-
随着我国工业产品的需求量急剧增加,在生产使用化学品的过程中排放污、废水比例也不断增大。对于煤化工、石油等行业废水来说,具有排放量大、废水污染程度高以及含有毒有害性物质等特点,属于典型难降解废水。由于我国工业品生产水平存在差异,部分企业生产技术落后,污染防控和治理措施不完善,低清洁生产水平下排放出的难降解废水,不仅会使河流、湖泊等水生态系统遭到破坏,也会影响周围动植物的生存质量。针对这一问题,我国早在2013年环境保护部印发的《化学品环境风险防控“十二五”规划》中就提到有关行业特征污染物的排放会引发周边环境状况的恶化,此类污染物在环境中降解速度慢,严重威胁人体的健康发展,必须加强特征污染物的环境监测。2018年起开始实施的《中华人民共和国水污染防治法》第二十五条规定国家要完善和加强水环境质量监测与水污染物排放监测。由于废水中的特定污染物对环境危害极大,我国在有毒有害污染物的监测及检测方面愈发重视。但是重金属、农药类有机物等毒性化学品在水体中含量低毒性大,给BOD(biochemical oxygen demand)、生物毒性等指标的检测带来一定的难度。其中BOD检测技术主要分为两部分,一种是以CO2或溶解氧量为定量基础的传统BOD检测技术;另一种是以电信号、光信号为定量基础的微生物传感器技术。以上方法在稳定检测与快速检测等方面具有优势,但不能同时满足。生物毒性检测技术通常受到受试生物的影响,具有检测时间长,重现性差,检测费用高等缺点。这两种传统方法共同存在的问题是,检测用时较长、无法实现在线监测、灵敏度低。为了克服以上问题,以微生物降解及电化学相结合的BOD和毒性一体化检测技术逐渐进入人们的视野,成为BOD、生物毒性等单指标及多指标检测领域的技术研究方向。
-
生化需氧量(BOD)是水质分析与检测中一种常见的理化参数,BOD的测定可广泛应用于工业废水、市政污水、地下水等常见水体[1-5],该参数不仅可以表征待测水样的可生化性能和污染强度,也可为水处理构筑物的设计提供参考[6]。目前,国内外常见的BOD检测方法有[7-8]:稀释接种法、压差法、增温法、微生物传感器法、微生物燃料电池法以及活性污泥曝气降解法等,如表1所示。
-
稀释与接种法是目前最常见的生化需氧量测定方法,该方法技术成熟适用于多种水质,检测范围在2—6000 mg·L−1,测量结果较为准确,在实际检测中得到广泛应用[9]。稀释与接种法是以微生物为媒介进行信号传导的一种方法,为了保证BOD5数值检测的准确性,待测水样不仅要在4 ℃内保存并进行去除余氯等预处理步骤,同时还要保证微生物在最适宜的条件下进行降解反应。经探究[10],废水中微生物的最适温度范围为16—30 ℃,因此稀释与接种法在密闭条件下的培养温度严格设置在(20±1) ℃。与此同时,pH也是影响微生物生存的重要因素,由于中性条件下的微生物生长状况最优,因此待测水样调节至pH7.0±0.5。
经以上探究可知,稀释接种法操作繁琐不能满足污水处理厂实时监测的需求,因此有研究人员提出利用压差法来测量BOD。压差法与稀释接种法的原理基本相同,主要差异是将溶解氧含量的测定转化为更加简单快捷的压力测定。微生物为了满足自身生长代谢所需的能量吸收并降解有机物,在此过程中吸收氧气并排出二氧化碳。根据此原理压差法测定BOD通常被分为两种形式,一是将待测水样充氧至饱和利用降解过程中氧气消耗产生的压差间接表征BOD。Hussain等[11]依靠该方法设计出了一种应用于养殖废水并实现对耗氧率(OUR)与BOD的实时监测的光学沼气再测量系统。二是无需处理待测水样,通过在密闭的培养瓶中添加氢氧化钠颗粒直接吸收微生物排出的二氧化碳,使得瓶中二氧化碳减少压力发生变化从而达到实时监测与测定BOD的目的[12-14],该部分的装置及原理如图1所示。
稀释接种法、压差法等传统方法虽具有较好测量精度,但为保证有机物可以被微生物完全降解检测用时均设定为5日,不能满足实际工况水样快速、简单的检测要求。经探究,光、电化学具有简便快速可实时观测的优点,因此有研究人员[15-16]提出可以利用光、电化学传感技术与微生物降解过程联合并研发出一种高效的BOD传感技术。
-
BOD生物传感器技术是一种将微生物作为识别元件并通过其自身反应与电极等转换器的作用,得到以电流/电量变化率、氧荧光猝灭效率以及耗氧率作为检测指标来评价BOD的技术[17-19]。其中根据检测指标的不同,选用的微生物种类也有所差异。常见的在以氧传导和电传导为基础的生物传感器中起到识别作用的微生物类别有Bacillus subtilis (枯草芽孢杆菌)、Escherichia coli (大肠埃希氏杆菌)、Trichosporon cutaneum (皮状丝孢酵母菌)、Candida albicans (白色念珠菌)、Saccharomyces cerevisiae (酿酒酵母菌)、Candidatropicalis (热带假丝酵母)等[20-23],以上微生物中大肠杆菌和酿酒酵母菌分别作为原核生物与真核生物的代表被广泛应用。由于两种菌群在细胞结构、生殖方式等方面具有较大差异。相比于大肠杆菌,酵母菌对有机物的降解更加广泛,同时在面对环境冲击以及水中毒性物质冲击时也具有良好的稳定性。但酵母在降解过程中受到酶作用机制的影响,电传导能力弱于大肠杆菌。为了弥补以上缺陷,有研究人员提出两种方案,一是通过添加酶等物质改善传感器性能[24]。Kim等[25]从活性污泥中提取出了一种Klebsiella sp. (克雷伯氏菌)该菌对乳酸具有较好的降解效果,但为了使以该菌为识别元件的BOD传感器对葡萄糖等有机物也具有较高的检测灵敏度,从牛血清蛋白中提取了β-半乳糖苷酶辅助降解反应的进行。二是将多类别的菌种混合共同参与反应[26]。Niyomdecha等[27]为了提升BOD传感器的检测性能探究并制备了一种以亚甲基蓝为介质,石墨烯为工作电极,壳聚糖-牛血清白蛋白(CHI-BSA)冷冻凝胶为载体,活性污泥混合菌群为生物识别元件的新型BOD生物传感器,该传感器的检测范围可达1.0—100 mg·L−1(O2),与GGA(葡萄糖+谷氨酸)标准溶液浓度相关系数R2=0.9993,具有良好的稳定性与重复性。经探究,活性污泥菌群不仅对有机物的降解具有广泛性,而且具有较强的耐冲击性,是良好的生物传感元件。但在长期的检测过程中活性污泥菌群不可避免地会对有机物进行争夺从而产生优、劣势菌种,使得菌群的多样性逐渐降低。为避免该情况的发生影响传感器检测性能,尽可能将混合微生物固定在电极表面后进行信号传导及BOD值的检测。
微生物菌群在创造良好降解效果并产生生物信号的同时,如何让生物信号最大效率的传递至转换元件是另一个需要探究的环节。目前,BOD反应器中最常见的微生物存在形式为游离态与固定态[26, 28]。当微生物处于游离态参与检测反应时既可避免转换元件表层被菌群堵塞,保持转换元件的信号传输强度,也可延长转换元件的寿命。但是由于菌群在传感器中较为分散,产生的生物信号大多需要通过添加一些介质辅助其进行集中传递。这些介质包括:中性红、亚甲基蓝、刃天青等[29-31],介质的添加不仅会对微生物产生微弱毒性,而且影响生物信号的生成。因此,有研究人员提出可以通过固定技术将微生物固定于转换元件表层,这样不仅可以加强生物信号的传输,也可以减少传输器的污染问题。如,Yudina等[32]利用包埋固定技术将酵母菌、细菌与酶共同固定在经过N-乙烯基吡咯烷酮改性的聚乙烯醇载体中,该传感器的检测用时仅为3—4 min,与BOD5的相关系数可达0.9988,具有良好的BOD检测性能。
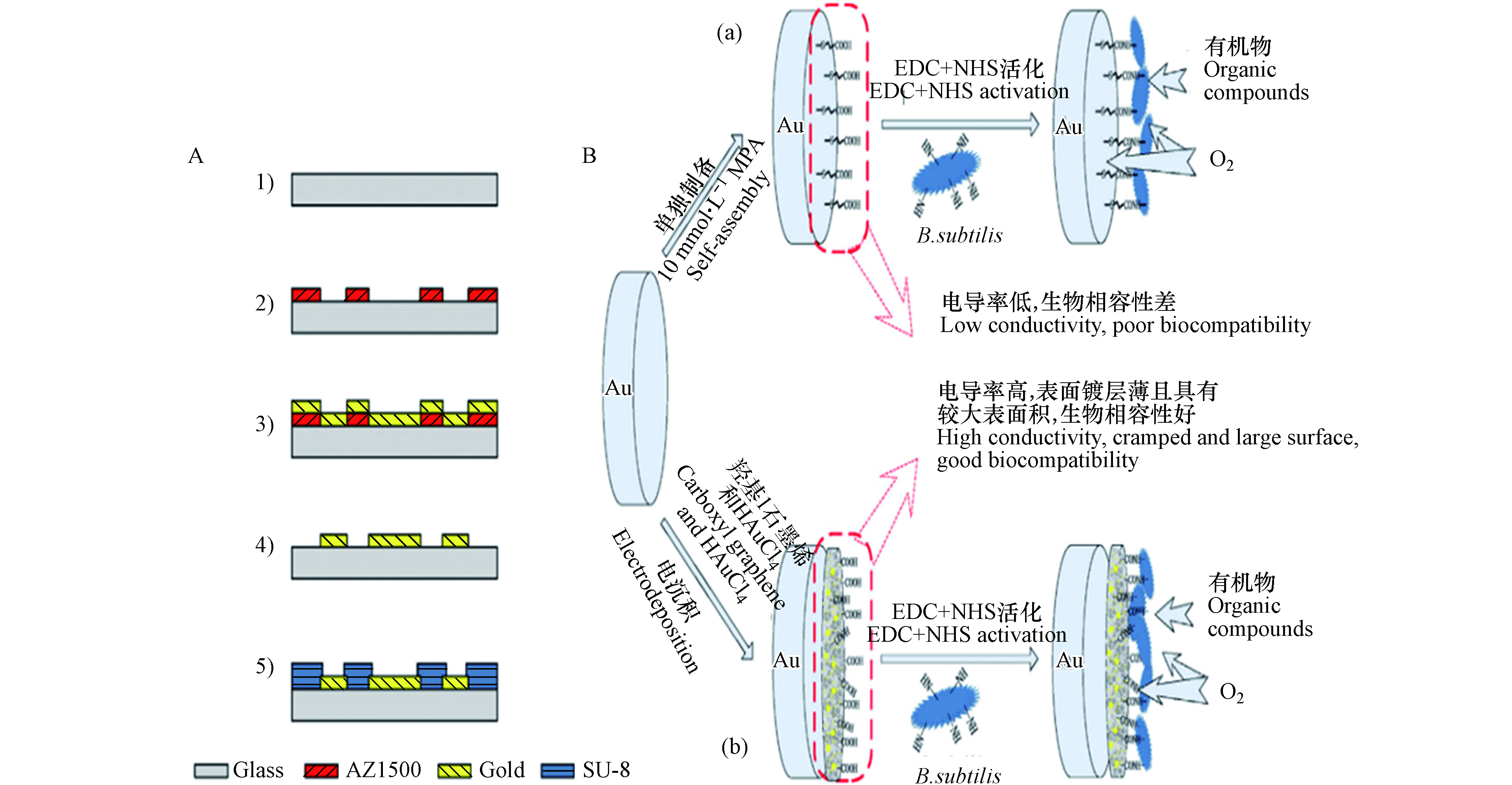
目前,常见的微生物固定方法有吸附固定、包埋固定、共价结合固定与交联固定等4种[33-35]。其中共价结合固定技术与交联结合技术属于化学方法,吸附固定技术与包埋技术属于物理方法。相比于交联技术,共价结合技术凭借其稳固的性能被更多学者所探究。共价结合技术是指利用载体表面带有的基团与细胞表面氨基基团匹配结合为共价键使微生物稳固在载体表面的一种固定方法。该固定方法制备的BOD电极可为微生物的附着提供更多点位,不仅延长了电极寿命而且提高了传感器的检测性能。图2为BOD传感器电极的制备A)与修饰B)过程图,由图可知以共价结合技术为基础的经羟基石墨烯(GN-COOH)与金纳米颗粒(AuNPs)改性的电极载体表面具有更多点位并且官能团的结合能力更强,相同条件下附着的微生物更多。但共价结合方法的制备过程过于复杂不适用于广泛应用,因此更加高效快速的包埋技术得到发展。
包埋固定技术中常以单一或复合形式的海藻酸钠(sodium alginate,SA)、聚乙烯醇(polyvinyl alcohol,PVA)、胶原纤维等物质作为微生物载体[36-38]。微生物被载体包裹固定,载体为工作菌群提供适宜稳定的生存与降解环境,两者的结合增强并提高了BOD传感器的传导性能与使用寿命。Zhao等[39]研制了一种负载Zr(Ⅳ)的胶原纤维载体,该载体不仅具有多孔结构,而且还有较好的亲水性与生物融合性,通过将该载体与大肠杆菌、酿酒酵母菌融合制备所得的BOD传感器具有42 d的较长寿命。近年来随着材料科学的深入发展,磁性材料以及纳米材料凭借其较强的造孔能力也逐渐进入人们的视野[40-41]。
-
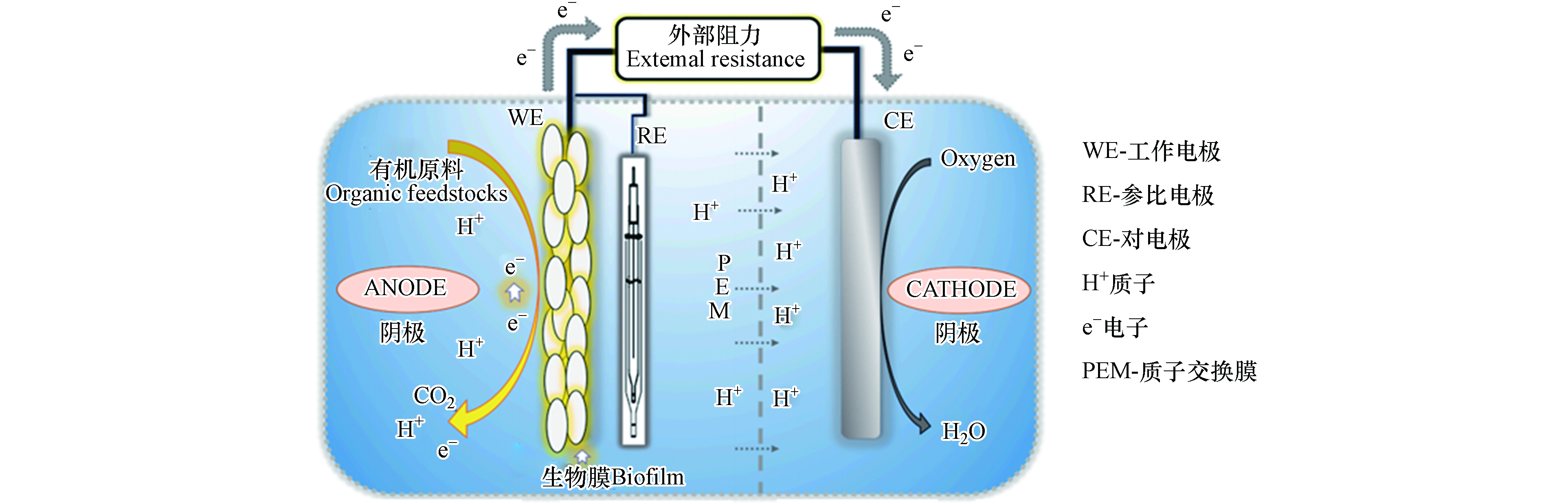
微生物燃料电池(microbial fuel cell,MFC)作为BOD传感技术中的重要分支。相比于其它方法,燃料电池技术主要通过作为阳极催化剂的电化学活性菌(electrochemically active bacteria,EAB)降解有机物,并利用降解过程中生成的生物电子为传感器系统提供能量,最终根据电流变化情况实现对BOD数值的监测与检测的一种技术方法[42-43]。常见的微生物燃料电池主要由阳极、阴极、分隔膜以及外接电路构成,其结构及工作流程如图3所示[44]。
根据其结构组成可知,阴、阳电极是影响微生物燃料电池性能产出的重要因素。因此对电极材料的探究尤为重要,阳极电极表面作为接收生物电子的重要点位需要具有较高的生物相容性、高的导电性以及耐腐蚀性。而阴极电极则需具备较高的氧还原性能,为了降低反应电势提高还原性能通常会在阴极表面负载一层高效催化剂来实现性能的提升[45]。经探究,常见的可用于传感导电的电极材料有以金刚石、碳纳米管、石墨烯为主的碳系列材料、天然生物质材料、以及钛、铂等金属材料[46-48]。其中,碳布、碳网、碳毡等传统碳系列材料凭借其廉价、具有较大的比表面等优点被广泛应用与研究[49-50]。如Guo等[51]为了探究电极的有效保存条件,建立了一种以碳布为电极材料用于检测BOD的微生燃料电池系统。有些研究人员为了进一步提升电极的电传导性能,在传统碳材料的基础上进行改性处理[52]。Liu等[53]将石墨烯颗粒电沉积于阳极碳布表面并以此构建了一种无介质微生物燃料电池,由于石墨烯的高生物相容性促使微生物在电极表面大量生长繁殖,增加了电子传递速率使得燃料电池的功率密度与能量转换率分别增加了2.7倍与3倍。
-
废水中的有机物根据微生物的降解特性可分为:包括葡萄糖、蛋白质、淀粉等物质在内的可生物降解有机物,以表面活性剂、烃类化合物、合成农药类化合物为主的难降解有机物,以塑料制品与尼龙制品为主的不可降解有机物[54-56]。活性污泥曝气降解法利用以上微生物的降解特性,分别对待测水样的原水COD值与降解反应后的出水COD值进行测定,将原水COD值视为总有机物含量,出水COD值视为难降解有机物与不可降解有机物的量。由于在曝气条件下活性污泥微生物较为活跃并大量降解废水中的可生化降解有机物,因此原水与出水间的COD差值理论上可表示为BOD。为了在短期内尽可能地完成对可生化有机物的降解,需要对活性污泥微生物的最佳反应条件进行探究。在常见的标准方法中,取3 mL预处理后的活性污泥与50 mL待测水样在30—35 ℃条件下连续曝气2 h既可达到最佳降解效果。本课题组也对此进行了探究,首先利用模拟废水对污泥进行培养驯化,待其成熟后分别探究降解时间、污泥量、pH以及温度等单因素的影响[57]。探究结果表明,当降解时间在180 min、污泥量为5 mL/100 mL、pH=7.0,温度保持在25 ℃时活性污泥对有机物的降解达到最大值并保持稳定。同时,在最佳条件下由BOD5与BODCOD的相关性探究可知,BODCOD的检测浓度范围为0—500 mg·L−1,相关系数R2=0.981,与传统BOD5具有良好的相关性。本课题组的探究为活性污泥曝气降解法提供了更加优异的检测条件。
活性污泥曝气降解法与传统的稀释接种法相比,检测用时从5 d缩减为2 h极大地提高了检测效率,同样具有良好的检测精度。与BOD传感器法相比,虽然检测用时稍长,但无需专门搭建反应器,减少了实验操作的复杂程度。综上所述,活性污泥曝气降解法的提出不仅提高了BOD的检测效率,而且为COD与BOD一体化检测提供了新的思路,在生活污水、市政污水以及工业废水等水质检测中具有良好的应用前景。
-
发光细菌毒性检测技术中菌群的发光能力是确保检测结果准确的重要条件。发光细菌的发光过程主要分为两个阶段[58],第一阶段:发光细菌受到体内荧光素酶与辅酶Ⅱ的共同催化作用,促使FMN(黄素单核苷酸)与H+发生反应,由氧化态的FMN变为还原态的FMNH2。第二阶段:微生物为了储存并获取满足自身生长所需的能量,在部分氧原子的参与下将长链脂肪醛(RCHO)合成为脂肪酸(RCOOH)。与此同时,体内剩余的氧原子在荧光素酶的催化作用下将FMNH2又氧化为FMN并释放出大量光子,该光子为波长在450—490 nm间的蓝绿色可见光。两阶段的反应方程如式1和2所示[59]。
目前,常选用的具有较强发光能力的菌群有Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 (青海弧菌)、Photobacterium luminum (明亮发光杆菌)、Vibrio fischeri(费氏弧菌)以及Heterobrevibacterium luminescens (发光异短杆菌)等[60-62],其中费氏弧菌与明亮发光杆菌作为主要的模式生物被列入各国的检测标准中,如国际标准(ISO 11348—2007)、欧盟标准(EN ISO 11348—2008)、美国标准(ASTM D5660—2004)和中国标准(GB/T 15441—1995)等[63]。由于Photobacterium luminum与Vibrio fischeri均属于海洋菌,只有在高盐分的条件下才具备较好的检测活性。近年来,淡水发光菌被越来越的人所探究,青海弧菌是少有的具备发光能力的淡水菌,该菌在检测过程中无需添加盐分来迎合微生物的生存环境,获取容易、价格低廉,较适宜用作发光细菌毒性试验中的受试生物并被广泛应用。Ma等[64]将青海弧菌作为受试生物,探究了制药废水在污水厂的不同处理阶段中的毒性水平。结果表明废水原水的荧光抑制率(IR)为60.96%具有较强毒性;TPC(三相催化氧化反应池)为毒性去除效果最优的构筑物去除率为48.3%;对于FSBBR(流动分离床生物反应器)来说处理后的废水毒性没有改观。由该探究可知发光细菌毒性检测方法可用于监测实际工况下所排放废水的毒性。
-
藻类毒性检测技术也是较为常见的生物毒性检测技术,该技术的检测指标包括:超氧化物歧化酶含量、细胞密度、细胞活力、叶绿素a含量、细胞色素含量、发光度以及抗氧化酶含量等[65-67]。以上指标在毒性检测试验中应用广泛且方法成熟,但是具有操作复杂、用时长等缺点。因此有研究人员提出了一种基于叶绿素荧光技术并以不同荧光参数为指标的藻类毒性检测新方法[68- 69]。
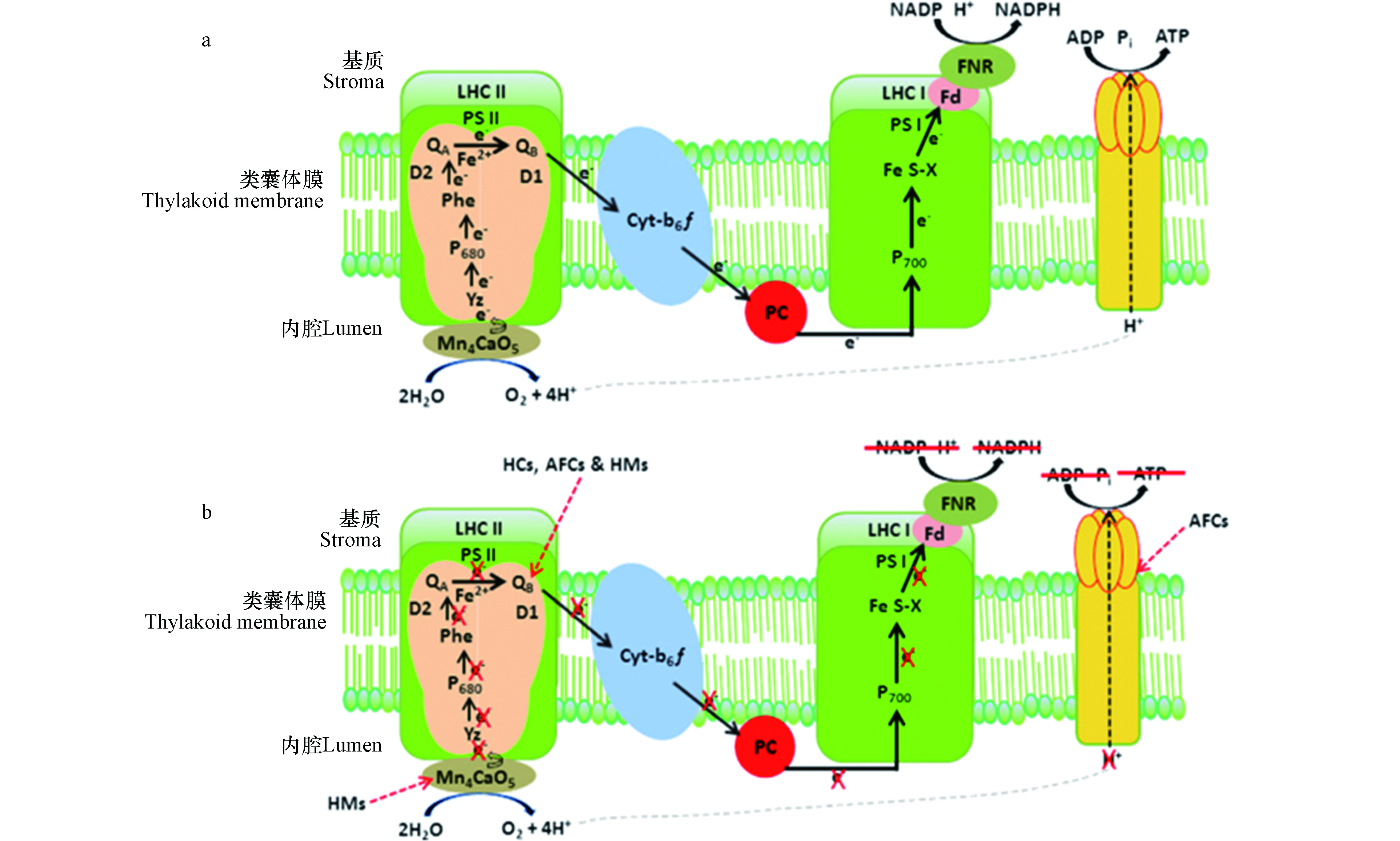
叶绿素荧光技术在实现快速、便捷的在线监测方面具有较大潜力,该技术是一种以藻类光合作用为理论基础,通过探究荧光参数变化情况来表征细胞光合代谢活性的测量技术。藻类进行光合作用的主要目的是获取能量,获取的能量被提供用于光化学反应、荧光生成以及热量散发。光合作用中的光反应过程为主要产能环节,光反应过程离不开电子的传递[70]。如图4所示,电子的传递过程主要分为3个阶段:① 光反应系统Ⅱ(PSⅡ)吸收了外界的光能并将光量子传递至以色素P680为主的光反应系统中心,该色素得到量子后跃迁为不稳定的激发态(
P*680 );② 处于激发态的P*680 会不断释放电子,电子全部转移至位于P680受体侧的脱镁叶绿素(Pheo),Pheo得到电子后变为P+680Pheo- 。③P+680Pheo- 在细胞色素b6f复合体与质体蓝素(PC)的作用下又将电子转移至光反应系统Ⅰ(PSⅠ)中的色素P700处。而PSⅡ中失去电子的P+680 与P680供体侧开始争夺多余的电子,迫使H2O继续裂解并释放大量的质子与电子。电子传递是生成NADPH与ATP等能量物质的重要环节。当藻类物质用于毒性检测并受到胁迫时,光合作用最先响应,主要表现在减少光化学反应得到的能量配比,多余的能量被用于荧光生成。因此,在藻类荧光动力学曲线中常表现为先上升后下降的趋势,该曲线可以对荧光测试结果进行辅助分析。鉴于叶绿素荧光技术具有对植物体无害、快速、精准等优良特性,该技术被大量用于毒性检测方面的研究,如Salas等[71]利用叶绿素荧光技术探究了在氨基酸的参与下银纳米粒子对莱茵衣藻(Chlamydomonas reinhardtii)的毒性强度变化情况。该实验首先通过荧光测定仪对
F′M 与F进行测定,其次将有效量子产量Y(Ⅱ)作为毒性检测指标,根据公式3进行计算。结果表明半胱氨酸具有减缓银毒性的作用。式中,
F′M 为饱和脉冲引起的最大荧光水平;F为饱和脉冲前的瞬时荧光水平。 -
从食物链的角度来说,发光细菌、藻类、鱼类之间属于分解者、生产者与消费者的关系,其中鱼类是消费者层级中最早用于毒性检测的生物之一。常见的受试鱼类有斑马鱼、日本清鳉鱼、稀有鮈鲫、虹鳟以及鲤鱼等[73-75]。在进行宏观与微观的分析中常以半数致死浓度(LC50)、游动行为强度(swimming behavior intensity,BS)、胚胎发育程度、血液中的物质含量等作为检测指标来描述受试水体的毒性强度。LC50是最早被用于毒性试验的指标,也是最常见且应用最广的急性毒性检测指标。陈建华等[76]利用斑马鱼探究了茶多酚对壬基酚急性毒性的缓解作用,结果表明当茶多酚浓度在2.5—20.0 mg·L−1时可对壬基酚的急性毒性起到缓解作用,使得斑马鱼死亡率下降,LC50明显上升。朱燕华等[77]则是利用斑马鱼胚胎对不同类别的食用油急性毒性进行了探究,探究结果表明未精炼的地沟猪油对斑马鱼胚胎毒性最大,LC50低至14.3 mL·L−1;正常精炼猪油的毒性最低LC50>173.3 mL·L−1。
虽然LC50可用于检测大多数的毒性物质,但是为了探究待测物质的累积毒性或遗传毒性只能通过血液指标与胚胎发育程度情况进行试验分析[78]。如硝酸盐类与亚硝酸盐类是废水处理中比较常见的低毒或无毒类污染物质,但是随着培养时间的增加,以上物质会逐渐在鱼体内积累,为了分析鱼体内对硝酸盐物质的毒性响应,可以从血液指标入手。Grabda等[79]将虹鳟鱼在含量为5—6 mg·L−1的硝酸盐溶液中培养数日,最后观察得到血液中的高铁血红蛋白水平增加,外周血和造血中心发生改变,肝脏受到损伤。还有研究人员[80]对醚菊酯的积累毒性进行了探究,结果表明长时间暴露在醚菊酯中致使鲤鱼的红细胞与血红蛋白含量减少、谷草转氨酶(glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase,AST)与谷丙转氨酶(alanine aminotransferase,ALT)含量增加,说明鲤鱼的肝脏可能受到了损伤。对于检测一些具有遗传毒性的物质来说,鱼胚胎技术具有可以靶向观察、快速、简便的特点是一种良好的技术手段。该技术通过鱼受精卵胚胎发育情况分析待测物质的遗传毒性强度。目前多被用于评估河流沉积物的遗传毒性,如Babić等[81]为了对萨瓦河河流沉积物的毒性进行了评估,将斑马鱼胚胎与沉积物分别接触24 h、48 h。观察发现不同斑马鱼胚胎的发育损伤程度不同,主要受到遗传损伤的部位为眼睛、肌肉、卵黄囊和尾巴。
LC50、胚胎发育损伤以及血液物质含量等指标可以实现对物质毒性的定性定量分析,但是对于有着在线监测需求的废水处理厂来说,以上指标并不能满足实际需求。因此游动行为强度这一可以实现在线监测目的指标被更多学者所探究[82-83]。游动行为强度以行为学为基础,从鱼类本身具有的趋流性出发对运动位置、运动速度等指标进行综合评价[84]。当水中含有毒性物质时,鱼的视、触神经系统最先遭受攻击,致使呼吸频率加快并出现与常规条件下不同的逆趋流行为[85]。基于该原理,现已开发出了可实现在线监测的3D生物监测装置,该装置主要以由运动轨迹、运动速度、出水频率组成的综合行为指标BS作为监测对象,具有简单、便捷等特点。图5为利用3D生物传感装置测得的不同毒性条件下斑马鱼活动规律数值分析图。
-
以上部分分别总结了以发光细菌毒性检测技术、藻类毒性检测技术以及鱼类毒性检测技术为主的国内外应用较早且较为普遍的几种生物毒性检测技术。随着时间的推移,越来越多的毒性检测技术被探究,本小节对常见的按照检测指标分类的生物毒性检测方法进行总结,总结结果如表2所示。
综上所述,在常见的生物毒性检测技术中虽然大多数方法具有较高的灵敏度,但是检测周期长不能满足在线监测以及多种指标一体化检测的实际需求等问题也不能被忽视,所以需要继续探究一种可以缩短检测用时、操作简便可以满足实际工况需求的生物毒性检测新方法。
-
就目前来说,国内外对于BOD与毒性一体化检测技术的探究较为欠缺,微生物燃料电池是目前仅有的已被探究具备一体化检测与制造成型设备能力的技术,该技术既可以实现对BOD的检测也可以满足毒性的检测需求。微生物燃料电池在进行毒性检测时其机理为:在相同条件下相比于无毒水体中微生物降解有机物时的产电量,由于受到重金属等毒性物质胁迫,电活性菌代谢过程受阻排出的生物电子随着毒性的渗透而逐渐减少,在一定时间内产电量大幅降低,降低的电量可间接地用于表征毒性。基于该原理分别对标准溶液下的微生物产电量(Q1)与受到重金属胁迫下的微生物产电量(Q2)进行测定并将数值代入式(4)进行计算求得产电抑制率(ICi),以产电抑制率评价毒性物质的毒性强度,实现微生物燃料电池对毒性的检测。
当微生物燃料电池作为毒性传感器时多将镉、铬、铜等重金属以及苯、醛等化学物质作为检测目标。基于微生物群落对毒性物质的特异性与耐受性,以不同类别或不同培养时间的菌种作为阳极生物膜的燃料电池得到的毒性检测结果也有所差异。如Lu等[94]为分析生物燃料电池在受到冲击后响应电压值下降原因,选用Flavobacterium(黄杆菌属)、Geobacter(地杆菌属)、Pseudomonas(假单胞菌属)、Acidovorax(嗜酸菌属)以上四种细菌暴露在不同浓度的甲醛溶液中进行毒性检测,探究表明Pseudomonas、Acidovorax对甲醛毒性较为敏感,在低浓度长时间的检测活动中活性抑制明显,进而导致电压值下降最大。Xu等[101]选用Pb作为毒性物质对不同检测时间下生物膜的毒性敏感度进行了探究,结果表明参加过多次检测活动的成熟生物膜在灵敏度及活性等方面均弱于新形成的生物膜。由以上可知当微生物燃料电池在作为毒性传感器使用时需要探究的因素较为广泛与复杂。与此同时,微生物燃料电池在毒性检测的实际应用中受到了电极恢复能力差、与标准毒性检测方法相关性差等因素的制约,不能得到广泛的发展。为此有研究人员[102]提出将群体传感诱导剂(C6-HSL,3-OXO-C12-HSL)应用于微生物燃料电池的阳极生物膜处以便增强微生物的传感能力与恢复能力,如图6所示,该方法不仅提高了检测范围与精度,同时也增强了微生物的耐冲击性。
对微生物燃料电池关于BOD与毒性检测的文献调研可知,电化学工作站接收微生物产生的电信号,最终以电量/电流/电压的形式表现出来。经过分析Q1可以用于表征可生化有机物BOD的量,ICi间接表征水体毒性。微生物燃料电池技术具备BOD与毒性一体化的能力,但由于制约因素较多很难在实际工况中广泛应用。
为了减弱指标检测的难度,韩严和课题组[57]提出了一种基于活性污泥法的BOD与毒性一体化检测技术,理论上将微生物降解前测定的COD值(COD原水)示为水样中总有机物的量,而微生物降解后测定的COD值(COD0)则为不可生物降解有机物的量。因此,微生物降解前后的COD之差为水样中可生物降解有机物的量即等于BOD (BODCOD=BOD)。毒性是微生物降解BOD时受到抑制的量,可以用毒性物质参与前后BOD的变化量(BOD0−BOD)表示,通过以上的理论分析可知对毒性量的检测最终可转化为对COD检测,即以BOD差值=(COD原水−COD0)−(COD原水−COD)=COD−COD0表示。该法将BOD、EC50的测定转化为对较简单、快速的COD测定,既达到了EC50快速检测的目的,又实现了BOD和EC50的一体化检测。
-
BOD与毒性一体化检测技术的实现不仅可以缩短BOD检测用时,丰富毒性检测方法,而且为实际工况提供更高效的选择。但一体化检测的方法较少且局限性较大,急需探究一种快速、简便的新方法。由上述基于活性污泥法的BOD与毒性一体化检测技术理论可知,该技术仅通过对COD值的测定与计算最终达到COD、BOD与毒性三者的一体化检测的目的,不仅可以避免COD标准检测方法的污染问题而且极大地缩短了BOD的检测用时,同时毒性检测技术的操作复杂以及重现性差等特点也得以改化。基于活性污泥法的BOD与毒性一体化检测技术主要是以在毒性物质胁迫下活性污泥微生物直接接触并降解废水中有机物为基础的实验分析方法,在适宜的曝气条件下活性污泥微生物受到废水中毒性物质的抑制作用,可通过有机物降解过程给予反馈。虽然活性污泥法的毒性检测灵敏度高,但是活性污泥在培养过程中容易老化需定期排泥并添加新泥,不适用于实际工况的应用。在接下来的探究中为了进一步优化该方法以达到更加便携快速的目的,可以通过培养陶粒生物膜替代活性污泥,生物膜法既可以满足微生物多样性的需求也可以实现便携快速检测。
水体生化需氧量、生物毒性及其一体化检测技术进展
The development of water biochemical oxygen demand, biological toxicity and its integrated detection technology
-
摘要: 随着国家对环境问题的不断重视,我国水污染状况已有了较大的改善,但为了进一步优化水质并使污水处理厂能够达标排放,水质检测是必要工作。由于在面对污、废水冲击时微生物的理化响应速度较快,因此与微生物相关的水质检测指标通常可以较好地反映出废水特性。本文围绕微生物理化指标,以常见的生化需氧量(biochemical oxygen demand,BOD)、水体生物毒性及其一体化检测方法为探究对象。依次总结了包括传统BOD检测方法、微生物传感器法、微生物燃料电池法以及活性污泥曝气降解法在内的BOD检测技术,以发光细菌、鱼类及藻类等不同营养级生物为主的毒性检测技术,并对以上技术的优缺点进行分析与总结。在综合分析的基础上提出BOD和生物毒性一体化检测技术在实际应用中具有较大发展前景并对技术研究方向进行展望。Abstract: With the continuous attention of the state to environmental problems, the water pollution situation in China has been greatly improved, but in order to further optimize the water quality and make the sewage treatment plant discharge up to the standard, water quality detection is necessary. Because microorganisms have the fastest response to the impact of sewage and wastewater, the water quality indicators related to microorganisms usually can better reflect the characteristics of wastewater. In this paper, the common biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), water biotoxicity and their integrated detection methods at home and abroad are studied, and the advantages and disadvantages of various technologies are analyzed and summarized. On the basis of comprehensive analysis, the integrated detection technology of the BOD and biotoxicity has a great development prospect in practical application, and the research direction of the technology is prospected.
-
Key words:
- biochemical oxygen demand /
- biological toxicity /
- integrated /
- detection technology
-
随着我国工业产品的需求量急剧增加,在生产使用化学品的过程中排放污、废水比例也不断增大。对于煤化工、石油等行业废水来说,具有排放量大、废水污染程度高以及含有毒有害性物质等特点,属于典型难降解废水。由于我国工业品生产水平存在差异,部分企业生产技术落后,污染防控和治理措施不完善,低清洁生产水平下排放出的难降解废水,不仅会使河流、湖泊等水生态系统遭到破坏,也会影响周围动植物的生存质量。针对这一问题,我国早在2013年环境保护部印发的《化学品环境风险防控“十二五”规划》中就提到有关行业特征污染物的排放会引发周边环境状况的恶化,此类污染物在环境中降解速度慢,严重威胁人体的健康发展,必须加强特征污染物的环境监测。2018年起开始实施的《中华人民共和国水污染防治法》第二十五条规定国家要完善和加强水环境质量监测与水污染物排放监测。由于废水中的特定污染物对环境危害极大,我国在有毒有害污染物的监测及检测方面愈发重视。但是重金属、农药类有机物等毒性化学品在水体中含量低毒性大,给BOD(biochemical oxygen demand)、生物毒性等指标的检测带来一定的难度。其中BOD检测技术主要分为两部分,一种是以CO2或溶解氧量为定量基础的传统BOD检测技术;另一种是以电信号、光信号为定量基础的微生物传感器技术。以上方法在稳定检测与快速检测等方面具有优势,但不能同时满足。生物毒性检测技术通常受到受试生物的影响,具有检测时间长,重现性差,检测费用高等缺点。这两种传统方法共同存在的问题是,检测用时较长、无法实现在线监测、灵敏度低。为了克服以上问题,以微生物降解及电化学相结合的BOD和毒性一体化检测技术逐渐进入人们的视野,成为BOD、生物毒性等单指标及多指标检测领域的技术研究方向。
1. BOD检测技术研究现状(Research status of BOD detection technology)
生化需氧量(BOD)是水质分析与检测中一种常见的理化参数,BOD的测定可广泛应用于工业废水、市政污水、地下水等常见水体[1-5],该参数不仅可以表征待测水样的可生化性能和污染强度,也可为水处理构筑物的设计提供参考[6]。目前,国内外常见的BOD检测方法有[7-8]:稀释接种法、压差法、增温法、微生物传感器法、微生物燃料电池法以及活性污泥曝气降解法等,如表1所示。
表 1 BOD检测技术现状Table 1. Current situation of BOD detection technologyBOD检测技术BOD detection technology 检测指标Detection index 适用范围Scope of application 优缺点Advantages and disadvantages 传统BOD技术 稀释接种法 二氧化碳/氧气消耗量 市政污水、工业废水、养殖废水、水质监测等 检测结果较为准确,技术较为成熟,但检测用时较长。 压差法 增温法 改进BOD技术 BOD生物传感器技术 光/电信号 模拟染料废水、工业废水 检测用时较短,但操作与制备过程复杂,该技术仍在探究与改进中。 活性污泥曝气降解法 COD变化量 工业废水、市政污水、模拟生活污水 检测时间为2 h,无需专门搭建反应器,减少了实验操作的复杂程度,检测精度较高。 微生物燃料电池技术 电量/电流值 工业废水、水质监测 检测效率与介质、微生物种类有关,检测时间较短,电极需要定期维护。 1.1 传统BOD5测定技术
稀释与接种法是目前最常见的生化需氧量测定方法,该方法技术成熟适用于多种水质,检测范围在2—6000 mg·L−1,测量结果较为准确,在实际检测中得到广泛应用[9]。稀释与接种法是以微生物为媒介进行信号传导的一种方法,为了保证BOD5数值检测的准确性,待测水样不仅要在4 ℃内保存并进行去除余氯等预处理步骤,同时还要保证微生物在最适宜的条件下进行降解反应。经探究[10],废水中微生物的最适温度范围为16—30 ℃,因此稀释与接种法在密闭条件下的培养温度严格设置在(20±1) ℃。与此同时,pH也是影响微生物生存的重要因素,由于中性条件下的微生物生长状况最优,因此待测水样调节至pH7.0±0.5。
经以上探究可知,稀释接种法操作繁琐不能满足污水处理厂实时监测的需求,因此有研究人员提出利用压差法来测量BOD。压差法与稀释接种法的原理基本相同,主要差异是将溶解氧含量的测定转化为更加简单快捷的压力测定。微生物为了满足自身生长代谢所需的能量吸收并降解有机物,在此过程中吸收氧气并排出二氧化碳。根据此原理压差法测定BOD通常被分为两种形式,一是将待测水样充氧至饱和利用降解过程中氧气消耗产生的压差间接表征BOD。Hussain等[11]依靠该方法设计出了一种应用于养殖废水并实现对耗氧率(OUR)与BOD的实时监测的光学沼气再测量系统。二是无需处理待测水样,通过在密闭的培养瓶中添加氢氧化钠颗粒直接吸收微生物排出的二氧化碳,使得瓶中二氧化碳减少压力发生变化从而达到实时监测与测定BOD的目的[12-14],该部分的装置及原理如图1所示。
稀释接种法、压差法等传统方法虽具有较好测量精度,但为保证有机物可以被微生物完全降解检测用时均设定为5日,不能满足实际工况水样快速、简单的检测要求。经探究,光、电化学具有简便快速可实时观测的优点,因此有研究人员[15-16]提出可以利用光、电化学传感技术与微生物降解过程联合并研发出一种高效的BOD传感技术。
1.2 BOD生物传感器技术
BOD生物传感器技术是一种将微生物作为识别元件并通过其自身反应与电极等转换器的作用,得到以电流/电量变化率、氧荧光猝灭效率以及耗氧率作为检测指标来评价BOD的技术[17-19]。其中根据检测指标的不同,选用的微生物种类也有所差异。常见的在以氧传导和电传导为基础的生物传感器中起到识别作用的微生物类别有Bacillus subtilis (枯草芽孢杆菌)、Escherichia coli (大肠埃希氏杆菌)、Trichosporon cutaneum (皮状丝孢酵母菌)、Candida albicans (白色念珠菌)、Saccharomyces cerevisiae (酿酒酵母菌)、Candidatropicalis (热带假丝酵母)等[20-23],以上微生物中大肠杆菌和酿酒酵母菌分别作为原核生物与真核生物的代表被广泛应用。由于两种菌群在细胞结构、生殖方式等方面具有较大差异。相比于大肠杆菌,酵母菌对有机物的降解更加广泛,同时在面对环境冲击以及水中毒性物质冲击时也具有良好的稳定性。但酵母在降解过程中受到酶作用机制的影响,电传导能力弱于大肠杆菌。为了弥补以上缺陷,有研究人员提出两种方案,一是通过添加酶等物质改善传感器性能[24]。Kim等[25]从活性污泥中提取出了一种Klebsiella sp. (克雷伯氏菌)该菌对乳酸具有较好的降解效果,但为了使以该菌为识别元件的BOD传感器对葡萄糖等有机物也具有较高的检测灵敏度,从牛血清蛋白中提取了β-半乳糖苷酶辅助降解反应的进行。二是将多类别的菌种混合共同参与反应[26]。Niyomdecha等[27]为了提升BOD传感器的检测性能探究并制备了一种以亚甲基蓝为介质,石墨烯为工作电极,壳聚糖-牛血清白蛋白(CHI-BSA)冷冻凝胶为载体,活性污泥混合菌群为生物识别元件的新型BOD生物传感器,该传感器的检测范围可达1.0—100 mg·L−1(O2),与GGA(葡萄糖+谷氨酸)标准溶液浓度相关系数R2=0.9993,具有良好的稳定性与重复性。经探究,活性污泥菌群不仅对有机物的降解具有广泛性,而且具有较强的耐冲击性,是良好的生物传感元件。但在长期的检测过程中活性污泥菌群不可避免地会对有机物进行争夺从而产生优、劣势菌种,使得菌群的多样性逐渐降低。为避免该情况的发生影响传感器检测性能,尽可能将混合微生物固定在电极表面后进行信号传导及BOD值的检测。
微生物菌群在创造良好降解效果并产生生物信号的同时,如何让生物信号最大效率的传递至转换元件是另一个需要探究的环节。目前,BOD反应器中最常见的微生物存在形式为游离态与固定态[26, 28]。当微生物处于游离态参与检测反应时既可避免转换元件表层被菌群堵塞,保持转换元件的信号传输强度,也可延长转换元件的寿命。但是由于菌群在传感器中较为分散,产生的生物信号大多需要通过添加一些介质辅助其进行集中传递。这些介质包括:中性红、亚甲基蓝、刃天青等[29-31],介质的添加不仅会对微生物产生微弱毒性,而且影响生物信号的生成。因此,有研究人员提出可以通过固定技术将微生物固定于转换元件表层,这样不仅可以加强生物信号的传输,也可以减少传输器的污染问题。如,Yudina等[32]利用包埋固定技术将酵母菌、细菌与酶共同固定在经过N-乙烯基吡咯烷酮改性的聚乙烯醇载体中,该传感器的检测用时仅为3—4 min,与BOD5的相关系数可达0.9988,具有良好的BOD检测性能。
目前,常见的微生物固定方法有吸附固定、包埋固定、共价结合固定与交联固定等4种[33-35]。其中共价结合固定技术与交联结合技术属于化学方法,吸附固定技术与包埋技术属于物理方法。相比于交联技术,共价结合技术凭借其稳固的性能被更多学者所探究。共价结合技术是指利用载体表面带有的基团与细胞表面氨基基团匹配结合为共价键使微生物稳固在载体表面的一种固定方法。该固定方法制备的BOD电极可为微生物的附着提供更多点位,不仅延长了电极寿命而且提高了传感器的检测性能。图2为BOD传感器电极的制备A)与修饰B)过程图,由图可知以共价结合技术为基础的经羟基石墨烯(GN-COOH)与金纳米颗粒(AuNPs)改性的电极载体表面具有更多点位并且官能团的结合能力更强,相同条件下附着的微生物更多。但共价结合方法的制备过程过于复杂不适用于广泛应用,因此更加高效快速的包埋技术得到发展。
包埋固定技术中常以单一或复合形式的海藻酸钠(sodium alginate,SA)、聚乙烯醇(polyvinyl alcohol,PVA)、胶原纤维等物质作为微生物载体[36-38]。微生物被载体包裹固定,载体为工作菌群提供适宜稳定的生存与降解环境,两者的结合增强并提高了BOD传感器的传导性能与使用寿命。Zhao等[39]研制了一种负载Zr(Ⅳ)的胶原纤维载体,该载体不仅具有多孔结构,而且还有较好的亲水性与生物融合性,通过将该载体与大肠杆菌、酿酒酵母菌融合制备所得的BOD传感器具有42 d的较长寿命。近年来随着材料科学的深入发展,磁性材料以及纳米材料凭借其较强的造孔能力也逐渐进入人们的视野[40-41]。
1.3 微生物燃料电池技术
微生物燃料电池(microbial fuel cell,MFC)作为BOD传感技术中的重要分支。相比于其它方法,燃料电池技术主要通过作为阳极催化剂的电化学活性菌(electrochemically active bacteria,EAB)降解有机物,并利用降解过程中生成的生物电子为传感器系统提供能量,最终根据电流变化情况实现对BOD数值的监测与检测的一种技术方法[42-43]。常见的微生物燃料电池主要由阳极、阴极、分隔膜以及外接电路构成,其结构及工作流程如图3所示[44]。
根据其结构组成可知,阴、阳电极是影响微生物燃料电池性能产出的重要因素。因此对电极材料的探究尤为重要,阳极电极表面作为接收生物电子的重要点位需要具有较高的生物相容性、高的导电性以及耐腐蚀性。而阴极电极则需具备较高的氧还原性能,为了降低反应电势提高还原性能通常会在阴极表面负载一层高效催化剂来实现性能的提升[45]。经探究,常见的可用于传感导电的电极材料有以金刚石、碳纳米管、石墨烯为主的碳系列材料、天然生物质材料、以及钛、铂等金属材料[46-48]。其中,碳布、碳网、碳毡等传统碳系列材料凭借其廉价、具有较大的比表面等优点被广泛应用与研究[49-50]。如Guo等[51]为了探究电极的有效保存条件,建立了一种以碳布为电极材料用于检测BOD的微生燃料电池系统。有些研究人员为了进一步提升电极的电传导性能,在传统碳材料的基础上进行改性处理[52]。Liu等[53]将石墨烯颗粒电沉积于阳极碳布表面并以此构建了一种无介质微生物燃料电池,由于石墨烯的高生物相容性促使微生物在电极表面大量生长繁殖,增加了电子传递速率使得燃料电池的功率密度与能量转换率分别增加了2.7倍与3倍。
1.4 活性污泥曝气降解法
废水中的有机物根据微生物的降解特性可分为:包括葡萄糖、蛋白质、淀粉等物质在内的可生物降解有机物,以表面活性剂、烃类化合物、合成农药类化合物为主的难降解有机物,以塑料制品与尼龙制品为主的不可降解有机物[54-56]。活性污泥曝气降解法利用以上微生物的降解特性,分别对待测水样的原水COD值与降解反应后的出水COD值进行测定,将原水COD值视为总有机物含量,出水COD值视为难降解有机物与不可降解有机物的量。由于在曝气条件下活性污泥微生物较为活跃并大量降解废水中的可生化降解有机物,因此原水与出水间的COD差值理论上可表示为BOD。为了在短期内尽可能地完成对可生化有机物的降解,需要对活性污泥微生物的最佳反应条件进行探究。在常见的标准方法中,取3 mL预处理后的活性污泥与50 mL待测水样在30—35 ℃条件下连续曝气2 h既可达到最佳降解效果。本课题组也对此进行了探究,首先利用模拟废水对污泥进行培养驯化,待其成熟后分别探究降解时间、污泥量、pH以及温度等单因素的影响[57]。探究结果表明,当降解时间在180 min、污泥量为5 mL/100 mL、pH=7.0,温度保持在25 ℃时活性污泥对有机物的降解达到最大值并保持稳定。同时,在最佳条件下由BOD5与BODCOD的相关性探究可知,BODCOD的检测浓度范围为0—500 mg·L−1,相关系数R2=0.981,与传统BOD5具有良好的相关性。本课题组的探究为活性污泥曝气降解法提供了更加优异的检测条件。
活性污泥曝气降解法与传统的稀释接种法相比,检测用时从5 d缩减为2 h极大地提高了检测效率,同样具有良好的检测精度。与BOD传感器法相比,虽然检测用时稍长,但无需专门搭建反应器,减少了实验操作的复杂程度。综上所述,活性污泥曝气降解法的提出不仅提高了BOD的检测效率,而且为COD与BOD一体化检测提供了新的思路,在生活污水、市政污水以及工业废水等水质检测中具有良好的应用前景。
2. 生物毒性检测技术研究现状(Research status of biotoxicity detection technology)
2.1 发光细菌毒性检测技术
发光细菌毒性检测技术中菌群的发光能力是确保检测结果准确的重要条件。发光细菌的发光过程主要分为两个阶段[58],第一阶段:发光细菌受到体内荧光素酶与辅酶Ⅱ的共同催化作用,促使FMN(黄素单核苷酸)与H+发生反应,由氧化态的FMN变为还原态的FMNH2。第二阶段:微生物为了储存并获取满足自身生长所需的能量,在部分氧原子的参与下将长链脂肪醛(RCHO)合成为脂肪酸(RCOOH)。与此同时,体内剩余的氧原子在荧光素酶的催化作用下将FMNH2又氧化为FMN并释放出大量光子,该光子为波长在450—490 nm间的蓝绿色可见光。两阶段的反应方程如式1和2所示[59]。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) 目前,常选用的具有较强发光能力的菌群有Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 (青海弧菌)、Photobacterium luminum (明亮发光杆菌)、Vibrio fischeri(费氏弧菌)以及Heterobrevibacterium luminescens (发光异短杆菌)等[60-62],其中费氏弧菌与明亮发光杆菌作为主要的模式生物被列入各国的检测标准中,如国际标准(ISO 11348—2007)、欧盟标准(EN ISO 11348—2008)、美国标准(ASTM D5660—2004)和中国标准(GB/T 15441—1995)等[63]。由于Photobacterium luminum与Vibrio fischeri均属于海洋菌,只有在高盐分的条件下才具备较好的检测活性。近年来,淡水发光菌被越来越的人所探究,青海弧菌是少有的具备发光能力的淡水菌,该菌在检测过程中无需添加盐分来迎合微生物的生存环境,获取容易、价格低廉,较适宜用作发光细菌毒性试验中的受试生物并被广泛应用。Ma等[64]将青海弧菌作为受试生物,探究了制药废水在污水厂的不同处理阶段中的毒性水平。结果表明废水原水的荧光抑制率(IR)为60.96%具有较强毒性;TPC(三相催化氧化反应池)为毒性去除效果最优的构筑物去除率为48.3%;对于FSBBR(流动分离床生物反应器)来说处理后的废水毒性没有改观。由该探究可知发光细菌毒性检测方法可用于监测实际工况下所排放废水的毒性。
2.2 藻类毒性检测技术
藻类毒性检测技术也是较为常见的生物毒性检测技术,该技术的检测指标包括:超氧化物歧化酶含量、细胞密度、细胞活力、叶绿素a含量、细胞色素含量、发光度以及抗氧化酶含量等[65-67]。以上指标在毒性检测试验中应用广泛且方法成熟,但是具有操作复杂、用时长等缺点。因此有研究人员提出了一种基于叶绿素荧光技术并以不同荧光参数为指标的藻类毒性检测新方法[68- 69]。
叶绿素荧光技术在实现快速、便捷的在线监测方面具有较大潜力,该技术是一种以藻类光合作用为理论基础,通过探究荧光参数变化情况来表征细胞光合代谢活性的测量技术。藻类进行光合作用的主要目的是获取能量,获取的能量被提供用于光化学反应、荧光生成以及热量散发。光合作用中的光反应过程为主要产能环节,光反应过程离不开电子的传递[70]。如图4所示,电子的传递过程主要分为3个阶段:① 光反应系统Ⅱ(PSⅡ)吸收了外界的光能并将光量子传递至以色素P680为主的光反应系统中心,该色素得到量子后跃迁为不稳定的激发态(
P*680 P*680 P+680Pheo- P+680Pheo- P+680 鉴于叶绿素荧光技术具有对植物体无害、快速、精准等优良特性,该技术被大量用于毒性检测方面的研究,如Salas等[71]利用叶绿素荧光技术探究了在氨基酸的参与下银纳米粒子对莱茵衣藻(Chlamydomonas reinhardtii)的毒性强度变化情况。该实验首先通过荧光测定仪对
F′M stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (3) 式中,
F′M 2.3 鱼类毒性检测技术
从食物链的角度来说,发光细菌、藻类、鱼类之间属于分解者、生产者与消费者的关系,其中鱼类是消费者层级中最早用于毒性检测的生物之一。常见的受试鱼类有斑马鱼、日本清鳉鱼、稀有鮈鲫、虹鳟以及鲤鱼等[73-75]。在进行宏观与微观的分析中常以半数致死浓度(LC50)、游动行为强度(swimming behavior intensity,BS)、胚胎发育程度、血液中的物质含量等作为检测指标来描述受试水体的毒性强度。LC50是最早被用于毒性试验的指标,也是最常见且应用最广的急性毒性检测指标。陈建华等[76]利用斑马鱼探究了茶多酚对壬基酚急性毒性的缓解作用,结果表明当茶多酚浓度在2.5—20.0 mg·L−1时可对壬基酚的急性毒性起到缓解作用,使得斑马鱼死亡率下降,LC50明显上升。朱燕华等[77]则是利用斑马鱼胚胎对不同类别的食用油急性毒性进行了探究,探究结果表明未精炼的地沟猪油对斑马鱼胚胎毒性最大,LC50低至14.3 mL·L−1;正常精炼猪油的毒性最低LC50>173.3 mL·L−1。
虽然LC50可用于检测大多数的毒性物质,但是为了探究待测物质的累积毒性或遗传毒性只能通过血液指标与胚胎发育程度情况进行试验分析[78]。如硝酸盐类与亚硝酸盐类是废水处理中比较常见的低毒或无毒类污染物质,但是随着培养时间的增加,以上物质会逐渐在鱼体内积累,为了分析鱼体内对硝酸盐物质的毒性响应,可以从血液指标入手。Grabda等[79]将虹鳟鱼在含量为5—6 mg·L−1的硝酸盐溶液中培养数日,最后观察得到血液中的高铁血红蛋白水平增加,外周血和造血中心发生改变,肝脏受到损伤。还有研究人员[80]对醚菊酯的积累毒性进行了探究,结果表明长时间暴露在醚菊酯中致使鲤鱼的红细胞与血红蛋白含量减少、谷草转氨酶(glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase,AST)与谷丙转氨酶(alanine aminotransferase,ALT)含量增加,说明鲤鱼的肝脏可能受到了损伤。对于检测一些具有遗传毒性的物质来说,鱼胚胎技术具有可以靶向观察、快速、简便的特点是一种良好的技术手段。该技术通过鱼受精卵胚胎发育情况分析待测物质的遗传毒性强度。目前多被用于评估河流沉积物的遗传毒性,如Babić等[81]为了对萨瓦河河流沉积物的毒性进行了评估,将斑马鱼胚胎与沉积物分别接触24 h、48 h。观察发现不同斑马鱼胚胎的发育损伤程度不同,主要受到遗传损伤的部位为眼睛、肌肉、卵黄囊和尾巴。
LC50、胚胎发育损伤以及血液物质含量等指标可以实现对物质毒性的定性定量分析,但是对于有着在线监测需求的废水处理厂来说,以上指标并不能满足实际需求。因此游动行为强度这一可以实现在线监测目的指标被更多学者所探究[82-83]。游动行为强度以行为学为基础,从鱼类本身具有的趋流性出发对运动位置、运动速度等指标进行综合评价[84]。当水中含有毒性物质时,鱼的视、触神经系统最先遭受攻击,致使呼吸频率加快并出现与常规条件下不同的逆趋流行为[85]。基于该原理,现已开发出了可实现在线监测的3D生物监测装置,该装置主要以由运动轨迹、运动速度、出水频率组成的综合行为指标BS作为监测对象,具有简单、便捷等特点。图5为利用3D生物传感装置测得的不同毒性条件下斑马鱼活动规律数值分析图。
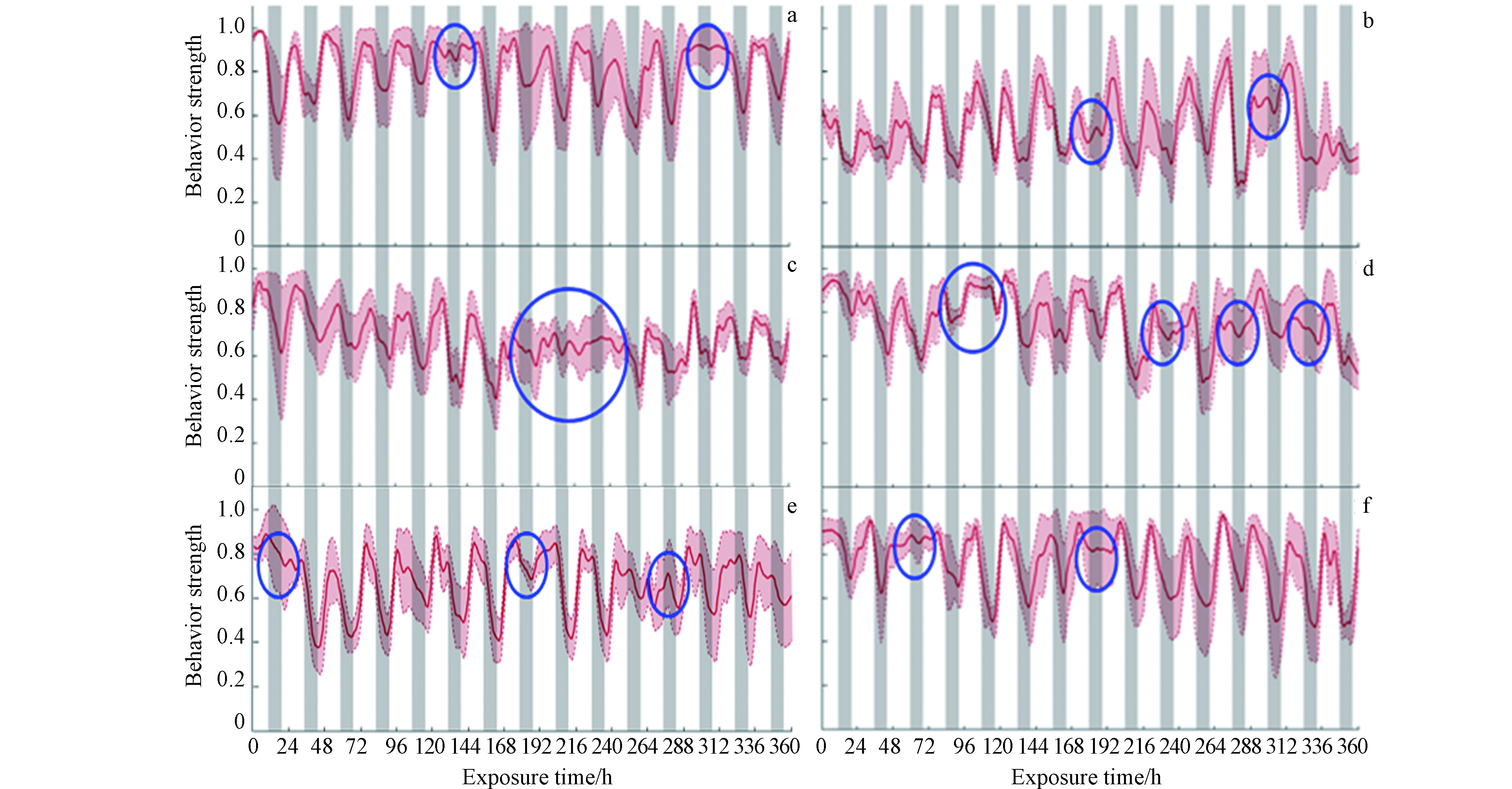 图 5 不同毒性条件下斑马鱼的BS值曲线[86] a) 对照组;b) 0.1 mg·L−1铊;c) 20 mg·L−1溴氰菊酯;d) 2 mg·L−1溴氰菊酯;e) 30 mg·L−1莠去津;f) 3 mg·L−1莠去津; 圈中为规律异常处Figure 5. BS value curve of zebrafish under different toxicity conditions [86] a) control group ;b) 0.1 mg·L−1 thallium; c) 20 mg·L−1 deltamethrin; d) 2 mg·L−1 deltamethrin; e) 30 mg·L−1 atrazine; f) 3 mg·L−1 atrazine; In the circle is the abnormal place
图 5 不同毒性条件下斑马鱼的BS值曲线[86] a) 对照组;b) 0.1 mg·L−1铊;c) 20 mg·L−1溴氰菊酯;d) 2 mg·L−1溴氰菊酯;e) 30 mg·L−1莠去津;f) 3 mg·L−1莠去津; 圈中为规律异常处Figure 5. BS value curve of zebrafish under different toxicity conditions [86] a) control group ;b) 0.1 mg·L−1 thallium; c) 20 mg·L−1 deltamethrin; d) 2 mg·L−1 deltamethrin; e) 30 mg·L−1 atrazine; f) 3 mg·L−1 atrazine; In the circle is the abnormal place2.4 生物毒性检测技术对比
以上部分分别总结了以发光细菌毒性检测技术、藻类毒性检测技术以及鱼类毒性检测技术为主的国内外应用较早且较为普遍的几种生物毒性检测技术。随着时间的推移,越来越多的毒性检测技术被探究,本小节对常见的按照检测指标分类的生物毒性检测方法进行总结,总结结果如表2所示。
表 2 几种常见的生物毒性检测方法对比Table 2. Comparison of several common biological toxicity detection methods表征指标 检测方法 检测用时 优点 缺点 致死/抑制浓度 鱼类、溞类、蚯蚓等动物检测方法[87-88] 24 、48 、96 h 操作较简便,灵敏度高,费用较低。 检测周期长,具有特异性,不能实现在线监测。 胚胎发育程度 鱼胚胎技术[89] 晶体期:120 —140 h;出膜期:163 —210 h 可实现对遗传毒性的研究。 试验操作复杂,需要具备一定的专业知识。 游动行为强度 鱼类、溞类等水生动物检测方法[90] 实时监测,数天 方法简单 检测周期长;数据分析难度大;鱼类具有特异性。 发光度 发光细菌法与叶绿素荧光法[91-92] 20—120 min/ 30—120 min 检测时间较短,反应灵敏,藻类无需预处理。 叶绿素荧光试验中需要控制的变量较多,不适宜广泛应用。 电流/电压/电量值 生物燃料电池法[93-94] 15—70 min 检测周期较短,可实现在线监测。 微生物易产生抗性,会影响检测结果。 吸光度 比色法与染色法[95-96] 数天 方便观察 比色法需要基因重组操作较复杂。 微核生成率/染色体畸变度 细胞微核法与SOS显色法[97-98] 数天 可用于探究遗传毒性 微核法的工作量大;不能实现定性、定量地分析污染物。 血液指标 鱼、虾、贝等水生动物检测法[79, 99] 数天 可用于测定累积毒性或损伤情况。 不能定量分析,且具有特异性。 酶活性、耗氧速率、硝化速率等 细菌菌群检测法[100] 60—150 min 可用于活性污泥的毒性测定 检测结果不稳定需多次测量。 综上所述,在常见的生物毒性检测技术中虽然大多数方法具有较高的灵敏度,但是检测周期长不能满足在线监测以及多种指标一体化检测的实际需求等问题也不能被忽视,所以需要继续探究一种可以缩短检测用时、操作简便可以满足实际工况需求的生物毒性检测新方法。
3. BOD与毒性一体化检测技术研究现状(Research status of BOD and toxicity integrated detection technology)
就目前来说,国内外对于BOD与毒性一体化检测技术的探究较为欠缺,微生物燃料电池是目前仅有的已被探究具备一体化检测与制造成型设备能力的技术,该技术既可以实现对BOD的检测也可以满足毒性的检测需求。微生物燃料电池在进行毒性检测时其机理为:在相同条件下相比于无毒水体中微生物降解有机物时的产电量,由于受到重金属等毒性物质胁迫,电活性菌代谢过程受阻排出的生物电子随着毒性的渗透而逐渐减少,在一定时间内产电量大幅降低,降低的电量可间接地用于表征毒性。基于该原理分别对标准溶液下的微生物产电量(Q1)与受到重金属胁迫下的微生物产电量(Q2)进行测定并将数值代入式(4)进行计算求得产电抑制率(ICi),以产电抑制率评价毒性物质的毒性强度,实现微生物燃料电池对毒性的检测。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (4) 当微生物燃料电池作为毒性传感器时多将镉、铬、铜等重金属以及苯、醛等化学物质作为检测目标。基于微生物群落对毒性物质的特异性与耐受性,以不同类别或不同培养时间的菌种作为阳极生物膜的燃料电池得到的毒性检测结果也有所差异。如Lu等[94]为分析生物燃料电池在受到冲击后响应电压值下降原因,选用Flavobacterium(黄杆菌属)、Geobacter(地杆菌属)、Pseudomonas(假单胞菌属)、Acidovorax(嗜酸菌属)以上四种细菌暴露在不同浓度的甲醛溶液中进行毒性检测,探究表明Pseudomonas、Acidovorax对甲醛毒性较为敏感,在低浓度长时间的检测活动中活性抑制明显,进而导致电压值下降最大。Xu等[101]选用Pb作为毒性物质对不同检测时间下生物膜的毒性敏感度进行了探究,结果表明参加过多次检测活动的成熟生物膜在灵敏度及活性等方面均弱于新形成的生物膜。由以上可知当微生物燃料电池在作为毒性传感器使用时需要探究的因素较为广泛与复杂。与此同时,微生物燃料电池在毒性检测的实际应用中受到了电极恢复能力差、与标准毒性检测方法相关性差等因素的制约,不能得到广泛的发展。为此有研究人员[102]提出将群体传感诱导剂(C6-HSL,3-OXO-C12-HSL)应用于微生物燃料电池的阳极生物膜处以便增强微生物的传感能力与恢复能力,如图6所示,该方法不仅提高了检测范围与精度,同时也增强了微生物的耐冲击性。
对微生物燃料电池关于BOD与毒性检测的文献调研可知,电化学工作站接收微生物产生的电信号,最终以电量/电流/电压的形式表现出来。经过分析Q1可以用于表征可生化有机物BOD的量,ICi间接表征水体毒性。微生物燃料电池技术具备BOD与毒性一体化的能力,但由于制约因素较多很难在实际工况中广泛应用。
为了减弱指标检测的难度,韩严和课题组[57]提出了一种基于活性污泥法的BOD与毒性一体化检测技术,理论上将微生物降解前测定的COD值(COD原水)示为水样中总有机物的量,而微生物降解后测定的COD值(COD0)则为不可生物降解有机物的量。因此,微生物降解前后的COD之差为水样中可生物降解有机物的量即等于BOD (BODCOD=BOD)。毒性是微生物降解BOD时受到抑制的量,可以用毒性物质参与前后BOD的变化量(BOD0−BOD)表示,通过以上的理论分析可知对毒性量的检测最终可转化为对COD检测,即以BOD差值=(COD原水−COD0)−(COD原水−COD)=COD−COD0表示。该法将BOD、EC50的测定转化为对较简单、快速的COD测定,既达到了EC50快速检测的目的,又实现了BOD和EC50的一体化检测。
4. 结语与展望(Conclusion and prospect)
BOD与毒性一体化检测技术的实现不仅可以缩短BOD检测用时,丰富毒性检测方法,而且为实际工况提供更高效的选择。但一体化检测的方法较少且局限性较大,急需探究一种快速、简便的新方法。由上述基于活性污泥法的BOD与毒性一体化检测技术理论可知,该技术仅通过对COD值的测定与计算最终达到COD、BOD与毒性三者的一体化检测的目的,不仅可以避免COD标准检测方法的污染问题而且极大地缩短了BOD的检测用时,同时毒性检测技术的操作复杂以及重现性差等特点也得以改化。基于活性污泥法的BOD与毒性一体化检测技术主要是以在毒性物质胁迫下活性污泥微生物直接接触并降解废水中有机物为基础的实验分析方法,在适宜的曝气条件下活性污泥微生物受到废水中毒性物质的抑制作用,可通过有机物降解过程给予反馈。虽然活性污泥法的毒性检测灵敏度高,但是活性污泥在培养过程中容易老化需定期排泥并添加新泥,不适用于实际工况的应用。在接下来的探究中为了进一步优化该方法以达到更加便携快速的目的,可以通过培养陶粒生物膜替代活性污泥,生物膜法既可以满足微生物多样性的需求也可以实现便携快速检测。
-
图 5 不同毒性条件下斑马鱼的BS值曲线[86] a) 对照组;b) 0.1 mg·L−1铊;c) 20 mg·L−1溴氰菊酯;d) 2 mg·L−1溴氰菊酯;e) 30 mg·L−1莠去津;f) 3 mg·L−1莠去津; 圈中为规律异常处
Figure 5. BS value curve of zebrafish under different toxicity conditions [86] a) control group ;b) 0.1 mg·L−1 thallium; c) 20 mg·L−1 deltamethrin; d) 2 mg·L−1 deltamethrin; e) 30 mg·L−1 atrazine; f) 3 mg·L−1 atrazine; In the circle is the abnormal place
表 1 BOD检测技术现状
Table 1. Current situation of BOD detection technology
BOD检测技术BOD detection technology 检测指标Detection index 适用范围Scope of application 优缺点Advantages and disadvantages 传统BOD技术 稀释接种法 二氧化碳/氧气消耗量 市政污水、工业废水、养殖废水、水质监测等 检测结果较为准确,技术较为成熟,但检测用时较长。 压差法 增温法 改进BOD技术 BOD生物传感器技术 光/电信号 模拟染料废水、工业废水 检测用时较短,但操作与制备过程复杂,该技术仍在探究与改进中。 活性污泥曝气降解法 COD变化量 工业废水、市政污水、模拟生活污水 检测时间为2 h,无需专门搭建反应器,减少了实验操作的复杂程度,检测精度较高。 微生物燃料电池技术 电量/电流值 工业废水、水质监测 检测效率与介质、微生物种类有关,检测时间较短,电极需要定期维护。 表 2 几种常见的生物毒性检测方法对比
Table 2. Comparison of several common biological toxicity detection methods
表征指标 检测方法 检测用时 优点 缺点 致死/抑制浓度 鱼类、溞类、蚯蚓等动物检测方法[87-88] 24 、48 、96 h 操作较简便,灵敏度高,费用较低。 检测周期长,具有特异性,不能实现在线监测。 胚胎发育程度 鱼胚胎技术[89] 晶体期:120 —140 h;出膜期:163 —210 h 可实现对遗传毒性的研究。 试验操作复杂,需要具备一定的专业知识。 游动行为强度 鱼类、溞类等水生动物检测方法[90] 实时监测,数天 方法简单 检测周期长;数据分析难度大;鱼类具有特异性。 发光度 发光细菌法与叶绿素荧光法[91-92] 20—120 min/ 30—120 min 检测时间较短,反应灵敏,藻类无需预处理。 叶绿素荧光试验中需要控制的变量较多,不适宜广泛应用。 电流/电压/电量值 生物燃料电池法[93-94] 15—70 min 检测周期较短,可实现在线监测。 微生物易产生抗性,会影响检测结果。 吸光度 比色法与染色法[95-96] 数天 方便观察 比色法需要基因重组操作较复杂。 微核生成率/染色体畸变度 细胞微核法与SOS显色法[97-98] 数天 可用于探究遗传毒性 微核法的工作量大;不能实现定性、定量地分析污染物。 血液指标 鱼、虾、贝等水生动物检测法[79, 99] 数天 可用于测定累积毒性或损伤情况。 不能定量分析,且具有特异性。 酶活性、耗氧速率、硝化速率等 细菌菌群检测法[100] 60—150 min 可用于活性污泥的毒性测定 检测结果不稳定需多次测量。 -
[1] BIRUK L N, MORETTON J, FABRIZIO de IORIO A, et al. Toxicity and genotoxicity assessment in sediments from the Matanza-Riachuelo river basin (Argentina) under the influence of heavy metals and organic contaminants [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 135: 302-311. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.09.024 [2] RASHEED T, BILAL M, NABEEL F, et al. Fluorescent sensor based models for the detection of environmentally-related toxic heavy metals [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 615: 476-485. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.126 [3] KIM S, ALIZAMIR M, ZOUNEMAT-KERMANI M, et al. Assessing the biochemical oxygen demand using neural networks and ensemble tree approaches in South Korea [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 270: 110834. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110834 [4] ABEYSIRIWARDANA-ARACHCHIGE I S A, NIRMALAKHANDAN N. Predicting removal kinetics of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and nutrients in a pilot scale fed-batch algal wastewater treatment system [J]. Algal Research, 2019, 43: 101643. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2019.101643 [5] JORDAN M A, WELSH D T, JOHN R, et al. A sensitive ferricyanide-mediated biochemical oxygen demand assay for analysis of wastewater treatment plant influents and treated effluents [J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(2): 841-849. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.010 [6] PONOMAREVA O N, ARLYAPOV V A, ALFEROV V A, et al. Microbial biosensors for detection of biological oxygen demand (a Review) [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 2011, 47(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1134/S0003683811010108 [7] JOUANNEAU S, RECOULES L, DURAND M J, et al. Methods for assessing biochemical oxygen demand (BOD): A review [J]. Water Research, 2014, 49: 62-82. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.066 [8] SU L, JIA W Z, HOU C J, et al. Microbial biosensors: A review [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2011, 26(5): 1788-1799. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.09.005 [9] 曹阳. 稀释与接种法测定BOD5的探讨[J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(增刊1): 138-140. CAO Y. Discussion on determination of BOD5 by means of dilution and inoculation[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2014, 32(Sup 1): 138-140(in Chinese).
[10] 康小虎, 冷艳, 曾小英, 等. 污水处理活性污泥微生物群落研究进展 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(5): 49-54. KANG X H, LENG Y, ZENG X Y, et al. Review on activated sludge microbial community in sewage treatment [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(5): 49-54(in Chinese).
[11] HUSSAIN F, YU H W, CHON K, et al. Real-time biomonitoring of oxygen uptake rate and biochemical oxygen demand using a novel optical biogas respirometric system [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 277: 111467. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111467 [12] 陈立湘, 柯水洲, 朱佳, 等. 亚铁活化过硫酸钠氧化预处理电镀废水 [J]. 化工环保, 2019, 39(2): 148-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2019.02.006 CHEN L X, KE S Z, ZHU J, et al. Pretreatment of electroplating wastewater by ferrous-activated sodium persulfate oxidation [J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(2): 148-152(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2019.02.006
[13] SARAVANAN N, SASIKUMAR K S K. Waste water treatment process using Nano TiO2 [J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2020, 33: 2570-2572. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2019.12.143 [14] FAISAL G H, JAEEL A J, AL-GASHAM T S. BOD and COD reduction using porous concrete pavements [J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2020, 13: e00396. doi: 10.1016/j.cscm.2020.e00396 [15] PAHLAVANZADEH S, ZOROUFCHI BENIS K, SHAKERKHATIBI M, et al. Performance and kinetic modeling of an aerated submerged fixed-film bioreactor for BOD and nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2018, 6(5): 6154-6164. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.09.045 [16] RAUD M, TENNO T, JÕGI E, et al. Comparative study of semi-specific Aeromonas hydrophila and universal Pseudomonas fluorescens biosensors for BOD measurements in meat industry wastewaters [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2012, 50(4/5): 221-226. [17] BURGE S R, HRISTOVSKI K D, BURGE R G, et al. Microbial potentiometric sensor: A new approach to longstanding challenges [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 742: 140528. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140528 [18] LIU J, MATTIASSON B. Microbial BOD sensors for wastewater analysis [J]. Water Research, 2002, 36(15): 3786-3802. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00101-X [19] ARLYAPOV V A, KHARKOVA A S, KURBANALIYEVA S K, et al. Use of biocompatible redox-active polymers based on carbon nanotubes and modified organic matrices for development of a highly sensitive BOD biosensor [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2021, 143: 109706. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2020.109706 [20] ARLYAPOV V, KAMANIN S, PONAMOREVA O, et al. Biosensor analyzer for BOD index express control on the basis of the yeast microorganisms Candida maltosa, Candida blankii, and Debaryomyces hansenii [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2012, 50(4/5): 215-220. [21] OOTA S, HATAE Y, AMADA K, et al. Development of mediated BOD biosensor system of flow injection mode for shochu distillery wastewater [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2010, 26(1): 262-266. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2010.06.040 [22] LI Y J, SUN J Z, WANG J F, et al. A microbial electrode based on the co-electrodeposition of carboxyl graphene and Au nanoparticles for BOD rapid detection [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 123: 86-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2017.03.015 [23] SAKAGUCHI T, KITAGAWA K, ANDO T, et al. A rapid BOD sensing system using luminescent recombinants of Escherichia coli [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2003, 19(2): 115-121. doi: 10.1016/S0956-5663(03)00170-2 [24] BOLLELLA P, LUDWIG R, GORTON L. Cellobiose dehydrogenase: Insights on the nanostructuration of electrodes for improved development of biosensors and biofuel cells [J]. Applied Materials Today, 2017, 9: 319-332. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2017.08.009 [25] KIM M N, PARK K H. Immobilization of enzymes for Klebsiella BOD sensor [J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2004, 98(1): 1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2003.07.001 [26] LIU L, DENG L, YONG D M, et al. Native biofilm cultured under controllable condition and used in mediated method for BOD measurement [J]. Talanta, 2011, 84(3): 895-899. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2011.02.025 [27] NIYOMDECHA S, LIMBUT W, NUMNUAM A, et al. A novel BOD biosensor based on entrapped activated sludge in a porous chitosan-albumin cryogel incorporated with graphene and methylene blue [J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2017, 241: 473-481. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.102 [28] IVANDINI T A, SAEPUDIN E, WARDAH H, et al. Development of a biochemical oxygen demand sensor using gold-modified boron doped diamond electrodes [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(22): 9825-9832. doi: 10.1021/ac302090y [29] ZAITSEVA A S, ARLYAPOV V A, YUDINA N Y, et al. Use of one-and two-mediator systems for developing a BOD biosensor based on the yeast Debaryomyces hansenii [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2017, 98: 43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2016.12.005 [30] LIU L, ZHAI J F, ZHU C Z, et al. One-pot synthesis of 3-dimensional reduced graphene oxide-based hydrogel as support for microbe immobilization and BOD biosensor preparation [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2015, 63: 483-489. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.07.074 [31] ZAITSEVA A S, ARLYAPOV V A, YUDINA N Y, et al. A novel Bod-mediator biosensor based on Ferrocene and Debaryomyces hansenii yeast cells [J]. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 2017, 53(3): 381-387. doi: 10.1134/S0003683817030152 [32] YUDINA N Y, ARLYAPOV V A, CHEPURNOVA M A, et al. A yeast co-culture-based biosensor for determination of waste water contamination levels [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2015, 78: 46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2015.06.008 [33] 徐忠强, 郝瑞霞, 任晓克, 等. 包埋法固定化细胞技术用于三维电极生物膜反应器 [J]. 中国给水排水, 2018, 34(19): 37-42. XU Z Q, HAO R X, REN X K, et al. Application of entrapping method in three-dimensional biofilm-electrode reactor for advanced nitrogen removal [J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2018, 34(19): 37-42(in Chinese).
[34] 李一锦, 夏善红. BOD微生物传感器关键技术及其发展 [J]. 传感器与微系统, 2015, 34(7): 5-10. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2015)07-0005-06 LI Y J, XIA S H. Key techniques of BOD microbial sensor and its development [J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2015, 34(7): 5-10(in Chinese). doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2015)07-0005-06
[35] DHALL P, KUMAR A, JOSHI A, et al. Quick and reliable estimation of BOD load of beverage industrial wastewater by developing BOD biosensor [J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2008, 133(2): 478-483. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2008.03.010 [36] KWOK N Y, DONG S J, LO W, et al. An optical biosensor for multi-sample determination of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) [J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2005, 110(2): 289-298. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2005.02.007 [37] JIA J B, TANG M Y, CHEN X, et al. Co-immobilized microbial biosensor for BOD estimation based on Sol-gel derived composite material [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2003, 18(8): 1023-1029. doi: 10.1016/S0956-5663(02)00225-7 [38] SAKAGUCHI T, MORIOKA Y, YAMASAKI M, et al. Rapid and onsite BOD sensing system using luminous bacterial cells-immobilized chip [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2007, 22(7): 1345-1350. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2006.06.008 [39] ZHAO L, HE L, CHEN S J, et al. Microbial BOD sensors based on Zr(Ⅳ)-loaded collagen fiber [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2017, 98: 52-57. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2016.11.010 [40] ISMAIL Z Z, KHUDHAIR H A. Biotreatment of real petroleum wastewater using non-acclimated immobilized mixed cells in spouted bed bioreactor [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 131: 17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2017.12.005 [41] 王永军, 付文强, 薛屏. 利用磁性固定化微生物降解水中微量油 [J]. 化学工程, 2017, 45(9): 7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2017.09.002 WANG Y J, FU W Q, XUE P. Degradation of trace oil in water using magnetic immobilized microorganism [J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2017, 45(9): 7-12(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2017.09.002
[42] ABREVAYA X C, SACCO N J, BONETTO M C, et al. Analytical applications of microbial fuel cells. Part I: Biochemical oxygen demand [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2015, 63: 580-590. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.04.034 [43] KIM M, YOUN S M, SHIN S H, et al. Practical field application of a novel BOD monitoring system [J]. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 2003, 5(4): 640-643. doi: 10.1039/b304583h [44] KUMAR S S, KUMAR V, KUMAR R, et al. Microbial fuel cells as a sustainable platform technology for bioenergy, biosensing, environmental monitoring, and other low power device applications [J]. Fuel, 2019, 255: 115682. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115682 [45] GAO Y Y, YIN F J, MA W Q, et al. Rapid detection of biodegradable organic matter in polluted water with microbial fuel cell sensor: Method of partial coulombic yield [J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2020, 133: 107488. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2020.107488 [46] PALANISAMY G, JUNG H Y, SADHASIVAM T, et al. A comprehensive review on microbial fuel cell technologies: Processes, utilization, and advanced developments in electrodes and membranes [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 221: 598-621. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.172 [47] ALMATOUQ A, BABATUNDE A O, KHAJAH M, et al. Microbial community structure of anode electrodes in microbial fuel cells and microbial electrolysis cells [J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2020, 34: 101140. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101140 [48] MOUSAVI M R, GHASEMI S, SANAEE Z, et al. Improvement of the microfluidic microbial fuel cell using a nickel nanostructured electrode and microchannel modifications [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 437: 226891. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.226891 [49] SIM J, REID R, HUSSAIN A, et al. Semi-continuous measurement of oxygen demand in wastewater using biofilm-capacitance [J]. Bioresource Technology Reports, 2018, 3: 231-237. doi: 10.1016/j.biteb.2018.08.009 [50] TRAN T V, LEE I C, KIM K. Electricity production characterization of a Sediment Microbial Fuel Cell using different thermo-treated flat carbon cloth electrodes [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(60): 32192-32200. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.10.076 [51] GUO F, LIU Y, LIU H. Hibernations of electroactive bacteria provide insights into the flexible and robust BOD detection using microbial fuel cell-based biosensors [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 753: 142244. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142244 [52] CHOUDHURY P, UDAY U S P, MAHATA N, et al. Performance improvement of microbial fuel cells for waste water treatment along with value addition: A review on past achievements and recent perspectives [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 79: 372-389. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.098 [53] LIU J, QIAO Y, GUO C X, et al. Graphene/carbon cloth anode for high-performance mediatorless microbial fuel cells [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 114: 275-280. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.02.116 [54] DERRIEN M, BROGI S R, GONÇALVES-ARAUJO R. Characterization of aquatic organic matter: Assessment, perspectives and research priorities [J]. Water Research, 2019, 163: 114908. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.114908 [55] 李彦澄, 刘邓平, 李蕾, 等. 难降解有机物微生物共代谢技术研究进展 [J]. 现代化工, 2019, 39(11): 25-28,34. doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2019.11.006 LI Y C, LIU D P, LI L, et al. Advances in co-metabolic technology of refractory organic pollutants and micro-organisms [J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(11): 25-28,34(in Chinese). doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2019.11.006
[56] 王梦乔, 周庆, 李爱民. 环境水体微污染有机物及其去除技术研究进展 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2012, 34(6): 71-76,96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2012.06.016 WANG M Q, ZHOU Q, LI A M. A review of organic micro pollutants in aquatic environment and its removal technologies [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2012, 34(6): 71-76,96(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2012.06.016
[57] 韩严和, 翟跃华, 阮修莉, 等. 微生物降解前后COD差值法快速测定BOD [J]. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(9): 4035-4039. HAN Y H, ZHAI Y H, RUAN X L, et al. Rapid detection of BOD with difference of COD before and after activated sludge aeration [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2014, 8(9): 4035-4039(in Chinese).
[58] JIN X W, LI Z Y, XU P P, et al. Advances in microfluidic biosensors based on luminescent bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(2): 181-189. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(19)61139-4 [59] MA X Y, WANG X C, NGO H H, et al. Bioassay based luminescent bacteria: Interferences, improvements, and applications [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468/469: 1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.028 [60] YE Z F, ZHAO Q L, ZHANG M H, et al. Acute toxicity evaluation of explosive wastewater by bacterial bioluminescence assays using a freshwater luminescent bacterium, Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. Nov [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(2/3): 1351-1354. [61] XU Y Q, LIU S S, LI K, et al. Polyethylene glycol 400 significantly enhances the stimulation of 2-phenoxyethanol on Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 bioluminescence [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 171: 240-246. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.087 [62] MOHSENI M, ABBASZADEH J, MAGHOOL S S, et al. Heavy metals detection using biosensor cells of a novel marine luminescent bacterium Vibrio sp. MM1 isolated from the Caspian Sea [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 148: 555-560. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.002 [63] MENZ J, SCHNEIDER M, KÜMMERER K. Toxicity testing with luminescent bacteria - Characterization of an automated method for the combined assessment of acute and chronic effects [J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 93(6): 990-996. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.05.067 [64] MA K, QIN Z, ZHAO Z Q, et al. Toxicity evaluation of wastewater collected at different treatment stages from a pharmaceutical industrial park wastewater treatment plant [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 158: 163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.052 [65] LIU X X, WANG Y, CHEN H, et al. Acute toxicity and associated mechanisms of four strobilurins in algae [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2018, 60: 12-16. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2018.03.021 [66] ROY B, SURESH P K, CHANDRASEKARAN N, et al. Antibiotic tetracycline enhanced the toxic potential of photo catalytically active P25 titanium dioxide nanoparticles towards freshwater algae Scenedesmus obliquus [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 267: 128923. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128923 [67] 郐安琪, 赵伟华, 李青云, 等. 典型污染物对藻类生态毒性效应研究进展 [J]. 长江科学院院报, 2015, 32(6): 100-109. KUAI A Q, ZHAO W H, LI Q Y, et al. Research advances in ecotoxicological effects of typical pollutants on algae [J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2015, 32(6): 100-109(in Chinese).
[68] GAN T T, ZHAO N J, YIN G F, et al. Optimal chlorophyll fluorescence parameter selection for rapid and sensitive detection of lead toxicity to marine microalgae Nitzschia Closterium based on chlorophyll fluorescence technology [J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B:Biology, 2019, 197: 111551. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111551 [69] 何莹, 楚梦玮, 刘洋, 等. 铜及氧化铜纳米颗粒对浮萍、藻类的毒性效应及机理研究进展 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2020, 15(4): 56-65. HE Y, CHU M W, LIU Y, et al. Toxicity and the underlying mechanisms of copper and copper oxide nanoparticles to duckweed and algae: A review [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2020, 15(4): 56-65(in Chinese).
[70] LI Y Y, LIU X L, ZHENG X W, et al. Toxic effects and mechanisms of PFOA and its substitute GenX on the photosynthesis of Chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 765: 144431. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144431 [71] SALAS P, ODZAK N, ECHEGOYEN Y, et al. The role of size and protein shells in the toxicity to algal photosynthesis induced by ionic silver delivered from silver nanoparticles [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 692: 233-239. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.237 [72] SURESH KUMAR K, DAHMS H U, LEE J S, et al. Algal photosynthetic responses to toxic metals and herbicides assessed by chlorophyll a fluorescence [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 104: 51-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.01.042 [73] CAMARGO J A, ALONSO A, SALAMANCA A. Nitrate toxicity to aquatic animals: A review with new data for freshwater invertebrates [J]. Chemosphere, 2005, 58(9): 1255-1267. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.044 [74] YANG C, SONG G, LIM W. A review of the toxicity in fish exposed to antibiotics [J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C:Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2020, 237: 108840. [75] CARNEY ALMROTH B, CARTINE J, JÖNANDER C, et al. Assessing the effects of textile leachates in fish using multiple testing methods: From gene expression to behavior [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 207: 111523. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111523 [76] 陈建华, 谢艳颖, 陈世红, 等. 茶多酚对壬基酚所致斑马鱼急性死亡和遗传损伤的保护作用 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2018, 40(10): 1126-1131. doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2018.10.010 CHEN J H, XIE Y Y, CHEN S H, et al. The protection of Danio rerio from acute lethal toxicity and genetic damage induced by nonylphenol through tea polyphenol [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2018, 40(10): 1126-1131(in Chinese). doi: 10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2018.10.010
[77] 朱燕华, 王钟凰, 李昱宗, 等. 基于斑马鱼胚胎急性毒性测试预测食用油毒性可行性研究 [J]. 中国油脂, 2020, 45(12): 71-75. doi: 10.12166/j.zgyz.1003-7969/2020.12.014 ZHU Y H, WANG Z H, LI Y Z, et al. A feasibility study on predicting the toxicity of edible oils using zebrafish embryos [J]. China Oils and Fats, 2020, 45(12): 71-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.12166/j.zgyz.1003-7969/2020.12.014
[78] MALEV O, LOVRIĆ M, STIPANIČEV D, et al. Toxicity prediction and effect characterization of 90 pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs measured in plasma of fish from a major European river (Sava, Croatia) [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 266: 115162. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115162 [79] GRABDA E, EINSZPORN-ORECKA T, FELIŃSKA C, et al. Experimental methemoglobinemia in rainbow trout [J]. Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria, 1974, 4(2): 43-71. doi: 10.3750/AIP1974.04.2.05 [80] 许阳光, 李学锋, 张文吉, 等. 低浓度醚菊酯对鲤鱼生长及生理生化指标的影响 [J]. 农药, 2005, 44(3): 105-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0413.2005.03.003 XU Y G, LI X F, ZHANG W J, et al. Effects of low concentrations of ethofenprox on physiological and bio- chemical parameters and growth of carp [J]. Pesticides, 2005, 44(3): 105-107(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0413.2005.03.003
[81] BABIĆ S, BARIŠIĆ J, STIPANIČEV D, et al. Assessment of river sediment toxicity: Combining empirical zebrafish embryotoxicity testing with in silico toxicity characterization [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 643: 435-450. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.124 [82] NEWBOLD L R, SHI X T, HOU Y Q, et al. Swimming performance and behaviour of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis): Application to fish passage and exclusion criteria [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2016, 95: 690-698. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.119 [83] ROUNTOS K J, KIM J J, HATTENRATH-LEHMANN T K, et al. Effects of the harmful algae, Alexandrium Catenella and Dinophysis acuminata, on the survival, growth, and swimming activity of early life stages of forage fish [J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2019, 148: 46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2019.04.013 [84] GOUNDADKAR B B, KATTI P. Environmental estrogen(s) induced swimming behavioural alterations in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2017, 54: 146-154. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2017.07.001 [85] AL SHURAIQI A, AL-HABSI A, BARRY M J. Time-, dose- and transgenerational effects of fluoxetine on the behavioural responses of zebrafish to a conspecific alarm substance [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 270: 116164. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116164 [86] ZHAO R B, HU Y Y, LI B, et al. Potential effects of internal physio-ecological changes on the online biomonitoring of water quality: The behavior responses with circadian rhythms of zebrafish (Danio rerio) to different chemicals [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 239: 124752. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124752 [87] CHAE Y, AN Y J. Toxicity and transfer of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silver nanowires in an aquatic food chain consisting of algae, water fleas, and zebrafish [J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2016, 173: 94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.01.011 [88] YU Y J, LI X F, YANG G L, et al. Joint toxic effects of cadmium and four pesticides on the earthworm (Eisenia fetida) [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 227: 489-495. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.064 [89] van der VEN L T M, SCHOONEN W G, GROOT R M, et al. The effects of aliphatic alcohols and related acid metabolites in zebrafish embryos - correlations with rat developmental toxicity and with effects in advanced life stages in fish [J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2020, 407: 115249. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115249 [90] ZHANG Y, MA J, ZHOU S Y, et al. Concentration-dependent toxicity effect of SDBS on swimming behavior of freshwater fishes [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2015, 40(1): 77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.05.005 [91] ZHANG Y, GUO X, SI X H, et al. Environmentally persistent free radical generation on contaminated soil and their potential biotoxicity to luminous bacteria [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 687: 348-354. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.137 [92] ZHAO L J, XIE J F, ZHANG H, et al. Enzymatic activity and chlorophyll fluorescence imaging of maize seedlings(Zea mays L.) after exposure to low doses of chlorsulfuron and cadmium [J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2018, 17(4): 826-836. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61717-9 [93] YU D B, BAI L, ZHAI J F, et al. Toxicity detection in water containing heavy metal ions with a self-powered microbial fuel cell-based biosensor [J]. Talanta, 2017, 168: 210-216. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.03.048 [94] LU H B, YU Y, XI H B, et al. Bacterial response to formaldehyde in an MFC toxicity sensor [J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 2020, 140: 109565. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2020.109565 [95] 吴立冬, 刘玲, 李丹, 等. 基于亚甲基蓝的水体急性毒性快速检测方法研究 [J]. 分析化学, 2016, 44(9): 1354-1358. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.160245 WU L D, LIU L, LI D, et al. A new microbial biosensor for detecting and monitoring water acute toxicity based on methylene blue [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 44(9): 1354-1358(in Chinese). doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.160245
[96] FUJIMOTO H, WAKABAYASHI M, YAMASHIRO H, et al. Whole-cell arsenite biosensor using photosynthetic bacterium Rhodovulum sulfidophilum [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 73(2): 332-338. doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0483-6 [97] LIMAN R, ACIKBAS Y, CIĞERCI İ H. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of cerium oxide micro and nanoparticles by Allium and Comet tests [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 168: 408-414. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.088 [98] ZHANG Z S, WANG X M, LI J F, et al. Inhibitory effects of Enteromorpha linza polysaccharide on micronucleus of Allium sativum root cells [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 87: 252-255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.065 [99] XIAN J N, WANG A L, MIAO Y T, et al. Flow cytometric analysis of in vitro cytotoxicity of cadmium in haemocytes from the tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2013, 90(1): 46-50. doi: 10.1007/s00128-012-0839-9 [100] 陈亚松, 张超, 陈振国, 等. 基于耗氧速率预警重金属对活性污泥的抑制性 [J]. 环境工程, 2015, 33(2): 27-31,52. CHEN Y S, ZHANG C, CHEN Z G, et al. Early warning of activated sludge inhibitory action by heavy metals based on oxygen uptake rate index [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2015, 33(2): 27-31,52(in Chinese).
[101] XU M, LI J F, LIU B C, et al. The evaluation of long term performance of microbial fuel cell based Pb toxicity shock sensor [J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 270: 129455. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129455 [102] PAN J Y, HU J P, LIU B C, et al. Enhanced quorum sensing of anode biofilm for better sensing linearity and recovery capability of microbial fuel cell toxicity sensor [J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 181: 108906. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108906 -






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: