-
邻苯二甲酸酯(Phthalates,PAEs)是重要的工业添加剂之一,主要用作塑料产品制造和加工的增塑剂[1]. PAEs与塑料分子之间没有化学键作用,仅通过范德华力(分子间力)连接在一起,相互作用较弱,因此很容易从塑料制品中泄露进入环境[2]. PAEs危害很大,不仅其生殖毒性类似于雌性激素, 还具有致畸致癌致突变的三致毒性, 可通过呼吸、饮食和皮肤接触进入人体, 危害人体健康[3]. 近年来,随着工业生产的迅速发展和塑料制品的广泛使用,PAEs已成为全球学界最关注的新兴有机污染物之一[4-6].
在我国,PAEs的消费量超过每年87万吨,占聚氯乙烯生产中增塑剂用量的90%[7],预计消费量还会增加[8]. PAEs目前使用较多的主要有14种[9],其中邻苯二甲酸(2-乙基己基)酯(di-(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate,DEHP)是农业土壤和蔬菜中最常检测到的PAEs化合物之一,其浓度在环境介质中高于大多数其他PAEs化合物[10],是我国优先控制的PAEs污染物[11]. 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(dibutylphthalate,DBP)是PAEs化合物中一种重要的增塑剂,在饮用水、地表水、室内外空气粉尘、河底沉积物和土壤中频频检出[12-13]. 蔡全英等[14]分析了我国内地和香港城市污泥中6种优先控制PAEs,其质量浓度为10.465—114.166 mg·kg−1. 张鸿郭等[15]分析了广州填埋场周边土壤中的DEHP、DBP和DEP等优先控制PAEs,其质量浓度为44.25—216.63 mg·kg−1. 由于土壤中的PAEs会通过各种途径流入水中,因此亟需研究一种有效去除水及土壤环境介质中PAEs的方法. 水中PAEs的去除方法包括吸附法[16]、生物降解法[17]、高级氧化法[18]等. Shaida等[19]以低碳高硅酸盐廉价煤为原料,通过壳聚糖的羟基与硅酸盐基团相互连接,制备了富矿物质煤与壳聚糖的复合物,该复合物在pH值为5.8时对邻苯二甲酸二乙酯(diethyl phthalate,DEP)的吸附率达到了91.1%. 魏丽琼等[20]研究了4种植物各自单作和分别间作对土壤中PAEs的降解,结果表明黑麦草和苏丹草对DEHP污染土壤的修复效率分别可以达到53.63%和50.55%. 晏晓旭等[21]使用Fe0在室温条件下活化过硫酸钠(persulfate sodium,PS)产生硫酸根自由基,3.5 h后邻苯二甲酸二甲酯(dimethyl phthalate,DMP)的去除率达到了50%. 其中高级氧化法的处理效率较高,PS是化学氧化修复技术中常用的氧化剂[22],具有较好的水溶性和稳定性,经活化后可分解生成硫酸盐自由基,其氧化能力较强,可以氧化大多数的有机污染物[23]. 活化PS的方式有很多,热活化过硫酸盐氧化技术是一种十分清洁的活化技术,相比于碱活化、金属活化、活性炭活化等方式,热活化不会对环境引入新的化学污染物,并且是在众多活化方式中较容易产生SO4·−的方式. [24].
目前,热活化PS降解去除PAEs的效果和机理尚不明确. 本文通过热活化PS的方式降解去除水中的PAEs,研究了污染物初始浓度、过硫酸钠活化温度及用量、助溶剂的添加量对PAEs降解去除的影响,分析了DBP的降解产物,为PS降解去除环境介质中DBP提供理论和实践依据.
-
主要仪器:高效液相色谱仪(HPLC,型号1260,美国安捷伦)、气相色谱质谱联用仪(GC/MS,型号8890/5977B,美国安捷伦)、涡旋仪(型号SCI-FS,美国赛洛捷克)和水浴锅(型号HWS-26,上海一恒).
试剂:邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(C16H22O4,分析纯,阿拉丁)、邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己基)酯(C24H38O4,分析纯,阿拉丁)、过硫酸钠(Na2S2O8,分析纯,麦克林)、甲醇(CH3OH,色谱纯,赛默飞世尔)、乙腈(C2H3N,色谱纯,赛默飞世尔)、二氯甲烷(CH2Cl2,农残级,上海星可)、无水硫酸钠(Na2SO4,分析纯,麦克林)和氯化钠(NaCl,分析纯,麦克林).
-
以乙腈作为助溶剂,配置一定浓度的DBP和DEHP混合母液备用(因为本实验是为研究场地污染物中PAEs的降解,将PAEs的浓度设置为50—200 mmol·L−1). 取一定量混合母液加超纯水稀释到一定浓度,然后加入一定质量的PS,涡旋振荡均匀后迅速置于不同温度的恒温水浴锅中进行反应. 实验设计如表1所示. 分别间隔一定时间取样,水样用甲醇淬灭后经0.22 μm的有机滤膜过滤,滤液用HPLC分析PAEs浓度.
-
实验中采用HPLC和GC/MS对PAEs及其降解产物进行鉴定分析.
HPLC条件: 色谱柱为Waters Symmetry C18 柱(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm),流动相为甲醇/水-95/5(V∶V),流速为1.0 mL·min−1,检测波长λ=225 nm,进样体积25 μL,柱温为25 ℃.
GC/MS条件:色谱柱为DB-5MS柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm),载气为高纯氦气,气体流速为1 mL·min−1,进样量1 μL,进样口温度280 ℃,不分流模式,炉温控制:以25 ℃·min-1升温至265 ℃,然后以6 ℃·min−1升温至285 ℃,再以10 ℃·min−1升温至320 ℃保持3 min. 离子源温度230 ℃,四极杆温度150 ℃.
DBP的初始浓度为50 mg·L−1,在最佳条件下反应30 min后,将水样倒入分液漏斗中,用少量二氯甲烷润洗样品瓶,并倒入分液漏斗,加入50 g氯化钠,再加入400 mL超纯水和50 mL二氯甲烷进行振荡萃取,静置,收集有机相,重复萃取1次. 调节水样pH<1,再次萃取1次,合并3次萃取液,经无水硫酸钠脱水后,浓缩至1 mL后用GC/MS扫描分析.
-
本研究利用OriginLab 2018进行数据统计分析.
-
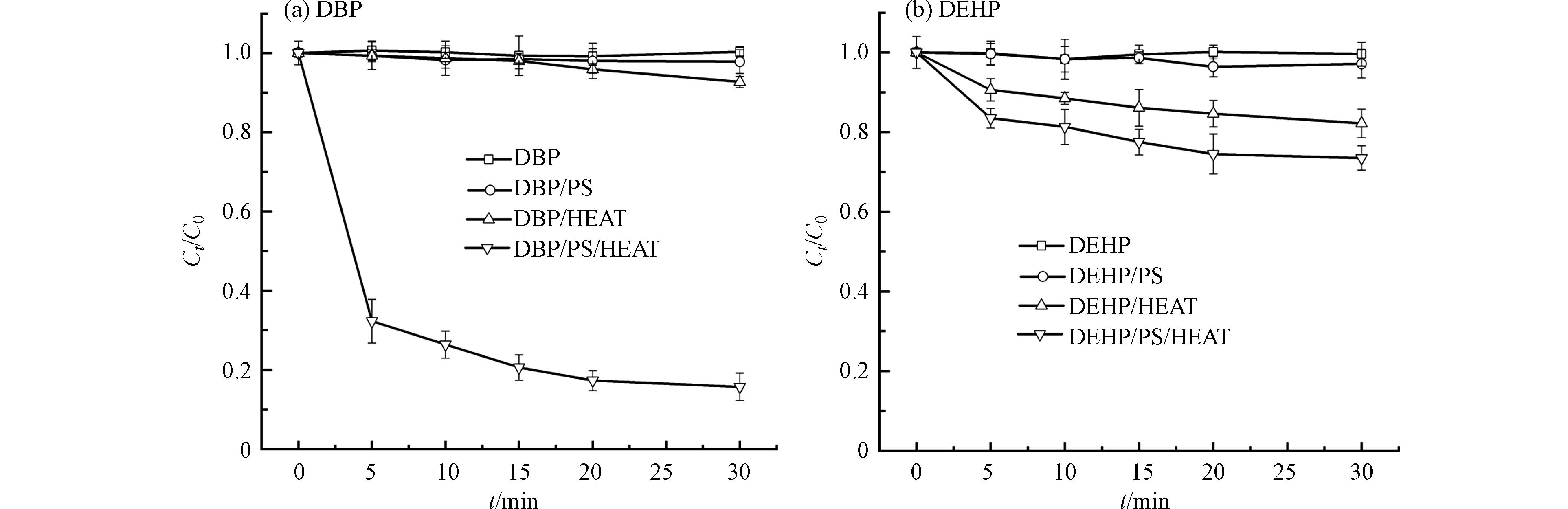
图1显示了不同氧化方式对水中PAEs的去除影响. 结果表明,热活化PS对PAEs的去除效果最佳,其次是单独使用热降解PAEs,而单独使用PS降解PAEs效果很差;热活化PS对DBP的降解效果要好于对DEHP的降解效果. 从图1可以看出,在单独使用PS时,30 min时DBP和DHEP几乎不降解,这是因为PS在常温下十分稳定,反应速率慢,因此在常温下对有机物的降解效果较差[25]. 在单独对PAEs加热时,30 min时DBP降解了7.3%,DEHP降解了17.8%,在只加热时DEHP的降解率高于DBP,是由于DEHP比DBP更难溶于水,所以DEHP在水体温度升高时,更容易从水中释放到大气中[26]. 在热活化PS的条件下,PAEs的降解率迅速增加,DBP在30 min时的降解率达到了84.3%,DEHP的降解率达到了26.5%,降解率相较于只加热时分别增加了10.5、0.5倍. Zhang等[27]的研究结果表明,PS氧化PAEs过程主要归因于SO4·−和·OH的自由基反应. 热活化过硫酸钠对PAEs的降解率迅速增加是由于温度的升高有利于PS发挥氧化降解作用,高温条件下使更多的PS分子中—O—O—键断裂,进而产生大量的SO4·−对PAEs进行降解[28]. 因为在这个体系中存在丰富的SO4·−和·OH,促进了邻苯二甲酸酯降解所必需的电子转移反应[29]. 以DBP为例,由于热活化PS体系的花费为纯热和纯PS的体系的花费相加,纯热和纯PS的体系DBP的降解率相加为9.5%,而热活化PS体系DBP的降解率为84.3%,且在纯热和纯PS的体系下,DBP很难达到热活化所达到的降解率,因此热活化体系更加经济.
-
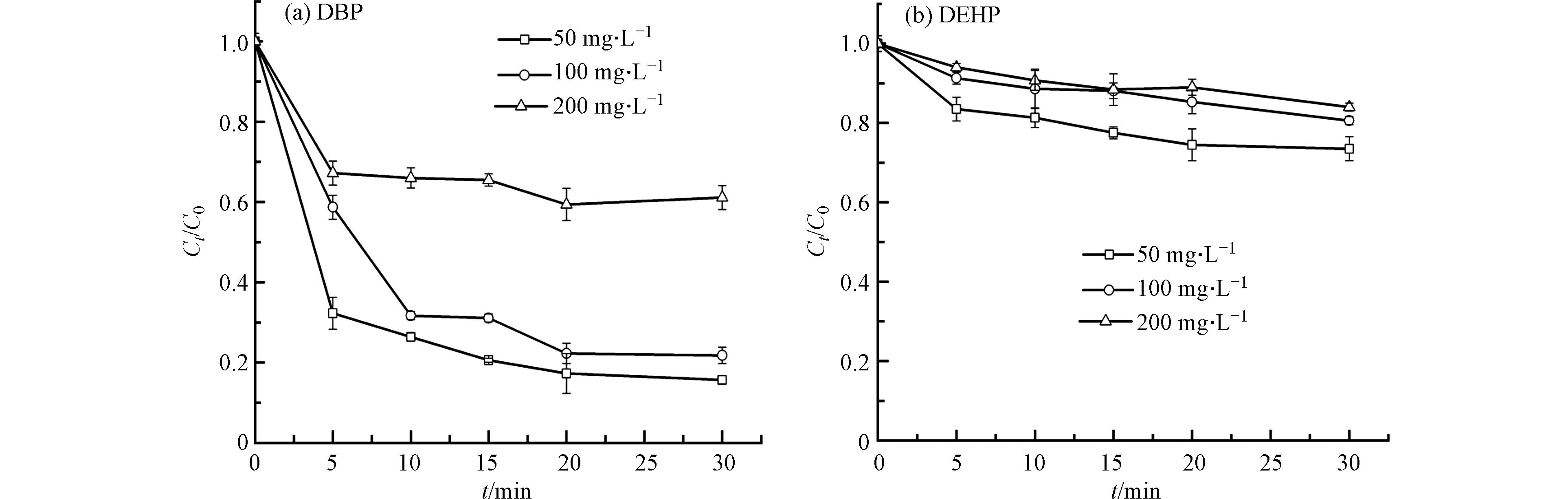
反应物的初始浓度也会影响其降解率,图2是在不同反应物浓度下热活化PS对PAEs的去除情况. 结果表明,反应物的初始浓度越大,其降解率越低. 从图2可以看出,随着PAEs的初始浓度由50 mg·L−1增加到200 mg·L−1,30 min时DBP的降解率由84.3%降至38.9%,DEHP的降解率由26.5%降至18.1%. 随着DBP和DHEP初始浓度的升高,在相同PS添加量时降解率都出现逐渐减小的情况,但是这两种污染物的降解量随初始浓度的增加有大幅度的提升. 这是因为在不改变PS投加量的条件下,SO4·−产生量是一定的,PAEs的初始浓度越高,自由基与PAEs的碰撞几率也越高,所以提高单位体积内有机污染物的量可以增加自由基的利用率,从而提高反应效率[30].
-
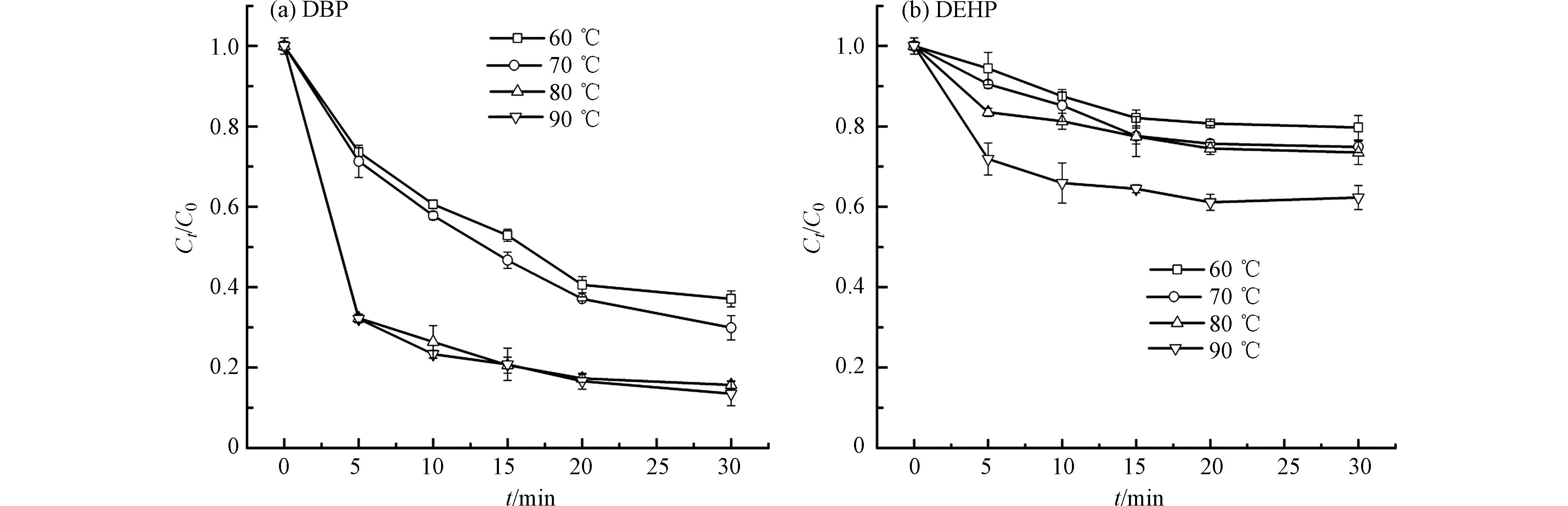
温度是氧化过程中的一个重要参数,因为它影响Ea和污染物的行为[31]. 图3显示了在不同温度下活化PS对PAEs降解情况. 结果表明,适当升高温度可以促进DBP和DEHP的降解. 从图3可以看出,DBP在60 ℃时30 min的降解率已经达到了62.9%,而在90 ℃时DEHP的降解率才达到了27.7%,说明在热活化PS的条件对DBP降解率明显高于DEHP,DBP在60 ℃到70 ℃降解率差距不大,在80 ℃时降解率有了大的飞跃,这时DBP的降解率达到了84.3%,而在高于80 ℃后,温度的增加对DBP去除率的提升已不显著. 与DBP相比,DEHP的降解规律有所不同,从60 ℃升温到90 ℃,DEHP的降解率从20.3%提高到37.7%,降解率的提高量低于DBP,从60 ℃升温到80 ℃时,DEHP的降解率提升不太明显,而从80 ℃上升到90 ℃,其降解率的提升有一个小的飞跃. DBP和DEHP的降解率都随着温度的升高,这说明,升高温度有利于S2O82-吸收更多的能量,从而生成更多的SO4·−,提高PAEs的降解率[32-33]. 随着温度的升高,水分子能量的增加被认为会促进反应的进行,因为液体向气体的转化会增加[34]. 从图中可以得知在兼顾DBP 去除率和经济效益的角度综合分析,其降解的最佳温度为80 ℃. 这可能是因为当温度较低时,温度能够提供足够的催化位点来激活PS产生自由基,当温度进一步增加时,PS的用量限制了催化氧化. 而DEHP所需要的温度更高可能是因为DEHP的分子量较大,水溶性较差,只有产生较多的自由基时才能更好的与DEHP接触促使其降解.
-
PS的初始投加量对污染物的降解也有着很大的影响. 从图4可以看出,随着PS浓度增加,PAEs的去除率也随之增加,当PS的浓度从42 mmol·L−1增加到210 mmol·L−1时,DBP的降解率从80.2%增加到89.8%,DEHP的降解率从22.3%增加到48.5%,这与Hung[35]与Xie[36]的研究结果一致,热活化PS处理污染物的降解率与PS的初始投加量呈正比关系. 当PS的浓度增加了4倍,DBP的降解率只提升了不到10%,而相同PS浓度的增加,DEHP的降解率比DBP降解率的增幅更大,这可能是因为PS也会与产生的SO4·−和·OH进行反应,从而减弱了自由基的利用效率,导致PS浓度较大时,PAEs的降解效率明显减慢. 结果表明,在热活化的条件下,增加PS的量会增加SO4·−和·OH的生成,且更容易与PAEs接触发生反应,从而提高了PAEs的降解率. 但是在实际应用时考虑到成本选择PS的浓度为42 mmol·L−1时就能达到降解目的,加入过多的PS并没有起到相应的效果.
-
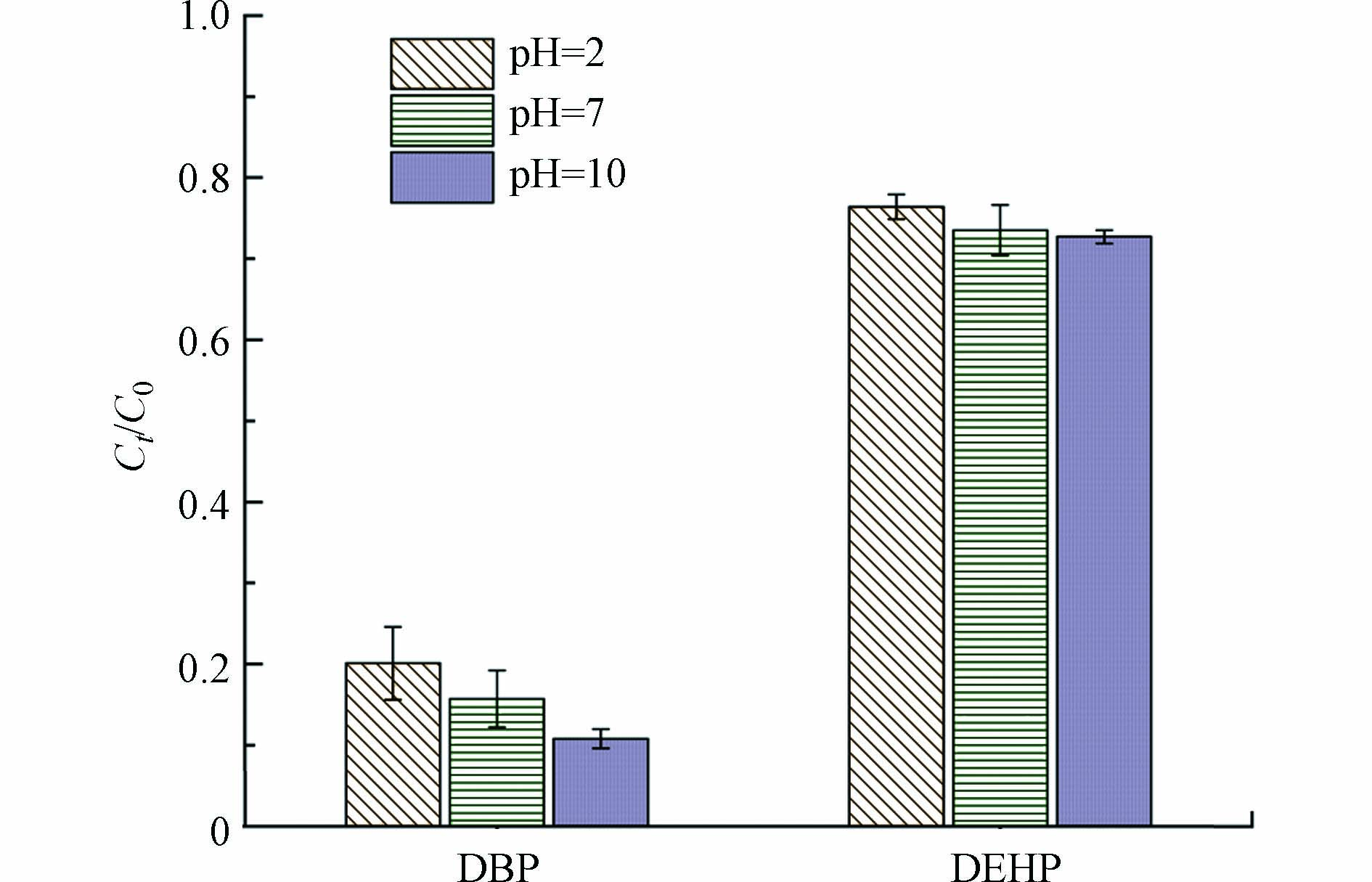
pH对水中污染物的降解也有很大的影响. 图5是在不同pH下热活化下30 min时PS对PAEs的去除情况. 结果表明,当污染物溶液的pH越大,DBP和DEHP的降解率越高. 从图5可以看出,DBP和DEHP在碱性(pH=10)的条件下,30 min时的降解率最高,此时DBP的降解率达到了89.2%,DEHP的降解率达到了27.3%. 在酸性(pH=2)条件下的降解率最低,此时DBP和DEHP的降解率分别为79.9%和23.6%. 这与吴楠等[37]的研究结果一致,碱热活化过硫酸钠对有机物的降解效果优于单一碱活化或热活化方式. 由Zhang等[27]的研究结果表明,在 pH = 2时,SO4·−是氧化PAEs的主要物种,当pH = 7时,SO4·−和·OH时氧化PAEs的主要物种,且·OH占主导地位,因此PAEs在中性时降解效果优于酸性可能是因为·OH对PAEs的降解效果更好.
-
上述结果表明即使在最优条件下,DBP降解到一定程度就基本不再降解,而DEHP在PS浓度为210 mmol·L−1时才降解了不到50%. 推测PAEs的溶解性较差,一部分PAEs无法和SO4·−进行接触而导致. 因此研究了助溶剂在热活化PS降解PAEs体系中的影响,图6显示了在不同助溶剂添加量时PAEs的降解情况. 从图6(a)可以看出,随着助溶剂添加量的增加,PAEs的降解率随之增加. 当助溶剂的添加量从5%增加到10%、20%和30%时,30 min时DBP的降解率分别达到了83.8%、99.2%和100%. 从图6(b)可以看出,在助溶剂的添加量增加到10%、20%时,DEHP的降解率分别是助溶剂添加量为5%的1.55、2.97倍;在添加量为30%时,DEHP的降解率达到了92.8%. 从图中可以明显看出,助溶剂的添加对DEHP降解率的影响更大. Wang等[38]利用UV/PS体系对DBP进行降解,在最佳条件下,DBP的降解率在20 min达到了94.7%. 而本研究在添加30%助溶剂时可以让DBP在20 min时降解99.2%,在30 min时全部降解. 图6表明,DBP和DEHP的降解率和助溶剂的添加量呈正相关关系,助溶剂的添加量对PAEs的降解起着决定性的影响,进一步说明PAEs的溶解度对其降解有着明显的影响. 低分子量PAEs(DBP)的脱除效率高于高分子量PAEs(DEHP),这是由于其水溶性较高,使得DBP更容易释放到存在丰富·OH的可溶性相,并在热活化PS条件下进行降解,这一结果与Hung等[39]一致. 由于DEHP的水溶性更差,且与水接触少,大量的DEHP无法与水相中的自由基接触,导致自由基无法降解DEHP,再加入助溶剂后,DEHP会存在于两相中,进一步与自由基进行接触,所以导致DEHP的进一步降解,而DBP本身水溶性大于DEHP的水溶液,与水接触多,因此在同样的PS浓度下,DBP能够接触到更多的自由基,从而有着更高的降解率. 因此,低分子量PAEs的降解比高分子量PAEs的降解更彻底.
-
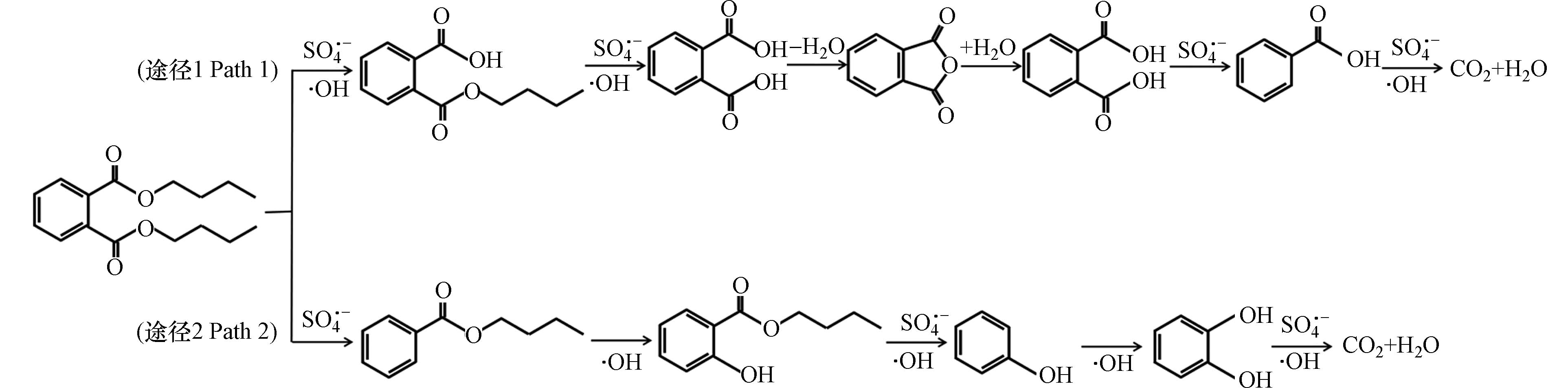
为了探索热活化PS氧化降解PAEs的过程,以DBP为例,采用GC-MS对溶液进行全扫描分析,在检测中检测到了苯酚、甲酸丁酯一些开链化合物以及大量的邻苯二甲酸酐、邻苯二甲酸等物质. 推测DBP的链结构首先受到硫酸根自由基和羟基自由基的攻击,DBP主要一部分被分解成了邻苯二甲酸丁酯,进而在·OH的加成反应下生成了邻苯二甲酸,又由于反应过程中快速脱水形成了邻苯二酸酐,这导致邻苯二酸酐大量积累[40]. 邻苯二甲酸在硫酸根自由基攻击下进而生成苯甲酸,最后苯环被打开氧化生成CO2和H2O(途径1). 另一部分DBP在受到硫酸根自由基和羟基自由基的攻击后,DBP被分解为苯甲酸丁酯,然后在羟基自由基加成反应下生成了2 -羟基苯甲酸丁酯,酯链在硫酸根自由基和羟基自由基的作用下不断发生裂解和氢化加成反应,生成苯酚和邻二苯酚等物质[41],最后苯环被打开氧化生成CO2和H2O(途径2)(图7).
-
(1)热活化过硫酸钠能有效的去除水中的邻苯二甲酸酯,在80℃,过硫酸钠浓度为84 mmol·L−1,助溶剂的添加量为30%时,DBP的去除率达到了100%,DEHP的去除率达到了92.8%.
(2)适度升高温度和PS浓度有利于提高PAEs的去除率;PAEs的初始浓度与去除率呈反比;pH与PAEs的去除率呈正比;提高PAEs溶解度可以明显提高PAEs的去除率;热活化过硫酸钠对溶解度较好的邻苯二甲酸酯去除率更高.
(3)通过GC/MS对降解产物的分析,推测了DBP的降解途径. 结果表明邻苯二甲酸和邻苯二甲酸酐时DBP降解的主要产物,脱烷基化和羟基化是DBP降解的主要机理.
热活化过硫酸钠氧化去除水中邻苯二甲酸酯
Removal of phthalates from water by thermally activated sodium persulfate oxidation
-
摘要: 邻苯二甲酸酯(PAEs)主要用作塑料产品制造和加工的增塑剂,是全球关注的新兴污染物之一. 本研究以邻苯二甲酸(2-乙基己基)酯(DEHP)和邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBP)为目标污染物,研究了在不同污染物初始浓度、过硫酸钠活化温度及浓度、助溶剂添加量对过硫酸钠氧化去除水中邻苯二甲酸酯的影响及机理. 结果表明,在实验条件下,邻苯二甲酸酯初始浓度与去除率呈反比,反应温度、过硫酸钠浓度和pH与邻苯二甲酸酯的去除率呈正比. 在80 ℃,过硫酸钠浓度为84 mmol·L-1,助溶剂的添加量为30%时,DBP的降解率达到了100%,DEHP的降解率达到了92.8%. GC/MS分析表明,在高温活化过硫酸钠的条件下,邻苯二甲酸和邻苯二甲酸酐是DBP降解的主要产物,脱烷基化和羟基化是DBP降解的主要机理. 本研究为过硫酸钠去除环境介质中的邻苯二甲酸酯提供了理论和实践依据.Abstract: Phthalates (PAEs) are mainly used as plasticizers in the manufacture and processing of plastic products. They are one of the emerging pollutants of global concern. Taking di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) and dibutyl phthalate (DBP) as target pollutants, the effects and mechanism of different initial concentrations of pollutants, activation temperature and concentration of persulfate sodium and the amount of cosolvent on the oxidative removal of phthalates in water were studied. The results showed that under the experimental conditions, the initial concentration of phthalate is inversely proportional to the removal rate, and the reaction temperature, sodium persulfate concentration and pH are directly proportional to the removal rate of phthalate. When the concentration of sodium persulfate was 84 mmol·L-1 at 80 ℃ and the amount of cosolvent was 30%, the degradation rate of DBP and DEHP reached 100% and 92.8%. GC/MS analysis showed that under the condition of high temperature activation of persulfate sodium, phthalic acid and phthalic anhydride were the main products of DBP degradation, and dealkylation and hydroxylation were the main mechanisms of DBP degradation. This study provides a theoretical and practical basis for the removal of phthalates from environmental media by persulfate sodium.
-
Key words:
- phthalate ester /
- persulfate sodium /
- thermal activation /
- degradation products.
-
邻苯二甲酸酯(Phthalates,PAEs)是重要的工业添加剂之一,主要用作塑料产品制造和加工的增塑剂[1]. PAEs与塑料分子之间没有化学键作用,仅通过范德华力(分子间力)连接在一起,相互作用较弱,因此很容易从塑料制品中泄露进入环境[2]. PAEs危害很大,不仅其生殖毒性类似于雌性激素, 还具有致畸致癌致突变的三致毒性, 可通过呼吸、饮食和皮肤接触进入人体, 危害人体健康[3]. 近年来,随着工业生产的迅速发展和塑料制品的广泛使用,PAEs已成为全球学界最关注的新兴有机污染物之一[4-6].
在我国,PAEs的消费量超过每年87万吨,占聚氯乙烯生产中增塑剂用量的90%[7],预计消费量还会增加[8]. PAEs目前使用较多的主要有14种[9],其中邻苯二甲酸(2-乙基己基)酯(di-(2-ethylhexyl)-phthalate,DEHP)是农业土壤和蔬菜中最常检测到的PAEs化合物之一,其浓度在环境介质中高于大多数其他PAEs化合物[10],是我国优先控制的PAEs污染物[11]. 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(dibutylphthalate,DBP)是PAEs化合物中一种重要的增塑剂,在饮用水、地表水、室内外空气粉尘、河底沉积物和土壤中频频检出[12-13]. 蔡全英等[14]分析了我国内地和香港城市污泥中6种优先控制PAEs,其质量浓度为10.465—114.166 mg·kg−1. 张鸿郭等[15]分析了广州填埋场周边土壤中的DEHP、DBP和DEP等优先控制PAEs,其质量浓度为44.25—216.63 mg·kg−1. 由于土壤中的PAEs会通过各种途径流入水中,因此亟需研究一种有效去除水及土壤环境介质中PAEs的方法. 水中PAEs的去除方法包括吸附法[16]、生物降解法[17]、高级氧化法[18]等. Shaida等[19]以低碳高硅酸盐廉价煤为原料,通过壳聚糖的羟基与硅酸盐基团相互连接,制备了富矿物质煤与壳聚糖的复合物,该复合物在pH值为5.8时对邻苯二甲酸二乙酯(diethyl phthalate,DEP)的吸附率达到了91.1%. 魏丽琼等[20]研究了4种植物各自单作和分别间作对土壤中PAEs的降解,结果表明黑麦草和苏丹草对DEHP污染土壤的修复效率分别可以达到53.63%和50.55%. 晏晓旭等[21]使用Fe0在室温条件下活化过硫酸钠(persulfate sodium,PS)产生硫酸根自由基,3.5 h后邻苯二甲酸二甲酯(dimethyl phthalate,DMP)的去除率达到了50%. 其中高级氧化法的处理效率较高,PS是化学氧化修复技术中常用的氧化剂[22],具有较好的水溶性和稳定性,经活化后可分解生成硫酸盐自由基,其氧化能力较强,可以氧化大多数的有机污染物[23]. 活化PS的方式有很多,热活化过硫酸盐氧化技术是一种十分清洁的活化技术,相比于碱活化、金属活化、活性炭活化等方式,热活化不会对环境引入新的化学污染物,并且是在众多活化方式中较容易产生SO4·−的方式. [24].
目前,热活化PS降解去除PAEs的效果和机理尚不明确. 本文通过热活化PS的方式降解去除水中的PAEs,研究了污染物初始浓度、过硫酸钠活化温度及用量、助溶剂的添加量对PAEs降解去除的影响,分析了DBP的降解产物,为PS降解去除环境介质中DBP提供理论和实践依据.
1. 材料及方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 主要仪器与试剂
主要仪器:高效液相色谱仪(HPLC,型号1260,美国安捷伦)、气相色谱质谱联用仪(GC/MS,型号8890/5977B,美国安捷伦)、涡旋仪(型号SCI-FS,美国赛洛捷克)和水浴锅(型号HWS-26,上海一恒).
试剂:邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(C16H22O4,分析纯,阿拉丁)、邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己基)酯(C24H38O4,分析纯,阿拉丁)、过硫酸钠(Na2S2O8,分析纯,麦克林)、甲醇(CH3OH,色谱纯,赛默飞世尔)、乙腈(C2H3N,色谱纯,赛默飞世尔)、二氯甲烷(CH2Cl2,农残级,上海星可)、无水硫酸钠(Na2SO4,分析纯,麦克林)和氯化钠(NaCl,分析纯,麦克林).
1.2 实验方法
以乙腈作为助溶剂,配置一定浓度的DBP和DEHP混合母液备用(因为本实验是为研究场地污染物中PAEs的降解,将PAEs的浓度设置为50—200 mmol·L−1). 取一定量混合母液加超纯水稀释到一定浓度,然后加入一定质量的PS,涡旋振荡均匀后迅速置于不同温度的恒温水浴锅中进行反应. 实验设计如表1所示. 分别间隔一定时间取样,水样用甲醇淬灭后经0.22 μm的有机滤膜过滤,滤液用HPLC分析PAEs浓度.
表 1 PAEs降解的因素实验设计Table 1. Experimental design of factors affecting the degradation of PAEs序号Serial number 实验设计Experimental design 污染物初始浓度/(mmol·L−1)Initial concentration of pollutants PS浓度/(mmol·L−1) PS concentration 温度/℃Temperature pH 助溶剂添加量/%Cosolvent addition 备注Remarks 1 氧化方式 50 — 25 7 5 空白 50 — 80 7 5 只加热,不加PS 50 84 25 7 5 添加未活化的PS 50 84 80 7 5 水浴活化PS 2 污染物初始浓度 50 84 80 7 5 — 100 84 80 7 5 — 200 84 80 7 5 — 3 活化温度 50 84 60 7 5 — 50 84 70 7 5 — 50 84 80 7 5 — 50 84 90 7 5 — 4 PS浓度 50 42 80 7 5 — 50 84 80 7 5 — 50 126 80 7 5 — 50 168 80 7 5 — 50 210 80 7 5 — 5 pH 50 84 80 2 5 — 50 84 80 7 5 — 50 84 80 10 5 — 6 助溶剂添加量 50 84 80 7 5 — 50 84 80 7 10 — 50 84 80 7 20 — 50 84 80 7 30 — 1.3 分析方法
实验中采用HPLC和GC/MS对PAEs及其降解产物进行鉴定分析.
HPLC条件: 色谱柱为Waters Symmetry C18 柱(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm),流动相为甲醇/水-95/5(V∶V),流速为1.0 mL·min−1,检测波长λ=225 nm,进样体积25 μL,柱温为25 ℃.
GC/MS条件:色谱柱为DB-5MS柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm),载气为高纯氦气,气体流速为1 mL·min−1,进样量1 μL,进样口温度280 ℃,不分流模式,炉温控制:以25 ℃·min-1升温至265 ℃,然后以6 ℃·min−1升温至285 ℃,再以10 ℃·min−1升温至320 ℃保持3 min. 离子源温度230 ℃,四极杆温度150 ℃.
DBP的初始浓度为50 mg·L−1,在最佳条件下反应30 min后,将水样倒入分液漏斗中,用少量二氯甲烷润洗样品瓶,并倒入分液漏斗,加入50 g氯化钠,再加入400 mL超纯水和50 mL二氯甲烷进行振荡萃取,静置,收集有机相,重复萃取1次. 调节水样pH<1,再次萃取1次,合并3次萃取液,经无水硫酸钠脱水后,浓缩至1 mL后用GC/MS扫描分析.
1.4 数据统计
本研究利用OriginLab 2018进行数据统计分析.
2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 热活化PS对PAEs的氧化动力学
图1显示了不同氧化方式对水中PAEs的去除影响. 结果表明,热活化PS对PAEs的去除效果最佳,其次是单独使用热降解PAEs,而单独使用PS降解PAEs效果很差;热活化PS对DBP的降解效果要好于对DEHP的降解效果. 从图1可以看出,在单独使用PS时,30 min时DBP和DHEP几乎不降解,这是因为PS在常温下十分稳定,反应速率慢,因此在常温下对有机物的降解效果较差[25]. 在单独对PAEs加热时,30 min时DBP降解了7.3%,DEHP降解了17.8%,在只加热时DEHP的降解率高于DBP,是由于DEHP比DBP更难溶于水,所以DEHP在水体温度升高时,更容易从水中释放到大气中[26]. 在热活化PS的条件下,PAEs的降解率迅速增加,DBP在30 min时的降解率达到了84.3%,DEHP的降解率达到了26.5%,降解率相较于只加热时分别增加了10.5、0.5倍. Zhang等[27]的研究结果表明,PS氧化PAEs过程主要归因于SO4·−和·OH的自由基反应. 热活化过硫酸钠对PAEs的降解率迅速增加是由于温度的升高有利于PS发挥氧化降解作用,高温条件下使更多的PS分子中—O—O—键断裂,进而产生大量的SO4·−对PAEs进行降解[28]. 因为在这个体系中存在丰富的SO4·−和·OH,促进了邻苯二甲酸酯降解所必需的电子转移反应[29]. 以DBP为例,由于热活化PS体系的花费为纯热和纯PS的体系的花费相加,纯热和纯PS的体系DBP的降解率相加为9.5%,而热活化PS体系DBP的降解率为84.3%,且在纯热和纯PS的体系下,DBP很难达到热活化所达到的降解率,因此热活化体系更加经济.
2.2 反应物初始浓度对PAEs降解的影响
反应物的初始浓度也会影响其降解率,图2是在不同反应物浓度下热活化PS对PAEs的去除情况. 结果表明,反应物的初始浓度越大,其降解率越低. 从图2可以看出,随着PAEs的初始浓度由50 mg·L−1增加到200 mg·L−1,30 min时DBP的降解率由84.3%降至38.9%,DEHP的降解率由26.5%降至18.1%. 随着DBP和DHEP初始浓度的升高,在相同PS添加量时降解率都出现逐渐减小的情况,但是这两种污染物的降解量随初始浓度的增加有大幅度的提升. 这是因为在不改变PS投加量的条件下,SO4·−产生量是一定的,PAEs的初始浓度越高,自由基与PAEs的碰撞几率也越高,所以提高单位体积内有机污染物的量可以增加自由基的利用率,从而提高反应效率[30].
2.3 温度对PAEs降解的影响
温度是氧化过程中的一个重要参数,因为它影响Ea和污染物的行为[31]. 图3显示了在不同温度下活化PS对PAEs降解情况. 结果表明,适当升高温度可以促进DBP和DEHP的降解. 从图3可以看出,DBP在60 ℃时30 min的降解率已经达到了62.9%,而在90 ℃时DEHP的降解率才达到了27.7%,说明在热活化PS的条件对DBP降解率明显高于DEHP,DBP在60 ℃到70 ℃降解率差距不大,在80 ℃时降解率有了大的飞跃,这时DBP的降解率达到了84.3%,而在高于80 ℃后,温度的增加对DBP去除率的提升已不显著. 与DBP相比,DEHP的降解规律有所不同,从60 ℃升温到90 ℃,DEHP的降解率从20.3%提高到37.7%,降解率的提高量低于DBP,从60 ℃升温到80 ℃时,DEHP的降解率提升不太明显,而从80 ℃上升到90 ℃,其降解率的提升有一个小的飞跃. DBP和DEHP的降解率都随着温度的升高,这说明,升高温度有利于S2O82-吸收更多的能量,从而生成更多的SO4·−,提高PAEs的降解率[32-33]. 随着温度的升高,水分子能量的增加被认为会促进反应的进行,因为液体向气体的转化会增加[34]. 从图中可以得知在兼顾DBP 去除率和经济效益的角度综合分析,其降解的最佳温度为80 ℃. 这可能是因为当温度较低时,温度能够提供足够的催化位点来激活PS产生自由基,当温度进一步增加时,PS的用量限制了催化氧化. 而DEHP所需要的温度更高可能是因为DEHP的分子量较大,水溶性较差,只有产生较多的自由基时才能更好的与DEHP接触促使其降解.
2.4 PS浓度对PAEs降解的影响
PS的初始投加量对污染物的降解也有着很大的影响. 从图4可以看出,随着PS浓度增加,PAEs的去除率也随之增加,当PS的浓度从42 mmol·L−1增加到210 mmol·L−1时,DBP的降解率从80.2%增加到89.8%,DEHP的降解率从22.3%增加到48.5%,这与Hung[35]与Xie[36]的研究结果一致,热活化PS处理污染物的降解率与PS的初始投加量呈正比关系. 当PS的浓度增加了4倍,DBP的降解率只提升了不到10%,而相同PS浓度的增加,DEHP的降解率比DBP降解率的增幅更大,这可能是因为PS也会与产生的SO4·−和·OH进行反应,从而减弱了自由基的利用效率,导致PS浓度较大时,PAEs的降解效率明显减慢. 结果表明,在热活化的条件下,增加PS的量会增加SO4·−和·OH的生成,且更容易与PAEs接触发生反应,从而提高了PAEs的降解率. 但是在实际应用时考虑到成本选择PS的浓度为42 mmol·L−1时就能达到降解目的,加入过多的PS并没有起到相应的效果.
2.5 pH对PAEs降解的影响
pH对水中污染物的降解也有很大的影响. 图5是在不同pH下热活化下30 min时PS对PAEs的去除情况. 结果表明,当污染物溶液的pH越大,DBP和DEHP的降解率越高. 从图5可以看出,DBP和DEHP在碱性(pH=10)的条件下,30 min时的降解率最高,此时DBP的降解率达到了89.2%,DEHP的降解率达到了27.3%. 在酸性(pH=2)条件下的降解率最低,此时DBP和DEHP的降解率分别为79.9%和23.6%. 这与吴楠等[37]的研究结果一致,碱热活化过硫酸钠对有机物的降解效果优于单一碱活化或热活化方式. 由Zhang等[27]的研究结果表明,在 pH = 2时,SO4·−是氧化PAEs的主要物种,当pH = 7时,SO4·−和·OH时氧化PAEs的主要物种,且·OH占主导地位,因此PAEs在中性时降解效果优于酸性可能是因为·OH对PAEs的降解效果更好.
2.6 不同助溶剂添加量对PAEs降解的影响
上述结果表明即使在最优条件下,DBP降解到一定程度就基本不再降解,而DEHP在PS浓度为210 mmol·L−1时才降解了不到50%. 推测PAEs的溶解性较差,一部分PAEs无法和SO4·−进行接触而导致. 因此研究了助溶剂在热活化PS降解PAEs体系中的影响,图6显示了在不同助溶剂添加量时PAEs的降解情况. 从图6(a)可以看出,随着助溶剂添加量的增加,PAEs的降解率随之增加. 当助溶剂的添加量从5%增加到10%、20%和30%时,30 min时DBP的降解率分别达到了83.8%、99.2%和100%. 从图6(b)可以看出,在助溶剂的添加量增加到10%、20%时,DEHP的降解率分别是助溶剂添加量为5%的1.55、2.97倍;在添加量为30%时,DEHP的降解率达到了92.8%. 从图中可以明显看出,助溶剂的添加对DEHP降解率的影响更大. Wang等[38]利用UV/PS体系对DBP进行降解,在最佳条件下,DBP的降解率在20 min达到了94.7%. 而本研究在添加30%助溶剂时可以让DBP在20 min时降解99.2%,在30 min时全部降解. 图6表明,DBP和DEHP的降解率和助溶剂的添加量呈正相关关系,助溶剂的添加量对PAEs的降解起着决定性的影响,进一步说明PAEs的溶解度对其降解有着明显的影响. 低分子量PAEs(DBP)的脱除效率高于高分子量PAEs(DEHP),这是由于其水溶性较高,使得DBP更容易释放到存在丰富·OH的可溶性相,并在热活化PS条件下进行降解,这一结果与Hung等[39]一致. 由于DEHP的水溶性更差,且与水接触少,大量的DEHP无法与水相中的自由基接触,导致自由基无法降解DEHP,再加入助溶剂后,DEHP会存在于两相中,进一步与自由基进行接触,所以导致DEHP的进一步降解,而DBP本身水溶性大于DEHP的水溶液,与水接触多,因此在同样的PS浓度下,DBP能够接触到更多的自由基,从而有着更高的降解率. 因此,低分子量PAEs的降解比高分子量PAEs的降解更彻底.
2.7 热活化PS降解PAEs的产物分析
为了探索热活化PS氧化降解PAEs的过程,以DBP为例,采用GC-MS对溶液进行全扫描分析,在检测中检测到了苯酚、甲酸丁酯一些开链化合物以及大量的邻苯二甲酸酐、邻苯二甲酸等物质. 推测DBP的链结构首先受到硫酸根自由基和羟基自由基的攻击,DBP主要一部分被分解成了邻苯二甲酸丁酯,进而在·OH的加成反应下生成了邻苯二甲酸,又由于反应过程中快速脱水形成了邻苯二酸酐,这导致邻苯二酸酐大量积累[40]. 邻苯二甲酸在硫酸根自由基攻击下进而生成苯甲酸,最后苯环被打开氧化生成CO2和H2O(途径1). 另一部分DBP在受到硫酸根自由基和羟基自由基的攻击后,DBP被分解为苯甲酸丁酯,然后在羟基自由基加成反应下生成了2 -羟基苯甲酸丁酯,酯链在硫酸根自由基和羟基自由基的作用下不断发生裂解和氢化加成反应,生成苯酚和邻二苯酚等物质[41],最后苯环被打开氧化生成CO2和H2O(途径2)(图7).
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)热活化过硫酸钠能有效的去除水中的邻苯二甲酸酯,在80℃,过硫酸钠浓度为84 mmol·L−1,助溶剂的添加量为30%时,DBP的去除率达到了100%,DEHP的去除率达到了92.8%.
(2)适度升高温度和PS浓度有利于提高PAEs的去除率;PAEs的初始浓度与去除率呈反比;pH与PAEs的去除率呈正比;提高PAEs溶解度可以明显提高PAEs的去除率;热活化过硫酸钠对溶解度较好的邻苯二甲酸酯去除率更高.
(3)通过GC/MS对降解产物的分析,推测了DBP的降解途径. 结果表明邻苯二甲酸和邻苯二甲酸酐时DBP降解的主要产物,脱烷基化和羟基化是DBP降解的主要机理.
-
表 1 PAEs降解的因素实验设计
Table 1. Experimental design of factors affecting the degradation of PAEs
序号Serial number 实验设计Experimental design 污染物初始浓度/(mmol·L−1)Initial concentration of pollutants PS浓度/(mmol·L−1) PS concentration 温度/℃Temperature pH 助溶剂添加量/%Cosolvent addition 备注Remarks 1 氧化方式 50 — 25 7 5 空白 50 — 80 7 5 只加热,不加PS 50 84 25 7 5 添加未活化的PS 50 84 80 7 5 水浴活化PS 2 污染物初始浓度 50 84 80 7 5 — 100 84 80 7 5 — 200 84 80 7 5 — 3 活化温度 50 84 60 7 5 — 50 84 70 7 5 — 50 84 80 7 5 — 50 84 90 7 5 — 4 PS浓度 50 42 80 7 5 — 50 84 80 7 5 — 50 126 80 7 5 — 50 168 80 7 5 — 50 210 80 7 5 — 5 pH 50 84 80 2 5 — 50 84 80 7 5 — 50 84 80 10 5 — 6 助溶剂添加量 50 84 80 7 5 — 50 84 80 7 10 — 50 84 80 7 20 — 50 84 80 7 30 — -
[1] 张悦, 袁骐, 蒋玫, 等. 邻苯二甲酸酯类毒性及检测方法研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(5): 1035-1046. doi: 10.1002/etc.4409 ZHANG Y, YUAN Q, JIANG M, et al. Research progress in toxicity and detection methods of phthalic acid esters [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(5): 1035-1046(in Chinese). doi: 10.1002/etc.4409
[2] 吴艳华, 周东美, 高娟, 等. 三种邻苯二甲酸酯在不同黏土矿物上的吸附 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(6): 1107-1114. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.06.013 WU Y H, ZHOU D M, GAO J, et al. Adsorption of three phthalic acid esters on different clay minerals [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(6): 1107-1114(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.06.013
[3] 廖健, 邓超, 陈怡, 等. 西湖景区土壤中邻苯二甲酸酯污染水平、来源分析和空间分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(7): 3378-3387. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201812207 LIAO J, DENG C, CHEN Y, et al. Pollution levels, sources, and spatial distribution of phthalate esters in soils of the west lake scenic area [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(7): 3378-3387(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201812207
[4] WANG J, LUO Y M, TENG Y, et al. Soil contamination by phthalate esters in Chinese intensive vegetable production systems with different modes of use of plastic film [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 180: 265-273. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.05.036 [5] WANG G Y, WANG J, ZHU L S, et al. Oxidative damage and genetic toxicity induced by DBP in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2018, 74(4): 527-538. doi: 10.1007/s00244-017-0451-4 [6] RAMZI A, GIREESHKUMAR T R, RAHMAN K H, et al. Distribution and contamination status of phthalic acid esters in the sediments of a tropical monsoonal estuary, Cochin - India [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 210: 232-238. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.182 [7] HE L Z, GIELEN G, BOLAN N S, et al. Contamination and remediation of phthalic acid esters in agricultural soils in China: A review [J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2015, 35(2): 519-534. doi: 10.1007/s13593-014-0270-1 [8] 王昱文, 柴淼, 曾甯, 等. 典型废旧塑料处置地土壤中邻苯二甲酸酯污染特征及健康风险 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(2): 364-372. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.02.2015072005 WANG Y W, CHAI M, ZENG N, et al. Contamination and health risk of phthalate esters in soils from a typical waste plastic recycling area [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(2): 364-372(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.02.2015072005
[9] 李彬, 吴山, 梁金明, 等. 珠江三角洲典型区域农产品中邻苯二甲酸酯(PAEs)污染分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(1): 317-324. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.01.041 LI B, WU S, LIANG J M, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of phthalic acid esters in agricultural products around the Pearl River Delta, South China [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(1): 317-324(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.01.041
[10] 梁浩花, 王亚娟, 陶红, 等. 银川市东郊设施蔬菜基地土壤中邻苯二甲酸酯污染特征及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(9): 3703-3713. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0215 LIANG H H, WANG Y J, TAO H, et al. Pollution characteristics of phthalate esters(PAEs) in soils of facility vegetable bases and health risk assessment in eastern suburb of Yinchuan [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(9): 3703-3713(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0215
[11] 黄文斌, 邱丽琪, 任方煜, 等. 过渡金属催化CO2氢化反应研究进展 [J]. 有机化学, 2021, 41(10): 3914-3934. doi: 10.6023/cjoc202105052 HUANG W B, QIU L Q, REN F Y, et al. Advances on transition-metal catalyzed CO2 hydrogenation [J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 41(10): 3914-3934(in Chinese). doi: 10.6023/cjoc202105052
[12] 杜娴, 罗固源, 许晓毅. 长江重庆段两江水相、间隙水和沉积物中邻苯二甲酸酯的分布与分配 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(2): 557-562. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2013.02.023 DU X, LUO G Y, XU X Y. Distribution and partition of phthalate esters in water phase, pore water and sediments from Chongqing section of the Yangtze River [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(2): 557-562(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2013.02.023
[13] 王成伟, 刘禹, 宋正国, 等. 微塑料对DBP胁迫下生菜光合作用及品质的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(3): 508-516. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1134 WANG C W, LIU Y, SONG Z G, et al. Effects of microplastics and DBP on photosynthesis and nutritional quality of lettuce [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(3): 508-516(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-1134
[14] 蔡全英, 莫测辉, 吴启堂, 等. 水稻土施用城市污泥盆栽通菜土壤中邻苯二甲酸酯(PAEs)的残留 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2003, 23(3): 365-369. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2003.03.015 CAI Q Y, MO C H, WU Q T, et al. Effect of municipal sludges and chemical fertilizers on the content of phthalic acid esters(PAEs) in paddy soils grown Ipomoea aquatic [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2003, 23(3): 365-369(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2003.03.015
[15] 张鸿郭, 陈迪云, 罗定贵, 等. 填埋场周边土壤邻苯二甲酸酯研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2010, 33(S2): 176-179. ZHANG H G, CHEN D Y, LUO D G, et al. Research on phthalic acid esters in soil around municipal solid waste landfill[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 33(Sup 2): 176-179(in Chinese).
[16] 李天翠, 王飞华, 梁威. 吸附法去除水环境中邻苯二甲酸酯类污染的研究进展 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(8): 1565-1573. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1601 LI T C, WANG F H, LIANG W. A review on phthalates removal using adsorption in aqueous environments [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(8): 1565-1573(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-1601
[17] 熊美昱, 夏雨琪, 彭程. 典型类雌激素的降解方法及其影响因素研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(3): 610-623. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101303 XIONG M Y, XIA Y Q, PENG C. Degradation methods and influence factors of typical estrogen-like substances [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(3): 610-623(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019101303
[18] SUN R X, WANG L, JIAO Y Q, et al. Metabolic process of di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) by Enterobacter sp. DNB-S2, isolated from Mollisol region in China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 255: 113344. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113344 [19] SHAIDA M A, DUTTA R K, SEN A K. Removal of diethyl phthalate via adsorption on mineral rich waste coal modified with chitosan [J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 261: 271-282. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.031 [20] 魏丽琼, 呼世斌, 王娇娇, 等. 甜菜-牧草体系对土壤中4种邻苯二甲酸酯的修复研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(6): 1097-1102. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016.06.011 WEI L Q, HU S B, WANG J J, et al. Phytoremediation of 4 phthalic acid esters in contaminated soil by beet-grass system [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(6): 1097-1102(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016.06.011
[21] 晏晓旭, 孙德栋, 于林, 等. 硫酸根自由基处理邻苯二甲酸酯类废水 [J]. 大连工业大学学报, 2013, 32(4): 263-266. doi: 10.19670/j.cnki.dlgydxxb.2013.04.009 YAN X X, SUN D D, YU L, et al. Treatment for phthalate esters wastewater with sulfate free radical [J]. Journal of Dalian Polytechnic University, 2013, 32(4): 263-266(in Chinese). doi: 10.19670/j.cnki.dlgydxxb.2013.04.009
[22] 蒲生彦, 吕雪, 张颖. 基于文献计量的全球活化过硫酸盐氧化技术研究趋势分析 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(10): 2895-2908. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201911102 PU S Y, LYU X, ZHANG Y. Global trends of activated persulfate oxidation technology based on bibliometric analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(10): 2895-2908(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201911102
[23] 吴昊, 孙丽娜, 李玉双, 等. 活化过硫酸钠去除长期污染土壤中的TPH [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(9): 5231-5237. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201504043 WU H, SUN L N, LI Y S, et al. Application of persulfate to remediatiate long-term TPH contaminated soils [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(9): 5231-5237(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201504043
[24] 于晓章, 乐东明, 任燕飞. 邻苯二甲酸酯在环境中的降解机制 [J]. 生态科学, 2015, 34(4): 180-187. doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2015.04.029 YU X Z, YUE D M, REN Y F. Possible mechanisms involved in degradation of phthalic acid esters in the environment [J]. Ecological Science, 2015, 34(4): 180-187(in Chinese). doi: 10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2015.04.029
[25] 吴昊, 孙丽娜, 王辉, 等. 活化过硫酸钠原位修复石油类污染土壤研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(11): 2085-2095. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.11.2015052601 WU H, SUN L N, WANG H, et al. Persulfate In-situ remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(11): 2085-2095(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.11.2015052601
[26] 刘庆, 杨红军, 史衍玺, 等. 环境中邻苯二甲酸酯类(PAEs)污染物研究进展 [J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(8): 968-975. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2012.00968 LIU Q, YANG H J, SHI Y X, et al. Research progress on phthalate esters (PAEs) organic pollutants in the environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 20(8): 968-975(in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2012.00968
[27] ZHANG D, WU L P, YAO J, et al. Carbon and hydrogen isotope fractionation of phthalate esters during degradation by sulfate and hydroxyl radicals [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 347: 111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.047 [28] 周阳, 应路瑶, 于欣, 等. 碱热联合活化过硫酸钠氧化降解2, 4-二氯苯酚研究 [J]. 水处理技术, 2021, 47(3): 68-72. ZHOU Y, YING L Y, YU X, et al. Study on oxidative degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by alkaline and thermal co-activated sodium persulfate [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2021, 47(3): 68-72(in Chinese).
[29] FEDOROV K, PLATA-GRYL M, KHAN J A, et al. Ultrasound-assisted heterogeneous activation of persulfate and peroxymonosulfate by asphaltenes for the degradation of BTEX in water [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 397: 122804. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122804 [30] 田东凡, 王玉如, 宋薇, 等. UV/PMS降解水中罗丹明B的动力学及反应机理 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(5): 1868-1876. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2017.0474 TIAN D F, WANG Y R, SONG W, et al. Degradation of Rhodamine B in aqueous solution by UV/PMS system: Kinetics and reaction mechanism [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(5): 1868-1876(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2017.0474
[31] CHOI J, CUI M C, LEE Y, et al. Application of persulfate with hydrodynamic cavitation and ferrous in the decomposition of pentachlorophenol [J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2020, 66: 105106. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105106 [32] 廖云燕, 刘国强, 赵力, 等. 利用热活化过硫酸盐技术去除阿特拉津 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(4): 931-937. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0153 LIAO Y Y, LIU G Q, ZHAO L, et al. Removal of atrazine in heat activated persulfate oxidation process [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(4): 931-937(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.0153
[33] CHOI J, CUI M C, LEE Y, et al. Hydrodynamic cavitation and activated persulfate oxidation for degradation of bisphenol A: Kinetics and mechanism [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 338: 323-332. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.018 [34] ZHAO L, MA K, YANG Z. Changes of water hydrogen bond network with different externalities [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2015, 16(4): 8454-8489. [35] HUNG C M, HUANG C P, LAM S S, et al. The removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from marine sediments using persulfate over a nano-sized iron composite of magnetite and carbon black activator [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 104440. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104440 [36] XIE X F, ZHANG Y Q, HUANG W L, et al. Degradation kinetics and mechanism of aniline by heat-assisted persulfate oxidation [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24(5): 821-826. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60844-9 [37] 吴楠, 王三反, 李乐卓, 等. 碱热活化过硫酸盐降解柴油精制废水中的有机硫化合物 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(4): 435-438,444. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2019.04.013 WU N, WANG S F, LI L Z, et al. Degradation of organosulfur compound in wastewater of diesel refining by alkali heat activated persulfate [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2019, 41(4): 435-438,444(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2019.04.013
[38] WANG Z Y, SHAO Y S, GAO N Y, et al. Degradation kinetic of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) by sulfate radical- and hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation process in UV/persulfate system [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 195: 92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2017.11.072 [39] HUNG C M, HUANG C P, CHEN C W, et al. Hydrodynamic cavitation activation of persulfate for the degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine sediments [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 286: 117245. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117245 [40] LI H X, WAN J Q, MA Y W, et al. Reaction pathway and oxidation mechanisms of dibutyl phthalate by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 562: 889-897. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.093 [41] ZHANG X F, LIN Q T, LUO H Y, et al. Activation of persulfate with 3D urchin-like CoO-CuO microparticles for DBP degradation: A catalytic mechanism study [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 655: 614-621. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.281 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: