-
近年来,许多环境工作者的研究成果表明水华的突然消亡可能与溶藻细菌的感染有关联[1],溶藻细菌具有种类多、繁殖快、分布广、代谢类型多样等特点,作为维持水生生态系统生物种群功能以及结构的重要组成部分,在维持藻的生物量平衡方面具有相当重要的作用;同时溶藻细菌高效、专一性强、二次污染低、对环境友好、制取成本低廉,把溶藻细菌当作水华的防治生物,已经引起许多环境工作者的关注[2]。
目前,国内外不乏利用溶藻细菌进行生物控藻的研究成果,其重点大多聚焦于对高效溶藻菌的获取以及对菌株特性的研究与溶藻条件优化上,对溶藻细菌生长以及在溶藻细菌作用下溶藻动力学的研究相对较少,通过建立菌株生长与铜绿微囊藻降解二者相应的生长模型及动力学机制,可为控制太湖水华提供理论支撑和技术支持[3-4]。同时,工程措施上应用于太湖蓝藻治理的高效溶藻菌鲜见报道,因此仍需对相关溶藻菌株的水体环境适应性及其溶藻过程中的进程调控作进一步深入研究[5-6]。从太湖土著水生动物体内筛选出能够有效溶藻并适应水体环境的菌株,可以起到有效溶藻、保护水体环境安全的作用[7-8]。
本文从太湖土著田螺消化道中筛选具备溶藻能力的微生物菌群,并通过系列溶藻条件对比优选出高效溶藻菌株,对菌株生长动力学、溶藻动力学进行实验分析,进而采用红外光谱分析技术研究溶藻菌的溶藻进程,从而了解溶藻产物的构成,以期为同类菌株的溶藻进程分析提供理论参考[9-10]。
-
实验菌种:筛选自太湖土著田螺消化道中,置于4 ℃冰箱中保存。
实验藻种:铜绿微囊藻购自中国科学院武汉水生生物研究所(FACHB-Collection,CAS),藻种编号为FACHB-905。设定铜绿微囊藻培养条件为光照周期比12 h:12 h、光照强度3000 Lux、温度25 ℃[11]。
-
净化工作台,立式压力蒸汽灭菌器,数显光照培养箱,恒温振荡培养箱,台式大型离心机等。
-
牛肉膏蛋白胨培养基:依次称取NaCl 1.25 g、鱼粉蛋白胨2.5 g、牛肉膏1.25 g、加入250 mL蒸馏水,调节pH值至7.0—7.2(固体培养基另加琼脂粉5 g);
培养基须经高温灭菌(121 ℃、20 min),冷却至室温后使用。
-
利用乙醇法提取藻液叶绿素a[12],测定并计算出每天的叶绿素a含量,叶绿素a(式1)以及溶藻率(式2)测定公式如下:
式(1)中,V2表示提取液体积(mL),即90%乙醇的体积,8 mL;D表示吸光度;V1表示藻液体积(L);δ比色皿光程,1 cm。
-
生长曲线的测定采用比浊法,具体操作详见文献[13]。
-
设置以下6种方式处理菌液:(1)培养18—24 h处于对数增长期菌液(以下皆简称为发酵液);(2)牛肉膏蛋白胨液体培养基(以下皆简称为液培);(3)将(1)中发酵液经6000 r·min−1处理10 min后的上清液过0.45 μm滤膜两次,过滤除菌(用牛肉膏蛋白胨固体培养基检测上清液是否除菌完全),即为上清液;(4)收集(3)中滤膜,用新鲜无菌水洗菌3遍,最后等体积重悬制备菌悬液;(5)将菌液(1)经高温高压(设定121 ℃、1.0×105 Pa)灭活处理25 min;(6)将菌液(1)经超声波破碎(设定10 W、20 min)。将上述6种菌液按照菌藻比1∶10的比例投加到100 mL新鲜铜绿微囊藻液中,每组样做3个平行样,连续测定7 d,每间隔24 h测1次藻液叶绿素a并计算溶藻率。
-
经过溶藻菌XMC处理后的铜绿微囊藻液与对照组铜绿微囊藻液分别离心后,取离心沉淀物用蒸馏水洗,重复3次,放入冷冻干燥机中过夜处理,用KBr固定后在红外光谱分析仪上(Nicolet iS50)进行红外光谱扫描并用origin9.0作出红外光谱图。
-
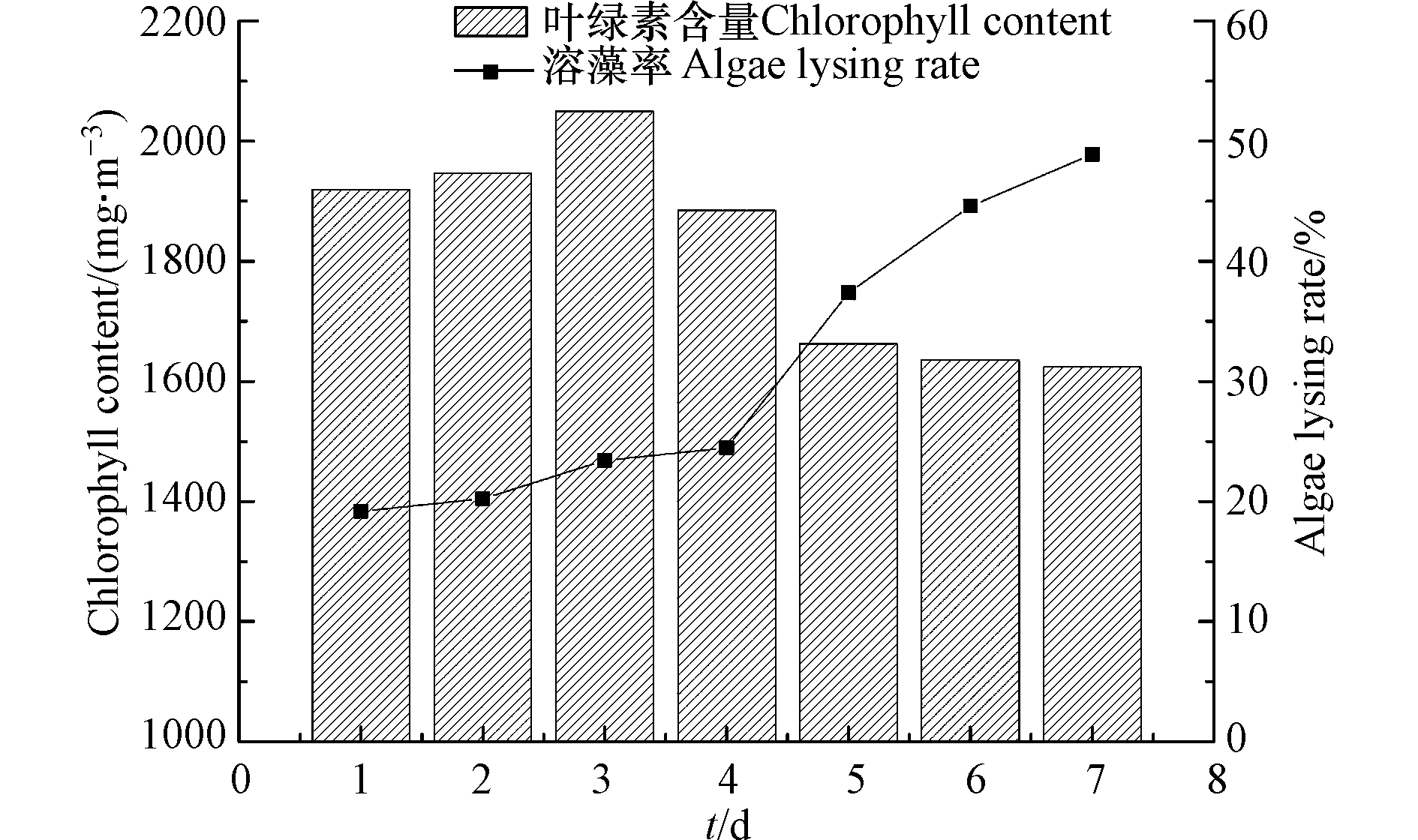
显微镜观察培养3 d左右菌株形态,筛选出5株性状明显的菌株。各菌株特征如表1所示。溶藻实验结果表明,1 #在7 d内的溶藻率远高于其他菌株,达到48.91%,因此选取1 #作为研究对象并命名为XMC。图1为溶藻菌XMC作用下7 d内藻液叶绿素a含量变化。
-
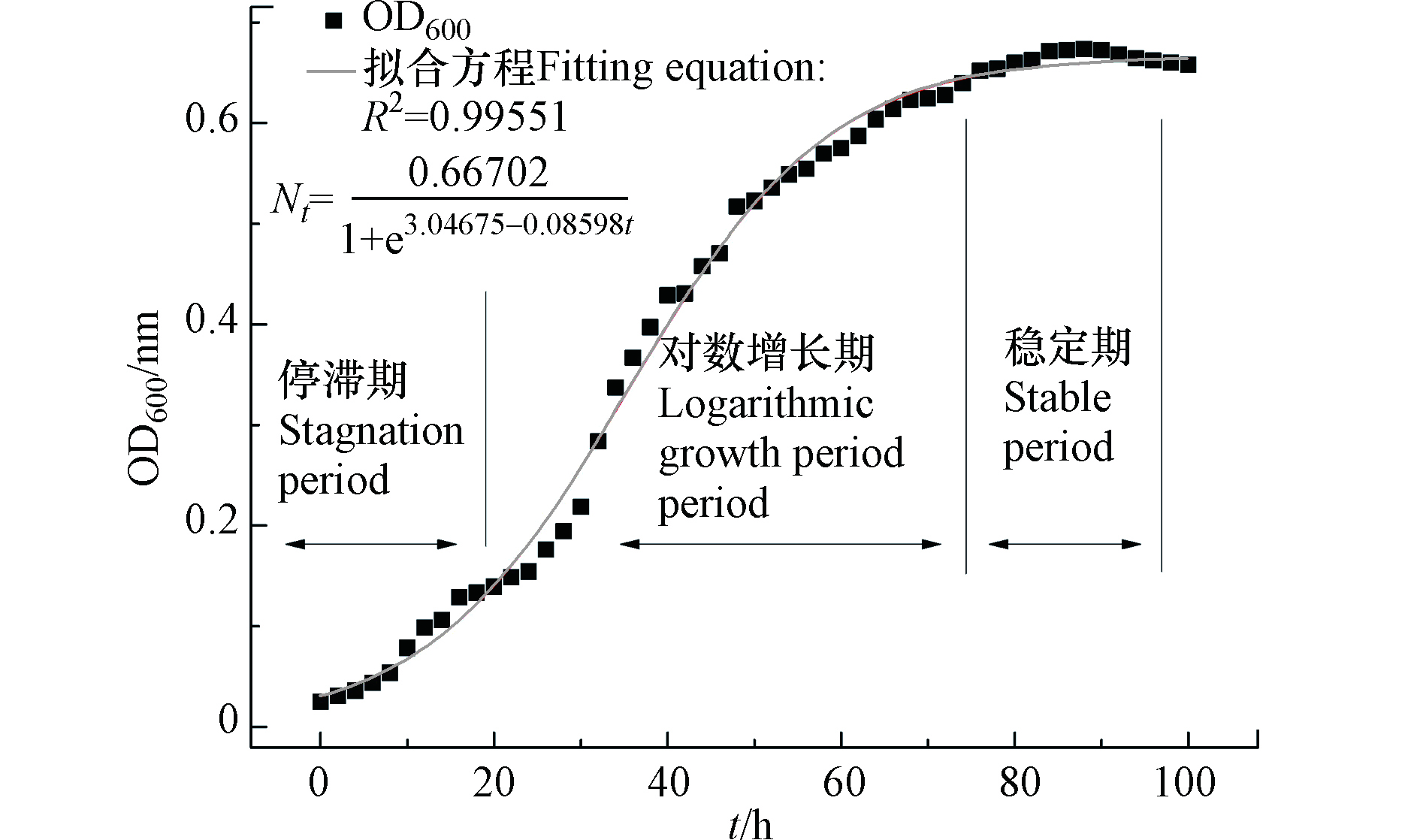
溶藻菌XMC生长曲线如图2所示,在理想条件下,溶藻菌XMC可破碎并利用藻细胞释放的物质作为自身生长的氮、碳源,进行生长代谢,但是在实验室规模下,溶藻菌并不能完全利用营养物质,因此有必要对菌株生长过程进行分析。
由实验结果可知,溶藻菌XMC的生长方式呈“S”型增长,与Logistic模型类似,因此采用该模型对菌株生长曲线进行拟合[14],如公式(3)所示:
式(3)中,Nt表示生长时间为t时的细菌细胞密度;K表示菌株生长的环境承载量;a是生长过程中一个参数;r表示溶藻菌XMC生长平均速率 (h−1);t表示细菌生长时间 (h)。由实验结果可知:K=0.66702,a=3.04675,r=0.08598。溶藻菌XMC生长Logistic模型如公式(4)所示:
溶藻菌XMC生长拟合曲线如图2所示,菌株在液培中培养5 d,其生长曲线与Logistic模型的相关性达到0.99551,处于对数增长期时,菌株增长略低于Logistic拟合方程,而处于停滞期、稳定期时,其增长则略高于理想条件下的数值。通过比对菌株生长曲线,控制实验期间溶藻菌处于对数增长期,从而使后续溶藻实验达到最佳溶藻效果[15]。
-
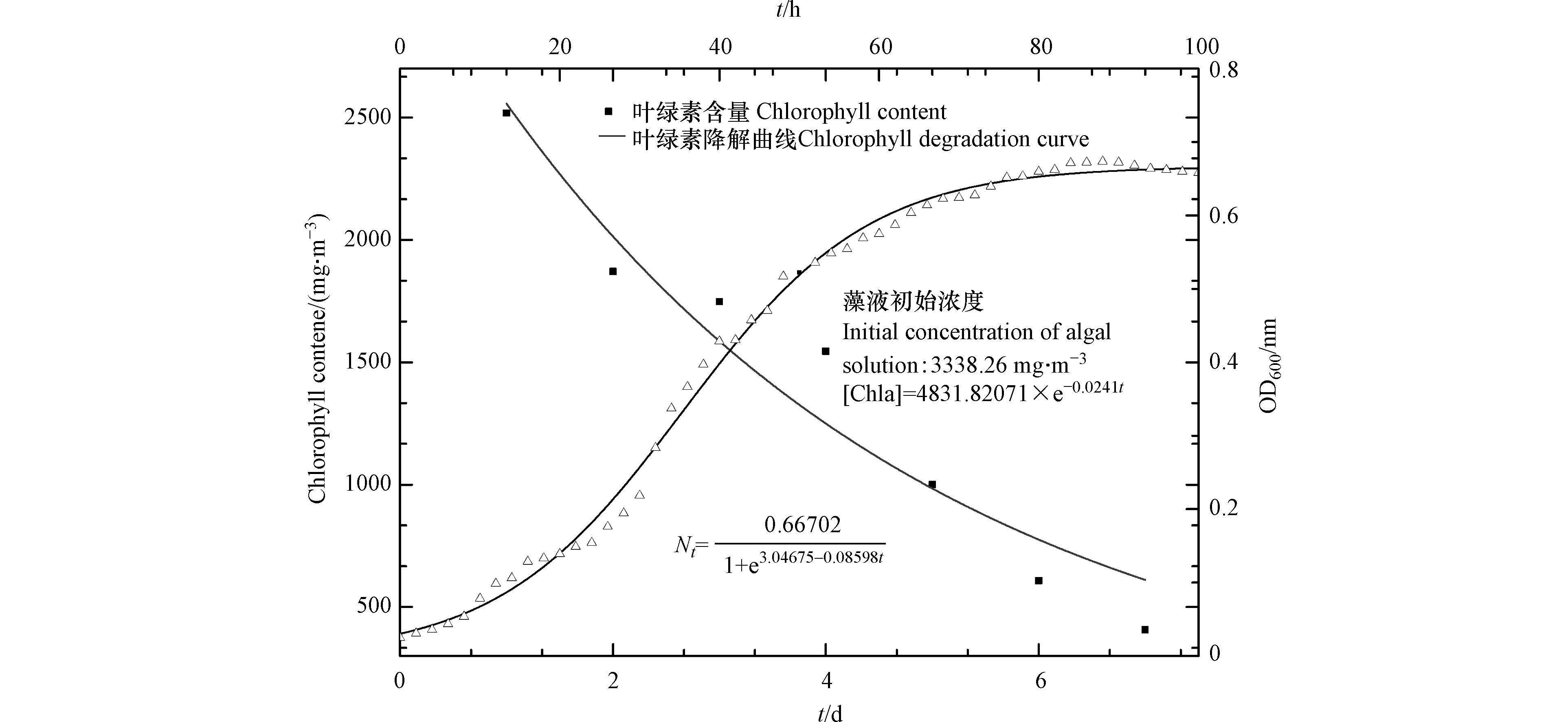
取发酵液混入藻液中,控制菌藻比1∶10、藻初始浓度为3338.26 mg·m−3,在此基础上研究溶藻菌XMC溶解铜绿微囊藻过程动力学,发现该菌株对铜绿微囊藻的降解过程与一级动力学模型相似,因此采用一级动力学模型进行拟合[16-18],如公式(5)所示:
式(5)中,Chl-a表示在时间为t时的藻液叶绿素a含量(mg·m−3);Chl-a0表示藻溶液初始叶绿素a含量(mg·m−3);w是一级动力学常数(d−1);t表示溶藻发生的时间(d)。由实验结果可知:[Chl-a0]=4831.82071,w=0.0241。藻液叶绿素a降解方程如公式(6)所示:
由图3可知,在溶藻菌XMC溶解铜绿微囊藻过程中,藻液叶绿素a含量变化与动力学拟合方程之间相关性达0.92729,其中藻液浓度与拟合方程中藻细胞浓度相差不大,溶藻完成藻液叶绿素a含量与溶藻时间呈反比关系。
对比溶藻菌XMC的生长曲线与叶绿素a降解方程可知:处于对数增长期时,溶藻菌表现出对不良环境的优秀抵抗能力,其细胞代谢活力最强,合成新物质的速度最快,藻液叶绿素a减少量最大,当菌株处于稳定期时,溶藻菌XMC的种间竞争关系会逐步降低其溶藻能力。
由实验结果可知,在溶藻过程中,处于对数期的溶藻菌溶藻能力最强,溶藻完成藻液叶绿素a含量与溶藻时间符合一级动力学模型[Chla]=4831.82071×e−0.0241t,这与李小彩等[19]在红球菌的溶藻特性及应用研究中的结论一致,此结论为溶藻菌XMC在实际工程应用中提供理论支持,该动力学模型可用于预测铜绿微囊藻溶藻过程的降解效果[20]。
-
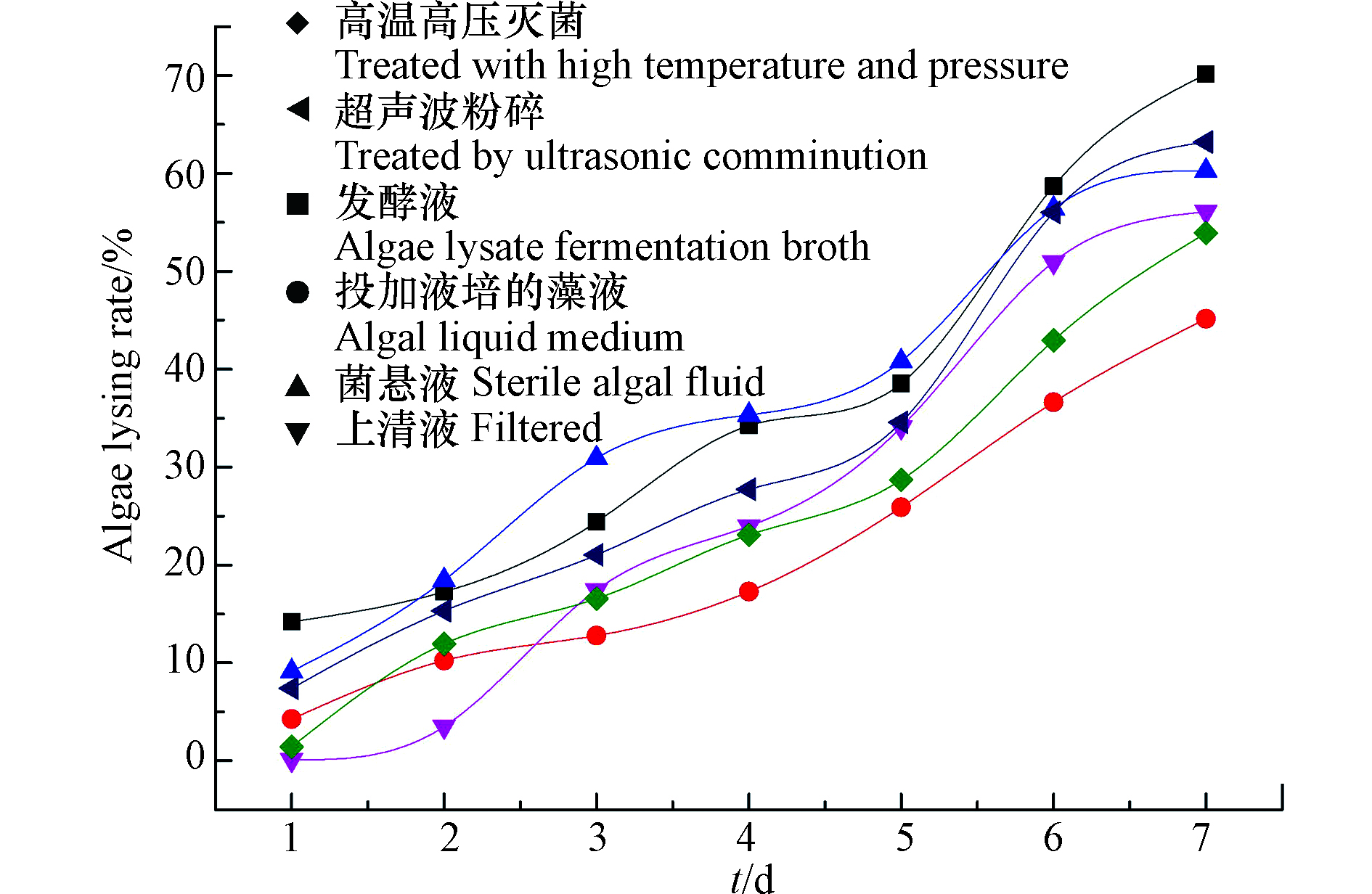
菌液处理方式不同,可能造成溶藻菌XMC的溶藻效果不同,为此设计了不同菌液处理方式研究对溶藻效果的影响,测定结果如图4所示。发酵液溶藻能力高于其它实验样本,液培本身具有一定的溶藻能力;经超声波粉碎处理与菌悬液溶藻效果显著,可见溶藻物质可能来源于菌株胞内物质;离心上清液中不含菌体但仍表现出溶藻能力,可能是菌株分泌与破碎物中的某些胞外非蛋白类物质具有溶藻作用,进行间接溶藻;经高温处理的菌液并不会丧失溶藻活性,说明这种溶藻物质可能具有耐高温的特性[21],或者是菌株通过自身特性在高温条件下分泌某种物质直接溶藻;
结合以上6种菌液处理方式的溶藻效果推测,溶藻菌XMC以间接溶藻为主,通过分泌耐高温的非蛋白类溶藻物质来裂解藻细胞,同时在特定情况下也能通过自身直接裂解藻细胞。
-
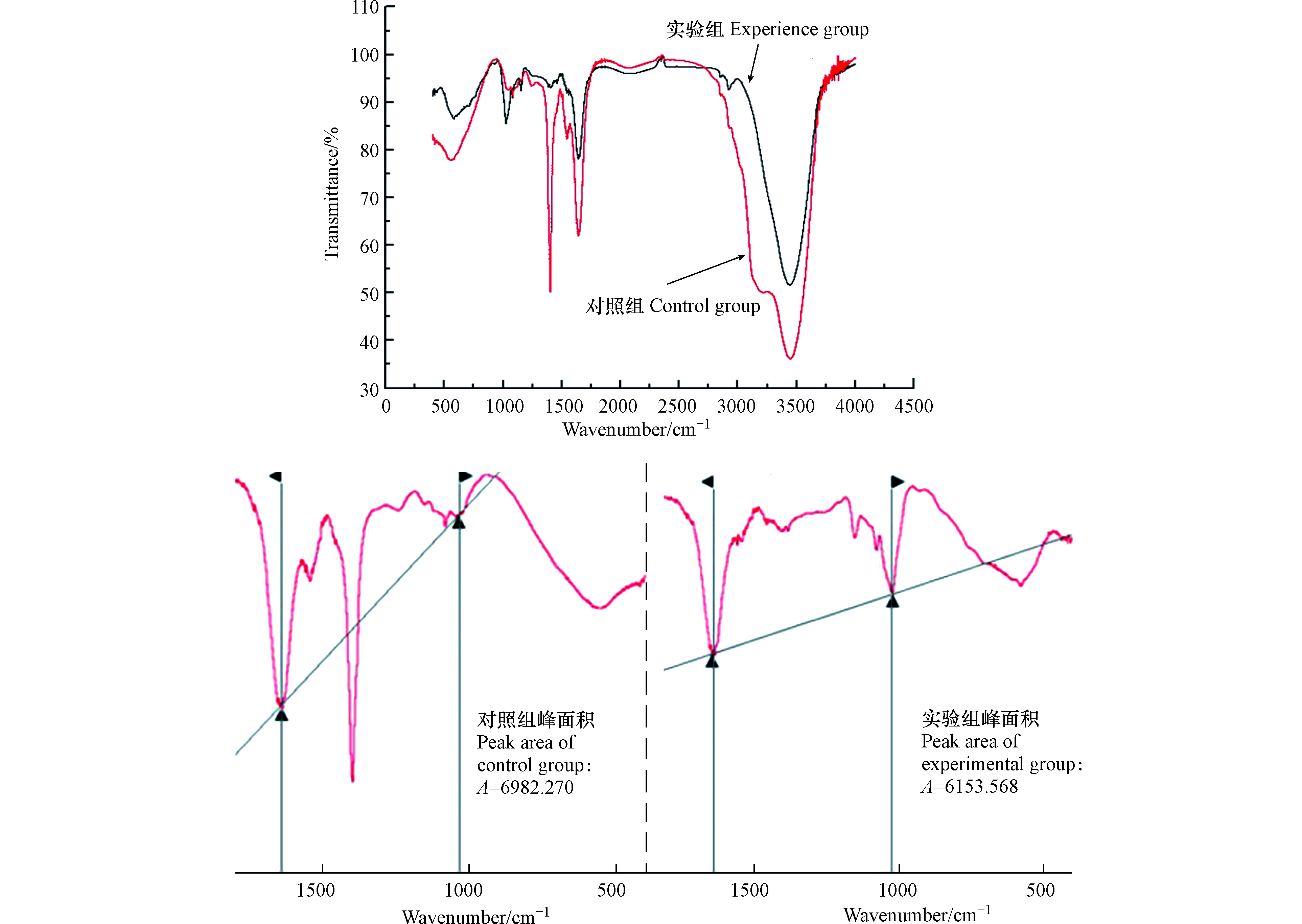
采用红外光谱对发酵液处理前后的铜绿微囊藻溶藻产物进行分析,结果如图5所示。空白对照组与经发酵液处理后的实验组溶藻产物在红外光谱图中吸收峰所在位置类似,吸收曲线形状趋同,但各吸收峰的相对强度之间存在差异。
从吸收峰的归属看,3452.56 cm−1处的吸收峰是铜绿微囊藻细胞壁壳聚糖和蛋白质中O—H− 键所在位置,表明细胞壁与蛋白质结构被破坏,藻细胞破裂[22];1637.49 cm−1处吸收峰处于酰胺Ⅰ带,代表C=O键的伸缩振动,而1545.22 cm−1处吸收峰位于酰胺Ⅱ带,是C—N的伸缩振动和N—H的弯曲振动,表明藻液中可能存在酰胺类物质,蛋白质中的酰胺类物质在溶藻过程中被破坏;波数在1400.42 cm−1处COO− 键对称伸缩,表明藻液中可能有芳香族氨基酸存在,藻细胞结构遭到破坏,溢出的细胞质被吸收。这与孔赟等对HJC-D1溶藻过程光谱学特征研究结果基本一致[23]。
如图5所示,波数在1000—1700 cm−1的区域内,实验组面积相比对照组面积下降约12%,表明溶藻菌导致藻细胞破裂,藻蛋白分解,结合不同峰位置来看,溶藻产物中存在芳环结构的氨基酸、酰胺类等物质。综合以上结论推测溶藻进程中,溶藻菌XMC分泌胞外物质(含有羟基、羧基基团的酸性物质)破坏铜绿微囊藻细胞壁,导致藻细胞内物质(蛋白质等)释放并失活,最终造成藻细胞的死亡。
-
(1)所筛选出的高效溶藻菌XMC取自太湖土著田螺消化道中,不会对太湖产生二次污染,其生长曲线符合Logistic模型,处对数增长期的菌株溶藻能力最强。在溶藻进程中,溶藻完成藻液叶绿素a含量与溶藻时间之间呈反比关系,该一级动力学模型[Chla]=4831.82071×e−0.0241t可用于预测溶藻过程中溶藻菌对铜绿微囊藻液叶绿素a的降解效果。
(2)经实验结果测定,溶藻菌XMC的溶藻进程是间接溶藻与直接溶藻相结合的方式,菌株通过分泌某些耐高温的溶藻物质或者自身直接裂解藻细胞进行溶藻。藻细胞破裂后分解出芳环结构的氨基酸、酰胺类等物质。
太湖土著田螺消化道中溶藻菌XMC溶藻进程与叶绿素a降解动力学研究
Study on algae-lysing process and chlorophyll-a degradation kinetics of algicidal bacteria XMC in the digestive tract of indigenous field snails of Taihu Lake
-
摘要: 在蓝藻爆发区域的太湖土著田螺消化道内,筛选出1株高效溶藻菌,命名为XMC。以铜绿微囊藻为受试对象,以叶绿素a含量检验溶藻菌XMC溶藻效果,考察了菌株溶藻能力、溶藻过程及其溶藻产物等。实验结果表明,溶藻菌XMC具有较强的溶藻能力,其生长曲线呈“S”型增长,符合Logistic动力学模型。菌藻共生环境中,藻液叶绿素a含量与溶藻时间两者之间符合一级动力学模型[Chla]=4831.82071×e−0.0241t,该模型可用于预测铜绿微囊藻溶藻过程的降解效果;溶藻菌XMC的溶藻进程以间接溶藻为主,通过分泌耐高温的非蛋白类溶藻物质来裂解藻细胞,菌液处理完的铜绿微囊藻液中,产物主要为藻细胞破裂分解出的芳环结构的氨基酸、酰胺类等物质。Abstract: A high-efficiency algicidal bacteria named XMC was selected from the native snails of Taihu Lake, which lived in the area of cyanobacteria outbreak for a long time. Microcystis aeruginosa was used as the test object, and the chlorophyll-a content was used to test the algae-lysing effect of the algicidal bacteria XMC, and the algae dissolving ability, process and products of the bacteria were investigated. The experimental results showed that the algicidal bacteria XMC had strong algicidal ability, and the growth curve of algicidal bacteria XMC showed an “S” shape which accords with the Logistic dynamic model. The relationship between chlorophyll-a content and algae lysis time in the symbiotic environment of bacteria and algae conformed to the first-order kinetic model ([Chla] = 4831.82071 × e− 0.0241t), which could be used to predict the degradation effect of Microcystis aeruginosa. The algicidal bacteria XMC was mainly an indirect algae lysate, which could lyse algal cells by secreting heat-resistant nonprotein lysates. In the treated Microcystis aeruginosa, the products were mainly amino acids and amides with aromatic ring structure broken down by algal cells.
-
Key words:
- algicidal bacteria /
- Microcystis aeruginosa /
- dynamic model /
- chlorophyll-a
-
抗生素在我国被广泛应用于水产、畜牧、养殖、医疗等行业,抗生素滥用造成的环境污染和生态风险越来越受到重视[1]。水产、畜牧、养殖、医疗等行业产生的废水经过处理排入自然水体,由于处理过程中无法去除抗生素污染物,往往会对河流、湖泊造成抗生素污染[2],水源地受到抗生素污染,对人体健康和生态环境会造成严重的危害。
磺胺甲恶唑(C10H11N3O3S,简称SMX)是一种非常典型的磺胺类抗生素,近年来常常在废水、湖泊、河流中被检出[3],因此,去除废水与自然水体中SMX十分重要。不同于传统的化学法、生物法、膜处理法,高级氧化技术(AOPs)处理磺胺类污染物效果好且不会产生二次污染[3]。芬顿法(Fenton)属于高级氧化技术的一种,利用亚铁盐、过氧化氢(H2O2)在催化剂的作用下产生活性羟基自由基(·OH),可以有效去除废水中的SMX[4]。电芬顿反应(electro-Fenton)的原理是溶解氧在阴极接受电子,还原生成H2O2,电芬顿体系能实现H2O2的阴极原位再生,处理过程中不需额外投加H2O2,处理过程易于控制且经济性良好[5-6]。
金属有机骨架(MOFs)是一种由机配体和金属离子组成的新型多孔材料,具有比表面积大、孔隙率高、孔结构可调等优点[7]。近年来,MOFs催化生成羟基自由基从而降解有机物的研究逐渐成为热点[8]。其中铁基MOFs作为芬顿反应催化剂产生·OH已被广泛用于去除水中有机污染物[9]。MIL-88B(Fe)是由对苯二甲酸 (C8H6O4,简称BDC)和铁三聚八面体簇(Fe3-μ3-OXO)构成的一种三维多孔铁基MOFs材料[10],MIL-88B(Fe)作为非均相芬顿催化剂用于催化降解SMX处理效率高、性能优异[11],但单一的MIL-88B(Fe)存在导电性较差的问题。
本文采用有机酸对MIL-88B(Fe)进行刻蚀,在晶体表面构造不饱和金属位点,对MOFs材料的结构和表面性质进行了调控,从而制备出高导电性、高活性且结构稳定的高效自组装的缺陷MOFs催化剂[12],并将制得的缺陷MOFs作为电芬顿催化剂在电芬顿体系下降解水中SMX,并利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、X射线衍射技术(XRD)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)技术对缺陷MOFs催化剂的理化性质进行了表征分析,深入研究了缺陷MOFs催化剂的比表面积、孔结构、电化学性能、降解动力学特征。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料
六水合三氯化铁(FeCl3·6H2O)、对苯二甲酸(C8H6O4)、甲酸(HCOOH)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)、无水乙醇(C2H5OH)、萘酚(Naphthol)、硫酸钠(Na2SO4)、磺胺甲恶唑(SMX)、硫酸(H2SO4)、冰乙酸(CH3COOH)、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)、异丙醇(C3H8O,简称IPA)、对苯醌(C6H4O2,简称BQ)
1.2 MIL-88B(Fe)材料的合成
根据文献[13]中提到的合成方法制备MIL-88B(Fe):称量0.756 g (2.770 mmol) FeCl3·6H2O 和0.231 g (1.385 mmol) 对苯二甲酸,溶解于60 mL DMF 中。在室温下磁力搅拌30 min后,将混合溶液转移至高压反应釜中,置于150 ℃恒温加热2 h。待加热结束后取出反应釜,自然冷却至室温,将所得固体离心分离并用乙醇洗涤数次。洗涤结束后将材料置于真空干燥箱中60 ℃条件下干燥12 h,干燥结束后取出材料,使用玛瑙研钵研磨后得到MIL-88B(Fe)粉末材料。
1.3 缺陷MOFs材料的制备
在所合成的MIL-88B(Fe)中加入有机酸进行刻蚀,可以对原有MOFs材料进行改性,在其表面引入不饱和金属位点,进而制备出具备高导电性、高活性且结构稳定的高效自组装的缺陷MOFs催化剂[14]。
本研究使用甲酸刻蚀MOFs材料从而引入缺陷,缺陷MOFs催化剂合成方法为:称量0.756 g (2.770 mmol) FeCl3·6H2O、0.231 g (1.385 mmol) 对苯二甲酸和 0.230~0.690 g (5.00~15.0 mmol) 甲酸,溶解于60 mL DMF中。在室温下磁力搅拌30 min后,将混合溶液转移至高压反应釜中,置于150 ℃恒温加热2 h。待加热结束后取出反应釜,自然冷却至室温,将所得固体离心分离并用乙醇洗涤数次。洗涤结束后将材料置于真空干燥箱中60 ℃条件下干燥12 h,干燥结束后取出材料,使用玛瑙研钵研磨后得到缺陷MOFs粉末材料。
使用5.0 mmol甲酸刻蚀制得的缺陷MOFs催化剂称为5A-MIL-88(Fe),使用10.0 mmol甲酸刻蚀制得的缺陷MOFs催化剂称为10A-MIL-88(Fe),使用15.0 mmol甲酸刻蚀制得的缺陷MOFs催化剂称为15A-MIL-88(Fe)。
1.4 抗生素污染物溶液的配制
本研究降解以磺胺甲恶唑(SMX)为代表的抗生素污染物,25 mg·L−1 SMX溶液的配制方法如下:配制好0.1 mol·L−1的Na2SO4 溶液,称取12.5 mg SMX于烧杯内,加入0.1 mol·L−1 Na2SO4溶液溶解SMX,缓慢加入0.5 mol浓硫酸,随后用保鲜膜封住烧杯口,并用铝箔完全包裹住烧杯,使用磁力搅拌器搅拌12 h直至溶液完全澄清。待搅拌结束后将澄清液移至500 mL容量瓶中,使用0.1 mol·L−1 Na2SO4溶液定容。
1.5 降解实验
将催化剂材料涂附在2 cm×2 cm大小的碳毡上,称量10 mg材料粉末,溶解于1 mL无水乙醇中,超声20 min,结束后加入30 μL 5%(质量分数)萘酚溶液,再次超声20 min。超声结束后使用滴管将液体逐滴滴在碳毡上,使液滴均匀分布在碳毡表面从而将材料完全涂附在碳毡上。碳毡电极作为本研究中MOFs和缺陷MOFs催化剂的载体,在先前的研究中呈现出比表面积大、吸附能力强、导电性能良好的优点[15]。
在降解池中按比例加入25 mg·L−1 SMX溶液和0.1 mol·L−1 Na2SO4溶液,金属铂片和碳毡插入到降解池液面以下,碳毡连接直流稳压电源的阴极,金属铂片连接直流稳压电源的阳极,控制电流为40 mA,电压保持在3.5 V。降解过程中,使用磁力搅拌器低速搅拌降解池内溶液,持续向阴极通氧气。
降解实验进行到0、10、20、30、40、60、90、120 min的时间,从降解池中取样,取出的样品经0.22 μm玻璃纤维滤头过滤后使用高效液相色谱仪(Waters 2695,美国 Waters公司)分析。样品过0.45 μm微孔滤膜后进入C18色谱柱( 4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm )进行分离,色谱柱温度为(25±5) ℃,使用标准工作曲线法进行定量,流动相为1% 冰乙酸,流速为1 mL·min−1,进样体积为10 μL,测量波长为289 nm处样品的吸光度,根据标准曲线计算样品浓度。SMX去除率按式(1)进行计算。
η=C0−CtC0×100% (1) 式中:η为SMX去除率,%;C0为SMX初始质量浓度,mg·L−1;Ct为t时刻对应的SMX质量浓度, mg·L−1。
1.6 表征手段
本实验采用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Bruker D8)对材料结构进行分析;采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,Merlin德国 卡尔·蔡司公司)观察材料晶形、晶貌;采用X射线光电子能谱(XPS,Thermo Scientific K-Alpha)对材料表面的元素组成及元素化学状态进行分析。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 材料形貌、结构表征
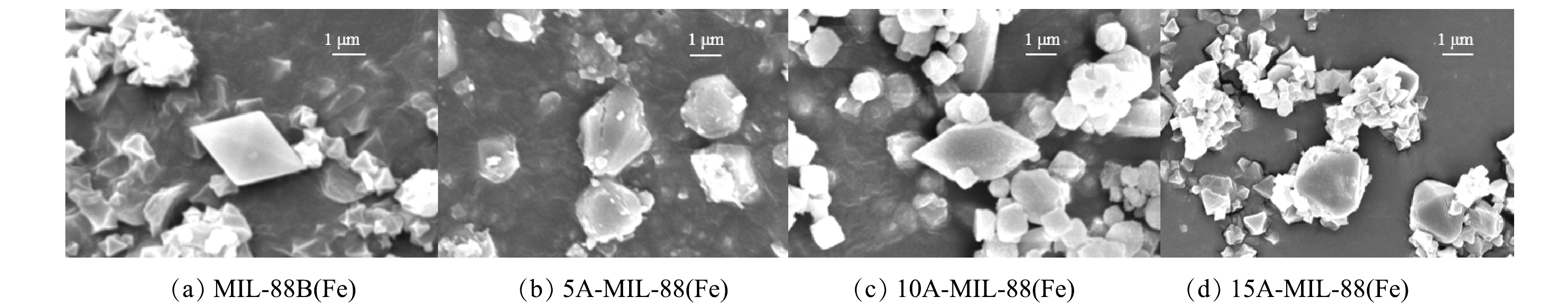
1) SEM分析。采用扫描电镜(SEM)观察催化剂材料的晶体形貌与结构。由图1(a)可见,MIL-88B(Fe) 的晶体结构呈均匀、高度对称的纺锤体形状,这与先前研究中的描述一致[16]。由图1(b)可见,5A-MIL-88(Fe)的晶体表面粗糙,出现明显的缺陷与孔隙结构,纺锤体棱角被有机酸蚀去,比表面积较之甲酸刻蚀前增大。由图1(c)可见,随着刻蚀甲酸量的增大,10A-MIL-88(Fe)晶体基本保留刻蚀前的纺锤体形状,晶粒逐渐成为球形且分布分散。由图1(d)可见,随着刻蚀甲酸量的进一步增大,15A-MIL-88(Fe)晶体难以生长成完整的纺锤体形状,晶粒分布高度分散。5A-MIL-88(Fe)、10A-MIL-88(Fe)、15A-MIL-88(Fe)材料的SEM分析结果表明,不同甲酸用量的刻蚀程度不同,过高的甲酸用量会影响缺陷MOFs材料的结晶度。
2) XPS分析。采用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)对催化剂材料的元素组成和电子层结构进行分析。由图2(a)可知,MIL-88B(Fe)和5A-MIL-88(Fe)主要组成元素均为C、O、Fe元素,此外,5A-MIL-88(Fe)中Fe元素的能谱峰强度高于MIL-88B(Fe),这表明5A-MIL-88(Fe)材料表面Fe元素含量增加,Fe元素暴露更充分。由图2(b)可知,MIL-88B(Fe)结合能为711.08 eV (Fe 2p3/2)、723.88 eV (Fe 2p1/2),Fe 2p3/2、Fe 2p1/2对应的卫星峰峰值分别出现在结合能为715.88 eV、728.68 eV处,这与先前研究中呈现的结果基本一致[17]。依据峰型特征判断,MIL-88B(Fe)中Fe元素为Fe(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅱ)混杂形态。5A-MIL-88(Fe)结合能为710.98 eV (Fe 2p3/2)、723.78 eV (Fe 2p1/2),Fe 2p3/2、Fe 2p1/2对应的卫星峰峰值分别出现在结合能为715.88 eV、728.68 eV处。依据峰型特征判断,材料中Fe元素为Fe(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅱ)混杂形态。5A-MIL-88(Fe)与MIL-88B(Fe)峰面积与峰值出现的位置基本一致,表明5A-MIL-88(Fe)保留了MIL-88B(Fe)不饱和金属位点富集度高、Fe位点电子密度高的优点[18-19]。
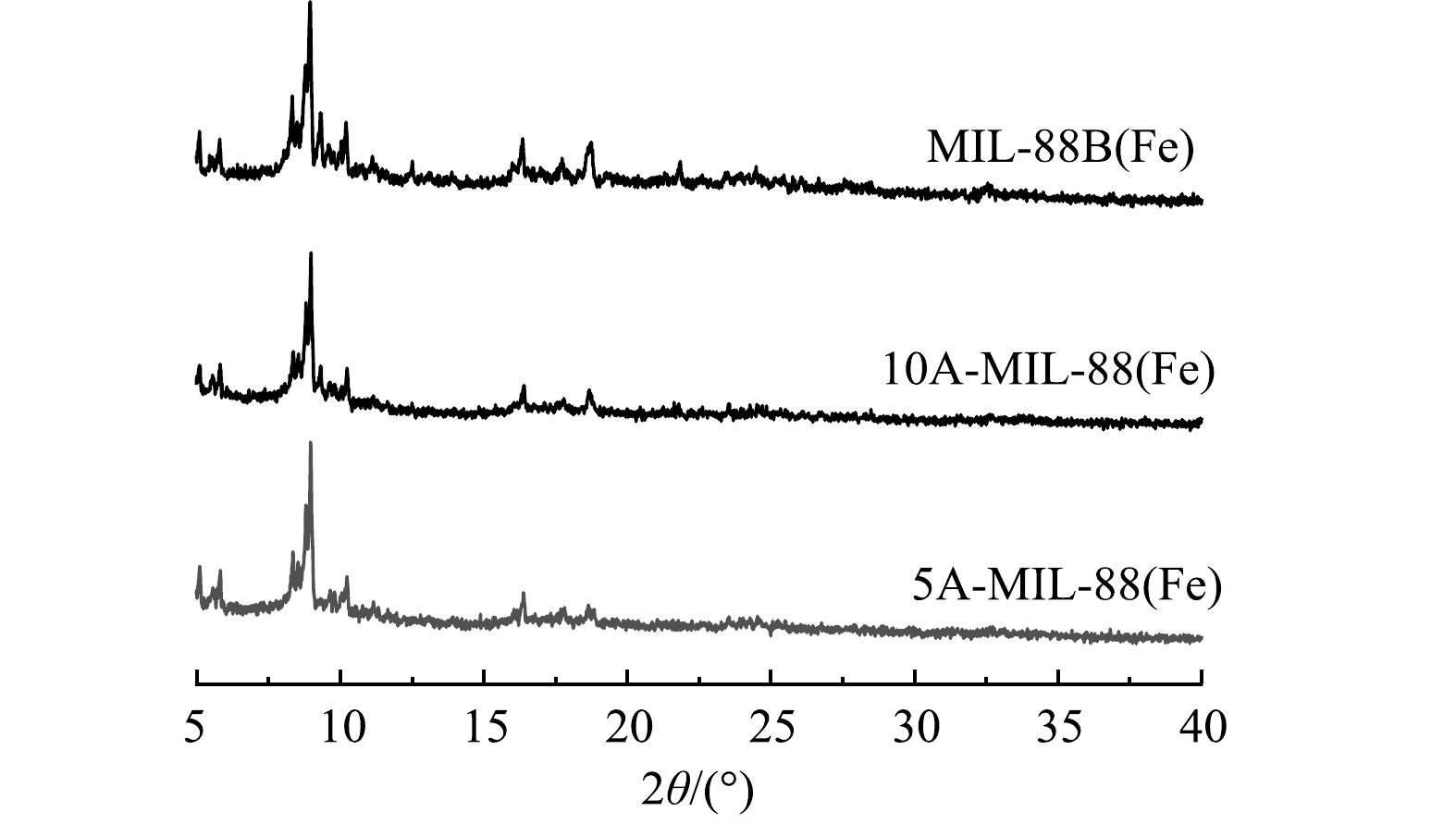
3) XRD分析。采用X射线衍射仪(XRD)对催化剂材料的晶体结构进行分析。由图3可见,MIL-88B(Fe) 在2θ=8.9°处衍射峰峰强最高,材料在2θ=8.9°、9.2°、10.2°、16.4°、18.7°处衍射峰的位置及特征与先前研究中呈现的结果基本一致[20]。5A-MIL-88(Fe)、10A-MIL-88(Fe)衍射峰的位置及特征与MIL-88B(Fe)基本一致,但部分衍射峰 (2θ=16.4°、18.7°)峰强相比MIL-88B(Fe)均略微有所减弱。结合SEM结果可知,缺陷MOFs材料的结构完整性和结晶形态基本保留,甲酸刻蚀没有导致材料晶体结构发生相变,部分衍射峰峰强减弱可能是因为引入缺陷过程中,缺陷MOFs材料结构轻微变形。
2.2 降解反应动力学分析
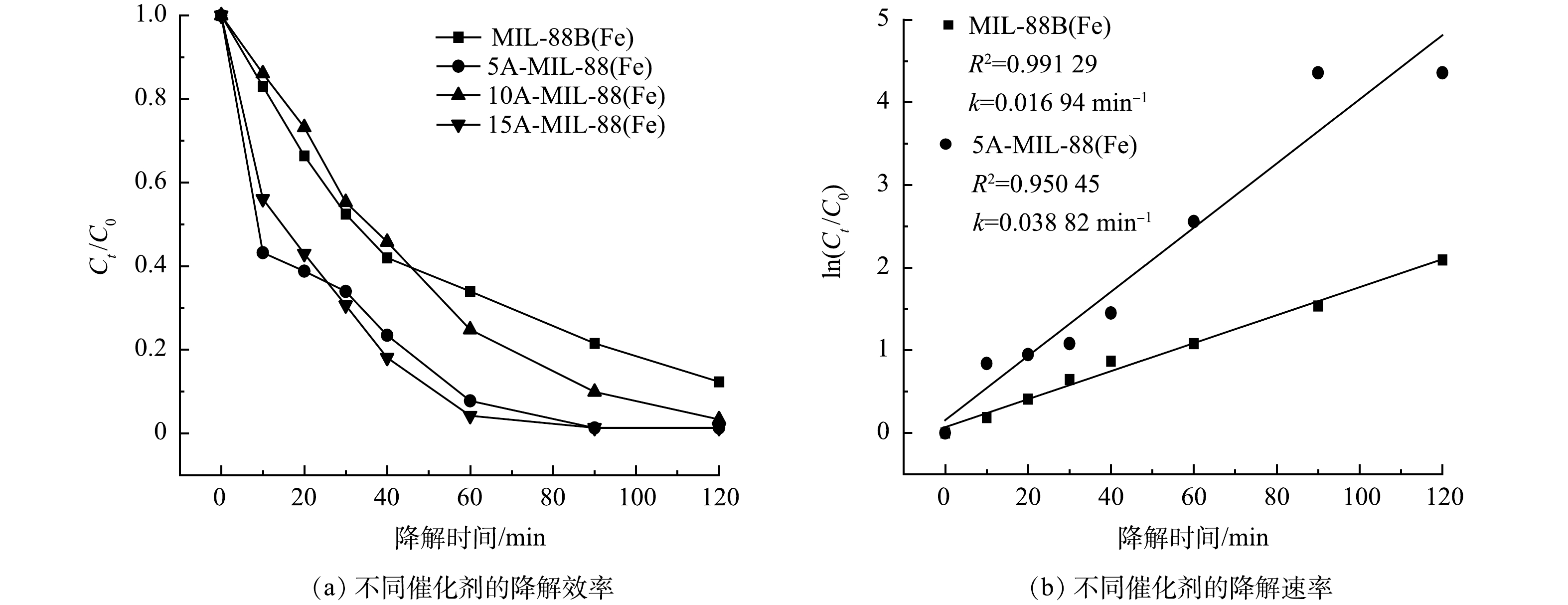
本研究进行了MIL-88B(Fe)催化剂和缺陷MOFs催化剂对10 mg·L−1 SMX的电催化降解实验。由图4(a)可见,反应120 min后,没有经过修饰的MIL-88B(Fe)对SMX去除率为87.67%;相比之下,缺陷MOFs对SMX去除率均高于98%,其中5 mmol甲酸刻蚀制得的5A-MIL-88(Fe)对SMX去除率最高,达98.72%。这是因为甲酸对MOFs材料表面进行修饰后,材料表面存在的不饱和金属位点的位置、数量和暴露程度均发生了改变,从而导致材料孔隙率增加、比表面积增大、电荷转移能力增强、电化学性能和催化性能得到增强[21]。但甲酸的过量添加则会导致MIL-88B(Fe)原有骨架的坍塌,影响其孔道结构,使得催化性能下降,故10A-MIL-88(Fe)、15A-MIL-88(Fe)对SMX去除率低于5A-MIL-88(Fe),这与SEM测试结果相互佐证。由图4(b)可见,MIL-88B(Fe)与缺陷MOFs催化降解SMX反应的动力学拟合曲线符合一级动力学模型,MIL-88B(Fe)对SMX催化降解速率为0.016 94 min−1,相比之下,降解效率最高的5A-MIL-88(Fe)对SMX催化降解速率为0.038 82 min−1,是MIL-88B(Fe)催化降解速率的2.29倍。这同样证明使用甲酸对MOFs刻蚀能够增强材料的电化学性能和催化性能。基于上述实验结果,后期研究均采用5A-MIL-88(Fe)作为最佳催化剂,分析5A-MIL-88(Fe)催化降解SMX的性能。
2.3 不同反应条件对降解反应的影响
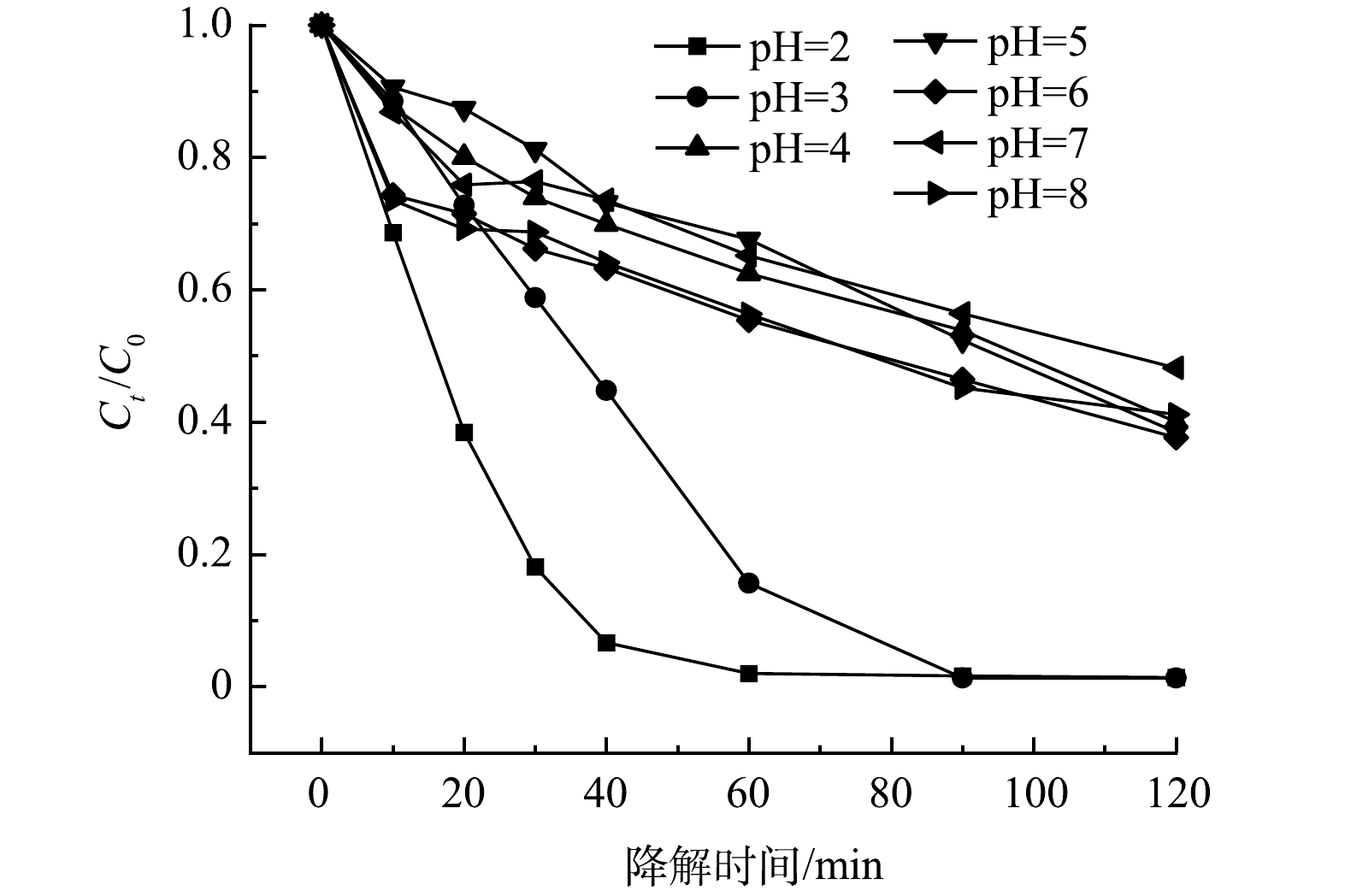
1) pH的影响。pH对5A-MIL-88(Fe)催化降解10 mg·L−1 SMX的影响结果如图5所示。可以看出,当pH为2时,SMX去除率为98.63%;当pH为3时,SMX去除率最高,达到了98.69%;当pH为4时,SMX去除率开始大幅度降低,仅有59.98%;随着环境pH继续升高,当pH为5~8时,SMX去除率均未超过65%。结果表明,5A-MIL-88(Fe)仅能在较强酸性环境中高效降解抗生素污染物,在弱酸性、中性或碱性环境下降解抗生素污染物效率较低。这是因为环境pH会影响溶液中SMX存在形态、材料表面电荷分布、电子转移速率及活性基团的生成速率导致,其中占主要因素的可能是活性基团的生成速率[22-23]。当pH呈弱酸性、中性或碱性时,溶液中H+含量低,不利于阴极产生H2O2,电芬顿体系中阴极产生H2O2的方程如式(2)所示。
O2+4H++4e−→2H2O2 (2) 当H2O2的产生受到抑制时,活性羟基自由基(·OH)、超氧自由基(·O2−)的产生也会受到影响,电芬顿体系中Fe(Ⅲ)、Fe(Ⅱ)产生·O2H、·OH的反应方程如式(3)和式(4)所示。
Fe(Ⅲ)+H2O2→Fe(Ⅱ)+⋅O−2+2H+ (3) Fe(Ⅱ)+H2O2→Fe(Ⅲ)+⋅OH+OH− (4) ·OH和·O2−是电芬顿体系中起主导氧化作用的自由基(见2.6反应机理分析),当体系中·OH和·O2−的含量降低时,SMX的去除率也会随之降低。因此,当pH呈弱酸性、中性或碱性时,SMX去除率低于pH呈较强酸性。
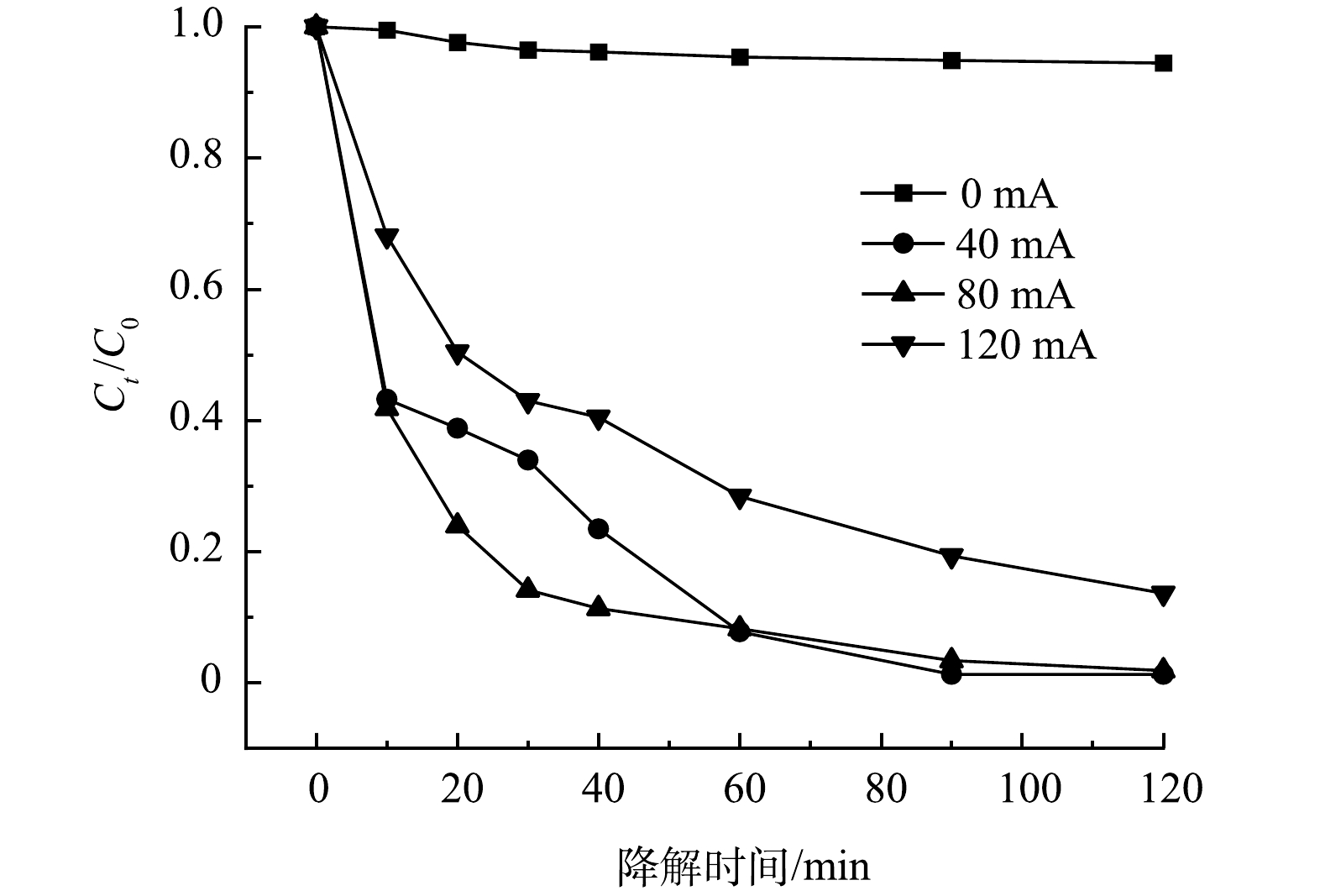
2)反应电流的影响。在不同的反应电流下,5A-MIL-88(Fe)对10 mg·L−1 SMX去除率如图6所示。可以看到,降解体系中没有电流流过(0 mA) 时,SMX几乎未被降解,这说明反应电流是构建SMX催化降解体系的必要条件。当反应电流为40 mA时,SMX去除率达到98.72%;当反应电流为80 mA时,SMX去除率达到98.14%;当反应电流为120 mA时,SMX去除率有所降低,为86.37%。对比反应电流40 mA与80 mA 这2组降解体系,前40 min内,80 mA电流去除率更高,达到了88.68%;后80 min内,40 mA 电流去除率更高。随着反应电流进一步提升至120 mA,SMX去除率降低,可能原因是H2O2在阳极表面(异向过程)或溶液中(均相过程)发生化学分解[24-25],从而造成溶液中·O2H、·OH产生速率降低。当溶液中·O2H、·OH含量降低,SMX去除率随之降低。随着反应电流增大,H2O2发生的分解方程如式(5)和式(6)所示。
H2O2→HO2⋅+H++e− (5) HO2⋅→O2+H++e− (6) 结果表明,5A-MIL-88(Fe)催化降解SMX反应有较宽的适宜电流范围(40~80 mA),5A-MIL-88(Fe)材料在不同反应电流下均有较高的稳定性及电化学活性。
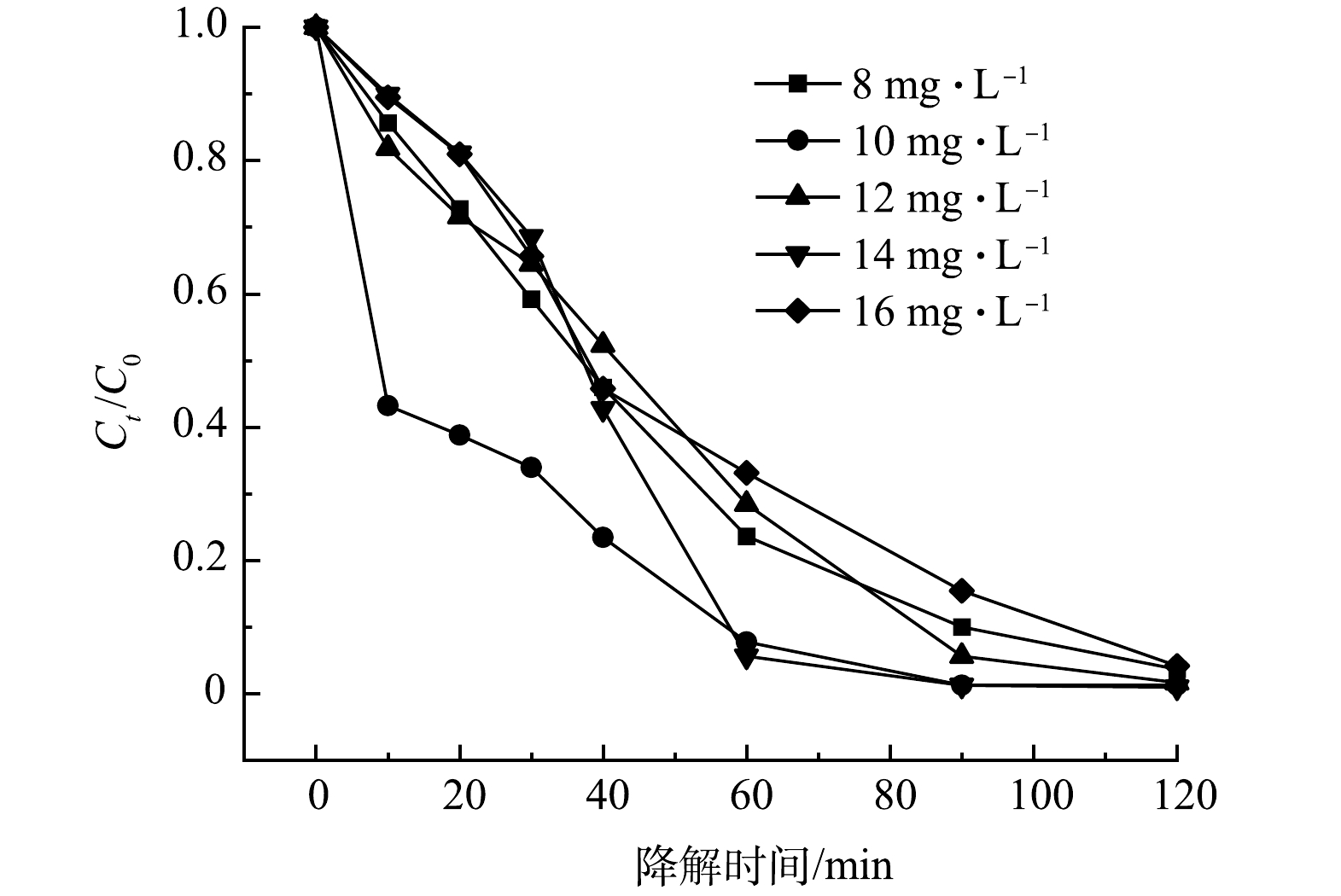
3) SMX初始浓度的影响。5A-MIL-88(Fe)对初始质量浓度为8、10、12、14、16 mg·L−1 SMX去除率如图7所示。可以看到,在120 min内,8~16 mg·L−1 SMX去除率均超过95%,14 mg·L−1 SMX去除率最高,达到99.04%。结果表明,对于一定质量浓度范围内的SMX抗生素污染物,以5A-MIL-88(Fe)作为催化剂构建的电化学降解体系均有较高的去除率,这说明5A-MIL-88(Fe)具有高效的催化降解性能能以及其在废水处理中潜在的应用前景。
2.4 材料循环利用和稳定性分析
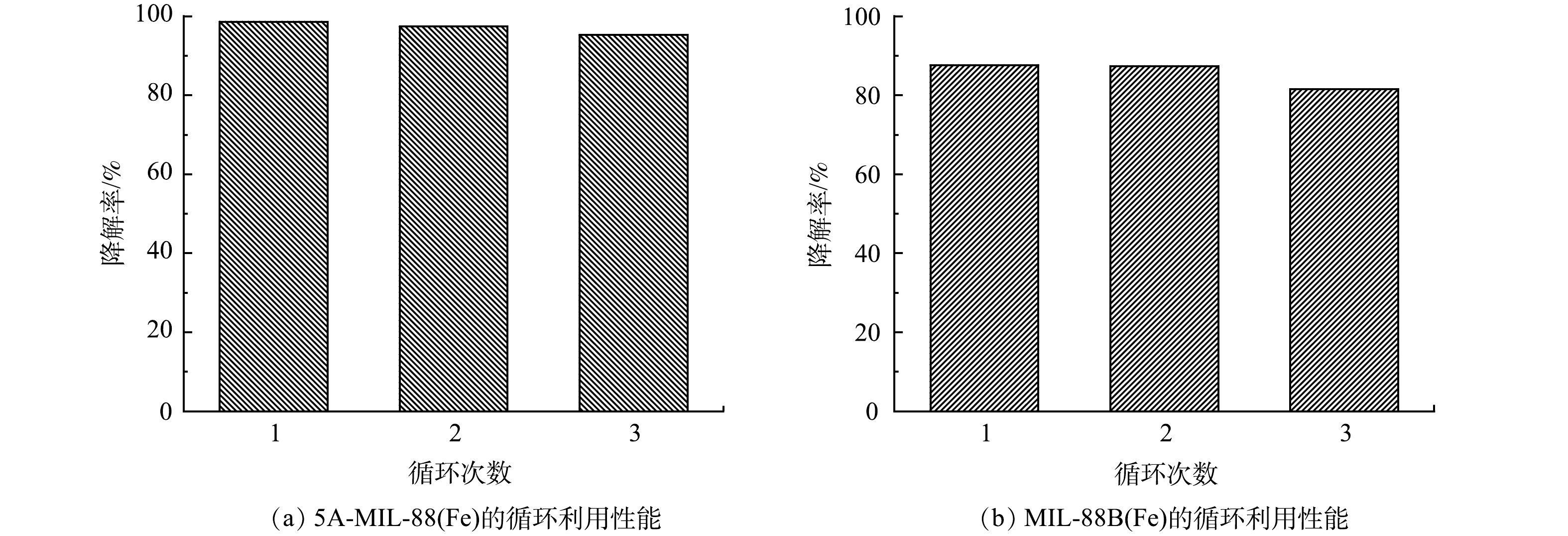
在工业污水处理领域,循环利用性能和稳定性是评价催化剂性能的重要指标,直接影响污水处理的效率和经济效益。控制电流40 mA、电压3.5 V,pH=3条件下,5A-MIL-88(Fe)和MIL-88B(Fe)催化降解10 mg·L−1 SMX的重复利用性能如图8所示。由图8(a)可见,5A-MIL-88B(Fe)连续3次催化降解10 mg·L−1 SMX效率分别为98.69%、97.44%、95.29%;由图8(b)可见,MIL-88B(Fe)连续3次催化降解10 mg·L−1 SMX效率分别为87.67%、87.42%、81.58%。可以看到,5A-MIL-88(Fe)和未经甲酸刻蚀的MIL-88B(Fe)循环利用和稳定性均良好,尤其是5A-MIL-88(Fe),对SMX的去除率始终保持在95%以上。MOFs材料一项显著的优点是结构稳定、重复利用性良好[26],上述实验结果证明,5A-MIL-88(Fe) 材料循环利用和稳定性良好可能是因为基本保持了原有MOFs材料的晶体骨架和结构完整性,这与XRD表征结果相互佐证。良好的循环利用性能为5A-MIL-88(Fe)在工业污水处理中的应用提供了潜能。
2.5 反应电流利用效率与能耗
在电化学反应中,法拉第电流效率是评价电化学反应的一项重要指标,通过计算产生H2O2的电流效率η,从而评价电极反应中消耗的电量与通过电路的总电量的比值。控制电流40 mA,电压3.5 V,pH=3条件下,5A-MIL-88(Fe)催化降解10 mg·L−1 SMX反应的法拉第电流效率η按式(7)计算。
η=(nFVΔC)4.32×107mIt (7) 式中:n为矿化每摩尔SMX所需要的电子数,n =61;F为法拉第常数,F=964 86 C·mol−1;V为反应体积,V=0.1 L;ΔC为降解反应前后SMX浓度的衰变,ΔC =9.872 mg·L−1;m为SMX碳原子数目,m=10;I为反应电流,I=0.04 A;t为反应时间,t=2 h。代入数值解得:SMX催化降解反应的法拉第电流利用效率η=16.81%。
在工业污水处理领域,能耗W是决定SMX电化学降解体系可行性的一项重要指标,结合电能的消耗和反应时间计算SMX电化学降解过程的能量消耗。控制电流40 mA,电压3.5 V,pH=3条件下,5A-MIL-88(Fe)催化降解10 mg·L−1 SMX反应的能耗W按公式(8)计算。
W=UIt1000V (8) 式中:U为反应电压,U=3.5 V;I为反应电流,I=0.04 A;t为反应时间,t=2 h;V为溶液体积,V=0.000 1 m3。代入数值解得:SMX催化降解反应能耗W=2.8 kW·h·m−3。
2.6 反应机理分析
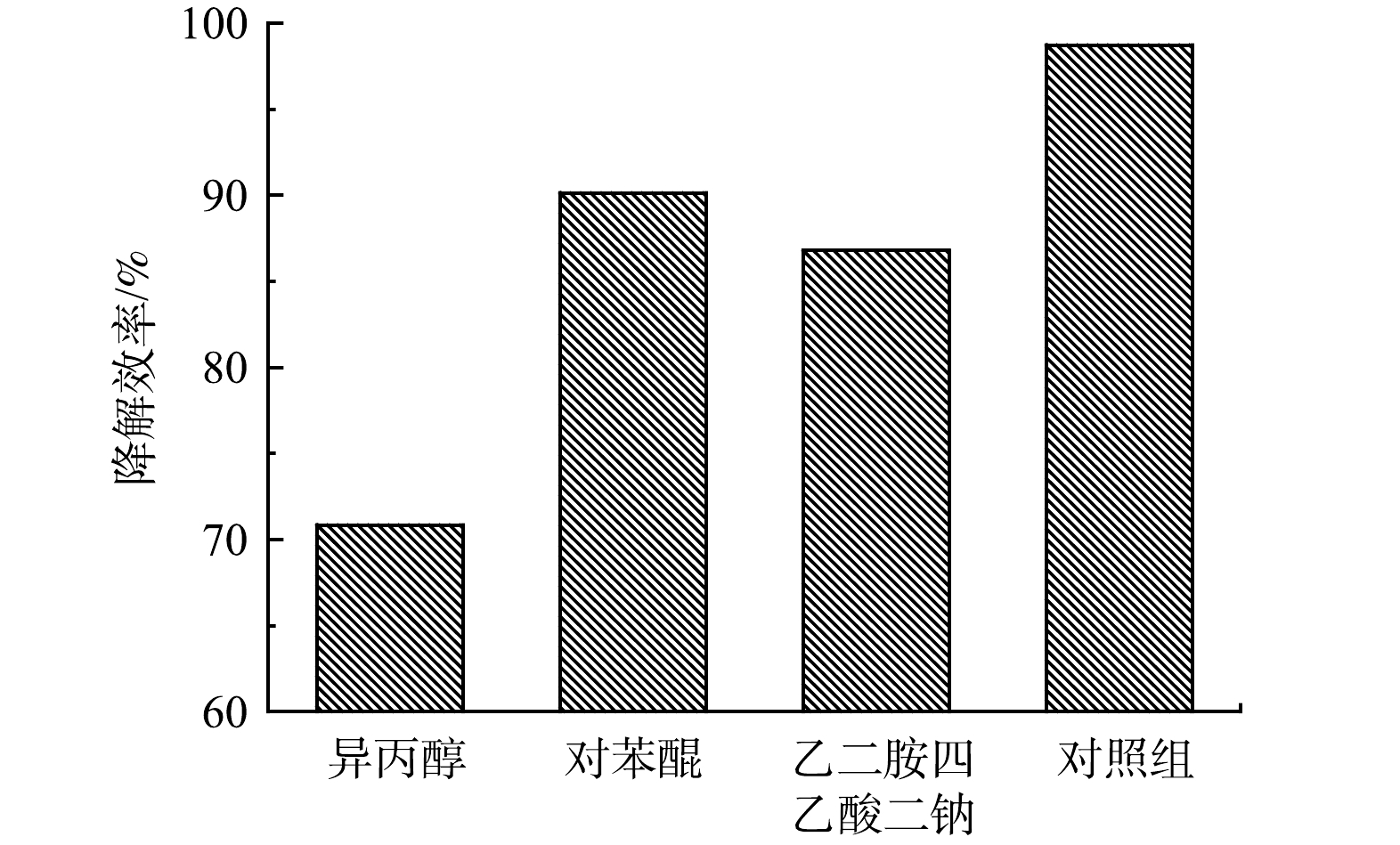
使用0.3 mmol 乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)、0.3 mmol 异丙醇(IPA)和对0.3 mmol对苯醌(BQ)分别作为空穴(h+) 、羟基自由基(·OH)和超氧自由基(·O2−)的淬灭剂,以探究SMX催化降解反应中起作用的活性物质以及反应可能的发生机理。加入0.3 mmol淬灭剂后,5A-MIL-88(Fe)对10 mg·L−1 SMX去除情况如图9所示。可以看出,反应进行120 min时,加入IPA的体系中SMX去除率降幅最大,去除率仅70.86%;加入BQ的体系中SMX去除率为90.14%;加入EDTA-2Na的体系中SXM去除率为86.79%。整体来看,以SMX去除率降低幅度由高至低排序为IPA>EDTA-2Na>BQ。结果表明,h+、·OH、·O2−在SMX催化降解过程中起到了共同氧化的作用,其中·OH起到的作用最大。h+具有强氧化性,阴极附近的大量e−将O2还原产生·OH、·O2−协同h+氧化降解SMX。5A-MIL-88(Fe)作为甲酸刻蚀制得的缺陷MOFs材料,保留了原有MOFs材料的多孔结构和内部框架可调功能,能够提供高密度的活性位点以产生h+、·OH、·O2−等活性自由基,在电流流通条件下,5A-MIL-88(Fe)内部分散性良好且可调节的活性位点阵列优化了材料的电子转移数目及电荷传输速率,从而能高效降解水中SMX为代表的抗生素污染物[27-28]。
2.7 其他催化剂对SMX去除率
表1列出了其他研究中的催化剂对SMX的去除情况。可以看出,综合考虑SMX初始浓度、降解时间和去除率,5A-MIL-88(Fe)催化降解SMX效果比其他催化剂具有一定的优势。表明5A-MIL-88(Fe)具有处理水中抗生素污染物的应用潜能。
表 1 其他催化剂对SMX的催化降解效果Table 1. Catalytic degradation efficiency of SMX by other catalysts3. 结论
1)通过甲酸刻蚀的方式制备了一系列缺陷MOFs,其中5 mmol甲酸刻蚀制得的5A-MIL-88(Fe)对SMX催化降解性能最优异,去除率、降解速率均优于未经刻蚀的MIL-88B(Fe)。以5A-MIL-88(Fe)作为催化剂构建的电芬顿降解体系具有处理废水中抗生素污染物的应用潜能。
2) pH、电流、SMX初始浓度是影响SMX去除率的重要因素。5A-MIL-88(Fe)催化剂对电流有较宽的适应范围、对一定质量浓度范围内波动的SMX均有较高的去除率,但仅能在较强酸性环境下高效催化降解SMX。
3) h+、·OH、·O2−对SMX的催化降解均有贡献,其中·OH的作用最为显著。适量甲酸的刻蚀会在MOFs材料表面引入缺陷位点,影响其形貌结构,从而构造出更多不饱和金属位点、改变Fe位点附近的电子密度、提升材料表面的电子传输速率以产生大量h+、·OH、·O2−,进而增强MOFs材料的导电性和电催化活性。
-
表 1 系列菌株形态特征
Table 1. Morphological characteristics of strains
菌株编号Strain number 大小/mmSize 形状Shape 颜色Color 表面形态Surface morphology 溶藻率/%Algae lysing rate 1# 1—3 圆形Circular 乳白Milky white 表面及边缘都光滑凸起Surface and edges are smooth and raised 48.91 2# 1—2 圆形Circular 白White 中间干瘪,凹The middle is shriveled and sunken 25.18 3# 3—4 圆形Circular 白White 表面及边缘都光滑凸起Smooth and convex surface and edge 9.73 4# 1—3 圆形Circular 橙黄Orange yellow 表面及边缘都光滑凸起Smooth and convex surface and edge 39.65 5# 1—2 圆形Circular 粉Pink 表面光滑smooth surface 4.52 -
[1] 景澄茗, 林涵, 陈庆丽, 等. 微生物控制水华藻的研究进展 [J]. 环境保护科学, 2014, 40(6): 34-37, 67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2014.06.007 JING C M, LIN H, CHEN Q L, et al. Progress in microbial control of water bloom [J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2014, 40(6): 34-37, 67(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2014.06.007
[2] 谢静, 潘伟斌, 曾嘉韫. 溶藻细菌L7代谢物对水华鱼腥藻的溶藻效应 [J]. 环境保护科学, 2014, 40(1): 36-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2014.01.009 XIE J, PAN W B, ZENG J Y. Algicidal Effect of Metabolites of Algicidal Bacteria Strain L7 on Anabaena Flosaquae [J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2014, 40(1): 36-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2014.01.009
[3] WANG L, WANG X, JIN X, et al. Analysis on algae growth mechanism and water blooms prediction under effect of multi-factor [J]. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 2017, 24(3): 556-562. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.01.026 [4] DANIEL J, JANA G, BLAHOSLAV M. Algicidal and cyanocidal effects of selected isoquinoline alkaloids [J]. Aquaculture Research, 2010, 41(5): 598-601. [5] LI Y, ZHU H, LEI X Q, et al. The first evidence of deinoxanthin from Deinococcus sp. Y35 with strong algicidal effect on the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 290: 87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.070 [6] SHU W, LING Z, HOU S, et al. Toxic effect on the membrane system and cell proliferation of Prorocentrum donghaiense caused by the novel algicidal fungus Talaromyces purpurogenus YL13 [J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2017, 29(1): 275-284. doi: 10.1007/s10811-016-0878-4 [7] GUO P Y, LIU Y, WEN X, et al. Effects of algicide on the growth of Microcystis flos-aquaeand adsorption capacity to heavy metals [J]. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 12(7): 2339-2348. [8] SON M, BAEK S H, SHIN K, et al. Effects of the algicide, thiazolidinedione derivative TD49, on microbial communities in a mesocosm experiment [J]. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 2015, 187(4): 162-171. [9] 程新, 李昆太, 黄林. 一株枯草芽孢杆菌的生长特性及抑藻效果研究 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(7): 120-125. CHENG X, LI K T, HUANG L. Study on the growth characteristics and algal inhibition of a Bacillus subtilis [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(7): 120-125(in Chinese).
[10] 王志勇, 石春芳, 曹菊梅. RZ1溶藻菌溶藻特性研究 [J]. 现代农业科技, 2016(1): 229-230. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2016.01.142 WANG Z Y, SHI C F, CAO J M. Study on the characteristics of RZ1 alginolytic bacteria [J]. Modern agricultural science and technology, 2016(1): 229-230(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2016.01.142
[11] 董小娜, 陈泽慧, 毛林强, 等. 太湖土著激浪鱼内脏中溶藻菌R1的筛选及其特性研究 [J]. 工业安全与环保, 2018, 44(8): 73-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2018.08.021 DONG X N, CHEN Z H, MAO L Q, et al. Screening and characterization of alginolytic bacteria R1 from the viscera of native surf fish in Taihu Lake [J]. Industrial safety and environmental protection, 2018, 44(8): 73-76(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2018.08.021
[12] 张志良. 植物生理学实验指导(第二版)[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1990. ZHANG Z L. Experimental guidance of plant physiology (second edition)[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1990(in Chinese).
[13] 全桂静, 雷晓燕, 李辉. 微生物学实验指导[M]]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2010. QUAN G J, LEI X Y, LI H. Experimental guidance of Microbiology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2010(in Chinese).
[14] 杨益民, 付必谦. 关于Logistic增长模型参数估计方法的再探讨 [J]. 统计与决策, 2015(13): 30-34. YANG Y M, FU B Q. Further discussion on the parameter estimation method of logistic growth model [J]. Statistics and decision making, 2015(13): 30-34(in Chinese).
[15] YAN R, JI H, WU Y, et al. An Investigation into the Kinetics and Mechanism of the removal of cyanobacteria by extract of ephedra equisetina root [J]. PLOS ONE, 2012, 7(8): e42285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042285 [16] 郑朔方, 杨苏文, 金相灿. 铜绿微囊藻生长的营养动力学 [J]. 环境科学, 2005, 26(2): 152-156. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.02.031 ZHENG S F, YANG S W, JIN X C. Nutritional dynamics of Microcystis aeruginosa growth [J]. Environmental Science, 2005, 26(2): 152-156(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2005.02.031
[17] 陈泽慧, 高志伟, 董小娜, 等. 藻毒素降解菌CQ5对MC-LR粗提液的降解动力学 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(1): 82-88. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017060403 CHEN Z H, GAO Z W, DONG X N, et al. Degradation kinetics of MC-LR crude extract by alginate degrading bacteria CQ5 [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(1): 82-88(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017060403
[18] LØNBORG C, ÁLVAREZSALGADO X. A, MARTÍNEZGARCÍA S, et al A, MARTÍNEZGARCÍA S, et al. Stoichiometry of dissolved organic matter and the kinetics of its microbial degradation in a coastal upwelling system [J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 2010, 58(2): 117-126. [19] 李小彩, 胡文容, 裴海燕, 等. 一株溶藻细菌(P15)的溶藻效应研究 [J]. 中国给水排水, 2006, 22(19): 8-11. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2006.19.003 LI X C, HU W R, PEI H Y, et al. Study on the algae dissolving effect of a algae dissolving bacteria (P15) [J]. Water Supply and Drainage in China, 2006, 22(19): 8-11(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2006.19.003
[20] 郭惠娟, 张伟, 张小梅, 等. 溶藻细菌Microbacterium oleivoran的溶藻进程与叶绿素降解动力学 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(6): 1274-1281. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018082801 GUO H J, ZHANG W, ZHANG X M, et al. The process of algal dissolution and the degradation kinetics of chlorophyll a of Microbacterium oleivoran [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(6): 1274-1281(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018082801
[21] 沈红池, 潘瑞松, 吴旭鹏, 等. 太湖芦苇根系中溶藻菌的分离鉴定及溶藻效果 [J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2017, 39(5): 123-128. SHEN H C, PAN R S, WU X P, et al. Isolation and identification of algae dissolving bacteria from reed roots of Taihu Lake [J]. Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2017, 39(5): 123-128(in Chinese).
[22] 孔赟. 溶藻菌分离鉴定、溶藻特性及作用机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. KONG Y. Isolation and Identification of Algae-lysing Bacteria[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013(in Chinese).
[23] 孔赟, 陈剑, 徐向阳, 等. Streptomyces sp. HJC-D1溶藻过程产物光谱学特征及机理 [J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 33(1): 167-171. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)01-0167-05 KONG Y, CHEN J, XU XY, et al. Spectroscopic characteristics and mechanism of products from algae dissolution process of Streptomyces sp. HJC-D1 [J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2013, 33(1): 167-171(in Chinese). doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)01-0167-05
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 任宝玉,戴东宸,钱超鸿. 间歇性投加Fe(Ⅱ)控制陶瓷膜MBR膜污染的机理分析. 化工环保. 2024(03): 362-370 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈作云,柴玉茜,姚宏. 铁路站段含油废水处理模式的碳排放研究. 铁道标准设计. 2024(09): 216-220 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 周兴. 海上低渗油田含油污水陶瓷膜处理现场试验与分析. 石油化工应用. 2024(11): 61-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 介志远,赵世凯,张久美,李亮,李洪达,李杰,李小勇,徐传伟,张珂珂,张子豪. 高精度陶瓷平板分离膜的制备及性能研究. 现代技术陶瓷. 2023(Z1): 509-516 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载: