-
毒品属于精神活性物质,是一类使人体在吸收后产生生理和心理依赖的物质[1],主要包括阿片类的海洛因及吗啡(MOR)制品,可卡因、苯丙胺类的甲基苯丙胺(METH)、苯丙胺和摇头丸等[2-3],截至2020年底,联合国毒品和犯罪办公室及欧洲药物与成瘾监测中心(EMCDDA)共鉴定出1000余种精神活性物质[4-6]。根据《2021年世界毒品问题报告》的数据显示,去年全球约有2.75亿人接触过毒品,相比2010年增加了22%,在2019年,吸毒直接导致近50万人死亡,超过 5400 万人患精神障碍疾病或丧失生命[6],引发了极其严峻的全球公共卫生问题[7-9]。《2020年中国毒品形势报告》指出,由于疫情扩散蔓延,毒品泛滥态势仍然复杂但整体向好 ,截至2020年底,中国现有吸毒人员180.1万名,海洛因、冰毒等滥用品种仍维持较大规模[10],严重影响了社会治安并造成了极大的社会危害[11-15]。
毒品滥用是对公共卫生和社会安全的巨大威胁[16],并严重威胁着人体健康[17],毒品滥用趋势的实时预测和社会危害的准确评价是当前亟待解决的问题[18],基于污水流行病学发展而来的污水验毒技术恰好能够解决这一难题。冰毒和海洛因等传统毒品,经过人体吸食和代谢后,随着尿液排入各级污水处理系统并最终汇入环境。通过对环境样品的采集、处理和分析,可以直观获取环境中毒品母体及其代谢物的种类、浓度及变化趋势,结合数学模型计算,可反推目标区域的毒品滥用种类和滥用量[19]。该方法所得数据客观、时效性高,可用于不同区域横向比较,在估算传统毒品滥用量等方面发挥了巨大作用[20-24]。但在污水及河流等的传输过程中,由于本底因素复杂,目标物可能存在生物化学降解、吸附或其他转化过程[25]。不同水环境性质的差异对传统毒品及其代谢产物的稳定存在具有不同程度的影响[26]。Baker等[26]认为,中性水样中,METH具有较好的稳定性倾向[27]。但海洛因代谢产物6-单乙酰吗啡(6-MAM)非常不稳定,可进一步转化为MOR[28],在污水流行病学范畴内,海洛因的估算通常是以其代谢产物6-MAM作为标准进行的[29],但污水中,6-MAM的损失比例高达42%[26],从而该方法失效。张小寒[30]则认为pH值可通过影响水底质中悬浮物的表面电荷,使得水样中传统毒品含量测量值偏低。张春水等[31]认为,海洛因在碱性条件下会加速降解。此外,吕昱帆等[32]在其研究中发现盐析剂NaCl的使用对6-MAM及MOR的回收率具有不同程度的影响。
为明确水环境对METH、6-MAM和MOR的基质效应,本研究选取了山东省潍坊市11条不同河流的实际水样,测定相关水质参数,采用内标法和主成分分析法探讨基本水质参数对3种精神活性物质METH、6-MAM和MOR定量分析准确度的影响;设计不同梯度pH及氯离子浓度的模拟水样,加入定量METH、6-MAM和MOR并储存不同时间,测试分析其中目标物含量,验证pH、氯离子浓度及存储时间对3种精神活性物质检出浓度的影响。
-
精神活性物质METH、6-MAM及MOR由山东省公安厅提供;氘代内标储备液MOR-D3、6-MAM-D3、METH-D8(100 μg·mL−1, 美国Cerilliant公司);实际水样来源于山东省潍坊市白浪河及利民河等处。主要化学试剂浓氨水、氢氧化钠、氯化钠、硝酸银、重铬酸钾、硫酸汞、高锰酸钾(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司),甲醇、二氯甲烷、甲酸(色谱纯,J&K百灵威公司)。
固相萃取仪(美国SUPELCO公司),Oasis MCX固相萃取小柱(美国Waters公司),0.45 μm微孔滤膜(天津津腾实验设备有限公司),氮吹仪(美国Organomation公司),XW-80A漩涡混合器(中国金昌实验仪器厂),三重四极杆液质联用仪(Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantiva LC-MS),水质多参仪(美国HACH公司),Milli-Q纯水机。
-
用分析天平分别称取0.0500 g METH、6-MAM及MOR,逐级稀释溶解于色谱纯的甲醇中,得到浓度均为50 ng·mL−1的毒品标准储备液,超声45 min使其溶解完全。
-
取浓盐酸和NaOH,加入Milli-Q水中,配制pH值分别为2、4、7、10的溶液备用。称取NaCl固体,配制质量浓度为0、1、2、3、4、5 g·L−1的溶液。在50 mL模拟水样中分别加入毒品标准储备液100 μL,使METH、6-MAM及MOR的质量浓度均为100 ng·L−1,常温(25℃)下存储12 、24、36、48、72、120 h。
-
实验样品于2019年12月在山东省潍坊市内白浪河及利民河等11条河流中采集。每个采样点取水样1000 mL, 分为两份,均置于提前用甲醇和Milli-Q水洗净并烘干的棕色玻璃瓶中。采样结束后立即运回实验室,于 4 ℃冷藏。1份样品在48 h内处理完毕,另1份加入定量毒品标准储备液,使METH、6-MAM及MOR的质量浓度均为100 ng·L−1,常温保存72 h。同步参照国家标准测试温度、pH、氯离子浓度,化学需氧量等6项相关水质参数。
-
①过滤:将水样经过玻璃纤维滤膜(Whatman GF/F)过滤,去除悬浮颗粒物,收集滤液至少100 mL。②MCX小柱活化:依次将甲醇、Milli-Q水和 pH=2的水溶液通过MCX小柱,控制流速为1—2 mL·min−1,充分活化并平衡柱子。③配制MOR-D3、6-MAM-D3、METH-D8的内标溶液,浓度均为200 μg·L−1。④于pH=2的条件下加载已过滤并添加内标的样品,控制流速为1—2 mL·min−1。⑤对淋洗后的SPE小柱持续抽气20 min,直至MCX小柱完全干燥。依次用甲醇和氨水/甲醇溶液(5/100,质量比)洗脱干燥的Oasis MCX柱,并控制流速为1—2 mL·min−1。⑥收集洗脱液,33 ℃水浴下置于柔和的氮气流下吹至近干,用注射器取0.5 mL 20%的甲醇水溶液复溶氮吹残留物,涡旋振荡1 min,用注射器吸取溶液,用0.45 μm针头过滤器(Whatman)过滤并转移至HPLC-MS/MS专用样品瓶中,重复此操作一次。⑦样品测试前用0.2 μm滤膜过滤,滤液上机测试。
-
流动相:0.12%甲酸和30 mmol·L−1甲酸铵超纯水溶液(A相);甲醇(B相),流速为0.3 mL·min−1,柱温为30 ℃,进样量为5 μL。以该液相色谱条件为初始方法[24],进一步手动优化,以获得对目标化合物的最高灵敏度(表1)。
质谱:离子源为电喷雾离子源(ESI),喷雾电压3500 V,离子传输管温度350 ℃,离子化模式为ESI(+);碰撞池气压(CAD)1.5 mTorr,鞘气压力(Sheath gas)为80 Arb,辅气压力(Aux gas)15 Arb。每种目标化合物及其相应内标的母离子和定量、定性离子的质荷比(m/z)见表2,其中,选取每种目标物丰度最大的离子对作为定量离子。
-
取3种毒品储备液适量,配制成低、中、高浓度(100 ng·L−1、300 ng·L−1、400 ng·L−1)的质控样品,分别按相同的前处理方法平行操作;每一浓度进行双样本分析,根据当日标准曲线,计算样品测定浓度,得出METH、6-MAM和MOR的方法回收率,结果见表3。数据结果表明METH、6-MAM和MOR的回收率良好。
-
将低浓度目标物混合标准溶液上机测定,仪器检出限(ILOD)和仪器定量限(ILOQ)分别以3倍信噪比(S/N=3)和10倍信噪比(S/N=10)确定。方法检出限(MLOD)和方法定量限(MLOQ)分别通过以下公式计算得到:
式中,200 μL为上机浓缩液的体积,50 mL为前处理所取水样的体积。
取混合毒品标准溶液适量,用流动相稀释,得质量浓度分别为1.5、3、6、12、25、50、100、150、200、250 ng·mL−1系列标准溶液。依次取上述各浓度标准溶液50 mL,按照相同的前处理方法操作,记录色谱图;以标准溶液中目标物的峰面积与同位素内标的峰面积之比为纵坐标(Y),进样浓度(X)为横坐标,进行线性回归运算,得METH、6-MAM和MOR回归方程:
结果表明METH、6-MAM及MOR质量浓度在1.5—250 ng·mL−1范围内线性关系良好,仪器的检出限和定量限见表3。
-
水样温度、pH值、氯离子浓度、化学需氧量、氨氮、高锰酸盐指数和溶解氧等水质参数见表4。
检测水样中METH、MOR及6-MAM浓度(记为c1),在样品中均加入定量毒品标准储备液,使METH、6-MAM及MOR的质量浓度均为100 ng·L−1,常温保存72 h后按照2.3所述方法进行样品前处理,并检测3种毒品目标物加标后的浓度(记为c2),见表5。
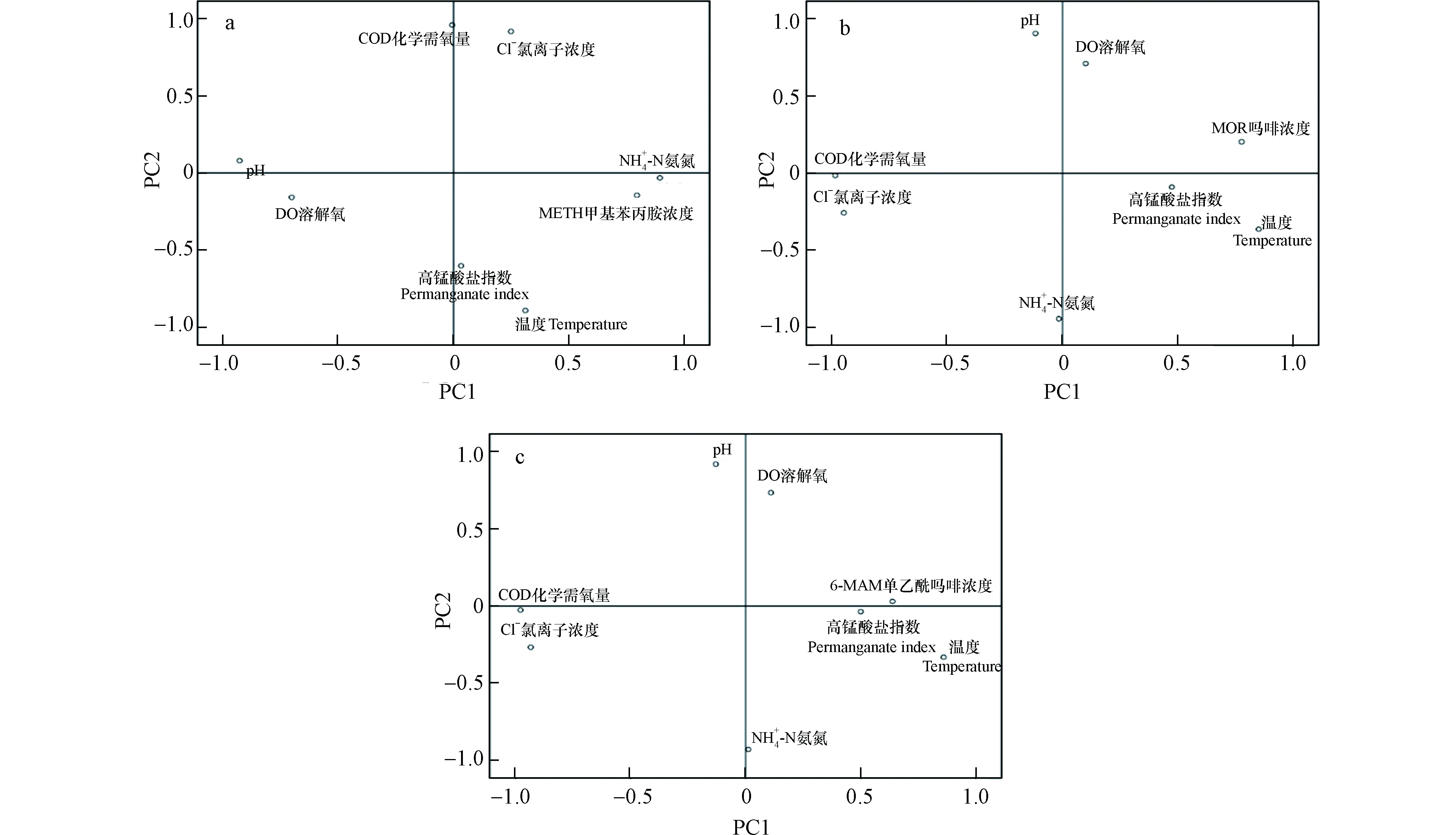
对河流水质参数及METH、6-MAM和MOR加标后的浓度分别进行主成分分析,探讨7个河流水质参数与污水样品中目标物检出浓度的相关性。主成分分析过程在 SPSS 20.0软件包中进行。对所有数据进行Bartlett球形度检验,相伴概率小于0.05,进行 PCA 以获得分数图和因子载荷,经变量最大旋转后,提取出特征值大于1的因子,主成分分析如图1所示。
METH与pH及溶解氧存在较强的负相关性,说明pH或溶解氧的升高可能会导致其检出浓度的下降。MOR与6-MAM均呈现出与化学需氧量及氯离子浓度的强负相关,说明较高浓度的氯离子浓度可能造成MOR及6-MAM检出浓度不准确。此外,METH与氨氮存在明显的正相关,而水体中氨氮的主要来源是生物体代谢所产生的尿素,与人口高度密切相关。METH是中国滥用人数最多且最为广泛的毒品,氨氮浓度较大的流域为人口聚集区域,METH浓度也呈现聚集趋势。MOR及6-MAM是海洛因的代谢产物,稳定性较低,在因子分析中表现为与温度及高锰酸盐指数相关。高锰酸盐指数是反映水体中有机和无机可氧化物质污染的常用指标,结果表明在较高温度及氧化性较强的水环境中,MOR及6-MAM易于分解。
-
根据实验结果,pH、氯离子浓度等均会不同程度影响3种毒品目标物的准确检出,故选取pH、氯离子浓度作为变量,设计单因素模拟实验验证其对毒品目标物稳定性的影响,此外,在应用污水验毒技术评估地区毒情及进行环境风险评估时,需要对污水及地表水中各毒品目标物进行精确定量,毒品母体及其生物标志物在不同水环境中驻留时间各不相同,也应考虑常温下不同存储时间对毒品目标物的检出影响。
-
取pH=2、pH=4、pH=7、pH=10的模拟水样各50 mL,分别向其加入METH、6-MAM及MOR标准溶液及内标,按照1.2.4进行前处理,3种目标物的检出浓度见表6。
当pH=2时,模拟样品中METH的回收率在71.97%—91.87%之间,pH值升高至4和7时,METH回收率为67.05%—99.51%,基本不变, pH升高至10时,METH的回收率明显降低,为57.63%—75.55%,即pH对METH的准确检出有影响,当水体呈现酸性及中性时,METH可以稳定存在并准确检出,在碱性水体中,METH稳定性发生改变,检出浓度下降,与实际水体因子分析的结论相符。原因可能为,在不同的pH体系中,METH的电离度及形态发生了变化。METH的结构中含有碱性的氨基官能团,溶液的pH会影响其质子化/去质子化的过程,此外,含胺类物质在水溶液中易发生光降解,且光解行为与氨基上N电子与三重激发物的转移有关,在低pH条件下,氢离子与N电子结合,阻碍了N电子向活性物的转化从而抑制其光降解,反之,N电子的可用性增强,加速了METH的降解[30]。模拟样品中,MOR在中性条件下检出浓度最高,酸性或碱性的条件下降低。6-MAM的变化趋势与其相反,中性条件下,其检出浓度最低,在酸性及碱性环境中,检出浓度较高,即pH也会干扰MOR和6-MAM在水体中的准确定量,张春水等[33]在研究中发现,海洛因的化学形式在不同pH环境下存在变化,当pH升高时,水解反应加剧,发生6-MAM向MOR的转化。实验结果对实际水体的主成分分析结果进行了补充,可知MOR在中性水体环境中较稳定,6-MAM在酸性条件下更稳定。
由图2可见,不同pH条件下, 6-MAM与MOR的浓度变化规律各不相同,两者呈现相反的趋势,在碱性水体环境中易发生6-MAM向MOR的转化,与张春水等[31]提出的海洛因在碱性条件下加速降解成MOR的结论一致。
在实际污水验毒工作中,6-MAM与MOR均被用来估算海洛因滥用量,在pH值为2、4、7、10时,6-MAM与MOR的回收率之和分别为95%、92%、89%和100%,可知pH对于二者的定量分析及海洛因滥用量的准确估算影响较小。
-
取不同氯离子浓度梯度的模拟水样各50 mL,分别加入METH、6-MAM及MOR标准溶液和内标,按照1.2.4节进行前处理,结果见表6。氯化钠浓度为0 g·L−1时,3种目标物都能在模拟水环境中稳定存在。METH的检出浓度随氯离子浓度升高基本不变;MOR的检出浓度在氯化钠浓度为1 g·L−1时最高,为47.74 ng·L−1,其它浓度时在31.94—39.79 ng·L−1范围内小幅波动,因此氯离子浓度的增大对MOR的稳定性存在负影响,与2.2主成分分析所得结论吻合;6-MAM的浓度随氯离子浓度的升高变化较大,在超过2 g·L−1的氯离子浓度的水环境中不能检出。吕昱帆等[32]在对腐败血中6-MAM和MOR的检出研究中发现,在2.5 mL样品中,加入盐析剂NaCl的质量大于30 mg时,6-MAM及MOR的回收率显著降低,与2.3.2节实验结果吻合,故氯离子浓度的影响在实际应用污水验毒技术的过程中不可忽略。
-
对常温(20℃)下存储不同时间的模拟水样进行前处理和定量分析,结果见表6。常温存储会使METH、6-MAM及MOR的浓度均下降,METH在120 h内降解35%左右,6-MAM在120 h内降解50%左右,MOR在120 h内降解达到了60%,即常温存储会造成METH、6-MAM及MOR在水中降解。
-
(1)本文研究了山东省潍坊市的11条河流中,不同水质参数与传统精神活性物质METH、MOR、6-MAM检出浓度的相关性,运用主成分分析法进行相关性评价。结果表明,METH与pH及溶解氧存在较强的负相关,与氨氮存在明显的正相关;MOR与6-MAM均与化学需氧量及氯离子浓度负相关,与其它水质参数相关性较小。
(2)根据实际水样主成分分析结果,选取相关性较大的水质参数进行单因素模拟实验,结果表明,METH在中性及酸性环境下较稳定,MOR在中性条件下较稳定,6-MAM在酸性和碱性条件下均能稳定存在和准确检出;METH的检出几乎不受氯离子浓度的影响,但6-MAM及MOR受氯离子浓度的影响较大;常温(20℃)保存120 h后,METH、6-MAM和MOR的含量均有不同程度的下降。
河流水质参数对甲基苯丙胺、吗啡及6-单乙酰吗啡定量分析的影响
Effects of river water quality parameters on quantitative analysis of methamphetamine, morphine and 6-monoacetylmorphine
-
摘要: 近年来,起源于污水流行病学的污水验毒技术逐渐成为涉毒评估的主流技术,但是该方法也存在一定的局限性。由于水样本底因素的复杂性使得目标物存在吸附、降解等过程,从而导致其定量分析不准确。本文通过固相萃取-液相色谱-多级质谱(SPE-LC-MS/MS)联用技术,检测了山东省潍坊市11条河流中甲基苯丙胺、吗啡和6-单乙酰吗啡等3种精神活性物质加标前后的质量浓度及水质参数,主成分分析法(PCA)评估了基本水质参数对这3种目标物的定量分析的影响,并设计单因素实验验证了pH、氯离子浓度和存储时间的影响。结果表明:甲基苯丙胺在低氯离子浓度、中性及酸性条件下具有较好的稳定性;吗啡在中性条件下较稳定,6-单乙酰吗啡在高氯离子浓度和中性环境中稳定性较差。因此水质参数的影响在传统精神活性物质的分析过程中不能忽略,这可为相关精神活性物质的定量分析提供参考。Abstract: In recent years, the sewage drug detection technology originating from sewage epidemiology has gradually become the mainstream technology of drug assessment, but it has some limitations. Due to the complexity of water sample background factors, the target substance maybe undergoes adsorption, degradation, etc., resulting in inaccurate quantitative analysis. In this paper, the mass concentrations of methamphetamine, morphine and 6-monoacetylmorphine in 11 rivers and water quality parameters in Weifang City, Shandong Province were detected by SPE-LC-MS/MS before and after methamphetamine, morphine and 6-monoacetylmorphine standards were added; and the effects of basic water quality parameters on the quantitative analysis of these three target substances were evaluated by principal component analysis (PCA), and single factor experiments were designed to verify the effects of pH, Cl- concentration and storage time. The results show that methamphetamine has good stability at low Cl- concentration and under neutral and acidic conditions; morphine has stability under neutral condition, and 6-monoacetylmorphine has poor stability at high Cl- concentration and under neutral condition. Therefore, the influences of water quality parameters can not be ignored during analysis of traditional psychoactive substances, which can provide a reference for quantitative analysis of relevant psychoactive substances.
-
毒品属于精神活性物质,是一类使人体在吸收后产生生理和心理依赖的物质[1],主要包括阿片类的海洛因及吗啡(MOR)制品,可卡因、苯丙胺类的甲基苯丙胺(METH)、苯丙胺和摇头丸等[2-3],截至2020年底,联合国毒品和犯罪办公室及欧洲药物与成瘾监测中心(EMCDDA)共鉴定出1000余种精神活性物质[4-6]。根据《2021年世界毒品问题报告》的数据显示,去年全球约有2.75亿人接触过毒品,相比2010年增加了22%,在2019年,吸毒直接导致近50万人死亡,超过 5400 万人患精神障碍疾病或丧失生命[6],引发了极其严峻的全球公共卫生问题[7-9]。《2020年中国毒品形势报告》指出,由于疫情扩散蔓延,毒品泛滥态势仍然复杂但整体向好 ,截至2020年底,中国现有吸毒人员180.1万名,海洛因、冰毒等滥用品种仍维持较大规模[10],严重影响了社会治安并造成了极大的社会危害[11-15]。
毒品滥用是对公共卫生和社会安全的巨大威胁[16],并严重威胁着人体健康[17],毒品滥用趋势的实时预测和社会危害的准确评价是当前亟待解决的问题[18],基于污水流行病学发展而来的污水验毒技术恰好能够解决这一难题。冰毒和海洛因等传统毒品,经过人体吸食和代谢后,随着尿液排入各级污水处理系统并最终汇入环境。通过对环境样品的采集、处理和分析,可以直观获取环境中毒品母体及其代谢物的种类、浓度及变化趋势,结合数学模型计算,可反推目标区域的毒品滥用种类和滥用量[19]。该方法所得数据客观、时效性高,可用于不同区域横向比较,在估算传统毒品滥用量等方面发挥了巨大作用[20-24]。但在污水及河流等的传输过程中,由于本底因素复杂,目标物可能存在生物化学降解、吸附或其他转化过程[25]。不同水环境性质的差异对传统毒品及其代谢产物的稳定存在具有不同程度的影响[26]。Baker等[26]认为,中性水样中,METH具有较好的稳定性倾向[27]。但海洛因代谢产物6-单乙酰吗啡(6-MAM)非常不稳定,可进一步转化为MOR[28],在污水流行病学范畴内,海洛因的估算通常是以其代谢产物6-MAM作为标准进行的[29],但污水中,6-MAM的损失比例高达42%[26],从而该方法失效。张小寒[30]则认为pH值可通过影响水底质中悬浮物的表面电荷,使得水样中传统毒品含量测量值偏低。张春水等[31]认为,海洛因在碱性条件下会加速降解。此外,吕昱帆等[32]在其研究中发现盐析剂NaCl的使用对6-MAM及MOR的回收率具有不同程度的影响。
为明确水环境对METH、6-MAM和MOR的基质效应,本研究选取了山东省潍坊市11条不同河流的实际水样,测定相关水质参数,采用内标法和主成分分析法探讨基本水质参数对3种精神活性物质METH、6-MAM和MOR定量分析准确度的影响;设计不同梯度pH及氯离子浓度的模拟水样,加入定量METH、6-MAM和MOR并储存不同时间,测试分析其中目标物含量,验证pH、氯离子浓度及存储时间对3种精神活性物质检出浓度的影响。
1. 实验部分(Experimental section)
1.1 实验试剂与仪器
精神活性物质METH、6-MAM及MOR由山东省公安厅提供;氘代内标储备液MOR-D3、6-MAM-D3、METH-D8(100 μg·mL−1, 美国Cerilliant公司);实际水样来源于山东省潍坊市白浪河及利民河等处。主要化学试剂浓氨水、氢氧化钠、氯化钠、硝酸银、重铬酸钾、硫酸汞、高锰酸钾(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司),甲醇、二氯甲烷、甲酸(色谱纯,J&K百灵威公司)。
固相萃取仪(美国SUPELCO公司),Oasis MCX固相萃取小柱(美国Waters公司),0.45 μm微孔滤膜(天津津腾实验设备有限公司),氮吹仪(美国Organomation公司),XW-80A漩涡混合器(中国金昌实验仪器厂),三重四极杆液质联用仪(Thermo Scientific TSQ Quantiva LC-MS),水质多参仪(美国HACH公司),Milli-Q纯水机。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 毒品标准储备液的配制
用分析天平分别称取0.0500 g METH、6-MAM及MOR,逐级稀释溶解于色谱纯的甲醇中,得到浓度均为50 ng·mL−1的毒品标准储备液,超声45 min使其溶解完全。
1.2.2 不同pH、氯离子浓度模拟水样配制
取浓盐酸和NaOH,加入Milli-Q水中,配制pH值分别为2、4、7、10的溶液备用。称取NaCl固体,配制质量浓度为0、1、2、3、4、5 g·L−1的溶液。在50 mL模拟水样中分别加入毒品标准储备液100 μL,使METH、6-MAM及MOR的质量浓度均为100 ng·L−1,常温(25℃)下存储12 、24、36、48、72、120 h。
1.2.3 实际水样的采集
实验样品于2019年12月在山东省潍坊市内白浪河及利民河等11条河流中采集。每个采样点取水样1000 mL, 分为两份,均置于提前用甲醇和Milli-Q水洗净并烘干的棕色玻璃瓶中。采样结束后立即运回实验室,于 4 ℃冷藏。1份样品在48 h内处理完毕,另1份加入定量毒品标准储备液,使METH、6-MAM及MOR的质量浓度均为100 ng·L−1,常温保存72 h。同步参照国家标准测试温度、pH、氯离子浓度,化学需氧量等6项相关水质参数。
1.2.4 样品前处理
①过滤:将水样经过玻璃纤维滤膜(Whatman GF/F)过滤,去除悬浮颗粒物,收集滤液至少100 mL。②MCX小柱活化:依次将甲醇、Milli-Q水和 pH=2的水溶液通过MCX小柱,控制流速为1—2 mL·min−1,充分活化并平衡柱子。③配制MOR-D3、6-MAM-D3、METH-D8的内标溶液,浓度均为200 μg·L−1。④于pH=2的条件下加载已过滤并添加内标的样品,控制流速为1—2 mL·min−1。⑤对淋洗后的SPE小柱持续抽气20 min,直至MCX小柱完全干燥。依次用甲醇和氨水/甲醇溶液(5/100,质量比)洗脱干燥的Oasis MCX柱,并控制流速为1—2 mL·min−1。⑥收集洗脱液,33 ℃水浴下置于柔和的氮气流下吹至近干,用注射器取0.5 mL 20%的甲醇水溶液复溶氮吹残留物,涡旋振荡1 min,用注射器吸取溶液,用0.45 μm针头过滤器(Whatman)过滤并转移至HPLC-MS/MS专用样品瓶中,重复此操作一次。⑦样品测试前用0.2 μm滤膜过滤,滤液上机测试。
1.2.5 分析方法优化
流动相:0.12%甲酸和30 mmol·L−1甲酸铵超纯水溶液(A相);甲醇(B相),流速为0.3 mL·min−1,柱温为30 ℃,进样量为5 μL。以该液相色谱条件为初始方法[24],进一步手动优化,以获得对目标化合物的最高灵敏度(表1)。
表 1 HPLC-MS流动相洗脱梯度Table 1. HPLC-MS mobile phase elution gradient时间/min Time A/% B/% 0.0 95 5 3.0 70 30 6.0 20 80 6.5 10 90 8.0 10 90 8.5 95 5 11.0 95 5 质谱:离子源为电喷雾离子源(ESI),喷雾电压3500 V,离子传输管温度350 ℃,离子化模式为ESI(+);碰撞池气压(CAD)1.5 mTorr,鞘气压力(Sheath gas)为80 Arb,辅气压力(Aux gas)15 Arb。每种目标化合物及其相应内标的母离子和定量、定性离子的质荷比(m/z)见表2,其中,选取每种目标物丰度最大的离子对作为定量离子。
表 2 目标物测试质谱参数Table 2. Mass spectral parameters of the target compound化合物Compound 母离子Parent ion 定量离子Quantitative ion 定性离子Qualitative ion 保留时间/minRetention time m/z m/z DP/V CE/V m/z DP/V CE/V MOR 286 152.1 82 55 165 82 32 2.73 MOR-D3 289.2 152.1 80 55 165 80 41 2.72 METH 150.1 91.1 30 16 119.1 30 16 4.62 METH-D8 158.2 93.2 40 19 124.2 40 10.3 4.59 6-MAM 328.1 165.3 90 36 211.3 90 36 4.35 6-MAM-D3 331.1 165.1 90 38.3 211.2 90 25 4.36 2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 分析方法的评价
2.1.1 回收率
取3种毒品储备液适量,配制成低、中、高浓度(100 ng·L−1、300 ng·L−1、400 ng·L−1)的质控样品,分别按相同的前处理方法平行操作;每一浓度进行双样本分析,根据当日标准曲线,计算样品测定浓度,得出METH、6-MAM和MOR的方法回收率,结果见表3。数据结果表明METH、6-MAM和MOR的回收率良好。
表 3 实验方法回收率、检出限及定量限Table 3. Experimental methods Recovery rate, detection limit and quantitation limit化合物Compound 加标浓度/(ng·L−1)Added 检出浓度/ (ng·L−1)Found 方法回收率/%Method recovery 检出限/(ng·mL−1) 定量限/(ng·mL−1) ILOD MLOD ILOQ MLOQ METH 400 377.0 94.25 0.2 0.0008 0.8 0.0032 300 304.9 101.63 100 102.6 102.60 6-MAM 400 384.2 96.05 0.2 0.0008 0.8 0.0032 300 283.7 94.57 100 101.4 101.4 MOR 400 418.0 104.50 0.2 0.0008 0.8 0.0032 300 294.8 98.27 100 102.3 102.3 2.1.2 线性范围、检出限及定量限
将低浓度目标物混合标准溶液上机测定,仪器检出限(ILOD)和仪器定量限(ILOQ)分别以3倍信噪比(S/N=3)和10倍信噪比(S/N=10)确定。方法检出限(MLOD)和方法定量限(MLOQ)分别通过以下公式计算得到:
MLOD(或MLOQ)=ILOD(或ILOQ)×200μL50mL 式中,200 μL为上机浓缩液的体积,50 mL为前处理所取水样的体积。
取混合毒品标准溶液适量,用流动相稀释,得质量浓度分别为1.5、3、6、12、25、50、100、150、200、250 ng·mL−1系列标准溶液。依次取上述各浓度标准溶液50 mL,按照相同的前处理方法操作,记录色谱图;以标准溶液中目标物的峰面积与同位素内标的峰面积之比为纵坐标(Y),进样浓度(X)为横坐标,进行线性回归运算,得METH、6-MAM和MOR回归方程:
Y=−0.040+0.033XR2=0.9996 Y=−0.044+0.023XR2=0.9998 Y=−0.042+0.023XR2=0.9992 结果表明METH、6-MAM及MOR质量浓度在1.5—250 ng·mL−1范围内线性关系良好,仪器的检出限和定量限见表3。
2.2 河流水质参数与毒品目标物检出浓度的相关性评价
水样温度、pH值、氯离子浓度、化学需氧量、氨氮、高锰酸盐指数和溶解氧等水质参数见表4。
表 4 样品水质参数Table 4. Water quality parameters of the samples样品名称Sample name 温度/℃Temperature pH 氯离子浓度/(mg·L−1)Chloride ion 化学需氧量/(mg·L−1)COD 氨氮/(mg·L−1)NH4+-N 高锰酸盐指数/(mg·L−1)Permanganate Index 溶解氧/(mg·L−1)DO YX 3.6 8.02 1.10×104 94.0 6.67 9.30 10.1 WS 7.0 8.27 9.09×102 9.50 3.81 11.6 9.50 BQ 2.6 8.34 2.25×102 24.0 1.22 6.70 13.1 GS 4.1 8.49 5.60×102 34.0 0.87 9.40 10.8 DH 2.6 8.50 1.30×103 41.0 0.89 10.0 11.6 BX 4.4 8.56 1.26×103 40.0 1.20 7.90 15.5 CZ 3.6 8.60 1.77×103 53.0 1.30 11.4 11.8 LZ -0.3 8.62 1.29×104 141 1.09 5.10 10.1 LX 0.6 8.64 1.24×104 126 0.88 10.5 14.0 XC 3.7 8.66 1.02×103 47.0 2.22 12.7 13.7 DX 4.3 8.68 1.13×103 39.0 1.08 10.5 14.2 检测水样中METH、MOR及6-MAM浓度(记为c1),在样品中均加入定量毒品标准储备液,使METH、6-MAM及MOR的质量浓度均为100 ng·L−1,常温保存72 h后按照2.3所述方法进行样品前处理,并检测3种毒品目标物加标后的浓度(记为c2),见表5。
表 5 样品加标前后三种毒品目标物的检出浓度Table 5. Detected concentrations of three drug targets before and after labeling样品名称Sample name METH/(ng·L−1) MOR/(ng·L−1) 6-MAM/(ng·L−1) c1 c2 c1 c2 c1 c2 YX 3.19 90.61 n.d. 6.99 n.d. 1.67 WS 2.15 98.73 1.97 25.15 1.25 23.85 BQ 1.13 103.19 3.05 44.63 n.d. 47.25 GS 3.35 99.54 n.d. 42.98 3.29 42.25 DH n.d. 91.70 n.d. 21.36 n.d. 7.37 BX 2.73 94.57 n.d. 19.41 3.12 11.03 CZ n.d. 90.50 3.26 20.41 n.d. 3.34 LZ n.d. 90.27 2.91 7.13 n.d n.d LX 1.59 92.11 2.29 4.59 n.d. 1.91 XC 3.41 95.85 n.d. 24.33 n.d. 26.29 DX 1.28 94.95 3.01 23.97 n.d. 4.01 对河流水质参数及METH、6-MAM和MOR加标后的浓度分别进行主成分分析,探讨7个河流水质参数与污水样品中目标物检出浓度的相关性。主成分分析过程在 SPSS 20.0软件包中进行。对所有数据进行Bartlett球形度检验,相伴概率小于0.05,进行 PCA 以获得分数图和因子载荷,经变量最大旋转后,提取出特征值大于1的因子,主成分分析如图1所示。
METH与pH及溶解氧存在较强的负相关性,说明pH或溶解氧的升高可能会导致其检出浓度的下降。MOR与6-MAM均呈现出与化学需氧量及氯离子浓度的强负相关,说明较高浓度的氯离子浓度可能造成MOR及6-MAM检出浓度不准确。此外,METH与氨氮存在明显的正相关,而水体中氨氮的主要来源是生物体代谢所产生的尿素,与人口高度密切相关。METH是中国滥用人数最多且最为广泛的毒品,氨氮浓度较大的流域为人口聚集区域,METH浓度也呈现聚集趋势。MOR及6-MAM是海洛因的代谢产物,稳定性较低,在因子分析中表现为与温度及高锰酸盐指数相关。高锰酸盐指数是反映水体中有机和无机可氧化物质污染的常用指标,结果表明在较高温度及氧化性较强的水环境中,MOR及6-MAM易于分解。
2.3 验证水质参数对模拟样品中毒品目标物的检出影响
根据实验结果,pH、氯离子浓度等均会不同程度影响3种毒品目标物的准确检出,故选取pH、氯离子浓度作为变量,设计单因素模拟实验验证其对毒品目标物稳定性的影响,此外,在应用污水验毒技术评估地区毒情及进行环境风险评估时,需要对污水及地表水中各毒品目标物进行精确定量,毒品母体及其生物标志物在不同水环境中驻留时间各不相同,也应考虑常温下不同存储时间对毒品目标物的检出影响。
2.3.1 pH对模拟样品中毒品目标物的检出影响
取pH=2、pH=4、pH=7、pH=10的模拟水样各50 mL,分别向其加入METH、6-MAM及MOR标准溶液及内标,按照1.2.4进行前处理,3种目标物的检出浓度见表6。
表 6 不同条件下模拟样品中目标物的检出浓度(ng·L−1)Table 6. Detected concentration of target in simulated samples under different conditions (ng ·L−1)条件梯度Condition Gradient METH/(ng·L−1) 回收率/%Recovery MOR/(ng·L−1) 6-MAM/(ng·L−1) MOR与6-MAM回收率/%Recovery pH 2 84.05±10.21 81.92±9.95 42.44±2.52 150.35±3.86 94.88±3.13 4 85.45±16.65 83.28±16.23 50.71±16.99 136.71±6.03 92.19±11.27 7 85.88±3.03 83.7±2.95 63.87±1.22 117.78±5.75 89.3±3.44 10 68.32±9.19 66.59±8.96 54.42±3.62 150.78±11.71 100.95±7.54 氯化钠浓度/(g·L−1) 0 57.33±1.71 55.88±1.67 34.57±0.04 81.45±0.26 57.06±0.15 1 66.99±5.53 65.29±5.39 46.97±0.77 17.49±1.13 31.58±0.94 2 54.11±1.22 52.74±1.19 33.16±1.22 0 16.21±0.6 3 53.39±1.86 52.04±1.81 38.10±0.74 0 18.62±0.36 4 50.96±3.76 49.67±3.66 35.46±1.04 0 17.33±0.51 5 55.85±0.94 54.43±0.92 37.54±2.25 0 18.35±1.1 存储时间/h 12 102.60±4.29 100±4.18 73.26±6.35 202.54±2.87 135.68±4.52 24 79.59±6.29 77.57±6.13 61.15±4.24 137.83±5.43 97.85±4.75 36 67.29±4.10 65.58±4 47.47±3.05 128.44±9.03 86.53±5.94 48 62.64±2.80 61.05±2.73 49.65±2.60 115.97±7.38 81.45±4.91 72 61.85±2.92 60.28±2.85 27.12±1.24 97.78±6.17 61.47±3.65 120 57.89±3.23 56.42±3.15 29.93±3.72 92.24±4.47 60.11±4.02 当pH=2时,模拟样品中METH的回收率在71.97%—91.87%之间,pH值升高至4和7时,METH回收率为67.05%—99.51%,基本不变, pH升高至10时,METH的回收率明显降低,为57.63%—75.55%,即pH对METH的准确检出有影响,当水体呈现酸性及中性时,METH可以稳定存在并准确检出,在碱性水体中,METH稳定性发生改变,检出浓度下降,与实际水体因子分析的结论相符。原因可能为,在不同的pH体系中,METH的电离度及形态发生了变化。METH的结构中含有碱性的氨基官能团,溶液的pH会影响其质子化/去质子化的过程,此外,含胺类物质在水溶液中易发生光降解,且光解行为与氨基上N电子与三重激发物的转移有关,在低pH条件下,氢离子与N电子结合,阻碍了N电子向活性物的转化从而抑制其光降解,反之,N电子的可用性增强,加速了METH的降解[30]。模拟样品中,MOR在中性条件下检出浓度最高,酸性或碱性的条件下降低。6-MAM的变化趋势与其相反,中性条件下,其检出浓度最低,在酸性及碱性环境中,检出浓度较高,即pH也会干扰MOR和6-MAM在水体中的准确定量,张春水等[33]在研究中发现,海洛因的化学形式在不同pH环境下存在变化,当pH升高时,水解反应加剧,发生6-MAM向MOR的转化。实验结果对实际水体的主成分分析结果进行了补充,可知MOR在中性水体环境中较稳定,6-MAM在酸性条件下更稳定。
由图2可见,不同pH条件下, 6-MAM与MOR的浓度变化规律各不相同,两者呈现相反的趋势,在碱性水体环境中易发生6-MAM向MOR的转化,与张春水等[31]提出的海洛因在碱性条件下加速降解成MOR的结论一致。
在实际污水验毒工作中,6-MAM与MOR均被用来估算海洛因滥用量,在pH值为2、4、7、10时,6-MAM与MOR的回收率之和分别为95%、92%、89%和100%,可知pH对于二者的定量分析及海洛因滥用量的准确估算影响较小。
2.3.2 氯离子浓度对模拟样品中毒品目标物的检出影响
取不同氯离子浓度梯度的模拟水样各50 mL,分别加入METH、6-MAM及MOR标准溶液和内标,按照1.2.4节进行前处理,结果见表6。氯化钠浓度为0 g·L−1时,3种目标物都能在模拟水环境中稳定存在。METH的检出浓度随氯离子浓度升高基本不变;MOR的检出浓度在氯化钠浓度为1 g·L−1时最高,为47.74 ng·L−1,其它浓度时在31.94—39.79 ng·L−1范围内小幅波动,因此氯离子浓度的增大对MOR的稳定性存在负影响,与2.2主成分分析所得结论吻合;6-MAM的浓度随氯离子浓度的升高变化较大,在超过2 g·L−1的氯离子浓度的水环境中不能检出。吕昱帆等[32]在对腐败血中6-MAM和MOR的检出研究中发现,在2.5 mL样品中,加入盐析剂NaCl的质量大于30 mg时,6-MAM及MOR的回收率显著降低,与2.3.2节实验结果吻合,故氯离子浓度的影响在实际应用污水验毒技术的过程中不可忽略。
2.3.3 存储时间对模拟样品中毒品目标物的检出影响
对常温(20℃)下存储不同时间的模拟水样进行前处理和定量分析,结果见表6。常温存储会使METH、6-MAM及MOR的浓度均下降,METH在120 h内降解35%左右,6-MAM在120 h内降解50%左右,MOR在120 h内降解达到了60%,即常温存储会造成METH、6-MAM及MOR在水中降解。
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)本文研究了山东省潍坊市的11条河流中,不同水质参数与传统精神活性物质METH、MOR、6-MAM检出浓度的相关性,运用主成分分析法进行相关性评价。结果表明,METH与pH及溶解氧存在较强的负相关,与氨氮存在明显的正相关;MOR与6-MAM均与化学需氧量及氯离子浓度负相关,与其它水质参数相关性较小。
(2)根据实际水样主成分分析结果,选取相关性较大的水质参数进行单因素模拟实验,结果表明,METH在中性及酸性环境下较稳定,MOR在中性条件下较稳定,6-MAM在酸性和碱性条件下均能稳定存在和准确检出;METH的检出几乎不受氯离子浓度的影响,但6-MAM及MOR受氯离子浓度的影响较大;常温(20℃)保存120 h后,METH、6-MAM和MOR的含量均有不同程度的下降。
-
表 1 HPLC-MS流动相洗脱梯度
Table 1. HPLC-MS mobile phase elution gradient
时间/min Time A/% B/% 0.0 95 5 3.0 70 30 6.0 20 80 6.5 10 90 8.0 10 90 8.5 95 5 11.0 95 5 表 2 目标物测试质谱参数
Table 2. Mass spectral parameters of the target compound
化合物Compound 母离子Parent ion 定量离子Quantitative ion 定性离子Qualitative ion 保留时间/minRetention time m/z m/z DP/V CE/V m/z DP/V CE/V MOR 286 152.1 82 55 165 82 32 2.73 MOR-D3 289.2 152.1 80 55 165 80 41 2.72 METH 150.1 91.1 30 16 119.1 30 16 4.62 METH-D8 158.2 93.2 40 19 124.2 40 10.3 4.59 6-MAM 328.1 165.3 90 36 211.3 90 36 4.35 6-MAM-D3 331.1 165.1 90 38.3 211.2 90 25 4.36 表 3 实验方法回收率、检出限及定量限
Table 3. Experimental methods Recovery rate, detection limit and quantitation limit
化合物Compound 加标浓度/(ng·L−1)Added 检出浓度/ (ng·L−1)Found 方法回收率/%Method recovery 检出限/(ng·mL−1) 定量限/(ng·mL−1) ILOD MLOD ILOQ MLOQ METH 400 377.0 94.25 0.2 0.0008 0.8 0.0032 300 304.9 101.63 100 102.6 102.60 6-MAM 400 384.2 96.05 0.2 0.0008 0.8 0.0032 300 283.7 94.57 100 101.4 101.4 MOR 400 418.0 104.50 0.2 0.0008 0.8 0.0032 300 294.8 98.27 100 102.3 102.3 表 4 样品水质参数
Table 4. Water quality parameters of the samples
样品名称Sample name 温度/℃Temperature pH 氯离子浓度/(mg·L−1)Chloride ion 化学需氧量/(mg·L−1)COD 氨氮/(mg·L−1)NH4+-N 高锰酸盐指数/(mg·L−1)Permanganate Index 溶解氧/(mg·L−1)DO YX 3.6 8.02 1.10×104 94.0 6.67 9.30 10.1 WS 7.0 8.27 9.09×102 9.50 3.81 11.6 9.50 BQ 2.6 8.34 2.25×102 24.0 1.22 6.70 13.1 GS 4.1 8.49 5.60×102 34.0 0.87 9.40 10.8 DH 2.6 8.50 1.30×103 41.0 0.89 10.0 11.6 BX 4.4 8.56 1.26×103 40.0 1.20 7.90 15.5 CZ 3.6 8.60 1.77×103 53.0 1.30 11.4 11.8 LZ -0.3 8.62 1.29×104 141 1.09 5.10 10.1 LX 0.6 8.64 1.24×104 126 0.88 10.5 14.0 XC 3.7 8.66 1.02×103 47.0 2.22 12.7 13.7 DX 4.3 8.68 1.13×103 39.0 1.08 10.5 14.2 表 5 样品加标前后三种毒品目标物的检出浓度
Table 5. Detected concentrations of three drug targets before and after labeling
样品名称Sample name METH/(ng·L−1) MOR/(ng·L−1) 6-MAM/(ng·L−1) c1 c2 c1 c2 c1 c2 YX 3.19 90.61 n.d. 6.99 n.d. 1.67 WS 2.15 98.73 1.97 25.15 1.25 23.85 BQ 1.13 103.19 3.05 44.63 n.d. 47.25 GS 3.35 99.54 n.d. 42.98 3.29 42.25 DH n.d. 91.70 n.d. 21.36 n.d. 7.37 BX 2.73 94.57 n.d. 19.41 3.12 11.03 CZ n.d. 90.50 3.26 20.41 n.d. 3.34 LZ n.d. 90.27 2.91 7.13 n.d n.d LX 1.59 92.11 2.29 4.59 n.d. 1.91 XC 3.41 95.85 n.d. 24.33 n.d. 26.29 DX 1.28 94.95 3.01 23.97 n.d. 4.01 表 6 不同条件下模拟样品中目标物的检出浓度(ng·L−1)
Table 6. Detected concentration of target in simulated samples under different conditions (ng ·L−1)
条件梯度Condition Gradient METH/(ng·L−1) 回收率/%Recovery MOR/(ng·L−1) 6-MAM/(ng·L−1) MOR与6-MAM回收率/%Recovery pH 2 84.05±10.21 81.92±9.95 42.44±2.52 150.35±3.86 94.88±3.13 4 85.45±16.65 83.28±16.23 50.71±16.99 136.71±6.03 92.19±11.27 7 85.88±3.03 83.7±2.95 63.87±1.22 117.78±5.75 89.3±3.44 10 68.32±9.19 66.59±8.96 54.42±3.62 150.78±11.71 100.95±7.54 氯化钠浓度/(g·L−1) 0 57.33±1.71 55.88±1.67 34.57±0.04 81.45±0.26 57.06±0.15 1 66.99±5.53 65.29±5.39 46.97±0.77 17.49±1.13 31.58±0.94 2 54.11±1.22 52.74±1.19 33.16±1.22 0 16.21±0.6 3 53.39±1.86 52.04±1.81 38.10±0.74 0 18.62±0.36 4 50.96±3.76 49.67±3.66 35.46±1.04 0 17.33±0.51 5 55.85±0.94 54.43±0.92 37.54±2.25 0 18.35±1.1 存储时间/h 12 102.60±4.29 100±4.18 73.26±6.35 202.54±2.87 135.68±4.52 24 79.59±6.29 77.57±6.13 61.15±4.24 137.83±5.43 97.85±4.75 36 67.29±4.10 65.58±4 47.47±3.05 128.44±9.03 86.53±5.94 48 62.64±2.80 61.05±2.73 49.65±2.60 115.97±7.38 81.45±4.91 72 61.85±2.92 60.28±2.85 27.12±1.24 97.78±6.17 61.47±3.65 120 57.89±3.23 56.42±3.15 29.93±3.72 92.24±4.47 60.11±4.02 -
[1] 魏英, 周波. 我国精神活性物质依赖治疗的现状及相关对策 [J]. 保健医学研究与实践, 2018, 15(6): 91-96. doi: 10.11986/j.issn.1673-873X.2018.06.025 WEI Y, ZHOU B. Current status and related countermeasures of psychoactive substance dependence treatment in my country [J]. Health Medicine Research and Practice, 2018, 15(6): 91-96(in Chinese). doi: 10.11986/j.issn.1673-873X.2018.06.025
[2] 李龙辉, 张建兵, 沈雯雯, 等. 苯丙胺类兴奋剂成瘾和成瘾严重认定标准的制订 [J]. 中国药物滥用防治杂志, 2015, 21(3): 125-128,132. doi: 10.15900/j.cnki.zylf1995.2015.03.001 LI L H, ZHANG J B, SHEN W W, et al. Establishment of Standards for Amphetamine-type Stimulant Addiction and Serious Addiction [J]. Chinese Journal of Drug Abuse Prevention and Treatment, 2015, 21(3): 125-128,132(in Chinese). doi: 10.15900/j.cnki.zylf1995.2015.03.001
[3] MEAD J, PARROTT A. Mephedrone and MDMA: A comparative review [J]. Brain Research, 2020, 1735: 146740. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146740 [4] SALOUROS H. Illicit drug chemical profiling: Current and future state [J]. Australian Journal of Forensic Sciences, 2018, 50(6): 689-696. [5] 陈祥勇. 我国毒品违法犯罪综合治理对策研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2016. CHEN X Y. Study on the comprehensive treatment of drug crimes in China[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2016 (in Chinese).
[6] BRIAN H. UNODC World Drug Report 2021[EB/OL]. [2021-06-24/2021-08-13].https://www.unodc.org/unodc/data-and-analysis/wdr2021. [7] RÖNKÄ S, KARJALAINEN K, VUORI E, et al. Personally prescribed psychoactive drugs in overdose deaths among drug abusers: A retrospective register study [J]. Drug and Alcohol Review, 2015, 34(1): 82-89. doi: 10.1111/dar.12182 [8] WODAK A. From failed global drug prohibition to regulating the drug market [J]. Addiction (Abingdon, England), 2018, 113(7): 1225-1226. doi: 10.1111/add.14111 [9] DAMIEN D A, THOMAS N, HÉLÈNE P, et al. First evaluation of illicit and licit drug consumption based on wastewater analysis in Fort de France urban area (Martinique, Caribbean), a transit area for drug smuggling [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 490: 970-978. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.090 [10] 马家佳. 2020年中国毒情形势报告[EB/OL]. [2021-07-16/2021-08-13]. http://www.nncc626.com/2021-07/16/c_1211244064.htm. MA J W. 2020 report on China’s drug situation [EB/OL]. [2021-07-16/2021-08-13]. http://www.nncc626.com/2021-07/16/c_1211244064.htm.
[11] 中国毒品问题治理的创新性举措[N]. 人民公安报, 2019-04-02(1). https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CCND&filename=RMGA201904020012 [12] 刘志民, 贾振军, 贾忠伟, 等. 全国七地区14城市毒品问题评估报告 [J]. 中国药物依赖性杂志, 2017, 26(4): 309-318,324. doi: 10.13936/j.cnki.cjdd1992.2017.04.013 LIU Z M, JIA Z J, JIA Z W, et al. Investigation of the situation of drug abuse and evaluation of the scale of drug users in 14 cities in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Drug Dependence, 2017, 26(4): 309-318,324(in Chinese). doi: 10.13936/j.cnki.cjdd1992.2017.04.013
[13] 解启文, 黄墩, 李婧, 等. 毒品形势分析及检测方法研究 [J]. 自然杂志, 2017, 39(6): 437-444. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2017.06.006 XIE Q W, HUANG D, LI J, et al. Study on drug situation analysis and detection methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2017, 39(6): 437-444(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2017.06.006
[14] 周帅. 我国毒品犯罪的研究热点及趋势分析 [J]. 云南警官学院学报, 2021(2): 32-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6057.2021.02.004 ZHOU S. Hotspots and trend of research on drug crimes in China [J]. The Journal of Yunnan Police College, 2021(2): 32-37(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6057.2021.02.004
[15] 张永礼. 我国防治合成毒品工作中面临的主要问题及对策 [J]. 湖北警官学院学报, 2015, 28(7): 127-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2391.2015.07.033 ZHANG Y L. he main problems and countermeasures in the prevention and control of synthetic drugs in my country [J]. Journal of Hubei University of Police, 2015, 28(7): 127-131(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2391.2015.07.033
[16] CHOU L W, CHANG K M, PUSPITASARI I. Drug abuse research trend investigation with text mining [J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2020, 2020: 1030815. [17] HERNÁNDEZ F, CASTIGLIONI S, COVACI A, et al. Mass spectrometric strategies for the investigation of biomarkers of illicit drug use in wastewater [J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 2018, 37(3): 258-280. doi: 10.1002/mas.21525 [18] RINALDI R, BERSANI G, MARINELLI E, et al. The rise of new psychoactive substances and psychiatric implications: A wide-ranging, multifaceted challenge that needs far-reaching common legislative strategies [J]. Human Psychopharmacology, 2020, 35(3): e2727. [19] 郑晓雨, 袁明俊, 王德高, 等. 基于污水流行病学的毒情研判技术研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2020, 15(4): 79-87. ZHENG X Y, YUAN M J, WANG D G, et al. Sewage epidemiology for drug situation assessment [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2020, 15(4): 79-87(in Chinese).
[20] 陈培培, 杜鹏, 周子雷, 等. 污水中新精神活性物质的分析方法优化及验证 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(8): 3736-3743. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201712251 CHEN P P, DU P, ZHOU Z L, et al. Optimization and validation of the analytical method to detect new psychoactive substances in wastewater [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(8): 3736-3743(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201712251
[21] LAI F Y, ORT C, GARTNER C, et al. Refining the estimation of illicit drug consumptions from wastewater analysis: Co-analysis of prescription pharmaceuticals and uncertainty assessment [J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(15): 4437-4448. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.05.042 [22] LI J, HOU L L, DU P, et al. Estimation of amphetamine and methamphetamine uses in Beijing through sewage-based analysis [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 490: 724-732. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.042 [23] KHAN U, van NUIJS A L N, LI J, et al. Application of a sewage-based approach to assess the use of ten illicit drugs in four Chinese megacities [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 487: 710-721. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.043 [24] ORT C, van NUIJS A L N, BERSET J D, et al. Spatial differences and temporal changes in illicit drug use in Europe quantified by wastewater analysis [J]. Addiction (Abingdon, England), 2014, 109(8): 1338-1352. doi: 10.1111/add.12570 [25] ROSI-MARSHALL E J, SNOW D, BARTELT-HUNT S L, et al. A review of ecological effects and environmental fate of illicit drugs in aquatic ecosystems [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 282: 18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.062 [26] BAKER D R, KASPRZYK-HORDERN B. Multi-residue analysis of drugs of abuse in wastewater and surface water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-positive electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218(12): 1620-1631. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.01.060 [27] LEE S, MIYAGUCHI H, HAN E, et al. Homogeneity and stability of a candidate certified reference material for the determination of methamphetamine and amphetamine in hair [J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2010, 53(4): 1037-1041. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2010.06.023 [28] HATTON M W, REGOECZI E. Studies of the metabolism of asialotransferrins: Nonspecific changes in the metabolic behaviour of human asialotransferrin in avians [J]. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry, 1976, 54(4): 336-340. doi: 10.1139/o76-049 [29] DU P, ZHOU Z L, BAI Y, et al. Estimating heroin abuse in major Chinese cities through wastewater-based epidemiology [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 605/606: 158-165. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.262 [30] 张小寒. 基于污水流行病学的精神活性物质消耗量计算及其在污水处理系统中的转化[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019. ZHANG X H. Consumption of psychoactive substances based on wastewater-based epidemiology and their transformation in wastewater treatment system[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[31] 张春水, 王蔚欣, 黄星, 等. 不同pH条件下海洛因毒品的溶解性研究 [J]. 化学分析计量, 2010, 19(1): 63-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2010.01.019 ZHANG C S, WANG W X, HUANG X, et al. Research OF heroin dissolution IN different pH condition [J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2010, 19(1): 63-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2010.01.019
[32] 吕昱帆, 王继芬, 常靖, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法检验腐败血中吗啡和6-单乙酰吗啡 [J]. 色谱, 2019, 37(1): 80-86. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2018.08004 LYU Y F, WANG J F, CHANG J, et al. Determination of morphine and 6-monoacetylmorphine in putrefied blood using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2019, 37(1): 80-86(in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2018.08004
[33] 张春水, 王蔚昕, 黄星, 等. 海洛因毒品水解机理的探讨 [J]. 化学分析计量, 2010, 19(2): 45-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2010.02.012 ZHANG C S, WANG W X, HUANG X, et al. Study on heroin hydrolysis mechanism [J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2010, 19(2): 45-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2010.02.012
-




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: