非抑制型离子色谱串联质谱法同时测定饮用水中卤乙酸和卤氧化物
Simultaneous determination of haloacetic acids and oxyhalides in drinking water by non-suppressed ion chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
-
摘要: 本文建立了一种基于非离子抑制型离子色谱-电喷雾离子化-串联质谱(IC-ESI-MS/MS)的卤乙酸和卤氧化物分析方法,解决了当前卤乙酸检测预处理过程复杂和卤氧化物检测灵敏度低的问题,本方法中仅需的样品前处理为0.45 μm滤膜过滤.样品采用Dionex IonPac AS16色谱柱进行分离,使用甲胺水溶液和乙腈作为混合流动相.采用电喷雾负离子(ESI-)模式,多反应监测模式(MRM)进行质谱分析.本文系统研究了甲胺水溶液的浓度及比例对分析物保留时间和响应值的影响,确定最优流动相条件为0.7 mol·L-1甲胺水溶液/乙腈,体积比30/70,等度洗脱.在此条件下,9种卤乙酸和3种卤氧化物在0.5-100 μg·L-1范围内均具有很好的线性关系(r>0.995),检出限为0.052-0.270 μg·L-1,检测下限为0.208-1.080 μg·L-1;在自来水中加标回收率为74.9%-114.9%,相对标准偏差为1.2%-8.7%.运用本方法对模拟加氯消毒水样及无锡市的自来水进行检测,两次测量结果偏差小,二氯乙酸和三氯乙酸检出浓度最高.本方法灵敏快速、操作简便,为国家标准《生活饮用水标准检验方法》(GB/T5750)中二氯乙酸、三氯乙酸、氯酸盐和溴酸盐等指标的检测方法修订提供了技术支撑.Abstract: An determination method of haloacetic acids (HAAs) and oxyhalides using non-suppressed ion chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (IC-ESI-MS/MS) was established to solve the problems of complex pretreatment for HAAs detection and the low sensitivity for oxyhalides detection. In this method, the only pretreatment was the process of 0.45 μm membrane filtration. The samples were separated by Dionex IonPac AS16 column, and aqueous methylamine solution and acetonitrile were used as the mixed mobile phases. Negative electrospray ionization (ESI-) mode and multiple reaction monitoring mode (MRM) were used for mass spectrometry analysis. The effects of concentration and proportion of aqueous methylamine solution on retention time and response value of the analytes were studied, and the optimal mobile phase condition was determined to be 0.7 mol·L-1 aqueous methylamine solution/acetonitrile, with a volume ratio of 30/70 and elution in equal degree. Under the optimal condition, all of the 12 analytes had good linear relationships(r>0.995)in the range of 0.5-100 μg·L-1, with the detection limits of 0.052-0.270 μg·L-1, the minimum quantitative detection limits of 0.208-1.080 μg·L-1. The recoveries of the spiked 12 analytes in tap water were 74.9%-114.9% with relative standard deviations ranging from 1.2% to 9.0%. This method was applied to analyze the simulated chlorinated water and tap water from Wuxi. The deviation of the duplicate analyses was small, and the concentrations of dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid were the highest. This method is sensitive, rapid and easy to operate, which provides technical support for the revision of the detection methods of dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, chlorate and bromate in the "Standard Examination Method for Drinking Water" (GB/T5750).
-
Key words:
- haloacetic acids /
- oxyhalides /
- disinfection by-products /
- IC-MS/MS
-
近年来,我国城市近地面大气臭氧(ozone,O3)污染形势严峻,尤其是在夏季,臭氧已成为导致部分城市空气质量超标的首要污染因子。挥发性有机物(volatile organic compounds,VOCs)和氮氧化物(nitrogen oxides,NOx)的光化学反应是对流层臭氧的主要来源[1-2]。NOx主要来自于发电厂、燃煤锅炉、机动车等排放过程,经过严格治理,近年来全国的NOx 污染状况明显转好,据2015—2019年《中国生态环境状况公报》报道,全国337个城市NO2超标天数比例从2015的1.6%降至2019年的0.6%,但是臭氧污染问题仍然突出,2019年全国337个城市O3-8 h年均浓度为148 μg·m−3,较2015年上升10.45%[3]。VOCs作为臭氧和二次有机气溶胶(secondary organic aerosol,SOA)生成的重要前体物被广泛关注。VOCs来源十分广泛,主要分为天然源和人为源两大类。天然源主要有植物排放,人为源主要有燃料燃烧、溶剂使用、机动车尾气排放、汽油等液体燃料挥发、工业排放等[4]。VOCs成分复杂,包含数百种组分,每种组分具有不同的光化学反应活性,因此,研究挥发性有机物污染特征及其光化学反应特性对臭氧和雾霾污染治理具有十分重要的指导意义。
目前,挥发性有机物的研究主要集中在珠三角、长三角、京津冀等经济高速发展的地区,而西部地区的相关研究相对较少。宁夏回族自治区因其具有丰富的煤炭等资源,成为西部大开发中的重要发展对象,西部大开发以来,宁夏的工业化进程不断加快,能源、新型煤化工、新材料等产业发展迅速,与此同时,光化学污染问题在宁夏日益突出,2015—2019年《宁夏生态环境公报》显示,2019年全区五地市PM10、PM2.5年均浓度较2015年分别下降了24.53%、31.91%,而2019年O3-8 h年均浓度较2015年上升了5.19%(142 μg·m−3),可见,O3正成为宁夏的主要大气污染物之一[5]。为建立协同联动的发展机制,宁夏回族自治区预计2022年前打造完成以银川为核心、辐射带动石嘴山、吴忠、宁东基地协同发展的银川都市圈,银川都市圈的臭氧污染成为大气污染治理的重要对象。
本研究在银川都市圈内6个典型站点开展了挥发性有机物的观测,分析了采样期间挥发性有机物的污染特征、臭氧生成潜势、二次有机气溶胶生成潜势及VOCs潜在来源等,以期为银川都市圈臭氧和雾霾污染治理提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 样品采集
本研究于2019年6月12日—17日、8月4日—9日在银川都市圈内对环境空气中挥发性有机物进行了观测。采样点分别位于银川都市圈内的灵武市、永宁县、银川市、大武口区、平罗县和青铜峡市(图1),涉及工业区、商业/交通/居民混合区和工业/交通混合区(表1)。宁东和永宁采样点位于工业区,大气污染源复杂。宁东采样点位于宁东煤化工基地的某烯烃公司内,周围分布有煤制油、煤制烯烃、煤制乙二醇及精细化加工等化工企业。永宁采样点位于望远镇工业园的某药业公司内,周围集聚有家具厂、彩钢厂等工厂。上海东路和大武口采样点位于商业/交通/居民混合区,两个采样点周边都集中有居民区和商场,人口密度及交通流量较大。平罗和青铜峡采样点位于工业/交通混合区,二者周围均分布有高速公路及少数工厂,平罗采样点位于某精细化工有限公司内,青铜峡采样点位于新材料基地内。样品采集按照美国国家环境保护局(USEPA)推荐的标准方法(TO-14A[6]和 TO-15[7]),利用苏玛罐采集环境空气样品。采样前用自动清罐仪(Entech 3100;Entech Instrument Inc,California, USA)对苏玛罐进行清洗,采样频率为全天24 h,采样高度距地面1.5 m左右。表2给出了观测期间2019年6、8月份各采样点温度、湿度和主导风向的统计结果,6、8月份的平均温度分别为26.6℃、28.8℃,平均湿度分别为37.9%、40.7%,各采样点6月份主导风向以东南风、西北风和西北转北风为主,8月份以西北风为主。除少数几天有阵雨外,观测期间各采样点多为晴朗或多云天气。
表 1 采样点信息汇总Table 1. Summary of sampling information功能区Functional area 采样点Sampling points 经纬度Latitude and longitude 样本量Sample size 工业区Industrial areas 宁东 106.62 °E,38.20 °N 12 永宁 106.26 °E,38.37 °N 12 商业/交通/居民混合区Commercial, traffic, and residential mixed areas 上海东路 106.29 °E,38.50 °N 12 大武口 106.38 °E,39.01 °N 12 工业/交通混合区Industrial and traffic mixed areas 平罗 106.50 °E,38.96 °N 12 青铜峡 105.89 °E,37.91 °N 12 表 2 观测期间各采样点气象条件Table 2. Meteorological conditions at each sampling point during the observation period采样点Sampling points 项目Project 2019年6月 2019年8月 最小值Minimum value 最大值Maximum value 平均值Average value 最小值Minimum value 最大值Maximum value 平均值Average value 宁东Ningdong 温度/℃ 19 31 26.5 19 32 27.17 相对湿度/% 24 70 40 33 67 44.5 主导风向 东南风 西北风 永宁Yongning 温度/℃ 19 33 27.67 — — — 相对湿度/% 26 81 44.33 — — — 主导风向 东南风 西北风 上海东路Shanghai East Road 温度/℃ 26 32 28.67 25 34 29.5 相对湿度/% 16 42 30.83 18 59 34 主导风向 东南风 西北风 大武口Dawukou 温度/℃ 20 25 22.33 — — — 相对湿度/% 17 33 25.5 — — — 主导风向 西北风 西北风 平罗Pingluo 温度/℃ 18 31 26.83 23 31 28.83 相对湿度/% 28 80 44.33 31 69 46.83 主导风向 西北转北风 西北风 青铜峡Qingtongxia 温度/℃ 22 32 27 21 33 29.5 相对湿度/% 32 62 42.67 21 64 37.5 主导风向 西北转北风 西北风 注:“—”代表数据缺失.means data is missing. 1.2 分析方法
本研究使用搭载微板流控技术(Dean-Switch)的GC-MS/FID分析样品[8]。环境空气样品通过预浓缩仪(Entech7200;Entech Instrument Inc, California, USA)进行富集浓缩。样品依次进入三级冷阱的M1、M2、M3模块,目标化合物在此过程中被富集浓缩,同时,水和二氧化碳也被去除[9]。浓缩后的样品被载气带入气相色谱系统(Trace 1300; Thermo fisher, USA)进行分离和检测。气相色谱内选用 TG-1MS 和 TG-BOND Alumina(Na2SO4)色谱柱分别对高碳(C6—C12)VOCs和低碳的(C2—C6)VOCs进行一级和二级分离,随后低碳组分(乙烷、乙烯、丙烷、丙烯和乙炔)载入FID检测并用外标法定量,高碳组分(碳数较高的烷烃、烯烃和芳香烃)载入MS检测并用内标法定量。本研究选取在光化学反应中活性较高的56种挥发性有机物(PAMS组分)为目标化合物。
1.3 质量控制与质量保证
本研究使用PAMS标准气体购自美国Linde Electronics and Specialty Gases公司。本方法按照5个浓度水平的混合标准气体(不含0点)建立标准曲线,标准曲线线性回归的决定系数R2均大于99.99%,所有目标化合物具有良好的重现性(相对标准偏差均小于10%)。利用信噪比 S/N=10为方法检出限,目标化合物的检出限范围为7
× × 2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 观测期间PM10、PM2.5 、O3、NO2浓度水平
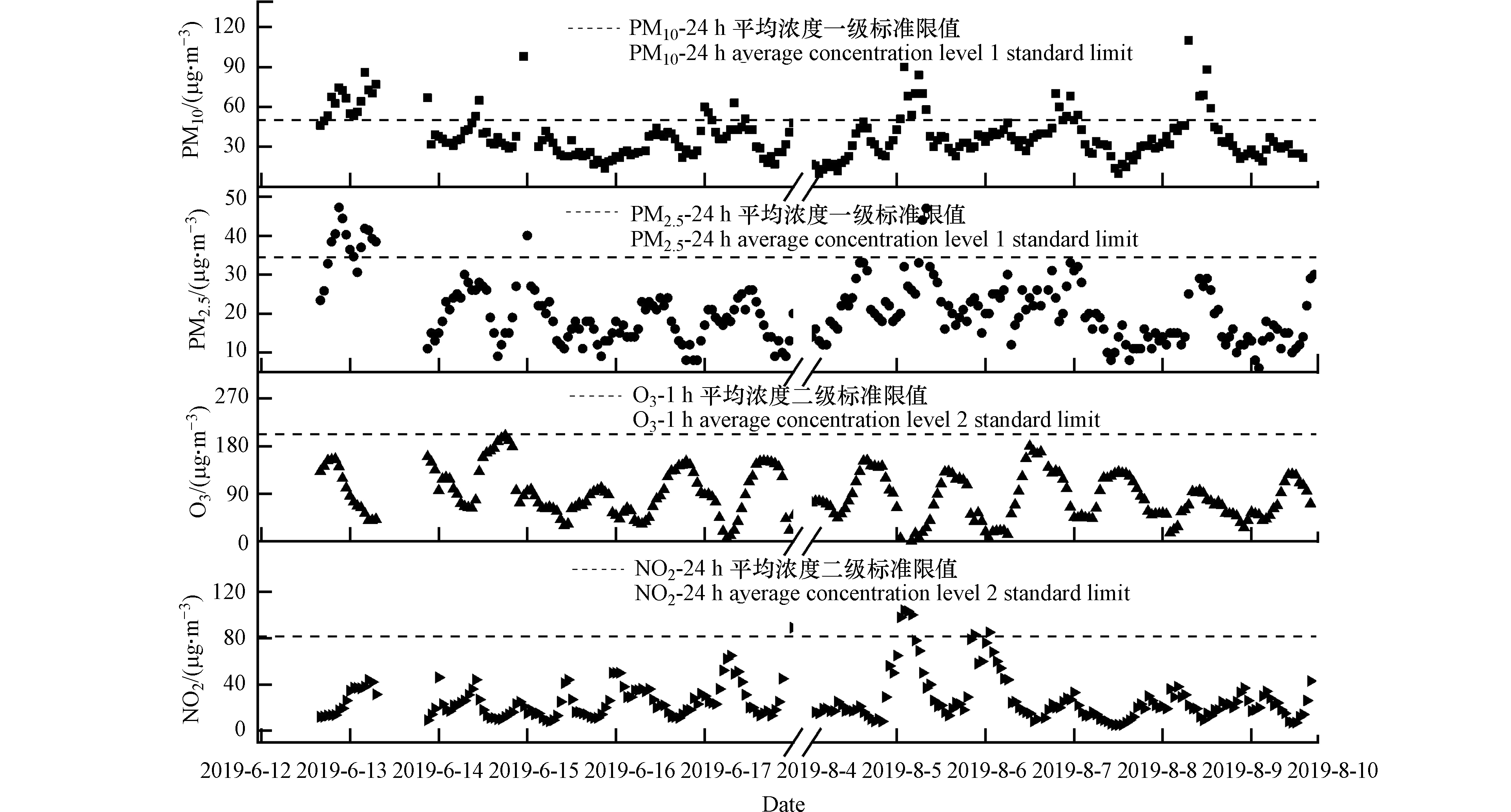
观测期间银川上海东路环境空气中PM10、PM2.5、O3、NO2浓度水平见图2。O3和NO2的浓度分别为(5.0—200.0)μg·m−3和(5.0—123.0)μg·m−3,O3的浓度呈现出昼高夜低的日变化特征,其峰值出现在15:00—18:00;而NO2在日间浓度较低,呈现出与O3相反的日变化趋势,这可能是随着日出后光照强度的增加,前夜积累在对流层的NO2发生光解,O3浓度开始升高,并在后续的光化学过程发展中达到峰值,随着光照强度减弱,由NO2光解生成O3的速率逐渐降低,O3与NO的反应导致O3浓度逐渐下降,NO2浓度在前半夜的升高。此外,夜间NO2浓度还可能与较低的混合层高度有关,NO2在低层大气中积累,随着日出后边界层的抬升,NO2等人为排放污染物的浓度得到稀释。观测期间,PM10和PM2.5的浓度分别为(10.0—110.0)μg·m−3和(6.0—47.2)μg·m−3,根据环保部《环境空气质量标准》(GB3095—2012),PM10和PM2.5的浓度均未超过污染物浓度限值二级标准。在8月8日的12:00左右PM10和PM2.5出现浓度峰值时,O3浓度峰值较其他天数略有降低,这可能是因为颗粒物浓度较高时,大气中光化学反应速率降低,不利于O3生成。
2.2 浓度水平与组成特征
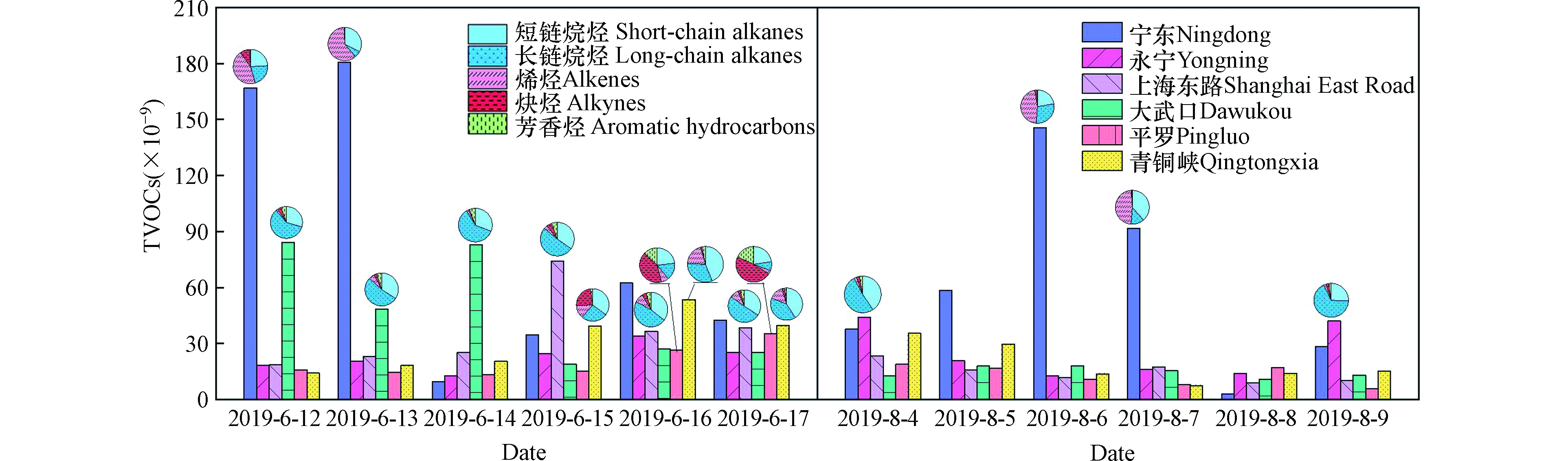
本研究根据VOCs各组分的分子结构及其与OH自由基(·OH)的反应活性,将测得的56种VOCs组分分成5个亚组,分别为短链烷烃(C ≤ 4)、长链烷烃(C > 4)、烯烃、炔烃和芳香烃。其中,短链烷烃、炔烃是低反应性烃,长链烷烃、烯烃和芳香烃(苯除外)是活性烃[10]。图3为观测期间各采样点环境空气中56种挥发性有机物总浓度水平(total volatile organic compounds,TVOCs),以及各采样点TVOCs浓度超过整个观测期间平均浓度水平时挥发性有机物的分类组成情况。各采样点TVOCs平均浓度分别为:宁东采样点(89.14
× × × × × × × × × × 而同为工业区的永宁采样点,其VOCs总浓度水平不高,表明不同类型工厂排放VOCs的强度存在一定差异。位于商业/交通/居民混合区的上海东路和大武口采样点的VOCs整体浓度水平相当,两个采样点TVOCs浓度在个别天内存在高值(例如6月12日—14日的大武口采样点和6月15日的上海东路采样点),其中,长链烷烃和短链烷烃的贡献最为明显,这可能是与某些非固定源异常排放有关,如机动车尾气排放等。位于工业/交通混合区的平罗和青铜峡采样点的TVOCs浓度之间存在一定差异,平罗采样点TVOCs浓度处于较低水平,而青铜峡采样点TVOCs浓度相对较高,且浓度较高时不同亚组VOCs的浓度占比差异明显,如6月15日炔烃的占比明显增大,这表明青铜峡采样点周围可能存在多个不同的VOCs排放源。
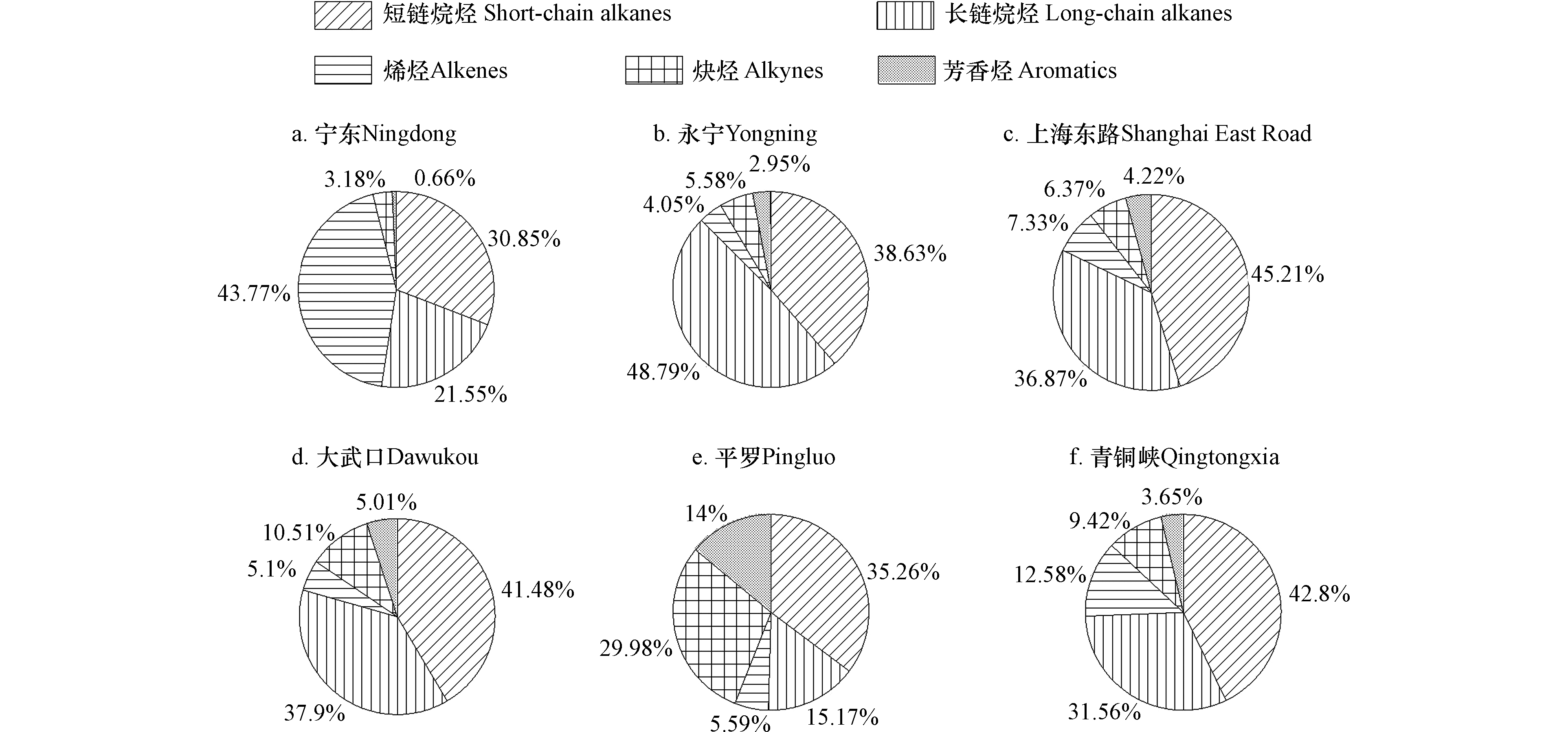
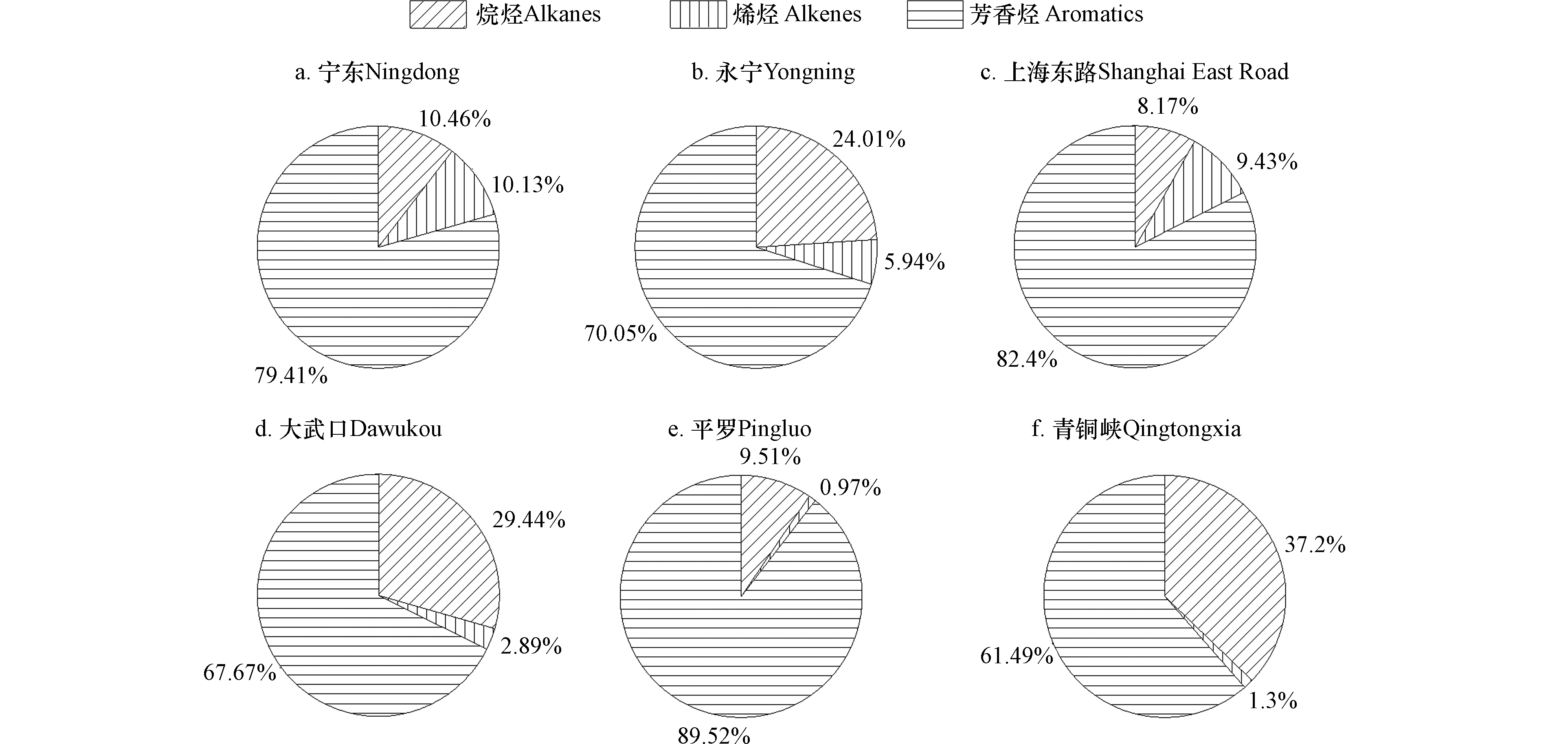
观测期间各采样点挥发性有机物分类组成如图4所示。短链烷烃、长链烷烃在6个采样点环境空气中均有较高占比,分别占TVOCs浓度的30.85%—45.21%、15.17%—48.79%;烯烃在宁东采样点的浓度占比最高,为43.77%;炔烃、芳香烃在平罗采样点的浓度占比最高,分别为29.98%和14.00%;其他采样点的炔烃和芳香烃的浓度占比均不高。
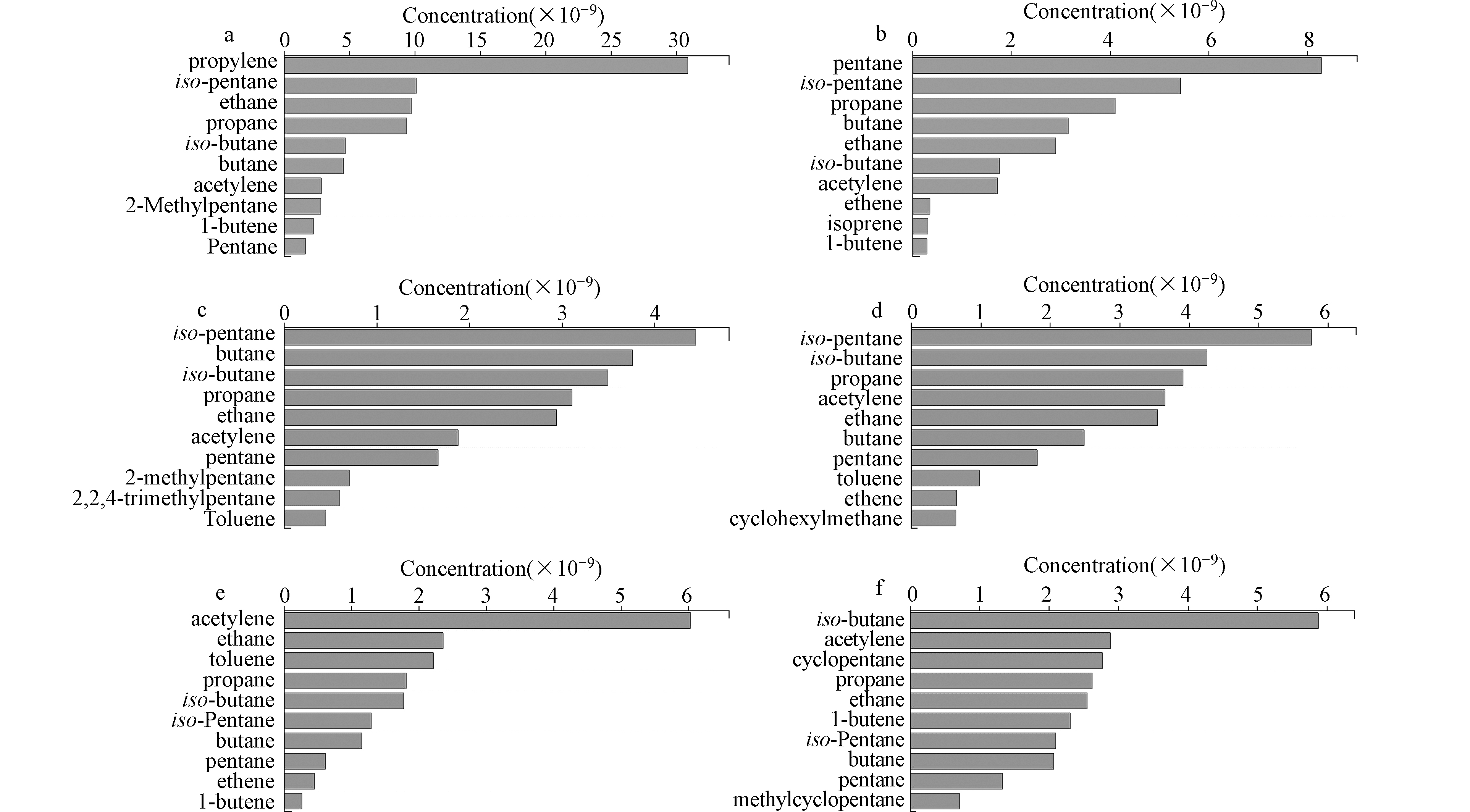
不同种类VOCs组成反映了各采样点VOCs来源具有差异,本研究通过各采样点浓度最大的前十位VOCs组分的对比(图5),进一步分析了各采样点VOCs可能来源及来源间差异。在6个采样点中,烷烃(包括短链烷烃和长链烷烃)总占比最大(50.43%—87.42%),其中,乙烷、丙烷、丁烷、异丁烷以及异戊烷在6个采样点均处于高浓度水平,乙烷、丙烷、丁烷和异丁烷是液化石油气(liquefied petroleum gas,LPG)助动车、汽油车和柴油车的主要排放物[11-12],异戊烷是汽油挥发的标志物[13],这反映出各采样点环境空气中的VOCs可能均受到来自机动车尾气排放的影响。宁东采样点烯烃占TVOCs的比例最大(43.77%),其中,丙烯浓度最为突出,平均浓度可以达到30.87
× 2.3 特征比值
不同采样点的污染源不同,并且不同污染源排放的VOCs特征组分间有一定差异,因此VOCs特征组分间的比值可初步判断VOCs的潜在来源。有研究发现,苯/甲苯(benzene/toluene, B/T)的比值在0.5左右时,机动车尾气排放为环境空气中VOCs主要来源[15];当B/T比值大于1时,煤或者生物质燃烧为主要贡献源[16];当B/T比值小于0.3时,工业排放的贡献较大[17]。本研究各采样点环境空气中苯/甲苯比值的箱线图如图6所示,可见永宁、上海东路和大武口采样点B/T比值的平均值都在0.5左右,表明这3个采样点环境空气中VOCs受机动车尾气排放的影响较大;平罗和青铜峡采样点的平均B/T比值分别为0.124、0.248,则这两个采样点VOCs主要受周围工业源排放的影响;宁东采样点平均B/T比值在1.5左右,表明宁东采样点环境空气中VOCs受到多种源的影响,其中煤或生物质燃烧的贡献较大,这可能与宁东采样点所处的煤化工基地有关。
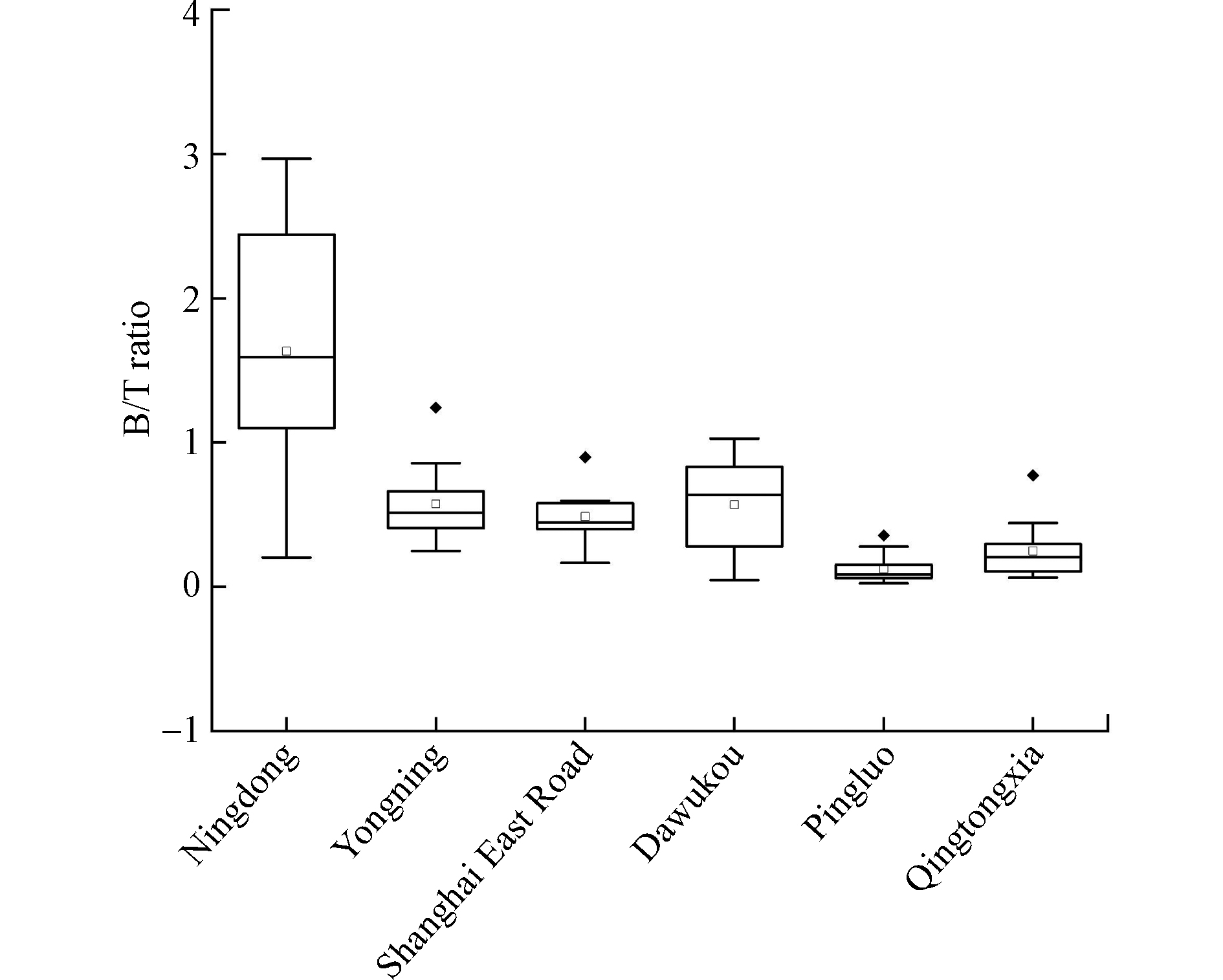 图 6 各采样点苯/甲苯比值箱线图Figure 6. Box and whisker plots of benzene/toluene ratio at each sampling site.框中实线代表中值浓度,框底部和顶部描绘了第25个(第一个四分位数)和第75个(第三个四分位数)百分位,空心点表示平均值,实心点表示异常值,晶须的末端分别对应在Q1和Q3的IQR的1.5倍之内的最低和最高数据The solid line in the box represents the median concentration. The bottom and top of the box depict the 25th (the first four Quantile) and the 75th (third quartile) percentile. The hollow dots represent the average value, and the solid dots represent the outliers. The ends of the whiskers correspond to the lowest and highest data still within 1.5 times the IQR of Q1 and Q3, respectively.
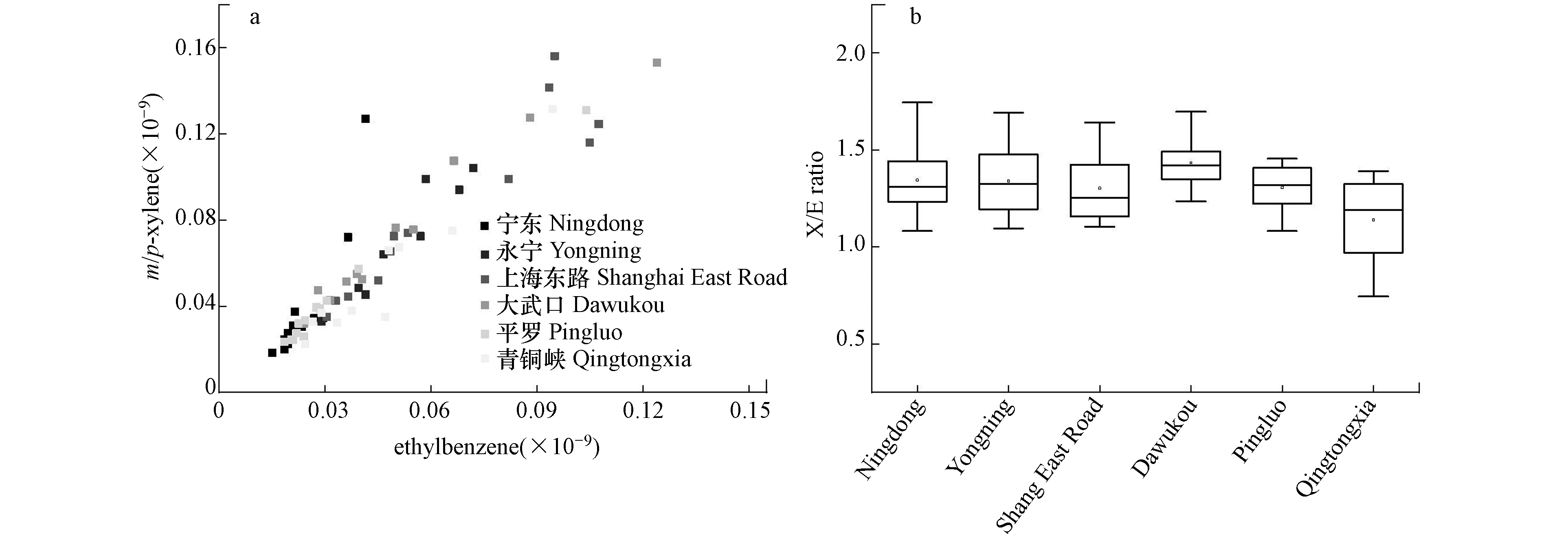
图 6 各采样点苯/甲苯比值箱线图Figure 6. Box and whisker plots of benzene/toluene ratio at each sampling site.框中实线代表中值浓度,框底部和顶部描绘了第25个(第一个四分位数)和第75个(第三个四分位数)百分位,空心点表示平均值,实心点表示异常值,晶须的末端分别对应在Q1和Q3的IQR的1.5倍之内的最低和最高数据The solid line in the box represents the median concentration. The bottom and top of the box depict the 25th (the first four Quantile) and the 75th (third quartile) percentile. The hollow dots represent the average value, and the solid dots represent the outliers. The ends of the whiskers correspond to the lowest and highest data still within 1.5 times the IQR of Q1 and Q3, respectively.一些VOCs组分虽然来源相似,但其光化学反应活性相差很大,因此,这些组分间的比值可用来反映光化学老化程度。图7为间/对-二甲苯/乙苯的散点图,结果表明,不同时间、不同采样点环境空气中间/对-二甲苯和乙苯对应浓度之间呈显著相关,说明观测期间这两种组分具有相似的来源[18-19]。间/对-二甲苯和乙苯可被·OH和·NO3氧化(白天主要与·OH反应,晚上主要与·NO3反应)[20-21]。间/对-二甲苯与·OH的反应速率大约是乙苯的3倍(间/对-二甲苯和乙苯与·OH的反应速率分别为18.90 × 10−12 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1、7.00 × 10−12 cm3∙molecule−1∙s−1)[22-23],随着间/对-二甲苯与·OH的反应速率的增大,间/对-二甲苯和乙苯间的比值(m/p-Xylene/ Ethylbenzene,X/E)逐渐减小,X/E的值越小,·OH暴露量越大,大气中光化学反应越活跃,空气质量老化的程度就越高[24-25]。从各采样点的间/对-二甲苯/乙苯比值的箱线图来看,青铜峡采样点的平均X/E比值最小(在1.10左右),其他5个采样点平均X/E比值相当,表明青铜峡采样点的挥发性有机物与·OH自由基光的光化学反应活性相对较强烈,该采样点空气的老化程度最大,更易受老化气团控制。
2.4 臭氧生成潜势
臭氧生成潜势(ozone formation potential,OFP)常被用来衡量VOCs组分生成臭氧的能力。本研究通过最大增量反应活性法(maximum incremental reactivity,MIR)来计算VOCs组分的臭氧生成潜势,并分析VOCs各组成成分对臭氧生成的贡献[26],臭氧生成潜势的计算公式:
OFPi=VOCsi×MIRi 式中,OFPi为VOCs组分i的臭氧生成潜势,
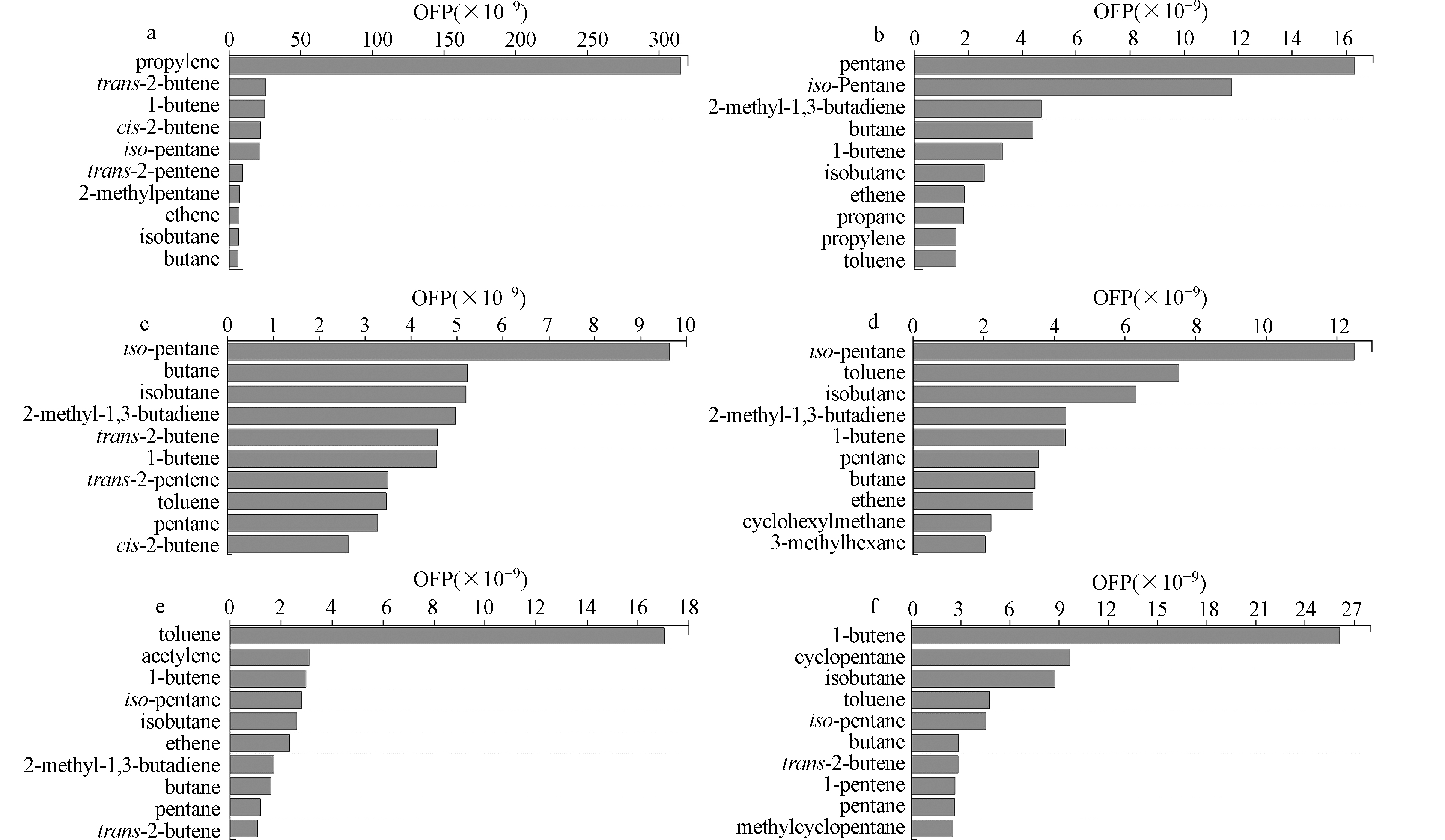
× × 图8显示了各采样点在观测期间不同类别挥发性有机物对臭氧生成潜势的贡献,结果表明,在6个采样点中烯烃对臭氧生成潜势都有较大贡献(23.20%—85.26%),其中,宁东采样点中烯烃对OFP的贡献率是6个采样点中最大,高达85.26%,这是由该采样点烯烃的高浓度及烯烃的高光化学反应活性共同导致的。与VOCs组成分析结果对比可知,不同VOCs组成的浓度占比与其对应的OFP贡献率之间存在一定关系。烯烃是主要的活性烃,在光照条件下能够产生大量自由基,从而对O3的生成产生重要贡献,从本研究结果看,烯烃对臭氧生成潜势的贡献情况与其浓度占比情况不一致,永宁、上海东路、大武口、平罗和青铜峡采样点中烯烃虽浓度占比不高,但其臭氧生成潜势贡献却十分明显,这主要与烯烃的高光化学反应活性有关。此外,在6个采样点中,短链烷烃的浓度占比高于长链烷烃,但短链烷烃对OFP的贡献率却低于长链烷烃,这与长链烷烃是活性烃,短链烷烃是低反应性烃有关。这些结果均表明VOCs组分的光化学反应活性在臭氧生成过程中起重要作用。
本研究中OFP贡献前10位的VOCs组分主要是烯烃和烷烃(图9),进一步与各采样点浓度最大的前10位VOCs组分(图5)比对可知,浓度较低的1-丁烯、顺式-2-丁烯、反式-2-丁烯等烯烃组分的对OFP的贡献反而较大,但不同采样点之间存在一定差异。
同处于工业区的宁东和永宁采样点,由于工业排放源种类以及污染物排放强度不同,对OFP贡献的主要VOCs组分也有所不同,宁东采样点中主要OFP贡献组分是丙烯(3.15
× × × × × × × × × × × × × × × × × 2.5 二次有机气溶胶生成潜势
为进一步了解环境空气中VOCs对银川都市圈地区二次有机气溶胶生成的影响,本研究采用气溶胶生成系数法(FAC法)估算观测期间各采样点的二次有机气溶胶生成潜势(SOAP),公式如下:
SOAP=VOCsi×FACi1−FVOCsi 式中,SOAP指SOA的生成潜势(μg·m−3);VOCsi指VOCs中i组分的浓度(μg·m−3);FACi指i组分的SOA的生成系数(%),FVOCsi为i组分参与氧化反应的份额(%)[27-28]。
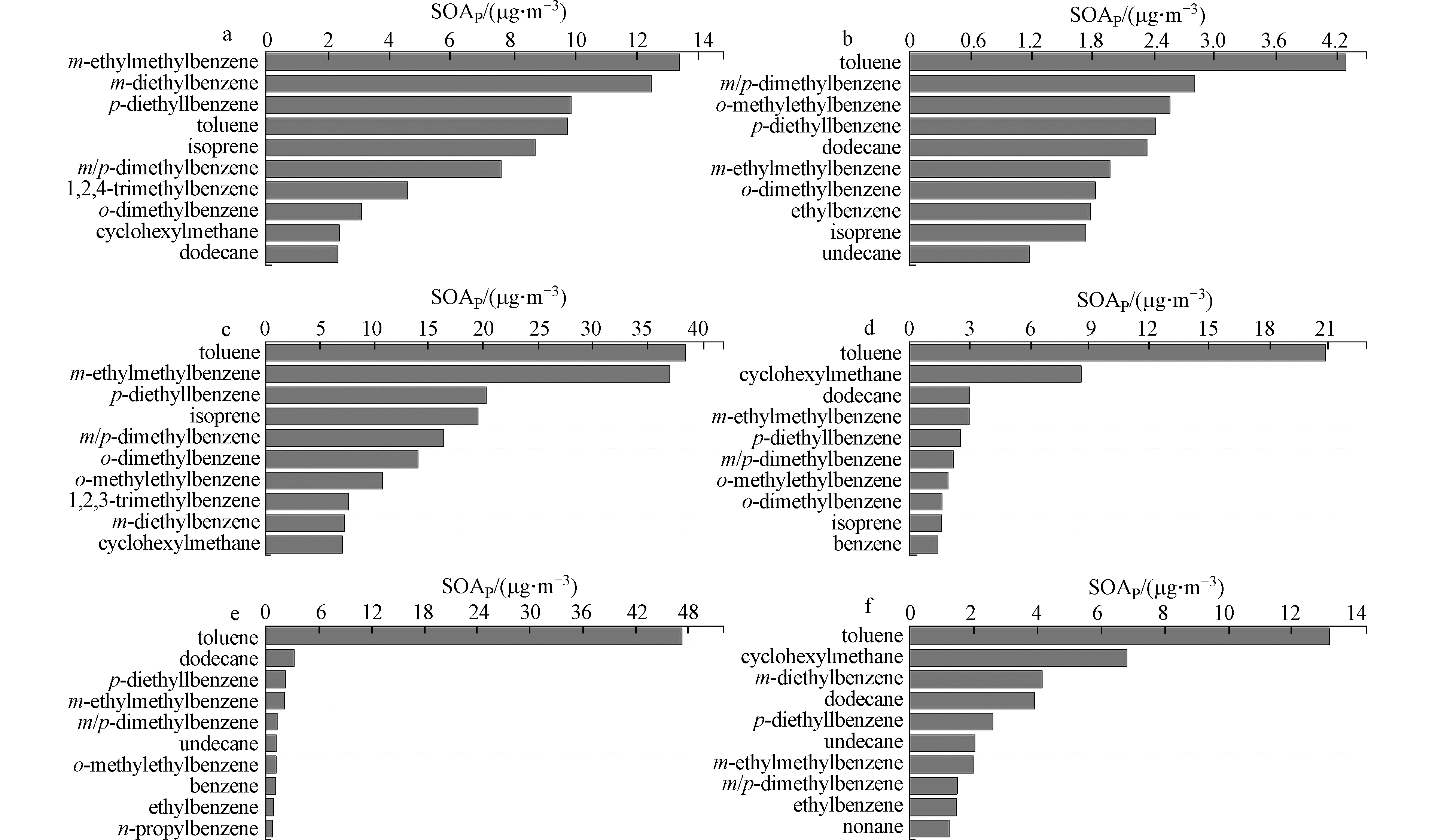
宁东、永宁、上海东路、大武口、平罗、青铜峡采样点SOAP均值分别为86.02、29.25、206.43、55.27、59.45、46.33 μg·m−3。6个采样点SOAP组成相似(图10),其中,芳香烃浓度占比最大(宁东79.41%、永宁70.05%、上海东路82.40%、大武口67.67%、平罗89.52%、青铜峡61.49%),而烷烃和烯烃的贡献相对较小。图11展示了各采样点对SOAP贡献前10的VOCs组分,结果表明,各采样点VOCs中对SOAP贡献较大的组分十分相似,均以芳香烃类居多,间/对-二甲苯、甲苯、间-乙基甲苯、对-二乙基苯对各采样点的SOAP中均有较大贡献,尤其在上海东路采样点中甲苯(3.85
× × × 3. 结论(Conclusion)
在银川都市圈工业区、商业/交通/居民混合区和工业/交通混合区中,尽管各采样点环境空气中VOCs的组分浓度及反应活性有所差异,但都以烯烃和长链烷烃组分为主;短链烷烃和长链烷烃在各点位都有较高的浓度占比,分别为30.85%—45.21%、15.17%—48.79%,这可能与机动车尾气排放有关。烯烃在宁东煤化工区采样点的浓度占比(43.77%)最为显著,炔烃、芳香烃在平罗采样点的浓度占比最高,分别为29.98%和14.00%,这可能与这些采样点的VOCs来源差异有关。宁东煤化工区采样点的VOCs总浓度水平高于其他5个采样点。尽管烯烃的浓度占比不高,但其生成臭氧的潜力较大,烯烃对臭氧生成潜势的贡献在23.2%—85.26%。6个采样点中各VOCs组成对SOAP的贡献相似,其中,芳香烃的贡献最大,贡献率在61.49%—89.52%。因此,O3污染和雾霾污染问题的改善需同时考虑VOCs组分浓度及其光化学反应活性。
-
[1] KRASNER S W, WEINBERG H S, RICHARDSON S D, et al. Occurrence of a new generation of disinfection byproducts[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(23):7175-7185. [2] PALS J A, ANG J K, WAGNER E D, et al. Biological mechanism for the toxicity of haloacetic acid drinking water disinfection by-products[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(13):5791-5797. [3] ESCOBARHOYOS L F, HOYOSGIRALD L S, LONDONOVELASCO E, et al. Genotoxic and clastogenic effects of monohaloacetic acid drinking water disinfection by-products in primary human lymphocytes[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(10):3282-3290. [4] XU X, GAO B Y, JIN B, et al. Study of microbial perchlorate reduction:Considering of multiple pH, electron cceptors and donors[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 285:228-235. [5] 尹江伟, 刘祖强, 李红华, 等. 离子色谱法测定饮用水中3种加氯消毒副产物[J]. 中国热带医学, 2004, 4(3):458-459. YIN J W, LIU Z Q, LI H H, et al. Determination of three by-products by using ion chromatography after adding chloride disinfectant in the drinking water[J]. China Tropical Medicine, 2004, 4(3):458-459(in Chinese).
[6] 陈际, 周永芳, 杜双双, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法检测饮用水中二氯乙酸和三氯乙酸[J]. 净水技术, 2018, 37(4):66-70. CHEN J, ZHOU Y F, DU S S, et al. Determination of dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid in drinking water by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry(UPLC-MS/MS)[J]. Water Purification Technology, 2018, 37(4):66-70(in Chinese).
[7] 李宗来, 何琴. 超高效液相色谱串联质谱法检测饮用水中卤乙酸[J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(2):574-576. LI Z L, HE Q. Determination of haloacetic acid in drinking water by ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(2):574-576(in Chinese).
[8] LIU Y, MOU S, CHEN D. Determination of trace-level haloacetic acids in drinking water by ion chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1039(1/2):89-95. [9] 苏宇亮, 冯兆敏, 胡克武, 等. 离子色谱法测定水中的卤代乙酸和卤素含氧酸[J]. 中国给水排水, 2006,22(12):86-88. SU Y L, FENG Z M, HU K W, et al. Determination of haloacetic acids and haloid oxyacids by ion chromatographic method[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2006,22(12):86-88(in Chinese).
[10] BRUZZONINITI M C, DE CARLO R M, HORVATH K, et al. High performance ion chromatography of haloacetic acids on macrocyclic cryptand anion exchanger[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2008, 1187(1/2):188-196. [11] 钟新林. 离子色谱法测定饮用水中亚氯酸盐、氯酸盐、溴酸盐、二氯乙酸及三氯乙酸[J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(7):1422-1423. ZHONG X L. Determination of chlorite, chlorate, bromate, dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid in drinking water by Ion Chromatography[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(7):1422-1423(in Chinese).
[12] MENG L P, WU S M, MA F J, et al. Trace determination of nine haloacetic acids in drinking water by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2010, 1217(29):4873-4876. [13] 雷颖, 八十岛诚, 王凌云, 等. 液相色谱-串联质谱法同时检测自来水中9种卤乙酸[J]. 中国给水排水, 2013, 29(20):124-129. LEI Y, YASOJIMA M, WANG L Y, et al. Determination of nine haloacetic acids in tap water by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2013, 29(20):124-129(in Chinese).
[14] 李建中, 陈伟, 薄涛,等. 生活饮用水中消毒副产物卤乙酸的UHPLC-MS/MS分析[J]. 环境化学, 2012, 31(5):757-759. LI J Z, CHEN W, BO T, et al. Analysis of haloacetic acid in drinking water by UHPLC-MS/MS[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(5):757-759(in Chinese).
[15] DUAN J, LI W, SI J, et al. Rapid determination of nine haloacetic acids in water using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in multiple reactions monitoring mode[J]. Analytical Methods, 2011, 3(7):1667-1673. [16] 贾娜, 张辰凌, 刘冰冰, 等. 离子色谱法快速测定饮用水中4种卤氧化合物[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2019, 55(11 ):1337-1340. JIA N, ZHANG C L, LIU B B, et al. Rapid determination of four oxyhalides in drinking water by ion chromatography[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis(Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2019, 55(11):1337-1340(in Chinese).
[17] TEH H B, LI S F Y. Simultaneous determination of bromate, chlorite and haloacetic acids by two-dimensional matrix elimination ion chromatography with coupled conventional and capillary columns[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1383:112-120. [18] USEPA, Method 557, Version 1.0. Determination of Haloacetic Acids, Bromate, and Dalapon in Drinking Water by Ion Chromatography Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry[S]. 2009. [19] LI W T, CAO M J, YOUNG T, et al. Application of UV absorbance and fluorescence indicators to assess the formation of biodegradable dissolved organic carbon and bromate during ozonation[J]. Water Research, 2017, 111:154-162. -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2873
- HTML全文浏览数: 2873
- PDF下载数: 42
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: