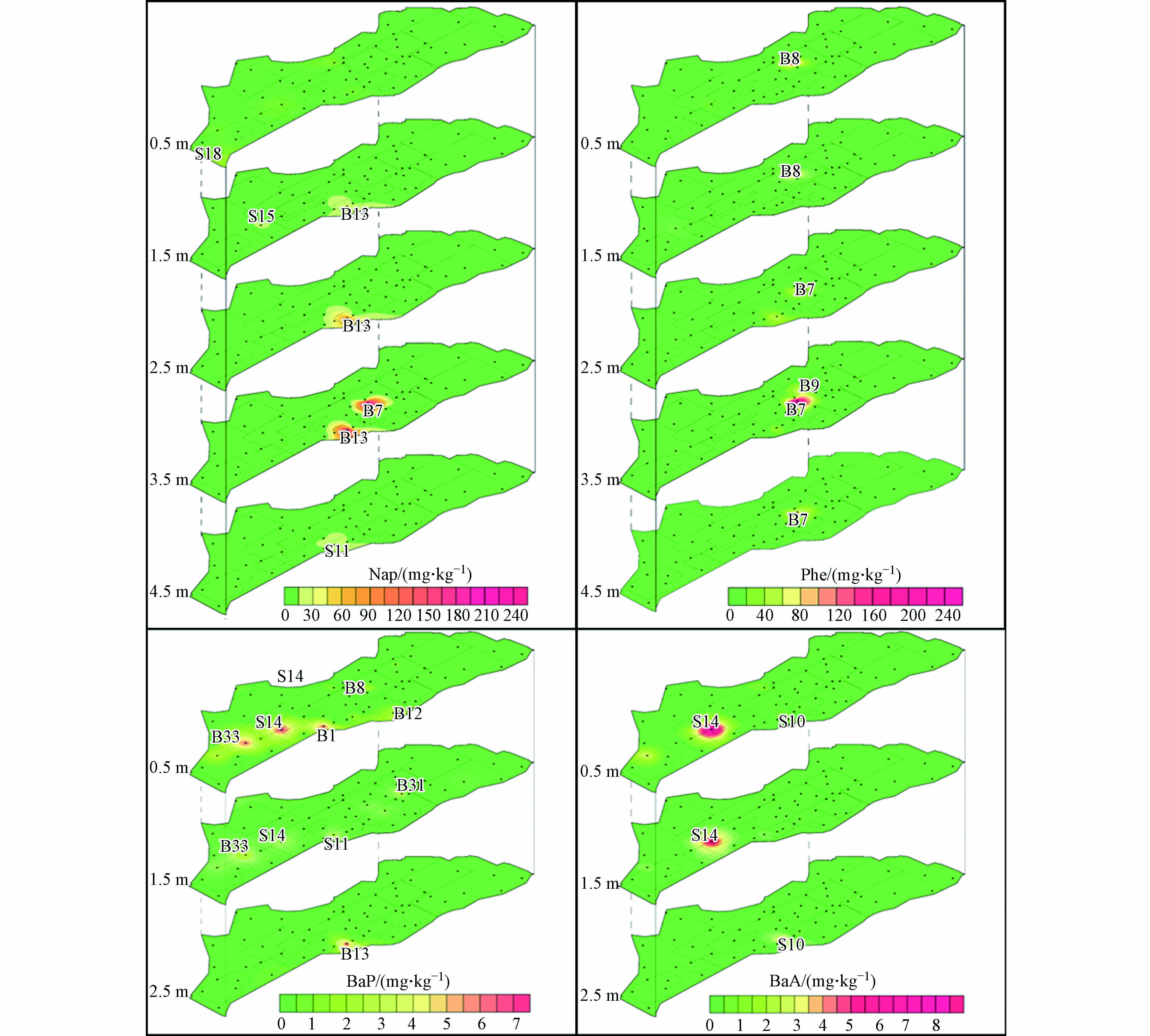
通过反距离插值法(IDW)分析厂区土壤PAHs的空间分布特征(图3). 场地PAHs的污染主要集中在场地的煤库/煤棚、鼓冷车间、洗苯脱苯车间、制冷站、沉淀池及气柜等区域. 场地不同区域中低环PAHs和高环PAHs分布存在着明显差异. 以Nap和Phe为代表的低环PAHs集中分布在洗苯脱苯车间、沉淀池及鼓冷车间附近区域,整体上随深度的增大呈现先升高再降低的变化规律,在深度3—4 m时出现最大值,最大污染深度为5 m. 以BaA和BaP为代表的高环PAHs分布在鼓冷车间和焦炉、煤仓附近,集中在表层土壤,浓度随深度增加而减小,最大污染深度为3 m. 总体来看,所有点位的低高环PAHs比值均大于1,且深层土壤的低环与高环PAHs比值高于表层,说明低环PAHs是场地多环芳烃污染的主体,这与孟祥帅等关于某工业区焦化厂PAHs分布特征的研究成果一致[22].
与低环PAHs相比,高环PAHs水溶性较低,不易随地下水迁移至土壤深部. 另外,土壤中有机质与高环PAHs通过Π-Π键结合更为紧密[23],阻止其向下迁移,因此多集中于土壤表层或次表层. 而低环PAHs水溶性强,具有较好的迁移性能[24],这使低环PAHs污染深度大于高环PAHs的污染深度. 低环PAHs浓度随深度增大呈现先增大后减小的变化规律,主要是因为场地内3—5 m内粉质粘土的阻隔作用,相对杂填土而言,粉质粘土具有更小的渗透系数和孔隙比,能够有效阻止低环PAHs的运移. 因此,粉质粘土层中的PAHs含量较少,而在杂填土和粉质粘土交界处,往往会出现低环PAHs的富集现象.
-
污染物的来源是否一致可通过相关性分析进行确定[25],利用皮尔逊相关系数对重金属Pb、As及PAHs中的Nap、Phe、BaA和BaP进行相关性分析(表5). 结果表明,PAHs之间均为显著正相关,低环PAHs之间的相关系数达0.94,高环PAHs之间的相关系数达0.802,而低高环PAHs之间的相关系数均小于0.6,为弱相关. 重金属之间也呈现显著正相关性,Pb、As之间的相关系数达0.648,重金属污染物与PAHs基本不相关,相关系数较低. 由此分析可知,重金属Pb与As可能具有相同的来源,各多环芳烃来源一致,但重金属与多环芳烃的来源不相同.
-
主成分分析是判别污染物来源的有效手段. 采用KMO和Bartlett法对土壤中重金属和PAHs含量进行检验,得到KMO为0.545(>0.5),Bartlett球度检验的相伴概率为0.000(<0.005),表明可以进行主成分分析[26]. 提取出两个特征值大于1的成分[27],为了提高数据真实性,使用最大方差法,计算出旋转后的成分矩阵,累计方差贡献率为75.28%,具有较高的代表性,结果如表6所示.
第一主成分的贡献率最高,为49.06%,4种PAHs在第一主成分上具有较大荷载. 结合表6可知,4种PAHs具有显著相关性,4种PAHs受到相同污染源的影响. 经分析判断认为,研究区焦化过程中的鼓冷、脱硫、冼氨、洗苯脱苯及沉淀过程产生的废气、废水和废渣都是PAHs的主要来源.
另外,在已有的研究中,可用低环PAHs与高环PAHs的比值来指示PAHs的来源,有研究认为[28-30],低环PAHs主要来源于石油、化石燃料的低温分解,而高环PAHs主要来自各类煤的高温燃烧. 综合场地PAHs污染羽的分布和场地环境调查结果,场地各个功能区的低环PAHs/高环PAHs的比值均大于1,推断认为这是焦油渣及萘油、苊油等油液副产品作为中间产物在堆存和生产过程中发生了遗撒泄露. 而高环PAHs主要来源为焦煤、气煤等生产原料的不充分燃烧. 在炼焦过程中,排放的烟尘为高环PAHs的富集相,在受到干、湿沉降作用后分布于表层土壤[31- 32],这也是造成高环PAHs主要集中于浅层土壤的原因之一.
第二主成分的贡献率为26.22%,较大荷载为重金属Pb和As,表6也显示Pb和As具有极显著相关性. 结合场地历史调查,认为重金属Pb、As主要来自厂区煤库/煤棚及仓库区堆存的铅精矿粉,由于厂区的煤仓处于半封闭状态,矿粉长期遭受雨水淋滤,其中的重金属成分在地表径流作用下水平运移和下渗扩散,导致周边环境的Pb和As污染.
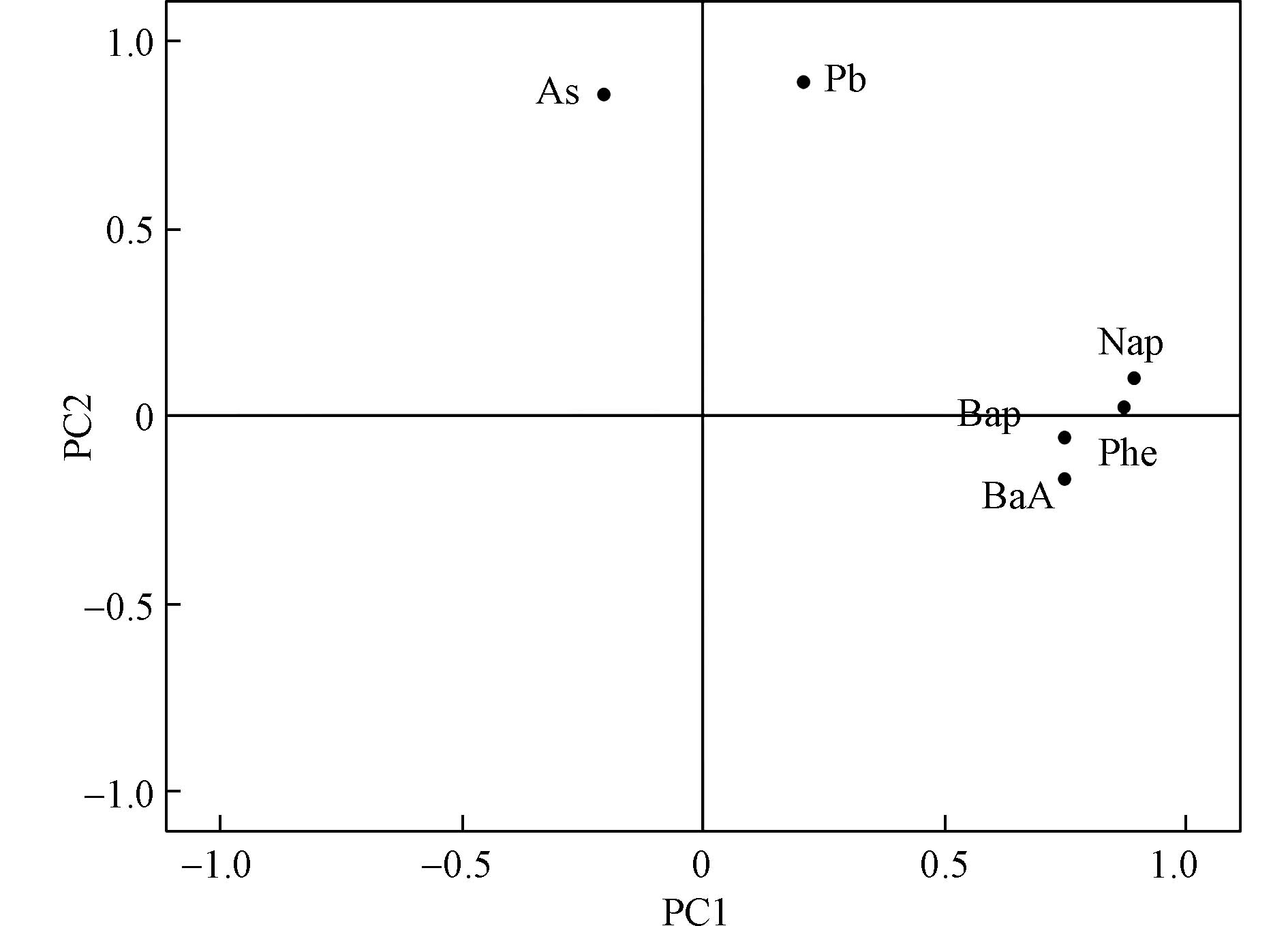
图4中污染物间的距离也反映了污染物之间的相关性,重金属Pb和As表现出较强的相关性;4种PAHs之间距离较近,具有很强的相关性,而重金属与PAHs则显示出较强的异源性.
由污染物污染羽分布状况分析,具有不同来源的重金属及PAHs在煤库/煤棚、制冷站及鼓冷车间等区域的土壤环境中相互共存,这种复合污染主要是由于重金属和高环PAHs均容易被吸附沉淀,在经过迁移后在场地部分区域形成复合污染[33],也可能由生产原料及废弃物的随意堆砌等多方面原因造成的.
-
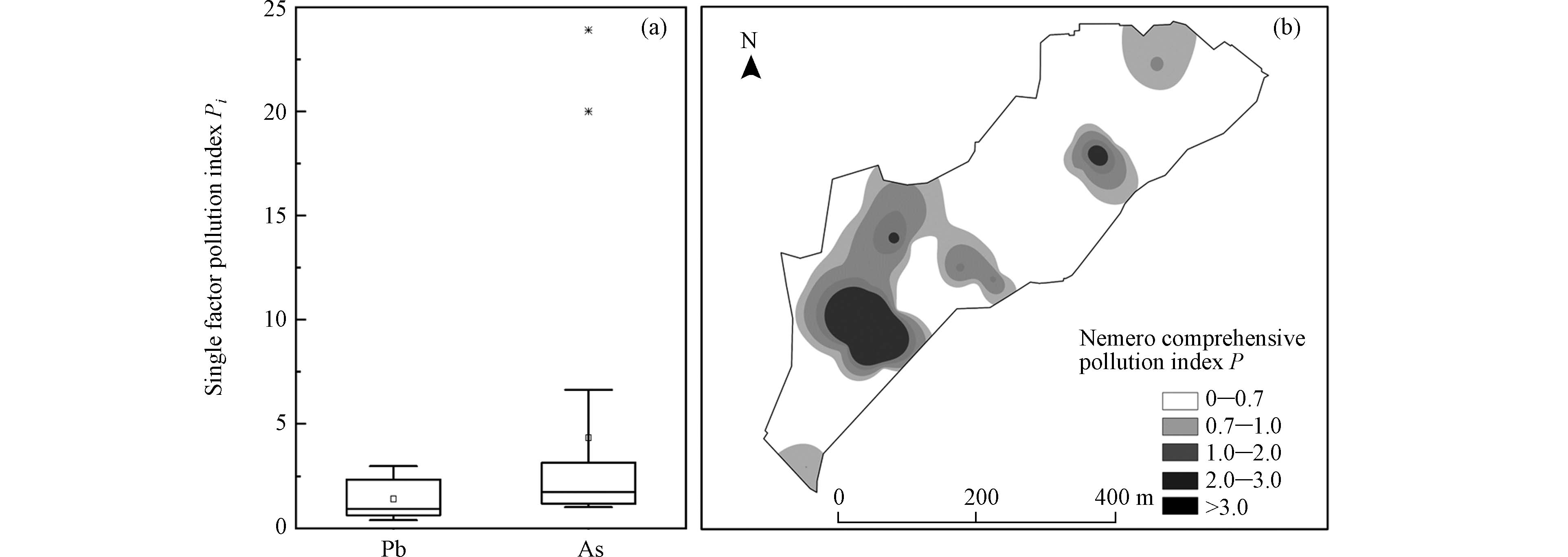
根据内梅罗综合污染指数法评价了场地土壤污染水平,如图5所示. 由5(a)图可以看出,重金属Pb的单因子污染指数在0.396—2.975之间,平均值1.49,基本上处于清洁—轻度污染,As的单因子污染指数范围为1.015—23.9,平均值4.34,整体上处于轻度—重度污染. 由图5(b)分析可知,场地大部分区域为清洁—轻度污染,中度风险及重度风险主要集中在煤棚/煤库、鼓冷车间及气柜等区域,与重金属Pb、As的空间分布具有高度一致性,表明场地土壤重金属污染主要受Pb、As元素的影响,进一步证实了Pb和As是场地重金属污染的主要元素.
-
采用质量基准法,计算场地土壤PAHs的QME值,计算结果如表7所示. 场地整体上处于低生态风险或无生态风险. 其中,洗苯脱苯车间、煤库/煤棚、制冷站的QME值分别高达21.07、15.69及3.36,远高于1.51,为高生态风险;气柜的QME值为1.42,属于中生态风险. 高生态风险区域与PAHs高浓度区域基本一致,洗苯脱苯车间为低环PAHs集中分布区域,其QME值为场地最高值,也证实了场地多环芳烃污染主要以菲、萘等低环PAHs为主.
-
(1)场地0—3 m土壤中,重金属Pb和As的最大超标倍数分别为1.98、22.9,超标率分别为17%和8.33%,PAHs中Nap、Phe、BaA及BaP的最大超标倍数分别为9.2、52.2、0.55及14.5,超标率分别为8.33%、14.3%、13.3%及15%. 重金属和PAHs污染在场地中分布均表现出明显的空间差异性,集中分布在煤库/煤棚、鼓冷车间、洗苯脱苯车间等区域.
(2)重金属Pb、As及高环PAHs集中分布在土壤表层,浓度随深度增加而呈现减小趋势;低环PAHs浓度随深度增加呈现先增大后减小的变化规律,浓度最大值分布在杂填土层与粉质粘土层交界处.
(3)污染物主要来源于原企业的生产活动,4种PAHs具有相同的来源,重金属与PAHs的来源不相同,但来源不同的重金属与PAHs经过土壤迁移后在场地的煤库/煤棚、鼓冷车间及制冷站等区域形成复合污染.
(4)内梅罗综合污染指数表明,场地大部分区域的重金属污染为轻度污染,气柜、煤库/煤棚、制冷站等区域基本处于中度—重度生态风险,质量基准法显示场地内PAHs在大部分区域为低生态风险或无生态风险,在气柜、制冷站、煤库/煤棚、鼓冷车间及洗苯脱苯车间等区域处于中—高生态风险状态.
某焦化场地重金属与多环芳烃复合污染特征与评价
Co-contaminated characteristics and assessment of heavy metal and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a coking site
-
摘要: 调查与分析焦化遗留场地的土壤复合污染特征是土地安全再利用的基础. 以某焦化场地为例,采集0—5 m深度范围内的土壤样品,测定其中的重金属与PAHs含量,并运用反距离插值法分析场地重金属与PAHs的污染特征,采用内梅罗综合污染指数法评估焦化场地重金属的污染程度,质量基准法评价PAHs的生态风险. 结果表明:污染物分布的空间差异性明显,重金属与高环PAHs集中分布在0—1 m表层土壤,低环PAHs在杂填土与粉质粘土交界处呈现富集状态;重金属与PAHs的来源不同,但经迁移后在场地煤库、鼓冷车间及制冷站等区域共存形成复合污染;内梅罗综合污染指数评价表明,场地内气柜、煤库/煤棚、制冷站区域为中度—重度污染,质量基准法表明气柜、鼓冷车间、洗苯脱苯车间及煤库/煤棚处于中—高生态风险. 本研究结果能够为焦化场地的后续土壤修复工程及生产工艺优化提供参考.Abstract: Investigating and analyzing the compound pollution characteristics of coking site is the basis of land safe reuse. Taking a coking site as an example, soil samples at 0—5 m depth were collected to measure the content of the heavy metals and PAHs, The pollution characteristics of heavy metals and PAHs in the site are analyzed by using the inverse distance interpolation method, and the pollution degree of heavy metals in the coking site is evaluated by using the Nemero comprehensive pollution index method, the ecological risk of PAHs is evaluated by using the quality benchmark method. The results show that the distribution of pollutants has obvious spatial differences. Heavy metals and high molecular weight PAHs are concentrated in the 0—1 m surface soil, then the concentration of low molecular weight PAHs presents an enrichment state at the junction of miscellaneous fill and silty clay; The sources of heavy metals and PAHs are different, but they coexist and form compound pollution in coal bunker, blast cooling workshop and refrigeration station of the coking site after migration. The evaluation results of the Nemero comprehensive index show that they are moderately—severely polluted in gasholder, coal depot/coal shed, refrigeration station. The quality benchmark method shows that the gasholder, refrigeration station, coal depot/coal shed, drum cooling workshop, and benzene washing and debenzylation workshop are in medium—high ecological risk. The results of this research can provide guidance for the subsequent soil remediation project and production process optimization of coking site.
-
Key words:
- co-contaminated site /
- PAHs /
- heavy metal /
- distribution characteristics /
- pollution assessment.
-
我国产业结构的优化升级和城市化进程的加速,促使传统工业企业转型,纷纷由城市中心搬迁至工业园区[1]. 然而原有企业在运营期间,环保意识淡薄、管理不当,使原址场地中的土壤和地下水受到不同程度的污染,不仅给周边环境和居民健康带来威胁和风险,也使遗留场地的再次开发利用受到限制. 企业生产工艺的多元化与生产活动的长期性,导致了大多遗留场地属于污染物种类复杂、风险程度高且累积性强的复合污染场地[2-3].
重金属与多环芳烃复合污染是典型的无机-有机型复合污染,不仅来源广泛、危害性大,且物化性质稳定,会长期滞留在土壤和地下水中,难以去除,因此受到国内外诸多学者的关注. 王耀锋等[4]对我国焦化场地中PAHs和重金属进行污染评价,发现山西与河北地区的焦化场地危害程度最高;刘颖等[5]研究重复合污染场地中重金属与PAHs的空间分布特征和健康风险评估,以此提出各类污染物的风险管控值;杨悦锁等[6]提出,目前针对重金属与PAHs复合污染场地的修复方法主要有淋洗修复、生物修复和联合修复,但行之有效的方法较少;Wong等[7]认为石油与焦化行业的废水排放是土壤复合污染的重要原因. 重金属与PAHs在土壤环境中,经过迁移至某一区域后,相互作用相互影响,从而形成复合污染,会对人体健康和土壤环境产生更大的危害[8-9],因此研究重金属与PAHs的污染特征及风险评价能够为复合污染场地提供理论科学依据,具有重要的理论与实际意义[10].
本文以湖南某焦化厂遗留的重金属-多环芳烃复合污染场地为研究对象,通过场地环境调查和地质勘探,明确了该场地的地层结构和地下水特征;通过对场地不同功能区的不同深度土壤样品中重金属及多环芳烃含量测试,分析了场地主要污染物的含量与空间分布特征;通过对重金属与多环芳烃的相关性分析,阐述了其共存特征与来源;通过内梅罗综合污染指数法、质量基准法分别对重金属、多环芳烃进行生态风险评价,以期为该焦化场地的土壤污染治理和修复提供科学依据.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区背景
本文研究的焦化场地属于丘岗地形,地表起伏较大,地势北高南低,属构造侵蚀红岩丘陵地带,场地内地层由上而下分别为:人工填土(Q4ml)、粉质粘土(Q4al)、强风化泥质粉砂岩(Kdld). 地下水主要有上层滞水和碎屑岩类孔隙裂隙水,地下水流向受单斜构造影响,整体呈北东流向南西,径流条件复杂,水位水量季节性变化明显,区域蓄水保水性能差,属于地下水贫乏区.
该焦化厂于1988年开始生产,2008年9月份停产,生产原料包括主焦煤、瘦煤、气煤、燃料煤、硫酸、轻柴油、纯碱和水等. 焦炉生产的荒煤气,经过鼓冷-脱硫-冼氨-洗苯脱苯等工艺,产生包括煤气、焦炭、焦油、硫铵、粗苯和硫磺等产品,原场地功能区布置如图1所示. 由于原工厂环境管理措施不当,存在废水乱排、废渣乱堆乱放等现象,造成场地污染. 目前,场地建(构)筑物拆除清理完毕,场地主要规划为住宅区,按照《土壤环境质量标准》(GB36600-2018),划分为第一类用地.
1.2 样品采集与保存
采样点布设参照《建设用地污染状况调查技术导则》(HJ25.1-2019),采用判断布点法,调查区域平均土壤布点密度为40 m×40 m,污染严重区域以20 m×20 m网格布点控制,共布设64个采样点位,采集463份土壤样品,样品深度范围0—5 m,每个采样点深度依污染源情况而定. 0—3 m 深度每隔0.5 m采集1个样品,深度超过3 m 时根据地层特性和光离子化检测仪(PID)快速检测数据,决定土壤样品的采集深度. 采样过程中,通过手持式GPS进行定位,SH-30型钻机钻取土壤样品,土壤样品从钻具中取出后,撇去植物根系与石块等杂物,装入250 mL棕色顶空瓶,加入保护剂,将样品瓶放入冷藏保温箱中低温避光保存(温度不超过4 ℃),当天送往实验室进行检测.
1.3 样品分析方法
1.3.1 重金属分析方法
依据《土壤和沉积物 12种金属元素的测定 王水提取-电感耦合等离子体质谱法》(HJ803-2016)测定土壤样品的重金属含量. 土壤研磨充分,过100目尼龙筛后,取0.1 g土样于消解罐中,加入6 mL王水(由1.19 g·mL−1的HCL溶液和1.42 g·mL−1的HNO3溶液按照体积比3 : 1混合配制而成),放入微波消解仪进行消解. 冷却后,将提取液收集于50 mL容量瓶,加蒸馏水定容,使用820—MS 型ICP—MS 质谱仪对重金属含量进行测定[11].
1.3.2 多环芳烃分析方法
参照《土壤和沉积物 多环芳烃的测定 气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ805-2016) 测定土壤中多环芳烃的含量.
(1)样品前处理
土壤样品中加入适量无水硫酸钠,进行脱水研磨成细粒状(约1 mm);取20 g土样于离心管,加入适量体积比为1:1的丙酮-正己烷混合溶液(ρ=500 µg·mL−1)进行加压流体萃取;将提取液转移至浓缩器皿中,浓缩至2.0 mL,并经硅酸镁净化小柱净化后,用丙酮-正己烷混合溶剂定容至1.0 mL,混匀后转入2 mL样品瓶中,待测[12].
(2)仪器分析与质量控制
土壤样品中的PAHs采用色谱-质谱仪(GC-MC)检测,色谱条件为:进样口温度为280 ℃,流量为1 mL·min−1,进样量1.0 μL,氦气为载气,不分流进样. 升温程序:柱起始温度80 ℃,保持2 min,然后以20 ℃·min−1速率上升至180 ℃,保持5 min,再以10 ℃·min−1的速率上升至290 ℃,保持5 min. 质谱条件:离子轰击电离源(EI源),电子能力70 eV,传输线温度为280 ℃,离子源温度为250 ℃,扫描范围(m/z)45—450 amu,全扫描模式.
1.4 污染评价方法
为评价污染物生态风险,对土壤中重金属采用内梅罗综合污染指数法评价,对多环芳烃污染物采用质量基准法评价.
1.4.1 内梅罗综合污染指数法
内梅罗综合污染指数法是当前国内外进行综合污染指数计算的最常用方法之一[13-14],该方法能够突出污染物最大含量对环境质量的影响和作用,综合反映多种重金属的联合污染水平. 计算公式如下:
Pi=Ci/C0 (1) P=√(Pmax)2+(Pave)22 (2) 式中,Ci、C0、Pi分别为土壤样品中污染物的实测值、《土壤环境质量 建设用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)》(GB366000-2018)中第一类用地筛选值(下文称筛选值)以及单因子污染指数;P、Pmax、Pave分别是内梅罗综合污染指数、单因子指数的最大值和平均值,依据《土壤环境监测技术规范》(HJ/T 166-2004),其分级标准见表1.
表 1 土壤污染分级标准Table 1. Soil pollution classification standard单因子污染指数Single pollution index 污染水平Pollution grade 内梅罗综合污染指数Nemerow comprehensive pollution index 污染水平Pollution grade Pi≤1 清洁 P≤0.7 清洁 1<Pi≤2 轻度污染 0.7<P≤1.0 尚清洁 2<Pi≤3 中度污染 1.0<P≤2.0 轻度污染 Pi>3 重度污染 2.0<P≤3.0 中度污染 P>3.0 重度污染 1.4.2 质量基准法
采用国内外常用的质量基准法对场地不同功能区的多环芳烃生态风险进行评价[4, 15],公式如下:
QME=∑(Ci/Ei)/n (3) 式中,QME为平均效应区间中值商;Ci为土壤中多环芳烃的实测值,mg·kg−1;Ei为多环芳烃的效应区间中值,mg·kg−1,见表2;n为多环芳烃的种类,此处为16;质量基准法风险等级划分见表3.
表 2 土壤中多环芳烃效应区间中值(Ei)参考值[4]( mg·kg−1)Table 2. Reference value of PAHs effect range median in soil(mg·kg−1)多环芳烃 Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons Ei 多环芳烃 Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons Ei 萘(Nap) 2.10 苯并(a)蒽(BaA) 1.60 苊烯(Acy) 0.64 䓛(Chry) 2.80 苊(Ace) 0.50 苯并(b)荧蒽(BbF) 1.62 芴(Flu) 5.10 苯并(k)荧蒽(BkF) 1.62 菲(Phe) 1.50 苯并(a)芘(BaP) 1.60 蒽(Ant) 1.10 二苯并(a,h)蒽(DahA) 0.26 荧蒽(Fla) 0.54 苯并(g,h,i)苝(BghiP) 1.60 芘(Pyr) 2.60 茚并(1,2,3-cd)芘(InP) 1.60 表 3 质量基准法风险等级划分Table 3. Soil average effect interval quotient QME risk classificationQME ≤0.1 0.1—0.5 0.5—1.5 ≥1.5 风险等级(Ecological risk) 无 低 中等 高 1.5 数据分析
采用SPSS 22.0和Excel 2019对土壤中重金属和多环芳烃含量数据进行统计分析,结合origin 2018制图;采用反距离插值法(IDW)[16]对场地的重金属和多环芳烃空间分布特征进行分析,并采用surfer 15绘制场地污染物空间分布图.
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 土壤污染物含量特征
场地中0—3 m土壤样品中的污染物含量如表4所示. 与筛选值相比,重金属中仅有Pb和As两种超过筛选值,最大检测值分别为1190 mg·kg−1和956 mg·kg−1,最大超标倍数分别为1.98、22.9,样品超标率分别为17%、8.33%;与湖南省土壤元素背景值[17](Pb=29.7 mg·kg−1、As=14 mg·kg−1)相比,最高含量分别是背景值的40.07倍和68.3倍. 多环芳烃中Nap、Phe、BaA及BaP超过筛选值,最大检测值分别为255、266、8.5、8.5 mg·kg−1,最大超标倍数分别为9.2、52.2、0.55及14.5,样品超标率分别为8.3%、14.3%、13.3%和15%,且场地内0—3 m土壤中的低环PAHs(2—3环)含量明显高于土壤高环PAHs(4环及以上)含量.
表 4 焦化厂遗留场地污染物含量分析Table 4. Pollutants concentration in soil of coking site土层Soil layer 污染物Pollutant 含量范围/(mg·kg−1)C 平均值/(mg·kg−1)Cave 变异系数Coefficient of variation 筛选值/(mg·kg−1)Cfil 最大超标倍数Maximum exceedance 上层(0—1 m) Pb 8.5—1190 703.2 0.83 400 1.98 As 2.96—956 123.6 2.92 40 22.9 Nap 0.12—28.6 3.74 1.77 25 0.15 Phe 9.2—128 55.23 1.1 5 24 BaA 0.28—8.5 1.86 1.95 5.5 0.55 BaP 0.6—6.4 2.18 1.46 0.55 10.6 中层(1—2 m) Pb 10.2—298 194.64 0.77 400 — As 1.23—800 249.88 2.32 40 7.95 Nap 0.09—47.7 8.3 1.86 25 0.91 Phe 6.3—35.2 12.45 1.34 5 6.04 BaA 0.3—6.6 1.61 2.26 5.5 — BaP 0.6—4.4 0.84 1.35 0.55 7.0 下层(2—3 m) As 8.47—126 94.9 0.72 40 2.15 Nap 0.1—255 48.2 0.98 25 9.2 Phe 0.2—266 80.1 1.79 5 52.2 BaA 0.13—4.9 1.33 2.0 5.5 — BaP 1.1—8.5 3.7 1.05 0.55 14.5 注:场地调查区域土壤属于红壤/黄棕壤,砷的筛选值为40 mg·kg−1. Note: The soil in the site investigation area belongs to red soil/yellow brown soil, the filter value of As is 40 mg·kg−1. 变异系数的大小能够反映污染物在土层间的平均变异程度以及污染物受外界因素的影响程度[18]. 如表4所示,场地表层、中层和下层的污染物变异系数范围分别为0.83—2.92、0.77—2.32、0.72—2.0,均属于高度变异,表明场地内污染物含量受焦化厂生产活动的影响很大,在土层间均具有波动幅度较大、连续性变化差的特点. 研究区整体偏弱碱性,0—1 m、1—2 m、2—3 m深度的土壤pH值范围分别为5.86—7.62、6.43—7.84、6.72—8.87,平均值分别为6.83、7.35和7.94.
2.2 土壤污染物空间分布特征
2.2.1 重金属空间分布特征
运用反距离插值法(IDW)分析获取了厂区土壤重金属的污染羽分布图(图2). 重金属Pb和As的污染主要集中在煤库/煤棚、焦炉、鼓冷车间等区域. Pb集中分布在B2点位(焦炉)、B13点位(鼓冷车间)、B15点位(煤库)及B26点位(气柜),以B2点位和B13点位的0.5 m污染物浓度最高,为1190 mg·kg−1,超标倍数为2.96倍,污染超标最大深度为2 m;As的污染范围较广,浓度最高值在煤棚附近S15点位的0.5 m,浓度为956 mg·kg−1,超标倍数为22.9倍,最大污染超标深度为4 m;另外,As在气柜、脱硫车间及食堂等区域零星分布,超标较轻,污染超标深度不超过2 m. 经调查分析可知,在本场地中,Pb和As集中分布在土壤表层,浓度随深度增大而逐渐减小,中层和下层的重金属浓度远小于表层,尤其在煤棚附近区域更加明显.
场地内土壤污染物的空间分布特征与土壤理化性质及污染物本身物化性质息息相关. Pb、As集中分布的土壤浅层,垂向上浓度随深度增大而减小,这可能与土壤质地有关,场地浅层(0—3 m)土壤以杂填土为主,渗透系数K较小,在一定程度上限制污染物的运移;而场地内表层土壤(0—1 m)的pH值在5.86—7.62之间,基本呈现弱酸性,较中层和下层的土壤pH小,有利于重金属在表层迁移[19];重金属污染深度一定程度上能够反映其在土壤中的迁移能力,Pb和As的最大污染深度分别为2 m和4 m, 即砷的迁移能力强于铅,这与Zheng关于郴州某大型有色冶炼厂重金属空间分布的研究一致[20-21].
2.2.2 PAHs空间分布特征
通过反距离插值法(IDW)分析厂区土壤PAHs的空间分布特征(图3). 场地PAHs的污染主要集中在场地的煤库/煤棚、鼓冷车间、洗苯脱苯车间、制冷站、沉淀池及气柜等区域. 场地不同区域中低环PAHs和高环PAHs分布存在着明显差异. 以Nap和Phe为代表的低环PAHs集中分布在洗苯脱苯车间、沉淀池及鼓冷车间附近区域,整体上随深度的增大呈现先升高再降低的变化规律,在深度3—4 m时出现最大值,最大污染深度为5 m. 以BaA和BaP为代表的高环PAHs分布在鼓冷车间和焦炉、煤仓附近,集中在表层土壤,浓度随深度增加而减小,最大污染深度为3 m. 总体来看,所有点位的低高环PAHs比值均大于1,且深层土壤的低环与高环PAHs比值高于表层,说明低环PAHs是场地多环芳烃污染的主体,这与孟祥帅等关于某工业区焦化厂PAHs分布特征的研究成果一致[22].
与低环PAHs相比,高环PAHs水溶性较低,不易随地下水迁移至土壤深部. 另外,土壤中有机质与高环PAHs通过Π-Π键结合更为紧密[23],阻止其向下迁移,因此多集中于土壤表层或次表层. 而低环PAHs水溶性强,具有较好的迁移性能[24],这使低环PAHs污染深度大于高环PAHs的污染深度. 低环PAHs浓度随深度增大呈现先增大后减小的变化规律,主要是因为场地内3—5 m内粉质粘土的阻隔作用,相对杂填土而言,粉质粘土具有更小的渗透系数和孔隙比,能够有效阻止低环PAHs的运移. 因此,粉质粘土层中的PAHs含量较少,而在杂填土和粉质粘土交界处,往往会出现低环PAHs的富集现象.
2.3 污染物来源分析
2.3.1 相关性分析
污染物的来源是否一致可通过相关性分析进行确定[25],利用皮尔逊相关系数对重金属Pb、As及PAHs中的Nap、Phe、BaA和BaP进行相关性分析(表5). 结果表明,PAHs之间均为显著正相关,低环PAHs之间的相关系数达0.94,高环PAHs之间的相关系数达0.802,而低高环PAHs之间的相关系数均小于0.6,为弱相关. 重金属之间也呈现显著正相关性,Pb、As之间的相关系数达0.648,重金属污染物与PAHs基本不相关,相关系数较低. 由此分析可知,重金属Pb与As可能具有相同的来源,各多环芳烃来源一致,但重金属与多环芳烃的来源不相同.
表 5 土壤多环芳烃相关性分析Table 5. Correlation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil因素Element Pb As Nap Phe BaA BaP Pb 1 As 0.648** 1 Nap −0.274 −0.163 1 Phe −0.161 −0.177 0.940** 1 BaA −0.048 −0.135 0.420* 0.418* 1 BaP −0.220 −0.111 0.594** 0.548** 0.802** 1 **. P<0.01; *. P<0.05. 2.3.2 主成分分析
主成分分析是判别污染物来源的有效手段. 采用KMO和Bartlett法对土壤中重金属和PAHs含量进行检验,得到KMO为0.545(>0.5),Bartlett球度检验的相伴概率为0.000(<0.005),表明可以进行主成分分析[26]. 提取出两个特征值大于1的成分[27],为了提高数据真实性,使用最大方差法,计算出旋转后的成分矩阵,累计方差贡献率为75.28%,具有较高的代表性,结果如表6所示.
表 6 污染物主成分分析矩阵Table 6. Component matrix of principal component analysis of pollutant因素Element 初始因子荷载Initial factor load 旋转后因子荷载Factor load rotation PC1 PC2 PC1 PC2 Pb 0.224 0.889 0.209 0.893 As −0.192 0.861 −0.207 0.858 Nap 0.894 0.085 0.892 0.100 Phe 0.872 0.010 0.871 0.025 BaA 0.744 −0.181 0.747 −0.169 BaP 0.862 0.019 0.862 0.034 特征值 2.944 1.573 2.072 1.793 累计方差贡献率% 49.06 75.28 40.06 75.28 第一主成分的贡献率最高,为49.06%,4种PAHs在第一主成分上具有较大荷载. 结合表6可知,4种PAHs具有显著相关性,4种PAHs受到相同污染源的影响. 经分析判断认为,研究区焦化过程中的鼓冷、脱硫、冼氨、洗苯脱苯及沉淀过程产生的废气、废水和废渣都是PAHs的主要来源.
另外,在已有的研究中,可用低环PAHs与高环PAHs的比值来指示PAHs的来源,有研究认为[28-30],低环PAHs主要来源于石油、化石燃料的低温分解,而高环PAHs主要来自各类煤的高温燃烧. 综合场地PAHs污染羽的分布和场地环境调查结果,场地各个功能区的低环PAHs/高环PAHs的比值均大于1,推断认为这是焦油渣及萘油、苊油等油液副产品作为中间产物在堆存和生产过程中发生了遗撒泄露. 而高环PAHs主要来源为焦煤、气煤等生产原料的不充分燃烧. 在炼焦过程中,排放的烟尘为高环PAHs的富集相,在受到干、湿沉降作用后分布于表层土壤[31- 32],这也是造成高环PAHs主要集中于浅层土壤的原因之一.
第二主成分的贡献率为26.22%,较大荷载为重金属Pb和As,表6也显示Pb和As具有极显著相关性. 结合场地历史调查,认为重金属Pb、As主要来自厂区煤库/煤棚及仓库区堆存的铅精矿粉,由于厂区的煤仓处于半封闭状态,矿粉长期遭受雨水淋滤,其中的重金属成分在地表径流作用下水平运移和下渗扩散,导致周边环境的Pb和As污染.
图4中污染物间的距离也反映了污染物之间的相关性,重金属Pb和As表现出较强的相关性;4种PAHs之间距离较近,具有很强的相关性,而重金属与PAHs则显示出较强的异源性.
由污染物污染羽分布状况分析,具有不同来源的重金属及PAHs在煤库/煤棚、制冷站及鼓冷车间等区域的土壤环境中相互共存,这种复合污染主要是由于重金属和高环PAHs均容易被吸附沉淀,在经过迁移后在场地部分区域形成复合污染[33],也可能由生产原料及废弃物的随意堆砌等多方面原因造成的.
2.4 土壤污染物评价结果分析
2.4.1 场地土壤重金属评价结果
根据内梅罗综合污染指数法评价了场地土壤污染水平,如图5所示. 由5(a)图可以看出,重金属Pb的单因子污染指数在0.396—2.975之间,平均值1.49,基本上处于清洁—轻度污染,As的单因子污染指数范围为1.015—23.9,平均值4.34,整体上处于轻度—重度污染. 由图5(b)分析可知,场地大部分区域为清洁—轻度污染,中度风险及重度风险主要集中在煤棚/煤库、鼓冷车间及气柜等区域,与重金属Pb、As的空间分布具有高度一致性,表明场地土壤重金属污染主要受Pb、As元素的影响,进一步证实了Pb和As是场地重金属污染的主要元素.
2.4.2 场地土壤PAHs风险评价结果
采用质量基准法,计算场地土壤PAHs的QME值,计算结果如表7所示. 场地整体上处于低生态风险或无生态风险. 其中,洗苯脱苯车间、煤库/煤棚、制冷站的QME值分别高达21.07、15.69及3.36,远高于1.51,为高生态风险;气柜的QME值为1.42,属于中生态风险. 高生态风险区域与PAHs高浓度区域基本一致,洗苯脱苯车间为低环PAHs集中分布区域,其QME值为场地最高值,也证实了场地多环芳烃污染主要以菲、萘等低环PAHs为主.
表 7 场地土壤QME评价结果Table 7. Soil QEM evaluation results of the site项目Project 煤库/煤棚Coal depot 鼓冷车间Drum cooling workshop 制冷站Refrigeration station 气柜Gas holder 洗苯脱苯车间Benzene washing and debenzylation workshop QME 15.69 18.91 3.36 1.42 21.07 污染程度 高生态风险 高生态风险 高生态风险 中生态风险 高生态风险 3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)场地0—3 m土壤中,重金属Pb和As的最大超标倍数分别为1.98、22.9,超标率分别为17%和8.33%,PAHs中Nap、Phe、BaA及BaP的最大超标倍数分别为9.2、52.2、0.55及14.5,超标率分别为8.33%、14.3%、13.3%及15%. 重金属和PAHs污染在场地中分布均表现出明显的空间差异性,集中分布在煤库/煤棚、鼓冷车间、洗苯脱苯车间等区域.
(2)重金属Pb、As及高环PAHs集中分布在土壤表层,浓度随深度增加而呈现减小趋势;低环PAHs浓度随深度增加呈现先增大后减小的变化规律,浓度最大值分布在杂填土层与粉质粘土层交界处.
(3)污染物主要来源于原企业的生产活动,4种PAHs具有相同的来源,重金属与PAHs的来源不相同,但来源不同的重金属与PAHs经过土壤迁移后在场地的煤库/煤棚、鼓冷车间及制冷站等区域形成复合污染.
(4)内梅罗综合污染指数表明,场地大部分区域的重金属污染为轻度污染,气柜、煤库/煤棚、制冷站等区域基本处于中度—重度生态风险,质量基准法显示场地内PAHs在大部分区域为低生态风险或无生态风险,在气柜、制冷站、煤库/煤棚、鼓冷车间及洗苯脱苯车间等区域处于中—高生态风险状态.
-
表 1 土壤污染分级标准
Table 1. Soil pollution classification standard
单因子污染指数Single pollution index 污染水平Pollution grade 内梅罗综合污染指数Nemerow comprehensive pollution index 污染水平Pollution grade Pi≤1 清洁 P≤0.7 清洁 1<Pi≤2 轻度污染 0.7<P≤1.0 尚清洁 2<Pi≤3 中度污染 1.0<P≤2.0 轻度污染 Pi>3 重度污染 2.0<P≤3.0 中度污染 P>3.0 重度污染 表 2 土壤中多环芳烃效应区间中值(Ei)参考值[4]( mg·kg−1)
Table 2. Reference value of PAHs effect range median in soil(mg·kg−1)
多环芳烃 Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons Ei 多环芳烃 Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons Ei 萘(Nap) 2.10 苯并(a)蒽(BaA) 1.60 苊烯(Acy) 0.64 䓛(Chry) 2.80 苊(Ace) 0.50 苯并(b)荧蒽(BbF) 1.62 芴(Flu) 5.10 苯并(k)荧蒽(BkF) 1.62 菲(Phe) 1.50 苯并(a)芘(BaP) 1.60 蒽(Ant) 1.10 二苯并(a,h)蒽(DahA) 0.26 荧蒽(Fla) 0.54 苯并(g,h,i)苝(BghiP) 1.60 芘(Pyr) 2.60 茚并(1,2,3-cd)芘(InP) 1.60 表 3 质量基准法风险等级划分
Table 3. Soil average effect interval quotient QME risk classification
Q ME≤0.1 0.1—0.5 0.5—1.5 ≥1.5 风险等级(Ecological risk) 无 低 中等 高 表 4 焦化厂遗留场地污染物含量分析
Table 4. Pollutants concentration in soil of coking site
土层Soil layer 污染物Pollutant 含量范围/(mg·kg−1)C 平均值/(mg·kg−1)Cave 变异系数Coefficient of variation 筛选值/(mg·kg−1)Cfil 最大超标倍数Maximum exceedance 上层(0—1 m) Pb 8.5—1190 703.2 0.83 400 1.98 As 2.96—956 123.6 2.92 40 22.9 Nap 0.12—28.6 3.74 1.77 25 0.15 Phe 9.2—128 55.23 1.1 5 24 BaA 0.28—8.5 1.86 1.95 5.5 0.55 BaP 0.6—6.4 2.18 1.46 0.55 10.6 中层(1—2 m) Pb 10.2—298 194.64 0.77 400 — As 1.23—800 249.88 2.32 40 7.95 Nap 0.09—47.7 8.3 1.86 25 0.91 Phe 6.3—35.2 12.45 1.34 5 6.04 BaA 0.3—6.6 1.61 2.26 5.5 — BaP 0.6—4.4 0.84 1.35 0.55 7.0 下层(2—3 m) As 8.47—126 94.9 0.72 40 2.15 Nap 0.1—255 48.2 0.98 25 9.2 Phe 0.2—266 80.1 1.79 5 52.2 BaA 0.13—4.9 1.33 2.0 5.5 — BaP 1.1—8.5 3.7 1.05 0.55 14.5 注:场地调查区域土壤属于红壤/黄棕壤,砷的筛选值为40 mg·kg−1. Note: The soil in the site investigation area belongs to red soil/yellow brown soil, the filter value of As is 40 mg·kg−1. 表 5 土壤多环芳烃相关性分析
Table 5. Correlation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil
因素Element Pb As Nap Phe BaA BaP Pb 1 As 0.648** 1 Nap −0.274 −0.163 1 Phe −0.161 −0.177 0.940** 1 BaA −0.048 −0.135 0.420* 0.418* 1 BaP −0.220 −0.111 0.594** 0.548** 0.802** 1 **. P<0.01; *. P<0.05. 表 6 污染物主成分分析矩阵
Table 6. Component matrix of principal component analysis of pollutant
因素Element 初始因子荷载Initial factor load 旋转后因子荷载Factor load rotation PC1 PC2 PC1 PC2 Pb 0.224 0.889 0.209 0.893 As −0.192 0.861 −0.207 0.858 Nap 0.894 0.085 0.892 0.100 Phe 0.872 0.010 0.871 0.025 BaA 0.744 −0.181 0.747 −0.169 BaP 0.862 0.019 0.862 0.034 特征值 2.944 1.573 2.072 1.793 累计方差贡献率% 49.06 75.28 40.06 75.28 表 7 场地土壤QME评价结果
Table 7. Soil QEM evaluation results of the site
项目Project 煤库/煤棚Coal depot 鼓冷车间Drum cooling workshop 制冷站Refrigeration station 气柜Gas holder 洗苯脱苯车间Benzene washing and debenzylation workshop QME 15.69 18.91 3.36 1.42 21.07 污染程度 高生态风险 高生态风险 高生态风险 中生态风险 高生态风险 -
[1] 廖晓勇, 崇忠义, 阎秀兰, 等. 城市工业污染场地: 中国环境修复领域的新课题 [J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(3): 784-794. LIAO X Y, CHONG Z Y, YAN X L, et al. Urban industrial contaminated sites: A new issue in the field of environmental remediation in China [J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(3): 784-794(in Chinese).
[2] 骆永明. 中国污染场地修复的研究进展、问题与展望 [J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2011, 23(3): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2011.03.002 LUO Y M. Contaminated site remediation in China: Progresses, problems and prospects [J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2011, 23(3): 1-6(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2011.03.002
[3] 骆永明, 滕应. 中国土壤污染与修复科技研究进展和展望 [J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(5): 1137-1142. LUO Y M, TENG Y. Research progresses and prospects on soil pollution and remediation in China [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(5): 1137-1142(in Chinese).
[4] 王耀锋, 何连生, 姜登岭, 等. 我国焦化场地多环芳烃和重金属分布情况及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(12): 5938-5948. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202105239 WANG Y F, HE L S, JIANG D L, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals in coking sites in China [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(12): 5938-5948(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202105239
[5] 刘颖, 周念清. 复合污染场地污染特征分析及健康风险评估 [J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(7): 934-943. LIU Y, ZHOU N Q. Pollution characteristics and health risk of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a Co-contaminated site [J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2018, 46(7): 934-943(in Chinese).
[6] 杨悦锁, 陈煜, 李盼盼, 等. 土壤、地下水中重金属和多环芳烃复合污染及修复研究进展 [J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(6): 2219-2232. YANG Y S, CHEN Y, LI P P, et al. Research progress on co-contamination and remediation of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil and groundwater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(6): 2219-2232(in Chinese).
[7] WONG M H, WU S C, DENG W J, et al. Export of toxic chemicals - A review of the case of uncontrolled electronic-waste recycling [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 149(2): 131-140. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.01.044 [8] 沈国清, 陆贻通, 周培. 土壤环境中重金属和多环芳烃复合污染研究进展 [J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2005, 23(1): 102-106. SHEN G Q, LU Y T, ZHOU P. Advances of research on combined pollution of heavy metals with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs) in soil environment [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Agricultural Science), 2005, 23(1): 102-106(in Chinese).
[9] 马佳燕, 马嘉伟, 柳丹, 等. 杭嘉湖平原水稻主产区土壤重金属状况调查及风险评价 [J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(2): 336-345. doi: 10.11833/j.issn.20950756.20200309 MA J Y, MA J W, LIU D, et al. Survey and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the main rice producing areas in Hangjiahu Plain [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2021, 38(2): 336-345(in Chinese). doi: 10.11833/j.issn.20950756.20200309
[10] 朱岗辉, 孙璐, 廖晓勇, 等. 郴州工业场地重金属和PAHs复合污染特征及风险评价 [J]. 地理研究, 2012, 31(5): 831-839. ZHU G H, SUN L, LIAO X Y, et al. Combined pollution of heavy metals and PAHs and its risk assessment in industrial sites of Chenzhou City [J]. Geographical Research, 2012, 31(5): 831-839(in Chinese).
[11] 毛盼, 王明娅, 孙昂, 等. 某典型废弃硫酸场地土壤重金属污染特征与评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(2): 511-525. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021071304 MAO P, WANG M Y, SUN A, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and assessment in soil of a typical abandoned sulfuric acid site [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(2): 511-525(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021071304
[12] 武海霞, 马栋. 工业污染场地土壤中多环芳烃测定方法研究 [J]. 内江科技, 2015, 36(12): 35-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1436.2015.12.026 WU H X, MA D. Study on determination method of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in contaminated site soil [J]. Nei Jiang Science & Technology, 2015, 36(12): 35-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1436.2015.12.026
[13] 吕占禄, 张金良, 张晗, 等. 生物质能电厂周边土壤中重金属元素污染特征及评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(12): 3480-3494. LV Z L, ZHANG J L, ZHANG H, et al. Pollution characteristics and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in surface soil around the Biomass Power Plant [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(12): 3480-3494(in Chinese).
[14] 廖晓勇, 陈同斌, 武斌, 等. 典型矿业城市的土壤重金属分布特征与复合污染评价: 以“镍都”金昌市为例 [J]. 地理研究, 2006, 25(5): 843-852. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2006.05.010 LIAO X Y, CHEN T B, WU B, et al. Mining urban soil pollution: Concentrations and patterns of heavy metals in the soils of Jinchang, China [J]. Geographical Research, 2006, 25(5): 843-852(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2006.05.010
[15] LONG E R, MACDONALD D D, SMITH S L, et al. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments [J]. Environmental Management, 1995, 19(1): 81-97. doi: 10.1007/BF02472006 [16] 刘庚, 毕如田, 张朝, 等. 某焦化场地苯并(a)芘污染空间分布范围预测的不确定性分析 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(2): 587-593. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2013.02.027 LIU G, BI R T, ZHANG C, et al. Uncertainty analysis on spatial distribution prediction of BaP in a coking plant site [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(2): 587-593(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2013.02.027
[17] 徐源, 师华定, 王超, 等. 湖南省郴州市苏仙区重点污染企业影响区的土壤重金属污染源解析 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(5): 1213-1222. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.11.03 XU Y, SHI H D, WANG C, et al. Heavy metal pollution sources in soil affected by key pollution enterprises in Suxian District, Chenzhou City, Hunan Province [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(5): 1213-1222(in Chinese). doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2020.11.03
[18] 段友春, 梁兴光, 臧浩, 等. 日照市典型农用地土壤重金属来源分析及环境质量评价 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(11): 1410-1414,1429. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.11.019 DUAN Y C, LIANG X G, ZANG H, et al. Source analysis and environmental quality assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil in a typical area of Rizhao City [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(11): 1410-1414,1429(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2020.11.019
[19] 韩张雄, 万的军, 胡建平, 等. 土壤中重金属元素的迁移转化规律及其影响因素 [J]. 矿产综合利用, 2017(6): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.06.002 HAN Z X, WAN D J, HU J P, et al. Migration and transformation of heavy metals in soil and its influencing factors [J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(6): 5-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.06.002
[20] YANG J J, WANG S Q, GUO Z W, et al. Spatial distribution of toxic metal(loid)s and microbial community analysis in soil vertical profile at an abandoned nonferrous metal smelting site [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(19): 7101. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17197101 [21] ZENG J Q, LUO X H, CHENG Y Z, et al. Spatial distribution of toxic metal(loid)s at an abandoned zinc smelting site, Southern China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 425: 127970. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127970 [22] 孟祥帅, 吴萌萌, 陈鸿汉, 等. 某焦化场地非均质包气带中多环芳烃(PAHs)来源及垂向分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 377-384. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201903142 MENG X S, WU M M, CHEN H H, et al. Vertical pollution characteristics and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a heterogeneous unsaturated zone under a coking plant [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 377-384(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201903142
[23] 李看看, 吴娟, 马东, 等. 表面活性剂对土壤中多环芳烃(PAHs)纵向迁移的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(7): 1545-1553. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017101301 LI K K, WU J, MA D, et al. Effects of surfactant on longitudinal migration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(7): 1545-1553(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017101301
[24] 韩志刚. 多环芳烃在土壤中的老化和迁移行为研究[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2009. HAN Z G. Aging and transport behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University, 2009(in Chinese).
[25] 吴志远, 张丽娜, 夏天翔, 等. 基于土壤重金属及PAHs来源的人体健康风险定量评价: 以北京某工业污染场地为例 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9): 4180-4196. WU Z Y, ZHANG L N, XIA T X, et al. Quantitative assessment of human health risks based on soil heavy metals and PAHs sources: Take a polluted industrial site of Beijing As an example [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(9): 4180-4196(in Chinese).
[26] 周艳, 陈樯, 邓绍坡, 等. 西南某铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属空间主成分分析及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. ZHOU Y, CHEN Q, DENG S P, et al. Principal component analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around a Pb-Zn mine in southwestern China [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892(in Chinese).
[27] 师荣光, 吕俊岗, 张霖琳. 天津城郊土壤中PAHs含量特征及来源解析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2012, 28(4): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2012.04.001 SHI R G, LV J G, ZHANG L L. Content character and source analyses of PAHs in soils of Tianjin suburbs [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2012, 28(4): 1-5(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2012.04.001
[28] 崔政武, 王洋, 于锐, 等. 吉林省电厂周边农田土壤中多环芳烃含量特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2018, 40(7): 806-811. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2018.07.015 CUI Z W, WANG Y, YU R, et al. Content characteristics and risk assessment of PAHs in agricultural soils around power plants in Jilin Province [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2018, 40(7): 806-811(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2018.07.015
[29] 李永霞, 刘燕, 王文刚, 等. 某钢铁企业表层土壤中多环芳烃含量特征与生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(6): 1320-1327. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.06.2016090802 LI Y X, LIU Y, WANG W G, et al. Concentration characteristic and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface soils of a steel plant [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(6): 1320-1327(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.06.2016090802
[30] 孔露露, 史明静, 梁晶晶, 等. 大港油田土壤中PAHs的组成特征及来源分析 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(5): 151-157. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2018.05.025 KONG L L, SHI M J, LIANG J J, et al. Concentration and origin of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the soil of dagang oil field [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(5): 151-157(in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2018.05.025
[31] 安永龙, 黄勇, 孙朝, 等. 北京通州某改造区土壤中PAHs的来源分析及风险评价 [J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2017, 44(5): 112-120. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.05.18 AN Y L, HUANG Y, SUN Z, et al. Source apportionment and risk assessment of PAHs in soil from a renewal area in the Tongzhou District of Beijing [J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(5): 112-120(in Chinese). doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2017.05.18
[32] 郝丽虹, 张世晨, 武志花, 等. 低山丘陵区焦化厂土壤中PAHs空间分布特征 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(7): 2625-2631. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.07.031 HAO L H, ZHANG S C, WU Z H, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of PAHs in soil at hilly areal coking plant [J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(7): 2625-2631(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.07.031
[33] 周玉璇, 龙涛, 祝欣, 等. 重金属与多环芳烃复合污染土壤的分布特征及修复技术研究进展 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2019, 35(8): 964-975. doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.0669 ZHOU Y X, LONG T, ZHU X, et al. Research progress on distribution and remediation technologies for the combined pollution of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2019, 35(8): 964-975(in Chinese). doi: 10.19741/j.issn.1673-4831.2018.0669
-




 下载:
下载: