-
Feammox是在厌氧的环境条件下以及微生物的催化作用下,能够实现以Fe(Ⅲ)为电子受体,NH4+为电子供体,发生类似于Anammox的氨氧化反应,且最终实现Fe(Ⅲ)还原和NH4+的氧化过程,也称之为厌氧铁氨氧化过程。Feammox作为一种新型的生物脱氮反应,其自然反应广泛存在于湿地、河流及湖泊底泥、稻田、旱地土壤等不同环境体系中[1-4]。Feammox反应过程中NH4+被氧化生成NO2−、NO3−和N2后,氮的损失可通过反硝化或Anammox进行[5],且其可直接产生N2的途径使得氮循环路径极大程度的缩短,并导致生态系统氮的损失[4]。此过程不但对陆地生态系统和水生生态系统具有重大意义,对整个自然界间氮的循环机制产生更深层次的认知和理解。
Feammox是由微生物驱使的生物脱氮过程,Feammox菌是Feammox反应的驱动者。Huang等[5]在2015年首次分离出了能够同时发生铵氧化和铁还原的嗜酸微生物科细菌A6(Acidimicrobiaceae bacterium A6)。Huang等[6]研究发现,A6能够以无机碳(CO2)作为碳源将NH4+氧化的同时还原Fe(Ⅲ),对NH4+的去除率可达52%。A6对重金属也具有一定的耐受性,Gilson等[7]研究发现在铀(U)污染的湿地沉积物中依然存在A6,并且其在厌氧状态下能将U(VI)作为电子受体还原和氧化NH4+。相比于氨氧化细菌,Feammox菌在厌氧条件下反应,以Fe(Ⅲ)替代氧作为电子受体,因此不需供氧且产生较少的N2O[8]。根据Feammox的脱氮特点,相比于传统的硝化反硝化脱氮,Feammox工艺应用于污水中可实现自养脱氮,不需要外加碳源和曝气,减少污泥量的生成,对解决低碳氮比(C/N)废水反硝化过程碳源不足问题,以及含重金属废水的处理具有一定的可行性和理论依据。
本文综述了Feammox反应机理以及Fe(Ⅲ)还原过程中电子传递机制,并探讨Feammox对自然界中氮损失的贡献程度及对生态环境的影响,最后分析了Feammox在污水脱氮领域的探索和应用,对其未来发展趋势进行了总结和归纳。
-
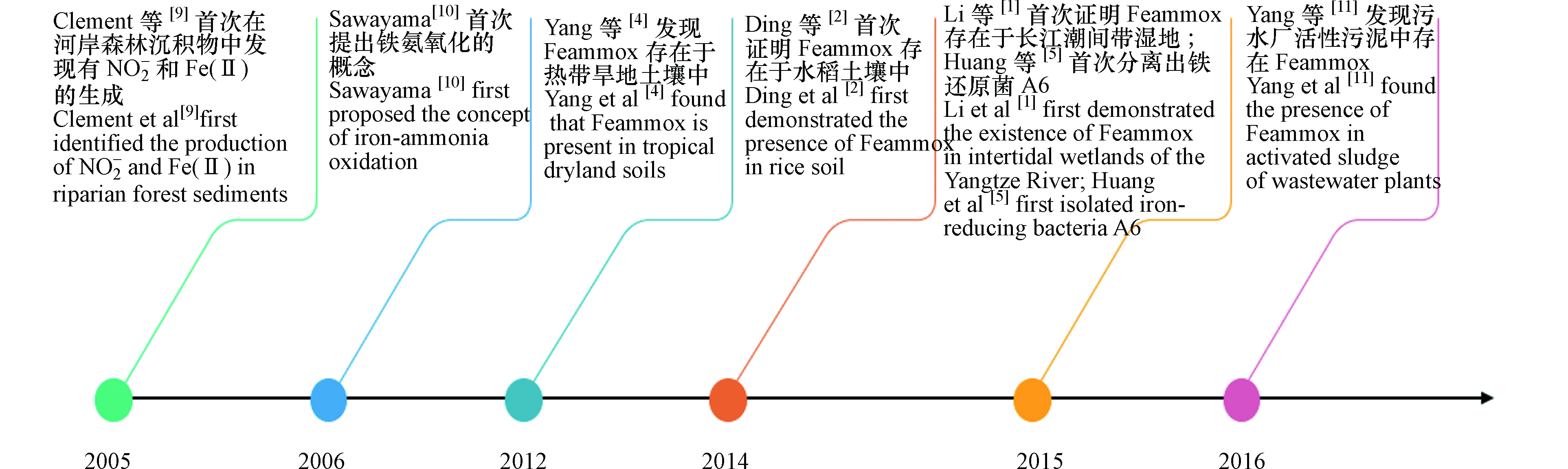
Feammox作为新发现的氮素转化机制,近几年来对其不断深入研究取得较多进展,Feammox主要研究历史节点如图1。Feammox反应最早发现在2005年,Clément等[9]在探索河岸森林沉积物中铁和氮循环的动力学时,发现在厌氧条件下,测定的沉积物样品中有NO2−和Fe(Ⅱ)的意外产生。因此猜测有一生物过程使用Fe(Ⅲ)作为电子受体,同时氧化NH4+生成NO2−,Fe(Ⅲ)被还原为Fe(Ⅱ)。在2006年,Sawayama通过实验研究,在厌氧的条件下含有NH4+、乙二胺四乙酸铁钠(EDTA-Fe)和碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)的固定床反应器流出物中有NO2−生成,且流出的NO2−浓度与添加的NaHCO3和EDTA-Fe的浓度呈正比,证明铁还原微生物以NaHCO3为无机碳源将NH4+转化为NO2−,Fe(Ⅲ)还原为Fe(Ⅱ),并将此反应命名为Feammox过程[10]。2012年,Yang等[4]使用同位素标记的铵和Fe(Ⅲ)培养热带旱地土壤泥浆,研究发现Feammox在热带旱地土壤中能产生N2、NO2−或NO3−,且Feammox的主要途径是产生N2。2014年,Ding等[2]使用15N标记的铵基同位素示踪和乙炔抑制技术,首次证明Feammox存在于水稻土壤中,且Feammox是造成水稻土壤中氮损失的一个重要途径。2015年,Li等[1]在长江潮间带湿地沉积物中检测到Feammox,其潜在速率为0.24—0.36 µg·g−1·d−1 。2017年,Yang等[11]对污水厂产生的污泥进行厌氧消化,通过添加磁铁矿、Fe2O3和Fe(OH)3的3种不同类型的Fe(Ⅲ)源可诱导Feammox发生,其中Fe(OH)3效果最佳且对总氮的去除率达到了20.1%。添加三价铁化合物使得活性污泥中含有的铁能够改善和强化污泥的絮体结构[12],不仅可减少污泥体积和增加甲烷产量也可诱导Feammox产生去除污泥中的铵,减轻活性污泥对环境的危害[11],给水厂污泥固体废弃物的处置提供了较好的方法和新颖的思路。
-
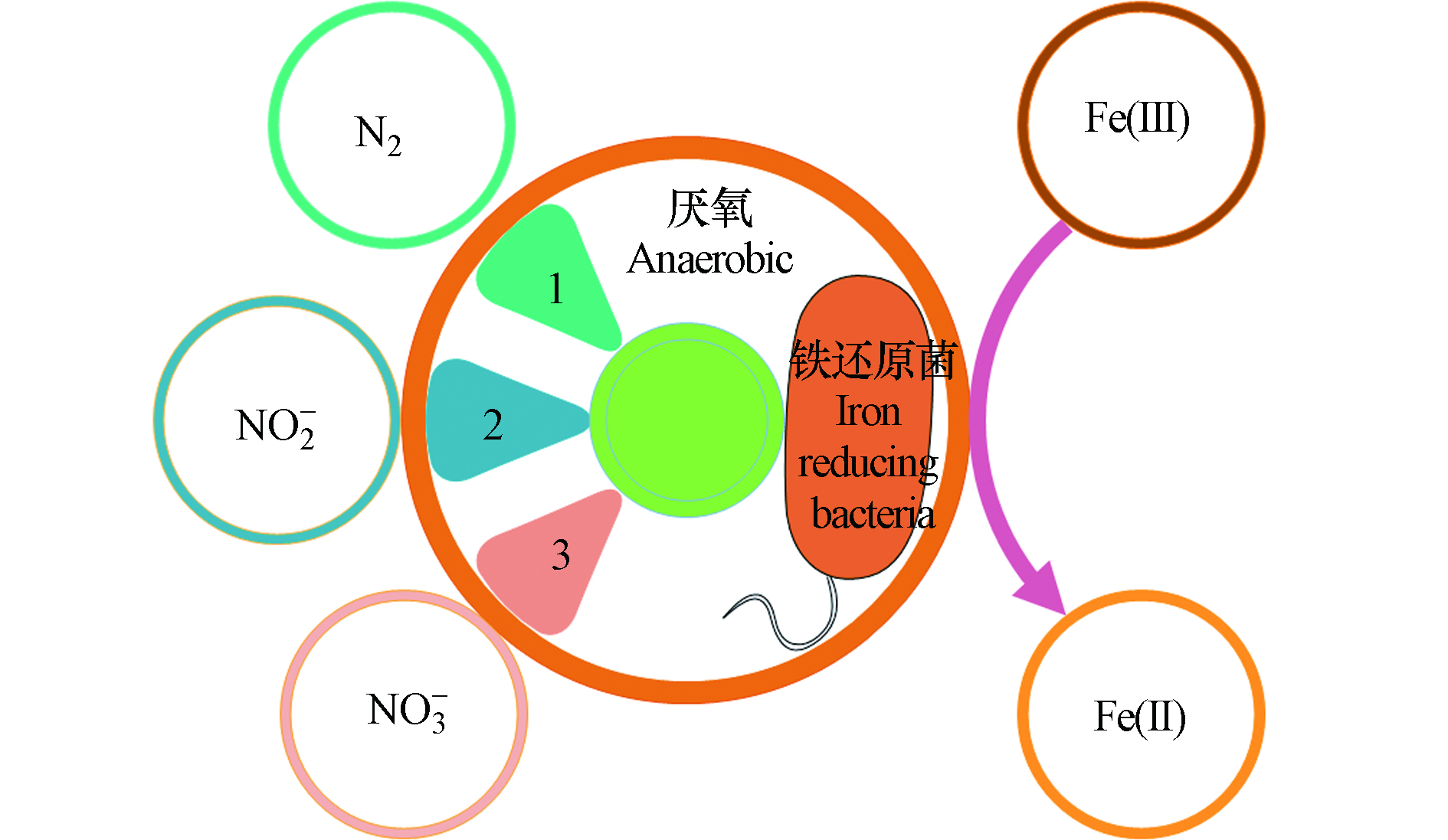
Feammox反应是在厌氧条件下,以及铁还原菌的驱使作用下,以三价铁为最终电子受体,氨氮为电子供体发生的生化反应,其反应产物有N2、NO2−、NO3−的3种不同形态的氮素(图2)。
Feammox反应机制极为复杂,致使Feammox产物氮素形态差异的原因尚不明确[13-14]。不同形态下的三价铁化合物作为电子供体Feammox的反应方程式及吉布斯自由能(ΔG)如表1。
不同形态的三价铁化合物作为电子受体,以及产物的不同其ΔG均有所差异。3种不同形态的铁化合物的ΔG均小于零,其反应均可自发进行。从热力学角度分析,电子受体为Fe(OH)3时,通过测定生成物为N2的反应ΔG为−245 kJ·mol−1 ,小于生成物为NO2−和NO3−的ΔG。另外生成N2的反应在相同条件下氧化NH4+所需Fe(Ⅲ)的量更少且产生能量更多,反应进程中消耗的铁氮比(Fe/N)为3∶1,而生成物为NO2−和NO3−的反应所消耗的Fe/N值分别为6∶1和8∶1。该反应又能够适应于较宽范围的pH,而NO2−和NO3−的生成要求pH值小于6.5,因此相比之下N2更易生成[4,15]。Yang等[4]研究证明了旱地土壤中N2的产生是Feammox主要反应途径。而Shrestha等[16]研究发现在没有任何NO2−或NO3−的湿地土壤中,并在厌氧和铁还原条件下,NH4+被氧化成了NO2−。在生成物为NO2−时,Fe(OH)3作为电子供体更易促进反应的进行,其反应ΔG为−164 kJ·mol−1,而FeOOH和Fe2O3·0.5H2O作为电子供体的Feammox反应ΔG为−30.90 kJ·mol−1和小于−145.08 kJ·mol−1,这也可为Feammox研究电子受体材料的选取提供一定理论依据。
-
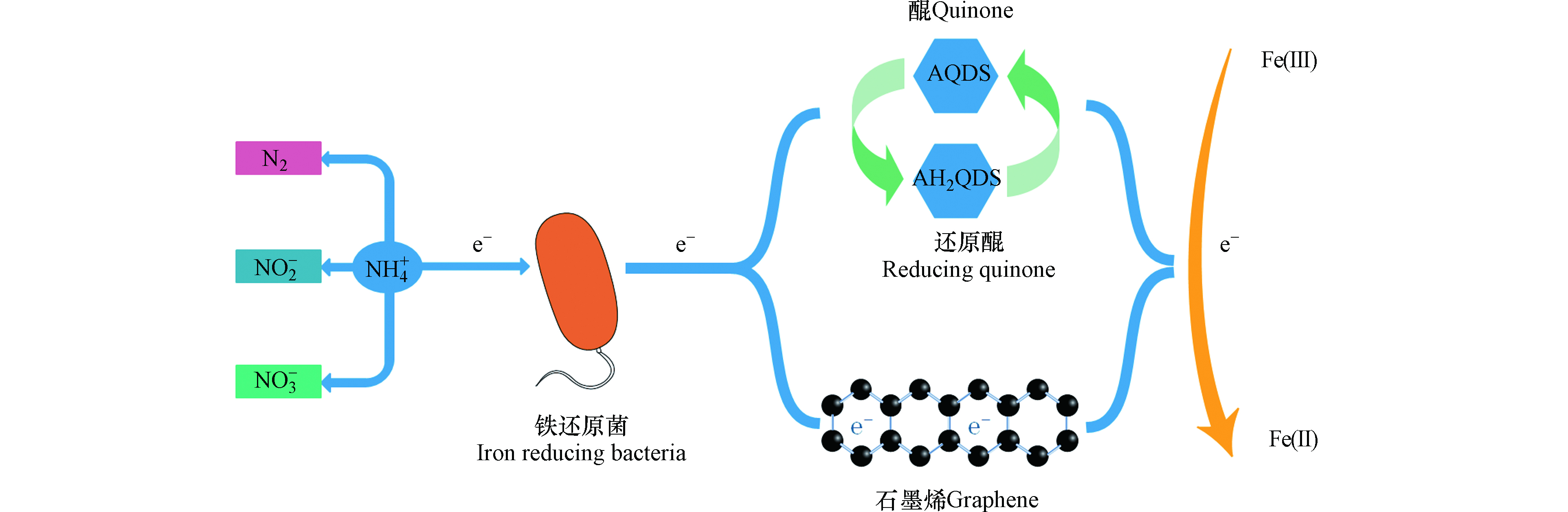
电子穿梭体是一种可溶性的小分子有机物或无机物,可通过自身的氧化还原作用加速微生物向细胞外部进行电子传递,间接电子传递和直接电子传递是胞外电子传递的两种主要方式,而穿梭体介导的电子传递属于间接电子传递[17-19]。电子穿梭体的来源可分为内生电子穿梭体(如黄素类化合物、黑色素、吩嗪化合物、醌类物质等)和外生电子穿梭体(如腐殖质、蒽醌、萘醌、半胱氨酸、硫单质、维生素等)[20-23],其中微生物自身能分泌的物质称为内生电子穿梭体,而能利用天然存在或人工合成的某些物质为外生电子穿梭体[24]。目前研究发现铁还原菌能够利用蒽醌、腐殖质和生物炭等作为电子穿梭体以其为电子载体向Fe(Ⅲ)输送电子(图3)[6,15,24]。Yang等[25]也通过实验证明AQDS和AH2QDS可作为铵与Fe2O3之间的电子传递体,能够成功地促进NH4+的氧化提升脱氮效率,并通过对比发现,添加AQDS的脱氮效率达到82.6%,而未添加AQDS的脱氮效率仅为64.3%。廖宏燕等[26]对螯合铁介导的Feammox脱氮效果进行了研究,研究发现腐殖酸铁介导的反应脱氮效果较好,总氮和氨氮去除率达到83.32%和83.68%,并推测N2是螯合铁介导Feammox反应的主要产物。腐殖酸的电子穿梭作用关键在于其所含有的醌基基团,而醌基基团可接受还原腐殖质的电子,并且研究发现腐殖质中醌基自由基的含量越高其电子接受能力也越高[27-28]。
通过固体导电介质的电子传导与电子穿梭体的分子扩散有一定的区别,固体材料的电子传导响应于电压差促使电子迁移,而水溶性的电子穿梭体在于浓度梯度产生的扩散[29]。生物炭作为一种固态材料,形态上虽区别于其它的水溶性电子穿梭体,其仍可以起到电子穿梭体的作用。Zhou等[30]研究了不同粒径的生物炭对异化铁还原菌(DIRB)和产甲烷菌的影响,发现在水铁矿富集物中加入生物炭后,DIRB菌和产甲烷菌均得到了富集,尺寸较小的粉末状生物炭对Fe(Ⅲ)还原效果更好。由于生物炭具有的芳香结构和氧化还原活性的醌类化合物有助于微生物细胞和不溶性矿物质之间的胞外电子转移,因此促进了Fe(Ⅲ)的还原效率[30-31]。另外Song等[32]研究发现活性炭表面的氧化还原活性含氧官能团对微生物还原Fe(Ⅲ)有促进作用,通过实验证明,经由HNO3改性处理的活性炭增加了表面官能团醌与氢醌的数量,并在兼性细菌MR-1的作用下Fe(Ⅲ)的还原率将近100%,与原始活性炭相比,Fe(Ⅲ)在还原率和还原程度上都有极大提高,活性炭具有的良好的氧化还原特性,使得其电子接受和电子供给能力发挥了极大作用。但是通过生物炭的电子传输不全归因于醌部分,Chen等[29]认为通过生物炭的电子传递也归因于生物炭自身材料的导电特性,并且发现附着在生物炭上的金属还原菌和巴氏杆菌可通过生物炭进行两个物种之间的电子转移,而不是通过细胞间的电子转移。显然生物炭能成为电子传递的通道,使得电子不通过细胞间的接触进行传递。另外Guan等[33]在红树林沉积物中加入石墨烯和9,10-蒽醌-2-磺酸酯(AQS),使得Feammox速率分别提高了31%和56%,但石墨烯参与的Feammox的Fe(Ⅲ)还原仅占总Fe(Ⅲ)还原的1.5%—4.9%,可能石墨烯具有的导电性能促使了部分电子转移给了Fe(Ⅲ),使得Fe(Ⅲ)得到还原。
石墨烯和生物炭作为固性材料均具有导电性能,但石墨烯不具有氢醌结构又能够促进Fe(Ⅲ)还原和Feammox反应速率,这也表明石墨烯和生物炭一样能够起到电子传递的桥梁作用,并与其它水溶性电子穿梭体的传递机制显著不同。目前对电子穿梭机制并没有完全的认知和了解,但随着对电子穿梭体传递电子机制的不断探究对Feammox的反应机理研究有极大帮助。
-
在土壤环境体系中最常见的氮去除是有机氮矿化,其次是硝化作用,然后是反硝化作用[34]。但Feammox在陆地生态系统中的显著活动,造成了土壤中一定量的氮损失(表2),大量的NH4+被直接或间接氧化生成N2,也在一定程度下缓轻了陆地生态系统生境破坏和水生生态系统中水体富营养化的现象[35]。
不同类型的土壤中Feammox速率和对氮损失的贡献占比略有差异,这与土壤的pH、总有机碳(TOC)、土壤Fe(Ⅲ)含量、土壤水分和铁还原微生物的丰度差异等诸多因素有关[2,5,36-37]。另外,Feammox速率也受季节和空间的影响。Ding等[38]对太湖流域万山地区的农田土壤、河岸土壤和河流沉积物在夏冬两季的Feammox速率以及铁还原菌的多样性和丰度进行了研究,结果发现,在夏季Feammox速率为0.05—0.19 µg·g−1·d−1大于冬季的0.02—0.09 µg·g−1·d−1,农田土壤中的Feammox速率最大,其后依次为河岸土壤和河流沉积物,土壤水分、Fe(Ⅲ)含量和TOC是影响Feammox速率和铁还原菌多样性的重要因素。而在水稻土壤中,由于其富含有Fe(Ⅲ)和高浓度的NH4+的特征,以及在水淹没状态下产生的厌氧环境,可能为Feammox发生过程及其相关的微生物提供了良好条件[39]。Li等[39]利用同15N同位素示踪技术证实了Feammox在我国南方水稻土中的存在,发现水稻土壤中约6.91%的施用氮肥的流失是由Feammox造成的,并对Feammox相关的微生物群落进行了研究,地杆菌属、GOUTA 19、 Nitrososphaeraceae和假单胞菌属为Feammox发生的潜在驱动力,而pH、土壤粒径、NH4+、C/N和TN是影响这些微生物组成的重要因素。Qin等[40]对位于太湖沿岸不同深度之间的水稻土的Feammox速率进行了研究,结果发现,Feammox在稻田深度为20—30 cm的区域活性最强,其速率为0.313—0.427 µg·g−1·d−1,在水稻表层土壤0—10 cm处,94.72%—96.89%的氮素流失是由反硝化造成的,反硝化作用是造成水稻表层土壤氮损失的最主要原因,而10 cm以下深层土壤的氮损失则由Feammox主导。Yi等[41]研究了施肥对水稻土中Feammox的影响,研究表明施肥可以丰富土壤中Fe(Ⅲ)和有机碳的含量,进而加速电子传递过程,刺激Feammox反应进程,并有助于微生物群落的转移,改变水稻土中微生物的氮转化过程。施肥能够导致反应底物NH4+和 NO3−含量升高,改变土壤理化性质,进而影响土壤微生物群落结构和功能微生物数量,尤其是有机肥对土壤中Feammox菌(A6)数量提升具有促进作用[42-43]。丁帮璟等[44]通过测定Feammox在菜地土壤中的反应速率,Feammox脱氮贡献占比为7.3%—12.4%,且Feammox速率与土壤Fe(Ⅲ)和TOC含量呈正相关性,约85%的N2生成是由反硝化和Anammox所贡献。在各项研究中可知,反硝化在土壤氮损失中起到最主要作用,而Feammox和Anammox等其它过程对土壤氮损失也占有一定比例,在土壤中Feammox和Anammox以及反硝化在各自反应过程中可能存在一定的联系。Ding等[36]研究发现在太湖河口地区Feammox、Anammox和反硝化分别约占总氮损失的3.5%—4.2%、2.8%—3.9%和92.6%—93.1%,并且发现Feammox速率和反硝化速率之间存在显著相关性,两者之间可能存在协同作用,但Feammox和Anammox之间并未发现具有明显的相关性。Feammox和Anammox可能会发生耦合作用,但是两者对NH4+的利用也会存在竞争[1,36],Feammox和反硝化存在关联可能是因为Feammox还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ)供给了反硝化利用[45],或者Feammox产生的NO3− 或NO2−被反硝化利用促进N2产生。
Feammox的发现和相关研究目前多在于陆地生态系统,其在海洋生态系统中的相关研究和报道较于陆地生态系统相对较少。海洋生态系统中的氮循环除了固氮和反硝化两大过程能够改变氮形态并起到关键的转化过程之外,氨化、硝化、Anammox和异化硝酸盐还原为铵(DNRA)等过程也是海洋生态系统氮循环和造成氮损失的重要途径[46]。此外,Toro等[47]在海洋沉积物中发现Anammox与依赖硫化物的反硝化之间的耦合作用,可同时去除与NO2−还原相关的铵和硫化物,这种耦合作用能力也可能会造成海洋中的氮损失。Emilia等[48]研究发现海洋沉积物中普遍存在依赖硫酸盐的厌氧氨氧化(Sulfammox)和Feammox反应过程,而沉积物中的Feammox速率达到2 µg·g−1·d−1N。这也表明了在极其复杂的海洋氮循环中,Feammox过程是参与氮循环和氮损失不可忽视的组成部分。Laufer等[49]在沿海海岸沉积物中研究发现存在自养的硝酸盐还原Fe(Ⅱ)氧化细菌,这种依赖于Fe(Ⅱ)的反硝化作用同样可能成为造成海洋氮损失的重要途径。另外,依赖型Fe(Ⅱ)反硝化的Fe(Ⅱ)源也可能来源于Feammox反应过程中还原产生的Fe(Ⅱ),在陆地土壤和海洋沉积物中,这两种反应极都有可能存在耦合作用。
不管Feammox存在于何种环境体系,其参与的氮转换途径已经成为计算全球氮损失不可缺少的一部分计算过程,并占有重要比例。Feammox过程的出现会改变以往反硝化和厌氧氨氧化等其它脱氮过程对自然界中氮去除的贡献格局,从而形成新的脱氮贡献格局,对氮污染的去除具有重大意义[50]。在实际环境体系中的复杂氮循环过程中,Feammox和其它各种复杂的反应过程之间存在怎样的关联,又如何通过相互之间的作用影响氮的损失,则需要进一步的探索和研究。
-
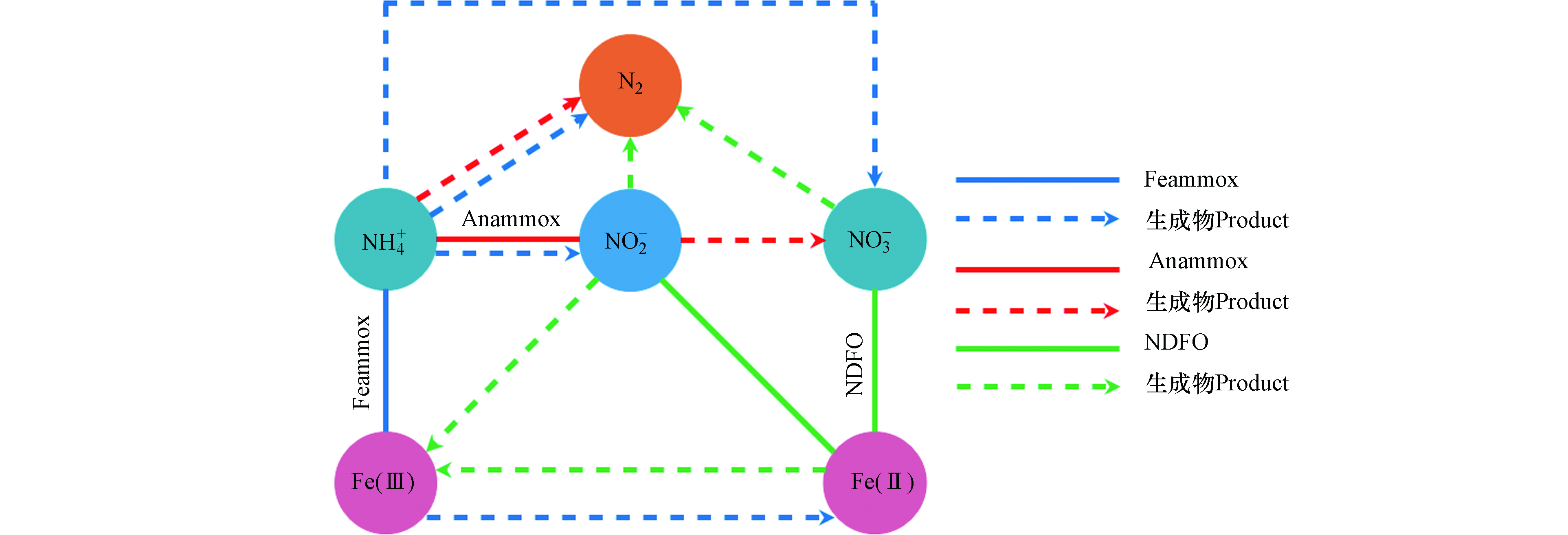
在污水处理中,氮素不同形态之间的转换是一个较为复杂的过程,微生物驱使作用下的污水生物脱氮主要包含有氨化、同化、硝化、反硝化、完全氨氧化(Comammox)、Anammox、Sulfammox、Feammox、亚硝酸盐/硝酸盐型厌氧甲烷氧化(n-DAMO)和DNRA等反应过程[51]。在污水生物脱氮过程中,Feammox反应生成的NO2−会被Anammox菌利用与NH4+反应生成N2,Anammox会伴随着Feammox反应进行而发生耦合作用(图4)。Li等[52]对Anammox与Feammox耦合的可行性及特点进行了研究,在含有Anammox的活性污泥的反应器中,以Fe(Ⅲ)作为电子受体进行厌氧反应,在反应器流出物中检测出有NO2−、NO3−和Fe(Ⅱ)的生成,且污泥中保留有Anammox菌,表明在Anammox污泥中存在Fe(Ⅲ)还原和NH4+氧化反应。另外,Park等[53]以养猪废水处理厂的厌氧污泥作为培养物的反应器中发现NH4+的氧化去除不仅促进了Fe(Ⅲ)的还原,而且有助于Anammox反应。刘恒蔚等[54]利用微生物技术对Anammox反应器和接种了Anammox污泥的Feammox反应器中的功能微生物进行了对比分析,发现Anammox菌均占主导地位,但Feammox反应器中微生物群落结构与Anammox反应器相比具明显的差异性。以上研究表明,以接种Anammox污泥启动的Feammox反应系统中,存在以NO2−或Fe(Ⅲ)为电子受体的氨氧化脱氮过程[55],但当NO2−与Fe(Ⅲ)同时作为电子受体反应时,Anammox优先于Feammox反应[56],其中Anammox脱氮占有重要比例,这也是Feammox与Anammox能够进行耦合反应的重要前提基础。另外值得注意的是,在反应系统中除了Feammox反应能够将Fe(Ⅲ)还原为Fe(Ⅱ)外,Anammox菌也具有还原Fe(Ⅲ)的能力,有研究报道称,Anammox菌能以有机物作为电子供体将Fe(Ⅲ)还原为Fe(Ⅱ),且其还原Fe(Ⅲ)的活性受pH、电子供体和受体种类的影响[57]。Zhao等[57]研究发现以甲酸盐和Fe(Ⅲ)-NTA分别作为电子受体和供体,在pH 7的条件下,Anammox菌具有较高的铁还原活性。在实际反应过程中,系统中会存在一定浓度的Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ),有关研究表明,适当的Fe(Ⅱ)浓度能够促进Anammox菌生长速率,显著提高Anammox活性[58]。Fe(Ⅱ)能够通过提高Anammox菌细胞内的总铁、血红素C和联氨脱氢酶活性,从而更好地刺激Anammox菌生长,不仅对其丰度有促进作用,还能够提升Anammox脱氮效率和诱导更多基因表达[59-62],并根据这一特点,有些研究者便通过投加适量的Fe(Ⅱ)来缩短Anammox反应器的启动时间[60]。同样研究发现,适量的Fe(Ⅲ)也能够提高Anammox菌16S rRNA及功能基因hzsB的丰度,并提升对氮的去除率[63],但过高的Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)浓度则均会抑制Anammox菌活性。
值得思考和研究的问题是,在Anammox与Feammox耦合反应过程中,NH4+作为电子供体,反应进程中是否对NH4+存在显著竞争,系统中存在的Fe(Ⅲ)和Feammox还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ),以及在合适条件下Anammox菌自身拥有的Fe(Ⅲ)还原能力所还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ),是否会对Anammox菌起到促进作用,以致使其更好的利用Feammox反应产生的NO2−,并促进Feammox和Anammox的耦合反应,这些可能受Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)形态的存留时间及相应浓度,系统反应条件等综合因素的影响。
Feammox和铁型反硝化(NDFO)也存在耦合反应(图4),在Feammox反应进程中通过氧化NH4+而还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ)可为亚铁氧化细菌还原NO3−提供电子供体,氧化生成的Fe(Ⅲ)可再次被铁还原菌利用[8,64-65]。Li等[66]将Feammox污泥接种在含有Fe(Ⅲ)、NH4+和NO3−的反应器中,通过同位素和微生物群落分析,证明了反应器中存在Feammox、Anammox和NDFO过程,在运行62d后发现,67.6%的NH4+和58.8%的NO3−能够同时进行转化去除,并且成功实现了Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)的循环转换。吴悦溪等[56]利用二沉池普通活性污泥培养Feammox,并分析了Feammox反应系统中存在的脱氮途径及其对NH4+的去除的贡献程度,结果发现,反应系统中是由Feammox主导并存在与Anammox和NDFO的耦合作用,57.7%的NH4+是由Feammox反应去除,而Anammox对NH4+的去除占42.3%。Feammox和NDFO的耦合反应,理论上可实现Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)的再生循环转换,但在实际反应中除了受各种复杂影响因素之外,值得注意的是Feammox的产物并不全是NOx−。因此,NDFO生成的Fe(Ⅲ)的量具有一定的局限性,Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)并不以等量的方式进行循环再生,需要补充额外的NO3−来氧化Fe(Ⅱ)产生Fe(Ⅲ)[67]。Yang等[67]便通过添加NaNO3提供NO3−,利用Feammox和NDFO的耦合作用触发Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)循环,进而去除NH4+。结果发现总氮的去除率达到了90.1%,而未提供NO3−的对照组总氮去除率仅为41.6%。NO3−的加入极大提升了脱氮效率,且NO3− 还原产生的NO2−可以进一步氧化Fe(Ⅱ)。但较高的NO2−浓度可能会对NO3−的还原起到抑制作用[68],由于Fe(Ⅱ)会被NO2−氧化生成Fe的氢氧化物,这种Fe的氢氧化物会附着在细胞表面造成细胞结壳,使得细胞的代谢和活性受到抑制而导致NO3−无法还原[69]。另外,有关研究者发现当使用螯合铁Fe(Ⅱ)-EDTA时,Fe(Ⅱ)的氧化则是由微生物催化,而不会被NO2−氧化致使细胞产生结壳现象[70]。Zhou等[68]利用可将硝酸盐还原和Fe(Ⅱ)氧化的NDFO菌株W5接种到海绵铁填充的生物滤池中,当进水NO2−浓度为10 mg·L−1时,NO3−的去除率达到最低为50.35%。另外以FeSO4作为Fe(Ⅱ)源,其浓度从800 mg·L−1增加到1500 mg·L−1时,细胞结壳严重NO3−去除率降低,而以Fe(Ⅱ)-EDTA做为Fe(Ⅱ)源且浓度为1100 mg·L−1时,脱氮效率可达到90%。NO3−和NO2−均能够将Fe(Ⅱ)氧化生成Fe(Ⅲ),除了通过补充NO3−之外,也可直接补充NO2−,这也是直接弥补系统中Fe(Ⅲ)量不足的有效方式,也避免通过直接投加Fe(Ⅲ)造成铁泥污染现象的发生。Yang等[71]便通过向Feammox反应系统间歇的添加NO2−,NO2−能够氧化Fe(Ⅱ),Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)的浓度在NO2−的添加下分别上升和减少,并随着NO2−的消耗以及Feammox的作用下分别下降和上升。NO2−的添加诱导了Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)之间的循环转换,并在Feammox的作用下,NH4+的去除率达到96%,且反应过程没有检测到Anammox菌,系统中没有发生Anammox反应。
Feammox和NDFO的耦合作用机制是触发系统中Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)循环的有利前提,也是通过利用Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)之间的循环转换而去除氮的主要启示来源,利用外来投加适量的NO3−和NO2−作为末端电子受体,保持系统中Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)循环平衡进而脱氮,其所具有的可行性使得Feammox运用于污水脱氮具有一定的理论和实践基础。Feammox与Anammox和NDFO的耦合作用能够强化脱氮过程,提升脱氮效率,但其作用机制及影响因素较为复杂,因此分析耦合作用影响因素,研究多变量因素之间的协同作用,确定最佳可控反应条件,以及深入研究各反应对氮去除的贡献程度,可为未来实际污水脱氮应用提供重要理论依据并具有重大实际意义。
-
目前,Feammox在污水脱氮中的应用仍处于初级探索阶段[72],利用Feammox处理实际废水的研究比较少,并且Feammox反应主要是NH4+和Fe(Ⅲ)之间发生的反应,因此对模拟废水中的NH4+去除研究较多。目前Feammox反应启动及对氮去除的主要技术手段有:(1)向反应器添加从土壤中富集培养出的Feammox菌液;(2)利用Anammox污泥培养驯化出Feammox污泥来启动Feammox反应;(3)利用微生物固定化技术将Feammox菌固定化。实验选取的反应器类型主要有ASBR、MBR和血清瓶等装置(表3)。
李海晖等[75]对实际污水进行了研究,通过向城市生活污水、和矿山废水中添加使用NH4+和Fe(Ⅲ)富集培养出的Feammox菌液,来探讨Feammox对实际废水中NH4+的去除效果。结果发现,经过10d的反应,城市生活污水中的NH4+浓度由初始203.94 mg·L−1降低至122.26 mg·L−1,去除率为40.05%,矿山废水中的NH4+去除率达到了44.64%。表明Feammox对实际废水中的NH4+去除起到了良好的效果。吴胤等[74]通过配置不同NH4+浓度的模拟废水来探讨对Feammox反应所产生的影响,向NH4+浓度分别为75 mg·L−1、150 mg·L−1和400 mg·L−1的模拟废水中加入Feammox菌液并进行厌氧反应。结果发现,反应15d后,初始NH4+浓度为75 mg·L−1和150 mg·L−1的反应器中,NH4+去除率分别为41.49%和7.45%,而在NH4+浓度为400 mg·L−1的模拟废水中Feammox反应受到抑制,表明在低氨氮废水中Feammox能起到较好的反应。姚海楠等[73]考虑到Feammox菌对重金属具有耐受性,便利用处理垃圾渗滤液的Anammox污泥作为接种污泥启动Feammox反应,并同样探究了不同NH4+浓度对Feammox反应的影响。当进水NH4+浓度为400 mg·L−1时,经过12 d反应,NH4+的转换量为40.69 mg·L−1,也同样证明了Feammox反应在高氨氮废水中对NH4+的去除率小于在低氨氮废水中,另外还发现反应器中的NO3−的生成量与NH4+的转化量差异不大,反应器中的NH4+主要转化为了NO3−。Feammox菌对重金属具有较强的耐受性,能对重金属起到固定效应并可降低其在污水中的毒性[73-74],这也可能是Feammox能够在NH4+浓度为400 mg·L−1和Fe(Ⅲ)浓度为500 mg·L−1的高浓度废水中仍能发生反应的重要原因[73]。此外,Feammox处理垃圾渗滤液过程也受pH的影响,Wang等[76]利用Feammox处理垃圾渗滤液的过程中研究发现,在pH 4.5时,垃圾渗滤液的反硝化效果最好,而在pH 3.5时的酸性环境中Feammox菌大量死亡。大量研究表明Feammox反应偏向于酸性环境,但过酸环境会抑制其反应,并导致微生物死亡。刘志文等[77]利用微生物固定化技术,使用磁性壳聚糖凝胶球(MCHBs)将Feammox菌固定化,并探讨其与游离菌液对NH4+的去除效果及差异。结果发现,在进水NH4+ 浓度为60 mg·L−1运行16 d后,粒径为1—2 mm的MCHBs 对NH4+的去除比游离细菌高出17.39%,达到了53.62%,实验过程中NH4+ 主要转换为了NO3−,而NO2−与N2只有少量的生成。Feammox反应过程中,由于NH4+作为电子供体,也是最佳的研究去除对象和目标污染物,对于低氨氮废水Feammox反应对NH4+的去除具有一定效果,但并不显著,因此对于高氨氮废水仍需求有效的解决方式。Yang等[78]向含有高NH4+的Feammox反应器中间歇的充气,在充气条件下,O2作为末端电子受体将Feammox还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ)氧化为Fe(Ⅲ),实现Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)循环,进而持续发生Feammox反应进行连续脱氮,最终总氮的去除率达到98.5%。与以往添加NO2−和NO3−实现铁循环进行脱氮不同的是,此充气方式简单且来源易得,可避免二次污染,对未来实际高氨氮废水的去除具有更简便的方式和广泛的适用性。虽然Feammox是自养脱氮过程,但Le等[79]研究了在有机碳源存在下的Feammox的氨氧化过程,研究发现Feammox能够与异养条件产生耦合作用,在进水COD与NH4+浓度分别为250 mg·L−1和200 mg·L−1,确定并控制两者最佳浓度比值为1.4,pH为中性的条件下,COD与NH4+的去除率达到了98.3%和58.8%,且反应最终产物为N2。此研究在有机碳的存在下显著提升了NH4+的去除,彻底实现了由NH4+转化为N2,并具有较高的去除率,对于一些NH4+和COD含量高的废水具有巨大的应用潜力。Feammox反应过程需要Fe(Ⅲ)源,铁的氧化物形态多样且廉价易得,Zhu等[80]通过添加不同的Fe(Ⅲ)化合物,以探索铁氧化物和碳源在废水处理中对NH4+的去除影响,结果表明,添加Fe2O3的反应器中引发的Feammox反应对NH4+去除效果最好,其去除负荷高达0.06 g·m−3·d−1。而与Le研究不同的是,在无COD的情况下NH4+的去除率为53%,比有COD的反应器高出23%,在反应器存在有机碳源的情况下,有机物抑制了Fe(Ⅲ)还原,也可能如Le的研究所示,当COD与NH4+浓度存在合适的比值时,才能对NH4+进行高效去除,但在有机碳源存在的情况下,其浓度大小如何影响对NH4+的去除需要进一步研究。
根据目前的研究现状,Feammox在污水处理方面的研究还相对单薄,且其所涉及的相关性功能微生物目前尚未统一[51]。除了目前已知的与Feammox相关的微小杆菌(Exiguobacterium spp)、A6菌、铁还原菌、以及利用Anammox污泥培养Feammox获得的Anammox菌之外,在污水处理领域中尚未分离出纯的Feammox菌种[10,24,52]。Feammox菌作为厌氧自养细菌,具有独特的代谢机制,在反应的过程中具有无需提供氧气和碳源并产生较少N2O的特点[66],有利于与其他脱氮反应联合应用于低碳氮比污水的处理[81]。Zhu等[82]便将Feammox与生物电化学系统相结合,两者的耦合反应对NH4+的去除率比单独Feammox反应高出38.8%,且此系统具有较低的能耗和运行成本。因此,一旦Feammox工艺成功运行于实际污水处理中,将会大幅减小污水厂曝气量和外投加碳源的经济成本,并减少污泥产量和温室气体排放[83],这也是Feammox应用于工程上所具有的独特优势和潜能。
-
Feammox作为新型的氮循环转换途径,在陆地和海洋沉积物中均有Feammox作用的发生,并参与其所在环境体系氮的损失,也是构成全球自然生态系统中氮损失的重要组成部分。经过近些年来的不断探索研究,Feammox在污水脱氮领域具有巨大的应用潜力,尤其是对废水中NH4+ 的去除具有较好的效果。另外,Feammox能够与Anammox和NDFO进行耦合脱氮,为污水中氮素的去除开辟了新的方法和途径,因此Feammox工艺脱氮也是继Anammox工艺脱氮之后备受瞩目的研究热点。
然而Feammox污水脱氮仍处于初步探索阶段,应用于实际工程中,仍具有一定的距离和面临着诸多挑战。在未来的发展中Feammox应注重以下研究:(1)目前发现的Feammox菌的种类比较少,与Feammox相关的功能性微生物没有统一,现已知的A6菌是唯一能起到纯Feammox作用的菌种。应从微生物宏基因和蛋白质组学领域作为出发点,研究Feammox的发生情景和其所处环境微生物的多样性,通过分析特定功能微生物及其所受影响因子,进一步剖析Feammox的作用机制。(2)Feammox反应的产物含有NO2−和NO3−,通过深入研究Feammox与Anammox和NDFO的耦合作用机制,确定耦合过程最佳反应条件,给污水中氮素的高效去除和精确的反应控制提供可靠的参考方案。有效地与NDFO反应进行结合,通过实现Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)的循环转换对氮素进行脱除,实现更加节约资源的绿色环保脱氮。(3)深入探究铁还原菌作用下的胞外电子传递机制,不仅对实现铁循环和加快Feammox反应速率具有重大意义,也对污水高效脱氮和Feammox作用机理的研究提供有力依据。
铁氨氧化研究进展及在污水脱氮中的应用探索
Research progress of Feammox and its application in wastewater denitrification
-
摘要: 近几年来,铁氨氧化(Feammox)反应在不同的环境体系中相继被发现。Feammox反应是在厌氧环境中以及微生物的驱使作用下,NH4+和Fe(Ⅲ)分别作为电子供体和电子受体,Fe(Ⅲ)被还原生成为Fe(Ⅱ),而NH4+则转化生成为亚硝酸盐(NO2−)、硝酸盐(NO3−)和氮气(N2)几种不同形态的氮素。Feammox的发现进一步揭示了氮素在自然界循环中的新的转化途径,这种新的氮素转换途径给污水领域中的脱氮技术方法带来了全新视角。另外,Feammox能够和厌氧氨氧化(Anammox)和铁型反硝化(NDFO)耦合或者通过实现Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)之间的循环转化进行脱氮,使得Feammox成为了一种潜在的新型脱氮技术。通过综述Feammox的发展历程、反应机制、以及对自然界生态系统所产生的的影响和其所受影响的物理性因素,最后,进一步探讨Feammox在污水脱氮中的应用,并对其未来发展进行总结和展望。Abstract: The Feammox reaction has been discovered in different environmental systems in recent years.The Feammox reaction occurs in an anaerobic environment and under the action of microorganisms. During the reaction, ammonia and Fe(Ⅲ) act as electron donors and electron acceptors respectively, Fe(Ⅲ) is reduced to Fe(Ⅱ), while ammonia is converted Nitrogen is produced in the form of nitrite (NO2−), nitrate (NO3−) and nitrogen (N2).The discovery of Feammox further reveals a new conversion pathway of nitrogen in the natural cycle, and this new conversion pathway of nitrogen brings a new perspective to the technology of denitrification in the sewage field.This process can also be coupled with Anammox and Iron Type Denitrification (NDFO) or through the cyclic conversion between Fe(Ⅲ) and Fe(Ⅱ) for nitrogen removal, which makes Feammox a potential Nitrogen removal technology.the article summarizes the development process and reaction mechanism of Feammox, as well as the impact on the natural ecosystem and the physical factors affected, and finally discusses its application and future development in wastewater denitrification.
-
Key words:
- Feammox /
- Nitrogen cycle /
- Denitrification technology /
- Anammox
-
Feammox是在厌氧的环境条件下以及微生物的催化作用下,能够实现以Fe(Ⅲ)为电子受体,NH4+为电子供体,发生类似于Anammox的氨氧化反应,且最终实现Fe(Ⅲ)还原和NH4+的氧化过程,也称之为厌氧铁氨氧化过程。Feammox作为一种新型的生物脱氮反应,其自然反应广泛存在于湿地、河流及湖泊底泥、稻田、旱地土壤等不同环境体系中[1-4]。Feammox反应过程中NH4+被氧化生成NO2−、NO3−和N2后,氮的损失可通过反硝化或Anammox进行[5],且其可直接产生N2的途径使得氮循环路径极大程度的缩短,并导致生态系统氮的损失[4]。此过程不但对陆地生态系统和水生生态系统具有重大意义,对整个自然界间氮的循环机制产生更深层次的认知和理解。
Feammox是由微生物驱使的生物脱氮过程,Feammox菌是Feammox反应的驱动者。Huang等[5]在2015年首次分离出了能够同时发生铵氧化和铁还原的嗜酸微生物科细菌A6(Acidimicrobiaceae bacterium A6)。Huang等[6]研究发现,A6能够以无机碳(CO2)作为碳源将NH4+氧化的同时还原Fe(Ⅲ),对NH4+的去除率可达52%。A6对重金属也具有一定的耐受性,Gilson等[7]研究发现在铀(U)污染的湿地沉积物中依然存在A6,并且其在厌氧状态下能将U(VI)作为电子受体还原和氧化NH4+。相比于氨氧化细菌,Feammox菌在厌氧条件下反应,以Fe(Ⅲ)替代氧作为电子受体,因此不需供氧且产生较少的N2O[8]。根据Feammox的脱氮特点,相比于传统的硝化反硝化脱氮,Feammox工艺应用于污水中可实现自养脱氮,不需要外加碳源和曝气,减少污泥量的生成,对解决低碳氮比(C/N)废水反硝化过程碳源不足问题,以及含重金属废水的处理具有一定的可行性和理论依据。
本文综述了Feammox反应机理以及Fe(Ⅲ)还原过程中电子传递机制,并探讨Feammox对自然界中氮损失的贡献程度及对生态环境的影响,最后分析了Feammox在污水脱氮领域的探索和应用,对其未来发展趋势进行了总结和归纳。
1. 铁氨氧化研究进展(Research progress of Feammox)
1.1 铁氨氧化发展历程
Feammox作为新发现的氮素转化机制,近几年来对其不断深入研究取得较多进展,Feammox主要研究历史节点如图1。Feammox反应最早发现在2005年,Clément等[9]在探索河岸森林沉积物中铁和氮循环的动力学时,发现在厌氧条件下,测定的沉积物样品中有NO2−和Fe(Ⅱ)的意外产生。因此猜测有一生物过程使用Fe(Ⅲ)作为电子受体,同时氧化NH4+生成NO2−,Fe(Ⅲ)被还原为Fe(Ⅱ)。在2006年,Sawayama通过实验研究,在厌氧的条件下含有NH4+、乙二胺四乙酸铁钠(EDTA-Fe)和碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)的固定床反应器流出物中有NO2−生成,且流出的NO2−浓度与添加的NaHCO3和EDTA-Fe的浓度呈正比,证明铁还原微生物以NaHCO3为无机碳源将NH4+转化为NO2−,Fe(Ⅲ)还原为Fe(Ⅱ),并将此反应命名为Feammox过程[10]。2012年,Yang等[4]使用同位素标记的铵和Fe(Ⅲ)培养热带旱地土壤泥浆,研究发现Feammox在热带旱地土壤中能产生N2、NO2−或NO3−,且Feammox的主要途径是产生N2。2014年,Ding等[2]使用15N标记的铵基同位素示踪和乙炔抑制技术,首次证明Feammox存在于水稻土壤中,且Feammox是造成水稻土壤中氮损失的一个重要途径。2015年,Li等[1]在长江潮间带湿地沉积物中检测到Feammox,其潜在速率为0.24—0.36 µg·g−1·d−1 。2017年,Yang等[11]对污水厂产生的污泥进行厌氧消化,通过添加磁铁矿、Fe2O3和Fe(OH)3的3种不同类型的Fe(Ⅲ)源可诱导Feammox发生,其中Fe(OH)3效果最佳且对总氮的去除率达到了20.1%。添加三价铁化合物使得活性污泥中含有的铁能够改善和强化污泥的絮体结构[12],不仅可减少污泥体积和增加甲烷产量也可诱导Feammox产生去除污泥中的铵,减轻活性污泥对环境的危害[11],给水厂污泥固体废弃物的处置提供了较好的方法和新颖的思路。
1.2 铁氨氧化反应原理
Feammox反应是在厌氧条件下,以及铁还原菌的驱使作用下,以三价铁为最终电子受体,氨氮为电子供体发生的生化反应,其反应产物有N2、NO2−、NO3−的3种不同形态的氮素(图2)。
Feammox反应机制极为复杂,致使Feammox产物氮素形态差异的原因尚不明确[13-14]。不同形态下的三价铁化合物作为电子供体Feammox的反应方程式及吉布斯自由能(ΔG)如表1。
表 1 Feammox反应方程式及吉布斯自由能Table 1. Feammox reaction equation and Gibbs free energy电子受体Electron acceptor 化学反应方程式Chemical reaction equation 吉布斯自由能ΔG/( kJ·mol−1 )Gibbs free energy 参考文献Reference FeOOH 6FeOOH+10H++NH4+—6Fe2++8H++NO2− −30.9 [9] 3Fe(OH)3+5H++NH4+—3Fe2++9H2O+0.5N2 −245 [4] Fe(OH)3 6Fe(OH)3+10H++NH4+—6Fe2++16H2O+NO2− −164 8Fe(OH)3+14H++NH4+—8Fe2++ 21H2O+ NO3− −207 Fe2O3·0.5H2O 3Fe2O3·0.5H2O+10H++NH4+—6Fe2++8.5H2O+NO2− ≤−145.08 [5] 不同形态的三价铁化合物作为电子受体,以及产物的不同其ΔG均有所差异。3种不同形态的铁化合物的ΔG均小于零,其反应均可自发进行。从热力学角度分析,电子受体为Fe(OH)3时,通过测定生成物为N2的反应ΔG为−245 kJ·mol−1 ,小于生成物为NO2−和NO3−的ΔG。另外生成N2的反应在相同条件下氧化NH4+所需Fe(Ⅲ)的量更少且产生能量更多,反应进程中消耗的铁氮比(Fe/N)为3∶1,而生成物为NO2−和NO3−的反应所消耗的Fe/N值分别为6∶1和8∶1。该反应又能够适应于较宽范围的pH,而NO2−和NO3−的生成要求pH值小于6.5,因此相比之下N2更易生成[4,15]。Yang等[4]研究证明了旱地土壤中N2的产生是Feammox主要反应途径。而Shrestha等[16]研究发现在没有任何NO2−或NO3−的湿地土壤中,并在厌氧和铁还原条件下,NH4+被氧化成了NO2−。在生成物为NO2−时,Fe(OH)3作为电子供体更易促进反应的进行,其反应ΔG为−164 kJ·mol−1,而FeOOH和Fe2O3·0.5H2O作为电子供体的Feammox反应ΔG为−30.90 kJ·mol−1和小于−145.08 kJ·mol−1,这也可为Feammox研究电子受体材料的选取提供一定理论依据。
1.3 铁氨氧化电子传递机理
电子穿梭体是一种可溶性的小分子有机物或无机物,可通过自身的氧化还原作用加速微生物向细胞外部进行电子传递,间接电子传递和直接电子传递是胞外电子传递的两种主要方式,而穿梭体介导的电子传递属于间接电子传递[17-19]。电子穿梭体的来源可分为内生电子穿梭体(如黄素类化合物、黑色素、吩嗪化合物、醌类物质等)和外生电子穿梭体(如腐殖质、蒽醌、萘醌、半胱氨酸、硫单质、维生素等)[20-23],其中微生物自身能分泌的物质称为内生电子穿梭体,而能利用天然存在或人工合成的某些物质为外生电子穿梭体[24]。目前研究发现铁还原菌能够利用蒽醌、腐殖质和生物炭等作为电子穿梭体以其为电子载体向Fe(Ⅲ)输送电子(图3)[6,15,24]。Yang等[25]也通过实验证明AQDS和AH2QDS可作为铵与Fe2O3之间的电子传递体,能够成功地促进NH4+的氧化提升脱氮效率,并通过对比发现,添加AQDS的脱氮效率达到82.6%,而未添加AQDS的脱氮效率仅为64.3%。廖宏燕等[26]对螯合铁介导的Feammox脱氮效果进行了研究,研究发现腐殖酸铁介导的反应脱氮效果较好,总氮和氨氮去除率达到83.32%和83.68%,并推测N2是螯合铁介导Feammox反应的主要产物。腐殖酸的电子穿梭作用关键在于其所含有的醌基基团,而醌基基团可接受还原腐殖质的电子,并且研究发现腐殖质中醌基自由基的含量越高其电子接受能力也越高[27-28]。
通过固体导电介质的电子传导与电子穿梭体的分子扩散有一定的区别,固体材料的电子传导响应于电压差促使电子迁移,而水溶性的电子穿梭体在于浓度梯度产生的扩散[29]。生物炭作为一种固态材料,形态上虽区别于其它的水溶性电子穿梭体,其仍可以起到电子穿梭体的作用。Zhou等[30]研究了不同粒径的生物炭对异化铁还原菌(DIRB)和产甲烷菌的影响,发现在水铁矿富集物中加入生物炭后,DIRB菌和产甲烷菌均得到了富集,尺寸较小的粉末状生物炭对Fe(Ⅲ)还原效果更好。由于生物炭具有的芳香结构和氧化还原活性的醌类化合物有助于微生物细胞和不溶性矿物质之间的胞外电子转移,因此促进了Fe(Ⅲ)的还原效率[30-31]。另外Song等[32]研究发现活性炭表面的氧化还原活性含氧官能团对微生物还原Fe(Ⅲ)有促进作用,通过实验证明,经由HNO3改性处理的活性炭增加了表面官能团醌与氢醌的数量,并在兼性细菌MR-1的作用下Fe(Ⅲ)的还原率将近100%,与原始活性炭相比,Fe(Ⅲ)在还原率和还原程度上都有极大提高,活性炭具有的良好的氧化还原特性,使得其电子接受和电子供给能力发挥了极大作用。但是通过生物炭的电子传输不全归因于醌部分,Chen等[29]认为通过生物炭的电子传递也归因于生物炭自身材料的导电特性,并且发现附着在生物炭上的金属还原菌和巴氏杆菌可通过生物炭进行两个物种之间的电子转移,而不是通过细胞间的电子转移。显然生物炭能成为电子传递的通道,使得电子不通过细胞间的接触进行传递。另外Guan等[33]在红树林沉积物中加入石墨烯和9,10-蒽醌-2-磺酸酯(AQS),使得Feammox速率分别提高了31%和56%,但石墨烯参与的Feammox的Fe(Ⅲ)还原仅占总Fe(Ⅲ)还原的1.5%—4.9%,可能石墨烯具有的导电性能促使了部分电子转移给了Fe(Ⅲ),使得Fe(Ⅲ)得到还原。
石墨烯和生物炭作为固性材料均具有导电性能,但石墨烯不具有氢醌结构又能够促进Fe(Ⅲ)还原和Feammox反应速率,这也表明石墨烯和生物炭一样能够起到电子传递的桥梁作用,并与其它水溶性电子穿梭体的传递机制显著不同。目前对电子穿梭机制并没有完全的认知和了解,但随着对电子穿梭体传递电子机制的不断探究对Feammox的反应机理研究有极大帮助。
1.4 铁氨氧化参与的氮损失
在土壤环境体系中最常见的氮去除是有机氮矿化,其次是硝化作用,然后是反硝化作用[34]。但Feammox在陆地生态系统中的显著活动,造成了土壤中一定量的氮损失(表2),大量的NH4+被直接或间接氧化生成N2,也在一定程度下缓轻了陆地生态系统生境破坏和水生生态系统中水体富营养化的现象[35]。
表 2 铁氨氧化在自然界产生的氮损失Table 2. Nitrogen loss in nature due to Feammox样品Sample 来源地点Source location 铁氨氧化速率/(µg·g−1·d−1)Feammox rate 氮损失/(kg·ha-1·a-1)Nitrogen loss pH 文献Reference 热带旱地土壤 美国卢基洛山脉 0.19—0.45 — 4.25—6.15 [4] 丘陵水稻土壤 中国江西省金县(28°10'—28°45'N,116°1'—116°34'E) 0.17—0.59 7.8—61(占国内常规施氮肥3.9%—31%) 4.69—5.72 [2] 水稻土壤 江苏省金坛市(31°39'49.42”N , 119°28'4.12”E) 0.047—0.319 3.64(施肥土壤),15.97—24.91(不施肥土壤),(占国内常规施氮肥7.99%—12.45%) 6.25—6.76 [12] 潮间带湿地 中国上海崇明(31°30'N,121°59'E) 0.24—0.36 115—180(占长江湿地无机氮的3.1%—4.9%) 春潮(8.32—8.46),小潮(8.48—8.75) [1] 太湖底泥 太湖梅梁湾(31°31'39— 31°32' 30 N,120°10' 26—120°11' 70 E) 0.29(无藻区底泥),0.01—0.05(聚藻区底泥) — 7.26—7.43 [3] 河岸带土壤 太湖贡湖湾(31°27'32—31°28'01N, 120°19'27—120°21'18E) 0.25—0.29 — 6.87—7.42 [13] 菜地土壤 太湖流域宛山荡(31°34'32—31°36'30N, 120°30'12—120°32'24E) 0.06—0.23 — (占产生氮气的7.3%—12.4%) 4.50—5.21 [44] 农田土壤 太湖万山地区(31°35′15—31°35′27 N,120°28′43—120°30′32 E) 0.12—0.18 17.8(占总氮损失的4.2%) 7.23—7.43 [36] 不同类型的土壤中Feammox速率和对氮损失的贡献占比略有差异,这与土壤的pH、总有机碳(TOC)、土壤Fe(Ⅲ)含量、土壤水分和铁还原微生物的丰度差异等诸多因素有关[2,5,36-37]。另外,Feammox速率也受季节和空间的影响。Ding等[38]对太湖流域万山地区的农田土壤、河岸土壤和河流沉积物在夏冬两季的Feammox速率以及铁还原菌的多样性和丰度进行了研究,结果发现,在夏季Feammox速率为0.05—0.19 µg·g−1·d−1大于冬季的0.02—0.09 µg·g−1·d−1,农田土壤中的Feammox速率最大,其后依次为河岸土壤和河流沉积物,土壤水分、Fe(Ⅲ)含量和TOC是影响Feammox速率和铁还原菌多样性的重要因素。而在水稻土壤中,由于其富含有Fe(Ⅲ)和高浓度的NH4+的特征,以及在水淹没状态下产生的厌氧环境,可能为Feammox发生过程及其相关的微生物提供了良好条件[39]。Li等[39]利用同15N同位素示踪技术证实了Feammox在我国南方水稻土中的存在,发现水稻土壤中约6.91%的施用氮肥的流失是由Feammox造成的,并对Feammox相关的微生物群落进行了研究,地杆菌属、GOUTA 19、 Nitrososphaeraceae和假单胞菌属为Feammox发生的潜在驱动力,而pH、土壤粒径、NH4+、C/N和TN是影响这些微生物组成的重要因素。Qin等[40]对位于太湖沿岸不同深度之间的水稻土的Feammox速率进行了研究,结果发现,Feammox在稻田深度为20—30 cm的区域活性最强,其速率为0.313—0.427 µg·g−1·d−1,在水稻表层土壤0—10 cm处,94.72%—96.89%的氮素流失是由反硝化造成的,反硝化作用是造成水稻表层土壤氮损失的最主要原因,而10 cm以下深层土壤的氮损失则由Feammox主导。Yi等[41]研究了施肥对水稻土中Feammox的影响,研究表明施肥可以丰富土壤中Fe(Ⅲ)和有机碳的含量,进而加速电子传递过程,刺激Feammox反应进程,并有助于微生物群落的转移,改变水稻土中微生物的氮转化过程。施肥能够导致反应底物NH4+和 NO3−含量升高,改变土壤理化性质,进而影响土壤微生物群落结构和功能微生物数量,尤其是有机肥对土壤中Feammox菌(A6)数量提升具有促进作用[42-43]。丁帮璟等[44]通过测定Feammox在菜地土壤中的反应速率,Feammox脱氮贡献占比为7.3%—12.4%,且Feammox速率与土壤Fe(Ⅲ)和TOC含量呈正相关性,约85%的N2生成是由反硝化和Anammox所贡献。在各项研究中可知,反硝化在土壤氮损失中起到最主要作用,而Feammox和Anammox等其它过程对土壤氮损失也占有一定比例,在土壤中Feammox和Anammox以及反硝化在各自反应过程中可能存在一定的联系。Ding等[36]研究发现在太湖河口地区Feammox、Anammox和反硝化分别约占总氮损失的3.5%—4.2%、2.8%—3.9%和92.6%—93.1%,并且发现Feammox速率和反硝化速率之间存在显著相关性,两者之间可能存在协同作用,但Feammox和Anammox之间并未发现具有明显的相关性。Feammox和Anammox可能会发生耦合作用,但是两者对NH4+的利用也会存在竞争[1,36],Feammox和反硝化存在关联可能是因为Feammox还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ)供给了反硝化利用[45],或者Feammox产生的NO3− 或NO2−被反硝化利用促进N2产生。
Feammox的发现和相关研究目前多在于陆地生态系统,其在海洋生态系统中的相关研究和报道较于陆地生态系统相对较少。海洋生态系统中的氮循环除了固氮和反硝化两大过程能够改变氮形态并起到关键的转化过程之外,氨化、硝化、Anammox和异化硝酸盐还原为铵(DNRA)等过程也是海洋生态系统氮循环和造成氮损失的重要途径[46]。此外,Toro等[47]在海洋沉积物中发现Anammox与依赖硫化物的反硝化之间的耦合作用,可同时去除与NO2−还原相关的铵和硫化物,这种耦合作用能力也可能会造成海洋中的氮损失。Emilia等[48]研究发现海洋沉积物中普遍存在依赖硫酸盐的厌氧氨氧化(Sulfammox)和Feammox反应过程,而沉积物中的Feammox速率达到2 µg·g−1·d−1N。这也表明了在极其复杂的海洋氮循环中,Feammox过程是参与氮循环和氮损失不可忽视的组成部分。Laufer等[49]在沿海海岸沉积物中研究发现存在自养的硝酸盐还原Fe(Ⅱ)氧化细菌,这种依赖于Fe(Ⅱ)的反硝化作用同样可能成为造成海洋氮损失的重要途径。另外,依赖型Fe(Ⅱ)反硝化的Fe(Ⅱ)源也可能来源于Feammox反应过程中还原产生的Fe(Ⅱ),在陆地土壤和海洋沉积物中,这两种反应极都有可能存在耦合作用。
不管Feammox存在于何种环境体系,其参与的氮转换途径已经成为计算全球氮损失不可缺少的一部分计算过程,并占有重要比例。Feammox过程的出现会改变以往反硝化和厌氧氨氧化等其它脱氮过程对自然界中氮去除的贡献格局,从而形成新的脱氮贡献格局,对氮污染的去除具有重大意义[50]。在实际环境体系中的复杂氮循环过程中,Feammox和其它各种复杂的反应过程之间存在怎样的关联,又如何通过相互之间的作用影响氮的损失,则需要进一步的探索和研究。
2. 铁氨氧化在污水脱氮中的应用探索(Application of feammox in wastewater denitrification)
2.1 铁氨氧化耦合脱氮理论基础
在污水处理中,氮素不同形态之间的转换是一个较为复杂的过程,微生物驱使作用下的污水生物脱氮主要包含有氨化、同化、硝化、反硝化、完全氨氧化(Comammox)、Anammox、Sulfammox、Feammox、亚硝酸盐/硝酸盐型厌氧甲烷氧化(n-DAMO)和DNRA等反应过程[51]。在污水生物脱氮过程中,Feammox反应生成的NO2−会被Anammox菌利用与NH4+反应生成N2,Anammox会伴随着Feammox反应进行而发生耦合作用(图4)。Li等[52]对Anammox与Feammox耦合的可行性及特点进行了研究,在含有Anammox的活性污泥的反应器中,以Fe(Ⅲ)作为电子受体进行厌氧反应,在反应器流出物中检测出有NO2−、NO3−和Fe(Ⅱ)的生成,且污泥中保留有Anammox菌,表明在Anammox污泥中存在Fe(Ⅲ)还原和NH4+氧化反应。另外,Park等[53]以养猪废水处理厂的厌氧污泥作为培养物的反应器中发现NH4+的氧化去除不仅促进了Fe(Ⅲ)的还原,而且有助于Anammox反应。刘恒蔚等[54]利用微生物技术对Anammox反应器和接种了Anammox污泥的Feammox反应器中的功能微生物进行了对比分析,发现Anammox菌均占主导地位,但Feammox反应器中微生物群落结构与Anammox反应器相比具明显的差异性。以上研究表明,以接种Anammox污泥启动的Feammox反应系统中,存在以NO2−或Fe(Ⅲ)为电子受体的氨氧化脱氮过程[55],但当NO2−与Fe(Ⅲ)同时作为电子受体反应时,Anammox优先于Feammox反应[56],其中Anammox脱氮占有重要比例,这也是Feammox与Anammox能够进行耦合反应的重要前提基础。另外值得注意的是,在反应系统中除了Feammox反应能够将Fe(Ⅲ)还原为Fe(Ⅱ)外,Anammox菌也具有还原Fe(Ⅲ)的能力,有研究报道称,Anammox菌能以有机物作为电子供体将Fe(Ⅲ)还原为Fe(Ⅱ),且其还原Fe(Ⅲ)的活性受pH、电子供体和受体种类的影响[57]。Zhao等[57]研究发现以甲酸盐和Fe(Ⅲ)-NTA分别作为电子受体和供体,在pH 7的条件下,Anammox菌具有较高的铁还原活性。在实际反应过程中,系统中会存在一定浓度的Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ),有关研究表明,适当的Fe(Ⅱ)浓度能够促进Anammox菌生长速率,显著提高Anammox活性[58]。Fe(Ⅱ)能够通过提高Anammox菌细胞内的总铁、血红素C和联氨脱氢酶活性,从而更好地刺激Anammox菌生长,不仅对其丰度有促进作用,还能够提升Anammox脱氮效率和诱导更多基因表达[59-62],并根据这一特点,有些研究者便通过投加适量的Fe(Ⅱ)来缩短Anammox反应器的启动时间[60]。同样研究发现,适量的Fe(Ⅲ)也能够提高Anammox菌16S rRNA及功能基因hzsB的丰度,并提升对氮的去除率[63],但过高的Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)浓度则均会抑制Anammox菌活性。
值得思考和研究的问题是,在Anammox与Feammox耦合反应过程中,NH4+作为电子供体,反应进程中是否对NH4+存在显著竞争,系统中存在的Fe(Ⅲ)和Feammox还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ),以及在合适条件下Anammox菌自身拥有的Fe(Ⅲ)还原能力所还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ),是否会对Anammox菌起到促进作用,以致使其更好的利用Feammox反应产生的NO2−,并促进Feammox和Anammox的耦合反应,这些可能受Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)形态的存留时间及相应浓度,系统反应条件等综合因素的影响。
Feammox和铁型反硝化(NDFO)也存在耦合反应(图4),在Feammox反应进程中通过氧化NH4+而还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ)可为亚铁氧化细菌还原NO3−提供电子供体,氧化生成的Fe(Ⅲ)可再次被铁还原菌利用[8,64-65]。Li等[66]将Feammox污泥接种在含有Fe(Ⅲ)、NH4+和NO3−的反应器中,通过同位素和微生物群落分析,证明了反应器中存在Feammox、Anammox和NDFO过程,在运行62d后发现,67.6%的NH4+和58.8%的NO3−能够同时进行转化去除,并且成功实现了Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)的循环转换。吴悦溪等[56]利用二沉池普通活性污泥培养Feammox,并分析了Feammox反应系统中存在的脱氮途径及其对NH4+的去除的贡献程度,结果发现,反应系统中是由Feammox主导并存在与Anammox和NDFO的耦合作用,57.7%的NH4+是由Feammox反应去除,而Anammox对NH4+的去除占42.3%。Feammox和NDFO的耦合反应,理论上可实现Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)的再生循环转换,但在实际反应中除了受各种复杂影响因素之外,值得注意的是Feammox的产物并不全是NOx−。因此,NDFO生成的Fe(Ⅲ)的量具有一定的局限性,Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)并不以等量的方式进行循环再生,需要补充额外的NO3−来氧化Fe(Ⅱ)产生Fe(Ⅲ)[67]。Yang等[67]便通过添加NaNO3提供NO3−,利用Feammox和NDFO的耦合作用触发Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)循环,进而去除NH4+。结果发现总氮的去除率达到了90.1%,而未提供NO3−的对照组总氮去除率仅为41.6%。NO3−的加入极大提升了脱氮效率,且NO3− 还原产生的NO2−可以进一步氧化Fe(Ⅱ)。但较高的NO2−浓度可能会对NO3−的还原起到抑制作用[68],由于Fe(Ⅱ)会被NO2−氧化生成Fe的氢氧化物,这种Fe的氢氧化物会附着在细胞表面造成细胞结壳,使得细胞的代谢和活性受到抑制而导致NO3−无法还原[69]。另外,有关研究者发现当使用螯合铁Fe(Ⅱ)-EDTA时,Fe(Ⅱ)的氧化则是由微生物催化,而不会被NO2−氧化致使细胞产生结壳现象[70]。Zhou等[68]利用可将硝酸盐还原和Fe(Ⅱ)氧化的NDFO菌株W5接种到海绵铁填充的生物滤池中,当进水NO2−浓度为10 mg·L−1时,NO3−的去除率达到最低为50.35%。另外以FeSO4作为Fe(Ⅱ)源,其浓度从800 mg·L−1增加到1500 mg·L−1时,细胞结壳严重NO3−去除率降低,而以Fe(Ⅱ)-EDTA做为Fe(Ⅱ)源且浓度为1100 mg·L−1时,脱氮效率可达到90%。NO3−和NO2−均能够将Fe(Ⅱ)氧化生成Fe(Ⅲ),除了通过补充NO3−之外,也可直接补充NO2−,这也是直接弥补系统中Fe(Ⅲ)量不足的有效方式,也避免通过直接投加Fe(Ⅲ)造成铁泥污染现象的发生。Yang等[71]便通过向Feammox反应系统间歇的添加NO2−,NO2−能够氧化Fe(Ⅱ),Fe(Ⅱ)和Fe(Ⅲ)的浓度在NO2−的添加下分别上升和减少,并随着NO2−的消耗以及Feammox的作用下分别下降和上升。NO2−的添加诱导了Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)之间的循环转换,并在Feammox的作用下,NH4+的去除率达到96%,且反应过程没有检测到Anammox菌,系统中没有发生Anammox反应。
Feammox和NDFO的耦合作用机制是触发系统中Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)循环的有利前提,也是通过利用Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)之间的循环转换而去除氮的主要启示来源,利用外来投加适量的NO3−和NO2−作为末端电子受体,保持系统中Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)循环平衡进而脱氮,其所具有的可行性使得Feammox运用于污水脱氮具有一定的理论和实践基础。Feammox与Anammox和NDFO的耦合作用能够强化脱氮过程,提升脱氮效率,但其作用机制及影响因素较为复杂,因此分析耦合作用影响因素,研究多变量因素之间的协同作用,确定最佳可控反应条件,以及深入研究各反应对氮去除的贡献程度,可为未来实际污水脱氮应用提供重要理论依据并具有重大实际意义。
2.2 铁氨氧化在污水脱氮中的探索研究
目前,Feammox在污水脱氮中的应用仍处于初级探索阶段[72],利用Feammox处理实际废水的研究比较少,并且Feammox反应主要是NH4+和Fe(Ⅲ)之间发生的反应,因此对模拟废水中的NH4+去除研究较多。目前Feammox反应启动及对氮去除的主要技术手段有:(1)向反应器添加从土壤中富集培养出的Feammox菌液;(2)利用Anammox污泥培养驯化出Feammox污泥来启动Feammox反应;(3)利用微生物固定化技术将Feammox菌固定化。实验选取的反应器类型主要有ASBR、MBR和血清瓶等装置(表3)。
表 3 不同反应装置和接种污泥下的氨氮转化效果Table 3. Transformation effect of NH4+-N under different reactor and inoculated sludge反应器类型Reactor type 废水类型Wastewater type 启动方式Start mode Fe(Ⅲ) Fe(Ⅲ)/(mg·L−1) pH 转化率/%Removal rate 文献Reference ASBR 模拟废水 接种二沉池污泥 FeCl3 27—33 7.4—7.6 53.8 [56] ASBR 模拟废水 接种Anammox污泥 FeCl3 12—24 7.4—7.6 52.73 [73] MBR 模拟废水 添加Feammox菌液 Fe(OH)3 573.2 4.5—5 41.49 [74] 生活污水 添加Feammox菌液 — 0.43—0.49 7.32 40.05 血清瓶 小榄江水 添加Feammox菌液 — 0.06—0.08 7.12 12.90 [75] 硫铁矿污水 添加Feammox菌液 — 13.43—13.55 4.5 44.64 李海晖等[75]对实际污水进行了研究,通过向城市生活污水、和矿山废水中添加使用NH4+和Fe(Ⅲ)富集培养出的Feammox菌液,来探讨Feammox对实际废水中NH4+的去除效果。结果发现,经过10d的反应,城市生活污水中的NH4+浓度由初始203.94 mg·L−1降低至122.26 mg·L−1,去除率为40.05%,矿山废水中的NH4+去除率达到了44.64%。表明Feammox对实际废水中的NH4+去除起到了良好的效果。吴胤等[74]通过配置不同NH4+浓度的模拟废水来探讨对Feammox反应所产生的影响,向NH4+浓度分别为75 mg·L−1、150 mg·L−1和400 mg·L−1的模拟废水中加入Feammox菌液并进行厌氧反应。结果发现,反应15d后,初始NH4+浓度为75 mg·L−1和150 mg·L−1的反应器中,NH4+去除率分别为41.49%和7.45%,而在NH4+浓度为400 mg·L−1的模拟废水中Feammox反应受到抑制,表明在低氨氮废水中Feammox能起到较好的反应。姚海楠等[73]考虑到Feammox菌对重金属具有耐受性,便利用处理垃圾渗滤液的Anammox污泥作为接种污泥启动Feammox反应,并同样探究了不同NH4+浓度对Feammox反应的影响。当进水NH4+浓度为400 mg·L−1时,经过12 d反应,NH4+的转换量为40.69 mg·L−1,也同样证明了Feammox反应在高氨氮废水中对NH4+的去除率小于在低氨氮废水中,另外还发现反应器中的NO3−的生成量与NH4+的转化量差异不大,反应器中的NH4+主要转化为了NO3−。Feammox菌对重金属具有较强的耐受性,能对重金属起到固定效应并可降低其在污水中的毒性[73-74],这也可能是Feammox能够在NH4+浓度为400 mg·L−1和Fe(Ⅲ)浓度为500 mg·L−1的高浓度废水中仍能发生反应的重要原因[73]。此外,Feammox处理垃圾渗滤液过程也受pH的影响,Wang等[76]利用Feammox处理垃圾渗滤液的过程中研究发现,在pH 4.5时,垃圾渗滤液的反硝化效果最好,而在pH 3.5时的酸性环境中Feammox菌大量死亡。大量研究表明Feammox反应偏向于酸性环境,但过酸环境会抑制其反应,并导致微生物死亡。刘志文等[77]利用微生物固定化技术,使用磁性壳聚糖凝胶球(MCHBs)将Feammox菌固定化,并探讨其与游离菌液对NH4+的去除效果及差异。结果发现,在进水NH4+ 浓度为60 mg·L−1运行16 d后,粒径为1—2 mm的MCHBs 对NH4+的去除比游离细菌高出17.39%,达到了53.62%,实验过程中NH4+ 主要转换为了NO3−,而NO2−与N2只有少量的生成。Feammox反应过程中,由于NH4+作为电子供体,也是最佳的研究去除对象和目标污染物,对于低氨氮废水Feammox反应对NH4+的去除具有一定效果,但并不显著,因此对于高氨氮废水仍需求有效的解决方式。Yang等[78]向含有高NH4+的Feammox反应器中间歇的充气,在充气条件下,O2作为末端电子受体将Feammox还原生成的Fe(Ⅱ)氧化为Fe(Ⅲ),实现Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)循环,进而持续发生Feammox反应进行连续脱氮,最终总氮的去除率达到98.5%。与以往添加NO2−和NO3−实现铁循环进行脱氮不同的是,此充气方式简单且来源易得,可避免二次污染,对未来实际高氨氮废水的去除具有更简便的方式和广泛的适用性。虽然Feammox是自养脱氮过程,但Le等[79]研究了在有机碳源存在下的Feammox的氨氧化过程,研究发现Feammox能够与异养条件产生耦合作用,在进水COD与NH4+浓度分别为250 mg·L−1和200 mg·L−1,确定并控制两者最佳浓度比值为1.4,pH为中性的条件下,COD与NH4+的去除率达到了98.3%和58.8%,且反应最终产物为N2。此研究在有机碳的存在下显著提升了NH4+的去除,彻底实现了由NH4+转化为N2,并具有较高的去除率,对于一些NH4+和COD含量高的废水具有巨大的应用潜力。Feammox反应过程需要Fe(Ⅲ)源,铁的氧化物形态多样且廉价易得,Zhu等[80]通过添加不同的Fe(Ⅲ)化合物,以探索铁氧化物和碳源在废水处理中对NH4+的去除影响,结果表明,添加Fe2O3的反应器中引发的Feammox反应对NH4+去除效果最好,其去除负荷高达0.06 g·m−3·d−1。而与Le研究不同的是,在无COD的情况下NH4+的去除率为53%,比有COD的反应器高出23%,在反应器存在有机碳源的情况下,有机物抑制了Fe(Ⅲ)还原,也可能如Le的研究所示,当COD与NH4+浓度存在合适的比值时,才能对NH4+进行高效去除,但在有机碳源存在的情况下,其浓度大小如何影响对NH4+的去除需要进一步研究。
根据目前的研究现状,Feammox在污水处理方面的研究还相对单薄,且其所涉及的相关性功能微生物目前尚未统一[51]。除了目前已知的与Feammox相关的微小杆菌(Exiguobacterium spp)、A6菌、铁还原菌、以及利用Anammox污泥培养Feammox获得的Anammox菌之外,在污水处理领域中尚未分离出纯的Feammox菌种[10,24,52]。Feammox菌作为厌氧自养细菌,具有独特的代谢机制,在反应的过程中具有无需提供氧气和碳源并产生较少N2O的特点[66],有利于与其他脱氮反应联合应用于低碳氮比污水的处理[81]。Zhu等[82]便将Feammox与生物电化学系统相结合,两者的耦合反应对NH4+的去除率比单独Feammox反应高出38.8%,且此系统具有较低的能耗和运行成本。因此,一旦Feammox工艺成功运行于实际污水处理中,将会大幅减小污水厂曝气量和外投加碳源的经济成本,并减少污泥产量和温室气体排放[83],这也是Feammox应用于工程上所具有的独特优势和潜能。
3. 结语(Conclusion)
Feammox作为新型的氮循环转换途径,在陆地和海洋沉积物中均有Feammox作用的发生,并参与其所在环境体系氮的损失,也是构成全球自然生态系统中氮损失的重要组成部分。经过近些年来的不断探索研究,Feammox在污水脱氮领域具有巨大的应用潜力,尤其是对废水中NH4+ 的去除具有较好的效果。另外,Feammox能够与Anammox和NDFO进行耦合脱氮,为污水中氮素的去除开辟了新的方法和途径,因此Feammox工艺脱氮也是继Anammox工艺脱氮之后备受瞩目的研究热点。
然而Feammox污水脱氮仍处于初步探索阶段,应用于实际工程中,仍具有一定的距离和面临着诸多挑战。在未来的发展中Feammox应注重以下研究:(1)目前发现的Feammox菌的种类比较少,与Feammox相关的功能性微生物没有统一,现已知的A6菌是唯一能起到纯Feammox作用的菌种。应从微生物宏基因和蛋白质组学领域作为出发点,研究Feammox的发生情景和其所处环境微生物的多样性,通过分析特定功能微生物及其所受影响因子,进一步剖析Feammox的作用机制。(2)Feammox反应的产物含有NO2−和NO3−,通过深入研究Feammox与Anammox和NDFO的耦合作用机制,确定耦合过程最佳反应条件,给污水中氮素的高效去除和精确的反应控制提供可靠的参考方案。有效地与NDFO反应进行结合,通过实现Fe(Ⅲ)和Fe(Ⅱ)的循环转换对氮素进行脱除,实现更加节约资源的绿色环保脱氮。(3)深入探究铁还原菌作用下的胞外电子传递机制,不仅对实现铁循环和加快Feammox反应速率具有重大意义,也对污水高效脱氮和Feammox作用机理的研究提供有力依据。
-
表 1 Feammox反应方程式及吉布斯自由能
Table 1. Feammox reaction equation and Gibbs free energy
电子受体Electron acceptor 化学反应方程式Chemical reaction equation 吉布斯自由能ΔG/( kJ·mol−1 )Gibbs free energy 参考文献Reference FeOOH 6FeOOH+10H++NH4+—6Fe2++8H++NO2− −30.9 [9] 3Fe(OH)3+5H++NH4+—3Fe2++9H2O+0.5N2 −245 [4] Fe(OH)3 6Fe(OH)3+10H++NH4+—6Fe2++16H2O+NO2− −164 8Fe(OH)3+14H++NH4+—8Fe2++ 21H2O+ NO3− −207 Fe2O3·0.5H2O 3Fe2O3·0.5H2O+10H++NH4+—6Fe2++8.5H2O+NO2− ≤−145.08 [5] 表 2 铁氨氧化在自然界产生的氮损失
Table 2. Nitrogen loss in nature due to Feammox
样品Sample 来源地点Source location 铁氨氧化速率/(µg·g−1·d−1)Feammox rate 氮损失/(kg·ha-1·a-1)Nitrogen loss pH 文献Reference 热带旱地土壤 美国卢基洛山脉 0.19—0.45 — 4.25—6.15 [4] 丘陵水稻土壤 中国江西省金县(28°10'—28°45'N,116°1'—116°34'E) 0.17—0.59 7.8—61(占国内常规施氮肥3.9%—31%) 4.69—5.72 [2] 水稻土壤 江苏省金坛市(31°39'49.42”N , 119°28'4.12”E) 0.047—0.319 3.64(施肥土壤),15.97—24.91(不施肥土壤),(占国内常规施氮肥7.99%—12.45%) 6.25—6.76 [12] 潮间带湿地 中国上海崇明(31°30'N,121°59'E) 0.24—0.36 115—180(占长江湿地无机氮的3.1%—4.9%) 春潮(8.32—8.46),小潮(8.48—8.75) [1] 太湖底泥 太湖梅梁湾(31°31'39— 31°32' 30 N,120°10' 26—120°11' 70 E) 0.29(无藻区底泥),0.01—0.05(聚藻区底泥) — 7.26—7.43 [3] 河岸带土壤 太湖贡湖湾(31°27'32—31°28'01N, 120°19'27—120°21'18E) 0.25—0.29 — 6.87—7.42 [13] 菜地土壤 太湖流域宛山荡(31°34'32—31°36'30N, 120°30'12—120°32'24E) 0.06—0.23 — (占产生氮气的7.3%—12.4%) 4.50—5.21 [44] 农田土壤 太湖万山地区(31°35′15—31°35′27 N,120°28′43—120°30′32 E) 0.12—0.18 17.8(占总氮损失的4.2%) 7.23—7.43 [36] 表 3 不同反应装置和接种污泥下的氨氮转化效果
Table 3. Transformation effect of NH4+-N under different reactor and inoculated sludge
反应器类型Reactor type 废水类型Wastewater type 启动方式Start mode Fe(Ⅲ) Fe(Ⅲ)/(mg·L−1) pH 转化率/%Removal rate 文献Reference ASBR 模拟废水 接种二沉池污泥 FeCl3 27—33 7.4—7.6 53.8 [56] ASBR 模拟废水 接种Anammox污泥 FeCl3 12—24 7.4—7.6 52.73 [73] MBR 模拟废水 添加Feammox菌液 Fe(OH)3 573.2 4.5—5 41.49 [74] 生活污水 添加Feammox菌液 — 0.43—0.49 7.32 40.05 血清瓶 小榄江水 添加Feammox菌液 — 0.06—0.08 7.12 12.90 [75] 硫铁矿污水 添加Feammox菌液 — 13.43—13.55 4.5 44.64 -
[1] LI X F, HOU L J, LIU M, et al. Evidence of nitrogen loss from anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with ferric iron reduction in an intertidal wetland [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(19): 11560-11568. [2] DING L J, AN X L, LI S, et al. Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction from paddy soils in a chronosequence [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(18): 10641-10647. [3] 罗文齐, 徐梦珊, 李丹丹, 等. 蓝藻暴发对太湖梅梁湾底泥中铁氨氧化速率的影响 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(8): 2828-2833. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0090 LUO W Q, XU M S, LI D D, et al. Effect of cyanobacteria outbreak on Feammox rates in the sediments of Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(8): 2828-2833(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0090
[4] YANG W H, WEBER K A, SILVER W L. Nitrogen loss from soil through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(8): 538-541. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1530 [5] HUANG S, JAFFÉ P R. Characterization of incubation experiments and development of an enrichment culture capable of ammonium oxidation under iron-reducing conditions [J]. Biogeosciences, 2015, 12(3): 769-779. doi: 10.5194/bg-12-769-2015 [6] HUANG S, JAFFÉ P R. Isolation and characterization of an ammonium-oxidizing iron reducer: Acidimicrobiaceae sp. A6 [J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(4): e0194007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194007 [7] GILSON E R, HUANG S, JAFFÉ P R. Biological reduction of uranium coupled with oxidation of ammonium by Acidimicrobiaceae bacterium A6 under iron reducing conditions [J]. Biodegradation, 2015, 26(6): 475-482. doi: 10.1007/s10532-015-9749-y [8] REN Y, HAO NGO H, GUO W S, et al. New perspectives on microbial communities and biological nitrogen removal processes in wastewater treatment systems [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 297: 122491. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122491 [9] CLÉMENT J C, SHRESTHA J, EHRENFELD J G, et al. Ammonium oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron under anaerobic conditions in wetland soils [J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2005, 37(12): 2323-2328. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.03.027 [10] SAWAYAMA S. Possibility of anoxic ferric ammonium oxidation [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2006, 101(1): 70-72. doi: 10.1263/jbb.101.70 [11] YANG Y F, ZHANG Y B, LI Y, et al. Nitrogen removal during anaerobic digestion of wasted activated sludge under supplementing Fe(III) compounds [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 332: 711-716. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.133 [12] JIA W L, WANG Q, ZHANG J, et al. Nutrients removal and nitrous oxide emission during simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal process: Effect of iron [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(15): 15657-15664. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6758-2 [13] GE J Y, HUANG S, HAN I, et al. Degradation of Tetra- and trichloroethylene under iron reducing conditions by Acidimicrobiaceae sp. A6 [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 247: 248-255. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.066 [14] 钟小娟, 王亚军, 唐家桓, 等. 铁氨氧化: 新型的厌氧氨氧化过程及其生态意义 [J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 47(1): 1-7. ZHONG X J, WANG Y J, TANG J H, et al. Feammox: a novel anammox process and ecological significance [J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 47(1): 1-7(in Chinese).
[15] ZHOU G W, YANG X R, LI H, et al. Electron shuttles enhance anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron(III) reduction [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(17): 9298-9307. [16] SHRESTHA J, RICH J J, EHRENFELD J G, et al. Oxidation of ammonium to nitrite under iron-reducing conditions in wetland soils [J]. Soil Science, 2009, 174(3): 156-164. doi: 10.1097/SS.0b013e3181988fbf [17] 陈丹丹, 罗小波, 李芳柏. 穿梭体影响微生物群落胞外电子传递过程的研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(8): 1419-1425. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2017.08.018 CHEN D D, LUO X B, LI F B. Effects of shuttles on extracellular electron transfer of microbial community [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(8): 1419-1425(in Chinese). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2017.08.018
[18] 张玉龙, 陈雪丽, 吴云当. 电子穿梭体及其介导的环境与地球化学过程研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(1): 213-222. ZHANG Y L, CHEN X L, WU Y D. Electron shuttle-mediated microbial extracellular electron transfer: Mechanisms and geochemical implications [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(1): 213-222(in Chinese).
[19] 李诗阳. 铁氧化物强化厌氧生物处理过程中胞外电子传递及其调控[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019. LI S Y. Enhancement and regulation of extracellular electron transfer in anaerobic biological treatment by iron oxides[D]. Dalian, China: Dalian University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[20] LOVLEY D R, COATES J D, BLUNT-HARRIS E L, et al. Humic substances as electron acceptors for microbial respiration [J]. Nature, 1996, 382(6590): 445-448. doi: 10.1038/382445a0 [21] NEVIN K P, LOVLEY D R. Potential for nonenzymatic reduction of Fe(III) via electron shuttling in subsurface sediments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2000, 34(12): 2472-2478. [22] KADEN J, ALEXANDER S G, SCHINK B. Cysteine-mediated electron transfer in syntrophic acetate oxidation by cocultures of Geobacter sulfurreducens and Wolinella succinogenes [J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2002, 178(1): 53-58. doi: 10.1007/s00203-002-0425-3 [23] 马金莲, 马晨, 汤佳, 等. 电子穿梭体介导的微生物胞外电子传递: 机制及应用 [J]. 化学进展, 2015, 27(12): 1833-1840. doi: 10.7536/PC150533 MA J L, MA C, TANG J, et al. Mechanisms and applications of electron shuttle-mediated extracellular electron transfer [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2015, 27(12): 1833-1840(in Chinese). doi: 10.7536/PC150533
[24] 吴彦成, 顾鑫, 朱继涛, 等. 铁氨氧化污水生物脱氮技术的研究进展 [J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(18): 38-44. WU Y C, GU X, ZHU J T, et al. Research advances of biological nitrogen removal from wastewater via Fe(Ⅲ) reduction coupled to anaerobic ammonium oxidation(feammox)process [J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2020, 36(18): 38-44(in Chinese).
[25] YANG Y F, PENG H, NIU J F, et al. Promoting nitrogen removal during Fe(III) reduction coupled to anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Feammox) by adding anthraquinone-2, 6-disulfonate (AQDS) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 247: 973-979. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.008 [26] 廖宏燕, 宋诚, 万柳杨, 等. 螯合铁对厌氧铁氨氧化脱氮效能及微生物群落的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(9): 4366-4373. LIAO H Y, SONG C, WAN L Y, et al. Effect of chelated iron on nitrogen removal efficiency and microbial community structure in the anaerobic ferric ammonium oxidation [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(9): 4366-4373(in Chinese).
[27] 柳广飞, 朱佳琪, 于华莉, 等. 电子穿梭体介导微生物还原铁氧化物的研究进展[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(增刊1): 157-170. LIU G F, ZHU J Q, YU H L, et al. Review on electron-shuttle-mediated microbial reduction of iron oxides minerals[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(Sup 1): 157-170(in Chinese).
[28] SCOTT D T, MCKNIGHT D M, BLUNT-HARRIS E L, et al. Quinone moieties act as electron acceptors in the reduction of humic substances by humics-reducing microorganisms [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1999, 33(2): 372. [29] CHEN S S, ROTARU A E, SHRESTHA P M, et al. Promoting interspecies electron transfer with biochar [J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 5019. [30] ZHOU G W, YANG X R, MARSHALL C W, et al. Biochar addition increases the rates of dissimilatory iron reduction and methanogenesis in ferrihydrite enrichments [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 589. [31] KAPPLER A, WUESTNER M L, RUECKER A, et al. Biochar as an electron shuttle between bacteria and Fe(III) minerals [J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2014, 1(8): 339-344. [32] WU S, FANG G D, WANG Y J, et al. Redox-active oxygen-containing functional groups in activated carbon facilitate microbial reduction of ferrihydrite [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(17): 9709-9717. [33] GUAN Q S, ZHANG Y L, TAO Y R, et al. Graphene functions as a conductive bridge to promote anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with iron reduction in mangrove sediment slurries [J]. Geoderma, 2019, 352: 181-184. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.05.044 [34] CANFIELD D E, GLAZER A N, FALKOWSKI P G. The evolution and future of Earth's nitrogen cycle [J]. Science, 2010, 330(6001): 192-196. doi: 10.1126/science.1186120 [35] TAN X, XIE G J, NIE W B, et al. Fe(III)-mediated anaerobic ammonium oxidation: A novel microbial nitrogen cycle pathway and potential applications [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2021: 1-33. [36] DING B J, CHEN Z H, LI Z K, et al. Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to Iron reduction from ecosystem habitats in the Taihu estuary region [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 662: 600-606. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.231 [37] DING B J, LI Z K, QIN Y B. Nitrogen loss from anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to Iron(III) reduction in a riparian zone [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 231: 379-386. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.027 [38] DING B J, QIN Y B, LUO W Q, et al. Spatial and seasonal distributions of Feammox from ecosystem habitats in the Wanshan region of the Taihu watershed, China [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 239: 124742. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124742 [39] LI H, SU J Q, YANG X R, et al. RNA stable isotope probing of potential feammox population in paddy soil [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(9): 4841-4849. [40] QIN Y B, DING B J, LI Z K, et al. Variation of Feammox following ammonium fertilizer migration in a wheat-rice rotation area, Taihu Lake, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.055 [41] YI B, WANG H H, ZHANG Q C, et al. Alteration of gaseous nitrogen losses via anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with ferric reduction from paddy soils in Southern China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 652: 1139-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.195 [42] 邹湘, 易博, 张奇春, 等. 长期施肥对稻田土壤微生物群落结构及氮循环功能微生物数量的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(12): 2158-2167. ZOU X, YI B, ZHANG Q C, et al. Effects of long-term fertilization on the microbial community structure and the population of N cycle-related functional microorganism in paddy soil [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(12): 2158-2167(in Chinese).
[43] LIU D M, ZHANG S R, FEI C, et al. Impacts of straw returning and N application on NH4+-N loss, microbially reducible Fe(III) and bacterial community composition in saline-alkaline paddy soils [J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2021, 168: 104115. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.104115 [44] 丁帮璟, 徐梦珊, 李丹丹, 等. 不同菜地土壤的铁氨氧化脱氮过程探究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(8): 3506-3511. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.08.030 DING B J, XU M S, LI D D, et al. Investigation of nitrogen removal by feammox in soils from different vegetable fields [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(8): 3506-3511(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.08.030
[45] LI T, WANG H J, DONG W Y, et al. Performance of an anoxic reactor proposed before BAF: Effect of ferrous sulfate on enhancing denitrification during simultaneous phosphorous removal [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 248: 41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.033 [46] 张日钊, 李斐然, 袁倩倩, 等. 海洋氮循环过程及基于基因组代谢网络模型的预测 [J]. 微生物学报, 2020, 60(6): 1130-1147. ZHANG R Z, LI F R, YUAN Q Q, et al. Marine nitrogen cycle and prediction based on genome-scale metabolic network model [J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2020, 60(6): 1130-1147(in Chinese).
[47] RIOS-DEL TORO E E, CERVANTES F J. Coupling between anammox and autotrophic denitrification for simultaneous removal of ammonium and sulfide by enriched marine sediments [J]. Biodegradation, 2016, 27(2/3): 107-118. [48] RIOS-DEL TORO E E, VALENZUELA E I, LÓPEZ-LOZANO N E, et al. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation linked to sulfate and ferric iron reduction fuels nitrogen loss in marine sediments [J]. Biodegradation, 2018, 29(5): 429-442. doi: 10.1007/s10532-018-9839-8 [49] LAUFER K, RØY H, JØRGENSEN B B, et al. Evidence for the existence of autotrophic nitrate-reducing Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria in marine coastal sediment [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2016, 82(20): 6120-6131. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01570-16 [50] 覃云斌. 农业氮污染迁移过程中铁氨氧化脱氮机理与应用研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2020. QIN Y B. Mechanism and application of feammox to nitrogen removal in the process of agricultural nitrogen pollution migration[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2020(in Chinese).
[51] 王彤, 汪涵, 周明达, 等. 污水脱氮功能微生物的组学研究进展 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(12): 4844-4870. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.210386 WANG T, WANG H, ZHOU M D, et al. Advances in omics of functional microorganisms for nitrogen removal in wastewater [J]. Microbiology China, 2021, 48(12): 4844-4870(in Chinese). doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.210386
[52] LI X, HUANG Y, LIU H W, et al. Simultaneous Fe(III) reduction and ammonia oxidation process in Anammox sludge [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 64: 42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.01.002 [53] PARK W, NAM Y K, LEE M J, et al. Anaerobic ammonia-oxidation coupled with Fe3+ reduction by an anaerobic culture from a piggery wastewater acclimated to NH4 +/Fe3+ medium [J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2009, 14(5): 680-685. doi: 10.1007/s12257-009-0026-y [54] 刘恒蔚, 毕玮, 李祥, 等. 厌氧氨氧化与铁氨氧化反应器功能微生物对比研究 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(6): 39-45. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.06.005 LIU H W, BI W, LI X, et al. Comparative analysis of functional bacteria communities in feammox and anammox reactors [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(6): 39-45(in Chinese). doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.06.005
[55] 杨朋兵. Feammox反应机理及功能微生物[D]. 苏州: 苏州科技大学, 2016. YANG P B. Study on reaction mechanism of feammox and the functional microbial community[D]. Suzhou, China: Suzhou University of Science and Technology, 2016(in Chinese).
[56] 吴悦溪, 曾薇, 刘宏, 等. Feammox系统内氮素转化途径的研究 [J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2265-2272,1935. WU Y X, ZENG W, LIU H, et al. Exploration of nitrogen transformation pathway in Feammox [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2265-2272,1935(in Chinese).
[57] ZHAO R, ZHANG H M, LI Y F, et al. Research of iron reduction and the iron reductase localization of anammox bacteria [J]. Current Microbiology, 2014, 69(6): 880-887. doi: 10.1007/s00284-014-0668-7 [58] LIU Y W, NI B J. Appropriate Fe (II) addition significantly enhances anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) activity through improving the bacterial growth rate [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 8204. doi: 10.1038/srep08204 [59] DING J, SEOW W, ZHOU J Z, et al. Effects of Fe(II) on anammox community activity and physiologic response [J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2020, 15(1): 1-11. [60] BI Z, QIAO S, ZHOU J T, et al. Fast start-up of Anammox process with appropriate ferrous iron concentration [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 170: 506-512. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.07.106 [61] BI Z, ZHANG W J, SONG G, et al. Iron-dependent nitrate reduction by anammox consortia in continuous-flow reactors: A novel prospective scheme for autotrophic nitrogen removal [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 692: 582-588. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.078 [62] QIAO S, BI Z, ZHOU J T, et al. Long term effects of divalent ferrous ion on the activity of anammox biomass [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 142: 490-497. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.05.062 [63] 王海月, 彭玲, 毛念佳, 等. 三价铁对有机物存在下厌氧氨氧化脱氮的影响 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(4): 1672-1680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.04.020 WANG H Y, PENG L, MAO N J, et al. Effect of Fe3+ on nitrogen removal of Anammox in the presence of organic matter [J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(4): 1672-1680(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.04.020
[64] KLUEGLEIN N, KAPPLER A. Abiotic oxidation of Fe(II) by reactive nitrogen species in cultures of the nitrate-reducing Fe(II) oxidizer Acidovorax sp. BoFeN1 - questioning the existence of enzymatic Fe(II) oxidation [J]. Geobiology, 2013, 11(2): 180-190. doi: 10.1111/gbi.12019 [65] OSHIKI M, ISHII S, YOSHIDA K, et al. Nitrate-dependent ferrous iron oxidation by anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) bacteria [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 79(13): 4087-4093. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00743-13 [66] LI X, YUAN Y, HUANG Y, et al. A novel method of simultaneous NH4+ and NO3− removal using Fe cycling as a catalyst: Feammox coupled with NAFO [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 631/632: 153-157. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.018 [67] YANG Y F, XIAO C C, LU J H, et al. Fe(III)/Fe(II) forwarding a new anammox-like process to remove high-concentration ammonium using nitrate as terminal electron acceptor [J]. Water Research, 2020, 172: 115528. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115528 [68] ZHOU J, WANG H Y, YANG K, et al. Autotrophic denitrification by nitrate-dependent Fe(II) oxidation in a continuous up-flow biofilter [J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2016, 39(2): 277-284. doi: 10.1007/s00449-015-1511-7 [69] COBY A J, PICARDAL F W. Inhibition of NO3- and NO2- reduction by microbial Fe(III) reduction: Evidence of a reaction between NO2- and cell surface-bound Fe2+ [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(9): 5267-5274. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.9.5267-5274.2005 [70] CHAKRABORTY A, PICARDAL F. Neutrophilic, nitrate-dependent, Fe(II) oxidation by a Dechloromonas species [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2013, 29(4): 617-623. doi: 10.1007/s11274-012-1217-9 [71] YANG Y F, XIAO C C, YU Q, et al. Using Fe(II)/Fe(III) as catalyst to drive a novel anammox process with no need of anammox bacteria [J]. Water Research, 2021, 189: 116626. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116626 [72] 李冠恒, 王宇佳, 史超, 等. 厌氧铁氨氧化工艺特性与控制策略的研究进展 [J]. 工业水处理, 2021, 41(8): 34-40. doi: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2020-0994 LI G H, WANG Y J, SHI C, et al. Research progress of Feammox's processing characteristics and control strategies [J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2021, 41(8): 34-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2020-0994
[73] 姚海楠, 张立秋, 李淑更, 等. 厌氧铁氨氧化处理模拟垃圾渗滤液的影响因素研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(9): 2953-2963. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0201 YAO H N, ZHANG L Q, LI S G, et al. Study on the factors affecting simulated landfill leachate treatment by anaerobic ferric ammonia oxidation [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(9): 2953-2963(in Chinese). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0201
[74] 吴胤, 陈琛, 毛小云, 等. 基于feammox的生物膜反应器性能研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(9): 3353-3362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.09.019 WU Y, CHEN C, MAO X Y, et al. Study on performance of the Feammox biofilm-reactor [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(9): 3353-3362(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.09.019
[75] 李海晖. 厌氧铁氨氧化反应在三类污水中对氨去除的探索[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2017. LI H H. Ammonium oxidation under iron-reducing conditions in three different wastewaters[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2017(in Chinese).
[76] WANG B, SUN B, LIU Y L, et al. Effect of feammox on landfill leachate treatment and its influence on pH [J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 770(1): 012007. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/770/1/012007 [77] 刘志文, 陈琛, 彭晓春, 等. 磁性壳聚糖凝胶球固定厌氧铁氨氧化菌对废水氨氮去除的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10): 4601-4611. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201801156 LIU Z W, CHEN C, PENG X C, et al. Effect of magnetic chitosan hydrogel beads with immobilized feammox bacteria on the removal of ammonium from wastewater [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(10): 4601-4611(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201801156
[78] YANG Y F, ZHAO Z Q, ZHANG Y B. Anaerobic ammonium removal pathway driven by the Fe(II)/Fe(III) cycle through intermittent aeration [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(11): 7615-7623. [79] LE C P, NGUYEN H T, NGUYEN T D, et al. Ammonium and organic carbon co-removal under feammox-coupled-with-heterotrophy condition as an efficient approach for nitrogen treatment [J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 784. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80057-y [80] ZHU T T, LAI W X, ZHANG Y B, et al. Feammox process driven anaerobic ammonium removal of wastewater treatment under supplementing Fe(III) compounds [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 804: 149965. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149965 [81] ZHU J X, LI T, LIAO C M, et al. A promising destiny for Feammox: From biogeochemical ammonium oxidation to wastewater treatment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 790: 148038. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148038 [82] ZHU T T, ZHANG Y B, LIU Y W, et al. Electrostimulation enhanced ammonium removal during Fe(III) reduction coupled with anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Feammox) process [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 751: 141703. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141703 [83] CHAN-PACHECO C R, VALENZUELA E I, CERVANTES F J, et al. Novel biotechnologies for nitrogen removal and their coupling with gas emissions abatement in wastewater treatment facilities [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 797: 149228. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149228 -





 下载:
下载: