-
矿业是经济和社会发展的重要支柱产业之一。随着我国采矿业的迅速发展,矿业活动导致的环境污染问题日益突出。矿山开采过程中产生的大量酸性矿山废水(acid mine drainage, AMD)未经处理直接排放进入河流、湖泊等水体会破坏水生生态系统,引起水体恶化、桥梁船舶和堤坝的腐蚀、微生物正常繁衍受损等问题[1]。除此之外,AMD含有的重金属离子会污染土壤,影响植被生长,长期使用酸性废水灌溉会导致土壤酸化,从而致使粮食减产。如果AMD处理不当会对自然环境以及人类社会产生巨大威胁[2]。因此,如何有效地处理AMD,防止其进入自然环境中产生污染是当前研究的热点之一。目前,处理AMD的常用方法有硫化法、化学中和法、微生物法等[3]。在使用硫化法时,AMD的pH值不会成为限制因素,产生的污染物呈固态,易去除,但使用硫化剂常常会产生对人体有害的H2S气体,且运行成本相对较高;化学中和法具有工艺简单、易操作、运行成本不高等优点,但在处理过程中会产生大量污泥和高浓度废水,去除效率低且极易对环境造成二次污染;相较于国外,国内微生物法起步较晚[2],但与其他AMD处理方法相比,微生物法的成本较低,适用范围较广,可以对AMD中的重金属或其他污染物进行有效的处理[4],但其处理效果受季节、气温、光照等自然因素影响较大。以上这些处理方法虽然处理效果好,但由于投资大、成本高、稳定性差、可能会产生二次污染等原因限制了其推广应用。生物炭修复技术具有低成本、高效率、环境友好等优点,近年来在环境修复领域受到广泛关注。
生物炭是生物质在缺氧或限氧条件下,经过高温慢热解或水热碳化制备的一类难熔、稳定、芳香化程度高、表面含氧官能团和碳含量丰富的固态物质[5-9]。作为一种新型的碳材料,生物炭具有高度的芳香性和多孔结构,其稳定性好、吸附能力强,已被广泛应用于环境修复和土壤改良[10-14]。目前,国内对生物炭在水环境中重金属离子的吸附方面已有大量研究报道,且发现生物炭对于废水中的重金属离子具有良好的吸附效果,但生物炭吸附去除AMD中的重金属离子方面则鲜有报道。如曹玮等[15]利用磁性谷壳生物炭吸附废水中的Cd2+和Zn2+,发现在磁性谷壳生物炭的吸附下,Zn2+和Cd2+的去除率分别达到了60.4%和61.1%。刘秀等[16]使用笼芯陶黑碳微珠生物炭去除模拟废水中的Cd2+,结果表明在适宜的条件下添加笼芯陶黑碳微珠生物炭有利于Cd2+的吸附去除。魏啸楠等[17]使用磷酸改性生物炭负载硫化锰去除废水中的Cd2+,发现在偏酸性条件下去除Cd2+的效果显著。在国外,已有利用生物炭处理AMD的相关研究报道。Mohapatra等[18]发现改性玉米芯生物炭可以较好地吸附铬铁矿废水和表土堆放场的Cd2+,当pH≤3且有Fe和S共存时,改性玉米芯生物炭的吸附效果更为显著。Giachini等[19]研究发现,与原始AMD相比,富含牛粪的生物炭可促进41%的硫酸盐还原,与其他处理(AMD沉积物、污泥)相比,硫酸盐减少了39%。Oh等[20]使用家禽粪便制备的生物炭处理韩国铜废弃矿产生的AMD,结果表明AMD内含有的高浓度Fe、Al、Mn、Cu、As被完全去除,Zn、Mn、SO42−的去除率分别达到了99%、61%和31%。Liatsou等[21]利用硫尿嘧啶改性前后的生物炭纤维对Cu2+的吸附,实验结果显示在一定酸性范围内,该改性生物炭纤维对当地铜矿排水样品中的Cu2+的去除率达100%。Mosley等[22]的实验结果表明,用芦苇制成的生物炭具有中和pH和从AMD中去除金属的能力。生物炭与酸性废水接触,渗滤液中的pH值得到中和,重金属含量也降低了97%,而生物炭渗滤液的pH值维持在6.5以上。综上可见,生物炭技术已逐渐被用于处理AMD,因此将其用于AMD的治理具有非常重要的意义。
由于AMD的pH值较低且成分复杂,其中含有不同的重金属离子,因此不同属性生物炭对AMD的吸附效果差异较大。目前已有许多研究者在实验室内进行了AMD的模拟吸附实验,由于不同材料、不同条件下制备的生物炭,其吸附特性有一定的差异,且不同类型的生物炭对于不同重金属离子的吸附能力也各相同。此外,尽管生物炭可以吸附水中的重金属离子,但现有文献中关于生物炭对AMD中重金属离子的吸附机理尚不清楚,许多吸附机制都可能在生物炭从水溶液中去除重金属的过程中发挥作用,如沉淀、络合、离子交换、静电相互作用和物理吸附等[23]。因此,在多种重金属离子共存的环境条件下,生物炭对多种重金属的吸附机理也有待进一步的研究。
基于以上原因,本文在对AMD的特征及其常用处理方法进行概述的基础上,介绍了生物炭的常规制备方法及理化性质表征,对生物炭处理AMD的影响因素、处理效果及其机理进行了综述,最后对生物炭技术在处理AMD方面的研究与应用提出了展望。
-
AMD是由于硫化矿物长期暴露于地表,与水、大气以及微生物相互作用形成的一种pH值较低,并含有高浓度金属离子的矿业废水[24]。在挖掘煤矿和各种有色金属矿以及废矿石堆放过程中,与矿层伴生的硫铁矿会暴露于空气,并通过地表径流渗透进入地下水或地表水中,经一系列化学与生物氧化过程,使得近中性的地下水转变为低pH、高Fe2+、Fe3+和SO42−,且多种重金属离子(Cd2+、Pb2+、Cu2+、Zn2+、As5+等)并存的AMD[25]。某些微生物也参与了AMD的形成,如嗜酸氧化硫硫杆菌可以将硫或硫化物氧化为SO42−,主要反应为:硫化物在O2的参与下,形成H2SO4和FeSO4:
Fe2+在游离氧或细菌的存在下,氧化成Fe3+:
由于Fe3+具有强氧化性,因此Fe3+对硫化物的影响比O2更为重要[26]。AMD的pH值一般为4.6—6.5,某些pH值可低至2.5—3.0,甚至达到2.0[3],这是因为在采矿过程中黄铁矿暴露在O2和水中时,会被氧化释放出Fe2+、SO42−和H+,反应方程式如下:
在O2充足的情况下,Fe2+会被进一步氧化成Fe3+,方程式如下:
Fe3+会以Fe(OH)3的形式沉淀,或者与黄铁矿直接反应产生更多的Fe2+和H+,方程式如下:
采矿会增加硫矿石在空气中暴露的机会,大量产生的酸性物质超出了岩石和水源的自然缓冲能力,因此导致了周围环境低pH的情况[27]。
AMD中有多种组分,其中包括多种重金属如Fe、Mn、Zn、Cu、Pb等,每升水中各离子含量不等。AMD的水量、水质随外界季节雨水变化以及开采情况不同而变化,因此难以对AMD进行有效控制。此外,AMD的性质还受到温度等外界因素的影响。AMD不仅不便于直接处理、回用,且直接排放会导致水体pH下降,破坏水体生态环境。长时间使用AMD浇灌会导致土壤酸化,严重影响农作物产量、食品安全及人体健康[28]。AMD还具有腐蚀性,它与含有不同类型矿物的岩石相互作用,容易引起有毒有害金属的溶解。产生的AMD提高了受纳地表水中溶解金属的含量,并对河流、湖泊等生态系统产生负面影响[29]。
-
(1)微生物燃料电池技术
微生物燃料电池(microbial fuel cell,MFC)技术的工作原理是电化学氧化还原过程。MFC是用微生物作为催化剂氧化有机物及无机物,转化化学能并产生电能的装置[30]。丁伟等[31]构建运行了微生物燃料电池处理模拟的AMD,实验结果显示,5 mg·L−1重金属离子(Cu2+、Zn2+、Ni2+、Cr6+)浓度对MFC出水pH无影响,COD去除率下降,SO42−去除率较低,MFC产电量也会逐渐降低。FADZLI等[32]构建的微生物燃料电池运行30 d后发现,Pb2+、Cd2+和Cr3+的修复效率分别为90.14%、88.00%和90.34%。尽管生物处理高浓度有机废水的治理技术有原料来源广且温和高效等优点,但是生物处理技术也有能耗大、运行费用高、输出电能低限制其工业化发展等缺点,且该方法对所需的电极材料,质子交换膜等限制较大。
(2)物理化学法
物理化学法是在污染组分形态不变时,浓缩、吸附、分离重金属离子的方法。常用的方法有离子交换法、膜分离技术、吸附法等。其中离子交换法是用树脂本身的氨基、羟基等活性基团与重金属离子进行螯合、交换反应,从而去除废水中重金属离子的方法。Fu等[33]制备的树脂用于合成金属溶液和铜矿酸性废水中,批量吸附试验结果表明,所制备的树脂在pH范围(1.0—6.0)内具有良好的吸附能力,重复利用性强且吸附容量大。使用真实AMD的固定床柱试验的穿透曲线表明该树脂能够容易地从AMD溶液中分离有毒重金属离子。离子交换法的选择性好、回收率高、装置简单,但也容易产生大量再生废液,且树脂需要经常更换,普遍适用性较差。膜分离法则是利用反渗透膜和电渗析等膜两侧产生的压力差及电位差为推动力,选择性地分离重金属离子。该方法的离子去除率高,容易操作和控制,温度控制灵活,但膜成本和运行费用较高,不适合处理量大的废水[34]。隋岩峰等[35]制备的反渗透装置对SO42−和PO43−的去除率都高于98%,选矿药剂的去除率在95%以上,F−的去除率略低。由此可知物理化学法对离子的去除率很高,但是该法对吸附材料以及膜的性能要求较高,而且运行成本偏高并且适用范围较窄。
(3)微生物法
微生物技术是广泛应用于AMD处理的方法之一。微生物法主要是通过微生物在适合的环境下将Fe2+氧化,并利用处理过程中产生的能量进行自身繁殖的特性,向AMD中加入适量的微生物用于氧化处理。同时,投加一定的中和剂及沉淀剂使金属离子沉淀,通过过滤最终达到废水处理的目的[25]。戴祥昕等[36]将SBR生物法应用于源头处理,阻断含硫矿物的风化,其中以乙醇和麦芽糊精做碳源时的SBR处理后的AMD水质符合《地下水质量标准GB/T 14848-93》中Ⅰ类水的pH标准(6.5—8.5)。外加碳源由强到弱依次为乙醇、麦芽糊精、乳酸钠和城市生活污水处理厂的污泥,对SO42−的去除率分别为91.9%、86.9%、83.4%和65.0%。Sahinkaya等[37]用垃圾填埋场渗滤液作为SRB的碳源处理AMD,结果发现可溶性金属去除率为82%—99.9%,总金属去除率为80%—99.9%。微生物法简单易行、成本低廉,不仅能去除金属离子,对N、P等营养物质也有良好的去除效果,无二次污染问题,但是,微生物法也存在对pH值、温度等条件要求较高等问题。
(4)湿地法
人工湿地是由基质、植物、微生物三者共同组成一个生态系统,通过物理、化学和生物作用将废水中的重金属从水体去除。其中,物理作用主要是利用由土壤、砾石、细沙等构成的基质层过滤和截留湿地的酸性水,并沉积悬浮物。化学作用主要包括化学沉淀、化学吸附和离子交换等,并在一系列复杂反应后将可溶性化合物转化为不溶状态,并将其分离出水体。生物作用是利用植物吸收、富集水中重金属的过程。龙中等[38]设计的多级复氧反应—垂直流人工湿地系统用于治理废弃石硐煤矿废水,研究显示,沉淀池中SS浓度明显下降,进出水的pH值由5.60—6.58上升到6.37—7.45时,Fe的去除率达到99.10%,Mn去除效率为69.80%—100%,Cu、Zn、Cd、As、Pb、Cr的去除效果也较为良好,但对SO42−的去除率则相对较低,仅为3.06%。湿地法处理AMD有运行成本低且缓冲性能强的优势,但占地面积大,对强酸性废水的适应性差,单独使用时常导致出水pH值未达标[39]。该方法对低浓度废水有明显的去除效果,但不能处理高浓度低pH废水,且对SO42−去除效果不佳。
(5)电化学技术
电化学法是通过电解废水,使得水中的重金属在阴极得到电子被还原,从而发生沉淀得以去除的过程。废水处理中最常用的电化学方法。主要是电解法、电絮凝法、电浮选法等。蒋文瑞等[40]的研究表明,黄铁矿表面氧化过程中会形成大量的SO42−,通过电化学技术探究SO42−对黄铁矿表面电化学氧化速率的影响,发现SO42−的引入及其浓度的升高并不会改变黄铁矿表面电化学氧化机理,但是其浓度的升高提高了电子转移电阻从而降低其氧化速率。当SO42−浓度为0.25 、0.50、0.75、1 mol·L−1时,黄铁矿的表面氧化速率分别约为空白组的52%、43%、28%和26%,即浓度越高黄铁矿表面氧化速率越慢。虽然电化学技术是一种较为清洁、效率高、占地少且不会发生二次污染的处理方式,但是该法存在投资大、电极材料寿命短等难以突破的问题,且耗能高,常用于处理中、小规模的电镀废水[34]。
(6)化学中和法
化学中和法是向AMD中投加适合的化学物质,提升水体pH值,使SO42−和金属离子反应并产生沉淀,进而去除重金属的方法。国外的AMD治理系统通常是使用包括石灰石在内的6种不同的化学药剂中和废水[41]。化学中和法虽然应用最为广泛,但生成的CaSO4较多,易造成二次污染。且硫化剂有毒,在反应时可能会有部分硫化物不能去除,残留在水中对水体再次造成污染。中和法对金属矿区已形成的废水有显著的处理效果,但未抑制产酸细菌的生长,矿山生态环境未得到根本性修复[42]。
(7)源头治理技术
源头控制的基本原理是控制铁氧化,且有中和法、杀菌法和表面钝化法等多种源头控制技术[43]。Yang等[44]研究发现生物炭可以促进钝化层的形成而抑制黄铜矿的生物溶解。该法处理既高效又经济,且不会对环境产生二次伤害。可源头治理虽然理论上先进可行,但在实际工程应用中也存在技术不够成熟且成本过高等问题。
综上,微生物氧化法、吸附法和人工湿地方法等新技术已逐渐应用于AMD的处理,但它们存在处理浓度低、工艺复杂、受环境条件限制等困难[45]。常用的处理方法及其优缺点如表1和图1所示。相比之下,生物炭技术成本较低、制备简便且原材料来源广泛,能对AMD中的金属离子进行有效吸附等优点。生物炭技术作为处理AMD的一个潜在的方法,近年来越来越受到国内外学者的广泛关注。
-
生物质碳化技术是指在缺氧或微氧条件下,加热生物质原料使其内部分子分解,并生成生物炭、生物油和不可冷凝气体产物的过程[46]。在此过程中,原料中的非碳物质逐渐去除,生物炭表面出现了以固定碳为基础的孔隙结构[47]。生物炭的制备方法通常有水热碳化技术和热解法(图2)。水热碳化又可以分为低温水热碳化法(低于30 ℃)和高温水热碳化法(300—800 ℃)[48]。热解法是在高温和限氧条件下,生物质被分解,且热解过程受操作温度、升温速率和停留时间的影响,产物的组成和理化性质随之改变[49]。热解法又可分为慢速热解、快速裂解、热解气化和微波裂解。①慢速热解的加热速率低于1 K·s−1,反应温度一般低于700 ℃。②快速热裂解指生物质在特定条件下,快速加热至较高温度,导致大分子分解,生成小分子气体以及可凝性挥发分和少量焦炭产物[50]。③热解气化条件温度大于700 ℃,气体为主要产物。④微波热裂解是采用微波对生物质加热,可用于生产大颗粒生物炭[51]。Oginni等[52]的研究结果表明,较高的碳化温度可改变生物炭的元素组成、pH值、电导率、比表面积、孔隙度和表面官能团含量。生物炭存在多级孔隙结构,且比表面积大、芳香程度高,含有羧基、酸酐和酚羟基等多种官能团[53-54]。
-
(1)物理性质
生物炭的基本物理性质包括比表面积、元素组成、孔隙率、总有机碳含量等[55]。其中生物质类型和碳化条件对生物炭的理化性质有直接影响。随着热解温度的提升,生物炭的孔隙结构越发达,孔隙排列也随之变得密集有序[56]。研究表明,在一定温度范围内,热解温度和生物炭的比表面积成正比,如李敏等[57]的研究发现,热解温度由400 ℃升高至600 ℃,小麦生物炭孔容积由小变大,均匀分布的表面孔隙形成大量微孔。肖琴等[58]研究发现,动植物生物炭碳化温度(≥300 ℃)增加后形成的比表面积和孔体积更大。但当温度达到一定程度后,生物炭的比表面积下降,如高凯芳等[59]研究发现,当制备稻秆生物炭的温度由初始的300 ℃升高时,生物炭的比表面积从6.11 m2·g−1开始快速增加,最终在700 ℃热解温度下表现下降趋势。此外,生物炭的pH、碳含量、碳氢比、氧碳比、灰分含量等都能直接影响生物炭的理化性质。
(2)化学性质
芳香烃和单质碳或具有石墨结构的碳是构成生物炭的主要因素,主要有H、O、N、C等元素。生物炭的羟基、羧基和苯环等主要官能团是生物炭具备强大吸附能力和较大离子交换量的主要原因[60]。生物炭的元素组成与碳化条件密切相关。在相同碳化温度下,即使生物炭的制备原料不同,但其表面含氧官能团种类和总量却类似,pH值和吸附能力存在较大差异[61]。刘青松等[62]发现对于玉米秸秆生物炭,热解温度升高则碳含量逐渐降低、氧含量逐渐增加。范士锁等[63]发现茶渣生物炭随着热解温度的增大,其亲水性和极性变差,芳香性增强。孙涛等[64]发现当碳化温度升高和碳化时间延长时,生物炭中有机碳含量和阳离子交换量减少,灰分和比表面积则缓缓增大。
生物炭的氧化硅成分会导致其灰分含量存在差异,而灰分则会影响生物炭的疏水性及化学持留性[65]。热解温度对生物炭的灰分含量有影响,尹云锋等[66]用阔叶树及针叶林的凋落物制备生成生物炭,发现该生物炭的含碳量、碳氮比以及灰分与热解温度基本呈正比。生物炭的灰分含量还取决于原料自身的灰分含量。胡华英等[67]在生物炭对杉木人工林土壤磷素吸附特性的影响中发现制备生物炭的原料不同,灰分含量也不相同。
生物炭一般呈碱性,随热解温度的升高生物炭的pH也有明显的升高。周强等[68]的研究结果显示,热解温度由250 ℃至350 ℃时,生物炭pH从6.96升高到9.64;当热解温度从350 ℃升高到650 ℃时,生物炭pH值从9.64升高到10.14。在特定环境中生物炭会氧化,此时生物炭表面形成了大量酸性基团,使得生物炭的pH降低。徐佳等[69]发现慢速热裂解条件存在差异时,制备的棉花秸秆生物炭的理化性质有很大不同,且当碳化温度增大时,生物炭的pH也渐渐升高。
综上,碳化温度、原料种类以及碳化方式等的差异性均会影响到生物炭的理化性质。生物质碳化之后,基本保留了生物质的孔隙结构,较大的孔隙度和比表面积等。
-
AMD的pH值较低,波动范围在2.0—6.5之间。针对不同的pH条件,生物炭对AMD的处理效果也有所不同。Meng等[70]利用猪粪生物炭研究去除废水中Cu2+的变化规律,结果显示随着pH值升高,猪粪生物炭对Cu2+吸附能力增大,在pH值为5.0时达到最大,然而在pH值为5.0—6.0时有所减小,在pH值低于3.0时,吸附能力最小。Wang等[71]通过黏土-生物炭复合吸附剂对AMD吸附能力进行研究,发现pH值增大(3.5—5.0)时,生物炭能较好的吸附Cu2+。当pH值为5.0—6.0时,吸附容量减少。Yoon等[72]研究在不同溶液pH的影响下,造纸厂污泥衍生生物炭在二元吸附体系中对As5+和Cd2+的吸附效果,结果发现随着pH值从8.6减小至2.4,Cd2+的吸附量快速减少,由31.2 mg·g−1降低到1.1 mg·g−1。同时发现在高pH条件下,As5+的去除略有增强,得出在单一吸附体系中,由于负电荷As5+与OH−之间的静电排斥,一般会降低As5+的吸附。而在二元吸附体系的相反趋势可归因于As5+和Cd2+之间可能的相互作用。
反应的环境温度也会对吸附过程产生影响。Pan等[73]研究了AMD中Cr3+吸附,结果表明秸秆生物炭对重金属的吸附一般为吸热过程,并且温度升高,吸附能力随之增加。在矿山开采过程中产生的AMD里,生物炭虽然可以在最佳吸附温度下将其中的污染物质高效去除,但是过高的温度会加剧离子的热运动,从而导致生物炭解吸反而使去除率下降,例如刘延湘等[74]用花生壳生物炭研究温度对模拟酸性废水中重金属Cr6+和Cu2+的吸附影响,研究结果表明,Cr6+和Cu2+的最佳吸附温度分别为30 ℃和40 ℃,之后随着温度的进一步升高,生物炭出现了解吸现象,去除率反而下降。
-
当AMD中多种离子同时存在时,可能会发生竞争吸附,从而致使生物炭吸附效果减弱[75]。Yoon等[72]研究造纸厂污泥衍生生物炭在最终pH为7.2条件下共存离子对As5+和Cd2+去除效率的影响,研究发现PO43−共存对As5+的吸附有负面影响。随着Ni2+浓度从0.5 mmol·L−1增加到3.0 mmol·L−1,Cd2+的去除率明显降低,由于竞争吸附,去除率从95.8%下降到64.3%。Park等[76]研究胡椒茎生物炭对多种重金属的吸附,发现吸附量的大小顺序为:Pb>Cu>Cr>Zn>Cd。因此在多种离子共存的情况下,溶液中的其他离子会对目标离子的吸附产生影响。因此,将生物炭应用于AMD处理时,需要考虑不同离子之间的竞争关系,从而根据实际情况,筛选出效果最佳的生物炭。
-
生物炭一般呈碱性,且不同原材料和热解温度下生物炭理化性质也各不相同。生物炭的酸碱性、表面基团和比表面积等都会影响生物炭的吸附性能。静电作用下生物炭的表面酸碱性会影响重金属离子吸附,且重金属离子极易在其表面发生沉淀作用[77]。Mosley等[22]发现生物炭对AMD中重金属的处理能力与生物炭的理化性质有关。肖琴等[58]研究发现,生物炭的表面官能团会对其表面酸碱度有影响,从而影响其对重金属离子的吸附。由于制备原料和制备条件的不同,生物炭的表面官能团种类多,主要包括羟基、醛基、羧基、羰基等含氧官能团,这些官能团会增强吸附性能。杨选民等[78]研究发现,生物炭热解温度越高,其孔隙结构也会更加致密且均匀,且比表面积也逐渐提高,使生物炭的吸附性能大大提升。因此生物炭自身的理化性质也是处理酸性废水的一种影响因素。
-
衡量生物炭吸附过程的主要指标是其吸附能力和吸附速度。蒋艳艳等[79]利用生物炭研究废水中重金属离子的吸附性能,推测吸附速度决定了污水接触所需要的时间。丁文川等[80]在研究富磷污泥生物炭去除水中Pb2+的研究结果中发现,其去除率在开始90 min内基本呈直线上升趋势,最大达到94%;反应时间到达180 min时,去除率为96%,往后去除率变化未明显改变,这主要是因为随着吸附的不断进行,生物炭表面的吸附位点逐渐被占满最终达到吸附平衡。徐楠楠等[81]生物炭对Cd2+吸附可分为快反应和慢反应2个阶段,0—10 min为快反应阶段,吸附量达到饱和吸附量的75%以上,此后为慢反应阶段,40 min时,吸附量基本达到平衡。
-
在AMD中,重金属离子的初始浓度较高,此时生物炭的吸附效果最大,当重金属离子浓度减小时,吸附效果也随之减小,重金属离子初始浓度不同会导致生物炭吸附效果不尽相同。Zhang等[82]在24.85 ℃的条件下研究不同初始U6+浓度对吸附过程的影响,结果表明生物炭吸附能力随初始U6+浓度的增加而增加。AMD中除了含有大量的Fe2+、Fe3+、SO42−外,还存在一定浓度的其他重金属离子,比如Cu2+、Cd2+、Pb2+、Zn2+、As5+等。沈州等[83]研究生物炭对AMD中氨氮初始浓度的影响,发现氨氮初始浓度与生物炭的吸附量成正比。前人对于AMD中Cu2+的吸附也进行了相关研究。如郭海艳等[84]将蚯蚓粪便生物炭添加到被重金属污染的酸性废水中,研究Cu2+的初始浓度对生物炭吸附性能的影响,结果显示Cu2+初始浓度增加,蚯蚓粪便生物炭与Cu2+的吸附量呈正比,与去除率呈反比。
-
生物炭添加量是影响AMD中重金属吸附效果的关键因素。生物炭添加量低于最适的添加量会导致重金属离子吸附位点不足,从而导致重金属离子去除率不高,而超过最适添加量,生物炭可能会发生颗粒聚集导致生物炭吸附位点的利用率降低。郭海艳等[84]研究了蚯蚓粪便生物炭添加量对被重金属污染的酸性废水中Cu2+的吸附性能的影响,研究发现当生物炭添加量为0.2 g·L−1时,对Cu2+去除率仅为7.99%,当添加量增加至5 g·L−1时,去除率可达98.50%,进一步添加生物炭时去除率保持稳定,但生物炭颗粒会发生团聚沉降从而影响吸附能力。王重庆等[77]在生物炭吸附重金属离子的研究中发现随着生物炭添加量的增加,对重金属离子的吸附能力逐渐提升。但同时也发现生物炭增加量较大时,生物炭吸附位点的利用率随之降低。故而在使用生物炭处理AMD时,需要针对AMD中的重金属含量,对生物炭的添加量进行反复实验从而得到最适宜生物炭添加量,才能在实际使用时节省成本,达到经济效益和处理工艺的最佳结合。
-
制备生物炭的材料不同和制备时的温度不同,会使生物炭的理化性质有差异[85]。Tong等[86]发现对Cu2+的最大吸附量顺序为:花生秸秆生物炭>豆秸秆生物炭>菜籽秸秆生物炭。Bandara等[87]用禽鸟窝(PBC)、苜蓿苗(LBC)、紫云英苗(VBC)、油菜苗(CBC)、麦秸(WBC)和糖胶木(SBC)生物炭对AMD中Cd2+和Cu2+的浓度和去除率进行研究,研究发现对AMD中Cd2+的去除率依次为:PBC(>99%)>LBC(82%)>VBC(55%)>CBC(20%)>WBC(6.5%)>SBC(6%),Cu2+的去除率由高到低依次为:PBC(99.9%)>LBC(99.8%)>VBC(99.7%)>CBC(95.0%)>WBC(0.55%)>SBC(0.34%)。结果表明禽鸟垃圾衍生的生物炭对矿井水中的Cd2+和Cu2+的去除率最高。
戴静等[88]利用木屑、米糠、稻秆和玉米秸秆为原料在300、400、500、600、700 ℃热解温度下制得生物炭,研究其对Pb2+和Cr2+的吸附效果,结果表明稻秆生物炭(700 ℃)对Pb2+和Cr2+的吸附效果最好。Sheng等[89]研究了4种原料在3种热解温度(300、450和600 ℃)下制备生物炭对水中As5+和Pb2+的吸附能力,研究表明所有生物炭中,在相同条件下不同生物炭对砷和Pb2+的吸附能力不同。在其他生物炭中,松树源生物炭吸收的As5+比相同条件下制备的其他生物炭吸附的As5+多,且Pb2+的吸附量高于As5+。
Li等[90]通过研究不同原料在不同热解温度下制备的生物炭的理化性质,发现不同原料的碳氢比、碳氧比和碳氮比随着热解温度的增加逐渐降低,表面官能团的数量会随热解温度的升高而减少,在吸附过程中会导致重金属离子与官能团之间的吸附作用降低。张继义等[91]研究了在不同温度条件下制备的小麦秸秆生物炭对污水中Cu2+吸附性能,结果显示,碳化温度提升会使生物炭表面粗糙程度随之提高,生物炭对Cu2+的吸附量同时增加。即不同原材料和热解温度直接影响生物炭对重金属的吸附效果。
-
目前,已有许多关于利用生物炭进行环境污染治理方面的研究报道[92],如土壤修复[93-96]、水体和土壤中有机污染物和重金属的吸附[77,97]等。生物炭已被用于AMD的处理,其本身的碱性对AMD有缓冲作用,可使AMD的pH值上升,同时对AMD中的重金属离子也有良好的去除效果。Mosley等[22]制备生物炭处理AMD,实验结果表明,AMD的pH值提高并保持在6.5以上,且重金属吸附大于97%。Giachini等[19]和Yang等[44]的研究中发现添加生物炭后的AMD也表现出类似效果。Oh等[20]的实验中,家禽粪便生物炭去除了AMD中Fe、Al等高浓度的重金属,Zn的去除率更是高达99%。若掌握生物炭在AMD中的作用机理,生物炭对各类AMD的处理应用将进一步完善。
通常情况下,生物炭对水环境中重金属的吸附去除机制主要有:离子交换、络合反应、静电吸附作用、表面沉淀作用和物理吸附等[11-12,60,98-99]。其中,离子交换是在适宜的pH条件下,生物炭表面官能团与重金属离子发生作用;络合反应主要是生物炭的官能团与重金属离子发生吸附作用;静电吸附作用是表面带负电的生物炭与带正电的重金属离子产生吸附;表面沉淀是生物炭在吸附重金属的过程中,在其表面或溶液中形成固体;当金属离子扩散到生物炭表面孔隙中时,微孔填充物理吸附作用发生。
一般情况下,水环境中生物炭对重金属离子的吸附是多种吸附机制共同作用的结果。Yang等[44]的研究结果表明,生物炭的吸附消耗Fe3+,从而促进黄钾铁矾形成,抑制黄铜矿的生物溶解,从而抑制AMD的形成;莫官海等[100]也发现,加入生物炭后废水pH值均有所提升;朱墨染[101]的研究也表明生物炭可吸附水中的Fe3+,且随着溶液的pH的升高去除率也升高。Giachini等[19]直接用生物炭处理AMD,发现生物炭的初始pH值对废水酸碱度的中和至关重要,当pH值变化,水环境中可与金属络合的硫化物离子将会产生,对去除AMD中的微量元素有一定贡献,另外AMD中的溶质移动到吸附剂的外表面,通过颗粒内扩散进入吸附剂的孔隙中,也是AMD中微量元素减少的原因,这可能是生物炭的静电相互作用、物理吸附、表面络合作用的结果。宋泽峰等[102]发现芦苇生物炭吸附Cu2+以静电作用力为主,溶液pH、离子强度等因素对于吸附过程有较大影响,且中性条件和低离子强度利于Cu2+的吸附。Wang等[103]利用松树林废弃物生物炭处理含高砷尾矿细颗粒与去离子水混合制备的尾矿水,发现溶液的pH值明显上升,AMD中的溶解铁氧化成Fe3+在生物炭表面沉淀,并形成用于除砷的山梨酸酯表面位点,AMD中的砷在生物炭上发生了表面络合反应。这说明了AMD中的某些离子与生物炭反应的先后顺序可能对后续离子的吸附有促进或者抑制作用。
常帅帅等[104]研究发现Pb2+的吸附量随pH的增加呈先增加后减少的趋势,且溶液的Na+、K+与Pb2+之间对生物炭上的吸附点位存在一定竞争,Ca2+则与前三者相反,可与Pb2+发生复合反应,促进Pb2+的吸附,这说明木屑生物炭对Pb2+的吸附机制可能有离子交换、静电作用、表面络合和沉淀作用。李瑞月等[105]通过对比三种生物炭对Pb2+、Cd2+的吸附发现,含较多碳酸盐、磷酸盐等无机矿物的生物炭的吸附主要以阳离子交换作用为主,比表面积较大、孔隙结构较好、含氧官能团较多的生物炭对重金属离子的吸附机制主要为络合作用。曹建华等[106]发现在生物炭对Cd2+吸附的反应机制中,离子交换和沉淀反应为主导,络合反应吸附量的占比最少。廖衡妍[107]用稀H2O2与铜尾矿混合,取其上清液进行吸附实验,实验中发现,加入生物炭后,溶液中由铜尾矿氧化释放的SO42−与Fe3+明显减少;在模拟实验中发现,经由生物炭处理后的尾矿滤液SO42−降低明显,去除率均达80%以上,对滤液中Fe3+的吸附也有显著成效。Ao等[108]的实验发现改性的柚子皮生物炭对硫酸盐吸附容量随pH的增加呈现下降趋势,这可归因于吸附剂的表面电荷。当硫酸盐溶液的pH值低于生物炭的零电荷点时,生物炭表面将被质子化并带正电,此时,生物炭容易通过静电作用捕获SO42−。反之,生物炭表面在高pH值环境中会去质子化,导致静电斥力增加,对硫酸盐的吸附减少。此外,在高pH时OH−会大量存在于溶液中,此时SO42−会争夺生物炭表面的活性吸附位点,这也导致生物炭对硫酸盐的吸附能力降低。敖涵婷[109]在实验中发现改性柚子皮生物炭上的羟基与SO42−发生配位交换反应,置换了羟基上的OH−。
以上研究表明,生物炭对AMD中重金属的吸附机制与已知的生物炭对水环境中重金属离子的吸附机制作用可能一致,但由于AMD中包含多种离子,其作用机制相对较复杂,可结合对不同重金属离子的吸附机制,对其处理机制进行进一步深入研究和探究。图3对生物炭处理AMD的主要机制进行了总结。
-
生物炭作为一种高效且低成本的新型吸附碳材料,如今在环境、能源、农业等领域得到广泛应用。迄今为止,生物炭在废水中去除污染物的相关研究大多是在实验室条件下进行的,实际应用和大面积的推广仍需要大量的研究工作。虽然生物炭的生产和应用在废水处理方面已经进行了大量的研究,但其在AMD应用方面的相关研究不多,主要集中在不同原料制备的生物炭的特性及其对水中单一离子的吸附研究,这些研究大多规模较小,且部分停留在实验室阶段的研究,尚未进行规模化或工程化的应用研究和示范,这方面国内外仍然存在空白。因此,生物炭对AMD中复合污染的研究和改性生物炭的研究可能是未来该领域极具发展潜力的方向。未来利用生物炭技术处理AMD研究领域可以从以下几个方面开展相关研究工作:
(1)处理效果方面:在不同条件、不同原料制备下的生物炭都有不同的吸附性能,可以通过对比不同制备条件下各种生物炭对AMD中离子的处理效果,选出该条件下性能最优的生物炭。
(2)实际应用方面:生物炭长期以来一直是活性炭的潜在原料,相较于活性炭,其成本相对较低、原材料来源广泛。但如何进一步降低其生产制备成本,提高其处理能力,还需要在未来的研究中解决实际运营成本和治理废水后生物炭的后续处理等问题。
(3)生物炭材料优化方面:为了进一步提高生物炭对水中重金属离子的吸附性能,将生物炭进行改性受到越来越多的关注。因此,针对不同的AMD理化性质,如何有针对性地对生物炭进行改性处理,以增强其对AMD中重金属的吸附性能也是未来的研究重点之一。
(4)尽管生物炭技术在处理AMD方面极具潜力,但其方式相对单一,其处理效果相对有限。因此,采用多级反应系统,与其他方法的联合运用(如微生物法、湿地法、高级氧化法)对AMD进行深度处理将是未来的发展趋势。
利用生物炭技术处理酸性矿山废水的研究进展
Progress on treatment of acid mine drainage by biochar technology
-
摘要: 随着社会经济的不断发展,矿业开发过程中产生的一系列环境问题引起国内外的广泛关注,其中采矿过程中产生的酸性矿山废水(acid mine drainage, AMD)问题尤为突出。AMD会导致水质酸化、土壤重金属污染以及植物枯萎死亡等问题。因此,如何对AMD进行有效处理已成为环境治理的焦点问题。现有的AMD处理方法主要包括中和法、人工湿地法和微生物法,但这些方法大多存在后续管理难、维护成本高、处理浓度低等问题。相比之下,生物炭技术因原料成本低、制备简便且原材料来源广泛等优点而被广泛应用于环境修复领域。近年来国内外已有关于利用生物炭技术处理AMD的研究报道,但其处理机制尚不清楚,许多研究还停留在实验室阶段,尚未形成规模化的应用模式。因此,本文首先对AMD的特征及其常用处理方法进行了概述,并介绍了生物炭的常规制备方法及理化性质表征,对生物炭处理AMD的影响因素、处理效果及其机理进行了综述,最后对生物炭技术在处理AMD方面的研究与应用进行了展望。Abstract: With the rapid development of society and economy, a series of environmental problems in mining development have attracted wide attention all over the world, especially the acid mine drainage (AMD) issue. AMD can cause a series of ecological environment problems, such as water acidification, soil contamination with heavy metals, and plant wilting and apoptosis. Therefore, the treatment of AMD has become the focus of environmental governance. The current disposal methods of AMD mainly include neutralization method, constructed wetland method and microbial method. However, most of these treatment methods have the problems of difficult follow-up management, high maintenance cost and low treatment concentration. In contrast, biochar technology has been widely used in the field of environmental remediation due to its advantages such as low cost, easy preparation and wide source of raw materials. In recent years, there have been some reports on the treatment of AMD with biochar technology, but the treatment mechanism is still unclear, and many studies are still in its infancy, which has not yet formed a large-scale application model. Therefore, in this paper, the characteristics of AMD and its common treatment methods are summarized, the conventional preparation methods and physicochemical properties of biochar are introduced, the influencing factors, effect and mechanism of biochar treatment of AMD are reviewed. Finally the prospect of the research and application of biochar in AMD treatment is proposed.
-
Key words:
- biochar /
- acid mine drainage /
- water acidification /
- treatment technology /
- Mechanism
-
印染废水成分复杂、排量大、色度高、碱度高、化学需氧量高、可生化性差,处理难度较大,常规生化处理很难实现稳定达标排放[1]。对印染废水生化出水采用吸附、催化臭氧氧化、芬顿/类芬顿氧化、光催化氧化、曝气生物滤池等方法进行深度处理,是印染废水处理的主要方法[2]。
芬顿/类芬顿氧化处理印染废水工艺在工业上应用较多。传统Fenton氧化在强酸条件下进行,存在Fe3+/Fe2+循环效率低、铁泥产生量大、H2O2利用率低等缺点[3-4]。用Fe3+代替Fe2+作为催化剂,则有机物降解速率降低。为减少反应过程中铁离子流失,异相光Fenton氧化技术备受关注,其采用固化铁离子催化剂,如天然含铁矿物、合成铁氧化物,或将铁离子负载于黏土、沸石、活性炭、Al2O3等载体表面[5-7]。
天然含铁矿物廉价易得,催化性能稳定,可以重复利用[8-9]。已报道作催化剂的含铁矿物主要有磁铁矿[10-12]、赤铁矿[13-14]、针铁矿[15-16]、黄铁矿[17-19]、磁黄铁矿[20]、钒钛磁铁矿[21]等。在光照条件下,通过光化学反应可以实现Fe3+/Fe2+循环和对部分有机物的光解,从而促进了H2O2分解产生·OH,提高了H2O2利用率,进而促使有机物快速、彻底被矿化[22]。
异相光Fenton体系分为异相UV-Fenton体系和异相可见光Fenton体系[23-25]。由于H2O2吸收波长小于320 nm才能产生·OH,故目前多采用中心波长为254 nm紫外灯光源。太阳光划分为紫外(100~400 nm)、可见(400~760 nm)和红外3个区段,其中,紫外光仅占3%~5%。在弱酸条件下,可见光照射铁离子的量子产率较低。因此,寻找太阳光利用率高的光催化材料,研究其在可见光下对异相Fenton体系的催化作用,可降低运行成本。
GUELOU等[26]采用FeOOH催化剂,比较了烷基苯硫酸基酸在不同氧化体系中的降解效果,其在均相Fenton体系中降解率为38%,在异相Fenton体系中几乎无法降解,在引入紫外光后,FeOOH表现出催化活性。张钰等[27]以天然赤铁矿为催化剂,在可见光照射、pH=3、H2O2浓度1.5 mmol·L−1的条件下,罗丹明B可在180 min内完全脱色,2,4-二氯苯酚在24 h后降解率可达56%,溶出铁对氧化作用贡献较小,赤铁矿可稳定循环使用6次。
陈芳艳等[28]的研究表明,在300 W高压汞灯照射和异相Fenton氧化的共同作用下,Fe/Al2O3/UV-Fenton体系在20 min时可使六氯苯的降解率达到94.5%。MUTHUVEL等[29]证实Fe(Ⅲ)-Al2O3催化剂在太阳光照射下,表面Fe3+会转变成Fe2+。MAZELLIER等[30]提出多相体系催化机理和铁循环机制,认为反应实质是均相Fenton氧化,但当溶出铁不足时,H2O2产·OH的过程以表面催化为主。刘婷[31]指出,催化剂表面Fe(III)光化学反应转变为Fe(II)是异相光Fenton反应的关键步骤之一,反应体系中·OH主要通过铁离子催化分解H2O2、H2O2直接光解及催化剂表面催化分解H2O2 3种途径生成。HE等[22]的研究表明,铁矿物催化剂具有多孔结构,除了吸收光子产生电子外,当H2O2被吸附到其表面时,会与催化剂表面上的电子空穴对结合反应产生·OH。
本研究以黄铜矿(CuFeS2)、磁铁矿(Fe3O4)、磁黄铁矿(Fe1-xS) 3种天然含铁矿物作为催化剂,分别选用300 W高压汞灯、400 W氙灯、400 W金卤灯作为光源,以无光条件下异相类Fenton体系作为对照,考察了不同类型的光源对异相光Fenton体系催化氧化效果的影响,并重点比较了不同氧化体系中Fe2+溶出量和COD去除率的变化。
1. 实验部分
1.1 废水性质
实验所用废水为通州某印染废水集中处理厂水解酸化-活性污泥好氧处理出水。在190~900 nm内进行光谱扫描,没有发现特征吸收峰。因此,根据现场经验,采用478 nm波长处的吸光度值对废水的色度进行表征,具体水质参数如下:pH为9.40、COD为81.32 mg·L−1、UV254=1.12、UV478=0.023、盐分为1.85 g·L−1、Cl−为227.80 mg·L−1、
SO2−4 1.2 天然矿物
实验所用天然矿物黄铜矿(CuFeS2)、磁铁矿(Fe3O4)、磁黄铁矿(Fe1-xS)均为工业品,所有矿物均过200目筛后备用,纯度在95%以上。X-射线衍射结果表明黄铜矿样品中含有少量黄铁矿杂质,Fe3O4样品中含有少量SiO2杂质,Fe1-xS样品中含有少量氟金云母杂质。
1.3 实验仪器和试剂
实验过程中用到的主要仪器有紫外可见分光光度计(T6新世纪,北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司),光化学反应仪(BL-GHX-V型,上海比朗仪器有限公司)和恒温水浴摇床(COS-110X50,上海比朗仪器有限公司)。所用试剂均为分析纯。
1.4 光Fenton降解实验
用氢氧化钠或硫酸调节废水pH,在250 mL石英试管中依次加入催化剂、废水和H2O2,放入光催化反应装置内,放有光源的石英冷阱置于中央。开启反应器,间隔一定时间用针筒取样,过滤测定铁离子浓度,用氢氧化钠将水样调至碱性,待H2O2没有残留后测定COD值,且计算COD的去除率。
光催化实验的光源有汞灯、氙灯、金卤灯,其中氙灯用于太阳光环境模拟,金卤灯分别用于太阳光、可见光环境模拟。实验分别采用18 W低压汞灯、300 W高压汞灯、400 W氙灯、400 W金卤灯作为光源,通过滤光片控制入射光波长。低压汞灯发热量小,实验时置于单层石英冷阱中;高压汞灯、氙灯、金卤灯功率大,发热量大,实验时置于双层石英冷阱中,冷阱接入20 ℃恒温水进行循环冷却。
1.5 分析测试方法
采用重铬酸钾-微波消解法测定COD。采用邻菲罗啉分光光度法测定铁离子浓度。通过测定Fe2+和1,10-邻菲罗啉的络合物在510 nm处的吸光度值以计算Fe2+的浓度。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 低压汞灯照射下异相光Fenton体系处理效果
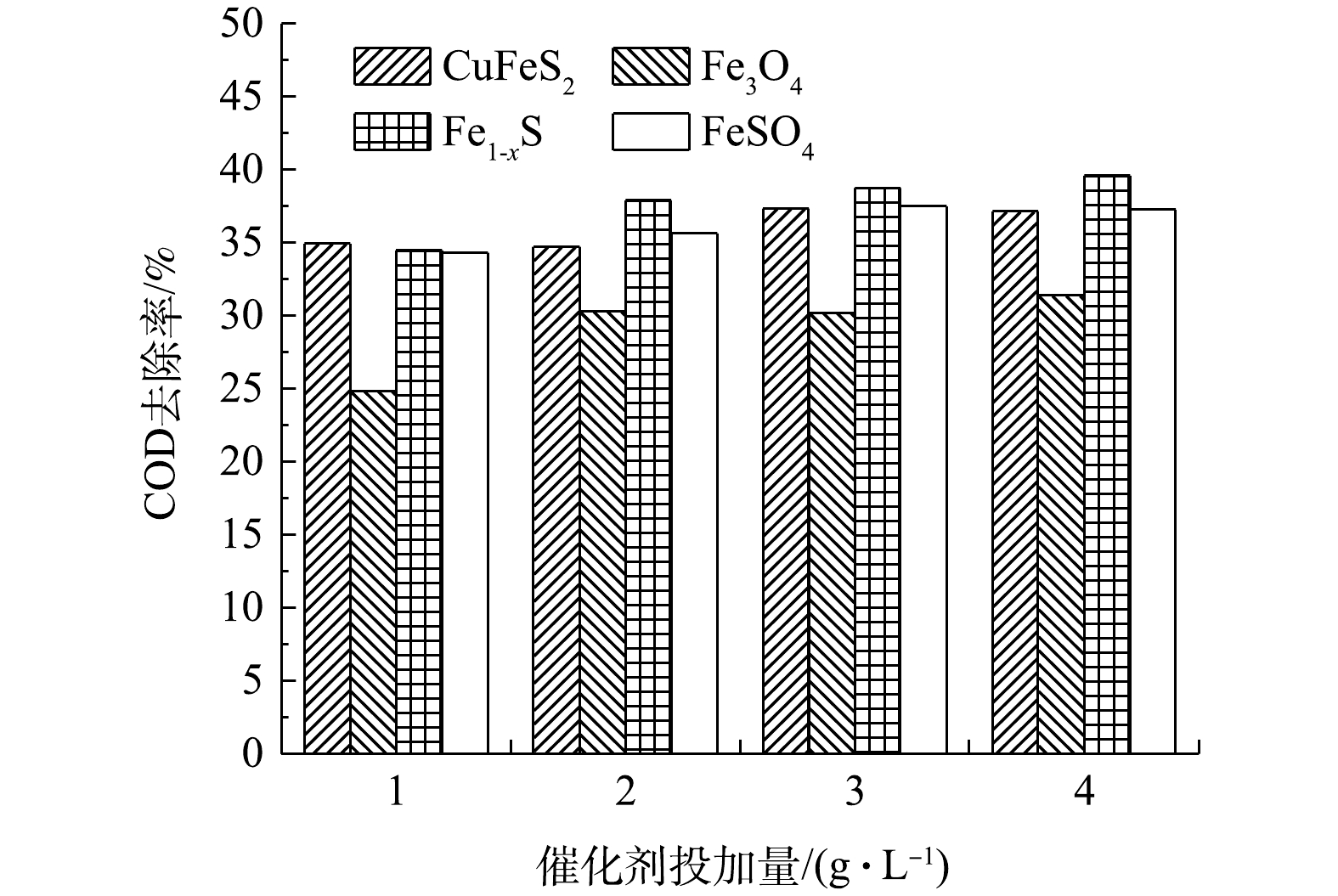
在pH为4时,以天然矿物为催化剂的异相UV-Fenton体系对废水有较好的处理效果[7, 10]。以主要发射波长为18 W低压汞灯作为辐照光源,在H2O2浓度为9.80 mmol·L−1的条件下反应2 h,催化剂投加量对COD去除效果的影响见图1。由图1可见,COD去除率随着催化剂投加量的增加而缓慢上升。因此,确定催化剂CuFeS2最佳用量为1 g·L−1、Fe3O4和Fe1-xS的最佳用量为2 g·L−1、FeSO4的最佳用量为1 g·L−1。
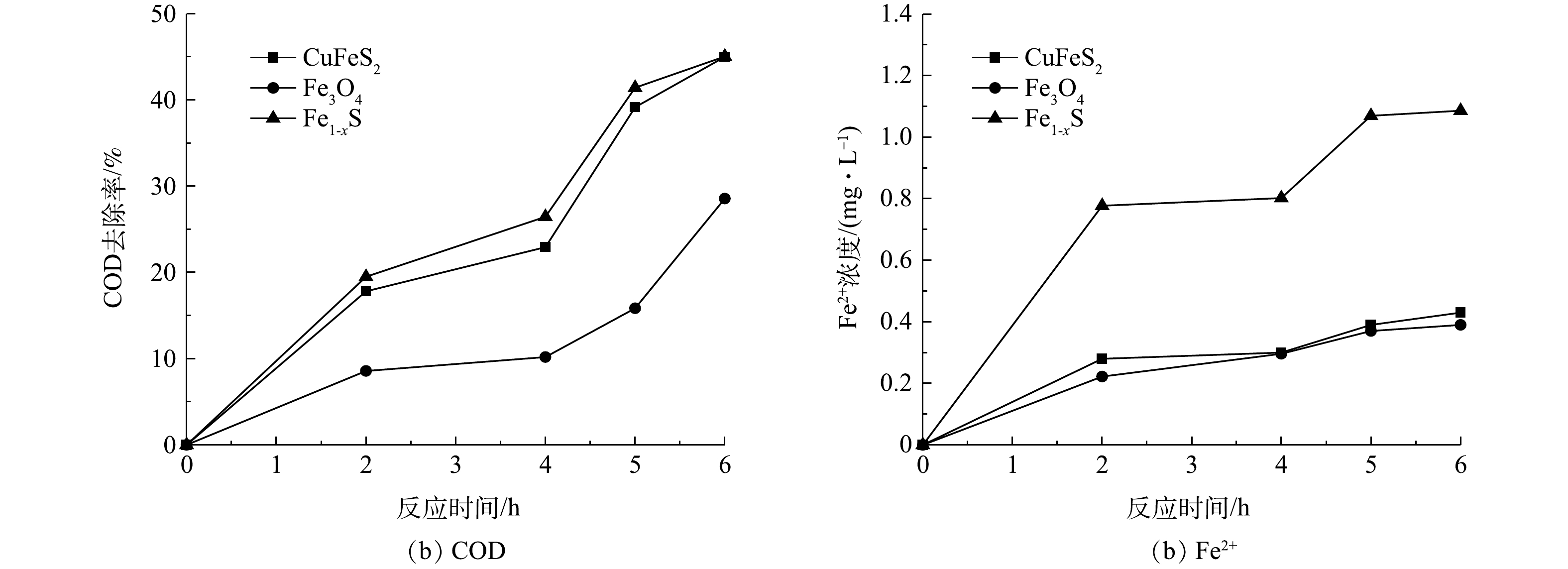
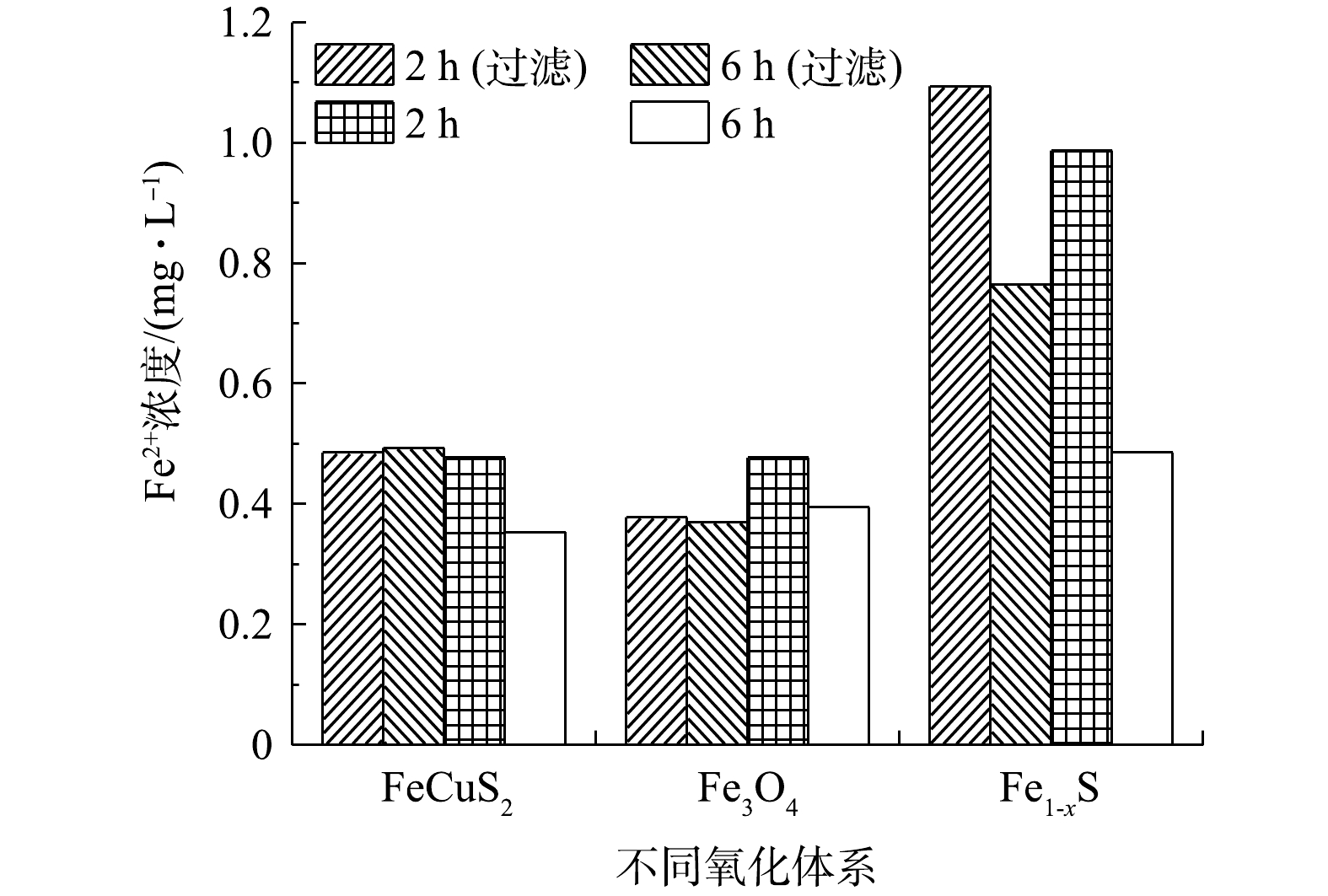
当pH为4时,首先考察在无光条件下,3种矿物异相类Fenton氧化体系对废水中COD的去除效果,其COD去除率、Fe2+浓度随反应时间的变化见图2。由图2(a)可见,Fe1-xS和CuFeS2催化体系中的COD去除率高于Fe3O4催化体系,在反应6 h后,Fe1-xS、CuFeS2、Fe3O4异相类Fenton体系对废水中COD的去除率分别达到45.91%、45.64%和28.57%。由图2(b)可见,3种矿物异相类Fenton体系中Fe2+浓度随着反应时间缓慢上升,CuFeS2、Fe3O4催化体系中Fe2+浓度始终保持在较低水平(0.40 mg·L−1左右),Fe1-xS催化体系中溶出Fe2+较多,在反应至2 h和6 h后,Fe2+浓度分别为0.78 mg·L−1和1.09 mg·L−1。综上结果可知,3种异相类Fenton体系在反应过程中溶出的Fe2+均较低[32]。
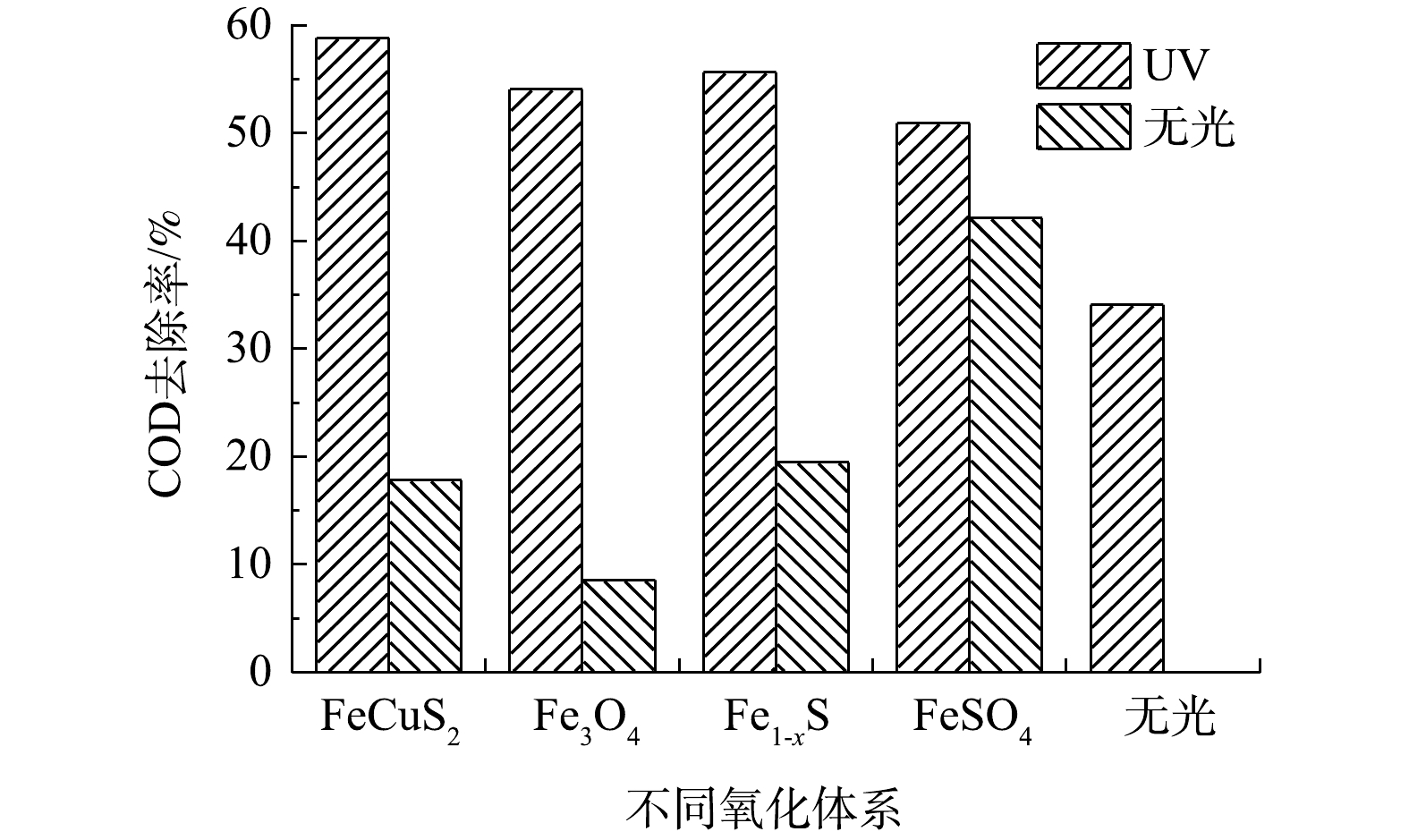
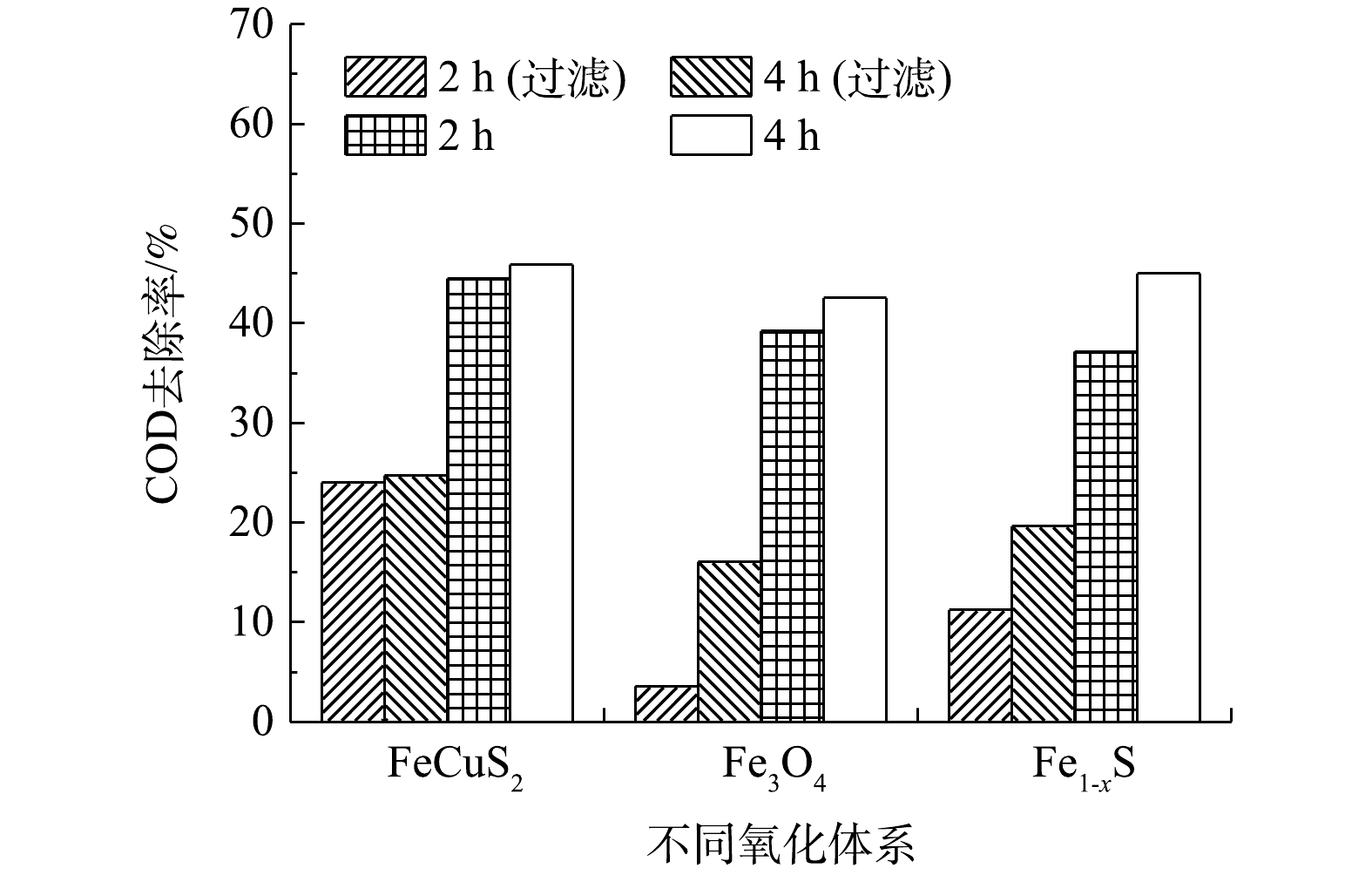
在pH为4、反应2 h时,有光和无光条件下,各催化氧化体系对COD的去除效果见图3。由图3可见,异相类Fenton体系的去除效果较差,各异相催化体系中COD的去除率均未达到20%,以Fe3O4作为催化剂时,COD去除率仅有8.58%。在低压汞灯光照后,UV-Fenton体系对COD的去除率比Fenton氧化体系去除率提高了8%;与无光异相Fenton反应相比,异相UV-Fenton体系对COD的去除率提高了40%左右。3种异相UV-Fenton体系均使COD降至30 mg·L−1左右,去除效果依次为CuFeS2(58.83%)>Fe1-xS(55.64%)>Fe3O4(54.07%)。在单独H2O2氧化的条件下,COD的去除率几乎为0,而UV-H2O2体系对COD的去除率为34.09%。这表明单独的H2O2几乎不能降解废水中的耗氧有机物(以COD计),但在紫外光作用下,H2O2通过光解产生·OH,以实现对部分耗氧有机物(以COD计)的降解。
2.2 高压汞灯照射下异相光Fenton体系处理效果
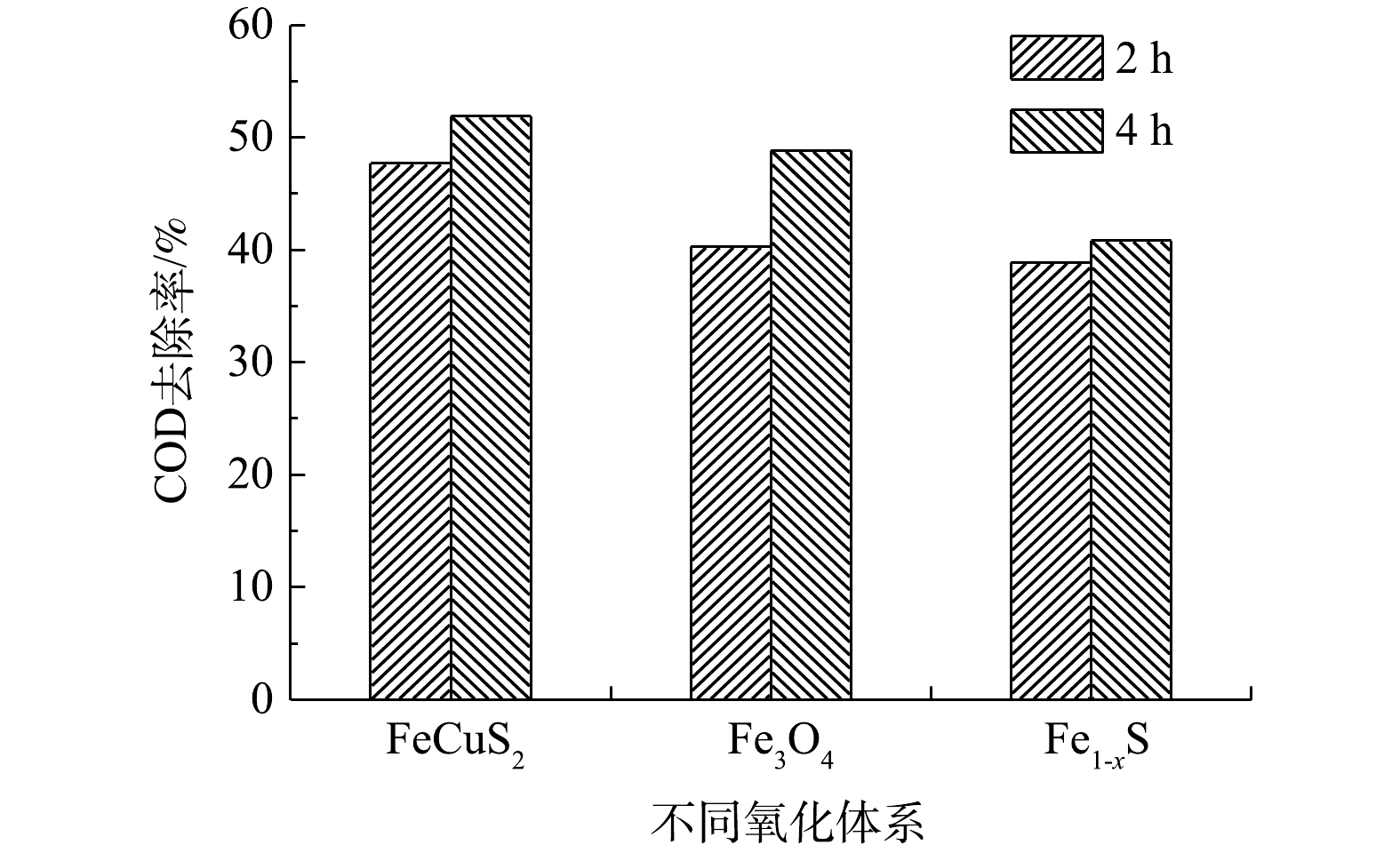
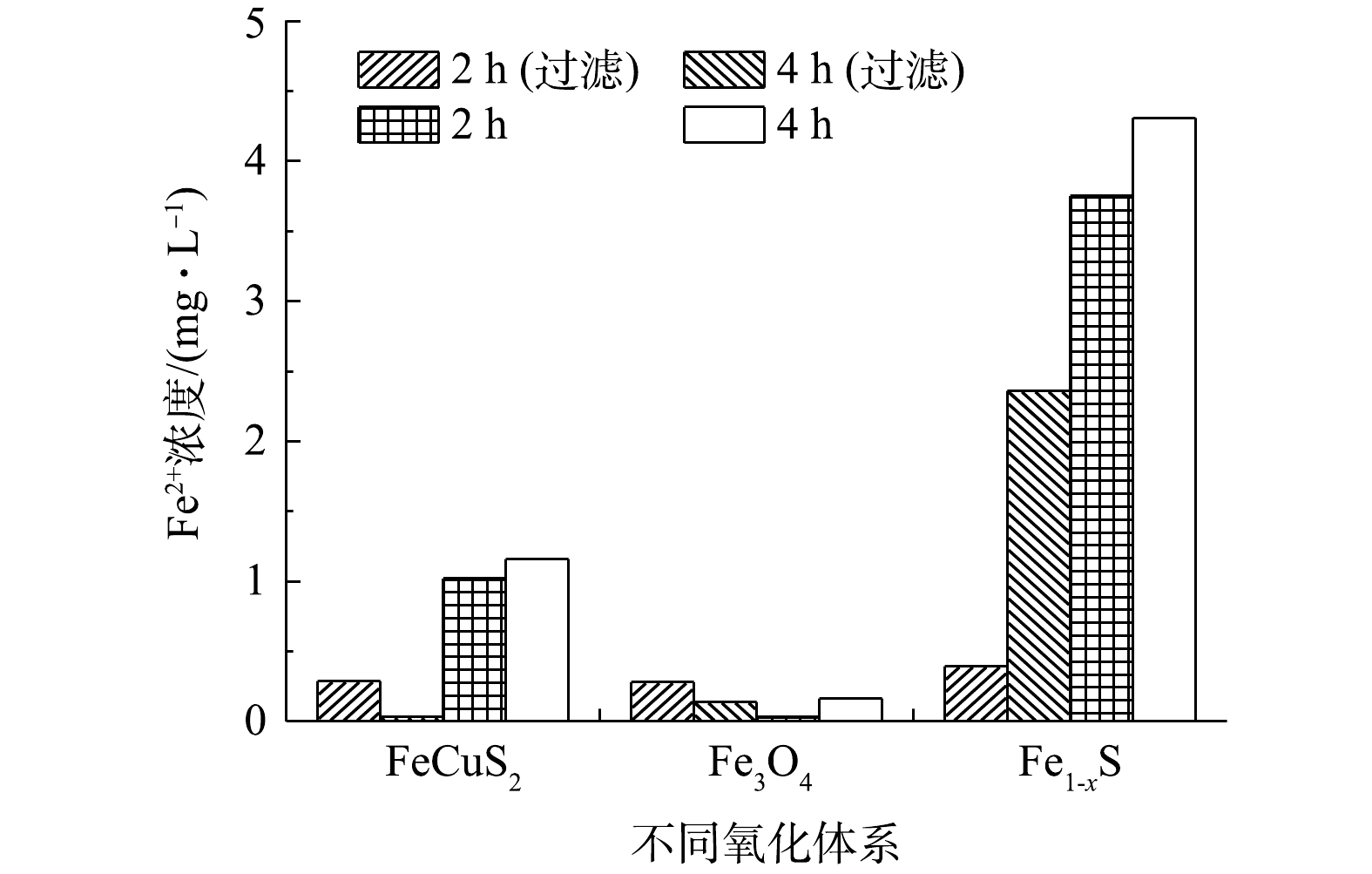
高压汞灯具有发射光谱波长范围宽、紫外辐射强度高等优点。以300 W高压汞灯为光源,考察了高压汞灯异相UV-Fenton体系对COD的去除效果。由图4可见,在反应2 h后,CuFeS2、Fe3O4、Fe1-xS催化体系对COD去除率分别为47.71%、40.31%和38.92%,COD去除率随着反应时间均有小幅上升。在3种催化剂中,CuFeS2催化氧化体系对COD的去除效果最佳,在反应4 h后,COD去除率可达51.95%。
在上述反应过程中Fe2+溶出量的变化见图5。由图5可见:在反应2 h后,各体系溶出的Fe2+很少;在反应4 h后,3种催化剂的Fe2+溶出量依次为Fe1-xS(3.00 mg·L−1)>CuFeS2(0.90 mg·L−1)>Fe3O4 (0.02 mg·L−1);溶出的Fe2+可与H2O2发生均相Fenton反应,但以矿物表面催化为主。
2.3 氙灯照射下异相光Fenton体系处理效果
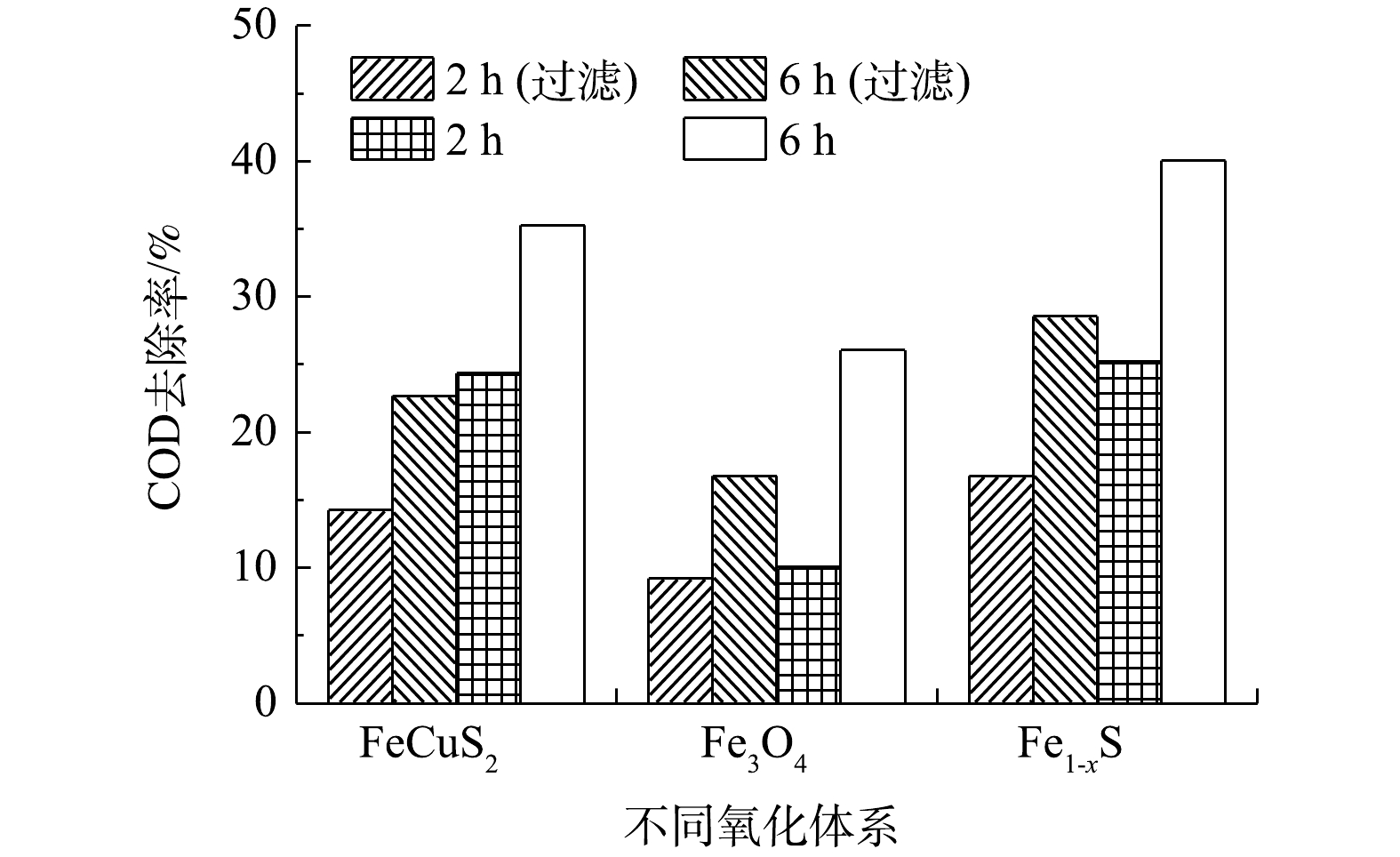
以400 W氙灯作为光源,用滤光片滤掉波长400 nm以下的光,考察了模拟异相太阳光Fenton体系对废水中COD的去除效果,结果见图6。由图6可见,尽管氙灯发射光谱中紫外光强度较低,但有无滤光片对COD去除率的影响较大。与有滤光片相比,在无滤光片时CuFeS2、Fe1-xS催化体系对COD的去除率有所增加,这表明紫外光可在一定程度上提高H2O2的利用率。随着反应时间延长至6 h时,CuFeS2、Fe3O4、Fe1-xS催化体系对COD去除率有所提高,分别为35.28%、26.04%、40.05%。
由图7可见,CuFeS2、Fe3O4催化体系中Fe2+浓度较小(<1.1 mg·L−1),有无滤光片对体系中Fe2+浓度的影响不大。Fe1-xS催化体系在反应6 h后,Fe2+浓度减少,这说明溶出Fe2+与H2O2发生均相Fenton反应。当以氙灯作为光源时,Fe1-xS体系中同时存在均相和异相催化作用。但由于体系中Fe2+浓度低于1.1 mg·L−1,均相催化作用的贡献十分有限。因此,Fe1-xS、CuFeS2、Fe3O4表面铁物种起主要催化作用,最终催化效果依次为Fe1-xS>CuFeS2>Fe3O4。
2.4 金卤灯照射下异相光Fenton体系处理效果
以400 W金卤灯作为光源,考察了在可见光下异相光Fenton体系对废水中COD的去除效果,结果见图8。设置一组对照实验,用滤光片过滤掉波长400 nm以下的紫外光。由图8可见,在无滤光片时,随着反应的进行,各氧化体系COD去除率有所增加,在4 h后的处理效果依次为CuFeS2(45.90%)≈Fe1-xS(45.13%)>Fe3O4(42.55%)。在加滤光片后,滤光片可滤去波长400 nm以下的紫外光,而波长大于320 nm的光不能使H2O2分解产生·OH。以CuFeS2为催化剂时,反应2 h后COD去除率为24%左右,Fe1-xS、Fe3O4催化效果更差,与无光条件下的异相类Fenton氧化结果相似,这说明3种异相催化体系对可见光的响应较弱。
由图9可见,在有滤光片时,与CuFeS2、Fe3O4相比,Fe1-xS溶出Fe2+较多,反应4 h体系中Fe2+浓度为2.36 mg·L−1,COD去除率仅为19.63%;Fe3O4催化体系反应速率最慢,反应2 h后 COD去除率仅为3.58%。在不加滤光片反应4 h后,3种催化剂的Fe2+溶出量依次为Fe1-xS(3.75 mg·L−1)>CuFeS2(1.02 mg·L−1)>Fe3O4(0.03 mg·L−1),而COD的去除效果为CuFeS2≈Fe1-xS>Fe3O4,表明异相光Fenton体系以矿物表面催化为主。
2.5 催化剂稳定性
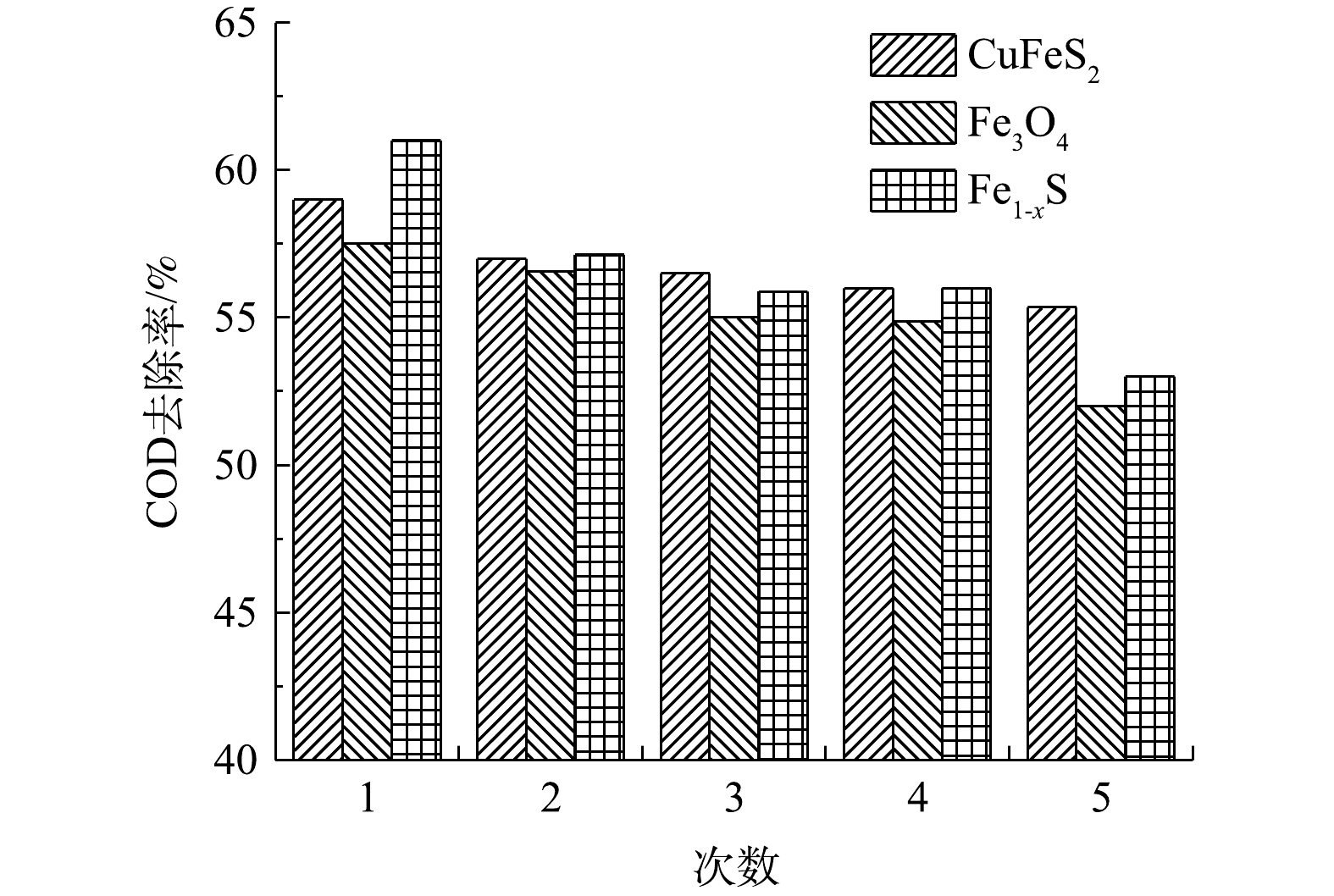
在低压汞灯照射下催化剂的循环使用对COD去除率的影响如图10所示。由图10可见,随着天然含铁矿物循环次数的增加,COD的去除率缓慢降低,但均保持在50%以上。这表明天然含铁矿物的光催化活性稳定,有效克服了均相UV-Fenton体系中催化剂无法重复利用的缺点,具有很好的应用价值。
2.6 催化机理
在pH为3~7时,CuFeS2、Fe3O4、Fe1-xS 3种矿物在光照6 h后,各体系中Fe2+溶出量均较小,H2O2浓度由9.8 mmol·L−1分别降低至3.22、3.76、2.38 mmol·L−1。这表明异相UV-Fenton体系中均相催化作用较弱,以矿物表面催化为主。在添加·OH的淬灭剂后,在低压汞灯照射下,在pH为4、CuFeS2、Fe3O4、Fe1-xS 3种矿物投加量分别为1、2、2 g·L−1、H2O2浓度为9.8 mmol·L−1的条件下,3种矿物对COD去除率分别由58.83%、55.64%和54.07%均降低到10%左右。这表明异相UV-Fenton体系·OH对有机物的氧化起主要作用。
·OH产生途径有H2O2光解、催化剂表面Fe(Ⅱ)催化H2O2分解、光致催化剂电荷分离和氧气二电子还原(式(1)~式(7)),其中
FeIIs FeIIIs H2O2+hv→2⋅OH (1) FeIIs+H2O2→FeIIIs+⋅OH+OH− (2) FeIIIs+H2O2→FeIIs+HOO⋅+H+ (3) 含铁矿物+hv→e−CB+h+VB (4) H2O+h+→⋅OH+H+ (5) O2+e−→O−2 (6) O−2+H2O2→⋅OH+OH−+O2 (7) 3. 结论
1)在无光条件下,COD的去除率较低,在反应6 h后,对废水中COD的去除效果为Fe1-xS≈CuFeS2>Fe3O4,在3种体系中COD去除率分别为45.91%、45.64%和28.57%,此时,Fe1-xS体系中的Fe2+溶出量最多(1.09 mg·L−1),其他2个体系中的Fe2+浓度均约为0.40 mg·L−1。
2) COD去除率对不同光源、不同催化剂的响应不同。以低压汞灯作为光源时,反应2 h后COD去除率为CuFeS2(58.83%)>Fe1-xS(55.64%)>Fe3O4(54.07%);以高压汞灯作为光源时,反应4 h后的COD去除率为CuFeS2(51.89%)>Fe3O4(48.86%)>Fe1-xS(40.83%);以氙灯为光源时(无滤光片),反应6 h后的COD去除率为Fe1-xS(40.05%)>CuFeS2(35.28%)>Fe3O4(26.04%);以金卤灯为光源时(无滤光片),反应4 h后的COD去除率为CuFeS2(45.90%)≈Fe1-xS(45.00%)>Fe3O4(42.55%)。
3)在3种天然矿物催化体系中,Fe1-xS、CuFeS2存在光腐蚀现象,在Fe1-xS体系中Fe2+溶出量最大;在以不同光源的异相光Fenton体系中,CuFeS2催化性能最为稳定,其次为Fe1-xS,均以表面催化作用为主。
4) 4种光源对异相类Fenton体系的强化作用依次为低压汞灯>高压汞灯>金卤灯>氙灯。在汞灯照射下,反应速率快,氧化效果好;以金卤灯作为光源时,加滤光片前后反应体系处理效果变化较大,这说明矿物异相类Fenton体系对可见光响应较弱;以氙灯作为光源时,各催化体系反应速率慢,对COD的去除效果与无光条件下的异相类Fenton体系相似。
-
表 1 AMD各种处理方法优缺点比较
Table 1. Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of various AMD processing methods
处理方法 Processing methods 优点 Advantages 缺点 Disadvantages 微生物燃料电池技术 原料来源广、温和高效 能耗大、运行费用高、设备要求高 物理化学法 离子去除率高 对吸附材料膜的性能要求较高,运行成本偏高,对水体、温度、停留时间等要求高 微生物法 简单易行、成本低廉、环境友好、适应性强、不会发生二次污染 操作环境不易控制 人工湿地法 环境友好、处理效果好、成本低、不会发生二次污染 占地面积大、时间长、各种作用难以控制 电化学法 清洁的去除方式、效率高、占地少、不会发生二次污染 初始投资大、电力供应大、电极材料寿命短等问题难以突破 中和法 初始成本低、操作简单、对设备要求相对简单、处理效果好 产生大量污泥易造成二次污染,增大处理成本 源头治理技术 高效经济、不会对环境产生二次伤害 技术不够成熟 -
[1] 王磊, 李泽琴, 姜磊. 酸性矿山废水的危害与防治对策研究 [J]. 环境科学与管理, 2009, 34(10): 82-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2009.10.020 WANG L, LI Z Q, JIANG L. Acidic mine waste water hazards and countermeasures research [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2009, 34(10): 82-84(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2009.10.020
[2] 牟力, 何腾兵, 黄会前, 等. 酸性矿山废水治理技术的研究进展 [J]. 天津农业科学, 2017, 23(2): 42-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2017.02.010 MOU L, HE T B, HUANG H Q, et al. Progress in research on the acid mine drainage treatment [J]. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 23(2): 42-45(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2017.02.010
[3] 刘志勇, 陈建中, 康海笑, 等. 酸性矿山废水的处理研究 [J]. 四川环境, 2004, 23(6): 50-53,57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2004.06.014 LIU Z Y, CHEN J Z, KANG H X, et al. Treatment and study of acid mine drainage [J]. Sichuan Environment, 2004, 23(6): 50-53,57(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2004.06.014
[4] 邓川, 陈韵竹, 李瑶. 矿山废水处理的研究综述 [J]. 当代化工研究, 2017(11): 57-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2017.11.035 DENG C, CHEN Y Z, LI Y. Review of research on mine wastewater treatment [J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2017(11): 57-58(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2017.11.035
[5] 钟晓晓, 王涛, 原文丽, 等. 生物炭的制备、改性及其环境效应研究进展 [J]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报, 2017, 40(5): 44-50. doi: 10.7612/j.issn.1000-2537.2017.05.007 ZHONG X X, WANG T, YUAN W L, et al. Progresses of preparation, modification and environmental behavior of biochar [J]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 2017, 40(5): 44-50(in Chinese). doi: 10.7612/j.issn.1000-2537.2017.05.007
[6] WANG B, MA Y N, LEE X, et al. Environmental-friendly coal gangue-biochar composites reclaiming phosphate from water as a slow-release fertilizer [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 758: 143664. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143664 [7] WANG B, WAN Y S, ZHENG Y L, et al. Alginate-based composites for environmental applications: A critical review [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 49(4): 318-356. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2018.1547621 [8] WANG B, GAO B, WAN Y S. Comparative study of calcium alginate, ball-milled biochar, and their composites on aqueous methylene blue adsorption [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(12): 11535-11541. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1497-1 [9] WANG B, GAO B, WAN Y S. Entrapment of ball-milled biochar in Ca-alginate beads for the removal of aqueous Cd(Ⅱ) [J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2018, 61: 161-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.12.013 [10] 马超然, 张绪超, 王朋, 等. 生物炭理化性质对其反应活性的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(11): 2425-2434. MA C R, ZHANG X C, WANG P, et al. Effect of physical and chemical properties of biochar on its reactivity [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(11): 2425-2434(in Chinese).
[11] TENG D Y, ZHANG B B, XU G M, et al. Efficient removal of Cd(Ⅱ) from aqueous solution by pinecone biochar: Sorption performance and governing mechanisms [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 265: 115001. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115001 [12] DAI W J, WU P, LIU D, et al. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous solution by organic montmorillonite sodium alginate nanocomposites [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 251: 126074. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126074 [13] WANG Q, WANG B, LEE X, et al. Sorption and desorption of Pb(Ⅱ) to biochar as affected by oxidation and pH [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 634: 188-194. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.189 [14] WANG B, LEHMANN J, HANLEY K, et al. Adsorption and desorption of ammonium by maple wood biochar as a function of oxidation and pH [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 138: 120-126. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.062 [15] 曹玮, 周航, 邓贵友, 等. 改性谷壳生物炭负载磁性Fe去除废水中Pb2+的效果及机制 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(3): 1437-1444. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201511081 CAO W, ZHOU H, DENG G Y, et al. Effects and mechanisms of magnetic iron supported on rice husk biochar removing Pb2+ in wastewater [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(3): 1437-1444(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201511081
[16] 刘秀, 刘立恒, 刘睿, 等. 笼芯陶黑碳微珠生物炭去除模拟废水中铬的实验研究[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 29(3): 75-81 LIU X, LIU L H, LIU R, et al. Experimental study on Cr removal from simulated wastewater by cage core black carbon beads[J/OL]. Environmental Engineering , 2021, 29(3): 75-81.
[17] 魏啸楠, 张倩, 李孟, 等. 磷酸改性生物炭负载硫化锰去除废水中重金属镉 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(5): 2095-2102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.05.028 WEI X N, ZHANG Q, LI M, et al. Removal of cadmium in wastewater by phosphoric acid modified biochar supported manganese sulfide [J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(5): 2095-2102(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.05.028
[18] MOHAPATRA S, KUMAR M, KARIM A A, et al. Biochars evaluation for chromium pollution abatement in chromite mine wastewater and overburden of Sukinda, Odisha, India [J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2020, 13(13): 1-14. [19] GIACHINI A J, SULZBACH T S, PINTO A L, et al. Microbially-enriched poultry litter-derived biochar for the treatment of acid mine drainage [J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2018, 200(8): 1227-1237. doi: 10.1007/s00203-018-1534-y [20] OH S Y, YOON M K. Biochar for treating acid mine drainage [J]. Environmental Engineering Science, 2013, 30(10): 589-593. doi: 10.1089/ees.2013.0063 [21] LIATSOU I, PASHALIDIS I, DOSCHE C. Cu(Ⅱ) adsorption on 2-thiouracil-modified Luffa cylindrica biochar fibres from artificial and real samples, and competition reactions with U(Ⅵ) [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 383: 120950. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120950 [22] MOSLEY L M, WILLSON P, HAMILTON B, et al. The capacity of biochar made from common reeds to neutralise pH and remove dissolved metals in acid drainage [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(19): 15113-15122. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4735-9 [23] INYANG M I, GAO B, YAO Y, et al. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal [J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 46(4): 406-433. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2015.1096880 [24] 辛瑞瑞. 不同酸性废水库中微生物群落季节变化及宏基因组学研究 [D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019. XIN R R. Seasonal variation of microbial community and metagenomics analysis in different acid mine drainage lakes [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2019.
[25] 白润才, 李彬, 李三川, 等. 矿山酸性废水处理技术现状及进展 [J]. 长江科学院院报, 2015, 32(2): 14-19. BAI R C, LI B, LI S C, et al. Development and status of the treatment technology for acid mine drainage [J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2015, 32(2): 14-19(in Chinese).
[26] 王颖南, 邓奇根, 王浩, 等. 硫酸盐还原菌胞外聚合物处理酸性矿山废水的研究进展 [J]. 水处理技术, 2020, 46(12): 7-11. WANG Y N, DENG Q G, WANG H, et al. Research progress on treatment of acid mine wastewater by extracellular polymeric substances of sulfate reducing bacteria [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2020, 46(12): 7-11(in Chinese).
[27] 洪思奇. 聚吡咯改性活性炭去除酸性矿山废水中的硫酸盐 [D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. HONG S Q. Sulfate removal from acid mine drainage using polypyrrole-grafted activated carbon [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2014.
[28] 王贺松. 酸性矿山废水中处理技术的研究进展 [J]. 民营科技, 2018(5): 62. WANG H S. Research progress of treatment technology in acid mine wastewater [J]. Private Technology, 2018(5): 62(in Chinese).
[29] KEFENI K K, MSAGATI T A M, MAMBA B B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 151: 475-493. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.082 [30] 郑琳姗, 张秀玲, 李惠雨, 等. 微生物燃料电池技术及其影响因素研究进展 [J]. 精细化工, 2021, 38(1): 1-8. ZHENG L S, ZHANG X L, LI H Y, et al. Research progress on microbial fuel cell technology and its influencing factors [J]. Fine Chemicals, 2021, 38(1): 1-8(in Chinese).
[31] 丁伟, 阿柔娜, 付志敏, 等. 重金属离子对微生物燃料电池产电性能的影响 [J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(7): 61-65. DING W, A R N, FU Z M, et al. The influence of heavy metal ions on the microbial fuel cell performance [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2016, 34(7): 61-65(in Chinese).
[32] FADZLI F S, RASHID M, YAQOOB A A, et al. Electricity generation and heavy metal remediation by utilizing yam (Dioscorea alata) waste in benthic microbial fuel cells (BMFCs) [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 172: 108067. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2021.108067 [33] FU W, JI G Z, CHEN H H, et al. Molybdenum sulphide modified chelating resin for toxic metal adsorption from acid mine wastewater [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 251: 117407. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117407 [34] 辛金豪. 离子交换法处理回用电镀含铬废水的研究进展 [J]. 资源节约与环保, 2015(7): 36,39. XIN J H. Ion exchange method and treatment of recycling the research progress of electroplating wastewater containing chromium [J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection, 2015(7): 36,39(in Chinese).
[35] 隋岩峰, 刘松林, 杨帆. 反渗透膜处理磷肥废水的实验研究 [J]. 应用化工, 2019, 48(4): 823-826. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.04.020 SUI Y F, LIU S L, YANG F. Experimental study on the treatment of phosphate fertilizer wastewater by reverse osmosis membrane [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(4): 823-826(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.04.020
[36] 戴祥昕, 桂梦瑶, 杜俊逸, 等. 硫酸盐还原菌包覆矿石控制酸性废水排放及碳源的优选研究 [J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(1): 73-81. DAI X X, GUI M Y, DU J Y, et al. Sulphate-reducing bacteria covered mine refuse to control acid mine drainage and the optimization of relevant carbon sources [J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(1): 73-81(in Chinese).
[37] SAHINKAYA E, DURSUN N, OZKAYA B, et al. Use of landfill leachate as a carbon source in a sulfidogenic fluidized-bed reactor for the treatment of synthetic acid mine drainage [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2013, 48: 56-60. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2012.10.019 [38] 龙中, 吴攀, 黄家琰, 等. 多级复氧反应-垂直流人工湿地深度处理煤矿酸性废水 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(6): 1391-1399. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201810086 LONG Z, WU P, HUANG J Y, et al. Advanced treatment of acid mine drainage by multi-stage reoxygenation reaction-vertical flow constructed wetland [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2019, 13(6): 1391-1399(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201810086
[39] 徐晶晶, 张继伟, 崔树军, 等. 煤矸石山酸性废水污染控制技术研究进展 [J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(1): 43-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2017.01.012 XU J J, ZHANG J W, CUI S J, et al. Research progress in pollution control technologies of acidic wastewater from coal gangue [J]. China Mining Magazine, 2017, 26(1): 43-48(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2017.01.012
[40] 蒋文瑞, 涂志红, 周姝, 等. 黄铁矿表面氧化机理及动力学影响因素研究进展 [J]. 金属矿山, 2021(3): 88-102. JIANG W R, TU Z H, ZHOU S, et al. A brief overview on the mechanism and kinetic influencing factors of the pyrite surface oxidation [J]. Metal Mine, 2021(3): 88-102(in Chinese).
[41] SKOUSEN J G, ZIEMKIEWICZ P F, MCDONALD L M. Acid mine drainage formation, control and treatment: Approaches and strategies [J]. The Extractive Industries and Society, 2019, 6(1): 241-249. doi: 10.1016/j.exis.2018.09.008 [42] 朱爱平, 田虎伟. 浅谈金属矿山酸性废水处理工艺 [J]. 现代矿业, 2020, 36(1): 204-206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2020.01.062 ZHU A P, TIAN H W. Discussion on acid mine waste water treatment process in metal mine [J]. Modern Mining, 2020, 36(1): 204-206(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2020.01.062
[43] 曾威鸿, 董颖博, 林海. 酸性矿山废水源头控制技术研究进展 [J]. 安全与环境工程, 2020, 27(1): 104-110. ZENG W H, DONG Y B, LIN H. Research progress of source control technologies of acid mine drainage [J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2020, 27(1): 104-110(in Chinese).
[44] YANG B J, LUO W, WANG X X, et al. The use of biochar for controlling acid mine drainage through the inhibition of chalcopyrite biodissolution [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 737: 139485. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139485 [45] CHAI Y Z, QIN P F, ZHANG J C, et al. Simultaneous removal of Fe(Ⅱ) and Mn(Ⅱ) from acid mine wastewater by electro-Fenton process [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 143: 76-90. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.06.026 [46] 丛宏斌, 赵立欣, 姚宗路, 等. 我国生物质炭化技术装备研究现状与发展建议 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2015, 20(2): 21-26. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2015.02.003 CONG H B, ZHAO L X, YAO Z L, et al. Research status of biomass carbonization technical equipment and proposals for its development in China [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2015, 20(2): 21-26(in Chinese). doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2015.02.003
[47] 孟凡彬, 孟军. 生物质炭化技术研究进展 [J]. 生物质化学工程, 2016, 50(6): 61-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2016.06.010 MENG F B, MENG J. Review of biomass carbonization technology [J]. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2016, 50(6): 61-66(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2016.06.010
[48] 韦思业. 不同生物质原料和制备温度对生物炭物理化学特征的影响 [D]. 广州: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院广州地球化学研究所), 2017. WEI S Y. Influence of biomass feedstocks and pyrolysis temperatures on physical and chemical properties of biochar [D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, , 2017(in Chinese).
[49] XIANG W, ZHANG X Y, CHEN J J, et al. Biochar technology in wastewater treatment: A critical review [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 252: 126539. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126539 [50] 王志鹏, 陈蕾. 秸秆生物炭的研究进展 [J]. 应用化工, 2019, 48(2): 444-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.02.045 WANG Z P, CHEN L. Research progress on straw-based biochar [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(2): 444-447(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.02.045
[51] 李湘萍, 张建光. 生物质热解制备多孔炭材料的研究进展 [J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2020, 36(5): 1101-1110. LI X P, ZHANG J G. Progress on biochar preparation through pyrolysis process [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2020, 36(5): 1101-1110(in Chinese).
[52] OGINNI O, SINGH K. Influence of high carbonization temperatures on microstructural and physicochemical characteristics of herbaceous biomass derived biochars [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 104169. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104169 [53] YUAN J H, XU R K. The amelioration effects of low temperature biochar generated from nine crop residues on an acidic Ultisol [J]. Soil Use and Management, 2011, 27(1): 110-115. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-2743.2010.00317.x [54] FENG Q W, WANG B, CHEN M, et al. Invasive plants as potential sustainable feedstocks for biochar production and multiple applications: A review [J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021, 164: 105204. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105204 [55] 盘丽珍. 大豆秸秆生物炭对金属硫化物尾矿污染土壤的修复作用[D]. 湘潭: 湖南科技大学, 2017. PAN L Z. The remediation of metal mine tailings contaminated siol by biochar derived from soybean straw[D]. Xiangtan: Hunan University of Science and Technology, 2017.
[56] 张天乐, 邱凌, 王雅君. 慢速热解对玉米秸秆炭理化特性的影响 [J]. 可再生能源, 2019, 37(10): 1423-1428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5292.2019.10.001 ZHANG T L, QIU L, WANG Y J. Study on process optimization of slow pyrolysis parameters of corn stalks [J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2019, 37(10): 1423-1428(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5292.2019.10.001
[57] 李敏, 赵立欣, 孟海波, 等. 慢速热解条件下生物炭理化特性分析 [J]. 农机化研究, 2015, 37(3): 248-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2015.03.061 LI M, ZHAO L X, MENG H B, et al. Analysis of biochar physical and chemical properties under the condition of slow pyrolysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015, 37(3): 248-253(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2015.03.061
[58] 肖琴, 刘有才, 曹占芳, 等. 生物炭吸附废水中重金属离子的研究进展 [J]. 环境科技, 2019, 32(1): 68-73. XIAO Q, LIU Y C, CAO Z F, et al. Research progress on the absorption of heavy metals from wastewater by biochar [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 32(1): 68-73(in Chinese).
[59] 高凯芳, 简敏菲, 余厚平, 等. 裂解温度对稻秆与稻壳制备生物炭表面官能团的影响 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(8): 1663-1669. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.08.2016010607 GAO K F, JIAN M F, YU H P, et al. Effects of pyrolysis temperatures on the biochars and its surface functional groups made from rice straw and rice husk [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(8): 1663-1669(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.08.2016010607
[60] 勾芒芒, 屈忠义. 生物炭对改善土壤理化性质及作物产量影响的研究进展 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2013(5): 1-5. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20130501 GOU M M, QU Z Y. Research on using biochar to agricultural soil amendment and crop yield [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2013(5): 1-5(in Chinese). doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20130501
[61] 王彤彤, 王晓琳, 任志胜, 等. 不同原料制备的生物炭形貌结构及表面特性研究 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2017, 40(1): 42-48. WANG T T, WANG X L, REN Z S, et al. Microscopic morphology and surface features of biochars derived from different raw materials [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 40(1): 42-48(in Chinese).
[62] 刘青松, 赵丽芳. 热解温度对生物炭表面性质及释放氮磷的影响 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2016, 33(2): 164-169. LIU Q S, ZHAO L F. Effects of biochar pyrolysis temperature on its surface characteristics and nitrogen and phosphorus release [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2016, 33(2): 164-169(in Chinese).
[63] 范世锁, 刘文浦, 王锦涛, 等. 茶渣生物炭制备及其对溶液中四环素的去除特性 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1308-1318. FAN S S, LIU W P, WANG J T, et al. Preparation of tea waste biochar and its application in tetracycline removal from aqueous solution [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3): 1308-1318(in Chinese).
[64] 孙涛, 朱新萍, 李典鹏, 等. 不同原料生物炭理化性质的对比分析 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2017, 34(6): 543-549. SUN T, ZHU X P, LI D P, et al. Comparison of biochars characteristics from different raw materials [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2017, 34(6): 543-549(in Chinese).
[65] 林珈羽, 张越, 刘沅, 等. 不同原料和炭化温度下制备的生物炭结构及性质 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(6): 3200-3206. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201501107 LIN J Y, ZHANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Structure and properties of biochar under different materials and carbonization temperatures [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(6): 3200-3206(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201501107
[66] 尹云锋, 张鹏, 雷海迪, 等. 不同热解温度对生物质炭化学性质的影响 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2014, 35(8): 1496-1500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2014.08.008 YIN Y F, ZHANG P, LEI H D, et al. Influence of different pyrolysis temperature on chemical properties of biochar [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2014, 35(8): 1496-1500(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2014.08.008
[67] 胡华英, 曹升, 杨靖宇, 等. 生物炭对杉木人工林土壤磷素吸附解吸特性的影响 [J]. 西北林学院学报, 2019, 34(4): 8-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2019.04.02 HU H Y, CAO S, YANG J Y, et al. Effects of biochar on phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation [J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2019, 34(4): 8-15(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2019.04.02
[68] 周强, 黄代宽, 余浪, 等. 热解温度和时间对生物炭pH值的影响 [J]. 地球环境学报, 2015, 6(3): 195-200. doi: 10.7515/JEE201503008 ZHOU Q, HUANG D K, YU L, et al. Effects of pyrolysis temperature, time and biochar mass ratio on pH value determination for four biochar solutions [J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2015, 6(3): 195-200(in Chinese). doi: 10.7515/JEE201503008
[69] 徐佳, 刘荣厚. 不同慢速热裂解工艺条件下棉花秸秆生物炭的理化特性分析 [J]. 上海交通大学学报(农业科学版), 2017, 35(2): 19-24. XU J, LIU R H. Physicochemical properties of cotton stalk biochar under different slow pyrolysis conditions [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Agricultural Science), 2017, 35(2): 19-24(in Chinese).
[70] MENG J, FENG X L, DAI Z M, et al. Adsorption characteristics of Cu(Ⅱ) from aqueous solution onto biochar derived from swine manure [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2014, 21(11): 7035-7046. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-2627-z [71] WANG H, TAN L Y, HU B W, et al. Removal of Cr(Ⅵ) from acid mine drainage with clay-biochar composite [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2019, 165: 212-221. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2019.24572 [72] YOON K, CHO D W, TSANG D C W, et al. Fabrication of engineered biochar from paper mill sludge and its application into removal of arsenic and cadmium in acidic water [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 246: 69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.020 [73] PAN J J, JIANG J, XU R K. Adsorption of Cr(Ⅲ) from acidic solutions by crop straw derived biochars [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 25(10): 1957-1965. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60305-2 [74] 刘延湘, 黄彪, 张丽. 花生壳生物炭对水中重金属Cr6+、Cu2+的吸附研究 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(13): 81-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.13.015 LIU Y X, HUANG B, ZHANG L. Adsorption of heavy metal Cr6+ and Cu2+ in aqueous solutions by peanut shell biochar [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(13): 81-85(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.13.015
[75] 王桂仙, 张启伟. 竹炭对水体中重金属离子的吸附规律研究 [J]. 化学与生物工程, 2008, 25(3): 66-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2008.03.019 WANG G X, ZHANG Q W. Adsorption law of bamboo-charcoal for heavy metal ions in aqueous solution [J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2008, 25(3): 66-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2008.03.019
[76] PARK J H, CHO J S, OK Y S, et al. Comparison of single and competitive metal adsorption by pepper stem biochar [J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2016, 62(5): 617-632. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2015.1074186 [77] 王重庆, 王晖, 江小燕, 等. 生物炭吸附重金属离子的研究进展 [J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(1): 692-706. WANG C Q, WANG H, JIANG X Y, et al. Research advances on adsorption of heavy metals by biochar [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(1): 692-706(in Chinese).
[78] 杨选民, 王雅君, 邱凌, 等. 温度对生物质三组分热解制备生物炭理化特性的影响 [J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(4): 284-290. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2017.04.037 YANG X M, WANG Y J, QIU L, et al. Effect of temperature on physicochemical properties of biochar prepared by pyrolysis of three components of biomass [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(4): 284-290(in Chinese). doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2017.04.037
[79] 蒋艳艳, 胡孝明, 金卫斌. 生物炭对废水中重金属吸附研究进展 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2013, 52(13): 2984-2988. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2013.13.003 JIANG Y Y, HU X M, JIN W B. Advances on absorption of heavy metals in the waste water by biochar [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 52(13): 2984-2988(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2013.13.003
[80] 丁文川, 杜勇, 曾晓岚, 等. 富磷污泥生物炭去除水中Pb(Ⅱ)的特性研究 [J]. 环境化学, 2012, 31(9): 1375-1380. DING W C, DU Y, ZENG X L, et al. Aqueous solution Pb(Ⅱ) removal by biochar derived from phosphorus-rich excess sludge [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(9): 1375-1380(in Chinese).
[81] 徐楠楠, 林大松, 徐应明, 等. 玉米秸秆生物炭对Cd2+的吸附特性及影响因素 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(5): 958-964. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2014.05.019 XU N N, LIN D S, XU Y M, et al. Adsorption of aquatic Cd2+ by biochar obtained from corn stover [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(5): 958-964(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2014.05.019
[82] ZHANG Z B, CAO X H, LIANG P, et al. Adsorption of uranium from aqueous solution using biochar produced by hydrothermal carbonization [J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2013, 295(2): 1201-1208. doi: 10.1007/s10967-012-2017-2 [83] 沈州, 罗仙平, 周丹, 等. 生物炭对离子型稀土矿山尾水中氨氮的吸附特性研究 [J]. 中国稀土学报, 2021, 17(5): 1-14. SHEN Z, LUO X P, ZHOU D, et al. Study on the adsorption characteristics of biochar to ammonia nitrogen in ionic rare earth mine tail water [J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2021, 17(5): 1-14(in Chinese).
[84] 郭海艳, 李雪琴, 王章鸿, 等. 蚯蚓粪生物炭对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附性能 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(7): 3811-3818. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201501229 GUO H Y, LI X Q, WANG Z H, et al. Performances of Cu(Ⅱ) adsorption by biochar derived from earthworm manure [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(7): 3811-3818(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201501229
[85] WANG B, LEHMANN J, HANLEY K, et al. Ammonium retention by oxidized biochars produced at different pyrolysis temperatures and residence times [J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(48): 41907-41913. doi: 10.1039/C6RA06419A [86] TONG X J, LI J Y, YUAN J H, et al. Adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ) by biochars generated from three crop straws [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 172(2/3): 828-834. [87] BANDARA T, XU J M, POTTER I D, et al. Mechanisms for the removal of Cd(Ⅱ) and Cu(Ⅱ) from aqueous solution and mine water by biochars derived from agricultural wastes [J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 254: 126745. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126745 [88] 戴静, 刘阳生. 四种原料热解产生的生物炭对Pb2+和Cd2+的吸附特性研究 [J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 49(6): 1075-1082. DAI J, LIU Y S. Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ onto biochars derived from pyrolysis of four kinds of biomasses [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2013, 49(6): 1075-1082(in Chinese).
[89] WANG S S, GAO B, ZIMMERMAN A R, et al. Physicochemical and sorptive properties of biochars derived from woody and herbaceous biomass [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 134: 257-262. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.04.062 [90] LI H B, DONG X L, da SILVA E B, et al. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 178: 466-478. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.072 [91] 张继义, 蒲丽君, 李根. 秸秆生物碳质吸附剂的制备及其吸附性能 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(增刊2): 104-109. ZHANG J Y, PU L J, LI G. Preparation of biochar adsorbent from straw and its adsorption capability [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2011, 27(Sup 2): 104-109.
[92] 林芳竹, 张珣. 生物炭在环境领域的研究与应用进展 [J]. 环境保护与循环经济, 2019, 39(10): 17-20,70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2019.10.006 LIN F Z, ZHANG X. Progress in research and application of biochar in the field of environment [J]. Environmental Protection and Circular Economy, 2019, 39(10): 17-20,70(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1021.2019.10.006
[93] 蒲生彦, 上官李想, 刘世宾, 等. 生物炭及其复合材料在土壤污染修复中的应用研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(3): 629-635. PU S Y, SHANGGUAN L X, LIU S B, et al. A review of the application of biochar and its composites in soil remediation [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(3): 629-635(in Chinese).
[94] WANG B, LEE X, THENG B K G, et al. Biochar addition can reduce NOx gas emissions from a calcareous soil [J]. Environmental Pollutants and Bioavailability, 2019, 31(1): 38-48. doi: 10.1080/09542299.2018.1544035 [95] FANG B, LEE X, ZHANG J, et al. Impacts of straw biochar additions on agricultural soil quality and greenhouse gas fluxes in Karst area, Southwest China [J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2016, 62(5/6): 526-533. [96] 李阳, 李心清, 王兵, 等. 四种改良剂对酸性黄壤土壤酸度和肥力的影响 [J]. 地球与环境, 2016, 44(6): 683-690. LI Y, LIN X Q, WANG B, et al. Effects of four soil amendments on improving soil quality and acidity of yellow soils [J]. Earth and Environment, 2016, 44(6): 683-690(in Chinese).
[97] 徐东昱, 周怀东, 高博. 生物炭吸附重金属污染物的研究进展 [J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2016, 14(1): 7-15. XU D Y, ZHOU H D, GAO B. Review of sorption of heavy metal contaminant on biochar [J]. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2016, 14(1): 7-15(in Chinese).
[98] 刘俊峰, 祝怡斌, 杨晓松, 等. 生物炭去除重金属的研究进展 [J]. 价值工程, 2015, 34(22): 149-152. LIU J F, ZHU Y B, YANG X S, et al. Research progress of dislodging heavy metals by biochar [J]. Value Engineering, 2015, 34(22): 149-152(in Chinese).
[99] QIN Y J, ZHU X L, SU Q, et al. Enhanced removal of ammonium from water by ball-milled biochar [J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020, 42(6): 1579-1587. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00474-5 [100] 莫官海, 谢水波, 曾涛涛, 等. 污泥基生物炭处理酸性含U(Ⅵ)废水的效能与机理 [J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2352-2362. MO G H, XIE S B, ZENG T T, et al. The efficiency and mechanism of U(Ⅵ) removal from acidic wastewater by sewage sludge-derived biochar [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2352-2362(in Chinese).
[101] 朱墨染. 农业废弃物改性生物炭对水中Fe2+和Mn2+去除的应用研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2017. ZHU M R. Study on the use of agricultural waste modified biochar removal of iron ions and manganese ions from water [D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2017.
[102] 宋泽峰, 石晓倩, 刘卓, 等. 芦苇生物炭的制备、表征及其吸附铜离子与双酚A的性能 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(8): 2196-2205. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019052001 SONG Z F, SHI X Q, LIU Z, et al. Synthesis and characterization of reed-based biochar and its adsorption properties for Cu2+ and bisphenol A (BPA) [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(8): 2196-2205(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019052001
[103] WANG D M, ROOT R A, CHOROVER J. Biochar-templated surface precipitation and inner-sphere complexation effectively removes arsenic from acid mine drainage [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021: 1-15. [104] 常帅帅, 张学杨, 王洪波, 等. 木屑生物炭的制备及其对Pb2+的吸附特性研究 [J]. 生物质化学工程, 2020, 54(3): 37-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2020.03.006 CHANG S S, ZHANG X Y, WANG H B, et al. Preparation of biochar from sawdust and it's adsorption property on Pb2+ [J]. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2020, 54(3): 37-44(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2020.03.006
[105] 李瑞月, 陈德, 李恋卿, 等. 不同作物秸秆生物炭对溶液中Pb2+、Cd2+的吸附 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(5): 1001-1008. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.05.025 LI R Y, CHEN D, LI L Q, et al. Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in aqueous solution by biochars derived from different crop residues [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(5): 1001-1008(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2015.05.025
[106] 曹健华, 刘凌沁, 黄亚继, 等. 原料种类和热解温度对生物炭吸附Cd2+的影响 [J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(9): 4183-4190. CAO J H, LIU L Q, HUANG Y J, et al. Effects of feedstock type and pyrolysis temperature on Cd2+ adsorption by biochar [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(9): 4183-4190(in Chinese).
[107] 廖衡妍. 生物炭和电石渣对矿区AMD污染的控制和修复作用[D]. 湘潭: 湖南科技大学, 2019. LIAO H Y. Control and remediation of AMD pollution by biochar and carbide slag in mining area [D]. Xiangtan: Hunan University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[108] AO H T, CAO W, HONG Y X, et al. Adsorption of sulfate ion from water by zirconium oxide-modified biochar derived from pomelo peel [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 708: 135092. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135092 [109] 敖涵婷. 锆改性柚子皮生物炭吸附硫酸根的性能及机理研究[D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2020. AO H T. Performance and mechanism of sulfate adsorption byzirconium-modified pomelo peel biochar [D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2020.
-







 下载:
下载: