-
畜禽饲料添加蓝矾或称胆矾(CuSO4·5H2O)、皓矾(ZnSO4·7H2O)等重金属化合物,以增强畜禽的免疫力,促进畜禽的生长[1-2],其中的Cu、Zn等重金属元素通过粪便排出体外[3],导致畜禽粪污中重金属含量超标,其中猪粪的Cu、Zn超标最为显著[4]. 我国一些地区对畜禽粪污排放管控不严,粪污未经处理就被排放到农田作为农肥,引起潜在的土壤重金属污染风险. 重金属Cu、Zn虽然是植物生长所需的微量元素,但过量的Cu、Zn会损害植物根系,抑制动植物生长,还会降低土壤中的生物量及生物活性,最终影响农作物的生长及农产品的安全.
为了减少猪粪农用风险,国家大力倡导利用厌氧发酵技术处理畜禽粪便[5],该技术不仅可以产生清洁能源、减少粪便体积,还能在一定程度上降低重金属生物有效性. 李轶等[6]研究表明,猪粪发酵过程中重金属钝化与发酵原料腐殖化存在着一定关系. 发酵原料腐殖化会产生腐殖质,腐殖质中含有大量羧基、羰基等官能团会与重金属发生吸附络合反应[7],从而降低重金属的生物有效性. 但由于重金属超标,发酵过程中微生物群落代谢功能会受到高浓度重金属的抑制[8],导致腐殖化程度低,钝化效果差. 单一的猪粪厌氧发酵对重金属钝化效果较差,因此就有学者研究在发酵过程中添加钝化剂来有效减少重金属的危害,提高重金属钝化效果[9-10].
腐殖酸(HA)本身就是腐殖化的产物,是农业废弃物转化的产品,可以作为园艺生物改良剂,促进种子萌发、根系发育和植物生长[11]. 同样,腐殖酸可以改善植物细胞内的生化反应并具有直接的营养价值. 此外,腐殖酸被认为是一种含有多种官能团的钝化剂,包括酚类、羧酸类和酮类,可以通过吸附和络合反应与重金属结合[12]. 但是,关于添加腐殖酸对猪粪厌氧发酵中重金属钝化的研究很少,主要都研究发酵前后变化,很少研究发酵过程中的动态变化. 同时在厌氧发酵过程中,腐殖化程度的高低是一个重要的评判标准. 目前由于光谱技术的快速发展,傅里叶红外光谱技术(FTIR)已成为分析厌氧发酵过程中有机物和腐殖质含量变化的常规技术,主要归功于其所需样品量少,测样速度快,灵敏度高等特点. 李轶等[13]就采用FTIR研究猪粪厌氧发酵沼渣中的光谱特性,FTIR可以有效反映猪粪厌氧发酵后的腐殖化程度.
本文主要研究添加腐殖酸对猪粪厌氧发酵过程中重金属及对厌氧发酵前后有机物结构变化的影响,涉及的主要研究内容包括:(1)采用BCR连续提取法来研究重金属(Cu、Zn)形态的动态变化;(2)利用傅里叶红外光谱技术(FTIR)探索猪粪发酵前后有机物结构的变化[14],揭示重金属钝化与有机物腐殖化程度的关系,为增加猪粪厌氧发酵产气量、减量化和重金属钝化提供理论依据,为降低猪粪中重金属Cu、Zn有效性、降低重金属污染风险和提高发酵质量提供技术指导.
-
新鲜猪粪取自常州市某养猪场;沼液取自常州市武农生态能源工程有限公司;玉米秸秆取自联丰农产品有限公司;腐殖酸购自合肥巴斯夫生物科技有限公司(表1).
-
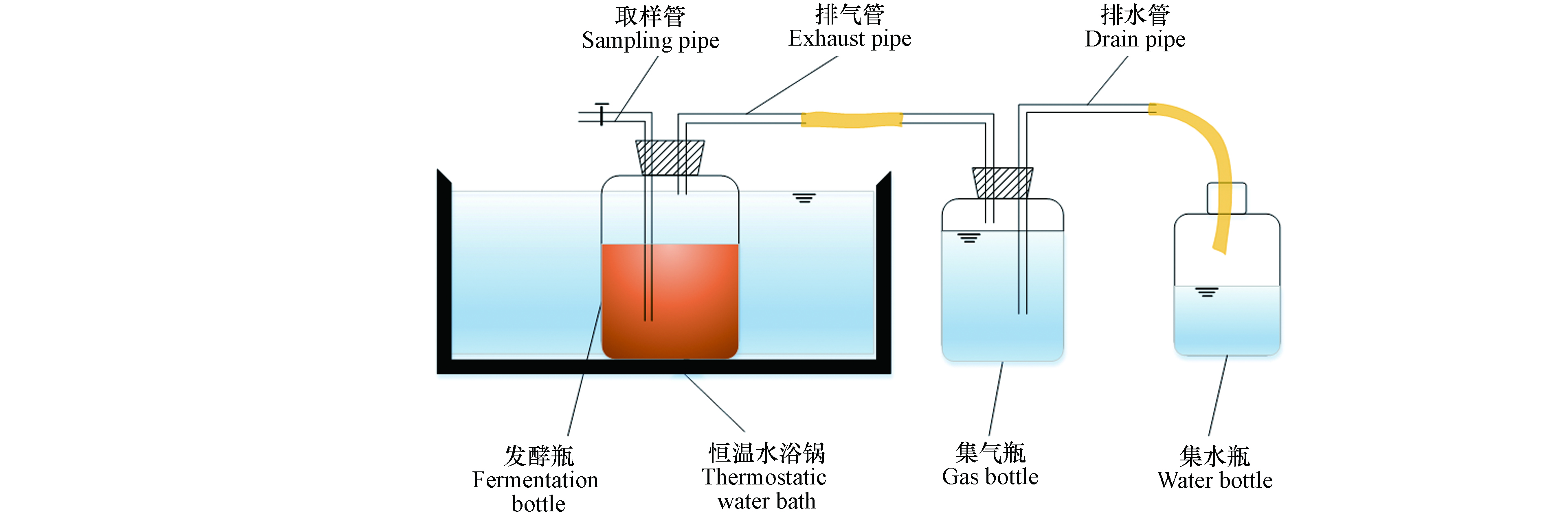
本实验厌氧发酵装置主要由发酵瓶、集气瓶和集水瓶3部分组成. 发酵瓶为有效容积0.8 L,规格1L的广口瓶. 集气瓶为有效容积0.6 L,规格0.8 L的广口瓶. 集水瓶为普通0.6 L的塑料瓶.
实验中发酵瓶和集气瓶分别用橡胶塞塞紧后用玻璃管和橡皮管连接,各接口处都严格密封,保证厌氧环境. 将装有发酵原料的发酵瓶放入(35±1)℃恒温水浴锅中厌氧发酵. 厌氧发酵装置如图1所示.
-
本实验发酵原料为猪粪和玉米秸秆,玉米秸秆用来控制C/N比,C/N为24[15],将粉碎后的秸秆与新鲜猪粪按均匀混合后装入发酵罐,沼液添加量为30%,加水调节使消化体系内的TS为10%,pH控制在 6.5—7.8之间,钝化剂添加量为发酵瓶内干物质含量的2.5%、5%、7.5%,试验共设计4组如表2所示,每组重复3次,结果取平均值. 分别在0、5、10、15、20、25、30 d取样,采用一次性进料,发酵周期为30 d.
-
沼渣的采取:先摇匀发酵瓶中发酵原料,然后取样,离心(3000 r·min−1,5 min)后上层清液为沼液,下层沉淀为沼渣,烘干研磨过100目筛,保存待测.
重金属形态含量结合欧共体标准司提出的BCR连续提取法和火焰原子吸收分光光度计来测定[16],BCR连续提取法将重金属分为4种形态,即:弱酸提取态、可还原态、可氧化态和残渣态. 其中,弱酸提取态和还原态进入环境后迁移性强,易被植物吸收利用,被称为生物有效形态;可氧化态和残渣态称为稳定态,不易被吸收和利用[16]. 发酵原料光谱特性采用傅里叶红外光谱法检测[17]. 根据测定结果计算以下指标[6]:
重金属形态占比(%)=各重金属形态含量/各重金属形态含量之和 × 100%
重金属生物有效形态(%)=弱酸提取态占比 + 可还原态占比
钝化效果(%)=(发酵前-发酵后)重金属有效形态/发酵前重金属有效形态 × 100%
-
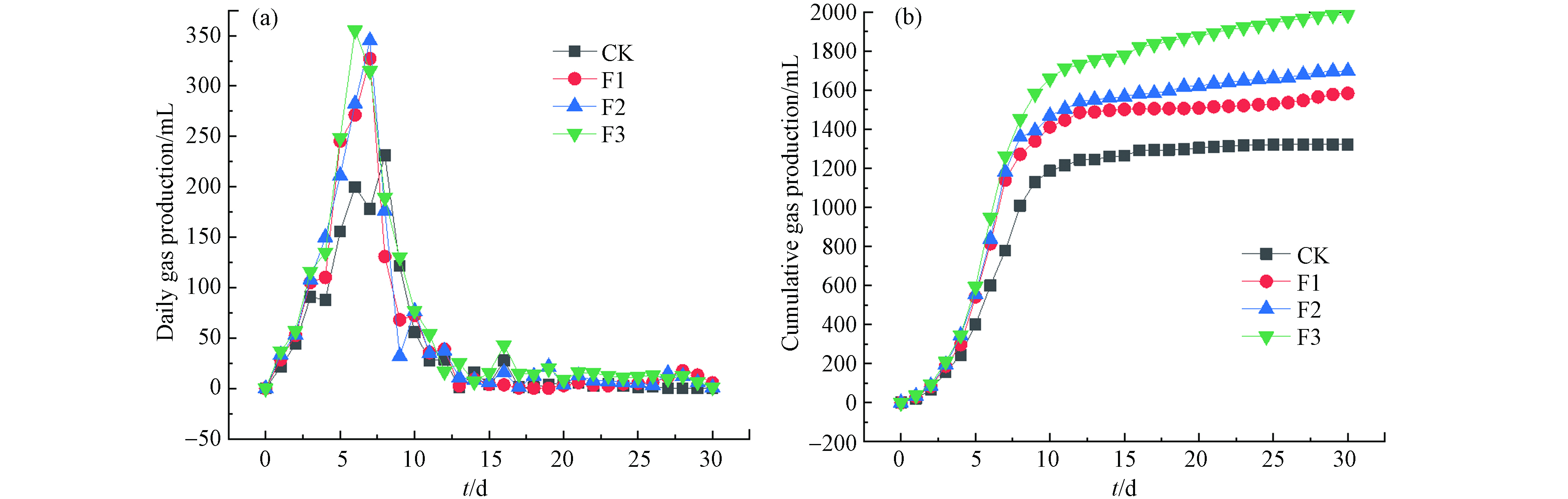
图2显示了猪粪/玉米秸秆厌氧发酵过程中日产气量和累计产气量的变化情况. 由图2(a)可知,随着时间的进行,各处理组厌氧发酵的日产气量在逐步上升,在第6天时,处理组F3达到了最高峰355.2 mL·d−1. 第7天时,处理组F1和F2日产气量相继达到了最高峰,分别是327.1 mL·d−1和345.1 mL·d−1. 到第8天时,对照组CK日产气量才达到最高峰231.2 mL·d−1. 接下来随着厌氧发酵的进行,由于发酵原料被微生物不断地消耗,日产气量逐渐呈下降趋势,到第30天时各组日产气量基本为0. 通过比较对照组与处理组,发现最大日产气量时间出现顺序:F3、F2、F1、CK,即对照组CK出现的时间最晚,说明腐殖酸的添加促进了发酵系统中微生物的代谢活动.
从图2(b)可知,各处理组的累计产气量的变化趋势. CK、F1、F2和F3最终总产气量分别是1321.9 、1583.72、1697.8、1986.2 mL. 各处理组F1、F2、F3总产气量均高于对照组CK,与对照组CK相比分别提高了19.81%、28.44%、50.25%. 其中,处理组F3提高最明显,添加7.5%腐殖酸产气效果最佳,说明腐殖酸促进了厌氧发酵,提高了有机物的降解效率,腐殖酸本身就是农业废弃物发酵后的产物,其很稳定,难以被微生物降解而导致产气量增多[18],产气量增多主要原因是腐殖酸中含有大量酚类和羧基基团能与重金属离子结合,添加的腐殖酸与重金属发生络吸附络合反应[19-21],降低了重金属的生物有效性,防止了重金属超标抑制微生物的活动.
-
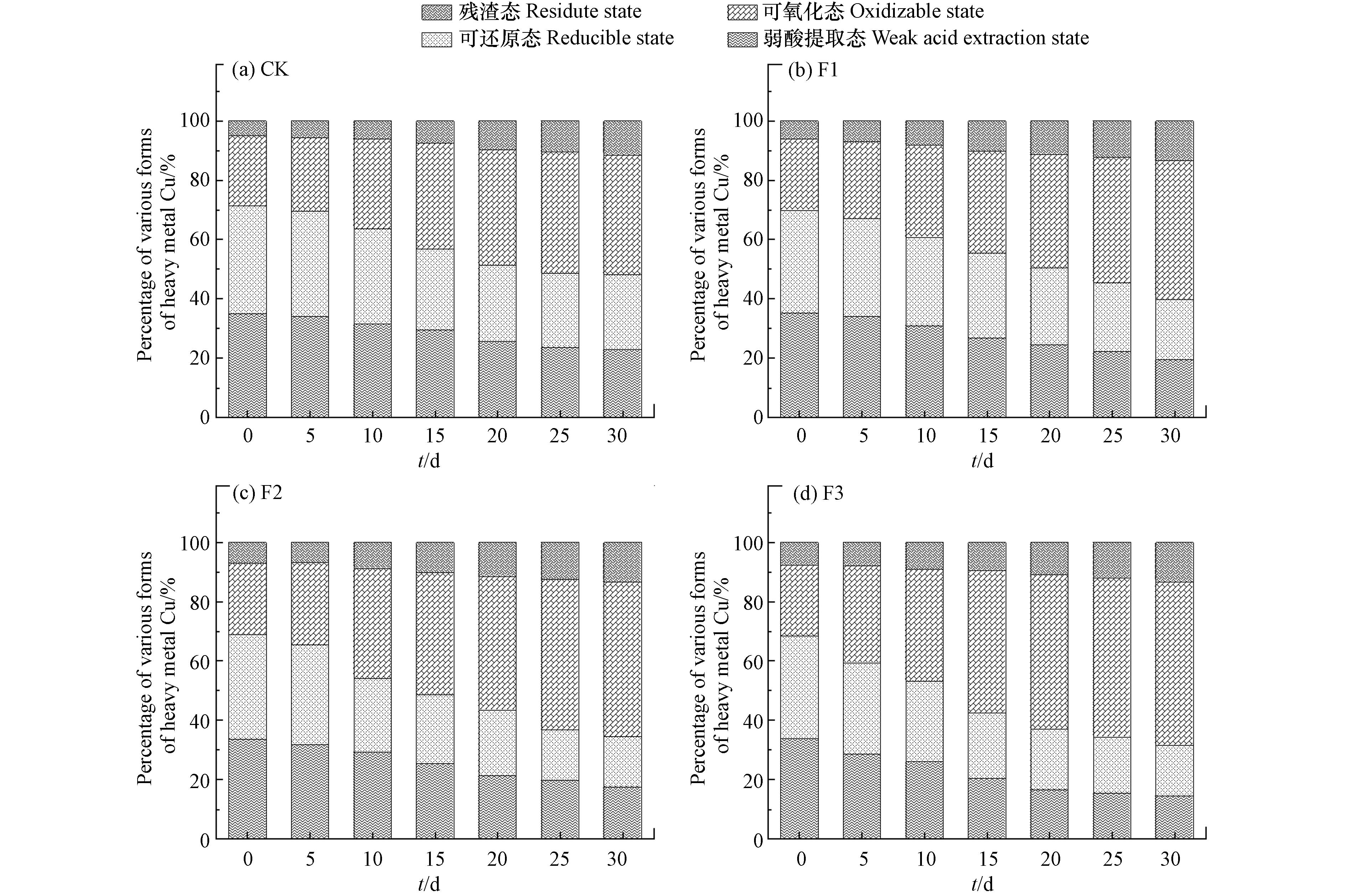
猪粪/玉米秸秆厌氧发酵过程中各处理组沼渣中重金属Cu各形态的变化如图3所示. 由图3可得出Cu形态的动态变化特征如下:
(1)从弱酸提取态来看,4组处理组中弱酸提取态Cu占比随着厌氧发酵的进行都呈下降的趋势. 发酵后CK中弱酸提取态Cu下降了9.01%,添加腐殖酸的处理组F1、F2、F3都分别下降了15.83%、16.38%、19.92%,下降幅度都明显高于CK.
(2)从可还原态来看,4组处理组中可还原态Cu占比下降趋势与弱酸提取态基本一致,呈下降趋势. 发酵前4组处理组可还原态Cu占比都差不多,发酵后4组处理组可还原态Cu占比从高到低依次为:CK>F1>F2>F3. 说明添加腐殖酸更易降低可还原态Cu含量.
(3)从可氧化态来看,4组处理组中可氧化态Cu都呈上升趋势,发酵结束后CK、F1、F2、F3可氧化态Cu都上升了14.13%、22.98%、27.50%、32.23%,上升幅度越来越大,其中F3上升幅度最大. 说明添加腐殖酸可以加速可氧化态Cu占比的增加.
(4)从残渣态来看,各处理组中残渣态Cu占比都较少,随着厌氧发酵的进行,各处理组中残渣态Cu呈上升趋势. 发酵结束后CK、F1、F2、F3残渣态Cu增幅分别为3.55%、7.22%、7.39%、7.99%. 添加腐殖酸的处理组的增幅明显高于对照组CK,说明腐殖酸对残渣态Cu的形成具有促进作用.
(5)从生物有效形态来看,各处理组中重金属Cu生物有效形态占比都逐渐减少,下降幅度有所不同. CK、F1、F2、F3生物有效形态Cu占比降幅分别为17.68%、30.20%、34.89%、40.22%. 添加腐殖酸显著降低重金属Cu的生物有效性,促进了重金属Cu的不稳定形态向稳定形态的转化. 其中,添加7.5%的腐殖酸使重金属Cu生物有效形态下降幅度可达40.22%,明显高于CK.
-
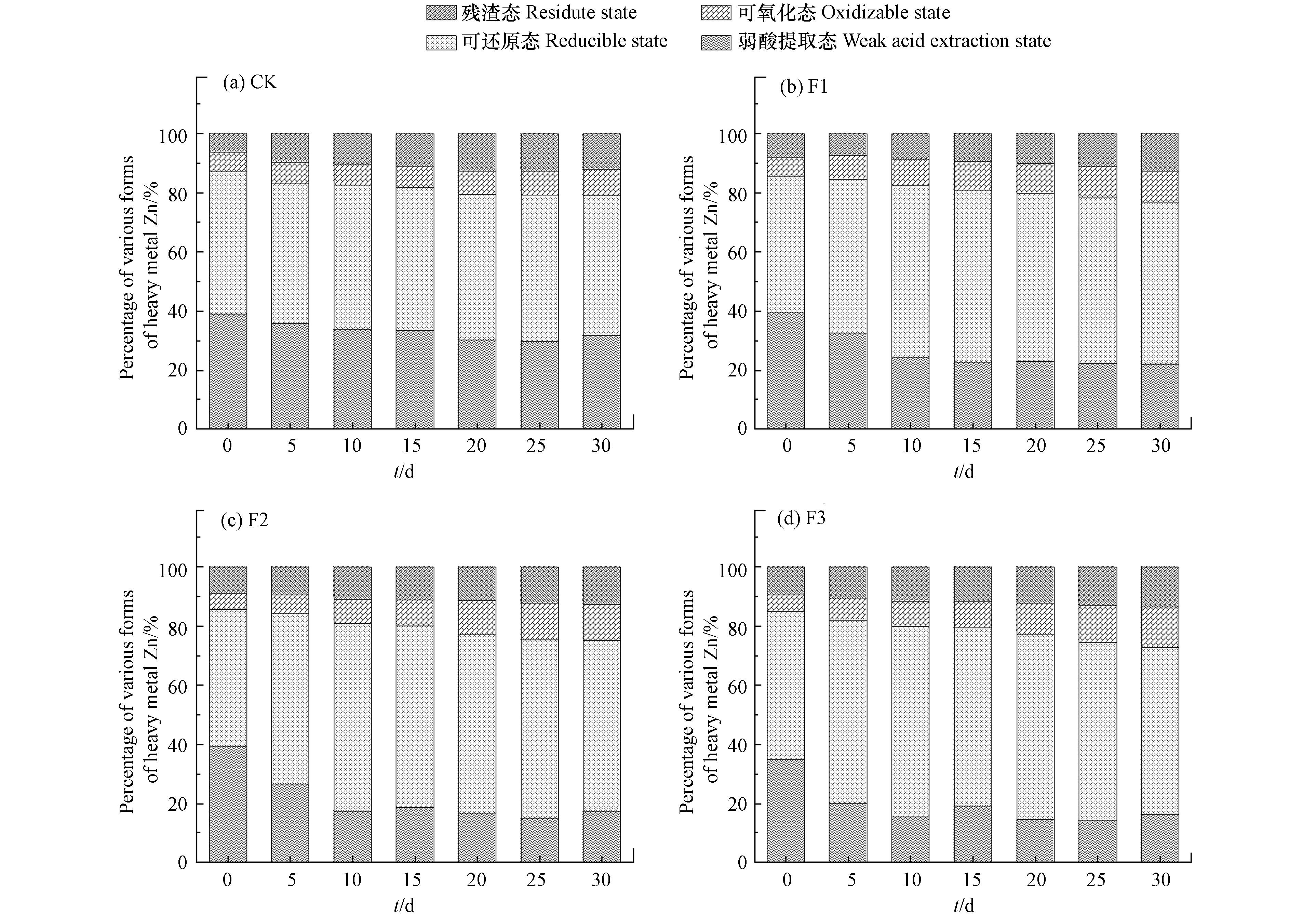
猪粪/玉米秸秆厌氧发酵过程中各处理组沼渣中重金属Zn各形态的变化如图4所示. 沼渣中重金属Zn主要是以弱酸提取态和可还原态的形式存在,由图4可得出Zn形态的动态变化特征如下:
(1)从弱酸提取态来看,厌氧发酵过程中对照组中弱酸提取态Zn占比下降比较平缓,下降幅度为6.25%. 然而,处理组F1、F2、F3都先是下降较快,接着保持平缓,下降幅度分别为15.27%、22.76%、19.76%,下降幅度都明显高于对照组CK.
(2)从可还原态来看,对照组CK中可还原态Zn占比并没有随着厌氧发酵的进行而变化,基本都维持在48%左右. 其他添加腐殖酸的处理组中可还原态Zn占比趋势都是先上升随后有所下降,发酵后可还原态Zn占比都比发酵前多. 说明腐殖酸并没有促进可还原态Zn的转化.
(3)从可氧化态来看,4组处理组中可氧化态Zn的占比明显小于可还原态Zn的,主要原因是Zn是两性金属,较活泼,与腐殖酸吸附络合的稳定性没有Cu高. 但可氧化态Zn的趋势与可氧化态Cu一样,呈上升趋势. 发酵结束后CK、F1、F2、F3可氧化态Zn分别上升了1.56%、4.78%、7.66%、8.89%. F1、F2、F3的上升幅度都明显高于CK.
(4)从残渣态来看,各处理组中残渣态Zn占比较少,随着厌氧发酵的进行,各处理组中残渣态Zn呈上升趋势. 发酵结束后CK、F1、F2、F3残渣态Zn增幅分别为3.53%、5.04%、5.15%、6.52%. 添加腐殖酸的处理组的增幅明显高于对照组CK,说明腐殖酸对残渣态的形成具有促进作用.
(5)从生物有效形态来看,各处理组中重金属Zn生物有效形态占比都逐渐减少,下降幅度有所不同. CK、F1、F2、F3生物有效形态Zn占比降幅分别为5.09%、9.82%、12.81%、15.41%. 腐殖酸的添加显著降低重金属Zn的生物有效性,促进了重金属Zn不稳定形态向稳定形态的转化.
综上实验结果表明,添加腐殖酸促进了厌氧发酵过程中重金属(Cu、Zn)有效形态含量的下降,钝化效果有了明显的提升. 这种现象主要是因为腐殖酸是一种离子交换能力很强的钝化剂,其主要结构是羧酸、醇羟基等多种活性官能团. 这些活性官能团会与阳离子重金属(Cu2+、Zn2+)发生络合反应形成络合物,从而降低生物有效性. 但对两种重金属的生物有效态下降有明显差别,在发酵系统中重金属Cu与Zn会有竞争关系. 根据Kerndorff等[22]研究,腐殖酸对重金属的吸附络合顺序为:Hg>Fe>Pb>Cu>Al>Ni>Cr>Zn>Cd>Co>Mn,可知腐殖酸对重金属Cu的吸附络合能力强于重金属Zn. 在发酵系统中腐殖酸会率先吸附络合重金属Cu,当腐殖酸中重金属Cu饱和后才会去吸附络合重金属Zn[19],因此可氧化态Zn的占比明显低于可氧化态Cu. 然而,发酵后可还原态Zn占比变化不明显,还略有所回升,这可能主要归因于Zn是两性金属化合物,其活性、迁移能力较强,在可还原条件下容易被释放,同时厌氧发酵过是一个极其复杂的过程,微生物在分解有机物时,会将本来与有机物相结合的Zn分解了,形成游离态,从而导致可还原态Zn略有增加.
-
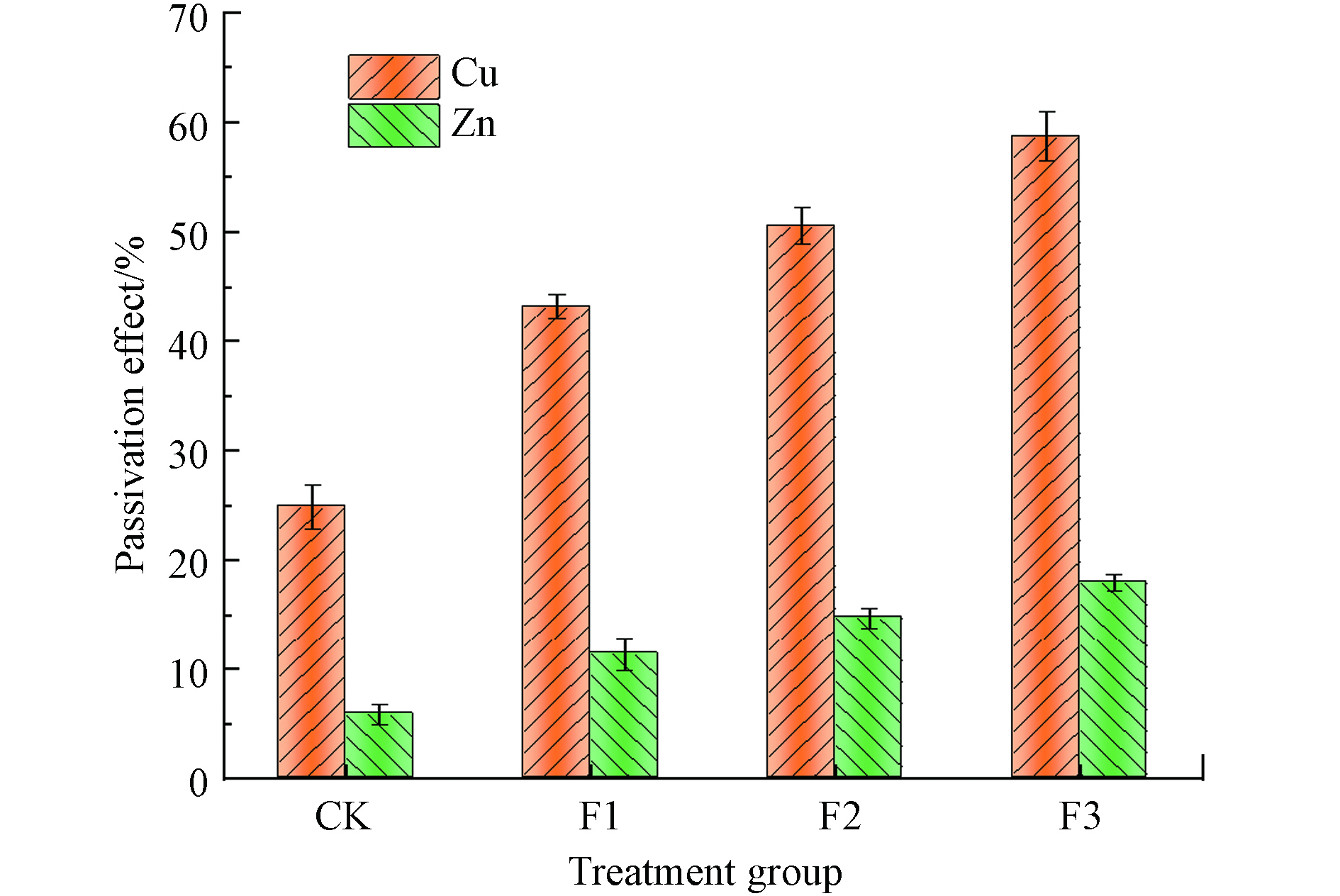
重金属钝化效果直观的反映了添加腐殖酸对厌氧发酵过程沼渣中重金属(Cu、Zn)钝化作用的强弱,图5为各处理组沼渣中重金属(Cu、Zn)钝化效果.
从图5可知,各处理组经过厌氧发酵结束后重金属Cu钝化效果由高到低的次序为:F3(58.72%)>F2(50.57%)>F1(43.18%)>CK(24.86%). 通过对重金属Cu钝化效果进行方差分析,结果表明添加腐殖酸对重金属Cu钝化效果有显著影响(P<0.05),其中处理组F3的影响最为显著,因此说明添加腐殖酸有效提高了对重金属Cu的钝化效果,促进了稳定态Cu的增多. 重金属Zn钝化效果顺序为:F3(17.95%)>F2(14.72%)>F1(11.37%)>CK(5.84%),对重金属Zn钝化效果方差分析,结果表明添加腐殖酸对重金属Cu、Zn钝化效果都有显著影响(P<0.05),其中F3的钝化效果较好,对重金属Cu、Zn的钝化效果分别为58.72%、17.95%.
综上实验结果,腐殖酸对重金属Cu的钝化效果明显优于对重金属Zn的钝化效果,这主要与重金属Zn的特性有关,重金属Zn是两性重金属,较为活泼,易在不同环境中流动,因此重金属Zn较难被钝化. 同时,在发酵系统中重金属Zn主要与小分子物质结合,并且结合不紧密易被植物吸收,重金属Cu则主要与大分子物质结合,并且结合紧密较为稳定[23-24],腐殖酸是一种大分子物质,因此重金属Cu更易被腐殖酸吸附络合形成稳定态,从而导致重金属Cu的钝化效果明显优于对重金属Zn.
-
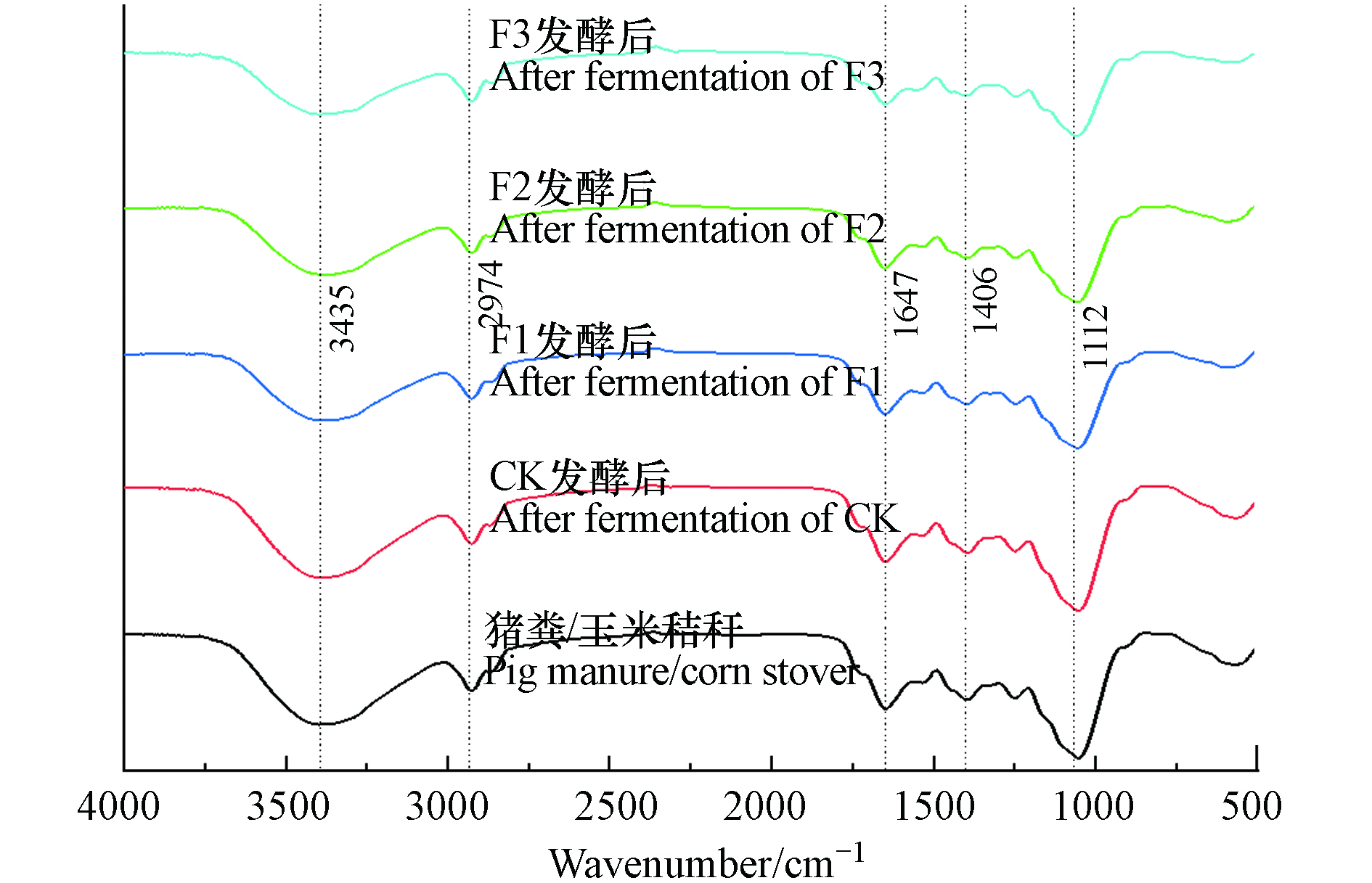
本实验利用傅里叶红外光谱技术(FTIR)来研究厌氧发酵过程中有机物的矿化和腐殖化程度. FTIR特征吸收带归属[25]见表3,厌氧发酵前后沼渣的红外光谱的变化情况如图6所示[13].
从图6可知,厌氧发酵前后的各个处理组沼渣的光谱特性都基本相似,只是在相对强度上有一些差异. 这主要可能与添加了不同比例的腐殖酸有关,但其主要的发酵原料还是猪粪,这一结果与栾润宇等[26]的研究一致. 图7中,3408—3450 cm−1、 2850—2922 cm−1、1600—1653 cm−1、1105—1160 cm−1这几个代表性峰值的强度变化比较明显.
结合表3和图7可知,在3408—3450 cm−1和2850—2922 cm−1峰处,厌氧发酵后各处理组在该两处峰的相对强度与未发酵的猪粪/玉米秸秆相比均有所降低,降幅由大到小依次为F3、F2、F1、CK. 前一峰表明添加腐殖酸促进了碳水化合物、酰胺化合物、蛋白质等有机物被分解为简单有机物,导致—OH基团的减少. 后一峰表明发酵原料中的碳水化合物与脂肪族化合物等有机物在微生物的矿化,代谢作用下被降解,导致—CH基团的减少. 此外,在1600—1653 cm−1峰处,发酵后各处理组在该处峰的相对强度与未发酵的猪粪/玉米秸秆相比均有所提高,F1、F2、F3在该处峰的相对强度均高于CK. 这表明添加腐殖酸促进被分解的简单有机物在微生物的作用下聚合成芳香环类、烯烃类腐殖质,加速了饱和碳向不饱和碳的形成[27],促使了腐殖质相对含量的增加. 综上,在厌氧发酵过程中,带有—OH、—CH2、—CH3的基团有机物在减少,带有C=O、—COO—、C—O—C和芳香环基团的有机物在增加. 表明了厌氧发酵促进了高分子有机物的分解和提高了沼渣的腐殖化程度. 添加腐殖酸后微生物的代谢活性更高,产生了更多的芳香族,腐殖化程度更高,其中F3腐殖化程度最佳.
近年来的众多学者研究结果显示[6, 13, 28],可用在芳香族碳(1647 cm−1)处的特征峰强度与碳水化合物碳(3435 cm−1)、脂肪族碳(2974 cm−1)、羧酸碳(1406 cm−1)、多糖碳(1112 cm−1)的比值(分别记为A、B、C、D)来表示厌氧发酵中有机物官能团结构的变化,来评价猪粪厌氧发酵的腐殖程度. 比值越高表明碳水化合物、脂肪族化合物、羧酸类、多糖类物质含量在减少,芳香族碳在增加,发酵原料中腐殖化程度越高.
由表4可知,未发酵的猪粪/玉米秸秆的A值为1.035,CK发酵后A值为1.037 ,添加腐殖酸的处理组厌氧发酵后A值依次上升均大于CK,表明厌氧发酵过程中添加腐殖酸有利于促进碳水化合物往芳香族化合物转化. 未发酵的猪粪/玉米秸秆B值为0.933,CK发酵后B值为0.951,增幅1.93%,F1、F2、F3的增幅依次为5.89%、7.40%、8.44%,都大于CK. 未发酵的猪粪/玉米秸秆的C值为0.950,厌氧发酵后各处理组C值由大到小的依次为F3、F2、F1、CK. 未发酵的猪粪/玉米秸秆的D值为1.031,与其相比,CK、F1、F2、F3的增幅分别为3.20%、3.30%、5.24%、10.18%. 综合分析以上各特征参数比值表明,添加腐殖酸促进碳水化合物和多糖物质向芳香族化合物转化,提高了猪粪/玉米秸秆厌氧发酵的腐殖化程度,其中7.5%添加比例最佳,F3腐殖化程度最高. 这可能由于添加的外源腐殖酸率先吸附钝化发酵系统中的超标的重金属,给微生物提供了适宜的环境,促进了有机物的分解以及厌氧发酵的腐殖化程度.
傅里叶红外光谱技术(FTIR)结果表明添加了腐殖酸,厌氧发酵后腐殖化程度越高. 主要原因:1)厌氧发酵是微生物参与的生物过程,腐殖酸能够疏松发酵原料[29-30],添加腐殖酸提高了发酵原料的孔隙率,为微生物提供了适宜的环境来分解有机物,加快了腐殖化程度. 2)厌氧发酵过程中发酵原料中重金属元素会抑制硝化反硝化过程[31-32],当这些元素浓度过高时会破坏微生物的结构和功能,甚至产生毒性抑制作用. 因此,腐殖酸在这起到了关键作用,厌氧发酵过程中钝化机理推测如图7所示,未添加腐殖酸时发酵系统中不稳定态Cu、Zn过高,将抑制微生物活性.
添加腐殖酸后,腐殖酸与发酵原料中的重金属吸附络合反应形成稳定的重金属形态,不稳定态重金属含量减少,降低了不稳定态重金属过高而破坏微生物结构和功能的风险,从而促进厌氧发酵,提高沼渣腐殖化程度. 腐殖化程度提高,进一步增加了发酵系统中腐殖质的含量,腐殖质分子富含羧基和羟基,可与金属阳离子形成稳定的络合物[33],从而进一步降低重金属(Cu、Zn)的生物有效性,由于腐殖酸络合重金属Cu的能力强于Zn,重金属Cu钝化效果要优于重金属Zn的. 就本实验研究结果而言,F3添加7.5%腐殖酸的处理组中腐殖化程度最高,重金属(Cu、Zn)钝化效果也最佳.
-
(1)厌氧发酵结果表明,添加腐殖酸对厌氧发酵产气量具有促进作用,添加腐殖酸的F1、F2、F3累计产气量分别比CK提高了19.81%、28.44%和50.25%.
(2)厌氧发酵过程中添加腐殖酸利于促进重金属(Cu、Zn)的有效态向稳定态转化,其中,重金属Cu生物有效性下降程度比重金属Zn明显,F3中重金属Cu生物有效形态下降幅度可达40.22%.
(3)厌氧发酵过程中添加腐殖酸有利于提高重金属Cu、Zn钝化效果,腐殖酸对重金属Cu的钝化效果优于对重金属Zn,F3钝化效果较好,对重金属Cu、Zn的钝化效果分别为58.72%、17.95%;通过方差分析,添加腐殖酸对重金属Cu、Zn钝化效果显著(P<0.05);F3的钝化效果优于其他处理组.
(4)傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)结果显示,猪粪厌氧发酵后各处理组沼渣中碳水化合物、脂肪族化合物等有机物分解、减少,芳香族化合物等腐殖质含量增多,腐殖化程度提高. 其中,F3添加7.5%腐殖酸的处理组中腐殖化程度最高.
(5)重金属钝化法只能缓解畜禽粪便重金属污染问题,为了能够从源头解决,促进绿色健康食品的发展,建议有关部门和科研单位大力开发、推广高效畜禽免疫制剂,替代重金属饲料添加剂,杜绝畜禽粪便重金属污染.
添加腐殖酸对猪粪/玉米秸秆厌氧发酵中铜、锌钝化效果的影响
Effect of adding humic acid on the passivation of copper and zinc during anaerobic digestion of pig manure/corn stover
-
摘要: 针对畜禽饲料添加蓝矾或称胆矾(CuSO4·5H2O)、皓矾(ZnSO4·7H2O)等重金属化合物,引起畜禽粪便重金属污染风险,本研究通过构建以猪粪/玉米秸秆为发酵原料、腐殖酸为钝化剂的发酵系统,考察添加腐殖酸对猪粪/玉米秸秆厌氧发酵过程中产气量、重金属(Cu、Zn)形态变化及沼渣光谱特性的影响. 结果表明,添加的腐殖酸对猪粪/玉米秸秆厌氧发酵产气具有显著促进作用,添加腐殖酸样本组(编号:F1、F2、F3)较未添加组(编号:CK)的累积产气量分别提高了19.81%、28.44%、50.25%;通过BCR提取法分析沼渣中的Cu、Zn形态动态变化,显示添加腐殖酸有利于Cu、Zn的有效态向稳定态转化,F3中Cu、Zn有效态转化为稳定态的效果最佳;显著性分析表明F3中Cu、Zn的钝化效果最佳,Cu、Zn的钝化效果分别为58.72%、17.95%,显著优于其他处理组;腐殖酸对Cu的钝化效果整体优于Zn;FTIR结果显示,厌氧发酵后各处理组沼渣中碳水化合物、脂肪族化合物等有机物分解、减少,芳香族化合物等腐殖质含量增多,且F3中腐殖化程度最高. 因此添加适量腐殖酸有利于降低Cu、Zn的生物有效性,提高腐殖化程度,可为降低猪粪中重金属Cu、Zn有效性、降低重金属污染风险和提高发酵质量提供技术指导.Abstract: The introduction of heavy metal compounds, such as blue vitriol (CuSO4·5H2O) and halo alum (ZnSO4·7H2O), in the livestock and poultry feeds could bring heavy metal pollution risk from livestock manure. This study established an anaerobic digestion system using pig manure/corn stalk and humic acid as fermentation raw materials and the passivator respectively. Effects of adding humic acid on the gas production, state transformation of heavy metals (Cu, Zn) and the spectral characteristics of the biogas residue were examined. The results show that the addition of humic acid can promote significantly gas production during the anaerobic digestion of pig manure/corn stover. The sample group with humic acid (serial number: F1, F2, F3) increased by 19.81%, 28.44%, and 50.25% comparing with the group without humic acid (serial number: CK). The state transformation of Cu and Zn is analyzed by BCR extraction method, adding humic acid is beneficial to the conversion of Cu and Zn from effective state to stable state, and conversion ratios of Cu and Zn from effective state to the stable state in F3 is maximum. Significance analysis shows that Cu and Zn have the best passivation effects in F3. 58.72% and 17.95% of Cu and Zn are passivated, the passivation of Cu by humic acid is better than Zn. FTIR results showed that organic matter in the biogas residue of each treatment group, such as carbohydrates and aliphatic compounds, decomposed accompanying with the increase in the content of humus such as aromatic compounds, and the degree of humification in F3 was the highest. Therefore, adding an appropriate amount of humic acid is beneficial to reduce the bioavailability of Cu and Zn and promote the humification degree. This study can provide technical guidance for reducing the effectiveness and pollution risk of Cu and Zn in pig manure and improving anaerobic digestion efficiency.
-
Key words:
- Pig manure /
- anaerobic digestion /
- heavy metal state /
- humic acid /
- FTIR.
-
近年来,我国一些发达地区的村落建设了分散式农村污水处理设施,并取得了较好的环境效益,但这些村落污水的治理,仍以COD、氨氮、总磷等污染物的降解为考核目标,而农村居民生活水平和医疗条件在不断提高,村落水环境中EDCs浓度水平也相应增加,其对水环境生态和人类健康危害日益严重[1],尤其是农村地区,EDCs通过灌溉形式,直接被稻、麦、瓜果等农作物吸收,进而进入食物链。EDCs是一种能扰乱生物体新陈代谢平衡的化学物质,主要分为天然产生(E1、E2、E3)及人工合成(EE2)[2]。据报道,各种环境基质中均检测到不同浓度的EDCs,水体中其质量浓度可低至10−6(1 μg·L−1)量级和10−9(1 ng·L−1)量级,而EDCs在极低浓度下就可引起水生生物的生殖发育障碍[3-4]。主要原因在于,EDCs与生物体内的雌激素受体结合而干扰生物内分泌系统正常代谢[5]。Legler等[6]研究发现,当自然水体中E2浓度达到1.0 ng·L−1时,可引起生物体内分泌紊乱。Cappiello等[7]发现不少猝死婴儿体内残留的EDCs含量相对普通新生婴儿较高;Clarke等[8]研究表明,妊娠期女性若接触过量EE2,则将増加母女患乳腺癌的风险。由此可见,当EDCs进入动物食物链,再经过层层传递,最终在人类体内积累,对人体健康损害威胁相应不断增大。
国内外众多学者研究表明,耕作型稻田复合生态系统通过“微生物-稻田湿地”耦合的复合系统对村落污水中的有机污染物进行生物降解,其主要依靠水稻复杂的根系及其附着的生物膜协同净化作用,不但可以达到净化村落污水的效果,还可以产生水稻增肥的效益[9]。但存在类固醇类激素(EDCs)环境污染及生态危害问题。现阶段,人为去除环境中雌激素类污染物主要通过吸附[10]、光催化氧化[11]、生物降解[12]的3种途径使EDCs在环境中迁移、降解。阳春等[10]研究表明,污泥对雌激素的吸附主要来自于污泥中的活性成分,而被生物表面所吸附的雌激素才能被生物降解。光解与氧化作用是EDCs真正的分解过程,因为它不可逆的改变了分子结构,强烈影响其在环境中的归趋,但光降解类固醇雌激素极易受pH的影响,近期有一些研究表明类固醇雌激素光氧化降解后产生的代谢产物仍具有雌激素活性[11]。生物降解通过微生物新陈代谢和自身与周围环境进行物质交换,达到将污染物去除或转化为无害无毒的物质[12],日益受到人们的重视。
本文针对村落污水中的类固醇类激素(EDCs)环境污染及生态危害问题,构建耕作型稻田湿地[13],并以本课题组筛选的农药降解菌HD为EDCs生物强化降解菌[14],考察其对EDCs的降解效能,以期为村落水环境中的EDCs降解机制及环境生态影响评价提供参考。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
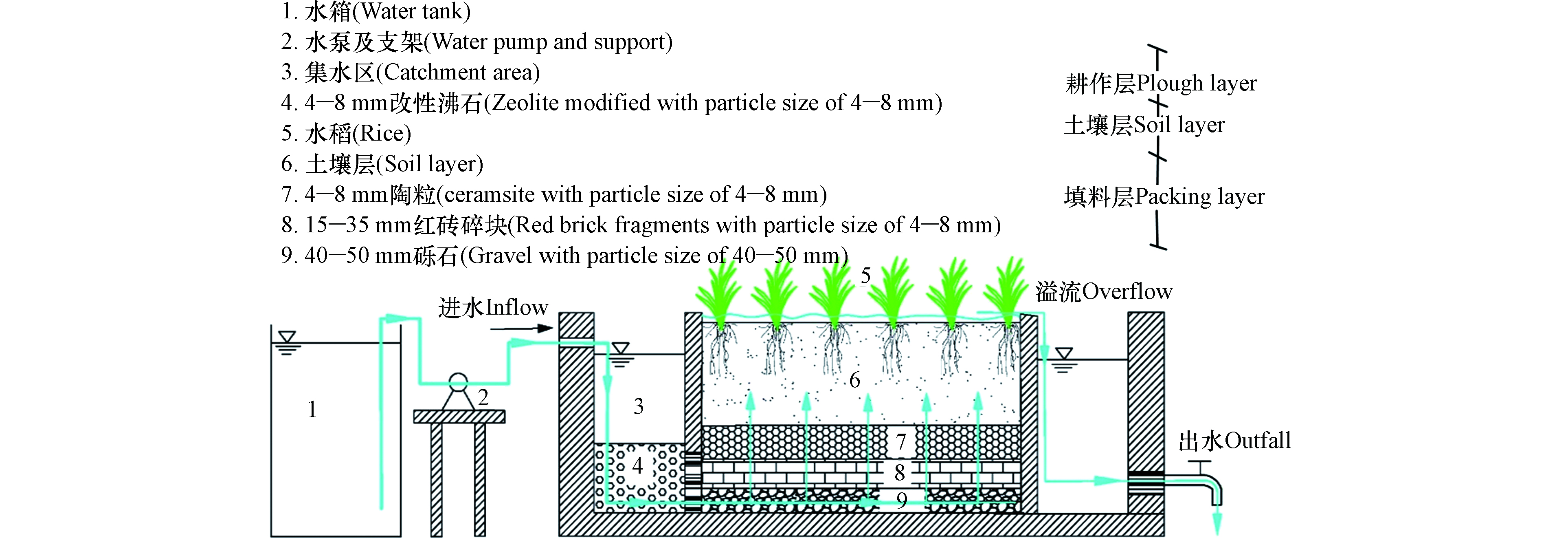
1.1 试验装置与进水水质
耕作型稻田湿地试验装置分2组,A组为空白对照组,B组为HD菌剂强化组。试验装置如图1所示,整个耕作型稻田湿地装置采用PP板(L×B×H=1 m×0.4 m×0.65 m),由集水区、湿地处理区和出水区3部分所组成,集水区沸石[15]层厚度200 mm,湿地填料层厚度300 mm,自下而上由40—50 mm砾石、15—35 mm红砖碎块、4—8 mm陶粒组成,孔隙率约30.8%;试验进水通过恒流水泵抽入集水区,经集水区的沸石层有效拦截后,再进入稻田湿地。装置内的土壤,取自常州洛阳镇薛家河周边稻田表层15—20 cm处土壤,所取土壤为该地区连年种植水稻土,装置内土壤层厚度为20 cm。耕作层厚度10 cm。水稻秧苗取自常州市洛阳镇薛家河周边水稻田中,种植密度为45株·m−2。
菌剂投加:A、B二组均采用自然进水法生物膜培养,当镜检可见填料上有褐色生物膜和原生动物及COD降解率超过60%时,认为生物挂膜成功。此时在B组中投加HD菌剂,配制100 mL的基础液体培养基(氯化钠:0.5 g,七水合硫酸镁:0.5 g,七水合硫酸亚铁:0.002 g,硫酸铵:1.5 g,氯化钙:0.04 g,磷酸氢二钾:1.5 g,磷酸二氢钾:1.5 g,蒸馏水:1 L,琼脂粉:20 g,pH:7.2—7.4),按照体积分数2.5%的比例接入菌种HD,培养48 h,将菌液混合后,再按照1%的投加比例混入进水中,随进水进入B组耕作型稻田湿地系统,连续投加2周,进行菌剂强化挂膜。A组不投菌,在正常条件下进行生物挂膜,为试验对照组。
农药降解菌HD筛选自南京某废弃农药厂的土壤中,是一株具有降解2,4-二氯苯酚能力的菌,现保藏于中国微生物菌种保藏管理委员会普通微生物中心,保藏编号:CGMCC No. 15123。经理化特性和分子鉴定判断属于摩式假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas mosselii)。
试验进水水质如表1所示。在生活污水的基础上添加少量内分泌干扰物,模拟进水内分泌干扰物浓度波动,如表2所示。
表 1 试验进水水质Table 1. Test water quality指标Index CODcr/(mg·L−1) 总磷/(mg L−1)TP 氨氮/(mg·L−1) NH+4 总氮/(mg·L−1)TN pH 范围 87—156 2.23—5.69 8.75—16.34 10.86—18.33 7.39—7.84 表 2 进水内分泌干扰物浓度(μg·L-1)Table 2. Concentration of endocrine disruptors in water inlet(μg·L-1)类固醇Steroid estrogen E1 Estrone E2 Estradiol EE2 17-α-ethinylestradiol E3 Estriol 原水浓度 10.13—15.25 0.79—1.1 0.88—1.82 6.31—9.58 模拟进水浓度 38.69—60.13 9.86—14.32 10.89—13.21 33.28—54.36 1.2 试验仪器与试剂
表 3 主要试验试剂Table 3. Main experimental reagents药品名称Drug names 分子式Molecular formula 规格Specification 生产单位Production unit E1 C18H22O2 — 阿拉丁 E2 C18H24O2 — 阿拉丁 E3 C18H24O3 — 阿拉丁 EE2 C20H24O3 — 阿拉丁 BSTFA C8H18F3NOSi2 — 阿拉丁 吡啶 C5H5N AR 永华化学科技(江苏) 丙酮 CH3COCH3 AR 国药 正己烷 C6H14 AR 江苏强盛功能化学 二氯甲烷 CH2Cl2 AR 永华化学科技(江苏) 雄烷 C19H23 — 北京谱析科技有限公司 表 4 试验主要仪器Table 4. Experimental main instruments仪器设备Instrument and equipment 型号Model number 生产单位Production unit 多用途高速离心机 SORVALL Thermo electron corporation 行星式球磨机 QM-1SP2 南京大学仪器厂 超声波细胞粉碎机 JY96-Ⅱ 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司 气质联用 Trace ISQLT 美国赛默飞科技有限公司 1.3 水样预处理
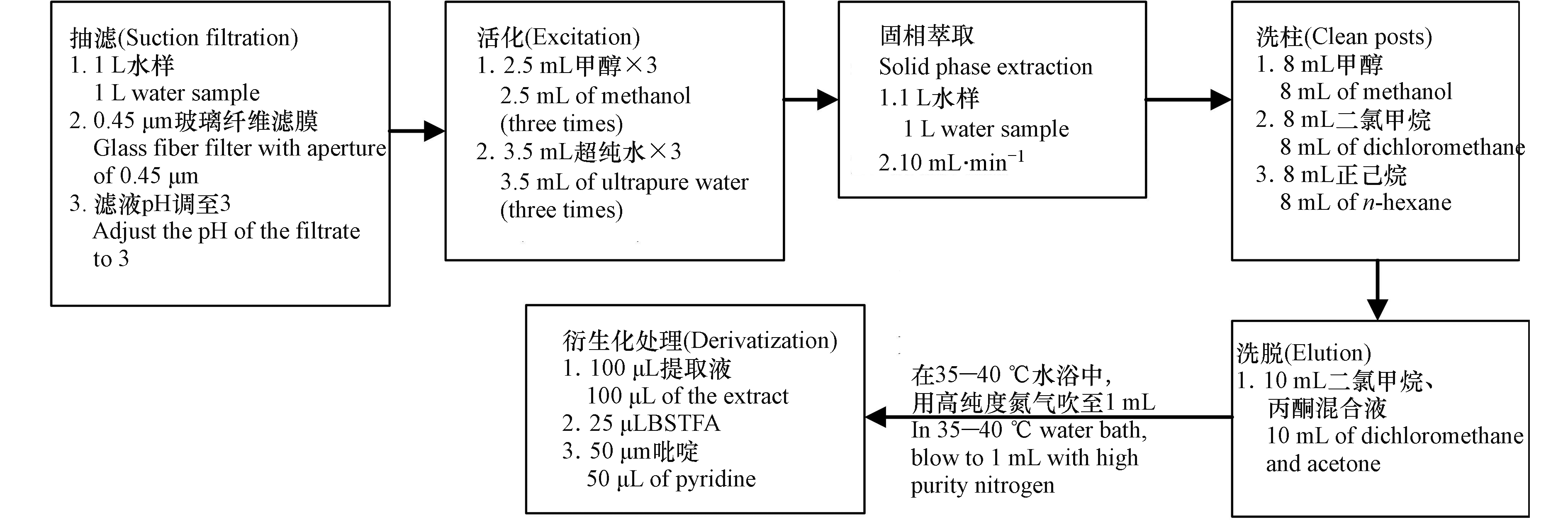
采集1 L水样,GF/F(0.45 μm)滤膜抽滤,滤液用99%的浓硫酸调节至pH3以下。
固相萃取:利用Simon Acti-Carb SPE柱进行固相萃取,首先活化SPE,分别加入2.5 mL甲醇3次,3.5 mL超纯水3次,控制流速在10 mL min−1,进行萃取,待水样萃取完,再分别加入8 mL甲醇、8 mL二氯甲烷、8 mL正己烷进行洗柱,最后用10 mL的二氯甲烷和丙酮的混合溶液淋洗,收集淋洗液,在35—40 ℃的水浴中,用高纯度氮气吹至1 mL,放入冰箱待用,具体步骤见图2。
1.4 土样预处理
稻田土壤采集后,自然风干,去除杂石杂草,用球磨机在400 r·min−1的条件下充分研磨,过20目筛网,混匀后放入冰箱待用。预处理时,称取1 g的样品,放入10 mL的离心管中,加入5 mL溶剂(甲醇∶丙酮=1∶1),超声波萃取10 min,随后以5000 r·min−1转速离心10 min,收集上清液至25 mL离心管中。重复以上步骤2次,合并上清液后,经高纯度氮气吹至1 mL后,定容至20 mL。最后按照图2水样预处理的方法,进行固相萃取。
1.5 衍生化处理
环境中类固醇类EDCs的含量相对较低,且由于这类化学物质都含有—OH官能团,极性较强,若直接采用气质联用测定,在测定过程中容易被色谱柱所吸附,从而造成实测浓度小于实际浓度,因此为降低该类物质的极性,提高其热稳定性,增加了衍生化步骤,即在正常衍生化的步骤中,又增添了吡啶,可以有效降低EE2的衍生产物转变为E1的衍生产物。黄成等[16]对某制药厂污水样品中E1、E2、E3和EE2衍生化后使用气相色谱/质谱法(GC-MS)分析表明,4种目标化合物的加标回收率达到(94.0%±2.9%)—(101.0%±3.8%),说明GC-MS法可应用于污水中雌激素化合物定量检测。
衍生化方法是在1.5 mL色谱进样瓶中加入100 μL的混合标液,通入高纯度氮气将其缓慢吹干,接着在进样瓶中加入25 μL BSTFA和50 μL吡啶,待其反应一定时间后吹干,最后加入V(二氯甲烷)∶V(正己烷)=1∶4的进样溶剂和10 μL 0.01 g·L−1的内标,取1 μL注入GC-MS分析,在空白污水样品中添加100,300、500 ng·L−1 等3个浓度水平的目标物,测定回收率。衍生化的具体反映结构变化如下:

1.6 EDCs的测定条件
试验中E1、E2、EE2、E3选用气质联用进行测定,色谱柱为TG-5MS(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm),气相条件如下:
GC:以氦气为载气,流速1 mL·min−1;不分流方式进样,进样口温度280 ℃,进样体积1 μL;柱初始温度为50 ℃,保持2 min,以12 ℃·min−1程序升温至260 ℃,保持8 min,再以3 ℃·min−1升温至280 ℃,保持5 min;
MS:接口温度280 ℃,传输线温度300 ℃,离子源为EI源,温度250 ℃,电子轰击能量70 eV,溶剂延迟时间12 min,以全扫描模式定性,扫描范围50—600 m/z,以选择离子扫描模式定量;
根据其衍生产物的特征碎片离子分布特征来确定目标产物的实际浓度,衍生产物实际参数如表5所示。
表 5 衍生产物的相应参数Table 5. corresponding parameters of derivative products衍生产物Derivative product 保留时间/min Retention time 特征碎片离子(m/z)Characteristic fragment ion 线性回归方程Equation of linear regression TMS-E1 24.28 342、327、285 Y=(9.43×108)x+(1.02×109);R2=0.91 di-TMS-E2 25.43 416、401、285 Y=(1.08×107))x+(7.55×106);R2=0.91 di-TMS-EE2 27.03 440、425、285 Y=(1.90×107))x+(3.92×106);R2=0.92 Tri-TMS-E3 28.43 504、489、285 Y=(1.14×106)x+(2.38×106);R2=0.90 注:x为目标产物的实际浓度,单位mg·L−1,Y为色谱峰面积. Note:x is the actual concentration of the target product, unit: mg·L−1, Y is the peak area. 2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 耕作型稻田湿地去除EDCs效能分析
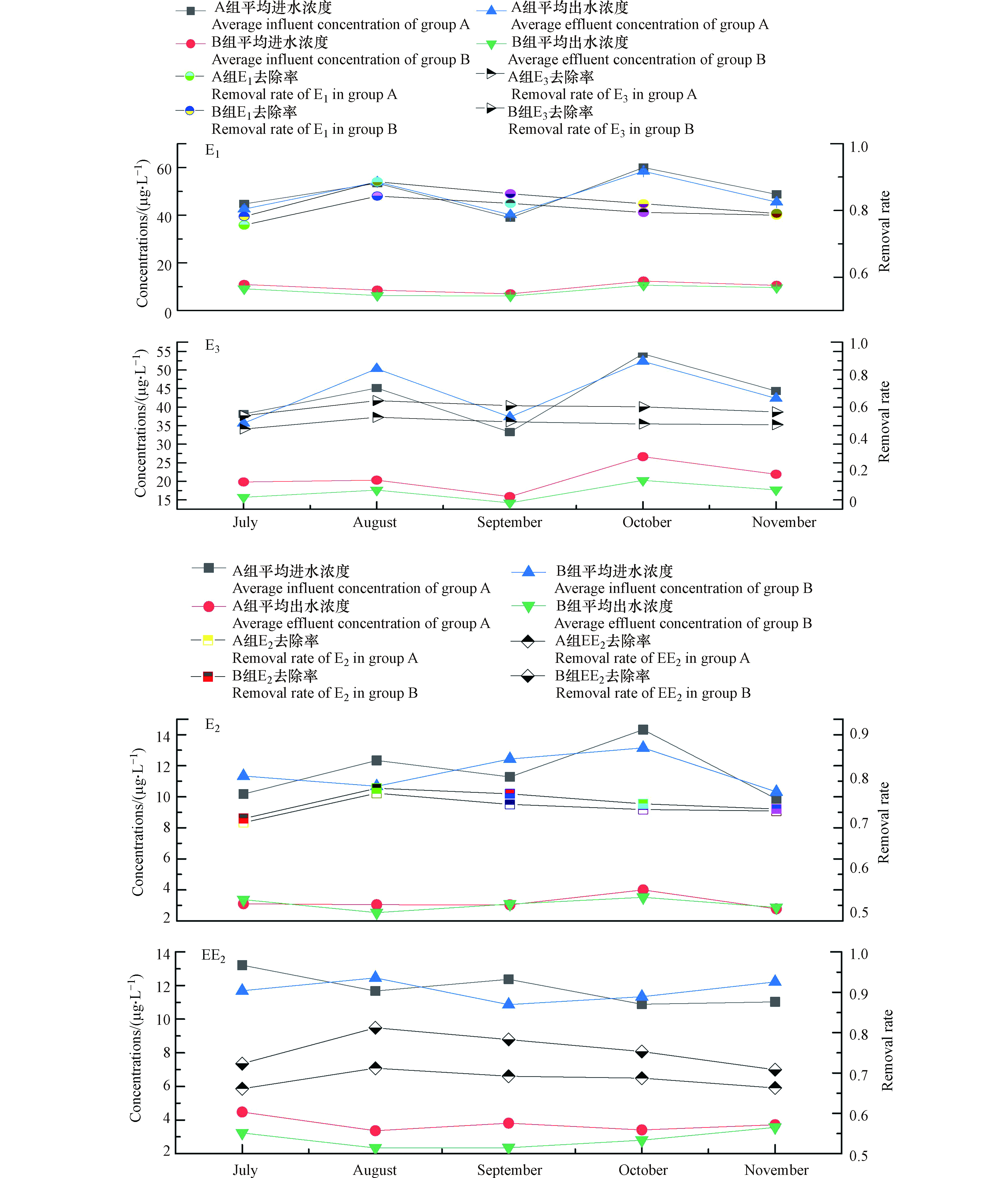
图3是2018年7月至11月,水稻生长过程中,耕作型稻田湿地对EDCs中E1、E2、EE2、E3的去除效果图。从图3可以看出,生活污水中EDCs通过耕作型稻田湿地吸附降解后,A组的E1、E2、EE2、E3的平均去除率为80.1%、72.4%、68.3%、51.4%,B组的平均去除率为82.6%、73.4%、75.6%、60.5%,除了E3外,其余各目标污染物的去除率均在65%以上,Baronti[17]在试验过程中发现E2在生物降解过程中,一部分的E2较易氧化转化成E1,遵循典型的醇氧化为酮原则,而E1通过水和作用又转化为E3,随着中间产物的不断产生,进而导致了出水E3浓度偏高。B组投加HD菌后,可能是假单胞菌HD诱导产生了羟基酶[18],相比A组E1、E2去除率未发生明显变化,EE2和E3去除率增高7%—9%,Huang等[19]发现,在BPA(双酚A)降解的河流底泥中,假单胞菌和鞘单胞菌占据了原有细菌群落的73%,由此可见,向湿地中投加假单胞菌HD有助于提高EDCs的去除率。
湿地经过5个月的连续运行后,投菌组B中的EDCs残留量明显低于未投菌组A。由图3中的实测数据,经计算B组湿地出水中E1、E2、E3和EE2含量相比A组分别降低约26.6%、17.1%、30.3%、13.3%。试验时间跨秋夏两季,夏季EDCs的去除效果要明显优于秋季,这主要是因为夏季正值水稻生长期,水稻根系对EDCs有一定吸收作用,夏季温度较高,微生物活性较强,微生物新陈代谢较为旺盛,运行至秋季时,温度降低,水稻收割,微生物活性逐渐降低,EDCs的降解率并未大幅下降,说明人工湿地中填料层及土壤层对EDCs的去除起到了一定作用。
2.2 HD菌剂强化后耕作型稻田湿地各生物单元对EDCs去除分析
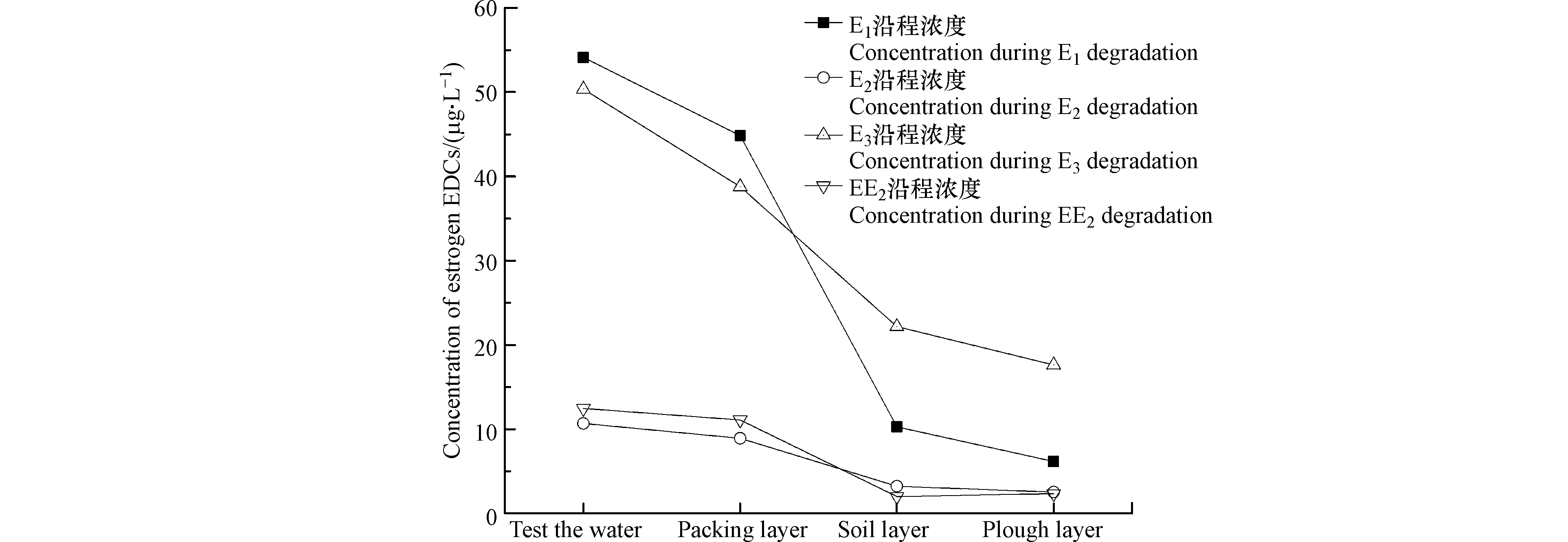
图4为耕作型稻田湿地经HD菌剂强化后EDCs浓度变化趋势图,沿程对E1、E2、E3和EE2的总去除率分别为88.6%、76.3%、64.8%和81.2%。3个生物单元填料层、土壤层、耕作层对E1去除率分别为16.2%、75.1%、28.2%,对E2去除率分别为14.5%、61.8%、18.7%,对E3去除率分别为20.6%、49.8%、10.4%,对EE2去除率分别为8.9%、43.4%、-8.1%,显然土壤层对EDCs的去除贡献占比相对最大,主要是因为土壤中微生物种群丰度要远高于填料层孔隙中生物膜上的微生物种群丰度,同时,土壤中还有分布广泛的水稻根系,通过其根系的泌氧作用,刺激微生物活性,促进微生物新陈代谢,进而加强了微生物降解能力,而填料层的填料作为微生物的代谢场所[20],其主要作用有二:一是直接吸附EDCs,二是作为微生物的载体,在其表面形成微生物集聚(生物膜),为生物膜微生物吸附、吸收、降解EDCs提供平台。其中E1、E2、E3的降解沿程越往后,目标污染物浓度越低,但EE2在经过土壤层的降解后,其浓度却略有提升,一方面,据Ascenzo等[21]研究显示,EE2的生物降解只发生在好氧段,因为EE2拥有乙炔基,从空间结构上来看,这对基团基质和受体的结合有阻碍作用,使得酶活性表达受阻,且在厌氧阶段,会使其由结合态变为游离态,导致EE2不易被降解,另一方面,Li等[22]研究发现,EE2在厌氧条件下更有利用吸附,耕作层分布有植物根系,植物根系的泌氧作用使得填料层吸附作用相比土壤层较弱。同时在降解过程中E3的含量在进水时略低于E1,但随着沿程越往后E3出水浓度高于E1,因为E2在生物降解过程中,一部分的E2较易氧化转化成E1,而E1通过水和作用又转化为E3,随着中间产物的不断产生,进而导致出水E3浓度偏高。
2.3 耕作型稻田湿地水芹种植期土壤中残留EDCs的变化特征
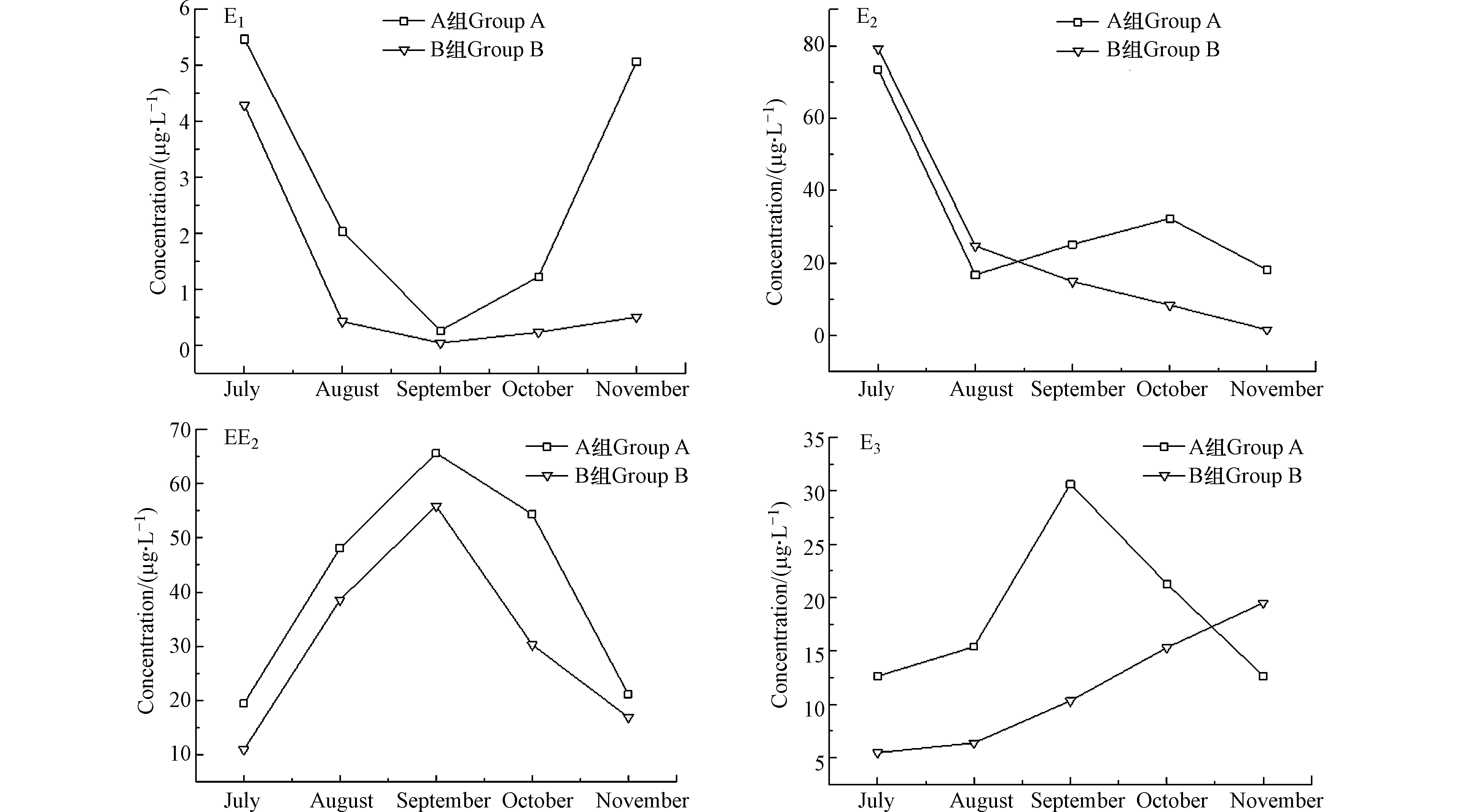
类固醇类EDCs多半有亲脂疏水的特性,易被土壤所吸附,一般类固醇类EDCs在环境中的半衰期为5—25 d不等,土壤中残留的EDCs会在一定时期,通过迁移、浸出到水体中,所以稻田湿地水体中EDCs含量通常偏高[23]。图5反应了耕作型稻田湿地净化过程中,土壤中残留EDCs含量的变化趋势,可看出投菌组B中E1、E2、EE2残留量明显小于A组,可见稻田湿地微生物对EDCs进行生物降解时,反硝化假单胞菌[24]使得反硝化细菌种群丰度提升,有利于E1的生物降解,说明HD菌促进了土壤层中羟基酶的产生,提高了其对EDCs的去除效率。从图5可看出,EE2浓度是先增后减,可能是由于EE2较为稳定不易降解。Ternes等[25]研究EE2的生物降解特性,发现1 mg·L−1的EE2经24 h后几乎无降解。10月水稻收割后,新种植了水芹,据Schroeder等[26]研究发现水芹在24 h内便能通过茎部富集近0.9 ng·L−1的EE2,所以后期EE2浓度又显下降趋势。B组中E3浓度一直呈上升趋势,任海燕等[27]研究发现,对EE2降解中间产物进行质谱分析推测,EE2在降解过程中首先被氧化为E1,后经过一系列生物催化作用生成2-羟基-2,4-二烯-戊酸和2-羟基-2,4-二烯-1,6-己二酸两种中间代谢产物,E1通过水合作转化为E3,又E2在生物降解过程中部分较易被氧化转化为E1,E1通过水合作用又转化为E3,故而导致土壤中E3浓度不断增高。湿地运行初期E1、E2浓度分别增加了85%、25%,EE2、E3浓度下降了60%、30%,这主要是因为生活污水中EDCs的构成主要以天然雌激素中的E1、E2为主,且其主要为结合态形式,极性更强,更易被土壤所吸收[28],且溶解性有机物的共轭物在经细菌酶分解时,亦会产生E1的衍生产物[29],进而导致E1浓度提高。虽然土壤层对于EDCs的降解效果较好,但初期由于土壤中生物种群尚未稳定,所以导致E1、E2的处理效果受限。
3. 结论(Conclusions)
(1)未投菌的A组对雌酮(E1)、雌二醇(E2)、雌三醇(E3)及17α-乙炔基雌二醇(EE2)的平均去除率分别为80.1%、72.4%、51.4%、68.3%,投加HD菌剂强化的B组平均去除率分别为82.6%、73.4%、60.5%、75.6%,A、B两组耕作型稻田湿地对E3去除率相比E1、E2、EE2最低。E2在生物降解过程中较易氧化转化成E1,而E1通过水和作用又转化为E3,随着中间产物的不断产生,出水E3浓度增大。A、B两组耕作型稻田湿地中,除E3外E1、E2、EE2去除率均在65%以上,EE2的生物降解只发生在好氧段,EE2拥有乙炔基,从空间结构上来看,这对基团基质和受体的结合有阻碍作用,使得酶活性表达受阻,且在厌氧阶段,会使其由结合态变为游离态,致使EE2不易被降解。
(2)投加HD菌后,耕作型稻田湿地对E1、E2、E3和EE2的总去除率分别为88.6%、76.3%、64.8%和81.2%。耕作层、土壤层、填料层3个生物单元对EDCs(E1、E2、E3、EE2)去除效果均有提升,其中:对E1去除率分别为16.2%、75.1%、28.2%;对E2去除率分别为14.5%、61.8%、18.7%;对E3去除率分别为20.6%、49.8%、10.4%;对EE2去除率分别为8.9%、43.4%、−8.1%。HD菌对耕作型稻田湿地中微生物群落产生影响,诱导产生的羟基酶有利于降解EDCs,从而提高了EDCs的去除效率。耕作型稻田湿地经HD菌剂强化后,3个生物单元中明显土壤层对EDCs去除贡献相对较大,土壤层微生物种群丰度更大,且土壤层中还分布有广泛的水稻根系,不仅为微生物代谢提供营养物质和氧气,还进一步提高了其生物分解能力。
(3)湿地运行初期,耕作型稻田背景土壤中残留的EDCs含量相对较高,经过5个月的连续运行后,土壤中EDCs含量明显下降,投菌组B中的EDCs残留量要明显低于未投菌组A,B组湿地出水中E1、E2、E3和EE2含量相比A组可分别降低约26.6%、17.1%、30.3%、13.3%。表明HD菌剂能强化耕作型稻田湿地土壤中EDCs的降解。本研究对于村落水环境中的EDCs降解机制及环境生态影响评价有一定的参考价值。
-
表 1 猪粪/玉米秸秆主要成分
Table 1. Main components of pig manure/corn stover
材料Material 含水率/%Water content 总有机碳含量/%Total organic carbon content 总氮含量/%Total nitrogen content C/N Cu含量/(mg·kg−1)Cu content Zn含量/(mg·kg−1)Zn content 猪粪 79.84 9.20 0.59 15.59 254.17 1039.83 玉米秸秆 4.45 15.13 0.36 42.03 ND ND 注:ND表示未检出. ND means not detected. 表 2 实验处理组
Table 2. Experimental treatment groups
编号Serial number 处理组Treatment group CK 猪粪+玉米秸秆 F1 猪粪+玉米秸秆+2.5%腐殖酸 F2 猪粪+玉米秸秆+5.0%腐殖酸 F3 猪粪+玉米秸秆+7.5%腐殖酸 表 3 FTIR特征吸收带归属
Table 3. Assignment of characteristic absorption bands of FTIR
波数/ cm−1 Wavenumber 振动峰 Vibration peak 基团 Group 3408—3450 O—H 碳水化合物、酰胺化合物、蛋白质、水 2850—2922 C—H 碳水化合物、脂肪族化合物的亚甲基 1600—1653 C=O、—COO—、C=C、N—H 羧酸盐、烯烃、酯类、酰胺类、芳香族 1400—1430 C—O、—COO—、—OH、—CH2 木质素、脂肪族化合物、羧酸盐 1105—1160 C—O—C、C—O、C—N 糖类、脂肪族化合物、氨基酸盐 表 4 各处理组的特征参数比值
Table 4. The ratio of characteristic parameters of each treatment group
处理组Treatment group 时间Time A芳香族碳/碳水化合物碳Aromatic carbon / Carbohydrate carbon B芳香族碳/脂肪族碳Aromatic carbon / Aliphatic carbon C芳香族碳/羧酸碳Aromatic carbon / Carboxylic carbon D芳香族碳/多糖碳Aromatic carbon / Polysaccharide carbon 猪粪/玉米秸秆 未发酵 1.035 0.933 0.950 1.031 CK 发酵后 1.037 0.951 0.982 1.064 F1 发酵后 1.046 0.988 1.014 1.065 F2 发酵后 1.049 1.002 1.027 1.085 F3 发酵后 1.144 1.012 1.028 1.136 -
[1] AWASTHI M K, DUAN Y M, AWASTHI S K, et al. Emerging applications of biochar: Improving pig manure composting and attenuation of heavy metal mobility in mature compost [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389: 122116. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122116 [2] 候月卿, 沈玉君, 刘树庆. 我国畜禽粪便重金属污染现状及其钝化措施研究进展 [J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2014, 16(3): 112-118. HOU Y Q, SHEN Y J, LIU S Q. Present status of heavy metal pollution from livestock waste and progress on passivation measures [J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2014, 16(3): 112-118(in Chinese).
[3] LI R, MENG H B, ZHAO L X, et al. Study of the morphological changes of copper and zinc during pig manure composting with addition of biochar and a microbial agent [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 291: 121752. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121752 [4] 贾武霞, 文炯, 许望龙, 等. 我国部分城市畜禽粪便中重金属含量及形态分布 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(4): 764-773. JIA W X, WEN J, XU W L, et al. Content and fractionation of heavy metals in livestock manures in some urban areas of China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(4): 764-773(in Chinese).
[5] . 国家发展改革委和农业部印发《全国农村沼气发展“十三五”规划》[J]. 能源研究与利用, 2017(2): 10. The national development and reform commission and the ministry of agriculture issued the "13th five-year plan for national rural biogas development [J]. Energy Research & Utilization, 2017(2): 10(in Chinese).
[6] 李轶, 宫兴隆, 郭敬阳, 等. 不同预处理玉米秸秆对猪粪厌氧发酵重金属镉钝化效果 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(11): 254-260. LI Y, GONG X L, GUO J Y, et al. Effects of various pretreated maize stovers on the passivation of cadmium by anaerobic fermentation of pig manure [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(11): 254-260(in Chinese).
[7] 卜贵军, 于静, 邸慧慧, 等. 鸡粪堆肥有机物演化对重金属生物有效性影响研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(11): 4352-4358. BU G J, YU J, DI H H, et al. Influence of organic matter evolution during composting on the bioavailability of heavy metals [J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(11): 4352-4358(in Chinese).
[8] 陈琳. Cu、Cd对农业废弃物发酵过程中微生物和酶活性的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2012. CHEN L. Effects of Cu, Cd on microorganisms and enzyme activities during agricultural waste fermentation process[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2012(in Chinese).
[9] 刘春软. 厌氧发酵条件下不同添加剂对猪粪产气特性以及重金属钝化效果研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽大学, 2019. LIU C R. Effects of different additives on gas-producting characteristics and passivation of heavy metals in pig manure during anaerobic fermentation[D]. Hefei: Anhui University, 2019(in Chinese).
[10] 刘艳杰. 钝化剂对猪粪厌氧发酵过程产气特性及重金属钝化效果的研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2017. LIU Y J. Study on gas-generating characteristics and passivation of heavy metals in anaerobic fermentation of pig manure by passivating agent[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2017(in Chinese).
[11] CANELLAS L P, OLIVARES F L, AGUIAR N O, et al. Humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants in horticulture [J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2015, 196: 15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2015.09.013 [12] HE E, LÜ C, HE J, et al. Binding characteristics of Cu2 + to natural humic acid fractions sequentially extracted from the lake sediments [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2016, 23(22): 22667-22677. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7487-2 [13] 李轶, 宫兴隆, 于嘉琪, 等. 硼泥对猪粪厌氧发酵重金属铬及其光谱特性的影响 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(24): 255-261. LI Y, GONG X L, YU J Q, et al. Effects of boron mud on anaerobic fermentation of heavy metal chromium and its spectral characteristics in pig manure [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(24): 255-261(in Chinese).
[14] CHEN X M, ZHAO Y, ZENG C C, et al. Assessment contributions of physicochemical properties and bacterial community to mitigate the bioavailability of heavy metals during composting based on structural equation models [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 289: 121657. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121657 [15] 李轶, 曲壮壮, 巩俊璐, 等. 海泡石对猪粪秸秆厌氧发酵产物中Cd的钝化效果研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(S1): 1-6. LI Y, QU Z Z, GONG J L, et al. Passivation effect of Cd by sepiolite in anaerobic fermentation products with pig manure and straw[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(Sup 1): 1-6(in Chinese).
[16] 巩俊璐. 钝化剂对猪粪/秸秆厌氧发酵中铜和锌减害化的影响研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2018. GONG J L. Effect of passivating agent on the reduction of Cu and Zn in anaerobic fermentation of pig manure/straw[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2018(in Chinese).
[17] 孙向平, 李国学, 肖爱平, 等. 添加不同比例玉米秸秆对猪粪高温堆肥过程中胡敏酸的结构组成及红外光谱特性影响分析 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2014, 34(9): 2413-2418. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)09-2413-06 SUN X P, LI G X, XIAO A P, et al. Analysis on the impact of composting with different proportions of corn stalks and pig manure on humic acid fractions and IR spectral feature [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2014, 34(9): 2413-2418(in Chinese). doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)09-2413-06
[18] WANG X Q, MUHMOOD A, LYU T, et al. Mechanisms of genuine humic acid evolution and its dynamic interaction with methane production in anaerobic digestion processes [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 408: 127322. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127322 [19] 贾黎, 张自立. 腐殖酸对La3+, Nd3+等重金属离子混合体系吸附的研究 [J]. 中国稀土学报, 2009, 27(6): 816-821. JIA L, ZHANG Z L. Adsorption of La3+, Nd3+ and some heavy metal ions by humic acid in A multi-metal-ion system [J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2009, 27(6): 816-821(in Chinese).
[20] 龙良俊. 污泥腐殖酸特性及其改性后对重金属的吸附研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018. LONG L J. Characteristics of humic acid from sewage sludge and adsorption of heavy metals after modification[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018(in Chinese).
[21] 袁飞, 张永霞, 徐恒山, 等. 腐植酸对环境中Cr(Ⅵ)去除机理探究及展望 [J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(2): 653-662. YUAN F, ZHANG Y X, XU H S, et al. Research and perspect on the removal mechanism of humic acid to Cr(Ⅵ) in the environment [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(2): 653-662(in Chinese).
[22] KERNDORFF H, SCHNITZER M. Sorption of metals on humic acid [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(11): 1701-1708. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90221-5 [23] 黄国锋, 张振钿, 钟流举, 等. 重金属在猪粪堆肥过程中的化学变化 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(1): 94-99. HUANG G F, ZHANG Z T, ZHONG L J, et al. Chemical changes of heavy metals in the process of pig manure composting [J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(1): 94-99(in Chinese).
[24] 张雪英, 周顺桂, 周立祥, 等. 堆肥处理对污泥腐殖物质形态及其重金属分配的影响 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2004, 23(1): 30-33. ZHANG X Y, ZHOU S G, ZHOU L X, et al. Component changes of humic substances and heavy metal distribution before and after sewage sludge composting [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2004, 23(1): 30-33(in Chinese).
[25] 曲壮壮, 猪粪厌氧发酵重金属镉/铬的形态转化及产气特性研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2020. QU Z Z, Study on the speciation transformation and gas production characteristics of heavy metals cadmium/chromium in anaerobic fermentation of pig manure[D]. Shenyang : Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020 (in Chinese).
[26] 栾润宇, 高珊, 徐应明, 等. 不同钝化剂对鸡粪堆肥重金属钝化效果及其腐熟度指标的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 469-478. LUAN R Y, GAO S, XU Y M, et al. Effect of different passivating agents on the stabilization of heavy metals in chicken manure compost and its maturity evaluating indexes [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 469-478(in Chinese).
[27] CUI H, OU Y, WANG L X, et al. Critical passivation mechanisms on heavy metals during aerobic composting with different grain-size zeolite [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 406: 124313. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124313 [28] 任秀娜, 王权, 赵军超, 等. 添加钙基膨润土对猪粪堆肥中水溶性有机物光谱特征的影响 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(6): 1856-1862. REN X N, WANG Q, ZHAO J C, et al. The effect of Ca-bentonite on spectra of dissolved organic matter during pig manure composting [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(6): 1856-1862(in Chinese).
[29] 陈静, 黄占斌. 腐植酸在土壤修复中的作用 [J]. 腐植酸, 2014(4): 30-34,65. CHEN J, HUANG Z B. Effect of humic acid on soil restoration [J]. Humic Acid, 2014(4): 30-34,65(in Chinese).
[30] 凌翔. 关于腐殖酸的应用化学研究 [J]. 中外企业家, 2019(8): 131. LING X. Applied chemistry research on humic acid [J]. Chinese & Foreign Entrepreneurs, 2019(8): 131(in Chinese).
[31] 荣宏伟, 王勤, 张朝升, 等. Cu2+、Zn2+对生物脱氮系统的影响 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(4): 617-620. RONG H W, WANG Q, ZHANG C S, et al. Effects of Cu2+ and Zn2+ on the biological nitrogen removal system [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2009, 3(4): 617-620(in Chinese).
[32] 张正哲. 重金属离子对厌氧氨氧化颗粒污泥的影响及其修复策略研究[D]. 杭州: 杭州师范大学, 2016. ZHANG Z Z. Effects of heavy metal ions on anammox granules and strategies for remediation[D]. Hangzhou: Hangzhou Normal University, 2016(in Chinese).
[33] PICCOLO A, SPACCINI R, de MARTINO A, et al. Soil washing with solutions of humic substances from manure compost removes heavy metal contaminants as a function of humic molecular composition [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 225: 150-156. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.019 -






 下载:
下载: