-
水华(algal bloom)是在一定的营养、气候和水文条件下藻类等浮游生物大量繁殖并在水体表面聚集,使水体颜色发生变化的现象[1]. 水华的发生可能引起严重的生态环境问题,大量繁殖的藻类死亡后耗氧分解会造成水体缺氧,这严重威胁了水体中其他生物的生存,从而导致生态失衡,而如果饮用水源发生水华则会影响饮用水安全,造成严重的经济损失[2]. 一直以来,水华都是国内外研究学者重点关注的生态环境问题之一.
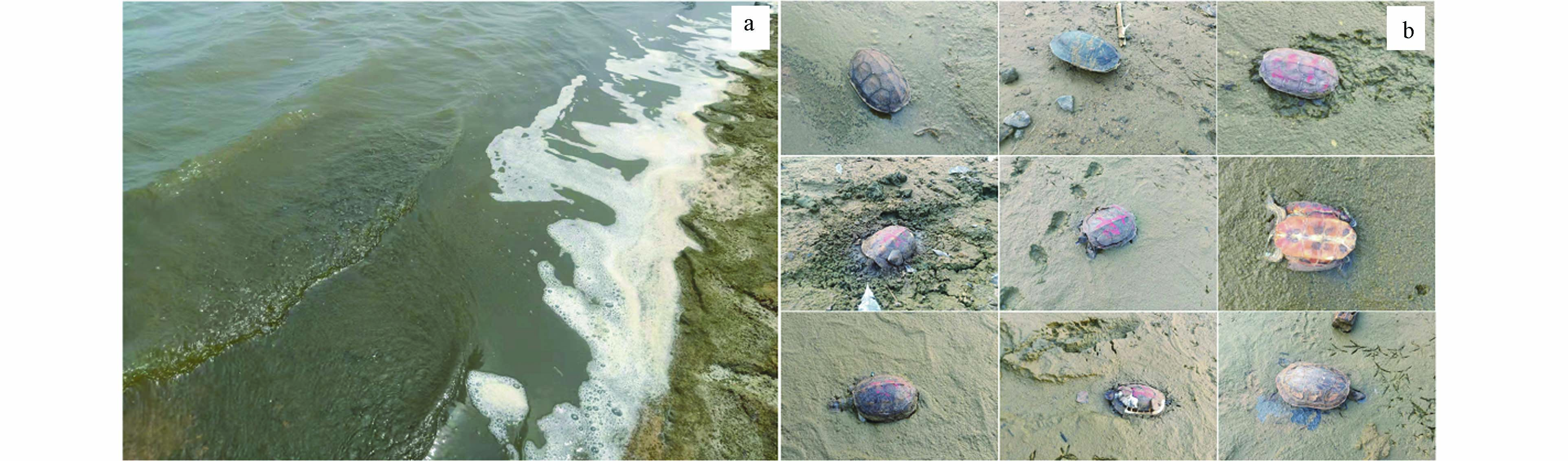
湖光岩玛珥湖(以下简称湖光岩)是距今14—16万年前由平地火山喷发后火山口下沉形成的湖泊,是世界上最大且保存最完整的玛珥湖[3]. 湖光岩是封闭性湖泊,四周被火山碎屑岩包围,且没有河流的注入与流出,湖水水位的变化主要取决于大气降水和地下水位的变化[4]. 前人有关湖光岩生态问题的研究主要集中在水体营养盐的时空分布[3]、浮游植物对溶解态氮的吸收[5]以及浮游植物种属的季节性变化[6]等方面,而有关湖光岩水华问题的研究尚未有过报道. 早在2009年以及2011年便有新闻报道关于湖光岩的湖面漂浮着蓝藻,但当时却未引起各学界的重视[7]. 2021年12月—2022年3月,笔者注意到湖光岩的湖面漂浮着大量的浮游藻类,东、北部水域的湖水浑浊且湖滩被一层绿色的藻泥所覆盖,此外在东、北部湖滩也发现了不少已经死亡的乌龟(图1),经观察确认湖光岩暴发了水华. 鉴于有关湖光岩水华现象的研究尚未有过报道,故本文对湖光岩的水华现象开展初步的研究分析,以期为认识湖光岩水华发生的机理提供科学依据.
湖光岩为封闭性湖泊,是研究认识较为单纯的水文条件下水华形成与发展的理想场所,对研究封闭性湖泊水华的发生具有独特的科学意义. 此外,湖光岩为国家4A级旅游景点,水华的发生必然对湖泊水体及周围的生态环境有所影响,因此分析和探讨湖光岩发生水华的原因具有积极的理论与实际意义. 本研究通过对湖光岩水华暴发的主要藻种鉴定以及水体样品的水质分析等,试图从营养盐、水文条件以及气象因素等方面探讨分析湖光岩发生水华的原因,以期认识玛珥湖水华发生的影响控制因素,同时也为湖光岩水华的治理与预防提供科学依据.
-
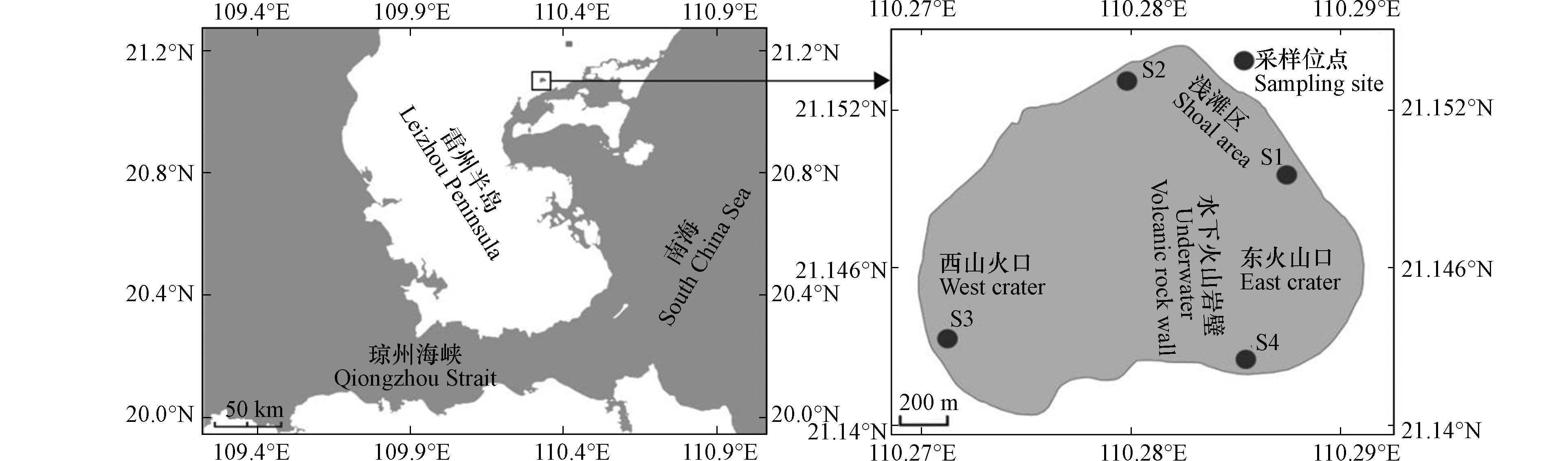
湖光岩(21°09′N,110°17′E)位于中国广东省湛江市,其外形呈心形形状,由紧邻的两个火山喷发口组合而成,在水下被火山岩壁分割成东、西两湖,东湖小且浅,西湖较大且深,湖泊水位较低时可看见东西两湖之间不连续的火山石出落于水中. 湖泊总面积为 2.3 km2,水深最深处约为 22 m[8]. 水华藻类样品及水样的采集主要是结合湖光岩的地形环境以及水华发生的位置进行采样点的布设,如图2所示,其中S1、S2站点位于浅滩区域,水深约1—2 m,该区域发生水华现象,湖水中漂浮着大量的浮游藻类并且湖滩有藻泥沉积覆盖,在S1、S2站点采集水华藻类样品和水样,S3站点位于西湖区域,S4站点位于东湖区域,由于S3、S4站点的区域没有发生水华,故在这两个样点只采集了水样.
-
样品的采集时间为2022年3月,使用采水器取水面以下约 0.5 m深处的水样1 L,完成后立即带回实验室,使用0.45 μm的醋酸纤维滤膜过滤,过滤后的水样冷冻保存于-20 ℃的冰箱,用于开展营养盐(硝态氮(NO3−-N)、亚硝态氮(NO2−-N)、铵态氮(NH4+-N)、磷酸盐(PO43−-P)和硅酸盐(SiO32−-Si))的分析. 另采集250 mL水样,加入3—5 mL的鲁哥试剂固定液,带回实验室经沉淀浓缩后进行镜下观察拍照,用于水华主要藻种的分析与鉴定.
-
湖水理化性质的测定包括现场水体的水温、pH值、盐度的测定,均使用便捷式多参数分析仪(上海雷磁有限公司,DZB—718L)进行现场测定. 营养盐的测定根据《水和废水监测分析方法》[9]进行测定,其中氨氮采用纳氏试剂分光光度法,亚硝酸盐采用萘乙二胺分光光度法,硝酸盐采用紫外分光光度法,磷酸盐采用磷钼蓝分光光度法,硅酸盐采用硅钼黄法分光光度法. 水华主要藻种的鉴定通过光学显微镜对采集的浮游藻类进行镜下观察和拍照,并参照《中国淡水藻类》[10]、《淡水微型生物图谱》[11]进行鉴定.
-
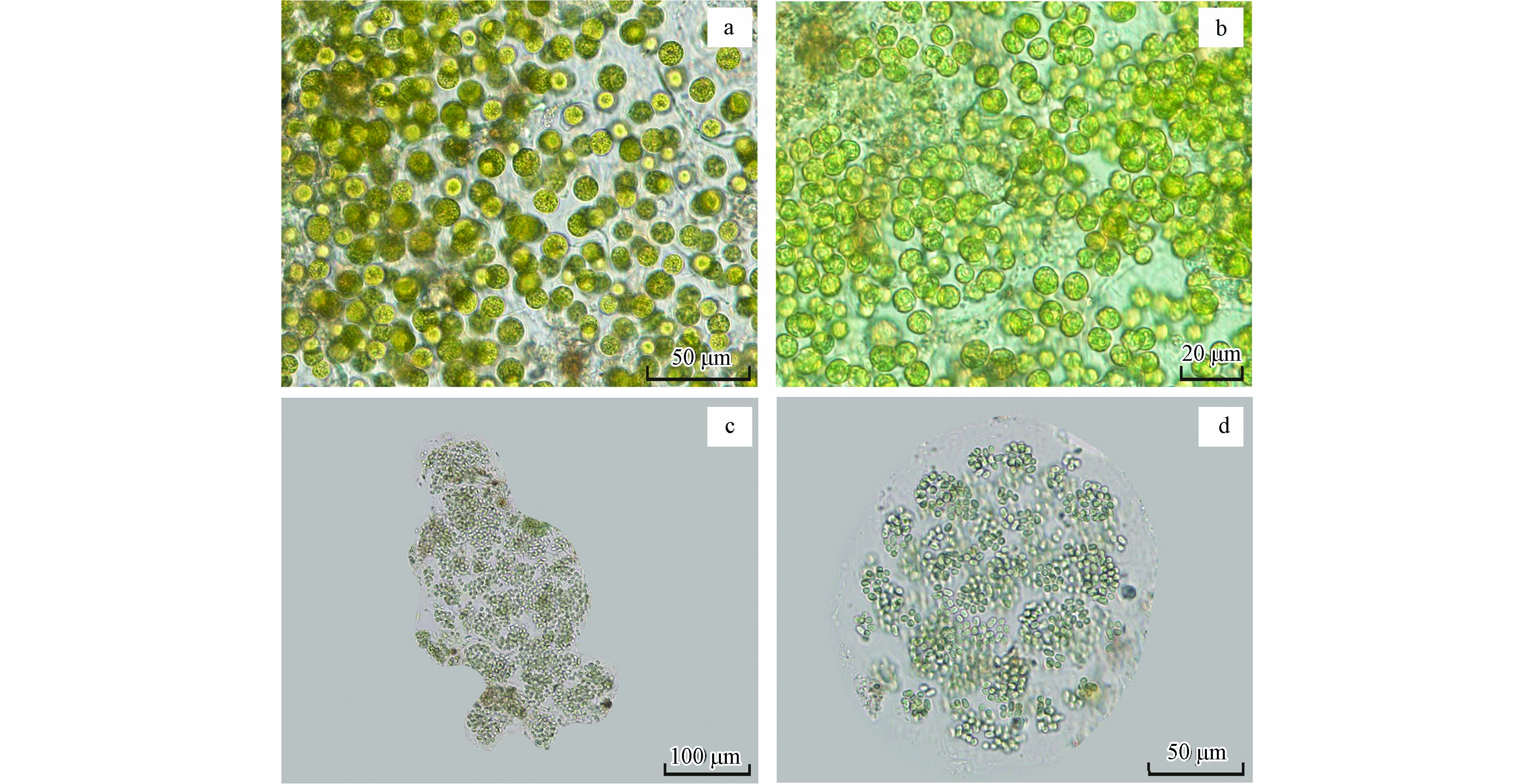
显微镜观察显示,构成湖光岩水华的藻种主要有两种,分别显示于图3a、b和图3c、d. 其中图3a、b显示的藻类为球形单细胞体,呈黄绿色,细胞壁薄,细胞直径5—10 μm;参照《中国淡水藻类》[10]和《淡水微型生物图谱》[11]进行鉴定,确定该藻种为绿藻门(Chlorophyta)、绿藻纲(Chlorophyceae)、绿球藻目(Chlorococcales)、小球藻科(Chlorellaceae)、小球藻属(Chlorella)中的小球藻(Chlorella vulgaris). 图c、d显示的藻类为多数细胞组成的群体,成熟的群体明显裂开,胶被的某些区域破裂或穿孔;群体中的细胞呈球形或椭圆形,直径3—7 μm,呈蓝绿色;经图谱鉴定该藻种为蓝藻门(Cyanophyceae)、蓝藻纲(Cyanophyceae)、色球藻目(Chroococcales)、色球藻科(Chroococcaceae)、微囊藻属(Microcystis)中的铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)[12]. 因此,引起湖光岩水华暴发的主要藻类为绿藻和蓝藻,且以绿藻占据优势,通过显微镜观察小球藻的数量占比可达60%.
张才学等[6]于2006年对湖光岩的浮游藻类进行周年的调查,结果检出湖光岩水体中浮游藻类260种,以绿藻门、蓝藻门、硅藻门为主,其中绿藻门占45%,硅藻门占30.4%,蓝藻门占16.5%,绿藻门的小球藻以及蓝藻门的小型色球藻、水华微囊藻、煤黑厚皮藻为全年广布优势种;2013年张国维等[13]检出湖光岩水体中浮游藻类135种,其中绿藻门占33.3%,蓝藻门占30.4%,硅藻门占22.2%,绿藻门的小球藻、蓝藻门的水华微囊藻、铜绿微囊藻以及硅藻门的颗粒直链藻为全年广布优势种. 可见,由于环境理化因子以及水质营养条件的改变,水华期间与没有发生水华期间浮游藻类的组成结构发生改变.
-
表1为2022年3月份湖光岩各站点理化状态的测定结果. 由表1可看出,湖光岩各站点的温度变化范围为25.10—29.20 ℃,平均温度为26.72 ℃,且水华发生区域的S1、S2站点的水温要比S3、S4站点的水温高2—4 ℃,这与湖光岩的地理环境有关,S3、S4站点位于湖光岩的南部,南部的植被较高且密集分布,阳光易被遮挡,因此湖泊的南部日照时间较短,接收的阳光较少,而S1、S2站点位于湖光岩的东北部,在一天中能接收更充足的阳光,因而S1、S2站点的水温更高[14].
温度是水体环境中最为重要的参数,也是诱发水华暴发的重要因素之一. 温度通过影响藻类的代谢强度和光合作用,控制着藻类的生长、发育和分布等[15]. 此次构成湖光岩水华暴发的两种主要藻种中,小球藻对温度的适应范围较广,而铜绿微囊藻在28—32 ℃的水温条件下生长速率最高,更适宜在较高温的条件下生长[16-17]. 由于湖光岩水华的暴发主要发生于冬春季节,冬季的湖水温度相对偏低,更适合小球藻的生长繁殖,这应是湖光岩水华暴发的主要藻种中小球藻占据优势的主要原因. 而发生水华区域的S1、S2站点位于湖光岩的北部,冬季期间能接收更充足的阳光,水温比位于日照少的南部区域的S3、S4站点要高,更有利于藻类进行光合作用.
-
表1显示湖光岩各站点的pH值变化范围为7.98—8.67,水质偏弱碱性,其中S2站点的pH值最高为8.67,而且S1、S2站点的pH值要比S3、S4站点的pH值高,这与浮游藻类在生长过程中吸收水体中的CO2进行光合作用有关,使得水体中的氢离子浓度降低,pH值升高. 一般情况下,藻类适宜生长在中性或者弱碱性的环境中,而水体的pH值也会随着藻类的增多而升高[18]. 小球藻对pH值的适应范围较广,适应能力较强. 而铜绿微囊藻在pH值为8.0—9.5的环境条件下生长繁殖能力较强,pH值过低或过高都会对铜绿微囊藻的生长有所影响[19]. 总体上看,湖光岩的酸碱度条件有利于小球藻和铜绿微囊藻的生长繁殖.
-
由表1可见,湖光岩各站点不同营养盐的含量中,SiO32−-Si的平均含量最高。4个站点的SiO32−-Si含量变化较大,范围为0.141—4.140 mg·L−1,S1站点的SiO32−-Si含量最高,为4.140 mg·L−1. PO43−-P的含量最低,含量范围为0.001—0.004 mg·L−1,其中S1站点的PO43−-P含量最高为0.004 mg·L−1. 在4个站点中NO2−-N的含量最稳定,4个站点的NO2−-N含量都为0.003 mg·L−1. NO3−-N的含量在4个站点中基本稳定,其中S1站点的NO3−-N含量最高,为0.192 mg·L−1. NH4+-N的含量变化在4个站点变化不大,变化范围为0.097—0.137 mg·L−1,其中S1站点的NH4+-N含量最高,为0.137 mg·L−1.
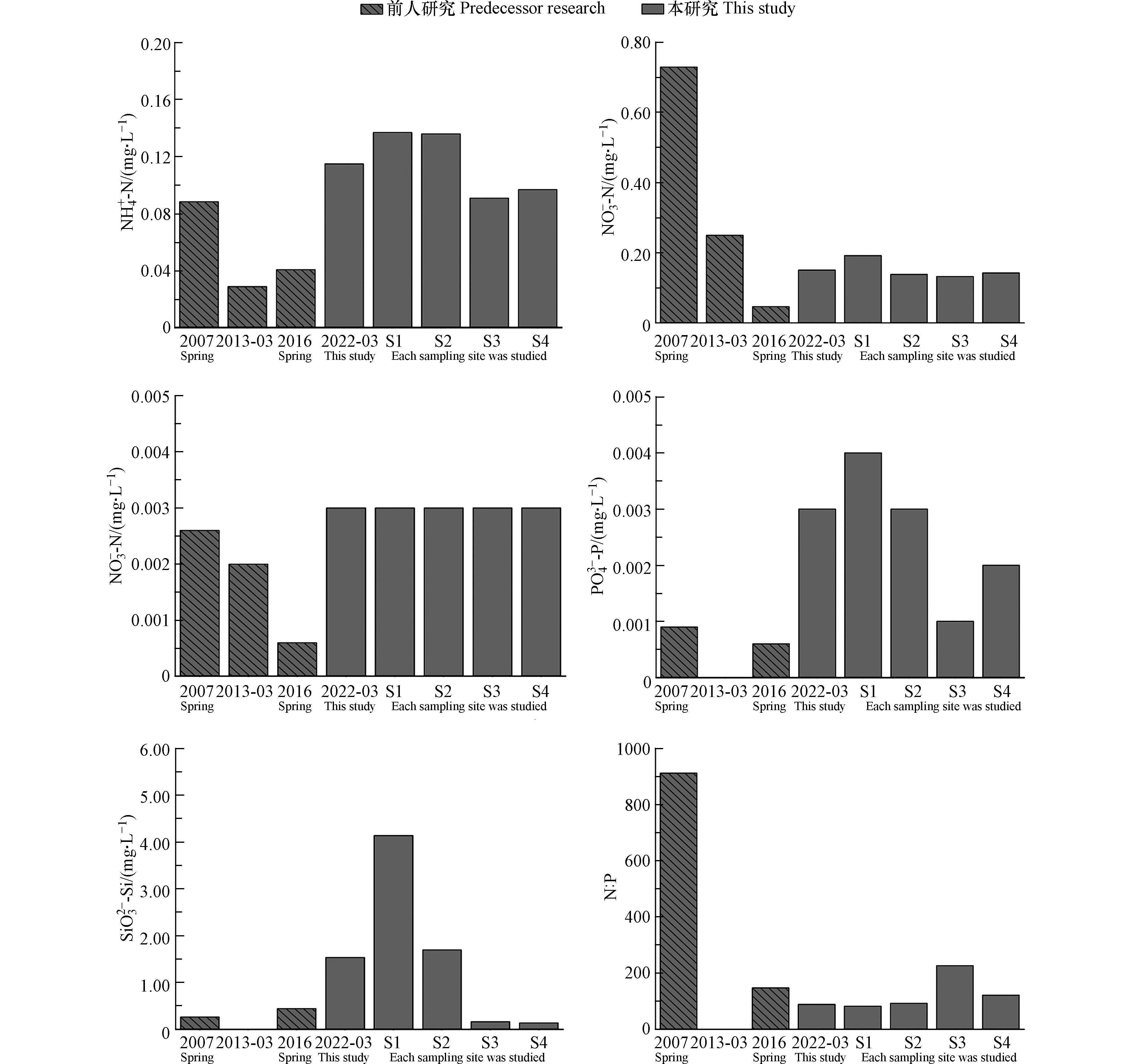
不同时期下湖光岩表层水营养盐含量的对比分析表明(表2),SiO32−-Si的含量在不同时期测定的营养盐组分中都是最高的,变化的范围为0.2674—1.5360 mg·L−1,PO43−-P含量最低,变化范围为0.0006—0.0030 mg·L−1. 图4为不同时期湖光岩表层水营养盐含量以及本研究不同采样点营养盐含量柱形图. 由图4中可明显看出,除了NO3−-N之外,本研究测定的NH4+-N、NO2−-N、PO43−-P、SiO32−-Si含量远高于前人测定的数值. 此外,从图4中可看出,除NO2−-N之外,水华发生区域S1、S2站点测定的NH4+-N、NO3−-N、PO43−-P、SiO32−-Si含量均高于S3、S4站点的含量. 营养盐是影响水体中藻类生长发育的重要条件,并在一定程度上导致水体中的优势藻类群落发生改变. 由此可见,相对较高的营养盐含量是引起湖光岩水华暴发的主要原因.
在分析的5种营养盐中,SiO32−-Si的含量最高,一方面这可能是由于湖泊底层沉积物中的有机质氧化分解产生的,另一方面可能是因为湖光岩四周为火山碎屑岩,火山碎屑岩的硅元素含量较高,岩石中的可溶性物质经雨水冲刷被带入水体中,从而使水体中的SiO32−-Si含量背景值较高[3]. 已有研究发现在浮游藻类中蓝藻和绿藻对磷有较高的需求,对硅没有明显的需求,而硅藻则对硅的需求较高[21-22]. 引发湖光岩水华暴发的两种主要藻类属于蓝藻和绿藻,因此,较高含量的SiO32−-Si对水华的形成没有明显的促进作用,其含量也可能没有达到让湖光岩水体暴发硅藻水华的浓度门限.
在本研究分析的5种营养盐中,PO43−-P含量最低,贝格最小值定律指出,植物生长取决于外界提供给它的所需养料中数量最少的一种[2]. Redfield[23]指出浮游藻类吸收利用氮、磷营养盐的最适宜比例为16:1,在研究中一般认为水体中的氮磷比大于16:1存在磷限制,而小于16:1则存在氮限制. 由表1可见,本研究中4个站点的N:P变化范围为83—227(N = DIN,P = PO43−-P),其中S3站点的氮磷比值最高为227,S1站点的氮磷比值最低为83,表现出明显的磷限制,这一分析结果与前人的研究结果一致[3, 6]. 且由表2及图4可见,相比于前人的研究,本研究的氮磷比相对较低. 因此,相比于氮营养盐含量的增加,磷营养盐含量的增加更有利于浮游藻类的生长繁殖. 由图4可见,相比于前人的研究,本研究的PO43−-P含量相对偏高,且水华发生区域的S1、S2站点的PO43−-P含量要比S3、S4站点的PO43−-P含量高. 因此,PO43−-P含量增加是导致湖光岩发生水华的重要因子之一.
张国维等[5]利用15N 稳定同位素示踪技术研究湖光岩浮游藻类对氮的吸收速率,结果发现湖光岩的浮游藻类对NH4+-N的吸收速率最高,更偏好利用NH4+-N,而对NO3−-N、NO2−-N则具有一定的亲和力. 由此推测,NH4+-N 也是调控湖光岩浮游藻类生长的重要营养盐因子之一. 由图4可知,相比于之前没有发生水华现象的研究,本研究中NH4+-N的含量相对较高,而且相比于S3、S4站点,水华发生区域的S1、S2站点的NH4+-N含量也是相对偏高的. 根据以上分析可见,水体中PO43−-P、NH4+-N含量的增加是造成水华现象发生的主要原因.
湖光岩为封闭性湖泊,其营养物质的循环主要是生态系统的内部循环,而外源营养物质的输入较少[6]. 湖光岩的营养物质内部循环受水体温度变化的影响较大,湖光岩的水体温度在垂向上具有季节性分层的现象,夏季表层水的温度高,表层水与较冷的深层水出现分层,阻碍了表层水与深层水及底层沉积物的营养盐循环交换,而到了冬春季节表层水的温度开始下降,水体的分层被破坏,水体发生混合,表层水的营养盐会有所增加[3, 24]. 此次湖光岩水华的暴发正值冬春季节,推测PO43−-P、NH4+-N等营养盐含量的增加主要是由于表层水与深层水发生垂直混合,从而使表层水的营养盐含量增加. 且S1、S2站点位于湖光岩浅滩区域,水深较浅,在冬季风的作用下其水体垂直混合更充分,因而其营养盐含量比S3、S4站点的高,更有利于水华的暴发.
-
浮游藻类的生长不仅受温度、光照、pH、营养盐、微量元素等影响因子的控制,水位的变化对藻类的生长也具有重要的调节作用[25]. 水位下降所引起的垂向轻微扰动能够使水体中的营养盐获得重新分配,激发底层水体和沉积物中营养盐的活性,为浮游藻类的生长提供了更持久的营养盐支撑条件[26]. 此外,水位的下降增强了水体的透光性,有利于浮游藻类进行光合作用,为浮游藻类的生长提供了有利的条件.
根据湛江市水文局的水文记录显示,在没有发生水华的年份湖光岩的平均水位多保持在20—21 m,而2021年以来湖光岩的水位在持续走低,2021—2022年最低水位出现在2022年4月中旬,为18.93 m,这表明在水华发生期间湖光岩的水位下降了近2 m. 湖光岩为封闭性湖泊,没有河流的注入与流出,水位的变化主要是取决于降雨和地下水位的变化. 湖光岩的气候属于典型的热带季风气候,干湿季分明,降雨主要集中在夏秋季节,冬春季节降雨量少,偏干旱[3]. 可见在冬春季节,水华发生期间降雨量偏少,减少了湖水的主要来源,长时间的干旱加快了湖水的蒸发速率,造成水位降低. 水位的下降使得水体中的营养盐得以重新分配,增强水体的透光性,为藻类的生长创造有利的条件. 此外,湖光岩为封闭性湖泊,在水位下降的条件下,水体中的营养盐得以富集,且更有利于水体的垂直混合,使表层的营养盐含量增加,加剧水华的暴发进程.
-
(1)引发2021—2022年湖光岩水华暴发的主要藻种为绿藻门中的小球藻以及蓝藻门中的铜绿微囊藻,其中小球藻的数量占比可达60%.
(2)2021—2022年湖光岩水华暴发的主要原因是在冬春季节,表层水体的温度下降,水体的分层被破坏,表层水体与深层水及底层沉积物的营养盐发生内部循环,导致表层水营养盐浓度增高,特别是PO43−-P和NH4+-N的增加,再加上适宜的水温、pH、光照条件以及水位的下降,为藻类的生长创造有利的条件,造成水华的发生. 因此,2021—2022年湖光岩水华的暴发是营养盐、水体环境因子以及气候因子等影响因子综合作用的结果.
致谢:感谢广东省湛江市水文局提供湖光岩水位数据资料和罗涛在藻类样品采集中给予的帮助,特别感谢广东海洋大学张才学教授和南宁师范大学徐轶肖教授对论文提出的宝贵修改意见,在此向他们表示衷心的感谢!
引发2021—2022年度湖光岩玛珥湖水华事件的主要藻种及原因分析
The dominant algal species and the controlling factors triggered 2021—2022 Huguangyan Maar Lake algal bloom event
-
摘要: 水华(algal bloom)是水体中藻类过度繁殖所引起的生态环境问题,水华的暴发会对水体环境以及水生生态平衡造成严重的破坏. 湖光岩玛珥湖是低平地区火山口形成的湖泊,具有相对封闭的水体环境,是研究认识较为单纯的水文条件下水华形成与发展的理想场所,研究其水华暴发期间的主要藻种构成及水生态环境条件对认识水华形成的原因具有积极的意义. 本文对2021年12月—2022年3月期间湖光岩水华暴发的主要藻类进行了分析鉴定,并从营养盐条件、水文条件、气象因素等方面探讨分析湖光岩水华暴发的原因. 结果表明:(1)湖光岩水华暴发的主要藻种为绿藻门中的小球藻(Chlorella vulgaris)以及蓝藻门中的铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa);(2)湖光岩表层水营养盐含量分析显示,SiO32−-Si的含量最高,PO43−-P的含量最低,NO2−-N、NO3−-N、NH4+-N的含量在不同采样点基本保持稳定,而与前人在没有发生水华的年份所做的湖光岩水体营养盐含量分析相比,水华期间SiO32−-Si、PO43−-P以及NH4+-N的含量显著增加,而其他营养盐组分则变化不大,PO43−-P、NH4+-N为调控湖光岩浮游藻类生长的重要营养盐因子,因此水体中PO43−-P、NH4+-N含量的增加是造成湖光岩发生水华的主要原因;(3)湖光岩水华的暴发主要与水体中营养盐的浓度变化有关,而适宜的水文环境以及气候条件等也有利于水华的暴发.Abstract: Algal bloom is an ecological and environmental problem caused by the overbreeding of algal in the water, and the outbreak of algal bloom will cause serious damage to the water environment and aquatic ecological balance. Huguangyan Maar lake is a lake formed by volcanic craters in low-flat areas, with a relatively closed hydrological environment, it is an ideal place to study the occurrence of algal bloom under relatively simple hydrological conditions, and the study of the main algal species and ecological conditions of lake water environmental conditions during the outbreaks of algal bloom is significance for understanding the causes of algal bloom. This study has analyzed and identified the dominant algal species which caused the algal bloom in Huguangyan Maar lake from December 2021 to March 2022, and discussed the outbreak causes of algal bloom in terms of nutrient conditions, hydrological conditions, meteorological factors. The results showed that (1) the dominant algal species that consisting of the algal bloom are chlorella vulgaris of the phylum Chlorellavulgaris and microcystis aeruginosa of the cyanobacteria phylum; (2) the analysis of the surface water nutrients show that the content of SiO32−-Si is the highest nutrient as the PO43−-P being the lowest one; the content of NO2−-N、NO3−-N、NH4+-N is basically same at all four sampling sites. By comparing with the earlier nutrient data of the surface water in Huguangyan Maar lake in previous studies, the content of SiO32−-Si, PO43−-P and NH4+-N show significant increase during the algal bloom, while other nutrients are generally remain same, PO43−-P、NH4+-N are important nutrient factors regulating the growth of the planktonic algal in Huguangyan Maar lake, therefore it seems that the increase content of PO43−-P and NH4+-N in the lake water are likely the main reason for the outbreak of algal bloom in Huguangyan Maar lake; (3) the outbreak of algal bloom in Huguangyan Maar lake is mainly related to the change of nutrients concentration in water, and the appropriate hydrological environment and climatic conditions aggravate the outbreak process.
-
Key words:
- algal bloom /
- dominant algal species /
- nutrients of surface water /
- Huguangyan Maar Lake.
-
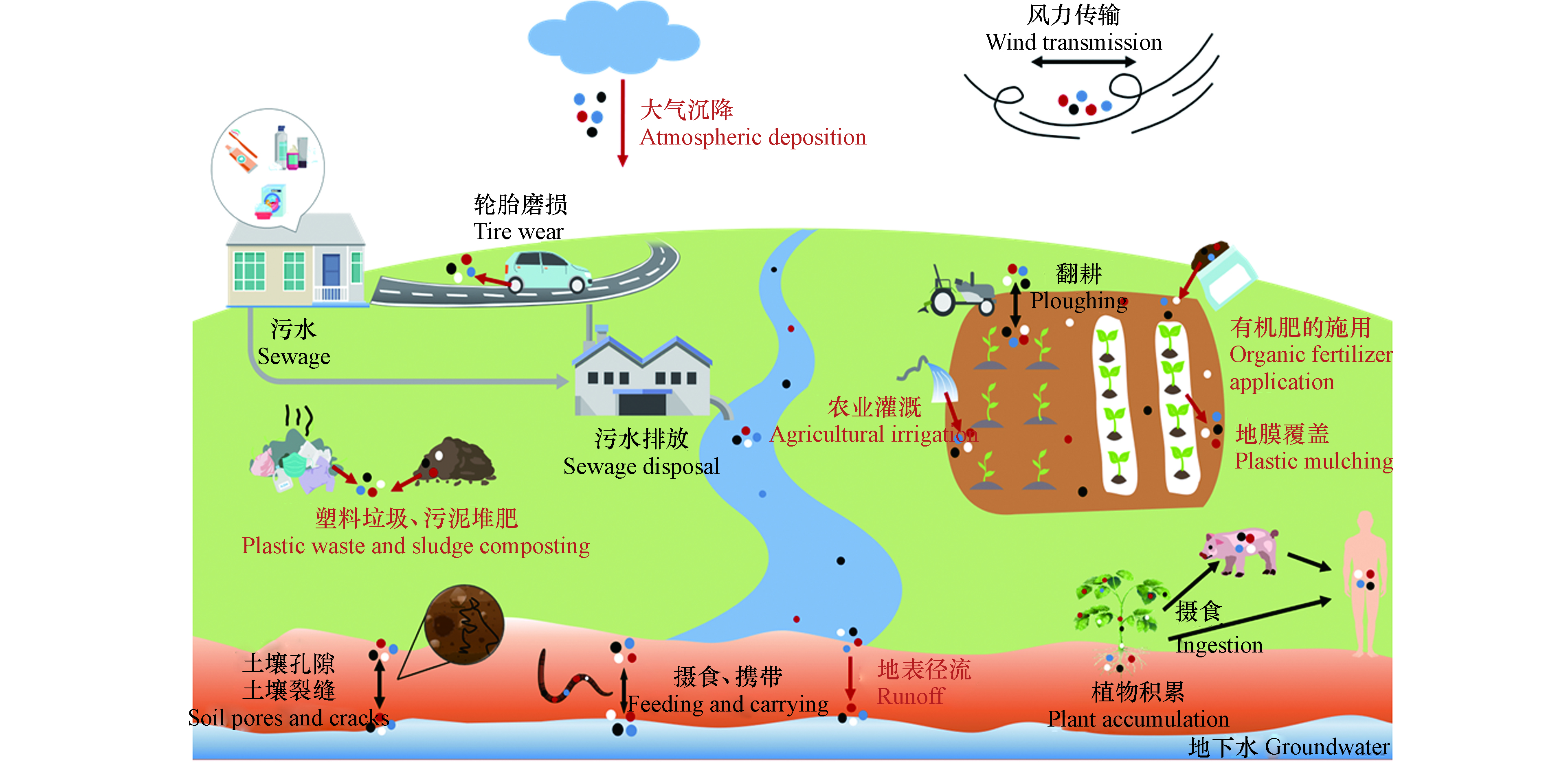
塑料的商业生产始于20世纪50年代[1],现广泛应用于包装、医疗、农业等行业,仅2019年全球塑料产量就高达3.68亿吨[2]。塑料在光照辐射、机械磨损、风化侵蚀、动物和微生物的作用下,可逐渐分解成粒径更小的塑料颗粒[3]。微塑料(microplastics, MPs)的概念最早出现在2004年Science发表的一篇文章[4],定义为粒径小于5 mm的塑料颗粒[5],粒径小于100 nm的被称为“纳米塑料”(nanoplastics, NPs)[6]。MPs通过大气、洋流等作用在全球范围内长距离运输[7],并在环境中持续存在和积累。水体[8]、沉积物[9]、土壤[10]、大气[11]甚至深海和极地都能检测到MPs[7]。尽管多项研究回顾了MPs在水环境中的发生、分布、生态风险及水体MPs与其他污染物的环境地球化学行为[8, 12-13],但关于陆地MPs的综述论文却很少[14-15]。陆地MPs是海洋MPs的主要来源,其MPs污染程度可能是海洋的4—23倍[16]。土壤作为陆地系统中MPs的汇[17],对MPs的储存和转移起着至关重要的作用[18]。因此,充分认识MPs在土壤环境中的丰度、来源、迁移和生态毒性对于科学评估和源头控制土壤MPs污染十分关键。
在Web of Science核心数据库中以“microplastics”和“soil”为关键词进行了搜索(截至2021年8月21日),产生了608篇文献。通过共现网络分析(图1),发现土壤环境MPs的研究始于2016年,相关研究主要包括:1)土壤类型,全球学者普遍注重农田土壤MPs的研究;2)MPs的来源,包括未合理处置的塑料垃圾、污泥堆肥、有机肥料的施用、污水灌溉和地膜覆盖等;3)MPs的分析方法,包括采样、分离(筛分、密度分离、消解等)、鉴定(目检法、光谱法、热解质谱分析法等);4)土壤MPs的丰度、类型(如聚丙烯(PP)、聚乙烯(PE)、聚苯乙烯(PS))、形状(如纤维、薄膜、碎片、颗粒等);5)MPs的生物效应,包括对植物、动物和微生物的影响。由此可见,MPs的来源、种类、分布、检测方法及生态健康风险是当前土壤MPs污染研究的热点方向。已发表的文献中,Praveena等[19]、陈雅兰等[20]较为全面的综述了土壤中MPs的提取与鉴定方法,郝爱红等[14]、Zhao等[15]从土壤中MPs的来源、迁移、分析方法、污染特征和生态风险等方面入手,揭示了土壤MPs的归宿和生态风险,但有关土壤MPs与多种有害污染物共同暴露的生物毒性、土壤中老化或降解MPs的生态风险鲜有报道。有学者对全球土壤MPs污染做了简单的总结[17, 21],但所收集的数据不够全面。因此,本文在总结最新国内外研究进展的基础上,从土壤环境中MPs的来源、丰度、迁移及其生态健康风险方面进行了综述,并提出了相关领域未来的研究重点。相比先前的研究,本文更加全面的总结了土壤中MPs的丰度,通过绘制分布图以更加直观的形式展现了全球土壤MPs污染,并将土壤老化/降解MPs的生态风险以及MPs的复合污染毒性和潜在生态风险展开了系统地回顾和展望,填补该领域综述论文的空白。本文将为评估土壤MPs潜在的生态健康风险提供有价值的参考。
 图 1 已发表论文中以“微塑料”、“土壤”为关键词的共现网络分析图[22]。Figure 1. Co-occurrence network analysis of published research papers with “microplastics” and “soil” as keywords每个节点(关键词)大小与其出现频次成正比,连线颜色表示论文发表年份,数据截至2021年8月21日
图 1 已发表论文中以“微塑料”、“土壤”为关键词的共现网络分析图[22]。Figure 1. Co-occurrence network analysis of published research papers with “microplastics” and “soil” as keywords每个节点(关键词)大小与其出现频次成正比,连线颜色表示论文发表年份,数据截至2021年8月21日1. 土壤MPs的来源、丰度和迁移 (Source, abundance and migration of soil MPs)
1.1 土壤MPs的来源
土壤中MPs的来源十分广泛(图2),人们日常生活(如未合理处置的塑料垃圾)和农业活动(如污泥堆肥、有机肥施用、地膜覆盖及农田灌溉等)产生的MPs会直接进入土壤[23-26],或通过地表径流[27]和大气沉降[28]间接输送到土壤环境。
1.1.1 未合理处置的塑料垃圾
土壤中存在着与水环境类似、种类繁多的MPs碎片[29],它们与塑料污染密不可分。根据目前的塑料废弃物管理趋势预测,2050年全球产生的塑料垃圾中将有120万吨进入垃圾填埋场或自然环境[30],必然会对生态环境造成影响。日常生活使用的一次性塑料袋/瓶、口罩/手套、衣服等均含有塑料,如使用后被随意丢弃在路边或非法倾倒地点[31],会造成附近土壤塑料污染。作为塑料垃圾的重要组成部分,塑料袋全球每年的消费量约为5000—10000亿个,其中900多亿个塑料袋不可回收[32],可在环境中老化降解生成MPs。自2020年新冠疫情爆发以来,大量一次性口罩排放到环境中。据估计,2020年全球生产的一次性口罩约520亿个[33]。每片新口罩中可释放(183.0±78.4)个MPs,而使用过的口罩因附着了空气中的MPs会释放更多的MPs(每片(1246.6±403.5) 个) [34]。由此,未合理处置的一次性口罩引起的土壤塑料和MPs污染不容忽视。
1.1.2 污泥堆肥的长期积累
污泥堆肥可能导致土壤MPs的增加[24]。生活废水经污水处理厂,可大大减少MPs(去除率约99%)向水环境直接排放[24],但未被处理的MPs通常积聚在污泥中[35],由于污泥含有丰富的N、P、K等营养元素[36],许多地区将污泥用作农田肥料[24],MPs便由此进入土壤。不同国家污泥中MPs的含量与经济发展水平、人口密度和废物处置等因素有关[37]。对于经济发达、人口密度高的国家,因使用药品、个人护理品(PPCPs)及洗衣产生的污水量大[38],污泥中MPs的含量相应较高。在欧洲和北美地区,每年通过污泥堆肥进入农田的MPs分别有约6.3×104—4.3×105和4.4×104—3.0×105吨[39]。土壤MPs的丰度随污泥施用量的增加而增加[24]。研究发现,在农田中仅施用一次污泥,15年后该区域土壤中仍可检测出塑料纤维[40],表明MPs在土壤中难以降解,会产生持久性污染。
1.1.3 有机肥料的施用
有机肥料的重复施用除了会引起重金属和抗生素等污染残留[41],还会导致土壤MPs污染,而后者常常被人们忽视[42]。研究发现,有机肥中普遍含有的MPs可能来自运输饲料的塑料管道、储存消毒剂或抗生素的塑料瓶[43]。江西鹰潭,猪粪中MPs的平均年丰度约为(1250±640)个·kg−1(干重),施用了猪粪的农田中MPs的年均累积量约为(1.25±0.61)个·kg−1[42];施用猪粪22年后的农田中MPs丰度((43.8±16.2)个·kg−1)明显高于未施用猪粪的农田((16.4±2.7)个·kg−1)[42]。德国是全球对肥料质量要求最严格的国家之一,但每年通过施用有机肥进入农田的MPs高达3.5×1010—2.2×1012个[26]。我国作为有机肥生产和使用大国,据估计,我国每年通过有机肥进入农田土壤中的MPs可达52.4—26400吨[3]。但该数据仅仅基于德国波恩、斯洛文尼亚等地区关于有机肥中塑料污染的报道[23, 26, 44],并结合我国有机肥每年实际施用量(2200万吨左右)来进行估算的,该估算忽略了粒径小于0.5 mm的MPs,且缺乏我国有机肥中关于MPs丰度的报道,因此,未来的研究中还应多关注我国有机肥中MPs的污染情况,以便全面评估我国通过有机肥进入土壤的MPs量。
1.1.4 农业灌溉和地表径流
农业灌溉是MPs进入土壤的又一重要途径。据统计,全球每年生活污水产生量超过356 km3,处理后的出水中有23.8 km3主要用于农业灌溉[45]。生活污水中含有大量源于PPCPs和衣物的MPs。虽然常规的处理工艺可有效去除污水中绝大部分MPs,但出水中仍有残留的MPs通过农业灌溉进入土壤环境[15]。在部分水资源匮乏的国家,未经处理的污水也会被用于灌溉农田[23]。据报道,全球约有3.6×105 km2的农田是使用未处理或者部分处理的生活污水进行灌溉的[46],必然会向土壤中输入更多的MPs。此外,天然水体中也存在MPs,例如:我国长江水中MPs高达6.6×103个·m−3[47],珠江水中MPs的丰度介于397—7924个·m−3之间[48],即使在偏远的内陆湖泊沿岸也有大量MPs存在,如青藏高原湖泊中MPs丰度可达(625±411)个·m−3[49]。这些水环境中的MPs也可通过灌溉或随地表径流进入土壤环境中。随着研究的深入,人们开始对生态环境敏感区(如青藏高原[49]、沙漠[50]、黄土高原[51])MPs污染进行研究,作为东南亚多条河流重要发源地的青藏高原,无处不在的MPs可能使其污染范围不断扩大到其他水系,或通过地表径流进入土壤环境,而该地区生态环境脆弱,存在调查难度大、恢复年限长等问题,未来的研究应该更加注重生态环境敏感区MPs污染及其健康风险评价。
1.1.5 地膜的广泛应用
地膜是农田土壤MPs污染的重要来源[23, 25]。2016年全球农用塑料薄膜市场交易量为400万吨,预计到2030年将以每年5.6%的速度增长[25]。全球约有1.29×105 km2的农田覆盖有地膜[52],我国地膜使用量最大,占全世界地膜覆盖面积的90%[17]。从田地中去除地膜费时费力,大量被残留的地膜在阳光辐射等作用下逐步破碎裂解,形成MPs[29]。农田土壤中MPs的含量随覆盖时间的延长逐渐增加[17]。在我国石河子市,随着地膜连续覆盖时间从5年增加至30年,MPs丰度从10.10 mg·kg−1增加到了61.05 mg·kg−1[53]。目前,大力研制与推广的环保型可降解地膜是解决塑料污染最有效的途径,但研究表明,MPs对污染物(如抗生素、农药等)的吸附能力大小排序为:老化可降解MPs>可降解MPs>非可降解MPs,且老化程度越高对污染物的吸附量越大[54-55],在这种情况下可降解地膜的使用,特别是地膜在环境中不可避免的老化行为,可能会给环境带来更大的生态危害,在未来的农业发展中应该重视这一问题。
1.1.6 大气沉降输入
土壤MPs也有部分来自大气中悬浮的塑料颗粒。多项研究表明,大气中存在MPs,如南海西北部大气中MPs的丰度为(0.035±0.015)n·m−3[56]。大气中的MPs主要来源于建筑材料、纺织品磨损、灰尘、道路油漆、轮胎和制动器磨损[57]。轮胎磨损产生的MPs主要来自各种车辆,全球车辆轮胎磨损的MPs排放量为人均0.81 kg·a−1[58],飞机轮胎磨损释放的MPs相对较少,约占荷兰轮胎磨损MPs排放总量的2%[58]。空气中密度小的大塑料颗粒和MPs可通过大气沉降和风力传输沉积在城市或乡村陆地表面[59],还可传输到偏远、人烟稀少的地区[28]。据报道,我国烟台市大气MPs沉降通量达1.5×105个·(m2 a)−1[60];法国巴黎大气MPs沉降通量达2—355个·(m2 d)−1,且该地区每年有3—10吨的纤维被大气沉降物沉积[59]。由此可见,大气沉降是MPs沉积到陆地的重要途径。值得思考的是,粒径小于50 μm的MPs可以重新悬浮到大气中[61],增加人体吸入MPs的风险,而多数国家并没有将大气中的MPs作为空气污染的一部分进行监测,为了明晰MPs对人类健康构成的潜在风险,将MPs纳入空气污染的监测范围迫在眉睫,尤其是在MPs污染严重的大城市。
总体来看,国内外大量关于土壤中MPs的来源研究仅停留在对来源的简单陈述,只有少部分做了MPs的溯源追踪方法。目前,环境中MPs的溯源方法主要集中于水体和沉积物,通过非仪器分析法(目视分析法、密度分析法、灼烧分析法等)从MPs的颜色、形状、密度等特性初步判识MPs的外观及用途[62],或通过仪器检测(光谱分析法、显微分析法、色谱质谱分析法等)判识MPs的化学成分及结构[63],两者相结合可追溯环境中MPs的来源。从已有研究成果来看,土壤MPs的溯源依旧没有可靠且简单易行的检测方法。值得注意的是,进入到环境的塑料碎片和MPs,由于各种物理化学作用,最终会破碎形成NPs,更小的粒径以及颜色、形状等特性不够显著增加了对MPs来源追溯的难度,因此亟需建立适合更小粒径的NPs的检测方法和理化指标。
1.2 土壤MPs的迁移行为
MPs在土壤中可发生水平和垂直迁移[64],其迁移行为受土壤和MPs理化性质的影响[21, 65]。土壤的理化性质(包括孔隙度、土壤质地、矿物和腐殖质含量等)对MPs的迁移有重要影响。土壤的孔隙大小由其质地决定,可直接影响MPs的迁移[30],砂土表面的MPs在渗透作用下可垂直迁移至距地表1.5—7.5 cm的土壤中[66]。由于土壤裂缝,干燥气候可能会加速MPs向下移动[66]。土壤矿物和腐殖酸共存时会增加MPs的垂直传输距离(9—10 cm)[67]。Wu等[68]发现, PS微球的迁移能力随土壤矿物(Fe/Al氧化物)含量的增高而降低,这是由于带负电的MPs与带正电的Fe/Al氧化物发生静电吸引所致。此外,MPs的特性(包括粒径、形状、电荷和表面化学等)也会影响其在土壤中的迁移。当MPs的粒径小于土壤孔隙尺寸时,MPs能通过土壤孔隙和裂缝向下移动,粒径小的MPs也容易被土壤动物摄食而转移到更深层的土壤中[69-70]。由于MPs与土壤团聚体的相互作用不同,不同形状的MPs可能对土壤中MPs的迁移产生阻塞作用影响其迁移行为[65]。如:塑料微球和微粒比微纤维更易下移到土壤深层,因为微纤维与土壤颗粒缠结形成土块后无法迁移[71]。高密度的MPs(如PET(聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯))可能会因重力作用而促进其在土壤中的迁移[72]。表面含有羧基、磺酸基、低密度氨基官能团的PS微球,比含有高密度氨基官能团的PS微球更易在海沙中迁移,这是由于带正电的高密度氨基MPs与带负电的沙粒之间存在静电吸引,从而阻碍MPs的迁移行为[73]。
除了在土壤内部迁移外,土壤中的MPs也会在风力、气流、地表径流等作用下迁移到空气和水等环境介质中[64, 66]。土壤表面的MPs尤其是微纤维等轻质塑料颗粒,可以被风和气流抬升到空气中,最终长距离传播到其他陆地或地表水中[59]。此外,地表径流可促使MPs进入深层土壤甚至含水层。据报道,澳大利亚维多利亚州地下水中MPs的平均丰度为38个·L−1[74],向地下水迁移的MPs可能带来新的环境问题,但目前仍缺乏对地下水MPs污染的环境风险预测、评估和防控研究。
1.3 全球土壤环境中MPs的丰度
我们收集了全球不同地区土壤环境中检出的MPs的理化性质和丰度,绘制了图3。目前,虽然只有少量研究报道了土壤环境中MPs的丰度情况,但可看出MPs广泛存在于多种土壤中(如农业土壤、公园土壤、湿地土壤、沙漠土壤等),其丰度从几个·kg−1到数万个·kg−1不等,多数地区土壤MPs丰度在0—5×103个·kg−1之间,粒径大多小于1 mm[75-77];MPs形状有纤维、薄膜、碎片、颗粒等,PP、PE、PS是土壤中最主要的聚合物类型。土壤环境中MPs的丰度普遍高于水和沉积物中的[8],说明土壤环境是MPs重要的汇。在全球范围内,亚洲、欧洲、北美、大洋洲的土壤环境中都发现了MPs,且不同地区丰度差异较大。从图3中可看出,智利梅利皮利亚县田地因长期施用污泥导致土壤MPs丰度高达18000—41000个·kg−1,明显高于其他地区[24];西班牙东南部穆尔西亚蔬菜农田土壤和墨西哥坎佩切家庭花园土壤中也检测到了数量较高的MPs,丰度分别为(2116±1024)个·kg−1和(870±1900)个·kg−1[78-79];但德国石勒苏益格-荷尔斯泰因州农田表层土壤中MPs仅有(5.8±8)个·kg−1[80],且该国弗兰科尼亚中部农田中MPs的丰度最低,仅为(0.34±0.36)个·kg−1[81]。
作为最大的塑料生产国和消费国[82],我国土壤MPs污染引起了越来越多的关注。在我国大多数受人为活动影响较少的土壤中MPs含量较低,如山东东营黄河三角洲湿地无植物覆盖的土壤和长江沿岸休耕的土壤中MPs丰度仅为60个·kg−1[83]和(28.4±22.0)个·kg−1[84];但农业土壤中MPs的含量通常较高,如:云南滇池柴河流域土壤MPs丰度为7100—42960个·kg−1[85];湖北武汉、山东寿光的农田土壤中也含有较高丰度的MPs(4.3×104—6.2×105、275—4165个·kg−1)[76-77],这可能是塑料地膜老化降解、污泥施用和污水灌溉所致。而少数地区如黄土高原[51]、上海菜地[75]等农田土壤中MPs丰度较小。在工业活动频繁的地区,也可能会引入较高丰度的MPs,广东贵屿电子废物拆解区土壤中MPs的丰度达34100个·kg−1[86]。沿海地区可通过海水养殖、旅游和港口建设等活动引入大量MPs[87]。一些偏远地区也存在少量MPs,可能是通过游客活动、卡车轮胎磨损和农用地膜引入的[88],或与大气传输有关。
土壤中MPs的垂直分布没有明显的规律[76]。例如我国上海郊区[75]、山东寿光[76]和德国石勒苏益格-荷尔斯泰因州[80]农田中表层土壤MPs丰度高于深层土壤MPs丰度,黄土高原[51]、山东胶州湾菜地和果园土壤[89]、毛里求斯农业土壤[90]中深层土壤含有更多的MPs,而我国云南滇池柴河流域农田[85]和墨西哥家庭花园[79]的表层和深层土壤MPs含量无显著差异。不同地区土壤MPs垂直分布可能会受到土壤翻耕、地表径流等因素的影响[51],动物的摄食和排泄行为也可能影响MPs在表层和深层土壤之间的垂直转移[58, 64]。此外,少数研究还报道了土壤质地、植被覆盖、栽培时间、恢复年限等与MPs丰度的关系[50, 76, 85]。例如: 我国山东寿光的农业土壤和砂质壤土中MPs丰度显著高于粉质壤土[76],毛乌素沙漠土壤MPs丰度高于草地和林地[50];设施栽培时间>25与<10年的农田土壤中MPs丰度差异不显著,表明早期的设施栽培措施导致土壤中MPs的累积数量不高[85]。由此可见,土壤中MPs无处不在,不同地区土壤MPs污染水平之间的差异是人类农业活动、工业生产等因素共同作用的结果。值得注意的是,已有研究采用的分离、计数MPs的方法不一,在单位上也有区别,可能会低估或高估了土壤中MPs的真实污染水平。因此,未来的研究亟需建立土壤MPs分离和检测标准。在深层土壤中,MPs受阳光辐照的影响减小,且可降解塑料的微生物种群较少[91],这意味着土壤深处MPs的老化降解可能减慢,其持久性可能会更长。那么,除了表层土壤,检测深层土壤中MPs的含量才能全面评估土壤中MPs的污染状况。
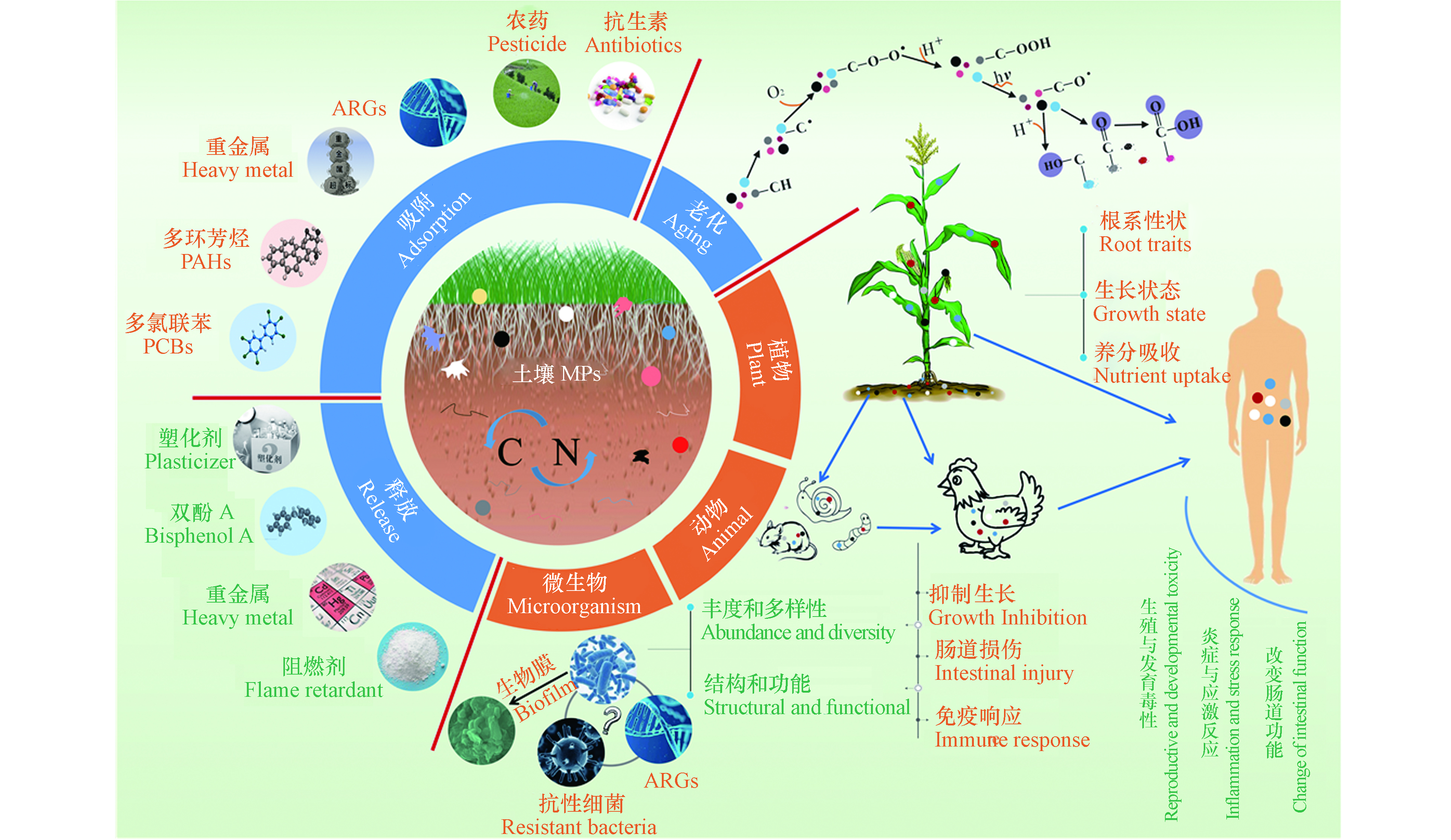
2. 土壤MPs污染的生态健康风险(Ecological health risks of soil MPs pollution)
土壤MPs可通过多种途径对生态系统构成潜在威胁(图4)。MPs的存在可直接影响土壤动植物、微生物的生长[92-94],后经食物链的积累和传递可能对人体健康构成潜在威胁[79]。土壤MPs在土壤环境中能够吸附多种污染物质(如重金属、抗生素、农药等)[58, 95],或与自身释放的添加剂(如增塑剂、抗氧化剂、阻燃剂等)形成复合污染[96],这会给土壤动植物的生长带来极大的危害,而土壤环境中的MPs大多处于老化/降解状态,较原生MPs对污染物表现为更高的吸附能力[97],可能会对土壤生态系统构成更大的威胁。
2.1 MPs对陆生植物的影响
MPs进入农业土壤会对植物产生暴露,阻塞种子孔隙、限制根吸收水和养分[92],影响植物的芽高、生物量和发芽率等[98-100]。Bosker 等[101]发现,绿色荧光塑料颗粒(50、500、4800 nm, 107个·mL−1)因堵塞种子的荚膜孔道会限制水芹种子发芽。而含PP、高密度聚乙烯(HDPE)、低密度聚乙烯(LDPE)和PET的土壤MPs能促进番茄植株的生长,但会延迟结果和降低果实产量[102]。MPs还可通过改变土壤结构、容重、持水能力和营养成分[103-104],间接影响植物根系性状、生长状态和养分吸收[99, 105]。de Souza Machado等[100]发现,MPs污染使得土壤容重降低,通气增加,有助于植物根系渗透到土壤中。然而,MPs(如微纤维)也会缠住幼根,阻碍幼苗的生长[92]。
MPs对植物生长的影响与其类型、暴露浓度、粒径等因素有关。de Souza Machado等[105]发现,PA、PE、HDPE、PP(均为2.0%)均会改变大葱的生物量、元素组成和根系性状,其影响程度因聚合物类型而异。Boots等[98]对比研究了生物降解的聚乳酸(PLA, 65.6 μm, 0.1% W/W)和难降解合成纤维((丙烯酸(AA)和尼龙混合物), 0.001% W/W)对黑麦草发芽的影响,发现两种MPs均会降低发芽率,PLA还会降低芽高。Qi等[99]也报道了类似的结果,即1%的淀粉基生物降解塑料和PE均抑制了小麦生长,且前者比后者的抑制作用更强。由此,生物降解材料来源的MPs对植物可能产生更强的毒性效应,值得进一步研究。一些研究表明粒径大小不同的MPs对植物的影响也不同,与5 μm PS(10、50、100 mg·L−1)相比,100 nm PS对蚕豆的生长抑制作用、遗传毒性和氧化损伤更强[106]。但目前,对于MPs在植物中的积累和转运以及对植物的毒性作用和机制等的认识仍不清楚。
2.2 MPs对陆生动物的影响
MPs被动物摄入后会影响其摄食行为、生长和繁殖[107]。与水生动物相比,MPs对陆生动物影响的生态毒理学研究非常有限,且主要集中在无脊椎动物(如蚯蚓)[93]。已有研究证实MPs暴露对蚯蚓的毒性作用主要包括抑制生长、体重减轻、肠道损伤、免疫响应、肠道微生物群落的改变,以及死亡率增加[70, 108-109]。少数研究报道了土壤MPs也会影响蜗牛[110]、土壤线虫[111]、小鼠[112]等的健康。MPs对动物的影响存在剂量-效应关系。Huerta Lwanga等[107]发现,0.2%的PE(<150 μm)对蚯蚓(Lumbricidae)的生长和存活没有影响,但较高的添加量(1.2%)有抑制作用。Cao等[108]同样发现,低剂量(≤0.5%)的PS(58 μm)对蚯蚓生长的影响不明显,但高剂量(1%、2%)的MPs显著抑制了蚯蚓的生长,死亡率达40%。PS(0.05—0.1 μm)在高暴露量(10%)下可观察到蚯蚓肠道微生物群的明显变化[113]。虽然低浓度MPs暴露不会明显影响动物的生长和引起动物死亡,但会诱使动物组织病理损伤和免疫响应[70]。在评估MPs对动物健康的影响时,粒径是除暴露剂量之外的重要影响因素,Lei等[111]研究了不同粒径的PS(0.1、0.5、1.0、2.0、5.0 μm)对土壤线虫(Caenorhabditis elegans)的影响,发现相同质量浓度(1 mg·L−1)下1.0 μm PS暴露后土壤线虫的存活率最低。然而,对于MPs对陆生动物的潜在影响,如MPs在动物组织中的积累和运输、MPs对动物的毒性作用和机制等方面的认识仍存在空白。
2.3 MPs对土壤微生物的影响
MPs内含或吸附的有机物可为微生物提供碳源[21],微生物在MPs表面定殖后形成生物膜[114],继而构成具有特殊微生物群落组成和功能的“塑料圈”[115]。研究发现,电子拆解厂区域的MPs(如PP、聚碳酸酯(PC)和ABS)及其周围环境的细菌群落存在显著差异,这可能是因为MPs为微生物提供了新的生态位[116],或通过改变土壤理化性质(如破坏土壤结构、降低土壤密度、改变土壤持水能力等)影响了微生物的群落结构和功能[65, 117]。添加MPs后土壤微生物群落多样性的影响研究还处于起步阶段,Huang、Judy等[118-119]认为,HDPE(<2 mm, 0.1%、0.25%、0.5%、1% W/W)、PVC(<2 mm, 0.01%、0.1%、0.25%、0.5%、1% W/W)、PET(<2 mm, 0.1%、0.25%、0.5%、1% W/W)和LDPE(2 mm×2 mm, 0.076 g·kg−1)的存在并没有显著改变土壤微生物群落的丰度和多样性。但也有研究发现土壤中添加低或高浓度(1%、5%)的LDPE(678 μm)和高浓度(5%)的PVC(18 μm)均显著增加了β变形杆菌目(Betaproteobacteriales)和假单胞菌目(Pseudomonadales)的相对丰度,而高浓度的PVC(18 μm, 5%)显著降低了鞘脂单胞菌科(Sphingomonadaceae)的丰度[120]。这些研究结果之间的差异可能与MPs的类型、浓度、以及土壤的理化性质有关。不同类型的MPs对微生物活性影响不同,PP颗粒(<180 μm, 7%、28%)对土壤微生物活性有积极影响[103],然而,Lozano等[94]发现PP碎片(<5 mm, 20%)会降低土壤微生物活性,PS颗粒(32.6 nm±11.9 nm, 1000 ng·g−1)、LDPE(643 μm, 17%)也对土壤微生物活性显示出负面影响[65, 121],de Souza Machado等[105]的研究也报道了类似的结果,但在这些研究中,MPs粒径、形状、大小和浓度各不相同,因此很难得出MPs对微生物毒性的一般性结论。
此外,MPs作为致病菌和耐药菌的载体[122],可能影响土壤中ARGs的分布和迁移。MPs与ARGs在环境中广泛共存,由于ARGs对人类健康的潜在不利影响,其传播越来越受到关注。水生环境中,多项研究表明MPs(如PVC、聚乙烯醇(PVA))可影响ARGs的分布和传播[123]。在土壤中,PS(0.08—0.10 mm, 0.1%)的存在已被证实会增加抗生素和ARGs的保留时间[124],Lu等[125]也得出了类似的结果,MPs可促进土壤中ARGs丰度和数量,但还需要更多的证据来证实MPs污染是否促进ARGs在土壤环境中传播的结论。此外,Zhu等[126]发现土壤温度和湿度的升高均显著提高了MPs上ARGs的丰度,因此,在全球气候变化的情况下,土壤MPs对ARGs影响需引起更多的关注。
2.4 MPs对人类健康的潜在影响
MPs可通过改变土壤理化性质、降低土壤肥力,影响土壤的生态功能和粮食生产[127],对人类的生存和发展产生潜在影响。MPs也可经陆生食物链传递进入人体。MPs及其吸附的污染物可在动植物体内积累[79],食用植物可以从土壤中吸收和积累微型(0.2 μm)荧光PS珠[128],100 nm PS可以在蚕豆、生菜根中积累,然后运输到茎叶[106]。一些重要的家禽(如鸡)也可食用MPs[79],而当人们食用被污染的家禽或蔬菜时,MPs可能在人体内大量积累。据估计,在墨西哥每人每年通过食用鸡肉就可摄入840个塑料颗粒[79],MPs一旦进入人体,可能引起炎症与应激反应、产生生殖与发育毒性,或改变肠道微生物的组成和功能[129]。MPs(<150 μm)可能会从肠腔转移到淋巴和循环系统,进而导致全身暴露[129]。Schirinzi等[130]证明了MPs(PS, 10 μm)和NPs(PS, 40、250 nm)可诱导人体细胞发生氧化应激,并在细胞水平上引起细胞毒性。MPs和NPs与免疫系统作用还可能会导致免疫毒性,进而引发不良反应(即免疫抑制、免疫激活和异常炎症反应)[131]。Prata[132]还发现,由于摄入MPs引起的慢性炎症和刺激可能会因DNA损伤而导致癌症。此外,常见的塑料添加剂,如邻苯二甲酸盐、阻燃剂、双酚A等,与生殖和发育障碍有关,可能引发乳腺癌、血液感染、青春期过早和生殖器缺陷[133]。目前开展的土壤MPs由食物链传递被吸食进入人体的研究还比较少,但已经在人类食物[129]和粪便[134]中检测到了MPs,甚至在人类胎盘、婴儿粪便、婴儿内脏中也发现了MPs的存在[135],虽然没有证据表明这些MPs是来源于土壤环境,但该结果应该足以引起人们对土壤MPs的重视。此外,大气MPs或许能通过反射阳光辐射对气候有冷却效果[136],而土壤中的MPs通过扬尘进入大气环境是否也有同样的效应,进而引起一系列的生态健康问题,如气候变化、水文调节及粮食安全等[137]。
2.5 MPs与其他污染物的复合污染毒性及生态风险
MPs因疏水性强、比表面积大[138],可以吸附多种有机和无机污染物,如多环芳烃(PAHs)、多氯联苯(PCBs)、重金属等[58, 95],或与自身释放的添加剂(如增塑剂、抗氧化剂、阻燃剂等)形成复合污染[96],从而影响土壤动植物的生长。对植物来说,Gao等[96]发现当加入邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBP)时,PS (100—1000 nm、>10000 nm)加重了DBP诱导的植物毒性,增强了对生菜(Lactuca sativa L. var . ramosa Hort)的负面影响,且小粒径PS(100—1000 nm)对生菜的不利影响略大。Liu等[139]发现土壤中PE(200—250 μm,0.5%、1%、2%、5%、8% W/W)和菲(100 mg·kg−1)共同污染比单一处理对小麦幼苗(Triticum aestivum L. cv. NAU 9918)的毒性更强,PE的单一污染破坏了小麦叶片的光合系统,而PE和菲复合污染则加剧了这种破坏。MPs与土壤中重金属等无机污染物的复合污染也引起了人们的关注。Dong等[140]研究发现,在As(Ⅲ)存在下,大尺寸的PS(5 µm)可以迁移到胡萝卜的叶和根部,这是由于As(Ⅲ)增加了PS表面的负电荷,同时As(Ⅲ)也会导致细胞壁扭曲和变形,并导致更多的MPs进入胡萝卜,降低其质量。另一项研究表明,PET(<2 mm)还可以作为载体将重金属运输到小麦根际区域[141]。而Zong等[142]的研究表明,与单一重金属处理相比,PS(0.5 µm, 100 mg·L−1)与Cu2+、Cd2+的结合增加了小麦中叶绿素含量,增强了光合作用,减少了活性氧(ROS)的积累,表明PS(0.5 µm, 100 mg·L−1)对Cu2+、Cd2+的生物利用度和毒性具有缓解作用。对动物来说,Zhou等[143]发现PP(<150 μm, 0.03%、0.3%、0.6%、0.9%)与重金属(Cd, 8 mg·kg−1)二者联合暴露会对蚯蚓(Eisenia foetida)产生更强的负面影响,降低蚯蚓的生长速度并增加其死亡率。而另一项研究却发现,PVC可能通过吸附/结合As(Ⅴ),降低As(Ⅴ)的生物利用度来缓解As(Ⅴ)对肠道菌群的影响,从而防止As(Ⅴ)的减少和总砷在肠道中的积累,降低对蚯蚓(Metaphire californica)的毒性[144]。然而,Sun等[145]发现,MPs(40—50 μm, 10 mg·kg−1、300 mg·kg−1)可显著增加毒氟磷杀虫剂在蚯蚓体(Eisenia fetida)内的生物蓄积性,加重对蚯蚓的氧化损伤和干扰代谢。Boughattas等[146]将MPs(100 µg·kg−1)和除草剂2,4-二氯苯氧乙酸(2-4-D)(7 mg·kg−1)共同暴露于土壤中,结果表明,MPs增加了蚯蚓中的2,4-D生物积累,破坏了溶酶体膜的稳定性和氧化状态,并增加了抗氧化基因的表达。
目前,不管是对MPs的单一毒性研究还是与其他污染物的复合毒性研究,都存在受试动植物类别有限、土壤类型单一、研究周期短等问题,且MPs的种类、大小和浓度与实际土壤环境有一定的差异,如实验室研究中所用MPs浓度往往会高于实际土壤环境中MPs的最大浓度(6.7%)[147],未来的研究应在环境相关浓度条件下评估生态效应。更重要的是,没有充分考虑自然环境因素,真实土壤环境中MPs更多是处于老化或被生物膜定殖的状态,这无疑增加了MPs上的吸附位点,可能使得MPs上吸附的污染物更多,对陆地生态系统构成更严重的威胁。此外,粒径较小的MPs,特别是NPs,可能对陆地生态系统的健康风险更大[21],应作为重点评估的对象。
2.6 MPs的老化/降解及其潜在生态风险
MPs在土壤中的长期积累可以进一步老化或降解[21]。除光照辐射、机械磨损、风化侵蚀外,土壤环境中动物群和微生物(如细菌和真菌)也可以降解MPs[21, 107, 148]。从土壤中分离得到的假单胞菌属细菌AKS2对LDPE的降解率在45 d内达到4%—6%[149],在地膜中分离得到的红球菌C208对PE塑料薄膜的降解率在30 d内达8%[150]。但目前从土壤中分离出能降解MPs的菌株种类较少,因此探究用于降解土壤MPs的微生物可能是进一步研究的方向之一。而生物体可以通过咬、咀嚼或消化碎片来物理降解MPs[151-152]。蜡螟(Waxworms)、印度谷螟(Indian Mealmoths)已被证实能吞食PE并在其肠道微生物的帮助下降解塑料聚合物[153]。此外,大麦虫(Zophobas Morio)、黄粉虫(Tenebrio molitor)、蚯蚓等均具有降解MPs的能力[154-156]。老化/降解会改变MPs的表面结构、疏水性、结晶度和比表面积,并增加MPs表面C—O、C=O、—OH等含氧官能团的数量[8, 97],导致老化或降解MPs具有更高的吸附能力,使其可以吸附其他污染物质,对土壤生态系统构成更大的威胁。
目前,关于土壤MPs的老化或降解对陆地生态系统的危害研究并不多,主要是以下几个方面。首先,长期风化会使MPs分解成为NPs,许多研究已证明粒径较小的NPs可能较MPs具有更大的环境流动性和毒性[111]。Muhammad等[157]发现家蚕(Bombyx mori)暴露于PS MPs(5—5.9 μm, 10 μg·mL−1)的个体在感染后存活得更好,而暴露于PS NPs(50—100 nm, 10 μg·mL−1)的个体则表现出更高的死亡率。Liu等[158]也得出了类似的结果,相较于100 nm PS NPs,20 nm PS NPs(0.1—100 μg·L−1)对线虫(Caenorhabditis elegans)表现出更强的毒性。其次,老化MPs对污染物表现为更强的吸附能力,且老化的可降解MPs更强[51, 159]。Zhang等[159]研究发现,搁浅的PS泡沫对土霉素的吸附能力高于原始PS泡沫的吸附能力,Fan等[55]的研究也发现通过紫外线的老化过程,PLA、PVC对四环素、环丙沙星的吸附能力增加,且可降解PLA表现出更好的吸附能力,这些研究表明更多的有机污染物可以吸附并浓缩到老化的MPs上,形成的复合污染可能对生物体造成更严重的危害。最后,一些研究还探究了在超纯水和模拟肠液中,抗生素在原生/老化MPs上的解吸行为,发现与原生MPs相比,抗生素在老化MPs上解吸量更大,且模拟肠液中的抗生素解吸量比超纯水中大,这可能会对生物体造成更严重的危害[55]。除了老化MPs对生物体的危害外,也可能会带来其他的环境问题,如老化后形成的NPs由于粒径太小,如何从土壤环境中检测丰度及去除也是一大难题。综上,老化MPs的生态毒性问题及其带来的环境污染问题值得高度关注。
3. 结论与展望(Conclusion and perspective)
(1)土壤MPs的来源途径很多,包括未合理处置的塑料垃圾、污泥堆肥、有机肥的施用、农业灌溉、地膜覆盖等,但当前的研究仅停留在对土壤MPs来源的描述上,很少聚焦MPs的溯源研究,现有的技术条件无法将MPs从环境中根除,因此从源头管控就显得尤为重要。但如今土壤MPs溯源几乎处于空白状态,建议加强这方面的研究,为土壤中MPs的源头控制提供关键支撑。
(2)MPs污染在全球土壤环境中普遍存在,应加大力度调查土壤MPs丰度。不同地点、土地类型、不同深度土壤中MPs污染水平和特征存在较大差异,频繁的农业活动导致农田土壤MPs污染较为严重,PE、PP、PS是土壤中最常见的MPs类型。通过大气传输、植物积累、动物摄食、翻耕等多种途径,MPs最终可迁移到深层土壤甚至含水层,因此检测深层土壤中MPs的含量才能全面评估土壤MPs的污染状况。迁移到地下水中的MPs可能带来新的环境问题,但相关的环境风险预测、评估和防控仍缺乏。
(3)土壤MPs的存在会对动植物的生长产生不同影响,关于这方面的研究存在暴露时间短、受试动植物类别有限、土壤类型单一以及MPs种类、粒径大小和浓度与实际土壤环境有一定差异等问题,未来应结合实际土壤环境状况加强这方面的研究。土壤MPs经陆生食物链的传递和积累,可能对人类健康构成严重威胁,但关于环境相关浓度土壤MPs对不同类型动植物的阈值毒性水平及其在食物链中转移的研究还不足,这些问题在后续研究中需重点考虑,以全面揭示陆地生态系统中MPs带来的生态风险。
(4)MPs因疏水性强、比表面积大,可以吸附多种有机和无机污染物,从而影响土壤生物的生长,MPs还可与自身释放的添加剂等形成复合污染,使得MPs的环境行为更加复杂。但目前关于土壤MPs与其携带的污染物结合和释放的机理尚不清楚,与多种有害污染物共同暴露对陆生生物的毒性效应和人体健康的风险亟待研究。未来的研究重点应关注MPs进入到土壤中如何参与其他元素(如重金属)和污染物的环境地球化学行为及生物效应。
(5)土壤MPs的存在可改变微生物的群落结构和功能,反过来,在微生物、土壤动物、光照辐射等作用下MPs可进一步老化或降解,可能对土壤生态系统构成更大的威胁。但MPs影响土壤微生物的机制和途径暂不明晰,未来探究MPs对微生物群落结构、微生物活性的影响,MPs对全球生态系统和生物地球化学循环及对ARGs的影响是研究的重点方向之一。此外,还应寻找绿色、高效且环保的控制措施,以减少生物体对MPs的吸收,并降低其在土壤生态系统中的迁移。
-
表 1 湖光岩不同采样站点理化因子的测定结果
Table 1. Determination results of physical and chemical factors at various stations of the Huguangyan
站点 Stations T/℃ pH S/% NH4+-N/ (mg·L−1) NO3--N/ (mg·L−1) NO2--N/ (mg·L−1) PO43--P/ (mg·L−1) SiO32--Si/ (mg·L−1) N:P S1 27.4 8.601 0.006 0.137 0.192 0.003 0.004 4.140 83 S2 29.2 8.665 0.006 0.136 0.139 0.003 0.003 1.700 93 S3 25.2 7.980 0.006 0.091 0.133 0.003 0.001 0.164 227 S4 25.1 8.017 0.006 0.097 0.143 0.003 0.002 0.141 122 表 2 湖光岩表层水营养盐含量历史对比分析表
Table 2. Table for historical comparison and analysis of nutrient content determination in the surface water of the Huguangyan
时间Time T/℃ pH NH4+-N/(mg·L−1) NO3--N/(mg·L−1) NO2--N/(mg·L−1) PO43--P/(mg·L−1) SiO32--Si/(mg·L−1) N:P 参考文献References 2007春季 27.00 8.40 0.0885 0.7295 0.0026 0.0009 0.2674 912 [6] 2013.03 20.30 7.88 0.0290 0.2500 0.0020 — — — [20] 2016春季 — 6.85—8.44 0.0410 0.0470 0.0006 0.0006 0.4460 148 [3] 2022.03 26.70 8.32 0.1150 0.1510 0.0030 0.0030 1.5360 89 本研究 -
[1] 牛晓君. 富营养化发生机理及水华暴发研究进展 [J]. 四川环境, 2006, 25(3): 73-76. NIU X J. Research progress of eutrophication mechanism and breakout of water bloom [J]. Sichuan Environment, 2006, 25(3): 73-76(in Chinese).
[2] 马健荣, 邓建明, 秦伯强, 等. 湖泊蓝藻水华发生机理研究进展 [J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(10): 3020-3030. doi: 10.5846/stxb201202140200 MA J R, DENG J M, QIN B Q, et al. Progress and prospects on cyanobacteria bloom-forming mechanism in lakes [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(10): 3020-3030(in Chinese). doi: 10.5846/stxb201202140200
[3] 陈法锦, 劳齐斌, 卞培旺, 等. 湖光岩玛珥湖水体中营养盐的时空分布特征及其影响因素 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(6): 1693-1706. doi: 10.18307/2018.0621 CHEN F J, LAO Q B, BIAN P W, et al. Spatial and temporal distributions of nutrients and their influencing factors in the Huguangyan Maar Lake [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(6): 1693-1706(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2018.0621
[4] 柏杨. 湖光岩玛珥湖多指标记录下的全新世气候环境演变[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017. BAI Y. A multi-proxy lacustrine record of Holocene climatic and environmental changes in Huguangyan, Maar Lake[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2017 (in Chinese).
[5] 张国维, 李长玲, 黄翔鹄, 等. 湖光岩玛珥湖春季浮游植物对溶解态氮的吸收 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2015, 27(3): 527-534. doi: 10.18307/2015.0321 ZHANG G W, LI C L, HUANG X H, et al. Uptake of dissolved nitrogen by phytoplankton in spring in Huguangyan Maar Lake [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2015, 27(3): 527-534(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2015.0321
[6] 张才学, 孙省利, 谢少英, 等. 湖光岩玛珥湖的浮游植物 [J]. 水生生物学报, 2008, 32(5): 620-630. ZHANG C X, SUN X L, XIE S Y, et al. The phytoplankton of the Huguangyan maar lake [J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2008, 32(5): 620-630(in Chinese).
[7] 蔡兴争. 湖光岩湖边惊现不明绿物[N]. 湛江日报, 2011-02-14. CAI X Z. Unknown green objects appear at the lakeside of Huguangyan[N]. Zhanjiang Daily, 2011-2-14 (in Chinese).
[8] 王倩, 周浩达, 胡建芳, 等. 湛江湖光岩玛珥湖中长链烷基二醇类化合物的检出及可能的环境意义 [J]. 地球化学, 2013, 42(2): 188-195. WANG Q, ZHOU H D, HU J F, et al. Identification and potential environmental implication of long-chain alkyl diols in Huguangyan maar Lake [J]. Geochimica, 2013, 42(2): 188-195(in Chinese).
[9] 国家环境保护总局《水和废水监测分析方法》编委会. 水和废水监测分析方法 (第四版) [M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. Editorial Board of Monitoring and Analysis Methods for Water and Wastewater of State Environmental Protection Administration. Monitoring and Analysis Methods for Water and Wastewater (Fourth Edition) [M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002 (in Chinese).
[10] 胡鸿钧, 李尧英, 魏印心, 等. 中国淡水藻类[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1980. HU H J, LI Y Y, WEI Y X, et al. Freshwater algae in China[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 1980(in Chinese).
[11] 周凤霞, 陈剑虹. 淡水微型生物图谱[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005. ZHOU F X, CHEN J H. Freshwater micro-biological atlas[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005(in Chinese).
[12] 王然, 朱传雪, 岳俊阳, 等. 巢湖铜绿微囊藻的分离鉴定及其生长特性研究 [J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 44(8): 1139-1145. WANG R, ZHU C X, YUE J Y, et al. Isolation, identification and growth characterization of Microcystis aeruginosa in Chaohu Lake [J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2021, 44(8): 1139-1145(in Chinese).
[13] 张国维. 湖光岩玛珥湖溶解态氮与浮游植物及其氮吸收的研究[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2014. ZHANG G W. Studies on dissovled nitrogen, phytoplankton and nitrogen uptake by phytoplankton in Huguangyan maar lake[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2014 (in Chinese).
[14] ABARIKE G A, SONG Z G, HAN Y Q, et al. Dissolved organic carbon concentration and its seasonal variation in the Huguangyan Maar Lake of Southern China[J]. Acta Geochimica, 2021, 40(5): 806-818. [15] 曹波. 铜绿微囊藻与小球藻种间竞争及其影响因素研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2010. CAO B. The interspecific competitions between Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella pyreniodosa and the factors affecting on this competition[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2010 (in Chinese).
[16] 马欠, 邓春暖, 郭锋锋. 温度对小球藻和铜绿微囊藻生长及叶绿素荧光特性的影响 [J]. 中州大学学报, 2018, 35(4): 108-112. MA Q, DENG C N, GUO F F. Effects of different temperature on growth of Chlorella and Microcystis meruginosa and chlorophyll fluorescence [J]. Journal of Zhongzhou University, 2018, 35(4): 108-112(in Chinese).
[17] ROBARTS R D, ZOHARY T. Temperature effects on photosynthetic capacity, respiration, and growth rates of bloom-forming cyanobacteria [J]. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 1987, 21(3): 391-399. doi: 10.1080/00288330.1987.9516235 [18] 金相灿, 李兆春, 郑朔方, 等. 铜绿微囊藻生长特性研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2004, 17(S1): 52-54, 61. JIN X C, LI Z C, ZHENG S F, et al. Studies on the growth characteristics of Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2004, 17(Sup 1): 52-54, 61 (in Chinese).
[19] 陈建中, 刘志礼, 李晓明, 等. 温度、pH和氮、磷含量对铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)生长的影响 [J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2010, 41(5): 714-718. CHEN J Z, LIU Z L, LI X M, et al. Effects of temperature, pH, nitrogen and phosphorus on growth of Microcystis aeruginosa [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2010, 41(5): 714-718(in Chinese).
[20] 张国维, 黄翔鹄, 李长玲, 等. 湖光岩玛珥湖叶绿素a与水质因子的相关分析及富营养化评价 [J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2015, 35(1): 69-75. ZHANG G W, HUANG X H, LI C L, et al. Correlation analysis between Chlorophylla and water quality indices in Huguangyan maar lake and its eutrophication evaluation [J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2015, 35(1): 69-75(in Chinese).
[21] 吴珊, 张晓萍, 张福萍. 2种藻类储磷释磷过程与生长情况对比 [J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(1): 15-19. WU S, ZHANG X P, ZHANG F P. Comparative study on phosphorus reserve and release process and growth of two kinds of algae [J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2010, 38(1): 15-19(in Chinese).
[22] KIM H S, HWANG S J, SHIN J K, et al. Effects of limiting nutrients and N: P ratios on the phytoplankton growth in a shallow hypertrophic reservoir [J]. Hydrobiologia, 2007, 589(1): 317. doi: 10.1007/s10750-007-0727-1 [23] REDFIELD A C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment [J]. Science Progress, 1960, 11: 150-170. [24] 贺艳艳, 李琴, 张瑜斌. 湖光岩玛珥湖浮游植物、浮游细菌生物量与可培养细菌数量的周年变化 [J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2015, 35(1): 62-68. HE Y Y, LI Q, ZHANG Y B. Annual dynamics of phytoplankon biomass, bacterioplankton biomass and densities of culturable bacteria in Huguangyan maar lake [J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2015, 35(1): 62-68(in Chinese).
[25] 张海涵, 王娜, 宗容容, 等. 水动力条件对藻类生理生态学影响的研究进展 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(1): 181-190. ZHANG H H, WANG N, ZONG R R, et al. Research progress on influence of hydrodynamic conditions on algal physiology and ecology [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(1): 181-190(in Chinese).
[26] 李祥华. 水位下降引起的微弱扰动对浮游藻类生长的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2010. LI X H. Research on the influence of algae growth under feeble disturbance caused by water level drop[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2010 (in Chinese).
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 贺凯凯,朱峰,王彦堂,郝春明. 湖南锡矿山高锑地下水稳定碳同位素特征及其富锑意义. 科学技术与工程. 2024(22): 9672-9680 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载: