-
土壤是陆地生态系统物质循环和能量传递的主要介质[1],也是人类生存和农业生产的重要资源。近年来,农田土壤重金属污染受到环境研究者的高度关注[2]。农田土壤重金属污染一方面是由于城市化、工业化和集约化农业的快速发展,重金属由工业“三废”、交通尾气、污水灌溉、化肥及农药使用等途径进入土壤环境,导致农田土壤重金属污染问题日益突出[3],中国农田土壤重金属点位超标率达19.4%,主要重金属污染元素为镉(Cd)、汞(Hg)、砷(As)、铅(Pb)和铬(Cr)等[4]。另一方面,土壤类型、地貌地形等自然因素也影响土壤环境质量,如喀斯特地区土壤重金属元素主要来源于区域高地质背景值和成土作用[5]。自然因素和人为活动共同增加了表层土壤中重金属的累积效应,而重金属的赋存形态与土壤环境生态风险又存在复杂的关系[6],因此,在评估土壤重金属环境质量时必须综合关注人为因素、自然因素(地形地貌、土壤类型)以及重金属赋存形态等。
目前国内外学者针对土壤重金属污染所开展的研究,多是综合统计学、地理学、地质学、生态学等学科知识,以工业区[7]、农业区[8]、矿区[9]、公园[10]等作为研究区域,采用统计学方法、数学模型、地理信息系统空间分析技术等分析重金属空间分布规律、污染程度、富集程度和生态风险评估,采用定性和定量方法确定污染来源,探究重金属的有效防治措施[11]。
银川平原地处我国西北干旱地区,位于贺兰山与鄂尔多斯高原之间[12],自东向西包括河漫滩、一级阶地、二级阶地、山前洪积扇等多个地貌类型,土地的利用方式多为农业耕地。由于长期的农业耕作与灌溉,大量的化肥、农药以及水体中的污染物被带入土壤,致使多种重金属在土壤中富集。因此,本文对银川平原按地貌单元对土壤进行采样,分析土壤中8种重金属5种赋存形态及其空间分布,探索可能的污染来源,从潜在生态风险、生物有效指数以及土壤RAC(risk assessment code)风险等方面对其评价,探明土壤重金属生态风险与地貌类型的空间关系,以期为银川平原重金属污染防控提供科学依据。
-
研究区位于宁夏回族自治区北部,地处黄河中上游,南起青铜峡,北至石嘴山,西依贺兰山,东靠鄂尔多斯高原。南北长165 km,东西宽42—60 km,总面积7790 km2。海拔高度1100—1200 m,地理坐标为东经105°45′—106°56′,北纬37°46′—39°23′。自南向北缓缓倾斜,地面坡降由0.6‰—1‰不等,地势平坦。属典型大陆性气候,多年来平均气温在7.14—11.51 ℃,平均降水量为194.55 mm[13]。经地壳升降运动、断裂运动和流水、风化等内外地质应力的综合作用,加之黄河的冲积和河道的变迁,阶地和洪积扇成为了银川平原地貌格局的基本特征。研究以面积较大的一级阶地、二级阶地和山前洪积扇为研究对象,其中东部的一级阶地因靠近黄河主河道,其土壤类型主要以盐化潮土为主;中部二级阶地土壤类型主要为灌淤土;西部山前洪积扇因地势较高,土壤类型主要为淡灰钙土[14]。
宁夏自治区是我国受到土壤盐渍化危害的重点地区,也是我国西部干旱半干旱区的典型代表区域,盐碱地占比达40%以上[15]。一级阶地盐化潮土,物理结构孔隙度及透水性等没有很好地一致性,pH 8.39,潮土的黏粒矿物均以水云母为主,土层颜色土色比心、底土层稍暗,浅灰棕色至暗灰棕色。潮土区垦殖率高,适种性广,适宜于轮作套种,宜种植耐碱的棉花、高粱等。其中二级阶地多为灌淤土,土层颜色较为均匀,一般为灰粽或浅灰棕色,物理黏性多为20%—60%,属壤质土,具有较一致的土壤结构和较多的孔隙,pH 8.07,黏土矿物多为水云母,粉土较多,含有一定的有机质和养分,含量显著高于母质层。灌淤土适宜性广泛,玉米、小麦、水稻、糜子和甜菜等作物、瓜果蔬菜及林木均可栽培。山前洪积扇多为淡灰钙土,pH 8.17,其特征为土壤母质主要为第四纪洪积冲击物,质地较粗,物理组成中细砂较多,粉粒较少;土壤肥力较低,在研究区,主要生长禾草和小半灌木[14]。
-
采样点设置原则是以各地貌单元划分,并兼顾各地貌单元相对面积大小,在银川平原北部、中部和南部形成3条剖面。具体采样点分布如图1所示。采集表层土0—20 cm的混合土样,其中一级阶地,二级阶地,山前洪积扇各采集4件、8件、5件,共采集样品17件。
采集的样品除去大块杂物后,自然风干,用玛瑙研钵研磨至过100目尼龙筛,得到粉末样品备用。采用Tessier法[16]连续提取土壤中重金属,依次提取离子交换态(F1)、碳酸盐结合态(F2)、铁-锰氧化物结合态(F3)、有机物结合态(F4)和残渣态(F5)五种形态。将不同的赋存形态归为可利用态(F1+F2)、潜在可利用态(F3+F4)和不可利用态(F5)[17]。Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb、Zn和Cd采用X Seris型等离子质谱仪测定,As和Hg采用DAG-9146A0原子荧光光度计测定。利用 Miniflex-600 型X射线多晶粉末衍射仪(XRD) 进行土壤矿物组成测试,扫描范围5°—90° (2θ),扫描速度0.1(°)·s−1(2θ)。利用X射线荧光分析仪(XRF)进行主要氧化物测定。用Vario EL Ⅲ型总有机碳分析仪测定总有机碳的含量。
-
富集系数(EF)是用来评价土壤和沉积物中重金属富集程度受人类活动影响程度的重要参数,自然衍生元素的EF值接近于1。通常选用化学性质比较稳定的元素,例如Al、Fe、Mn、Ti和Sc[18]。本文以研究区重金属背景值为基础,Al为参考元素,按公式(1)计算EF:
式中,(C/Al)s表示土壤中元素与Al实测浓度的比值;(C/Al)b为背景值的比值。为更客观真实的表现出重金属的富集程度,本文采用2007年国土资源部对宁夏土壤基准值的调查结果作为背景值[19],富集程度的分级标准如表1所示[20]。
-
基于重金属的总量选用潜在生态危害指数法(RI)[21],引入了不同重金属的毒性系数,各参数分别为:Zn=1,Cr=2,Cu、Ni、Pb=5,As=10,Cd=30和Hg=40。RI法中的参比值选用宁夏重金属背景值[19]。
-
除去重金属的残渣态,其余形态(F1+F2+F3+F4)与总量的比值作为生物有效系数,对单因子污染指数法[22]进行修正,将其称为生物有效指数评价法。生物有效指数法突出重金属元素的可移动性和生物有效性。公式如下:
其中,PKi为生物有效指数,Ki为重金属的生物有效系数,Ci、Cs分别为重金属元素的实测值和参比值[19],生物有效指数PKi划分为4个等级,分别为:PKi ≤1,无污染;1<PKi≤2,轻污染;2< PKi≤3,中度污染;PKi>3;重污染。
-
风险评价指数(risk assessment code,RAC)是通过计算重金属的活性形态(可交换态和碳酸盐态) 在总量中的所占比例来定量分析重金属的生态风险,其占比越高,重金属生态危害风险越大[23]。依据RAC大小划分为5个等级,分别为:RAC <1%,无风险;1%≤ RAC <10%,低风险;10%≤ RAC <30%,中等风险;30%≤ RAC <50%,高风险;RAC ≥50%,极高风险。
-
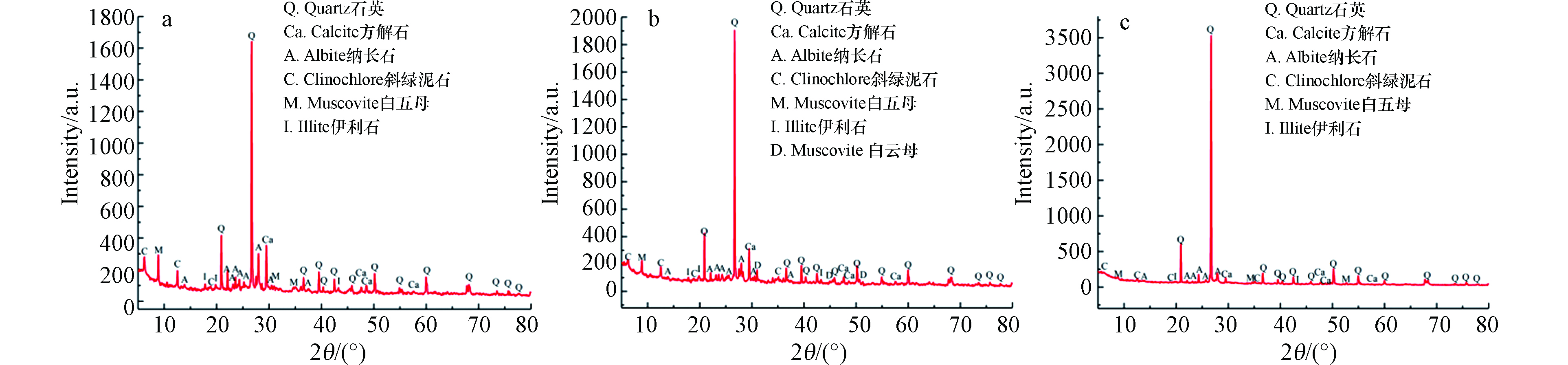
银川平原不同地貌单元土壤的矿物组成、pH、TOC以及主要氧化物统计结果见表2和表3。总体上,银川平原土壤pH值介于8.07—8.39之间,平均值为8.21,土壤处于偏碱性环境。根据X射线衍射图谱分析结果(表2和图2),土壤中所含矿物主要以石英(32.26%—39.16%)、长石(12.06%—19.58%)和黏土矿物(28.5%—47.54%)为主,其中黏土矿物以云母为主,伊利石和绿泥石次之。结合不同地貌单元来看,石英的含量为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,白云母含量与之相反,为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇。山前洪积扇中的石英含量最多,可能是由于山前洪积扇中砾石、粗砂含量较高;而白云母含量较多的土壤表明其土壤粒径较细,因此在一级和二级阶地中白云母含量明显比山前洪积扇中多。不同地貌类型的TOC含量有所差异,其中一级阶地、二级阶地和山前洪积扇中的TOC含量分别为29%、21.74%和7%。一级阶地与二级阶地的TOC含量较高,而山前洪积扇的TOC含量较低,可能是由于岩性特征不同所致,与山前洪积扇中粗砂、砾石含量较多相比,一级阶地和二级阶地多为黏土、粉砂,易吸附固持有机物。
土壤中主要氧化物含量统计结果(表3)表明,氧化物SiO2、Al2O3、CaO、MgO、K2O等的含量变化相对稳定(n=17,CV<0.20),而Fe2O3和Na2O的变化幅度相对较大(n=17,CV>0.20)。相比于中国平均土壤,银川平原中明显富集MgO、CaO、Al2O3等组分,相对亏损SiO2、Fe2O3等组分。
-
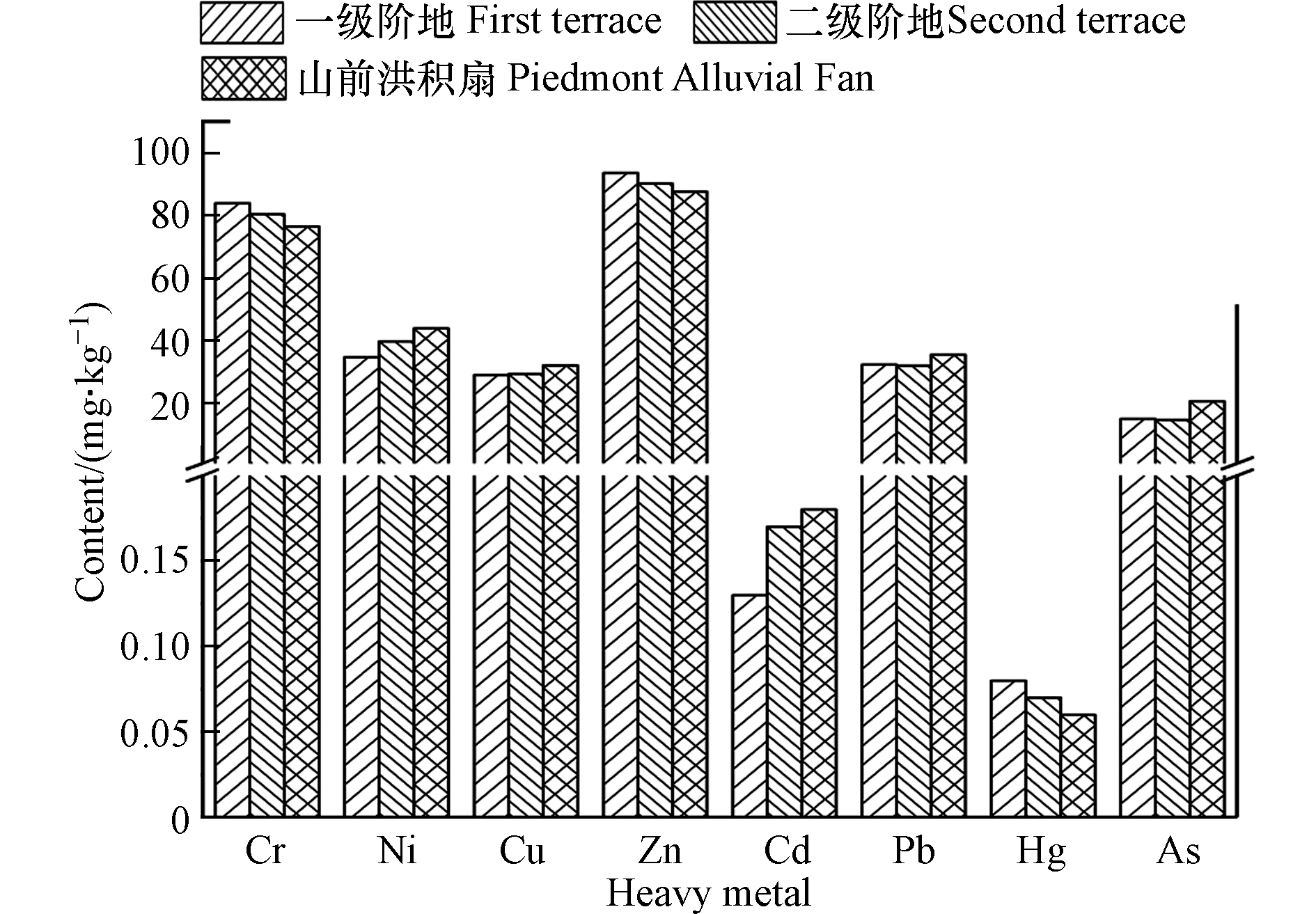
银川平原的3种地貌单元土壤中8种重金属含量(mg·kg−1)如表4和图3所示。从变异系数来看[25],3种地貌单元中,一级阶地重金属除Hg外,其余的变化幅度均较小(CV<20%),二级阶地中Cr、Ni、Cd、Hg等重金属含量变化幅度相对较大(CV>20%),山前洪积扇中除Cr、Zn外,其余重金属变化幅度均较大(CV>20%)。总体上,研究区重金属Ni、Cd、Hg、As含量变化较大(n=17,CV>20%),其中Hg的变化幅度最大接近50%。重金属在不同土壤中的分布相对不均一,可能与农业生产活动等因素影响有关。
由表4可知,银川平原中重金属的平均含量(mg·kg−1)大小为Zn(90.49)>Cr(81.84)>Ni(39.08)>Pb(32.70)>Cu(29.69)>As(15.91)>Cd(0.16)>Hg(0.08),含量差异较大。根据(GB15618—2018)中的农用地土壤风险筛选值 (pH>7.5),土壤中重金属 Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Hg、As平均含量均未超标。但对比宁夏土壤重金属的区域背景值,含量均超过了区域背景值,其超标分别达到了50.28%、79.76%、84.64%、104.77%、60.00%、89.57%、515.38%、74.64%。其中 Hg 超标最为严重,其余各金属的依次为:Hg > Zn > Pb > Cu > Ni > As > Cd > Cr。与其他地区土壤重金属研究进行对比,银川平原大多数重金属含量水平并不高,基本处于同一水平(Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Hg),但Cr和As的浓度相较于其他地区偏高,有研究表明,As元素作为农药和化肥等农业活动的标志元素[33],长期的使用会导致土壤中As的增加。
从图3中可以看出,不同地貌单元中重金属的含量不同,重金属Hg、Zn、Cr的含量由大到小依次为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,其中Hg、Zn、Cr在一级阶地含量相对较高可能是因为有机质含量高的土壤对重金属的吸附能力较强,但对不同的重金属也会有所差异[34]。不同地貌类型中土壤原生结构的差异,可能导致重金属含量的不同,其中山前洪积扇中可能是由于贺兰山岩土风化带来的,重金属大多来自于母质层本身所带来的;一级阶地主要受到黄河的冲击,可能从上游水中带来;主要是物源不同导致重金属总量的差异。重金属Ni、Cu、Cd的排序都为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,Pb和As的排序为山前洪积扇>一级阶地>二级阶地。pH会影响土壤中重金属的含量,研究区土壤 pH 值均大于7,在碱性条件下,土壤中As多以HASO4−存在[35],pH越高越不利于As在土壤中的存留,二级阶地土壤中pH较高,故在3种土壤中含量较低。
基于ArcGIS10.2软件绘制研究区土壤重金属空间分布图(图4),结果显示,8种土壤重金属在空间分布上具有一定的差异性。Cr、Cd、As、Cu的分布较为相似,主要特征表现为在西北部地区山前洪积扇中重金属含量较高,南部和东部的阶地中含量较低。Hg的空间分布与之相反,高值主要表现在中东部地区的阶地中,在西部地区山前洪积扇中含量较低。Ni的分布高值在西北部山前洪积扇中,低值主要分布在东南部的一级阶地中。Pb的高值主要表现在中部地区呈条带状分布在山前洪积扇和二级阶地中,在南北部含量相对较低。
-
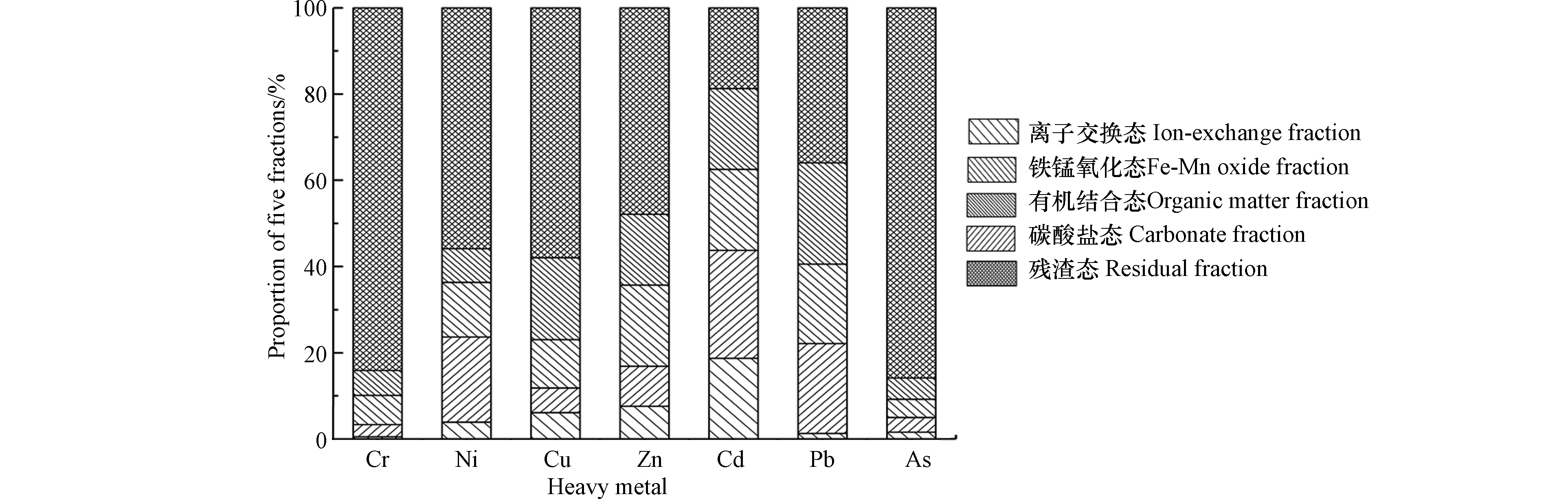
土壤中重金属的赋存形态特征是研究重金属的来源和生物有效性的重要信息[36],其迁移能力和赋存形态密切相关,并能对生态环境质量产生直接影响。重金属的离子交换态和碳酸盐结合态可被植物直接利用,铁锰氧化态和有机结合态在一定条件下可转化被植物吸收利用,而残渣态能长期稳定的存在于土壤中,不易被生物所利用,也不易发生迁移转化,对环境危害较小。
重金属各形态分布情况见图5。银川平原不同地貌单元土壤中As、Cr、Ni、Cu和Zn的赋存形态会有所差异,但均以残渣态为主,平均占比分别达到86.13%、83.59%、56.26%、58.47%、48.13%,生态环境危害均较低,这与已有的报道相似[35]。Cd的可利用态和潜在可利用组分远高于其他重金属,与大多数地区土壤中重金属Cd的赋存形态具有一定的相似性,即含量分布大多具有相对较低的残渣态和相对较高的活性态的特征[37]。Pb的潜在可利用态占63%,在还原环境中或pH值降低情况下,重金属会向有效态转化而增加土壤重金属风险,与麻冰涓[38]和韦壮绵[39]的研究结果相似,这可能是因为土壤中Fe和Mn的氢氧化物对 Pb2+有很强的专项吸附能力[40]。总体而言,除了Cd与Pb外,研究区土壤重金属多以残渣态形式存在,重金属元素生物活性组分占比相对较低。
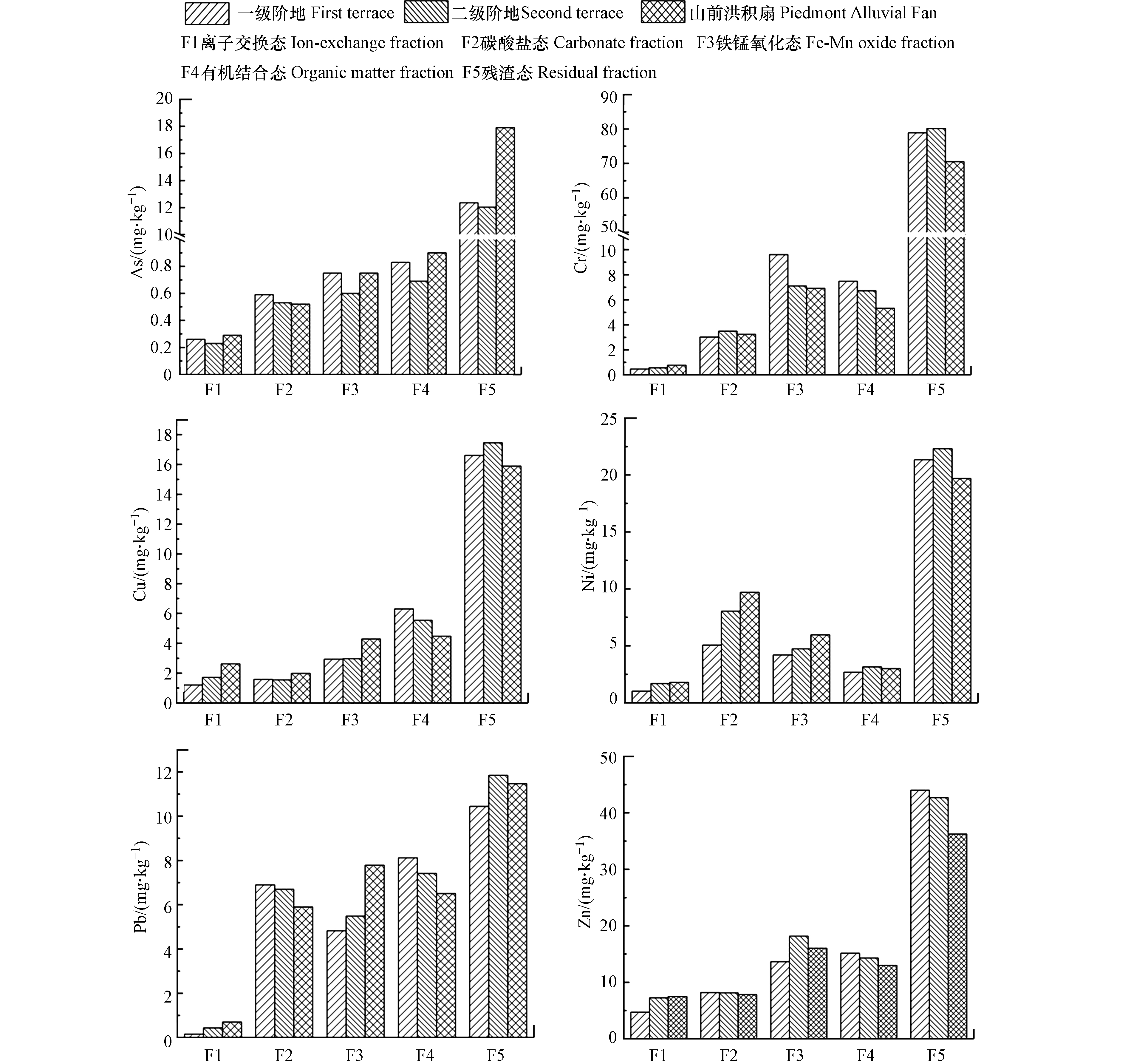
由图6可知,不同地貌单元中的重金属赋存形态各不相同,其中:离子交换态Cr、Ni、Pb、Zn、Cu含量均为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,可能是由于种植结构的差异所导致,其中山前洪积扇 种植葡萄经济作物,农药化肥用量较大,灌溉也相对较多,导致其离子交换态含量赋存较多。还可能是由于在一级阶地中的有机质含量最高而在山前洪积扇中的含量较低有关,彭敏等的研究表明,土壤有机质能通过吸附金属络合物而降低重金属的生物活性[37]。碳酸盐态Zn、Pb、As含量均表现出一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,pH是影响碳酸盐态的关键因素,而pH的升高有利于碳酸盐态的形成,一级阶地的pH相对较高,因此碳酸盐态含量较多。铁锰结合态Ni、Pb、Cu含量均表现出山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,而As含量却表现出一级阶地>山前洪积扇>二级阶地,这是由于土壤pH值升高,土壤中铁锰氧化物(土壤矿质胶体中吸附阴离子的重要部分)增加,导致其吸附能力增强[41],因此pH相对较高的土壤中As的铁锰态含量高。在活性相对较低的有机结合态中Cr、Pb、Zn、Cu含量均为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,而Ni含量表现出二级阶地>一级阶地>山前洪积扇。在惰性最大的残渣态中Cr、Ni、Pb、Cu均表现出二级阶地>一级阶地>山前洪积扇。
总体来看,在3种地貌单元中,重金属的赋存形态为:Ni、Pb、Cu的离子交换态和铁锰态表现为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地;Zn和Pb的碳酸盐结合态和有机态表现为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇;Cr、Ni、Pb和Cu残渣态表现为二级阶地>一级阶地>山前洪积扇。
-
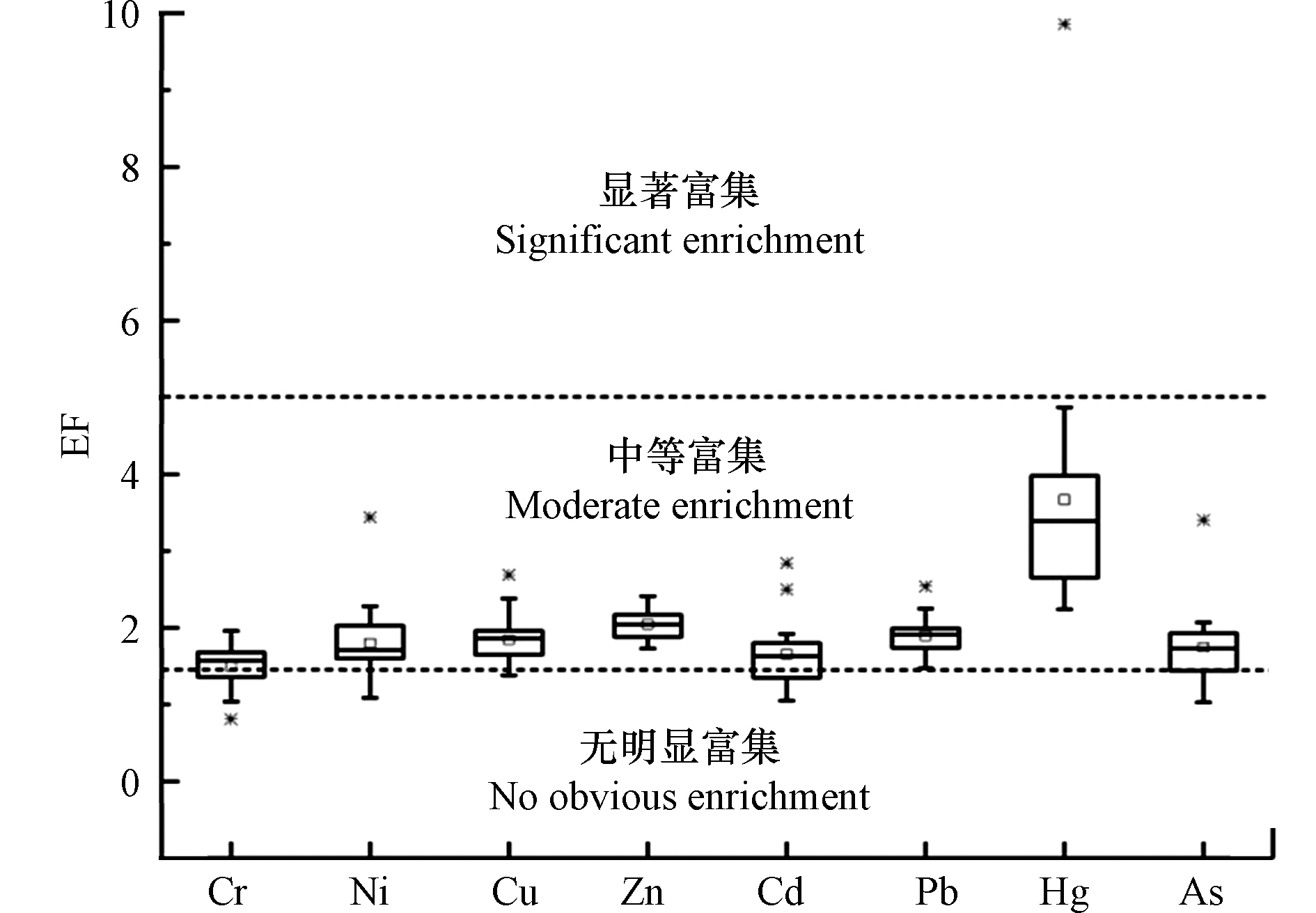
由图7可知,银川平原土壤中重金属均为中等富集程度(1.5<EF≤5),其中Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Hg和As的中位值分别为1.53、1.74、1.86、2.10、1.62、1.87、3.43、1.70,说明银川平原土壤存在重金属污染。其中Hg的富集系数较大,富集程度相比于其他重金属较为明显,且部分Hg的EF值可达偏高富集,属于偏高污染程度,应予以关注。
-
表5是银川不同地貌单元土壤重金属生态风险指数,从单因子风险指数可以看出研究区土壤样品中As、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni和 Cr的潜在风险指数均小于40,为轻微生态风险。而Cd的潜在生态风险指数范围为27.24—73.83,均值为42.72,存在轻微至中等生态风险等级,以轻微生态危害为主,个别点处在中等危害水平。Hg的潜在生态风险指数范围为89.71—394.48,均值为142.02,风险等级为强度生态危害。整体上Cd处在中度危害水平,Hg因其较高的含量和强烈的毒性,处在强度危害水平;其余各金属的毒性相对较低,都处在轻微危害状态,危害水平从大到小依次为As、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni、Cr。
从潜在生态风险指数RI上看(表5),土壤中重金属的RI值为165.09—485.00,最大值(485.00)出现在二级阶地土壤中,属于强生态危害等级,一级阶地和山前洪积扇均处在中等生态风险。其中,Hg和Cd对潜在生态风险指数RI的贡献最为主要,而其他元素贡献率相对较低,这与北方地区土壤重金属生态风险评价结果一致[42]。孙变变采用潜在生态风险指数法对银川土壤重金属生态风险进行评价,结果也表明Hg是最主要的风险来源[43]。主要原因一方面是由于Hg的毒性相应系数数值较高,另一方面土壤Hg的背景值较低,而该区域土壤Hg的含量超标点位较多。
-
银川平原土壤重金属生物有效指数具有明显的差异性,如表6所示,其中Cr(0.19—0.46)、Ni(0.18—1.04)、Cu(0.40—0.96)、Zn(0.58—0.91)、As(0.11—0.32),均值分别为0.31、0.46、0.56、0.76、0.20,在3种地貌单元中的生物有效指数结果均处于0—1之间,表明这5种重金属均处在无污染状态。Cd的生物有效指数在0.72—1.66,均值为1.13,整体上处于无污染状态的占29.41%,其余处在轻微污染状态的占70.59%,表明主要以轻微污染状态为主。Pb的生物有效指数位于0.74—1.27之间,其中一级阶地和二级阶地的均在无污染状态,而山前洪积扇地貌单元土壤处在轻微污染状态,整体上处在无污染状态占比为52.94%,轻微污染状态的占47.06%。
-
大量研究表明,重金属的生物毒性和生物可利用度不仅与总量有关,更与其赋存形态密切相关。不同形态的重金属在土壤中的迁移能力不同,对植物的生物有效性也不同。研究区土壤多为碱性,碳酸盐态不易转化为离子交换态被生物所利用,因此研究区重金属元素的生物有效性主要考虑植物易吸收的离子交换态。研究区土壤重金属的RAC风险等级如图8所示。
根据风险指数平均值银川平原土壤重金属RAC风险系数由强到弱分别Cd > Zn > Cu > Ni > Cr > Pb,重金属Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn和Pb元素RAC风险等级均为低风险或无风险,仅Cd 元素RAC 风险等级以中等风险为主,这与其他地区的研究结果相一致[23]。Cd 的可交换态百分比高,生物活性高,对环境可能造成的有害效应较强,因此其风险较高。其他重金属生物活性较低,对环境可能造成的有害效应有限,因此风险水平较低。
-
以上分析表明,银川平原土壤中重金属具有富集现象。土壤重金属的来源既与自然条件有关,也与工业、农业等人为活动有关[44]。研究区土壤重金属含量数据经KMO检验和Bartlett’s球体检验,结果显示KMO检验系数为0.674>0.5,Bartlett's球体检验P值<0.05,表明各重金属元素相关性强,适合进行主成分分析。土壤8种重金属污染物主成分分析显示(图9),第一主成分(PC1)与第二主成分的特征值为(PC2)特征值分别为3.213和1.859,对应方差贡献率分别为40.164%和23.244%,说明所有数据的绝大部分信息能够由前2个主成分反映(63.41%)。
第一主成分的方差贡献率为40.164%,表现为重金属Cu、Pb、Cd、As有较高的正载荷,分别为0.870、0.826、0.704、0.682。研究区土壤多为农业用地,大量使用的有机肥中Pb含量偏高可能造成土壤中Pb升高[45]。宋波等[46]对广西农田研究发现污灌对土壤中Cd含量的影响较为突出;Cu是载荷值最大的元素,畜禽饲料中经常添加Cu用来防治疾病和促进生长,且95%会随粪便排出,施用到土壤中时,也会相应地增加土壤中Cu的含量[47];Lu等[48]的研究也发现, Cd和Cu主要来自农业活动,同时灌溉用水也是农业土壤中重金属 Cd和Cu含量升高的重要原因[49]。赵东杰等[33]的研究也指出,As元素是农药和化肥等农业活动的标志元素。银川平原是历史悠久的老灌区,长期接受黄河水灌溉补给,水体中不可避免存在微量重金属,因此推测第一主成分4 种重金属具有相同或相似的来源,重金属的来源主要受农业的灌溉、化肥以及农药的使用等人类生产活动的影响。第二主成分的方差贡献率为23.24%,表现为重金属Cr、Ni、Zn有较高的正载荷,分别为0.720、0.656、0.673,且变异系数均较低,受人为因素影响程度较小,潜在生态风险评价结果可知,Cr、Ni、Zn均造成轻微生态危害水平,进一步表明这三种重金属受人类活动影响较小[50],主要是由日照强烈,岩石风化严重从而进入土壤中。结合Sheng[51]、纪冬丽等[52]的研究,发现Cr和Ni在土壤中可能来源于成土母质或母岩的风化与破碎等观点,推断这3种重金属主要由岩石风化进入成土母质中,为自然来源。
-
(1)在空间分布上,土壤中Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Hg、As 含量高于背景值,分别达到背景值1.51、1.80、1.85、2.05、1.60、1.91、6.15和1.75倍。其中,Cr、Zn、Hg的含量依次为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,Ni、Cu、Cd的含量由大到小为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,Pb和As的含量依次为山前洪积扇>一级阶地>二级阶地,可能由于不同地貌单元中的有机质含量和pH值不同导致。
(2)研究区重金属Cd的可利用态占比达42.3%,生物有效性相对较高,其余重金属赋存形态以残渣态为主,对生态环境危害较低。重金属的赋存形态表现为:在不同地貌单元中Ni、Pb、Cu的交换态和铁锰结合态均为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地;Zn和Pb的碳酸盐态和有机结合态为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇;Cr、Ni、Pb和Cu残渣态为二级阶地>一级阶地>山前洪积扇。
(3)潜在生态风险结果显示,重金属Hg和Cd的风险水平较高,分别处于强度和中度生态危害水平,其余各金属危害指数较小,都处于轻度生态危害水平;生态有效指数法和RAC指数法均显示,仅Cd元素以中等风险为主,其他各元素均为低风险或无风险。初步判定Cd和Hg为银川平原土壤重金属污染防治的优先控制对象.其他重金属含量也呈现出明显增加的趋势,仍需引起重视。
(4)土壤重金属主成分分析结果表明,重金属Cu、Pb、Cd、As的来源主要与农业生产等人类活动带入有关,对环境带来的风险较大,而Cr、Ni、Zn主要与岩石风化等自然过程有关。
银川平原不同地貌单元土壤重金属的分布特征及其风险评价
Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in different geomorphological units of Yinchuan Plain
-
摘要: 为了解银川平原不同地貌单元土壤重金属不同形态分布特征及生态风险状况,按一级阶地、二级阶地和山前洪积扇的3种类型进行采样. 利用X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析土壤的矿物组成,采用Tessier法分析As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Hg、Ni、Pb 和 Zn总量及赋存形态特征,利用潜在生态风险指数法、生物有效指数法和风险评估编码法对土壤生态风险进行评价,并采用主成分分析对重金属来源解析. 结果表明,Cr、Zn、Hg的含量一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,Ni、Cu、Cd的含量山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,Pb和As的含量山前洪积扇>一级阶地>二级阶地. 不同形态重金属的含量规律为,Ni、Pb、Cu可交换态和铁锰态均为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,Zn和Pb碳酸盐态与有机结合态为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,Cr、Ni、Pb和Cu残渣态为二级阶地>一级阶地>山前洪积扇. 潜在生态风险评价法结果表明Hg和Cd分别处在高度和中度生态危害水平,其余各金属均处于轻度危害水平,依次为As、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni、Cr. 生态有效指数法和风险评估编码法分析结果相同:Cd为中等风险,其他各元素均为低风险或无风险状态. 评价结果表明应重点关注Hg和Cd引起的污染. 主成分分析结果表明,土壤中的Cu、Pb、Cd、As可能与农业施肥、施药等人为活动有关,而Cr、Ni、Zn可能与岩石风化等自然过程有关.Abstract: In order to understand the distribution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metals in different geomorphic units of Yinchuan Plain, the samples were taken according to three types of first terrace, second terrace and piedmont alluvial fan. The mineral composition of soil was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The total amount and speciation of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb and Zn were analyzed by Tessier method. The potential ecological risk index,biological effectiveness index and risk assessment coding method were used to evaluate the soil ecological risk, and principal component analysis was used to analyze the sources of heavy metals. The results showed that the order of the content of Cr, Zn, and Hg was: first terrace> second terrace> piedmont alluvial fan. The content of Ni, Cu, and Cd was: piedmont alluvial fan> second terrace> first terrace. The order of Pb and As content was: piedmont alluvial fan>first terrace>second terrace. Different forms of heavy metals have different content rules. The contents of Ni, Pb, Cu exchangeable states and iron-manganese states were all piedmont alluvial fan>second terrace>first terrace. The carbonate and organic bound content of Zn and Pb are first terrace> second terrace> piedmont alluvial fan, the content of Cr, Ni, Pb and Cu residue states was second terrace> first terrace> piedmont alluvial fan. The potential ecological risk assessment method showed that Hg and Cd were at high and moderate ecological risk levels, respectively, and the other metals were at mild risk levels, followed by As, Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr. Both the ecological effective index method and risk assessment coding method showed that Cd was medium risk, and other elements were low risk or no risk. The evaluation results suggested that the pollution caused by Hg and Cd should be paid more attention. The principal component analysis results showed that Cu, Pb, Cd and As in soil might be related to human activities, such as agricultural fertilization and pesticide application, while Cr, Ni and Zn might be related to natural processes such as rock weathering.
-
土壤是陆地生态系统物质循环和能量传递的主要介质[1],也是人类生存和农业生产的重要资源。近年来,农田土壤重金属污染受到环境研究者的高度关注[2]。农田土壤重金属污染一方面是由于城市化、工业化和集约化农业的快速发展,重金属由工业“三废”、交通尾气、污水灌溉、化肥及农药使用等途径进入土壤环境,导致农田土壤重金属污染问题日益突出[3],中国农田土壤重金属点位超标率达19.4%,主要重金属污染元素为镉(Cd)、汞(Hg)、砷(As)、铅(Pb)和铬(Cr)等[4]。另一方面,土壤类型、地貌地形等自然因素也影响土壤环境质量,如喀斯特地区土壤重金属元素主要来源于区域高地质背景值和成土作用[5]。自然因素和人为活动共同增加了表层土壤中重金属的累积效应,而重金属的赋存形态与土壤环境生态风险又存在复杂的关系[6],因此,在评估土壤重金属环境质量时必须综合关注人为因素、自然因素(地形地貌、土壤类型)以及重金属赋存形态等。
目前国内外学者针对土壤重金属污染所开展的研究,多是综合统计学、地理学、地质学、生态学等学科知识,以工业区[7]、农业区[8]、矿区[9]、公园[10]等作为研究区域,采用统计学方法、数学模型、地理信息系统空间分析技术等分析重金属空间分布规律、污染程度、富集程度和生态风险评估,采用定性和定量方法确定污染来源,探究重金属的有效防治措施[11]。
银川平原地处我国西北干旱地区,位于贺兰山与鄂尔多斯高原之间[12],自东向西包括河漫滩、一级阶地、二级阶地、山前洪积扇等多个地貌类型,土地的利用方式多为农业耕地。由于长期的农业耕作与灌溉,大量的化肥、农药以及水体中的污染物被带入土壤,致使多种重金属在土壤中富集。因此,本文对银川平原按地貌单元对土壤进行采样,分析土壤中8种重金属5种赋存形态及其空间分布,探索可能的污染来源,从潜在生态风险、生物有效指数以及土壤RAC(risk assessment code)风险等方面对其评价,探明土壤重金属生态风险与地貌类型的空间关系,以期为银川平原重金属污染防控提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法( Materials and methods)
1.1 研究区域概况
研究区位于宁夏回族自治区北部,地处黄河中上游,南起青铜峡,北至石嘴山,西依贺兰山,东靠鄂尔多斯高原。南北长165 km,东西宽42—60 km,总面积7790 km2。海拔高度1100—1200 m,地理坐标为东经105°45′—106°56′,北纬37°46′—39°23′。自南向北缓缓倾斜,地面坡降由0.6‰—1‰不等,地势平坦。属典型大陆性气候,多年来平均气温在7.14—11.51 ℃,平均降水量为194.55 mm[13]。经地壳升降运动、断裂运动和流水、风化等内外地质应力的综合作用,加之黄河的冲积和河道的变迁,阶地和洪积扇成为了银川平原地貌格局的基本特征。研究以面积较大的一级阶地、二级阶地和山前洪积扇为研究对象,其中东部的一级阶地因靠近黄河主河道,其土壤类型主要以盐化潮土为主;中部二级阶地土壤类型主要为灌淤土;西部山前洪积扇因地势较高,土壤类型主要为淡灰钙土[14]。
宁夏自治区是我国受到土壤盐渍化危害的重点地区,也是我国西部干旱半干旱区的典型代表区域,盐碱地占比达40%以上[15]。一级阶地盐化潮土,物理结构孔隙度及透水性等没有很好地一致性,pH 8.39,潮土的黏粒矿物均以水云母为主,土层颜色土色比心、底土层稍暗,浅灰棕色至暗灰棕色。潮土区垦殖率高,适种性广,适宜于轮作套种,宜种植耐碱的棉花、高粱等。其中二级阶地多为灌淤土,土层颜色较为均匀,一般为灰粽或浅灰棕色,物理黏性多为20%—60%,属壤质土,具有较一致的土壤结构和较多的孔隙,pH 8.07,黏土矿物多为水云母,粉土较多,含有一定的有机质和养分,含量显著高于母质层。灌淤土适宜性广泛,玉米、小麦、水稻、糜子和甜菜等作物、瓜果蔬菜及林木均可栽培。山前洪积扇多为淡灰钙土,pH 8.17,其特征为土壤母质主要为第四纪洪积冲击物,质地较粗,物理组成中细砂较多,粉粒较少;土壤肥力较低,在研究区,主要生长禾草和小半灌木[14]。
1.2 样品采集与预处理
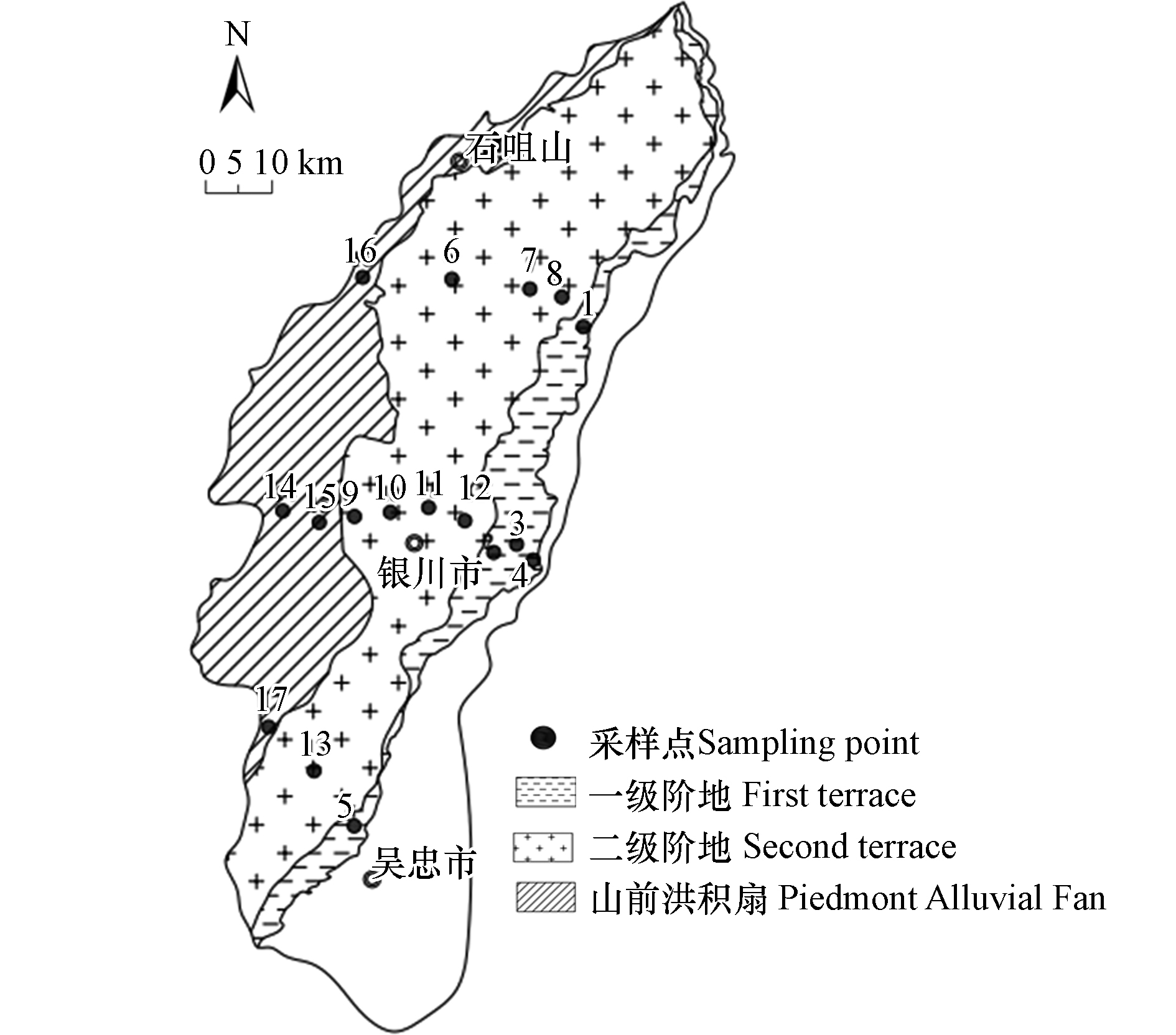
采样点设置原则是以各地貌单元划分,并兼顾各地貌单元相对面积大小,在银川平原北部、中部和南部形成3条剖面。具体采样点分布如图1所示。采集表层土0—20 cm的混合土样,其中一级阶地,二级阶地,山前洪积扇各采集4件、8件、5件,共采集样品17件。
采集的样品除去大块杂物后,自然风干,用玛瑙研钵研磨至过100目尼龙筛,得到粉末样品备用。采用Tessier法[16]连续提取土壤中重金属,依次提取离子交换态(F1)、碳酸盐结合态(F2)、铁-锰氧化物结合态(F3)、有机物结合态(F4)和残渣态(F5)五种形态。将不同的赋存形态归为可利用态(F1+F2)、潜在可利用态(F3+F4)和不可利用态(F5)[17]。Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb、Zn和Cd采用X Seris型等离子质谱仪测定,As和Hg采用DAG-9146A0原子荧光光度计测定。利用 Miniflex-600 型X射线多晶粉末衍射仪(XRD) 进行土壤矿物组成测试,扫描范围5°—90° (2θ),扫描速度0.1(°)·s−1(2θ)。利用X射线荧光分析仪(XRF)进行主要氧化物测定。用Vario EL Ⅲ型总有机碳分析仪测定总有机碳的含量。
1.3 评价方法
1.3.1 富集因子法
富集系数(EF)是用来评价土壤和沉积物中重金属富集程度受人类活动影响程度的重要参数,自然衍生元素的EF值接近于1。通常选用化学性质比较稳定的元素,例如Al、Fe、Mn、Ti和Sc[18]。本文以研究区重金属背景值为基础,Al为参考元素,按公式(1)计算EF:
EF=(C/Al)s/(C/Al)b (1) 式中,(C/Al)s表示土壤中元素与Al实测浓度的比值;(C/Al)b为背景值的比值。为更客观真实的表现出重金属的富集程度,本文采用2007年国土资源部对宁夏土壤基准值的调查结果作为背景值[19],富集程度的分级标准如表1所示[20]。
表 1 富集因子和污染等级Table 1. Enrichment factor and pollution level富集因子Enrichment factor EF≤1.5 1.5<EF≤5 5<EF≤20 20<EF≤40 富集程度 无或低富集 中度富集 偏高富集 高富集 污染程度 无或低 中度 偏高 高 1.3.2 潜在生态风险评价指数
基于重金属的总量选用潜在生态危害指数法(RI)[21],引入了不同重金属的毒性系数,各参数分别为:Zn=1,Cr=2,Cu、Ni、Pb=5,As=10,Cd=30和Hg=40。RI法中的参比值选用宁夏重金属背景值[19]。
1.3.3 生物有效指数评价
除去重金属的残渣态,其余形态(F1+F2+F3+F4)与总量的比值作为生物有效系数,对单因子污染指数法[22]进行修正,将其称为生物有效指数评价法。生物有效指数法突出重金属元素的可移动性和生物有效性。公式如下:
PKi=Ki⋅Pi=Ki⋅Ci/Cs (2) Ki=C潜在可利用C总量 (3) 其中,PKi为生物有效指数,Ki为重金属的生物有效系数,Ci、Cs分别为重金属元素的实测值和参比值[19],生物有效指数PKi划分为4个等级,分别为:PKi ≤1,无污染;1<PKi≤2,轻污染;2< PKi≤3,中度污染;PKi>3;重污染。
1.3.4 风险评价指数法
风险评价指数(risk assessment code,RAC)是通过计算重金属的活性形态(可交换态和碳酸盐态) 在总量中的所占比例来定量分析重金属的生态风险,其占比越高,重金属生态危害风险越大[23]。依据RAC大小划分为5个等级,分别为:RAC <1%,无风险;1%≤ RAC <10%,低风险;10%≤ RAC <30%,中等风险;30%≤ RAC <50%,高风险;RAC ≥50%,极高风险。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 土壤的理化性质
银川平原不同地貌单元土壤的矿物组成、pH、TOC以及主要氧化物统计结果见表2和表3。总体上,银川平原土壤pH值介于8.07—8.39之间,平均值为8.21,土壤处于偏碱性环境。根据X射线衍射图谱分析结果(表2和图2),土壤中所含矿物主要以石英(32.26%—39.16%)、长石(12.06%—19.58%)和黏土矿物(28.5%—47.54%)为主,其中黏土矿物以云母为主,伊利石和绿泥石次之。结合不同地貌单元来看,石英的含量为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,白云母含量与之相反,为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇。山前洪积扇中的石英含量最多,可能是由于山前洪积扇中砾石、粗砂含量较高;而白云母含量较多的土壤表明其土壤粒径较细,因此在一级和二级阶地中白云母含量明显比山前洪积扇中多。不同地貌类型的TOC含量有所差异,其中一级阶地、二级阶地和山前洪积扇中的TOC含量分别为29%、21.74%和7%。一级阶地与二级阶地的TOC含量较高,而山前洪积扇的TOC含量较低,可能是由于岩性特征不同所致,与山前洪积扇中粗砂、砾石含量较多相比,一级阶地和二级阶地多为黏土、粉砂,易吸附固持有机物。
表 2 银川平原不同地貌单元矿物组成(%)、pH及TOC含量(%)Table 2. Statistic results of mineral composition (%),pH value and TOC content (%) of different geomorphic units in Yinchuan Plain地貌单元Geomorphological unit 石英Quartz 方解石Calcite 钠长石Albite 白云母Muscovite 伊利石Illite 绿泥石Chlorite pH TOC 一级阶地 32.26 8.16 12.06 31.26 7.96 8.32 8.39 29.00 二级阶地 32.52 8.96 14.32 24.02 8.49 7.07 8.07 21.74 山前洪积扇 39.16 11.18 19.58 18.38 6.50 3.62 8.17 7.00 银川平原 34.65 9.43 15.32 24.55 7.65 6.34 8.21 19.23 表 3 土壤主要氧化物含量统计结果(%)Table 3. Statistic results of major oxide concentration (%)地貌单元Geomorphological unit SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O 一级阶地 60.46 15.14 4.55 10.32 3.25 3.02 1.71 二级阶地 59.23 14.58 4.69 11.14 3.89 3.1 1.75 山前洪积扇 59.39 13.56 4.28 13.43 3.55 2.9 1.59 银川平原 59.58 14.46 11.51 4.49 3.70 3.01 1.72 CV 8 8 29 19 18 10 26 CS[24] 65.00 12.60 4.60 3.20 1.80 2.50 1.60 注:CS:中国平均土壤,CV:变异系数. Note:CS:China average soil,CV:Coefficient of variation. 土壤中主要氧化物含量统计结果(表3)表明,氧化物SiO2、Al2O3、CaO、MgO、K2O等的含量变化相对稳定(n=17,CV<0.20),而Fe2O3和Na2O的变化幅度相对较大(n=17,CV>0.20)。相比于中国平均土壤,银川平原中明显富集MgO、CaO、Al2O3等组分,相对亏损SiO2、Fe2O3等组分。
2.2 重金属含量特征
2.2.1 土壤重金属总量
银川平原的3种地貌单元土壤中8种重金属含量(mg·kg−1)如表4和图3所示。从变异系数来看[25],3种地貌单元中,一级阶地重金属除Hg外,其余的变化幅度均较小(CV<20%),二级阶地中Cr、Ni、Cd、Hg等重金属含量变化幅度相对较大(CV>20%),山前洪积扇中除Cr、Zn外,其余重金属变化幅度均较大(CV>20%)。总体上,研究区重金属Ni、Cd、Hg、As含量变化较大(n=17,CV>20%),其中Hg的变化幅度最大接近50%。重金属在不同土壤中的分布相对不均一,可能与农业生产活动等因素影响有关。
表 4 银川平原土壤重金属全量统计分析(mg·kg-1)Table 4. Statistical analysis of total heavy metals in soils in Yinchuan Plain(mg·kg-1)地貌单元Geomorphological unit Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb Hg As 一级阶地 Min 56.82 26.94 22.59 77.24 0.10 29.94 0.05 9.34 Max 101.28 38.11 32.34 106.60 0.16 34.40 0.10 16.60 Mean 83.87 34.49 28.91 93.50 0.13 32.13 0.08 14.78 CV 19.96% 13.02% 13.57% 13.80% 17.91% 5.05% 25.29% 20.68% 二级阶地 Min 44.02 23.75 22.23 78.35 0.13 26.35 0.05 11.70 Max 106.74 49.59 38.21 102.45 0.24 36.21 0.21 18.04 Mean 80.33 39.62 29.08 90.08 0.17 31.78 0.08 14.38 CV 23.57% 21.29% 16.55% 7.46% 20.18% 12.20% 62.68% 17.10% 山前洪积扇 Min 71.24 26.43 26.06 76.57 0.12 25.36 0.05 14.04 Max 92.80 74.71 43.25 96.01 0.28 43.79 0.07 30.94 Mean 82.31 43.76 31.86 87.56 0.18 35.25 0.06 20.37 CV 13.70% 48.50% 24.70% 10.67% 38.12% 22.48% 14.32% 36.04% 银川平原 Min 44.02 23.75 22.23 76.57 0.10 25.36 0.05 9.34 Max 106.74 74.71 43.25 106.60 0.28 43.79 0.21 30.94 Mean 81.84 39.08 29.69 90.49 0.16 32.70 0.08 15.91 CV 19.44% 29.49% 17.55% 10.06% 27.77% 14.06% 48.73% 29.23% 参考体 中国背景值[26] 60 36.5 22.1 58.8 0.11 20.6 0.021 11.8 宁夏背景值[19] 54.46 21.74 16.08 44.19 0.10 17.25 0.013 9.11 风险筛选值[27] 250 190 100 300 0.6 170 3.4 25 天津[28] 51.0 39 33 148 0.18 45 0.43 11 北京[29] 52.1 22.9 — 68.3 0.153 23.8 0.046 8.3 珠江平原[30] 44.18 14.26 21.27 64.57 0.15 42.29 0.13 14.6 陕西[31] 71.00 32.00 — 83.00 0.20 24.00 0.13 14.00 松嫩平原[32] 53.62 23.34 18.59 55.96 0.1 22.00 0.03 8.69 由表4可知,银川平原中重金属的平均含量(mg·kg−1)大小为Zn(90.49)>Cr(81.84)>Ni(39.08)>Pb(32.70)>Cu(29.69)>As(15.91)>Cd(0.16)>Hg(0.08),含量差异较大。根据(GB15618—2018)中的农用地土壤风险筛选值 (pH>7.5),土壤中重金属 Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Hg、As平均含量均未超标。但对比宁夏土壤重金属的区域背景值,含量均超过了区域背景值,其超标分别达到了50.28%、79.76%、84.64%、104.77%、60.00%、89.57%、515.38%、74.64%。其中 Hg 超标最为严重,其余各金属的依次为:Hg > Zn > Pb > Cu > Ni > As > Cd > Cr。与其他地区土壤重金属研究进行对比,银川平原大多数重金属含量水平并不高,基本处于同一水平(Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Hg),但Cr和As的浓度相较于其他地区偏高,有研究表明,As元素作为农药和化肥等农业活动的标志元素[33],长期的使用会导致土壤中As的增加。
从图3中可以看出,不同地貌单元中重金属的含量不同,重金属Hg、Zn、Cr的含量由大到小依次为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,其中Hg、Zn、Cr在一级阶地含量相对较高可能是因为有机质含量高的土壤对重金属的吸附能力较强,但对不同的重金属也会有所差异[34]。不同地貌类型中土壤原生结构的差异,可能导致重金属含量的不同,其中山前洪积扇中可能是由于贺兰山岩土风化带来的,重金属大多来自于母质层本身所带来的;一级阶地主要受到黄河的冲击,可能从上游水中带来;主要是物源不同导致重金属总量的差异。重金属Ni、Cu、Cd的排序都为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,Pb和As的排序为山前洪积扇>一级阶地>二级阶地。pH会影响土壤中重金属的含量,研究区土壤 pH 值均大于7,在碱性条件下,土壤中As多以HASO4−存在[35],pH越高越不利于As在土壤中的存留,二级阶地土壤中pH较高,故在3种土壤中含量较低。
基于ArcGIS10.2软件绘制研究区土壤重金属空间分布图(图4),结果显示,8种土壤重金属在空间分布上具有一定的差异性。Cr、Cd、As、Cu的分布较为相似,主要特征表现为在西北部地区山前洪积扇中重金属含量较高,南部和东部的阶地中含量较低。Hg的空间分布与之相反,高值主要表现在中东部地区的阶地中,在西部地区山前洪积扇中含量较低。Ni的分布高值在西北部山前洪积扇中,低值主要分布在东南部的一级阶地中。Pb的高值主要表现在中部地区呈条带状分布在山前洪积扇和二级阶地中,在南北部含量相对较低。
2.2.2 土壤重金属赋存形态特征
土壤中重金属的赋存形态特征是研究重金属的来源和生物有效性的重要信息[36],其迁移能力和赋存形态密切相关,并能对生态环境质量产生直接影响。重金属的离子交换态和碳酸盐结合态可被植物直接利用,铁锰氧化态和有机结合态在一定条件下可转化被植物吸收利用,而残渣态能长期稳定的存在于土壤中,不易被生物所利用,也不易发生迁移转化,对环境危害较小。
重金属各形态分布情况见图5。银川平原不同地貌单元土壤中As、Cr、Ni、Cu和Zn的赋存形态会有所差异,但均以残渣态为主,平均占比分别达到86.13%、83.59%、56.26%、58.47%、48.13%,生态环境危害均较低,这与已有的报道相似[35]。Cd的可利用态和潜在可利用组分远高于其他重金属,与大多数地区土壤中重金属Cd的赋存形态具有一定的相似性,即含量分布大多具有相对较低的残渣态和相对较高的活性态的特征[37]。Pb的潜在可利用态占63%,在还原环境中或pH值降低情况下,重金属会向有效态转化而增加土壤重金属风险,与麻冰涓[38]和韦壮绵[39]的研究结果相似,这可能是因为土壤中Fe和Mn的氢氧化物对 Pb2+有很强的专项吸附能力[40]。总体而言,除了Cd与Pb外,研究区土壤重金属多以残渣态形式存在,重金属元素生物活性组分占比相对较低。
由图6可知,不同地貌单元中的重金属赋存形态各不相同,其中:离子交换态Cr、Ni、Pb、Zn、Cu含量均为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,可能是由于种植结构的差异所导致,其中山前洪积扇 种植葡萄经济作物,农药化肥用量较大,灌溉也相对较多,导致其离子交换态含量赋存较多。还可能是由于在一级阶地中的有机质含量最高而在山前洪积扇中的含量较低有关,彭敏等的研究表明,土壤有机质能通过吸附金属络合物而降低重金属的生物活性[37]。碳酸盐态Zn、Pb、As含量均表现出一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,pH是影响碳酸盐态的关键因素,而pH的升高有利于碳酸盐态的形成,一级阶地的pH相对较高,因此碳酸盐态含量较多。铁锰结合态Ni、Pb、Cu含量均表现出山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,而As含量却表现出一级阶地>山前洪积扇>二级阶地,这是由于土壤pH值升高,土壤中铁锰氧化物(土壤矿质胶体中吸附阴离子的重要部分)增加,导致其吸附能力增强[41],因此pH相对较高的土壤中As的铁锰态含量高。在活性相对较低的有机结合态中Cr、Pb、Zn、Cu含量均为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,而Ni含量表现出二级阶地>一级阶地>山前洪积扇。在惰性最大的残渣态中Cr、Ni、Pb、Cu均表现出二级阶地>一级阶地>山前洪积扇。
总体来看,在3种地貌单元中,重金属的赋存形态为:Ni、Pb、Cu的离子交换态和铁锰态表现为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地;Zn和Pb的碳酸盐结合态和有机态表现为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇;Cr、Ni、Pb和Cu残渣态表现为二级阶地>一级阶地>山前洪积扇。
2.3 土壤重金属生态风险评价
2.3.1 富集因子法
由图7可知,银川平原土壤中重金属均为中等富集程度(1.5<EF≤5),其中Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Hg和As的中位值分别为1.53、1.74、1.86、2.10、1.62、1.87、3.43、1.70,说明银川平原土壤存在重金属污染。其中Hg的富集系数较大,富集程度相比于其他重金属较为明显,且部分Hg的EF值可达偏高富集,属于偏高污染程度,应予以关注。
2.3.2 潜在生态风险评价
表5是银川不同地貌单元土壤重金属生态风险指数,从单因子风险指数可以看出研究区土壤样品中As、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni和 Cr的潜在风险指数均小于40,为轻微生态风险。而Cd的潜在生态风险指数范围为27.24—73.83,均值为42.72,存在轻微至中等生态风险等级,以轻微生态危害为主,个别点处在中等危害水平。Hg的潜在生态风险指数范围为89.71—394.48,均值为142.02,风险等级为强度生态危害。整体上Cd处在中度危害水平,Hg因其较高的含量和强烈的毒性,处在强度危害水平;其余各金属的毒性相对较低,都处在轻微危害状态,危害水平从大到小依次为As、Pb、Zn、Cu、Ni、Cr。
表 5 不同地貌单元潜在生态风险评价Table 5. Potential ecological risk assessment of different geomorphic units地貌单元Geomorphological unit Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb Hg As RI 一级阶地 Min 1.89 3.69 5.11 6.57 27.24 7.27 89.71 7.92 167.70 Max 3.38 5.22 7.32 9.06 42.38 8.35 194.95 14.07 275.89 Mean 2.80 4.72 6.54 7.95 34.45 7.80 152.76 12.52 229.54 二级阶地 Min 1.47 3.25 5.03 6.66 35.08 6.40 95.43 9.92 165.09 Max 3.56 6.79 8.64 8.71 64.91 8.79 394.48 15.29 485.00 Mean 2.68 5.43 6.58 7.66 45.77 7.71 158.82 12.19 246.83 山前洪积扇 Min 2.37 3.62 5.89 6.51 32.06 6.16 99.24 11.90 177.34 Max 3.09 10.23 9.79 8.16 73.83 10.63 137.33 26.22 233.74 Mean 2.74 5.99 7.21 7.45 47.95 8.55 114.48 17.26 211.63 银川平原 Min 1.47 3.25 5.03 6.51 27.24 6.16 89.71 7.92 165.09 Max 3.56 10.23 9.79 9.06 73.83 10.63 394.48 26.22 485.00 Mean 2.74 5.38 6.78 7.69 42.72 8.02 142.02 13.99 229.33 从潜在生态风险指数RI上看(表5),土壤中重金属的RI值为165.09—485.00,最大值(485.00)出现在二级阶地土壤中,属于强生态危害等级,一级阶地和山前洪积扇均处在中等生态风险。其中,Hg和Cd对潜在生态风险指数RI的贡献最为主要,而其他元素贡献率相对较低,这与北方地区土壤重金属生态风险评价结果一致[42]。孙变变采用潜在生态风险指数法对银川土壤重金属生态风险进行评价,结果也表明Hg是最主要的风险来源[43]。主要原因一方面是由于Hg的毒性相应系数数值较高,另一方面土壤Hg的背景值较低,而该区域土壤Hg的含量超标点位较多。
2.3.3 生物有效指数评价
银川平原土壤重金属生物有效指数具有明显的差异性,如表6所示,其中Cr(0.19—0.46)、Ni(0.18—1.04)、Cu(0.40—0.96)、Zn(0.58—0.91)、As(0.11—0.32),均值分别为0.31、0.46、0.56、0.76、0.20,在3种地貌单元中的生物有效指数结果均处于0—1之间,表明这5种重金属均处在无污染状态。Cd的生物有效指数在0.72—1.66,均值为1.13,整体上处于无污染状态的占29.41%,其余处在轻微污染状态的占70.59%,表明主要以轻微污染状态为主。Pb的生物有效指数位于0.74—1.27之间,其中一级阶地和二级阶地的均在无污染状态,而山前洪积扇地貌单元土壤处在轻微污染状态,整体上处在无污染状态占比为52.94%,轻微污染状态的占47.06%。
表 6 生态有效指数法评价结果Table 6. Ecological effectiveness index method evaluation results地貌单元Geomorphological unit Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb As 一级阶地 Min 0.25 0.23 0.45 0.61 0.72 0.83 0.11 Max 0.44 0.49 0.66 0.76 1.12 1.19 0.26 Mean 0.34 0.35 0.54 0.71 0.91 0.97 0.21 二级阶地 Min 0.19 0.18 0.42 0.75 1.02 0.80 0.13 Max 0.46 0.67 0.72 0.91 1.55 1.07 0.22 Mean 0.30 0.48 0.53 0.81 1.28 0.97 0.17 山前洪积扇 Min 0.23 0.27 0.40 0.58 0.82 0.74 0.17 Max 0.39 1.04 0.96 0.87 1.66 1.27 0.32 Mean 0.29 0.56 0.61 0.75 1.20 1.01 0.21 银川平原 Min 0.19 0.18 0.40 0.58 0.72 0.74 0.11 Max 0.46 1.04 0.96 0.91 1.66 1.27 0.32 Mean 0.31 0.46 0.56 0.76 1.13 0.98 0.20 2.3.4 土壤RAC风险评价
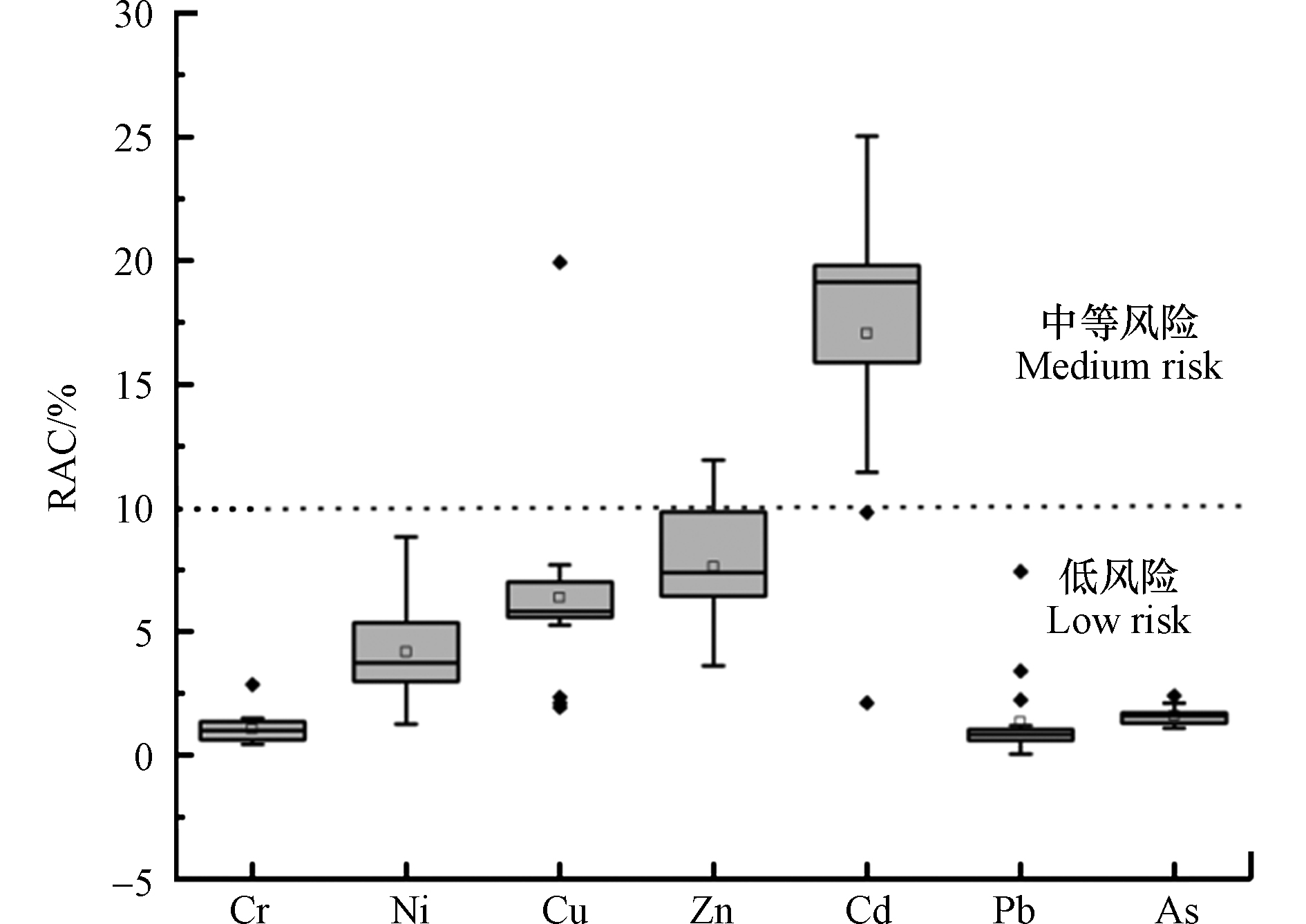
大量研究表明,重金属的生物毒性和生物可利用度不仅与总量有关,更与其赋存形态密切相关。不同形态的重金属在土壤中的迁移能力不同,对植物的生物有效性也不同。研究区土壤多为碱性,碳酸盐态不易转化为离子交换态被生物所利用,因此研究区重金属元素的生物有效性主要考虑植物易吸收的离子交换态。研究区土壤重金属的RAC风险等级如图8所示。
根据风险指数平均值银川平原土壤重金属RAC风险系数由强到弱分别Cd > Zn > Cu > Ni > Cr > Pb,重金属Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn和Pb元素RAC风险等级均为低风险或无风险,仅Cd 元素RAC 风险等级以中等风险为主,这与其他地区的研究结果相一致[23]。Cd 的可交换态百分比高,生物活性高,对环境可能造成的有害效应较强,因此其风险较高。其他重金属生物活性较低,对环境可能造成的有害效应有限,因此风险水平较低。
2.4 重金属来源分析
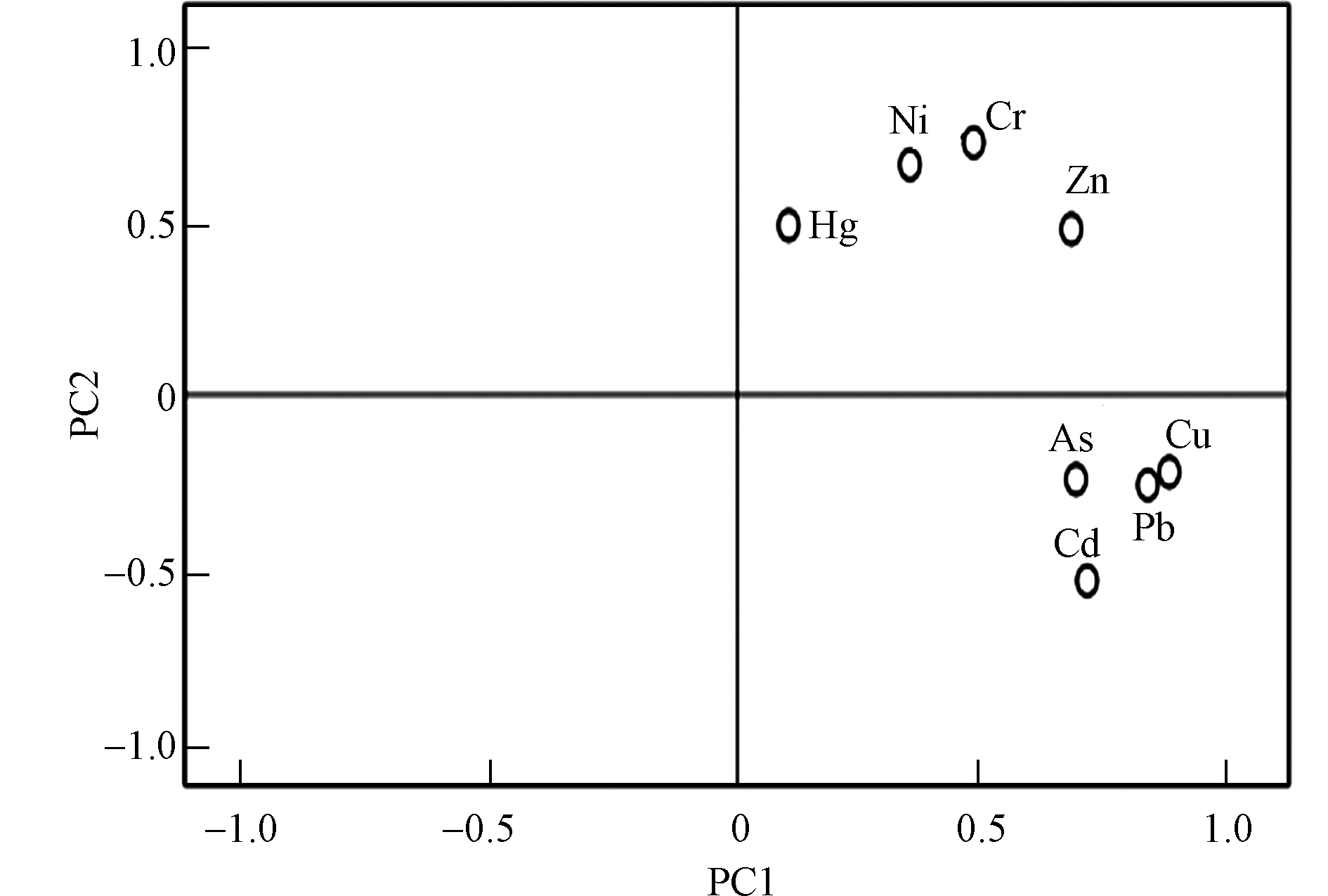
以上分析表明,银川平原土壤中重金属具有富集现象。土壤重金属的来源既与自然条件有关,也与工业、农业等人为活动有关[44]。研究区土壤重金属含量数据经KMO检验和Bartlett’s球体检验,结果显示KMO检验系数为0.674>0.5,Bartlett's球体检验P值<0.05,表明各重金属元素相关性强,适合进行主成分分析。土壤8种重金属污染物主成分分析显示(图9),第一主成分(PC1)与第二主成分的特征值为(PC2)特征值分别为3.213和1.859,对应方差贡献率分别为40.164%和23.244%,说明所有数据的绝大部分信息能够由前2个主成分反映(63.41%)。
第一主成分的方差贡献率为40.164%,表现为重金属Cu、Pb、Cd、As有较高的正载荷,分别为0.870、0.826、0.704、0.682。研究区土壤多为农业用地,大量使用的有机肥中Pb含量偏高可能造成土壤中Pb升高[45]。宋波等[46]对广西农田研究发现污灌对土壤中Cd含量的影响较为突出;Cu是载荷值最大的元素,畜禽饲料中经常添加Cu用来防治疾病和促进生长,且95%会随粪便排出,施用到土壤中时,也会相应地增加土壤中Cu的含量[47];Lu等[48]的研究也发现, Cd和Cu主要来自农业活动,同时灌溉用水也是农业土壤中重金属 Cd和Cu含量升高的重要原因[49]。赵东杰等[33]的研究也指出,As元素是农药和化肥等农业活动的标志元素。银川平原是历史悠久的老灌区,长期接受黄河水灌溉补给,水体中不可避免存在微量重金属,因此推测第一主成分4 种重金属具有相同或相似的来源,重金属的来源主要受农业的灌溉、化肥以及农药的使用等人类生产活动的影响。第二主成分的方差贡献率为23.24%,表现为重金属Cr、Ni、Zn有较高的正载荷,分别为0.720、0.656、0.673,且变异系数均较低,受人为因素影响程度较小,潜在生态风险评价结果可知,Cr、Ni、Zn均造成轻微生态危害水平,进一步表明这三种重金属受人类活动影响较小[50],主要是由日照强烈,岩石风化严重从而进入土壤中。结合Sheng[51]、纪冬丽等[52]的研究,发现Cr和Ni在土壤中可能来源于成土母质或母岩的风化与破碎等观点,推断这3种重金属主要由岩石风化进入成土母质中,为自然来源。
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)在空间分布上,土壤中Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Cd、Pb、Hg、As 含量高于背景值,分别达到背景值1.51、1.80、1.85、2.05、1.60、1.91、6.15和1.75倍。其中,Cr、Zn、Hg的含量依次为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇,Ni、Cu、Cd的含量由大到小为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地,Pb和As的含量依次为山前洪积扇>一级阶地>二级阶地,可能由于不同地貌单元中的有机质含量和pH值不同导致。
(2)研究区重金属Cd的可利用态占比达42.3%,生物有效性相对较高,其余重金属赋存形态以残渣态为主,对生态环境危害较低。重金属的赋存形态表现为:在不同地貌单元中Ni、Pb、Cu的交换态和铁锰结合态均为山前洪积扇>二级阶地>一级阶地;Zn和Pb的碳酸盐态和有机结合态为一级阶地>二级阶地>山前洪积扇;Cr、Ni、Pb和Cu残渣态为二级阶地>一级阶地>山前洪积扇。
(3)潜在生态风险结果显示,重金属Hg和Cd的风险水平较高,分别处于强度和中度生态危害水平,其余各金属危害指数较小,都处于轻度生态危害水平;生态有效指数法和RAC指数法均显示,仅Cd元素以中等风险为主,其他各元素均为低风险或无风险。初步判定Cd和Hg为银川平原土壤重金属污染防治的优先控制对象.其他重金属含量也呈现出明显增加的趋势,仍需引起重视。
(4)土壤重金属主成分分析结果表明,重金属Cu、Pb、Cd、As的来源主要与农业生产等人类活动带入有关,对环境带来的风险较大,而Cr、Ni、Zn主要与岩石风化等自然过程有关。
-
表 1 富集因子和污染等级
Table 1. Enrichment factor and pollution level
富集因子Enrichment factor EF≤1.5 1.5<EF≤5 5<EF≤20 20<EF≤40 富集程度 无或低富集 中度富集 偏高富集 高富集 污染程度 无或低 中度 偏高 高 表 2 银川平原不同地貌单元矿物组成(%)、pH及TOC含量(%)
Table 2. Statistic results of mineral composition (%),pH value and TOC content (%) of different geomorphic units in Yinchuan Plain
地貌单元Geomorphological unit 石英Quartz 方解石Calcite 钠长石Albite 白云母Muscovite 伊利石Illite 绿泥石Chlorite pH TOC 一级阶地 32.26 8.16 12.06 31.26 7.96 8.32 8.39 29.00 二级阶地 32.52 8.96 14.32 24.02 8.49 7.07 8.07 21.74 山前洪积扇 39.16 11.18 19.58 18.38 6.50 3.62 8.17 7.00 银川平原 34.65 9.43 15.32 24.55 7.65 6.34 8.21 19.23 表 3 土壤主要氧化物含量统计结果(%)
Table 3. Statistic results of major oxide concentration (%)
地貌单元Geomorphological unit SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O 一级阶地 60.46 15.14 4.55 10.32 3.25 3.02 1.71 二级阶地 59.23 14.58 4.69 11.14 3.89 3.1 1.75 山前洪积扇 59.39 13.56 4.28 13.43 3.55 2.9 1.59 银川平原 59.58 14.46 11.51 4.49 3.70 3.01 1.72 CV 8 8 29 19 18 10 26 CS[24] 65.00 12.60 4.60 3.20 1.80 2.50 1.60 注:CS:中国平均土壤,CV:变异系数. Note:CS:China average soil,CV:Coefficient of variation. 表 4 银川平原土壤重金属全量统计分析(mg·kg-1)
Table 4. Statistical analysis of total heavy metals in soils in Yinchuan Plain(mg·kg-1)
地貌单元Geomorphological unit Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb Hg As 一级阶地 Min 56.82 26.94 22.59 77.24 0.10 29.94 0.05 9.34 Max 101.28 38.11 32.34 106.60 0.16 34.40 0.10 16.60 Mean 83.87 34.49 28.91 93.50 0.13 32.13 0.08 14.78 CV 19.96% 13.02% 13.57% 13.80% 17.91% 5.05% 25.29% 20.68% 二级阶地 Min 44.02 23.75 22.23 78.35 0.13 26.35 0.05 11.70 Max 106.74 49.59 38.21 102.45 0.24 36.21 0.21 18.04 Mean 80.33 39.62 29.08 90.08 0.17 31.78 0.08 14.38 CV 23.57% 21.29% 16.55% 7.46% 20.18% 12.20% 62.68% 17.10% 山前洪积扇 Min 71.24 26.43 26.06 76.57 0.12 25.36 0.05 14.04 Max 92.80 74.71 43.25 96.01 0.28 43.79 0.07 30.94 Mean 82.31 43.76 31.86 87.56 0.18 35.25 0.06 20.37 CV 13.70% 48.50% 24.70% 10.67% 38.12% 22.48% 14.32% 36.04% 银川平原 Min 44.02 23.75 22.23 76.57 0.10 25.36 0.05 9.34 Max 106.74 74.71 43.25 106.60 0.28 43.79 0.21 30.94 Mean 81.84 39.08 29.69 90.49 0.16 32.70 0.08 15.91 CV 19.44% 29.49% 17.55% 10.06% 27.77% 14.06% 48.73% 29.23% 参考体 中国背景值[26] 60 36.5 22.1 58.8 0.11 20.6 0.021 11.8 宁夏背景值[19] 54.46 21.74 16.08 44.19 0.10 17.25 0.013 9.11 风险筛选值[27] 250 190 100 300 0.6 170 3.4 25 天津[28] 51.0 39 33 148 0.18 45 0.43 11 北京[29] 52.1 22.9 — 68.3 0.153 23.8 0.046 8.3 珠江平原[30] 44.18 14.26 21.27 64.57 0.15 42.29 0.13 14.6 陕西[31] 71.00 32.00 — 83.00 0.20 24.00 0.13 14.00 松嫩平原[32] 53.62 23.34 18.59 55.96 0.1 22.00 0.03 8.69 表 5 不同地貌单元潜在生态风险评价
Table 5. Potential ecological risk assessment of different geomorphic units
地貌单元Geomorphological unit Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb Hg As RI 一级阶地 Min 1.89 3.69 5.11 6.57 27.24 7.27 89.71 7.92 167.70 Max 3.38 5.22 7.32 9.06 42.38 8.35 194.95 14.07 275.89 Mean 2.80 4.72 6.54 7.95 34.45 7.80 152.76 12.52 229.54 二级阶地 Min 1.47 3.25 5.03 6.66 35.08 6.40 95.43 9.92 165.09 Max 3.56 6.79 8.64 8.71 64.91 8.79 394.48 15.29 485.00 Mean 2.68 5.43 6.58 7.66 45.77 7.71 158.82 12.19 246.83 山前洪积扇 Min 2.37 3.62 5.89 6.51 32.06 6.16 99.24 11.90 177.34 Max 3.09 10.23 9.79 8.16 73.83 10.63 137.33 26.22 233.74 Mean 2.74 5.99 7.21 7.45 47.95 8.55 114.48 17.26 211.63 银川平原 Min 1.47 3.25 5.03 6.51 27.24 6.16 89.71 7.92 165.09 Max 3.56 10.23 9.79 9.06 73.83 10.63 394.48 26.22 485.00 Mean 2.74 5.38 6.78 7.69 42.72 8.02 142.02 13.99 229.33 表 6 生态有效指数法评价结果
Table 6. Ecological effectiveness index method evaluation results
地貌单元Geomorphological unit Cr Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb As 一级阶地 Min 0.25 0.23 0.45 0.61 0.72 0.83 0.11 Max 0.44 0.49 0.66 0.76 1.12 1.19 0.26 Mean 0.34 0.35 0.54 0.71 0.91 0.97 0.21 二级阶地 Min 0.19 0.18 0.42 0.75 1.02 0.80 0.13 Max 0.46 0.67 0.72 0.91 1.55 1.07 0.22 Mean 0.30 0.48 0.53 0.81 1.28 0.97 0.17 山前洪积扇 Min 0.23 0.27 0.40 0.58 0.82 0.74 0.17 Max 0.39 1.04 0.96 0.87 1.66 1.27 0.32 Mean 0.29 0.56 0.61 0.75 1.20 1.01 0.21 银川平原 Min 0.19 0.18 0.40 0.58 0.72 0.74 0.11 Max 0.46 1.04 0.96 0.91 1.66 1.27 0.32 Mean 0.31 0.46 0.56 0.76 1.13 0.98 0.20 -
[1] ZHANG P Y, QIN C Z, HONG X, et al. Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of Yellow River irrigation in China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 633: 1136-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.228 [2] CHEN H Y, TENG Y G, LU S J, et al. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 512/513: 143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025 [3] HUANG Y, WANG L Y, WANG W J, et al. Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: A meta-analysis [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 651: 3034-3042. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.185 [4] LIANG X F, HAN J, XU Y M, et al. In situ field-scale remediation of Cd polluted paddy soil using sepiolite and palygorskite [J]. Geoderma, 2014, 235/236: 9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.06.029 [5] 张富贵, 彭敏, 王惠艳, 等. 基于乡镇尺度的西南重金属高背景区土壤重金属生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9): 4197-4209. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201912241 ZHANG F G, PENG M, WANG H Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals at township scale in the high background of heavy metals, Southwestern, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(9): 4197-4209(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201912241
[6] BHATTI S S, KUMAR V, SAMBYAL V, et al. Comparative analysis of tissue compartmentalized heavy metal uptake by common forage crop: A field experiment [J]. CATENA, 2018, 160: 185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.09.015 [7] 钟萍, 张家泉, 占长林, 等. 华中冶金工业走廊表层土壤、道路尘重金属污染特征及健康风险 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(1): 87-96. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018020103 ZHONG P, ZHANG J Q, ZHAN C L, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and health risks of topsoil and road dust in Central China Metallurgical Industry Corridor [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(1): 87-96(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018020103
[8] 孙彤, 纪艺凝, 李可, 等. 弱碱性玉米地土壤重金属赋存形态及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(9): 2469-2478. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019061701 SUN T, JI Y N, LI K, et al. The speciation distributions of heavy metals in weakly alkaline maize soils and its potential ecological risk [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(9): 2469-2478(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019061701
[9] 张成丽, 张伟平, 程红丹, 等. 禹州市煤矿区周边土壤和农作物重金属污染状况及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(4): 805-812. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018060502 ZHANG C L, ZHANG W P, CHENG H D, et al. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment of farmland soil around coal mines in Yuzhou City [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(4): 805-812(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018060502
[10] 范刘丹, 王明仕, 宋党育, 等. 部分中国城市公园重金属生态风险及健康风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(4): 793-804. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018061701 FAN L D, WANG M S, SONG D Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in some China urban Parks [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(4): 793-804(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018061701
[11] 姬超, 侯大伟, 李发志, 等. 耕地土壤重金属健康风险空间分布特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1440-1448. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201908163 JI C, HOU D W, LI F Z, et al. Assessment and spatial characteristics analysis of human health risk of heavy metals in cultivated soil [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1440-1448(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201908163
[12] 周勤利, 王学东, 李志涛, 等. 宁夏贺兰县土壤重金属分布特征及其生态风险评价 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2019, 36(4): 513-521. ZHOU Q L, WANG X D, LI Z T, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metal in Helan County of Ningxia, China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2019, 36(4): 513-521(in Chinese).
[13] 石天池, 王志强, 曹园园, 等. 农用地土壤中重金属水平及潜在生态风险评价: 以宁夏石嘴山地区为例 [J]. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(2): 180-183. SHI T C, WANG Z Q, CAO Y Y, et al. Evaluation on heavy metal levels and potential ecological risks in agricultural soils—A case study of Shizuishan region of ningxia [J]. Journal of Ningxia University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 42(2): 180-183(in Chinese).
[14] 张敏. 宁夏平原引黄灌区重金属污染特征及其两种土地利用类型源解析研究[D]. 北京: 中央民族大学, 2020. ZHANG M. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution and source analysis of two land use types in the Yellow River Irrigation Area of Ningxia Plain [D]. Beijing: Central University for Nationalities, 2020(in Chinese).
[15] 张松林. 西北工业园区盐土重金属污染的盐生植物生态修复研究 : 以宁夏石嘴山惠农区为例[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2020. ZHANG S L. Research on phytoremediation of halophytes for heavy metal pollution of saline soil in northwest industrial park —A case study of Huinong district, ningxia, China[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2020(in Chinese).
[16] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [17] 严明书, 李武斌, 杨乐超, 等. 重庆渝北地区土壤重金属形态特征及其有效性评价 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(1): 64-70. YAN M S, LI W B, YANG L C, et al. Speciation characteristics and effectiveness assessment of heavy metals in soils in Yubei district, Chongqing [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(1): 64-70(in Chinese).
[18] ZHANG H H, CHEN J J, ZHU L, et al. Anthropogenic mercury enrichment factors and contributions in soils of Guangdong Province, South China [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 144: 312-319. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.01.031 [19] 高宇, 杨智敏. 银川平原土壤地球化学基准值研究 [J]. 农业科学研究, 2009, 30(1): 10-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0747.2009.01.003 GAO Y, YANG Z M. Datum values of soil geochemistry in Yinchuan Plain [J]. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 30(1): 10-12(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0747.2009.01.003
[20] SUTHERLAND R A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii [J]. Environmental Geology, 2000, 39(6): 611-627. doi: 10.1007/s002540050473 [21] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [22] NEMEROW N L. Stream, lake, estuary, and ocean pollution [M]. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Publishing, 1985. [23] 杨新明, 庄涛, 韩磊, 等. 小清河污灌区农田土壤重金属形态分析及风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(3): 644-652. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051001 YANG X M, ZHUANG T, HAN L, et al. Fraction distribution and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the farmland soil from the sewage irrigated area of Xiaoqing River [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(3): 644-652(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018051001
[24] 鄢明才, 迟清华. 中国东部地壳与岩石的化学组成[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 126-127. YAN M C, CHI Q H. The chemical compositions of crust and rocks in the eastern part of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 126-127(in Chinese).
[25] 曹宏杰, 王立民, 罗春雨, 等. 三江平原地区农田土壤中几种重金属空间分布状况 [J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2014, 30(2): 155-161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2014.02.003 CAO H J, WANG L M, LUO C Y, et al. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Sanjiang plain [J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2014, 30(2): 155-161(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2014.02.003
[26] 国家环境保护局主持中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990: 326-359. National Environmental Protection Agency, China Environmental Testing Center. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 1990: 326-359(in Chinese).
[27] 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 中华人民共和国国家标准: 土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准 GB 15618—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. Ministry of Ecology and Environment. National Standard (Mandatory) of the People's Republic of China: Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land. GB 15618—2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018 (in Chinese).
[28] ZHAO L, XU Y, HOU H, et al. Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468-469: 654-662. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.094 [29] 余洪慧. 北京市顺义区表层土壤重金属地球化学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019. YU H H. Geochemical characteristics of heavy metals in topsoil of Shunyi district in Beijing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2019(in Chinese).
[30] 宗庆霞, 窦磊, 侯青叶, 等. 基于土地利用类型的土壤重金属区域生态风险评价: 以珠江三角洲经济区为例 [J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(8): 875-884. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.08.0875 ZONG Q X, DOU L, HOU Q Y, et al. Regional ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in Pearl River Delta economic zone based on different land uses [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(8): 875-884(in Chinese). doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2017.08.0875
[31] PAN L B, MA J, WANG X L, et al. Heavy metals in soils from a typical County in Shanxi Province, China: Levels, sources and spatial distribution [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 148: 248-254. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.049 [32] 张慧, 马鑫鹏, 苏航, 等. 松嫩平原黑龙江省南部土壤重金属背景值及污染程度分析 [J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2018, 36(6): 230-236. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2018.06.34 ZHANG H, MA X P, SU H, et al. Soil heavy metal background values and pollution degree in southern Songnen Plain of Heilongjiang Province [J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2018, 36(6): 230-236(in Chinese). doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2018.06.34
[33] 赵东杰, 王学求. 滇黔桂岩溶区河漫滩土壤重金属含量、来源及潜在生态风险 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(4): 1609-1619. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.028 ZHAO D J, WANG X Q. Distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the floodplain soils of the Karst area of Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(4): 1609-1619(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.028
[34] 高太忠, 张昊, 周建伟. 溶解性有机物对土壤中重金属环境行为的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(4): 652-658. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.04.011 GAO T Z, ZHANG H, ZHOU J W. Effect of dissolved organic matter on the environmental behaviors of heavy metals in soils [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(4): 652-658(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.04.011
[35] 周亚龙, 杨志斌, 王乔林, 等. 雄安新区农田土壤-农作物系统重金属潜在生态风险评估及其源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4): 2003-2015. ZHOU Y L, YANG Z B, WANG Q L, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in soil-crop system in Xiongan new district [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4): 2003-2015(in Chinese).
[36] ADAMO P, IAVAZZO P, ALBANESE S, et al. Bioavailability and soil-to-plant transfer factors as indicators of potentially toxic element contamination in agricultural soils [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 500/501: 11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.085 [37] 马宏宏, 彭敏, 刘飞, 等. 广西典型碳酸盐岩区农田土壤-作物系统重金属生物有效性及迁移富集特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 449-459. MA H H, PENG M, LIU F, et al. Bioavailability, translocation, and accumulation characteristic of heavy metals in a soil-crop system from a typical carbonate rock area in Guangxi, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 449-459(in Chinese).
[38] 麻冰涓, 王海邻, 李小超, 等. 河南省武陟县大田土壤重金属形态分布及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(4): 363-367. MA B J, WANG H L, LI X C, et al. Fractional distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil, Wuzhi, Henan [J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(4): 363-367(in Chinese).
[39] 韦壮绵, 陈华清, 张煜, 等. 湘南柿竹园东河流域农田土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(10): 2753-2764. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019073103 WEI Z M, CHEN H Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils at Shizhuyuan Donghe River basin of Southern Hunan [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(10): 2753-2764(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019073103
[40] 陈岩, 季宏兵, 朱先芳, 等. 北京市得田沟金矿和崎峰茶金矿周边土壤重金属形态分析和潜在风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(11): 2142-2151. CHEN Y, JI H B, ZHU X F, et al. Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils around the gold mine of detiangou-qifengcha, Beijing city, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(11): 2142-2151(in Chinese).
[41] 李月芬, 王冬艳, 汤洁, 等. 吉林西部土壤砷的形态分布及其与土壤性质的关系研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(3): 516-522. LI Y F, WANG D Y, TANG J, et al. Speciation of soil arsenic and its correlation with soil properties in western Jilin Province, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(3): 516-522(in Chinese).
[42] 李小牛, 周长松, 杜斌, 等. 北方污灌区土壤重金属污染特征分析 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 42(6): 205-212. LI X N, ZHOU C S, DU B, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in sewage irrigated soil of Northern China [J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(6): 205-212(in Chinese).
[43] 孙变变, 赵银鑫, 常丹, 等. 银川市城市绿地土壤重金属分布特征及其生态风险评价 [J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(6): 262-268,277. SUN B B, ZHAO Y X, CHANG D, et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in green spaces of Yinchuan city [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(6): 262-268,277(in Chinese).
[44] BAI J H, CUI B S, CHEN B, et al. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a typical plateau lake wetland, China [J]. Ecological Modelling, 2011, 222(2): 301-306. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.12.002 [45] LV J, LIU Y, ZHANG Z L, et al. Identifying the origins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in soils of Ju country (Eastern China) using multivariate and geostatistical approach [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2015, 15(1): 163-178. doi: 10.1007/s11368-014-0937-x [46] 宋波, 张云霞, 庞瑞, 等. 广西西江流域农田土壤重金属含量特征及来源解析 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(9): 4317-4326. SONG B, ZHANG Y X, PANG R, et al. Analysis of characteristics and sources of heavy metals in farmland soils in the Xijiang River Draining of Guangxi [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(9): 4317-4326(in Chinese).
[47] 李有文, 莫治新, 薛江鹏, 等. 喀什地区土壤重金属污染评价及来源解析 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(8): 147-153. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2020.223 LI Y W, MO Z X, XUE J P, et al. Pollution evaluation and source apportionment of heavy metals in soils from Kashgar region, Xinjiang, China [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(8): 147-153(in Chinese). doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2020.223
[48] LU A X, WANG J H, QIN X Y, et al. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 425: 66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.03.003 [49] MICÓ C, RECATALÁ L, PERIS M, et al. Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis [J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 65(5): 863-872. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.016 [50] 王美娥, 彭驰, 陈卫平. 宁夏干旱地区工业区对农田土壤重金属累积的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(9): 3532-3539. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.09.035 WANG M E, PENG C, CHEN W P. Impacts of industrial zone in arid area in ningxia Province on the accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(9): 3532-3539(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2016.09.035
[51] SHENG J J, WANG X P, GONG P, et al. Heavy metals of the Tibetan top soils [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2012, 19(8): 3362-3370. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-0857-5 [52] 纪冬丽, 曾琬晴, 张新波, 等. 天津近郊农田土壤重金属风险评价及空间主成分分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(9): 1955-1965. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018111201 JI D L, ZENG W Q, ZHANG X B, et al. Ecological risk assessment and principal component analysis of heavy metals in suburban farmland soils of Tianjin [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(9): 1955-1965(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018111201
-




 下载:
下载: