-
随着城乡水环境保护治理要求日益严格,农村水环境污染治理问题逐渐成为关注的焦点[1]。现有的城市污水处理工艺不适宜在污水总量小、分散且经济条件差、技术匮乏的农村地区采用,因此针对农村地区开发出水稳定达标、能耗低、运行管理简单的分散污水处理工艺对强化农村地区生活污水处理具有重要意义。
多级A/O工艺是一种高效的脱氮除磷污水处理工艺,在水处理中应用广泛,但由于好氧段的硝化液需要回流至缺氧段进行反硝化脱氮,能耗相对较高[2-3]。分段进水多级A/O工艺通过将污水分段加入各缺氧段实现反硝化过程中的碳源补充,可有效降低工艺运行成本,具有操作灵活简便的特点,但传统的分段进水多级A/O工艺主要基于活性污泥法开发。多级生物接触氧化工艺具有填料固定生物量大、挂膜周期短、水力停留时间短、体积小等特点,在分散生活污水处理方面表现出优异潜力[4-5]。将生物接触氧化工艺与多点进水技术相结合,实现生物接触氧化系统中碳源、溶解氧的再分配,有望进一步强化多级生物接触氧化工艺对低碳氮比生活污水的净化效能。
本研究针对传统生物接触氧化工艺的弊端,结合农村分散型生活污水的特点,设计多点进水的多级生物接触氧化工艺,将进水以不同比例投加到不同的生物接触氧化工艺段,利用原水中的有机物实现对缺氧段碳源补给和溶解氧的再分配,以实现对农村生活污水的高效低耗净化。
-
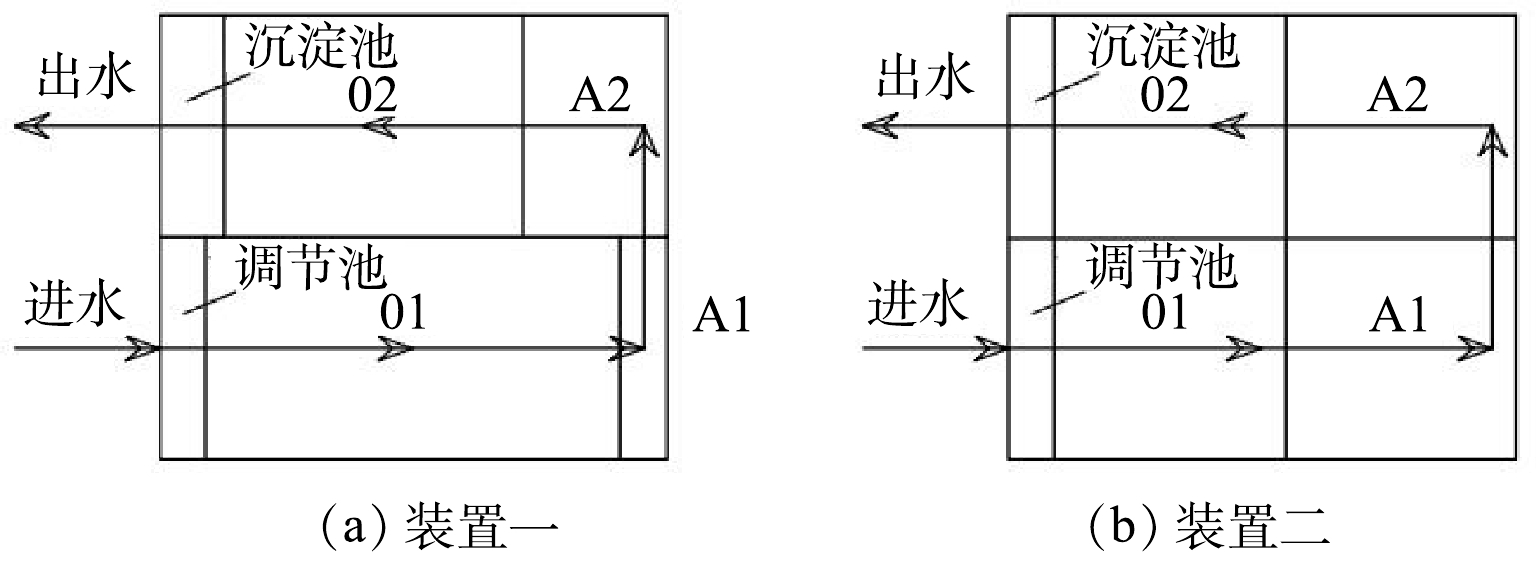
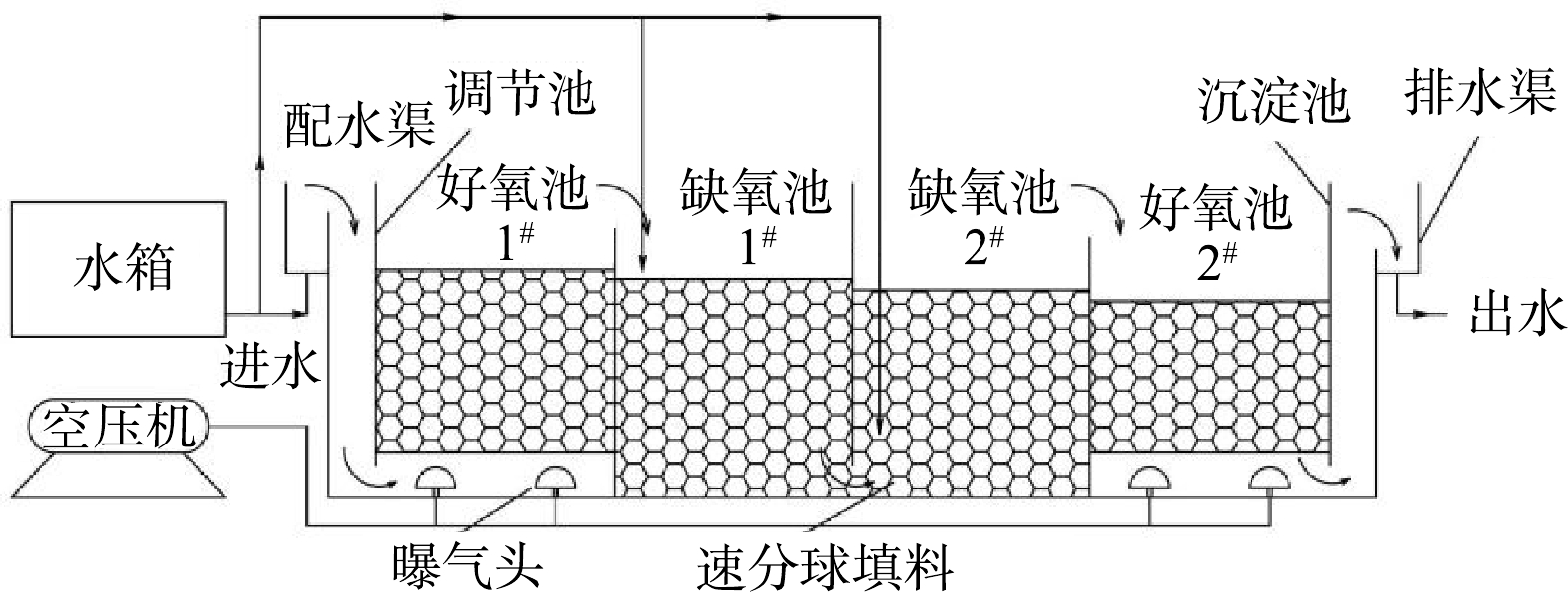
实验装置由不锈钢钢板加工制作而成,分为6个反应区,即调节池、好氧池1# (O1)、缺氧池1# (A1)、缺氧池2# (A2)、好氧池2# (O2)及沉淀池(图1),装置总尺寸为1.225 m×1.2 m×0.7 m,反应区的有效容积为770 L。内填充速分球作为填料,外为直径10 cm的PVC壳体,内为火山岩碎块,填充率采用经验值,即每立方米装填1 000个直径10 cm的速分球。空压机通过与空气管相连的微孔曝气盘向好氧池1#(O1池)和好氧池2#(O2池)充氧曝气。装置污水采用上进下出、下进上出的方式,单点进水时,由自吸泵通过进水管进入配水渠;多点进水时,自吸泵中的污水部分从进水管进入配水渠,部分进入缺氧池1#(A1池)或缺氧池2#(A2池)。
本研究设计2套总体积相同、各段体积不同的装置。装置一各段的水力停留时间比为O1∶A1∶A2∶O2=9∶1∶3∶6,即每个工艺段的体积比为9∶1∶3∶6;装置二各段水力停留时间比为O1∶A1∶A2∶O2=1∶1∶1∶1,即每个工艺段的体积相等。2套装置平面设计图如图2所示。
-
生物接触氧化装置采用活性污泥挂膜法,接种的活性污泥取自北京市郊区某污水处理厂好氧池,污泥浓度约5.5 g·L−1。将活性污泥闷曝48 h,静置沉淀后排出上清液,然后将接种的活性污泥与生活污水以体积比约1∶20混合后注入生物接触氧化池,好氧池溶解氧控制在4 mg·L−1左右,缺氧池不曝气。继续在池内污水闷曝24 h后,排出底部老化的活性污泥,连续通入生活污水,挂膜至24 d时,可观察到好氧池填料上有棕黄色的生物膜,缺氧池内的生物膜呈黑色(图3),此时COD和氨氮的去除率均高于75%,出水水质良好,表明挂膜成功[6-7],可以进行下一阶段实验。
-
实验进水取自北京市郊区某污水处理厂进水口,污水源为周边农村居民生活污水,实验期间进水水质指标:COD、TN、NH4+-N质量浓度为101~364、22~42、4~25.8 mg·L−1,温度为18.3~31.3 ℃,pH为7.69~7.98。实验周期为5个月。
-
装置运行参数为:生物接触氧化系统进水流量为120 L·h−1,不设回流。O1段溶解氧控制为(4.0±0.1) mg·L−1,O2段溶解氧控制为(3.0±0.1) mg·L−1。由于装置不设回流,多点进水时将污水以4∶1及2∶1的比例进入O1段、A1段或O1段、A2段,把系统进水分为O1∶A1=4∶1 (工况I),O1∶A1=2∶1 (工况II),O1∶A2=4∶1 (工况III),O1∶A2=2∶1 (工况IV)4个工况。
-
温度、pH、DO采用YSI ProPlus便携式多参数水质分析仪,COD采用快速消解法,TN采用过硫酸钾氧化法,NH4+-N采用纳氏试剂法。
-
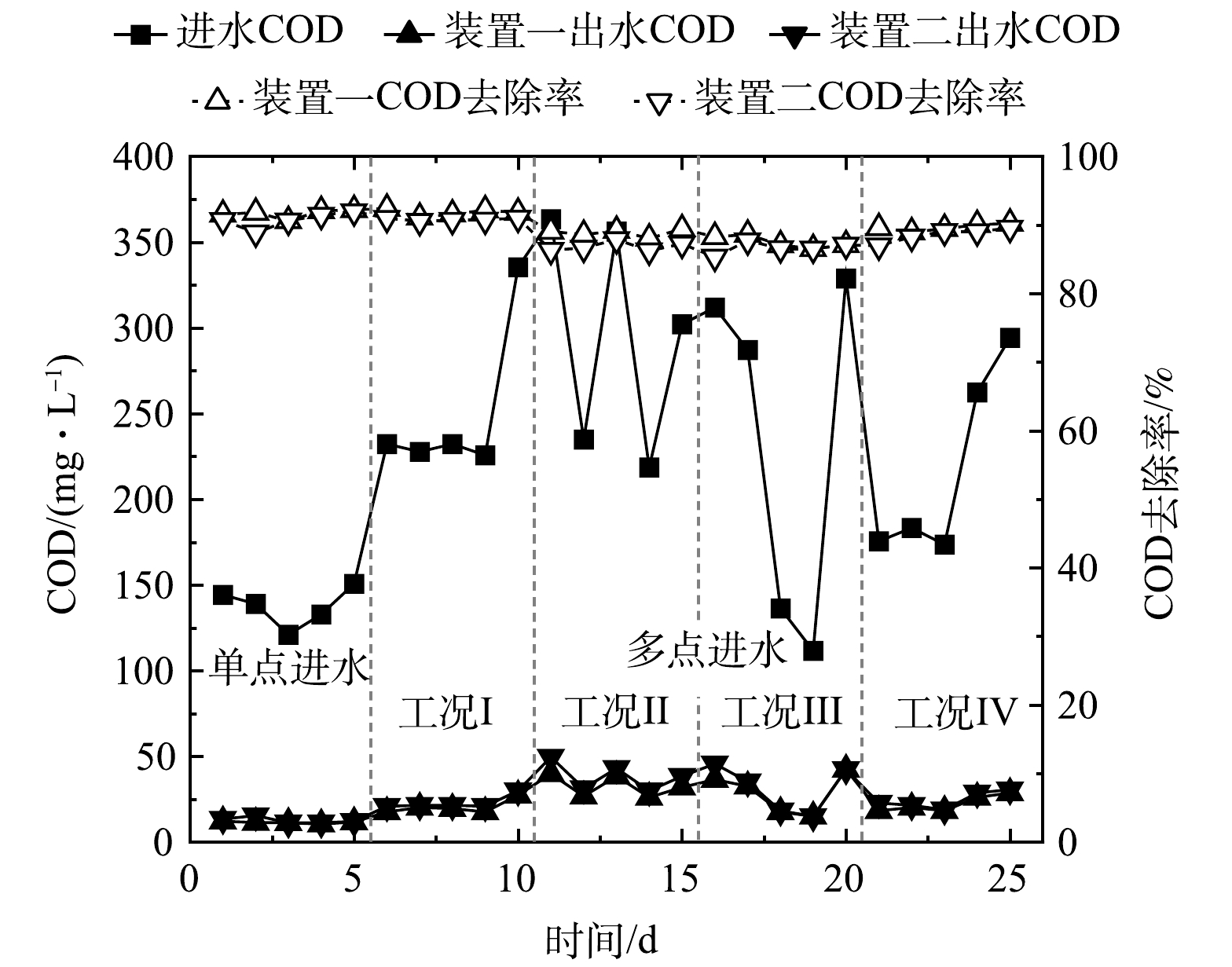
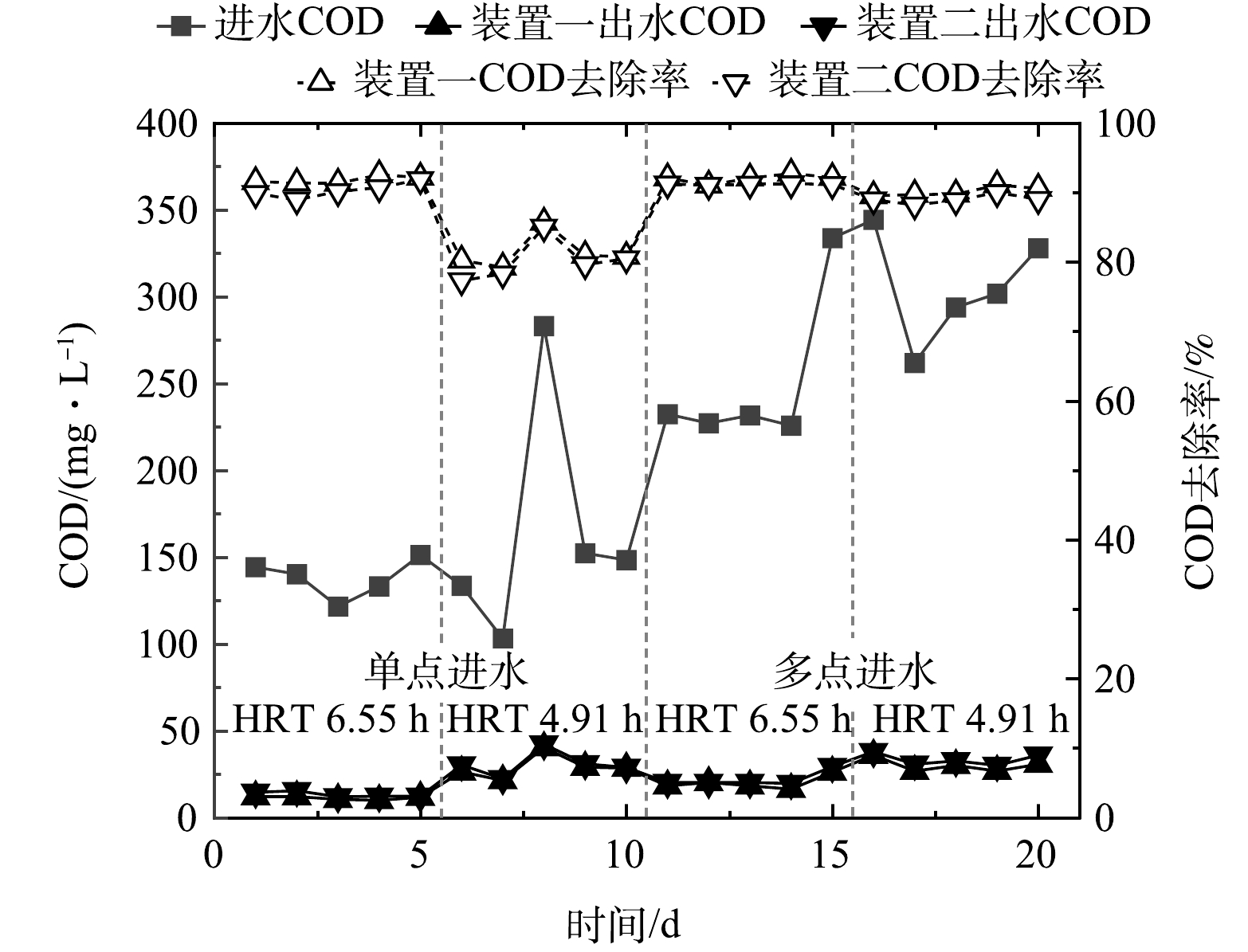
图4所示为单点和多点进水情况下生物接触氧化工艺对生活污水中COD的去除效果变化情况。尽管进水COD波动较大,但单点和多点进水情况下出水COD值始终在30 mg·L−1左右。单点进水与多点进水下的出水COD值相差不大,甚至在多点进水情况下出现出水COD值升高的现象。多点进水时,装置一在工况I时的出水COD值最低,为20.2 mg·L1,平均去除率为92.0%。
多点进水时,对比工况I和工况II,进水位置相同、进水比例不同时出水COD值相差不大,但工况I的进水COD去除率较工况II高,很可能是因为O1段进水在装置中停留时间较长,有较好的生化效果;对比工况I和工况III,相同的进水比例在不同的进水位置也会有不同的出水COD值,进水O1段流量相同,A1段进水较A2段进水时COD的去除率高,很可能是缺氧段时间越长,反硝化作用越强;对比工况I和工况IV,尽管进水位置及比例均不同,但出水COD值均稳定在30 mg·L−1以下,且去除率处于较高的水平。
-
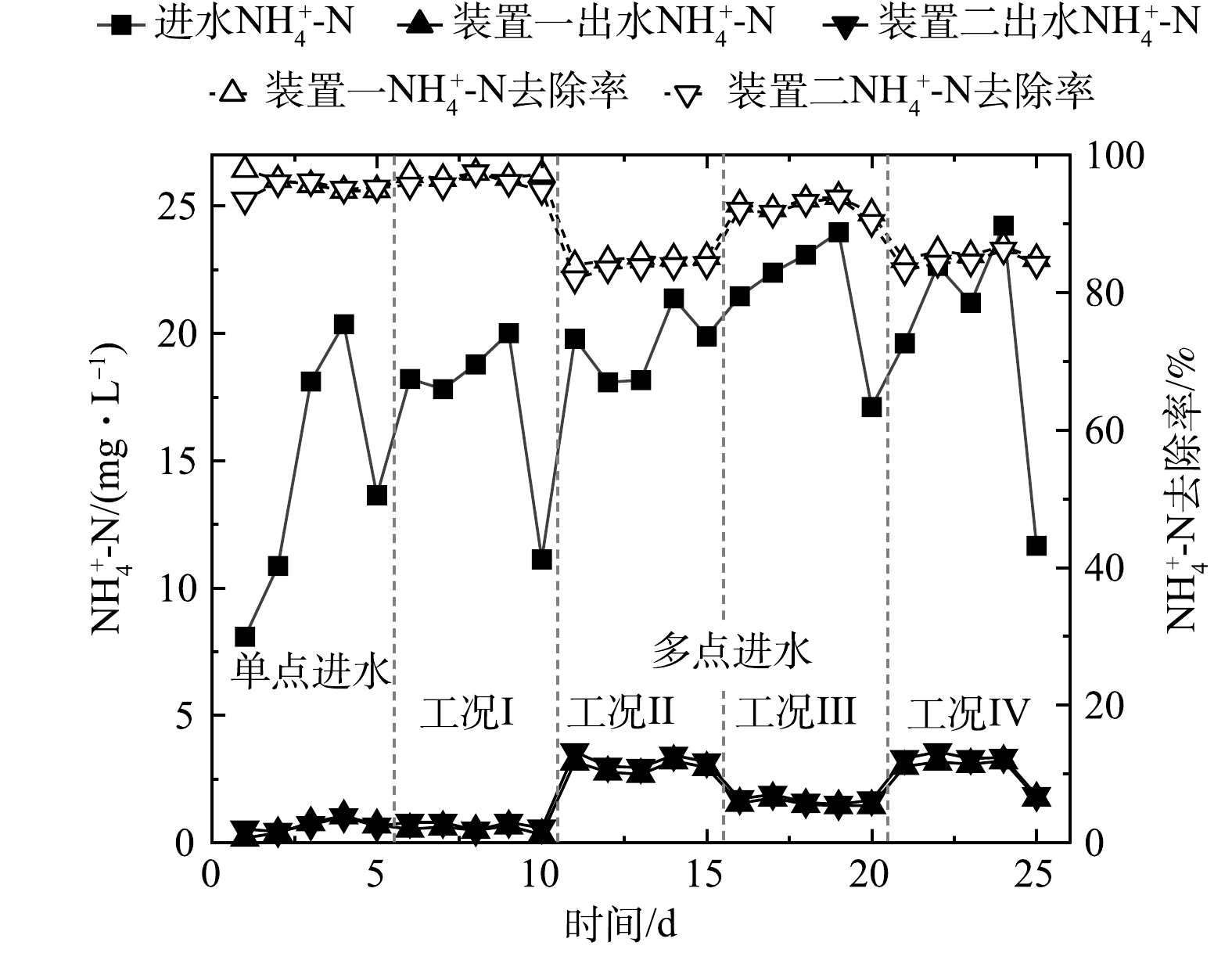
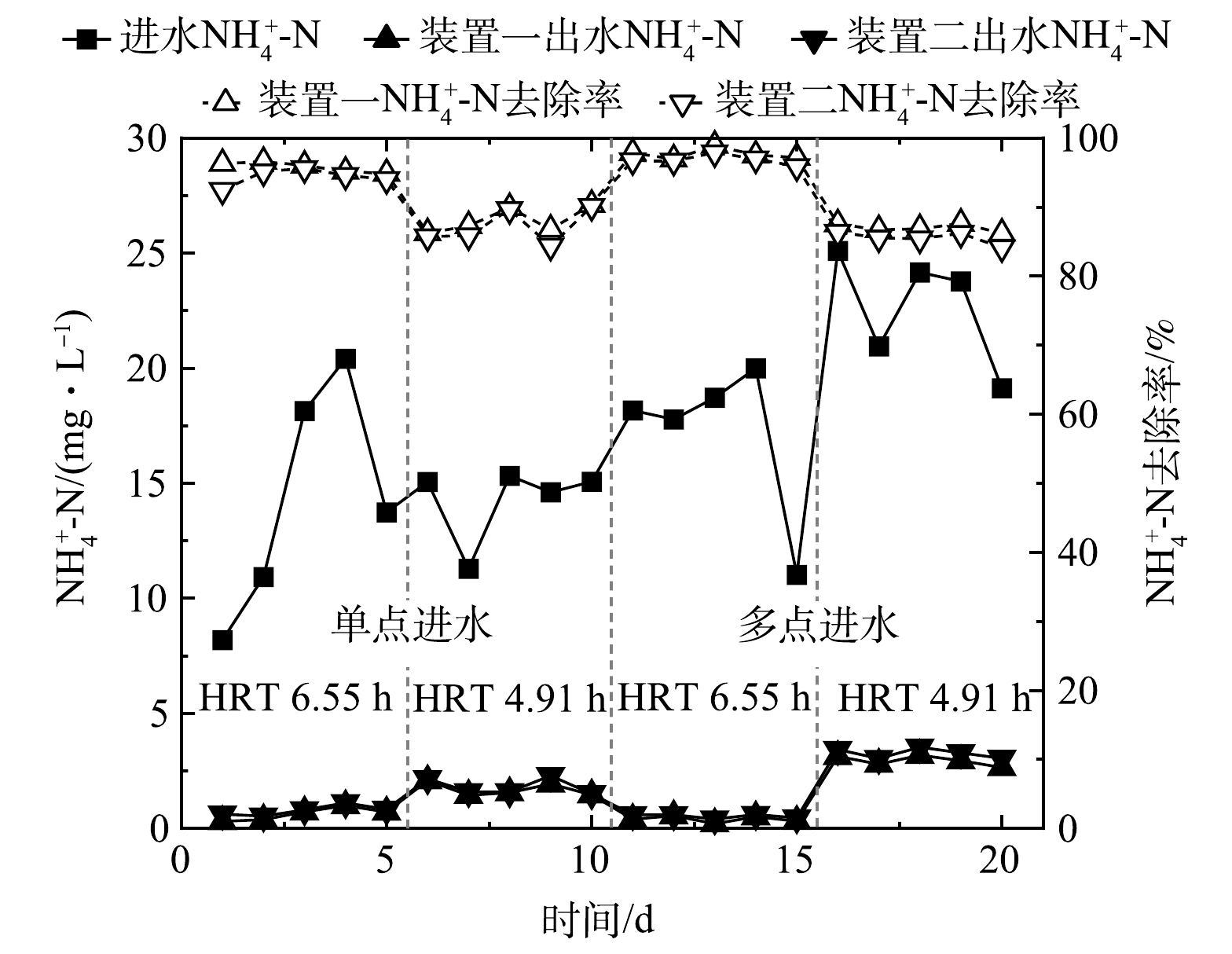
图5为单点和多点进水情况下生物接触氧化工艺对生活污水中氨氮的去除效果。单点进水条件下2套装置对氨氮的去除率相近,平均去除率为95.5%。多点进水时在不同的工况下,氨氮的出水浓度有所差异,去除率变化明显。当进水位置及比例有所改变时,装置一在工况I时对氨氮的处理效果最好,出水平均浓度为0.5 mg·L−1,平均去除率为97.1%。
对比工况I和工况II,进水位置相同、进水比例不同时,O1段进水流量较高,A1段进水较低时的氨氮去除率较高;对比工况I和工况III,进水比例相同、进水位置不同时,进水A1段较A2段的氨氮去除率稍高;对比工况I和工况IV,在进水总量相同,进水位置及比例均不同时,工况I对氨氮的去除率较高,原因是好氧段水力停留时间越长,氨氮的出水效果越好[7]。
-
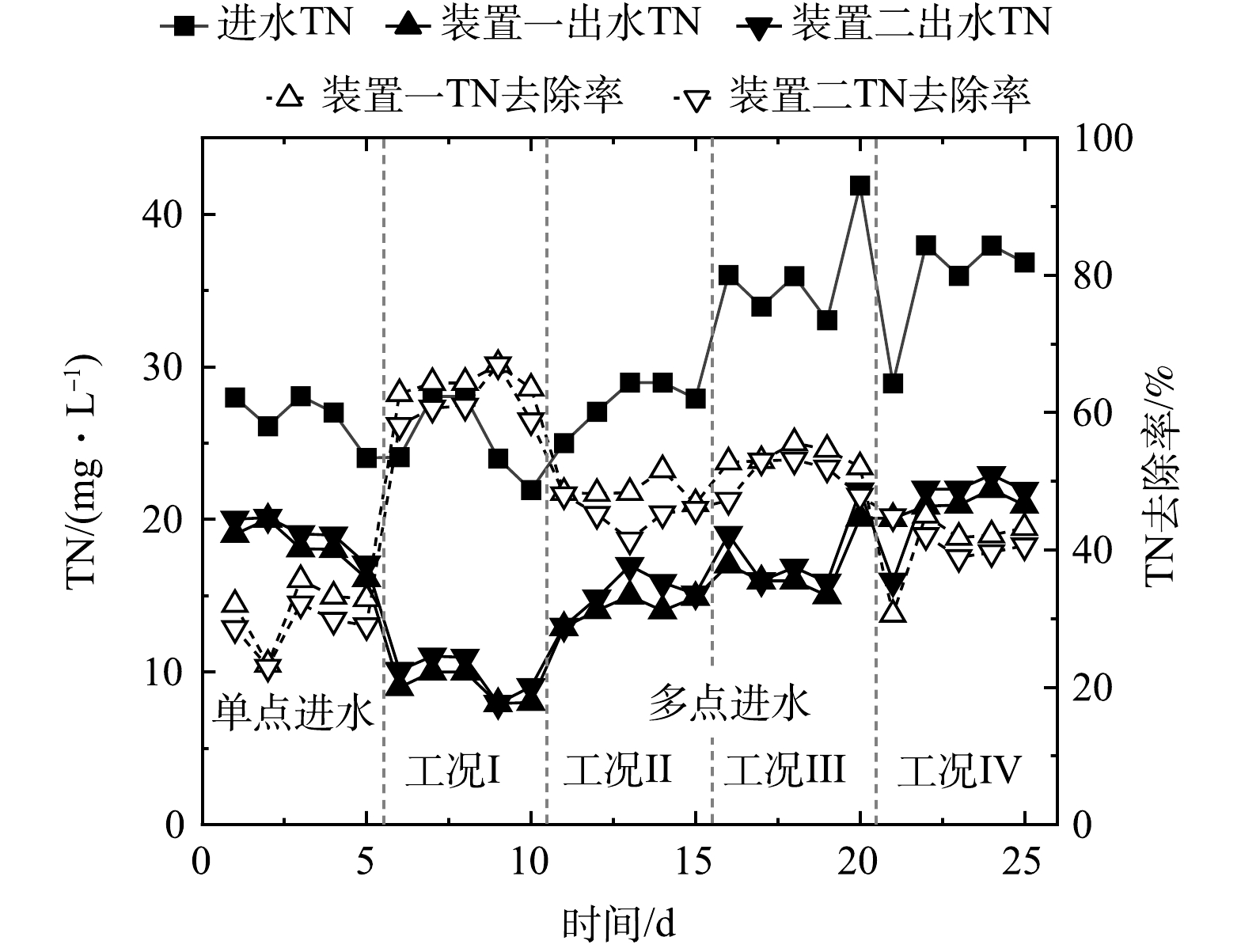
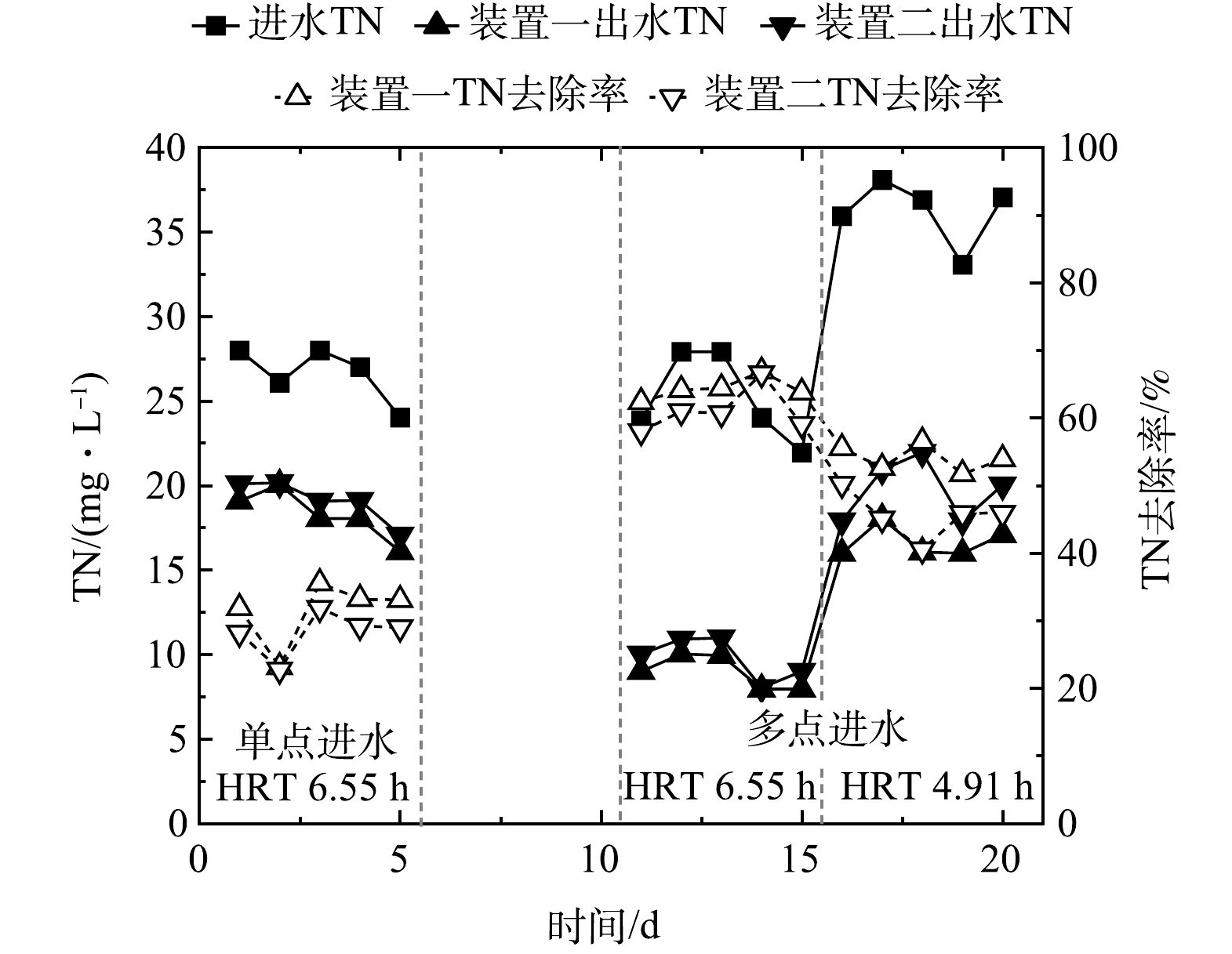
图6所示为单点和多点进水情况下生物接触氧化工艺对生活污水中TN的去除效果变化情况。单点进水时,进水总氮在24~28 mg·L−1,2套装置对总氮的去除效果均不佳,平均出水浓度为18.2 mg·L−1,平均去除率为31.5%,不能达到排放标准。多点进水时,2套装置在4个工况下的出水总氮浓度变化幅度较大,总体来说,装置一的总氮去除效果优于装置二,且在工况I时的装置一总氮平均出水浓度为9.0 mg·L−1,平均去除率为64.3%,可以稳定达到北京市地标农村生活污水一级A排放标准,这在不设回流、不外加碳源的情况下是较难实现的。
对比工况I和工况II,进水位置相同、进水比例不同时,O1段进水流量越大,出水总氮越低;对比工况I和工况III,进水比例相同、进水位置不同时,原水进入A1段时的总氮去除率较进入A2段时高;对比工况I和工况IV,在进水总量相同,进水位置及比例都不相同时,工况I运行时出水总氮浓度较低,脱氮效果最好。多点进水模式实现了碳源在多级A/O工艺中的再分配,A1或A2段进水弥补了厌氧段由于碳源不足导致的反硝化能力不足问题,但同时当缺氧段存在大量有机物时,容易造成缺氧段异养菌繁殖,进而与反硝化细菌产生竞争作用,限制反硝化细菌的生长,在一定程度上抑制反硝化效率[8-9]。
综上可知,多点进水时多级生物接触氧化工艺对生活污水的处理效果优于单点进水。在工况I(O1∶A1=4∶1)的进水情况下出水效果最优,且装置一的出水效果优于装置二,最优的COD、氨氮、总氮的出水平均浓度分别为20.2、0.5、9 mg·L−1,平均去除率分别为92.0%、97.1%、64.3%。
-
图7所示不同水力停留时间下多级生物接触氧化工艺COD去除变化曲线。单点进水时,2套装置出水的COD值相近,COD的去除率随着水力停留时间(HRT)的减小而降低,当HRT为6.55 h时,装置一中出水COD平均值为10.8 mg·L−1,平均去除率为92.1%;当HRT为4.91 h时,装置一中出水COD平均值为28.4 mg·L−1,平均去除率为81.8%。多点进水下,当HRT从6.55 h减少到4.91 h时,装置一的出水COD平均值由20.2 mg·L−1增加至31.2 mg·L−1,平均去除率随之降低。
随着HRT的减小,反应器的水力负荷有所增加,必然会影响有机物的处理效率。缩短HRT,使得反应器内的生物膜受到气流的扰动作用和水力的剪切作用加强,接触时间变短,生物氧化作用不完全,再加上生物量流失增加,导致反应不完全,出水水质下降[8]。同时发现减少HRT时,COD去除下降效果不太显著,表明系统对COD的去除有较高的抗冲击负荷能力,增加水力负荷时,对COD仍有较高的去除率。
-
图8所示为不同水力停留时间下多级生物接触氧化工艺氨氮去除变化曲线。单点进水时,装置一对氨氮的去除率略好于装置二。当HRT为6.55 h时,装置一中氨氮的平均出水浓度为0.66 mg·L−1,平均去除率为95.5%;当HRT为4.91 h时,装置一中氨氮的平均出水浓度为1.76 mg·L−1,平均去除率为87.7%。多点进水时,装置一对氨氮的去除率稍高于装置二,其在水力停留时间较长的6.55 h时,氨氮的出水效果最好,平均出水浓度为0.5 mg·L−1,平均去除率高达97.1%。随着水力停留时间的减少,反应器内硝化菌去除氨氮的作用减弱,当水力停留时间减少至4.91 h时,氨氮平均出水浓度为3.10 mg·L−1,平均去除率减至86.8%。
HRT是影响氨氮去除效果的重要影响因素。在一定范围内,HRT越长,氨氮的去除率越高;HRT越短,氨氮的去除率越低。HRT由6.55 h降低为4.91 h时,系统对氨氮的去除有所下降,下降幅度较小。这可能是随着进水流量的增加,O2段可供利用的有机物含量升高,加快了微生物的新陈代谢,使得生物活性得到提高,使得出水氨氮浓度下降的幅度较小。
-
图9所示为2套生物接触氧化装置的总氮去除变化情况。在单点进水条件下,当水力停留时间为6.55 h时,平均出水总氮浓度为18.2 mg·L−1,平均去除率仅为31.5%。多点进水时,随着水力停留时间逐渐减少,总氮的去除率呈现直线下降的趋势,且装置一较装置二对总氮的去除率稍高。当水力停留时间为6.55 h时,装置一中总氮的出水浓度最低,去除率最高,平均出水浓度为9.0 mg·L−1,平均去除率可达到64.3%,随着水力停留时间减少至4.91 h,总氮的平均出水浓度增加至16.6 mg·L−1,平均去除率降低为54.1%。
总氮的去除依靠同步硝化反硝化过程和缺氧段的反硝化过程。当系统的水力负荷随水体停留时间的减少而逐渐增加时,水流的水力冲刷作用增强,生物膜的附着性变差,缺氧段生物膜分泌物质的粘性作用不足以抗拒水流的冲刷,将会加快生物膜的脱落,使得反硝化菌随水流流失严重,反硝化脱氮的效果减弱,总氮的去除率降低[9-10]。另外,水力负荷的增加,使得好氧段微生物对氨氮的转化能力减弱,氨氮转化为硝态氮和亚硝态氮的效率较低,反硝化过程受到制约,从而降低总氮的去除效果。
-
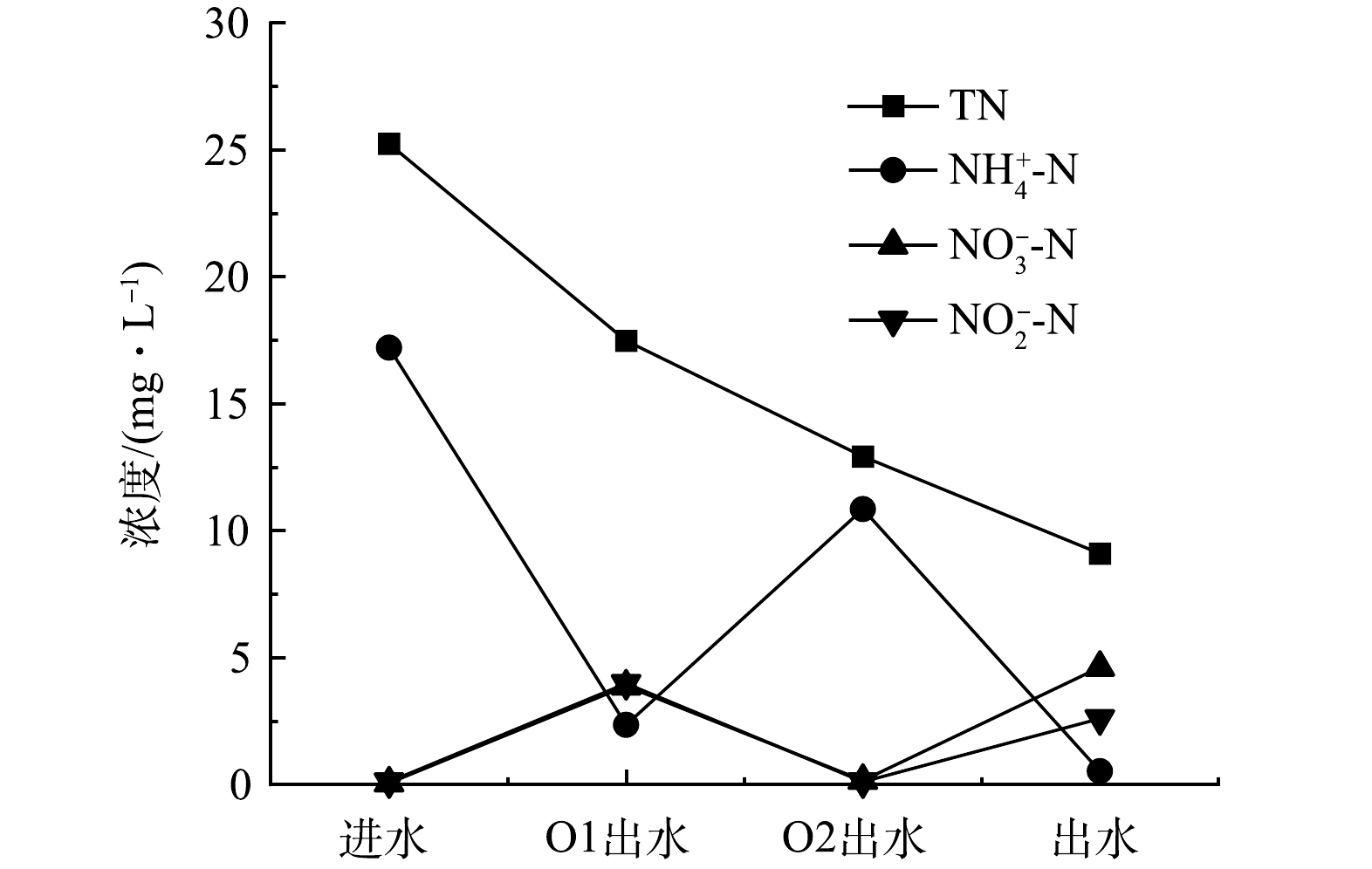
由多点进水条件下多级生物接触氧化工艺对COD、氨氮及总氮的去除效果的影响结果表明,进水位置及比例为O1∶A1=4∶1,水力停留时间为6.55 h的运行工况下的出水效果最好,因此,以装置一中工况I的氮浓度变化来探究总氮的去除机理。
图10所示为多级生物接触氧化工艺不同段出水中氮浓度变化曲线。进水中的总氮及氨氮浓度较高,硝态氮和亚硝态氮浓度较低,经好氧段O1后,总氮及氨氮值均有明显下降,且氨氮降幅较大,硝态氮及亚硝态氮值均有提高,说明氨氮在O1段硝化菌的作用下转化为硝态氮和亚硝态氮[10],同时总氮在在O1段有所减少表明在好氧段O1段发生了反硝化作用。值得注意的是,由于进水中有机物浓度较高,导致硝化速度不及反硝化速度,导致在O1段存在一定的亚硝酸盐累计;同时,O1段内的微生物可以获取进水中的有机物质供给自身进行增殖,随着生物膜厚度的逐渐增加,水中的溶解氧穿透生物膜表层的能力越来越弱,使得填料内部火山岩上生长的微生物处于缺氧的环境,在生物膜内外形成一定的缺氧区和好氧区,同步硝化反硝化作用得以进行[10]。
当污水经好氧段O1流入缺氧段A1的同时,部分原水进入A1段,由于原水中的氨氮及总氮浓度较高,直接进入A1段时,提高了缺氧段出水的总氮和氨氮值。然而缺氧段的反硝化菌可利用原水中的有机物将好氧段提供的硝态氮、亚硝态氮还原为氮气,从而降低了总氮及硝态氮和亚硝态氮的浓度,所以在A2段出水时很难检测到硝态氮和亚硝态氮的存在。但总氮在缺氧段呈现下降的趋势,表明缺氧段的反硝化作用强于进水和O1段出水浓度的混合提高,因此,总氮的去除效果较为明显。污水流出O2段时,氨氮在好氧的条件下得到转化,硝态氮及亚硝态氮的浓度均有所提高;总氮浓度的降低也表明了O2段内同步硝化反硝化过程依然存在,因此,系统对总氮的去除效果较好。
-
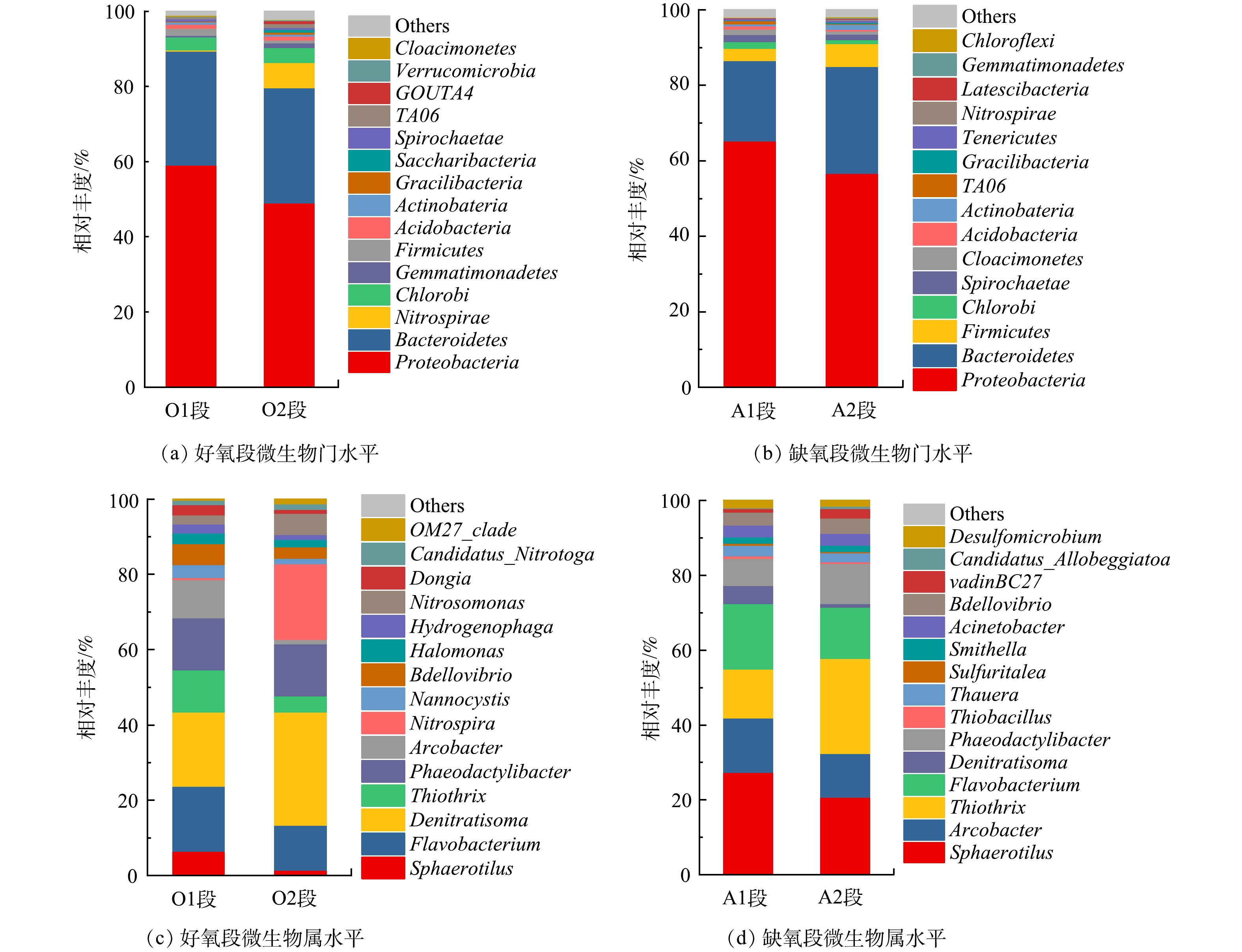
当反应器运行至稳定状况时,填料上的生物膜经长期运行后达到稳定,分析装置一中O1段、A1段、A2段、O2段中生物膜中微生物的菌群结构。图11(a)为好氧段生物膜门水平上微生物top15及相对丰度。相对丰度最高的为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes),二者可有效去除水中的有机污染物,同时具有脱氮功能。此外,在好氧段生物膜中也存在较高的硝化螺旋菌门,是重要的亚硝酸盐氧化细菌,是污水处理中执行亚硝酸盐氧化功能的关键菌群。图11(b)所示为缺氧段生物膜门水平上微生物组成情况。与好氧段类似,相对丰度最高的为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes),其次相对丰度较高的是厚壁菌门(Firmicutes),厚壁菌门中大都可以产生芽孢,可用以抵抗外部极端环境,是污水处理中被的重要功能菌群。
图11(c)所示为好氧段生物膜属水平上微生物top15及相对丰度。相对丰度较高的黄杆菌属(Flavobacterium)、Denitratisoma菌属、Phaeodactylibacter菌属、硝化螺旋菌属(Nitrospira)、噬氢菌属(Hydrogenophaga)等都有利于生物脱氮反应的进行,而球衣菌属(Sphaerotilus)具有降解有机污染物的功能,可促进COD去除;亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)可以调节酶来控制硝化过程。在反应器的好氧段生物膜中存在部分反硝化菌属,表明好氧段内存在缺氧甚至是厌氧环境,证实了好氧段同步硝化反硝化过程的存在。
图11(d)所示为缺氧段生物膜属水平上微生物群落结构。属水平上相对丰度较高的为球衣菌属(Sphaerotilus),具有降解有机污染物的功能;丝硫菌属(Thiothrix)常出现在氮源较少,碳源及能源丰富的环境中;弓形杆菌属(Arcobacter)、黄杆菌属(Flavobacterium)、Denitratisoma菌属、Phaeodactylibacter菌属、索氏菌属(Thauera)等菌属均为重要的脱氮微生物。缺氧段中存在的丰富弓形杆菌属(Arcobacter)、黄杆菌属(Flavobacterium)、Phaeodactylibacter菌属、和Denitratisoma菌属等微生物,有利于生物的反硝化过程,进而提高总氮去除率。
-
1)多点进水的多级生物接触氧化条件下,进水位置及比例对污染物去除效果具有明显影响。进水位置及比例为O1∶A1=4∶1时的出水效果最好,COD、NH4+-N及TN的平均出水浓度分别为20.2、0.5、9.0 mg·L−1,平均去除率分别为92.0%、97.1%、64.3%。
2) HRT对COD、氨氮和总氮去除效果有显著影响。随着HRT的减少,COD、氨氮和总氮的出水浓度逐渐升高,去除率逐渐降低,出水水质恶化,实验得出的最优水力停留时间为6.55 h。
3)多点进水条件下多级生物接触氧化工艺在好氧段内存在同步硝化反硝化过程,对总氮去除具有一定的提升作用,经缺氧段后总氮出水继续降低,末端好氧段后COD、氨氮及总氮均可达标出水。
多点进水多级生物接触氧化工艺处理农村生活污水
Multi-stage biological contact oxidation process with multi-point influent for rural domestic sewage treatment
-
摘要: 针对农村地区生活污水的特点,设计好氧-缺氧-缺氧-好氧的多级生物接触氧化工艺,通过控制进水位置及比例、水力停留时间等参数,分别考察了单点进水和多点进水条件下生物接触氧化工艺的除碳脱氮性能。结果表明:当进水比例为好氧池1#与缺氧池1# = 4:1,HRT为6.55 h时,生物接触氧化工艺出水水质最优,COD、NH4+-N及TN的出水平均浓度分别为20.2、0.5、9.0 mg·L−1,平均去除率分别为92.0%、97.1%、64.3%。出水水质达到北京市《农村生活污水处理设施水污染物排放标准》(DB11/ 1612-2019)》一级A标准。Abstract: According to the characteristics of rural domestic sewage, a multi-stage biological contact oxidation process including aerobic, anoxic, anoxic and aerobic processes was designed. Through controlling the parameters such as inlet position, proportion and hydraulic retention time, the carbon and nitrogen removal performance of the biological contact oxidation process under single point and multiple point inlet conditions were investigated. The results showed that when the inlet ratio of aerobic tank 1# to anaerobic tank 1# was 4:1, and HRT was 6.55 hours, the effluent quality of the biological contact oxidation process was optimal. The average values of COD, NH4+-N, and TN in the effluent were 20.2, 0.5, and 9.0 mg·L−1 with the average removal rates of 92.0%, 97.1%, and 64.3%, respectively. The effluent water quality meets the Grade One A-level discharge standard of the Beijing local standard “Discharge standard of water pollutants for rural sewage treatment facilities” (DB11/ 1612-2019).
-
随着城乡水环境保护治理要求日益严格,农村水环境污染治理问题逐渐成为关注的焦点[1]。现有的城市污水处理工艺不适宜在污水总量小、分散且经济条件差、技术匮乏的农村地区采用,因此针对农村地区开发出水稳定达标、能耗低、运行管理简单的分散污水处理工艺对强化农村地区生活污水处理具有重要意义。
多级A/O工艺是一种高效的脱氮除磷污水处理工艺,在水处理中应用广泛,但由于好氧段的硝化液需要回流至缺氧段进行反硝化脱氮,能耗相对较高[2-3]。分段进水多级A/O工艺通过将污水分段加入各缺氧段实现反硝化过程中的碳源补充,可有效降低工艺运行成本,具有操作灵活简便的特点,但传统的分段进水多级A/O工艺主要基于活性污泥法开发。多级生物接触氧化工艺具有填料固定生物量大、挂膜周期短、水力停留时间短、体积小等特点,在分散生活污水处理方面表现出优异潜力[4-5]。将生物接触氧化工艺与多点进水技术相结合,实现生物接触氧化系统中碳源、溶解氧的再分配,有望进一步强化多级生物接触氧化工艺对低碳氮比生活污水的净化效能。
本研究针对传统生物接触氧化工艺的弊端,结合农村分散型生活污水的特点,设计多点进水的多级生物接触氧化工艺,将进水以不同比例投加到不同的生物接触氧化工艺段,利用原水中的有机物实现对缺氧段碳源补给和溶解氧的再分配,以实现对农村生活污水的高效低耗净化。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置
实验装置由不锈钢钢板加工制作而成,分为6个反应区,即调节池、好氧池1# (O1)、缺氧池1# (A1)、缺氧池2# (A2)、好氧池2# (O2)及沉淀池(图1),装置总尺寸为1.225 m×1.2 m×0.7 m,反应区的有效容积为770 L。内填充速分球作为填料,外为直径10 cm的PVC壳体,内为火山岩碎块,填充率采用经验值,即每立方米装填1 000个直径10 cm的速分球。空压机通过与空气管相连的微孔曝气盘向好氧池1#(O1池)和好氧池2#(O2池)充氧曝气。装置污水采用上进下出、下进上出的方式,单点进水时,由自吸泵通过进水管进入配水渠;多点进水时,自吸泵中的污水部分从进水管进入配水渠,部分进入缺氧池1#(A1池)或缺氧池2#(A2池)。
本研究设计2套总体积相同、各段体积不同的装置。装置一各段的水力停留时间比为O1∶A1∶A2∶O2=9∶1∶3∶6,即每个工艺段的体积比为9∶1∶3∶6;装置二各段水力停留时间比为O1∶A1∶A2∶O2=1∶1∶1∶1,即每个工艺段的体积相等。2套装置平面设计图如图2所示。
1.2 微生物挂膜
生物接触氧化装置采用活性污泥挂膜法,接种的活性污泥取自北京市郊区某污水处理厂好氧池,污泥浓度约5.5 g·L−1。将活性污泥闷曝48 h,静置沉淀后排出上清液,然后将接种的活性污泥与生活污水以体积比约1∶20混合后注入生物接触氧化池,好氧池溶解氧控制在4 mg·L−1左右,缺氧池不曝气。继续在池内污水闷曝24 h后,排出底部老化的活性污泥,连续通入生活污水,挂膜至24 d时,可观察到好氧池填料上有棕黄色的生物膜,缺氧池内的生物膜呈黑色(图3),此时COD和氨氮的去除率均高于75%,出水水质良好,表明挂膜成功[6-7],可以进行下一阶段实验。
1.3 实验水质
实验进水取自北京市郊区某污水处理厂进水口,污水源为周边农村居民生活污水,实验期间进水水质指标:COD、TN、NH4+-N质量浓度为101~364、22~42、4~25.8 mg·L−1,温度为18.3~31.3 ℃,pH为7.69~7.98。实验周期为5个月。
1.4 运行工况
装置运行参数为:生物接触氧化系统进水流量为120 L·h−1,不设回流。O1段溶解氧控制为(4.0±0.1) mg·L−1,O2段溶解氧控制为(3.0±0.1) mg·L−1。由于装置不设回流,多点进水时将污水以4∶1及2∶1的比例进入O1段、A1段或O1段、A2段,把系统进水分为O1∶A1=4∶1 (工况I),O1∶A1=2∶1 (工况II),O1∶A2=4∶1 (工况III),O1∶A2=2∶1 (工况IV)4个工况。
1.5 仪器与方法
温度、pH、DO采用YSI ProPlus便携式多参数水质分析仪,COD采用快速消解法,TN采用过硫酸钾氧化法,NH4+-N采用纳氏试剂法。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 不同工况下多级生物接触氧化工艺的COD去除效果
图4所示为单点和多点进水情况下生物接触氧化工艺对生活污水中COD的去除效果变化情况。尽管进水COD波动较大,但单点和多点进水情况下出水COD值始终在30 mg·L−1左右。单点进水与多点进水下的出水COD值相差不大,甚至在多点进水情况下出现出水COD值升高的现象。多点进水时,装置一在工况I时的出水COD值最低,为20.2 mg·L1,平均去除率为92.0%。
多点进水时,对比工况I和工况II,进水位置相同、进水比例不同时出水COD值相差不大,但工况I的进水COD去除率较工况II高,很可能是因为O1段进水在装置中停留时间较长,有较好的生化效果;对比工况I和工况III,相同的进水比例在不同的进水位置也会有不同的出水COD值,进水O1段流量相同,A1段进水较A2段进水时COD的去除率高,很可能是缺氧段时间越长,反硝化作用越强;对比工况I和工况IV,尽管进水位置及比例均不同,但出水COD值均稳定在30 mg·L−1以下,且去除率处于较高的水平。
2.2 不同工况下多级生物接触氧化工艺的氨氮去除效果
图5为单点和多点进水情况下生物接触氧化工艺对生活污水中氨氮的去除效果。单点进水条件下2套装置对氨氮的去除率相近,平均去除率为95.5%。多点进水时在不同的工况下,氨氮的出水浓度有所差异,去除率变化明显。当进水位置及比例有所改变时,装置一在工况I时对氨氮的处理效果最好,出水平均浓度为0.5 mg·L−1,平均去除率为97.1%。
对比工况I和工况II,进水位置相同、进水比例不同时,O1段进水流量较高,A1段进水较低时的氨氮去除率较高;对比工况I和工况III,进水比例相同、进水位置不同时,进水A1段较A2段的氨氮去除率稍高;对比工况I和工况IV,在进水总量相同,进水位置及比例均不同时,工况I对氨氮的去除率较高,原因是好氧段水力停留时间越长,氨氮的出水效果越好[7]。
2.3 不同工况下多级生物接触氧化工艺的总氮去除效果
图6所示为单点和多点进水情况下生物接触氧化工艺对生活污水中TN的去除效果变化情况。单点进水时,进水总氮在24~28 mg·L−1,2套装置对总氮的去除效果均不佳,平均出水浓度为18.2 mg·L−1,平均去除率为31.5%,不能达到排放标准。多点进水时,2套装置在4个工况下的出水总氮浓度变化幅度较大,总体来说,装置一的总氮去除效果优于装置二,且在工况I时的装置一总氮平均出水浓度为9.0 mg·L−1,平均去除率为64.3%,可以稳定达到北京市地标农村生活污水一级A排放标准,这在不设回流、不外加碳源的情况下是较难实现的。
对比工况I和工况II,进水位置相同、进水比例不同时,O1段进水流量越大,出水总氮越低;对比工况I和工况III,进水比例相同、进水位置不同时,原水进入A1段时的总氮去除率较进入A2段时高;对比工况I和工况IV,在进水总量相同,进水位置及比例都不相同时,工况I运行时出水总氮浓度较低,脱氮效果最好。多点进水模式实现了碳源在多级A/O工艺中的再分配,A1或A2段进水弥补了厌氧段由于碳源不足导致的反硝化能力不足问题,但同时当缺氧段存在大量有机物时,容易造成缺氧段异养菌繁殖,进而与反硝化细菌产生竞争作用,限制反硝化细菌的生长,在一定程度上抑制反硝化效率[8-9]。
综上可知,多点进水时多级生物接触氧化工艺对生活污水的处理效果优于单点进水。在工况I(O1∶A1=4∶1)的进水情况下出水效果最优,且装置一的出水效果优于装置二,最优的COD、氨氮、总氮的出水平均浓度分别为20.2、0.5、9 mg·L−1,平均去除率分别为92.0%、97.1%、64.3%。
2.4 水力停留时间对多级生物接触氧化工艺去除COD效果的影响
图7所示不同水力停留时间下多级生物接触氧化工艺COD去除变化曲线。单点进水时,2套装置出水的COD值相近,COD的去除率随着水力停留时间(HRT)的减小而降低,当HRT为6.55 h时,装置一中出水COD平均值为10.8 mg·L−1,平均去除率为92.1%;当HRT为4.91 h时,装置一中出水COD平均值为28.4 mg·L−1,平均去除率为81.8%。多点进水下,当HRT从6.55 h减少到4.91 h时,装置一的出水COD平均值由20.2 mg·L−1增加至31.2 mg·L−1,平均去除率随之降低。
随着HRT的减小,反应器的水力负荷有所增加,必然会影响有机物的处理效率。缩短HRT,使得反应器内的生物膜受到气流的扰动作用和水力的剪切作用加强,接触时间变短,生物氧化作用不完全,再加上生物量流失增加,导致反应不完全,出水水质下降[8]。同时发现减少HRT时,COD去除下降效果不太显著,表明系统对COD的去除有较高的抗冲击负荷能力,增加水力负荷时,对COD仍有较高的去除率。
2.5 水力停留时间对多级生物接触氧化工艺去除氨氮效果的影响
图8所示为不同水力停留时间下多级生物接触氧化工艺氨氮去除变化曲线。单点进水时,装置一对氨氮的去除率略好于装置二。当HRT为6.55 h时,装置一中氨氮的平均出水浓度为0.66 mg·L−1,平均去除率为95.5%;当HRT为4.91 h时,装置一中氨氮的平均出水浓度为1.76 mg·L−1,平均去除率为87.7%。多点进水时,装置一对氨氮的去除率稍高于装置二,其在水力停留时间较长的6.55 h时,氨氮的出水效果最好,平均出水浓度为0.5 mg·L−1,平均去除率高达97.1%。随着水力停留时间的减少,反应器内硝化菌去除氨氮的作用减弱,当水力停留时间减少至4.91 h时,氨氮平均出水浓度为3.10 mg·L−1,平均去除率减至86.8%。
HRT是影响氨氮去除效果的重要影响因素。在一定范围内,HRT越长,氨氮的去除率越高;HRT越短,氨氮的去除率越低。HRT由6.55 h降低为4.91 h时,系统对氨氮的去除有所下降,下降幅度较小。这可能是随着进水流量的增加,O2段可供利用的有机物含量升高,加快了微生物的新陈代谢,使得生物活性得到提高,使得出水氨氮浓度下降的幅度较小。
2.6 水力停留时间对多级生物接触氧化工艺去除总氮效果的影响
图9所示为2套生物接触氧化装置的总氮去除变化情况。在单点进水条件下,当水力停留时间为6.55 h时,平均出水总氮浓度为18.2 mg·L−1,平均去除率仅为31.5%。多点进水时,随着水力停留时间逐渐减少,总氮的去除率呈现直线下降的趋势,且装置一较装置二对总氮的去除率稍高。当水力停留时间为6.55 h时,装置一中总氮的出水浓度最低,去除率最高,平均出水浓度为9.0 mg·L−1,平均去除率可达到64.3%,随着水力停留时间减少至4.91 h,总氮的平均出水浓度增加至16.6 mg·L−1,平均去除率降低为54.1%。
总氮的去除依靠同步硝化反硝化过程和缺氧段的反硝化过程。当系统的水力负荷随水体停留时间的减少而逐渐增加时,水流的水力冲刷作用增强,生物膜的附着性变差,缺氧段生物膜分泌物质的粘性作用不足以抗拒水流的冲刷,将会加快生物膜的脱落,使得反硝化菌随水流流失严重,反硝化脱氮的效果减弱,总氮的去除率降低[9-10]。另外,水力负荷的增加,使得好氧段微生物对氨氮的转化能力减弱,氨氮转化为硝态氮和亚硝态氮的效率较低,反硝化过程受到制约,从而降低总氮的去除效果。
2.7 多点进水多级生物接触氧化工艺的除氮过程分析
由多点进水条件下多级生物接触氧化工艺对COD、氨氮及总氮的去除效果的影响结果表明,进水位置及比例为O1∶A1=4∶1,水力停留时间为6.55 h的运行工况下的出水效果最好,因此,以装置一中工况I的氮浓度变化来探究总氮的去除机理。
图10所示为多级生物接触氧化工艺不同段出水中氮浓度变化曲线。进水中的总氮及氨氮浓度较高,硝态氮和亚硝态氮浓度较低,经好氧段O1后,总氮及氨氮值均有明显下降,且氨氮降幅较大,硝态氮及亚硝态氮值均有提高,说明氨氮在O1段硝化菌的作用下转化为硝态氮和亚硝态氮[10],同时总氮在在O1段有所减少表明在好氧段O1段发生了反硝化作用。值得注意的是,由于进水中有机物浓度较高,导致硝化速度不及反硝化速度,导致在O1段存在一定的亚硝酸盐累计;同时,O1段内的微生物可以获取进水中的有机物质供给自身进行增殖,随着生物膜厚度的逐渐增加,水中的溶解氧穿透生物膜表层的能力越来越弱,使得填料内部火山岩上生长的微生物处于缺氧的环境,在生物膜内外形成一定的缺氧区和好氧区,同步硝化反硝化作用得以进行[10]。
当污水经好氧段O1流入缺氧段A1的同时,部分原水进入A1段,由于原水中的氨氮及总氮浓度较高,直接进入A1段时,提高了缺氧段出水的总氮和氨氮值。然而缺氧段的反硝化菌可利用原水中的有机物将好氧段提供的硝态氮、亚硝态氮还原为氮气,从而降低了总氮及硝态氮和亚硝态氮的浓度,所以在A2段出水时很难检测到硝态氮和亚硝态氮的存在。但总氮在缺氧段呈现下降的趋势,表明缺氧段的反硝化作用强于进水和O1段出水浓度的混合提高,因此,总氮的去除效果较为明显。污水流出O2段时,氨氮在好氧的条件下得到转化,硝态氮及亚硝态氮的浓度均有所提高;总氮浓度的降低也表明了O2段内同步硝化反硝化过程依然存在,因此,系统对总氮的去除效果较好。
2.8 多点进水多级生物接触氧化工艺微生物分析
当反应器运行至稳定状况时,填料上的生物膜经长期运行后达到稳定,分析装置一中O1段、A1段、A2段、O2段中生物膜中微生物的菌群结构。图11(a)为好氧段生物膜门水平上微生物top15及相对丰度。相对丰度最高的为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes),二者可有效去除水中的有机污染物,同时具有脱氮功能。此外,在好氧段生物膜中也存在较高的硝化螺旋菌门,是重要的亚硝酸盐氧化细菌,是污水处理中执行亚硝酸盐氧化功能的关键菌群。图11(b)所示为缺氧段生物膜门水平上微生物组成情况。与好氧段类似,相对丰度最高的为变形菌门(Proteobacteria)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes),其次相对丰度较高的是厚壁菌门(Firmicutes),厚壁菌门中大都可以产生芽孢,可用以抵抗外部极端环境,是污水处理中被的重要功能菌群。
图11(c)所示为好氧段生物膜属水平上微生物top15及相对丰度。相对丰度较高的黄杆菌属(Flavobacterium)、Denitratisoma菌属、Phaeodactylibacter菌属、硝化螺旋菌属(Nitrospira)、噬氢菌属(Hydrogenophaga)等都有利于生物脱氮反应的进行,而球衣菌属(Sphaerotilus)具有降解有机污染物的功能,可促进COD去除;亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)可以调节酶来控制硝化过程。在反应器的好氧段生物膜中存在部分反硝化菌属,表明好氧段内存在缺氧甚至是厌氧环境,证实了好氧段同步硝化反硝化过程的存在。
图11(d)所示为缺氧段生物膜属水平上微生物群落结构。属水平上相对丰度较高的为球衣菌属(Sphaerotilus),具有降解有机污染物的功能;丝硫菌属(Thiothrix)常出现在氮源较少,碳源及能源丰富的环境中;弓形杆菌属(Arcobacter)、黄杆菌属(Flavobacterium)、Denitratisoma菌属、Phaeodactylibacter菌属、索氏菌属(Thauera)等菌属均为重要的脱氮微生物。缺氧段中存在的丰富弓形杆菌属(Arcobacter)、黄杆菌属(Flavobacterium)、Phaeodactylibacter菌属、和Denitratisoma菌属等微生物,有利于生物的反硝化过程,进而提高总氮去除率。
3. 结论
1)多点进水的多级生物接触氧化条件下,进水位置及比例对污染物去除效果具有明显影响。进水位置及比例为O1∶A1=4∶1时的出水效果最好,COD、NH4+-N及TN的平均出水浓度分别为20.2、0.5、9.0 mg·L−1,平均去除率分别为92.0%、97.1%、64.3%。
2) HRT对COD、氨氮和总氮去除效果有显著影响。随着HRT的减少,COD、氨氮和总氮的出水浓度逐渐升高,去除率逐渐降低,出水水质恶化,实验得出的最优水力停留时间为6.55 h。
3)多点进水条件下多级生物接触氧化工艺在好氧段内存在同步硝化反硝化过程,对总氮去除具有一定的提升作用,经缺氧段后总氮出水继续降低,末端好氧段后COD、氨氮及总氮均可达标出水。
-
-
[1] RAHIMI Y, TORABIAN A, MEHRDADI N, et al. Simultaneous nitrification–denitrification and phosphorus removal in a fixed bed sequencing batch reactor (FBSBR)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(2/3): 852-857. [2] 阳琪琪. A/O生物接触氧化工艺处理城市污水试验研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2013. [3] LIM E T, JEONG G T, BHANG S H, et al. Evaluation of pilot-scale modified A2O processes for the removal of nitrogen compounds from sewage[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100(24): 6149-6154. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.06.072 [4] ZHENG T, XIONG R, LI W, et al. An enhanced rural anoxic/oxic biological contact oxidation process with air-lift reflux technique to strengthen total nitrogen removal and reduce sludge generation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 348: 131371. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131371 [5] 徐建明. 生物接触氧化强化脱氮净化微污染水源水的工艺优化实验与中试设计[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2017. [6] 罗峰, 盛得洋, 张忠祥, 等. 生物接触氧化法去除微污染水中氨氮的中试研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(20): 109-115. [7] QIN W, LUO Y, ZHAO W, et al. Performance and microbial characteristics of a novel pilot-scale tubing biological contact oxidation reactor for rural drinking water[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 43: 102290. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102290 [8] ZHOU J, WU Y, PAN J, et al. Pretreatment of pig manure liquid digestate for microalgae cultivation via innovative flocculation-biological contact oxidation approach[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 694: 133720. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133720 [9] 边德军, 李清哲, 王帆, 等. 低温下分段进水多级A/O工艺脱氮规律分析[J]. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 2021, 53(4): 106-112. [10] 徐军, 史新星, 李坤, 等. 微氧生化—生物接触氧化法对癸二酸废水的处理特性研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2023,DOI: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2023-0288. -




 下载:
下载: