-
随着工业化的发展,采矿、工业和农业生产等人为活动逐渐成为环境水体中重金属的主要来源[1]. 例如,电镀、制革、燃煤等工业活动会产生大量含铬废水,燃煤和焚烧污泥排放大量含镉废水,酸性电池、含铅汽油的普遍使用导致含铅废水的增多[1-2]等. 废水中的重金属具有毒性大、无法降解的特点,能够通过食物链被水生生物富集,再由食物摄入的途径进入人体,造成发育迟缓、内分泌紊乱、神经系统异常、癌症等严重危害[3-4]. 水中重金属的去除方法主要有物理法和化学法两类. 物理法是利用膜孔截留、静电作用和其他作用将重金属离子从污水中浓缩并分离出来,不发生化学反应,具有操作简单、灵活、不受污水规模影响等优点,但材料回收和膜再生等问题是限制物理法大规模应用的因素[5]. 化学法的原理是通过投加化学药剂使水中的重金属离子改变形态或降低毒性,适用于重金属浓度较高的废水,包括化学沉淀法、电解法、氧化还原法、气浮法等. 然而,由于耗费电能、使用大量化学品、产生大量污泥等等缺点,化学法的成本较高[6]. 吸附法能兼顾处理效果和成本效益,对高低浓度的重金属污染物都适用,且基本不产生二次污染,具有多方面的优势[6-7].
传统吸附剂(活性炭等)受处理效率和成本等因素的限制,难以满足废水处理的需要[8],近年来新型吸附剂的设计开发成为研究热点. 这些材料可分为低成本吸附剂、生物吸附剂、无机纳米材料和合成多孔材料四类[9-10]. 需要注意的是,对天然材料或传统吸附材料改性处理得到的多孔材料属于低成本吸附剂的范畴. 合成多孔材料是由人工设计并合成的吸附剂,既具有疏松、多孔的结构特性,又能根据应用水体进行灵活的结构调控,增加吸附位点. 废水中的重金属离子被截留在合成多孔吸附剂表面,然后进入颗粒内的孔道并扩散,最终与吸附活性位点发生结合[11]. 合成多孔材料对重金属的吸附容量和选择性远胜于其他材料,有极大的发展空间. 为指导高效、高选择性吸附剂的设计合成,通过理论模拟和实验结合,确定吸附剂和重金属离子之间的相互作用机制,是此类研究中的关键步骤. 常用的实验方法是对吸附前后的吸附剂进行表征和对比(如FT-IR和XPS),理论模拟是对吸附过程进行DFT计算,其重点在于针对不同研究目的选择合适的计算、分析方法.
本文介绍了近年来典型合成多孔材料的开发和对重金属吸附的应用进展,并对这些新材料未来的研究方向进行了展望. 另外,总结了DFT计算的四个常用功能,并列举文献实例说明具体分析方法,为此类理论模拟研究提供参考和帮助.
-
石墨烯、过渡金属硫化物等无机纳米材料均能作为重金属吸附剂,但其孔径和表面化学特性很难提前设计和调控,在研究中大多制成复合材料来提高吸附效果[9-12]. 相比之下,人工设计合成的多孔材料具有合适而均匀的孔径和良好的化学稳定性,并可通过添加官能团修饰的方式提高材料对某些重金属的特异性亲和力,因此合成多孔材料具有很大的研究空间[13]. 根据组成和结构,这类材料主要分为无机介孔吸附剂、金属有机框架和多孔有机聚合物,各种合成多孔材料吸附重金属的效果见表1.
-
孔径在2—50 nm范围内的材料称为介孔材料,二氧化硅是最常见的介孔材料之一,其结构高度有序,合成方法简单,具有大比表面积和丰富的吸附位点. 介孔二氧化硅的吸附能力主要与形貌和表面化学特性有关,因此,可以从孔道大小和表面官能团两方面调节吸附剂的理化性质. 对材料扩孔的常用方法是“溶胀-萃取”法,即先用溶胀剂填充孔道,待其溶胀后用溶剂萃取除去溶胀剂得到扩孔后的吸附剂,从而适应不同尺寸的目标污染物[33].
由于介孔二氧化硅表面富含羟基,容易团聚,不利于实际应用,目前许多研究用偶联剂对其进行表面化学修饰,改性方法有共缩聚法和后嫁接法等[33]. Awual等[14]通过后嫁接法将6-((2-(2-羟基-1-萘甲酰基)肼基)甲基)苯甲酸(HMBA)包覆在二氧化硅上得到一种光学介孔吸附剂. Cu(Ⅱ)或Pb(Ⅱ)与HMBA结合会使吸附剂的反射光谱红移,溶液出现明显的颜色变化. 利用这一光学特性,该材料能快速检测水中痕量的Cu(Ⅱ)和Pb(Ⅱ)并去除,实验测得最大吸附容量分别为182 mg·g−1和173 mg·g−1,且再生后循环使用8次仍能保持90%以上去除率,对低浓度含铜、铅废水的大规模检测和处理有很大的应用潜力. Betiha等[15]同样采用后嫁接法,对介孔二氧化硅SBA-15表面接枝3-氨丙基三甲氧基硅烷,部分氨基再与聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)发生希夫碱缩合反应得到复合介孔材料PVP-SBA-15. 该材料表面含有丰富的官能团,能够通过多种机理的联合作用实现高效吸附,包括端位氨基与重金属的络合作用;质子化氨基与重金属的离子交换作用;PVP结构中C=O、C—N—C共振产生的C—O、C=N+—C对金属离子的螯合作用等. 实验证明,PVP-SBA-15对Pb(Ⅱ)、Cu(Ⅱ)、Ni(Ⅱ)等3种金属离子有良好的吸附效果,最大吸附容量分别为175 mg·g−1、128 mg·g−1、72 mg·g−1. 由于后嫁接法的稳定性、可控性,目前在介孔二氧化硅吸附重金属的研究中应用较多,但仍存在反应条件苛刻、成本偏高、改性后对重金属的吸附容量仍低于有机材料等局限性. 未来还需优化介孔二氧化硅的改性方法,进一步提高其吸附容量.
-
介孔碳是一种新型碳基吸附剂材料,具有比表面积大、孔体积大、表面可调控等优点,在污染物去除领域已有大量研究. 介孔碳的制备方法分为硬模板法和软模板法两种[34],硬模板法是以介孔二氧化硅作为模板,用选定的碳源物质浸渍并填充模板孔,在高温下对碳-硅复合材料进行碳化,最后用NaOH/HF除去模板物质. 这种方法成本较高,操作复杂,且用到有害化学品氢氟酸,因此,通过有机物自组装的软模板法逐渐成为主流,该方法需要先形成胶束单元,再与碳源物质发生交联聚合反应,在高温、氮气环境中,聚合物逐步转化得到介孔碳.
介孔碳的孔径调节和表面改性方法与介孔二氧化硅类似,通过调节合成中的各种参数来优化材料的理化性质,从而增强吸附能力. 此外,还可以用酸碱对介孔碳进行表面化学改性. Marciniak等[16]用硬模板法和软模板法制备了介孔碳吸附剂,并分别在70 ℃和100 ℃下用5 mol·L−1的硝酸氧化改性. 氧化后材料的比表面积和孔体积降低,但表面含氧官能团增多. 实验发现,两种方法合成的材料吸附效果接近,而氧化后的吸附剂对水中Co(Ⅱ)和Ni(Ⅱ)的吸附容量显著增加,且温度越高氧化程度越高(经过100 ℃硝酸氧化,对Co(Ⅱ)的吸附量从66 mg·g−1和71 mg·g−1分别增加到135 mg·g−1和148 mg·g−1),说明化学吸附可能是介孔碳吸附剂的主要吸附作用.
-
金属有机框架(MOFs)是由金属盐溶液与有机配体混合原位反应得到的有机-无机杂化多孔晶体材料,合成方法简便,有溶剂热法、微波法、扩散法、模板法、超声波法、机械搅拌法等等[35]. 金属离子或金属簇与有机配体通过配位键结合,形成的MOF网络兼具稳定性和多孔性,通过调节金属与有机配体的比例即可调控多孔结构[36]. MOF对重金属的吸附一般是多种物理和化学机理联合作用的结果,物理作用包括静电作用、范德华力和分子扩散作用等,化学作用有有离子交换、络合作用、形成化学键等[37]. 根据软硬酸碱理论,稳定的MOF材料可以分为两种:一种是硬碱配体(例如羧基)与硬酸离子结合,主要有MIL系列和UiO系列;另一种是软碱配体(咪唑、吡唑、三唑盐等)与软酸离子结合,以沸石咪唑骨架(ZIFs)为代表[38].
UiO系列材料的结构中含有较强的Zr—O键和大量的吸附位点,能在不同溶剂、不同酸碱环境中保持结构的稳定性,是比较理想的重金属吸附材料[35]. 许多研究表明,用有机化合物改性UiO材料能够显著提升吸附效果. Liu等[17]用2,5-二巯基-1,3,4-噻二唑(DMTD)改性UiO-66-NH2制备了一种新型MOF吸附剂,DMTD能够引入大量的巯基和氮原子,利用这些官能团的络合作用提高吸附剂结合Hg(Ⅱ)的能力,使UiO-66-DMTD的吸附量从改性前的不到200 mg·g−1增至671 mg·g−1,并对Hg(Ⅱ)表现出较好的吸附选择性和循环利用性,5次循环后去除率为93.8%,10次循环后降至85.4%. Yan等[18]用乙二胺四亚甲基膦酸(EDTMPA)改性UiO-66,引入氮、氧原子作为吸附位点,使UiO-66-EDTMPA对Pb(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ)、Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附容量分别增至改性前的8.77、5.63、5.19倍. Ahmadijokani等[19]用乙二胺(EDA)改性UiO-66后,对Pb(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ)、Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附容量分别为243.90、217.39、208.33 mg·g−1. Morcos等[20]用氨基硫脲(AT)改性UiO-66和UiO-67,对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附容量分别增加了5倍和6.5倍,用EDTA-2Na再生循环4次后去除率仍保持在90%以上,表现出优良的吸附和循环利用效果. Wang等[21]用富含氮原子的聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)和具有磁性的Ni0.6Fe2.4O4改性UiO-66-NH2得到一种新型磁性MOF吸附剂,实现了对Pb(Ⅱ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的高容量、高选择性吸附. 该材料的磁性有利于进行分离和再生,5次吸附循环后对Pb(Ⅱ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率分别为92.32%和99.79%,表明Ni0.6Fe2.4O4-UiO-66-PEI具有突出的大规模应用潜力.
MIL系列和ZIF材料也有类似的特点,例如,Lv等[22]设计的氨基改性材料MIL-101-NH2,兼具吸附和荧光传感器两种功能,对Fe(Ⅲ) 、Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)的最大吸附容量分别为195、57 、228 mg·g−1. Huang等[23]通过溶剂热法制备了ZIF-8和ZIF-67吸附剂,其中ZIF-67的孔更均匀,且比表面积很大(1289 m2·g−1),对重金属Pb(Ⅱ)和Cu(Ⅱ)的最大吸附容量高达1348 mg·g−1和618 mg·g−1. 可见,表面官能团改性是提高MOF材料吸附容量的关键方法,而在结构相似的情况下材料的吸附容量受比表面积影响较大.
目前多数研究致力于对单一重金属的选择性去除,而Peng等[39]设计的广谱吸附剂BS-HMT对22种重金属离子都有非常好的去除效果. BS-HMT的合成方法如图1所示,以MOF-808为原料,用乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)取代其表面的甲酸从而接枝到MOF-808表面. EDTA能与各种软酸、硬酸、临界酸金属离子发生络合,因此这种材料对几乎所有重金属都有捕获作用. 在19种金属离子共存的溶液中,BS-HMT对所有金属的静态吸附去除率都接近100%;在固定床动态吸附条件下,出水中所有金属均降到极低浓度(1.9×10−9 mg·L−1以下),表现出巨大的水处理应用潜力. 实际废水中往往存在多种重金属污染物,因此,未来广谱吸附剂的开发可能会成为重要的研究方向.
-
多孔有机聚合物(POPs)是通过共价键桥联等反应人工合成的具有多孔结构的有机高分子材料. POPs包含许多种类,其中共价有机框架(COFs)为晶体材料,其他大多数是无定形的非晶体材料[40]. POPs对重金属的吸附效率、容量、选择性和循环利用性都远高于天然材料,且合成和调控方法多样,近年来在污染物去除领域受到广泛关注.
-
共价有机框架是一种骨架密度低、由强共价键相连的多孔聚合物,分子结构长程有序,热稳定性和化学稳定性良好,是理想的吸附材料. 羟基、三嗪、偶氮、亚胺、卟啉、噻吩等官能团以共价键连接在多孔网络上,成为重金属的吸附活性位点[41-42].
与MOFs类似,COFs对重金属的吸附依靠多孔结构和官能团的共同作用,其中官能团一般起决定性作用. 巯基是典型的软碱,对软酸离子有较强的亲和力. Cao等[24]用巯基改性COF,对Pb(Ⅱ)最大吸附容量为239 mg·g−1,实现了高效、高选择性吸附. Ma等[25]制备的COF-SH 对Hg(Ⅱ)的吸附容量高达1283 mg·g−1,并且由于合成过程中发生了烯醇向酮的转变,COF-SH还具有良好的化学稳定性和循环吸附能力,循环使用10次后去除率仍保持97%以上. Cui等[26]用羟基修饰双孔COF吸附剂,具有1.27 nm和2.2 nm两种大小的孔,在酸性溶液中对Cr(Ⅵ)的最大吸附容量达到384 mg·g−1,并且吸附后小孔径的分布变宽,出现更小的孔,而2.2 nm的大孔几乎不变. 根据孔径分布的变化和XPS表征可以推测,羟基密度较高的小孔能提供更多的吸附位点,并且Cr(Ⅵ)能被羟基部分还原,因此表现出良好的去除效果. Jiang等[43]将TpPa-NO2表面的硝基还原为氨基,再接枝EDTA,得到广谱吸附剂TpPa-NH2@EDTA. 利用EDTA的强络合能力,TpPa-NH2@EDTA在5 min内对6种软酸、硬酸、临界酸金属离子都能达到85%以上的去除率. 由此可见,吸附剂结构中巯基、羟基的引入能显著强化对特定金属离子的吸附;设计重金属广谱吸附剂材料时,可以考虑用EDTA改性.
-
共轭微孔聚合物(CMPs)具有扩展的π共轭骨架结构,因此孔道结构具有刚性,化学稳定性和热稳定性较好[44]. 除了常规的化学交联法,还能通过微波合成、机械力化学合成和基质上合成等非常规方法制备CMPs[40]. 与上述多孔材料类似,通过调节单体的结构、比例、反应条件,以及合成后修饰等方法可以对CMPs分子的形貌和孔结构进行灵活的设计以实现不同的功能[44-45]. Qiao等[27]向CMP结构中同时引入氰基和吡啶得到两种孔径不同的吸附剂CMP-2a(孔径较小)和CMP-3a(孔径较大),对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附容量分别为63 mg·g−1和93 mg·g−1. 两种含氮基团能与Pb(Ⅱ)配位,使原有的多孔结构具有更高的吸附容量和吸附选择性,且孔大、比表面积较大的CMP-3a效果更佳. Wang等[28]设计的PTIA吸附剂以三元吲哚结构为重复单元,具有高度富电子的π平面. 研究表明,它主要通过阳离子-π相互作用吸附重金属离子,每个单元可结合6个金属阳离子(如图2所示),对Ni(Ⅱ)、Cu(Ⅱ)、Cr(Ⅲ)、Zn(Ⅱ)的最大吸附量在179—324 mg·g−1之间,体现出较好的广谱吸附效果. 可见,在设计开发广谱吸附剂时,可以利用阳离子-π或其他非特异性相互作用,同时提高对各种金属离子的亲和力.
-
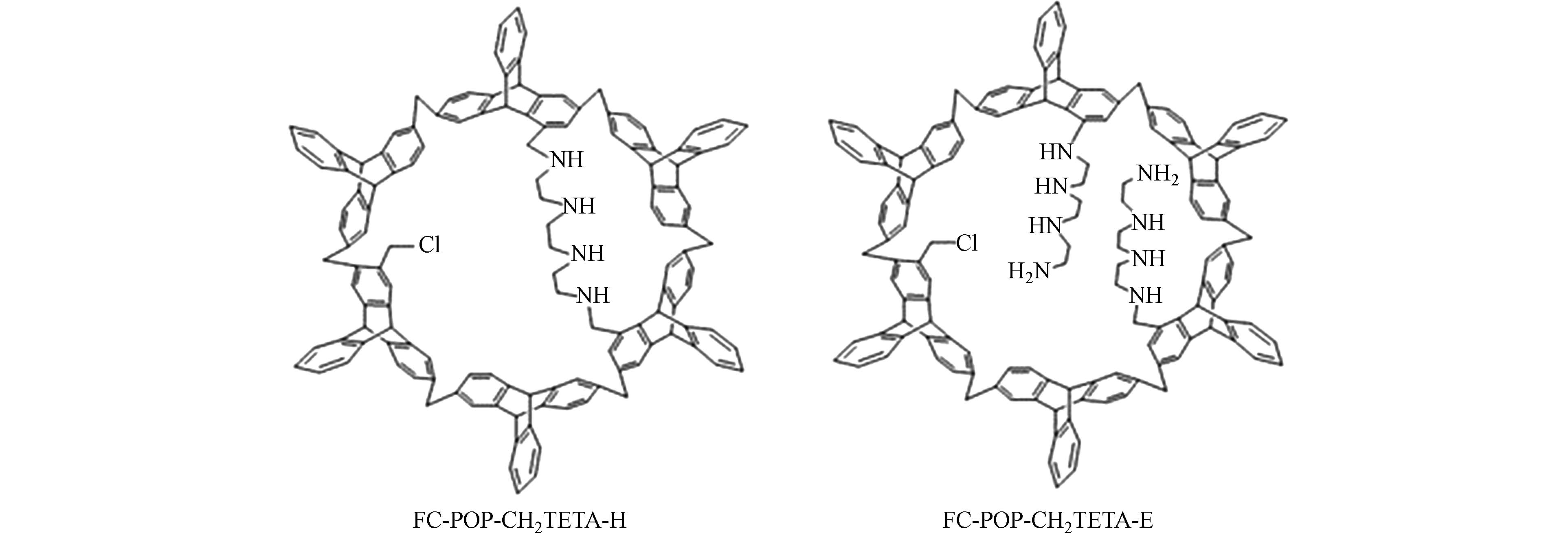
除了COFs和CMPs这些特殊结构,一般在聚合时引入氮、硫、氧等杂原子作为重金属的吸附活性位点,也同样能提高聚合物材料对重金属离子的亲和力,其中含硫的材料多适用于水中Hg(Ⅱ)的去除. Xu等[29]制备了富含硫的微孔聚合物SMP(硫含量为31.4% wt)去除痕量Hg(Ⅱ),SMP结构中的硫与Hg(Ⅱ)形成配合物,能在3 min内将Hg(Ⅱ)从0.2 mg·L−1降至饮用水标准以下,且SMP再生循环使用4次后吸附效率仍高达98%. Aguila等[30]制备的吸附剂含大量硫醇基团,在较宽的pH范围内稳定性良好,对水中Hg(Ⅱ)的吸附容量高达1216 mg·g−1,循环吸附4个周期后去除率在90%以上. 类似的还有Ryu等[31]制备的含硫醇介孔聚合物4AS-MBP,对Hg(Ⅱ)的最大吸附容量为312 mg·g−1,实验发现,4AS-MBP对Hg(Ⅱ)与其他几种重金属离子(Pb(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ)、Cu(Ⅱ)、Zn(Ⅱ))的选择性系数在54—823之间,验证了吸附剂对Hg(Ⅱ)的高选择性,并且4AS-MBP循环使用5次后对Hg(Ⅱ)的去除率为92.13%,体现出良好的循环利用性. Zhao等[32]通过三联苯的傅克烷基化反应产生聚合物骨架,再接枝三亚乙基四胺(TETA)得到具有环形氨基链和延伸氨基链的两种多孔聚合物(分子结构见图3). 用Langmuir模型拟合得到两种材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的最大吸附容量分别为1134 mg·g−1 和561 mg·g−1,经过6次循环对Pb(Ⅱ)的去除率均保持在90%以上. 利用DFT计算解释了两种结构的吸附效果差异:经过构型优化,FC-POP-CH2TETA-H的氮原子与Pb(Ⅱ)距离更近,对Pb(Ⅱ)的结合能为-2624 kJ·mol−1,远大于FC-POP-CH2TETA-E(-988 kJ·mol−1),即环形氨基链结构对Pb(Ⅱ)有更强的亲和力. 可见,在多孔聚合物中引入杂原子可以显著提高吸附量,而官能团引入的不同位置和形式也可能导致吸附量的巨大差异. 今后的研究中,可以通过DFT计算筛选出几种合适的吸附剂结构,再进行合成和测试,使官能团改性最大化地发挥作用,同时提高研究效率.
-
近年来,量子化学计算的相关模型和方法已经逐渐成熟,特别是DFT计算,在物理、化学、材料科学和工程各领域中已经成为重要的研究方法[46]. 合成多孔材料吸附重金属是多种机理共同影响的过程,包括配位络合作用、氢键作用、静电作用、氧化还原作用、扩散作用等. 吸附剂的结构和重金属的种类决定了吸附的主要机理,DFT计算作为一种辅助手段,主要是为了与吸附实验结果相互验证,为吸附机理的推断提供有说服力的证据. 吸附研究中常用的DFT计算方法可以归为四类:结构优化、结合能计算、吸附剂的电子特性分析、吸附剂与金属离子的相互作用分析.
-
Gaussian程序能对物质的结构进行优化,即得到能量最低时分子中各原子的空间排布. 结构优化是进行后续计算的基础,对于合成多孔吸附剂来说,构建完整的分子结构计算量太大,也没有必要,因此通常取吸附剂的一个重复单元为计算对象. 例如1.3.2节中图2所示,Wang等优化后的构型中PTIA结构单元能与6个金属阳离子结合,验证了阳离子-π作用在吸附机理中的主导地位[28].
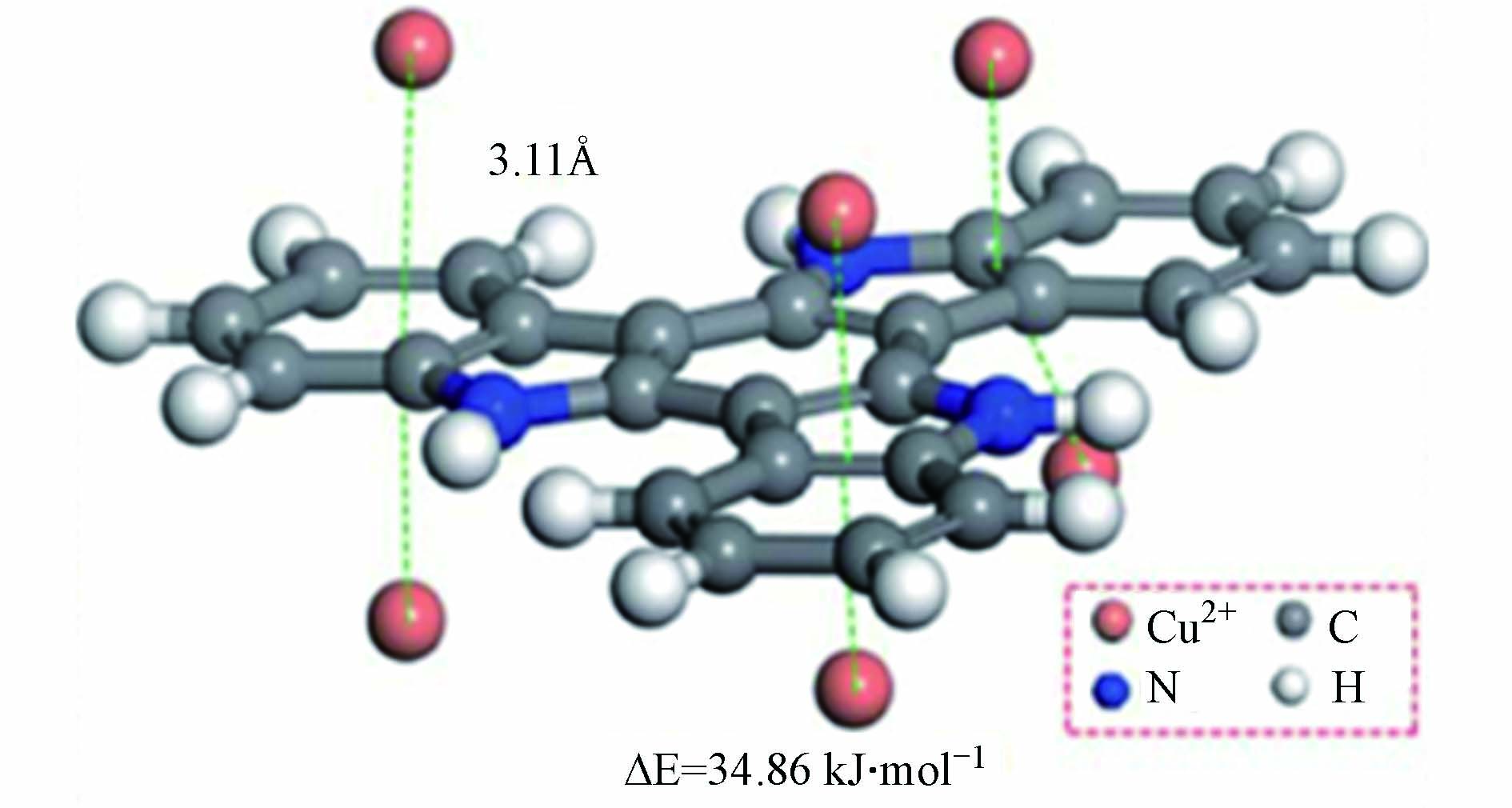
利用结构优化后的原子间距信息能初步推测原子间的相互作用. 例如,He等[47]发现吸附剂POP-NH2中的氮原子与Pb(Ⅱ)间的距离小于两者的范德华半径之和;另一项研究中,结构优化后Cu(Ⅱ)与硫原子和吸附剂TSP-NS中氮原子的距离分别为0.2237 nm和0.2159 nm,均小于对应的范德华半径之和,说明吸附过程中可能有化学键形成[48]. Yang等[49]制备了共轭微孔材料PFCMP-0,其中苯环大π键与炔键之间的π-π共轭效应有利于其与金属离子结合,同时氟原子电负性较强,增强了吸引力. PFCMP-0吸附Pb(Ⅱ)和Ca(Ⅱ)的优化构型如图4所示,PFCMP-0与Pb(Ⅱ)的距离明显更近,相互作用更强,很好地解释了对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附选择性.
结构优化后的键角数据可以解释某些官能团对重金属的结合能力. Shao等[50]分别用五种官能团(EDTA、羧基、磺酸基、巯基、氨基)改性二氧化硅制备了水中Pb(Ⅱ)的高效吸附剂,并对SiO2-EDTA的最佳吸附效果给出了合理的解释. 通过比较结构优化后Pb(Ⅱ)单独结合官能团和Pb(Ⅱ)结合官能团改性的二氧化硅的键角数据发现,只有EDTA-Pb(键角为100.37°)和SiO2-EDTA-Pb(键角为101.37°)键角基本相同,而其他几组键角变化较大,表明SiO2-EDTA相比其余4种吸附剂几何适应性更好,与Pb(Ⅱ)结合时基本不发生结构扭曲,有利于吸附Pb(Ⅱ).
此外,结构优化与表征方法相结合,可以初步推测吸附机理,验证某些官能团的作用. Halder等[51]为了探究吸附剂[Ni(3-bpd)2(NCS)2]n的—SCN基团是否为Hg(Ⅱ)的吸附位点,尝试将多个汞原子与其结合并优化结构,发现—SCN中的硫原子最多同时结合两个汞原子,多余的汞原子之间存在弱的Hg···Hg相互作用. 吸附前后的理论红外光谱中—SCN特征峰的位置偏移了89 cm−1,与实验得到的-SCN特征峰位移(69 cm−1)十分接近,验证了—SCN在吸附中的贡献. 利用结构优化得到稳定构型是后续计算的基础,但也能从中获取一些有价值的信息.
-
结合能,或称吸附能(Ead),计算方法见式(1),其中Etotal为吸附后体系的总能量,Eadsorbent和Emetal分别代表吸附剂单元和金属离子单独的能量[52-54]. 结合能的计算结果一般为负值,根据热力学原理,结合能越小代表结构越稳定,由结合能大小分析官能团的亲和力强弱、吸附选择性顺序、最佳吸附构型等信息,在吸附研究中十分常见.
计算结合能可以比较不同官能团对金属离子的亲和力大小. 例如,Xu等[55]发现含三嗪、羟基双官能团的COF-Tz-OH对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附能为−70.4 kcal·mol−1,明显小于单官能团吸附剂COF-Tz (−51.4 kcal·mol−1)和COF-OH(-39.9 kcal·mol−1),表明三嗪基团亲和力较强且两种官能团具有协同作用. 同样,He等[56]用Gaussian09程序计算并比较了氨基、羧基改性POP的效果,POP-NH2对Pb(Ⅱ)的结合能为−540.71 kJ·mol−1,小于POP-COOH(−467.49 kJ·mol−1)和未修饰的POP (−257.52 kJ·mol−1),证明氨基改性可以提高对Pb(Ⅱ)的亲和力,且效果优于羧基,很好地解释了实验结果.
计算结合能还可以预测或解释同一吸附剂对不同金属离子的选择性. 例如,Li等[52]比较了单簇纳米片CoCNSP分别结合不同金属离子的情况,对Hg(Ⅱ)、U(VI)、Pb(Ⅱ)、Co(Ⅱ)的吸附能分别为−9.43、−10.77、−8.75、−0.97 kcal·mol−1,与实验中CoCNSP对Co(Ⅱ)的吸附选择性最差结果相符. 然而,计算得到的吸附选择性顺序与实验结果并不完全对应,这是因为仅对单簇结构进行计算很难精确地模拟整体材料的吸附行为.
对于确定的吸附剂和金属离子来说,可能的结合方式也有多种,计算结合能可以推断最稳定的吸附构型. Ren等[57]计算了改性介孔二氧化硅G1.0与Cd(Ⅱ)的6种结合方式的结合能,结果见表3,G1.0-Cd(Ⅱ)-6的结合能最低,表明G1.0的氮、氧原子与Cd(Ⅱ)的六配位模式是最稳定的吸附构型. Wei等[54]计算了Cr(Ⅲ)以3种水合离子形式分别结合5种吸附剂的结合能,结果见图5. 可以看出,A和D两种吸附剂对Cr(Ⅲ)的亲和力更强,水合离子中Cr(H2O)43+与各吸附剂之间的络合最稳定,并且水合分子数增加会降低吸附量. 由此可见,结合能计算既可以验证实验得出的官能团改性效果和吸附选择性顺序,还能提供一些实验无法测定的信息(如吸附构型).
-
静电势(ESP)分析是通过作吸附剂分子的ESP图得到各原子周围的电荷情况,帮助确定吸附活性位点的一种常用方法,多用于分析静电作用导致的吸附行为. 一般在ESP图中,红色区域代表带负电荷,蓝色表示带正电,静电势越低就越容易结合金属阳离子. Wei等[54]作了5种吸附剂片段的ESP图,推测这些分子中的红色区域,即C=N键、氧原子和芳香环都可能是Cr(Ⅲ)的吸附位点. Wang等[56]从MOF-MA的静电势图中发现负电荷集中分布在硫原子周围,说明这些位点对金属阳离子的亲和力最强,应当是主要的吸附位点. Esrafili等[58]合成的MOF吸附剂表面静电势为负值的区域都与氮或氧原子有关,因此,这些原子很可能是Pb(Ⅱ)吸附的位点. 可见一般电负性强的杂原子和富电子的芳香环对金属阳离子的静电作用较强,是主要的吸附位点,当吸附剂分子含有这类官能团时,可以采用静电势分析.
-
选择合适的方法计算出原子电荷,并在分子结构中用不同的颜色标记(颜色与电性的对应关系与ESP图相同),这种方法能够直观地分析原子之间的静电作用,在吸附研究中可以预测吸附位点和比较吸附选择性等. 计算原子电荷的方法有许多种[59],其中,ADCH是以原子偶极距校正来计算Hirshfeld电荷的方法. Li等[52]对CoCNSP分别结合4种金属进行了ADCH电荷分析,发现金属原子均位于带负电荷的硫原子周围,并且钴原子的ADCH电荷明显低于其他3种金属,说明硫原子是吸附位点,且在4种金属中对Co(Ⅱ)的选择性最差,验证了实验结果.
-
HOMO和LUMO分别是最高占据分子轨道和最低未占据分子轨道的缩写,二者之间的能级差称为禁带. HOMO、LUMO的能量大小和禁带宽度不仅能反映出分子的导电性,还能在相似的结构间比较化学稳定性. Esrafili等[58]比较了4个结构类似的吸附剂分子的HOMO能量(见表2),从结构稳定性角度解释了TMU-23对6种金属的最佳吸附能力:TMU-6和TMU-21的结构存在共振效应,分子比较稳定,与金属离子结合的倾向更低;而TMU-24的HOMO能量低于TMU-23,表明含萘环的结构比苯环更稳定,因此,4种结构中TMU-23与金属结合的能力最强.
-
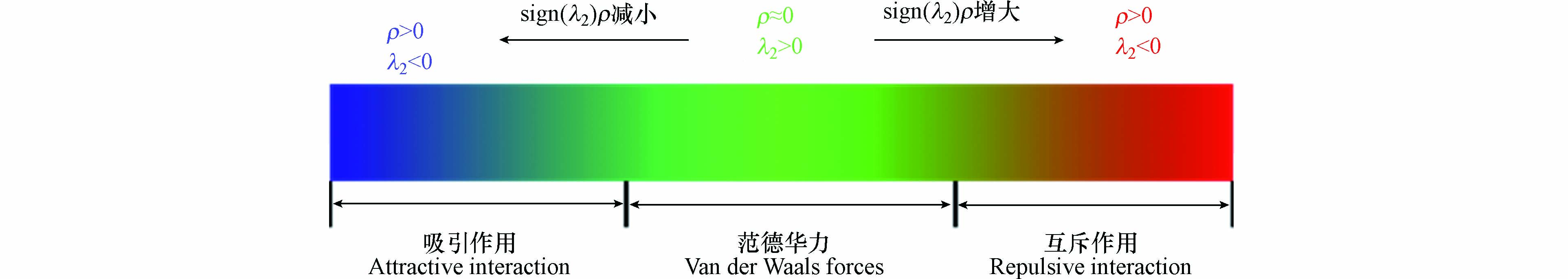
NCI(非共价相互作用指数)分析,也称为RDG(约化密度梯度函数)法,是对体系中弱相互作用的区域和类型进行可视化的研究方法. RDG函数的表达式见式(2). NCI方法是通过ρ和λ2两个参数来定性地表示一个区域内的各种相互作用的,其中ρ代表电子密度,反映相互作用的强弱;λ2反映相互作用的类型,λ2<0代表吸引作用,λ2>0代表互斥作用. 对不同的类型和强弱用不同的颜色区分,将Sign(λ2)绘制成RDG填色等值面图,就能直观地看出结构内或分子间的非成键相互作用情况[60]. 绘制RDG等值面图的对应关系见图6,若出现蓝色区域代表周围原子之间存在吸引作用,红色代表互斥作用,以此推测金属原子与吸附剂之间的相互作用类型. 在Wei等[54]的研究中,发现Cr(H2O)43+的氢原子与吸附剂的氮原子之间出现盘状的蓝色区域,据此推测氢键可能是吸附机理之一. Li等[52]用三维RDG等值面图解释了吸附剂CoCNSP对Co(Ⅱ)吸附选择性差的原因,当4种不同金属分别与吸附剂的硫原子结合时,Co(II)与硫原子之间出现绿色区域,其余3种金属与硫原子之间为蓝色,表明吸附剂对Co(II)的作用力明显较弱.
-
自然键轨道(NBO)分析是考察成键原子之间电子离域情况的一种方法,是将薛定谔方程的计算解转化为化学键概念的手段之一[61],常用于分析重金属与吸附剂之间的络合作用. NBO分析常用到二阶微扰校正能E(2),即通过二阶微扰理论近似估计电子占据的NBO轨道向相邻的非占据NBO轨道发生离域而使体系降低的能量,E(2)的值越大说明相互作用越强. 例如,吸附剂G1.0含有的多个氮、氧原子能与Cd(Ⅱ)以6种方式络合,Ren等[57]对这些构型进行了NBO分析,结果见表3. 从部分电荷和Cd(Ⅱ)电子排布的变化可以看出,氮、氧原子的孤对电子部分转移至Cd(Ⅱ)的5s、5p、6p空轨道上,大部分转移至5s轨道;计算得到LP(N)→LP*(Cd)过程的E(2)明显大于LP(O)→LP*(Cd),表明氮原子与Cd(Ⅱ)的结合能力比氧原子更强,在吸附中的贡献更大.
-
合成多孔材料根据化学组成可分为无机介孔材料、金属-有机框架和多孔有机聚合物三类,通过改变反应物或合成条件、合成后修饰等方法能够对吸附剂的孔结构和表面化学特性进行灵活调控. 表面化学特性是影响吸附的关键因素,在研究中大多采用有机物进行化学改性. 通过向吸附剂的分子结构中引入含杂原子(氮、氧、硫等)的官能团,利用它们对重金属的特异性亲和力,可有效增加吸附剂表面的活性位点,从而显著提高吸附效果. 近年来,DFT计算在吸附研究中的应用越来越普遍,主要用于从微观角度分析和阐明吸附过程中的络合作用、静电作用以及其他弱相互作用,预测或解释实验结果. 然而,合成多孔吸附剂的开发和DFT计算探究吸附机理仍存在许多挑战和局限性,今后的研究中应关注以下问题:
(1)合成多孔材料的改性条件比较苛刻,为了适应实际废水的大规模处理需求,研究者们应考虑开发更简便高效的合成与改性方法.
(2)新材料产生的环境影响未被重视. 目前,仅有少数研究在开发新材料时关注了毒性或金属浸出情况,未来合成多孔材料的开发研究应包含毒性测试或环境影响评估,避免产生二次污染.
(3)许多研究的吸附机理分析比较简略,多数文献仅通过DFT计算的结构优化和结合能解释实验现象并推测机理. 研究者们应充分利用DFT计算的强大功能进一步分析可能存在的相互作用,或预测吸附剂的吸附效果,为新型吸附剂的设计提供参考.
合成多孔材料吸附水中重金属的研究进展
Research progress on adsorption of heavy metals in water by synthetic porous materials
-
摘要: 重金属吸附新材料的开发是废水处理技术的一大挑战,合成多孔材料由于高吸附容量、高选择性和结构调控的灵活性受到关注. 本文以无机介孔材料、金属有机框架和多孔有机聚合物为代表,介绍了合成多孔材料作为重金属吸附剂研究的最新成果,包括新材料的制备、结构调控的方法和吸附效果. 与常用的确定吸附机理的研究方法如傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等相比,基于密度泛函理论(density functional theory,DFT)的计算可以更清晰地阐述吸附位点与材料中的官能团或原子之间的关系,己成为当前深入探究吸附机理和解释实验结果的重要手段. 本文列举了DFT计算中常用的代表性功能的原理和应用于合成多孔吸附材料研究中的文献实例,包括结构优化、计算结合能、分析吸附剂电子特性、研究分子间相互作用,以期为类似的新材料开发和吸附机理研究提供参考.Abstract: The development of new materials for heavy metal adsorption is a major challenge for wastewater treatment technology. Synthetic porous materials have attracted much attention due to their high adsorption capacity, high selectivity, and flexibility of structural regulation. Represented by inorganic mesoporous materials, metal-organic frameworks and porous organic polymers, the latest achievements in the research of synthetic porous materials as heavy metal adsorbents are introduced in this paper, including the preparation of new materials, methods of structure regulation and adsorption effects. Compared with the commonly used research methods to determine the adsorption mechanism, such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), etc., the calculation based on density functional theory (DFT) can be more efficient. Clearly expounding the relationship between adsorption sites and functional groups or atoms in materials has become an important means for in-depth exploration of adsorption mechanisms and interpretation of experimental results. This paper lists the principles of representative functions commonly used in DFT calculations and literature examples applied to the study of synthetic porous adsorbents, including structure optimization, calculation of binding energies, analysis of adsorbent electronic properties, and study of intermolecular interactions. Provide reference for new material development and adsorption mechanism research.
-
Key words:
- porous material /
- heavy metal adsorption /
- structural regulation /
- DFT calculation.
-
近年来,塑料制品生产及使用量急剧增加,加之塑料垃圾处理不当和回收率低的原因,导致塑料在自然环境中大量积累[1]. 据报道至2050年,全球每年塑料产量可能达到330亿吨[2]. 数量巨大的塑料制品在光照、海浪冲击、侵蚀、风化等外界作用下会逐渐分解为直径小于5 mm的小塑料颗粒,即微塑料. 微塑料在环境中具有持久性且不易降解的特点[3],其长时间暴露在环境中[4]易造成潜在的环境风险[5-6]. 作为一种新型污染物,微塑料所引发的生态安全已成为全球关注的热点环境问题之一[7].
目前,微塑料已在水生态系统中被广泛检出[8]. 如中国南海、渤海、东海等海域[9-10],黄河、长江等河流[11-12],鄱阳湖、南湖等湖泊均发现不同程度的微塑料污染[13-14]. 已有研究表明,沉积物是淡水生态系统微塑料的“汇”[15]. 沉积物中微塑料的累积、迁移和分布受气象条件、水流和水生生物等在内的多种因素的影响[16-18]. 此外,微塑料的数量也与人口和人类活动(如船舶、港口作业、捕鱼、塑料生产和污水处理)密切相关[19-20]. 可见,沉积物微塑料的分布与所在水域自然及人为因素的影响密不可分,针对特定水域开展湖泊沉积物中微塑料分布特征的调查,将对该水域微塑料污染背景数据的积累具有重要意义.
本研究以金山湖沉积物为研究对象,研究金山湖沉积物微塑料的丰度、分布特征和季节变化规律,评估微塑料在金山湖沉积物中的污染情况,研究结果将为半封闭式闸坝型城市湖泊沉积物中微塑料的污染状况提供基础数据.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区概况
研究区域位于江苏省镇江市金山湖,该区域属于亚热带湿润气候,平均气温14.8—15.3 ℃,平均年降水量为1044.6 mm[21].
金山湖(32°13'4.652"—32°14'35.79"N ,119°25'5.711"—119°29'48.049"E)位于江苏省镇江市内,金山湖东西方向长约4 km,南北宽约2 km,湖泊丰水期面积为8.8 km2,在镇江城市地表水中所占面积约80%以上[22],是镇江市最大的景观湖泊和重要的防洪水体,且是镇江市金山、焦山、北固山“三山”名胜景区的核心所在[23]. 该湖泊为闸坝型水体,1987年来开通了连接金山湖与长江的引航道[24],引航道闸坝从长江引水进入金山湖,并穿过下游胶南坝使水回流至长江,从而实现金山湖水位的调控[25].
1.2 样品采集及预处理
在综合考虑镇江市金山湖水体分布特征、水域面积及人类活动的程度等基础上,在金山湖共选取10个点位进行样品采集,具体点位见图1所示.
采用彼德森抓泥斗抓取沉积物,在2019年1月(冬季)和7月(夏季)在选取的10个点位采集表层沉积物样品,每个点位采集3个平行样,将同一采点位样品充分混匀,带回实验室. 将样品在45 ℃的烘箱中烘干、砸碎、过5 mm筛,并用铝箔包好,保存在干燥处储存,用于微塑料的样品前处理.
1.3 微塑料提取
采用密度分离法提取沉积物中微塑料[26]. 首先将50 g沉积物样品(干重)转移到一个干净的锥形瓶中,加入500 mL饱和氯化钠溶液,用干净的玻璃棒搅拌2 min,直到沉积物和溶液完全混匀. 瓶子用铝箔密封,以防止样品污染,并静置24 h,等待固体和液体分离完全,确保微塑料完全悬浮在上清液中. 随后,将上清液转移到另一个干净的锥形瓶中,并在剩余的沉积物中加入饱和碘化钠溶液,进行二次浮选. 重复上述相同的步骤来分离固体和液体. 为避免有机质的干扰,在提取的上清液总加入30%的过氧化氢溶液,然后用铝箔将瓶子密封,在45 ℃的水浴中加热48 h. 待有机质消解后,使用Φ50 mm×0.45 μm醋酸纤维素膜对上清液进行真空过滤,将滤膜置于培养皿中保存,以备后续对微塑料的观测.
1.4 微塑料的鉴别
采用金相显微镜(CX40M, Ningbo Sunny, China)在放大50—100倍下通过软件IMSA-2000对干燥滤膜上的微塑料进行拍照计数. 研究表明[27],微塑料按形态特征分为即纤维、颗粒、碎片、薄膜状微塑料共4种类型. 按颜色分为红色、蓝色、绿色、透明、白色和黑色共6类[28]. 根据其粒径不同可分为<0.5、0.5—1、1—2、2—3、3—4、4—5 mm等类型[28-29].
选择具有代表性的微塑料样品,采用拉曼光谱仪(DXR, Thermo Fisher, USA),根据已知的聚合物光谱确定微塑料的聚合物类型,对微塑料样品的化学组成进行识别[30]. 由于样本量较大,采用所有颜色及形状的微塑料组合,以确保所有类型都被检测到,并且根据显微镜的观察进行微塑料聚合物类型的统计分析.
本研究中,利用扫描电子显微镜结合能量光谱仪(SEM/EDS),研究了微塑料样品的表面性质. 即:用拉曼分析对微塑料进行鉴定后,将样品涂上铂薄膜,用20 kV扫描电镜(S-3400N,Hitachi, Japan)与可变真空钨丝观察. 由于微塑料表面的侵蚀程度不同,在不同的表面位置和粗糙度下至少进行了3次可视化分析.
1.5 数据计算与分析
使用软件 WPS Office 进行数据的处理和表格的绘制. 本研究采用双因素方差分析来确定在P<为0.05时,微塑料的季节变化和空间变化是否具有统计学意义. 采用SPSS v. 27(IBM公司,Armonk,NY,USA)进行空间与季节的双因素方差分析. 微塑料丰度数值采用平均值表示,丰度采用每kg干重沉积物的颗粒数表示,单位为n·kg−1 .
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 微塑料的季节与空间分布
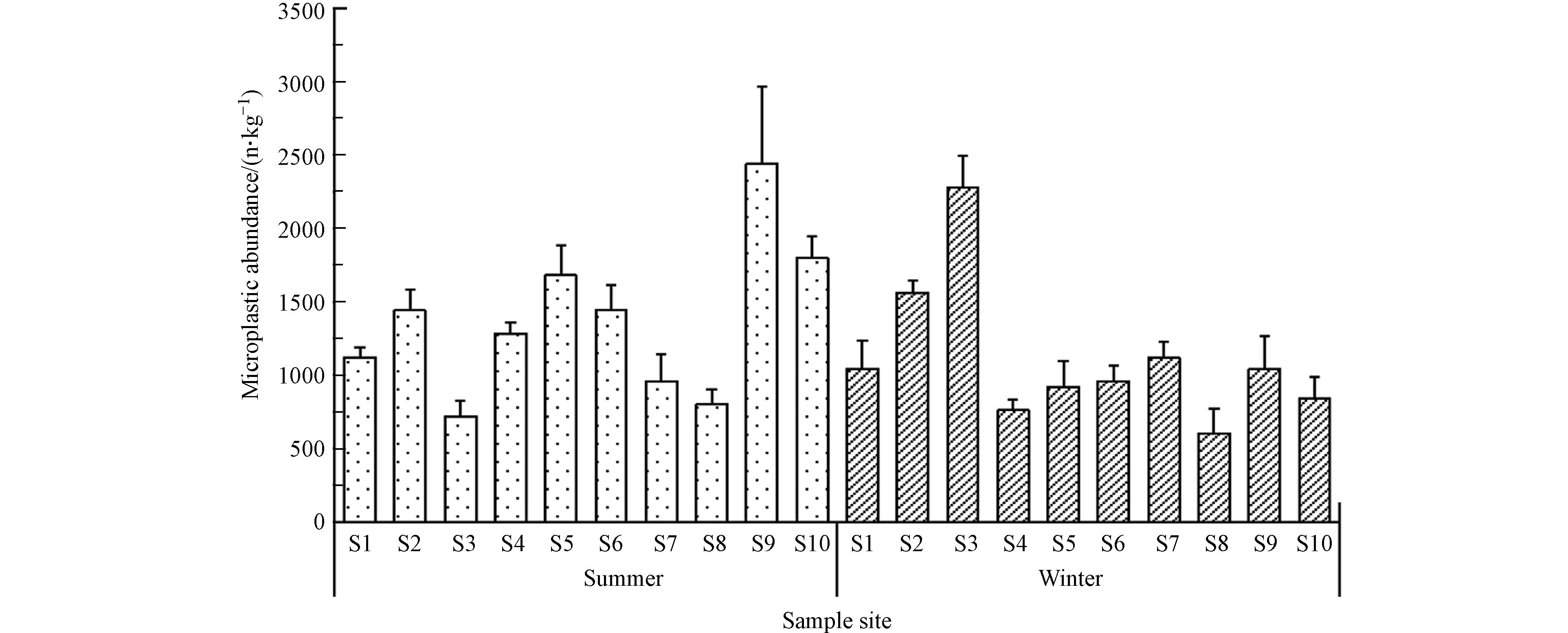
由图2可知,金山湖所有点位表层沉积物均检测到了微塑料,夏季沉积物中微塑料丰度范围为720—2440 n·kg−1干重沉积物,平均丰度为1368 n·kg−1,冬季则为600 — 2280 n·kg−1,平均丰度为1112 n·kg−1干重沉积物. 对比其他湖泊沉积物微塑料丰度值后发现,金山湖微塑料丰度低于牛轭湖沉积物(347—4031 n·kg−1和507—7593 n·kg−1)[31],高于太湖沉积物微塑料丰度(11.0—234.6 n·kg−1)[32]、雨山湖(278.9、277.1 n·kg−1)[33]和洞庭湖(180—693 n·kg−1)[34]. 金山湖沉积物微塑料丰度平均值与鄱阳湖相近(921.6 n·kg−1和996.2 n·kg−1)[15]. 总体而言,本研究所测金山湖沉积物微塑料丰度值在中国已观测的沉积物微塑料丰度范围之内.
金山湖沉积物微塑料丰度值冬季两季变化明显. 冬夏两季10个采样点沉积物微塑料丰度值的方差分析结果表明,S3、S4、S5、S6、S9和S10点位在两个季节丰度值存在显著差异(P<0.05). 其中,S2、S3和S7采样点沉积物微塑料丰度平均值表现为冬季>夏季,其余点位则表现为夏季>冬季,由此可判断,金山湖70%沉积物在夏季微塑料丰度略高于冬季,这与夏季降雨量较大等有一定的关系. 研究表明,降雨充沛时微塑料可从陆地转移到湖泊沉积物,从而使湖泊沉积物中微塑料丰度升高[35].
除了季节差异,沉积物中微塑料丰度在空间分布上亦表现出显著的差异(P<0.01). 已有研究表明,河流和湖泊等环境中微塑料丰度与人类活动等因素密切相关[36-37]. 人类活动较为频繁的地区往往会造成严重的塑料堆积和污染[19]. 如研究发现人流量增加引起微塑料的丰度显著升高[38-39]. 而城市较高的人口密度引起的塑料制品消费增加也会产生更多的微塑料污染[40]. 金山湖位于镇江市中心,作为镇江市的著名风景区吸引大量游客,尤其是夏季,大量的游客在金山湖水域开展各项活动,增加了塑料制品的污染风险. 其次,城市建筑材料、汽车轮胎等频繁使用,将导致微塑料随大气干、湿沉降以及随地表径流等从陆地进入湖泊生态系统[41].
2.2 微塑料的形态分布特征
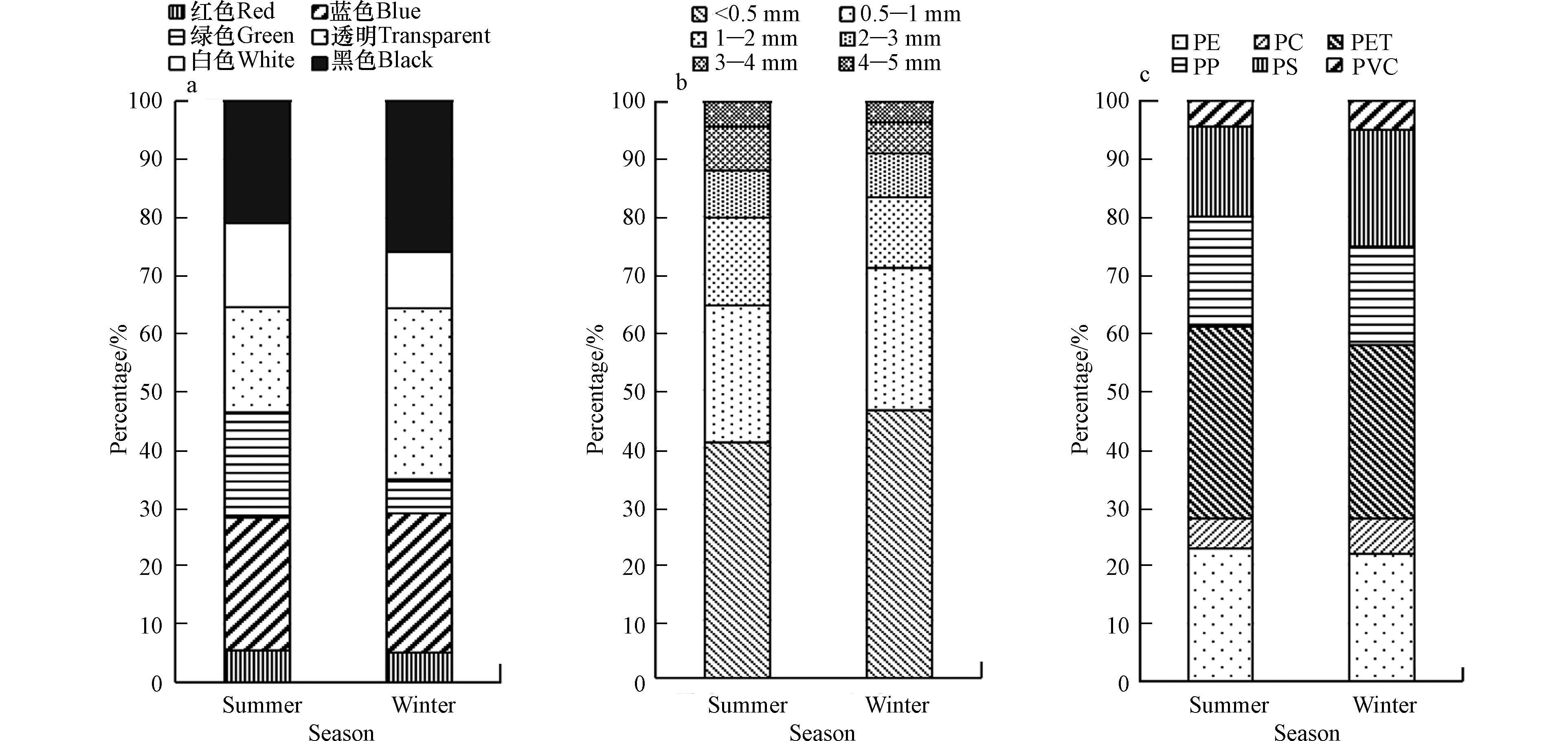
金山湖表层沉积物微塑料从形态上主要分为4类:纤维状、颗粒状、碎片状和薄膜状(图3). 夏季沉积物微塑料中,纤维状微塑料占比57.3%,其次是碎片状(26.3%)、颗粒状(11.1%)和薄膜状(5.3%);冬季沉积物微塑料中,纤维状微塑料占比70.5%,其次是碎片状(16.2%)、颗粒状(7.9%)和薄膜状(5.4%). 冬夏两季微塑料形状占比均表现为:纤维状>碎片状>颗粒状>薄膜状,表明冬夏两个季节金山湖沉积物中微塑料形态组成均以纤维状为主,这与Malla-Pradhan等[42]在费瓦湖沉积物的研究结果类似. 已有研究表明,纤维状微塑料具有大的比表面积,因此生物膜易附着在其表面,可降低纤维状微塑料的浮力[43],促使其沉降. 此外,纤维状微塑料还可能与渔业和生活污水排放有关. 研究表明[44],洗衣机出水中纤维状微塑料丰度可达100 n·L−1;其次,老化的渔网渔具也会形成纤维状的微塑料[45]. 除了纤维状微塑料,其他形态如碎片状和薄膜状等主要是塑料制品自然分解所产生,如塑料包装袋、农用地膜和塑料容器[46]. 颗粒状微塑料主要来源于个人护理及化妆品等,如调查发现面部擦洗产品中微塑料平均含量约为20.86 n·mg−1[47].
2.3 微塑料的颜色和粒径分布特征
金山湖沉积物中共检出6种颜色微塑料,其中红色、蓝色、绿色归类为彩色微塑料. 如图4(a)夏季沉积物微塑料颜色占比分别为蓝色(22.81%)>黑色(21.05%)>绿色(18.13%)=透明(18.13%)>白色(14.33%)>红色(5.56%);冬季沉积物微塑料颜色则表现为透明(29.50%)>黑色(25.90%)>蓝色(24.10%)>白色(9.71%)>绿色(5.76%)>红色(5.04%). 夏季蓝色微塑料占优势,而冬季透明微塑料占比最高,此外,夏季彩色微塑料显著高于冬季的彩色微塑料,如绿色微塑料可能来源于渔网、渔具等. 此外,目前市场上彩色塑料制品占比较高也是沉积物彩色微塑料丰度较高的重要原因之一[48]. 黑色微塑料可能是农用地膜和轮胎使用所产生. 已有研究表明,在光照的作用下环境中微塑料易发生风化,含氧官能团的增加导致微塑料发生褪色[49]. 基于多种因素,金山湖沉积物微塑料颜色呈现出多样性的特征. 而彩色微塑料与营养水平较低的生物体类似,更易被生物摄食[50],从而增加了生态风险.
微塑料按其粒径可分为<0.5、0.5—1、1—2、2—3、3—4、4—5 mm共6个范围[51]. 如图4(b)所示,金山湖沉积物冬夏两季微塑料丰度均随粒径的增加而减小,这与洞庭湖[52],三峡水库[53]等研究结果一致. <0.5 mm微塑料的丰度最高,冬夏季分别占微塑料总量的46.40%和40.94%,这与其他研究结果类似,如鄱阳湖沉积物中<0.5 mm粒径的微塑料>70%[54],雨山湖和南湖沉积物粒径<0.5 mm的微塑料分别占比46.02%和62.79%的[33].
此外,将<1 mm的微塑料定义为较小尺寸的微塑料[55],按此标准,冬季<1 mm(71.22%)的微塑料占比略高于夏季(64.62%),表明在两个季节中较小尺寸微塑料占主要优势,这可能与金山湖的水位调控,以及长江支流等[56]水体中<1 mm的微塑料占主要优势有关. 研究已证实,小尺寸微塑料占比高的原因可能由于污水处理厂不能对小尺寸微塑料进行很好的去除[57];此外,小尺寸的微塑料可能是大尺寸的塑料经过机械磨损、氧化和生物等作用下发生碎裂和降解所形成[58]. 由于小尺寸微塑料具有较大的比表面积,能对环境中的重金属离子等有害元素进行吸附,往往成为这些有害元素的载体,极易被水生生物摄食并在食物链中循环,从而产生生物毒性效应[59-60],并最终对人类健康造成危害. 由于较小尺寸的微塑料粒径小,沉积物中的较小尺寸微塑料更容易二次悬浮至水中,加剧水体危害[61]. 因此,沉积物中较小尺寸的微塑料在湖泊生态系统中具有更大的潜在生态风险.
2.4 微塑料的聚合物类型及其表面形貌
利用拉曼光谱仪对微塑料成分进行检测后发现,金山湖沉积物微塑料共有6种聚合物类型,分别为聚乙烯(polyethylene PE)、聚碳酸酯(polycarbonate PC)、聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(polyethylene terephthalate PET)、聚丙烯(polypropylene PP)、聚苯乙烯(polystyrene PS)和聚氯乙烯(polyvinyl chloride PVC). 金山湖冬夏两季沉积物微塑料聚合物类型较为相似,冬季沉积物中PET占优势(29.86%),其次为PE(21.94%)、PS(20.14%)、PP(16.91%)、PC(6.12%)和PVC(5.04%),夏季沉积物PET、PE、PP、PS、PC、PVC占比分别为33.04%、22.81%、19.01%、15.50%、5.26%和4.39%,占比最少的为PC和PVC. 以上微塑料都是较为常见的聚合物类型. 其中,PE主要用于农用地膜、网和钓鱼线等;PC主要来源于建筑材料、汽车和其他工业用途,PET是纺织品常见的组成部分,其可以通过洗涤废水进入湖泊中,这可能是湖泊沉积物PET微塑料占比较高的主要原因;PP是服装、医疗等生活必须品的主要原材料;PS和PVC则通常用于包装和工业目的[62]. 由此可推测金山湖沉积物中微塑料污染可能主要来源于洗涤废水、包装和老旧渔具等,在今后的研究中需进一步追溯其源头. 扫描电镜的结果显示金山湖沉积物中的微塑料均呈现表面粗糙、多孔、撕裂和裂缝,表明由于水流及沉积物的运动,微塑料经历了不同程度的侵蚀和风化(图5).
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)金山湖沉积物中微塑料夏冬季平均丰度分别为1368 n·kg−1 和1112 n·kg−1,夏季表面沉积物中微塑料丰度平均值高于冬季.
(2)金山湖沉积物中微塑料的形状包括纤维状、碎片状、颗粒状和薄膜状,其中纤维状微塑料在夏季和冬季沉积物中均占比最高,分别为57.3%和70.5%.
(3)金山湖冬季沉积物中微塑料颜色分别为透明(29.50%)、黑色(25.90%)、蓝色(24.10%)、白色(9.71%)、绿色(5.76%)和红色(5.04%);夏季沉积物微塑料颜色分别为蓝色(22.81%)、黑色(21.05%)、绿色(18.13%)、透明(18.13%)、白色(14.33%)和红色(5.56%).
(4)金山湖冬季和夏季沉积物中微塑料以较小尺寸(<1 mm)微塑料为主,占比分别为71.22%和64.62%.
(5)冬季和夏季金山湖沉积物中微塑料聚合物类型均以PET和PE为主,冬季沉积物中PET和PE分别占总数的29.86%和21.94%;夏季沉积物微塑料PET和PE分别占总数的33.04%和22.81%.
(6)冬夏两季金山湖沉积物中微塑料均存在表面粗糙、多孔、撕裂和裂缝等情况.
-
表 1 合成多孔材料对重金属的吸附性能比较
Table 1. Comparison of the adsorption properties of synthetic porous materials for heavy metals
类型Type 吸附剂Adsorbents BET比表面积/(m2·g−1)Specific surface area 重金属Heavy metals 最佳pHOptimum pH 吸附容量/(mg·g−1)Adsorption capacity 循环效果Reusability 参考文献Ref. 无机介孔材料 介孔二氧化硅(HMBA改性) 552 Cu(Ⅱ) 5.2 182 8次,>90% [14] Pb(Ⅱ) 3.5 173 无机介孔材料 PVP-SBA-15 378 Cu(Ⅱ) 5 128 — [15] Pb(Ⅱ) 175 Ni(Ⅱ) 72 CKIT-6-100-5 23 Co(Ⅱ) 5 156 — [16] Ni(Ⅱ) 149 CST-100-5 0.66 Co(Ⅱ) 141 Ni(Ⅱ) 130 金属有机框架 UiO-66-DMTD — Hg(Ⅱ) 3 671 10次,85.4% [17] UiO-66-EDTMPA 131 Pb(Ⅱ) 5.5 559 5次,73.92% [18] Cd(Ⅱ) 271 5次,70.28% Cu(Ⅱ) 211 5次,66.56% UiO-66-EDA — Pb(Ⅱ) 6 244 4次,84% [19] Cd(Ⅱ) 217 4次,76% Cu(Ⅱ) 208 4次,67% UiO-66-AT 887 Pb(Ⅱ) 5—5.5 246 4次,>90% [20] UiO-67-AT 920 Pb(Ⅱ) 367 4次,>90% Ni0.6Fe2.4O4-UiO-66-PEI 22 Pb(Ⅱ) 5.5 273 5次,92.32% [21] Cr(Ⅵ) 3 429 5次,99.79% MIL-101-NH2 455 Fe(Ⅲ) 3 195 6次,初次的88.1% [22] Cu(Ⅱ) 5 57 6次,初次的78.8% Pb(Ⅱ) 5 228 6次,初次的76.9% ZIF-8 937 Pb(Ⅱ) 5.1 1120 — [23] Cu(Ⅱ) 455 ZIF-67 1289 Pb(Ⅱ) 5.2 1348 Cu(Ⅱ) 618 多孔有机聚合物 COF-SH 40.4 Pb(Ⅱ) 5-6 239 — [24] COF-SH 235 Hg(Ⅱ) 7 1283 10次,>97% [25] COF-BTA-DHBZ 816 Cr(Ⅵ) 1 384 — [26] CMP-2a 118 Pb(Ⅱ) ≥4 63 — [27] CMP-3a 168 93 5次,>80% PTIA 139 Ni(Ⅱ) 6 290 4次,初次的74.6% [28] Cu(Ⅱ) 324 4次,初次的80.2% Cr(Ⅲ) 179 4次,初次的75.0% Zn(Ⅱ) 204 4次,初次的81.4% SMP 517 Hg(Ⅱ) 1 596 4次,>98% [29] POP-SH 1061 Hg(Ⅱ) — 1216 4次,>90% [30] 4AS-MBP 167 Hg(Ⅱ) 5 312 5次,92.13% [31] FC-POP-CH2TETA-H 599 Pb(Ⅱ) 2—8 1134 6次,>90% [32] FC-POP-CH2TETA-E 413 561 6次,>90% 络合构型Complexes 结合能/(kcal·mol−1)Binding energy NBO部分电荷NBO partial charge Cd(II)电子构型Cd(Ⅱ) electron configuration 配体Ligand Cd(Ⅱ) G1.0-Cd(II)-1 −224.53 0.81 1.19 5s0.84d9.995p0.026p0.01 G1.0-Cd(II)-2 −260.79 0.36 1.64 5s0.364d9.986p0.02 G1.0-Cd(II)-3 −271.73 0.35 1.65 5s0.354d9.995p0.016p0.01 G1.0-Cd(II)-4 −280.36 0.30 1,70 5s0.294d9.996p0.02 G1.0-Cd(II)-5 −291.85 0.29 1.71 5s0.294d9.986p0.02 G1.0-Cd(II)-6 −300.12 0.33 1.67 5s0.324d9.995p0.016p0.01 -
[1] ALI H, KHAN E, ILAHI I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation [J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 2019: 6730305. [2] VAREDA J P, VALENTE A J M, DURÃES L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: A review [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 246: 101-118. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.126 [3] 刘金燕, 刘立华, 薛建荣, 等. 重金属废水吸附处理的研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(9): 2016-2024. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017110105 LIU J Y, LIU L H, XUE J R, et al. Research progress on treatment of heavy metal wastewater by adsorption [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(9): 2016-2024(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017110105
[4] SALL M L, DIAW A, GNINGUE-SALL D, et al. Toxic heavy metals: Impact on the environment and human health, and treatment with conducting organic polymers, a review [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(24): 29927-29942. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09354-3 [5] ZHU Y, FAN W H, ZHOU T T, et al. Removal of chelated heavy metals from aqueous solution: A review of current methods and mechanisms [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 678: 253-266. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.416 [6] VARDHAN K H, KUMAR P S, PANDA R C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 290: 111197. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111197 [7] AZIMI A, AZARI A, REZAKAZEMI M, et al. Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: A review [J]. ChemBioEng Reviews, 2017, 4(1): 37-59. doi: 10.1002/cben.201600010 [8] CRINI G, LICHTFOUSE E, WILSON L D, et al. Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment [J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2019, 17(1): 195-213. doi: 10.1007/s10311-018-0786-8 [9] SARMA G K, SEN GUPTA S, BHATTACHARYYA K G. Nanomaterials as versatile adsorbents for heavy metal ions in water: A review [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(7): 6245-6278. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-04093-y [10] AYANGBENRO A S, BABALOLA O O. A new strategy for heavy metal polluted environments: A review of microbial biosorbents [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(1): 94. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14010094 [11] BARAKAT M A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2011, 4(4): 361-377. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.07.019 [12] 周雯, 佟珊珊. 新型吸附材料分离和富集贵金属的研究进展 [J]. 应用化学, 2021, 38(8): 897-910. ZHOU W, TONG S S. Research progress on novel adsorbent materials for separation and enrichment of noble metals [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2021, 38(8): 897-910(in Chinese).
[13] WU Z X, ZHAO D Y. Ordered mesoporous materials as adsorbents [J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2011, 47(12): 3332-3338. doi: 10.1039/c0cc04909c [14] AWUAL M R, RAHMAN I M M, YAITA T, et al. pH dependent Cu(II) and Pd(II) ions detection and removal from aqueous media by an efficient mesoporous adsorbent [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 236: 100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.083 [15] BETIHA M A, MOUSTAFA Y M, EL-SHAHAT M F, et al. Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Aminopropyl-SBA-15 schiff Base hybrid for efficient removal of divalent heavy metal cations from wastewater [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 397: 122675. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122675 [16] MARCINIAK M, GOSCIANSKA J, FRANKOWSKI M, et al. Optimal synthesis of oxidized mesoporous carbons for the adsorption of heavy metal ions [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 276: 630-637. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.042 [17] FU L K, WANG S X, LIN G, et al. Post-functionalization of UiO-66-NH2 by 2, 5-Dimercapto-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole for the high efficient removal of Hg(II) in water [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 368: 42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.025 [18] YAN Y H, CHU Y T, KHAN M A, et al. Facile immobilization of ethylenediamine tetramethylene-phosphonic acid into UiO-66 for toxic divalent heavy metal ions removal: An experimental and theoretical exploration [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 806: 150652. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150652 [19] AHMADIJOKANI F, TAJAHMADI S, BAHI A, et al. Ethylenediamine-functionalized Zr-based MOF for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from water [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 264: 128466. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128466 [20] MORCOS G S, IBRAHIM A A, EL-SAYED M M H, et al. High performance functionalized UiO metal organic frameworks for the efficient and selective adsorption of Pb (II) ions in concentrated multi-ion systems [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(3): 105191. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105191 [21] WANG C, XIONG C, HE Y L, et al. Facile preparation of magnetic Zr-MOF for adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) from water: Adsorption characteristics and mechanisms [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 415: 128923. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128923 [22] LV S W, LIU J M, LI C Y, et al. A novel and universal metal-organic frameworks sensing platform for selective detection and efficient removal of heavy metal ions [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 375: 122111. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122111 [23] HUANG Y, ZENG X F, GUO L L, et al. Heavy metal ion removal of wastewater by zeolite-imidazolate frameworks [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 194: 462-469. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2017.11.068 [24] CAO Y, HU X, ZHU C Q, et al. Sulfhydryl functionalized covalent organic framework as an efficient adsorbent for selective Pb (II) removal [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020, 600: 125004. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125004 [25] MA Z Y, LIU F Y, LIU N S, et al. Facile synthesis of sulfhydryl modified covalent organic frameworks for high efficient Hg(II) removal from water [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124190. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124190 [26] CUI F Z, LIANG R R, QI Q Y, et al. Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by a dual-pore covalent organic framework [J]. Advanced Sustainable Systems, 2019, 3(4): 1800150. doi: 10.1002/adsu.201800150 [27] QIAO X X, LIU G F, WANG J T, et al. Highly efficient and selective removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions by conjugated microporous polymers with functionalized heterogeneous pores [J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2020, 20(1): 337-344. [28] WANG Q, LI R, OUYANG X, et al. A novel indole-based conjugated microporous polymer for highly effective removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution via double cation-π interactions [J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(69): 40531-40535. doi: 10.1039/C9RA07970J [29] XU D, WU W D, QI H J, et al. Sulfur rich microporous polymer enables rapid and efficient removal of mercury(II) from water [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 196: 174-181. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.186 [30] AGUILA B, SUN Q, PERMAN J A, et al. Efficient mercury capture using functionalized porous organic polymer [J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(31): 1700665. doi: 10.1002/adma.201700665 [31] RYU J, LEE M Y, SONG M, et al. Highly selective removal of Hg(II) ions from aqueous solution using thiol-modified porous polyaminal-networked polymer [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 250: 117120. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117120 [32] ZHAO K Q, KONG L K, YANG W W, et al. Hooped amino-group chains in porous organic polymers for enhancing heavy metal ion removal [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(47): 44751-44757. [33] LI H, CHEN X P, SHEN D Q, et al. Functionalized silica nanoparticles: Classification, synthetic approaches and recent advances in adsorption applications [J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(38): 15998-16016. doi: 10.1039/D1NR04048K [34] GANG D, UDDIN AHMAD Z, LIAN Q Y, et al. A review of adsorptive remediation of environmental pollutants from aqueous phase by ordered mesoporous carbon [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 403: 126286. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126286 [35] RU J, WANG X M, WANG F B, et al. UiO series of metal-organic frameworks composites as advanced sorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions: Synthesis, applications and adsorption mechanism [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 208: 111577. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111577 [36] KOBIELSKA P A, HOWARTH A J, FARHA O K, et al. Metal-organic frameworks for heavy metal removal from water [J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2018, 358: 92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.12.010 [37] WEN J, FANG Y, ZENG G M. Progress and prospect of adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution using metal-organic frameworks: A review of studies from the last decade [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 201: 627-643. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.047 [38] FENG M B, ZHANG P, ZHOU H C, et al. Water-stable metal-organic frameworks for aqueous removal of heavy metals and radionuclides: A review [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 209: 783-800. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.114 [39] PENG Y G, HUANG H L, ZHANG Y X, et al. A versatile MOF-based trap for heavy metal ion capture and dispersion [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 187. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02600-2 [40] LEE J S M, COOPER A I. Advances in conjugated microporous polymers [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(4): 2171-2214. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00399 [41] MODAK A, BHANJA P, SELVARAJ M, et al. Functionalized porous organic materials as efficient media for the adsorptive removal of Hg(ii) ions [J]. Environmental Science:Nano, 2020, 7(10): 2887-2923. doi: 10.1039/D0EN00714E [42] LV S W, LIU J M, WANG Z H, et al. Recent advances on porous organic frameworks for the adsorptive removal of hazardous materials [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 80: 169-185. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.12.010 [43] JIANG Y Z, LIU C Y, HUANG A S. EDTA-functionalized covalent organic framework for the removal of heavy-metal ions [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(35): 32186-32191. [44] KHAKBAZ M, GHAEMI A, MIR MOHAMAD SADEGHI G. Synthesis methods of microporous organic polymeric adsorbents: A review [J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2021, 12(48): 6962-6997. doi: 10.1039/D1PY01145F [45] SHENG X, SHI H, YANG L M, et al. Rationally designed conjugated microporous polymers for contaminants adsorption [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 750: 141683. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141683 [46] AL-MAHAYNI H, WANG X, HARVEY J P, et al. Experimental methods in chemical engineering: Density functional theory [J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 99(9): 1885-1911. doi: 10.1002/cjce.24127 [47] HE Y, LIU Q Q, HU J, et al. Efficient removal of Pb(II) by amine functionalized porous organic polymer through post-synthetic modification [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 180: 142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2017.01.026 [48] HE Y, LIU Q Q, LIU F, et al. Porous organic polymer bifunctionalized with triazine and thiophene groups as a novel adsorbent for removing Cu (II) [J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016, 233: 10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.06.024 [49] YANG R X, WANG T T, DENG W Q. Extraordinary capability for water treatment achieved by a perfluorous conjugated microporous polymer [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 10155. doi: 10.1038/srep10155 [50] SHAO P H, LIANG D H, YANG L M, et al. Evaluating the adsorptivity of organo-functionalized silica nanoparticles towards heavy metals: Quantitative comparison and mechanistic insight [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 387: 121676. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121676 [51] HALDER S, MONDAL J, ORTEGA-CASTRO J, et al. A Ni-based MOF for selective detection and removal of Hg2+ in aqueous medium: A facile strategy [J]. Dalton Transactions (Cambridge, England:2003), 2017, 46(6): 1943-1950. doi: 10.1039/C6DT04722J [52] LI J, DUAN Q Y, WU Z, et al. Few-layered metal-organic framework nanosheets as a highly selective and efficient scavenger for heavy metal pollution treatment [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 383: 123189. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123189 [53] GENG S Y, LIU J, WANG C, et al. Experimental analysis and theoretical studies by density functional theory of aminopropyl-modified ordered mesoporous carbon [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 351: 911-919. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.034 [54] WEI D L, ZHANG A R, AI Y J, et al. Adsorption properties of hydrated Cr3+ ions on schiff-base covalent organic frameworks: A DFT study [J]. Chemistry - an Asian Journal, 2020, 15(7): 1140-1146. doi: 10.1002/asia.201901686 [55] XU T, ZHOU L, HE Y, et al. Covalent organic framework with triazine and hydroxyl bifunctional groups for efficient removal of lead(Ⅱ) ions [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(42): 19642-19648. [56] WANG C, LIN G, XI Y H, et al. Development of mercaptosuccinic anchored MOF through one-step preparation to enhance adsorption capacity and selectivity for Hg(II) and Pb(Ⅱ) [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2020, 317: 113896. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113896 [57] REN B, WANG K, ZHANG B S, et al. Adsorption behavior of PAMAM dendrimers functionalized silica for Cd(II) from aqueous solution: Experimental and theoretical calculation [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2019, 101: 80-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2019.04.037 [58] ESRAFILI L, SAFARIFARD V, TAHMASEBI E, et al. Functional group effect of isoreticular metal-organic frameworks on heavy metal ion adsorption [J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 42(11): 8864-8873. doi: 10.1039/C8NJ01150H [59] 卢天, 陈飞武. 原子电荷计算方法的对比 [J]. 物理化学学报, 2012, 28(1): 1-18. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB2012281 LU T, CHEN F W. Comparison of computational methods for atomic charges [J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2012, 28(1): 1-18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB2012281
[60] BOTO R A, CONTRERAS-GARCÍA J, TIERNY J, et al. Interpretation of the reduced density gradient [J]. Molecular Physics, 2016, 114(7/8): 1406-1414. [61] WEINHOLD F, LANDIS C R, GLENDENING E D. What is NBO analysis and how is it useful? [J]. International Reviews in Physical Chemistry, 2016, 35(3): 399-440. doi: 10.1080/0144235X.2016.1192262 -





 下载:
下载: