-
氯代苯酚类化合物具有高毒性、难降解和生物累积性的特征,是一种常见的持久性有机污染物[1-3],且广泛存在于土壤、沉积物、地表和地下水中。为了降低对受纳水体的污染,氯酚废水的处理至关重要。目前对于氯酚类废水的处理方法主要有生物降解法[4-6]、物理吸附法[7-8]、高级氧化法[9-11]等。近年来,高级氧化技术以其氧化能力强、反应速度快、限制少和处理效率高等优点受到众多学者的青睐[12]。臭氧氧化法是目前最具代表性且最有效的高级氧化法之一。众所周知,臭氧氧化有机物主要的两种方式:一是臭氧分子与有机物的直接反应;二是臭氧分解产生的羟基自由基(OH·)与有机物的间接反应[13]。纳米二氧化锰作为催化剂能有效促进臭氧催化氧化过程中羟基自由基等活性物质的形成,使其对难降解有机污染物的去除更加迅速、彻底,是催化臭氧化中最常使用的催化剂之一[14-17]。
目前,很多学者已经对催化臭氧化的降解效率及降解动力学等[18-19]进行了研究,但鲜有研究其降解过程中的生物毒性变化及其关键的致毒因子。已有研究发现,由于臭氧的部分氧化特性,生成的大量降解中间产物的生物毒性可能大于母体污染物,造成母体污染物浓度降低而总体生物毒性升高的现象[20].
本研究以3-CP作为模型污染物,探究二氧化锰催化臭氧化中生物毒性的变化规律,并识别高毒性的中间产物。在此基础上,研究催化臭氧化体系处理各类有机化合物过程中自由氯浓度的变化,以揭示高毒性中间产物的产生机理。
-
3-CP(分析纯)购自中国能源化工有限公司;一水合硫酸锰(MnSO4∙H2O,分析纯)和叔丁醇(t-BuOH,分析纯)由迈瑞尔化学技术有限公司提供;高锰酸钾(KMnO4,分析纯)购于上海斯信生物科技有限公司。配制模拟湖水所用药品(CaCl2、NaHCO3、KCl、CH3COONa和MgSO4)和亚硫酸钠(Na2SO3)等均购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司且均为分析纯。
-
以高锰酸钾和一水合硫酸锰为原料,采用水化学沉积法制备了MnO2纳米粒子[21-22],其反应方程式为式(1)。取物质的量比为2:3的KMnO4和MnSO4∙H2O在80 ℃下分别溶解于125 mL去离子水中;将上述两溶液缓慢滴入装有250 mL去离子水的三口瓶中,并在油浴锅中恒温(80 ℃)缓慢搅拌反应2 h;将得到的黑色或棕色悬浮液自然冷却1 h,随后超声分散10 min;将制备好的悬浮液进行抽滤,去离子水洗涤,重复3次;将洗涤抽滤后的产物在80 ℃下干燥过夜至恒重,制得纳米二氧化锰样品。
-
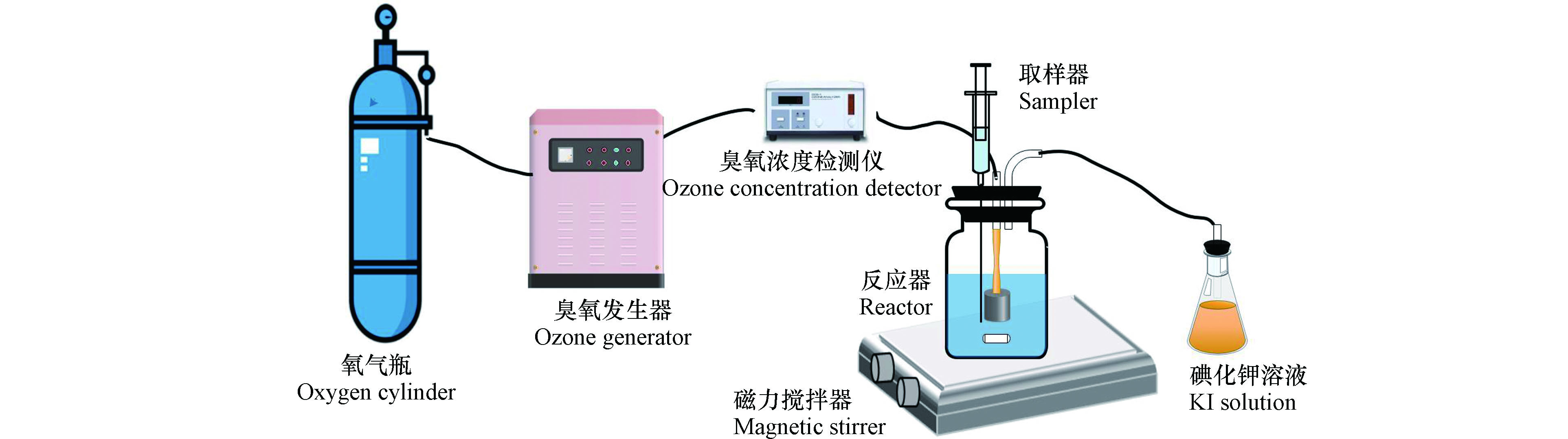
在有效容积为2 L的玻璃反应器中进行半静态催化臭氧氧化实验,实验装置如图1所示。实验以纯氧为气源在臭氧发生器(中国青岛国林环保科技有限公司,CF-G-3-10G)中产生臭氧,使用在线检测仪(中国朗科公司,LT-200B)测定气相中臭氧浓度。臭氧与氧气的混合物以0.5 L∙min−1的流速,通过固定在反应器底部的烧结曝气头分散到溶液中,臭氧尾气用KI溶液进行吸收。3-CP的初始浓度为40 mg∙L−1,臭氧浓度为28 mg∙L−1,MnO2投加量为1 g∙L−1,反应溶液pH值为1—12。不同pH的氯酚溶液用10 mmol∙L−1磷酸缓冲液配制,并使用1 mol∙L−1 H2SO4和1 mol∙L−1 NaOH调节至相应的pH。反应过程中以固定的时间间隔取样,在取样后,立即用氮气吹脱臭氧化水样[23],以消除溶解在溶液中未反应的臭氧,然后再进行下一步操作。
-
使用灵敏度高的发光细菌青海弧菌(Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.NovQ67)[24],进行发光菌发光抑制实验测定急性生物毒性。具体的测试方法根据已有的研究方法[25-27]进行了适当的调整。
取-80 ℃条件下保存的Q67菌种(1 mL菌液)接入装有液体培养基的锥形瓶,于22 ℃条件下,振荡(180 r∙min−1)培养16—18 h。取100 μL菌液于96孔板测定发光强度(RLU),离心(200 r∙min−1,10 min)后收集菌体,用模拟湖水将菌体制成菌悬液。调整菌悬液的密度,使其发光强度在20万—60万RLU∙mL−1之间,待用。实验前,将水样pH值调至7,并用人工配制的模拟湖水将样品稀释成一系列的浓度梯度。样品的相对浓度以稀释倍数的倒数表示。将180 μL水样和20 μL调整后的菌液先后加入96孔板中,模拟湖水设置空白对照,每个浓度设置3个平行。振荡15 min后,用酶标仪(Ifinite-200,Tecan,瑞士)测定各孔的发光强度。使用公式(2)计算发光抑制率IR(%):
式中,RLIBC表示空白对照组中发光细菌发出的相对发光强度,RLIS表示原始和稀释的样品中发光细菌发出的相对发光强度。
剂量-效应浓度曲线和最大半抑制浓度利用Origin软件的logistic模型来进行拟合和计算:
式中,x表示稀释溶液中初始样品的百分比;y表示发光抑制率;Slope为斜率参数;IC50表示相对半数效应浓度。
根据公式(4)计算毒性单元:
式中:TU表示毒性单元;TOC表示总有机碳浓度。
-
纳米二氧化锰的晶相结构采用XRD表征,仪器型号为D8ADVANCED,最大输出功率≥2.2 kV,最大管流80 mA,靶材为铜靶,扫描方式θ/θ或θ/2θ速,测量仪最小度数0.0001°。场发射扫描电镜(FESEM)(FEI Quanta 250F,美国)用于表征纳米二氧化锰的表面形貌。采用Zeta电位仪(Zeta Sizer 3000型,Malvern,英国)对纳米二氧化锰的表面零点电荷(pHzpc)进行测定。总有机碳分析仪(Multi N/C 3100,Elementar,德国)测定TOC浓度。自由氯由哈希余氯/总氯水质测试检测仪(PC-II,美国)测定。3-CP浓度通过配备有UV检测器(SPD-M20A,波长为180 nm至800 nm)的高效液相色谱仪(岛津LC-20A,日本)测得。在改良的C18柱(Lnertsil ODS-SP,250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm)上进行分析,3-CP的计算波长为275 nm;进样体积为10 μL,流动相为流速1 mL∙min−1的甲醇与水的混合液,比例为6.5:3.5,柱温保持在40 ℃,保留时间约为7.0 min。
-
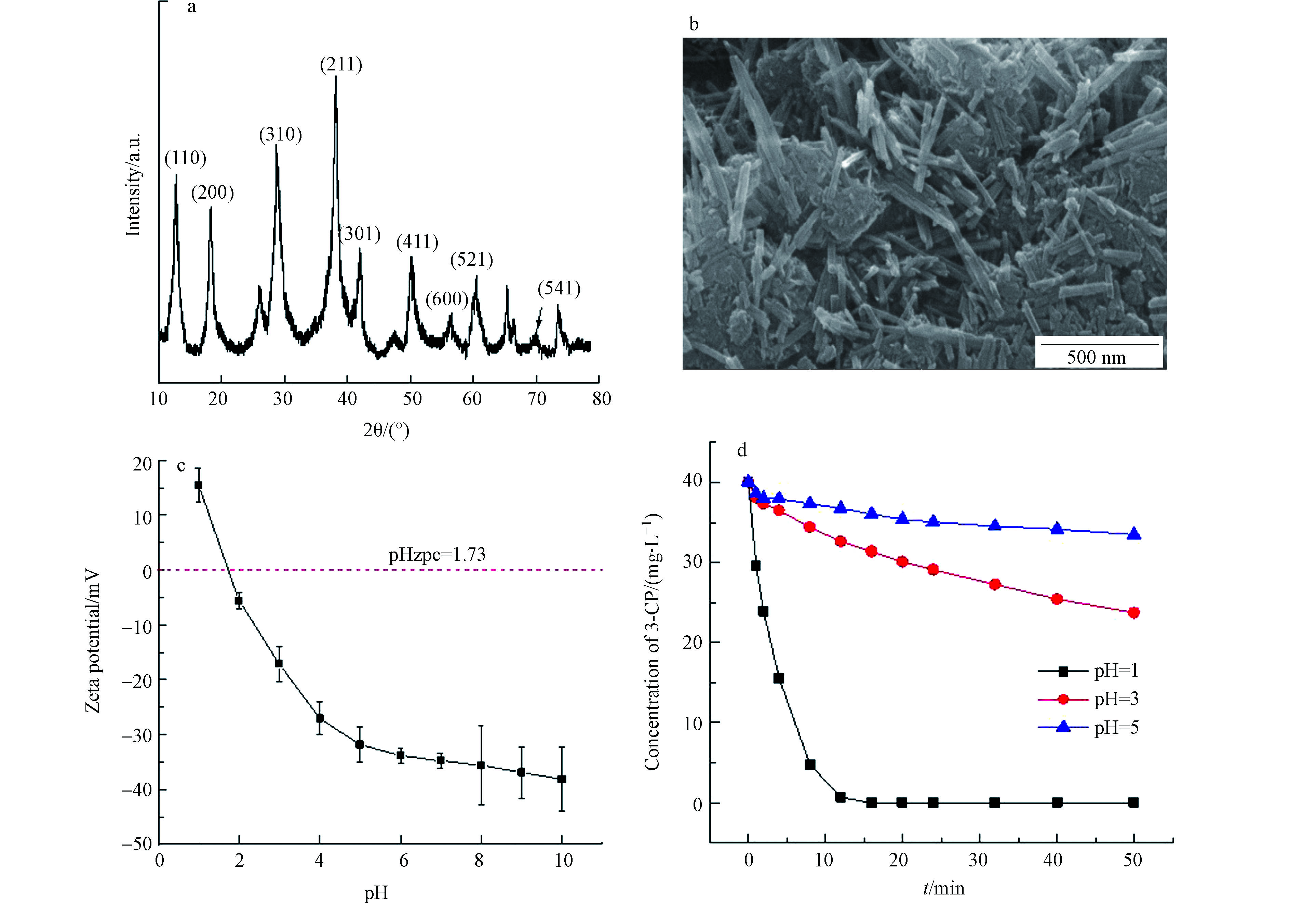
图2(a)为催化剂样品的X射线衍射光谱谱图,催化剂在2θ为12.6°、18.2°、28.8°、37.5°、41.9°、49.8°、56.4°、60.2°和69.7°处分别表现出了对应α-MnO2的(110)、(200)、(310)、(211)、(301)、(411)、(600)、(521)和(541)晶面的特征衍射峰[28],与α-MnO2(JCPDS 44-0141)匹配度高。图2(b)为纳米二氧化锰的FESEM图,可以看出所制备的纳米二氧化锰有团簇现象,但主要为松散的纳米线状,其直径约50—100 nm,长约0.2—1 μm。
如图2(c)所示,通过表面的电势的测量,催化剂的pHzpc=1.73(R2=0.998),与参考文献接近[29]。所以pH<1.73时,催化剂表面带正电;当pH>1.73时,催化剂表面带负电。如图2(d),纳米MnO2对3-CP的吸附反应进行8 min(pH=1、3、5)时,对3-CP的吸附率分别为89%、15%和5%,即随着本体溶液pH的升高,纳米MnO2催化剂对3-CP的吸附能力逐渐减弱。而3-CP的pKa为8.8—9.1[30],酸性条件下以未解离的分子形式存在。因而静电作用是导致3-CP在纳米二氧化锰表面吸附的主要原因。
-
本实验在不同pH(pH=1、3、5、7、10、12)下,考察了催化臭氧氧化3-CP过程中急性毒性、3-CP浓度、TOC浓度和自由氯浓度的变化。实验结果如图3所示。
-
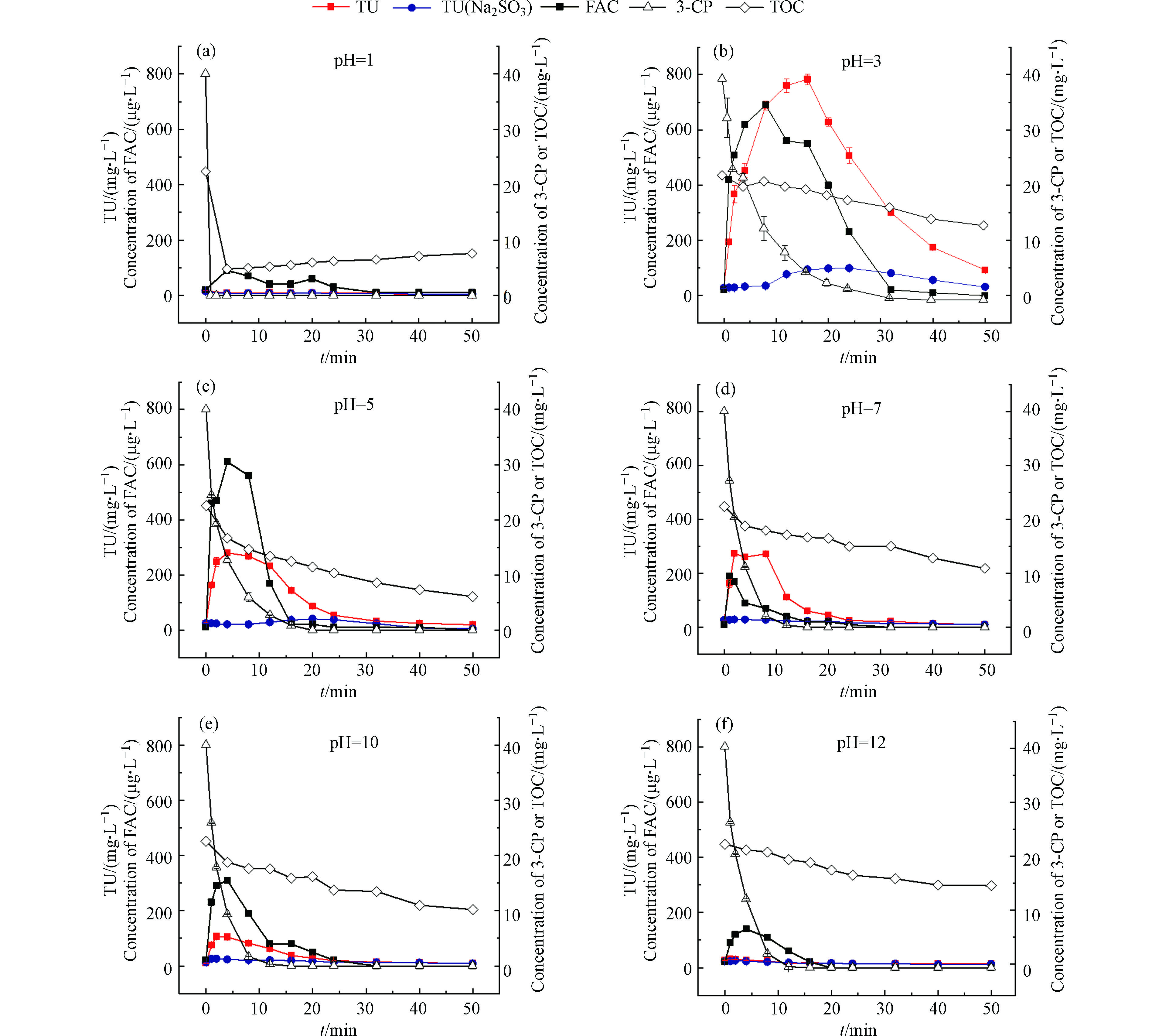
从图3(a)中可以看出,当pH=1时,在1 min内3-CP降解率接近100%,且TOC浓度迅速下降,随着反应时间推移,TOC含量保持在5 mg∙L−1左右。3-CP的迅速去除一方面是由于催化剂MnO2在pH=1时有较强吸附能力,另一方面,酸性条件下MnO2能够催化臭氧对3-CP的氧化降解,但并未被完全矿化,而是生成了其它中间产物。
如图3(b)—(e)所示,当pH=3—12时,3-CP浓度和TOC浓度逐渐降低。pH=3时,3-CP完全降解需要约32 min,随着pH逐渐增大,3-CP完全降解所需时间随之减少。一方面,随着pH的升高,臭氧分子更容易分解生成氧化性更强的羟基自由基[30]。另一方面,Poznyak和Vivero[31]指出,氯酚类物质在高pH下发生解离,生成的离子形式与氧化剂臭氧分子和羟基自由基的反应速率大于分子形式。
-
如图3(a)所示,当pH=1时,实验过程中生物毒性没有升高,这可能是因为3-CP的去除主要是MnO2的吸附作用,高毒性中间产物没有累积。如图3(b)—3(e)所示,当pH=3—10时,生物毒性都呈现先升高后下降的变化,且生物毒性的最高值随pH的增加呈下降的趋势。当pH=3时,生物毒性最高值约为初始值的26倍,而当pH=12时,生物毒性没有明显升高的现象发生。造成这一现象的原因可能随着pH的升高,臭氧分解生成的大量羟基自由基能够和高毒性中间产物迅速反应,减少了中间产物的累积。
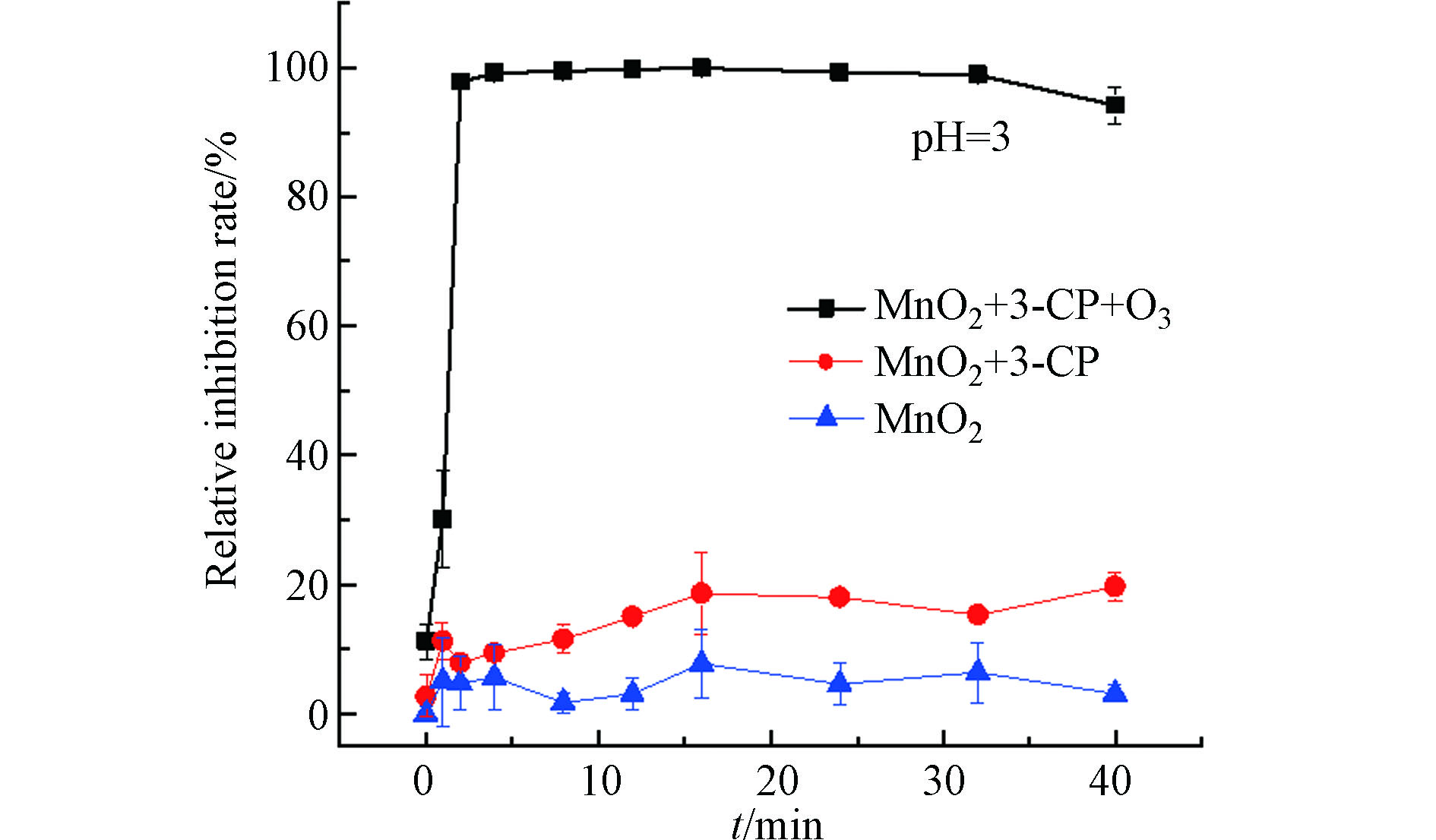
为了确定体系中的MnO2催化剂是否是造成毒性升高的原因,在pH=3的情况下,研究了MnO2催化臭氧化3-CP、吸附3-CP以及臭氧化MnO2过程中的生物毒性变化。如图4所示,当反应体系中不通入臭氧或不加入污染物3-CP时,没有明显的生物毒性升高的现象发生。由此可以得出结论,在3-氯酚的催化臭氧氧化过程中,MnO2催化剂本身对生物毒性没有影响,仅作催化作用。
-
为了识别催化臭氧化中的关键致毒因子,监测了反应过程中自由氯的浓度变化,如图3(a)—(f),自由氯浓度的变化与生物毒性的变化一致,在pH=3—10时也呈现了先升高后下降的趋势。为了说明生物毒性与各指标的相关性,通过皮尔森相关系数法,对生物毒性和3-CP残留浓度、TOC浓度及自由氯浓度的相关性进行了分析,分析结果如表1所示。
从表1中可以看出,在生物毒性显著增加的4组(pH=3、5、7和10)中,生物毒性和自由氯浓度在0.01水平上显著相关,生物毒性与3-CP残留浓度及TOC基本不存在相关性。另外,已有研究发现,在相同浓度下,自由氯对发光细菌的毒性比3-CP大得多[32]。由此推断,催化臭氧化3-CP中生成的高毒性中间产物可能为自由氯。为了验证自由氯在体系生物毒性变化中的作用,取反应后的溶液1.2 mL,加入10 mmol∙L−1亚硫酸钠溶液36 μL,以研究自由氯去除后生物毒性的变化规律。如图3(a)—(f)所示,加入自由氯去除剂亚硫酸钠后,生物毒性显著下降。在pH=3—10时,生物毒性的去除率最高达到100%。但在pH=3时,加入亚硫酸钠后的水样生物毒性仍显著高于初始值。有研究表明[33],在臭氧氧化氯酚类物质中能够生成某些有机中间转化产物,如氯代邻二酚、氯代己二烯二酸等,它们可能是除无机高毒性中间产物自由氯外,会造成催化/臭氧化过程中生物毒性升高的物质。因此,MnO2催化臭氧化3-氯酚中生成的自由氯是急性毒性升高的关键致毒因子。
-
自由氯作为一种强氧化剂,长期以来一直是抑制市政和工业废水中微生物生长的有效消毒剂[32]。然而,如果经处理后的废水中含有自由氯,则可能对水生生物具有不良影响,引起一定的健康和安全问题。以往研究表明,使用Fenton处理含氯酚类的焦化废水时,自由氯会导致急性毒性增加[24]。高级氧化处理中自由氯的生成并导致处理后生物毒性升高需要进一步重视,这对高级氧化处理工艺的安全运行至关重要。在2.2催化臭氧化实验所有实验组中,当pH=3时生物毒性最高值最大,约为初始值的26倍。因此,将进一步探究pH=3时自由氯的生成机制。
-
氯酚在臭氧化中会脱氯,形成氯离子[32]。臭氧氧化氯离子过程中主要的氧化剂有两种:一是羟基自由基,羟基自由基在酸性条件下,与氯离子反应生成氯自由基,最终生成氯气;二是臭氧分子,臭氧分子与氯离子反应,生成次氯酸根,在酸性条件下,再生成次氯酸,次氯酸分解产生氯气;在碱性条件下,次氯酸根被氧化成亚氯酸根和氯酸根,反应方程式及速率常数如表2所示。但O3对氯离子的氧化作用一般可以忽略,因为反应速率常数小于10−3 L·mol−1·s−1[32]。为了确定单独催化臭氧化氯离子对自由氯生成的影响,在pH=3的条件下,对浓度为2、5、10、50、100 mg·L−1的氯离子溶液进行催化臭氧化实验。如图5(a)所示,实验过程中没有明显的自由氯的生成。因此,催化臭氧化氯酚中自由氯的生成,不是通过单独的催化臭氧化氯酚脱氯形成的氯离子。
-
如图5(b),为了探究自由氯生成中起作用的氧化剂,在催化臭氧氧化3-CP的体系中加入20 mL羟基自由基淬灭剂叔丁醇(TBA)后,发现反应过程中自由氯浓度明显升高。同时,臭氧氧化含氯离子的苯酚溶液实验结果与臭氧化3-CP类似,检测到明显的自由氯的生成;且加入TBA后,自由氯浓度也明显升高。如体系中不存在TBA,羟基自由基会与氯离子反应最终生成氯气,消耗一部分氯离子。在加入TBA后,羟基自由基被迅速反应,增加了直接与臭氧分子反应的氯离子,因而造成自由氯浓度增大。因此,在催化臭氧氧化3-CP的体系中,自由氯生成的主要氧化剂是臭氧分子。
-
为探究有机物共存对自由氯生成的影响,研究了不同有机物和氯离子共存时催化臭氧化中自由氯浓度的变化。其中氯离子浓度均为11 mg·L−1,有机物分别为乙醇(14.3 mg·L−1)、乙酸(18.7 mg·L−1)、富马酸(36.1 mg·L−1)、苯(24.3 mg·L−1)、苯酚(29.3 mg·L−1)和对苯二酚(34.3 mg·L−1)。
如图5(c)所示,小分子酸乙酸,不饱和酸富马酸,以及苯加氯离子的体系中没有检测到明显的自由氯。苯酚和苯二酚加氯离子的体系中检测到自由氯明显升高,且在同等摩尔浓度下,自由氯在苯二酚加氯离子的体系中浓度约为苯酚加氯离子体系中的两倍。在氯含量相同的情况下,苯酚加氯离子的催化臭氧臭氧化实验中,自由氯生成的最大值与3-氯酚催化臭氧化相当。因此,可以推测出催化臭氧化氯离子与一些酚类有机物的混合体系中会产生自由氯。
-
基于以上分析,推测催化臭氧氧化中自由氯生成机理,如图6所示。MnO2催化剂带负电,具有很强的吸附性能,能够吸附污染物3-CP和氧化剂臭氧分子。一部分被吸附的臭氧分子能够直接与污染物发生反应,生成有机中间产物及脱氯生成氯离子。另一部分臭氧分子可以在催化剂表面分解,生成高氧化性的羟基自由基。羟基自由基能够氧化氯离子,生成氯气,如表2(1)—(4)反应,由于反应体系连续曝气,氯气逸出,不会造成反应体系生物毒性的明显升高。
臭氧分子直接与氯离子反应,在pH<7.5时,主要生成HClO[36],如反应(5)和(6),但由于臭氧分子与氯离子反应常数仅为2.48×10−3 L∙mol−1∙s−1[32],因而不会造成自由氯的明显升高。根据2.3.1—2.3.3节,当酚类有机污染物及其中间产物与氯离子共存时,在催化剂MnO2的作用下,臭氧分子氧化污染物时共氧化氯离子,提高了反应(5)的反应速率,生成次氯酸,造成自由氯升高,因而生物毒性升高。如反应(7),生成的次氯酸与氯离子及氢离子反应生成氯气,在体系连续曝气的条件下,氯气逸出,进而使得生物毒性随着反应时间增加而下降。实验中,在尾气吸收装置碘化钾溶液中检测到氯离子的存在,间接证明了自由氯生成机制推测的正确性。
-
MnO2催化臭氧化3-氯酚时,生物毒性不随母体污染物和TOC浓度同比例降低而是出现了先升高后下降的现象,尤其是当pH=3时,生物毒性最高值约为初始值的26倍。通过生物毒性与常规指标的相关性分析发现,催化臭氧化3-CP过程中生物毒性的大小和自由氯浓度在pH=3—10时显著相关。催化臭氧化溶液中加入自由氯去除剂亚硫酸钠后,生物毒性几乎全部去除,最高点生物毒性去除率达到100%。故造成生物毒性升高的关键致毒因子是自由氯。在MnO2催化剂的作用下,3-氯酚发生脱氯作用生成氯离子。当与酚类有机污染物及其中间产物共存时,臭氧分子能够迅速共氧化氯离子,生成次氯酸,造成生物毒性升高。
催化臭氧化3-氯酚中生物毒性的变化
Study on the biological toxicity evolution during catalytic ozonation of 3-chlorophenol
-
摘要: 氯酚类化合物具有高毒性、难生物降解的特性,催化臭氧化是处理氯酚类废水的重要方法,但催化臭氧化部分氧化的特性常会导致生物毒性升高。为了识别催化臭氧化3-氯酚(3-CP)过程中的关键致毒因子,研究了不同pH下二氧化锰(MnO2)催化臭氧化降解3-CP过程中总体生物毒性的变化规律,探究了急性生物毒性与常规污染指标3-CP浓度、总有机碳浓度(TOC)以及自由氯(FAC)浓度的相关性。结果表明,MnO2催化臭氧化3-CP时,生物毒性不随母体污染物和TOC浓度同比例降低而是出现了先升高后下降的现象,尤其是当pH=3时,生物毒性最高值约为初始值的26倍。通过生物毒性与常规指标的相关性分析发现,处理过程中生物毒性的大小和自由氯浓度在pH=3—10时显著相关。催化臭氧化溶液中加入自由氯去除剂亚硫酸钠后,生物毒性几乎全部去除,最高点生物毒性去除率达到100%。由此推测,自由氯是MnO2催化臭氧化3-CP中生成的高毒性中间产物,在生物毒性演变中起了关键作用。进一步研究发现,体系中的自由氯是由于臭氧分子氧化形成的,它的生成可能与共存的酚类有机物有关。Abstract: Chlorophenols are highly toxic and difficult to biodegrade. Catalytic ozonation is an critical method to degrade chlorophenols in wastewater, but the partial oxidation of catalytic ozonation often lead to the increased biological toxicity. In order to identify the key toxic factors in the degradation of 3-chlorophenol (3-CP) by catalytic ozonation of manganese dioxide (MnO2), the acute toxicity evolution at different pH and its relationship with conventional pollution parameters including 3-CP concentration, total organic carbon (TOC) concentration and free active chlorine (FAC) concentration were studied. It was found that the acute toxicity of ozonated effluents increased firstly and then decreased during ozonation. The highest toxic unit was about 26 times of the initial value at pH=3. The biological toxicity and the free chlorine concentration during catalytic ozonation of 3-CP were significantly correlated at pH=3—10. After adding the free chlorine quencher sodium sulfite to the catalytic ozonated solution, the biological toxicity was almost completely removed, and the highest removal rate of biological toxicity reached 100%. Therefore, it is speculated that free chlorine is a highly toxic intermediate produced in MnO2-catalyzed ozonation of 3-CP and plays a key role in the evolution of biological toxicity. Further study found that the free chlorine in the system was formed by the oxidation of ozone molecules, and its generation might be related to the coexisted phenolic organics.
-
Key words:
- catalytic ozonation /
- chlorophenol degradation /
- biological toxicity /
- free chlorine.
-
氯代苯酚类化合物具有高毒性、难降解和生物累积性的特征,是一种常见的持久性有机污染物[1-3],且广泛存在于土壤、沉积物、地表和地下水中。为了降低对受纳水体的污染,氯酚废水的处理至关重要。目前对于氯酚类废水的处理方法主要有生物降解法[4-6]、物理吸附法[7-8]、高级氧化法[9-11]等。近年来,高级氧化技术以其氧化能力强、反应速度快、限制少和处理效率高等优点受到众多学者的青睐[12]。臭氧氧化法是目前最具代表性且最有效的高级氧化法之一。众所周知,臭氧氧化有机物主要的两种方式:一是臭氧分子与有机物的直接反应;二是臭氧分解产生的羟基自由基(OH·)与有机物的间接反应[13]。纳米二氧化锰作为催化剂能有效促进臭氧催化氧化过程中羟基自由基等活性物质的形成,使其对难降解有机污染物的去除更加迅速、彻底,是催化臭氧化中最常使用的催化剂之一[14-17]。
目前,很多学者已经对催化臭氧化的降解效率及降解动力学等[18-19]进行了研究,但鲜有研究其降解过程中的生物毒性变化及其关键的致毒因子。已有研究发现,由于臭氧的部分氧化特性,生成的大量降解中间产物的生物毒性可能大于母体污染物,造成母体污染物浓度降低而总体生物毒性升高的现象[20].
本研究以3-CP作为模型污染物,探究二氧化锰催化臭氧化中生物毒性的变化规律,并识别高毒性的中间产物。在此基础上,研究催化臭氧化体系处理各类有机化合物过程中自由氯浓度的变化,以揭示高毒性中间产物的产生机理。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 试剂
3-CP(分析纯)购自中国能源化工有限公司;一水合硫酸锰(MnSO4∙H2O,分析纯)和叔丁醇(t-BuOH,分析纯)由迈瑞尔化学技术有限公司提供;高锰酸钾(KMnO4,分析纯)购于上海斯信生物科技有限公司。配制模拟湖水所用药品(CaCl2、NaHCO3、KCl、CH3COONa和MgSO4)和亚硫酸钠(Na2SO3)等均购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司且均为分析纯。
1.2 纳米二氧化锰的制备
以高锰酸钾和一水合硫酸锰为原料,采用水化学沉积法制备了MnO2纳米粒子[21-22],其反应方程式为式(1)。取物质的量比为2:3的KMnO4和MnSO4∙H2O在80 ℃下分别溶解于125 mL去离子水中;将上述两溶液缓慢滴入装有250 mL去离子水的三口瓶中,并在油浴锅中恒温(80 ℃)缓慢搅拌反应2 h;将得到的黑色或棕色悬浮液自然冷却1 h,随后超声分散10 min;将制备好的悬浮液进行抽滤,去离子水洗涤,重复3次;将洗涤抽滤后的产物在80 ℃下干燥过夜至恒重,制得纳米二氧化锰样品。
2MnO−4+3Mn2++2H2O⟶5MnO2↓+4H+ (1) 1.3 实验装置
在有效容积为2 L的玻璃反应器中进行半静态催化臭氧氧化实验,实验装置如图1所示。实验以纯氧为气源在臭氧发生器(中国青岛国林环保科技有限公司,CF-G-3-10G)中产生臭氧,使用在线检测仪(中国朗科公司,LT-200B)测定气相中臭氧浓度。臭氧与氧气的混合物以0.5 L∙min−1的流速,通过固定在反应器底部的烧结曝气头分散到溶液中,臭氧尾气用KI溶液进行吸收。3-CP的初始浓度为40 mg∙L−1,臭氧浓度为28 mg∙L−1,MnO2投加量为1 g∙L−1,反应溶液pH值为1—12。不同pH的氯酚溶液用10 mmol∙L−1磷酸缓冲液配制,并使用1 mol∙L−1 H2SO4和1 mol∙L−1 NaOH调节至相应的pH。反应过程中以固定的时间间隔取样,在取样后,立即用氮气吹脱臭氧化水样[23],以消除溶解在溶液中未反应的臭氧,然后再进行下一步操作。
1.4 急性毒性的测定
使用灵敏度高的发光细菌青海弧菌(Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.NovQ67)[24],进行发光菌发光抑制实验测定急性生物毒性。具体的测试方法根据已有的研究方法[25-27]进行了适当的调整。
取-80 ℃条件下保存的Q67菌种(1 mL菌液)接入装有液体培养基的锥形瓶,于22 ℃条件下,振荡(180 r∙min−1)培养16—18 h。取100 μL菌液于96孔板测定发光强度(RLU),离心(200 r∙min−1,10 min)后收集菌体,用模拟湖水将菌体制成菌悬液。调整菌悬液的密度,使其发光强度在20万—60万RLU∙mL−1之间,待用。实验前,将水样pH值调至7,并用人工配制的模拟湖水将样品稀释成一系列的浓度梯度。样品的相对浓度以稀释倍数的倒数表示。将180 μL水样和20 μL调整后的菌液先后加入96孔板中,模拟湖水设置空白对照,每个浓度设置3个平行。振荡15 min后,用酶标仪(Ifinite-200,Tecan,瑞士)测定各孔的发光强度。使用公式(2)计算发光抑制率IR(%):
IR(%)=RLIBC−RLISRLIBC 式中,RLIBC表示空白对照组中发光细菌发出的相对发光强度,RLIS表示原始和稀释的样品中发光细菌发出的相对发光强度。
剂量-效应浓度曲线和最大半抑制浓度利用Origin软件的logistic模型来进行拟合和计算:
y=Bottom+Top - Bottom1+(IC50x)Slope (3) 式中,x表示稀释溶液中初始样品的百分比;y表示发光抑制率;Slope为斜率参数;IC50表示相对半数效应浓度。
根据公式(4)计算毒性单元:
TU=TOCIC50 (4) 式中:TU表示毒性单元;TOC表示总有机碳浓度。
1.5 分析测试
纳米二氧化锰的晶相结构采用XRD表征,仪器型号为D8ADVANCED,最大输出功率≥2.2 kV,最大管流80 mA,靶材为铜靶,扫描方式θ/θ或θ/2θ速,测量仪最小度数0.0001°。场发射扫描电镜(FESEM)(FEI Quanta 250F,美国)用于表征纳米二氧化锰的表面形貌。采用Zeta电位仪(Zeta Sizer 3000型,Malvern,英国)对纳米二氧化锰的表面零点电荷(pHzpc)进行测定。总有机碳分析仪(Multi N/C 3100,Elementar,德国)测定TOC浓度。自由氯由哈希余氯/总氯水质测试检测仪(PC-II,美国)测定。3-CP浓度通过配备有UV检测器(SPD-M20A,波长为180 nm至800 nm)的高效液相色谱仪(岛津LC-20A,日本)测得。在改良的C18柱(Lnertsil ODS-SP,250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm)上进行分析,3-CP的计算波长为275 nm;进样体积为10 μL,流动相为流速1 mL∙min−1的甲醇与水的混合液,比例为6.5:3.5,柱温保持在40 ℃,保留时间约为7.0 min。
2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 纳米二氧化锰的表征
图2(a)为催化剂样品的X射线衍射光谱谱图,催化剂在2θ为12.6°、18.2°、28.8°、37.5°、41.9°、49.8°、56.4°、60.2°和69.7°处分别表现出了对应α-MnO2的(110)、(200)、(310)、(211)、(301)、(411)、(600)、(521)和(541)晶面的特征衍射峰[28],与α-MnO2(JCPDS 44-0141)匹配度高。图2(b)为纳米二氧化锰的FESEM图,可以看出所制备的纳米二氧化锰有团簇现象,但主要为松散的纳米线状,其直径约50—100 nm,长约0.2—1 μm。
如图2(c)所示,通过表面的电势的测量,催化剂的pHzpc=1.73(R2=0.998),与参考文献接近[29]。所以pH<1.73时,催化剂表面带正电;当pH>1.73时,催化剂表面带负电。如图2(d),纳米MnO2对3-CP的吸附反应进行8 min(pH=1、3、5)时,对3-CP的吸附率分别为89%、15%和5%,即随着本体溶液pH的升高,纳米MnO2催化剂对3-CP的吸附能力逐渐减弱。而3-CP的pKa为8.8—9.1[30],酸性条件下以未解离的分子形式存在。因而静电作用是导致3-CP在纳米二氧化锰表面吸附的主要原因。
2.2 催化臭氧化实验
本实验在不同pH(pH=1、3、5、7、10、12)下,考察了催化臭氧氧化3-CP过程中急性毒性、3-CP浓度、TOC浓度和自由氯浓度的变化。实验结果如图3所示。
2.2.1 不同pH下纳米二氧化锰的催化降解效果
从图3(a)中可以看出,当pH=1时,在1 min内3-CP降解率接近100%,且TOC浓度迅速下降,随着反应时间推移,TOC含量保持在5 mg∙L−1左右。3-CP的迅速去除一方面是由于催化剂MnO2在pH=1时有较强吸附能力,另一方面,酸性条件下MnO2能够催化臭氧对3-CP的氧化降解,但并未被完全矿化,而是生成了其它中间产物。
如图3(b)—(e)所示,当pH=3—12时,3-CP浓度和TOC浓度逐渐降低。pH=3时,3-CP完全降解需要约32 min,随着pH逐渐增大,3-CP完全降解所需时间随之减少。一方面,随着pH的升高,臭氧分子更容易分解生成氧化性更强的羟基自由基[30]。另一方面,Poznyak和Vivero[31]指出,氯酚类物质在高pH下发生解离,生成的离子形式与氧化剂臭氧分子和羟基自由基的反应速率大于分子形式。
2.2.2 不同pH下催化降解过程中毒性变化
如图3(a)所示,当pH=1时,实验过程中生物毒性没有升高,这可能是因为3-CP的去除主要是MnO2的吸附作用,高毒性中间产物没有累积。如图3(b)—3(e)所示,当pH=3—10时,生物毒性都呈现先升高后下降的变化,且生物毒性的最高值随pH的增加呈下降的趋势。当pH=3时,生物毒性最高值约为初始值的26倍,而当pH=12时,生物毒性没有明显升高的现象发生。造成这一现象的原因可能随着pH的升高,臭氧分解生成的大量羟基自由基能够和高毒性中间产物迅速反应,减少了中间产物的累积。
为了确定体系中的MnO2催化剂是否是造成毒性升高的原因,在pH=3的情况下,研究了MnO2催化臭氧化3-CP、吸附3-CP以及臭氧化MnO2过程中的生物毒性变化。如图4所示,当反应体系中不通入臭氧或不加入污染物3-CP时,没有明显的生物毒性升高的现象发生。由此可以得出结论,在3-氯酚的催化臭氧氧化过程中,MnO2催化剂本身对生物毒性没有影响,仅作催化作用。
2.2.3 毒性与常规指标相关性分析
为了识别催化臭氧化中的关键致毒因子,监测了反应过程中自由氯的浓度变化,如图3(a)—(f),自由氯浓度的变化与生物毒性的变化一致,在pH=3—10时也呈现了先升高后下降的趋势。为了说明生物毒性与各指标的相关性,通过皮尔森相关系数法,对生物毒性和3-CP残留浓度、TOC浓度及自由氯浓度的相关性进行了分析,分析结果如表1所示。
表 1 急性毒性与各指标的相关性Table 1. Correlation between acute toxicity and each index常规指标Conventional index 皮尔森相关系数Pearson correlation coefficient (r) pH=1 pH=3 pH=5 pH=7 pH=10 pH=12 3-CP浓度 0.957** −0.344 0.118 0.232 0.175 0.822** TOC 0.963** 0.267 0.503 0.542 0.600* 0.924** 自由氯 −0.282 0.764** 0.872** 0.759** 0.969** 0.760** 注:* P<0.05;** P<0.01。 Note: * means P<0.05; ** means P<0.01. 从表1中可以看出,在生物毒性显著增加的4组(pH=3、5、7和10)中,生物毒性和自由氯浓度在0.01水平上显著相关,生物毒性与3-CP残留浓度及TOC基本不存在相关性。另外,已有研究发现,在相同浓度下,自由氯对发光细菌的毒性比3-CP大得多[32]。由此推断,催化臭氧化3-CP中生成的高毒性中间产物可能为自由氯。为了验证自由氯在体系生物毒性变化中的作用,取反应后的溶液1.2 mL,加入10 mmol∙L−1亚硫酸钠溶液36 μL,以研究自由氯去除后生物毒性的变化规律。如图3(a)—(f)所示,加入自由氯去除剂亚硫酸钠后,生物毒性显著下降。在pH=3—10时,生物毒性的去除率最高达到100%。但在pH=3时,加入亚硫酸钠后的水样生物毒性仍显著高于初始值。有研究表明[33],在臭氧氧化氯酚类物质中能够生成某些有机中间转化产物,如氯代邻二酚、氯代己二烯二酸等,它们可能是除无机高毒性中间产物自由氯外,会造成催化/臭氧化过程中生物毒性升高的物质。因此,MnO2催化臭氧化3-氯酚中生成的自由氯是急性毒性升高的关键致毒因子。
2.3 自由氯生成机制研究
自由氯作为一种强氧化剂,长期以来一直是抑制市政和工业废水中微生物生长的有效消毒剂[32]。然而,如果经处理后的废水中含有自由氯,则可能对水生生物具有不良影响,引起一定的健康和安全问题。以往研究表明,使用Fenton处理含氯酚类的焦化废水时,自由氯会导致急性毒性增加[24]。高级氧化处理中自由氯的生成并导致处理后生物毒性升高需要进一步重视,这对高级氧化处理工艺的安全运行至关重要。在2.2催化臭氧化实验所有实验组中,当pH=3时生物毒性最高值最大,约为初始值的26倍。因此,将进一步探究pH=3时自由氯的生成机制。
2.3.1 氯离子对自由氯生成的影响
氯酚在臭氧化中会脱氯,形成氯离子[32]。臭氧氧化氯离子过程中主要的氧化剂有两种:一是羟基自由基,羟基自由基在酸性条件下,与氯离子反应生成氯自由基,最终生成氯气;二是臭氧分子,臭氧分子与氯离子反应,生成次氯酸根,在酸性条件下,再生成次氯酸,次氯酸分解产生氯气;在碱性条件下,次氯酸根被氧化成亚氯酸根和氯酸根,反应方程式及速率常数如表2所示。但O3对氯离子的氧化作用一般可以忽略,因为反应速率常数小于10−3 L·mol−1·s−1[32]。为了确定单独催化臭氧化氯离子对自由氯生成的影响,在pH=3的条件下,对浓度为2、5、10、50、100 mg·L−1的氯离子溶液进行催化臭氧化实验。如图5(a)所示,实验过程中没有明显的自由氯的生成。因此,催化臭氧化氯酚中自由氯的生成,不是通过单独的催化臭氧化氯酚脱氯形成的氯离子。
表 2 催化臭氧化氯离子过程反应方程式及速率常数Table 2. Reaction equation and rate constant of catalytic ozonation of chloride ion编号Number 反应方程式Reaction equation 速率常数Rate constant (k) 参考文献Reference (1) OH⋅+Cl−⟶ClOH−⋅ k1=(4.2±0.2)×109 L·mol−1·s−1 [35] (2) ClOH−⋅+H+⟶Cl−+OH⋅ k2=(2.4±0.4)×1010 L·mol−1·s−1 [35] (3) Cl⋅+Cl−⟶Cl−2⋅ k3=(7.8±0.8)×109 L·mol−1·s−1 [35] (4) 2Cl−2⋅⟶Cl−+Cl2↑ k4=(3.5±2.7)×109 L·mol−1·s−1 [35] (5) O3+Cl−⟶ClO−+O2 k5=2.48×10−3 L·mol−1·s−1 [32] (6) ClO−+H+⟶HClO k6=5.0×1010 L·mol−1·s−1 [36] (7) HClO+H++Cl−⟶Cl2↑+H2O k7=2.14×104 L2·mol−2·s−1 [36] 注:反应(1)—(4)温度为297±2 K,反应(5)—(7)温度为298 K. Note: The temperature of reactions (1)—(4) is 297 ± 2 K, and reactions (5)—(7) is 298 K. 2.3.2 羟基自由基对自由氯生成的影响
如图5(b),为了探究自由氯生成中起作用的氧化剂,在催化臭氧氧化3-CP的体系中加入20 mL羟基自由基淬灭剂叔丁醇(TBA)后,发现反应过程中自由氯浓度明显升高。同时,臭氧氧化含氯离子的苯酚溶液实验结果与臭氧化3-CP类似,检测到明显的自由氯的生成;且加入TBA后,自由氯浓度也明显升高。如体系中不存在TBA,羟基自由基会与氯离子反应最终生成氯气,消耗一部分氯离子。在加入TBA后,羟基自由基被迅速反应,增加了直接与臭氧分子反应的氯离子,因而造成自由氯浓度增大。因此,在催化臭氧氧化3-CP的体系中,自由氯生成的主要氧化剂是臭氧分子。
2.3.3 共存有机物对自由氯生成的影响
为探究有机物共存对自由氯生成的影响,研究了不同有机物和氯离子共存时催化臭氧化中自由氯浓度的变化。其中氯离子浓度均为11 mg·L−1,有机物分别为乙醇(14.3 mg·L−1)、乙酸(18.7 mg·L−1)、富马酸(36.1 mg·L−1)、苯(24.3 mg·L−1)、苯酚(29.3 mg·L−1)和对苯二酚(34.3 mg·L−1)。
如图5(c)所示,小分子酸乙酸,不饱和酸富马酸,以及苯加氯离子的体系中没有检测到明显的自由氯。苯酚和苯二酚加氯离子的体系中检测到自由氯明显升高,且在同等摩尔浓度下,自由氯在苯二酚加氯离子的体系中浓度约为苯酚加氯离子体系中的两倍。在氯含量相同的情况下,苯酚加氯离子的催化臭氧臭氧化实验中,自由氯生成的最大值与3-氯酚催化臭氧化相当。因此,可以推测出催化臭氧化氯离子与一些酚类有机物的混合体系中会产生自由氯。
2.3.4 催化臭氧化中自由氯的生成机制
基于以上分析,推测催化臭氧氧化中自由氯生成机理,如图6所示。MnO2催化剂带负电,具有很强的吸附性能,能够吸附污染物3-CP和氧化剂臭氧分子。一部分被吸附的臭氧分子能够直接与污染物发生反应,生成有机中间产物及脱氯生成氯离子。另一部分臭氧分子可以在催化剂表面分解,生成高氧化性的羟基自由基。羟基自由基能够氧化氯离子,生成氯气,如表2(1)—(4)反应,由于反应体系连续曝气,氯气逸出,不会造成反应体系生物毒性的明显升高。
臭氧分子直接与氯离子反应,在pH<7.5时,主要生成HClO[36],如反应(5)和(6),但由于臭氧分子与氯离子反应常数仅为2.48×10−3 L∙mol−1∙s−1[32],因而不会造成自由氯的明显升高。根据2.3.1—2.3.3节,当酚类有机污染物及其中间产物与氯离子共存时,在催化剂MnO2的作用下,臭氧分子氧化污染物时共氧化氯离子,提高了反应(5)的反应速率,生成次氯酸,造成自由氯升高,因而生物毒性升高。如反应(7),生成的次氯酸与氯离子及氢离子反应生成氯气,在体系连续曝气的条件下,氯气逸出,进而使得生物毒性随着反应时间增加而下降。实验中,在尾气吸收装置碘化钾溶液中检测到氯离子的存在,间接证明了自由氯生成机制推测的正确性。
3. 结论(Conclusion)
MnO2催化臭氧化3-氯酚时,生物毒性不随母体污染物和TOC浓度同比例降低而是出现了先升高后下降的现象,尤其是当pH=3时,生物毒性最高值约为初始值的26倍。通过生物毒性与常规指标的相关性分析发现,催化臭氧化3-CP过程中生物毒性的大小和自由氯浓度在pH=3—10时显著相关。催化臭氧化溶液中加入自由氯去除剂亚硫酸钠后,生物毒性几乎全部去除,最高点生物毒性去除率达到100%。故造成生物毒性升高的关键致毒因子是自由氯。在MnO2催化剂的作用下,3-氯酚发生脱氯作用生成氯离子。当与酚类有机污染物及其中间产物共存时,臭氧分子能够迅速共氧化氯离子,生成次氯酸,造成生物毒性升高。
-
表 1 急性毒性与各指标的相关性
Table 1. Correlation between acute toxicity and each index
常规指标Conventional index 皮尔森相关系数Pearson correlation coefficient (r) pH=1 pH=3 pH=5 pH=7 pH=10 pH=12 3-CP浓度 0.957** −0.344 0.118 0.232 0.175 0.822** TOC 0.963** 0.267 0.503 0.542 0.600* 0.924** 自由氯 −0.282 0.764** 0.872** 0.759** 0.969** 0.760** 注:* P<0.05;** P<0.01。 Note: * means P<0.05; ** means P<0.01. 表 2 催化臭氧化氯离子过程反应方程式及速率常数
Table 2. Reaction equation and rate constant of catalytic ozonation of chloride ion
编号Number 反应方程式Reaction equation 速率常数Rate constant (k) 参考文献Reference (1) OH⋅+Cl−⟶ClOH−⋅ k1=(4.2±0.2)×109 L·mol−1·s−1 [35] (2) ClOH−⋅+H+⟶Cl−+OH⋅ k2=(2.4±0.4)×1010 L·mol−1·s−1 [35] (3) Cl⋅+Cl−⟶Cl−2⋅ k3=(7.8±0.8)×109 L·mol−1·s−1 [35] (4) 2Cl−2⋅⟶Cl−+Cl2↑ k4=(3.5±2.7)×109 L·mol−1·s−1 [35] (5) O3+Cl−⟶ClO−+O2 k5=2.48×10−3 L·mol−1·s−1 [32] (6) ClO−+H+⟶HClO k6=5.0×1010 L·mol−1·s−1 [36] (7) HClO+H++Cl−⟶Cl2↑+H2O k7=2.14×104 L2·mol−2·s−1 [36] 注:反应(1)—(4)温度为297±2 K,反应(5)—(7)温度为298 K. Note: The temperature of reactions (1)—(4) is 297 ± 2 K, and reactions (5)—(7) is 298 K. -
[1] PIETER V A, ROB V D B, DEGREVE J, et al. A pilot-scale coupling of ozonation and biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol-containing wastewater: The effect of biomass acclimation towards chlorophenol and intermediate ozonation products [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 161: 1432-1441. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.124 [2] AKHARAME M O, FATOKI O S, OPEOLU B O, et al. Comparative time-based intermediates study of ozone oxidation of 4-chloro- and 4-nitrophenols followed by LCMS-TOF [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 2019, 55(4): 385-401. [3] 蔡应康, 刘茂春, 李卫星, 等. 臭氧催化氧化降解2,4,6-三氯苯酚研究 [J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2018, 32(3): 725-730. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2018.03.030 CAI Y K, LIU M C, LI W X, et al. Study on catalytic ozonation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol [J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2018, 32(3): 725-730(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2018.03.030
[4] CARUCCI A, MILIA S, CAPPAI G, et al. A direct comparison amongst different technologies (aerobic granular sludge, SBR and MBR) for the treatment of wastewater contaminated by 4-chlorophenol [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 177(1-3): 119-1125. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.004 [5] WANG Y K, PAN X R, SHENG G P, et al. Development of an energy-saving anaerobic hybrid membrane bioreactors for 2-chlorophenol-contained wastewater treatment [J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 140: 79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.101 [6] 罗艳, 何仕均, 王建龙. 4-氯酚对厌氧颗粒污泥产甲烷活性的影响研究 [J]. 西南给排水, 2012, 34(2): 36-39. LUO Y, HE S J, WANG J L. Effect of 4-monochlorophenol on methanogenic activity of anaerobic granular sludge [J]. Southwest Water & Wastewater, 2012, 34(2): 36-39(in Chinese).
[7] RONG Y, HAN R. Adsorption of p-chlorophenol and p-nitrophenol in single and binary systems from solution using magnetic activated carbon [J]. The Korean journal of chemical engineering, 2019, 36(6): 942-953. doi: 10.1007/s11814-019-0267-1 [8] 钟少芬, 莫健文, 李阳苹, 等. 粉末活性炭对水中氯酚的吸附 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(6): 2927-2932. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201501023 ZHONG S F, MO J W, LI Y P, et al. Adsorption of chlorophenols in water by powdered activated carbon [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(6): 2927-2932(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201501023
[9] 徐蕾. 高级氧化方法降解2,4,6-三氯苯酚的研究进展 [J]. 资源节约与环保, 2015(5): 76-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2015.05.070 XU L. Advances in degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by advanced oxidation methods [J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection, 2015(5): 76-77(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2251.2015.05.070
[10] NAWROCKI J, KASPRZYK-HORDERN B. The efficiency and mechanisms of catalytic ozonation [J]. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2010, 99(1-2): 27-42. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.06.033 [11] CHEN C, HAN C, WANG P, et al. Investigation on titanium silicalite ETS-4 catalyzed ozonation for chemicals in wastewater, exemplified with 4-chlorophenol [J]. Clean-Soil Air Water, 2016, 44(12): 1644-1651. doi: 10.1002/clen.201500282 [12] 雷利荣. 化学浆制浆废水污染特性及催化臭氧深度处理研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012. LEI L R. Pollution characteristics of chemical pulp effluent and its tertiary treatment with catalytic ozonation[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2012 (in Chinese).
[13] LIOTTA L F, GRUTTADAURIA M, DI C G, et al. Heterogeneous catalytic degradation of phenolic substrates: catalysts activity [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(2): 588-606. [14] IKHLAQ A, BROWN D R, KASPRZYK H. Mechanisms of catalytic ozonation: An investigation into superoxide ion radical and hydrogen peroxide formation during catalytic ozonation on alumina and zeolites in water [J]. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2013, 129: 437-449. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.09.038 [15] 童少平, 杜桂荣, 张鉴清. 液相中MnO2催化臭氧化降解磺基水杨酸 [J]. 环境化学, 2003, 22(5): 454-458. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2003.05.008 TONG S P, DU G R, ZHANG J Q. Performances of different types of MnO2 catalytic ozonation of sulfosalicylic acid in aqueous solution [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2003, 22(5): 454-458(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2003.05.008
[16] CHEN Y H, HSIEH D C, SHANG N C. Efficient mineralization of dimethyl phthalate by catalytic ozonation using TiO2/Al2O3 catalyst [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192(3): 1017-1025. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.005 [17] LIU B, LI A M, XIA M F, et al. Preparation of manganese oxide supported on activated carbon and its application in catalytic ozonation of 4-chlorophenol [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 538-541: 2285-2288. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.538-541.2285 [18] 冯冬梅, 高乃云, 王希诚, 等. 臭氧(O3)氧化降解2,4,6-三氯酚的动力学研究 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(5): 2130-2135. FENG D M, GAO N Y, WANG X C, et al. Kinetics of 2,4,6-TCP degradation by ozonation [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(5): 2130-2135(in Chinese).
[19] 金鑫, 许建军, 解明媛, 等. 五氯酚的臭氧催化氧化特性 [J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(4): 572-576. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.04.006 JING X, XU J J, XIE M Y, et al. The characteristics of pentachlorophenol decomposition by catalytic ozonation [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(4): 572-576(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.04.006
[20] MA D H, LIU C, ZHU X B, et al. Acute toxicity and chemical evaluation of coking wastewater under biological and advanced physicochemical treatment processes [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(18): 18343-18352. [21] 王春雨. 纳米二氧化锰的表面形貌调控及其催化氧化性能研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2016. WANG C Y. Study on surface morphology control and catalytic oxidation performance of manganese dioxide[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2016 (in Chinese).
[22] 刘世斌, 周娴娴, 池永庆, 等. 纳米二氧化锰的制备及其形貌调控 [J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2011, 42(4): 369-374. LIU S B, ZHOU X X, CHI Y Q, et al. Preparation and structure regulation of nano-manganese dioxide [J]. Journal of Taiyuan university of technology, 2011, 42(4): 369-374(in Chinese).
[23] ZHAO Y, YU G, CHEN S Y, et al. Ozonation of antidepressant fluoxetine and its metabolite product norfluoxetine: Kinetics, intermediates and toxicity [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 316: 951-963. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.032 [24] YE Z F, ZHAO Q L, ZHANG M H, et al. Acute toxicity evaluation of explosive wastewater by bacterial bioluminescence assays using a freshwater luminescent bacterium, Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. Nov [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(2/3): 1351-1354. [25] MA D H, WEI J J, ZHANG H B, et al. Acute toxicity evolution during ozonation of mono-chlorophenols and initial identification of highly toxic intermediates [J]. Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2019, 21(9): 1509-1518. [26] 张松, 李菲菲, 史晨, 等. 生活污水的臭氧深度处理及其急性毒性 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(6): 3468-3474. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201603108 ZHANG S, LI F F, SHI C, et al. Ozonation of domestic wastewater and acute toxicity [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(6): 3468-3474(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201603108
[27] SHANG N C, YU Y H, MA H W, et al. Toxicity measurements in aqueous solution during ozonation of mono-chlorophenols [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2006, 78(3): 216-222. [28] 李经纬, 宋灿, 刘善堂. 不同晶型二氧化锰纳米棒催化氧化氯苯性能的研究 [J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70(22): 2347-2352. doi: 10.6023/A12080562 LI J W, SONG C, LIU S T. Catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over MnO2 nanorods with different phase structures [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(22): 2347-2352(in Chinese). doi: 10.6023/A12080562
[29] 陈高, 赵玲, 董元华. 二氧化锰氧化降解金霉素的动力学研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(9): 2773-2778. CHEN G, ZHAO L, DONG Y H. Oxidative kinetics of chlortetracycline by manganese dioxide [J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(9): 2773-2778(in Chinese).
[30] PIETER V A, ROB V D B, DEGGREVE J, et al. The effect of ozonation on the toxicity and biodegradability of 2, 4-dichlorophenol-containing wastewater [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 280: 728-736. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.019 [31] POZNYAK T, VIVERO J. Degradation of aqueous phenol and chlorinated phenols by ozone [J]. Ozone:Science & Engineering, 2005, 27(6): 447-458. [32] LEVANOV A V, ANTIPENKO E E, LUNIN V V. Primary stage of the reaction between ozone and chloride ions in aqueous solution: Oxidation of chloride ions with ozone through the mechanism of oxygen atom transfer [J]. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2012, 86(3): 519-522. doi: 10.1134/S0036024412030193 [33] SHANG N C, YU Y H, MA H W. Variation of toxicity during the ozonation of monochlorophenolic solutions [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 2002, 37(2): 261-271. [34] MACEDO L P R, DORNELAS A S P, VIEIRA M M, et al. Comparative ecotoxicological evaluation of peracetic acid and the active chlorine of calcium hypochlorite: Use of Dugesia tigrina as a bioindicator of environmental pollution [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 233: 273-281. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.286 [35] YU X Y. Critical evaluation of rate constants and equilibrium constants of hydrogen peroxide photolysis in acidic aqueous solutions containing chloride ions [J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 2004, 33(3): 747-763. doi: 10.1063/1.1695414 [36] LEVANOV A V, ISAYKINA O Y, AMIROVA N K, et al. Photochemical oxidation of chloride ion by ozone in acid aqueous solution [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(21): 16554-16569. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4832-9 -





 下载:
下载: