-
传统污水处理工艺如A/O、CASS、氧化沟等采用单一污泥悬浮生长体系因其具有工艺简单、氮磷去除效果较好得到广泛应用,但采用单污泥体系的污水处理工艺在培养硝化菌、反硝化菌进行脱氮除磷过程中存在有机负荷、泥龄以及碳源需求上的竞争与矛盾,很难获得良好的污染物去除效果[1-2]。因此,在20世纪80年代JONES等[3-4]提出了构建双污泥体系工艺即A2N(厌氧/缺氧-硝化)工艺的思路,通过将硝化菌和反硝化菌分别独立培养,从而提高生物脱氮工艺对污水中碳源的利用效率,解决了硝化菌和反硝化菌泥龄矛盾等问题。
与单污泥体系的传统生物脱氮工艺相比,双污泥体系生物脱氮工艺具有污泥产量低、不同功能菌分开培养、有效利用碳源等优点[5],但是也存在固有缺陷。目前双污泥体系生物脱氮工艺包含间歇式和连续式两种模式,间歇式A2N工艺采用2座SBR(sequencing batch reactor)分别培养硝化菌和反硝化菌,工序较长,且有效污水处理时长受到污泥沉降性等因素影响,如果采用膜生物反应器,膜污染问题也会增加运行成本。而连续式A2N工艺由于处理设施较多,工艺流程与一般单污泥体系生物脱氮工艺更长,实际应用中建设成本和运行成本有所增加,同时间歇式和连续式A2N工艺均存在出水氨氮浓度较高的问题[6]。
本研究利用自主设计的实验室规模泥水分离反应器替代SBR,在反应器内截留污泥,富集培养功能微生物,将双污泥体系与A/O工艺相结合,构建缺氧和好氧污泥完全独立的双污泥生物脱氮工艺,根据运行模式特点称为A/O双污泥工艺。通过连续稳定运行实验,验证A/O双污泥工艺的脱氮性能,根据批次实验研究了工艺运行过程的氮素转化规律,并通过16S rRNA测序手段揭示了工艺运行过程中微生物群落结构对脱氮性能的影响方式。最后基于以上实验结果评估A/O双污泥工艺进一步开发研究的潜力,总结工艺需要优化的问题点,为工艺实际应用研究提供数据支撑。
-
缺氧池和好氧池接种污泥分别取自运行一段时间的好氧SBR和缺氧SBR。在第1阶段(1~7 d)开始前分别倒入缺氧池和好氧池启动A/O双污泥工艺,工艺启动后污泥浓度(MLSS)大约为2 000 mg·L−1。
工艺启动及运行阶段均采用模拟废水,其主要组分NH4+-N浓度为400 mg·L−1,其他组分有0.8 g·L−1 K2CO3、1.5 g·L−1 Na2HPO4、1 m L·L−1 营养液(2.5 g·L−1 FeSO4·7H2O、0.44 g·L−1 CaCl2、0.19 g·L−1 MgCl2、0.06 g·L−1 ZnCl2、0.045 g·L−1 MnSO4·H2O、0.06 g·L−1 H3BO3、0.11 g·L−1 CoSO4·7H2O、0.06 g·L−1 CuSO4·5H2O、0.04 g·L−1 NiCl2·6H2O、0.034 g·L−1 钼酸铵)[7],模拟废水碳源采用乙酸钠和蔗糖按1:1配制。
-
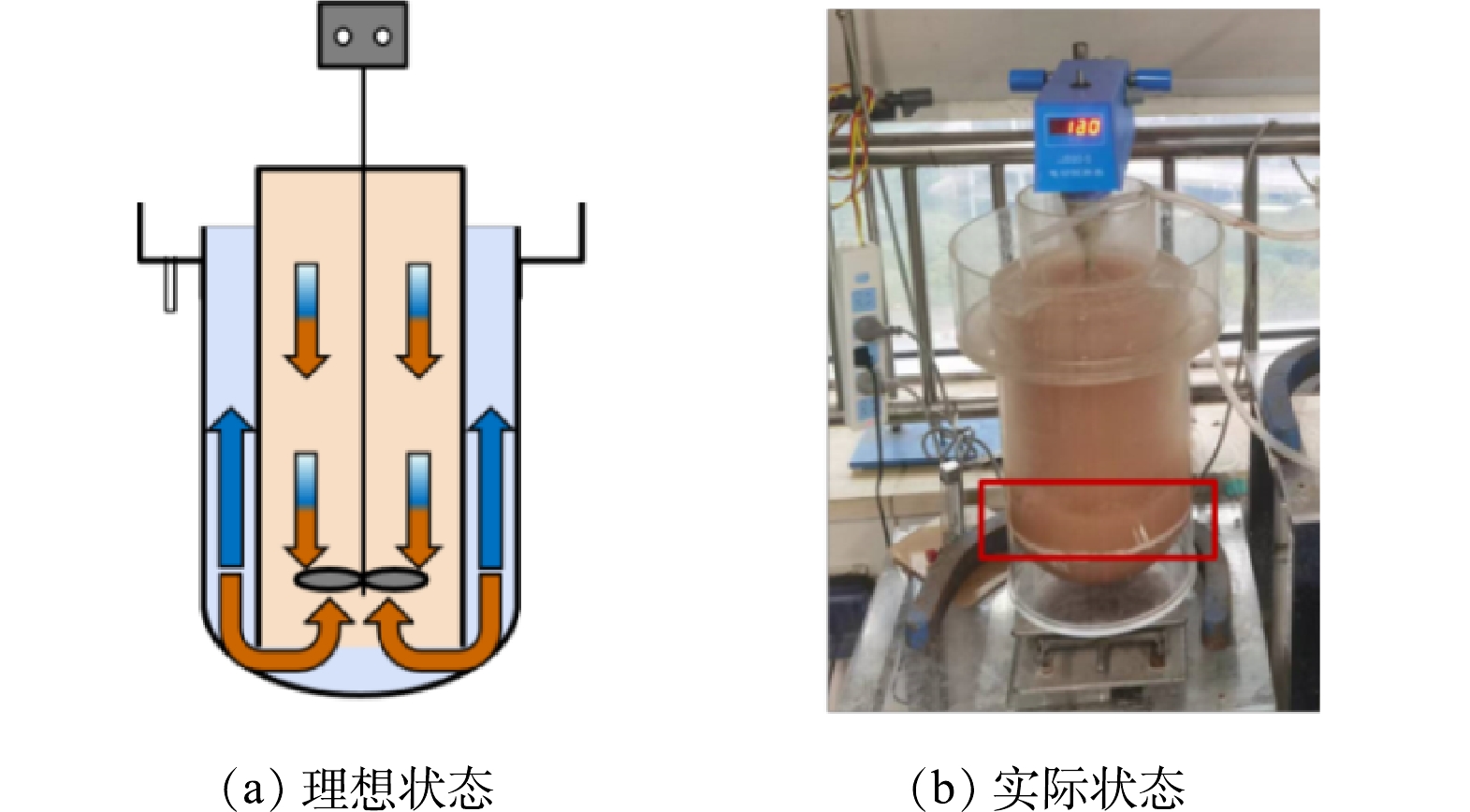
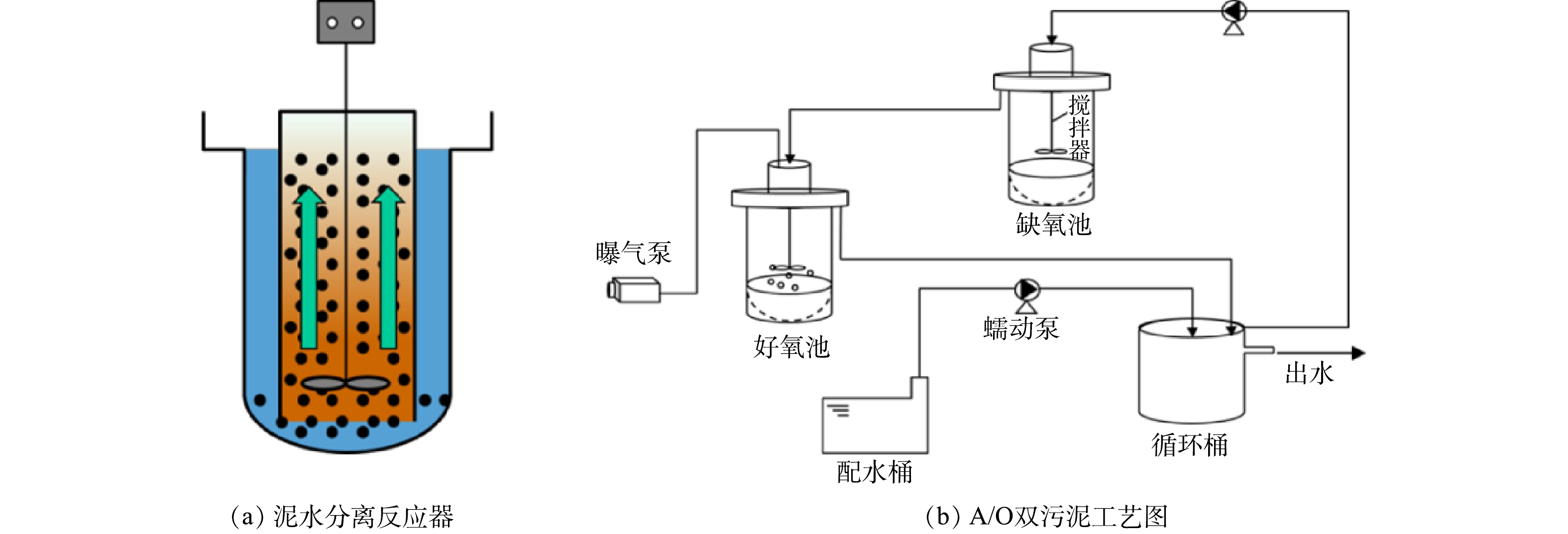
反应器总有效体积为13.2 L,缺氧池和好氧池有效体积均为6.6 L,采用课题组设计的泥水分离反应器,反应器结构如图1(a)所示。该反应器通过搅拌桨旋转提供的升力将沉降性能良好的活性污泥截留在图1(a)黄色区域和反应器底部,废水在反应器下部完成泥水分离过程,最后从外圈出水堰进入下一构筑物。
A/O双污泥工艺流程如图1(b)所示。实验装置由有机玻璃制成,每个运行周期通过蠕动泵(Longer, BT101L,UK)从配水桶抽水进入循环桶,然后泵入缺氧池,再利用高度差重力流作用从缺氧池出水堰流入好氧池,最后在高度差重力流作用下返回循环桶,完成一次废水在工艺的内循环过程。循环桶内每个周期均预留4 L水,工艺启动及运行过程中进水体积与排水体积均为2 L。工艺运行采用时间继电器控制,每个周期总时长为8~12 h,模拟废水进水时长固定为50 min,排水时长固定为10 min,在整个运行周期内一直保持废水在工艺不同构筑物之间连续循环流动的过程。
-
第Ⅰ阶段(1~7 d),从SBR转移活性污泥至对应的泥水分离反应器,然后启动工艺。第Ⅱ阶段增大废水内循环速度,提高工艺整体的脱氮效率。第Ⅲ阶段缩短水力停留时间,增加日进水负荷,避免低负荷运行影响工艺功能菌活性,加快污泥老化。在第Ⅲ阶段结束后,设置进水NH4+-N浓度为200 mg·L−1,其他条件不变,选择乙酸钠作为碳源,在4种C/N比(5、7、9、11)条件进行批次实验,研究工艺运行过程的氮素转化规律。本研究A/O双污泥工艺启动及运行阶段运行参数详见表1。
-
水质指标 NH4+-N、NO2−-N、NO3−-N、COD指标均采用国家规定的标准方法监测。包括纳氏试剂分光光度法(NH4+-N)、(1-萘基)-乙二胺分光光度法、(NO2−-N)和氨基磺酸紫外分光光度法(NO3−-N)、重铬酸钾法(COD)。
-
利用16SrRNA技术分析活性污泥微生物群落结构组成,包括微生物丰度占比及微生物多样性变化(上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司)。使用上游引物338F(5'-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3')和下游引物806R (5'- GGACTACH VGGGTWTCTAAT-3')扩增细菌16S rRNA基因的V3~V4区域。扩增程序如下:95 ℃预变性3 min,25个循环(95 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火30 s, 72 ℃ 延伸45 s),然后72 ℃稳定延伸10 min,最后在10 ℃进行保存(PCR仪:ABI GeneAmp® 9700 型)。
聚合酶链式反应(PCR)扩增产物利用Illumina MiSeq测序仪(中国上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司所有)进行测序,将高通量测序结果得到的有效序列进行聚类分析,利用Uparse平台(版本7.1)按照97%相似性对非重复序列进行OUT(operational taxonomic units)聚类,然后利用Silva数据库对不同的OTU代表性序列进行标注和评价。
-
图2反映了工艺运行过程中泥水分离反应器的运行效果。在理想状态下,污水从进水管流入内筒与污泥混合,在泥水混合液向外筒扩散过程中,搅拌桨旋转提供向上升力将大部分污泥截留在内筒,最后在到达外筒底部时,剩余污泥在自身重量作用下被截留在底部半球形区域运动,仅有极少量衰亡或活性变差的污泥与水一起流入出水堰到达下一反应器。由图2(b)中所示的反应器实际运行效果来看,大部分污泥能够被截留在内筒进行培养,经过取样检测,缺氧池出水SS保持在44 mg·L−1,好氧池出水SS保持在40 mg·L−1,大幅减少了混合回流液中污泥的含量。以上结果证明实际运行效果基本符合理想状态下设计该反应器的运行目标,但出水SS与一级出水A标准仍有一定差距,后续反应器需要进一步优化,降低出水SS。
-
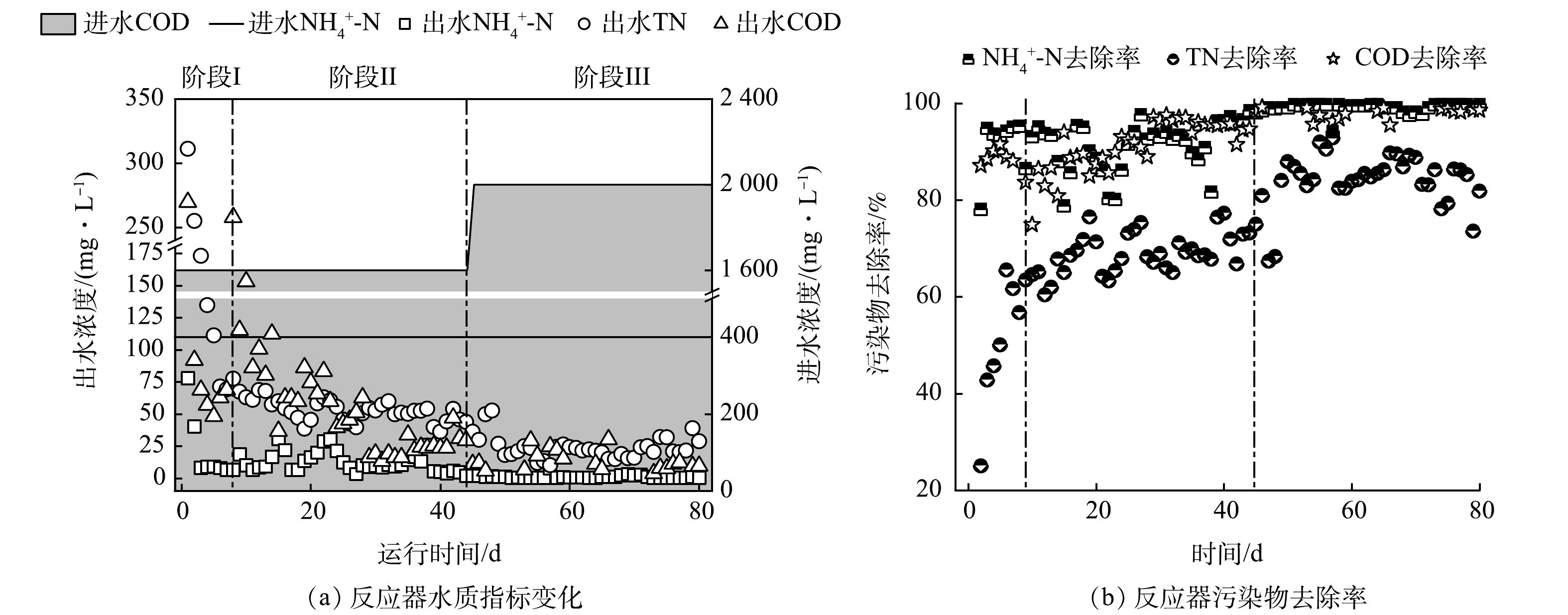
图3反映了A/O双污泥工艺在不同运行阶段各项水质指标变化过程,不同阶段运行参数如表1所示。阶段Ⅰ(0~7 d)是在进水NH4+-N浓度为400 mg·L−1、C/N为4条件下启动工艺,在工艺启动前分别对好氧池和缺氧池污泥进行一段时间的驯化恢复操作,因此,阶段Ⅰ(0~7 d)工艺的NH4+-N、TN出水浓度和出水COD快速下降,NH4+-N和COD去除率达到80%以上,TN去除率达到60%,这说明工艺已具有一定污染物去除能力。阶段Ⅱ(8~44 d)将内循环速度提高至78 mL·min−1,TN出水浓度由超过60 mg·L−1降至40 mg·L−1,出水COD值从68 mg·L−1降至29 mg·L−1,由于进水采用模拟废水,NH4+-N出水浓度整体较低,因此,TN出水浓度主要与缺氧池的反硝化脱氮效率有关,与传统A/O工艺相比,本研究采用泥水分离反应器可以减少好氧池出水混合液回流时含有的污泥量,从而降低回流液携带的溶解氧,因此,单座反应器的水力停留时间可以从3.55 h缩短至1.41 h,回流比提高至4以上,让缺氧池单位时间内流入的TN浓度、COD值更高,从而提升缺氧池反硝化细菌的有机物利用效率。阶段Ⅲ(45~80 d)将C/N从4提高至5,运行周期从12 h缩短至8 h,出水NH4+-N浓度和COD值与阶段Ⅱ基本一致,有机负荷和氨氮负荷提高并未对反应器内功能菌活性造成冲击。这表明泥水分离反应器可以通过截留污泥保持污泥浓度,为功能菌生长提供稳定的环境,保证工艺对负荷提高产生的冲击具有良好的耐受性。同时工艺的运行模式对高氨氮进水能够产生一定稀释作用,能够降低高氨氮废水中游离氨的浓度,减轻游离氨对好氧池硝化细菌脱氮效率的抑制作用,让A/O双污泥工艺在80 d运行过程中始终保持较高的氨氮去除效率。这表明A/O双污泥工艺运行模式在高氨氮废水处理方面具有一定应用潜力。
经过80 d的稳定运行,A/O双污泥工艺在进水氨氮负荷为0.11 kg·(m3·d)−1、C/N比为5、内循环速度为78 mL·min−1条件下,COD和NH4+-N去除率均达到90%以上,TN去除率超过80%,因此,上述运行参数可以认为是保持工艺高去除效率的适宜条件。
A/O双污泥工艺脱氮性能对比如表2所示。与表中文献报道的A2/O(anaerobic/anoxic/oxic)、A/O等工艺相比,A/O双污泥工艺的氨氮负荷和氮去除负荷更高,无需二沉池,没有污泥回流路径,同时采用泥水分离反应器构建独立培养功能菌的双污泥体系,极大减少了污水循环流动过程中混合的污泥量,降低了污水快速流动过程中污泥携带溶解氧对缺氧区环境的影响。与采用SBR的双污泥体系工艺(A2NSBR工艺)相比,A/O双污泥工艺采用泥水分离反应器精简了SBR的控制流程,提高了工艺处理污水的有效时间,在C/N更低的条件下达到更高的处理负荷。在高浓度氨氮废水处理应用方面,总计80 d的水质指标表明工艺具有一定应用价值,但与已有研究相比,还应进一步研究反应器结构优化及调控运行参数,在工艺最优运行参数下,通过提升进水负荷来判断工艺能够达到的处理负荷上限从而准确评估在高浓度氨氮废水处理实际应用的潜力。综上所述,表2脱氮性能数据对比说明采用泥水分离反应器搭建的A/O双污泥工艺在生活污水处理方面具有进一步开发的价值和潜力。
-
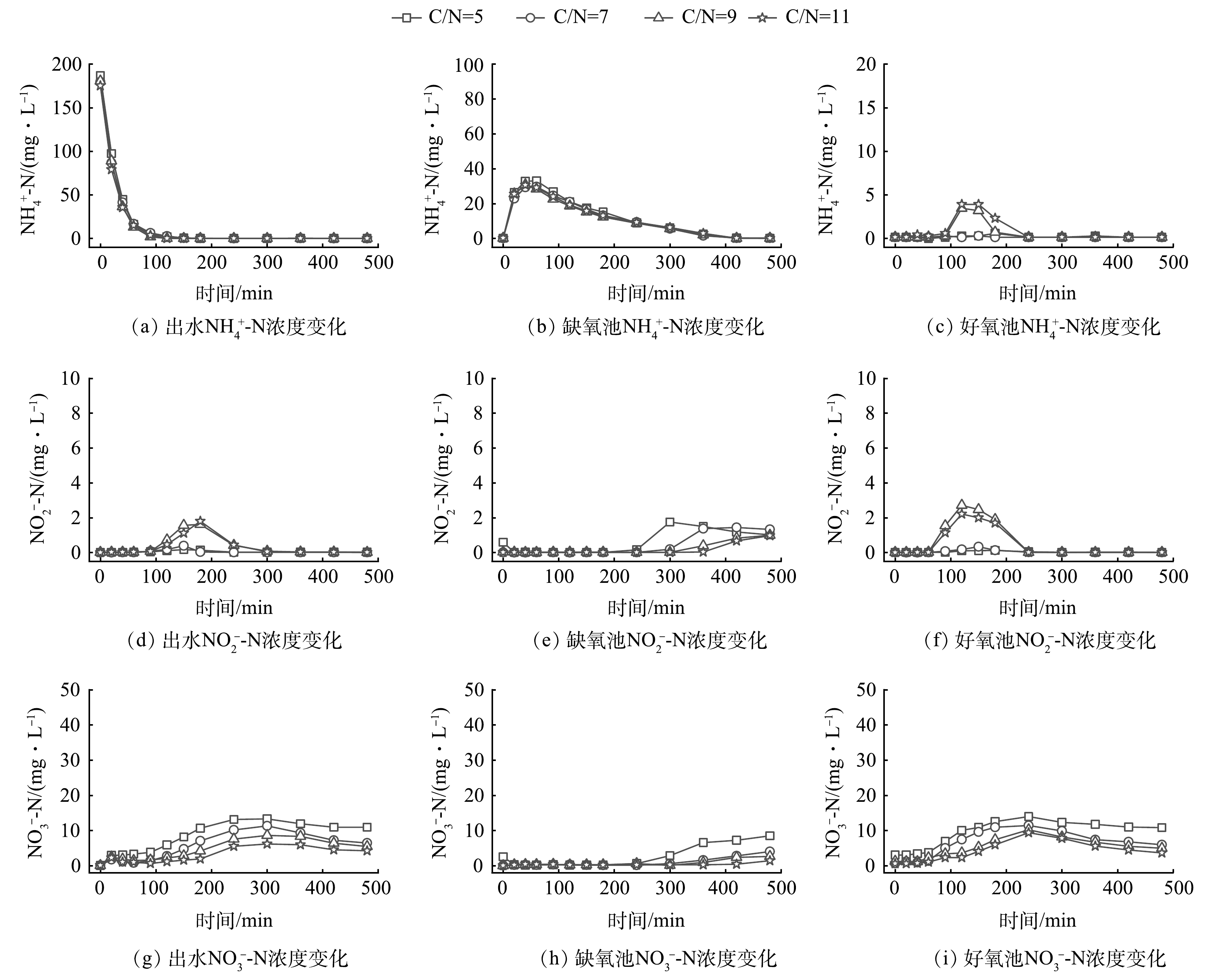
图4为以乙酸钠为碳源时,A/O双污泥工艺在不同C/N条件下脱氮过程的指标变化。图4(a)~(f)反映了不同反应器NH4+-N、NO2−-N浓度变化,在4种C/N条件下,循环桶出水区、缺氧池NH4+-N浓度变化无显著差异,好氧池在C/N为9、11时出现NH4+-N、NO2−-N短暂积累。这说明C/N较高时对好氧池脱氮功能菌产生抑制作用,因为乙酸钠结构简单,通过三羧酸循环即可参与细胞代谢[16],碳源过量时无法在缺氧池被完全分解利用流入了好氧池,造成异养菌能够利用碳源迅速增殖与脱氮功能菌竞争溶解氧[17],导致水中溶解氧浓度不足,在好氧池出现NH4+-N、NO2−-N浓度短暂积累的现象。
图4(g)~(i)反映了NO3−-N浓度随时间在不同反应器的变化过程。从最终产物浓度在不同反应器的分布情况来看,反硝化过程是限制工艺体系脱氮效率提高的关键因素。随着C/N升高,出水NO3−-N浓度下降幅度逐渐减小,说明过多有机物加入超出了反硝化菌的代谢能力,过量碳源被其他代谢途径消耗,无法参与反硝化过程;而在C/N较低的条件下,有机物在C/N比为5、7、9时,仅需4 h即在缺氧池降至较低水平,无法平均分配到整个工艺运行过程,导致运行周期后半段有机物不足,NO3−-N浓度升高。因此,优化碳源投加方式是提高缺氧池反硝化菌对有机物利用效率的有效途径之一。A/O双污泥工艺在运行过程中采用乙酸钠加蔗糖的复合碳源组合,利用高分子有机物分解代谢时间较长的特点,让每个周期运行后半段仍有一定比例的碳源能被反硝化细菌利用。但在实际应用时面对水质有机物组成复杂,C/N低的条件,还应考虑其他优化方式,例如,延长碳源投加时间,避免一次性投加过量,保证碳源投加过程中主要在缺氧池被反硝化功能菌快速利用去除NO3−-N,避免单位时间投加碳源量超出功能菌承受能力,导致碳源被其他代谢途径消耗。
-
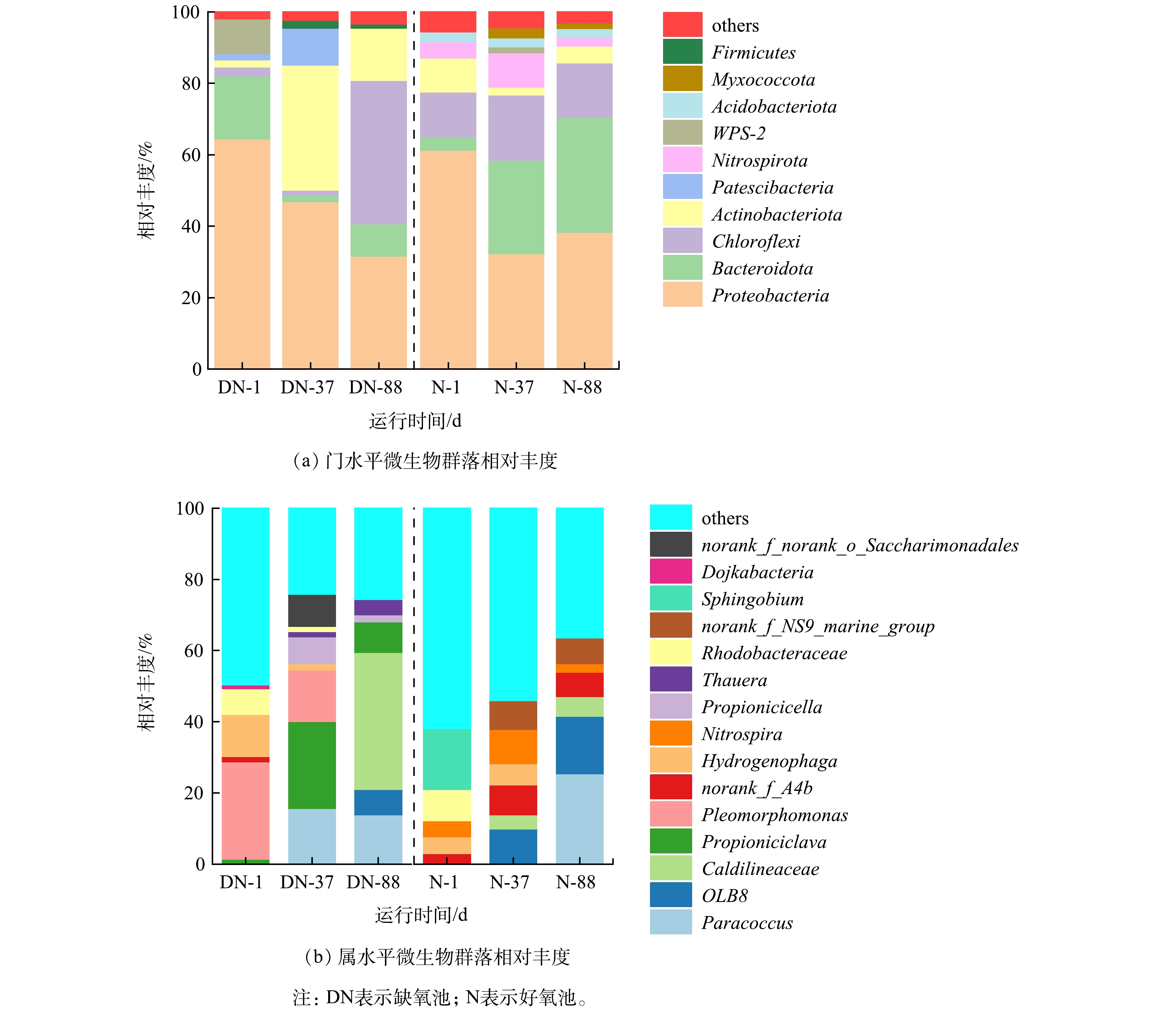
图5为工艺缺氧池和好氧池取样得到不同阶段的微生物群落指标。由图5(a)表示的门水平微生物群落结构可知,变形菌门(Proteobacteria)在所有样品中均保持优势,是传统污水处理厂最常见、丰度最高的细菌之一[18],对有机物和氮元素具有良好的去除效果。绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi) 、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)和放线菌门(Actinobacterota)的细菌可以将难降解有机物进行降解[19-22],分解成易于微生物利用的简单有机物,放线菌门(Actinobacterota)除了可以分解有机物,门下某些细菌也会参与到反硝化脱氮过程中[23]。在好氧池的硝化螺旋杆菌门(Nitrospirota)则是硝化反应常见的硝化菌种,在运行阶段丰度减少可能与变形菌门包含的好氧脱氮菌竞争有关。与其他研究[24-25]相比,变形菌门(Proteobacteria)在工艺体系下没有大幅度高于其它菌门的原因可能是,投加碳源为乙酸钠加蔗糖的复合碳源,蔗糖分解需要其他微生物参与,而工艺采用的泥水分离反应器为截留富集不同种类微生物提供了有利条件,因此,产生了多种菌门相对丰度与主要脱氮菌种变形菌门(Proteobacteria)丰度比较接近的现象。
从属水平分析,经过88 d的运行,缺氧池具有反硝化功能或反硝化潜力的菌属包括副球菌 (Paracoccus)、陶厄氏菌(Thauera)以及Caldilineaceae菌[26-28]在缺氧池的相对丰度升高,其中Caldilineaceae菌属相对丰度达到了38.47%,这可能是因为其属于具有分解有机物能力的绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi),对蔗糖类高分子碳源适应性更强,在竞争中逐渐占据优势。在好氧池中与硝化相关的菌属有硝化螺菌(Nitrospira)和副球菌(Paracoccus) ,目前,副球菌(Paracoccus)已有关于异养硝化-好氧反硝化菌种被报道,ZHENG等、MEDHI等[29-30]研究中利用副球菌(Paracoccus)细菌实现了同步硝化反硝化过程,减少了脱氮所需碳源。本研究利用泥水分离反应器有效富集了全程硝化功能菌硝化螺菌(Nitrospira)[31-32]和实现异养硝化-好氧反硝化过程的副球菌(Paracoccus),这可能是工艺能够实现氨氮去除率达到90%以上的重要原因。因此,通过设计新型反应器,调整运行工况培养富集脱氮所需功能菌群是A/O双污泥工艺实现较低C/N比条件下高效处理高氨氮废水,NH4+-N、COD去除率超过90%、TN去除率超过80%的原因之一。
-
经过80 d的运行实验,A/O双污泥工艺在较低C/N条件下表现出良好的脱氮性能,与传统脱氮工艺相比,具有一定实际应用的潜力,但在实际中试前也存在以下需要改进的问题。首先是现有反应器结构存在有效体积在总体积占比不足的问题,反应器总体积为11 L,有效体积只有6.6 L;其次,反应器出水SS浓度与一级出水A标准还有一定差距,上述2个问题需要研究其它方法来解决,比如筛选合适的填料、利用CFD软件进行模拟实验来优化结构等;同时在“双碳”背景下,急需开发节能降耗的污水处理工艺,面对污水C/N比低的处理难题,还应该将泥水分离反应器与新型脱氮技术相结合,如短程硝化、短程反硝化及厌氧氨氧化等,进一步降低脱氮所需碳源,同时保持高效的脱氮效率以及氮去除负荷。
-
1)结合双污泥体系的A/O双污泥工艺与传统A/O、A2/O等工艺相比,可以在更低的C/N比下保持良好的TN去除率,与采用SBR的A2N工艺相比,采用泥水分离反应器的A/O双污泥工艺精简了处理工序,简化了操作流程,取消了污泥回流过程,具有进一步开发优化的潜力。
2)根据工艺运行过程的氮素转化规律表明,A/O双污泥工艺脱氮效能主要受反硝化过程脱氮效率限制,应考虑改变碳源投加方式或进水方式提高有机物在缺氧池的停留时间,优化工艺体系利用有机物的效率。
3)微生物群落结构分析结果表明,A/O双污泥工艺的主要功能菌包括变形菌门、绿弯弧菌门、拟杆菌门在门水平上相对丰度占比较高,在属水平上缺氧池反硝化相关菌属相对丰度较高,好氧池既存在硝化相关菌属,还存在主导异养硝化-好氧反硝化过程的副球菌(Paracoccus),这种异养硝化-好氧反硝化过程可能是工艺维持较高TN去除率的原因之一。
4)泥水分离反应器和A/O双污泥工艺还存在较大优化空间,在后续研究中应结合流场模拟技术、新型脱氮技术等手段向节能降耗、智能化调控的方向继续发展。
A/O双污泥工艺脱氮性能
Nitrogen removal performance of A/O process with two-sludge system
-
摘要: 针对传统A/O(anaerobic/oxic)工艺中反硝化细菌对有机物的利用效率低、A2N(anaerobic/anoxic-nitrification)工艺工序繁琐和出水氨氮浓度较高的问题,提出了一种泥水分离反应器,将双污泥体系与A/O工艺结合构建A/O双污泥工艺。对工艺运行过程的脱氮性能、微生物群落变化及氮素转化规律进行了研究,根据研究结果评估泥水分离反应器和A/O双污泥工艺在实际应用中的开发潜力,并总结工艺和反应器需要优化的问题,提出解决问题的思路。结果表明:在进水氮负荷为0.11 kg·(m3·d)−1条件下,工艺的氮去除负荷可以达到0.089 kg·(m3·d)−1,NH4+-N去除率超过95%、COD去除率超过90%,TN去除率达到80%以上,该工艺能够实现长期稳定运行。反硝化过程反应速率是提升A/O双污泥工艺脱氮效率的限速步骤,强化有机物在缺氧池中的接触停留是有机物利用率提高的关键。因此,需要对现有碳源的投加方式、污水的进水方式或工艺的反应器数量进行优化,进一步提高工艺对碳源的利用效率。微生物群落结构表明陶厄氏菌(Thauera)、硝化螺杆菌(Nitrospira)、Caldilineaceae等硝化反硝化功能菌属与主导异养硝化-好氧反硝化过程的副球菌(Paracoccus)共同协作是维持高NH4+-N去除率和TN去除率的原因之一。综上所述,A/O双污泥工艺具有良好的脱氮性能,具备实际应用价值,同时该研究结果可为工艺及反应器存在的缺陷进行后续优化研究提供参考。Abstract: To address the low utilization efficiency of organic matter by denitrifying bacteria in traditional A/O processes, the complexity of A2N(anaerobic/anoxic-nitrification) process steps, and the high concentration of effluent ammonia nitrogen, a sludge-water separation reactor was proposed. The two-sludge system and A/O process were combined to build the A/O two-sludge process to tackle these challenges. The denitrification performance, variations in microbial communities, and nitrogen transformation patterns during the process operation were studied, the development potential of the sludge-water separation reactor and the A/O two-sludge process based on the research results were evaluated. Additionally, the issues that require optimization in both the process and reactors were summarized and the strategies to address these challenges were raised. The result showed that at an influent nitrogen loading of 0.11 kg·(m3·d)−1, the nitrogen removal load of the process could reach 0.089 kg·(m3·d)−1. The NH4+-N removal efficiency exceeded 95%, COD removal rate surpassed 90%, and TN removal rate exceeded 80%, which could ensure the long-term stable operation of systems. Analysis of the nitrogen transformation patterns indicates that the reaction rate of the denitrification process was the limiting factor in improving the denitrification efficiency of A/O two-sludge process. Increasing the contact time of organic matter in the anoxic tank was crucial for improving the organic matter utilization rates. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize the current carbon source addition method, influent mode, or the number of reactors in the process for further increasing the process efficiency in utilizing carbon sources. The microbial community structure suggests that the cooperative action of denitrifying bacteria, such as Thauera, Nitrospira, Caldilineaceae, along with the predominant heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacterium Paracoccus, was the key factor in maintaining high removal efficiencies of NH4+-N and TN. In conclusion, the A/O two-sludge process had an excellent denitrification performance and a practical application value. The results of this study can provide a reference for subsequent optimization research to address existing deficiencies in both the process and reactors.
-
表 1 不同阶段工艺运行条件
Table 1. Conditions of process operation at different stages
阶段 时间/d 运行周期/h DO/(mg·L−1) 内循环速度/(mL·min−1) C/N 氨氮负荷/(kg·(m3·d)−1) Ⅰ 1~7 12 2~4 31 4 0.073 Ⅱ 8~44 12 2~4 78 4 0.073 Ⅲ 45~80 8 2~4 78 5 0.11 表 2 泥水分离反应器脱氮性能对比
Table 2. Comparing the nitrogen removal performance of sludge-water separating reactors
工艺 进水水质 NH4+-N进水/(mg·L−1) TN进水/(mg·L−1) C/N 氮容积负荷/(kg·(m3·d)−1) 氮去除负荷/(kg·(m3·d)−1) 来源 A/O双污泥 合成废水 400 400 5 0.11 0.089 本研究 A/O 合成废水 60 83 9 0.083 0.071 [8] A2NSBR 生活污水 35.31 37.28 6~7 0.074 0.061 [9] MBBR 合成废水 50 100 10 0.2 0.16 [10] MBR 生活污水 85~115 — 6~10 0.11~0.15 0.0847~0.12 (仅氨氮) [11] A2/O 合成废水 31 31 >10 0.124 0.074 [12] A/O 合成废水 45 45 6~7 0.12 0.1056 [13] UMSR 猪场废水 393 394 0.93 0.179 0.164 [14] A2/O 猪场废水 (575±116) (688±143) (2.83±0.67) (0.057±0.012) (0.037±0.003) [15] -
[1] 张杰, 臧景红, 杨宏, 等. A2O工艺的固有缺欠和对策研究[J]. 给水排水, 2003, 29(3): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2003.03.008 [2] FIGDORE B A, DAVID STENSEL H, WINKLER M-K H. Bioaugmentation of sidestream nitrifying-denitrifying phosphorus-accumulating granules in a low-SRT activated sludge system at low temperature[J]. Water Research, 2018, 135: 241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.035 [3] JONES W L, SCHROEDER E D, WILDERER P A. Denitrification in a batch wastewater treatment system using sequestered organic substances[J]. Research Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 1990, 62(3): 259-67. [4] WANNER J, ČECH J S, KOS M. New process design for biological nutrient removal[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1992, 25(4/5): 445-8. [5] LI X K, HUANG R X, BAO L L, et al. Simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal in a continuous-flow two-sludge system[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 18: 52-7. [6] 刘莹, 彭永臻, 王淑莹. A2N工艺的固有弊端分析及其对策研究[J]. 工业用水与废水, 2010, 41(6): 1-5. [7] WANG Q, DUAN H, WEI W, et al. Achieving Stable Mainstream Nitrogen Removal via the Nitrite Pathway by Sludge Treatment Using Free Ammonia[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(17): 9800-7. [8] JI B, ZHANG H, ZHOU L, et al. Effect of the rapid increase of salinity on anoxic-oxic biofilm reactor for treatment of high-salt and high-ammonia–nitrogen wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 337: 125363. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125363 [9] 王亚宜, 彭永臻, 殷芳芳, 等. 双污泥SBR工艺反硝化除磷脱氮特性及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(6): 1526-32. [10] BIAN X, WU Y, LI J, et al. Effect of dissolved oxygen on high C/N wastewater treatment in moving bed biofilm reactors based on heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification: Nitrogen removal performance and potential mechanisms[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 365: 128147. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128147 [11] 张西旺, 金奇庭. 一体式MBR处理高氨氮小区生活污水中试研究[J]. 环境工程, 2003, 21(1): 23-26. [12] BAEZA J A, GABRIEL D, LAFUENTE J. Effect of internal recycle on the nitrogen removal efficiency of an anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (A2/O) wastewater treatment plant (WWTP)[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2004, 39(11): 1615-24. doi: 10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00300-5 [13] 陈燕, 刘国华, 范强, 等. 不同溶解氧条件下A/O系统的除碳脱氮效果和细菌群落结构变化[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(7): 2610-2616. [14] TIAN Y, LI J, FAN Y, et al. Performance and nitrogen removal mechanism in a novel aerobic-microaerobic combined process treating manure-free piggery wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 345: 126494. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126494 [15] CHEN Y, ZHENG R, SUI Q, et al. Coupling anammox with denitrification in a full-scale combined biological nitrogen removal process for swine wastewater treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 329: 124906. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124906 [16] GE S, PENG Y, WANG S, et al. Nitrite accumulation under constant temperature in anoxic denitrification process: The effects of carbon sources and COD/NO3-N[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 114: 137-43. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.016 [17] 郑冰玉, 张树军, 张亮, 等. 一体化厌氧氨氧化工艺处理垃圾渗滤液的性能研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(7): 1728-1733. [18] ZHOU A, LIU W, VARRONE C, et al. Evaluation of surfactants on waste activated sludge fermentation by pyrosequencing analysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 192: 835-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.017 [19] ZHANG Y-T, WEI W, HUANG Q-S, et al. Insights into the microbial response of anaerobic granular sludge during long-term exposure to polyethylene terephthalate microplastics[J]. Water Research, 2020, 179: 115898. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115898 [20] XIAO Y, ZENG G-M, YANG Z-H, et al. Changes in the actinomycetal communities during continuous thermophilic composting as revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and quantitative PCR[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102: 1383-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.034 [21] JIA W, CHEN Y, ZHANG J, et al. Response of greenhouse gas emissions and microbial community dynamics to temperature variation during partial nitrification[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 261: 19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.137 [22] LIU Y, LI X, KANG X, et al. Effect of extracellular polymeric substances disintegration by ultrasonic pretreatment on waste activated sludge acidification[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2015, 102: 131-6. [23] 杨浩, 张国珍, 杨晓妮, 等. 16S rRNA高通量测序研究集雨窖水中微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(4): 1704-1716. [24] LONG Y, MA Y, WAN J, et al. Denitrification efficiency, microbial communities and metabolic mechanisms of corn cob hydrolysate as denitrifying carbon source[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 221: 115315. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115315 [25] JIANG F, QI Y, SHI X. Effect of liquid carbon sources on nitrate removal, characteristics of soluble microbial products and microbial community in denitrification biofilters[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 339: 130776. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130776 [26] MAO Y, XIA Y, ZHANG T. Characterization of Thauera-dominated hydrogen-oxidizing autotrophic denitrifying microbial communities by using high-throughput sequencing[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 128: 703-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.106 [27] BLASZCZYK M. Effect of Medium Composition on the denitrification of nitrate by paracoccus denitrificans[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1993, 59(11): 3951-3. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.11.3951-3953.1993 [28] LIU H, DONG W, ZHAO Z, et al. Advanced nitrogen removal from low carbon nitrogen ratio domestic sewage via continuous plug-flow anaerobic/oxic/anoxic system: Enhanced by endogenous denitrification[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 378: 128987. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.128987 [29] ZHENG L, DONG Y, LI B, et al. Simultaneous removal of high concentrations of ammonia nitrogen and calcium by the novel strain Paracoccus denitrificans AC-3 with good environmental adaptability[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 359: 127457. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127457 [30] MEDHI K, SINGHAL A, CHAUHAN D K, et al. Investigating the nitrification and denitrification kinetics under aerobic and anaerobic conditions by Paracoccus denitrificans ISTOD1[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 242: 334-343. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.084 [31] 李强, 沈逸豪, 陈传垒, 等. 同步硝化反硝化中试装置脱氮及微生物特性研究[J]. 给水排水, 2023, 59(S1): 111-118. [32] VAN KESSEL M A H J, SPETH D R, ALBERTSEN M, et al. Complete nitrification by a single microorganism[J]. Nature, 2015, 528(7583): 555-559. doi: 10.1038/nature16459 -






 下载:
下载: