-
纺织工业生产过程中往往会产生大量的印染废水. 其中偶氮染料毒性大、难降解、易致癌,该废水可生化性弱,常规的生物处理很难去除[1]. 基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·−)高级氧化技术(SR-AOP)在光照下协同处理难降解污染物被认为是一种有前景的方法[2]. 硫酸根自由基(SO4·−)(E0=2.5—3.1 V)比传统Fenton法中羟基自由基(E0=1.8—2.7 V)的氧化还原电位要高,pH适用范围广,能够高效的降解水中污染物[3-4]. 过一硫酸盐(PMS)在水体中较为稳定,通常采用加热、光辐射、过渡金属等方法来活化产生SO4·−. 在这些技术中,光催化具有绿色、低耗能等优点[5]. 随着可见光催化剂的发展,PMS光活化的光源也从紫外光扩展到可见光甚至是太阳光.
钼酸铋(Bi2MoO6)是一种典型的铋系光催化剂,作为一种层状Aurivillius氧化物,Bi2MoO6的[Bi2O2]2+和MoO42−呈层状的交替结构,具有较窄的带隙(2.6—2.9 eV)和可见光催化性能,能够在可见光光照下产生电子-空穴对,各种含氧活性物种来降解污染物. 但是由于其比表面积低、光生电子-空穴对易复合,导致Bi2MoO6的应用受到限制[6-7]. 十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)是一种能有效控制铋基催化剂生长的阳离子表面活性剂,且CTAB作为卤素源,溴离子(Br−)可以影响氧空位(OVs)结构[8].
本文通过水热法用CTAB辅助合成Bi2MoO6,并对其晶体形貌、结构等进行分析;研究了光照下Bi2MoO6协同PMS在不同体系、不同条件下对水体中AO7的降解效果;通过自由基消除实验,探索了光照/PMS/Bi2MoO6系统中主要的活性物种.
-
二水合钼酸钠(Na2MoO4·2H2O,天津恒兴化学试剂有限公司),乙二醇((CH2OH)2,江苏强盛功能化学股份有限公司),十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB,C19H42BrN,上海润捷化学试剂有限公司);五水合硝酸铋(Bi(NO3)3·5H2O)、乙醇(C2H5OH)、金橙Ⅱ(AO7)(C16H11N2NaO4S)、亚硝酸钠(NaNO2)、过氧单磺酸钾(PMS)(KH3S4O18)、叔丁醇(C4H10O)、对苯醌(C6H4O2)、糠醇(C5H6O2)、异丙醇(C3H8O)、腐殖酸均购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司;以上药品均为分析纯;实验用水为去离子水.
-
称取2 mmol Bi(NO3)3·5H2O加入到20 mL乙二醇溶液中,超声30 min使其分散. 称取1 mmol Na2MoO4·2H2O加入到10 mL乙二醇溶液中,磁力搅拌30 min,将铋盐溶液移至上述溶液中搅拌均匀,加入0.05、0.10、0.15 g的CTAB,继续40 ℃恒温搅拌1 h. 随后将混合溶液移至50 mL聚四氟乙烯高压反应釜中,在150 ℃下水热反应24 h. 自然条件下冷却并过滤,用乙醇和去离子水分别洗涤3次后,在60 ℃下干燥12 h,最终得到样品0.05CTAB-BMO、0.1CTAB-BMO、0.15CTAB-BMO. 重复上述操作时不添加CTAB,得到样品BMO.
-
吸附-光催化降解:选用14 W的氙灯模拟可见光. 将1 mL的AO7溶液(10 mmol·L−1)稀释到100 mL去离子水中,取一定量的催化剂分散到水溶液中,反应温度控制在(25±2) ℃. 在黑暗中磁力搅拌30 min,完成吸附-脱附平衡实验. 然后打开氙灯进行反应,每隔一段时间用针管抽取一定量的溶液,用0.45 μm滤头过滤. 过滤液用石英比色皿在波长484 nm下的紫外可见分光光度计测试AO7浓度.
协同体系降解:选用14 W的氙灯模拟可见光. 将1 mL 的AO7溶液(10 mmol·L−1)稀释到100 mL去离子水中,放于磁力搅拌器上,反应温度控制在(25±2) ℃. 取一定量的催化剂分散到水溶液中,打开氙灯,同时加入1 mmol·L−1的PMS开始反应. 每隔一段时间用针管抽取一定量的溶液,用0.45 μm滤头过滤,并加入1 mL亚硝酸钠猝灭剂. 过滤液用石英比色皿在波长484 nm下的紫外可见分光光度计测试AO7浓度.
-
采用Smartlab TM型号的X射线衍射测试仪来测试样品的物相结构;采用Nicolet 6700型的傅立叶红外光谱仪表征样品表面的官能团;采用Quanta FEG 250型的扫描分析仪对所有样品进行拍摄;采用Thermo Scientific Nexsa型的X射线光电子能谱仪对样品表面的元素价态进行分析;采用麦克ASAP 2460型号的全自动比表面积及孔隙率分析仪测定样品的比表面积及孔径;采用岛津UV3600IPLUS型的紫外/可见/近红外漫反射仪获得样品的吸收波长.
-
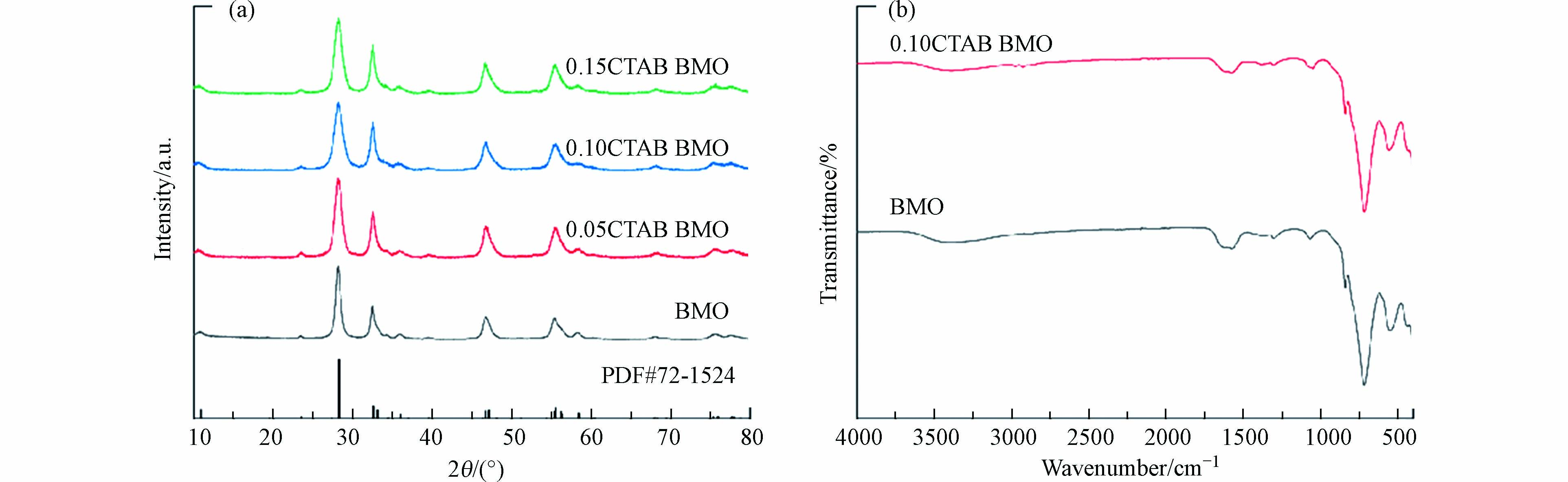
采用X射线衍射(XRD)的方法研究催化剂的物相结构. 不同CTAB添加量BMO光催化剂的XRD谱图如图1a所示. 在纯BMO的情况下,2θ衍射峰约为10.9°、23.5°、28.3°、32.5°、32.6°、33.1°、47.1°、55.6°、58.4°. 所有的衍射峰均与正交相的Bi2MoO6标准卡片(PDF#72-1524)一致,对应(020)、(111)、(131)、(200)、(002)、(060)、(062)、(133)和(262)晶格面. CTAB-BMO的XRD衍射谱图与BMO的相似,未检测到杂质峰,说明样品纯度较高. 但与纯BMO相比,CTAB-BMO的衍射峰强度明显降低,表明对应晶面的结晶度降低. 这可能是由于氧空位在相应晶面产生,破坏了晶体的晶面结构.
图1b中傅立叶变换红外吸收光谱图 (FT-IR)可以清楚看出,在3387.41 cm−1和1571.6 cm−1处观察到的BMO特征峰归因于O—H的振动拉伸和收缩. 910—650 cm−1和630—430 cm−1的特征峰分别为Mo—O和Bi—O键拉伸振动引起的. 位于715 cm−1和547 cm−1处的特征峰分别代表MoO6结构中O2分子的不对称拉伸和MoO6的弯曲振动. 此外,0.10CTAB-BMO的FT-IR谱图与BMO的峰同样具有高度一致性.
-
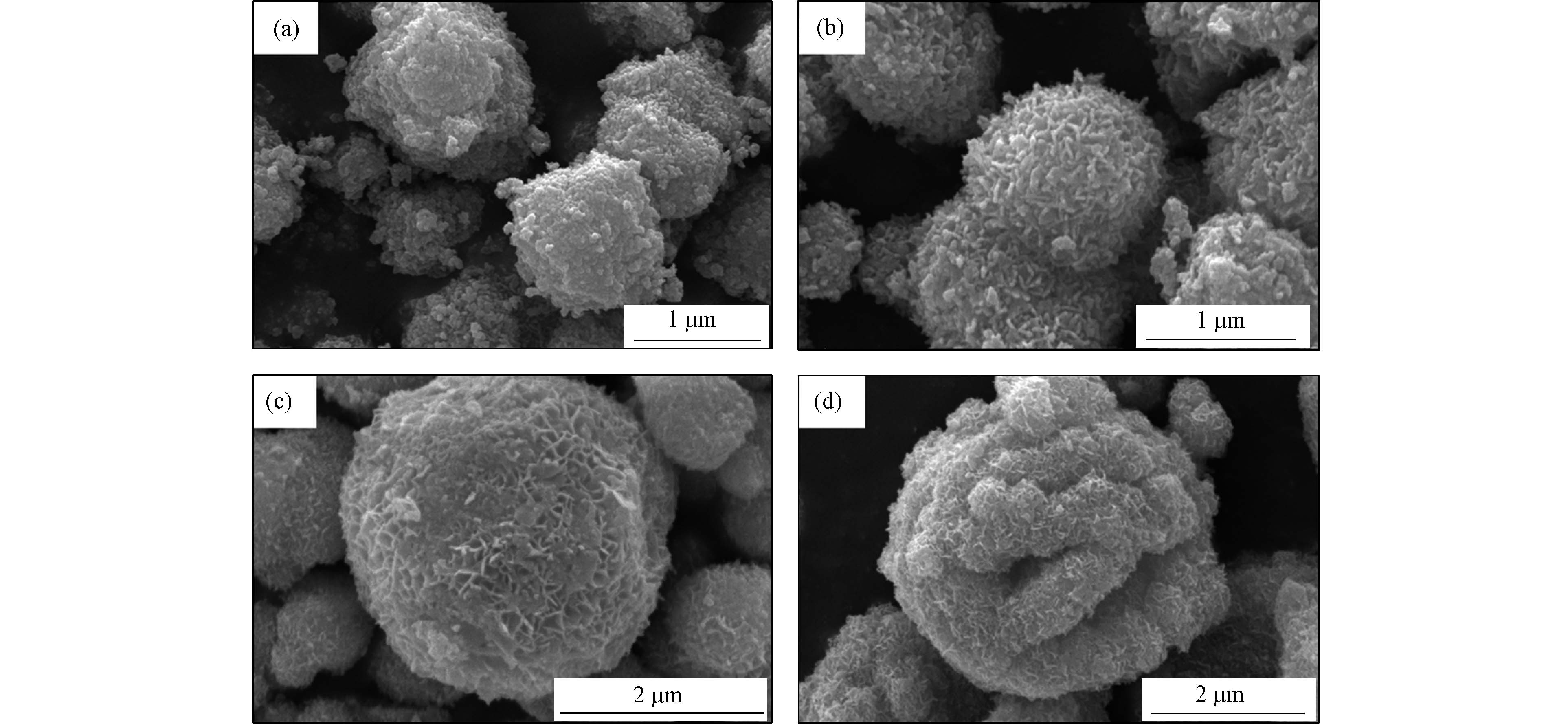
通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)可以看出,CTAB的加入对BMO的形貌特征产生了很大的变化,如图2所示. 不论是否添加CTAB,最终样品的形态均为球形,主要是因为乙二醇(EG)的贡献. 乙二醇具有很强的螯合能力,当Bi(NO3)3·5H2O和Na2MoO4·2H2O溶于乙二醇中,可以在乙二醇中螯合形成醇盐,醇氧化物的生成大大的降低了溶液中游离Bi3+的浓度和反应速率. 另外乙二醇具有较高的溶剂黏度,产生较大的空间位阻,从而抑制纳米粒子的转移和团聚[9-10]. 图2a可以看出,纯BMO的平均直径在1 μm左右,由许多纳米球形微晶组成. 而在添加不同浓度CTAB之后,其纳米颗粒由球状变成了片状结构,微球的平均直径也有所增加. 0.05CTAB-BMO与纯BMO形貌相似,是因为CTAB的添加量较低,不足以改变其形貌特征. 而当CTAB的含量增加到0.1 g时,BMO微球中纳米粒子形状变成了片状结构,比表面积、平均直径也有所增加. 0.15CTAB-BMO的表面结构比较疏松,具有更高的孔隙结构,平均直径也达到了5 μm左右. BMO微球平均直径的增加有可能是因为CTAB与[MoO4]2−相互作用,抑制Bi2O3与[MoO4]2−的反应,形成更大的结构[11]. 本次实验主要对0.10CTAB-BMO进行分析,因为该催化剂具有形貌较好的纳米片状结构,催化性能有望增加.
-
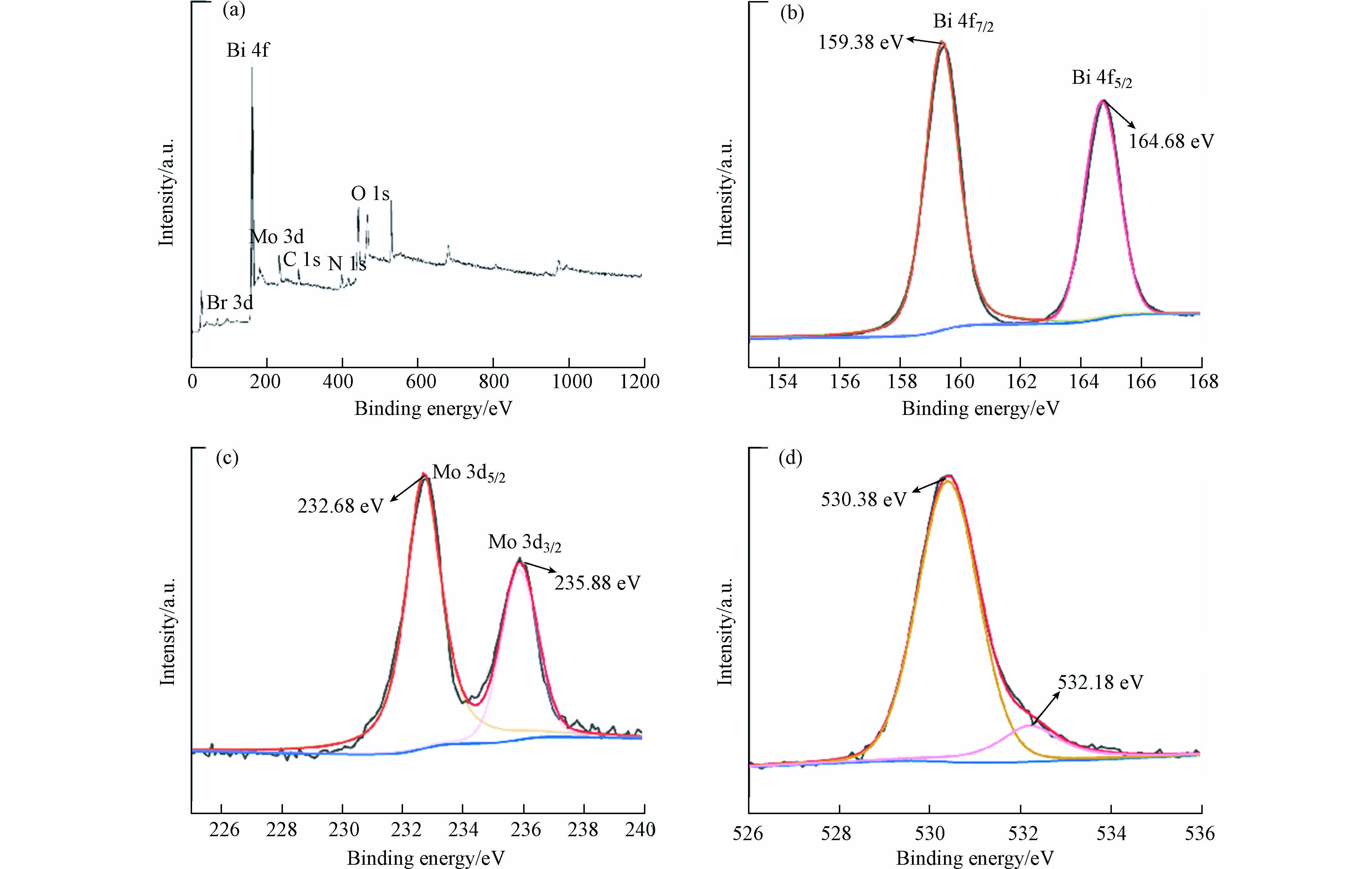
通过XPS进一步对0.10CTAB-BMO催化材料的表面元素组成和化学价态进行深入分析. 图3a的全谱图检测到0.10CTAB-BMO的核心组成为Bi 4f、Mo 3d、O 1s、C 1s、N 1s和Br 3d. 值得注意的是,N 1s和Br 3d元素的峰可能是由于CTAB的添加. 然而,XRD的结果表明,CTAB-BMO没有发现多余的峰,可能原因是Br以非晶态存在,没有形成新的晶体取向. 首先用C 1s(284.8 eV)矫正各元素的结合能. Bi 4f的XPS谱图如图3b所示,电子结合能在159.38 eV和164.4 eV处的特征峰分别对应于Bi 4f7/2和Bi 4f5/2,,这主要是Bi3+的特点[12]. 图3c中,232.68 eV和235.88 eV处的结合能可以归因于Mo6+的Mo 3d5/2和Mo 3d3/2. 图3d为O 1s的XPS谱图,O 1s可以拟合为530.38 eV和532.18 eV处的两个分峰,在530.38 eV处的峰可以归结于晶格氧,在532.18eV处的峰可以归结于材料表面的羟基和吸附水形成的表面氧[13].
-
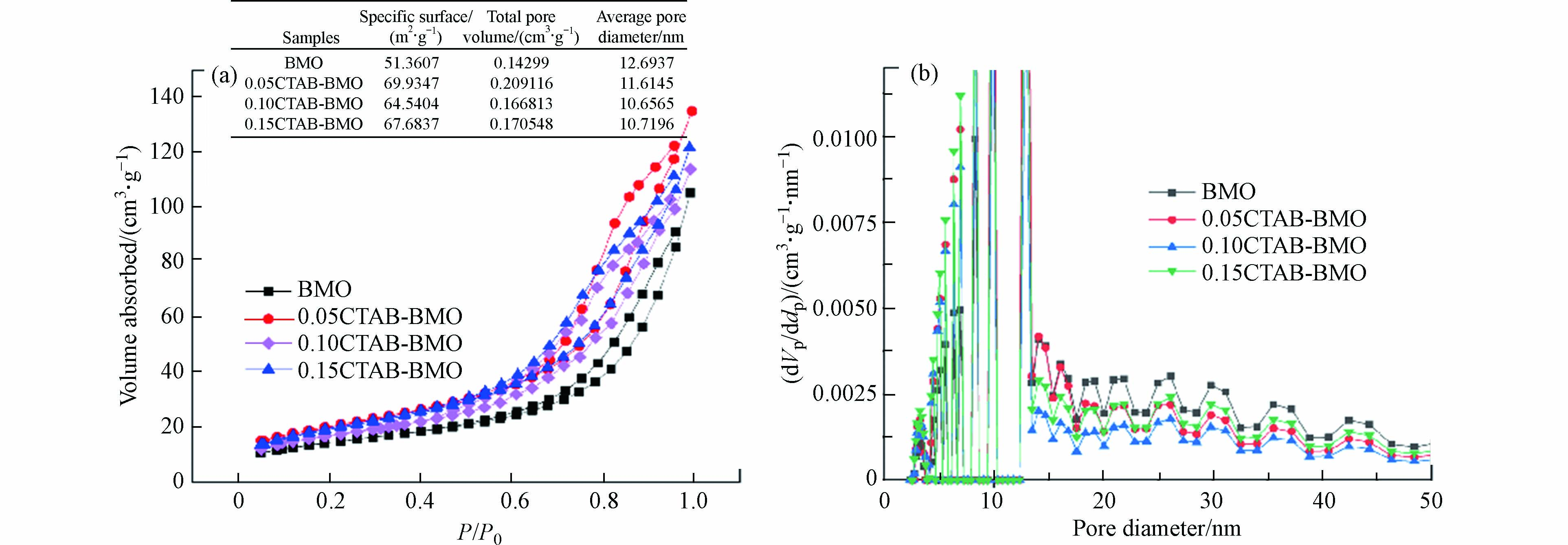
通过N2吸附-脱附等温线和BJH孔径分布来分析合成催化剂的结构性质. 如图4a所示,催化剂吸附量随着压力的上升而增加,表现为Ⅲ型吸附等温线. 当催化剂处于脱附状态时表现为H3型回滞环,表明催化剂是纳米片堆叠而成的介孔结构. 图4b证明所有催化剂的孔径均在10 nm至50 nm之间. 从图4a的表格可以看到,BMO、0.05CTAB-BMO、0.10CTAB-BMO和0.15CTAB-BMO的比表面积、孔体积和平均孔径. CTAB的添加导致催化剂比表面积的增加,而孔径有所下降. 以上现象可能是由于CTAB的加入使氧空位浓度增加从而引起晶体结构破坏,产生更多的纳米片堆叠形成的介孔,此结果也符合SEM中催化剂的形貌. 比表面积的增加,有利于催化反应的活性点位增加,促进反应物的吸附及中间产物的脱附,从而提高催化活性.
-
采用UV-Vis DRS技术进一步研究了合成催化材料的光学性能,BMO及0.10CTAB-BMO催化剂的UV-Vis DRS谱图如图5所示. 图5a可以看出,两种材料的吸收边界均位于450 nm以上,对可见光都有明显的吸收作用. 此外,有CTAB添加的催化剂吸收波发生红移,说明可以吸收波长更长的光.
合成样品的禁带宽度(Eg)可从Kubelka-Munk方程近似得到:
式中,A为比例常数,h为普朗克常数,ν为光频率,α为吸收系数. 由图5b可以清楚地看出,BMO和0.10CTAB-BMO的直接禁带宽度分别为2.68 eV和2.75 eV. 根据Mulliken电负性理论方程估计了0.10CTAB-BMO的边带位置,具体的价带(VB)和导带(CB)可由下列公示计算:
式中,E0为氢电子自由能(4.5 eV),X为半导体的电负性,即组成原子电负性的几何平均值(5.17 eV),EVB为价带(VB),ECB为导带(CB),Eg为半导体的禁带宽度. 通过图5c VB-XPS计算可以得到0.10CTAB-BMO的VB和CB电位分别为2.05 eV和-0.70 eV. 结果表明,该材料具有合适的禁带宽度,是一种适合在可见光下催化降解污染物的催化剂.
-
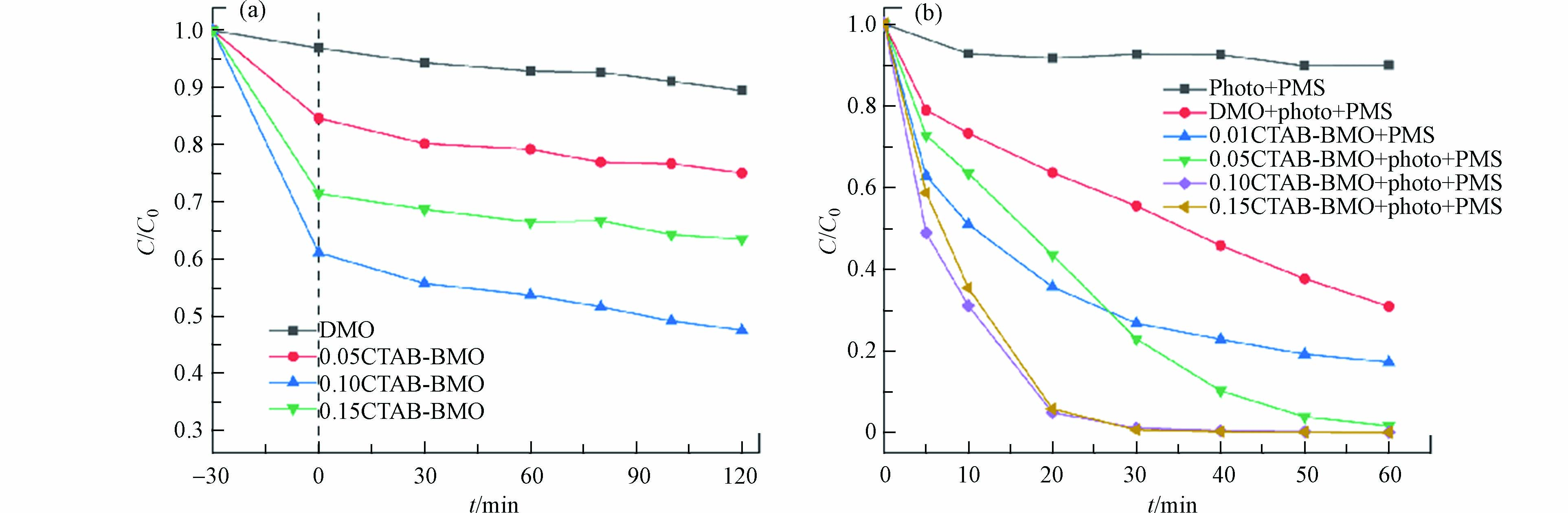
通过不同CTAB改性后的催化剂在14 W的氙灯照射下降解AO7的效果来探究其光催化性能. 从表1及图6a可以看出,CTAB改性的催化剂表现出了较强的吸附性,在暗反应30 min后,0.10CTAB-BMO对AO7的吸附率达到了38.9%. 结合图4a中数据,CTAB-BMO吸附量的提高有可能是因为添加CTAB使纳米颗粒的片状结构具有更多的比表面积和合适的氧空位浓度. 但是,0.15CTAB-BMO的吸附量少于0.10CTAB-BMO,可能是由于CTAB添加过多,导致其表面结构过于疏松. CTAB改性后的BMO光催化性能同样有所提高. 一是因为吸附对光降解效率是非常有利的,可以增大光催化剂与染料的接触,协同促进染料分子的降解[14]. 二是因为合适的氧空位浓度可以提供更多的反应活性位点.
为探究CTAB改性后的CTAB-BMO在可见光下与过一硫酸盐(PMS)的协同性能,设计了不同的反应体系,如图6b所示. 在光与PMS体系中,AO7的降解率为10.1%,由于光照条件下PMS可以被催化裂解产生具有活性的硫酸根自由基(SO4·−). 在黑暗条件下,0.10CTAB-BMO/PMS体系中的AO7降解率达到82.8%,说明在钼酸铋除了作为光催化剂外,在活化PMS降解污染物时,也具备良好的催化性能. 在可见光照射下,非均相0.10CTAB-BMO/PMS体系表现出最优的降解速率,对AO7的降解率可以在30 min达到99%以上. 由于0.10CTAB-BMO具有较大的比表面积和合适的氧空位浓度,提供了更多的吸附及反应活性位点. 此外,可见光的引入也能够对非均相过硫酸盐体系有良好的协同作用.
-
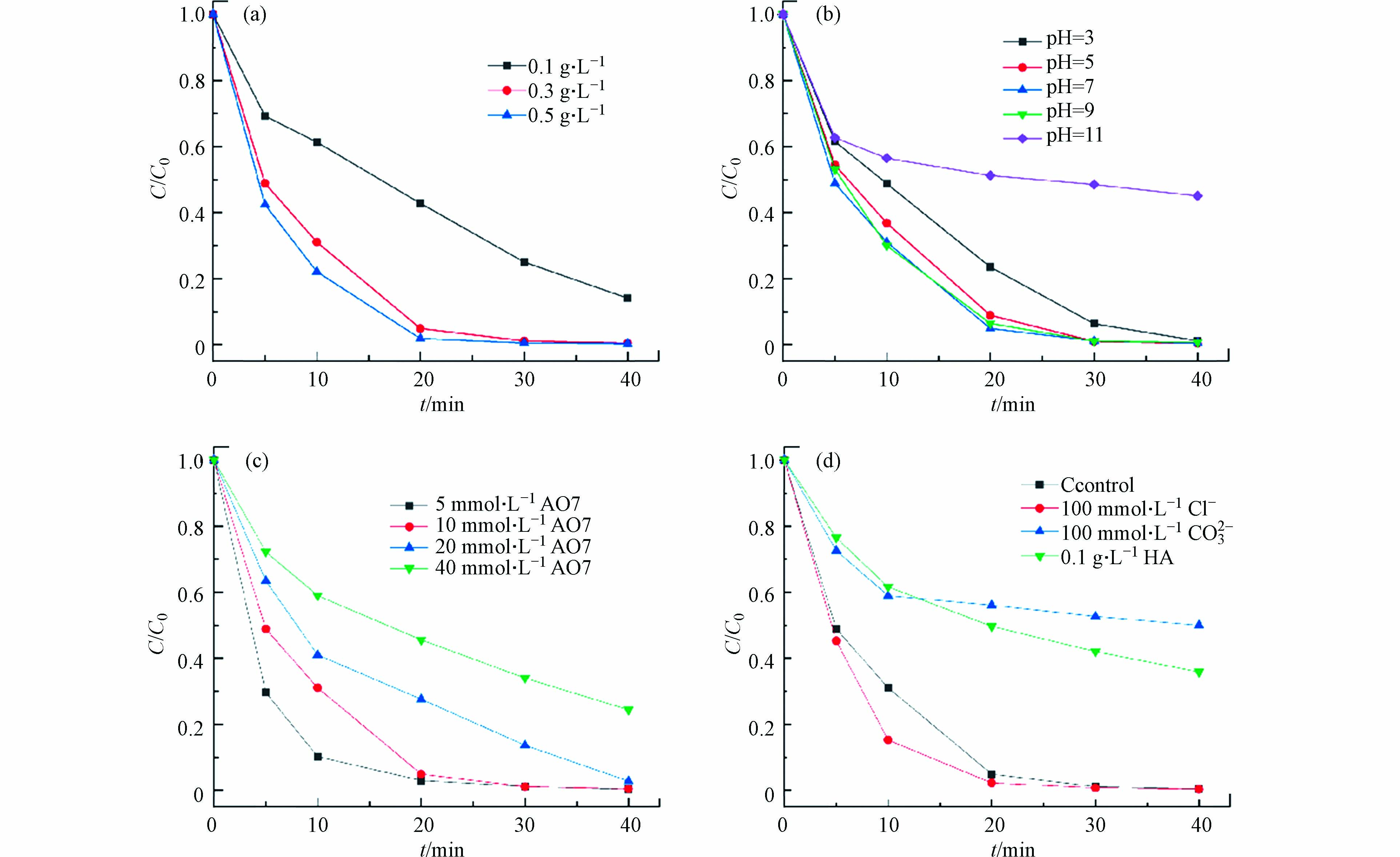
图7a考察了不同0.10CTAB-BMO催化剂投加量(0.1、0.3、0.5 g·L−1)对AO7降解的影响.
当催化剂的投加量从0.1 g·L−1增加到0.5 g·L−1时,AO7在30 min时的降解率也从74.9%提高到了大于99%. 但是,当投加量从0.3 g·L−1增加到0.5 g·L−1时,后者的降解速率并没有提升过多. 是因为在一定浓度的PMS产生的自由基有限,导致AO7的降解速率没有增加过快. 另外,过量的催化剂可能会在悬浮液中过量聚集,增加反应溶液的浊度,从而影响可见光的透射率并降低可见光的吸收率.
-
许多文献报道,溶液的pH会影响污染物的降解效率. 与传统的Fenton相比,SR-AOP在较宽的pH范围内具有良好的反应活性. 图7b评估了0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系中在不同初始pH值下(3.0—11.0)的催化降解性能. 当pH值在3.0—9.0范围内,AO7可以在40 min内降解99%,说明该pH范围内AO7的降解效率没有受到太大影响. 但是当pH调至11时,AO7的降解率仅为58.5%. 因为在酸性和中性条件下,PMS主要以HSO5−为主,而在碱性条件下SO52−的浓度会迅速增加. 当溶液pH值在3.0—9.0时,SO4·−与OH−和H2O以适当的速率生成·OH,增强了AO7的降解速率. 而当溶液pH为11时,催化剂表面负电荷的增加会阻碍PMS的吸附;此外,由于SO52−的活化效果比HSO5−要弱,也会导致AO7的降解速率减慢[15-16].
-
为了研究AO7初始浓度影响,在AO7浓度为5—40 mmol·L−1范围内进行实验. 如图7c所示,随着AO7浓度的增加,降解效果明显下降. 随着AO7的初始浓度从5 mmol·L−1增加到40 mmol·L−1,AO7从20 min大于99%的降解率下降到40 min的75.6%. 主要是因为初始浓度较高的AO7溶液中缺乏足够的活性自由基.
-
实际水体中存在许多可溶性的无机阴离子,会对0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系催化反应造成一定的影响. 本实验选用0.1 mmol·L−1的NaCl、Na2CO3作为Cl−、CO32−的来源,具体结果如图7所示. 印染废水中往往存在着大量的Cl−,部分文献说Cl−的存在可能会抑制污染物的降解. 而在本实验中Cl−存在条件下,0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系对AO7的降解有促进作用,大致可以归为一下两点:①Cl−除孔洞的能力,可以降低光生电子-空穴的复合率(式4)[17]. ②Cl−会与·OH和SO4·−发生一系列反应反生成氯自由基及二氯自由基,进一步生成具有氧化性质的HCIO(式5—9)[18].
溶液中存在一定量的CO32−会对AO7的降解起到明显的抑制作用,当加入100 mmol·L−1 Na2CO3时,AO7在60 min内仅降解了52.4%,去除效率降低的主要原因是CO32−与目标污染物竞争·OH和SO4·−,生成活性较低的CO3·−(式10—11)[19-20],但是CO3·−的稳定性较差,AO7对其反应活性较低,导致去除率不高.
引入自然有机物(NOM)模型化合物腐殖酸(HA)对污染物的降解有着重要的影响. 当加入0.1 g·L−1 HA后,AO7的降解受到了抑制,45 min反应时间内的去除率为73.2%. 分析原因认为因为HA是天然的有机质,在反应体系内与目标污染物竞争活性物种.
-
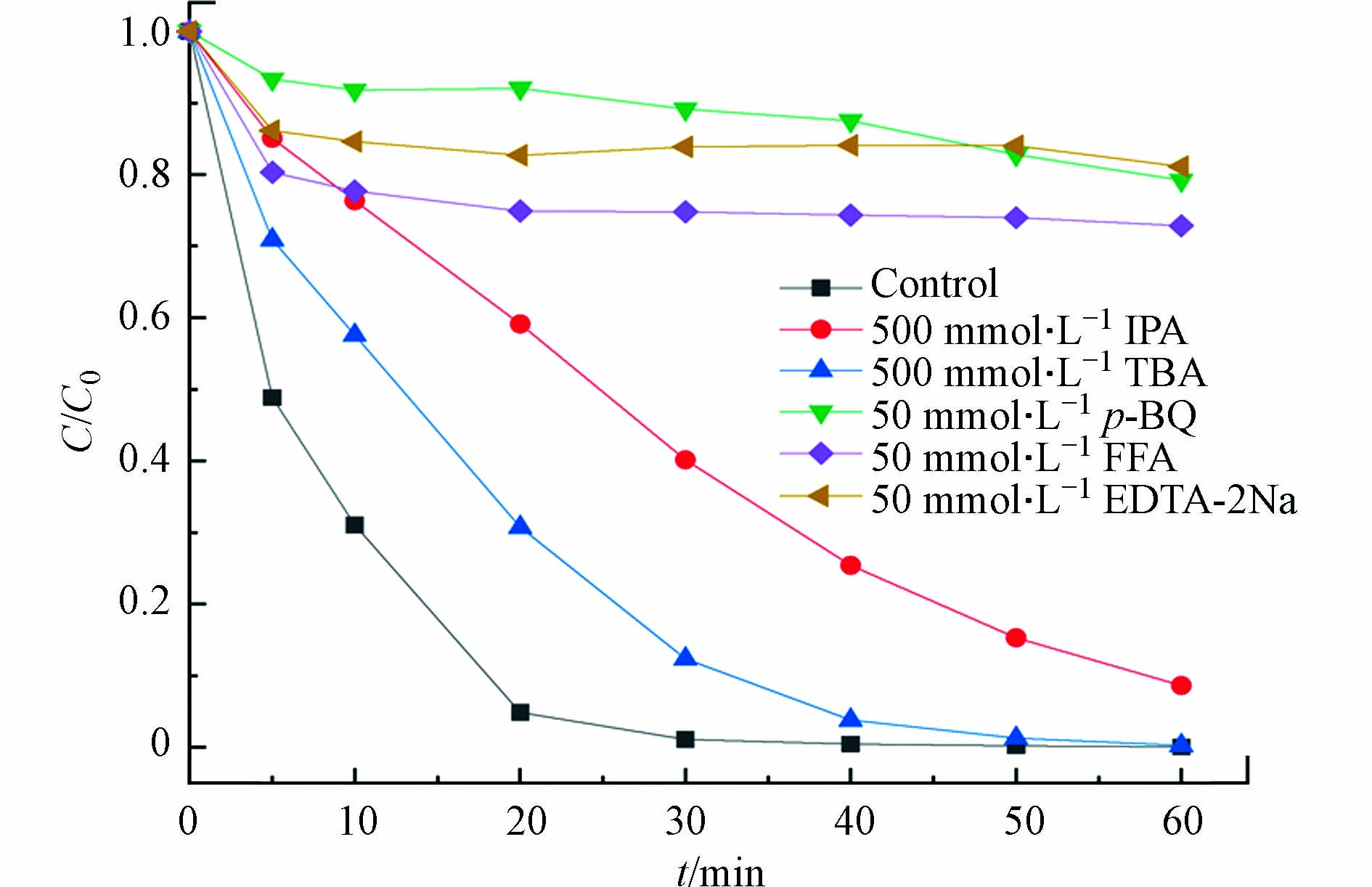
为了研究0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系降解AO7过程中活性物种,采用乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)、对苯醌(p-BQ)、糠醇(FFA)、叔丁醇(TBA)、异丙醇(IPA)分别作为h+、·O2−、1O2、·OH和·OH/SO4·−的猝灭剂来进行捕获实验. 如图8所示,体系内不存在任何猝灭剂时,30 min内99%的AO7的被降解. 当溶液中加入IPA、TBA后,在30 min时AO7的降解率分别降低至59.8%和87.6%. 而在添加EDTA-2Na、p-BQ、FFA后可以看出明显的抑制了AO7的降解,降解率在60 min内均不超过30%. 结果表明,在0.1CTAB-BMO/光/PMS降解AO7体系中产生的活性物质有h+、·O2−、1O2、·OH和SO4·−,其中h+、·O2−、1O2对于AO7降解的贡献要高于·OH和SO4·−.
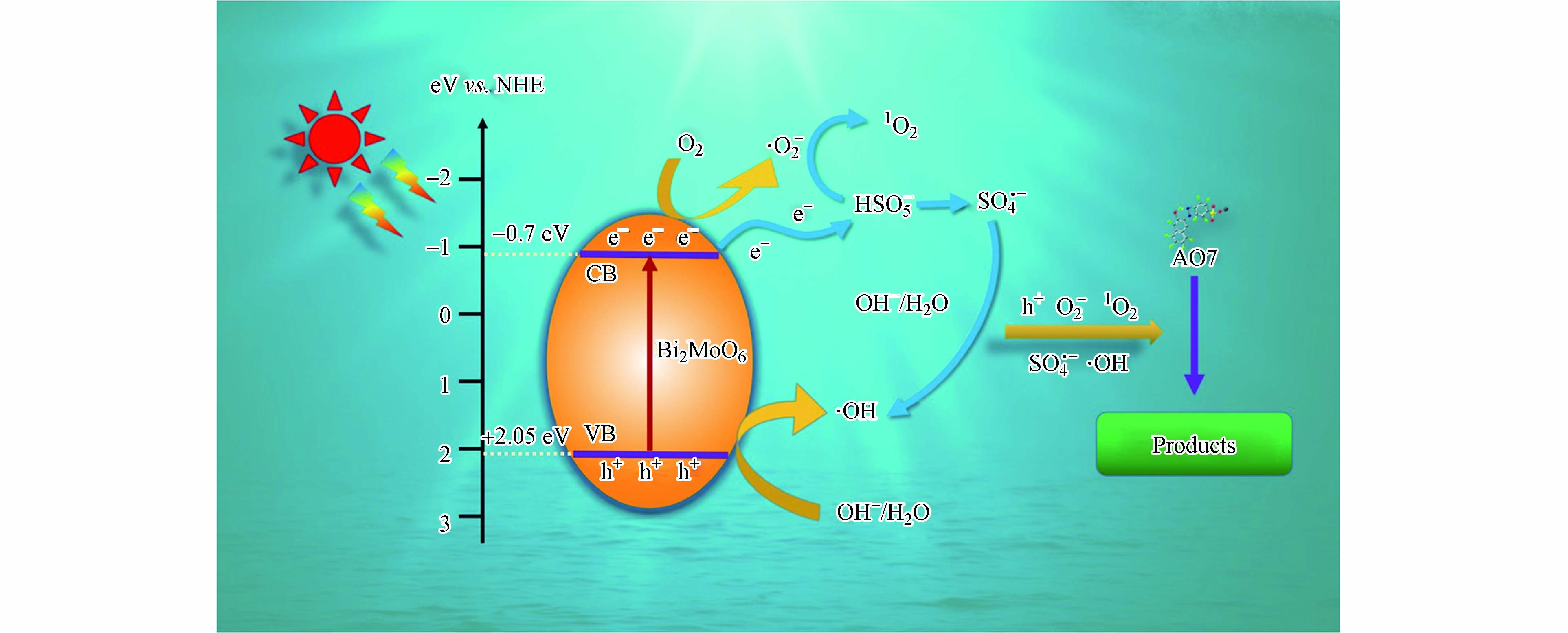
根据实验及分析结果,本研究提出0.1CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系催化降解AO7可能的催化反应机理. 该体系CTAB-BMO微球具有较大的比表面积和合适的氧空位浓度,能够提供更多的吸附反应活性位点,用于吸附活性物质. 同时,PMS在水中的溶解度远大于氧气在水中的溶解度,所以氧空位能够更好地吸收离子态的HSO5−. 可见光照射下,0.1CTAB-BMO光催化剂被激发产生光生电子(e−)和空穴(h+)(式12)[21],合适浓度的氧空位可以作为电子捕获中心,阻止光生电子和空穴的复合. 由于0.1CTAB-BMO的CB电位为-0.70 eV,低于O2/·O2−的电位值(E0=-0.33 V),故光生电子e−不仅能与PMS反应生成SO4·−(式13),而且能与O2反应生成·O2−(式14)[22]. 通过加入FFA消除实验我们得到1O2在AO7的降解过程中也起到了非常重要的作用. 已有研究报道,1O2是PMS活化过程中的一种选择性活性氧,1O2可以通过PMS自身分解产生,也可以通过与超氧自由基重组形成(式15—17) [23]. 生成·OH的方法主要有两种,一方面,h+可以与H2O/OH−生成H+和·OH(式18). 另一方面,由于SO4·−/SO42−的氧化还原电位(2.5—3.1 eV)高于·OH,所以也可以与H2O/OH−生成·OH(式19—20)[24-25]. 最终,AO7在活性物种(h+、·O2−、1O2、·OH和SO4·−)的共同作用下分解成更小的分子物质甚至是无毒无害的CO2和H2O(式21). 图9提供了0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系降解AO7过程中的反应机理示意图.
-
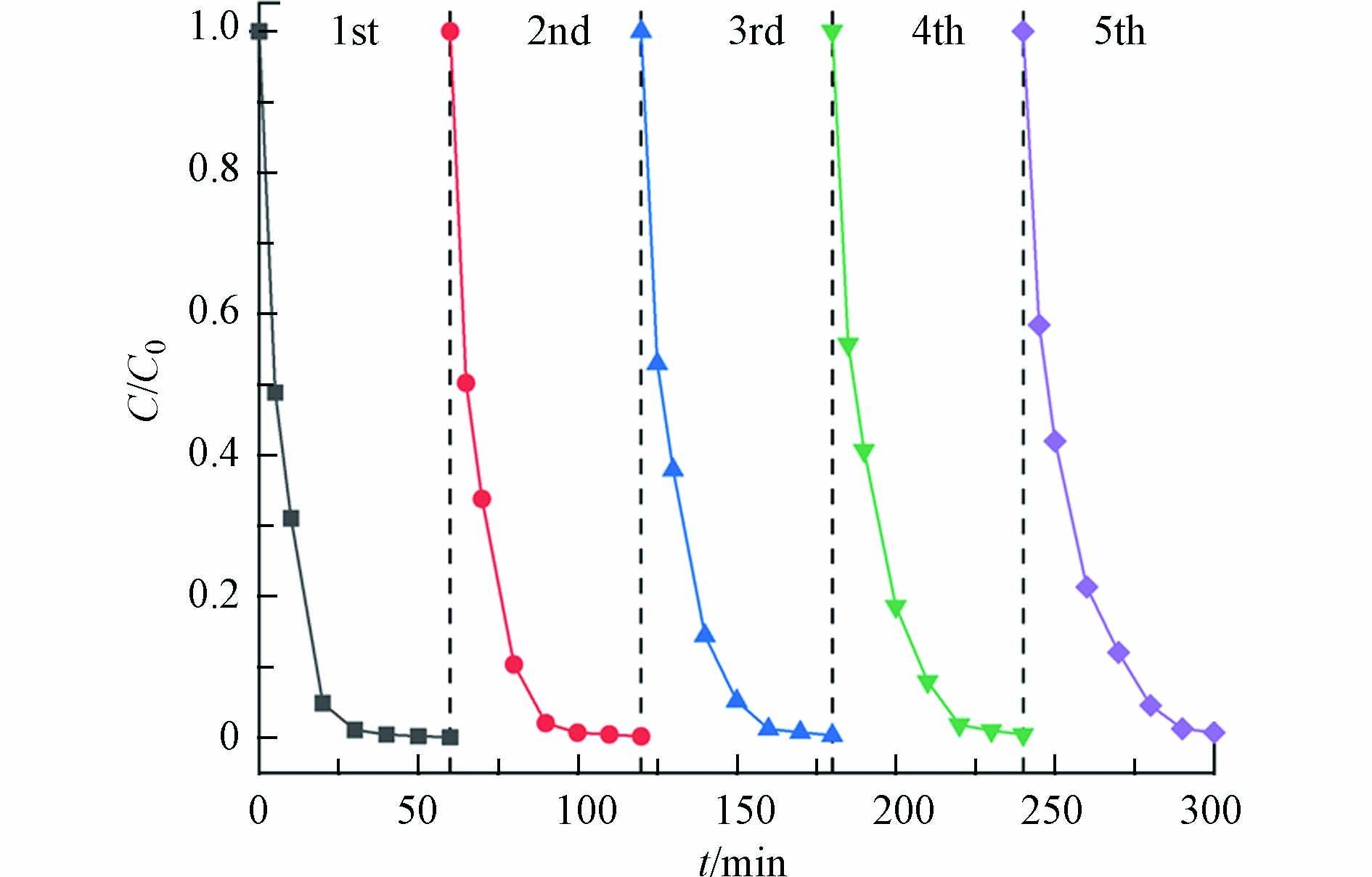
为了考察0.1CTAB-BMO催化剂的可回收性和稳定性,进行了连续去除实验. 在每次实验条件相同下反应60 min后,通过抽滤装置收集材料颗粒,用酒精和去离子水洗涤若干次,放入60 ℃烘箱干燥6 h后,重新分散到新的AO7溶液中进行下次实验. 图10可以看到,在重复了5次实验后,AO7依然可以在60 min内达到99%以上的去除率. 结果表明0.1CTAB-BMO纳米微球催化剂是一种良好且稳定的催化剂.
-
(1)通过水热法成功制备了CTAB-BMO催化剂,CTAB的引入改变了钼酸铋的形貌特征,提供了合适的氧空位浓度. 当0.10CTAB-BMO为0.3 g·L−1、AO7为0.1 mmol·L−1、PMS为1 mmol·L−1、14 W氙灯的照射下,AO7可以在30 min内完全去除(>99%),0.1CTAB-BMO在被重复利用5次后,60 min内对AO7的降解率仍然高达99%,说明催化剂具有高效性和稳定性.
(2)0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系可以在较宽的初始pH(3.0—9.0)范围内表现出较高的AO7降解率. 一定量的Cl−可以促进AO7的降解,而CO32−和HA的加入会起明显的抑制作用.
(3)通过猝灭表明,催化剂存在多个活性物种(h+、·O2−、1O2、·OH和SO4·−)并协同降解AO7污染物,其中h+、·O2−和1O2起着主要作用.
表面活性剂 (十六烷基三甲基溴化铵) 辅助合成Bi2MoO6光催化剂协同PMS降解AO7
Surfactant ( cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide ) assisted synthesis of Bi2MoO6 photocatalyst and PMS assisted degradation of AO7
-
摘要: 采用CTAB辅助水热法合成钼酸铋(Bi2MoO6,BMO)微球,并将其用于活化过一硫酸盐(PMS),在可见光下降解废水中的偶氮染料金橙Ⅱ(AO7). 利用X 射线衍射 (XRD),傅里叶红外光谱仪(FT-IR),扫描电子显微镜(SEM),X射线能谱(XPS),透射电子显微镜(TEM)和紫外-可见漫反射光谱(UV-vis)对催化剂进行了表征,并通过降解实验测试其催化性能. 结果表明,合成的催化剂具有良好的吸附、催化降解AO7的性能. 在中性条件下,催化剂投加量0.3 g·L−1,AO7浓度0.1 mmol·L-1,PMS浓度1 mmol·L−1,可以在30 min内完全降解AO7. 研究了催化剂含量、pH、共存阴离子等对AO7降解效果的影响. 通过自由基消除实验,探索了0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系中存在的活性物种(h+、·O2−、1O2、·OH和SO4·−)和可能的降解途径. 通过5次连续去除实验,该体系仍然可以在60min内完全降解AO7.Abstract: Bismuth molybdate (Bi2MoO6, BMO) microspheres were synthesized by CTAB-assisted hydrothermal method. The degradation of azo dye OrangeⅡ (AO7) by the BMO-activated persulfate (PMS) in wastewater under visible light was studied. The catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray energy spectrum (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and UV-visible diffuse reflection spectroscopy (UV-vis), respectively. The catalytic performance of catalysts was tested by degradation experiments. Results show that the catalyst as prepared show a good adsorption and degradation performance for AO7. Under the neutral condition, AO7 could be completely degraded within 30min as the catalyst dosage was 0.3 g·L−1, AO7 concentration was 0.1 mmol·L−1 and PMS concentration was 1 mmol·L−1, respectively. The effects of catalyst content, pH and coexisting anions on the degradation of AO7 were studied. The active species (h+, ·O2−, 1O2, ·OH和SO4·−) and possible degradation pathways of 0.10CTAB-BMO/photo/PMS system were explored by free radical elimination experiments. The AO7 could be degraded completely by this system in 60 mins after 5 consecutive removal experiments.
-
Key words:
- CTAB /
- bismuth molybdate /
- photocatalytic /
- peroxymonosulfate /
- AO7
-
纺织工业生产过程中往往会产生大量的印染废水. 其中偶氮染料毒性大、难降解、易致癌,该废水可生化性弱,常规的生物处理很难去除[1]. 基于硫酸根自由基(SO4·−)高级氧化技术(SR-AOP)在光照下协同处理难降解污染物被认为是一种有前景的方法[2]. 硫酸根自由基(SO4·−)(E0=2.5—3.1 V)比传统Fenton法中羟基自由基(E0=1.8—2.7 V)的氧化还原电位要高,pH适用范围广,能够高效的降解水中污染物[3-4]. 过一硫酸盐(PMS)在水体中较为稳定,通常采用加热、光辐射、过渡金属等方法来活化产生SO4·−. 在这些技术中,光催化具有绿色、低耗能等优点[5]. 随着可见光催化剂的发展,PMS光活化的光源也从紫外光扩展到可见光甚至是太阳光.
钼酸铋(Bi2MoO6)是一种典型的铋系光催化剂,作为一种层状Aurivillius氧化物,Bi2MoO6的[Bi2O2]2+和MoO42−呈层状的交替结构,具有较窄的带隙(2.6—2.9 eV)和可见光催化性能,能够在可见光光照下产生电子-空穴对,各种含氧活性物种来降解污染物. 但是由于其比表面积低、光生电子-空穴对易复合,导致Bi2MoO6的应用受到限制[6-7]. 十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)是一种能有效控制铋基催化剂生长的阳离子表面活性剂,且CTAB作为卤素源,溴离子(Br−)可以影响氧空位(OVs)结构[8].
本文通过水热法用CTAB辅助合成Bi2MoO6,并对其晶体形貌、结构等进行分析;研究了光照下Bi2MoO6协同PMS在不同体系、不同条件下对水体中AO7的降解效果;通过自由基消除实验,探索了光照/PMS/Bi2MoO6系统中主要的活性物种.
1. 实验部分 ( Experimental section )
1.1 实验药品
二水合钼酸钠(Na2MoO4·2H2O,天津恒兴化学试剂有限公司),乙二醇((CH2OH)2,江苏强盛功能化学股份有限公司),十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB,C19H42BrN,上海润捷化学试剂有限公司);五水合硝酸铋(Bi(NO3)3·5H2O)、乙醇(C2H5OH)、金橙Ⅱ(AO7)(C16H11N2NaO4S)、亚硝酸钠(NaNO2)、过氧单磺酸钾(PMS)(KH3S4O18)、叔丁醇(C4H10O)、对苯醌(C6H4O2)、糠醇(C5H6O2)、异丙醇(C3H8O)、腐殖酸均购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司;以上药品均为分析纯;实验用水为去离子水.
1.2 材料的制备
称取2 mmol Bi(NO3)3·5H2O加入到20 mL乙二醇溶液中,超声30 min使其分散. 称取1 mmol Na2MoO4·2H2O加入到10 mL乙二醇溶液中,磁力搅拌30 min,将铋盐溶液移至上述溶液中搅拌均匀,加入0.05、0.10、0.15 g的CTAB,继续40 ℃恒温搅拌1 h. 随后将混合溶液移至50 mL聚四氟乙烯高压反应釜中,在150 ℃下水热反应24 h. 自然条件下冷却并过滤,用乙醇和去离子水分别洗涤3次后,在60 ℃下干燥12 h,最终得到样品0.05CTAB-BMO、0.1CTAB-BMO、0.15CTAB-BMO. 重复上述操作时不添加CTAB,得到样品BMO.
1.3 降解实验
吸附-光催化降解:选用14 W的氙灯模拟可见光. 将1 mL的AO7溶液(10 mmol·L−1)稀释到100 mL去离子水中,取一定量的催化剂分散到水溶液中,反应温度控制在(25±2) ℃. 在黑暗中磁力搅拌30 min,完成吸附-脱附平衡实验. 然后打开氙灯进行反应,每隔一段时间用针管抽取一定量的溶液,用0.45 μm滤头过滤. 过滤液用石英比色皿在波长484 nm下的紫外可见分光光度计测试AO7浓度.
协同体系降解:选用14 W的氙灯模拟可见光. 将1 mL 的AO7溶液(10 mmol·L−1)稀释到100 mL去离子水中,放于磁力搅拌器上,反应温度控制在(25±2) ℃. 取一定量的催化剂分散到水溶液中,打开氙灯,同时加入1 mmol·L−1的PMS开始反应. 每隔一段时间用针管抽取一定量的溶液,用0.45 μm滤头过滤,并加入1 mL亚硝酸钠猝灭剂. 过滤液用石英比色皿在波长484 nm下的紫外可见分光光度计测试AO7浓度.
1.4 材料的表征
采用Smartlab TM型号的X射线衍射测试仪来测试样品的物相结构;采用Nicolet 6700型的傅立叶红外光谱仪表征样品表面的官能团;采用Quanta FEG 250型的扫描分析仪对所有样品进行拍摄;采用Thermo Scientific Nexsa型的X射线光电子能谱仪对样品表面的元素价态进行分析;采用麦克ASAP 2460型号的全自动比表面积及孔隙率分析仪测定样品的比表面积及孔径;采用岛津UV3600IPLUS型的紫外/可见/近红外漫反射仪获得样品的吸收波长.
2. 结果与讨论 ( Results and discussion )
2.1 催化剂表征分析
2.1.1 XRD分析及FT-IR分析
采用X射线衍射(XRD)的方法研究催化剂的物相结构. 不同CTAB添加量BMO光催化剂的XRD谱图如图1a所示. 在纯BMO的情况下,2θ衍射峰约为10.9°、23.5°、28.3°、32.5°、32.6°、33.1°、47.1°、55.6°、58.4°. 所有的衍射峰均与正交相的Bi2MoO6标准卡片(PDF#72-1524)一致,对应(020)、(111)、(131)、(200)、(002)、(060)、(062)、(133)和(262)晶格面. CTAB-BMO的XRD衍射谱图与BMO的相似,未检测到杂质峰,说明样品纯度较高. 但与纯BMO相比,CTAB-BMO的衍射峰强度明显降低,表明对应晶面的结晶度降低. 这可能是由于氧空位在相应晶面产生,破坏了晶体的晶面结构.
图1b中傅立叶变换红外吸收光谱图 (FT-IR)可以清楚看出,在3387.41 cm−1和1571.6 cm−1处观察到的BMO特征峰归因于O—H的振动拉伸和收缩. 910—650 cm−1和630—430 cm−1的特征峰分别为Mo—O和Bi—O键拉伸振动引起的. 位于715 cm−1和547 cm−1处的特征峰分别代表MoO6结构中O2分子的不对称拉伸和MoO6的弯曲振动. 此外,0.10CTAB-BMO的FT-IR谱图与BMO的峰同样具有高度一致性.
2.1.2 SEM分析
通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)可以看出,CTAB的加入对BMO的形貌特征产生了很大的变化,如图2所示. 不论是否添加CTAB,最终样品的形态均为球形,主要是因为乙二醇(EG)的贡献. 乙二醇具有很强的螯合能力,当Bi(NO3)3·5H2O和Na2MoO4·2H2O溶于乙二醇中,可以在乙二醇中螯合形成醇盐,醇氧化物的生成大大的降低了溶液中游离Bi3+的浓度和反应速率. 另外乙二醇具有较高的溶剂黏度,产生较大的空间位阻,从而抑制纳米粒子的转移和团聚[9-10]. 图2a可以看出,纯BMO的平均直径在1 μm左右,由许多纳米球形微晶组成. 而在添加不同浓度CTAB之后,其纳米颗粒由球状变成了片状结构,微球的平均直径也有所增加. 0.05CTAB-BMO与纯BMO形貌相似,是因为CTAB的添加量较低,不足以改变其形貌特征. 而当CTAB的含量增加到0.1 g时,BMO微球中纳米粒子形状变成了片状结构,比表面积、平均直径也有所增加. 0.15CTAB-BMO的表面结构比较疏松,具有更高的孔隙结构,平均直径也达到了5 μm左右. BMO微球平均直径的增加有可能是因为CTAB与[MoO4]2−相互作用,抑制Bi2O3与[MoO4]2−的反应,形成更大的结构[11]. 本次实验主要对0.10CTAB-BMO进行分析,因为该催化剂具有形貌较好的纳米片状结构,催化性能有望增加.
2.1.3 XPS分析
通过XPS进一步对0.10CTAB-BMO催化材料的表面元素组成和化学价态进行深入分析. 图3a的全谱图检测到0.10CTAB-BMO的核心组成为Bi 4f、Mo 3d、O 1s、C 1s、N 1s和Br 3d. 值得注意的是,N 1s和Br 3d元素的峰可能是由于CTAB的添加. 然而,XRD的结果表明,CTAB-BMO没有发现多余的峰,可能原因是Br以非晶态存在,没有形成新的晶体取向. 首先用C 1s(284.8 eV)矫正各元素的结合能. Bi 4f的XPS谱图如图3b所示,电子结合能在159.38 eV和164.4 eV处的特征峰分别对应于Bi 4f7/2和Bi 4f5/2,,这主要是Bi3+的特点[12]. 图3c中,232.68 eV和235.88 eV处的结合能可以归因于Mo6+的Mo 3d5/2和Mo 3d3/2. 图3d为O 1s的XPS谱图,O 1s可以拟合为530.38 eV和532.18 eV处的两个分峰,在530.38 eV处的峰可以归结于晶格氧,在532.18eV处的峰可以归结于材料表面的羟基和吸附水形成的表面氧[13].
2.1.4 BET分析
通过N2吸附-脱附等温线和BJH孔径分布来分析合成催化剂的结构性质. 如图4a所示,催化剂吸附量随着压力的上升而增加,表现为Ⅲ型吸附等温线. 当催化剂处于脱附状态时表现为H3型回滞环,表明催化剂是纳米片堆叠而成的介孔结构. 图4b证明所有催化剂的孔径均在10 nm至50 nm之间. 从图4a的表格可以看到,BMO、0.05CTAB-BMO、0.10CTAB-BMO和0.15CTAB-BMO的比表面积、孔体积和平均孔径. CTAB的添加导致催化剂比表面积的增加,而孔径有所下降. 以上现象可能是由于CTAB的加入使氧空位浓度增加从而引起晶体结构破坏,产生更多的纳米片堆叠形成的介孔,此结果也符合SEM中催化剂的形貌. 比表面积的增加,有利于催化反应的活性点位增加,促进反应物的吸附及中间产物的脱附,从而提高催化活性.
2.1.5 UV-Vis DRS分析
采用UV-Vis DRS技术进一步研究了合成催化材料的光学性能,BMO及0.10CTAB-BMO催化剂的UV-Vis DRS谱图如图5所示. 图5a可以看出,两种材料的吸收边界均位于450 nm以上,对可见光都有明显的吸收作用. 此外,有CTAB添加的催化剂吸收波发生红移,说明可以吸收波长更长的光.
合成样品的禁带宽度(Eg)可从Kubelka-Munk方程近似得到:
αhν=A(hν−Eg)1/2 (1) 式中,A为比例常数,h为普朗克常数,ν为光频率,α为吸收系数. 由图5b可以清楚地看出,BMO和0.10CTAB-BMO的直接禁带宽度分别为2.68 eV和2.75 eV. 根据Mulliken电负性理论方程估计了0.10CTAB-BMO的边带位置,具体的价带(VB)和导带(CB)可由下列公示计算:
EVB=X−E0+0.5Eg (2) ECB=EVB−Eg (3) 式中,E0为氢电子自由能(4.5 eV),X为半导体的电负性,即组成原子电负性的几何平均值(5.17 eV),EVB为价带(VB),ECB为导带(CB),Eg为半导体的禁带宽度. 通过图5c VB-XPS计算可以得到0.10CTAB-BMO的VB和CB电位分别为2.05 eV和-0.70 eV. 结果表明,该材料具有合适的禁带宽度,是一种适合在可见光下催化降解污染物的催化剂.
2.2 催化降解性能分析
2.2.1 吸附-光催化和不同体系对AO7的降解性能
通过不同CTAB改性后的催化剂在14 W的氙灯照射下降解AO7的效果来探究其光催化性能. 从表1及图6a可以看出,CTAB改性的催化剂表现出了较强的吸附性,在暗反应30 min后,0.10CTAB-BMO对AO7的吸附率达到了38.9%. 结合图4a中数据,CTAB-BMO吸附量的提高有可能是因为添加CTAB使纳米颗粒的片状结构具有更多的比表面积和合适的氧空位浓度. 但是,0.15CTAB-BMO的吸附量少于0.10CTAB-BMO,可能是由于CTAB添加过多,导致其表面结构过于疏松. CTAB改性后的BMO光催化性能同样有所提高. 一是因为吸附对光降解效率是非常有利的,可以增大光催化剂与染料的接触,协同促进染料分子的降解[14]. 二是因为合适的氧空位浓度可以提供更多的反应活性位点.
表 1 各种催化剂的吸附/光催化性能Table 1. Adsorption / photocatalytic properties of various samples样品Sample AO7吸附率/%AO7 adsorption rate AO7光催化降解率/%AO7 photocatalytic degradation rate 总去除率/%The total removal rate kapp/min−1 BMO 3.1 7.4 10.5 0.00074 0.05CTAB-BMO 15.3 9.7 25.0 0.00192 0.10CTAB-BMO 38.9 13.6 52.5 0.00497 0.15CTAB-BMO 28.5 8.1 36.6 0.00304 为探究CTAB改性后的CTAB-BMO在可见光下与过一硫酸盐(PMS)的协同性能,设计了不同的反应体系,如图6b所示. 在光与PMS体系中,AO7的降解率为10.1%,由于光照条件下PMS可以被催化裂解产生具有活性的硫酸根自由基(SO4·−). 在黑暗条件下,0.10CTAB-BMO/PMS体系中的AO7降解率达到82.8%,说明在钼酸铋除了作为光催化剂外,在活化PMS降解污染物时,也具备良好的催化性能. 在可见光照射下,非均相0.10CTAB-BMO/PMS体系表现出最优的降解速率,对AO7的降解率可以在30 min达到99%以上. 由于0.10CTAB-BMO具有较大的比表面积和合适的氧空位浓度,提供了更多的吸附及反应活性位点. 此外,可见光的引入也能够对非均相过硫酸盐体系有良好的协同作用.
2.2.2 催化剂投加量的影响
图7a考察了不同0.10CTAB-BMO催化剂投加量(0.1、0.3、0.5 g·L−1)对AO7降解的影响.
当催化剂的投加量从0.1 g·L−1增加到0.5 g·L−1时,AO7在30 min时的降解率也从74.9%提高到了大于99%. 但是,当投加量从0.3 g·L−1增加到0.5 g·L−1时,后者的降解速率并没有提升过多. 是因为在一定浓度的PMS产生的自由基有限,导致AO7的降解速率没有增加过快. 另外,过量的催化剂可能会在悬浮液中过量聚集,增加反应溶液的浊度,从而影响可见光的透射率并降低可见光的吸收率.
2.2.3 初始pH的影响
许多文献报道,溶液的pH会影响污染物的降解效率. 与传统的Fenton相比,SR-AOP在较宽的pH范围内具有良好的反应活性. 图7b评估了0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系中在不同初始pH值下(3.0—11.0)的催化降解性能. 当pH值在3.0—9.0范围内,AO7可以在40 min内降解99%,说明该pH范围内AO7的降解效率没有受到太大影响. 但是当pH调至11时,AO7的降解率仅为58.5%. 因为在酸性和中性条件下,PMS主要以HSO5−为主,而在碱性条件下SO52−的浓度会迅速增加. 当溶液pH值在3.0—9.0时,SO4·−与OH−和H2O以适当的速率生成·OH,增强了AO7的降解速率. 而当溶液pH为11时,催化剂表面负电荷的增加会阻碍PMS的吸附;此外,由于SO52−的活化效果比HSO5−要弱,也会导致AO7的降解速率减慢[15-16].
2.2.4 初始污染物浓度的影响
为了研究AO7初始浓度影响,在AO7浓度为5—40 mmol·L−1范围内进行实验. 如图7c所示,随着AO7浓度的增加,降解效果明显下降. 随着AO7的初始浓度从5 mmol·L−1增加到40 mmol·L−1,AO7从20 min大于99%的降解率下降到40 min的75.6%. 主要是因为初始浓度较高的AO7溶液中缺乏足够的活性自由基.
2.2.5 水中共存离子及腐殖酸的影响
实际水体中存在许多可溶性的无机阴离子,会对0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系催化反应造成一定的影响. 本实验选用0.1 mmol·L−1的NaCl、Na2CO3作为Cl−、CO32−的来源,具体结果如图7所示. 印染废水中往往存在着大量的Cl−,部分文献说Cl−的存在可能会抑制污染物的降解. 而在本实验中Cl−存在条件下,0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系对AO7的降解有促进作用,大致可以归为一下两点:①Cl−除孔洞的能力,可以降低光生电子-空穴的复合率(式4)[17]. ②Cl−会与·OH和SO4·−发生一系列反应反生成氯自由基及二氯自由基,进一步生成具有氧化性质的HCIO(式5—9)[18].
2Cl−+2h+→Cl2 (4) Cl−+SO⋅−4→SO2−4+Cl⋅ (5) Cl⋅+Cl−→Cl⋅−2 (6) Cl−+⋅OH→OH−+Cl⋅ (7) Cl⋅+Cl⋅−2→Cl2+Cl− (8) Cl2+H2O→HClO (9) 溶液中存在一定量的CO32−会对AO7的降解起到明显的抑制作用,当加入100 mmol·L−1 Na2CO3时,AO7在60 min内仅降解了52.4%,去除效率降低的主要原因是CO32−与目标污染物竞争·OH和SO4·−,生成活性较低的CO3·−(式10—11)[19-20],但是CO3·−的稳定性较差,AO7对其反应活性较低,导致去除率不高.
SO⋅−4+CO2−3→CO⋅−3+SO2−4 (10) ⋅OH+CO2−3→CO⋅−3+OH− (11) 引入自然有机物(NOM)模型化合物腐殖酸(HA)对污染物的降解有着重要的影响. 当加入0.1 g·L−1 HA后,AO7的降解受到了抑制,45 min反应时间内的去除率为73.2%. 分析原因认为因为HA是天然的有机质,在反应体系内与目标污染物竞争活性物种.
2.3 AO7降解机理
为了研究0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系降解AO7过程中活性物种,采用乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)、对苯醌(p-BQ)、糠醇(FFA)、叔丁醇(TBA)、异丙醇(IPA)分别作为h+、·O2−、1O2、·OH和·OH/SO4·−的猝灭剂来进行捕获实验. 如图8所示,体系内不存在任何猝灭剂时,30 min内99%的AO7的被降解. 当溶液中加入IPA、TBA后,在30 min时AO7的降解率分别降低至59.8%和87.6%. 而在添加EDTA-2Na、p-BQ、FFA后可以看出明显的抑制了AO7的降解,降解率在60 min内均不超过30%. 结果表明,在0.1CTAB-BMO/光/PMS降解AO7体系中产生的活性物质有h+、·O2−、1O2、·OH和SO4·−,其中h+、·O2−、1O2对于AO7降解的贡献要高于·OH和SO4·−.
根据实验及分析结果,本研究提出0.1CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系催化降解AO7可能的催化反应机理. 该体系CTAB-BMO微球具有较大的比表面积和合适的氧空位浓度,能够提供更多的吸附反应活性位点,用于吸附活性物质. 同时,PMS在水中的溶解度远大于氧气在水中的溶解度,所以氧空位能够更好地吸收离子态的HSO5−. 可见光照射下,0.1CTAB-BMO光催化剂被激发产生光生电子(e−)和空穴(h+)(式12)[21],合适浓度的氧空位可以作为电子捕获中心,阻止光生电子和空穴的复合. 由于0.1CTAB-BMO的CB电位为-0.70 eV,低于O2/·O2−的电位值(E0=-0.33 V),故光生电子e−不仅能与PMS反应生成SO4·−(式13),而且能与O2反应生成·O2−(式14)[22]. 通过加入FFA消除实验我们得到1O2在AO7的降解过程中也起到了非常重要的作用. 已有研究报道,1O2是PMS活化过程中的一种选择性活性氧,1O2可以通过PMS自身分解产生,也可以通过与超氧自由基重组形成(式15—17) [23]. 生成·OH的方法主要有两种,一方面,h+可以与H2O/OH−生成H+和·OH(式18). 另一方面,由于SO4·−/SO42−的氧化还原电位(2.5—3.1 eV)高于·OH,所以也可以与H2O/OH−生成·OH(式19—20)[24-25]. 最终,AO7在活性物种(h+、·O2−、1O2、·OH和SO4·−)的共同作用下分解成更小的分子物质甚至是无毒无害的CO2和H2O(式21). 图9提供了0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系降解AO7过程中的反应机理示意图.
Catalyst+hv→e−+h+ (12) e−+HSO−5→SO⋅−4+OH− (13) O2+e−→⋅O−2 (14) ⋅O−2+⋅O−2+2H+→1O2+H2O2 (15) ⋅O−2+H2O2→1O2+OH−+⋅OH (16) ⋅O−2+⋅OH→1O2+OH− (17) h++H2O→H++⋅OH (18) SO⋅−4+H2O→H++⋅OH+SO2−4 (19) SO⋅−4+OH−→⋅OH+SO2−4 (20) (h+、⋅O−2、1O2、⋅OHandSO⋅−4)+AO7→Products (21) 2.4 材料的重复利用性与稳定性
为了考察0.1CTAB-BMO催化剂的可回收性和稳定性,进行了连续去除实验. 在每次实验条件相同下反应60 min后,通过抽滤装置收集材料颗粒,用酒精和去离子水洗涤若干次,放入60 ℃烘箱干燥6 h后,重新分散到新的AO7溶液中进行下次实验. 图10可以看到,在重复了5次实验后,AO7依然可以在60 min内达到99%以上的去除率. 结果表明0.1CTAB-BMO纳米微球催化剂是一种良好且稳定的催化剂.
3. 结论 ( Conclusion )
(1)通过水热法成功制备了CTAB-BMO催化剂,CTAB的引入改变了钼酸铋的形貌特征,提供了合适的氧空位浓度. 当0.10CTAB-BMO为0.3 g·L−1、AO7为0.1 mmol·L−1、PMS为1 mmol·L−1、14 W氙灯的照射下,AO7可以在30 min内完全去除(>99%),0.1CTAB-BMO在被重复利用5次后,60 min内对AO7的降解率仍然高达99%,说明催化剂具有高效性和稳定性.
(2)0.10CTAB-BMO/光/PMS体系可以在较宽的初始pH(3.0—9.0)范围内表现出较高的AO7降解率. 一定量的Cl−可以促进AO7的降解,而CO32−和HA的加入会起明显的抑制作用.
(3)通过猝灭表明,催化剂存在多个活性物种(h+、·O2−、1O2、·OH和SO4·−)并协同降解AO7污染物,其中h+、·O2−和1O2起着主要作用.
-
表 1 各种催化剂的吸附/光催化性能
Table 1. Adsorption / photocatalytic properties of various samples
样品Sample AO7吸附率/%AO7 adsorption rate AO7光催化降解率/%AO7 photocatalytic degradation rate 总去除率/%The total removal rate kapp/min−1 BMO 3.1 7.4 10.5 0.00074 0.05CTAB-BMO 15.3 9.7 25.0 0.00192 0.10CTAB-BMO 38.9 13.6 52.5 0.00497 0.15CTAB-BMO 28.5 8.1 36.6 0.00304 -
[1] NOORIMOTLAGH Z, MIRZAEE S A, MARTINEZ S S, et al. Adsorption of textile dye in activated carbons prepared from DVD and CD wastes modified with multi-wall carbon nanotubes: Equilibrium isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic study [J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2019, 141: 290-301. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2018.11.007 [2] HAN F, KAMBALA V S R, DHARMARAJAN R, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dye acid orange 7 using different light sources over Fe3+-doped TiO2 nanocatalysts [J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2018, 12: 27-42. [3] 毕文龙, 郝茜华, 刘奋武, 等. 硫酸根自由基对活性炭吸附刚果红的影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(1): 190-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.01.021 BI W L, HAO X H, LIU F W, et al. Effect of sulfate radical on adsorption of Congo red by activated carbon [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(1): 190-197(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.01.021
[4] ZHAO G Q, ZOU J, CHEN X Q, et al. Iron-based catalysts for persulfate-based advanced oxidation process: Microstructure, property and tailoring [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 421: 127845. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127845 [5] PELAEZ M, NOLAN N T, PILLAI S C, et al. A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 125: 331-349. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.05.036 [6] ZHENG Y, ZHOU T, ZHAO X, et al. Atomic interface engineering and electric-field effect in ultrathin Bi2MoO6 nanosheets for superior lithium ion storage [J]. Advanced Materials , 2017, 29(26): 1700396. [7] 张琴, 汪晓凤, 段芳, 等. Bi2MoO6中空微球的制备及其光催化性能 [J]. 无机化学学报, 2015, 31(11): 2152-2158. ZHANG Q, WANG X F, DUAN F, et al. Bi2MoO6 hollow microspheres preparation and photocatalytic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 31(11): 2152-2158(in Chinese).
[8] WANG S Y, DING X, YANG N, et al. Insight into the effect of bromine on facet-dependent surface oxygen vacancies construction and stabilization of Bi2MoO6 for efficient photocatalytic NO removal [J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 265: 118585. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118585 [9] BI J H, CHE J G, WU L, et al. Effects of the solvent on the structure, morphology and photocatalytic properties of Bi2MoO6 in the solvothermal process [J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2013, 48(6): 2071-2075. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.02.033 [10] CHANKHANITTHA T, SOMAUDON V, PHOTIWAT T, et al. Preparation, characterization, and photocatalytic study of solvothermally grown CTAB-capped Bi2WO6 photocatalyst toward photodegradation of Rhodamine B dye [J]. Optical Materials, 2021, 117: 111183. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111183 [11] YANG Z X, SHEN M, DAI K, et al. Controllable synthesis of Bi2MoO6 nanosheets and their facet-dependent visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 430: 505-514. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.072 [12] 徐梦秋, 柴波, 闫俊涛, 等. Bi2MoO6/Ag3PO4复合光催化剂的制备及其光催化性能 [J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2018, 46(1): 93-100. XU M Q, CHAI B, YAN J T, et al. Preparation of Bi2MoO6/Ag3PO4 composites with enhanced photocatalytic activities [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 46(1): 93-100(in Chinese).
[13] GUO J, SHEN C H, SUN J, et al. Highly efficient activation of peroxymonosulfate by Co3O4/Bi2MoO6 p-n heterostructure composites for the degradation of norfloxacin under visible light irradiation [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 259: 118109. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118109 [14] 王丹军, 申会东, 郭莉, 等. BiOBr/Bi2MoO6异质结的构筑及对甲基橙的吸附/光催化性能的协同作用机制 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(5): 1751-1762. WANG D J, SHEN H D, GUO L, et al. The fabrication of BiOBr/Bi2MoO6 heterojunction with enhanced adsorption performance for methyl-orange via synergistic adsorption/photocatalysis effect [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(5): 1751-1762(in Chinese).
[15] HAN F M, YE X, CHEN Q, et al. The oxidative degradation of diclofenac using the activation of peroxymonosulfate by BiFeO3 microspheres—Kinetics, role of visible light and decay pathways [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 232: 115967. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115967 [16] XU M J, LI J, YAN Y, et al. Catalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole through peroxymonosulfate activated with expanded graphite loaded CoFe2O4 particles [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 369: 403-413. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.075 [17] MAHMOODI N M, ARAMI M, LIMAEE N Y, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of agricultural N-heterocyclic organic pollutants using immobilized nanoparticles of titania [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 145(1/2): 65-71. [18] 王柯晴, 徐劼, 陈家斌, 等. 氧基氯化铁非均相活化过一硫酸盐降解金橙Ⅱ [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(8): 3385-3393. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.08.016 WANG K Q, XU J, CHEN J B, et al. Degradation of AO7 by PMS activated by FeOCl [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(8): 3385-3393(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.08.016
[19] JI Y F, DONG C X, KONG D Y, et al. New insights into atrazine degradation by cobalt catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation: Kinetics, reaction products and transformation mechanisms [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 285: 491-500. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.026 [20] LIANG C J, WANG Z S, MOHANTY N. Influences of carbonate and chloride ions on persulfate oxidation of trichloroethylene at 20 ℃ [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 370(2/3): 271-277. [21] ZHU L, ZHENG L, XIE H, et al. Design and properties of FeAl/Al2O3/TiO2 composite tritium-resistant coating prepared through pack cementation and Sol-gel method [J]. Materials Today Communications, 2021, 26: 101848. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101848 [22] SHEIKHMOHAMMADI A, ASGARI E, NOURMORADI H, et al. Ultrasound-assisted decomposition of metronidazole by synthesized TiO2/Fe3O4 nanocatalyst: Influencing factors and mechanisms [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(5): 105844. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105844 [23] ZHANG X, CHEN S H, LIAN X Y, et al. Efficient activation of peroxydisulfate by g-C3N4/Bi2MoO6 nanocomposite for enhanced organic pollutants degradation through non-radical dominated oxidation processes [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 607: 684-697. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.08.198 [24] JI Y F, KONG D Y, LU J H, et al. Cobalt catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation of tetrabromobisphenol A: Kinetics, reaction pathways, and formation of brominated by-products [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 313: 229-237. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.033 [25] GHORAI K, BHATTACHARJEE M, MANDAL D, et al. Facile synthesis of CuCr2O4/BiOBr nanocomposite and its photocatalytic activity towards RhB and tetracycline hydrochloride degradation under household visible LED light irradiation [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 867: 157947. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157947 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王静,李喜兰,丘宇锴,刘续兴,陈成志. Nb_2O_5/Nb_2C催化剂的制备及其光催化NO转化的性能. 当代化工. 2024(05): 1148-1152 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 褚一威,靳凤先,马同宇,郭盛祺. 十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)辅助水热法制备介孔Nb_2O_5及其光催化性能. 环境化学. 2024(10): 3527-3537 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载: