-
随着城市化和工业化的快速发展,大量来自人为来源的重金属被排放到水生环境中[1-5]。水生环境中的金属是不可生物降解的。而重金属可以通过物理、化学和生物过程在沉积物和悬浮颗粒中积累[6]。然而,当沉积物中的环境条件发生变化时,化学和生物过程可能会使累积的重金属再循环回水柱,从而将沉积物变成内部污染源[7]。因此,研究沉积物重金属对评价人类活动对水环境的影响具有重要意义。重金属主要来源于自然输入或人为活动。通过多元统计分析,可以追踪这些重金属的来源。地质累积指数和潜在生态风险指数被广泛用于评估它们所构成的风险[8]。然而,以往的研究表明,不同评估方法的结果有时并不一致[9]。因此,采用多种方法对沉积物质量进行评价,以获得更全面、更准确的信息是十分必要的。
海河流域是一个农业、工业和城市化迅速发展的流域,在我国的国民经济发展中占有举足轻重的地位。其水生态环境受到广泛的关注[10-11]。漳卫河水系多年平均水资源总量为5.36×109 m3,是海河流域水资源量最大的子流域,主要由漳河、卫河两大支流组成。其水环境和水生态安全对海河具有重要影响。近年来,河流沉积物中的重金属污染已得到广泛研究[12]。Tang等对海河流域的滦河等9个主要子流域的表层沉积物的重金属污染、风险、毒性进行了综合评价[13],Cao等也对海河干流的有毒金属污染进行评价[14],结果均表明,人为输入是金属富集的一个重要贡献者,其中沉积物中Cd的污染程度较高。Zhang等对海河流域的大中型城市河流沉积物中的重金属(Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn)污染及其危害进行了评价,表明城市化水平的提高会导致城市河流沉积物中Cr、Zn的污染加剧[15]。赵海萍等对漳河上游水质及污染进行分析,浊漳南源的有机污染物污染程度远大其他河段[16]。郝红等对海河流域的漳河、卫河、卫运河、南运河及漳卫新河的表层沉积物中的 As、Hg、Cd、Cu、Cr、Pb、Zn 等重金属进行了评价,结果表明多数河段都具有较高的生态风险[17]。多数学者主要以海河及其流域内主要河流为研究对象开展重金属分析及污染评价的相关研究,但是针对漳河上游流域的重金属相关研究较少。
认识沉积物重金属的污染特征和潜在生态风险,以及确定可能的来源和控制因素,对于污染预防和生物多样性保护管理至关重要。因此,研究漳河沉积物中重金属的污染水平对保障海河流域水资源安全具有重要影响。Cr、Cu、Ni在人体代谢过程中发挥着重要作用,过度接触这些金属会对人体健康产生有害影响,并增加慢性中毒的可能性。Pb虽然不参与人体代谢,但在非常低的水平上具有毒性作用。本研究选取这4种常见的重金属对地球化学基线及其生态风险进行评价。
-
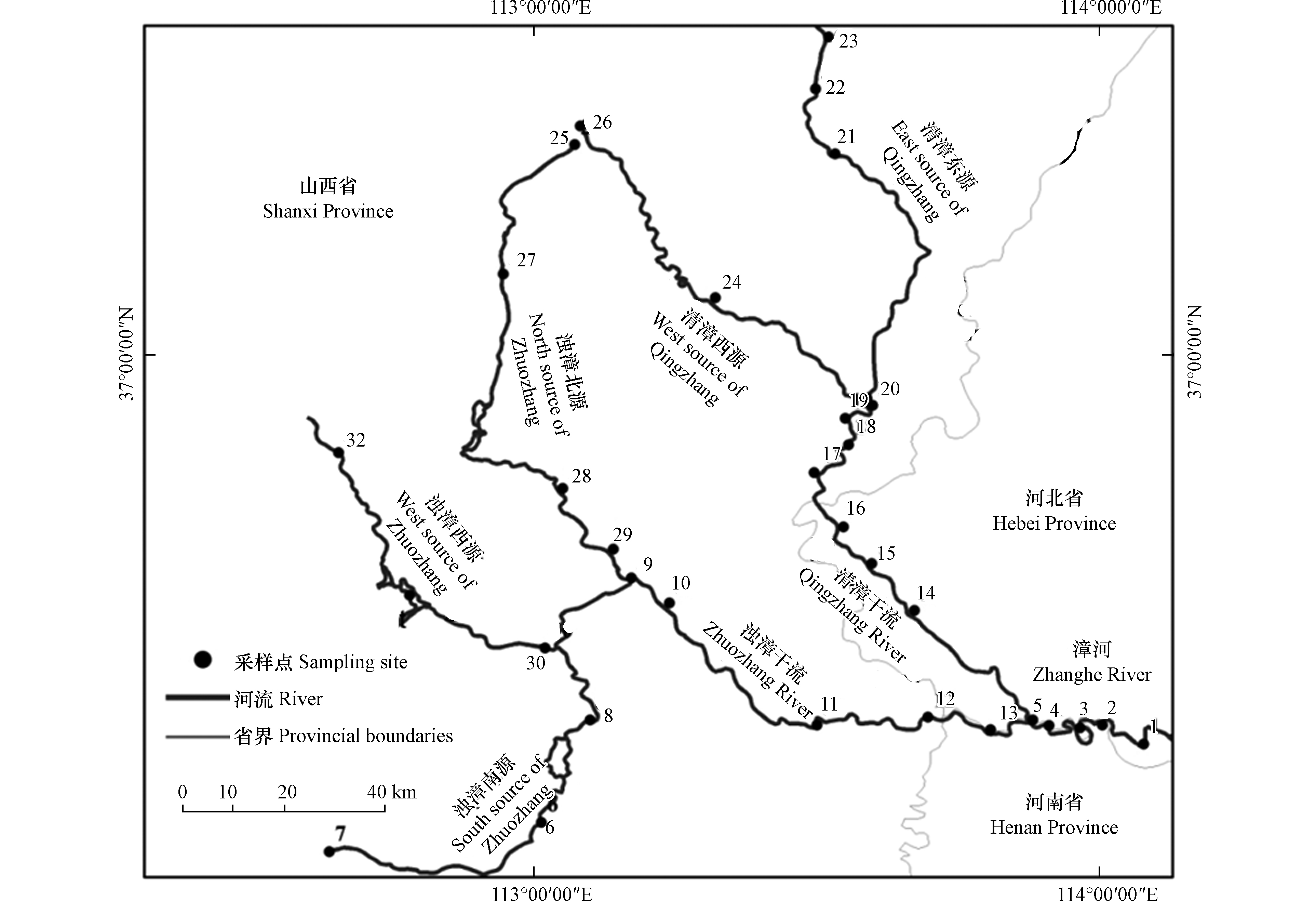
漳河上游有清漳河、浊漳河两条支流,均出山西省东南部,在河北省南部边境汇合后称漳河。清漳河分东西两源。浊漳河上游分南源、西源和北源。采样时间为2019年9月,结合漳河、清漳河、浊漳河的分布情况,共设置32个采样点,采样点位置如图1所示。漳河干流有5个采样点即1号至5号,浊漳河干流有5个采样点即9号至13号,清漳河干流有7个采样点即14号至20号,浊漳源头有10个采样点即6号至8号和26号至32号,清漳源头有5个采样点即21号至25号。使用抓斗式采样器采集河流表层沉积物,每一点采集3处混合均匀并放入自封袋中,记录编号,避光保存运回实验室分析。
-
沉积物样品经过冷冻干燥,去除石头和植物碎片,经研钵研磨后过100目尼龙筛备用。对于元素含量测定,精确称量0.2 g沉积物子样品,并将其放入聚四氟乙烯容器中,用6 mL HNO3和2 mL HF进行消化。微波消解后150℃赶酸,冷却后用去离子水将残渣稀释至25 mL,然后使用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)分析重金属含量[18]。
-
采用相对累积频率和归一化法计算沉积物重金属的地球化学基线。标准化和线性回归分析中使用的数据集必须完全基于自然浓度,以获得金属和参考元素之间可靠的统计关系。许多作者将铝作为参考元素,因为铝在地壳中的自然丰度很高,通常不受人为输入的影响,而铁浓度可能受人为输入的影响。当河底氧化还原电位发生变化时,铁氧化物被还原为Fe2+。在本研究中,使用参照元素Al对金属进行地球化学归一化。Al作为参考元素可以补偿粒度和矿物学的差异[6]。
建立地球化学基线包括四个步骤:首先,绘制金属浓度(Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb)的分布直方图,用于消除极端异常值(严重污染的现场数据)。其余数据点用于计算地球化学基线。其次,在剔除所有异常样本点后,绘制Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb的累积分布函数图,将数据集识别为地质背景浓度集、人为无影响浓度集以及人为影响的浓度集。第三步,利用线性回归模型得到重金属(Cr、Cu、Ni、Pb)与参考元素Al的关系,剔除95%置信区间以外的数据点。剔除这些异常值后,对剩余数据集再次进行线性回归模拟,得到地球化学基线函数[19]。
-
地质累积指数Igeo值由以下公式计算得出:
式中,
Cn 是沉积物样品所测金属浓度,Bn 是地球化学背景值。引入系数1.5,是金属成岩变化的校正系数。在以前的研究中,选择了全球页岩平均值或区域背景值作为
Bn ,这是一个恒定值。然而,不同采样点的自然源贡献不同。因此,在本研究中,修正的地质累积指数用公式(2)表示:其中,使用回归方程计算的32个采样点的区域地球化学基线值
CRGB 代替Bn 。此外,为了避免自然变化的双重校正,修正的地质累积指数中省略了系数1.5。评价等级:
⩽0 :未污染;0—1:轻度污染;1—2:偏中度污染;2—3:中度污染;3—4:偏重度污染;4—5:严重污染;>5 :极重污染。 -
EI用于评估重金属污染程度[20],并使用以下公式计算:
C0 为参考值;Tn 为重金属的毒性系数。Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb的毒性系数分别为2、5、5、5。风险等级:
<40 :轻微生态危害;40—80:中等生态危害;80—160:强生态危害;160—320:很强生态危害;320:极强生态危害。 -
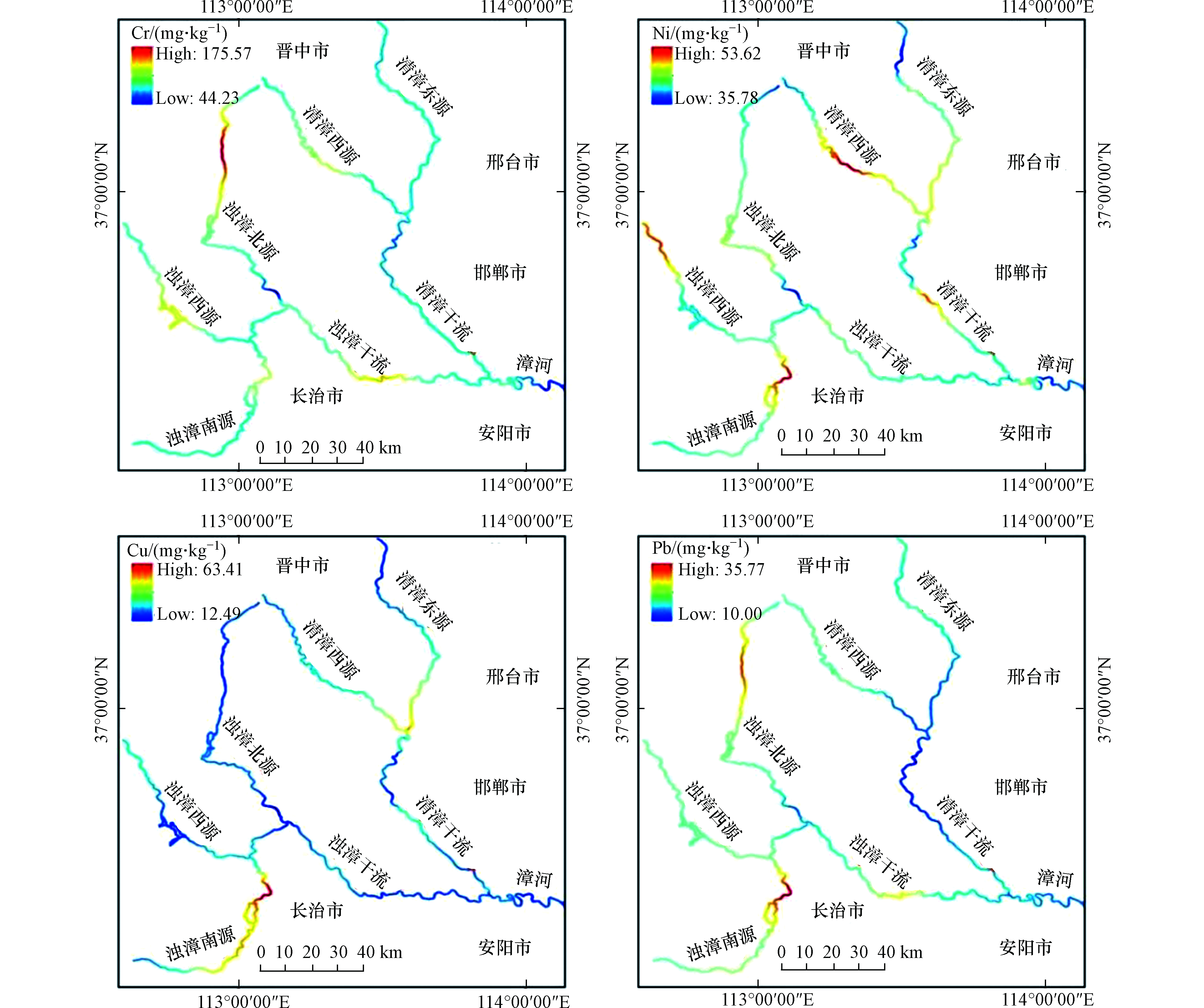
漳河上游流域沉积物中重金属的浓度分布如表1和图2所示。Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb的平均浓度分别为91.51(44.13—175.57)mg·kg−1、43.33(35.78—53.62)mg·kg−1、21.93(12.49—63.41)mg·kg−1、18.30(10.00—35.77)mg·kg−1。沉积物中Cr、Pb的平均浓度与上大陆地壳浓度相似,而Ni、Cu的平均浓度低于上大陆地壳浓度[8, 21]。根据相对标准偏差,Cr、Cu、Pb变化范围很广(相对标准偏差:27%—48%),表明Cr、Cu、Pb受外界影响的表现相似,而Ni的含量变化范围不大(相对标准偏差<20%)。根据漳卫南运河管理局资料显示,漳河上游流域所在水系非点源污染物包括的范围极广,其中农药和化肥占了很大的比重。农药、化肥不合理的大量施用,不仅造成农药和化肥的浪费,而且通过流失和下渗,污染地表水和地下水。同时,清漳河和浊漳河两岸存在城镇及工厂,其中长治、安阳、邯郸、邢台等城市工业发展迅速。因此重金属的空间差异性可能是因为该区的人为活动、点源和非点源以及地球化学过程造成的[22]。
表2显示了中国和世界其他地区沉积物中重金属的浓度。沉积物中除Cr的浓度略高于土壤背景值外,Ni、Cu、Pb的平均浓度接近中国的土壤背景值。Cr、Ni的含量较其他地区含量属偏高水平,Cu、Pb的含量较其他地区含量属中等偏低水平。各区域重金属浓度的差异可能反映了地球化学背景下的区域差异。
-
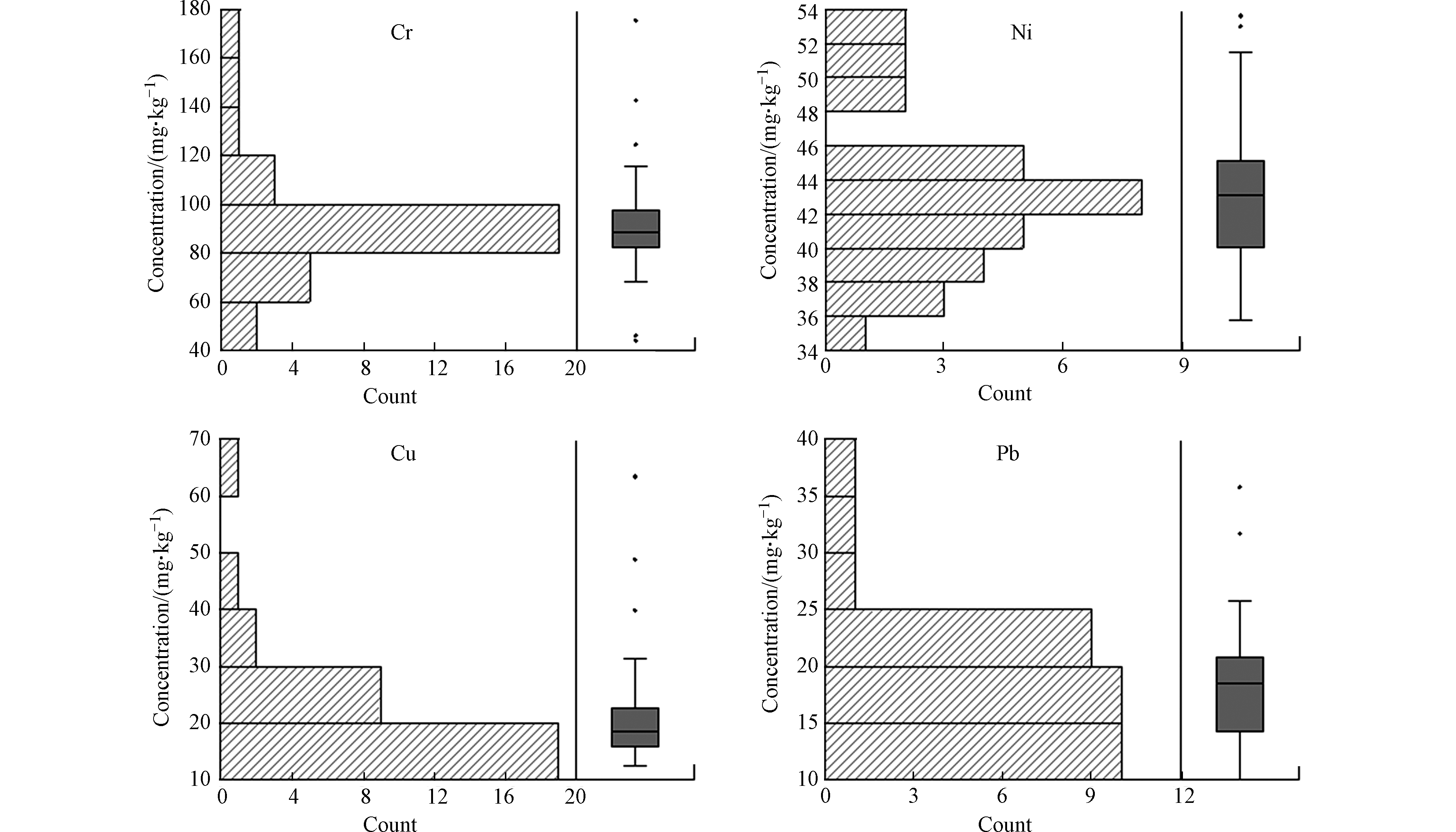
采用归一化法和相对累积频率法计算了表层沉积物的基线值。在进行线性回归之前,应去除异常值和人为影响样本。从而将原始数据集缩减为相对干净的数据集。这个数据集显示了或多或少的正态分布(图3)。表层沉积物中重金属的基线能够表示局部沉积物中金属的现状(表3)。值得注意的是,除Cu外,表层沉积物中Cr、Pb、Ni的基线值均高于背景值,原因为基线值所研究的表层沉积物比深层沉积物(背景值)更易受外部环境影响[35]。
在本研究中,根据基线函数计算每个采样点的基线浓度。测量的金属浓度和基线值之间的正差表示人为输入,而负值表明测量重金属来自自然来源。根据区域地球化学基线值,人为贡献率(ACR)可使用以下公式计算[20]:
地球化学基线代表了受人为干扰地区元素含量的相对自然变化,主要由背景含量和不可避免的均匀非点源组成。高于基线的部分称为局部污染源,包括一些水域的固定排放点,如入河口、工厂排水口和农田排水沟。与自然来源的金属相比,人为来源的污染贡献可以量化。
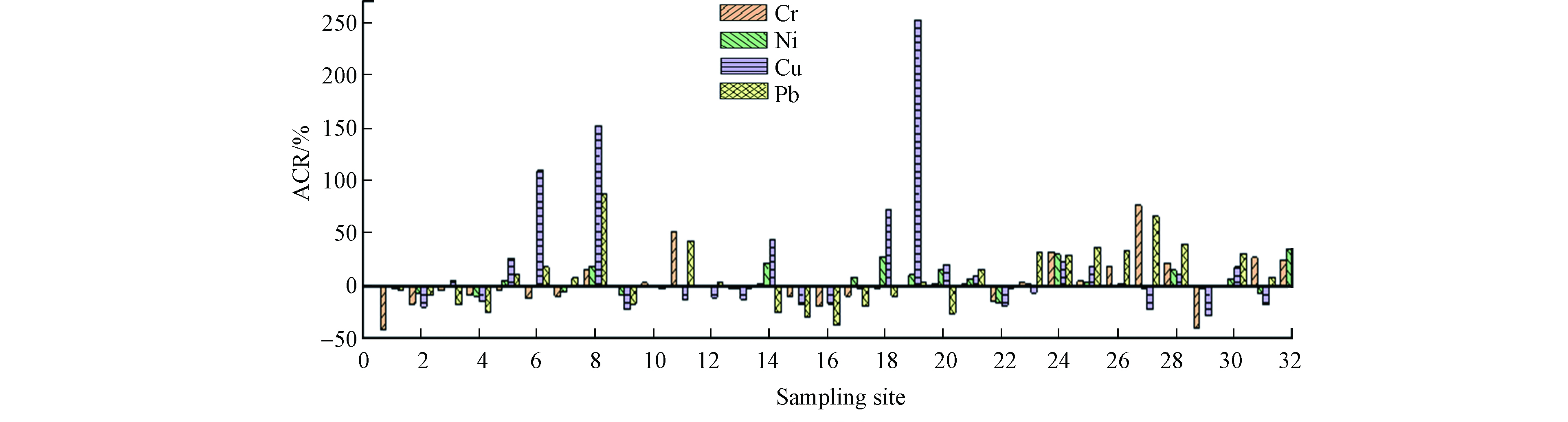
各采样点重金属的人为贡献率(ACR)如图4所示,人类活动影响大多集中在浊漳源头和清漳源头的位置。浊漳源头和清漳源头处于城镇周边,与人类活动、工业生产排放存在一定的相关性。Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb受人为因素影响的地点分别占66%、63%、50%、56%。在受人类活动影响的地点中,Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb人为贡献率的平均值为17.14%(0.36%—79.9%)、11.16%(0.01%—36.08%)、50.92%(1.72%—252.79%)、29.35%(0.52%—88.31%),表明人为活动的影响较小。
金属间的相关性反映了河流系统中金属的来源和迁移行为。所研究金属之间的皮尔逊相关性表明,沉积物中的大多数金属之间具有显著的相关性。沉积物中Cr与Fe(P<0.05,r=0.82)、Al(P<0.05,r=0.61)的正相关表明它们的行为相似、来源相同,主要来源于天然成岩源[36]。而沉积物中的Ni和Cu(P<0.05,r=0.50)呈正相关,表明这些金属存在共同成因,受地质背景控制。沉积物中Pb与Cr(P<0.05,r=0.73)呈强正相关,表明人类活动可能是他们的共同来源,受人为因素影响。
-
建立沉积物中微量元素的可靠背景浓度一直是生态风险评估中的一个重要问题。以往的研究都采用算术平均值±标准差或中值作为沉积物中金属的地球化学背景浓度。本研究应用Igeo和EI对漳河上游底泥重金属污染程度进行了评价。根据不同背景值(背景值、中值、区域地球化学基线值)的污染评估结果如图5所示。基于区域地球化学基线值作为参考背景值时,计算Igeo采用的为修正后的公式,如采用修正前的公式,则4种重金属的Igeo值除个别点外均为负值,这可能是数据校正过度导致的数值偏小。在本研究中,风险评估结果没有显著差异。区域地球化学基线值随区域的变化而变化,并随人类活动强度的增加而增加,而背景值是一个固定值。因此,当一个地区受到人类活动的显著影响时,区域地球化学基线值将远高于背景值。因此,在污染评估期间,区域地球化学基线的风险值将明显低于背景值的风险值,尤其是EI。
污染评价结果与参考背景浓度密切相关。参考背景值越高,生态风险越低。在这项研究中,土壤背景值和中值是固定的,而区域地球化学基线值随采样点的不同而变化。土壤背景值参考了山西省土壤背景值,它没有考虑到区域差异。虽然中位数是从现有的重金属浓度值中选择的,但它没有考虑由颗粒大小引起的金属的自然变化。相比之下,区域地球化学基线值不仅考虑了每个采样点的特性,而且消除了粒度的影响。因此,在风险评估中使用区域地球化学基线作为背景值是合理的,特别是在没有区域背景测量系统的受人类活动影响的地区。
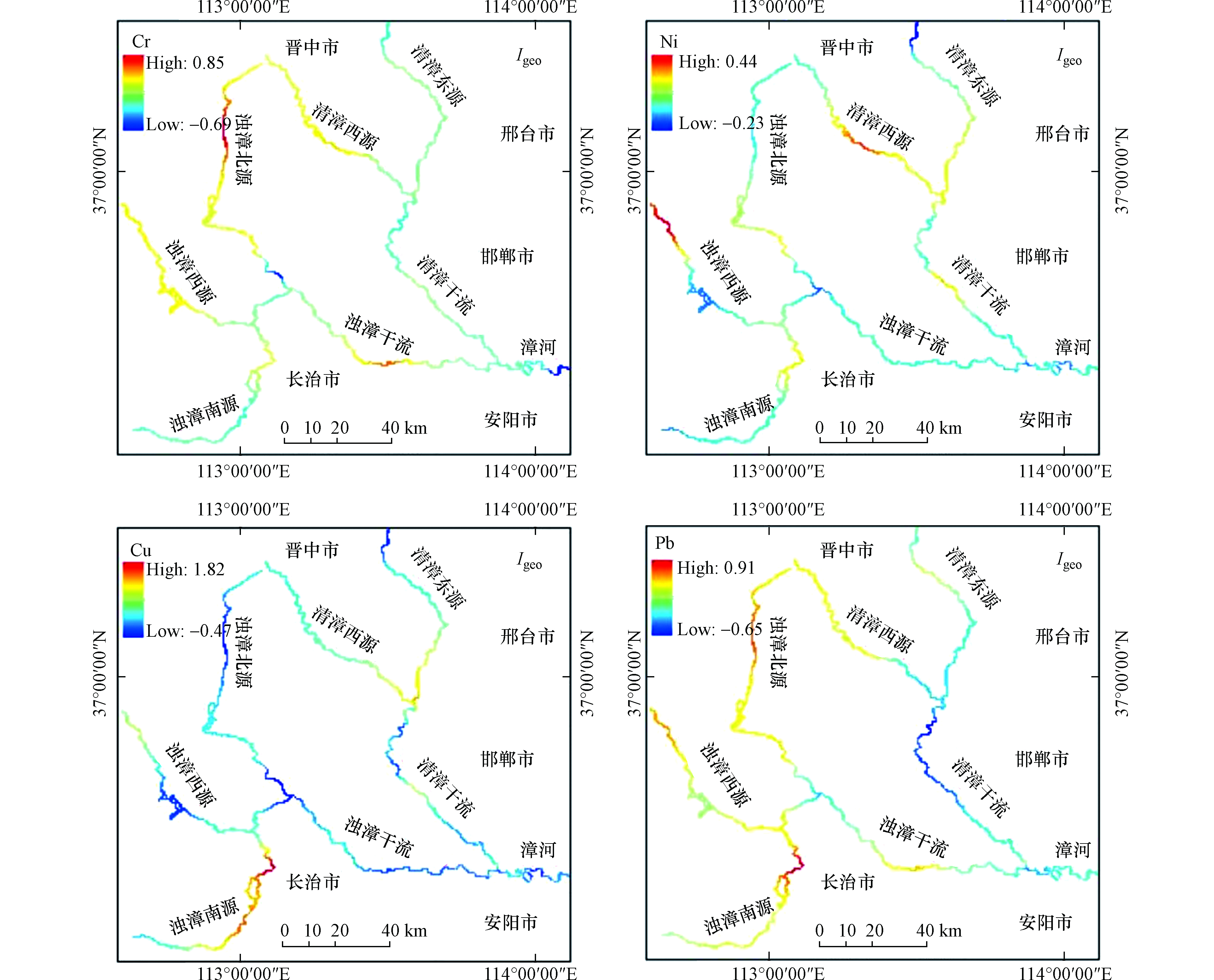
就Igeo而言,所有重金属的Igeo的平均值均在0—1之间(图6),表明漳河上游沉积物中在重金属方面处于轻微污染状态。在各采样点所有金属的Igeo中,总体污染级别为:Cu>Pb>Ni>Cr。Cr的Igeo范围为−0.69—0.85,均值为0.06。Ni的Igeo范围为−0.23—0.44,均值为0.07。Pb的Igeo范围为−0.65—0.91,均值为0.09。Cu的Igeo范围为−0.47—1.82,均值为0.14,值最大的地点是6、8和19,污染水平达到中度污染(1.07、1.34和1.82)。3个地点(6、8和19)的Cu污染可能与附近工厂有关。此外,还与人类活动加剧导致生活污水和其他垃圾的产生有关[23]。在浊漳南源,Cu和Pb的地质累积指数分别为0.81和0.42,污染状态为轻微富集轻微污染,与张茜等[37]在浊漳南源漳泽水库的评价结果一致。
在所有重金属的潜在生态风险方面,EI值在1.24—17.64之间(图7)。因此,漳河上游沉积物中重金属的生态风险较低。每种重金属的EI平均值依次为:Cu>Pb>Ni>Cr,与Igeo评价结果一致。而且重金属的毒性系数值影响其顺序。Cr的EI范围为1.24—3.60,均值为2.13。Ni的EI范围为4.26—6.80,均值为5.26。Pb的EI范围为3.19—9.42,均值为5.49。Cu的EI范围为3.62—17.64,均值为5.94。EI值表明,所有重金属都具有较低的生态风险。与侯沁文[38]在浊漳北源的研究结果相似。总的来说,根据Igeo和EI的综合风险评估结果,沉积物中重金属的富集程度很小,表明漳河流域中重金属(Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb)处于无污染至轻度污染状态,具有较低的生态风险。
根据沉积物质量指南的阈值效应水平(TEL)和可能效应水平(PEL)(表4),如果10%的值超过TEL,则每个地点都视为受到污染。在本研究中,沉积物中的Cr、Ni、Cu的有10%采样点的含量超过TEL值。有84.37%的Cr、81.25%的Ni和12.5%的Cu在TEL和PEL之间,有15.63%的Cr和18.75%的Ni高于PEL。因此,结果表明,Cu和Pb预计不会对漳河的生物群造成不利的影响。而在大部分研究点的表层沉积物中,Cr和Ni则可能会对河流生物构成威胁。
-
(1)漳河上游流域表层沉积物中Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb的浓度范围分别为44.13—175.57、35.78—53.6、12.49—63.41、10.00—35.77 mg·kg−1,平均值为91.51、43.33、21.93、18.30 mg·kg−1。重金属浓度空间分布差异较大,人类活动影响大多集中在浊漳源头和清漳源头的位置。
(2)用相对累积频率法和归一化法计算了重金属的区域地球化学基线值。结果表明,区域地球化学基线值不仅考虑了每个采样点的特性,而且消除了粒度的影响。区域地球化学基线值被认为是沉积物风险评估的合理区域背景值。
(3)应用Igeo和EI对漳河上游底泥重金属污染程度进行了评价。污染程度和风险评价显示,漳河上游沉积物中重金属处于轻度累积轻微污染状态,具有低生态风险。
漳河上游流域沉积物中重金属生态风险评价
Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the upper reaches of Zhanghe River
-
摘要: 海河流域人口密集,大中城市众多,在我国政治经济中具有重要地位。漳河,属海河流域漳卫南运河水系,是漳卫河的一大支流。本研究以漳河上游流域表层沉积物为研究对象,采用相对累积频率法和归一化法建立了4种重金属(Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb)的区域地球化学基线。根据区域地球化学基线值定量计算了漳河上游流域沉积物中重金属污染的人为贡献率。根据不同背景参考值(土壤背景值、重金属浓度中值和区域地球化学基线值)采用地质累积指数和潜在生态风险指数对沉积物中重金属的污染水平和生态风险进行评价。沉积物中Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb的平均含量分别为91.51、43.33、21.93、18.30 mg·kg−1,接近中国土壤背景值。计算的区域地球化学基线值略低于沉积物中重金属的平均含量。Cr、Ni、Cu、Pb的平均人为贡献率为17.14%、11.16%、50.92%、29.35%,表明人为影响较小。此外,Igeo和EI结果表明,沉积物重金属处于无污染至轻度污染状态,具有较低的生态风险。Abstract: Haihe River Basin plays an important role in China's politics and economy. Zhanghe River is the largest tributary of Zhangwei River, which belongs to Zhangweinan Canal in Haihe River Basin. In this study, the regional geochemical baselines of four heavy metals (Cr, Ni, Cu, Pb) were established by relative cumulative frequency and normalization methods. The anthropogenic contribution rate of sediment in the upper reaches of Zhanghe River was quantitatively calculated by using the baseline value of regional geochemistry. The geological accumulation index (Igeo) and potential ecological risk index (EI) were used to evaluate the pollution level and ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments according to different background reference values (soil background value, median concentration of heavy metals and regional geochemical baseline value). The average contents of Cr, Ni, Cu and Pb in sediments are 91.51 mg·kg−1, 43.33 mg·kg−1, 21.93 mg·kg−1 and 18.30 mg·kg−1, respectively, which are close to the background values of soil in China. The calculated regional geochemical baseline value is slightly lower than the average content of heavy metals in sediments. The average anthropogenic contribution rates of Cr, Ni, Cu and Pb are 17.14%, 11.16%, 50.92% and 29.35%, indicating that the anthropogenic influence is relatively small. In addition, the results of Igeo and EI show that heavy metals in sediments are in a state of no pollution to slight pollution, and the ecological risk is low.
-
Key words:
- Zhanghe River /
- sediments /
- heavy metals /
- regional geochemical baseline /
- pollution assessment
-
表 1 表层沉积物重金属浓度汇总统计
Table 1. Summary statistics of the heavy metal concentrations of the surface sediments
Cr Ni Cu Pb 最小值/(mg·kg−1) 44.23 35.78 12.49 10.00 最大值/(mg·kg−1) 175.57 53.62 63.41 35.77 均值/(mg·kg−1) 91.51 43.33 21.93 18.30 中值(mg·kg−1) 88.43 43.08 18.64 18.47 标准偏差/(mg·kg−1) 24.30 4.64 10.48 5.43 相对标准偏差/% 0.27 0.11 0.48 0.30 表 2 其他区域沉积物重金属含量的比较(mg·kg−1)
Table 2. Comparison of heavy metal content in sediments of other regions (mg·kg−1)
位置Location Cr Cu Ni Pb 参考文献References 漳河上游流域 The upper reaches of Zhanghe River 91.51 21.93 43.33 18.30 本研究 中国淮河流域Huaihe River, Anhui, China — 31.30 32.79 53.43 [6] 中国白洋淀Baiyangdian Lake,china 62.50 26.50 29.10 23.10 [23] 长江和淮河流域中下游浅水湖泊Freshwater lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze and Huai River Basins 74.60 47.60 38.30 37.7 [3] 中国胶州湾Jiaozhou Bay, China 86.17 27.31 32.35 38.54 [7] 东阳江Dongyang River 71.90 86.20 28.10 79.10 [24] 三峡库区支流汝溪河Ruxi Tributary of the Three Gorges Reservoir 79.60 32.69 41.34 29.12 [25] 宝鸡市渭河Weihe River in Baoji City 57.57 48.89 31.80 15.70 [26] 长江中下游底泥Middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River 77.20 46.47 — 37.75 [27] 柳江中下游流域The middle and lower reaches of Liujiang River 53.70 21.60 22.50 32.70 [28] 印度喀拉拉邦Kerala, India — 18.20 50.40 21.60 [29] 埃及红海海岸Coastal sediments, Red Sea, Egypt — 9.43 17.52 11.43 [30] 越南西贡河 Saigon River, Vietnam — — 4.02 1.27 [31] 沙特阿拉伯红海Red Sea, Saudi Arabia — 2.10 2.16 2.75 [32] 韩国西南沿海河流River sediments of southwestern coastal Korea 62.20 29.70 26.10 32.10 [33] 山西省土壤背景值Soil background value ,Shanxi Province 61.8 32.0 26.9 15.8 [34] 中国土壤背景值Soil background value,china 66.8 25.5 33.8 21.9 [34] 表 3 表层沉积物的区域地球化学基线
Table 3. Regional geochemical baseline of surface sediments
重金属Heavy metal 地球化学基线函数 Geochemical baseline functions 地球化学基线值/(mg·kg−1)Geochemical baseline value R2 Cr Cr(mg·kg-1)=60.75+6.69 × 85.56 0.89 Ni Ni(mg·kg-1)=35.29+1.62 × 41.46 0.98 Cu Cu(mg·kg-1)=16.76+0.47 × 18.39 0.84 Pb Pb(mg·kg-1)=11.95+1.28 × 16.33 0.96 表 4 淡水沉积物质量指南的汇总统计
Table 4. Summary statistics of the and guideline freshwater sediment quality values
重金属 Heavy metal Cr Ni Cu Pb TEL/(mg·kg−1,干重) 43.3 22.7 31.6 35.8 PEL/(mg·kg−1,干重) 111.0 48.6 149.0 128.0 <TEL/% 0 0 87.50 100 TEL – PEL/% 84.37 81.25 12.50 0 >PEL/% 15.63 18.75 0 0 TEL:阈值效应水平Threshold effects level;PEL:可能影响水平Probable effects level[39]. -
[1] WEI X, HAN L F, GAO B, et al. Distribution, bioavailability, and potential risk assessment of the metals in tributary sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir: The impact of water impoundment [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2016, 61: 667-675. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.10.018 [2] LI L, JIANG M, LIU Y, et al. Heavy metals inter-annual variability and distribution in the Yangtze River estuary sediment, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 141: 514-520. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.03.008 [3] XU M, WANG R, YANG X D, et al. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments from shallow lakes in East China [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 213: 106490. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106490 [4] SHI C, DING H, ZAN Q J, et al. Spatial variation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in mangrove sediments across China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 143: 115-124. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.04.043 [5] DASH S, BORAH S S, KALAMDHAD A S. Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk assessment for surficial sediments of Deepor Beel, India [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 122: 107265. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107265 [6] WANG J, LIU G J, LU L L, et al. Geochemical normalization and assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, and Ni) in sediments from the Huaihe River, Anhui, China [J]. CATENA, 2015, 129: 30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2015.02.008 [7] LIANG X M, SONG J M, DUAN L Q, et al. Source identification and risk assessment based on fractionation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 128: 548-556. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.02.008 [8] ISLAM M A, DAS B, QURAISHI S B, et al. Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessment in water and sediments of the Halda river, Bangladesh: A natural fish breeding ground [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 160: 111649. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111649 [9] XIA P H, MA L, SUN R G, et al. Evaluation of potential ecological risk, possible sources and controlling factors of heavy metals in surface sediment of Caohai Wetland, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 740: 140231. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140231 [10] KONG P R, CHENG X, SUN R H, et al. The synergic characteristics of surface water pollution and sediment pollution with heavy metals in the Haihe river basin, Northern China [J]. Water, 2018, 10(1): 73. doi: 10.3390/w10010073 [11] ZHAO Y, SHAN B Q, TANG W Z, et al. Nitrogen mineralization and geochemical characteristics of amino acids in surface sediments of a typical polluted area in the Haihe River Basin, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(22): 17975-17986. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4873-0 [12] ZHU A M, LIU J H, QIAO S Q, et al. Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Bohai Sea of China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 153: 110901. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.110901 [13] TANG W Z, ZHANG W Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Basin-scale comprehensive assessment of cadmium pollution, risk, and toxicity in riverine sediments of the Haihe Basin in North China [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 81: 295-301. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.06.011 [14] CAO Y X, LEI K, ZHANG X, et al. Contamination and ecological risks of toxic metals in the Hai River, China [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 164: 210-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.009 [15] ZHANG C, SHAN B Q, TANG W Z, et al. Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 139: 263-271. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.047 [16] 赵海萍, 陈旺, 李清雪, 等. 漳河上游水质时空分异特征及污染源识别 [J]. 水资源保护, 2017, 33(4): 47-54. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2017.04.008 ZHAO H P, CHEN W, LI Q X, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of water quality and pollutant source identification in upper reaches of Zhanghe River [J]. Water Resources Protection, 2017, 33(4): 47-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2017.04.008
[17] 郝红, 周怀东, 王剑影, 等. 漳卫南运河沉积物重金属污染及其潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2005, 3(2): 109-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3031.2005.02.007 HAO H, ZHOU H D, WANG J Y, et al. Assessment on potential ecological risk due to heavy metals pollution in sediment in the South Zhangwei Canal [J]. Journal of China Institute of Water, 2005, 3(2): 109-115(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3031.2005.02.007
[18] CHEN H Y, TENG Y G, LI J, et al. Source apportionment of trace metals in river sediments: A comparison of three methods [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 211: 28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.12.037 [19] JIANG J B, WANG J, LIU S Q, et al. Background, baseline, normalization, and contamination of heavy metals in the Liao River Watershed sediments of China [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 73: 87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.014 [20] ZHOU Y, GAO L, XU D Y, et al. Geochemical baseline establishment, environmental impact and health risk assessment of vanadium in lake sediments, China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 660: 1338-1345. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.093 [21] RUDNICK R L, HOLLAND H D, TUREKIAN K K. Treatise on geochemistry, volume 3[EB/OL]. 2003 [22] BHUYAN M S, BAKAR M A. Seasonal variation of heavy metals in water and sediments in the Halda River, Chittagong, Bangladesh [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(35): 27587-27600. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0204-y [23] GAO L, HAN L F, PENG W Q, et al. Identification of anthropogenic inputs of trace metals in lake sediments using geochemical baseline and Pb isotopic composition [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 164: 226-233. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.014 [24] 龚亚玲, 胡忠行, 周云鹏, 等. 东阳江表层沉积物重金属污染评价及来源分析 [J]. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(4): 466-473. GONG Y L, HU Z X, ZHOU Y P, et al. On pollution assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Dongyang River [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 41(4): 466-473(in Chinese).
[25] 方志青, 王永敏, 王训, 等. 三峡库区支流汝溪河沉积物重金属空间分布及生态风险 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1338-1345. FANG Z Q, WANG Y M, WANG X, et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the ruxi tributary of the Three Gorges reservoir [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1338-1345(in Chinese).
[26] 耿雅妮, 杨宁宁, 戴恩华, 等. 宝鸡市河流表层沉积物重金属空间分布、风险评价及源解析 [J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(10): 102-110. GENG Y N, YANG N N, DAI E H, et al. Spatial distribution, ecological risk and source of heavy metals in surface sediments of Baoji river [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(10): 102-110(in Chinese).
[27] 易雨君, 王文君, 宋劼. 长江中下游底泥重金属污染特征、潜在生态风险评价及来源分析 [J]. 水利水电技术, 2019, 50(2): 1-7. YI Y J, WANG W J, SONG J. Pollution characteristics, potential ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals of sediment in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2019, 50(2): 1-7(in Chinese).
[28] 钟晓宇, 吴天生, 李杰, 等. 柳江流域沉积物重金属生态风险评价及来源分析 [J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(1): 191-198. ZHONG X Y, WU T S, LI J, et al. Ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments of Liujiang River Catchment [J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(1): 191-198(in Chinese).
[29] SHIBINI MOL P A, SUJATHA C H. Distribution and geochemical speciation of sediment bound heavy metals in the specific zones of central Kerala, India [J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 2020, 14: 100358. [30] NOUR H E, EL-SOROGY A S, ABD EL-WAHAB M, et al. Contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals pollution from the Shalateen coastal sediments, Red Sea, Egypt [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 144: 167-172. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.04.056 [31] NGUYEN B T, DO D D, NGUYEN T X, et al. Seasonal, spatial variation, and pollution sources of heavy metals in the sediment of the Saigon River, Vietnam [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 256: 113412. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113412 [32] AL-MUR B A. Geochemical fractionation of heavy metals in sediments of the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia [J]. Oceanologia, 2020, 62(1): 31-44. doi: 10.1016/j.oceano.2019.07.001 [33] YANG H J, JEONG H J, BONG K M, et al. Organic matter and heavy metal in river sediments of southwestern coastal Korea: Spatial distributions, pollution, and ecological risk assessment [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 159: 111466. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111466 [34] 中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 中国环境科学出版, 1990. China National Environmental Monitoring Station. Background value of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science, 1990(in Chinese).
[35] 贾晗, 刘军省, 王春光, 等. 基于铜陵地区地球化学基线的土壤重金属污染评价及分析 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(5): 50-55. JIA H, LIU J X, WANG C G, et al. Evaluation and analysis of soil heavy metal pollution based on geochemical baseline in Tongling area [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(5): 50-55(in Chinese).
[36] TAMIM U, KHAN R, JOLLY Y N, et al. Elemental distribution of metals in urban river sediments near an industrial effluent source [J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 155: 509-518. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.099 [37] 张茜, 冯民权, 郝晓燕. 漳泽水库沉积物重金属污染特征与生态风险评价 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(1): 11-17. ZHANG Q, FENG M Q, HAO X Y. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of zhangze reservoir [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(1): 11-17(in Chinese).
[38] 侯沁文. 浊漳河北源河道沉积物中6种重金属污染特征与源解析 [J]. 长治学院学报, 2017, 34(2): 17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2014.2017.02.005 HOU Q W. Characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metal contamination in the channel sediment of the northern source, Zhuozhang river [J]. Journal of Changzhi University, 2017, 34(2): 17-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2014.2017.02.005
[39] MACDONALD D D, INGERSOLL C G, BERGER T A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems [J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2000, 39(1): 20-31. doi: 10.1007/s002440010075 -




 下载:
下载: