-
新烟碱类杀虫剂(neonicotinoid insecticides,NEOs)属于氯化烟酰类杀虫剂,广泛应用于农业生产、市政绿化、城镇家居害虫防治,尤其是刺吸式害虫、小型鳞翅目和鞘翅目等害虫[1]。新烟碱类杀虫剂已成为全球第一大类杀虫剂[2]。目前,商品化的新烟碱类杀虫剂有多种,其中吡虫啉(imidacloprid, IMI)、噻虫嗪(thiamethoxam, THM)、啶虫脒(acetamiprid, ACE)、噻虫啉(thiacloprid, THA)和噻虫胺(clothianidin, CLO)等典型新烟碱类杀虫剂在我国使用广泛,近年来市场销售额及占有率均排在先列。然而,大多数新烟碱类杀虫剂在施用后并未被动植物吸收代谢,而随着降水、径流或市政排水进入河流、湖泊等受纳水体和城镇污水处理系统中,因其结构稳定、难以降解,具有环境持久性,对非靶标生物(如蜜蜂等授粉昆虫、水生生物等)及水生生态环境造成潜在危害[1, 3-4],属新型有机污染物。
水生生态系统中残留新烟碱类杀虫剂对生态环境及人类健康的潜在不利影响日益明显并引起了世界范围的关注。有研究表明,全球环境,包括土壤和水体均受到了不同程度的新烟碱类杀虫剂的污染[1-2, 5]。新烟碱类杀虫剂可以通过削弱蜜蜂觅食与归巢能力,影响蜜蜂种群数量[5-7]。同时,新烟碱类杀虫剂对水生及陆生无脊椎动物也有一定的致死作用[5],此外,也有研究报道,大量接触新烟碱类杀虫剂会对人体健康产生危害[6]。有研究表明,新烟碱类杀虫剂污染已成为全球范围内普遍存在的环境问题[7]。目前,欧盟、法国、美国、加拿大等组织与国家已颁布相关法令限制或禁止新烟碱类杀虫剂的使用以减缓其危害。我国作为新烟碱类杀虫剂的第一生产和使用大国,有必要在多环境介质中开展其污染状况、环境行为及归趋的研究。
新烟碱类杀虫剂在水中的溶解度很大,易在水体中积累,造成水体污染,可能会转移到水生生物体中会对生物造成危害[6-7]。城镇污水处理厂作为污染物重要的“源”和“汇”,为研究此类物质污染特征、迁移转化行为提供了有效途径。然而,目前针对城镇污水处理过程中新烟碱类杀虫剂迁移转化行为和生物降解等相关报道较少。有研究显示活性污泥法,如A2/O工艺、氧化沟等常规污水处理工艺难以实现有效去除。Sadaria等[8]研究发现噻虫啉、啶虫脒、吡虫啉在常规活性污泥处理系统中去除效果较差,在污水处理系统中具有持久存在性;Iancu等[9]研究发现常规污水处理工艺对新烟碱类农药的去除率较低,效果有限。循环活性污泥工艺(CASS)集曝气、沉淀功能于一体,其曝气、沉淀、排水在同一池子内依次进行,周期循环,并能实现程序化控制,自动化程度高,操作简便,CODCr去除率较高,抗冲击能力强,能实现良好的脱氮除磷。在我国南方地区生活污水处理中有较广泛的应用,其对新烟碱类杀虫剂去除特性有待开展。
全文HTML
-
选取5种使用广泛的新烟碱类杀虫剂作为目标化合物,分别为吡虫啉、噻虫嗪、噻虫胺、啶虫脒和噻虫啉,详细信息如表1所示。5种典型新烟碱类杀虫剂标准品均为固态粉末状。其中吡虫啉(99.5%)、噻虫嗪(99.0%)、噻虫胺(99.0%)、啶虫脒(98.1%)购自德国Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH公司,噻虫啉(98.6%)购自美国AccuStandard Inc公司。内标物IMI-d4(99.9%)、THM-d3(98.0%)、CLO-d3(97.0%)、ACE-d3(98.0%)和THA-d4(98.0%)均购自美国Sigma-Aldrich Chemical公司。乙腈(色谱纯,99.9%)、二氯甲烷(色谱纯,99.8%)和甲醇(色谱纯,99.9%)购自上海安谱(ANPEL Laboratory Technologies)公司。氯化钠(分析纯,99.9%)购自天津市大茂化学试剂厂。HLB型固相萃取小柱(500 mg,6 mL)购自上海安谱(ANPEL Laboratory Technologies)公司。实验过程中均使用美国Millipore公司Milli-Q系统制备的超纯水。
标准储备液制备:所有标准品均溶解于乙腈中配置成浓度为100 mg·L−1的标准品储备液。所有储备液于−20 ℃下避光保存。
-
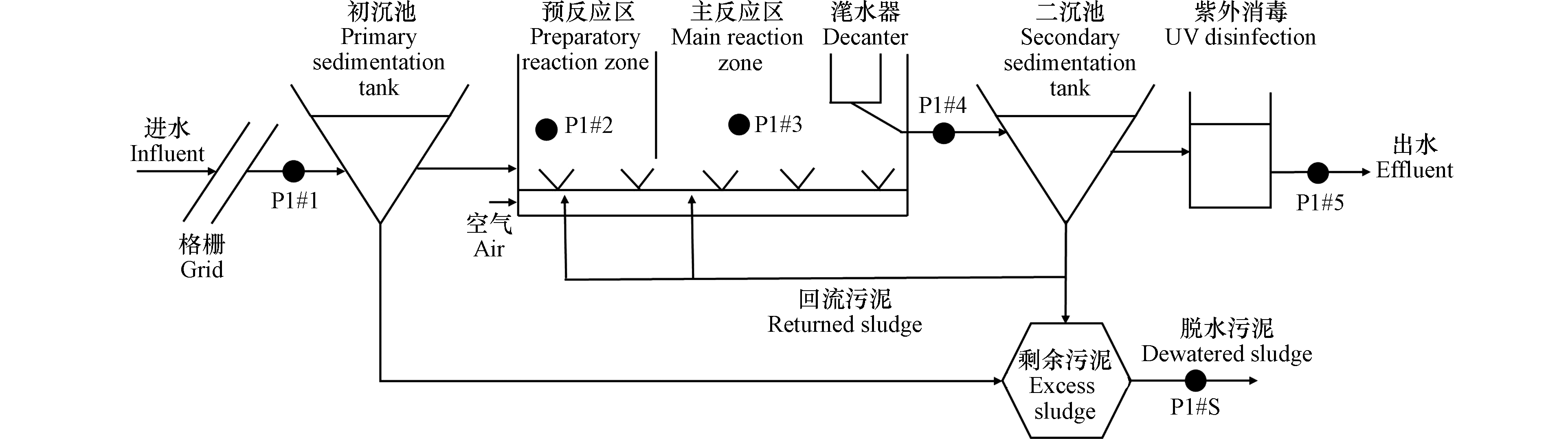
选取华南地区中山市某城镇污水处理系统作为采样地。所选取城镇污水处理系统工艺主要包括格栅、初沉池、循环活性污泥生物处理反应池(CASS)、二沉池以及紫外消毒池等,其中循环活性污泥生物处理反应池前部为生物选择区也称预反应区,后部为主反应区,在主反应区后部安装了可升降的自动滗水装置,曝气、沉淀、排水等过程在同一池子内周期循环运行,其操作时间为:进水曝气2.0 h,沉淀1.0 h,滗水闲置1.0 h。采集处理系统各工艺段中污水和污泥样品,采样点分布如图1所示,进水(P1#1)、厌氧阶段出水/缺氧阶段前进水(P1#2)、缺氧阶段出水/好氧阶段进水(P1#3)、好氧阶段出水(P1#4)、出水(P1#5)以及脱水污泥(P1#S)。其中P1#2位于预反应区附近,P1#2、P1#3位于主反应区附近、P1#4位于滗水器后端。当处理系统达到稳态时开始试验,采集连续3—6个运行周期内(水力停留时间)样品分析。
按照各反应阶段的进出水时间点采集反应池进、出水附近样品3—6次。使用便携式取样器和塑料小桶从污水处理系统中采集泥水混合样品,垂直静止15 min,分别收集污水和污泥样品,储存在聚丙烯(polypropylene, PP)采样瓶中,分别添加适量甲醇和叠氮化钠抑制微生物活性。脱水污泥(P1#S)采用不锈钢采样器收集,储存在聚丙烯(polypropylene, PP)宽口采样瓶中。收集完成后将样品放置于便携式冰箱中,并尽快转移到实验室,分别储存在4 ℃和−20 ℃冰箱中。在1周内完成样品前处理及分析。所有样品储存用容器在采样前均使用甲醇和超纯水清洗2—3次。在样品采集同时记录各工艺段操作参数及运行状况,其中温度(T)、pH、溶解氧(DO)、电导率(COND)和氧化还原电位(ORP)采用哈希多参数水质监测仪原位测定。
-
每0.5 L水样用孔径为0.45 μm滤膜过滤,加入内标混合均匀,水样使用固相萃取法作为前处理提取新烟碱类杀虫剂。依次用10 mL甲醇与10 mL超纯水活化HLB小柱,以3—5 mL·min−1流速加载水样,整个过程中始终保持水样液面高于小柱填料上表面。待样品装载完成后,用25 mL 5%甲醇/水溶液润洗样品瓶2次,并过柱。然后,用5 mL超纯水清洗小柱以去除盐分和残留杂质,并在抽真空条件下对小柱进行干燥5—10 min。待小柱抽干后,用5 mL甲醇洗脱富集在小柱上的新烟碱类杀虫剂,洗脱液用轻柔氮气吹至近干,并以1 mL乙腈定容至棕色进样小瓶,于−20 ℃下避光保存。
污泥样本风干后,捣碎,过100目筛。准确称取5.00 g过筛后污泥样品,转移至50 mL带密封盖塑料瓶中,加入20 mL乙腈:二氯甲烷(2∶1,V/V)混合溶液,涡旋震荡1 min混匀,超声提取15 min。以5000 r·min−1转速,离心8 min,将溶液转移到梨形瓶中,转移至旋转蒸发仪浓缩至近干,用1 mL乙腈定容待用。将上述1 mL乙腈提取液转入10 mL去离子水中(pH=7),依次加入0.8 g NaCl和2 mL二氯甲烷,涡旋振荡1 min后,超声萃取10 min,5000 r·min−1转速离心5 min,然后用微量注射器取走沉底乳化液珠,用轻柔氮气吹至近干,并以1 mL 乙腈定容至棕色进样小瓶,于−20 ℃下避光保存。
-
水样和污泥中待测新烟碱类杀虫剂浓度采用色谱质谱联用技术(Thermo LC TSQ Quantum Ultra三重四极杆液质联用仪)进行检测[10-11],色谱柱为Thermo Hypersil GOLD C18柱(100 mm×2.1 mm,1.9 μm),色谱柱上游端连接在线过滤器以除去流动相和样品中的细小颗粒物,柱温箱维持在40°C,待测样品进样量为3 μL;采用0.1%甲酸水溶液(A相)与乙腈(B相)为流动相,流速为300 μL·min−1。质谱检测采用正离子模式;喷雾电压(spray voltage)为+3200 V;喷雾温度(vaporizer temperature)为350 ℃;鞘气(sheath gas flow rate, N2)为45 arb;辅气(aux gas flow rate, N2)为8 arb;碰撞气(Ar)为1.5 mTorr。
采用外标法定量,各目标化合物标准曲线相关系数均大于0.99。现场空白、实验室空白、加标样品以及样品平行均与样品同时进行前处理和仪器分析。空白中均未检出任何目标化合物;检出限为0.01—0.05 ng·L−1(水样)、0.001—0.005 ng·g−1(污泥样品),加标回收率为83%—106%(水样)和81%—112%(污泥样品),相对标准偏差小于12%。
-
污水处理系统水相中新烟碱类杀虫剂的去除率计算式为:
其中,Cinf、Ceff分别为处理系统进、出水中新烟碱类杀虫剂平均质量浓度(ng·L−1)。
1.1. 材料和试剂
1.2. 样本采集
1.3. 样品前处理
1.4. 仪器分析
1.5. 去除率计算
-
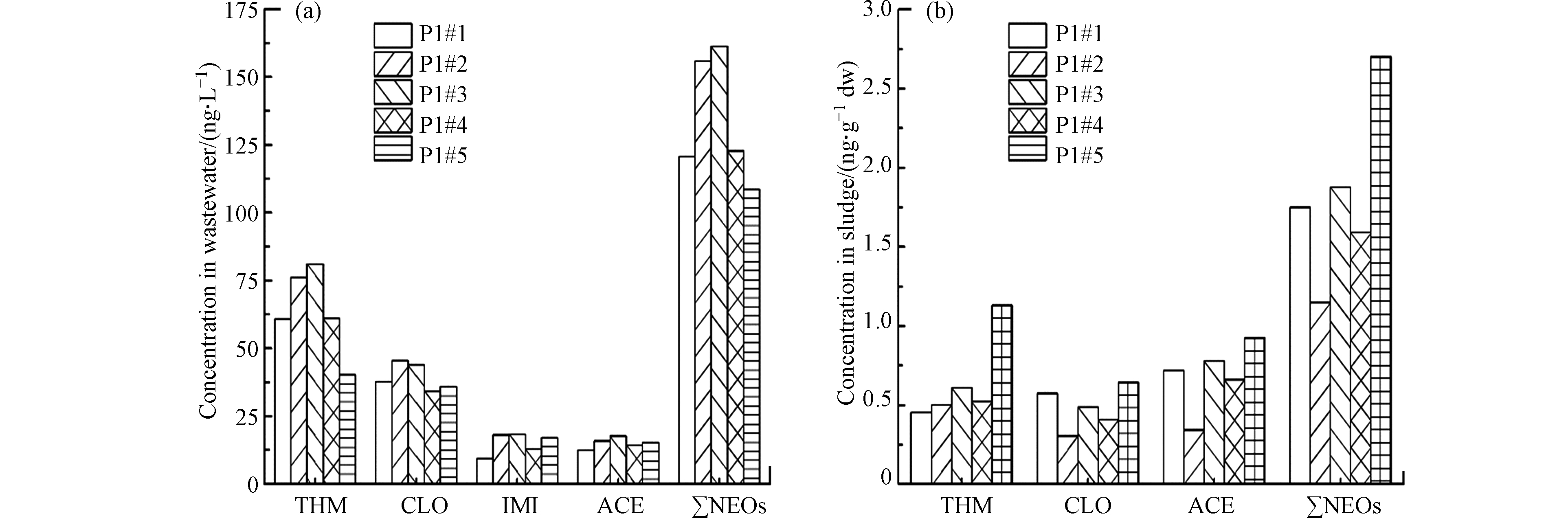
在城镇污水处理系统各工艺段样品中均检测到有典型新烟碱类杀虫剂残留(噻虫啉除外),详见表2。在污水中主要检出类型有噻虫嗪、噻虫胺、吡虫啉和啶虫脒(检出率100%),未检测到噻虫啉。其中,检出浓度最高的是噻虫嗪,其平均浓度达到63.9 ng·L−1,其次是噻虫胺,平均浓度为39.5 ng·L−1。吡虫啉与啶虫脒的检出浓度较低,平均浓度分别为15.3 ng·L−1和15.3 ng·L−1。与污水中检出情况不同的是,在污泥中只检出有噻虫嗪、噻虫胺、啶虫脒等3种新烟碱类杀虫剂,未检测出噻虫啉与吡虫啉。其中,啶虫脒在5种典型新烟碱类杀虫剂中检出浓度最高,平均浓度为0.685 ng·g−1 dw,噻虫嗪与啶虫脒相差不大,平均浓度为0.644 ng·g−1 dw,噻虫胺浓度最低,仅为0.484 ng·g−1 dw。
在整个处理过程中,污水中新烟碱类杀虫剂的浓度总体上呈现先增加后减少的趋势(图2a)。进水中5种新烟碱类杀虫剂总检出浓度为120.7 ng·L−1,厌氧阶段出水(P1#2)中新烟碱类杀虫剂总检出浓度有所上升,为155.9 ng·L−1,缺氧阶段出水(P1#3)中新烟碱类杀虫剂总浓度达到最高,为161.3 ng·L−1;经过曝气处理后浓度逐渐降低,好氧阶段出水(P1#4)为122.8 ng·L−1,出水(P1#5)中新烟碱类杀虫剂总浓度降低至约108.7 ng·L−1。在污泥中新烟碱类杀虫剂总体上则呈上升趋势(图2b)。初沉池污泥中新烟碱类杀虫剂总检出浓度为1.748 ng·g−1 dw,厌氧阶段污泥中新烟碱类杀虫剂总检出浓度最低,为1.15 ng·g−1 dw,缺氧与好氧阶段污泥中新烟碱类杀虫剂总检出浓度分别为1.876 ng·g−1 dw和1.589 ng·g−1 dw,在末端脱水污泥中总检出浓度达到最大,为2.700 ng·g−1 dw。相比初沉池污泥,脱水污泥中5种新烟碱类杀虫剂总浓度增加约35%。
-
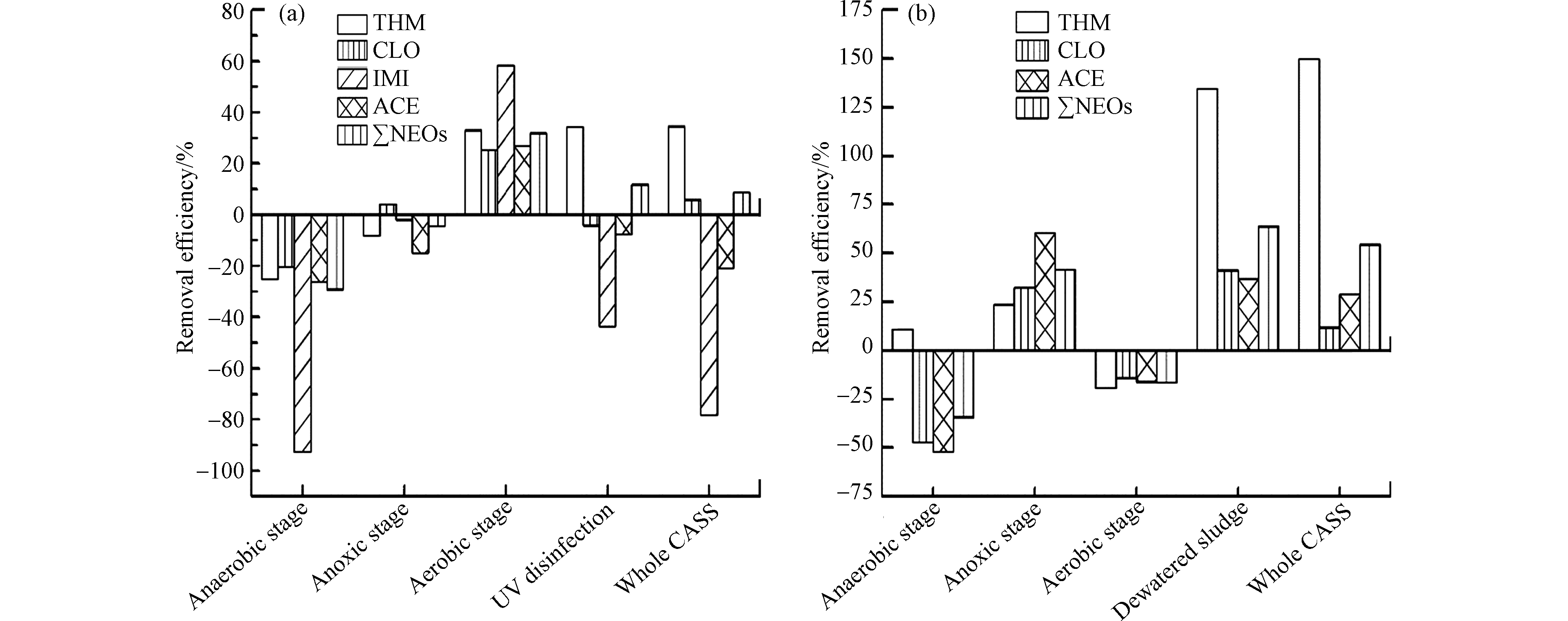
在试验过程多个水力停留时间内,循环活性污泥生物处理工艺(CASS)对污水中COD、氮、磷具有较好的去除效果,出水COD在55—68 mg·L−1,去除率为65%—83%,氮、磷可达标排放。而污水中新烟碱类杀虫剂总去除效率仅为9%(图3a),效果不佳,其余部分(91%)随出水排入受纳河流水体。对于各工序阶段而言,新烟碱类杀虫剂在厌氧与缺氧阶段去除率均为负数,分别是-29%和-5%,其可能与污泥中新烟碱类杀虫剂解离脱附有关;好氧阶段对∑NEOs去除效率最高,平均去除率达到32%;其次是紫外消毒阶段,去除率大致为12%,其表明水中紫外线可能对新烟碱类杀虫剂有一定的降解作用,同时也说明有氧条件可能有利于新烟碱类杀虫剂的去除。
大多数研究表明污泥对新烟碱类杀虫剂有较好的吸附作用,本试验中CASS工艺中污泥对新烟碱类杀虫剂的吸附效果较理想,吸附率达到54%(图3b)。厌氧与好氧阶段可能存在一定的解离脱附作用导致污泥中新烟碱类杀虫剂浓度降低,出现负吸附率,平均吸附率分别为-34%和-16%;缺氧阶段污泥平均吸附率为41%,脱水污泥中新烟碱类杀虫剂的吸附效果最好,平均吸附率达64%,其可能与不同工艺条件下污泥理化性质等有关。
通过整个处理流程后,吡虫啉与啶虫脒的去除率分别为-78%和-20%,噻虫胺的去除率为6%,噻虫嗪去除率最高,为34%。吡虫啉未在污泥中被发现,而啶虫脒在污泥中吸附率为28%,噻虫胺在污泥中吸附率为12%,结果表明在CASS工艺中噻虫胺的去除效果不理想;而噻虫嗪在污泥中吸附率则为150%,其原因可能是污泥不仅吸附了污水中输入的噻虫嗪,还可能吸附在厌氧与好氧阶段中解离脱附的噻虫嗪,结合上文中噻虫胺去除效果差异、结果表明CASS工艺可能对某类特定的新烟碱类杀虫剂(如噻虫嗪),有较好的处理效果,但对其它新烟碱类杀虫剂去除效果有限。Sadaria等[8]在对美国西南部一座大型活性污泥污水处理厂的研究中发现,出水中吡虫啉和噻虫胺的去除率分别为11%和12%,并得出了曝气池中微生物降解、水解、氧化等工艺对废水中吡虫啉和噻虫胺去除效果不明显的结论;类似地,Iancu等[9]对Bucharest污水处理厂研究发现新烟碱类杀虫剂从进水中去除比例较低,啶虫脒去除率为23.2%,吡虫啉平均去除率为22.4%,噻虫嗪平均去除率为20.3%。综上,新烟碱类杀虫剂在传统的污水处理系统中难以得到有效去除[12],CASS处理过程中操作条件差异可能促进某类特定新烟碱类杀虫剂的去除或吸附(如噻虫嗪)。新烟碱类杀虫剂随污水处理系统出水外排很可能对周围生态环境造成威胁。
-
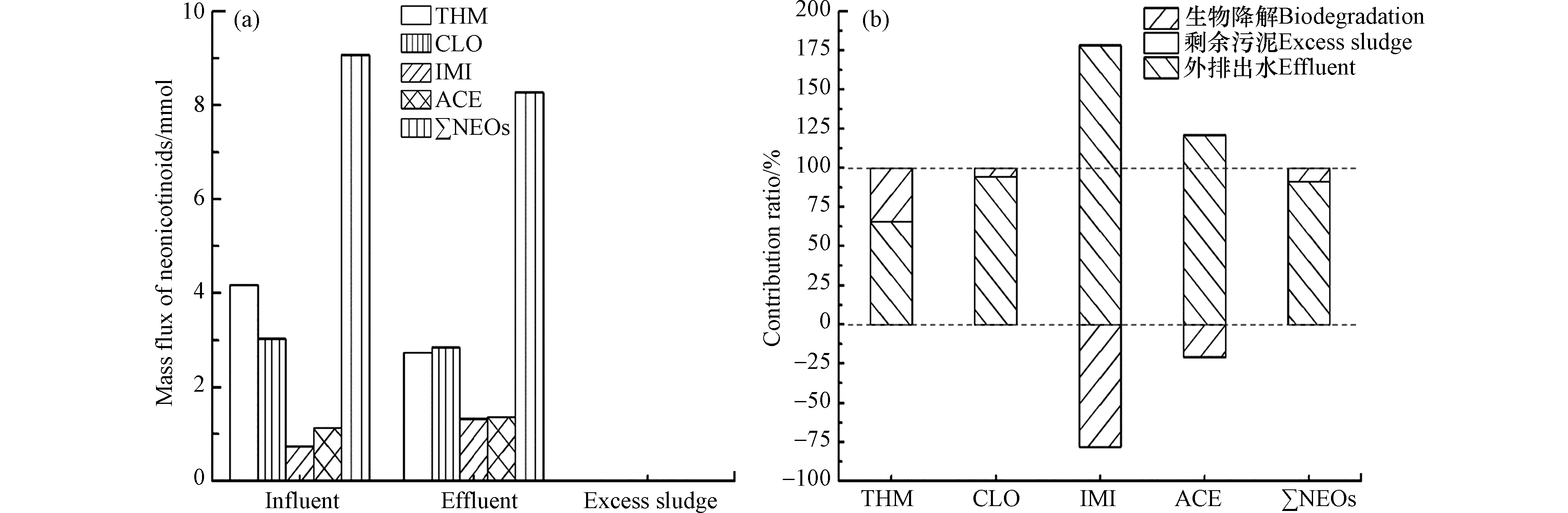
由上文知通过CASS主体生物处理流程后,新烟碱类杀虫剂物质量有所减少。根据运行数据,此城镇污水处理厂日进水量为2万吨,出水量为1.98万吨,日脱水污泥(80%质量含水率)10吨,则可知污水处理厂进水中新烟碱类杀虫剂总量约为9.07 mmol,其中0.44 mmol被吸附到脱水污泥中,出水中新烟碱类杀虫剂剩余约8.27 mmol(图4a),有一部分新烟碱类杀虫剂被生物降解去除,其中噻虫嗪、噻虫胺、吡虫啉、啶虫脒被降解量分别为1.44、0.18、-0.58、-0.23 mmol,∑NEOs生物降解量为0.80 mmol。为了阐明各种去除途径对新烟碱类杀虫剂去除的贡献,根据目标新烟碱类杀虫剂质量流量计算CASS工艺中各去除路径贡献率(图4b)。生物降解是CASS工艺中去除新烟碱类杀虫剂最重要的途径。对于∑NEOs,出水中剩余量约为91.2%,生物降解路径的贡献率为8.8%,而转移到污泥中量仅占0.02%,绝大部分新烟碱类杀虫剂仍残留在出水中,而污泥吸附贡献率极低,污泥对于新烟碱类杀虫剂吸附效率极差,几乎可以忽略不计。另外,CASS工艺中生物降解的贡献率不高(8.8%),并不能有效实现新烟碱类杀虫剂的去除。对于噻虫嗪而言,出水中剩余量约为65.5%,参与生物降解量约为34.5%,是5种典型新烟碱类杀虫剂中生物降解贡献率最大值,对噻虫嗪的去除效果处于领先;出水中噻虫胺剩余量为94.2%,参与生物降解的占5.8%,去除效果不佳;然而,出水中吡虫啉与啶虫脒剩余量则高于其在进水中量,吡虫啉剩余量为178.3%,啶虫脒剩余量为120.8%,其物质量增加主要由于生物降解量为负值,如吡虫啉生物降解贡献率为−78.3%,啶虫脒生物降解贡献率为−20.9%,可能与污泥中新烟碱类杀虫剂由污泥中解离脱附有关。
类似地,Sadaria等[8]研究发现干重污泥中新烟碱类杀虫剂的浓度较低,仅占总质量的1%,对质量平衡分析不起作用。进一步证明,CASS工艺对新烟碱类杀虫剂的处理效果不佳。
在水样采集同时对水样主要理化指标,包括T(℃)、pH、DO(μmol·L−1)、COND(μS·cm−1)、ORP(mV)等进行了检测。对新烟碱类杀虫剂浓度与理化指标进行单因子分析(表3)发现系统中T((30.4±0.3) ℃)、pH(6.7±0.3)变化不大,与新烟碱类杀虫剂浓度相关系数较小(r<0.8),相关性较弱。COND与ORP相关性系数绝对值均小于0.8,同样和新烟碱类杀虫剂浓度有弱相关性或没有相关性。综合各种理化指标,溶解氧DO与噻虫嗪和新烟碱类杀虫剂总浓度呈现强相关性,且为线性负相关(P <0.01),也即DO与新烟碱类杀虫剂的去除率正相关(P<0.01),进一步证明有氧条件可能有利于新烟碱类杀虫剂的生物降解。
2.1. 新烟碱类杀虫剂在污水处理系统中检出类型及污染水平
2.2. 新烟碱类杀虫剂在不同处理过程中去除效率
2.3. 新烟碱类杀虫剂在不同处理过程中去除途径及关联环境因子
-
(1)当前城镇污水处理系统(CASS处理工艺)对新烟碱类杀虫剂去除效果不理想,大多数(91%)随出水排入受纳河流水体,可能会对周边水环境及水生态造成潜在巨大危害。
(2)污泥吸附和生物降解可能是城镇污水处理系统中新烟碱类杀虫剂的主要去除途径。
(3)缺氧阶段污泥对新烟碱类杀虫剂吸附作用较好,好氧生物处理可能有利于新烟碱类杀虫剂的降解。





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: