-
抗菌剂的长期滥用导致了细菌耐药性问题不断加剧,致使抗菌剂的抗菌效果降低,对人类的健康生存和长期发展造成潜在的威胁。如何缓解细菌耐药性成为了大多数研究者在治疗细菌感染和治理环境污染过程中的主要问题[1]。抗菌剂的联合治疗不仅可以增加抗菌剂的治疗效果,还可以防止和减少细菌耐药性[2]。因此,探索抗菌剂之间的联合作用效应,对提高抗菌剂的抗菌疗效并减少细菌耐药性问题具有重要意义。
常用的抗菌剂可分为无机抗菌剂和有机抗菌剂[3]。银系抗菌剂为不易产生耐药性的无机抗菌材料,具有抗菌广谱性、持久性、热稳定性好和安全性高等优势。硝酸银(AgNO3)和纳米银(AgNPs)作为两种常见的银系抗菌剂,被广泛应用于抗感染的伤口敷料、牙齿治疗、泌尿系统感染和慢性溃疡等临床治疗的多个方面[4]。如丁刚等[5]总结了硝酸银涂布治疗真菌性角膜炎的诊治经验,发现硝酸银涂布对于病变位于浅中基质层的真菌性角膜炎具有良好疗效,可缩短溃疡愈合时间,减少抗真菌药物的应用等。冯瑶等[6]研究纳米银在牙科根管应用中,发现纳米银与氢氧化钙联合作用于饥饿期的粪肠球菌生物膜呈现显著的抑菌效果。由此看出AgNO3和AgNPs在抗菌治疗中具有广泛的应用前景,可以表现出良好的抗菌效果。
有机抗菌剂通常是指以有机物为抗菌物质的抗菌剂。由于具有抗菌效果好、抗菌作用迅速等优点,有机抗菌剂被广泛应用于制造业、医疗以及水处理等多个行业[7]。抗生素是一种常见的有机抗菌剂,其主要包括β-内酰胺类、四环素类、氨基糖苷类、大环内酯类以及多肽类抗生素等,被广泛应用于农业、畜牧业和医疗卫生等多个领域,对防治感染性疾病起到重要的作用。表面活性剂是一类具有两亲性质的有机抗菌剂,通过与细菌生物膜蛋白质的强烈相互作用使细菌变性或失去功能,在医药、洗涤、农药等方面有着广泛的应用[8];唑啉类有机抗菌剂因其具有抗菌能力强、药效持久、对环境安全以及抗菌谱宽广等优良性能,在工业、农业、医药等行业中广泛使用[9]。基于有机抗菌剂广泛的应用前景,AgNO3和AgNPs和不同的有机抗菌剂联合会产生什么样的抗菌效果呢?是否可以从这些不同的有机抗菌剂中筛选出与AgNO3和AgNPs联合产生协同效应的抗菌剂,从而提高抗菌剂的联合抗菌效果呢?
近几年,对于银系抗菌剂与有机抗菌剂的联合研究报道逐渐增多。如Xu等[10]对AgNO3与抗生素万古霉素、利福平、庆大霉素和左氧氟沙星分别进行抗菌性能测试,发现其联合治疗的抗菌活性均得到了提高。Deng等[11]探讨了AgNPs分别与氨苄青霉素、青霉素、依诺沙星、卡那霉素、新霉素和四环素对耐多药菌伤寒沙门氏菌的联合抗菌作用,依诺沙星、卡那霉素、新霉素和四环素在与AgNPs联合时对沙门氏菌表现出协同作用,而氨苄西林和青霉素则没有。由此可以看出,银系抗菌剂和有机抗菌剂的联合抗菌治疗效果会由于有机抗菌剂的结构及单一作用机制的不同而不同。此外,当化合物之间以不同比例混合时会呈现不同的联合作用方式。如仇爱锋等[12]在研究克百威、镉和铜对费氏弧菌的联合毒性效应中,发现克百威和镉的二元混合体系在以毒性单位为1∶1和1∶2的混合下联合毒性作用部分呈现相加效应,而在2∶1混合时产生协同效应。因此,有必要开展银系抗菌剂与不同有机抗菌剂在不同毒性比混合下的联合效应研究,以进一步提高抗菌剂在细菌感染治疗中的抗菌效果,并为评估它们在进入环境后可能产生的联合暴露风险给予参考依据。
大肠杆菌是生物体内最常见的细菌之一,由于它具有分裂增殖能力强、发育周期短以及结构简单等特点,已作为一种重要的模式生物在现代生命科学研究领域起着重要的作用。因此,本文以大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)为模式生物,通过联合毒性实验,测定AgNO3和AgNPs分别与抗生素、表面活性剂和唑啉类杀菌剂等有机抗菌剂的联合毒性效应,并对它们的联合毒性作用机制进行了初步的讨论,以期在未来为银系抗菌剂与有机抗菌剂联合用药以及环境联合暴露风险评价提供参考。
-
测试化合物中,四环素类抗生素购自Sigma-Aldrich化学制品有限公司,硝酸银、β-内酰胺类、氨基糖苷类、多肽类、大环内酯类抗生素以及唑啉类杀菌剂、表面活性剂均购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司,纳米银溶液购自宇瑞(上海)化学有限公司,纯度均为分析纯以上,化合物的基本信息如表1。
本实验中使用的模式生物E.coli(Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655),菌种冻干粉购自Biovector生物科技有限公司(北京)。
-
受试化合物在毒性试验中采用不超过总体积0.1%的二甲基亚砜(DMSO)助溶后,用1 %NaCl溶液配制成待测化合物母液。实验时再用1%NaCl溶液将待测化合物母液稀释成等对数梯度系列,将化合物溶液加入96孔酶标板中,每孔包含80 μL的待测化合物溶液(作为实验组)或1 %的NaCl溶液(作为对照组),80 μL的2.5倍LB培养基和40 μL工作菌液。最后将96孔酶标板放置在37ºC下,转速为165 r·min−1的培养箱中培养24 h至E.coli到平台期后,用酶标仪测定波长600 nm处,96孔板每孔的光密度(optical density,OD600)。通过剂量-效应曲线得到抑制率达到50 %时对应的化合物浓度即为EC50,根据单一化合物的EC50,配制化合物A与化合物B在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比的混合溶液,然后按照单一毒性测定方法测定系列混合溶液的联合毒性。
-
单一毒性结果采用抑制率Inhibition(%)来表征,联合毒性作用采用毒性单位(Toxicity Unit TU)值来表述,抑制率及TU值的计算如下式:
式(1)中,OD600,0为E.coli在无染毒作用下的对照组OD平均值,OD600,i为测试化合物作用下实验组的OD平均值。式(2)中,CA、CB是混合体系产生50 %抑制效应时化合物A、B各自的摩尔浓度(mol·L−1),EC50A和EC50B是单一化合物A、B分别作用产生50%抑制效应时的浓度。根据采用Broderius的联合毒性作用判别标准[13],当 TU<0.8认为两组分间为协同效应;0.8≤TU≤1.2认为两组分间为相加效应;TU>1.2认为两组分间为拮抗效应。
-
银系抗菌剂与8种有机抗菌剂对大肠杆菌的单一毒性数据如表1所示。其中,毒性最大的为多肽类抗生素PMX,其−lgEC50为6.59 mol·L−1。所有抗菌剂中的毒性大小排序为:多肽类抗生素PMX>氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN>四环素类抗生素TC>大环内酯类抗生素ERY>AgNPs>唑啉类杀菌剂MIT>AgNO3>糖肽类抗生素VA>表面活性剂DTAB>β-内酰胺类抗生素PVP。
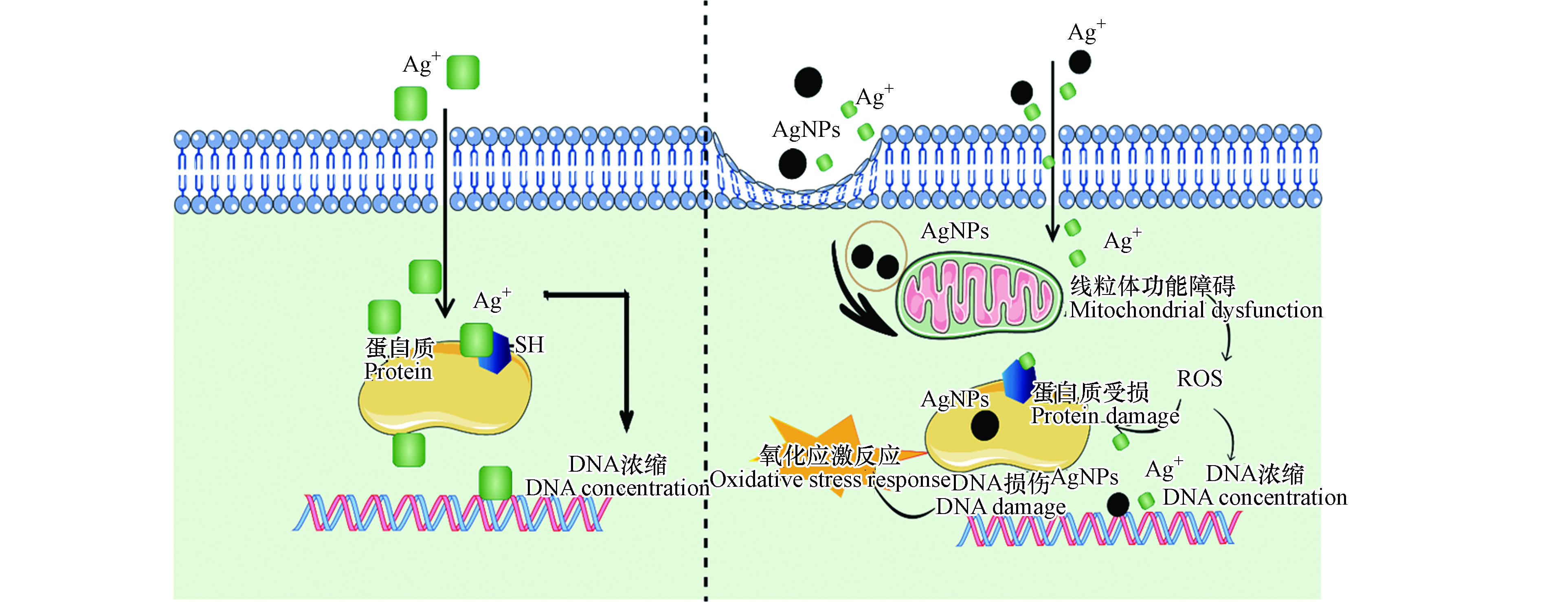
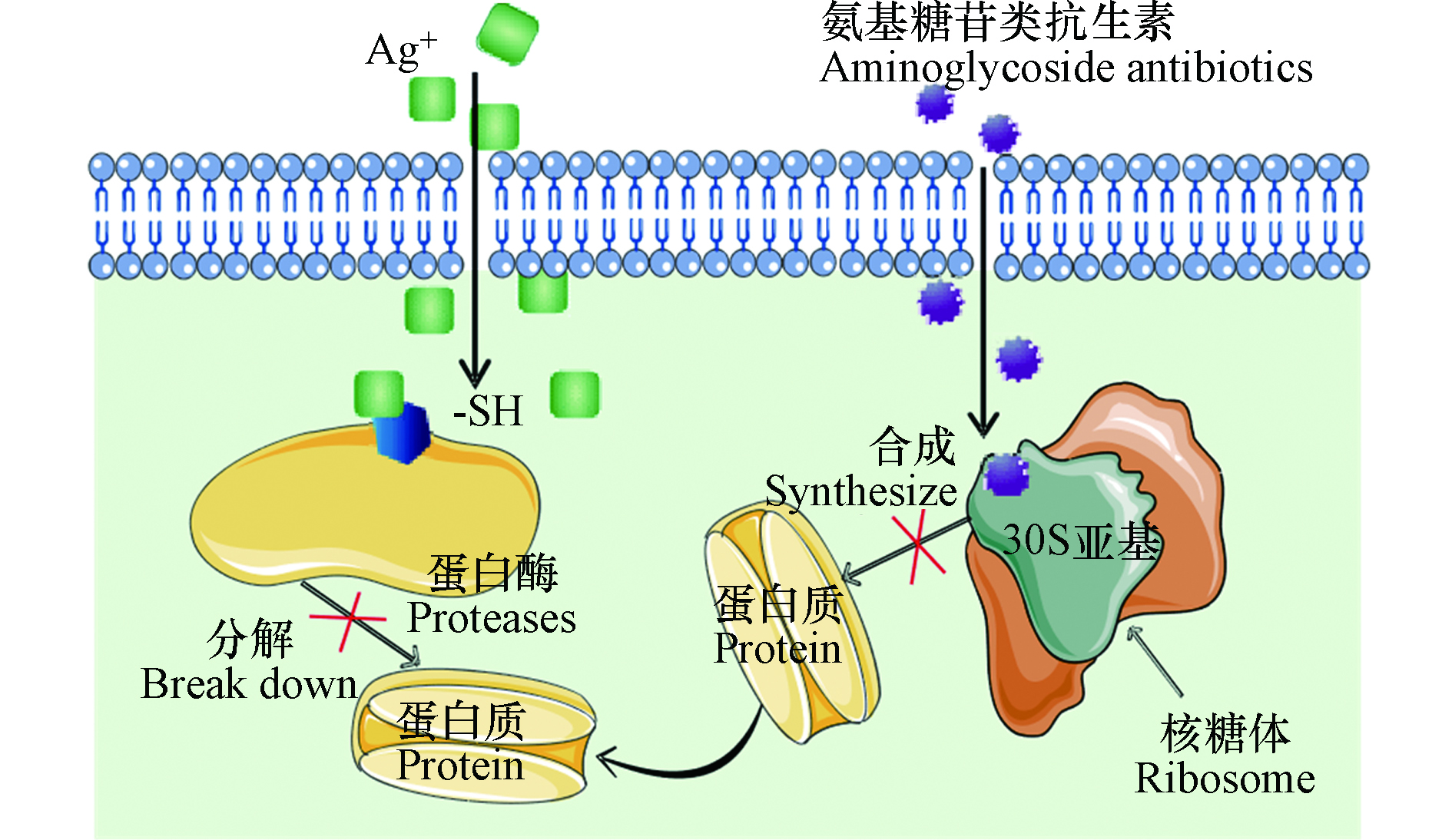
基于前人对于银系抗菌剂的研究,纳米银和硝酸银的作用机制如图1所示,AgNO3通过释放Ag+来发挥其抗菌性,Ag+能吸附在带负电的细菌细胞壁上,并能够穿透细胞膜进入细胞内部,与细菌中蛋白酶上的巯基(—SH)迅速结合,使蛋白酶丧失活性,同时,也可以通过浓缩DNA使其失去复制能力而引起DNA的降解来抑制细菌的生长繁殖[14-15]。AgNPs抗菌机理主要由于其自身的尺寸很小而具有较高比表面积,从而呈现较高的反应活性,释放出Ag+发挥其抗菌作用;同时,AgNPs还可以通过扩散或内吞作用进入细胞,引起线粒体功能障碍,造成线粒体呼吸链的破坏,增加活性氧(ROS)的产生并抑制了三磷酸腺苷ATP的合成,从而导致DNA损伤、细胞内的蛋白质受损,当生成的ROS超过细胞抗氧化防御系统的能力时,发生氧化损伤,最终抑制细菌的增殖[16]。本研究中,AgNO3和AgNPs的-logEC50分别为4.51 mol·L−1和4.78 mol·L−1,说明AgNO3与AgNPs的抗菌活性相差不大。因此,推测实验中AgNO3与AgNPs的可能都是主要Ag+来发挥毒性作用。该推测与已有研究[17-18]中表明AgNO3和AgNPs主要是通过释放Ag+来发挥其抗菌性的结论一致。
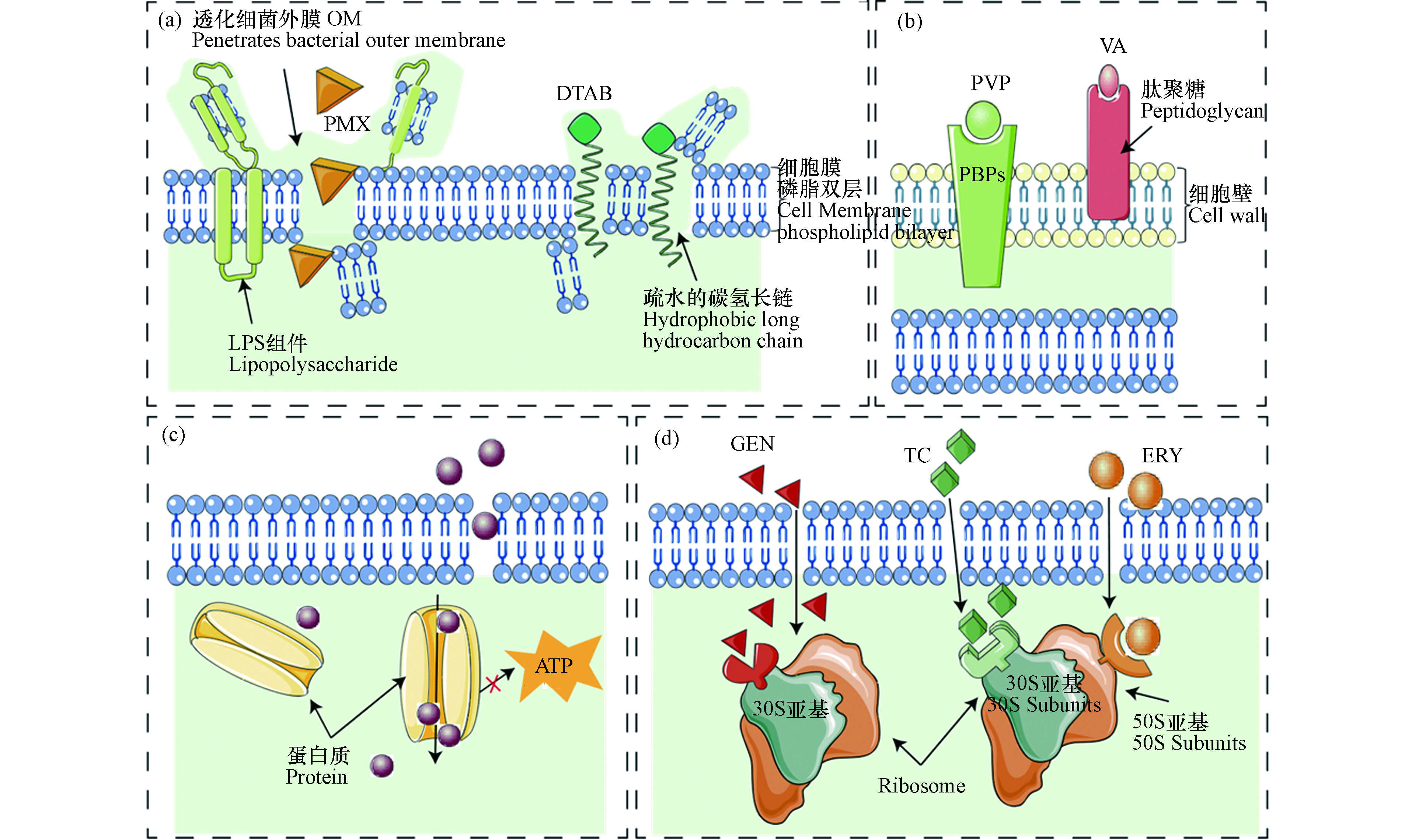
基于前人对于有机抗菌剂的作用机理的研究,将本文研究的有机抗菌的作用机理归纳为以下两个方面:一是与细胞壁和细胞膜系统相互作用;二是与细菌核糖体相互作用。
多肽类抗生素PMX和表面活性剂DTAB主要通过作用于细菌的细胞膜上来表达毒性(图2(a))。多肽类抗生素PMX的靶标是在膜的脂多糖(LPS)组件上,通过与LPS的脂质A成分直接相互作用来透化细菌外膜OM,随后插入并破坏内膜磷脂双分子层的物理完整性,使细胞内成分外漏而造成细菌死亡[19-20]。表面活性剂DTAB由于其分子中疏水的碳氢长链容易插入到细胞膜磷脂双层,从而引起细胞膜损伤,最终导致细菌死亡[21]。β-内酰胺类抗生素PVP和糖肽类抗生素VA主要通过作用于细菌的细胞壁上来发挥其抗菌性(图2(b))。β-内酰胺类抗生素PVP主要靶位为青霉素结合蛋白(PBPs),由于其结构可充当粘肽D-丙氨酰-D-丙氨酸(D-Ala-D-Ala)的末端的-CO-N-,从而竞争性地与PBPs结合,阻碍了细菌细胞壁肽聚糖生物合成,使细胞的外形难以维持,引起溶菌,最终导致细菌死亡[22-23]。糖肽类抗生素VA通过与D-Ala-D-Ala末端的肽聚糖前体小肽特异性结合,抑制细菌细胞壁肽聚糖的延伸与交联,从而使细菌细胞发生溶解死亡[24]。唑啉类杀菌剂MIT的抗菌机理(图2(c))区别于其他抗菌剂的作用机理,其主要通过断开微生物细胞中的蛋白质键,并迅速与之发生作用,从而抑制细胞呼吸和ATP的合成,最终导致细菌死亡[25]。
氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN、四环素类抗生素TC和大环内酯类抗生素ERY主要通过作用于核糖体来发挥其毒性(图2(d))。氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN穿过细胞后,与核糖体30s亚基的氨基酰-tRNA位点(A位点)的密码子-反密码子识别区附近的保守序列结合,从而导致翻译的准确性下降,最终抑制细菌蛋白质的合成,导致细菌死亡[26]。四环素TC进入细菌胞后作用于核糖体中提供遗传密码翻译场所的30S亚基上,通过阻止氨基酰–tRNA与A位点结合,从而抑制蛋白质合成[27-28]。大环内酯类抗生素ERY可以与50S亚单位结合从而抑制50S核糖体大亚基的形成,进而阻碍50S大亚基内的催化肽酰转移反应,最终导致蛋白合成能力降低,抑制细菌生长[29-30]。
-
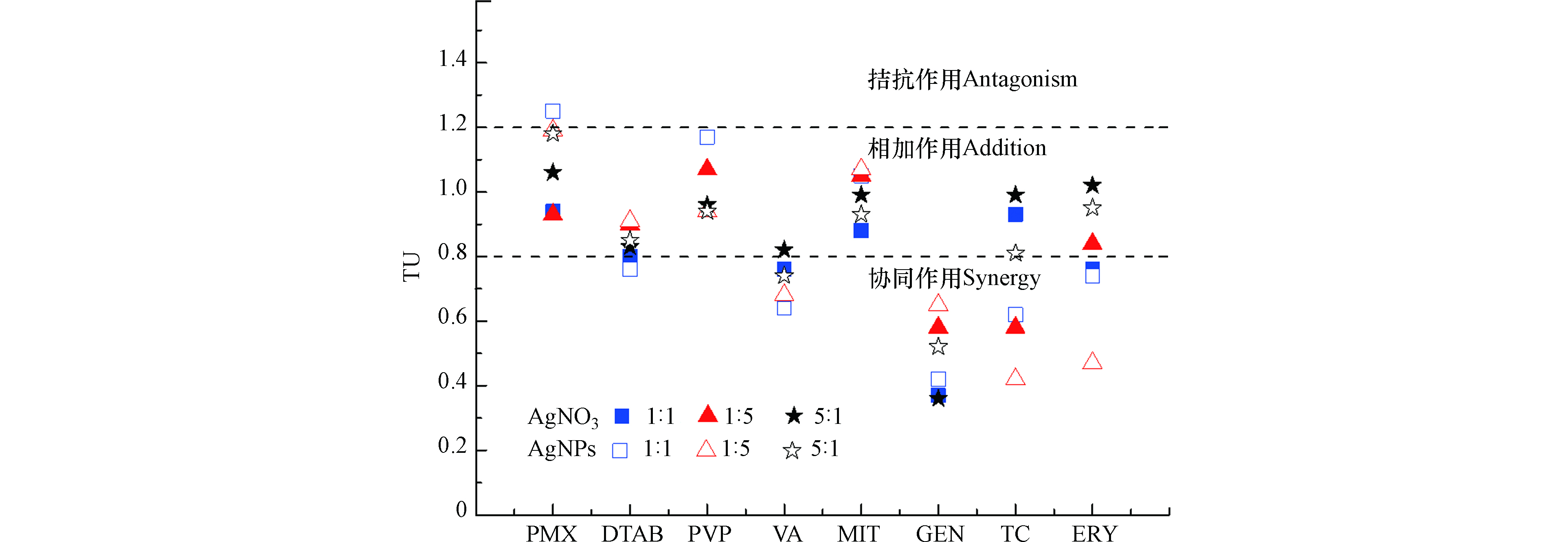
AgNO3和AgNPs与8种有机抗菌剂的二元联合(1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比)毒性实验结果如表2所示,结合实验结果绘制抗菌剂联合作用的TU分布图(图3),可以看出,AgNO3和AgNPs与多肽类抗生素PMX、表面活性剂DTAB、β-内酰胺类抗生素PVP和唑啉类杀菌剂MIT对E.coli在所有毒性比的联合作用下呈现相加效应,而与糖肽类抗生素VA混合作用会产生较弱的协同效应(TU值越大协同效应越弱)。同时,AgNO3和AgNPs与氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN在所有毒性比(1∶1、1∶5和5∶1)混合作用下均产生了明显的协同效应,与四环素类抗生素TC和大环内酯类抗生素ERY在1∶1和1∶5毒性比的作用下呈现协同效应。
为了探究联合毒性实验中银系抗菌剂中的主要抗菌因子,对这8种有机抗菌剂分别与AgNO 3和AgNPs在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比联合作用的
TUAgNO3 和TUAgNPs 进行了回归分析:通过线性回归分析发现,
TUAgNO3 和TUAgNPs 之间有较好的相关性(R2=0.703,P>0.01)。因此,推测在本研究的联合毒性实验中AgNO3和AgNPs在混合体系中的抗菌性可能也主要Ag+来发挥其毒性作用。基于AgNO3和AgNPs与8种有机抗菌剂的二元联合毒性实验结果,可以看出氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN与银系抗菌剂的联合在所有毒性比混合下均呈现协同效应。那么银系抗菌剂与其他的氨基糖苷类抗生素联合可以产生协同效应吗?它们的联合协同机制又是怎样的呢?这些问题还有待进一步的讨论。因此,需进一步开展银系抗菌剂与多种氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合毒性效应研究。
-
为了探索银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素联合协同作用是否具有普遍性,选择5种氨基糖苷类抗生素(STR、NEO、TM、KAN和ISE)与AgNO3和AgNPs在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比联合的毒性作用,5种氨基糖苷类抗生素的单一毒性如表1中所示,其中,毒性最大的为妥布霉素TM,其−lgEC50为6.36 mol·L−1。这5种氨基糖苷类抗生素的毒性大小排序为:TM>NEO>STR>ISE>KAN。
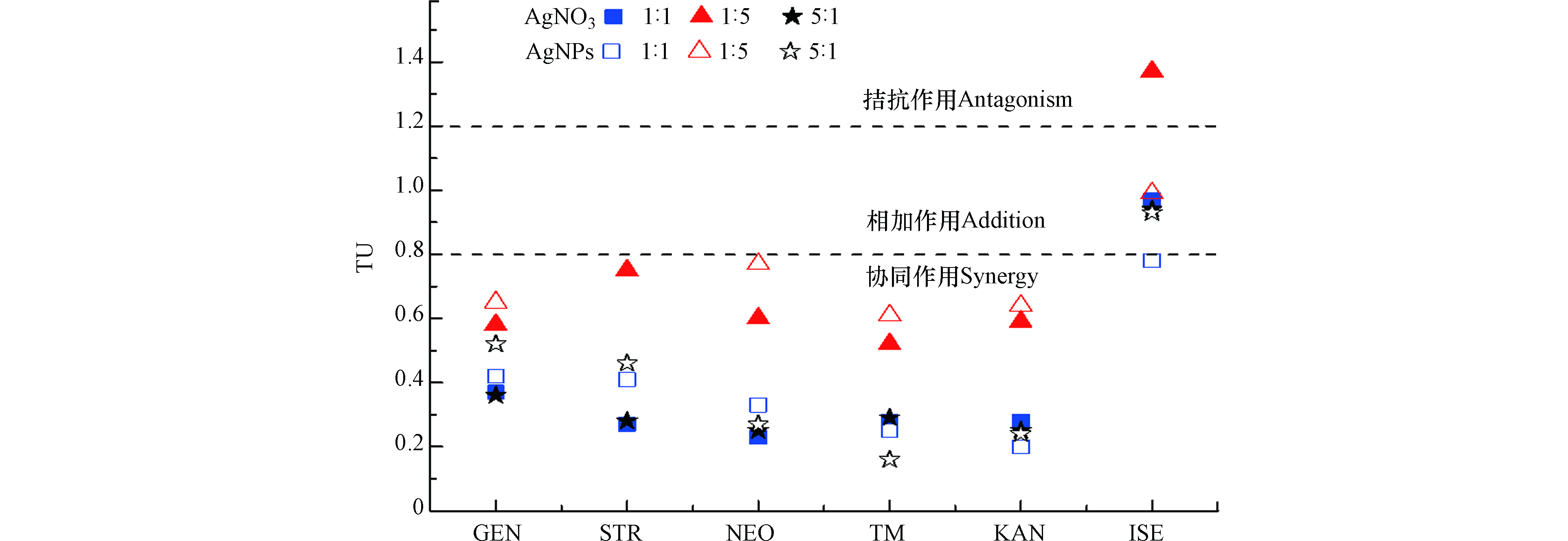
银系抗菌剂与这5种氨基糖苷类抗生素联合毒性实验结果如表3所示,结合实验结果绘制抗菌剂联合作用的TU分布图(图4)。可以看出,AgNO3和AgNPs与4种氨基糖苷类抗生素(TM、NEO、STR、KAN)对大肠杆菌的二元联合效应在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比混合时均呈现协同效应。而AgNO3和AgNPs与氨基糖苷类抗生素ISE在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比混合时基本呈现相加效应,且ISE仅与AgNPs(5 nm)在1∶1毒性比混合作用呈现协同效应。
-
基于以上的实验研究可知,银系抗菌剂与大部分的氨基糖苷类抗生素对大肠杆菌的二元联合毒性作用呈现协同效应。结合银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素单一毒性作用机制,银系抗菌剂的主要抗菌因子Ag+的作用靶点在蛋白酶上,使蛋白质无法有效分解,导致细菌死亡。而氨基糖类抗生素通过作用在核糖体上,最终抑制细菌蛋白质的合成,从而发挥其毒性。银系抗菌剂与氨基糖类抗生素的二元混合体系共同阻碍了蛋白质的合成与降解,破坏了蛋白质合成与代谢的整个过程。因此,推测银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合协同效应可能是由于它们单一毒性作用的靶蛋白具有通路一致性,从而相互促进,共同作用产生协同作用(图5)。
此外,结合AgNO3和AgNPs与5种氨基糖苷类抗生素联合毒性结果(图4),可以看出AgNO3和AgNPs与氨基糖苷类抗生素在1∶1和5∶1毒性比混合时比1∶5毒性比混合作用呈现更强的协同效应(TU值越小表明协同效应越强),基于Herisse等[31]的研究所表明的Ag+可以增加大肠杆菌对氨基糖苷类抗生素的吸收,推测在AgNO3和AgNPs与氨基糖苷类抗生素混合体系中,银系抗菌剂的主要抗菌因子Ag+可能会促进大肠杆菌摄入更多的氨基糖苷类抗生素的从而产生更强的协同效应。
基于上述研究,可以看出将具有作用通路一致性的银系抗菌剂和氨基糖苷类抗生素混合能够达到协同抗菌的目的。此外,在本文研究中,四环素类抗生素TC和大环内酯类抗生素ERY也都是通过作用于核糖体来表现毒性效应,而它们与银系抗菌剂的联合毒性也能在很大程度上表现出协同效应,这也进一步印证了作用通路一致性对于抗菌剂联用表现协同效应的重要性。因此,在今后的临床治疗中可以考虑银系抗菌剂与作用在核糖体上的抗菌剂联合用药。同时还可以进一步探索作用靶蛋白具有通路一致性的其他种抗菌剂之间的联合效应,以期可以寻找更多的抗菌治疗方案以提高抗菌剂抗菌疗效,并减少细菌耐药性问题。
本文所研究的受试生物为大肠杆菌,而大肠杆菌作为一种革兰氏阴性菌,其细胞壁有一层外膜,由脂蛋白、β-barrel蛋白、脂多糖和磷脂等组成。研究表明,革兰氏阴性菌的病原能力通常与其细胞壁组成相关,同种抗菌剂对于革兰氏阴性菌可能具有类似的抑菌效果[32]。因此,本文研究的银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素对大肠杆菌的协同作用与机制,可以为常见的克雷白杆菌、绿脓杆菌、流感嗜血杆菌和沙门氏菌等革兰氏阴性菌的感染治疗提供参考。革兰氏阳性菌与革兰氏阴性菌的细胞壁组成成分和结构不同,使得这两类细菌对于抗菌剂会产生不同的敏感性。对于金黄色葡萄菌、链球菌、肠球菌和利斯特菌等常见的革兰氏阳性菌,本文研究的银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合抗菌效果还需要开展相关的毒性实验进行探索验证。
此外,本文所研究的银系抗菌剂和多种有机抗菌剂的联合效应可以为环境中抗菌剂混合暴露的风险评价提供依据。抗菌剂主要通过医疗废水、生活污水、生产厂家以及畜禽和水产养殖业等废弃排放进入生态环境中,并通过食物链在整个环境中产生毒害作用,对微生物、水生生物和人类造成潜在危害[33-34]。同时,多种抗菌剂在进入环境后会存在联合暴露的可能,而抗菌剂以不同种类和不同比例联合暴露时可能会产生不同的联合毒性作用。基于本文的研究结果,可以推测银系抗菌剂与不同的有机抗菌剂以不同比例在环境中混合暴露是可能会造成不同程度的环境风险,而银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素由于作用靶蛋白的通路一致性在环境中联合暴露时可能会带来更大的环境风险。因此,当作用靶蛋白具有通路一致性的抗菌剂在环境中联合暴露时,其环境风险值得研究与关注。
-
(1)AgNO3和AgNPs无论在单一毒性实验中,还是与有机抗菌剂的混合作用中,它们都主要通过释放Ag+来发挥其对E.coli的毒性作用。
(2)不同有机抗菌剂与银类抗菌剂混合会产生不同的联合效应,其中氨基糖苷类抗生素与银系抗菌剂联合作用呈现更好的联合抗菌效果,且混合体系中银系抗菌剂占比更多时,其协同效应更强。
(3)银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的协同作用机制可能是由于作用在蛋白酶上的银系抗菌剂与作用在核糖体上的氨基糖苷类抗生素的二元混合体系共同阻碍了蛋白质的降解与合成,它们的作用靶蛋白具有通路一致性。本研究能够为探索更多抗菌剂的联合协同治疗方案以及评价多种抗菌剂在环境中可能产生的混合暴露风险提供参考依据。
银系抗菌剂与有机抗菌剂对大肠杆菌的联合毒性效应
A study on the combined toxicities of silver antibacterial agents and organic antibacterial agents against Escherichia coli
-
摘要: 抗菌剂的长期滥用导致细菌耐药性问题不断加剧,这对人类的健康生存和长期发展构成巨大威胁。银系抗菌剂作为不易产生耐药性的无机抗菌材料,可以将其与有机抗菌剂联合使用以提高抗菌效果,从而达到减少抗菌剂滥用的目的。但由于有机抗菌剂的结构及单一作用机制不同,使得银系抗菌剂与其联合后会产生不同的抗菌效果,因此有必要研究银系抗菌剂与不同的有机抗菌剂的联合毒性效应。本文以大肠杆菌为模式生物,硝酸银(AgNO3)和纳米银(AgNPs)作为常见的银类抗菌剂,测定了AgNO3、AgNPs与8种有机抗菌剂(多肽类、表面活性剂类、糖肽类、β-内酰胺类、唑啉类、氨基糖苷类、四环素类和大环内酯类)在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比混合下的联合毒性。结果表明,AgNO3和AgNPs在单一毒性实验和混合毒性中主要通过释放Ag+来发挥其对大肠杆菌的毒性作用。此外,8种有机抗菌剂中仅有氨基糖苷类抗生素与银系抗菌剂在所有毒性比的联合作用下均呈现协同效应。为了进一步验证这一协同作用的普遍性,测定了AgNO3和AgNPs与另外5种氨基糖苷类抗生素在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比联合的毒性效应。结果显示AgNO3和AgNPs与大部分氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合毒性作用呈现协同效应。基于银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的毒性作用机理,推测这两者的协同抗菌效应可能是由于银系抗菌剂作用的蛋白酶与氨基糖苷类抗生素作用的核糖体具有通路一致性,它们联合作用协同破坏了蛋白质合成与代谢的整个过程。本研究可以为今后抗菌剂的联合用药和探索更多的抗菌剂联合协同治疗方案提供参考和新思路,并为多种抗菌剂在环境中联合暴露的风险评价提供参考。Abstract: The abuse of antibiotics has caused increasingly serious bacterial resistance, which poses a great threat to human health and long-term development. Silver antimicrobial is a kind of inorganic antibacterial material and is not easy to induce drug resistance, which is suggested to be used together with organic antibacterial agents to improve the antibacterial effect and reduce the use of antibiotics. However, due to the different structures and single action mechanisms of organic antibacterial agents, their combined use with silver antimicrobials may trigger different antibacterial effects. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the combined toxic effects between silver antimicrobials and different organic antibacterial agents. In this paper, Escherichia coli (E.coli) was used as the model organism, while silver nitrate (AgNO3) and nano silver (AgNPs) were chosen as the test silver antimicrobials. The combined toxicity of 2 silver antimicrobials (AgNO3, and AgNPs) and 8 organic antibacterial agents (Polypeptide, Surfactant, β-lactam, Glycopeptide, Azoline fungicide, Tetracycline, Macrolide, Aminoglycoside) were determined as the toxicity ratios setting at 1∶1, 1∶5 and 5∶1. The results indicated that the toxic effects of AgNO3 and AgNPs in single and combined toxicity are mainly derived from the release of Ag+. Among the 8 organic antibacterial agents, only aminoglycoside exhibited synergistic effect with silver antimicrobials at all toxicity ratios. To further verify the universality of this synergism, the combined toxicity of silver antimicrobials and five other aminoglycosides were tested as the toxicity ratios setting at 1∶1, 1∶5 and 5∶1, which all showed the synergism in these mixtures. Based on the toxic mechanisms of silver antimicrobials and aminoglycoside, it was speculated that the synergistic effects of silver antimicrobials and aminoglycosides might result from that the target of silver antimicrobials (protease) and the target of aminoglycoside (ribosome) lie in the same signaling pathway, and thus their combined use synergistically destroyed the whole process of protein synthesis and metabolism. This study can provide a reference and new insights for the future combined use of antibacterial agents and the exploration of collaborative treatment programs among more antibacterial agents. Furthermore, this study may benefit the risk assessment for the combined exposure of antibacterial agents in the environment.
-
抗菌剂的长期滥用导致了细菌耐药性问题不断加剧,致使抗菌剂的抗菌效果降低,对人类的健康生存和长期发展造成潜在的威胁。如何缓解细菌耐药性成为了大多数研究者在治疗细菌感染和治理环境污染过程中的主要问题[1]。抗菌剂的联合治疗不仅可以增加抗菌剂的治疗效果,还可以防止和减少细菌耐药性[2]。因此,探索抗菌剂之间的联合作用效应,对提高抗菌剂的抗菌疗效并减少细菌耐药性问题具有重要意义。
常用的抗菌剂可分为无机抗菌剂和有机抗菌剂[3]。银系抗菌剂为不易产生耐药性的无机抗菌材料,具有抗菌广谱性、持久性、热稳定性好和安全性高等优势。硝酸银(AgNO3)和纳米银(AgNPs)作为两种常见的银系抗菌剂,被广泛应用于抗感染的伤口敷料、牙齿治疗、泌尿系统感染和慢性溃疡等临床治疗的多个方面[4]。如丁刚等[5]总结了硝酸银涂布治疗真菌性角膜炎的诊治经验,发现硝酸银涂布对于病变位于浅中基质层的真菌性角膜炎具有良好疗效,可缩短溃疡愈合时间,减少抗真菌药物的应用等。冯瑶等[6]研究纳米银在牙科根管应用中,发现纳米银与氢氧化钙联合作用于饥饿期的粪肠球菌生物膜呈现显著的抑菌效果。由此看出AgNO3和AgNPs在抗菌治疗中具有广泛的应用前景,可以表现出良好的抗菌效果。
有机抗菌剂通常是指以有机物为抗菌物质的抗菌剂。由于具有抗菌效果好、抗菌作用迅速等优点,有机抗菌剂被广泛应用于制造业、医疗以及水处理等多个行业[7]。抗生素是一种常见的有机抗菌剂,其主要包括β-内酰胺类、四环素类、氨基糖苷类、大环内酯类以及多肽类抗生素等,被广泛应用于农业、畜牧业和医疗卫生等多个领域,对防治感染性疾病起到重要的作用。表面活性剂是一类具有两亲性质的有机抗菌剂,通过与细菌生物膜蛋白质的强烈相互作用使细菌变性或失去功能,在医药、洗涤、农药等方面有着广泛的应用[8];唑啉类有机抗菌剂因其具有抗菌能力强、药效持久、对环境安全以及抗菌谱宽广等优良性能,在工业、农业、医药等行业中广泛使用[9]。基于有机抗菌剂广泛的应用前景,AgNO3和AgNPs和不同的有机抗菌剂联合会产生什么样的抗菌效果呢?是否可以从这些不同的有机抗菌剂中筛选出与AgNO3和AgNPs联合产生协同效应的抗菌剂,从而提高抗菌剂的联合抗菌效果呢?
近几年,对于银系抗菌剂与有机抗菌剂的联合研究报道逐渐增多。如Xu等[10]对AgNO3与抗生素万古霉素、利福平、庆大霉素和左氧氟沙星分别进行抗菌性能测试,发现其联合治疗的抗菌活性均得到了提高。Deng等[11]探讨了AgNPs分别与氨苄青霉素、青霉素、依诺沙星、卡那霉素、新霉素和四环素对耐多药菌伤寒沙门氏菌的联合抗菌作用,依诺沙星、卡那霉素、新霉素和四环素在与AgNPs联合时对沙门氏菌表现出协同作用,而氨苄西林和青霉素则没有。由此可以看出,银系抗菌剂和有机抗菌剂的联合抗菌治疗效果会由于有机抗菌剂的结构及单一作用机制的不同而不同。此外,当化合物之间以不同比例混合时会呈现不同的联合作用方式。如仇爱锋等[12]在研究克百威、镉和铜对费氏弧菌的联合毒性效应中,发现克百威和镉的二元混合体系在以毒性单位为1∶1和1∶2的混合下联合毒性作用部分呈现相加效应,而在2∶1混合时产生协同效应。因此,有必要开展银系抗菌剂与不同有机抗菌剂在不同毒性比混合下的联合效应研究,以进一步提高抗菌剂在细菌感染治疗中的抗菌效果,并为评估它们在进入环境后可能产生的联合暴露风险给予参考依据。
大肠杆菌是生物体内最常见的细菌之一,由于它具有分裂增殖能力强、发育周期短以及结构简单等特点,已作为一种重要的模式生物在现代生命科学研究领域起着重要的作用。因此,本文以大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)为模式生物,通过联合毒性实验,测定AgNO3和AgNPs分别与抗生素、表面活性剂和唑啉类杀菌剂等有机抗菌剂的联合毒性效应,并对它们的联合毒性作用机制进行了初步的讨论,以期在未来为银系抗菌剂与有机抗菌剂联合用药以及环境联合暴露风险评价提供参考。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 模式生物与试剂
测试化合物中,四环素类抗生素购自Sigma-Aldrich化学制品有限公司,硝酸银、β-内酰胺类、氨基糖苷类、多肽类、大环内酯类抗生素以及唑啉类杀菌剂、表面活性剂均购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司,纳米银溶液购自宇瑞(上海)化学有限公司,纯度均为分析纯以上,化合物的基本信息如表1。
表 1 试剂的理化参数和单一毒性数据Table 1. The physicochemical parameters and the single toxicity data of the reagents类别Class 序号No. 名称及简称Name and abbreviation CAS 结构式Structural formula 相对分子质量/ (g·mol−1)Relative molecular mass −lgEC50/(mol·L−1) 银系抗菌剂Silver antibacterial agents 1 硝酸银AgNO3 7761-88-8 — 169.87 4.51 2 纳米银AgNPs(5 nm) 7440-22-4 — 107.87 4.78 多肽类抗生素Polypeptide antibiotic 3 硫酸多粘菌素B Polymyxin B sulfate PMX 1405-20-5 
1301.56 6.59 表面活性剂Surfactant 4 十二烷基三甲溴化铵Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide DTAB 1119-94-4 
308.34 3.88 β-内酰胺类抗生素β-lactam antibiotic 5 青霉素V钾Phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium PVP 132-98-9 
388.48 3.74 糖肽类抗生素Glycopeptide antibiotic 6 盐酸万古霉素Vancomycin hydrochloride VA 1404-93-9 
1485.71 3.95 唑啉类杀菌剂Azoline fungicide 7 甲基异噻唑啉酮Methylisothiazolinone MIT 2682-20-4 
115.15 4.60 四环素类抗生素Tetracycline antibiotic 8 盐酸四环素Tetracycline hydrochloride TC 64-75-5 
480.90 6.25 大环内酯类抗生素Macrolide antibiotic 9 红霉素Erythromycin ERY 114-07-8 
733.93 4.86 氨基糖苷类抗生素Aminoglycoside antibiotics 10 硫酸庆大霉素Gentamycin sulfate GEN 1405-41-0 
1506.80 6.26 11 硫酸链霉素Streptomycin sulfate STR 3810-74-0 
1457.38 5.94 12 硫酸新霉素Neomycin sulfate NEO 1405-10-3 
712.72 6.25 13 妥布霉素Tobramycin TM 32986-56-4 
467.51 6.36 氨基糖苷类抗生素Aminoglycoside antibiotics 14 硫酸卡那霉素Kanamycin sulfate KAN 70560-51-9 
582.58 5.71 15 异帕米星Isepamicin ISE 58152-03-7 
569.60 5.93 本实验中使用的模式生物E.coli(Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655),菌种冻干粉购自Biovector生物科技有限公司(北京)。
1.2 毒性试验及数据的表征
1.2.1 毒性试验
受试化合物在毒性试验中采用不超过总体积0.1%的二甲基亚砜(DMSO)助溶后,用1 %NaCl溶液配制成待测化合物母液。实验时再用1%NaCl溶液将待测化合物母液稀释成等对数梯度系列,将化合物溶液加入96孔酶标板中,每孔包含80 μL的待测化合物溶液(作为实验组)或1 %的NaCl溶液(作为对照组),80 μL的2.5倍LB培养基和40 μL工作菌液。最后将96孔酶标板放置在37ºC下,转速为165 r·min−1的培养箱中培养24 h至E.coli到平台期后,用酶标仪测定波长600 nm处,96孔板每孔的光密度(optical density,OD600)。通过剂量-效应曲线得到抑制率达到50 %时对应的化合物浓度即为EC50,根据单一化合物的EC50,配制化合物A与化合物B在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比的混合溶液,然后按照单一毒性测定方法测定系列混合溶液的联合毒性。
1.2.2 毒性数据的表征
单一毒性结果采用抑制率Inhibition(%)来表征,联合毒性作用采用毒性单位(Toxicity Unit TU)值来表述,抑制率及TU值的计算如下式:
Inhibition(%)=OD600,0−OD600,iOD600,0×100% (1) TU=CAEC50A+CBEC50B (2) 式(1)中,OD600,0为E.coli在无染毒作用下的对照组OD平均值,OD600,i为测试化合物作用下实验组的OD平均值。式(2)中,CA、CB是混合体系产生50 %抑制效应时化合物A、B各自的摩尔浓度(mol·L−1),EC50A和EC50B是单一化合物A、B分别作用产生50%抑制效应时的浓度。根据采用Broderius的联合毒性作用判别标准[13],当 TU<0.8认为两组分间为协同效应;0.8≤TU≤1.2认为两组分间为相加效应;TU>1.2认为两组分间为拮抗效应。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 银系抗菌剂与8种有机抗菌剂的联合毒性效应
2.1.1 银系抗菌剂与8种有机抗菌剂对大肠杆菌的单一毒性作用
银系抗菌剂与8种有机抗菌剂对大肠杆菌的单一毒性数据如表1所示。其中,毒性最大的为多肽类抗生素PMX,其−lgEC50为6.59 mol·L−1。所有抗菌剂中的毒性大小排序为:多肽类抗生素PMX>氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN>四环素类抗生素TC>大环内酯类抗生素ERY>AgNPs>唑啉类杀菌剂MIT>AgNO3>糖肽类抗生素VA>表面活性剂DTAB>β-内酰胺类抗生素PVP。
基于前人对于银系抗菌剂的研究,纳米银和硝酸银的作用机制如图1所示,AgNO3通过释放Ag+来发挥其抗菌性,Ag+能吸附在带负电的细菌细胞壁上,并能够穿透细胞膜进入细胞内部,与细菌中蛋白酶上的巯基(—SH)迅速结合,使蛋白酶丧失活性,同时,也可以通过浓缩DNA使其失去复制能力而引起DNA的降解来抑制细菌的生长繁殖[14-15]。AgNPs抗菌机理主要由于其自身的尺寸很小而具有较高比表面积,从而呈现较高的反应活性,释放出Ag+发挥其抗菌作用;同时,AgNPs还可以通过扩散或内吞作用进入细胞,引起线粒体功能障碍,造成线粒体呼吸链的破坏,增加活性氧(ROS)的产生并抑制了三磷酸腺苷ATP的合成,从而导致DNA损伤、细胞内的蛋白质受损,当生成的ROS超过细胞抗氧化防御系统的能力时,发生氧化损伤,最终抑制细菌的增殖[16]。本研究中,AgNO3和AgNPs的-logEC50分别为4.51 mol·L−1和4.78 mol·L−1,说明AgNO3与AgNPs的抗菌活性相差不大。因此,推测实验中AgNO3与AgNPs的可能都是主要Ag+来发挥毒性作用。该推测与已有研究[17-18]中表明AgNO3和AgNPs主要是通过释放Ag+来发挥其抗菌性的结论一致。
基于前人对于有机抗菌剂的作用机理的研究,将本文研究的有机抗菌的作用机理归纳为以下两个方面:一是与细胞壁和细胞膜系统相互作用;二是与细菌核糖体相互作用。
多肽类抗生素PMX和表面活性剂DTAB主要通过作用于细菌的细胞膜上来表达毒性(图2(a))。多肽类抗生素PMX的靶标是在膜的脂多糖(LPS)组件上,通过与LPS的脂质A成分直接相互作用来透化细菌外膜OM,随后插入并破坏内膜磷脂双分子层的物理完整性,使细胞内成分外漏而造成细菌死亡[19-20]。表面活性剂DTAB由于其分子中疏水的碳氢长链容易插入到细胞膜磷脂双层,从而引起细胞膜损伤,最终导致细菌死亡[21]。β-内酰胺类抗生素PVP和糖肽类抗生素VA主要通过作用于细菌的细胞壁上来发挥其抗菌性(图2(b))。β-内酰胺类抗生素PVP主要靶位为青霉素结合蛋白(PBPs),由于其结构可充当粘肽D-丙氨酰-D-丙氨酸(D-Ala-D-Ala)的末端的-CO-N-,从而竞争性地与PBPs结合,阻碍了细菌细胞壁肽聚糖生物合成,使细胞的外形难以维持,引起溶菌,最终导致细菌死亡[22-23]。糖肽类抗生素VA通过与D-Ala-D-Ala末端的肽聚糖前体小肽特异性结合,抑制细菌细胞壁肽聚糖的延伸与交联,从而使细菌细胞发生溶解死亡[24]。唑啉类杀菌剂MIT的抗菌机理(图2(c))区别于其他抗菌剂的作用机理,其主要通过断开微生物细胞中的蛋白质键,并迅速与之发生作用,从而抑制细胞呼吸和ATP的合成,最终导致细菌死亡[25]。
氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN、四环素类抗生素TC和大环内酯类抗生素ERY主要通过作用于核糖体来发挥其毒性(图2(d))。氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN穿过细胞后,与核糖体30s亚基的氨基酰-tRNA位点(A位点)的密码子-反密码子识别区附近的保守序列结合,从而导致翻译的准确性下降,最终抑制细菌蛋白质的合成,导致细菌死亡[26]。四环素TC进入细菌胞后作用于核糖体中提供遗传密码翻译场所的30S亚基上,通过阻止氨基酰–tRNA与A位点结合,从而抑制蛋白质合成[27-28]。大环内酯类抗生素ERY可以与50S亚单位结合从而抑制50S核糖体大亚基的形成,进而阻碍50S大亚基内的催化肽酰转移反应,最终导致蛋白合成能力降低,抑制细菌生长[29-30]。
2.1.2 银系抗菌剂与8种有机抗菌剂的二元联合毒性效应
AgNO3和AgNPs与8种有机抗菌剂的二元联合(1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比)毒性实验结果如表2所示,结合实验结果绘制抗菌剂联合作用的TU分布图(图3),可以看出,AgNO3和AgNPs与多肽类抗生素PMX、表面活性剂DTAB、β-内酰胺类抗生素PVP和唑啉类杀菌剂MIT对E.coli在所有毒性比的联合作用下呈现相加效应,而与糖肽类抗生素VA混合作用会产生较弱的协同效应(TU值越大协同效应越弱)。同时,AgNO3和AgNPs与氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN在所有毒性比(1∶1、1∶5和5∶1)混合作用下均产生了明显的协同效应,与四环素类抗生素TC和大环内酯类抗生素ERY在1∶1和1∶5毒性比的作用下呈现协同效应。
表 2 硝酸银、纳米银分别和抗菌剂的二元联合毒性数据Table 2. Data on the combined toxicity of AgNO3, AgNPs with antibacterial agents respectively分类 B A∶B A∶AgNO3 A∶AgNPs(5 nm) −lgEC50mix TU 联合效应 −lgEC50mix TU 联合效应 多肽类抗生素 PMX 1∶1 4.81 0.99 相加 4.99 1.21 拮抗 1∶5 5.30 0.93 相加 5.47 1.13 相加 多肽类抗生素 PMX 5∶1 4.56 1.06 相加 4.80 1.13 相加 表面活性剂 DTAB 1∶1 4.19 0.80 相加 4.25 0.76 协同 1∶5 3.99 0.90 相加 3.99 0.91 相加 5∶1 4.40 0.83 相加 4.52 0.85 相加 β-内酰胺类抗生素 PVP 1∶1 3.90 1.17 相加 3.93 1.17 相加 1∶5 3.80 1.02 相加 3.84 0.94 相加 5∶1 4.27 0.96 相加 4.38 0.94 相加 糖肽类抗生素 VA 1∶1 4.26 0.76 协同 4.35 0.69 协同 1∶5 4.17 0.68 协同 4.18 0.68 协同 5∶1 4.44 0.82 相加 4.62 0.74 协同 唑啉类杀菌剂 MIT 1∶1 4.61 0.88 相加 4.68 1.01 相加 1∶5 4.56 1.05 相加 4.60 1.07 相加 5∶1 4.53 0.99 相加 4.78 0.93 相加 氨基糖苷类抗生素 GEN 1∶1 5.24 0.37 协同 5.44 0.42 协同 1∶5 5.49 0.58 协同 5.68 0.65 协同 5∶1 5.03 0.36 协同 5.14 0.52 协同 四环素类抗生素 TC 1∶1 4.86 0.88 相加 5.27 0.62 协同 1∶5 5.49 0.58 协同 5.82 0.47 协同 5∶1 4.61 0.94 相加 4.95 0.81 相加 大环内酯类抗生素 ERY 1∶1 4.77 0.76 协同 4.95 0.74 协同 1∶5 4.86 0.82 相加 5.15 0.50 协同 5∶1 4.54 1.02 相加 4.81 0.95 相加 为了探究联合毒性实验中银系抗菌剂中的主要抗菌因子,对这8种有机抗菌剂分别与AgNO 3和AgNPs在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比联合作用的
TUAgNO3 TUAgNPs TUAgNO3=0.9398TUAgNPs+0.0376 (3) n=24,R2=0.703,SE=0.115,F=52.184,P=0.000 通过线性回归分析发现,
TUAgNO3 TUAgNPs 基于AgNO3和AgNPs与8种有机抗菌剂的二元联合毒性实验结果,可以看出氨基糖苷类抗生素GEN与银系抗菌剂的联合在所有毒性比混合下均呈现协同效应。那么银系抗菌剂与其他的氨基糖苷类抗生素联合可以产生协同效应吗?它们的联合协同机制又是怎样的呢?这些问题还有待进一步的讨论。因此,需进一步开展银系抗菌剂与多种氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合毒性效应研究。
2.2 银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合毒性效应与机制初探
2.2.1 银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合毒性效应
为了探索银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素联合协同作用是否具有普遍性,选择5种氨基糖苷类抗生素(STR、NEO、TM、KAN和ISE)与AgNO3和AgNPs在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比联合的毒性作用,5种氨基糖苷类抗生素的单一毒性如表1中所示,其中,毒性最大的为妥布霉素TM,其−lgEC50为6.36 mol·L−1。这5种氨基糖苷类抗生素的毒性大小排序为:TM>NEO>STR>ISE>KAN。
银系抗菌剂与这5种氨基糖苷类抗生素联合毒性实验结果如表3所示,结合实验结果绘制抗菌剂联合作用的TU分布图(图4)。可以看出,AgNO3和AgNPs与4种氨基糖苷类抗生素(TM、NEO、STR、KAN)对大肠杆菌的二元联合效应在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比混合时均呈现协同效应。而AgNO3和AgNPs与氨基糖苷类抗生素ISE在1∶1、1∶5和5∶1毒性比混合时基本呈现相加效应,且ISE仅与AgNPs(5 nm)在1∶1毒性比混合作用呈现协同效应。
表 3 硝酸银、纳米银分别和氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合毒性数据Table 3. Data on the combined toxicity of AgNO3、AgNPs with aminoglycoside antibiotics respectivelyB∶氨基糖苷类抗生素 A∶B毒性比 A∶AgNO3 A∶AgNPs(5 nm) −lgEC50mix TU 联合效应 −lgEC50mix TU 联合效应 STR 1∶1 5.36 0.27 协同 5.44 0.41 协同 1∶5 5.34 0.75 协同 5.55 0.75 协同 5∶1 5.14 0.28 协同 5.19 0.46 协同 NEO 1∶1 5.45 0.23 协同 5.55 0.33 协同 1∶5 5.48 0.60 协同 5.60 0.77 协同 5∶1 5.18 0.25 协同 5.42 0.27 协同 TM 1∶1 5.36 0.28 协同 5.67 0.25 协同 1∶5 5.54 0.52 协同 5.72 0.61 协同 5∶1 5.13 0.29 协同 5.67 0.16 协同 KAN 1∶1 5.35 0.28 协同 5.72 0.20 协同 1∶5 5.40 0.59 协同 5.55 0.64 协同 5∶1 5.18 0.25 协同 5.47 0.24 协同 ISE 1∶1 4.81 0.97 相加 5.16 0.78 协同 1∶5 5.08 1.37 拮抗 5.43 0.99 相加 5∶1 4.61 0.94 相加 4.88 0.93 相加 2.2.2 银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的协同效应机制初探
基于以上的实验研究可知,银系抗菌剂与大部分的氨基糖苷类抗生素对大肠杆菌的二元联合毒性作用呈现协同效应。结合银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素单一毒性作用机制,银系抗菌剂的主要抗菌因子Ag+的作用靶点在蛋白酶上,使蛋白质无法有效分解,导致细菌死亡。而氨基糖类抗生素通过作用在核糖体上,最终抑制细菌蛋白质的合成,从而发挥其毒性。银系抗菌剂与氨基糖类抗生素的二元混合体系共同阻碍了蛋白质的合成与降解,破坏了蛋白质合成与代谢的整个过程。因此,推测银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合协同效应可能是由于它们单一毒性作用的靶蛋白具有通路一致性,从而相互促进,共同作用产生协同作用(图5)。
此外,结合AgNO3和AgNPs与5种氨基糖苷类抗生素联合毒性结果(图4),可以看出AgNO3和AgNPs与氨基糖苷类抗生素在1∶1和5∶1毒性比混合时比1∶5毒性比混合作用呈现更强的协同效应(TU值越小表明协同效应越强),基于Herisse等[31]的研究所表明的Ag+可以增加大肠杆菌对氨基糖苷类抗生素的吸收,推测在AgNO3和AgNPs与氨基糖苷类抗生素混合体系中,银系抗菌剂的主要抗菌因子Ag+可能会促进大肠杆菌摄入更多的氨基糖苷类抗生素的从而产生更强的协同效应。
基于上述研究,可以看出将具有作用通路一致性的银系抗菌剂和氨基糖苷类抗生素混合能够达到协同抗菌的目的。此外,在本文研究中,四环素类抗生素TC和大环内酯类抗生素ERY也都是通过作用于核糖体来表现毒性效应,而它们与银系抗菌剂的联合毒性也能在很大程度上表现出协同效应,这也进一步印证了作用通路一致性对于抗菌剂联用表现协同效应的重要性。因此,在今后的临床治疗中可以考虑银系抗菌剂与作用在核糖体上的抗菌剂联合用药。同时还可以进一步探索作用靶蛋白具有通路一致性的其他种抗菌剂之间的联合效应,以期可以寻找更多的抗菌治疗方案以提高抗菌剂抗菌疗效,并减少细菌耐药性问题。
本文所研究的受试生物为大肠杆菌,而大肠杆菌作为一种革兰氏阴性菌,其细胞壁有一层外膜,由脂蛋白、β-barrel蛋白、脂多糖和磷脂等组成。研究表明,革兰氏阴性菌的病原能力通常与其细胞壁组成相关,同种抗菌剂对于革兰氏阴性菌可能具有类似的抑菌效果[32]。因此,本文研究的银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素对大肠杆菌的协同作用与机制,可以为常见的克雷白杆菌、绿脓杆菌、流感嗜血杆菌和沙门氏菌等革兰氏阴性菌的感染治疗提供参考。革兰氏阳性菌与革兰氏阴性菌的细胞壁组成成分和结构不同,使得这两类细菌对于抗菌剂会产生不同的敏感性。对于金黄色葡萄菌、链球菌、肠球菌和利斯特菌等常见的革兰氏阳性菌,本文研究的银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合抗菌效果还需要开展相关的毒性实验进行探索验证。
此外,本文所研究的银系抗菌剂和多种有机抗菌剂的联合效应可以为环境中抗菌剂混合暴露的风险评价提供依据。抗菌剂主要通过医疗废水、生活污水、生产厂家以及畜禽和水产养殖业等废弃排放进入生态环境中,并通过食物链在整个环境中产生毒害作用,对微生物、水生生物和人类造成潜在危害[33-34]。同时,多种抗菌剂在进入环境后会存在联合暴露的可能,而抗菌剂以不同种类和不同比例联合暴露时可能会产生不同的联合毒性作用。基于本文的研究结果,可以推测银系抗菌剂与不同的有机抗菌剂以不同比例在环境中混合暴露是可能会造成不同程度的环境风险,而银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素由于作用靶蛋白的通路一致性在环境中联合暴露时可能会带来更大的环境风险。因此,当作用靶蛋白具有通路一致性的抗菌剂在环境中联合暴露时,其环境风险值得研究与关注。
3. 结论(Conclusion)
(1)AgNO3和AgNPs无论在单一毒性实验中,还是与有机抗菌剂的混合作用中,它们都主要通过释放Ag+来发挥其对E.coli的毒性作用。
(2)不同有机抗菌剂与银类抗菌剂混合会产生不同的联合效应,其中氨基糖苷类抗生素与银系抗菌剂联合作用呈现更好的联合抗菌效果,且混合体系中银系抗菌剂占比更多时,其协同效应更强。
(3)银系抗菌剂与氨基糖苷类抗生素的协同作用机制可能是由于作用在蛋白酶上的银系抗菌剂与作用在核糖体上的氨基糖苷类抗生素的二元混合体系共同阻碍了蛋白质的降解与合成,它们的作用靶蛋白具有通路一致性。本研究能够为探索更多抗菌剂的联合协同治疗方案以及评价多种抗菌剂在环境中可能产生的混合暴露风险提供参考依据。
-
表 1 试剂的理化参数和单一毒性数据
Table 1. The physicochemical parameters and the single toxicity data of the reagents
类别Class 序号No. 名称及简称Name and abbreviation CAS 结构式Structural formula 相对分子质量/ (g·mol−1)Relative molecular mass −lgEC50/(mol·L−1) 银系抗菌剂Silver antibacterial agents 1 硝酸银AgNO3 7761-88-8 — 169.87 4.51 2 纳米银AgNPs(5 nm) 7440-22-4 — 107.87 4.78 多肽类抗生素Polypeptide antibiotic 3 硫酸多粘菌素B Polymyxin B sulfate PMX 1405-20-5 1301.56 6.59 表面活性剂Surfactant 4 十二烷基三甲溴化铵Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide DTAB 1119-94-4 308.34 3.88 β-内酰胺类抗生素β-lactam antibiotic 5 青霉素V钾Phenoxymethylpenicillin potassium PVP 132-98-9 388.48 3.74 糖肽类抗生素Glycopeptide antibiotic 6 盐酸万古霉素Vancomycin hydrochloride VA 1404-93-9 1485.71 3.95 唑啉类杀菌剂Azoline fungicide 7 甲基异噻唑啉酮Methylisothiazolinone MIT 2682-20-4 115.15 4.60 四环素类抗生素Tetracycline antibiotic 8 盐酸四环素Tetracycline hydrochloride TC 64-75-5 480.90 6.25 大环内酯类抗生素Macrolide antibiotic 9 红霉素Erythromycin ERY 114-07-8 733.93 4.86 氨基糖苷类抗生素Aminoglycoside antibiotics 10 硫酸庆大霉素Gentamycin sulfate GEN 1405-41-0 1506.80 6.26 11 硫酸链霉素Streptomycin sulfate STR 3810-74-0 1457.38 5.94 12 硫酸新霉素Neomycin sulfate NEO 1405-10-3 712.72 6.25 13 妥布霉素Tobramycin TM 32986-56-4 467.51 6.36 氨基糖苷类抗生素Aminoglycoside antibiotics 14 硫酸卡那霉素Kanamycin sulfate KAN 70560-51-9 582.58 5.71 15 异帕米星Isepamicin ISE 58152-03-7 569.60 5.93 表 2 硝酸银、纳米银分别和抗菌剂的二元联合毒性数据
Table 2. Data on the combined toxicity of AgNO3, AgNPs with antibacterial agents respectively
分类 B A∶B A∶AgNO3 A∶AgNPs(5 nm) −lgEC50mix TU 联合效应 −lgEC50mix TU 联合效应 多肽类抗生素 PMX 1∶1 4.81 0.99 相加 4.99 1.21 拮抗 1∶5 5.30 0.93 相加 5.47 1.13 相加 多肽类抗生素 PMX 5∶1 4.56 1.06 相加 4.80 1.13 相加 表面活性剂 DTAB 1∶1 4.19 0.80 相加 4.25 0.76 协同 1∶5 3.99 0.90 相加 3.99 0.91 相加 5∶1 4.40 0.83 相加 4.52 0.85 相加 β-内酰胺类抗生素 PVP 1∶1 3.90 1.17 相加 3.93 1.17 相加 1∶5 3.80 1.02 相加 3.84 0.94 相加 5∶1 4.27 0.96 相加 4.38 0.94 相加 糖肽类抗生素 VA 1∶1 4.26 0.76 协同 4.35 0.69 协同 1∶5 4.17 0.68 协同 4.18 0.68 协同 5∶1 4.44 0.82 相加 4.62 0.74 协同 唑啉类杀菌剂 MIT 1∶1 4.61 0.88 相加 4.68 1.01 相加 1∶5 4.56 1.05 相加 4.60 1.07 相加 5∶1 4.53 0.99 相加 4.78 0.93 相加 氨基糖苷类抗生素 GEN 1∶1 5.24 0.37 协同 5.44 0.42 协同 1∶5 5.49 0.58 协同 5.68 0.65 协同 5∶1 5.03 0.36 协同 5.14 0.52 协同 四环素类抗生素 TC 1∶1 4.86 0.88 相加 5.27 0.62 协同 1∶5 5.49 0.58 协同 5.82 0.47 协同 5∶1 4.61 0.94 相加 4.95 0.81 相加 大环内酯类抗生素 ERY 1∶1 4.77 0.76 协同 4.95 0.74 协同 1∶5 4.86 0.82 相加 5.15 0.50 协同 5∶1 4.54 1.02 相加 4.81 0.95 相加 表 3 硝酸银、纳米银分别和氨基糖苷类抗生素的联合毒性数据
Table 3. Data on the combined toxicity of AgNO3、AgNPs with aminoglycoside antibiotics respectively
B∶氨基糖苷类抗生素 A∶B毒性比 A∶AgNO3 A∶AgNPs(5 nm) −lgEC50mix TU 联合效应 −lgEC50mix TU 联合效应 STR 1∶1 5.36 0.27 协同 5.44 0.41 协同 1∶5 5.34 0.75 协同 5.55 0.75 协同 5∶1 5.14 0.28 协同 5.19 0.46 协同 NEO 1∶1 5.45 0.23 协同 5.55 0.33 协同 1∶5 5.48 0.60 协同 5.60 0.77 协同 5∶1 5.18 0.25 协同 5.42 0.27 协同 TM 1∶1 5.36 0.28 协同 5.67 0.25 协同 1∶5 5.54 0.52 协同 5.72 0.61 协同 5∶1 5.13 0.29 协同 5.67 0.16 协同 KAN 1∶1 5.35 0.28 协同 5.72 0.20 协同 1∶5 5.40 0.59 协同 5.55 0.64 协同 5∶1 5.18 0.25 协同 5.47 0.24 协同 ISE 1∶1 4.81 0.97 相加 5.16 0.78 协同 1∶5 5.08 1.37 拮抗 5.43 0.99 相加 5∶1 4.61 0.94 相加 4.88 0.93 相加 -
[1] NORDMANN P, NAAS T, FORTINEAU N, et al. Superbugs in the coming new decade; multidrug resistance and prospects for treatment of Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus spp. and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in 2010 [J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2007, 10(5): 436-440. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.07.004 [2] 陈志芳, 赵斌. 抗菌药物联合用药与单药治疗的对比及临床决策 [J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2010, 20(15): 2353-2355. CHEN Z F, ZHAO B. Comparison and clinical decision of antibiotic combination therapy and single drug therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, 2010, 20(15): 2353-2355(in Chinese).
[3] 常建国. 新型有机抗菌剂及抗菌高分子材料的合成、制备及表征[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2016. CHANG J G. Synthesis, preparation and characterization of novel organic antimicrobial agents and antimicrobial polymeric materials[D], Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2016 (in Chinese). .
[4] 刘艺楠, 孙昊宇, 沈洪艳, 等. 新型抗菌剂——群体感应抑制剂与传统抗菌剂对大肠杆菌的联合毒性效应 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(4): 941-949. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019040104 LIU Y N, SUN H Y, SHEN H Y, et al. A study on the combined toxicities of a new antimicrobials-quorum sensing inhibitors and traditional antimicrobials against Escherichia coli [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(4): 941-949(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019040104
[5] 丁刚, 高芯, 位宁, 等. 硝酸银涂布治疗真菌性角膜炎的经验 [J]. 中华眼外伤职业眼病杂志, 2020, 42(8): 624-627. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn116022-20191210-00406 DING G, GAO X, WEI N, et al. Experience of local infriction of silver nitrate for the treatment of fungal keratitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Ocular Trauma and Occupational Eye Disease, 2020, 42(8): 624-627(in Chinese). doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn116022-20191210-00406
[6] 冯瑶, 薛钢, 董波. 纳米银在牙科根管应用中对粪肠球菌抑制效果评价 [J]. 黑龙江医药科学, 2019, 42(2): 212-214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0104.2019.02.102 FENG Y, XUE G, DONG B. Evaluation of the inhibitory effect of silver nanoparticles on enterococcus faecalis in dental root canal application [J]. Heilongjiang Medicine and Pharmacy, 2019, 42(2): 212-214(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0104.2019.02.102
[7] 刘利, 龙必强, 周亮, 等. 抗菌材料研究进展 [J]. 科技视界, 2017(7): 220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2457.2017.07.173 LIU L, LONG B Q, ZHOU L, et al. Research progress of antibacterial materials [J]. Science Technology Vision, 2017(7): 220(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2457.2017.07.173
[8] 刘慧. 壳聚糖及其表面活性剂复合物的抗菌性与抗菌机理的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2004. LIU H. Antimicrobial activity and mechanism of chitosan and its combinations with surfactants[D]. Wuhan : Wuhan University, 2004 (in Chinese).
[9] 付旭锋, 李圆圆, 苏红巧, 等. 异噻唑啉酮类杀菌剂对黑斑蛙胚胎和蝌蚪的急性毒性 [J]. 生态毒理学报, 2014, 9(6): 1097-1103. FU X F, LI Y Y, SU H Q, et al. Acute toxicity of isothiazolinone biocides to pelophylax nigromaculatus embryos and tadpoles [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2014, 9(6): 1097-1103(in Chinese).
[10] XU N, CHENG H, XU J W, et al. Silver-loaded nanotubular structures enhanced bactericidal efficiency of antibiotics with synergistic effect in vitro and in vivo[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2017, 12: 731-743. [11] DENG H, MCSHAN D, ZHANG Y, et al. Mechanistic study of the synergistic antibacterial activity of combined silver nanoparticles and common antibiotics [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(16): 8840-8848. [12] 仇爱锋, 王玉涛, 张树秋, 等. 克百威、镉和铜对费氏弧菌的联合毒性效应[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(5): 869-875. QIU AI F, WANG Y T, ZHANG S Q, et al. Joint toxic effects of carbofuran, Cd and Cu to Vibrio fischeri[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(5): 869-875 (Chinese).
[13] BRODERIUS S J, KAHL M D, HOGLUND M D. Use of joint toxic response to define the primary mode of toxic action for diverse industrial organic chemicals [J]. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, 1995, 14(9): 1591-1605. [14] SLAWSON R M, LEE H, TREVORS J T. Bacterial interactions with silve [J]. Biology of Metals, 1990, 3(3-4): 151-154. doi: 10.1007/BF01140573 [15] JUNG W K, KOO H C, KIM K W, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 74(7): 2171-2178. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02001-07 [16] MCSHAN D, RAY P C, YU H. Molecular toxicity mechanism of nanosilver [J]. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 2014, 22(1): 116-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.010 [17] VAZQUEZ-MUÑOZ R, BORREGO B, JUÁREZ-MORENO K, et al. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in biological systems: Does the complexity of biological systems matter? [J]. Toxicology Letters, 2017, 276: 11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.05.007 [18] 赵清风, 陈介南, 张林, 等. AgNO3对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌作用及机制 [J]. 生物加工过程, 2011, 9(3): 52-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2011.03.011 ZHAO Q F, CHEN J N, ZHANG L, et al. Antimicrobial activity and mechanism of silver nitrate on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2011, 9(3): 52-56(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2011.03.011
[19] VELKOV T, THOMPSON P E, NATION R L, et al. Structure−activity relationships of polymyxin antibiotics [J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2010, 53(5): 1898-1916. doi: 10.1021/jm900999h [20] CLAUSELL A, GARCIA-SUBIRATS M, PUJOL M, et al. Gram-negative outer and inner membrane models: Insertion of cyclic cationic lipopeptides [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2007, 111(3): 551-563. doi: 10.1021/jp064757+ [21] 刘珏玲, 杨伟峰, 王毅. 细菌生物膜与表面活性剂抗菌的研究进展 [J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2016, 11(9): 858-860. LIU J L, YANG W F, WANG Y. Advance in the study of biofilmsand and the effect of surfactants on biofilm removal [J]. Journal of Pathogen Biology, 2016, 11(9): 858-860(in Chinese).
[22] 于海军. β-内酰胺类抗生素作用机制及头孢菌素发展 [J]. 石家庄职业技术学院学报, 2009, 21(2): 12-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4873.2009.02.005 YU H J. The mechanism of β-lactam antibiotics and the development of cephalosporins [J]. Journal of Shijiazhuang Vocational Technology Institute, 2009, 21(2): 12-16(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4873.2009.02.005
[23] KING D T, SOBHANIFAR S, STRYNADKA N C J. The mechanisms of resistance to β-lactam antibiotics//GOTTE M, BERGHUIS A, MATLASHEWSKI G, et al. Handbook of Antimicrobial Resistance[M]. New York: Springer New York, 2014: 1-22. [24] 胡兴戎. 糖肽类抗生素的作用机制及肠球菌的糖肽耐药机制 [J]. 国外医药(抗生素分册), 2001(3): 116-121. HU X G. The mechanism of action of glycopeptide antibiotics and the mechanism of glycopeptide resistance in enterococcus [J]. World Notes on Antibiotics, 2001(3): 116-121(in Chinese).
[25] 丁晓京. 新型二甲基异噻唑啉酮MIT杀菌剂 [J]. 日用化学品科学, 2004(5): 40-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7264.2004.05.015 DING X J. A new fungicide of dimethyl isothiazolinone MIT [J]. Detergent & Cosmetics, 2004(5): 40-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7264.2004.05.015
[26] FOURMY D, YOSHIZAWA S, PUGLISI J D. Structural origins of gentamicin antibiotic action [J]. The EMBO Journal, 1998, 17(22): 6437-6448. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.22.6437 [27] SCHNAPPINGER D, HILLEN W. Tetracyclines: Antibiotic action, uptake, and resistance mechanisms [J]. Archives of microbiology, 1996, 165(6): 359-369. doi: 10.1007/s002030050339 [28] CHOPRA I, HAWKEY P M, HINTON M. Tetracyclines, molecular and clinical aspects [J]. The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 1992, 29(3): 245-277. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.3.245 [29] CHAMPNEY W S, MILLER M. Inhibition of 50S ribosomal subunit assembly in haemophilus influenzae cells by azithromycin and erythromycin [J]. Current Microbiology, 2002, 44(6): 418-424. doi: 10.1007/s00284-001-0016-6 [30] 郭磊艳, 赵旦, 桂嘉烯, 等. 核糖体的组成、结构、功能和检测 [J]. 科技通报, 2020, 36(5): 1-12. GUO L Y, ZHAO D, GUI J X, et al. Composition, structure, function and detection of ribosome [J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2020, 36(5): 1-12(in Chinese).
[31] HERISSE M, DUVERGER Y, MARTIN-VERSTRARTA I, et al. Silver potentiates aminoglycoside toxicity by enhancing their uptake [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2017, 105(1): 115-126. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13687 [32] LUKACIK P, BARNARD T J, KELLER P W, et al. Structural engineering of a phage lysin that targets Gram-negative pathogens [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(25): 9857-9862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203472109 [33] 曾庆军. 抗生素在生态环境中的污染转归以及应对措施[J]. 湖南畜牧兽医, 2017(5): 49-52. ZENG Q J. The pollution and transformation of antibiotics in ecological environment and the response measures [J]. Hunan Journal of Animal Science & Veterinary Medicine, 2017(5): 49-52 (Chinese).
[34] 殷光权, 赵扬, 戴前梅. 我国水体中抗生素的污染现状、危害及防治建议[J]. 安徽卫生职业技术学院学报, 2017, 16(5): 6-8. YIN G Q, ZHAO Y, DAI Q M. Pollution Status, hazard and control suggestions of antibiotics in water of China (Summary) [J]. Journal of Anhui Health Vocational & Technical College, 2017, 16(5): 6-8 (Chinese).
-






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: