-
煤矸石是采煤和洗煤过程中排放的固体废物,是在成煤过程中与煤层伴生的一种含碳量较低、比煤坚硬的黑灰色岩石[1],可通过堆积、风化、淋溶等多种作用对周边大气、土壤和水体造成不同程度的污染[2- 3]。长期以来,煤矸石被用于低洼地区的垃圾填埋,形成了大量露天堆积物,造成植被破坏、水土流失等环境污染问题。煤矸石长时间的堆积以及治理措施经验的不足,造成门头沟区尾矿库附近的矸石山存在严重的重金属污染,尤其是汞(Hg)[4]。汞是一种毒性很强的重金属元素,在自然界中呈现多种赋存形态,如金属汞、无机结合态汞和有机结合态汞。无机汞的毒性较弱但进入环境后将经历一系列的转化为甲基汞,甲基汞是毒性最强的汞化合物[5]。为有效解决汞污染,联合国环境规划部于2013年制定了国际汞公约《水俣公约》;我国政府于2011年颁布的《重金属污染综合防治“十二五”规划》(国函〔2011〕13号)中,将汞列为重点管理重金属,并制定了汞污染排放量额指标,随后于2013年正式启动973汞污染特性以及环境和减排技术项目[6]。
国内外学者对煤矸石利用方面的研究[7-23]较多,如建材(包括制作水泥、混凝土,制砖,作路基材料,井下填充,土地复垦等)、高值化利用(包括合成陶瓷,制备氧化铝,提取镓、锂等稀有稀土元素)、吸附剂作用、碳回收等,但在环境污染方面的研究较少。对于重金属总量、赋存形态、淋溶等研究[24-29]主要集中于矿区中煤的研究和周边土壤重金属污染评价;对煤矸石中汞的研究主要讨论不同的加热速率、停留时间、气氛条件(N2、O2、CO2)、氧气体积分数等影响因素对煤矸石中汞的热释放[30-32],并表明煤矸石中汞释放的主要因素为温度。然而,北京门头沟区煤矸石中汞的空间分布、迁移富集规律及潜在环境风险却没有被系统地研究过。本次研究区域位于门头沟区的西南和中东部矿集区,具有百年多的煤炭开采历史[33],该地拥有煤和非金属矿产等多种资源,大规模的开采曾带动了当地区域的发展,同时也改变和破坏了当地的地质环境,产生了一系列的环境问题。在煤炭开采过程中遗留下大量煤矸石裸露堆积在地表已成为门头沟矿区的主要污染源,这些露天堆放的煤矸石经过风化和淋滤等作用,成为矿区水土污染的重要来源,对北京市门头沟矿区周边环境造成了严重影响。因此,研究北京市门头沟煤矸石堆放过程中汞的环境效应有着重要的理论和现实意义。
本文以北京市门头沟典型矿区堆积的煤矸石为研究对象,探讨煤矸石中汞的含量及影响因子,并采用改进的BCR连续提取法提取汞的赋存形态,探究在酸雨条件下初始pH、粒径、固液比等因素对汞的溶出特征的影响,为重金属汞的污染监测、矿区的进一步治理及生态修复提供理论依据。
-
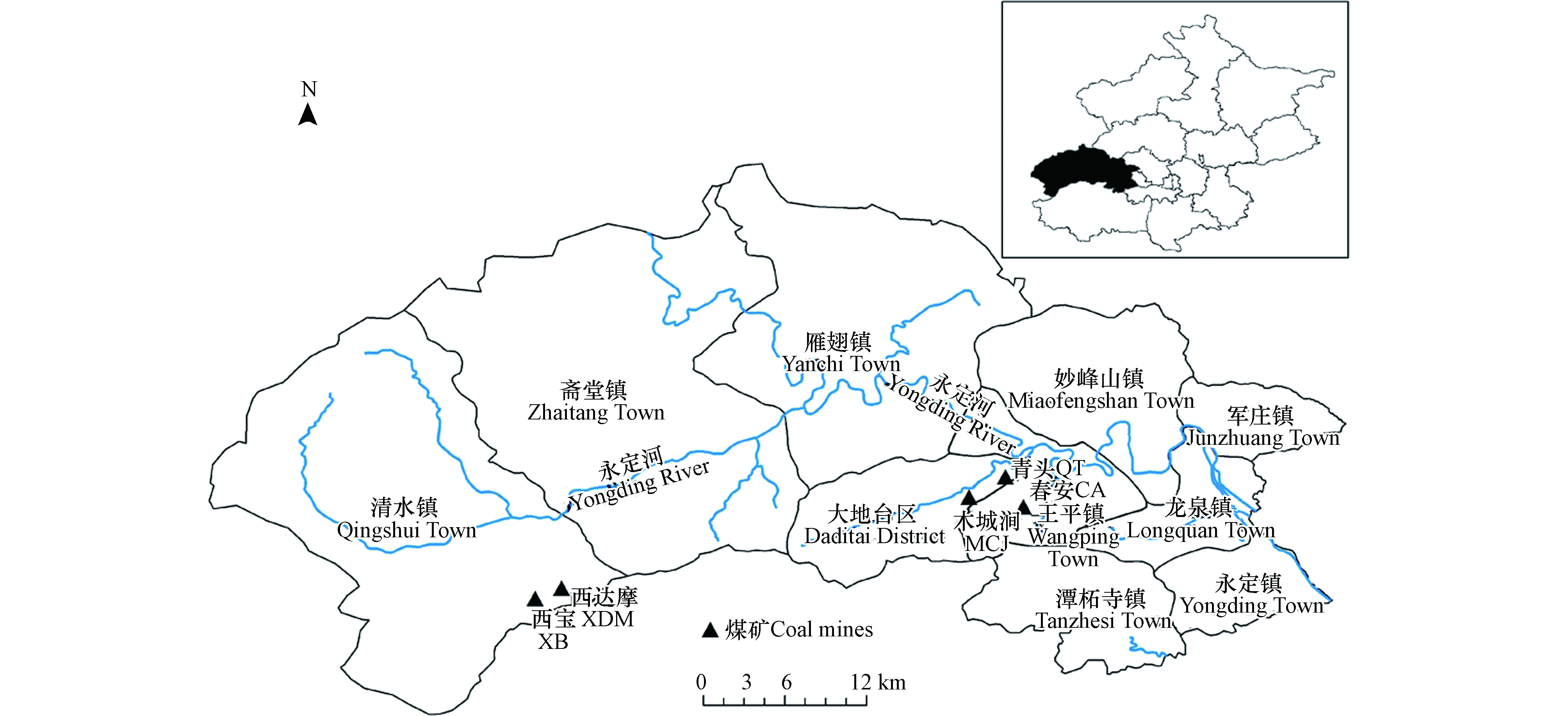
门头沟区蕴藏着丰富的煤炭资源,煤的储藏面积近700 km2, 占全区总面积的一半, 是中国五大无烟煤产地之一, 曾经是首都的能源基地[34]。但随着门头沟“首都西部生态涵养区”定位的确定, 各类矿山在2020年9月已经全部关闭, 在此过程中产生了大量的矿业废弃地。其中, 煤矿废弃地是主要的废弃地类型,煤矿废弃类型包括煤矸石压占、塌陷坑、废弃房屋压占等[35],大部分的煤矸石堆停止排矸后就地露天堆放,其中的重金属经过长年淋溶逐渐释放到周边环境中,造成重金属污染。研究区位于北京城区正西偏南,山地面积占98.5%,是北京唯一的纯山区。该地区气候为温带季风气候,冬季干燥寒冷, 最低温度−15 ℃,7—8月份温度最高, 在35 ℃以上。年均降水量600—700 mm, 多集中7—8月份,无霜期170—200 d左右[36]。本文选择清水镇、大地台区、王平镇3个镇的5个矿区进行研究,分别为西达摩(简称“XDM”)、西宝(简称“XB”)、青头(简称“QT”)、春安(简称“CA”)和木城涧(简称“MCJ”)(见图1)。
-
2019年4月沿永定河上游向依次对清水镇、大地台区、王平镇等地的矿区矸石山采集45个自然风化煤矸石固态样品,选用5点采样法采集表层0—20 cm矸石,其中XDM矿区5个(1—5),XB矿区9个(5—14),MCJ矿区4个(15—18),CA矿区9个(19—27),QT矿区18个(28—45)样品,分别保存在聚乙烯塑封袋中,依次编号。去除样品中根系、石块和虫体等杂物,于干净通风处自然风干,切割磨碎后分别过20目、100目和200目尼龙筛,密封于自封袋中保存待测。
-
风化煤矸石总汞用王水水浴消解-冷原子荧光测定[37]。其主要步骤为:称取0.5 g过100目筛的样品,加入10 mL(1+1)王水,加塞后摇匀,于沸水浴中消解2 h,取出冷却,立即加入10 mL的保存液,用稀释液稀释至刻度,摇匀后放置,取上清液待测,同时做空白实验。每组实验带有平行样品,且每次实验均重复3次,实验结果的不确定性低于5%。pH值用雷磁PHS-3C测量,Eh值测试配夹ORP计复合电极。
煤矸石中汞(Hg)采用AFS-930双道原子荧光光度计(北京吉天)测定;采用扫描电镜(SEM)(SU8100型冷场扫描电镜,日本日立)测定浸出前后矸石样的表面结构;pH的测定参照王萍[38]等的实验方法(固液比为1∶2.5);总有机碳(TOC)含量采用重铬酸钾氧化-分光光度法(HJ615—2011)测定;含水率按照国家《煤和岩石物理力学测定方法》(GB/T 23561)测定。
煤矸石形态采用欧共体标准物质局提出的BCR连续提取法测定[39],其提取步骤为:
(1)弱酸提取态(F1):准确称取0.5000 g 200目矸石样置于50mL离心管中,加入25 mL 0.11 mol·L−1醋酸溶液,设定温度(22±5)℃,放于摇床上220 r·min−1振荡16 h,再3000 r·min−1离心20 min获得上清液,待测,其残渣供下一步提取。
(2)可还原态(F2):将上一步的残渣物加入25 mL 0.5 mol·L−1的盐酸羟胺溶液,用HNO3调至pH为2,(22±5)℃再以220 r·min−1的转速振荡16 h,同上离心洗涤,取上清液供下一步提取。
(3)可氧化态(F3):将F2的残渣物加入5 mL H2O,摇匀,加入10 mL 30% H2O2。离心管加盖在室温下反应1 h,间歇振荡,然后去盖在85 ℃水浴中继续加热1h,直到试管中H2O2体积减少到1—2 mL,再向其中加入10 mL H2O2,在85 ℃水浴中加热1 h,直到H2O2蒸发近干。待冷却后,向其中加入25 mL醋酸铵溶液(1 mol·L−1,pH=2)。同前两步,再次振荡16 h后转移上清液
(4)残渣态(F4):其提取步骤参考土壤汞的消解步骤。
-
重金属含量描述性统计分析与Person相关性分析由SPSS 24.0实现;样点分布图与Hg的空间分布图由ArcGIS 10.3.1实现;折线图等由Excel 2013和Origin 2017实现。所有实验设置空白对照和平行试验,回收率86%—110%,将BCR提取的4种Hg形态含量之和与煤矸中Hg总量相比,其回收率在80%—115%之间。
-
富集因子(enrichment factor,EF)可定量表示元素富集程度并识别来源,计算方法如下:
式中,Ci为重金属i的含量(mg·kg−1);Cref为参比元素的含量(mg·kg−1)。
EF分级标准为:EF≤2,无或轻微富集;2<EF≤5,中度富集;5<EF≤20,显著富集;20<EF≤40,强烈富集;EF>40,极强富集[40]。研究表明,Sc的分布稳定,变异系数小[41],因此将Sc作为参比元素。
-
地质累积指数法(geoindex,Igeo)是由海德堡大学沉积物研究所MÜLLER[42]在1969年提出,不仅考虑了自然地质过程造成的背景值影响,也充分注意了人为活动对重金属污染的影响,是区分人为活动影响的重要参数,计算方法如下:
式中,Cn表示样品中测量到的重金属含量(mg·kg−1),Bn表示重金属的背景值(mg·kg−1),引入因子k(k=1.5)是为了减小背景值可能变化的影响。Igeo分级标准为:Igeo≤0,无污染;0<Igeo≤1,轻度污染;1<Igeo≤2,中度污染;2<Igeo<3,中度-重度污染;3≤Igeo<4,重度污染;4≤Igeo<5,重度-极度污染;Igeo≥5,极度污染。
根据重金属赋存形态,将弱酸溶态称为生物可利用态,可还原态和可氧化态称为潜在生物可利用态,残渣态称为生物不可利用态[43]。基于煤矸石中Hg的赋存形态,采用风险编码法(risk assessment coding method,RAC)和次生相和原生相分布比值法(ration of secondary phase and primary phase,RSP)对Hg进行有效性评价。
-
风险编码法主要通过计算弱酸态含量(F1)占总量的比例来评价环境风险[44],其计算公式如下:
式中,RAC为F1占总量的质量分数,%;CF1为F1弱酸溶态重金属含量(mg·kg−1);CT为BCR四态含量之和(mg·kg−1)。根据RAC大小,将风险程度分为5个等级:RAC<1%(无风险), 1%≤RAC<10%(低风险),10%≤RAC<30%(中等风险),30%≤RAC<50%(高风险),RAC≥50%(极高风险)。
-
次生相和原生相比值法(RSP)是通过计算原生矿物的风化产物和外来次生产物的比值来评价重金属对煤矸石环境的污染程度[45-47],其计算公式下:
式中,RSP为次生相和原生相的比值,Msec为次生相的重金属含量,Mprim为原生相重金属的含量,本文以BCR前三态含量之和为次生相重金属含量(mg·kg−1),原生相重金属含量为残渣态(mg·kg−1),其风险等级为:RSP<1(无污染),1<RSP<2(轻度污染),2<RSP<3(中度污染),RSP>3(重度污染)。
-
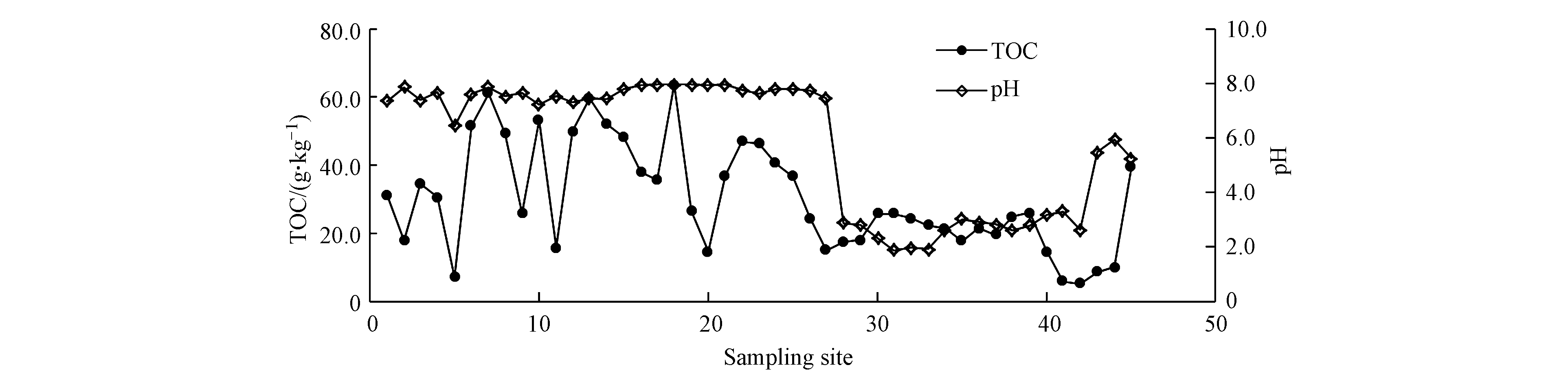
研究区煤矸石的pH和TOC含量如图2所示,除QT煤矿外,其余4个矿区pH值变化范围为6.42—8.05,均值为7.63,属于中性偏碱范围;QT煤矿周边堆积的矸石pH均值为3.13,在1.88—5.94之间,呈现出较强的酸性,这是由于QT煤矿在多年自然恢复作用下暴露在大气中,经风化淋溶作用使得矸石表面酸化,从而呈现出酸性[48]。矸石TOC含量变化范围为5.19—63.72 g·kg−1,均值为30.33 g·kg−1,最大值出现在18号采样点,该点位于矸石山堆积下方河流附近,周边生物残体、凋落物[49]及耕地土壤施肥等因素导致有机质含量较高。
-
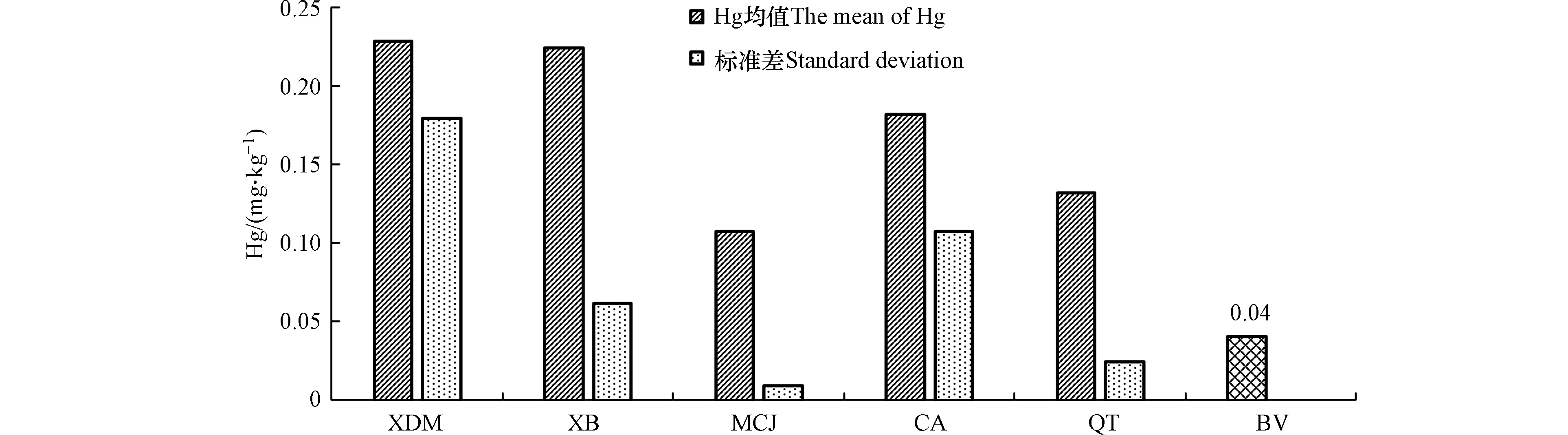
研究区45个样品中Hg含量的描述性统计结果如表1、图3所示。由表1,Hg的含量为0.085—0.519 mg·kg−1,均值为0.169 mg·kg−1,标准差为0.089 mg·kg−1,变异系数为52.09%,属于高变异(50%—100%),空间异质性强,各矿区均值从大到小依次为XDM>XB>CA>QT>MCJ。Hg的平均值含量超过了北京市土壤背景值[50],超标倍数为4.225,表明Hg对该研究区有一定的污染,各矿区单因子超标倍数均值从大到小依次为XB>XDM>CA>QT>MCJ。富集系数和地累积指数的大小能体现出研究区的污染程度[51-52],其中Hg的平均富集系数和地累积指数分别为4.53和1.35,属于中度污染,各矿区Hg的平均EF依次为XB>XDM>QT>CA>MCJ,平均Igeo依次为XDM>CA>QT>XB>MCJ。
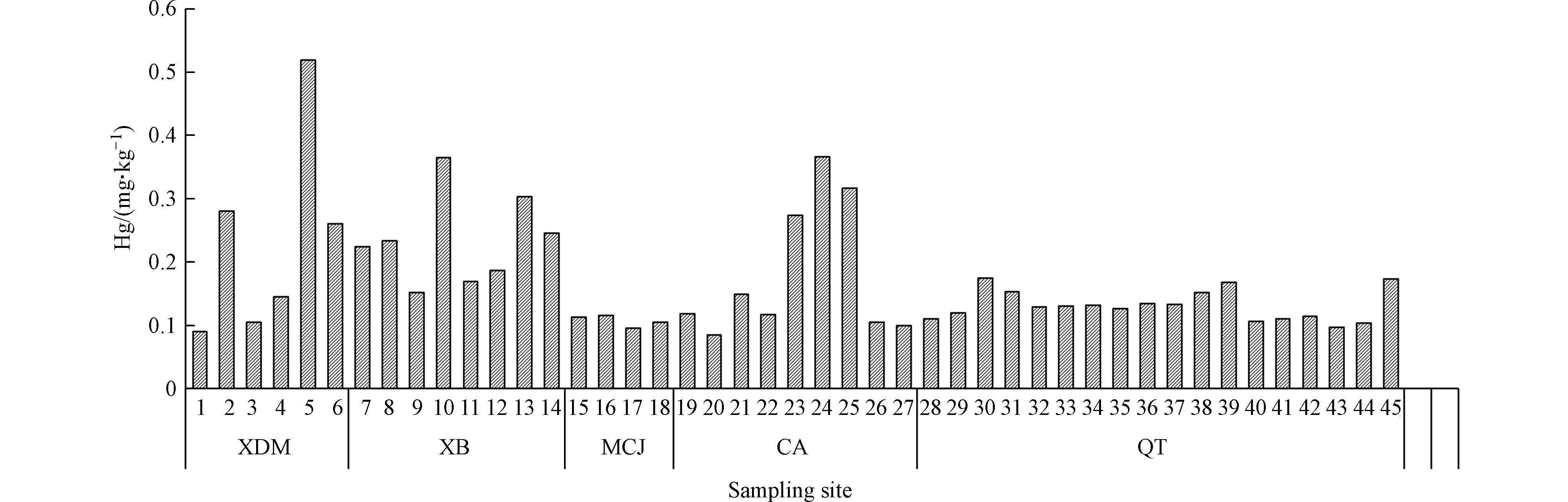
根据各样点汞元素的含量,对汞的分布做柱状图,结果如图4所示,Hg含量分布较为均匀的是MCJ矿区和QT矿区,含量不高;同样可见,5、10、13、24、25号的5个样点含量较高,这几个点主要分布在XDM、XB和CA矿区,呈现局部污染态势,这与Li等[53-54]的研究一致;k-s检验表明,MCJ和CA矿区的均值存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。在空间位置上,研究区Hg含量高的区域主要集中在矿区边缘,并以该区域向周围扩散,这可能是由于大气沉降、矿山开采、冶炼、运输等活动产生的固体废物在矿区边缘堆积,经过雨水的冲刷和风力等物理条件的作用向四周扩散而成。
-
煤矸石的理化性质(总有机碳含量、含水率、pH、Eh)会影响重金属的总量和迁移转化能力,因此,总有机碳、含水率、pH、Eh是重金属含量分析时的重要指标。由研究区Hg的含量与pH、Eh、TOC和矸石含水率(
ωH2O )间的Person相关系数可见(表2), Eh与Hg呈现为负相关,即当矸石通气状况不好时,Hg的含量较高,说明在厌氧条件下,Hg易产生沉淀,还原Hg,降低其毒性[55]。 矸石含水率(ωH2O )对重金属的毒性和生物的可利用性有一定的影响[49],由表2可见,ωH2O 与Hg间存在显著正相关,说明ωH2O 在一定条件下能影响矸石中的微生物,促进Hg的积累。而Hg与TOC、pH之间不存在相关性。 -
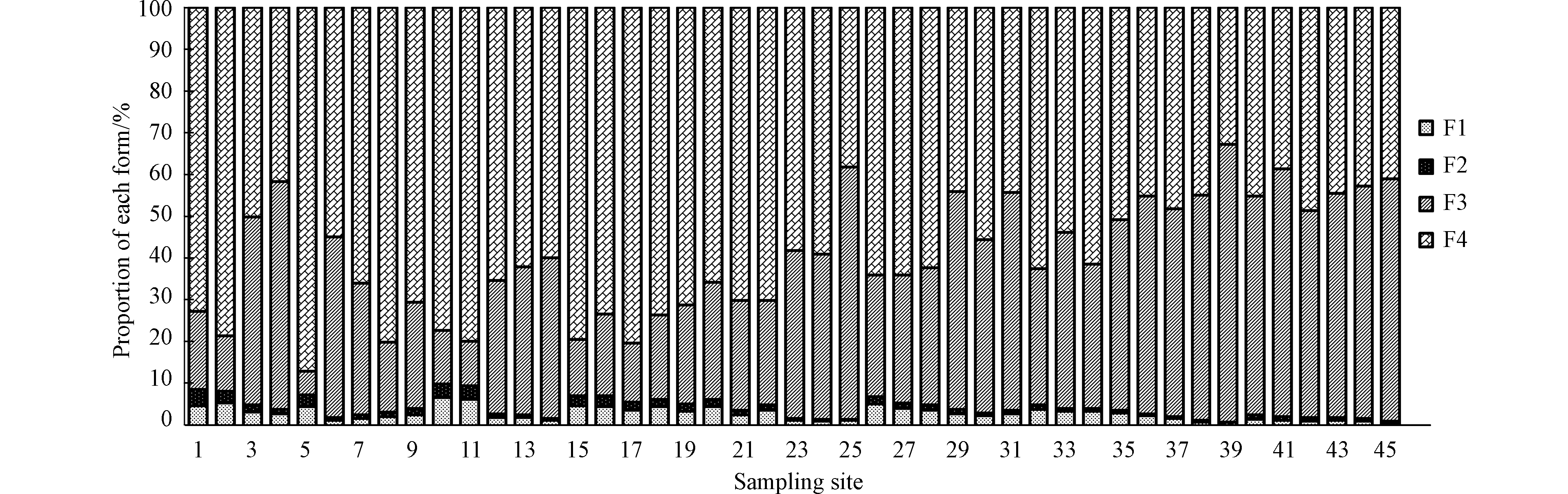
为了解研究区Hg的污染状况,采用改进BCR连续提取法对研究区表层煤矸石Hg的赋存形态进行分析,其提取形态分为4种:弱酸提取态(F1)、可还原态(F2)、可氧化态(F3)和残渣态(F4)。研究区煤矸石中Hg元素的F1占0.35%—6.45%,F2占0.28%—3.92%,F3占5.71%—66.46%,F4占32.91%—87.20%,Hg的主要形态为F3和F4,各形态之和占总量的83.53%—97.71%。由图5不难看出,Hg的赋存形态特征表现为F4(59.66%)>F3(36.37%)>F1(2.68%)>F2(1.29%),对环境的危害较小[26]。由此可见,煤矸石中Hg元素的化学性质较为稳定,可给性极弱,难以被生物吸收利用[56],但F3占比较高,易与矸石中有机物络合,导致Hg2+释放并被植物吸收利用[57],造成周边环境污染。
表3中F2与F3呈显著负相关(P<0.01),当环境处于缺氧状态时,F2被释放,当环境处于氧化条件时,F3被释放;且F2与TOC、pH呈现显著正相关(P<0.01),表明在某种条件下,TOC、pH能影响F2的含量;F3与F4呈显著正相关(P<0.01);F4与全量Hg呈显著正相关(P<0.01),表明全量Hg是影响F4的主要因素,Hg的潜在活性随全量的增加而增加;F4与TOC呈显著正相关,表明F4受TOC影响较大,易与有机质结合,但从有机质中解吸Hg需要克服较大的活化能。
-
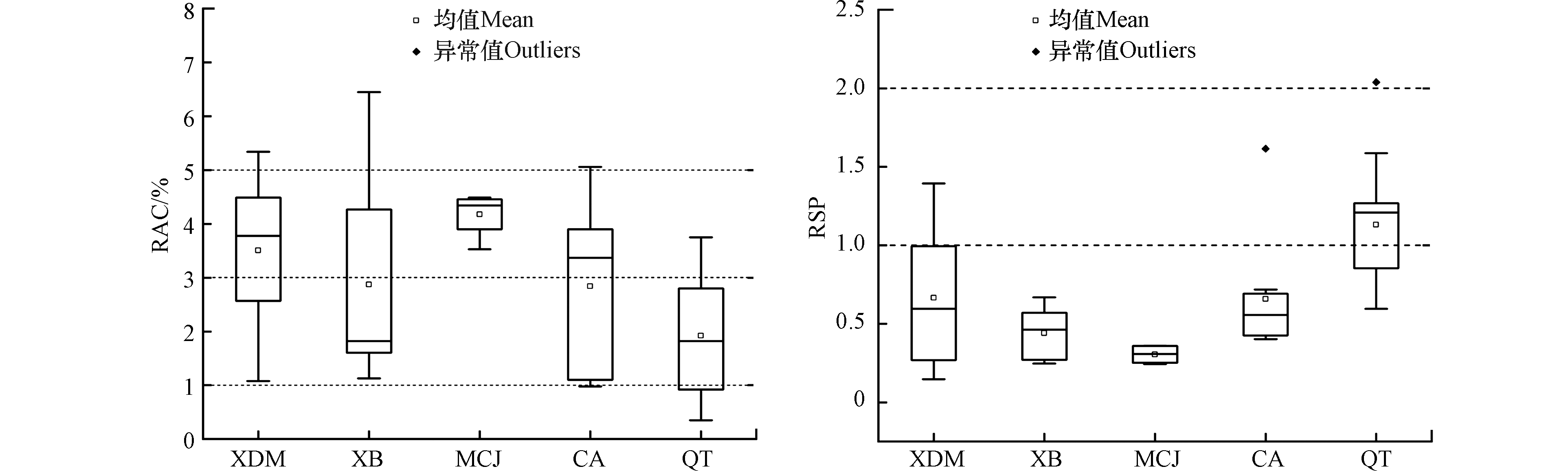
煤矸石中重金属元素迁移能力的强弱与其化学形态密切相关[58]。由2.1.2节得知,该研究区Hg富集严重。故选择Hg元素为研究对象,探究其潜在风险。不同矿区Hg形态的潜在风险结果如图6所示。比较RAC可看出,5个矿区中有39个样品的RAC值在1%—10%,为低风险程度,占总量的86.67%,其中MCJ矿区分布较为均匀,每个样品保持在4.18%左右,相对其他矿区,环境风险相对较高;其中10号样点Hg的RAC值最大,为6.45%;总体而言,各矿区中Hg的平均RAC值由强到弱分别为MCJ>XDM>CA>XB>QT,属于低风险。比较RSP计算结果,不同矿区也存在着差异,基本属于无污染,其中QT矿区Hg的平均RSP值最大,为1.13,属于轻度污染,表明QT矿区的污染程度相对较高,可还原态Hg和可氧化态Hg极大可能会迁移到环境中;总体而言,各矿区Hg的平均RSP值由大到小依次为QT>XDM>CA>XB>MCJ,轻度污染的占比为31.11%,其余均为无污染;整体而言,研究区Hg的潜在风险程度较低,但仍存在风险,需引起重视。
-
选取XDM和CA两个矿区中总汞含量较高的4个煤矸石样(23号、22号、5号、2号)对其进行淋溶试验。从淋溶时间、初始pH、粒径、固液比的4个方面看其溶出特征并进行原因分析。将初始淋溶液pH设定为5.60和3.11[59-60]置于500 mL锥形瓶中与矸石样混合浸泡,浸泡后对样品进行早中晚3次均匀搅拌,用封口膜将锥形瓶封口,对不同初始pH、粒径和固液比的样品进行同样操作。在第1、3、5、8、12、18、22、29、36 d分别取样5 mL测试Hg的浓度(王水消解法),保持室内温度为20℃左右,每组实验设置3组平行样。
-
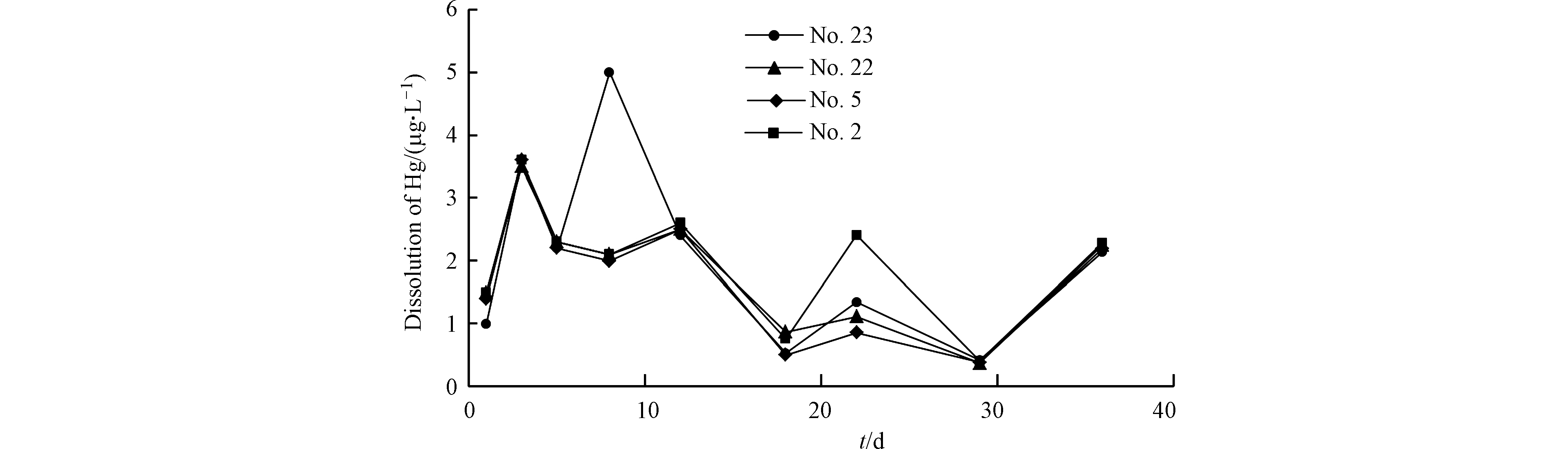
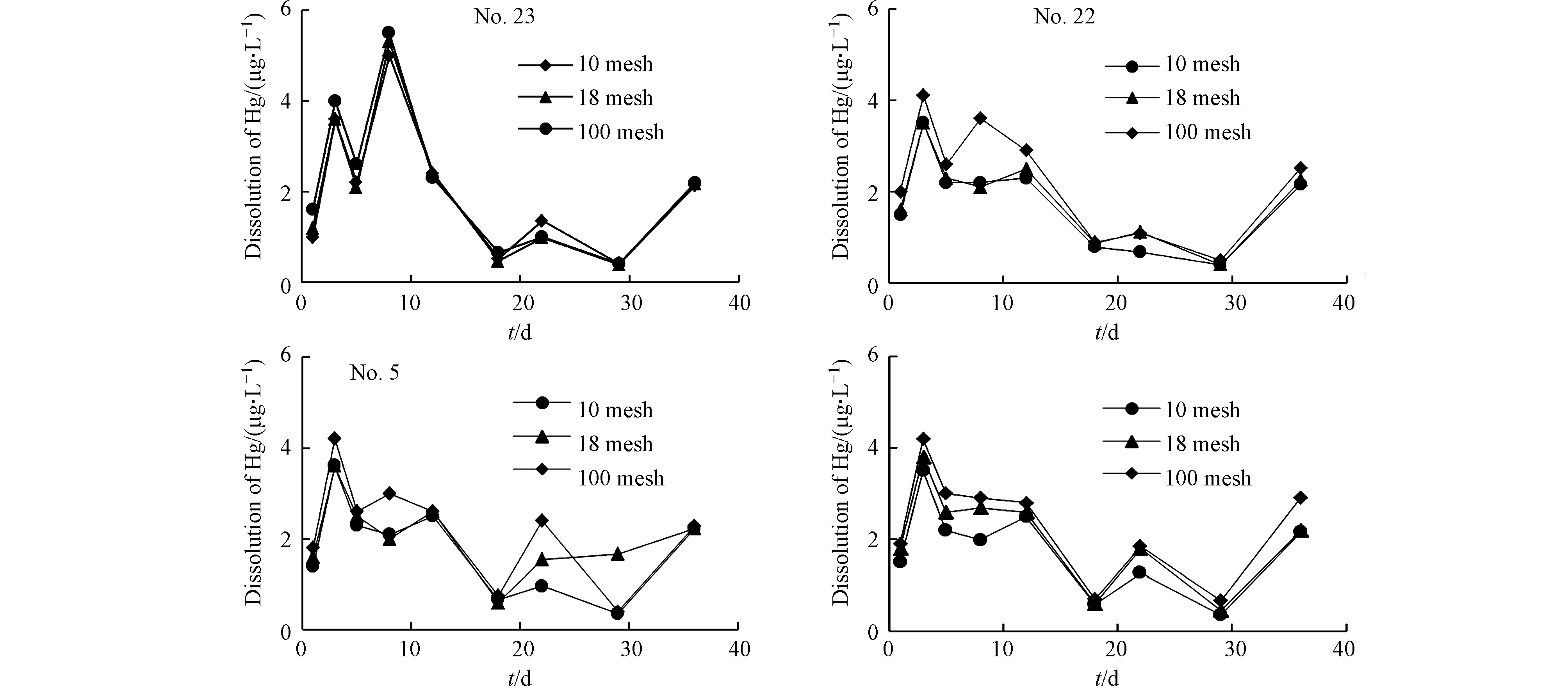
门头沟地区多年连续降雨时间最长为18 d,但降雨过程持续时间短且雨量较小,而地势较低处的煤矸石受雨水的浸泡时间较长,故选择浸泡测验时间为1、3、5、8、12、18、22、29、36 d。由图7可看出,4个样品在30 d前整体均有两个明显的峰值,在第3 天首次出现溶出高峰,溶出量在3.6 μg·L−1左右,出现原因主要为弱酸提取态Hg在酸性条件下极易发生溶解释放到上清液中,加之搅拌时间间隔较长造成缺氧环境使得可还原态Hg被溶解释放。在第22 天迎来第二次高峰,且第一次峰值约为第二次的2.54倍,可能出现的原因是该样品中Hg在搅拌过程中伴随着O2的进入被氧化释放所得。
-
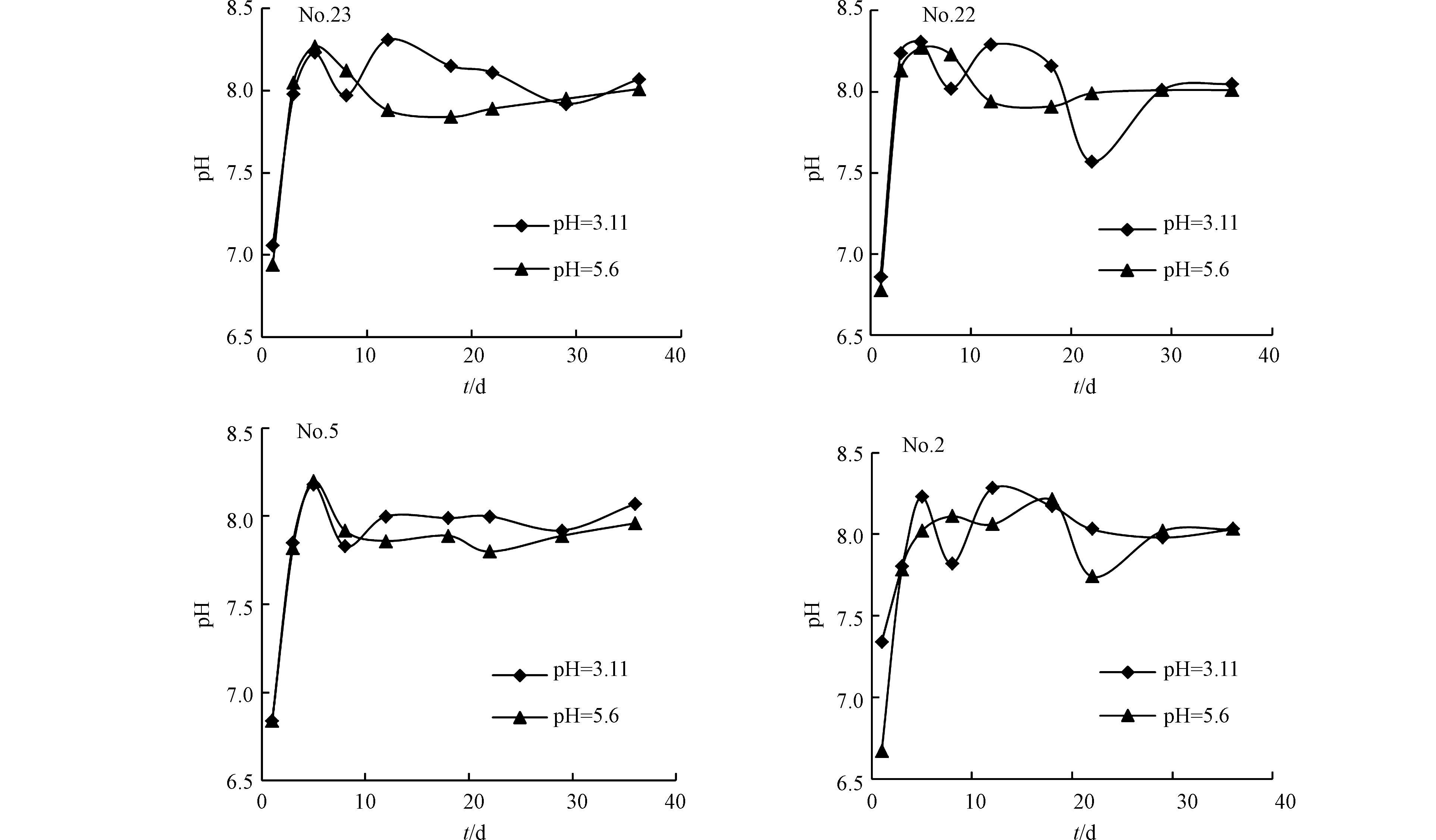
pH值是评价环境污染程度的重要指标之一,它影响着元素的价态和形态。该地区多年降水的平均pH值和最低pH值分别为5.6和3.11,因此选择初始pH值为3.11和5.6的浸泡液。研究区处于山地,汽车较少,主要影响因子为煤中的硫元素,故初始pH采用硫酸∶硝酸=3∶1的混合液,并用去离子水稀释配制。由图8可知,无论初始pH为多少,均在第5天浸出液的pH值达到第一个峰值,之后便维持在8.0左右,为弱碱性,此时的氧化还原电位也达到稳定状态,说明矿物在该体系中的溶解和沉淀达到一个动态平衡的状态,这与LIN等[62]的研究一致。当初始pH 3.11时,4个样品的起伏较大,当初始pH 5.6时,走势均为先增再减,且样品后期均有pH下降的现象,这是因为煤矸石中本身带有消耗碱性矿物,长期浸泡会导致pH有短暂时期的降低[63]。
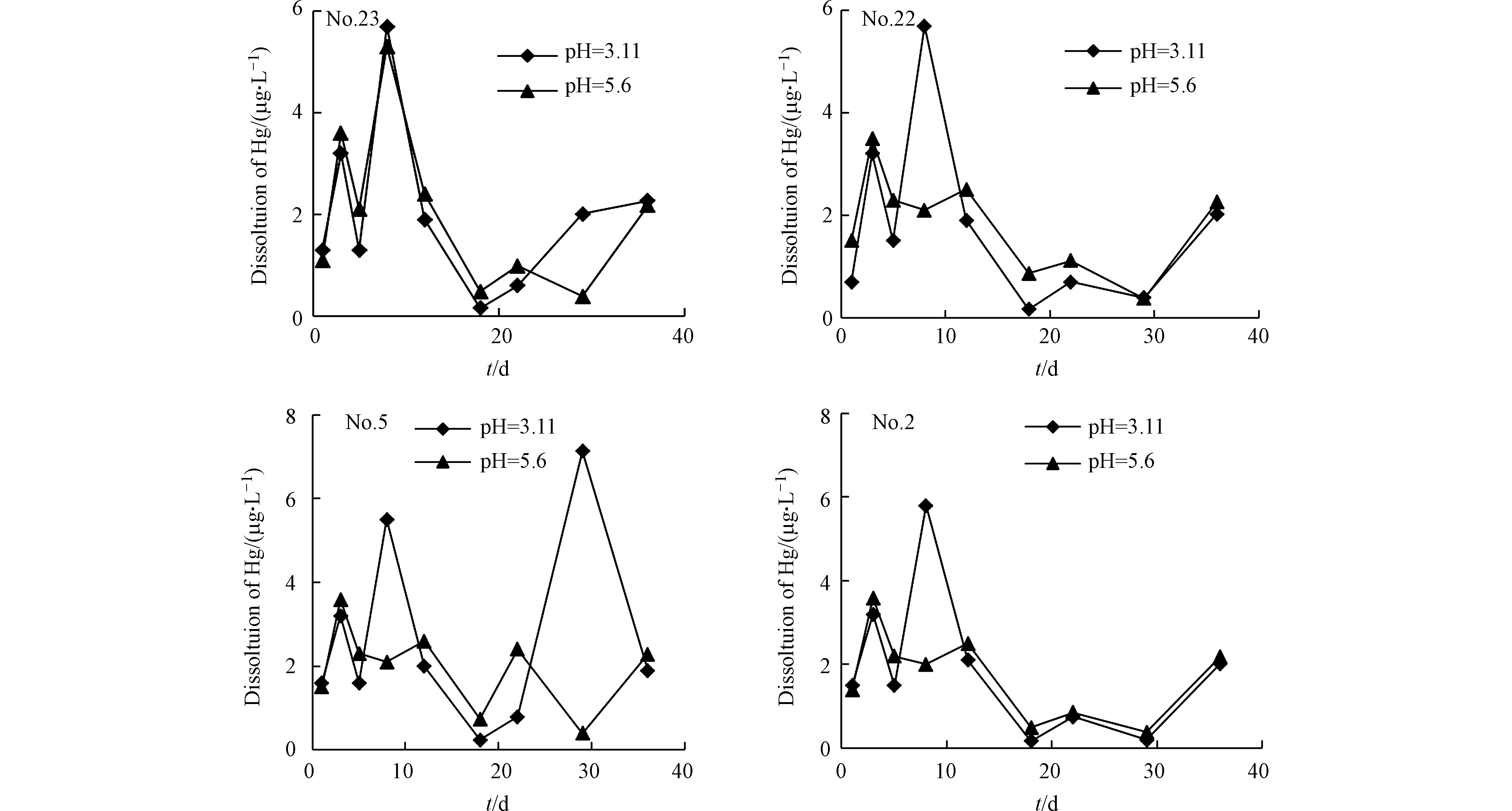
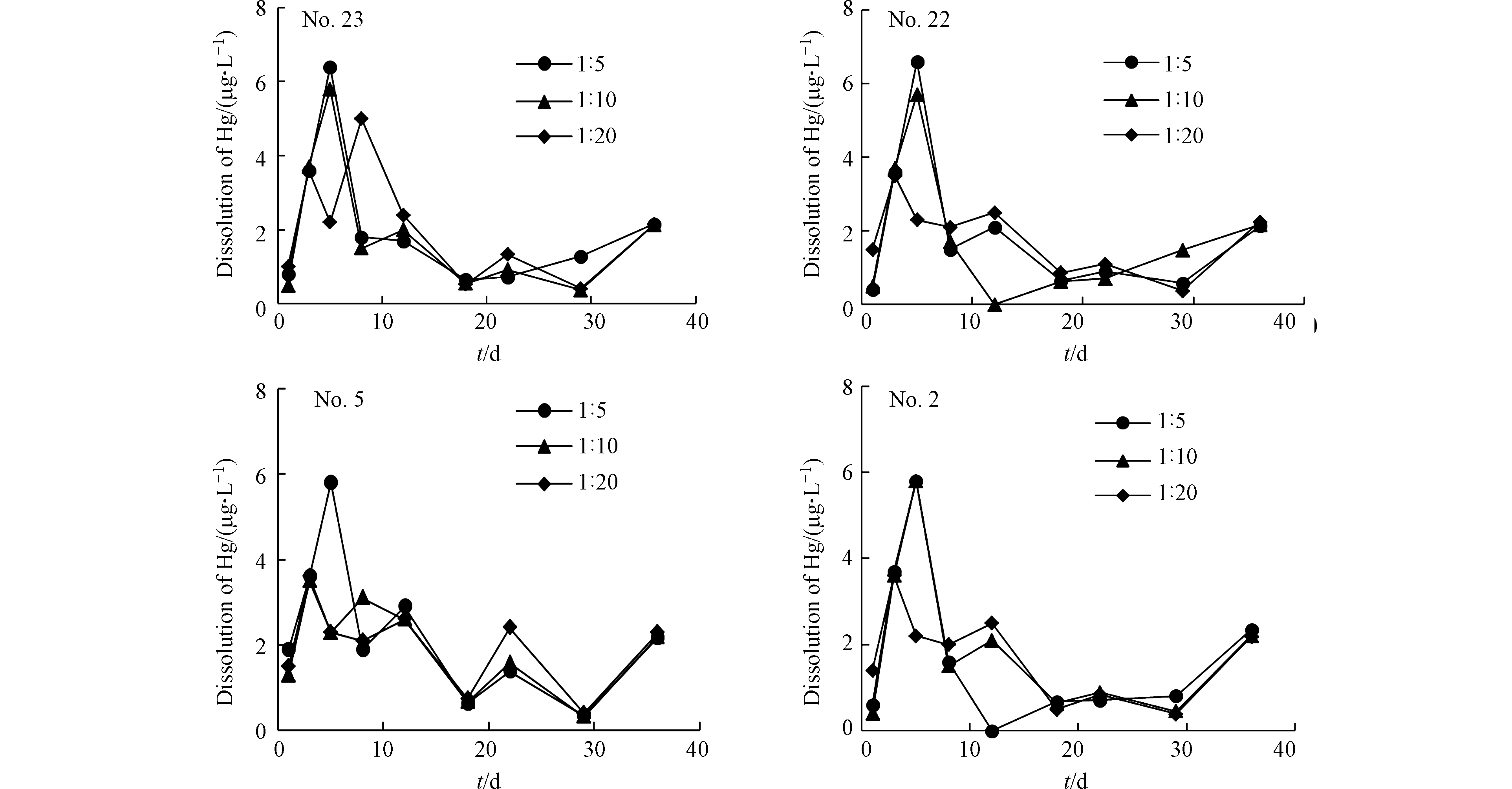
由图9可知,第1天,初始pH3.11时Hg的溶出量较初始pH5.6时多,这是由于在酸性条件下,Hg的溶出量大于沉淀量[62-63],溶出量主要为F1,F1与矸石结合最不稳定,最易溶解到渗滤液中,且酸性条件可以极大地增加环境中Hg和有机物的迁移转化;而在第8—12天Hg的溶出量出现了第二个高峰期,这是因为在实验过程中搅拌次数不多,造成锥形瓶中出现缺氧状态,从而使得F2被释放出来,溶解到渗滤液中[62]。因而在酸性条件下,Hg更易析出溶解并释放到环境中,影响周边环境。
-
煤矸石的粒径对重金属的溶解量有较大影响。因而分别选择80 g 10目、18目和100目(相当于粗粒度、中粒度、细粒度)的矸石样置于500 mL的锥形瓶中,分别加入pH为5.6、固液比为1∶5的淋溶液,将样品与去离子水混合均匀后浸泡,并进行充分搅拌。结果见图10,可以看出不同粒径的煤矸石中Hg的溶出量有所差异,4个样品在第3天和第8天有两次溶出峰值。整体而言,3个粒径中Hg的溶出量随浸泡时间的变化不大,但显而易见的是,100目的细颗粒相对粗颗粒而言,溶出量最大,这是由于细颗粒的比表面积大,与液体接触的表面积大,反应速率加快,因而溶解快[64];后期由于溶解出来的Hg向溶液中扩散,一部分被基质吸附,故而溶出量减小。
-
按照煤矸石质量与浸泡液体积比(固液比)为1∶5、1∶10、1∶20,准确称取100目煤矸石样品80 g、40 g、20 g分别置于3个500 mL的锥形瓶中,加入400 mL去离子水,将样品与去离子水混合均匀后浸泡,并进行充分搅拌。由图11可知,固液比为1∶5时Hg的溶出量最大,说明固液比对煤矸石中Hg的溶解释放有重要影响,固液比越大,浸泡液中Hg的溶出量越高。
-
为研究酸雨侵蚀和重金属析出对样品表面形貌的影响,对原始样品、浸泡中样品和浸泡后样品进行电镜扫描分析,由图12a可观察到,原始样品粒形整体规则、光滑,且表层附有高亮颗粒;淋溶中期(图12b)受酸溶液浸泡侵蚀使得样品发生化学损伤,表面凹凸不平,并出现微孔;在淋溶后期(12c),煤矸石出现了严重的腐蚀现象,表面大颗粒较少,碎裂状较多,煤矸石内部间隙在淋溶后期酸雨作用下得到进一步的发育和扩展,进而煤矸石内部在淋溶后期得到了严重损伤,可能导致煤矸石物理性质发生变化[65],且表面高亮颗粒较多,可能是淋溶过程中析出的重金属物质[64]。
-
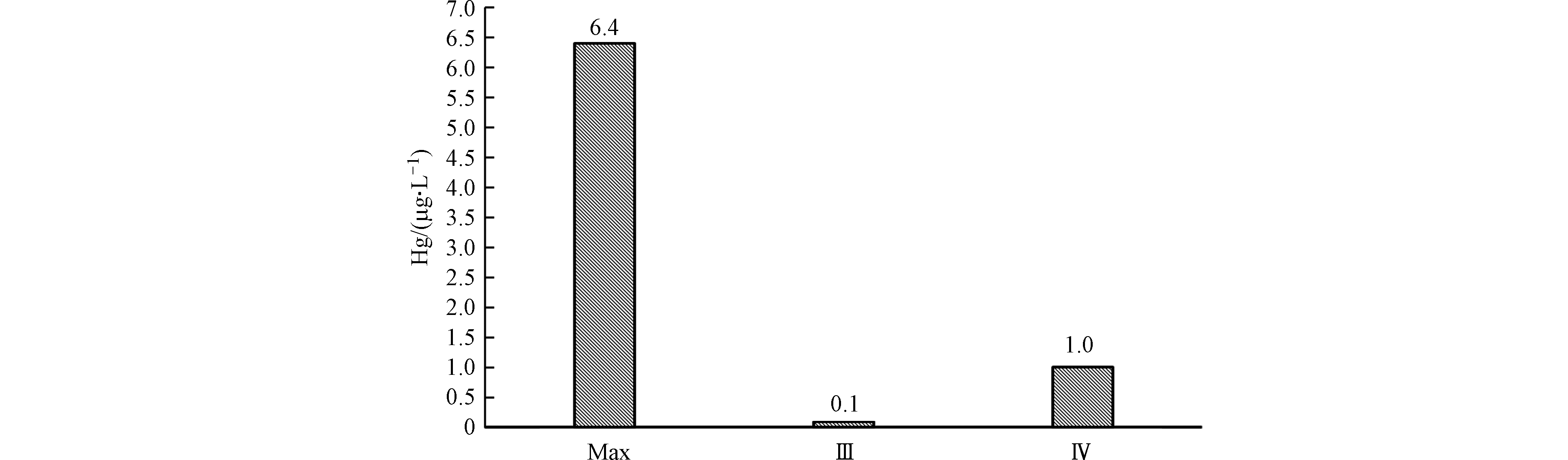
汞元素的溶出最大量为6.4 μg·L−1,为22号样点在固液比为1∶5、粒径为100目、初始pH为3.11时所达到,占该样品总量的1.75%,占比较小。该研究区毗邻永定河,因此对永定河地表水的保护也极其重要,如图13所示,淋溶液中Hg的最大溶出量与GB3838—2002《地表水环境质量标准基本项目标准限制》中Ⅲ类、Ⅳ类水质指标数值相比较得出,Hg元素严重超出国家标准,为Ⅳ类水质的6.4倍,且此次淋溶时间较短,可见煤矸石在短期淋溶下的重金属释放较为明显,加之各地区煤矸石中Hg元素的含量差异较大,Hg 的污染具有长期累积性[66]。因此煤矸石中Hg元素通过地表径流和地下渗流对永定河污染的可能性较大,且不容忽视。
-
(1)研究区中Hg的平均含量均超过北京市土壤背景值,其单因子指数、富集因子指数和地累积指数分别为4.225、4.39和1.32,属于中度污染,Hg为强变异水平,XDM矿区变异水平最大,表明XDM矿区受人类活动影响强烈。
(2)该研究区煤矸石中Hg以残渣态Hg为主,对环境危害较小;可氧化态Hg次之,具有二次污染的风险。
(3)风险编码法和次生相与原生相分布比值法均表明各矿区中Hg的污染程度较低,污染风险较小。
(4)静态淋溶试验和SEM扫描电镜分析结果表明,淋溶初期Hg的溶解量较大;酸度越强,初期Hg的溶出量越大;固液比越大,溶出量越高;淋溶时间在5 d达到最大,而后减小;粒径越大,溶出越小。
(5)该研究区中Hg的最大溶出量为Ⅳ类水质的6.4倍,严重超出国家标准,故煤矸石中Hg元素在自然条件下淋溶,通过地表径流和地下渗流对永定河污染的可能性较大。
综合评价结果表明XDM矿区为风险最高矿区,处于中低风险区;MCJ为风险最低矿区,基本属于无污染区;应优先控制对象,并采取相关措施进行改善。综合赋存形态与静态溶出结果,Hg元素中可氧化态与残渣态占比较高,且溶出最大量已超过国家Ⅳ类水质标准,应对矸石山周边已经污染的土壤进行原位或异位修复,并且采取土壤固化技术,防止重金属造成更大面积的地表水与地下水污染。
北京市门头沟风化煤矸石中汞的赋存形态与溶出特征分析
Analysis on the occurrence and dissolution characteristics of mercury in weathered coal gangue in Mentougou, Beijing
-
摘要: 为探究堆积煤矸石所产生的重金属的污染问题,本文以北京市门头沟5个典型矿区为研究对象,采集矸石山堆积表面风化煤矸石共45个样品,分析测试矸石样品中汞(Hg)的含量,对不同理化性质下各重金属的变化规律进行了初步探讨;利用改进BCR连续提取法,研究样品中Hg的赋存形态,分析其生物可利用性;采用富集因子法、地累积指数法、风险编码法和个体污染因子法对Hg进行有效性评价;再模拟酸雨条件下Hg的溶出特征及影响因素。结果表明,该研究区Hg的含量为0.085—0.519 mg·kg−1,均值为0.169 mg·kg−1,超过了北京市土壤背景值,超标倍数为4.225;Hg的平均富集系数与地累积指数分别为4.53和1.35,均表现为中度污染;风险编码法和次生相与原生相比值法结果显示为低风险和轻度污染,占比分别为86.67%和31.11%;Hg与Eh呈显著负相关,与含水率呈显著正相关;煤矸石中Hg的主要赋存形态为可氧化态Hg和残渣态Hg,其中可还原态Hg与可氧化态Hg存在显著负相关,TOC、pH与可还原态Hg呈显著正相关;静态淋溶试验表明,雨水酸度、粒径、固液比均会影响Hg的溶出量,在一定条件范围内,煤矸石浸泡液中Hg的溶出量随pH的增大而减小,随粒径的增大而增大,随固液比的增大而增大;在静态淋溶模拟试验中,Hg的最大溶出量严重超出国家标准,为Ⅳ类水质的6.4倍。该研究结果可为进一步了解Hg 在煤矸石中的活性、迁移规律、赋存形态及永定河Hg的污染治理提供科学依据。Abstract: In order to explore the pollution of heavy metals caused by the accumulation of coal gangue, this paper takes 5 typical mining areas in Mentougou, Beijing as the research object. A total of 45 samples of weathered coal gangue on the surface of the gangue hill were collected to analyze and test the content of mercury (Hg) in the gangue samples, and a preliminary discussion on the changing laws of various heavy metals under different physical and chemical properties were investigated; using the improved BCR continuous extraction method to study the occurrence of Hg in the sample and analyze its bioavailability; and the enrichment factor method, the geoaccumulation index method, risk coding method and individual pollution factor method were used to evaluate the effectiveness of Hg; the dissolution characteristics and factors affecting Hg under acid rain conditions were then simulated. The results showed that the content of Hg in the study area was 0.085—0.519 mg·kg−1, with an average value of 0.169 mg·kg−1, which exceeded the Beijing soil background value with a multiple of 4.225; the average enrichment coefficient of Hg and land accumulation index are 4.53 and 1.35 respectively, both of which are moderate pollution; the results of risk coding method and secondary phase to primary phase ratio method show low risk and light pollution, accounting for 86.67% and 31.11% respectively; Hg are significantly negatively correlated with Eh, and positively correlated with moisture content; the main occurrence forms of Hg in coal gangue are oxidizable Hg and residual Hg, among which there is a significant negative correlation between reducible Hg and oxidizable Hg, there is a significant positive correlation between TOC, pH and the reducible Hg; the static leaching test shows that the acidity of rainwater, particle size, and solid-liquid ratio will all affect the dissolution of Hg. Within a certain range of conditions, the dissolution of Hg in the coal gangue soaking solution decreases with pH increases, and it increases with the increase of particle size and solid-liquid ratio; In the static leaching simulation test, the maximum dissolution of Hg seriously exceeded the national standard, and it was 6.4 times as much as the value of Class Ⅳ water quality. The research results can provide a scientific basis for further understanding of the activity, migration law, occurrence form of Hg in coal gangue and the Hg pollution control of Yongding River.
-
Key words:
- mercury /
- coal gangue /
- occurrence states /
- static leaching
-
多环芳烃(polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, PAHs)是一类环境中广泛存在的有机污染物,主要来自于人为源,如石油泄漏、汽车排放、化石燃料和生物质燃烧、工业过程以及化学制造,也有部分来自火山活动、森林火灾和成岩作用等自然源[1-2]. 这类污染物因其分布广、生物累积性和对人类的潜在生态风险[3]而受到广泛关注. 16种PAHs被美国环境保护署(USEPA)列为优先控制的污染物[4]. 其中,含有2—3个苯环的低分子量PAHs被认为是非致癌物,而含有4—6个环的7个高分子量PAHs被列为致癌物[5]. PAHs一旦释放到环境中,能够通过水和空气进行长距离的迁移,扩散到全球范围的土壤[6-7]、沉积物[8-9]、水[10]和大气[11-12]中. PAHs不易降解,容易被土壤颗粒吸附[13-14],因此土壤埋藏了环境中90%以上的PAHs,是一个重要的汇[15].
尽管存在一些自然来源,造成全球范围内PAHs污染的主要原因仍是与城市化密切相关的人为排放[16]. 许多发展中国家,尤其是中国,正处于城市化兴起与快速发展的过渡时期. 由于大规模的城市化和工业化,我国城市地区大量人口密集,随之出现工业活动加剧、汽车使用激增等现象,从而导致大量PAHs通过大气沉降进入城市土壤[17-18]. 此外,PAHs在城市土壤中的分布主要归因于其释放源的类型和位置[19-20]. 因此,加剧的人类活动可能会改变城市土壤环境中PAHs的组成和分布. 基于不同PAH毒性的差异性,组成的改变也可能会引起暴露人群健康风险的变化. 然而,这个问题迄今为止较少引起关注[21].
研究表明,城市化可能是影响城市土壤中PAHs环境行为的关键因素. Wang等[22]通过分析土壤PAHs浓度、城市化指标以及土壤理化性质之间的相关性,提出人口密度是影响南京城市土壤PAHs含量的关键因素之一. Cao等[21]基于苏南一个快速发展的城镇土壤中2009年和2014年PAHs的浓度,将其含量、组成和来源的变化归因于城市化进程. Jensen等[23]发现挪威南部邻近奥斯陆的地区,因其人口较多和城市化程度较高,土壤中PAHs浓度高于位于挪威北部,人口较少的地区. 此外,也有一些学者[19, 24-26]利用湖泊和水库中的柱状沉积物,以及不同城市化阶段或不同深度的土壤样品,探讨PAHs的环境行为与城市化过程之间的关系. 然而,深入探讨某个特定时期城市化进程对城市土壤中PAHs浓度、来源和暴露风险影响的研究却很少.
2008年至2012年,天津市处在城市化最快的时期[27],且2012年以前,全市生产总值(GDP)增速均保持在16%以上,为近15年来最高水平[28]. 本研究基于天津市近郊地区(包括西青区、津南区、北辰区和东丽区)土壤中的16种优先控制PAHs的浓度数据,利用正定矩阵因子分解(positive matrix factorization, PMF)模型和终身累积癌症风险(incremental lifetime cancer risk, ILCR)模型定量解析出2008年和2012年天津市近郊地区土壤中PAHs的来源组成以及人体暴露风险,并将两个年份的解析结果进行对比分析. 旨在通过定点定期的监测结果,探讨在经济高速发展的背景下,快速城市化过程中区域土壤中PAHs排放源的变化及其引起的浓度、组成和生态风险的改变,进而揭示人类活动对城市环境的影响.
1. 材料和方法(Material and methods)
1.1 样品采集
2008年8月[29]和2012年10月[30]在天津市近郊地区(西青区、津南区、北辰区和东丽区)使用不锈钢勺分别采集获得83个和60个土壤样品(表层0—10 cm,各1 kg),并储存在聚乙烯密封袋中. 每1个样品由10—20个采自于站位点周边10×10 m2范围内的子样品混合而成. 每次采样之前使用丙酮冲洗不锈钢勺防止沾污. 所有土壤样品均放置在暗处,并尽快运送到实验室,经风干、研磨、过筛(50目)之后,于−20 ℃环境下保存.
1.2 PAHs的测定
采用加速溶剂萃取法(accelerated solvent extraction, ASE)对土壤样品进行萃取. 取16 g冻干土壤样品和5 g二氧化硅混匀后倒入34 mL ASE样品瓶,以丙酮与二氯甲烷(1:1体积比)混合溶液为萃取溶剂,将样品在温度和压力分别为120 °C和1500 psi的条件下萃取2次,每次5分钟,所得的提取液蒸发至近干,加入9 mL环己烷与丙酮(1:1体积比)的混合溶液. 替换溶剂之后的提取液依次使用凝胶色谱(LCTech Geremany)和弗罗里硅固相萃取柱进行纯化,所得洗脱液经氮吹浓缩至1 mL转入棕色安捷伦进样瓶中上机分析. 采用GC-MS方法对PAHs进行定量分析,仪器参数和分析方法的质量控制见文献[29]. 16种PAHs包括萘(NAP)、苊(ACE)、芴(FLO)、二氢苊(ACY)、菲(PHE)、蒽(ANT)、荧蒽(FLA)、芘(PYR)、䓛(CHR)、苯并(a)蒽(BaA)、苯并(b)荧蒽(BbF)、苯并(k)荧蒽(BkF)、苯并(a)芘(BaP)、二苯并(a,h)蒽(DahA)、苯并(g,h,i)苝(BghiP)和茚苯(1,2,3-cd)芘(IcdP). PAHs加标回收率和指示物回收率分别为62.2%—116.7%和70.6%—119.1%.
1.3 PMF源解析
PMF是由Paatero和Tapper[31]开发的,基于主成分分析的非负约束受体模型,常用于环境中PAHs的源解析[32]. 该模型的矩阵方程式为:
X=G×F+E 式中,X代表由n个样品的m种化合物的浓度组成的样品浓度数据矩阵;G代表主要源的贡献率矩阵(n×p,p为源的个数);F代表主要源的成分谱矩阵(p×m);E代表残差矩阵(n×m),定义为:
eij=xij−p∑k=1gikfkj 式中,eij、xij、gik和fkj分别为E、X、G和F中的对应元素. 在对F和G进行非负约束的同时,对每个数据点的不确定性进行加权. Q是模型的判据之一,当其收敛时才可进一步分析,且多次运行选Q较小的值来继续分析. Q的计算公式为:
Q=n∑i=1m∑j=1(eijσij)2 式中σij为第i个样品中第j种化合物的不确定性,其他项含义如前文所述.
本研究利用USEPA开发的PMF模型软件5.0,基于83(样品)×16(PAHs)数据集和60(样品)×16(PAHs)数据集,分别对2008年和2012年天津市近郊地区土壤中PAHs来源进行识别. 模型解析目标设置为计算出3到6个因子,且每次运行都用不同的起始点进行初始化. 对于每次运行,正定矩阵因子分解模型的样品数符合模型对最少样本量的需求,即样本数大于物种数的3倍[33].
1.4 风险评估
利用ILCR模型可定量评估城市居民通过摄入、皮肤接触和吸入3种方式暴露于土壤PAHs的潜在健康风险[34-35]. 基于USEPA标准模型计算潜在癌症风险的方程式[36-37]如下.
ILCRingestion=CS×(CSFingestion×3√BW/70)×IRingestion×EF×EDBW×AT×106ILCRdermal=CS×(CSFdermal×3√BW/70)×SA×AF×ABS×EF×EDBW×AT×106ILCRinhalation=CS×(CSFinhalation×3√BW/70)×IRinhalation×EF×EDBW×AT×106 其中,CS是土壤中PAHs基于BaP的毒性当量[1](toxic equivalency factor, TEF)计算的转换浓度之和(mg·kg−1);CSF是致癌物斜率因子(mg·kg−1·d−1)−1, 根据BaP的致癌能力进行测定;BW是体重;IRingestion和IRinhalation人体土壤摄入效率和吸入效率;EF代表暴露频率;ED是暴露时长;SA是皮肤表面积;AF是真皮粘附因子;ABS为真皮吸附因子;AT为平均寿命;PEF为颗粒释放因子(见表1). BaP的CSFingestion、CSFdermal和CSFinhalation分别为7.3、25、3.85(mg·kg−1·d−1)-1[38].
暴露参数Exposure parameter 单位Unit 儿童Child 青少年Adolescent 成人Adult BW kg 13.95 46.75 58.78 IRingestion mg·d−1 200 100 100 IRinhalation m3·d−1 10.9 17.7 17.5 EF d·a−1 350 350 350 ED a 6 14 30 SA cm2 2800 2800 5700 AF mg·cm−2 0.2 0.2 0.07 ABS — 0.13 0.13 0.13 AT d 25550 25550 25550 PEF m3·kg−1 1.36×109 1.36×109 1.36E×109 1991年USEPA发布的指南指出[37],百万分之一的癌症发病几率(ILCR = 10−6)是可接受的阈值. 因此,依据ILCR的判断标准如下:ILCR ≤ 10−6时代表可忽略风险;10−6 < ILCR < 10−4表示低风险;ILCR ≥ 10−4表示癌症高风险,需要特别关注. 在本研究中,依据年龄将居民分为儿童(0—10岁)、青少年(11—18岁)和成人(19—70岁)的3个群体进行癌症风险评估.
1.5 数据分析
利用Origin2019软件进行数据记录、数据处理以及表格制作;利用USEPA PMF 5.0软件进行PAHs来源识别及贡献计算. 天津市及其区县社会经济发展的数据分别引自2009年、2013年、2014年和2015年天津统计年鉴[28].
2. 结果与讨论( Results and discussion)
2.1 PAHs含量及组成的变化趋势
2008年至2012年,天津市近郊地区表层土壤中16种PAHs浓度呈倍数增长,7种致癌PAHs浓度也呈上升趋势. 如表2所示,五环化合物的浓度占比大幅度下降,而二环和四环化合物的占比均显著增加, 低分子量组分的比例由28.6%上升到34.8%. 优势化合物由苯并(b)荧蒽、荧蒽和苯并(g, h, i)苝转变为菲、萘和荧蒽. 萘、二氢苊、菲等低分子量PAHs的浓度明显增加. 虽然PAHs被认为是持久性有机污染物能长期存在于环境中,但其仍可通过光化学降解、生物降解和挥发作用从土壤中去除[40]. 以往的研究发现[21, 41],PAHs在土壤中长期埋藏后,浓度会显著下降. 另外,具有不同个数苯环的PAHs在土壤中表现出不同的环境行为[15]. 高分子量的PAHs通常能在土壤中埋藏较长时间,其降解速率随着分子量的增加而降低[42],而低分子量的更容易被光降解或生物降解. 因此,总浓度以及低分子量组分占比的增加,表明土壤环境中存在持续不断的PAHs输入,且污染状况趋于严重,这与该地区5年内经济高速发展,城市化进程加快有着密切的关系. 2008年西青区、津南区、北辰区和东丽区的常住人口总计228.59万,区县生产总值(GDP)共计1336.66亿元[28]. 2012年,4个区的常住人口增加到283.03万,区县生产总值(GDP)增加了近一倍,达到2552.27亿元[28]. 通常来说,人为源是环境中PAHs急剧增加的主要原因. 城市土壤中的PAHs主要来源于工业活动、机动车排放以及居民烹饪和取暖,因此,其受到区域经济发展水平、人口和工业化程度的影响[22, 43].
表 2 天津市近郊区土壤中PAHs毒性当量因子、含量及组成Table 2. Toxic equivalent factors, composition, and concentrations of PAHs in surface soils from suburban Tianjin in 2008 and 2012PAHs 环数Aromatic ring 毒性当量因子TEF 2008(n = 83) 2012(n = 60) 均值/(ng·g−1)Mean 范围/(ng·g−1)Range 组成占比/%Proportion 均值/(ng·g−1)Mean 范围/(ng·g−1)Range 组成占比/%Proportion 萘 2 0.001 18.7 2.72—133 6.0 68.2 ND—441 10.8 二氢苊 3 0.001 3.96 ND—42.6 1.0 35.2 ND—697 4.1 苊 3 0.001 3.10 ND—19.2 1.3 4.44 ND—31.0 0.5 芴 3 0.001 17.0 1.23—86.5 8.4 12.8 ND—78.0 2.0 菲 3 0.001 36.5 1.98—336 8.4 131 7.45—1091 16.4 蒽 3 0.01 16.6 0.502—306 3.6 11.6 0.450—107 1.0 荧蒽 4 0.001 63.4 2.39—792 9.4 255 ND—3278 15.6 芘 4 0.001 56.9 1.17—728 8.0 154 1.00—1977 9.0 苯并(a)蒽* 4 0.1 33.1 0.225—386 5.2 68.7 0.470—841 3.9 䓛* 4 0.01 46.1 0.717—506 6.4 97.9 0.850—1210 6.7 苯并(b)荧蒽* 5 0.1 103 ND—1010 13.6 118 1.38—1362 8.1 苯并(k)荧蒽* 5 0.1 43.6 ND—669 5.5 43.3 0.230—549 2.6 苯并(a)芘* 5 1 52.2 ND—728 6.8 86.6 0.370—1118 4.8 二苯并(a, h)蒽* 5 1 22.9 ND—252 4.0 33.4 ND—348 2.4 茚苯(1, 2, 3-cd)芘* 6 0.1 23.3 ND—244 3.1 106 2.37—1237 7.1 苯并(g, h, i)苝 6 0.01 66.3 ND—886 9.2 70.0 1.23—775 4.9 二环化合物 — — 18.7 2.72—133 6.0 68.2 ND—441 10.8 三环化合物 — — 77.2 6.34—701 22.6 195 7.90—1586 24.0 四环化合物 — — 199 8.53—2413 29.1 575 2.32—7306 35.2 五环化合物 — — 221 ND—2445 30.0 281 1.98—3377 17.9 六环化合物 — — 89.6 ND—1129 12.3 176 4.90—2012 12.0 Σ7-carPAHs — — 324 5.03—3582 44.7 554 7.98—6666 35.6 Σ16PAHs — — 606 29.7—6705 100 1296 22.9—14722 100 注:“*”代表7种具有致癌作用的PAHs;“ND”代表未检出;“Σ7-carPAHs”代表7种具有致癌作用PAHs总含量;“Σ16PAHs”代表16种PAHs总含量. * stands for 7 carcinogenic PAHs, ND stands for not detected, Σ7-carPAHs stands for total concentrations of 7 carcinogenic PAHs, Σ16PAHs stands for total concentrations of 16 PAHs. 2.2 PAHs的来源
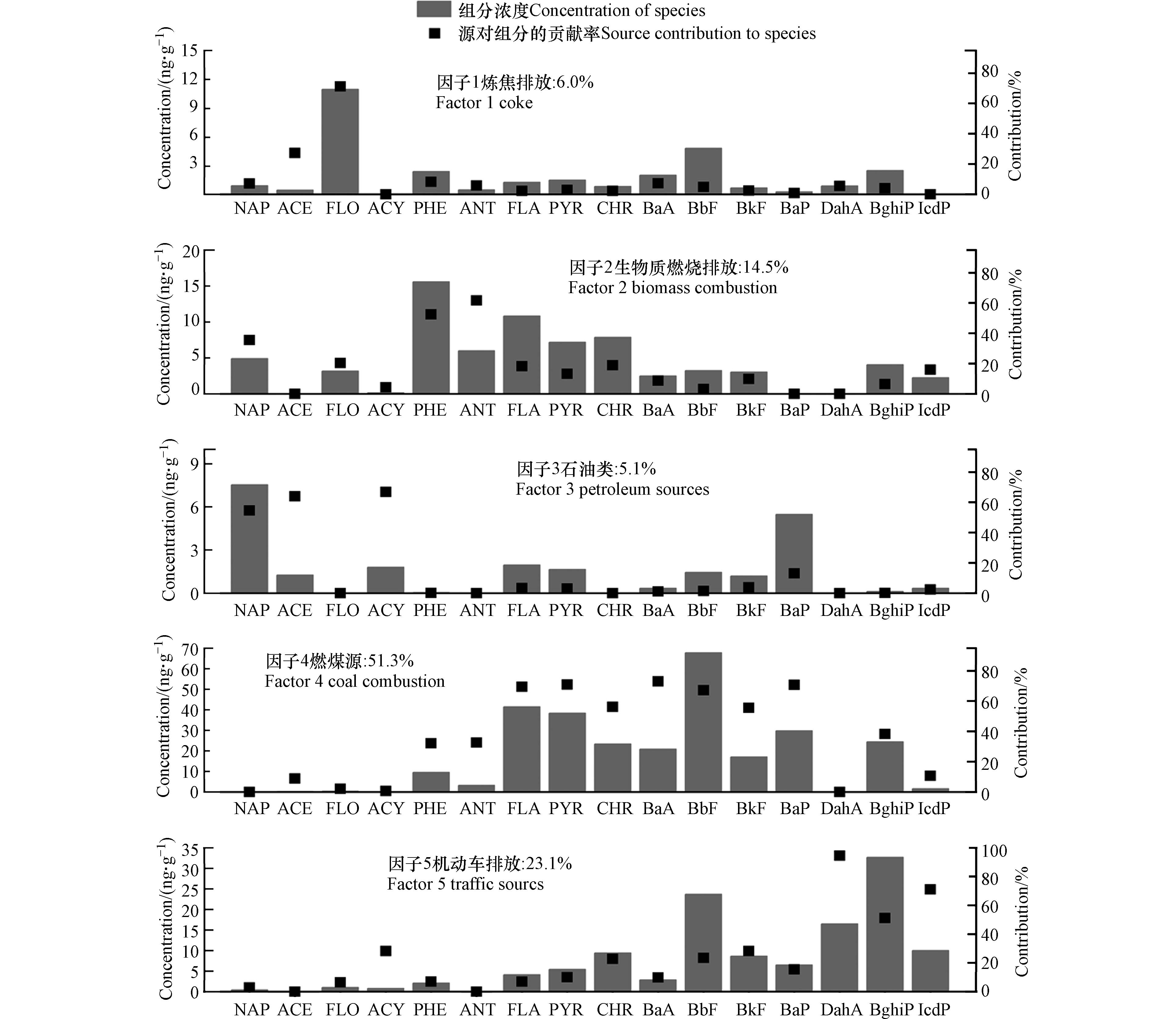
2008年PAHs来源成分谱如图1所示,模型筛选出5个因子. 因子1中表征炼焦生产的芴[44]占比达到71.2%,推断该因子代表炼焦排放,其贡献为6.0%. 因子2中蒽和菲的占比较高,分别为61.6%和52.5%,符合生物质燃烧的排放特征[16, 45],推断因子2为生物质燃烧排放,其贡献为14.5%. 因子3中优势组分为萘、苊和二氢苊,占比分别为54.6%、63.9%和66.9%. 萘是原油和石油产品的重要组成部分[46-48],并且二环和三环PAHs多与石油类来源有关[49-51]. 因此,因子3表示石油源,其贡献为5.1%. 因子4中荧蒽(69.5%)、芘(70.8%)、䓛(56.2%)、苯并(a)蒽(72.9%)、苯并(b)荧蒽(67.1%)、苯并(k)荧蒽(55.6%)和苯并(a)芘(70.7%)占比较高,符合煤燃烧排放特征[16, 52-55]. 因此,因子4表示燃煤源,其贡献为51.3%. 因子5中表征汽车尾气[16, 56-57]的二苯并(a,h)蒽、茚苯(1,2,3-cd)芘和苯并(g,h,i)苝占比较高,分别为94.6%、51.2%和71.0%,推断该因子代表机动车排放,其贡献为23.1%.
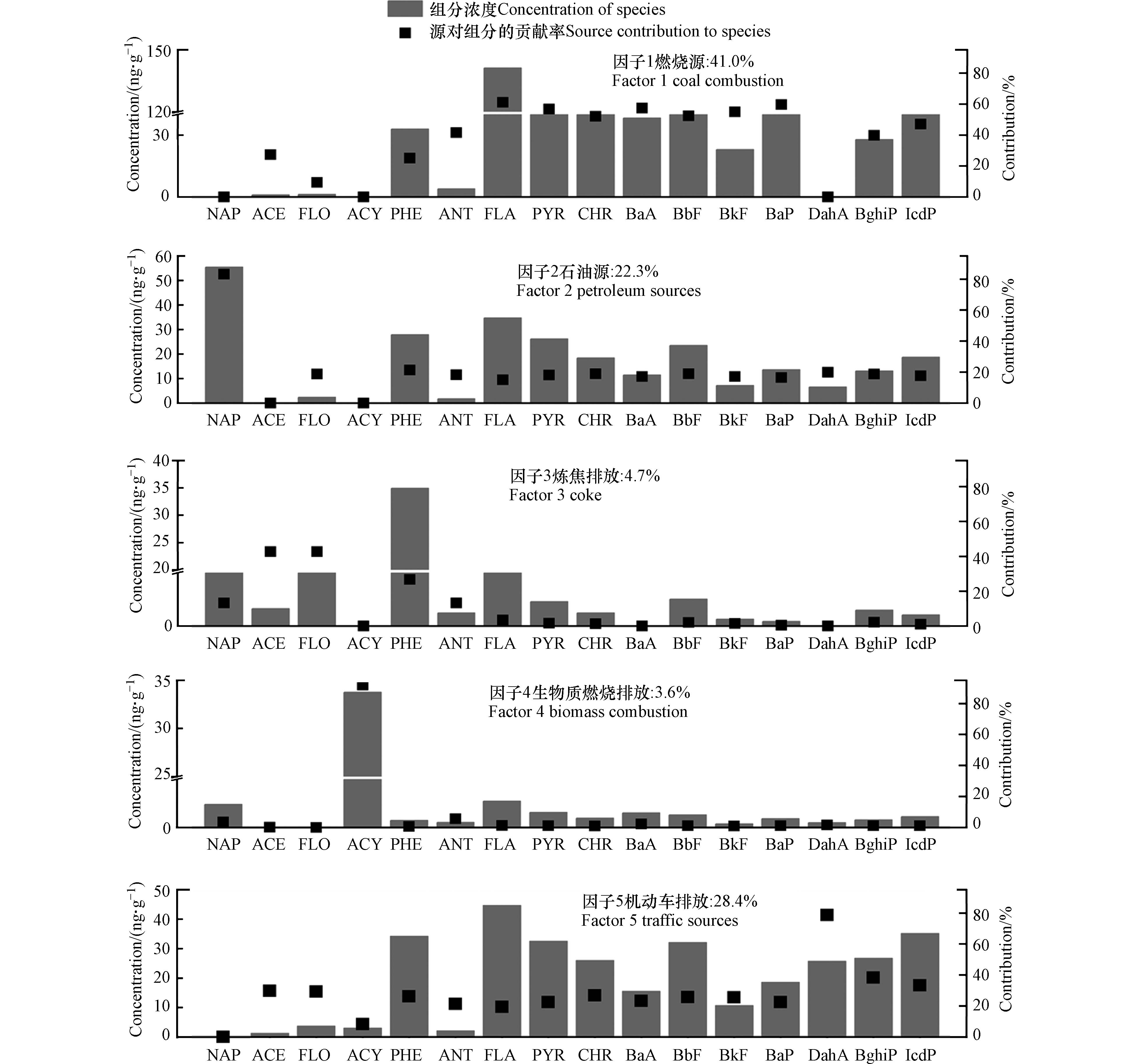
2012年PAHs来源成分谱如图2所示,模型也筛选出5个因子. 因子1中荧蒽、芘、䓛、苯并(a)蒽、苯并(b)荧蒽、苯并(k)荧蒽和苯并(a)芘占比较高,分别为61.1%、56.8%、52.0%、57.5%、52.4%、55.0%和59.6%,符合煤燃烧排放特征[16, 52-55]. 因此,因子1表示燃煤源,其贡献为41.0%. 因子2中表征原油和石油产品的萘[46-48]占比达83.2%,推断该因子为石油源,其贡献为22.3%. 因子3中苊、芴和菲占比相对较高,其中芴和菲的占比分别为42.6%和26.8%,是炼焦生产的表征化合物[44, 55]. 因此,因子3应该与焦炭的生产密切相关,其贡献为4.7%. 因子4中生物质燃烧过程排放的优势化合物二氢苊[44-45]占比高达91.8%,推断该因子代表生物质燃烧排放,其贡献为3.6%. 因子5中的优势组分为二苯并(a,h)蒽、茚苯(1,2,3-cd)芘和苯并(g,h,i)苝,占比分别为78.7%、38.3%和33.2%,符合汽车尾气排放特征[16, 56-57]. 因此,推断该因子代表机动车排放,其贡献为28.4%.
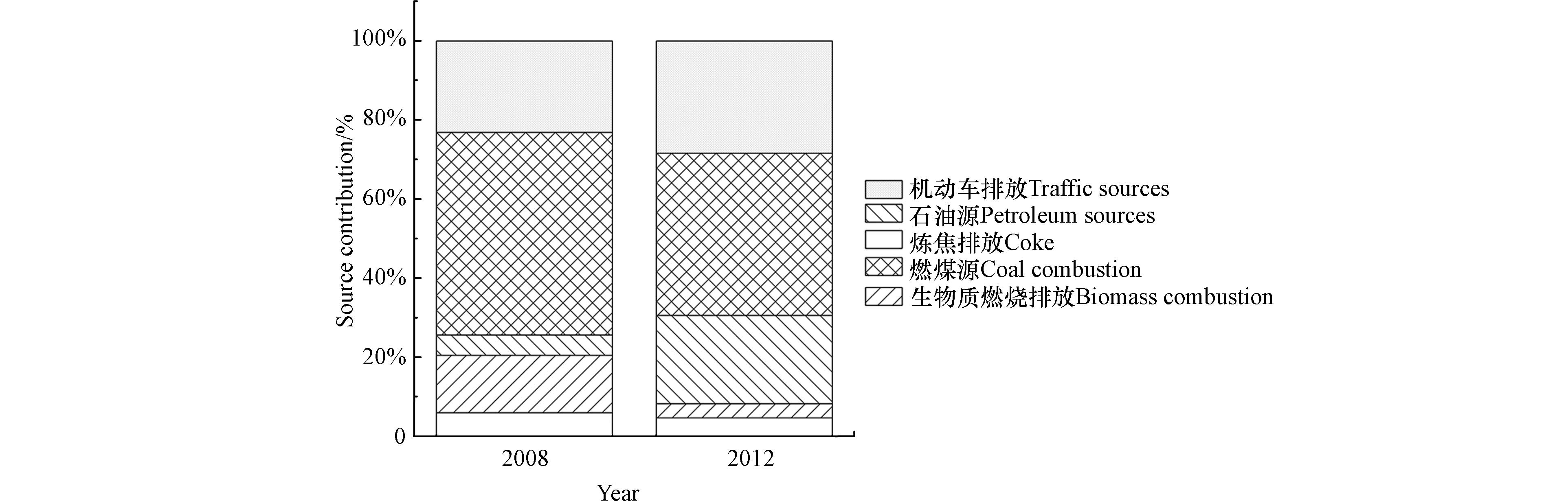
基于上述PMF的解析结果发现,天津市近郊区域土壤中PAHs来源贡献率变化较大的是燃煤源、生物质燃烧排放和石油源. 其中,燃煤源和生物质燃烧排放的贡献率分别由2008年的51.3%和14.5%下降到2012年的41.0%和3.6%(图3). 虽然煤炭是天津市工业的主要能源,但是燃煤源的贡献率在5年内下降了10.3%. 此外,根据地理位置和居民的生活习惯,调查区域的生物质燃烧应与露天焚烧秸秆和居民烹饪有关. 2008年天津市启动生态城市建设行动计划,包括生态区县建设,改善水、空气、生态环境质量,提升固体废物综合利用水平,加强农村环境污染防治,发展循环经济等7个方面. 为了实现节能减排、改善城市环境质量,很多企业在生产过程中使用电力、天然气等清洁能源取代了煤炭,到2012年,天津市单位工业增加值能耗由2008年的1.16吨标准煤每万元下降到0.95吨标准煤每万元. 因此,燃煤源贡献率的下降可能与该区域工业化发展过程中能源结构的变化、装备和技术的不断发展有关. 另一方面,生物质燃烧排放贡献率的下降则可能与禁止露天生物质燃烧,以及电力和液化石油气取代了生物质作为烹饪燃料有关.
但是,5年内石油源的贡献率却由5.1%上升到22.3%. 天津作为我国北部重要的工业城市,石油化工是其优势产业之一. 2008年天津市石油化工联合其他五大优势产业完成工业总产值8323.89亿元,而到2012年仅石油化工这一项优势产业就完成产值3626.63亿元. 2017年发布的天津市石油和化学工业发展“十三五”规划纲要指出,2015年全市拥有石化企业711家,资产总额3756.57亿元,全年实现产值4024.32亿元,约占全市规模以上工业的15%. 到2020年,石油化工产业总产值将超过6000亿元. 同时,天津市也因天津港成为我国北部最重要的国际航运物流中心之一. 2020年天津港口货物吞吐量突破5亿吨,集装箱吞吐量突破1800万标准箱,均在全国港口中居第六位,“十三五”时期集装箱吞吐量年均增长5.4%,稳居全球集装箱港口十强. 因此,石油化工产业和航运物流产业的快速扩张与发展可能是石油源贡献率迅速增长的一个重要原因.
2.3 健康风险评估
ILCR模型解析结果表明,2008年和2012年天津市近郊地区居民土壤PAHs暴露风险值ILCRsinhalation的数量级在10-14—10-10之间,远低于10−6. 因此,居民通过吸入方式接触到土壤中PAHs而导致的健康风险可以忽略.
如表3所示,2008年近郊地区居民土壤PAHs暴露风险值ILCRsingestion和ILCRsdermal的范围分别为1.19 × 10−9—5.89 × 10−6和2.84 × 10−9—1.00 × 10−5,它们最大值分别出现在儿童和成人. 根据不同年龄段暴露人群的统计结果,分别有32.5%、24.1%和36.1%的土壤样品的儿童、青少年和成人暴露总风险值ILCRstotal处于低风险判定区间内. 2012年居民各暴露途径的风险值ILCRs均高于2008年,ILCRsingestion的范围为2.84 × 10−9—9.51 × 10−6,ILCRsdermal的范围为6.79 × 10−9—1.62 × 10−5,两者最大值出现的年龄段和2008年一致. 儿童、青少年和成人暴露总风险值ILCRstotal大于10−6的土壤样品比例分别为41.7%、36.7%和45.0%,较2008年均有不同程度的增长. 值得注意的是,2008年和2012年居民土壤PAHs暴露风险值ILCRsdermal均高于ILCRsingestion,并且2012年青少年和成人暴露风险值ILCRsdermal的均值较2008年增长了一个数量级. 上述结果表明,2008年到2012年,天津市近郊地区居民土壤PAHs暴露风险在不断增加,且皮肤接触是主要的暴露途径;儿童因其对致癌物的高敏感性应归为最敏感的亚群体. 人群暴露风险的增加可能与机动车排放源贡献率增加有关. 根据PMF解析结果,虽然2012年机动车排放贡献率较2008年仅增加了5.3%,但是其估算排放量是2008年的2.6倍. 机动车排放量大幅度的增加导致更多的具有强致癌效力的特征组分[1, 56-57],如苯并(a)芘、二苯并(a, h)蒽和茚苯(1, 2, 3-cd)芘进入到土壤中,增加暴露人群的健康风险. 另一方面,石油源的贡献率和估算排放量的增幅虽然最大,但其排放至环境中的组分主要是致癌效力较低的低分子量PAHs.
表 3 不同群体暴露于土壤PAHs的潜在癌症风险Table 3. Age-specific potential cancer risk via exposure to soil PAHs in 2008 and 20122008 2012 人群Population 均值Mean 最小值Min 最大值Max 均值Mean 最小值Min 最大值Max 儿童Child ILCRingestion 4.87 × 10−7 2.28 × 10−9 5.89 × 10−6 7.84 × 10−7 5.45 × 10−9 9.51 × 10−6 ILCRdermal 6.07 × 10−7 2.84 × 10−9 7.34 × 10−6 9.78 × 10−7 6.79 × 10−9 1.19 × 10−5 ILCRtotal 1.09 × 10−6 5.12 × 10−9 1.32 × 10−5 1.76 × 10−6 1.22 × 10−8 2.14 × 10−5 青少年Adolescent ILCRingestion 2.53 × 10−7 1.19 × 10−9 3.07 × 10−6 4.09 × 10−7 2.84 × 10−9 4.95 × 10−6 ILCRdermal 6.32 × 10−7 2.96 × 10−9 7.65 × 10−6 1.02 × 10−6 7.08 × 10−9 1.24 × 10−5 ILCRtotal 8.85 × 10−7 4.14 × 10−9 1.07 × 10−5 1.43 × 10−6 9.92 × 10−9 1.73 × 10−5 成人Adult ILCRingestion 4.66 × 10−7 2.18 × 10−9 5.65 × 10−6 7.52 × 10−7 5.22 × 10−9 9.11 × 10−6 ILCRdermal 8.28 × 10−7 3.88 × 10−9 1.00 × 10−5 1.34 × 10−6 9.28 × 10−9 1.62 × 10−5 ILCRtotal 1.29 × 10−6 6.06 × 10−9 1.57 × 10−5 2.09 × 10−6 1.45 × 10−8 2.53 × 10−5 注:ILCRtotal = ILCRingestion + ILCRdermal 3. 结论(Conclusions)
2008年至2012年,天津市近郊地区城市化发展在一定程度上改变了土壤中PAHs的来源、含量和组成.
(1) 土壤中16种PAHs的总含量均值增加了1倍,菲、萘和荧蒽取代苯并(b)荧蒽、荧蒽和苯并(g, h, i)苝成为优势组分,萘、二氢苊、菲等低分子量PAHs的浓度明显增加.
(2) 五环化合物占比大幅度下降,而二环和四环化合物占比均显著增加.
(3) PMF解析结果表明,燃煤源和生物质燃烧排放的贡献率均减少10%以上,石油源的贡献率增加17.2%.
(4) 当地居民土壤PAHs暴露风险在不断增加,儿童作为最敏感的亚群体应受到关注,皮肤接触是主要的暴露途径. 机动车排放源贡献率的增加可能的导致暴露风险上升的重要原因.
-
表 1 煤矸石中汞含量描述性统计分析(mg·kg−1)
Table 1. Descriptive statistical analysis of Hg content in coal gangue (mg · kg−1)
重金属元Heavy metal elements 最小值Minimum 最大值Maximum 平均值Mean 标准差Standard deviation 偏度Skewness 峰度Kurtosis 变异系数Coefficient of variation EF Igeo Hg 0.085 0.519 0.169 0.089 5.17 5.55 52.09% 4.53 1.35 表 2 煤矸石中重金属含量与各理化指标间的相关系数
Table 2. Correlation coefficients between Hg content in coal gangue and various physical and chemical indicators
Hg TOC pH Eh ωH2O Hg 1 TOC 0.251 1 pH 0.256 .531** 1 Eh −.326* −.513** −.972** 1 ωH2O .440** .401** −0.147 0.135 1 **. 在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性显著;*. 在 0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著。 **Significance level P < 0.01; * Significance level P < 0.05. 表 3 煤矸石中Hg的不同形态与pH、TOC的相关性关系
Table 3. Correlation between different forms of Hg in coal gangue and pH and TOC
F1 F2 F3 F4 Hg TOC pH F1 1 F2 0.242 1 F3 −0.225 −.403** 1 F4 0.111 −0.023 .653** 1 Hg 0.015 0.133 0.203 .437** 1 TOC 0.206 .419** 0.055 .475** 0.29 1 pH 0.098 .702** −0.258 0.157 0.266 .531** 1 *. 在 0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著;**. 在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性显著。 **Significance level P < 0.01; * Significance level P < 0.05 -
[1] 曹艳芝, 郭少青, 翟晋栋. 煤矸石中汞和砷的赋存形态研究 [J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2017, 45(1): 26-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.01.005 CAO Y Z, GUO S Q, ZHAI J D. The mode of occurrence of mercury and arsenic in coal gangues [J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2017, 45(1): 26-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.01.005
[2] SZCZEPANSKA J, TWARDOWSKA I. Distribution and environmental impact of coal-mining wastes in Upper Silesia, Poland [J]. Environmental Geology, 1999, 38(3): 249-258. doi: 10.1007/s002540050422 [3] 杨建, 陈家军, 王心义. 煤矸石堆周围土壤重金属污染空间分布及评价 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2008(3): 873-878. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2008.03.007 YANG J, CHEN J J, WANG X Y. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils around the coal waste rock pile and their environmental pollution assessment [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2008(3): 873-878(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2008.03.007
[4] 任建莉, 周劲松, 骆仲泱, 等. 煤中汞燃烧过程析出规律试验研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2002, 22(3): 289-293. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2002.03.004 REN J L, ZHOU J S, LUO Z Y, et al. Study of mercury emission during coal combustion [J]. Acta Science Circumstantiae, 2002, 22(3): 289-293(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2002.03.004
[5] 邢宇鑫, 闫广新, 侯秋丽, 等. 北京门头沟矿集区土壤重金属空间分布及污染特征 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2016, 33(6): 499-507. XING Y X, YAN G X, HOU Q L, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in soil of Mentougou mining area of Beijing city, China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2016, 33(6): 499-507(in Chinese).
[6] 冯新斌, 陈玖斌, 付学吾, 等. 汞的环境地球化学研究进展 [J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(5): 503-530. FENG X B, CEHN J B, FU X W, et al. Progresses on environmental geochemistry of mercury [J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(5): 503-530(in Chinese).
[7] BANDURA L, FRANUS M, PANEK R, et al. Characterization of zeolites and their use as adsorbents of petroleum substances [J]. Przem Chem, 2015, 94(3): 323-327. [8] CAO Z, CAO Y, DONG H, et al. Effect of calcination condition on the microstructure and pozzolanic activity of calcined coal gangue [J]. Int J Miner Process, 2016, 146: 23-28. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2015.11.008 [9] GUO Y, YAN K, CUI L, et al. Improved extraction of alumina from coal gangue by surface mechanically grinding modification [J]. Powder Technol, 2016, 302: 33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.08.034 [10] UCURUM M. Influences of Jameson flotation operation variables on the kinetics and recovery of unburned carbon [J]. Powder Technol, 2009, 191(3): 240-246. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2008.10.014 [11] IVINDRA P, WILL H. Investigation of blended cement hydration by isothermal calorimetry and thermal analysis [J]. Cement Concrete Res, 2005, 35: 1155-1164. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.10.027 [12] LEE J H, CHOI H J, YOON S Y, et al. Porous mullite ceramics derived from coal fly ash using a freeze-gel casting/polymer sponge technique [J]. J Porous Mat, 2013, 20(1): 219-226. doi: 10.1007/s10934-012-9591-0 [13] YU J L, MENG F R, LI X C, et al. Power generation from coal gangue in China: Current status and development [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 550/553: 443-446. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.550-553.443 [14] BERNARDO E, SCARINCI G, BERTUZZI P, et al. Recycling of waste glasses into partially crystallized glass foams [J]. J Porous Mat, 2010, 17(3): 359-365. doi: 10.1007/s10934-009-9286-3 [15] QIU G, LUO Z, SHI Z, et al. Utilization of coal gangue and copper tailings as clay for cement clinker calcinations [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci Ed, 2011, 26(6): 1205-1210. doi: 10.1007/s11595-011-0391-1 [16] PANDEY Y, SANGITA, TARE V. Utilization of coal mixed waste aggregates available at thermal power plants for GSB and asphalt mixtures [J]. Procedia engineering, 2016, 143: 170-177. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.022 [17] 秦倩, 王金满, 胡斯佳. 利用煤矸石粉煤灰制成农田排水混凝土材料的研制实验 [J]. 中国矿业, 2015, 24(7): 39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.07.010 QIN Q, WANG J M, HU S J. Adevelopment test on porous concrete material with coal gangue and fly ash used for farmland drainage in coal mining subsidence area with high ground-water level [J]. China Minging Magazine, 2015, 24(7): 39-43(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.07.010
[18] 谷玲钰, 刘振英, 刘银. 利用煤矸石制备多孔陶瓷的及力学性能研究 [J]. 矿产综合利用, 2018(5): 135-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.05.030 GU L Y, LIU Z Y, LIU Y. The Investigation on preparation of porous ceramic by using coal gangue as the raw materials [J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(5): 135-137(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.05.030
[19] 刘曙光, 徐良骥, 余礼仁. 煤矸石充填复垦地土壤理化性质的时空变化特征 [J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(2): 173-177. LIU S G, XU L J, YU L R. Spatiotemporal variation of physical and chemical properties of reclaimed soil in coal fangue filling land [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(2): 173-177(in Chinese).
[20] 任雪娇, 夏举佩, 张召述. 煤矸石酸解制备氢氧化铝的实验研究 [J]. 非金属矿, 2012, 35(2): 12-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2012.02.004 REN X J, XIA J P, ZHANG Z S. Experimental study on producing alumina hydroxide with acid hydrolysis from coal gangue [J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2012, 35(2): 12-14(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2012.02.004
[21] 郭彦霞, 张圆圆, 程芳琴. 煤矸石综合利用的产业化及其展望 [J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(7): 2443-2453. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2014.07.006 GUO Y X, ZHANG Y Y, CHENG F Q. Industrial development and prospect about comprehensive utilization of coal gangue [J]. Ciesc Journa, 2014, 65(7): 2443-2453(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2014.07.006
[22] 郭海桥, 程伟, 尚志, 等. 水分和冻融循环对酷寒矿区煤矸石风化崩解速率影响的定量研究 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(12): 3859-3864. GUO H Q, CHENG W, SHANG Z, et al. Quantitative determination of the effect of moisture and freeze / thaw cycles on coal gaugue decay rate in severe cold mining areas [J]. Jour Nal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(12): 3859-3864(in Chinese).
[23] 陈东, 曹坤. 准格尔矿区煤矸石综合利用新途径 [J]. 中国煤炭, 2017, 43(10): 132-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2017.10.026 CHEN D, CAO K. New method for coal gangue comprehensive utilization in Jungar mining area [J]. China Coal, 2017, 43(10): 132-136(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-530X.2017.10.026
[24] OCHEDI F O, LIU Y, HUSSAIN A. A review on coal fly ash-based adsorbents for mercury and arsenic removal [J]. J Clean Prod, 2020, 267: 122143. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122143 [25] ZHOU Y, REN B, HURSTHOUSE A, et al. Antimony ore tailings: Heavy metals, chemical speciation, and leaching characteristics [J]. Pol J Environ Stud, 2018, 28(1): 485-495. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/85006 [26] LIANG L, XU X, HAN J, et al. Characteristics, speciation, and bioavailability of mercury and methylmercury impacted by an abandoned coal gangue in southwestern China [J]. Environmental science and pollution research international, 2019, 26(36): 37001-37011. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06775-7 [27] LI W H, MA Z Y, HUANG Q X, et al. Distribution and leaching characteristics of heavy metals in a hazardous waste incinerator [J]. Fuel, 2018, 233: 427-441. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.041 [28] ZHANG Y J, ZHANG Y L, ZHANG Y, et al. Study on speciation and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soil around typical coal gangue in Fengfeng Mining Area [J]. IOP conference series. Earth and environmental science, 2019, 371(3): 032081. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/371/3/032081 [29] 籍永华, 秦丙克, 黄沈丹. 汪家寨煤矿煤中汞的含量分布与赋存状态 [J]. 煤炭技术, 2019, 38(7): 156-159. JI Y H, QIN B K, HUANG S D. Distribution and occurrence state of mercury in coal of Wangjiazhai coal mine [J]. Coal Technology, 2019, 38(7): 156-159(in Chinese).
[30] GUO S, NIU X, ZHAI J. Mercury release during thermal treatment of two Chinese coal gangues [J]. Environ Sci Pollut R, 2017, 24(30): 23578-23583. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9980-7 [31] LI B, WANG J H, BI M S, et al. Experimental study of thermophysical properties of coal gangue at initial stage of spontaneous combustion [J]. J Hazard Mater, 2020, 400: 123251. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123251 [32] 赵文鑫, 刘瑞卿, 张建利, 等. 煤矸石热处理过程中汞的释放行为 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(4): 842-849. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112904 ZHAO W X, LIU R Q, ZHANG J L, et al. Release behaviors of mercury during thermal treatment of three coal gangues [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(4): 842-849(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018112904
[33] 齐鸿浩. 京西门头沟煤矿简述 [J]. 首都博物馆丛刊, 2010(1): 59-60. QI H H. Brief introduction of Mentougou coal mine in western Beijing [J]. A Collection of Essays about Capital Museum of China, 2010(1): 59-60(in Chinese).
[34] 程琳琳, 李继欣, 徐颖慧, 等. 基于综合评价的矿业废弃地整治时序确定 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(4): 222-229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.04.027 CHENG L L, LI J X, XU Y H, et al. Determination of reclamation sequence for mining wasteland based on comprehensive evaluation [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(4): 222-229(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.04.027
[35] 程琳琳, 刘昙昙, 杨丽铃, 等. 产业转型背景下的矿业废弃地开发利用模式和战略: 以北京市门头沟区为例 [J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(7): 70-74. CHEN L L, LIU T T, YANG L L, et al. Development and utilization of models and strategies of mining wasteland in the background of industrial transformation: taking Mentougou district as an example [J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(7): 70-74(in Chinese).
[36] 林英华, 宋百敏, 韩茜, 等. 北京门头沟废弃采石矿区地表土壤动物群落多样性 [J]. 生态学报, 2007(11): 4832-4839. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.11.053 LIN Y H, SONG B M, HAN Q, et al. The community diversity of ground-dwelling soil animals in abandoned quarry in Mentougou, Beijing [J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 2007(11): 4832-4839(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.11.053
[37] 宋文, 何天容. 贵州盘县煤矸石中汞的环境效应 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(8): 1589-1593. SONG W, HE T G. Environmental effects of mercury in coal mine spoils in Panxian of Guizhou Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2009, 28(8): 1589-1593(in Chinese).
[38] 王萍, 胡振琪, 马保国, 等. 煤矸石浸水后pH值测定方法及结果比较 [J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2010, 38(2): 108-112. WANG P, HU Z Q, MA B G, et al. Comparison on pH value measuring methods and results of coal rejects after immersion in water [J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2010, 38(2): 108-112(in Chinese).
[39] 宋文, 何天容, 鲁生. 贵州水城煤矸石风化土壤-农作物系统中汞分布规律研究 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(7): 1326-1332. SONG W, HE T R, LU S. Distribution of mercury species in the soils from weathered coal mine spoils and crops in Shuicheng, Guizhou Province, China [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2010, 29(7): 1326-1332(in Chinese).
[40] 耿雅妮, 梁青芳, 杨宁宁, 等. 宝鸡市城区灰尘重金属空间分布、来源及健康风险 [J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(5): 696-706. GENG Y N, LIANG Q F, YANG N N, et al. Distribution, sources and health risk assessment of heavy metals in uusts of the urban area of the Baoji City [J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47(5): 696-706(in Chinese).
[41] 田和明, 代世峰, 李大华, 等. 重庆南川晚二叠世凝灰岩的元素地球化学特征 [J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(1): 169-177. TIAN H M, DAI S F, LI D H, et al. Geochemical features of the late permian tuff in Nanchuan District, Chongqing, Southwestern China [J]. Geological Review, 2014, 60(1): 169-177(in Chinese).
[42] 陈文轩, 李茜, 王珍, 等. 中国农田土壤重金属空间分布特征及污染评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6): 2822-2833. CHEN W X, LI Q, WANG Z, et al. Spatial Distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in arable land soil of China [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6): 2822-2833(in Chinese).
[43] 秦延文, 张雷, 郑丙辉, 等. 太湖表层沉积物重金属赋存形态分析及污染特征 [J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(12): 4291-4299. QIN Y W, ZHANG L, ZHENG B H, et al. Speciation and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in the sediment of Taihu Lake [J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(12): 4291-4299(in Chinese).
[44] 林承奇, 黄华斌, 胡恭任, 等. 九龙江流域水稻土重金属赋存形态及污染评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(1): 453-460. LIN C Q, HUANG H B, HU G R, et al. ssessment of the speciation and pollution of heavy metals in paddy soils from the Jiulong River Basin [J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(1): 453-460(in Chinese).
[45] 孙境蔚, 胡恭任, 于瑞莲, 等. 铁观音茶园土壤-茶树体系中重金属的生物有效性 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(10): 2765-2776. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020022403 SUN J W, HU G W, YU R L, et al. Bioavailability of heavy metals in soil-tea plant system of Tieguanyin tea garden [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(10): 2765-2776(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020022403
[46] 冯精兰, 胡鹏抟, 刘群, 等. 黄河中下游干流沉积物中重金属的赋存形态及其生态风险 [J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(1): 178-185. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.01.2014032102 FENG J L, HU P T, LIU Q, et al. Chemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments from the mainstream of middle and lower reaches of Yellow River [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(1): 178-185(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.01.2014032102
[47] 王闯, 单保庆, 唐文忠, 等. 官厅水库典型入库河流(洋河)表层沉积物重金属赋存形态特征 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(9): 3471-3479. WANG C, SHAN B Q, TANG W Z, et al. Heavy metal speciation in the surface sediments of Yang River System (Guanting Reservoir) [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(9): 3471-3479(in Chinese).
[48] 马芳, 秦俊梅, 白中科. 不同风化程度对煤矸石盐分与pH值的影响 [J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007(1): 55-57,70. MA F, QIN J M, BAI Z K. Effects of weathering degree on the total salt and ph of weathering coal waste rock [J]. J. Shanxi Agric Univ(Natural Science Edition), 2007(1): 55-57,70(in Chinese).
[49] 刘沙沙, 付建平, 蔡信德, 等. 重金属污染对土壤微生物生态特征的影响研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(6): 1173-1178. LIU S S, FU J P, CAI X D, et al. Effect of heavy metals pollution on ecological characteristics of soil microbes: A review [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(6): 1173-1178(in Chinese).
[50] 魏复盛, 杨国治, 蒋德珍, 等. 中国土壤元素背景值基本统计量及其特征[J]. 中国环境监测, 1991, 7(1): 1: 6. . [51] QIAO P, YANG S, LEI M, et al. Quantitative analysis of the factors influencing spatial distribution of soil heavy metals based on geographical detector [J]. Sci Total Environ, 2019, 664: 392-413. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.310 [52] 胡青青, 沈强, 陈飞, 等. 重构土壤垂直剖面重金属Cd赋存形态及影响因素 [J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6): 2878-2888. HU Q Q, SHEN Q, CHEN F, et al. Reconstructed soil vertical profile heavy metal Cd occurrence and its influencing factors [J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6): 2878-2888(in Chinese).
[53] LI H X, JI H B. Chemical speciation, vertical profile and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from coal-mine brownfield, Beijing, China [J]. J Geochem Explor, 2017, 183: 22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.09.012 [54] LI H X, JI H B, SHI C J, et al. Distribution of heavy metals and metalloids in bulk and particle size fractions of soils from coal-mine brownfield and implications on human health [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 172: 505-515. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.021 [55] 毛凌晨, 叶华. 氧化还原电位对土壤中重金属环境行为的影响研究进展 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2018, 31(10): 1669-1676. MAO L C, YE H. Influence of redox potential on heavy metal behavior in soils: A review [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31(10): 1669-1676(in Chinese).
[56] 毛海涛. 贵州典型矿区煤矸石自然风化及资源化过程中汞的环境效应初步分析[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2009. MAO H T. Environmental effects of mercury on natural weathering and resource utilization of coal gangue in typical mining areas of Guizhou Province[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2009(in Chinese).
[57] 夏毅民, 郑刘根, 邱征, 等. 铜陵某富硫尾矿库周边土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(4): 493-499. XIA Y M, ZHENG L G, QIU Z, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and risk assessment of soil around a sulfur-rich tailings pond in Tongling [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(4): 493-499(in Chinese).
[58] 庞文品, 秦樊鑫, 吕亚超, 等. 贵州兴仁煤矿区农田土壤重金属化学形态及风险评估 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(5): 1468-1478. PANG W P, QIN F X, LV Y C, et al. Chemical speciations of heavy metals and their risk assessment in agricultural soils in a coal mining area from Xingren County, Guizhou Province, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(5): 1468-1478(in Chinese).
[59] 乔晓燕, 尹佳莉, 李林, 等. 2003—2015年北京市观象台酸雨特征及长期趋势分析 [J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2018, 12(4): 52-57. doi: 10.12057/j.issn.1002-0799.2018.04.008 QIAO X Y, YIN J L, L L, et al. Characteristics and trend analysis of acid rain from 2003 to 2015 in Beijing Meteorological Observatory [J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2018, 12(4): 52-57(in Chinese). doi: 10.12057/j.issn.1002-0799.2018.04.008
[60] 徐梅, 祝青林, 朱玉强, 等. 近20年天津市酸雨变化特征及趋势分析 [J]. 气象, 2016, 42(4): 436-442. doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2016.04.006 XU M, ZHU Q L, ZHU Y Q, et al. Characteristics and variation trend of acid rain in Tianjin during the last 20 years [J]. Meteorlolgical Monthly, 2016, 42(4): 436-442(in Chinese). doi: 10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2016.04.006
[61] 吴代赦, 郑宝山, 康往东, 等. 煤矸石的淋溶行为与环境影响的研究——以淮南潘谢矿区为例 [J]. 地球与环境, 2004(1): 55-59. WU D S, ZHENG B S, KANG W D, et al. Leaching behavior of coal spoils and environmengtal impacts [J]. Earth and Environment, 2004(1): 55-59(in Chinese).
[62] LIN H, LI G Y, DONG Y B, et al. Effect of pH on the release of heavy metals from stone coal waste rocks [J]. Int J Miner Process, 2017, 165: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2017.05.001 [63] 金肇岩. 煤中砷、汞的淋滤迁移规律研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2011. JIN Z Y. The leaching and transformation of As, Hg in coal[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2011(in Chinese).
[64] DONG Y, LIU Y, LIN H. Leaching behavior of V, Pb, Cd, Cr, and As from stone coal waste rock with different particle sizes [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2018, 25(8): 861-870. doi: 10.1007/s12613-018-1635-2 [65] 尹升华, 吴爱祥, 王少勇, 等. 溶液对斑岩铜矿废石的浸蚀机理及其力学特性 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(1): 309-314. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2013.01.037 YIN S H, WU A X, WANG S Y, et al. Erosion mechanism of waste rocks and its mechanical properties during dump leaching [J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2013, 44(1): 309-314(in Chinese). doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2013.01.037
[66] 岳娟. 煤矸石中重金属元素的形态及淋溶实验研究[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2010. YUE J. Chemical forms and leaching experiment of heavy metals in coal gangue[D]. Taiyuan: Shan'xi University, 2010(in Chinese).
-






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: