-
大气氮磷沉降是陆地和水体生态系统重要的营养来源. 在过去几十年,随着全球社会经济的快速发展,人类活动明显改变了氮磷的“地球−化学”循环,增加了大气中氮磷含量[1],导致大气沉降超过了生态系统的临界负荷,从而造成了水体富营养化、土壤酸化等一系列的负面生态效应[2]. 大气中活性氮主要来源于化石燃料燃烧和农业活动,磷主要来源于矿物尘、生物颗粒和燃烧源[3]. 大气沉降是氮磷等营养元素“地球−化学”循环的重要途经,分为干沉降和湿沉降. 干沉降以气态和颗粒态通过空气动力和自身重力迁移到地表的形式,湿沉降是通过雨、雪、雹等形式迁移到地表的过程[4]. 其中,湿沉降中营养元素多为水溶性,迁移到生态系统中可以被直接利用而备受关注[5].
关于营养盐湿沉降特征研究较多集中在沿海海域和内陆湖泊. Xing等[6]研究了胶州湾大气湿沉降中氨氮
(NH+4−N) 、硝氮(NO−3−N) 、亚硝氮(NO−2−N) 、可溶性有机氮(DON)、可溶性无机磷(DIP)和有机磷(DOP)的沉降特征,结果表明胶州湾大气氮磷多来源于农业活动和土壤扬尘,突发暴雨的氮磷贡献将增加海域初级生产力,影响浮游植物群落结构. 黄河三角洲滨海湿地研究结果表明,随着氮沉降水平的增加,微生物α多样性显著降低,高浓度的氮沉降虽然会增加土壤中的养分,但会降低土壤微生物的多样性,对黄河滨海湿地系统造成负面影响[7]. 武汉东湖大气氮磷沉降占入湖总量的7.28%和4.41%,春季沉降量显著偏高[8]. 此外,在云南滇池[9]、洱海[10]和阳宗海[11],以及安徽巢湖也有相似的研究[12]. 这些研究为我国大气营养盐沉降提供了宝贵的理论基础和数据. 由于氮磷等营养盐大气沉降空间差异较大,许多敏感区域还缺乏相关数据.三峡库区地处长江上游,水库蓄水造成水流变缓,水体富营养化突出. 因此,探究三峡库区大气氮磷沉降规律、负荷及其影响对于区域水环境污染控制具有重要意义. 一些研究者曾在三峡典型区域开展了氮沉降研究工作[13-14],本团队也曾报道了三峡库区湿沉降沉降中无机氮的时空变化和来源[15-16],但这些研究均缺乏亚硝态氮和磷的沉降研究. 为完善区域在营养盐沉降上的不足,本研究于2017年1月—2017年12月在三峡库区腹地3个典型区域进行了湿沉降样品收集,测定了其中氮磷形态浓度(
NO−3−N 、NH+4−N 、NO−2−N 、DTN、DTP),探讨了湿沉降中各形态氮磷浓度和沉降通量特征,明确了其时空变化和来源. -
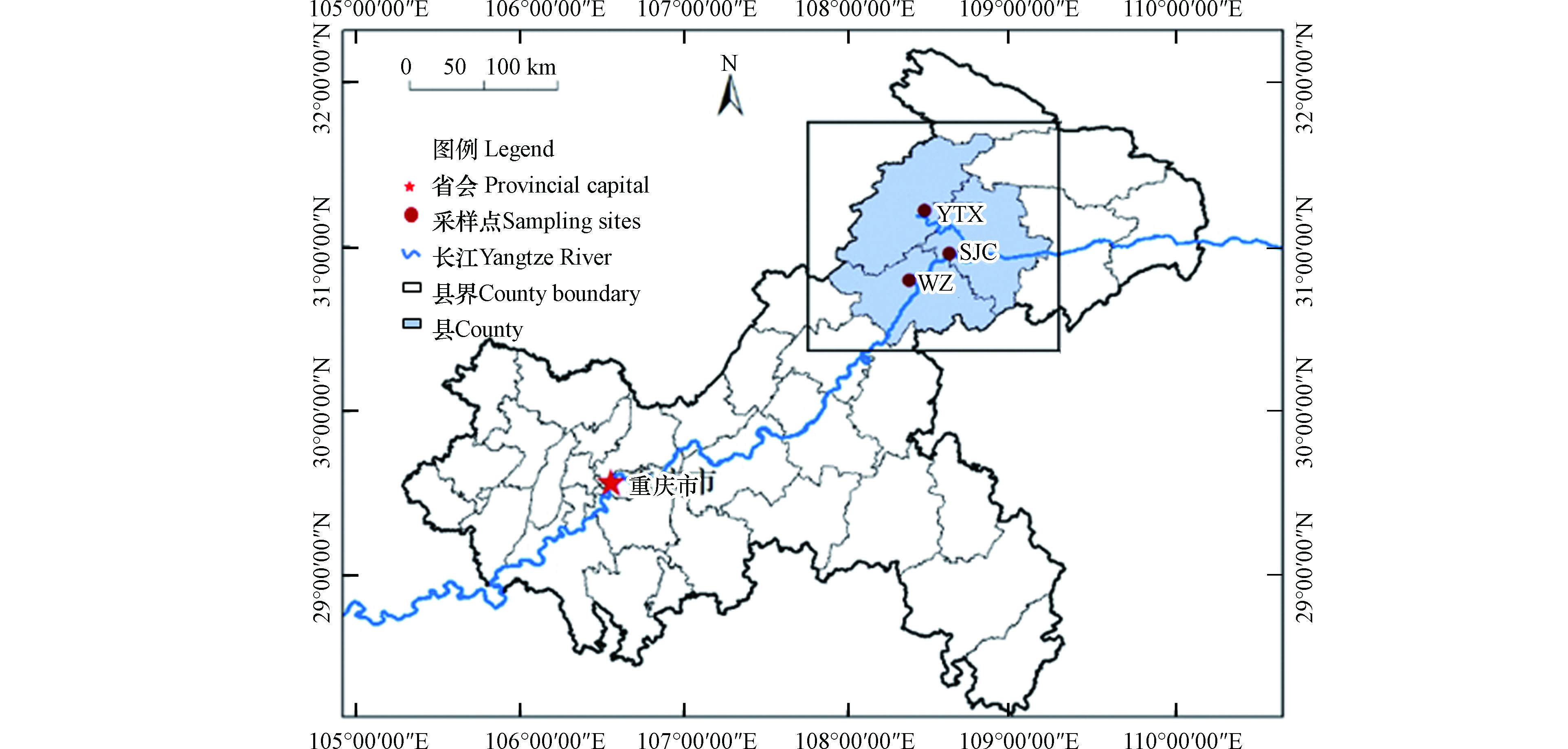
本研究3个采样点分别位于三峡库区重庆市万州区、开州区和云阳县(图1). 万州城区站点(WZ)设置在重庆三峡学院老校区S教教学楼楼顶,距离地面高约27 m,站点周边居住区和商业区,站点东侧约100 m有一条城市交通主干道沙龙路二段,该站点为代表典型城区环境;晒经村站点(SJC)位于云阳县人和街道晒经村,距离云阳县城约3 km,距离长江干流约400 m,代表郊区站点;野塘溪站点(YTX)位于开州区厚坝镇野塘溪村,距离彭溪河约2 km,代表农业区域.
-
用降水降尘自动采样器(APS−3A,长沙湘蓝)收集降水样品,在无降水发生时,盖板遮住降水收集桶,在发生降水时自动打开盖板开始采样,样品以天为单位(9:00—翌日9:00)收集,一天之间发生多次降水则合并为1个样品. 同时仪器配备精度为0.1 mm的雨量计,用以记录降雨量. 样品每周收集1次,带回实验室后立即经0.45 µm滤膜过滤,并置于冰柜中冷冻保存尽快测量. 采样及盛装样品所用聚乙烯塑料桶在使用前用10%盐酸浸泡3 d,然后用超纯水洗净烘干备用.
-
用全自动连续流动分析仪(荷兰SKALARSan++)分析了样品中的
NO−3−N 、NH+4−N 、NO−2−N 、DTN、DTP含量进行测定,它们的检出限分别为0.01 mg·L −1、0.01 mg·L −1、1 µg·L −1、0.01 mg·L −1和1.00 µg·L −1. 样品测试时每10个样品插入标准物质,方法精密度要求小于5.0%,加标回收率在95.0%—105.0%之间. -
沉降通量Dpp(kg·hm−2·a−1)计算方法如下:
式中,Ci为次降雨中每种氮素或磷素的浓度(mg·L−1),Pi为次降雨量(mm),100为单位换算系数.
湿沉降的年均浓度是用年降雨量进行加权平均计算:
式中,Cr为年加权平均浓度(mg·L−1),Ci和Pi与沉降通量计算公式相同.
氮素浓度关系为:
式中,DIN为溶解性无机氮,DON为溶解性有机氮,单位均为mg·L −1.
本研究采用Microsoft Excel 2016和Origin 2017数据进行统计分析及制图,后向轨迹模拟分析采用Trajstat(中国气象科学研究院大气成分研究所王亚强团队开发)进行计算. Trajstat内置的轨迹计算模块与NOAAHYSPLIT一致,HYSPLIT(Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated)是由美国国家海洋和大气管理局(NOAA)的空气资源实验室(ARL)与澳大利亚气象局共同研制的专业气象轨迹模式,广泛用于多种污染物在区域中传输和扩散的研究中[3,17-18]. 考虑到边界层的影响,本研究轨迹计算高度取1200 m,此高度高于混合层平均高度约3 km,比较适用于降水云层[19]. 气团以降水发生日的世界标准时间(UTC)0:00为起始时间,向后推算72 h,然后导入轨迹营养盐浓度,并将所有轨迹进行聚类,最后提取出主要方位后向轨迹,同时得到每条聚类轨迹的占比和营养盐浓度. 气象数据来源于NOAAARL预测数据,可在网上自行下载(ftp://arlftp.arlhq.noaa.gov/pub/archives/gdas1/).
-
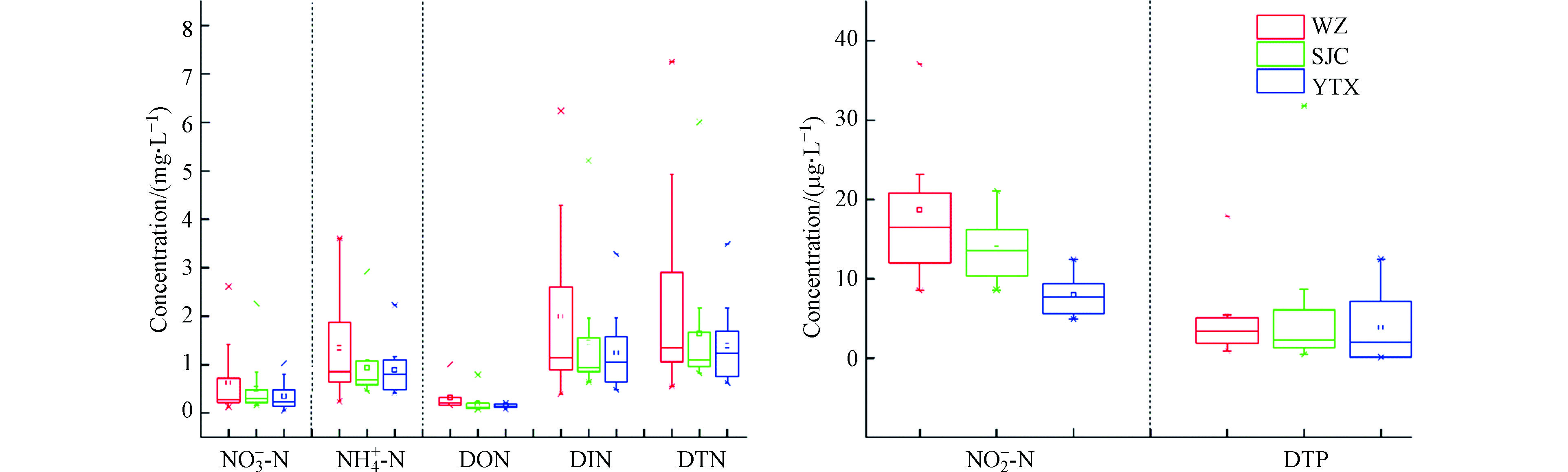
表1为三峡库区腹地
NO−3−N 、NH+4−N 、DON、DTN、DTP、NO−2−N 的浓度统计特征,区域各形态营养盐的浓度表现为算术均值大于加权均值,尤其NO3−−N算术均值为加权均值两倍,表明浓度受降雨量的影响较大,特别是氮浓度与降雨量均呈现显著负相关关系,皮尔逊相关系数(r)位于0.38和0.77之间,虽然DTP受降雨量影响不显著,但也呈现一定的负相关关系(r= −0.19),因此下文均用加权均值进行讨论. 三峡库区腹地大气湿沉降中,NO−3−N 年均浓度为0.24 mg·L −1,NH+4−N 为0.68 mg·L −1,DON为0.16 mg·L −1,DTN为1.09 mg·L −1,而DTP和NO−2−N 则分别为3.36 μg·L −1和11.14 μg·L −1. 其中,NH+4−N 浓度在DTN中占比最高,达到62.4%;NO−3−N 次之,为22.0%;而DON浓度占比为14.7%,NO−2−N 最低,为1.0%. 可见三峡库区氮湿沉降中DIN占据主要地位,而磷湿沉降含量则较低.用《地表水环境质量标准》(GB3838−2002)评价三峡库区腹地降水氮磷浓度,结果显示,DTP满足Ⅰ类水质标准,
NH+4−N 满足Ⅱ水质标准,而DTN仅满足Ⅳ水质标准.与国内其他同类区域(表2)相比,三峡库区湿沉降中DTN浓度水平要远低于南京和西宁郊区,也低于沿海地区的太湖和杭嘉湖地区以及盐亭和秣陵的农区,与滇池、黑龙江凉水国家自然保护区水平相近,但要高于西藏林芝市,也高于同为水库生态区的大河口水库以及戴云山国家自然保护区,总的来说处于中等偏下的水平. 在
NO−3−N 和NH+4−N 浓度方面,三峡库区与长沙县农业区和黑龙江凉水国家自然保护区相一致,NO−3−N 和NH+4−N 浓度值分别仅为南京郊区的0.1倍和0.5倍,为西宁近郊0.1倍和0.3倍左右,这可能和城市周边的工厂污染物排放有关. 而DON浓度方面,三峡库区仅高于盐亭县和长沙县的农区,处于比较区域中的较低水平,说明库区内受到有机氮影响有限,NO2−−N浓度也仅比黑龙江凉水国家自然保护区稍高. 在DTP浓度方面,可以明显看出三峡库区要远低于其他区域,其水平为杭嘉湖地区的16.8%,而仅为滇池的3.1%,达到了国家地表水环境质量标准(GB3838−2002)中I类水总磷标定限值(≤10.00 μg·L −1),说明库区内大气中磷含量水平较低. -
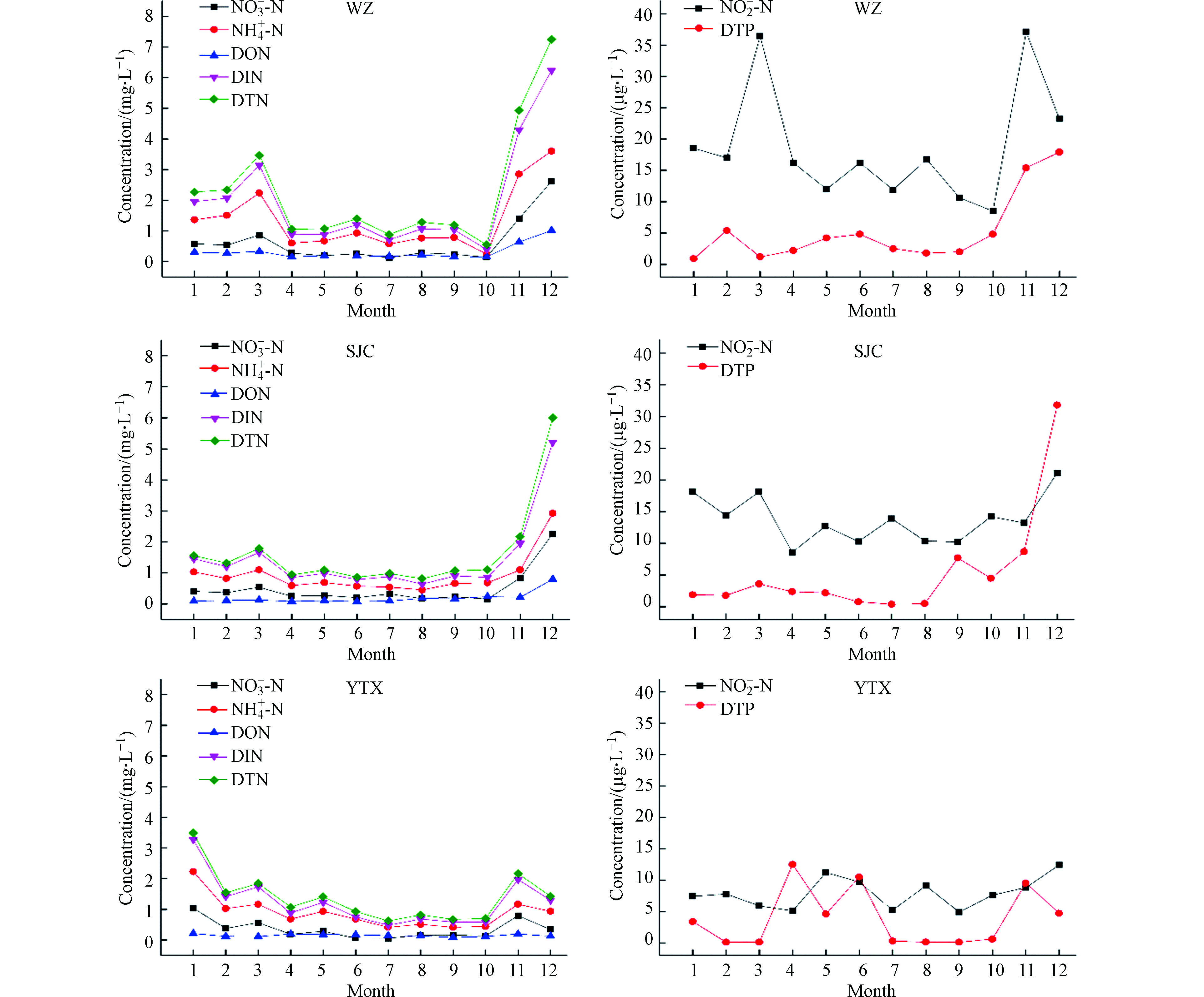
如图2所示,从时间变化上来看,三峡库区湿沉降中氮磷浓度月变化趋势有明显的差异. 较高的氮浓度主要呈现在冬季,其次为秋季和春季,夏季最低. 万州和晒经村的DTN浓度峰值出现在12月份,而野塘溪则出现在1月,从浓度峰值大小来看,WZ>SJC>YTX,分别为7.25 mg·L −1、6.01 mg·L −1和3.49 mg·L −1. 在季节分布上,冬季万州DTN浓度占全年比值高达42.8%,晒经村则达到45.1%,趋近全年一半的贡献量,野塘溪采样点也达到了38.6%,可以明显看出冬季是三峡库区高浓度氮沉降高发季节. 磷沉降方面,DTP浓度月变化起伏比较大的是野塘溪的4月份、6月份和11月份,由于野塘溪采样点处于农业区域,农村有焚烧秸秆的习惯,根据时间节点分析DTP浓度有可能是受生物质燃烧以及陆源气团影响而产生比较大的波动[27]. 高浓度的磷沉降也主要呈现在冬季,除了野塘溪DTP浓度峰值在4月份(12.5 μg·L −1)外,万州和晒经村DTP浓度最大值均出现在12月份,分别为17.90 μg·L −1、31.80 μg·L −1. 放眼全年,冬季DTP浓度在万州和高阳分别占比38.4%和53.5%,为四季最高;野塘溪最高在春季,为36.99%. 库区夏季磷浓度占比最低,为12.34%. 总体来说,库区内氮和磷的高浓度沉降都主要集中在冬季,一方面是因为冬季燃烧供暖导致活性氮释放增加;另一方面夏季高降雨量也加剧了大气中氮磷物质稀释效应从而削弱了夏季浓度[4].
从湿沉降的区域变化特征(图3)来看,整体上三峡库区的DTN浓度为0.55−7.25 mg·L −1,DTP浓度为0.10−31.80 μg·L −1. 而不同类型氮磷在3个站点湿沉降中不同分布表现为,DTN年均浓度方面WZ>SJC>YTX,分别为1.22、1.07、0.97 mg·L −1;DTP年均浓度方面WZ>YTX>SJC,分别为3.45、3.35、3.28 μg·L −1;DIN年均浓度方面WZ>SJC>YTX,分别为1.03、0.93、0.83 mg·L −1;DON年均浓度方面WZ>SJC≈YTX,分别为0.19、0.14、0.14 mg·L −1. 氮磷浓度变化趋势总体符合城区>郊区>农区. 3个站点中,DIN在DTN中占比都超过了80.0%,而DON只维持在10.0%左右的水平. DIN中
NH+4−N 起着主导作用,占比为60.0%左右,万州、晒经村、野塘溪的NH+4−N 浓度分别为0.76、0.66、0.64 mg·L −1;NO−2−N 占比最少,仅维持在1.0%水平. -
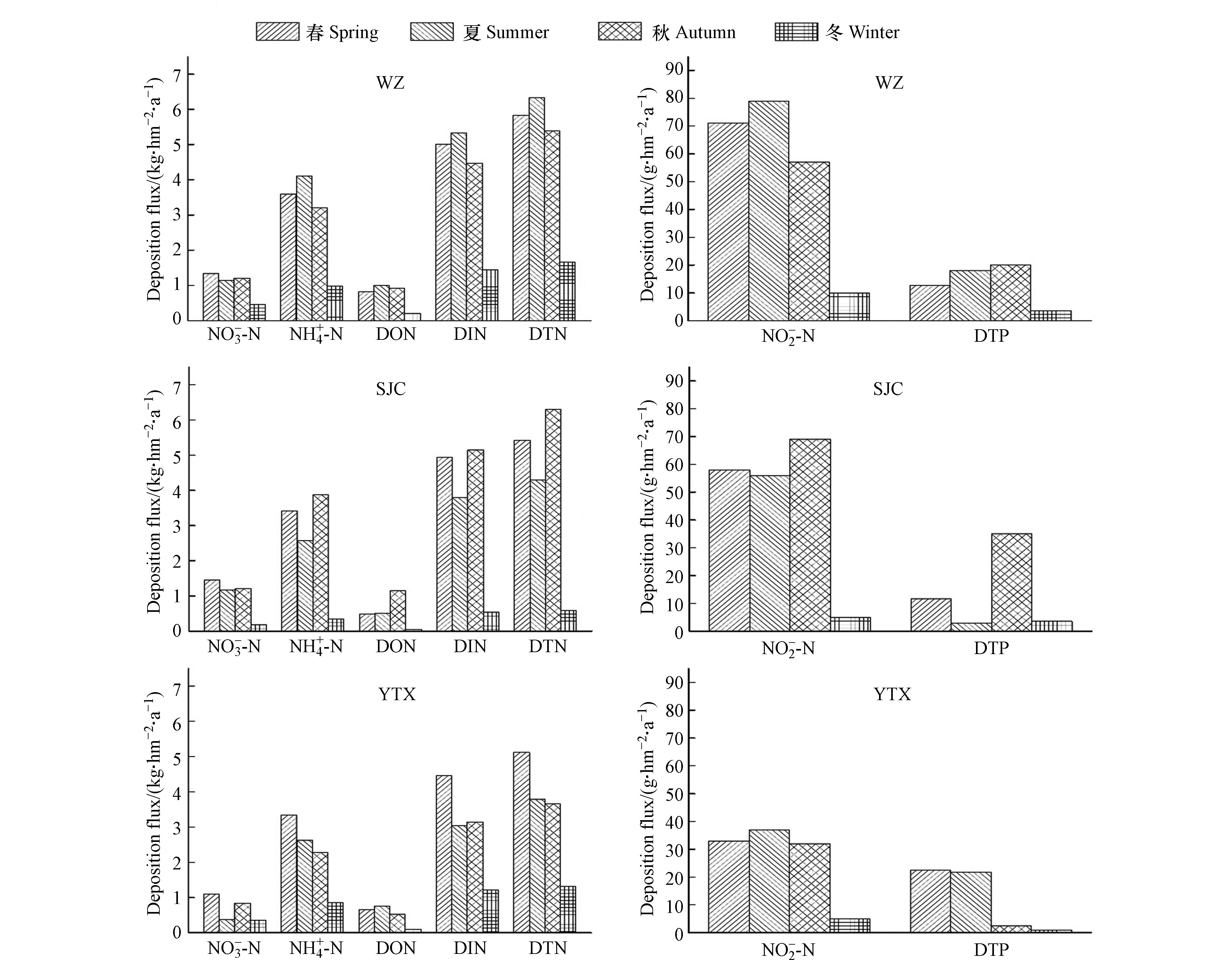
除了探讨氮磷的浓度,氮磷沉降通量也是反映区域氮磷水平的一个重要特征. 3个站点氮磷湿沉降通量随季节变化的关系如图4所示. 由图4可知,氮和磷沉降通量呈现出比较显著的季节性差异,但是两者在四季分布情况不尽相同.
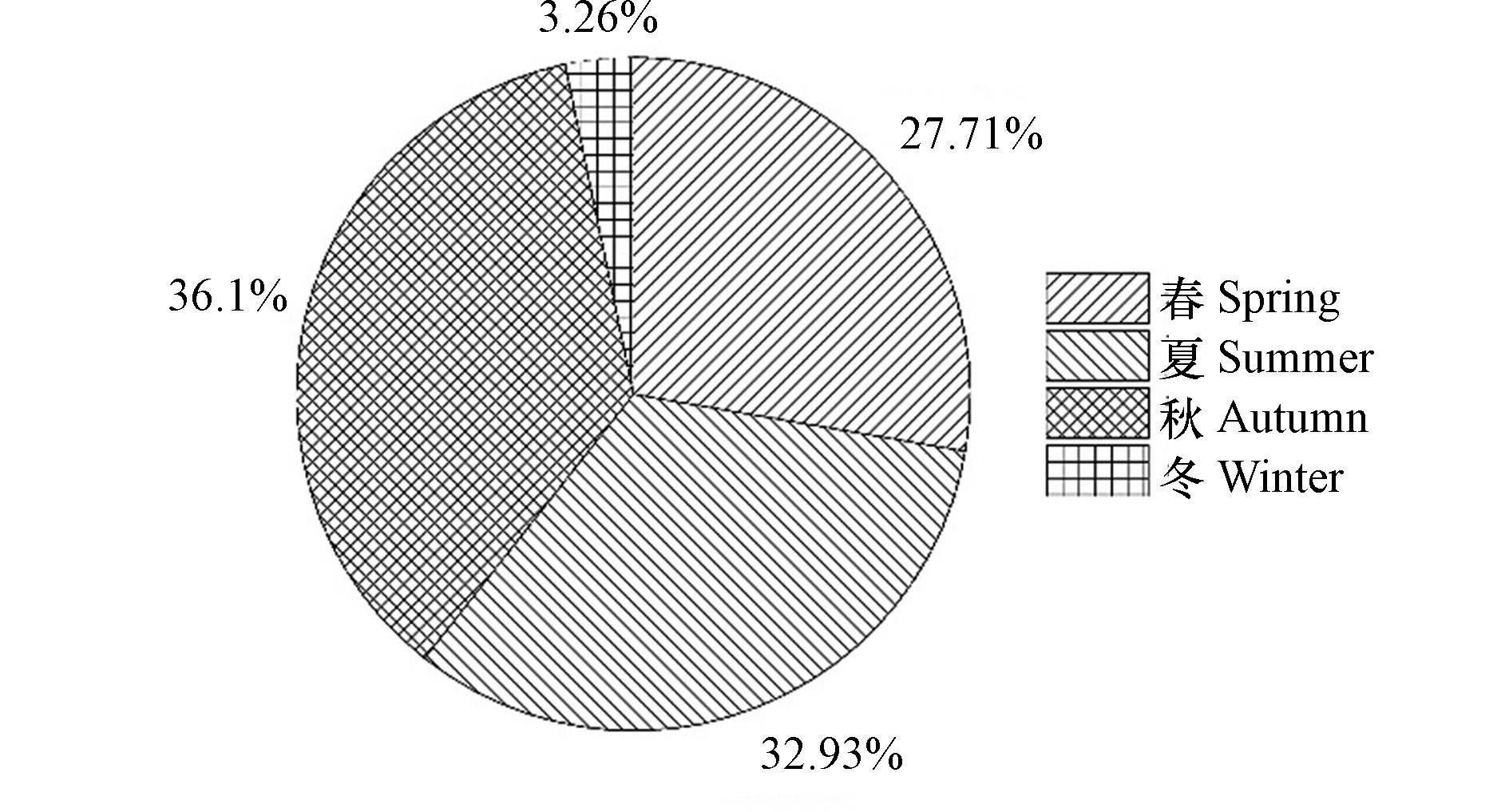
总体上看,区域氮沉降量季节分布特征基本为春、夏、秋三季相当,冬季最少. 其中春季沉降占比最高,为32.9%;秋季次之,为30.9%. 春季区域DTN沉降通量均值为5.45 kg·hm −2·a −1,DIN沉降通量均值为4.8 kg·hm −2·a −1,DON沉降通量均值为0.66 kg·hm −2·a −1;秋季区域DTN沉降通量均值为5.12 kg·hm −2·a −1,
NH+4−N 沉降通量均值为3.12 kg·hm −2·a −1,占DTN输入的60.9%,硝态氮与亚硝态氮占DTN输入的22.4%. 区域磷沉降通量表现为秋季最高,占比为37.7%,沉降通量均值为19.17 g·hm −2·a-1;春、夏两季相当,占比分别为30.7%、27.8%;冬季占比最低,为3.9%,沉降通量均值为1.97 g·hm −2·a −1. 可见,区域高频氮磷沉降集中在春、夏、秋三季.降雨量是影响氮磷沉降通量的一个重要因素. 如图5所示,区域内降水主要集中在春、夏、秋三季,三季降雨量超过全年的90.0%,而氮、磷沉降通量与降雨量都呈显著正相关关系(r=0.90,P<0.05;r=0.63,P<0.05),结合前述氮磷沉降通量季节分布特征可以推测降雨量一定程度上影响着区域内氮磷湿沉降通量.
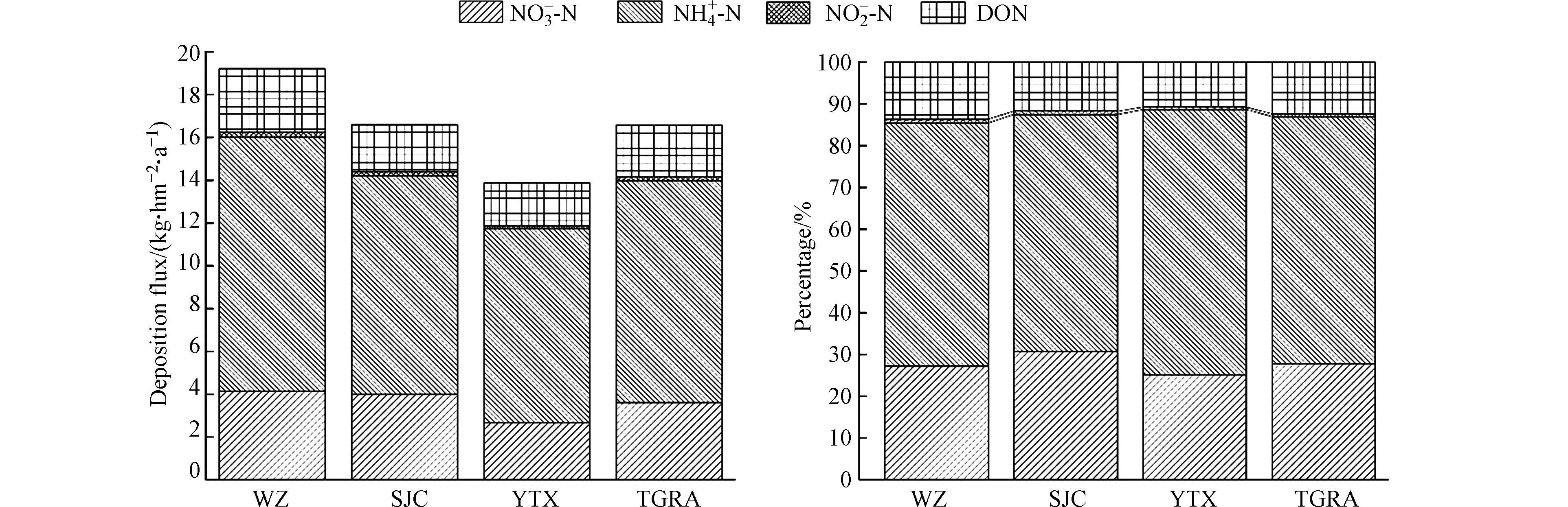
图6呈现了3个站点
NO−3−N 、NH+4−N 、NO−2−N 、DON沉降通量值及其占比. 由图6可知,区域内DTN沉降通量WZ>SJC>YTX,分别为19.21、16.60、13.87 kg·hm −2·a −1,区域均值为16.56 kg·hm −2·a-1,与太湖(16.71 kg·hm −2·a −1)[31]和青海湖区域相当(16.82 kg·hm −2·a −1)[32],略低于丹江口库区(18.73 kg·hm −2·a −1)[33],远高于九寨沟(7.65 kg·hm −2·a −1)[34]和滇池地区(13.63 kg·hm −2·a −1)[9].NO−3−N 、NH+4−N 、NO−2−N 、DON沉降通量也均表现为WZ>SJC>YTX. 区域内DIN和DON分别占DTN的85.6%和14.4%,本研究无机氮沉降占绝对优势,这与DIN和DON的占比相当的珠江口横门(DIN占50.5%,DON占49.5%)存在较大区别[35]. 区域内各站点DTP沉降通量相当,为50.00 g·hm −2·a −1,远低于九寨沟(140.00 g·hm −2·a −1)、太湖(260.00 g·hm −2·a −1)等区域,三峡库区可溶性磷沉降通量处于较低水平. -
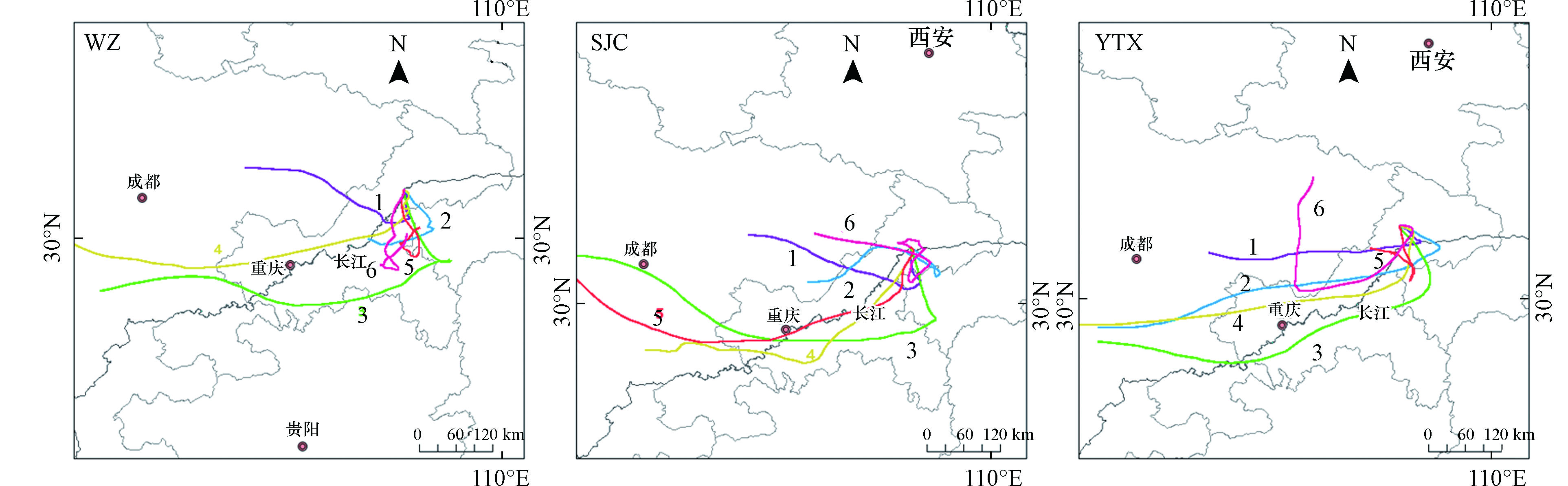
大气湿沉降中的氮磷浓度不仅会受到区域内生产生活排放性污染的影响,气团的运动轨迹以及气溶胶的浓度都可能对湿沉降中的组分含量产生影响[36]. 不同来源的气团会直接影响地区营养盐沉降,多数研究表明,来自陆地的气团会引起高氮沉降[37-38]. 因此,本研究利用王亚强团队开发的Trajstat(MeteoInfo插件版)进行气团后向轨迹模拟分析,探究研究区域气团来源以及走向趋势. 设置起始高度为1200 m,将所有雨天到达采样站点的气团后向推移72 h得到气团的后向轨迹,对每个地点的所有轨迹进行聚类后得到6条主要轨迹,如图7所示. 由图7可知,3个站点的气团都主要来自重庆、四川和湖北.
在万州站点,气团主要来自于重庆与湖北交界处以及四川东部,大部分的气团都经过了这两个区域. Cluster1起源于四川东部,途经南充、达州,然后在重庆东北部进入万州站点,该类轨迹占比31.0%,仅次于Cluster5(34.5%). Cluster2起源于重庆丰都县,途经重庆石柱县、湖北利川,北上抵达站点. Cluster3则源于四川盆地中部,经渝南、黔北、恩施南部区域后到达万州. 由表3可知,Cluster2(13.8%)和Cluster3(11.7%)占比相近,两者气团中
NO−3−N 、NH+4−N 、DON浓度也居于次位,其中Cluster2气团中DTP浓度为所有聚类轨迹中最高. Cluster4占比最低,仅为3.5%,气团中氮磷浓度水平也处于最低位,说明Cluster4的气团较为清洁,其起源于川西北,穿越四川中部、重庆中东部,然后抵达万州站点. Cluster5起源于湖北利川西部地区,经由重庆与湖北交界区域到达万州,该类轨迹占比最高,Cluster5和Cluster1反映出万州大气活性氮主要来自于鄂西、川东以及万州南部区域. Cluster6占比5.5%,但是其气团中NO−3−N 、NH+4−N 、DON浓度最高,该类气团起于重庆石柱县东部,向南行进一段后,北上穿越石柱县、忠县,沿长江干流抵达万州,其间穿越万州工业聚集区可能是其气团中浓度水平较高的主要原因,可见万州大气高浓度活性氮主要受本地排放影响.晒经村站点气团主要来自于四川东部,这类气团占所有聚类轨迹的65.5%,说明川东地区是影响晒经村大气活性氮的主要区域,其中Cluster1占比51.7%,而Cluster2虽然仅占比13.8%,但是气团中
NO−3−N 、NH+4−N 、DON、DTP浓度均为所有轨迹中最高,这与四川盆地较高的含氮污染物排放有关[39]. Cluster3起源于四川中部,Cluster4起源于四川南部,最后都经由重庆中南部进入晒经村站点,Cluster3气团中氮磷浓度相对较高. Cluster5和Cluster6占比相等,均为4.8%. Cluster5源于青藏高原东侧,途经四川盆地中心地带以及重庆中部地区,最后从云阳南部进入站点. Cluster6源于四川达州附近,经重庆东北部进入,而后从云阳北部进入站点.野塘溪站点气团来源比例与万州相似,但是来源比例有所差异. 占比最大的是Cluster5,为38.6%,气团起源于重庆梁平区附近,途经万州、利川后进入野塘溪站点,Cluster1占比为26.9%,源于四川南充附近,气团较为清洁. Cluster4和Cluster6两类轨迹气团占比最低,分别为3.5%和5.5%. Cluster4气团源于青藏高原中部,穿越成渝城市群,无机氮含量最高,Cluster6气团源于四川盆地东部,DON和DTP含量最高. 而Cluster2和Cluster3都源于四川盆地中南部,Cluster2途经重庆中北部及广安以南区域进入站点,Cluster3则经过重庆中南部和恩施西部地区到达野塘溪站点,两类气团中氮磷浓度都处于较低水平.
气团后向轨迹分析表明,四川盆地是东南部区域是三峡库区腹地降水营养盐的主要潜在源区. 然而,区域营养盐还是主要来自于本地及周边区域的源排放. 已有研究表明,大气中的
NH+4−N 主要来源于农业活动,而NO−3−N 则来源于汽车尾气和工业排放,土壤中微生物的活动也是NO−3−N 的一个重要来源[40]. 结合采样点周边实际情况可推断,万州城区大气中的氮主要来源于周边生产性活动以及城市汽车交通尾气复合型排放,而晒经村和野塘溪由于处于农村郊区地带,农业活动比较频繁,所以其氮主要来源于施肥过程中化肥的挥发以及养殖过程中畜禽粪便的氮素排放,晒经村所处的蜂箱加工厂偶有木屑燃烧也是影响其氮素浓度的一个因素. 氨硝比(NH+4−N /NO−3−N )可粗略地判断工业源和农业源的相对贡献[41],本研究城区、郊区和农业区的氨硝比分别为2.87、2.55和3.41,可见库区腹地总体上呈现农业源为主导的区域排放特征,农业区域更为显著.大气中磷的来源主要分为自然源和人为源,包括地壳源、火山源、海洋源、生物质及化石燃料的燃烧、化肥的挥发等[42]. 3个站点居于内陆,受到火山源和海洋源的影响很小,所以其磷的来源主要是地壳源和人为源. 具体来说,万州站点位于城区,周边工厂居多,化石燃料燃烧可能处于磷贡献首位;野塘溪和晒经村则可能是生物质燃烧和施肥引起的磷含量增加.
-
三峡库区腹地大气湿沉降中DTN、DTP年均浓度分别为1.09 mg·L −1、3.36 μg·L−1,
NH+4−N 浓度在DTN中占比最高,达到62.4%,NO−2−N 最低,为1.0%. 与国内其他研究区域相比,三峡库区腹地氮磷浓度都处于较低水平. 库区内氮磷浓度都呈现出冬季高、夏季低的趋势,且都符合城区>郊区>农区的特性. 库区DTN沉降通量为16.56 kg·hm−2·a−1,季节分布特征基本为春、夏、秋三季相当,冬季最少;磷沉降通量为50 g·hm−2·a−1,表现为秋季最高,冬季最低. 万州城区大气氮磷主要来源于化石燃料的燃烧以及城市交通尾气排放,晒经村和野塘溪大气中氮磷主要受生物质燃烧和施肥影响. 万州、晒经村、野塘溪3个站点的气团都主要来自于重庆、四川、湖北,万州站点大气中活性氮主要受到源于鄂西、川东以及万州南部区域气团影响,晒经村站点主要受到源于川东地区气团影响,野塘溪站点则主要受到源于重庆梁平和四川南充气团的双重影响. 区域外源性输入高浓度氮磷都主要来自于四川盆地.
三峡库区腹地大气氮磷营养盐湿沉降特征
Characteristics of atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus in wet deposition in the hinterland of the Three Gorges Reservoir area
-
摘要: 为探明三峡库区大气营养盐湿沉降特征,在三峡库区腹地设置城区(万州)、郊区(晒经村)和农区(野塘溪)的3个功能区采样点,于2017年1月—12月同步采集湿沉降样品并测定氨氮(NH4+-N)、硝氮(NO3−-N)、亚硝氮(NO2−-N)、可溶性总氮(DTN)和可溶性总磷(DTP)的浓度,分析氮磷营养盐沉降的时空分布、组成特征及其影响因素. 三峡库区腹地大气湿沉降中DTN、DTP年均浓度分别为1.09 mg·L −1、3.36 μg·L−1,其中在DTN中NH4+-N占比最高(62.4%),NO2−-N最低(1.0%). 与国内其他研究区域相比,三峡库区腹地氮磷浓度均处于较低水平. 区域氮磷浓度均呈现冬季高、夏季低的趋势,且浓度水平均为城区>郊区>农区. 万州城区大气氮磷主要来源于化石燃料燃烧以及城市交通排放,郊区和农区则主要受生物质燃烧和施肥的影响. 三峡库区腹地DTN沉降通量为16.56 kg·hm −2·a −1,其季节分布特征基本为春、夏、秋三季相当,冬季最少;磷沉降通量为50 g·hm −2·a −1,表现为秋季最高,冬季最低. 四川盆地东部是三峡库区腹地氮磷营养盐的潜在源区之一.Abstract: In order to investigate the characteristics of atmospheric nutrients in wet deposition in the Three Gorges Reservoir area (TGRA), one-year precipitation samples (from January to December 2017) were collected simultaneously at three functional sampling sites, including urban area (Wanzhou), suburban area (Shaijingcun), and agricultural area (Yetangxi) in the hinterland of the TGRA, and their concentrations of ammonia nitrogen (NH4+-N), nitrate nitrogen (NO3--N), nitrite nitrogen (NO2--N), dissolved total nitrogen (DTN), and dissolved total phosphorus (DTP) were determined. The spatiotemporal distribution, composition characteristics and influencing factors of regional nitrogen and phosphorus in wet deposition were analyzed as well. The average annual concentrations of DTN and DTP were 1.09 mg·L-1 and 3.36 μg·L-1, respectively. The concentration of NH4+-N accounted for the highest proportion of DTN (62.4%), while that of NO2--N was the lowest (1.0%). Compared with other regions in China, the concentration of nitrogen and phosphorus in the hinterland of the TGRA was at a relatively low level. Both nitrogen and phosphorus showed a temporal trend of higher levels in winter and lower levels in summer, and a spatial distribution from high to low levels of urban > suburban > agricultural areas. The atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus were mainly from the combustion of fossil fuels and traffic emissions in urban area, whereas they were mainly affected by biomass combustion and fertilization in suburban and agricultural areas. The DTN flux of wet deposition was 16.56 kg·hm-2·a-1, of which the fluxes in spring, summer and autumn were comparable, while the lowest flux appeared in winter. The TDP flux was 50 g·hm-2·a-1, with the highest in autumn and the lowest in winter. The eastern part of the Sichuan Basin was one of the potential sources of both nitrogen and phosphorus in the hinterland of the TGRA.
-
表 1 湿沉降中氮磷浓度统计
Table 1. Statistics of nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in wet deposition
营养盐 Nutrients 算术平均Arithmetic mean 加权平均Weighted average 标准差Standard deviation 变异系数Coefficient of variation 最小值Minimum 中位数Median 最大值Maximum NO3−−N/(mg·L−1) 0.49 0.24 0.56 1.14 0.06 0.28 2.61 NH4+−N/(mg·L−1) 1.05 0.68 0.78 0.74 0.24 0.78 3.60 NO2−−N/(μg·L−1) 13.46 11.14 7.31 0.54 4.90 11.95 37.10 DON/(mg·L−1) 0.22 0.16 0.20 0.90 0.08 0.17 1.01 DTN/(mg·L−1) 1.78 1.09 1.51 0.85 0.55 1.24 7.25 DTP/(μg·L−1) 4.89 3.36 6.37 1.30 0.10 2.45 31.80 表 2 国内典型区域湿沉降氮磷浓度
Table 2. Wet deposition concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus in typical regions in China
地点 Sites 采样点类型 Type of sampling site 监测时间Monitoring time NO−3−N NH+4−N NO−2−N DON/(mg·L−1) DTN/(mg·L−1) DTP/(μg·L−1) 文献Reference 戴云山国家自然保护区 林区(保护区) 2015.3.27—2015.10.09 0.24 0.44 — 0.31 0.99 — [20] 黑龙江凉水国家自然保护区 林区(保护区) 2015.5—2015.10 0.41 0.68 9.00 0.45 1.54 — [21] 滇池 水域 2014.1—2014.12 — — — 0.22 1.36 130.00 [9] 太湖 水域 2009.8—2010.7 — — — — 3.17 77.00 [22] 2017.8—2018.7 — — — — 3.16 56.00 大河口水库 水域 2014.3—2016.2 0.15 0.20 25.00 — 0.50 80.00 [23] 盐亭县 农区 2008—2013 1.05 1.48 — 0.02 2.55 [24] 秣陵县 农区 2010.3—2012.2 1.03 1.26 — — — 117.50 [25] 长沙县 农区 2010.9—2011.8 0.40 0.68 − 0.13 1.21 — [26] 南京郊区 郊区 2005.6—2006.5 2.77 1.74 210 5.36 10.08 — [27] 西宁近郊 郊区 2014.1—2015.12 1.8 2.2 — — — — [28] 杭嘉湖地区 城区 2013.9—2014.8 — — — — 2.60 20.00 [29] 林芝市 城区 2017.3—2017.10 0.13 0.22 — 0.39 0.74 108.80 [30] 三峡库区腹地 城区 2017.1—2017.12 0.26 0.76 13.80 0.19 1.22 3.50 本研究 郊区 2017.1—2017.12 0.26 0.66 12.20 0.14 1.07 3.30 农区 2017.1—2017.12 0.19 0.64 7.50 0.14 0.97 3.40 混合 2017.1—2017.12 0.24 0.68 11.14 0.16 1.09 3.36 表 3 轨迹中氮磷平均浓度
Table 3. Average concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus in the clusters of trajectories
地点Sites Cluster 占比/%Percentage NO−3−N NH+4−N DON/(mg·L−1) DTP/(μg·L−1) 万州(WZ) 1 31.0 0.47 1.11 0.27 3.69 2 13.8 0.74 1.54 0.36 5.86 3 11.7 0.61 1.31 0.31 4.63 4 3.5 0.44 1.10 0.25 2.72 5 34.5 0.54 1.20 0.29 5.05 6 5.5 0.97 1.87 0.40 5.34 晒经村(SJC) 1 51.7 0.46 0.90 0.17 4.96 2 13.8 0.58 1.00 0.21 5.92 3 11.7 0.49 0.93 0.19 5.15 4 13.1 0.46 0.93 0.14 3.95 5 4.8 0.4 0.92 0.11 2.46 6 4.8 0.29 0.56 0.14 1.31 野塘溪(YTX) 1 26.9 0.35 0.89 0.16 3.62 2 13.8 0.36 0.91 0.15 4.04 3 11.7 0.34 0.88 0.15 3.63 4 3.5 0.72 1.56 0.15 1.42 5 38.6 0.35 0.97 0.17 5.94 6 5.5 0.38 1.03 0.18 6.85 -
[1] DECINA S M, TEMPLER P H, HUTYRA L R. Atmospheric inputs of nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus across an urban area: Unaccounted fluxes and canopy influences [J]. Earth's Future, 2018, 6(2): 134-148. doi: 10.1002/2017EF000653 [2] BARON J S, DRISCOLL C T, STODDARD J L, et al. Empirical critical loads of atmospheric nitrogen deposition for nutrient enrichment and acidification of sensitive US lakes [J]. BioScience, 2011, 61(8): 602-613. doi: 10.1525/bio.2011.61.8.6 [3] MAHOWALD N, JICKELLS T D, BAKER A R, et al. Global distribution of atmospheric phosphorus sources, concentrations and deposition rates, and anthropogenic impacts [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2008, 22(4): GB003240. doi: 10.1029/2008gb003240 [4] ZHANG L Y, TIAN M, PENG C, et al. Nitrogen wet deposition in the Three Gorges Reservoir area: Characteristics, fluxes, and contributions to the aquatic environment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 738: 140309. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140309 [5] DU E Z. A database of annual atmospheric acid and nutrient deposition to China's forests [J]. Scientific Data, 2018, 5: 180223. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2018.223 [6] XING J W, SONG J M, YUAN H M, et al. Fluxes, seasonal patterns and sources of various nutrient species (nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon) in atmospheric wet deposition and their ecological effects on Jiaozhou Bay, North China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 576: 617-627. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.134 [7] 张智渊. 太湖大气湿沉降氮、磷营养盐特征及其对浮游植物的影响[D]. 北京: 中国环境科学研究院, 2018. ZHANG Z Y. Atmospheric wet deposition characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in Taihu lake and its influence on phytoplankton[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Environmental Sciences, 2018(in Chinese).
[8] 彭秋桐, 李中强, 邓绪伟, 等. 城市湖泊氮磷沉降输入量及影响因子: 以武汉东湖为例 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(8): 2635-2643. PENG Q T, LI Z Q, DENG X W, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus deposition in urban lakes and its impact factors: A case study of East Lake in Wuhan [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(8): 2635-2643(in Chinese).
[9] 任加国, 贾海斌, 焦立新, 等. 滇池大气沉降氮磷形态特征及其入湖负荷贡献 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(2): 582-589. REN J G, JIA H B, JIAO L X, et al. The characteristics of atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus in Dianchi Lake and its contribution to the lake load [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(2): 582-589(in Chinese).
[10] 高蓉, 韩焕豪, 崔远来, 等. 降雨量对洱海流域稻季氮磷湿沉降通量及浓度的影响 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(22): 191-198. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002−6819.2018.22.024 GAO R, HAN H H, CUI Y L, et al. Effects of rainfall on wet deposition flux and concentration of nitrogen and phosphorus in rice season in Erhai Lake Basin [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(22): 191-198(in Chinese). doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002−6819.2018.22.024
[11] 余功友, 杨常亮, 刘楷, 等. 云南阳宗海大气氮、磷沉降特征 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2017, 29(5): 1134-1142. doi: 10.18307/2017.0511 YU G Y, YANG C L, LIU K, et al. Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorous in Lake Yangzonghai, Yunnan Province [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2017, 29(5): 1134-1142(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2017.0511
[12] 魏东霞, 李璇, 赵禹恒, 等. 合肥科学岛大气氮磷沉降及对巢湖影响的分析 [J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(9): 1259-1266. WEI D X, LI X, ZHAO Y H, et al. Analyses of atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus deposition at Hefei Science Island and its impact on Chaohu Lake [J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2018, 41(9): 1259-1266(in Chinese).
[13] 袁玲, 周鑫斌, 辜夕容, 等. 重庆典型地区大气湿沉降氮的时空变化 [J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(11): 6095-6101. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000−0933.2009.11.042 YUAN L, ZHOU X B, GU X R, et al. Variation in wet deposition of nitrogen from atmosphere in typical areas of Chongqing [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(11): 6095-6101(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000−0933.2009.11.042
[14] LIU L, ZHANG X Y, LU X H. The composition, seasonal variation, and potential sources of the atmospheric wet sulfur (S) and nitrogen (N) deposition in the southwest of China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(7): 6363-6375. doi: 10.1007/s11356−015−5844−1 [15] LENG Q M, CUI J, ZHOU F W, et al. Wet-only deposition of atmospheric inorganic nitrogen and associated isotopic characteristics in a typical mountain area, southwestern China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 616/617: 55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.240 [16] WANG H B, SHI G M, TIAN M, et al. Wet deposition and sources of inorganic nitrogen in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 233: 520-528. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.085 [17] 胡春阳, 樊曙先, 王小龙, 等. 庐山2016年冬季三级分档雾水化学特征 [J]. 气象学报, 2019, 77(4): 745-757. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2019.034 HU C Y, FAN S X, WANG X L, et al. The chemical characteristics of fog water in three grades of Lushan in the winter of 2016 [J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2019, 77(4): 745-757(in Chinese). doi: 10.11676/qxxb2019.034
[18] 石春娥, 姚叶青, 张平, 等. 合肥市PM10输送轨迹分类研究 [J]. 高原气象, 2008, 27(6): 1383-1391. SHI C E, YAO Y Q, ZHANG P, et al. Transport trajectory classifying of PM10 in Hefei [J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2008, 27(6): 1383-1391(in Chinese).
[19] LUCEY D, HADJIISKI L, HOPKE P K, et al. Identification of sources of pollutants in precipitation measured at the mid−Atlantic US Coast using potential source contribution function (PSCF) [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2001, 35(23): 3979-3986. doi: 10.1016/S1352−2310(01)00185−6 [20] 袁磊, 李文周, 陈文伟, 等. 戴云山国家级自然保护区大气氮沉降特点 [J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(11): 4142-4146. YUAN L, LI W Z, CHEN W W, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen deposition in Daiyun mountain national nature reserve [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(11): 4142-4146(in Chinese).
[21] 宋蕾, 田鹏, 张金波, 等. 黑龙江凉水国家级自然保护区大气氮沉降特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10): 4490-4496. SONG L, TIAN P, ZHANG J B, et al. Characteristics of nitrogen deposition in Heilongjiang Liangshui national nature reserve [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(10): 4490-4496(in Chinese).
[22] 牛勇, 牛远, 王琳杰, 等. 2009−2018年太湖大气湿沉降氮磷特征对比研究 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(1): 122-129. NIU Y, NIU Y, WANG L J, et al. Comparative study on nitrogen and phosphorus characteristics of atmospheric wet deposition in lake Taihu from 2009 to 2018 [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(1): 122-129(in Chinese).
[23] 张晓晶, 卢俊平, 马太玲, 等. 大气氮磷湿沉降特征及对沙源区水库水环境的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(12): 2093-2101. ZHANG X J, LU J P, MA T L, et al. Wet deposition of atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus and its impact on water environment of reservoir in sand source area [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(12): 2093-2101(in Chinese).
[24] KUANG F H, LIU X J, ZHU B, et al. Wet and dry nitrogen deposition in the central Sichuan Basin of China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 143: 39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.08.032 [25] SUN L Y, LIU Y L, WANG J Y, et al. Atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus deposition at three sites in Nanjing, China, and possible links to nitrogen deposition sources [J]. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water, 2014, 42(11): 1650-1659. doi: 10.1002/clen.201300692 [26] SHEN J L, LI Y, LIU X J, et al. Atmospheric dry and wet nitrogen deposition on three contrasting land use types of an agricultural catchment in subtropical central China [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 67: 415-424. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.10.068 [27] 邓君俊, 王体健, 李树, 等. 南京郊区大气氮化物浓度和氮沉降通量的研究 [J]. 气象科学, 2009, 29(1): 25-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009−0827.2009.01.004 DENG J J, WANG T J, LI S, et al. Study on atmospheric nitrogen oxidant and deposition flux in suburban of Nanjing [J]. Scientia Meteorologica Sinica, 2009, 29(1): 25-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009−0827.2009.01.004
[28] 许稳, 金鑫, 罗少辉, 等. 西宁近郊大气氮干湿沉降研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(4): 1279-1288. XU W, JIN X, LUO S H, et al. Research on atmospheric nitrogen deposition in the suburbs of Xining [J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(4): 1279-1288(in Chinese).
[29] 王江飞, 周柯锦, 汪小泉, 等. 杭嘉湖地区大气氮、磷沉降特征研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(9): 2754-2763. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000−6923.2015.09.030 WANG J F, ZHOU K J, WANG X Q, et al. Research on atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus deposition characteristics in Hangjiahu area [J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(9): 2754-2763(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000−6923.2015.09.030
[30] WANG W, LIU X J, XU J, et al. Imbalanced nitrogen and phosphorus deposition in the urban and forest environments in southeast Tibet [J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2018, 9(4): 774-782. doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2018.02.002 [31] 王燕, 刘宁锴, 王骏飞. 太湖流域氮磷等大气沉降研究 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2015, 40(5): 103-105. WANG Y, LIU N K, WANG J F. Study on atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus in Taihu lake [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2015, 40(5): 103-105(in Chinese).
[32] ZHANG X, LIN C Y, ZHOU X L, et al. Concentrations, fluxes, and potential sources of nitrogen and phosphorus species in atmospheric wet deposition of the Lake Qinghai Watershed, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 682: 523-531. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.224 [33] 刘冬碧, 张小勇, 巴瑞先, 等. 鄂西北丹江口库区大气氮沉降 [J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(10): 3419-3427. LIU D B, ZHANG X Y, BA R X, et al. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition in Danjiangkou Reservoir area of Northwest Hubei [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(10): 3419-3427(in Chinese).
[34] 乔雪, 江丽君, 唐亚, 等. 九寨沟大气氮、磷和硫沉降的通量及水环境意义 [J]. 山地学报, 2014, 32(5): 633-640. QIAO X, JIANG L J, TANG Y, et al. The fluxes and possible aquatic impacts of atmospheric nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorous deposition in Jiuzhaigou [J]. Mountain Research, 2014, 32(5): 633-640(in Chinese).
[35] 樊敏玲, 王雪梅, 王茜, 等. 珠江口横门大气氮、磷干湿沉降的初步研究 [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2010, 29(1): 51-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009−5470.2010.01.008 FAN M L, WANG X M, WANG Q, et al. Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus into the Hengmen of Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(1): 51-56(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009−5470.2010.01.008
[36] 韩丽君, 朱玉梅, 刘素美, 等. 黄海千里岩岛大气湿沉降营养盐的研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(7): 1174-1184. HAN L J, ZHU Y M, LIU S M, et al. Nutrients of atmospheric wet deposition from the Qianliyan Island of the Yellow Sea [J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(7): 1174-1184(in Chinese).
[37] AVILA A, ALARCÓN M. Relationship between precipitation chemistry and meteorological situations at a rural site in NE Spain [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1999, 33(11): 1663-1677. doi: 10.1016/S1352−2310(98)00341−0 [38] 王茜, 王雪梅, 钟流举, 等. 珠江口无机氮湿沉降规律及大气输送的研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(6): 1156-1163. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253−2468.2009.06.005 WANG Q, WANG X M, ZHONG L J, et al. Wet deposition of inorganic nitrogen and atmospheric transport at the estuary of the Pearl River [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2009, 29(6): 1156-1163(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253−2468.2009.06.005
[39] 郑丹楠, 王雪松, 谢绍东, 等. 2010年中国大气氮沉降特征分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(5): 1089-1097. ZHENG D N, WANG X S, XIE S D, et al. Simulation of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China in 2010 [J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(5): 1089-1097(in Chinese).
[40] 宋玉芝, 秦伯强, 杨龙元, 等. 大气湿沉降向太湖水生生态系统输送氮的初步估算 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2005, 17(3): 226-230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003−5427.2005.03.006 SONG Y Z, QIN B Q, YANG L Y, et al. Primary estimation of atmospheric wet deposition of nitrogen to aquatic ecosystem of lake Taihu [J]. Journal of Lake Science, 2005, 17(3): 226-230(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003−5427.2005.03.006
[41] 谢迎新, 张淑利, 赵旭, 等. 长江三角洲地区雨水中NH4+−N/NO3−−N和δ15NH4+值的变化 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(9): 2035-2041. XIE Y X, ZHANG S L, ZHAO X, et al. Seasonal variation patterns of NH4+−N/NO3−−N ratio and δ15NH4+ value in rainwater in Yangtze River Delta [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(9): 2035-2041(in Chinese).
[42] 王楠, 马淼, 石金辉, 等. 夏季青岛大气气溶胶中不同形态磷的浓度、来源及沉降通量 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(9): 4034-4041. WANG N, MA M, SHI J H, et al. Concentrations, sources, and dry deposition fluxes of different forms of phosphorus in Qingdao aerosols in summer [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(9): 4034-4041(in Chinese).
-




 下载:
下载: