-
重金属因其在环境中的持久性、高毒性以及生物蓄积性等特性,广泛的分布于全球各环境介质中,成为全球性的环境公害。重金属可由大气沉降、地表径流、污水直排等途径进入海洋环境[1-4]。海水中的重金属易吸附于颗粒物中,通过络合、沉淀等过程转移并富集于沉积物中[5-6]。当水环境改变时,富集于沉积物中的重金属可再次释放至水环境中,形成“二次污染”[7-8],这种“源”与“汇”之间的转化,对海洋生态系统造成严重危害。因此,海洋沉积物环境中重金属可作为海域重金属污染程度的“指示剂”,蕴含着丰富的环境信息和海洋地质过程,对评价环境生态风险具有重要的意义[6, 9]。
北部湾位于南海西北部,该海域生产力高,生物多样性丰富,是沿海地区重要的渔场及渔业产品的主要来源[10-11]。但由于北部湾是一个半封闭海湾,水动力条件弱,污染物不容易扩散而易富集于海湾内。近年来,随着广西沿海工业化、城市化的快速发展,北部湾近海生态也正面临着日益严重的重金属污染压力[3, 12]。例如,北部湾部分近海港口、潮间带、油田等区域也发现了不同程度的重金属污染[11-13]。此外,北部湾入海河流中,部分河流(如大风江和南流江)污染物含量在雨季处于较高水平,该时期大量的污染物排入北部湾近岸[14]。研究显示,北部湾沉积物芯中重金属含量从1985年至2008年呈显著上升趋势[15],这很可能与陆源污染物输入增加有关。但对于广西北部湾整体海域重金属的相关研究仍相对较少,对海域重金属来源及影响因素的认识仍相对较弱。因此,对北部湾重金属研究及生态风险评价具有重要的意义。
本研究以广西北部湾采集的表层沉积物为对象,分析沉积物中6种重金属(As、Cd、Cu、Hg、Pb和Zn)的污染特征、潜在来源以及生态风险评价,揭示人类活动对北部湾海洋生态的影响,对维护北部湾生态环境提供科学依据。
-
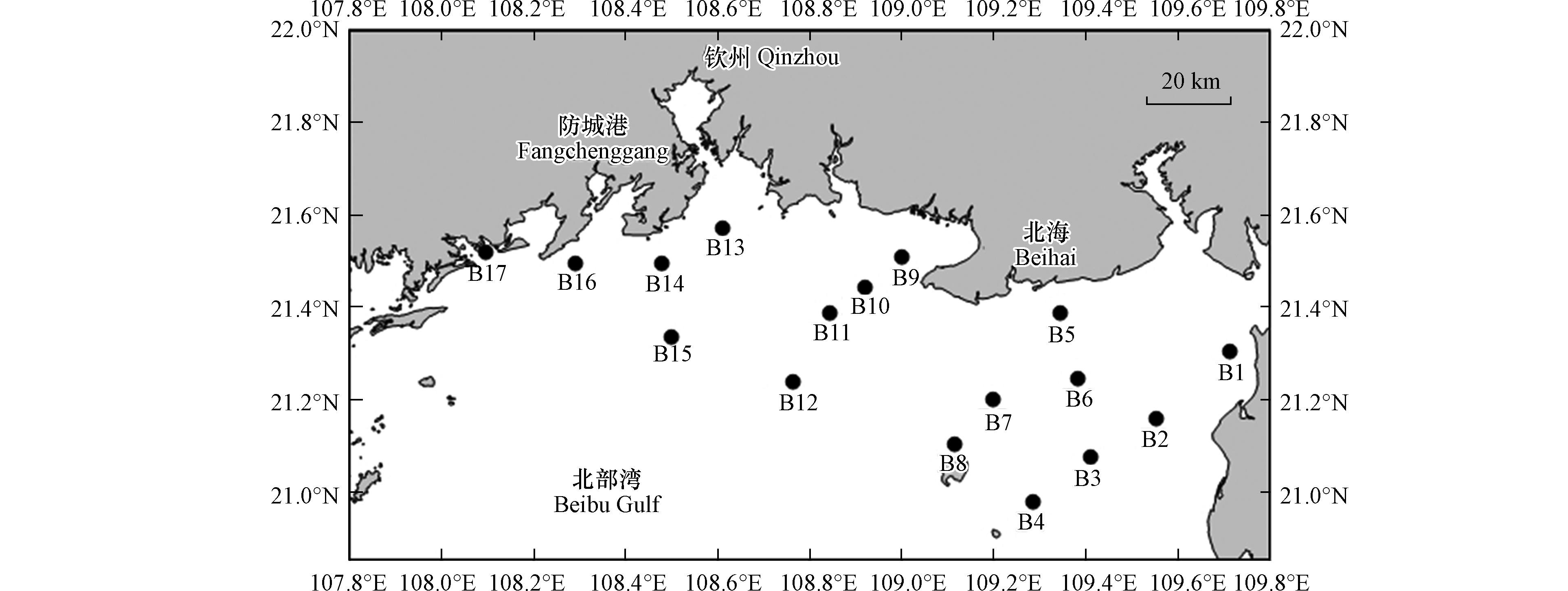
本研究位于广西北海、钦州和防城港沿海的北部湾近海区域(图1),该海湾属于半封闭海湾,水动力条件较弱,易受到人类活动的影响,污染物质难以扩散,使得海湾生态系统极易受到破坏。
于2018年8月(夏季)使用抓斗式采样器在该区域共采集17个表层沉积物样品(0—5 cm),并将采集好的沉积物样品置于聚乙烯密封袋中,密封冷藏(4℃)保存,用以分析重金属和总有机碳(TOC)。
-
沉积物样品的处理及分析检测方法按照《海洋监测规范第5部分:沉积物分析》(GB 17378.5-2007)进行。一部分沉积物样品在105℃条件下的烘箱干燥,用于检测Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd和As,检测Hg的样品在自然室温条件下烘干。烘干并除去石头等大颗粒物后,用玛瑙研磨样品,通过160目筛网筛出Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd和As样品,通过80目的筛网筛出Hg样品,待测。另一部分沉积物样品进行冷冻干燥,用以测定TOC含量。在整个实验分析过程中均使用超纯水,实验所用的玻璃器皿均在1:3的硝酸溶液中浸泡至少7 d,然后使用超纯水清洗。
处理后的沉积物样品,取0.5 g,用硝酸和盐酸混合溶液在95℃条件下消解1 h,然后用超纯水稀释至50 mL,待分析。Cd、Cu、Pb和Zn采用原子吸收光谱法(ZEENH700P, Jena, German)测定,As和Hg采用原子荧光光谱法(AFS-9530,北京海光仪器,中国)测定。Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Hg和As的检出限分别为2.0、1.0、6.0 、0.04、0.002、0.06 μg·g−1。TOC含量采用重铬酸钾氧化硫酸亚铁滴定法测定,检出限为0.01%。
-
根据《海洋沉积物质量标准》(GB 18668-2002)中Ⅰ类沉积物标准值,对As、Cd、Cu、Hg、Pb和Zn进行单因子污染评价,计算如下:
其中,
Cif 为重金属i的污染指数;Ci 为实测浓度(μg·g−1),Cin 为重金属评价标准值(见表1)。当Cif ≤1时,代表污染程度低,其含量符合标准;当Cif >1时,其含量超出标准评价,其中1<Cif ≤3代表中等污染程度,3<Cif ≤6代表重污染程度,Cif >6位严重污染程度。 -
根据沉积物中重金属浓度及毒性响应特征和污染物类型,针对不同地域环境背景差异,Hakanson于20世纪80年代提出了生态风险指数评价法[16],该方法被广泛应用于海洋环境重金属危害程度及潜在生态风险评价[6, 17-18]。方法如下:
其中,
Pi 表示沉积物重金属总体污染指数;Cif 表示重金属i的污染指数;Ci 表示重金属i实测值(μg·g−1);Cin 表示重金属i的评价标准值(μg·g−1),本研究采用北部湾区域重金属的背景值[18],Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Hg和As的背景值分别为15.8、28.9、75.8、0.09、0.029、7.8 μg·g−1;Tir 表示重金属i的毒性系数,其反应该重金属毒性水平及生物对该重金属污染的敏感度,Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Hg和As的毒性系数分别为5、5、1、30、40和10;Eir 表示重金属的潜在风险系数;RI表示沉积物中重金属的潜在生态风险指数。Eir 和RI的值可以反应沉积物中重金属的不同程度的风险危害,等级划分见表2。 -
北部湾沉积物中重金属含量及分布特征见表3和图2。Hg的浓度范围为0.023—0.037 μg·g−1,平均为0.030 μg·g−1,Hg浓度的高值主要分布在钦州和涠洲岛近岸区域。Cd的浓度范围为0.04—0.09 μg·g−1,平均为0.06 μg·g−1,其浓度的分布特征表现为涠洲岛近岸区域、大风江口和南流江口外海域较高,而钦州和北海近岸区域较低。Pb的浓度范围为12.1—26.7 μg·g−1,平均为18.9 μg·g−1,其浓度的分布表现为外海区域高于近岸区域。As、Cu和Zn浓度的分布趋势相似,As的浓度范围为0.39—9.21 μg·g−1,平均为3.73 μg·g−1;Cu的浓度范围为3.59—16.90 μg·g−1,平均为11.16 μg·g−1;Zn的浓度范围为ND—62.3 μg·g−1,平均为27.8 μg·g−1。As、Cu和Zn浓度的分布呈现北部湾西部(钦州、防城港近岸区域)和涠洲岛近岸区域较高,而东部海域(北海近岸区域)的浓度较低。北部湾重金属分布特征的差异,表明不同重金属间的来源可能不同。
与其他区域对比(表3),北部湾重金属含量明显低于厦门湾[19]、广东近岸[20]和珠江口[21]区域,与海南岛近岸浓度相当[6],但明显高于20世纪90年代时期北部湾沉积物的浓度[22],表明近些年来,北部湾沉积物重金属呈现一定程度富集。
-
沉积物中重金属含量受环境背景、生物过程、海洋物理过程以及人类活动等多方面的影响。此外,TOC主要为沉积物中有机质,其对重金属具有极强的吸附和络合作用[23-24]。因此,在讨论沉积物中重金属潜在来源时,常用利用TOC含量通过与重金属浓度的相关性分析,可对它们的来源进行初步判断[3,18,23]。沉积物中Cu和Zn的含量与TOC含量呈显著正相关性(表4),表明Cu和Zn在沉积物中的富集受到TOC含量的影响。Cu和As、Cu和Zn、Pb和Zn、Pb和Cd之间呈显著正相关性(表4),表明这些元素之间具有同源性;而Hg与其他元素均无相关性,说明Hg与其他重金属的来源方式可能不同。
为进一步了解重金属的潜在来源及主控因素,对沉积物中重金属含量进行主成份分析,结果如表5所示,当特征值大于1时,可提取3个成份,可分别解释总因子的43.54%、21.23%和18.66%,累积贡献率为83.43%。在成份1中,TOC、Zn、Cu和Pb具有很高载荷,这些重金属元素组合的高值区主要分布在钦州、防城港和涠洲岛近岸区域,表明这些金属元素在沉积物中的富集受到沉积物中有机质含量的影响。Zn、Cu和Pb主要来源于交通运输和工业生产[9]。钦州和防城港是北部湾沿海主要的工业活动区域,表明这些元素来源可能受到近海工业活动的影响。成份2中,Hg和As具有较高的载荷。As的富集受到低温热液成矿的影响,主要来源于农药残留、网箱养殖和工业生产[6,9]。Hg主要来源于石化产品、金属冶炼和煤炭燃烧[9]。As含量的高值主要分布于钦州和防城港近岸区域,其来源仍为近海人类活动为主;而外海较远区域As浓度的高值可能受控于自然地质背景因素,或于外海物质来源有关[9]。成份3仅Cd具有高载荷,其主要用于杀虫剂、化工业、电镀业等,通过河流排污入海并富集于沉积物中[6]。Cd浓度的高值主要分布在大风江口和南流江口外海域,反映了北部湾城市发展进程导致的区域污染差异性影响。
-
对北部湾沉积物中重金属含量进行单因子分析,结果显示,所有站位的重金属污染因子均小于1,其含量低于Ⅰ类沉积物标准,污染程度低。北部湾沉积物中重金属单因子污染影响程度如表6所示,依次为Cu>Pb>As>Zn>Hg>Cd。
各重金属潜在生态风险系数(
Eir )除了Hg外,均小于40(表6),潜在危害程度低,沉积物中重金属潜在生态危害影响依次为Hg>Cd>As>Cu>Pb>Zn。沉积物中计算总体污染程度指数(Pi)范围在2.25—7.13,平均为4.45,高值主要分布在钦州和防城港近岸区域(图3),但其最大值小于8,评价为低程度污染。沉积物重金属的潜在生态风险指数(RI)范围为54.71—105.12,平均为76.99,其分布与Pi相似(图3),但低于150,重金属总体潜在生态危害属低程度范围,反映了北部湾海域较好的低质生态环境。但值得注意的是,大部分沉积物样品中Hg的潜在生态风险指数大于40,处于中等潜在生态危害程度。综上评价,尽管北部湾沉积物中重金属处于低程度污染和底潜在生态危害风险,但随着北部湾经济区城市化、工业化的不断发展,局部海域污染程度和潜在生态风险程度处于较高水平,仍需警惕。
-
(1)北部湾沉积物中不同重金属的分布特征差异明显,其中As、Cu、Hg和Zn的分布总体呈现西部和涠洲岛近岸海域高于东部海域,Cd浓度的高值主要分布在涠洲岛近岸区域、大风江口和南流江口外海域,Pb浓度的分布表现为外海区域高于近岸区域,表明北部湾重金属的来源可能存在差异。
(2)与其他区域相比,北部湾沉积物中重金属含量处于较低水平,但与历史数据相比呈现增长趋势,表现一定程度的富集。
(3)Zn、Cu、Pb、Hg和As的来源主要受到近海人类活动的影响,而Cd反映了北部湾城市发展进程导致的区域污染差异性影响。
(3)北部湾沉积物重金属的污染评价显示,局部海域污染程度和潜在生态风险程度处于较高水平,重金属的污染仍需警惕。
广西北部湾沉积物重金属污染特征及生态风险评价
Evaluation on sediment pollution and potential ecological risks in Guangxi Beibu Gulf
-
摘要: 于2018年夏季采集了广西北部湾表层沉积物样品,分析沉积物中6种重金属(Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Hg和As)含量的分布特征,利用数理统计方法研究其来源及主控因素,并评价了重金属的总体污染状况和潜在生态风险。结果显示,北部湾沉积物中Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Hg和As浓度的平均值分别为11.16、18.9、27.8、0.06、0.030、3.73 μg·g−1。不同重金属含量的分布呈现区域性的差异,但其来源主要受到近海人类活动的影响。与其他区域相比,北部湾沉积物重金属含量处于较低水平,但明显高于北部湾历史监测值,表现一定程度的富集。北部湾沉积物重金属含量均符合Ⅰ类沉积物标准,单因子污染影响程度依次为Cu>Pb>As>Zn>Hg>Cd,总体处于低程度污染。除了Hg处于中等潜在生态危害程度外,其他重金属潜在生态危害程度低,生态危害影响依次为Hg>Cd>As>Cu>Pb>Zn,Hg对海域环境污染及潜在危害影响程度最高。Abstract: The distribution characteristics of the concentration of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, Hg and As were analyzed based on the geochemical analisis of surface sidement samples in Guangxi Beibu Gulf. The sources, main controlling factors and the potential ecological risks for heavy metal distribution were discussed in this study. The results showed that the average concentrations of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, Hg and As were 11.16, 18.9, 27.8, 0.06, 0.030, 3.73 μg·g−1, respectively. The distribution of different heavy metals showed regional differences, but their sources were mainly affected by human activities in the coastal area. Compared with other areas, although the heavy metals in the sediments of Guangxi Beibu Gulf were at relatively low level, those level in the gulf were significantly higher than that historical monitoring level. The level of heavy metals in the sediments of Guangxi Beibu Gulf reached China’s national first-class benchmark of marine sediment quality, and the degree of pollution for six metals were arranged in the following order: Cu>Pb>As>Zn>Hg>Cd, and caused low levels of pollution generally. Except for the medium potential ecological risk of Hg, other metals were at a low ecological risk level, and the order for the ecological risk of the six metals was Hg>Cd>As>Cu>Pb>Zn, and Hg was the primary potential ecological risk factor.
-
Key words:
- Beibu Gulf /
- sediment /
- heavy metals /
- ecological risk assessment
-
重金属因其在环境中的持久性、高毒性以及生物蓄积性等特性,广泛的分布于全球各环境介质中,成为全球性的环境公害。重金属可由大气沉降、地表径流、污水直排等途径进入海洋环境[1-4]。海水中的重金属易吸附于颗粒物中,通过络合、沉淀等过程转移并富集于沉积物中[5-6]。当水环境改变时,富集于沉积物中的重金属可再次释放至水环境中,形成“二次污染”[7-8],这种“源”与“汇”之间的转化,对海洋生态系统造成严重危害。因此,海洋沉积物环境中重金属可作为海域重金属污染程度的“指示剂”,蕴含着丰富的环境信息和海洋地质过程,对评价环境生态风险具有重要的意义[6, 9]。
北部湾位于南海西北部,该海域生产力高,生物多样性丰富,是沿海地区重要的渔场及渔业产品的主要来源[10-11]。但由于北部湾是一个半封闭海湾,水动力条件弱,污染物不容易扩散而易富集于海湾内。近年来,随着广西沿海工业化、城市化的快速发展,北部湾近海生态也正面临着日益严重的重金属污染压力[3, 12]。例如,北部湾部分近海港口、潮间带、油田等区域也发现了不同程度的重金属污染[11-13]。此外,北部湾入海河流中,部分河流(如大风江和南流江)污染物含量在雨季处于较高水平,该时期大量的污染物排入北部湾近岸[14]。研究显示,北部湾沉积物芯中重金属含量从1985年至2008年呈显著上升趋势[15],这很可能与陆源污染物输入增加有关。但对于广西北部湾整体海域重金属的相关研究仍相对较少,对海域重金属来源及影响因素的认识仍相对较弱。因此,对北部湾重金属研究及生态风险评价具有重要的意义。
本研究以广西北部湾采集的表层沉积物为对象,分析沉积物中6种重金属(As、Cd、Cu、Hg、Pb和Zn)的污染特征、潜在来源以及生态风险评价,揭示人类活动对北部湾海洋生态的影响,对维护北部湾生态环境提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法 (Material and mathods)
1.1 研究区域及样品采集
本研究位于广西北海、钦州和防城港沿海的北部湾近海区域(图1),该海湾属于半封闭海湾,水动力条件较弱,易受到人类活动的影响,污染物质难以扩散,使得海湾生态系统极易受到破坏。
于2018年8月(夏季)使用抓斗式采样器在该区域共采集17个表层沉积物样品(0—5 cm),并将采集好的沉积物样品置于聚乙烯密封袋中,密封冷藏(4℃)保存,用以分析重金属和总有机碳(TOC)。
1.2 样品的处理及分析检测
沉积物样品的处理及分析检测方法按照《海洋监测规范第5部分:沉积物分析》(GB 17378.5-2007)进行。一部分沉积物样品在105℃条件下的烘箱干燥,用于检测Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd和As,检测Hg的样品在自然室温条件下烘干。烘干并除去石头等大颗粒物后,用玛瑙研磨样品,通过160目筛网筛出Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd和As样品,通过80目的筛网筛出Hg样品,待测。另一部分沉积物样品进行冷冻干燥,用以测定TOC含量。在整个实验分析过程中均使用超纯水,实验所用的玻璃器皿均在1:3的硝酸溶液中浸泡至少7 d,然后使用超纯水清洗。
处理后的沉积物样品,取0.5 g,用硝酸和盐酸混合溶液在95℃条件下消解1 h,然后用超纯水稀释至50 mL,待分析。Cd、Cu、Pb和Zn采用原子吸收光谱法(ZEENH700P, Jena, German)测定,As和Hg采用原子荧光光谱法(AFS-9530,北京海光仪器,中国)测定。Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Hg和As的检出限分别为2.0、1.0、6.0 、0.04、0.002、0.06 μg·g−1。TOC含量采用重铬酸钾氧化硫酸亚铁滴定法测定,检出限为0.01%。
1.3 重金属污染评价
1.3.1 单因子污染指数法
根据《海洋沉积物质量标准》(GB 18668-2002)中Ⅰ类沉积物标准值,对As、Cd、Cu、Hg、Pb和Zn进行单因子污染评价,计算如下:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) 其中,
Cif Ci Cin Cif Cif Cif Cif Cif 表 1 国家海洋沉积物重金属含量标准值Table 1. National standard values of heavy metals in marine sediments指标Index 海洋沉积物质量标准值/(μg·g−1)Standard value of marine sediment Cu Hg Pb Zn Cd As Ⅰ类Class I 35 0.2 60 150 0.5 20 Ⅱ类Class Ⅱ 100 0.5 130 350 1.5 65 1.3.2 生态风险指数法
根据沉积物中重金属浓度及毒性响应特征和污染物类型,针对不同地域环境背景差异,Hakanson于20世纪80年代提出了生态风险指数评价法[16],该方法被广泛应用于海洋环境重金属危害程度及潜在生态风险评价[6, 17-18]。方法如下:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) 其中,
Pi Cif Ci Cin Tir Eir Eir 表 2 重金属污染程度及潜在生态风险等级Table 2. Contaminant grades and potential ecological risk levels of heavy metalsPi 重金属总体污染程度Overall pollution level Eir 单个重金属潜在生态危害程度Potential ecological hazard of single metal RI 重金属总体潜在生态危害程度Overall potential ecological hazard of metals <8 低度污染 <40 低危害 <150 低危害 8—16 中等污染 40—80 中等危害 150—300 中等危害 16—32 重污染 80—160 较重危害 300—600 重危害 ≥32 严重污染 160—320 重危害 ≥600 严重危害 — — >320 严重危害 — — 2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 沉积物中重金属分布特征
北部湾沉积物中重金属含量及分布特征见表3和图2。Hg的浓度范围为0.023—0.037 μg·g−1,平均为0.030 μg·g−1,Hg浓度的高值主要分布在钦州和涠洲岛近岸区域。Cd的浓度范围为0.04—0.09 μg·g−1,平均为0.06 μg·g−1,其浓度的分布特征表现为涠洲岛近岸区域、大风江口和南流江口外海域较高,而钦州和北海近岸区域较低。Pb的浓度范围为12.1—26.7 μg·g−1,平均为18.9 μg·g−1,其浓度的分布表现为外海区域高于近岸区域。As、Cu和Zn浓度的分布趋势相似,As的浓度范围为0.39—9.21 μg·g−1,平均为3.73 μg·g−1;Cu的浓度范围为3.59—16.90 μg·g−1,平均为11.16 μg·g−1;Zn的浓度范围为ND—62.3 μg·g−1,平均为27.8 μg·g−1。As、Cu和Zn浓度的分布呈现北部湾西部(钦州、防城港近岸区域)和涠洲岛近岸区域较高,而东部海域(北海近岸区域)的浓度较低。北部湾重金属分布特征的差异,表明不同重金属间的来源可能不同。
表 3 北部湾表层沉积物中重金属的监测结果及与其他区域对比(μg·g-1)Table 3. The results of measured metals values in the surface sediments of Beibu Gulf and comparison with other regins数据统计Data statistics Hg As Cu Zn Pb Cd 参考文献 Reference 最小值 Minimum value 0.023 0.39 3.59 ND 12.1 0.04 本研究This study 最大值 Maximum value 0.037 9.21 16.90 62.3 26.7 0.09 平均值 Mean value 0.030 3.73 11.16 27.8 18.9 0.06 标准偏差 Standard deviation 0.005 3.40 4.74 25.4 4.6 0.02 Ⅰ类沉积物/个Class I 17 17 17 17 17 17 湛江湾 Zhanjiang Bay 18.7 73.60 43.89 0.15 [10] 厦门湾 Xiamen Bay 44.0 139.0 54.0 0.33 [19] 广东近岸 Coast of Guangdong Province 0.13 20.83 43.83 139.93 44.29 0.38 [20] 珠江口 Pearl River Estuary 348.0 383.4 102.6 1.72 [21] 北部湾 Beibu Gulf(1998年) 0.03 1.74 1.7 19.9 1.26 0.05 [22] 海南岛北部 Northern Hainan Island 0.02 8.40 8.32 35.87 18.77 0.06 [6] 注:ND为未检出. 与其他区域对比(表3),北部湾重金属含量明显低于厦门湾[19]、广东近岸[20]和珠江口[21]区域,与海南岛近岸浓度相当[6],但明显高于20世纪90年代时期北部湾沉积物的浓度[22],表明近些年来,北部湾沉积物重金属呈现一定程度富集。
2.2 重金属的来源与主控因素分析
沉积物中重金属含量受环境背景、生物过程、海洋物理过程以及人类活动等多方面的影响。此外,TOC主要为沉积物中有机质,其对重金属具有极强的吸附和络合作用[23-24]。因此,在讨论沉积物中重金属潜在来源时,常用利用TOC含量通过与重金属浓度的相关性分析,可对它们的来源进行初步判断[3,18,23]。沉积物中Cu和Zn的含量与TOC含量呈显著正相关性(表4),表明Cu和Zn在沉积物中的富集受到TOC含量的影响。Cu和As、Cu和Zn、Pb和Zn、Pb和Cd之间呈显著正相关性(表4),表明这些元素之间具有同源性;而Hg与其他元素均无相关性,说明Hg与其他重金属的来源方式可能不同。
表 4 北部湾表层沉积物中重金属和TOC 相关性分析Table 4. Correlation analysis of heavy metals and TOC in surface sediments of Beibu GulfTOC Hg As Cu Zn Pb Cd TOC 1 Hg −0.255 1 As 0.159 0.394 1 Cu 0.706** 0.183 0.532* 1 Zn 0.574* 0.086 0.327 0.792** 1 Pb 0.445 −0.018 0.000 0.397 0.573* 1 Cd −0.081 0.104 −0.019 0.222 0.367 0.547* 1 注:*在0.05水平上显著相关;**在0.01水平上显著相关. 为进一步了解重金属的潜在来源及主控因素,对沉积物中重金属含量进行主成份分析,结果如表5所示,当特征值大于1时,可提取3个成份,可分别解释总因子的43.54%、21.23%和18.66%,累积贡献率为83.43%。在成份1中,TOC、Zn、Cu和Pb具有很高载荷,这些重金属元素组合的高值区主要分布在钦州、防城港和涠洲岛近岸区域,表明这些金属元素在沉积物中的富集受到沉积物中有机质含量的影响。Zn、Cu和Pb主要来源于交通运输和工业生产[9]。钦州和防城港是北部湾沿海主要的工业活动区域,表明这些元素来源可能受到近海工业活动的影响。成份2中,Hg和As具有较高的载荷。As的富集受到低温热液成矿的影响,主要来源于农药残留、网箱养殖和工业生产[6,9]。Hg主要来源于石化产品、金属冶炼和煤炭燃烧[9]。As含量的高值主要分布于钦州和防城港近岸区域,其来源仍为近海人类活动为主;而外海较远区域As浓度的高值可能受控于自然地质背景因素,或于外海物质来源有关[9]。成份3仅Cd具有高载荷,其主要用于杀虫剂、化工业、电镀业等,通过河流排污入海并富集于沉积物中[6]。Cd浓度的高值主要分布在大风江口和南流江口外海域,反映了北部湾城市发展进程导致的区域污染差异性影响。
表 5 北部湾表层沉积物中重金属和TOC 主成份分析Table 5. Principal component analysis of heavy metals and TOC in surface sediments of Beibu Gulf元素Element 因子载荷 Factor load 成分1 成分2 成分3 TOC 0.720 −0.272 −0.557 Hg 0.133 0.775 0.417 As 0.458 0.737 −0.140 Zn 0.902 −0.038 0.015 Cu 0.909 0.196 −0.204 Cd 0.421 −0.229 0.798 Pb 0.697 −0.420 0.353 特征值 3.047 1.486 1.306 贡献率/ % 43.54 21.23 18.66 累积贡献率/% 43.54 64.77 83.43 2.3 重金属污染评价
对北部湾沉积物中重金属含量进行单因子分析,结果显示,所有站位的重金属污染因子均小于1,其含量低于Ⅰ类沉积物标准,污染程度低。北部湾沉积物中重金属单因子污染影响程度如表6所示,依次为Cu>Pb>As>Zn>Hg>Cd。
表 6 北部湾沉积物中重金属污染指数和潜在生态风险评价Table 6. Contaminant index and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in the sediments of Beibu Gulf元素Element Cif Eir 最小值Minimum 最大值Maximum 平均值Mean 最小值Minimum 最大值Maximum 平均值Mean Hg 0.100 0.205 0.150 27.59 56.55 41.31 As 0.020 0.721 0.290 0.50 18.47 7.43 Zn 0.000 0.415 0.240 0 0.82 0.47 Cu 0.103 0.837 0.401 1.14 9.27 4.44 Cd 0.080 0.180 0.121 13.33 30.00 20.17 Pb 0.202 0.445 0.305 2.09 4.62 3.17 Cd 2.25 7.13 4.45 RI 54.71 105.12 76.99 各重金属潜在生态风险系数(
Eir 综上评价,尽管北部湾沉积物中重金属处于低程度污染和底潜在生态危害风险,但随着北部湾经济区城市化、工业化的不断发展,局部海域污染程度和潜在生态风险程度处于较高水平,仍需警惕。
3. 结论 (Conclusion)
(1)北部湾沉积物中不同重金属的分布特征差异明显,其中As、Cu、Hg和Zn的分布总体呈现西部和涠洲岛近岸海域高于东部海域,Cd浓度的高值主要分布在涠洲岛近岸区域、大风江口和南流江口外海域,Pb浓度的分布表现为外海区域高于近岸区域,表明北部湾重金属的来源可能存在差异。
(2)与其他区域相比,北部湾沉积物中重金属含量处于较低水平,但与历史数据相比呈现增长趋势,表现一定程度的富集。
(3)Zn、Cu、Pb、Hg和As的来源主要受到近海人类活动的影响,而Cd反映了北部湾城市发展进程导致的区域污染差异性影响。
(3)北部湾沉积物重金属的污染评价显示,局部海域污染程度和潜在生态风险程度处于较高水平,重金属的污染仍需警惕。
-
表 1 国家海洋沉积物重金属含量标准值
Table 1. National standard values of heavy metals in marine sediments
指标Index 海洋沉积物质量标准值/(μg·g−1)Standard value of marine sediment Cu Hg Pb Zn Cd As Ⅰ类Class I 35 0.2 60 150 0.5 20 Ⅱ类Class Ⅱ 100 0.5 130 350 1.5 65 表 2 重金属污染程度及潜在生态风险等级
Table 2. Contaminant grades and potential ecological risk levels of heavy metals
Pi 重金属总体污染程度Overall pollution level Eir 单个重金属潜在生态危害程度Potential ecological hazard of single metal RI 重金属总体潜在生态危害程度Overall potential ecological hazard of metals <8 低度污染 <40 低危害 <150 低危害 8—16 中等污染 40—80 中等危害 150—300 中等危害 16—32 重污染 80—160 较重危害 300—600 重危害 ≥32 严重污染 160—320 重危害 ≥600 严重危害 — — >320 严重危害 — — 表 3 北部湾表层沉积物中重金属的监测结果及与其他区域对比(μg·g-1)
Table 3. The results of measured metals values in the surface sediments of Beibu Gulf and comparison with other regins
数据统计Data statistics Hg As Cu Zn Pb Cd 参考文献 Reference 最小值 Minimum value 0.023 0.39 3.59 ND 12.1 0.04 本研究This study 最大值 Maximum value 0.037 9.21 16.90 62.3 26.7 0.09 平均值 Mean value 0.030 3.73 11.16 27.8 18.9 0.06 标准偏差 Standard deviation 0.005 3.40 4.74 25.4 4.6 0.02 Ⅰ类沉积物/个Class I 17 17 17 17 17 17 湛江湾 Zhanjiang Bay 18.7 73.60 43.89 0.15 [10] 厦门湾 Xiamen Bay 44.0 139.0 54.0 0.33 [19] 广东近岸 Coast of Guangdong Province 0.13 20.83 43.83 139.93 44.29 0.38 [20] 珠江口 Pearl River Estuary 348.0 383.4 102.6 1.72 [21] 北部湾 Beibu Gulf(1998年) 0.03 1.74 1.7 19.9 1.26 0.05 [22] 海南岛北部 Northern Hainan Island 0.02 8.40 8.32 35.87 18.77 0.06 [6] 注:ND为未检出. 表 4 北部湾表层沉积物中重金属和TOC 相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation analysis of heavy metals and TOC in surface sediments of Beibu Gulf
TOC Hg As Cu Zn Pb Cd TOC 1 Hg −0.255 1 As 0.159 0.394 1 Cu 0.706** 0.183 0.532* 1 Zn 0.574* 0.086 0.327 0.792** 1 Pb 0.445 −0.018 0.000 0.397 0.573* 1 Cd −0.081 0.104 −0.019 0.222 0.367 0.547* 1 注:*在0.05水平上显著相关;**在0.01水平上显著相关. 表 5 北部湾表层沉积物中重金属和TOC 主成份分析
Table 5. Principal component analysis of heavy metals and TOC in surface sediments of Beibu Gulf
元素Element 因子载荷 Factor load 成分1 成分2 成分3 TOC 0.720 −0.272 −0.557 Hg 0.133 0.775 0.417 As 0.458 0.737 −0.140 Zn 0.902 −0.038 0.015 Cu 0.909 0.196 −0.204 Cd 0.421 −0.229 0.798 Pb 0.697 −0.420 0.353 特征值 3.047 1.486 1.306 贡献率/ % 43.54 21.23 18.66 累积贡献率/% 43.54 64.77 83.43 表 6 北部湾沉积物中重金属污染指数和潜在生态风险评价
Table 6. Contaminant index and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in the sediments of Beibu Gulf
元素Element Cif Eir 最小值Minimum 最大值Maximum 平均值Mean 最小值Minimum 最大值Maximum 平均值Mean Hg 0.100 0.205 0.150 27.59 56.55 41.31 As 0.020 0.721 0.290 0.50 18.47 7.43 Zn 0.000 0.415 0.240 0 0.82 0.47 Cu 0.103 0.837 0.401 1.14 9.27 4.44 Cd 0.080 0.180 0.121 13.33 30.00 20.17 Pb 0.202 0.445 0.305 2.09 4.62 3.17 Cd 2.25 7.13 4.45 RI 54.71 105.12 76.99 -
[1] ISLAM M S, AHMED M K, RAKNUZZAMAN M, et al. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2015, 48: 282-291. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.016 [2] CHEN L, ZHOU S L, WU S H, et al. Concentration, fluxes, risks, and sources of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in the Lihe River watershed, Taihu region, Eastern China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 255: 113301. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113301 [3] LAO Q B, SU Q Z, LIU G Q, et al. Spatial distribution of and historical changes in heavy metals in the surface seawater and sediments of the Beibu Gulf, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 146: 427-434. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.06.080 [4] 王萧, 张文思, 迟光希, 等. 辽东湾及其附近海域重金属污染研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(10): 2317-2326. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112606 WANG X, ZHANG W S, CHI G X, et al. The heavy metals contamination in Liaodong Bay and its adjacent waters [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(10): 2317-2326(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112606
[5] ARIKIBE J E, PRASAD S. Determination and comparison of selected heavy metal concentrations in seawater and sediment samples in the coastal area of Suva, Fiji [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 157: 111157. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111157 [6] 曾维特, 杨永鹏, 张东强, 等. 海南岛北部海湾沉积物重金属来源、分布主控因素及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(3): 1085-1094. ZENG W T, YANG Y P, ZHANG D Q, et al. Sources, distribution of main controlling factors, and potential ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in the surface sediment of Hainan island north bay, South China [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(3): 1085-1094(in Chinese).
[7] 张伟, 张洪, 单保庆. 北运河源头区沙河水库沉积物重金属污染特征研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(12): 4284-4290. ZHANG W, ZHANG H, SHAN B Q. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in the sediments from Shahe reservoir, the upper reach of the north canal river [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(12): 4284-4290(in Chinese).
[8] LI S Y, ZHANG Q F. Risk assessment and seasonal variations of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the Upper Han River, China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1/2/3): 1051-1058. [9] 陈思杨, 宋琍琍, 刘希真, 等. 浙江典型海湾潮间带沉积物污染及生态风险评价 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(4): 1771-1781. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.045 CHEN S Y, SONG L L, LIU X Z, et al. Evaluation on sediment pollution and potential ecological risks in the intertidal zone of typical bays in Zhejiang Province [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(4): 1771-1781(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.04.045
[10] CHEN F J, LIN J, QIAN B H, et al. Geochemical assessment and spatial analysis of heavy metals in the surface sediments in the eastern beibu gulf: A reflection on the industrial development of the South China Coast [J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(3): 496. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15030496 [11] LIU G Q, LAO Q B, SU Q Z, et al. Spatial and seasonal characteristics of dissolved heavy metals in the aquaculture areas of Beibu Gulf, South China [J]. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment:an International Journal, 2020, 26(7): 1957-1969. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2019.1629273 [12] 付文超, 孟范平, 王志峰, 等. 北部湾潮间带沉积物和双壳类动物中的重金属: 污染特征与生物积累 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(5): 1401-1409. FU W C, MENG F P, WANG Z F, et al. Heavy metals in the intertidal sediments and two marine bivalves along the Beibu Bay: Contamination status and bioaccumulation [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(5): 1401-1409(in Chinese).
[13] YANG J C, WANG W G, ZHAO M W, et al. Spatial distribution and historical trends of heavy metals in the sediments of petroleum producing regions of the Beibu Gulf, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 91(1): 87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.12.023 [14] 劳齐斌, 刘国强, 申友利, 等. 北部湾入海河流营养盐的分布特征及入海通量研究 [J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(12): 93-100. LAO Q B, LIU G Q, SHEN Y L, et al. Distribution characteristics and fluxes of nutrients in the rivers of the Beibu Gulf [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(12): 93-100(in Chinese).
[15] GAN H Y, LIN J Q, LIANG K, et al. Selected trace metals (As, Cd and Hg) distribution and contamination in the coastal wetland sediment of the northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 66(1/2): 252-258. [16] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [17] 罗松英, 邢雯淋, 梁绮霞, 等. 湛江湾红树林湿地表层沉积物重金属形态特征、生态风险评价及来源分析 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(2): 348-358. LUO S Y, XING W L, LIANG Q X, et al. Speciation, ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in the surface sediments of mangrove wetland in Zhanjiang bay [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(2): 348-358(in Chinese).
[18] 蓝先洪, 孟祥君, 梅西, 等. 辽东湾表层沉积物的重金属污染特征与质量评价 [J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(6): 60-73. LAN X H, MENG X J, MEI X, et al. Pollution characteristics and quality assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Liaodong Bay [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 40(6): 60-73(in Chinese).
[19] ZHANG L P, YE X, FENG H, et al. Heavy metal contamination in western Xiamen Bay sediments and its vicinity, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2007, 54(7): 974-982. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.02.010 [20] ZHAO G M, LU Q Y, YE S Y, et al. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of the west Guangdong coastal region, China [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2016, 108(1/2): 268-274. [21] NIU H Y, DENG W J, WU Q H, et al. Potential toxic risk of heavy metals from sediment of the Pearl River in South China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 21(8): 1053-1058. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62381-5 [22] LIAN X, WANG Y, CHEN Q. Assessment on heavy metals in seawater, surface sediments and organisms at Guangxi inshore [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2001, 20(2): 59-62. [23] 唐得昊, 刘兴健, 邹欣庆. 海湾表层沉积物重金属污染与潜在生态危害评价: 以深圳湾为例 [J]. 环境化学, 2014, 33(8): 1294-1300. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.08.002 TANG D H, LIU X J, ZOU X Q. Heavy metals pollution and their potential ecological risk assessment in the surface sediment from Shenzhen Bay [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(8): 1294-1300(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2014.08.002
[24] 李庆召, 李国新, 罗专溪, 等. 厦门湾海域表层沉积物重金属和多环芳烃污染特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境化学, 2009, 28(6): 869-875. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2009.06.019 LI Q Z, LI G X, LUO Z X, et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs) in sediment from Xiamen bay [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2009, 28(6): 869-875(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2009.06.019
-




 下载:
下载:







































