-
底泥是湖泊及其流域中重金属等污染物的重要归宿和蓄积库,底泥中的重金属形态和分布不仅能够反映自然和人类活动对湖泊的影响,也反映底泥对水体生态系统的威胁[1-3]。重金属在底泥的垂向分布与水平分布研究同样重要,它们在底泥某层位中的分布可反映某一历史时段内湖泊流域自然和人为活动所造成的重金属流失与污染强度 [4]。重金属是相对保守的物质,具有潜在危害性,一般认为底泥中重金属的毒性几乎与总量无关,而与间隙水中可生物利用的金属组分相关,间隙水中重金属离子浓度与底泥中重金属形态关系紧密[5-6]。底泥中重金属形态主要为金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态、有机质及硫化物结合态和残渣晶格态,它们各自表现出不同的物理化学稳定性、生物可利用性及潜在生态毒害性 [7-8]。重金属的可交换态最易被生物利用,毒性最强,碳酸盐结合态也较易重新释放进入水相,因而可以用底泥中金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态重金属占重金属总量的百分数来评价底泥中重金属的稳定程度 [6, 9]。
南四湖是我国华北平原上面积最大的淡水湖,湖泊面积1266 km2,自北向南依次由南阳、独山、昭阳和微山4个湖串联而成,平均水深约1.46 m。作为华东最重要的煤炭能源基地,南四湖周边地区的城市发电、民用煤燃烧,造纸、食品、化工、医药等行业企业的迅速发展,以及航运交通等方面的影响,南四湖近20年来底泥中Hg、Pb 、Cd和As的含量呈快速增长趋势,尤其是Hg和Pb的污染最为严重 [10-11]。底泥典型重金属对环境的危害除了与其总量有关外,更大程度上取决于其在环境系统中的形态和分布,其元素赋存形态是判断底泥中重金属的毒性响应以及生态风险的重要指标[3, 8]。作为南水北调东线工程最重要的输水通道和京杭大运河最重要的航运路段,对南四湖底泥典型重金属污染物的形态和污染程度进行分析评价具有重要意义[3]。然而,目前针对南四湖不同湖区底泥重金属污染研究多集中在总量水平分布上,而对其形态和垂向分布研究则较少[3, 12]。
本文以南四湖4个湖区为研究对象,在探讨4种典型重金属元素(Pb、Cd 、Hg 、As)主要生物有效形态垂向分布特征的基础上,对其表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属污染程度、潜在生态风险性及稳定性进行评价,揭示南四湖近年来的重金属污染状况,为其水环境保护和底泥污染治理提供参考依据。
-
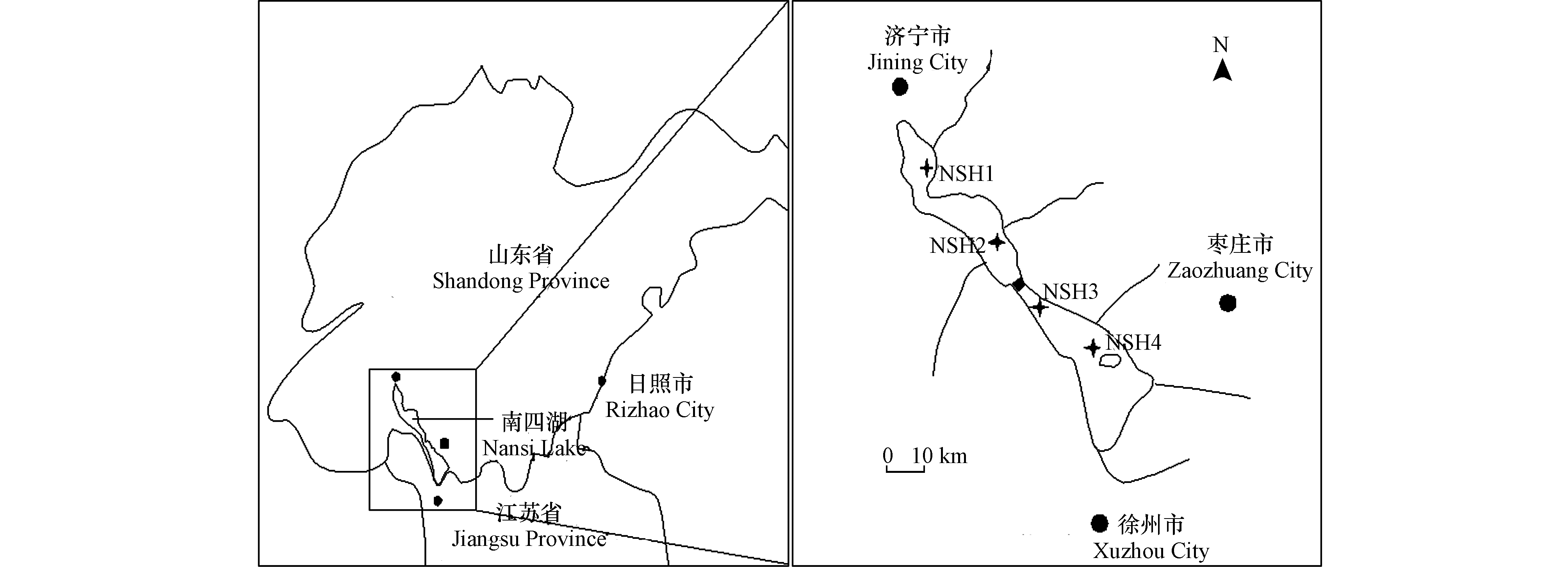
为充分反映南四湖不同湖区底泥性质的差异,结合现场环境条件,在南阳、独山、昭阳和微山等4个湖区的湖心分别设置代表性采样点,采样点布设应避免航运船只扰动及人工养殖的影响,具体采样点见图1。4个采样点位置及经纬度从北向南依次为:南阳湖区(NSH1,35°9′5.64″N,116°39′39″E)、独山湖区(NSH2,35°2′13.08″N,116°50′31.8″E)、昭阳湖区(NSH3,34°50′12.96″N,117°2′8.5″E)和微山湖区(NSH4,34°41′16.26″N,117°13′18.3″E)。
-
2015年1月采集底泥样品,ϕ85 mm×600 mm有机玻璃管的柱状采样器每点采集3根平行样,上部用原样点水样注满后两端用橡皮塞塞紧,垂直放置,小心带回实验室[3]。在室内按10 cm以内间距为2 cm和10 cm以下间距为5 cm进行切样,自然风干至恒重,研磨后过100目筛备用。
-
用Tessier分级提取法对底泥重金属进行形态含量分析[13],本文主要分析生物效应较强的3种形态:金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态和铁锰氧化物结合态。因通过分级提取重金属各形态含量总和往往与实际总量有差异,本文采用三酸提取法对相应重金属总量进行一次性提取[14]。用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES VISTA-MPX,美国Varian公司)检测重金属Pb、Cd、Hg和As总量及各形态含量。ICP-OES 工作前采用双内标Rh 和Re 对分析信号进行校正,RSD 在3%以下,测定前验证标准曲线,每种元素的线性相关系数达到0.9999以上,每批样品做1个平行空白和2个标准参考物质,全程采用空白样品进行对照,用以验证数据的准确性[15]。ICP-OES 测定Pb、Cd、Hg、As 等4种元素的检出限分别为0.01、0.01、0.02、0.05 μg·L−1。
-
底泥重金属污染评价方法很多,地积累指数法[16]与潜在生态危害指数法[17]因简单易行而被广泛应用[3]。地积累指数法能直观的判定重金属污染级别,但该法侧重单一金属元素,潜在生态危害指数法能够综合反映底泥中重金属对生态环境的影响,但其生物毒性加权系数存在主观性,因此将地积累指数(Igeo)和生态危害指数(RI)相互补充进行风险评价更为合理[3, 5]。
南四湖流域原为黄河泛滥平原,本文综合考虑黄河干流底泥和南四湖流域未受污染土壤的化学元素含量选取湖泊底泥中元素分析的环境背景值[3, 18]。参照相关研究,各重金属生物毒性响应因子分别为: Pb5、 Cd30、 Hg30、As10[3, 19]。
-
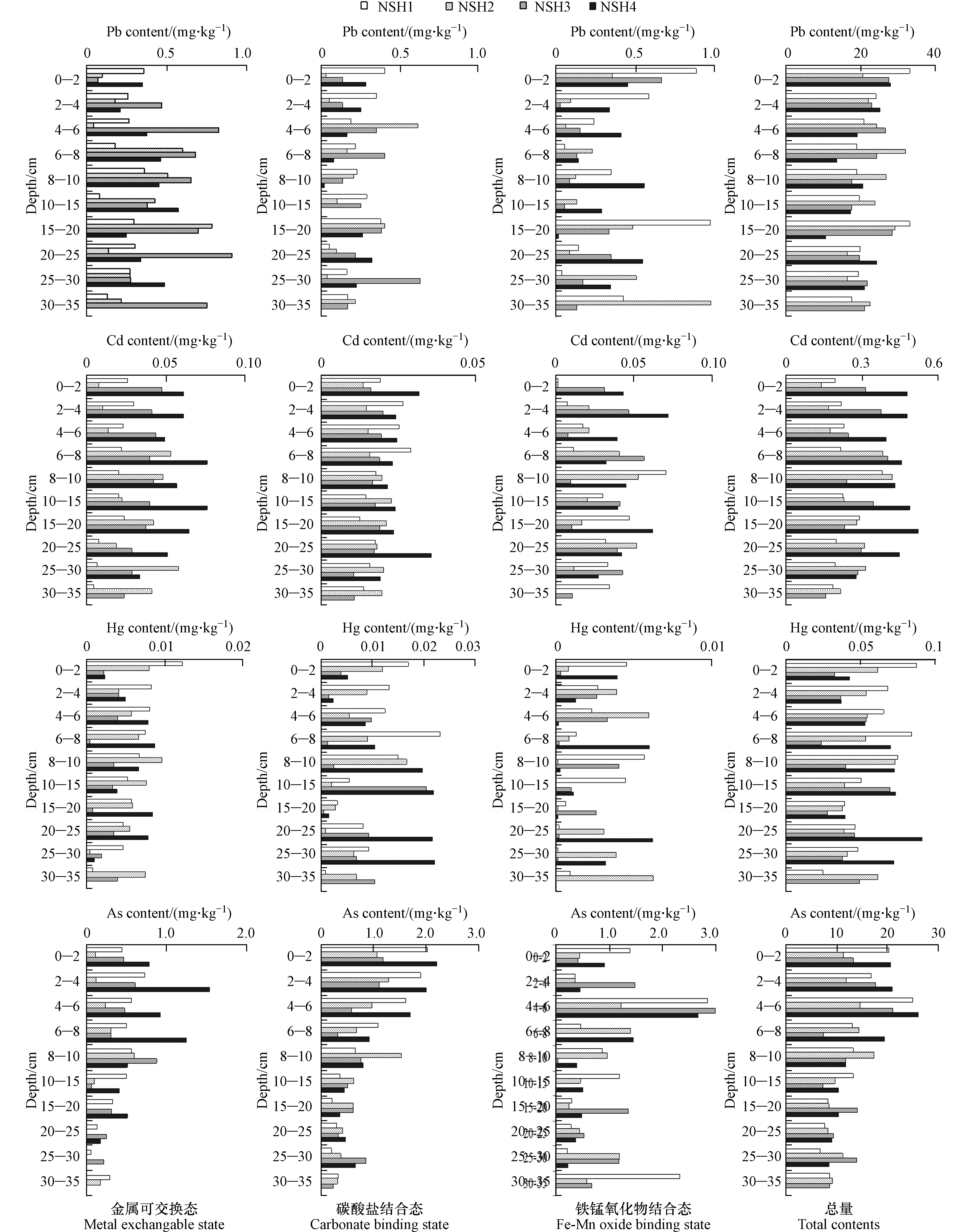
底泥重金属中的金属可交换态和碳酸盐结合态因其生物有效性大,能够更直接的反映底泥重金属的赋存现状与风险;铁锰氧化物比表面积大,吸附重金属能力强,在特定年份受铁锰浓度及重金属污染影响而沉积在相应层次中,铁锰氧化物结合态能反映出沉积各层对应年份的外源污染状况[20-21]。南四湖4个湖区采样点底泥典型重金属Pb、Cd、Hg、As的金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态和铁锰氧化物结合态含量及总量的垂向分布见图2。重金属在底泥的垂向分布特征可反映某一历史时段内湖泊流域自然和人为活动所造成的重金属流失与污染强度,由图2可见,南四湖的4个湖区不同采样点典型重金属形态与含量在垂向分布上差异较大,各元素各形态未表现出一致的变化规律,说明各湖区采样点典型重金属近年来的污染状况亦有所差异。
4个湖区采样点Pb的金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态含量较低,且差异不大,都在1 mg·kg−1的范围内波动,各形态仅占Pb总量的2%左右,底泥Pb的潜在风险相对较小。垂向上,南阳湖区采样点Pb的3种形态和总量有较为一致的变化趋势,即随深度增加呈波动下降,但存在15—20 cm处的相对高值,表明南阳湖区Pb在该层年份污染较重,而且近几年污染未有明显降低,南四湖东部地区是我国重要的煤田能源基地,煤炭燃烧过程和冶金、电镀等工业产生的大量废水是底泥Pb的主要来源[22]。独山湖和昭阳湖采样点表层底泥Pb的金属可交换态与碳酸盐结合态含量较底层明显降低,Pb的总量在表层亦表现出降低趋势,表明近几年这两个湖区Pb污染有所降低;微山湖采样点Pb各形态垂向分布较为复杂,可交换态随深度增加而增加,碳酸盐结合态和铁锰氧化物结合态随深度波动较大,无明显规律,从总量上看,微山湖表层底泥Pb含量有增加趋势。总体上,随着近几年南四湖的综合治理,独山湖和昭阳湖底泥Pb污染有所降低,南阳湖和微山湖降低不明显,但南四湖底泥Pb的含量总体不高,污染风险相对较低。
南四湖各湖区采样点Cd的金属可交换态占比较高,约占总量的15%左右,说明底泥Cd具有较高的释放风险,研究表明,冶金、电镀等工业产生的大量废水和湖区周边农药与化肥的大量使用等是南四湖底泥Cd 的主要来源[22]。垂向上,各湖区差异明显,南阳湖、昭阳湖、微山湖的金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态有随深度增加呈波动下降的趋势,而独山湖表层6 cm内该赋存形态含量明显小于下层,表明独山湖表层底泥Cd的生物有效性明显降低。铁锰氧化物结合态变化趋势可以看出,南阳湖、独山湖表层赋存含量明显小于深层底泥,表明这两个区域当前污染状况有所好转,而微山湖、昭阳湖则相反,近年表现出一定程度的污染,且波动性大。总量上,南阳湖、独山湖、昭阳湖Cd含量峰值出现在6—8 cm,微山湖Cd含量峰值出现在15—20 cm,4个湖区表层0—2 cm含量均略小于2—4 cm,这一现象也见于以上3种结合态,表明近几年湖区外源Cd污染负荷有降低趋势。
南四湖各湖区样点底泥Hg的金属可交换态和碳酸盐结合态占总量的比例在20%以上,底泥中Hg的迁移性较强,具有较大的释放风险,值得关注。垂向上,南阳湖采样点Hg的金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态呈现出随深度增加而减小的趋势,铁锰氧化物结合态15 cm以上含量也明显高于下层,表明该湖区近几年Hg污染没有得到缓解;独山湖金属交换态与碳酸盐结合态有较为一致的变化趋势,即8—10 cm含量最高;昭阳湖三形态垂向分布规律不明显,整体各赋存形态含量要小于其他湖区。微山湖采样点金属交换态与碳酸盐结合态表层含量均较下层低,该湖区近年Hg污染有所降低。总量上,南阳湖、独山湖Hg均有随深度增大而波动减小的趋势,微山湖则相反,昭阳湖不明显,总体上,南阳湖底泥Hg污染较为严重,且近几年未见明显好转,而独山湖、昭阳湖和微山湖Hg污染有降低趋势。南阳湖位于南四湖最北段,靠近济宁市区,除城区煤炭燃烧产生大量Hg外,城区生活污水和工业废水的大量排放应亦是其Hg含量增加的主要原因[22]。
南四湖各湖区采样点As的垂向分布特征明显,除独山湖外,其他湖区金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态均有随深度增加而呈波动减小的趋势;独山湖三种形态含量在6—8 cm层出现峰值,采样点位该层As污染曾经较重,这和当时地方大力发展水产养殖,鱼类饵料中含有微量的As有关,该湖区禁渔后,As污染有所好转,这从总量的垂向分布中亦能得到验证。总量上,虽然4个湖区采样点As有随深度增加而波动递减,但As污染峰值均出现在2—8 cm区间,说明近几年南四湖各湖区As污染开始逐步降低。
-
表层底泥对上覆水影响最为直接,研究表明,风力等动力扰动对底泥理化指标的影响主要集中在表层0—3 cm[23-24]。本研究选择0—4 cm深度的表层底泥作为分析对象,即取0—2 cm和2—4 cm底泥重金属含量的平均值,具体结果见表1。从表1可见,Pb、Cd、Hg、As的4种重金属在4个湖区的含量分别为21.31—28.46、0.16—0.50、0.037—0.079和12.91—20.81 mg·kg−1,对比《土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(GB15618—2018)》,4种重金属含量均低于该标准水田风险筛选值(6.5<pH<7.5)。根据底泥富集系数法[25]对4种重金属进行污染程度评价,4种重金属的富集系数均大于1,4个湖区采样点底泥均受到不同程度的重金属污染,Cd和Hg富集最明显,其次为As和Pb。4个湖区采样点Cd富集系数均在2以上,其中以微山湖污染最为突出,富集系数达到6.44,为显著污染,其次是昭阳湖、南阳湖和微山湖,富集系数依次为3.95、3.03和2.07,均为中度污染。4个湖区采样点Hg污染程度也较重,富集系数均在2以上,污染大小顺序为南阳湖>独山湖>微山湖>昭阳湖,南阳湖富集系数为5.26,为显著污染。各采样点As污染程度由高到低依次为微山湖、南阳湖、昭阳湖和独山湖,微山湖富集系数为2.78,为中度污染。南阳湖Pb的富集最明显,富集系数为1.9,然后依次是微山湖、昭阳湖和独山湖,均为无—弱污染等级。总体上,底泥富集系数法显示,南四湖底泥典型重金属Hg、Cd、As和Pb均有一定程度污染,污染较重的区域为南阳湖和微山湖,独山湖和昭阳湖相对较轻,这与刘良等的研究结果一致[11]。
通过相关公式[26]计算出的南四湖各采样点表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属地积累指数Igeo和潜在生态风险因子Ei、生态风险指数RI结果见表2。由表2看出,根据地积累指数Igeo进行评价,南四湖4个湖区表层底泥普遍受到Hg、Cd、As污染,Pb相对较轻。昭阳湖和微山湖Cd污染较重,分别达到中等污染和中-强污染等级,其中微山湖最严重,南阳湖和独山湖Cd污染相对较轻,为轻-中等级。南阳湖Hg污染最为突出。As在4个湖区均为轻-中污染水平,独山湖最轻。Pb污染独山湖最轻,其他3个湖区均为轻-中污染等级,其中南阳湖最重。
从潜在生态风险因子评价可以看出,4种元素在4个湖区的污染风险等级与地积累指数法得到的污染等级较为接近,但因引入了生物毒性响应因子,生物毒性较强的元素污染风险等级较地积累指数法的污染等级高,说明潜在生态危害指数法更注重污染对生态的危害,同时,生物毒性加权系数亦具有一定的主观性。从表2中Ei看出,4个湖区采样点都明显受到Hg和Cd的污染,为中—强污染风险等级,As、Pb相对较轻,为轻微生态污染风险等级。具体来看,南阳湖区Hg污染风险最强,微山湖Cd污染风险最强,均达到很强等级。从潜在生态风险指数RI看,南阳湖、微山湖达到了重污染生态风险等级,其中Hg和Cd分别是最主要的生态风险贡献因子,昭阳湖、独山湖为中等污染生态风险强度,各湖区污染风险强度大小顺序表现为:微山湖>南阳湖>昭阳湖>独山湖。这与孟祥华等[10]和刘良等[11]的研究基本一致,但也有差异,主要在于微山湖重金属Cd污染因子的贡献加大。另外,底泥中重金属元素各形态组成差异较大,各形态迁移转化能力不同,评价时综合考虑以上因素,才能对其生态风险做出更科学的评价[27],由各湖区底泥Pb、Cd、Hg、As的形态分析得知,南阳湖和独山湖区Cd和Hg的金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态含量占比分别高达36%和33%,具有较高的迁移性,存在生态风险相对较大,应予以重视。
-
底泥中重金属的形态分布不是一成不变的,它们会随着周围环境条件的变化,如:水体温度、pH、底泥有机质和外源重金属等的改变而发生转化[6]。基于重金属可交换态最易被生物利用,毒性最强,碳酸盐结合态也较易重新释放进入水相的特点,很多学者用底泥中金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态重金属占重金属总量的百分数来评价底泥中重金属的稳定程度[6, 9]。本文采用该法得到的南四湖各湖区表层0—4 cm底泥重金属的稳定度(SAC)见表3。由表3看出,Pb、Cd、Hg、As等4种重金属元素的稳定度差异较大,Hg、Cd、As的稳定性较小,Pb相对比较稳定。结合表1重金属富集系数及表2重金属污染评价发现,重金属的稳定性评价与总量污染评价有一定相关性,但并不一致,如微山湖Cd富集系数为6.44,南阳湖为3.03,微山湖Cd污染要明显重于南阳湖,但其稳定度(18.6%)却明显小于南阳湖(25.0%),说明南阳湖底泥Cd中金属可交换态和碳酸盐结合态占比更高、更活跃,对湖泊水环境的变化更敏感,释放风险亦更大 [28]。4个湖区Pb虽然受到一定程度的污染,但考虑到稳定度,其二次释放潜力较小,潜在生态危害并不高。Hg在南阳湖采样点最不稳定,稳定度大小顺序为昭阳湖>微山湖>独山湖>南阳湖。4个湖区各采样点As稳定度均为中等稳定,大小顺序为昭阳湖>独山湖>南阳湖>微山湖,其中,微山湖最不稳定。
-
(1)底泥富集系数法显示,典型重金属Pb、Cd、Hg、As在南四湖4个湖区表层底泥(0—4 cm)中富集系数均大于1,均受到不同程度的污染,其中,Cd、Hg富集最为明显,其次为As和Pb,4个湖区采样点表层底泥污染较重的为南阳湖和微山湖,独山湖和昭阳湖相对较轻。
(2)南四湖4个湖区采样点Pb的金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态含量较低,在1 mg·kg−1的范围内波动,约占Pb总量的2%左右,潜在风险较小,Cd的金属可交换态占比较高,约占总量的15%左右,Hg的金属可交换态和碳酸盐结合态占总量的比例在20%以上,Hg和Cd的潜在风险较大。垂向分布上,4个湖区各重金属形态差异较大,无明显规律,有的随深度增加而波动下降,如As在南阳湖、昭阳湖和微山湖的垂向分布,总体上,除南阳湖表层底泥Hg含量外,其他湖区采样点表层底泥Cd、Hg、As含量均下降,近几年南四湖各湖区重金属污染有降低趋势。
(3)地积累指数评价结果显示,南四湖4个湖区采样点表层底泥普遍受到Hg、Cd、As污染,Pb污染相对较轻。微山湖Cd污染最重,南阳湖Hg污染最为突出,As在4个湖区均为轻—中污染水平,独山湖污染最轻。从潜在生态风险指数RI看出,南阳湖、微山湖为重污染生态风险强度,昭阳湖、独山湖为中等污染风险强度,污染风险程度大小顺序为:微山湖>南阳湖>昭阳湖>独山湖。
(4)南四湖各采样点表层底泥Pb、Cd、Hg、As的稳定度差异较大,其中,Hg、Cd、As稳定性较小,Pb最为稳定。4个湖区Cd均为中等稳定,稳定度大小顺序为独山湖>昭阳湖>微山湖>南阳湖。Hg在南阳湖最不稳定,各湖区大小顺序为昭阳湖>微山湖>独山湖>南阳湖。As的稳定度大小为昭阳湖>独山湖>南阳湖>微山湖。综合比较,南阳湖区底泥Hg污染应引起足够重视。
山东南四湖底泥典型重金属的形态分布、稳定度与风险评价
Fraction distribution, stability and risk assessment of typical heavy metals in sediment of Nansi Lake, Shandong Province, China
-
摘要: 为研究南四湖底泥重金属赋存形态与稳定度的空间差异,利用柱状底泥采样器分别在南阳湖、独山湖、昭阳湖和微山湖采集原位柱状样,在对典型重金属Pb、Cd、Hg、As形态分析的基础上,结合地积累指数法和潜在生态风险指数法,对表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属污染程度进行评价,并对其稳定性进行分析。结果表明,南四湖的4个湖区采样点位表层底泥Pb、Cd、Hg、As均存在一定程度的富集,Hg、Cd富集最为明显,Pb、As次之;Cd和Hg的金属可交换态占比较高,约占总量的10%—15%,潜在风险较大。垂向分布上,4个湖区采样点各重金属形态差异较大,无明显规律。总体上,除南阳湖Hg污染外,其他湖区重金属污染均有降低趋势;地积累指数评价显示,4个湖区采样点表层底泥普遍受到Hg、Cd、As污染,Pb污染相对较轻,微山湖Cd污染和南阳湖Hg污染最为突出;潜在生态风险指数显示,南阳湖、微山湖为重污染生态风险强度,昭阳湖、独山湖为中等污染生态风险强度,污染风险顺序为:微山湖>南阳湖>昭阳湖>独山湖;各湖区采样点4种重金属元素稳定度差异较大,Hg、Cd、As稳定性较小,Pb比较稳定,四湖区各重金属稳定度顺序:Cd为独山湖>昭阳湖>微山湖>南阳湖,Hg为昭阳湖>微山湖>独山湖>南阳湖,As为昭阳湖>独山湖>南阳湖>微山湖。综合比较,南阳湖区底泥Hg污染应引起足够重视。Abstract: In order to study the space differences of heavy metal fraction and stability of sediments in Nansi Lake, columnar sediment sampler was used to collect the intact in situ sediment cores from Nanyang Lake, Dushan Lake, Zhaoyang Lake and Weishan Lake, respectively. On the basis of analyzing the fractions of typical heavy metal Pb, Cd, Hg, As, using geographical accumulation index method and potential ecological risk index method, the heavy metal pollution level of surface sediment (0—4 cm) was evaluated, and the stability of them was analyzed. Results showed that Pb, Cd, Hg, As in the surface sediments of four lakes were all enriched to a certain extent, and Hg, Cd enrichement was the most obvious, followed by Pb and As. The metal exchangeable state amounts of Cd and Hg, accounting for about 10—15% of the total amount, were very high with highly potential risk. The vertical distribution of heavy metal forms in four lakes was quite different with no obvious rules, and in general, the heavy metal pollution had the decreasing trend in Nansi Lake in recent years except for Hg in Nanyng Lake. According to the evaluation of geographical accumulation index, the surface sediments of four lakes were polluted by Hg, Cd and As, and the Cd pollution in Weishan Lake and Hg pollution in Nanyang Lake were the most serious. The potential ecological risk index showed that the sediments of Nanyang Lake and Weishan Lake had heavy ecological pollution risks, Zhaoyang Lake and Dushan Lake had moderate pollution risks, and the pollution risk order was Weishan Lake> Nanyang Lake>Zhaoyang Lake>Dushan Lake. The stability of sediment Hg, Cd and As was poor, the Pb was relatively stable, and the order of Cd stability in four lakes was Dushan Lake>Zhaoyang Lake>Weishan Lake>Nanyang Lake, the Hg was Zhaoyang Lake>Weishan Lake>Dushan Lake>Nanyang Lake, and the As was Zhaoyang Lake>Dushan Lake>Nanyang Lake>Weishan Lake, respectively. Comprehensive comparison, more attention should be paid to Hg pollution in sediment of Nanyang Lake.
-
Key words:
- heavy metals /
- fraction distribution /
- pollution assessment /
- stability /
- Nansi Lake
-
底泥是湖泊及其流域中重金属等污染物的重要归宿和蓄积库,底泥中的重金属形态和分布不仅能够反映自然和人类活动对湖泊的影响,也反映底泥对水体生态系统的威胁[1-3]。重金属在底泥的垂向分布与水平分布研究同样重要,它们在底泥某层位中的分布可反映某一历史时段内湖泊流域自然和人为活动所造成的重金属流失与污染强度 [4]。重金属是相对保守的物质,具有潜在危害性,一般认为底泥中重金属的毒性几乎与总量无关,而与间隙水中可生物利用的金属组分相关,间隙水中重金属离子浓度与底泥中重金属形态关系紧密[5-6]。底泥中重金属形态主要为金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态、有机质及硫化物结合态和残渣晶格态,它们各自表现出不同的物理化学稳定性、生物可利用性及潜在生态毒害性 [7-8]。重金属的可交换态最易被生物利用,毒性最强,碳酸盐结合态也较易重新释放进入水相,因而可以用底泥中金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态重金属占重金属总量的百分数来评价底泥中重金属的稳定程度 [6, 9]。
南四湖是我国华北平原上面积最大的淡水湖,湖泊面积1266 km2,自北向南依次由南阳、独山、昭阳和微山4个湖串联而成,平均水深约1.46 m。作为华东最重要的煤炭能源基地,南四湖周边地区的城市发电、民用煤燃烧,造纸、食品、化工、医药等行业企业的迅速发展,以及航运交通等方面的影响,南四湖近20年来底泥中Hg、Pb 、Cd和As的含量呈快速增长趋势,尤其是Hg和Pb的污染最为严重 [10-11]。底泥典型重金属对环境的危害除了与其总量有关外,更大程度上取决于其在环境系统中的形态和分布,其元素赋存形态是判断底泥中重金属的毒性响应以及生态风险的重要指标[3, 8]。作为南水北调东线工程最重要的输水通道和京杭大运河最重要的航运路段,对南四湖底泥典型重金属污染物的形态和污染程度进行分析评价具有重要意义[3]。然而,目前针对南四湖不同湖区底泥重金属污染研究多集中在总量水平分布上,而对其形态和垂向分布研究则较少[3, 12]。
本文以南四湖4个湖区为研究对象,在探讨4种典型重金属元素(Pb、Cd 、Hg 、As)主要生物有效形态垂向分布特征的基础上,对其表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属污染程度、潜在生态风险性及稳定性进行评价,揭示南四湖近年来的重金属污染状况,为其水环境保护和底泥污染治理提供参考依据。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and Methods)
1.1 采样点布设
为充分反映南四湖不同湖区底泥性质的差异,结合现场环境条件,在南阳、独山、昭阳和微山等4个湖区的湖心分别设置代表性采样点,采样点布设应避免航运船只扰动及人工养殖的影响,具体采样点见图1。4个采样点位置及经纬度从北向南依次为:南阳湖区(NSH1,35°9′5.64″N,116°39′39″E)、独山湖区(NSH2,35°2′13.08″N,116°50′31.8″E)、昭阳湖区(NSH3,34°50′12.96″N,117°2′8.5″E)和微山湖区(NSH4,34°41′16.26″N,117°13′18.3″E)。
1.2 底泥的采集与预处理
2015年1月采集底泥样品,ϕ85 mm×600 mm有机玻璃管的柱状采样器每点采集3根平行样,上部用原样点水样注满后两端用橡皮塞塞紧,垂直放置,小心带回实验室[3]。在室内按10 cm以内间距为2 cm和10 cm以下间距为5 cm进行切样,自然风干至恒重,研磨后过100目筛备用。
1.3 底泥重金属形态分析
用Tessier分级提取法对底泥重金属进行形态含量分析[13],本文主要分析生物效应较强的3种形态:金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态和铁锰氧化物结合态。因通过分级提取重金属各形态含量总和往往与实际总量有差异,本文采用三酸提取法对相应重金属总量进行一次性提取[14]。用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES VISTA-MPX,美国Varian公司)检测重金属Pb、Cd、Hg和As总量及各形态含量。ICP-OES 工作前采用双内标Rh 和Re 对分析信号进行校正,RSD 在3%以下,测定前验证标准曲线,每种元素的线性相关系数达到0.9999以上,每批样品做1个平行空白和2个标准参考物质,全程采用空白样品进行对照,用以验证数据的准确性[15]。ICP-OES 测定Pb、Cd、Hg、As 等4种元素的检出限分别为0.01、0.01、0.02、0.05 μg·L−1。
1.4 重金属污染评价方法
底泥重金属污染评价方法很多,地积累指数法[16]与潜在生态危害指数法[17]因简单易行而被广泛应用[3]。地积累指数法能直观的判定重金属污染级别,但该法侧重单一金属元素,潜在生态危害指数法能够综合反映底泥中重金属对生态环境的影响,但其生物毒性加权系数存在主观性,因此将地积累指数(Igeo)和生态危害指数(RI)相互补充进行风险评价更为合理[3, 5]。
南四湖流域原为黄河泛滥平原,本文综合考虑黄河干流底泥和南四湖流域未受污染土壤的化学元素含量选取湖泊底泥中元素分析的环境背景值[3, 18]。参照相关研究,各重金属生物毒性响应因子分别为: Pb5、 Cd30、 Hg30、As10[3, 19]。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and Discussion)
2.1 底泥重金属形态的垂向分布
底泥重金属中的金属可交换态和碳酸盐结合态因其生物有效性大,能够更直接的反映底泥重金属的赋存现状与风险;铁锰氧化物比表面积大,吸附重金属能力强,在特定年份受铁锰浓度及重金属污染影响而沉积在相应层次中,铁锰氧化物结合态能反映出沉积各层对应年份的外源污染状况[20-21]。南四湖4个湖区采样点底泥典型重金属Pb、Cd、Hg、As的金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态和铁锰氧化物结合态含量及总量的垂向分布见图2。重金属在底泥的垂向分布特征可反映某一历史时段内湖泊流域自然和人为活动所造成的重金属流失与污染强度,由图2可见,南四湖的4个湖区不同采样点典型重金属形态与含量在垂向分布上差异较大,各元素各形态未表现出一致的变化规律,说明各湖区采样点典型重金属近年来的污染状况亦有所差异。
4个湖区采样点Pb的金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态含量较低,且差异不大,都在1 mg·kg−1的范围内波动,各形态仅占Pb总量的2%左右,底泥Pb的潜在风险相对较小。垂向上,南阳湖区采样点Pb的3种形态和总量有较为一致的变化趋势,即随深度增加呈波动下降,但存在15—20 cm处的相对高值,表明南阳湖区Pb在该层年份污染较重,而且近几年污染未有明显降低,南四湖东部地区是我国重要的煤田能源基地,煤炭燃烧过程和冶金、电镀等工业产生的大量废水是底泥Pb的主要来源[22]。独山湖和昭阳湖采样点表层底泥Pb的金属可交换态与碳酸盐结合态含量较底层明显降低,Pb的总量在表层亦表现出降低趋势,表明近几年这两个湖区Pb污染有所降低;微山湖采样点Pb各形态垂向分布较为复杂,可交换态随深度增加而增加,碳酸盐结合态和铁锰氧化物结合态随深度波动较大,无明显规律,从总量上看,微山湖表层底泥Pb含量有增加趋势。总体上,随着近几年南四湖的综合治理,独山湖和昭阳湖底泥Pb污染有所降低,南阳湖和微山湖降低不明显,但南四湖底泥Pb的含量总体不高,污染风险相对较低。
南四湖各湖区采样点Cd的金属可交换态占比较高,约占总量的15%左右,说明底泥Cd具有较高的释放风险,研究表明,冶金、电镀等工业产生的大量废水和湖区周边农药与化肥的大量使用等是南四湖底泥Cd 的主要来源[22]。垂向上,各湖区差异明显,南阳湖、昭阳湖、微山湖的金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态有随深度增加呈波动下降的趋势,而独山湖表层6 cm内该赋存形态含量明显小于下层,表明独山湖表层底泥Cd的生物有效性明显降低。铁锰氧化物结合态变化趋势可以看出,南阳湖、独山湖表层赋存含量明显小于深层底泥,表明这两个区域当前污染状况有所好转,而微山湖、昭阳湖则相反,近年表现出一定程度的污染,且波动性大。总量上,南阳湖、独山湖、昭阳湖Cd含量峰值出现在6—8 cm,微山湖Cd含量峰值出现在15—20 cm,4个湖区表层0—2 cm含量均略小于2—4 cm,这一现象也见于以上3种结合态,表明近几年湖区外源Cd污染负荷有降低趋势。
南四湖各湖区样点底泥Hg的金属可交换态和碳酸盐结合态占总量的比例在20%以上,底泥中Hg的迁移性较强,具有较大的释放风险,值得关注。垂向上,南阳湖采样点Hg的金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态呈现出随深度增加而减小的趋势,铁锰氧化物结合态15 cm以上含量也明显高于下层,表明该湖区近几年Hg污染没有得到缓解;独山湖金属交换态与碳酸盐结合态有较为一致的变化趋势,即8—10 cm含量最高;昭阳湖三形态垂向分布规律不明显,整体各赋存形态含量要小于其他湖区。微山湖采样点金属交换态与碳酸盐结合态表层含量均较下层低,该湖区近年Hg污染有所降低。总量上,南阳湖、独山湖Hg均有随深度增大而波动减小的趋势,微山湖则相反,昭阳湖不明显,总体上,南阳湖底泥Hg污染较为严重,且近几年未见明显好转,而独山湖、昭阳湖和微山湖Hg污染有降低趋势。南阳湖位于南四湖最北段,靠近济宁市区,除城区煤炭燃烧产生大量Hg外,城区生活污水和工业废水的大量排放应亦是其Hg含量增加的主要原因[22]。
南四湖各湖区采样点As的垂向分布特征明显,除独山湖外,其他湖区金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态均有随深度增加而呈波动减小的趋势;独山湖三种形态含量在6—8 cm层出现峰值,采样点位该层As污染曾经较重,这和当时地方大力发展水产养殖,鱼类饵料中含有微量的As有关,该湖区禁渔后,As污染有所好转,这从总量的垂向分布中亦能得到验证。总量上,虽然4个湖区采样点As有随深度增加而波动递减,但As污染峰值均出现在2—8 cm区间,说明近几年南四湖各湖区As污染开始逐步降低。
2.2 表层底泥重金属的分布与污染风险评价
表层底泥对上覆水影响最为直接,研究表明,风力等动力扰动对底泥理化指标的影响主要集中在表层0—3 cm[23-24]。本研究选择0—4 cm深度的表层底泥作为分析对象,即取0—2 cm和2—4 cm底泥重金属含量的平均值,具体结果见表1。从表1可见,Pb、Cd、Hg、As的4种重金属在4个湖区的含量分别为21.31—28.46、0.16—0.50、0.037—0.079和12.91—20.81 mg·kg−1,对比《土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(GB15618—2018)》,4种重金属含量均低于该标准水田风险筛选值(6.5<pH<7.5)。根据底泥富集系数法[25]对4种重金属进行污染程度评价,4种重金属的富集系数均大于1,4个湖区采样点底泥均受到不同程度的重金属污染,Cd和Hg富集最明显,其次为As和Pb。4个湖区采样点Cd富集系数均在2以上,其中以微山湖污染最为突出,富集系数达到6.44,为显著污染,其次是昭阳湖、南阳湖和微山湖,富集系数依次为3.95、3.03和2.07,均为中度污染。4个湖区采样点Hg污染程度也较重,富集系数均在2以上,污染大小顺序为南阳湖>独山湖>微山湖>昭阳湖,南阳湖富集系数为5.26,为显著污染。各采样点As污染程度由高到低依次为微山湖、南阳湖、昭阳湖和独山湖,微山湖富集系数为2.78,为中度污染。南阳湖Pb的富集最明显,富集系数为1.9,然后依次是微山湖、昭阳湖和独山湖,均为无—弱污染等级。总体上,底泥富集系数法显示,南四湖底泥典型重金属Hg、Cd、As和Pb均有一定程度污染,污染较重的区域为南阳湖和微山湖,独山湖和昭阳湖相对较轻,这与刘良等的研究结果一致[11]。
表 1 南四湖表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属含量及富集系数Table 1. Heavy metal contents and enrichment factors in surface sediments (0—4 cm) of Nansi Lake项目 Project Pb Cd Hg As 南阳湖 含量/(mg·kg−1) 28.46±4.17 0.23±0.01 0.079±0.011 18.64±2.01 富集系数 1.90 3.03 5.26 2.49 污染程度 无—弱污染 中度污染 显著污染 中度污染 独山湖 含量/(mg·kg−1) 21.31±0.89 0.16±0.02 0.058±0.007 12.91±0.29 富集系数 1.42 2.07 3.87 1.72 污染程度 无—弱污染 中度污染 中度污染 无—弱污染 昭阳湖 含量/(mg·kg−1) 25.14±3.86 0.30±0.03 0.037±0.019 15.50±1.84 富集系数 1.68 3.95 2.43 2.07 污染程度 无—弱污染 中度污染 中度污染 中度污染 微山湖 含量/(mg·kg−1) 26.51±1.28 0.50±0.01 0.041±0.003 20.81±3.02 富集系数 1.77 6.44 2.72 2.78 污染程度 无—弱污染 显著污染 中度污染 中度污染 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准值(水田,6.5<pH<7.5) 140 0.6 0.6 25 环境背景值/(mg ·kg−1) 15 0.077 0.015 7.5 注:富集系数为底泥重金属含量同环境背景值的比值. Note: Enrichment coefficient is the ratio of sediment heavy metal contents to environmental background values. 通过相关公式[26]计算出的南四湖各采样点表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属地积累指数Igeo和潜在生态风险因子Ei、生态风险指数RI结果见表2。由表2看出,根据地积累指数Igeo进行评价,南四湖4个湖区表层底泥普遍受到Hg、Cd、As污染,Pb相对较轻。昭阳湖和微山湖Cd污染较重,分别达到中等污染和中-强污染等级,其中微山湖最严重,南阳湖和独山湖Cd污染相对较轻,为轻-中等级。南阳湖Hg污染最为突出。As在4个湖区均为轻-中污染水平,独山湖最轻。Pb污染独山湖最轻,其他3个湖区均为轻-中污染等级,其中南阳湖最重。
表 2 南四湖表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属地积累指数Igeo及潜在生态风险指数RITable 2. The index of geoaccumulation (Igeo) and potential ecological risk index (RI) of heavy metals in surface sediments (0—4 cm) of Nansi Lake区域District 潜在生态风险因子EiPotential ecological risk index Ei RI 地积累指数IgeoIndex of geoaccumulation Igeo Pb Cd Hg As Pb Cd Hg As 南阳湖 9.49 80.93 156.44 24.85 272.97 0.34 0.85 1.80 0.73 轻微 强 强 轻微 重污染 轻—中 轻—中 中 轻—中 独山湖 7.10 59.88 115.40 15.61 199.09 −0.08 0.41 1.36 0.06 轻微 中 强 轻微 中等污染 无 轻—中 中 轻—中 昭阳湖 8.38 134.61 69.15 20.67 233.88 0.16 1.58 0.62 0.46 轻微 强 中 轻微 中等污染 轻—中 中 轻—中 轻—中 微山湖 8.84 186.95 80.41 27.75 304.99 0.24 2.05 0.84 0.89 轻微 很强 强 轻微 重污染 轻—中 中—强 轻—中 轻—中 从潜在生态风险因子评价可以看出,4种元素在4个湖区的污染风险等级与地积累指数法得到的污染等级较为接近,但因引入了生物毒性响应因子,生物毒性较强的元素污染风险等级较地积累指数法的污染等级高,说明潜在生态危害指数法更注重污染对生态的危害,同时,生物毒性加权系数亦具有一定的主观性。从表2中Ei看出,4个湖区采样点都明显受到Hg和Cd的污染,为中—强污染风险等级,As、Pb相对较轻,为轻微生态污染风险等级。具体来看,南阳湖区Hg污染风险最强,微山湖Cd污染风险最强,均达到很强等级。从潜在生态风险指数RI看,南阳湖、微山湖达到了重污染生态风险等级,其中Hg和Cd分别是最主要的生态风险贡献因子,昭阳湖、独山湖为中等污染生态风险强度,各湖区污染风险强度大小顺序表现为:微山湖>南阳湖>昭阳湖>独山湖。这与孟祥华等[10]和刘良等[11]的研究基本一致,但也有差异,主要在于微山湖重金属Cd污染因子的贡献加大。另外,底泥中重金属元素各形态组成差异较大,各形态迁移转化能力不同,评价时综合考虑以上因素,才能对其生态风险做出更科学的评价[27],由各湖区底泥Pb、Cd、Hg、As的形态分析得知,南阳湖和独山湖区Cd和Hg的金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态含量占比分别高达36%和33%,具有较高的迁移性,存在生态风险相对较大,应予以重视。
2.3 底泥重金属稳定度评价
底泥中重金属的形态分布不是一成不变的,它们会随着周围环境条件的变化,如:水体温度、pH、底泥有机质和外源重金属等的改变而发生转化[6]。基于重金属可交换态最易被生物利用,毒性最强,碳酸盐结合态也较易重新释放进入水相的特点,很多学者用底泥中金属可交换态及碳酸盐结合态重金属占重金属总量的百分数来评价底泥中重金属的稳定程度[6, 9]。本文采用该法得到的南四湖各湖区表层0—4 cm底泥重金属的稳定度(SAC)见表3。由表3看出,Pb、Cd、Hg、As等4种重金属元素的稳定度差异较大,Hg、Cd、As的稳定性较小,Pb相对比较稳定。结合表1重金属富集系数及表2重金属污染评价发现,重金属的稳定性评价与总量污染评价有一定相关性,但并不一致,如微山湖Cd富集系数为6.44,南阳湖为3.03,微山湖Cd污染要明显重于南阳湖,但其稳定度(18.6%)却明显小于南阳湖(25.0%),说明南阳湖底泥Cd中金属可交换态和碳酸盐结合态占比更高、更活跃,对湖泊水环境的变化更敏感,释放风险亦更大 [28]。4个湖区Pb虽然受到一定程度的污染,但考虑到稳定度,其二次释放潜力较小,潜在生态危害并不高。Hg在南阳湖采样点最不稳定,稳定度大小顺序为昭阳湖>微山湖>独山湖>南阳湖。4个湖区各采样点As稳定度均为中等稳定,大小顺序为昭阳湖>独山湖>南阳湖>微山湖,其中,微山湖最不稳定。
表 3 南四湖各采样点表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属稳定程度Table 3. The stable risks of heavy metals in surface sediment (0—4 cm) of Nansi Lake区域District Pb Cd Hg As 南阳湖 SAC 2.4% 25.0% 32.7% 13.6% 分级 稳定 中等稳定 不稳定 中等稳定 独山湖 SAC 0.8% 14.9% 28.6% 11.0% 分级 极稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 昭阳湖 SAC 1.6% 18.1% 16.9% 10.9% 分级 稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 微山湖 SAC 2.1% 18.6% 18.6% 15.7% 分级 稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)底泥富集系数法显示,典型重金属Pb、Cd、Hg、As在南四湖4个湖区表层底泥(0—4 cm)中富集系数均大于1,均受到不同程度的污染,其中,Cd、Hg富集最为明显,其次为As和Pb,4个湖区采样点表层底泥污染较重的为南阳湖和微山湖,独山湖和昭阳湖相对较轻。
(2)南四湖4个湖区采样点Pb的金属可交换态、碳酸盐结合态、铁锰氧化物结合态含量较低,在1 mg·kg−1的范围内波动,约占Pb总量的2%左右,潜在风险较小,Cd的金属可交换态占比较高,约占总量的15%左右,Hg的金属可交换态和碳酸盐结合态占总量的比例在20%以上,Hg和Cd的潜在风险较大。垂向分布上,4个湖区各重金属形态差异较大,无明显规律,有的随深度增加而波动下降,如As在南阳湖、昭阳湖和微山湖的垂向分布,总体上,除南阳湖表层底泥Hg含量外,其他湖区采样点表层底泥Cd、Hg、As含量均下降,近几年南四湖各湖区重金属污染有降低趋势。
(3)地积累指数评价结果显示,南四湖4个湖区采样点表层底泥普遍受到Hg、Cd、As污染,Pb污染相对较轻。微山湖Cd污染最重,南阳湖Hg污染最为突出,As在4个湖区均为轻—中污染水平,独山湖污染最轻。从潜在生态风险指数RI看出,南阳湖、微山湖为重污染生态风险强度,昭阳湖、独山湖为中等污染风险强度,污染风险程度大小顺序为:微山湖>南阳湖>昭阳湖>独山湖。
(4)南四湖各采样点表层底泥Pb、Cd、Hg、As的稳定度差异较大,其中,Hg、Cd、As稳定性较小,Pb最为稳定。4个湖区Cd均为中等稳定,稳定度大小顺序为独山湖>昭阳湖>微山湖>南阳湖。Hg在南阳湖最不稳定,各湖区大小顺序为昭阳湖>微山湖>独山湖>南阳湖。As的稳定度大小为昭阳湖>独山湖>南阳湖>微山湖。综合比较,南阳湖区底泥Hg污染应引起足够重视。
-
表 1 南四湖表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属含量及富集系数
Table 1. Heavy metal contents and enrichment factors in surface sediments (0—4 cm) of Nansi Lake
项目 Project Pb Cd Hg As 南阳湖 含量/(mg·kg−1) 28.46±4.17 0.23±0.01 0.079±0.011 18.64±2.01 富集系数 1.90 3.03 5.26 2.49 污染程度 无—弱污染 中度污染 显著污染 中度污染 独山湖 含量/(mg·kg−1) 21.31±0.89 0.16±0.02 0.058±0.007 12.91±0.29 富集系数 1.42 2.07 3.87 1.72 污染程度 无—弱污染 中度污染 中度污染 无—弱污染 昭阳湖 含量/(mg·kg−1) 25.14±3.86 0.30±0.03 0.037±0.019 15.50±1.84 富集系数 1.68 3.95 2.43 2.07 污染程度 无—弱污染 中度污染 中度污染 中度污染 微山湖 含量/(mg·kg−1) 26.51±1.28 0.50±0.01 0.041±0.003 20.81±3.02 富集系数 1.77 6.44 2.72 2.78 污染程度 无—弱污染 显著污染 中度污染 中度污染 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准值(水田,6.5<pH<7.5) 140 0.6 0.6 25 环境背景值/(mg ·kg−1) 15 0.077 0.015 7.5 注:富集系数为底泥重金属含量同环境背景值的比值. Note: Enrichment coefficient is the ratio of sediment heavy metal contents to environmental background values. 表 2 南四湖表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属地积累指数Igeo及潜在生态风险指数RI
Table 2. The index of geoaccumulation (Igeo) and potential ecological risk index (RI) of heavy metals in surface sediments (0—4 cm) of Nansi Lake
区域District 潜在生态风险因子EiPotential ecological risk index Ei RI 地积累指数IgeoIndex of geoaccumulation Igeo Pb Cd Hg As Pb Cd Hg As 南阳湖 9.49 80.93 156.44 24.85 272.97 0.34 0.85 1.80 0.73 轻微 强 强 轻微 重污染 轻—中 轻—中 中 轻—中 独山湖 7.10 59.88 115.40 15.61 199.09 −0.08 0.41 1.36 0.06 轻微 中 强 轻微 中等污染 无 轻—中 中 轻—中 昭阳湖 8.38 134.61 69.15 20.67 233.88 0.16 1.58 0.62 0.46 轻微 强 中 轻微 中等污染 轻—中 中 轻—中 轻—中 微山湖 8.84 186.95 80.41 27.75 304.99 0.24 2.05 0.84 0.89 轻微 很强 强 轻微 重污染 轻—中 中—强 轻—中 轻—中 表 3 南四湖各采样点表层底泥(0—4 cm)重金属稳定程度
Table 3. The stable risks of heavy metals in surface sediment (0—4 cm) of Nansi Lake
区域District Pb Cd Hg As 南阳湖 SAC 2.4% 25.0% 32.7% 13.6% 分级 稳定 中等稳定 不稳定 中等稳定 独山湖 SAC 0.8% 14.9% 28.6% 11.0% 分级 极稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 昭阳湖 SAC 1.6% 18.1% 16.9% 10.9% 分级 稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 微山湖 SAC 2.1% 18.6% 18.6% 15.7% 分级 稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 中等稳定 -
[1] CHATTERJEE M, SILVA F E V, SARKAR S K, et al. Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance [J]. Environment International, 2007, 33(3): 346-356. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2006.11.013 [2] 马长城, 孙竹梅, 胥军, 等. 湖北菱角湖沉积物中重金属垂直分布及形态分析 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2014, 37(3): 136-139. MA C C, SUN Z M, XU J, et al. Vertical distribution and speciation analysis of heavy metals in sediments of Lingjiao Lake, Hubei [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2014, 37(3): 136-139(in Chinese).
[3] 张智慧, 李宝, 梁仁君. 南四湖南阳湖区河口与湖心沉积物重金属形态对比研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(5): 1408-1416. ZHANG Z H, LI B, LIANG R J. Comparison of sediment heavy metal fractions at estuary and center of Nanyang Zone from Nansi Lake, China [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(5): 1408-1416(in Chinese).
[4] 杨丽原, 沈吉, 张祖陆, 等. 南四湖表层底泥重金属污染及其风险性评价 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2003, 15(3): 252-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2003.03.009 YANG L Y, SHEN J, ZHANG Z L, et al. Distribution and ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in superficial sediments of Nansihu Lake [J]. Journal of Lake Science, 2003, 15(3): 252-256(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2003.03.009
[5] 范成新, 张路. 太湖-沉积物污染与修复原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 162—165. FAN C X, ZHANG L. Principles of sediment pollution and remediation in Lake Taihu[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 162—165 (in Chinese).
[6] 汪玉娟, 吕文英, 刘国光, 等. 沉积物中重金属的形态及生物有效性研究进展 [J]. 安全与环境工程, 2009, 16(4): 27-29,37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2009.04.007 WANG Y J, LV W Y, LIU G G, et al. Progress in research on heavy metal speciation and bioavailability in sediment [J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2009, 16(4): 27-29,37(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2009.04.007
[7] ALCOCK S, BARCELO D, HANSEN P-D. Monitoring freshwater sediments [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2003, 18(8): 1077-1083. doi: 10.1016/S0956-5663(02)00210-5 [8] 章骅, 何品晶, 吕凡, 等. 重金属在环境中的化学形态分析研究进展 [J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(1): 130-137. ZHANG H, HE J J, LV F, et al. A review on the methods for investigating heavy metal speciation in environmental chemistry [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(1): 130-137(in Chinese).
[9] SINGH K P, MOHAN D, SINGH V K, et al. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river Sediments-a tributary of the Ganges, India [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 312: 14-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.01.021 [10] 孟祥华, 刘恩峰, 杨丽原, 等. 南四湖及主要入湖河流沉积物金属空间分布特征与污染评价 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2010, 23(1): 1-6. MENG X H, LIU E F, YANG L Y, et al. Spatial distribution and contamination evaluation of metals in sediments from Nansihu Lake and its main inflow rivers [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 23(1): 1-6(in Chinese).
[11] 刘良, 张祖陆. 南四湖表层沉积物重金属的空间分布、来源及污染评价 [J]. 水生态学杂志, 2013, 34(6): 7-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3075.2013.06.002 LIU L, ZHANG Z L. Spatial distribution, sources metals in the surface and pollution assessment of heavy sediments of Nansihu Lake [J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2013, 34(6): 7-15(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3075.2013.06.002
[12] 刘恩峰, 沈吉, 王建军, 等. 南四湖表层沉积物重金属的赋存形态及底部界面扩散通量的估算 [J]. 环境化学, 2011, 29(5): 870-874. LIU E F, SHEN J, WANG J J, et al. Chemical forms of the heavy metals in surface sediment from Nansihu Lake and their diffusion flux at the sediment-water interface [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 29(5): 870-874(in Chinese).
[13] TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M, et al. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7): 844-852. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017 [14] 张霖琳, 梁宵, 加那尔别克·西里甫汗, 等. 在土壤及底泥重金属测定中不同前处理和分析方法的比较 [J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(2): 302-306. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.02.018 ZHANG L L, LIANG X, JANARBEK X L F H, et al. Comparison of different pretreatment and analytical method of heavy metals in soil and sediment samples [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(2): 302-306(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.02.018
[15] 邱继彩, 梁仁君, 孙爱德, 等. 祊河下游河水中重金属污染评价 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(20): 176-180. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2013-0721 QIU J C, LIANG R J, SUN A D, etal. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the Beng downstream river water [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013, 29(20): 176-180(in Chinese). doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2013-0721
[16] MULLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of Rhine River [J]. GeoJournal, 1969, 2(3): 109-118. [17] HKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control:a sedimentological approach [J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8 [18] 张朝生, 章申, 王立军, 等. 长江与黄河沉积物金属元素地球化学特征及其比较 [J]. 地理学报, 1998, 53(4): 314-322. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1998.04.005 ZHANG C S, ZHANG S, WANG L J, et al. Geochemistry of metals in sediments from Changjiang River and Huanghe River and their comparison [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1998, 53(4): 314-322(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1998.04.005
[19] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2): 112-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.02.030 XU Z Q, NI S J, TUO X G, et al. Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2008, 31(2): 112-115(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2008.02.030
[20] KALNEJAIS L H, MARTIN W R, SIGNELL R P, et al. Role of sediment resuspension in the remobilization of particulate-phase metals from coastal sediments [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(7): 2282-2288. [21] 俞慎, 历红波. 沉积物再悬浮-重金属释放机制研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(7): 1724-1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.07.038 YU S, LI H B. Perspectives on the release of heavy metals via sediment resuspension [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2010, 19(7): 1724-1731(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.07.038
[22] 沈吉, 张祖陆, 杨丽原, 等. 南四湖-环境与资源研究[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2008: 141—159. SHEN J, ZHANG Z L, YANG L Y, et al. Nansi Lake-environmental and resource studies[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2008, 141—159 (in Chinese).
[23] 李宝, 孙春意, 张智慧, 等. 小埠东橡胶坝对沂河临沂城区蓄水段沉积物重金属分布的影响 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(4): 243-246. LI B, SUN C Y, ZHANG Z H, et al. Effects of Xiaobudong rubber dam on the distribution of sediment heavy metals in Yihe River at Linyi City, Shandong Province [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(4): 243-246(in Chinese).
[24] LOPEZ-GALVAN E, BARCELO-QUINTAL I, SOLIS-CORREA H E, et al. Calculation of the ecological risk index in the José Antonio Alzate Dam, State of Mexico, Mexico [J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2010, 135: 121-135. doi: 10.1007/s12011-009-8501-z [25] 王霞. 黄河上游典型地区底泥重金属调查与污染评价[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2014, 22—24. WANG X. Investigation and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from typical regions in upstream of Yellow River[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2014, 22—24 (in Chinese).
[26] 毛志刚, 谷孝鸿, 陆小明, 等. 太湖东部不同类型湖区疏浚后沉积物重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(1): 187-193. MAO Z G, GU X H, LU X M, et al. Pollution distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from the different eastern dredging regions of Lake Taihu [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2014, 35(1): 187-193(in Chinese).
[27] 田林锋, 胡继伟, 罗桂林, 等. 贵州百花湖沉积物重金属稳定性及潜在生态风险性研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(4): 886-894. TIAN L F, HU J W, LUO G L, et al. Ecological risk and stability of heavy metals in sediments from Lake Baihua in Guizhou Province [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012, 32(4): 886-894(in Chinese).
[28] 程晓东, 郭明新. 河流底泥重金属不同形态的生物有效性 [J]. 农业环境保护, 2001, 20(1): 19-22. CHEN X D, GUO M X. Bioavailability of heavy metals at different forms in sediment [J]. Agro-Environmental Protection, 2001, 20(1): 19-22(in Chinese).
-




 下载:
下载: