-
混凝是水处理中应用最广泛的技术之一,混凝药剂投加量的控制是影响混凝效果、提升出水水质的关键。实现对混凝过程药剂投加量的快速准确预测对于给水处理厂节约运行成本和控制水质安全稳定具有重要意义[1]。
传统的混凝药剂投加量控制多采用烧杯试验法和经验目测法[2],具有时间滞后和受人为干扰大等特点[3],且伴有化学试剂的二次污染等问题。随着人工智能技术的发展,由数据驱动的机器学习模型被广泛应用于混凝投药量预测。张凯[4]提出多模型Stacking与时序特征的混凝剂投加量预测方法,并利用水厂运行3年的15×104条数据进行验证。LIN等[5]在时间序列模型的基础上引入了图注意力网络,对水厂11年的6×104条数据进行学习和预测。刘洪波等[6]提出贝叶斯优化BP神经网络的混凝剂加药量预测方法,并以华东地区某给水厂的31×104条数据进行建模和验证。以上研究均为基于长时间序列和充足的样本数据量开展的。然而,由于数据采集方式和传感器设备测量精度的限制,许多水厂从实际运行或者模拟实验中获取的数据量往往难以满足机器学习模型的大数据要求[7-9],这导致所建立预测模型的精度较低,无法指导实际工艺运行。同时,混凝药剂投加量受温度和原水水质的季节性变化影响大,冬季低温和夏季高浊度时水处理难度增大,对混凝剂的需求量相比其他时期也有所增加[10-11]。极端天气变化和水位升高会导致水体浊度增加,为达到快速降浊的目的,混凝剂投加量也会相应增加[12]。对不同水质条件数据进行分类建模与预测有助于提高药剂投加量的预测准确度,然而已有的研究很少在模型构建过程中考虑不同水质条件的影响。
集成学习能够将若干学习器组合得到更全面的学习器,在提高小样本预测的泛化能力问题方面具有良好的表现[13-14]。K-Means聚类是一种无监督学习算法,能够根据指定特征将数据划分为若干类别[15]。因此,为了提高小样本数据下混凝投药量的预测精度,本研究提出一种K-Means聚类结合集成学习的混凝投药量预测方法。根据原水水质特征进行数据分类,结合分类结果采用分层抽样划分测试集和训练集,利用Bagging方法构建包含多种学习器的PAC投加量集成预测模型,并与其他常用模型进行对比分析。研究结果可为小样本数据下的水厂混凝投药量的建模与预测提供参考。
-
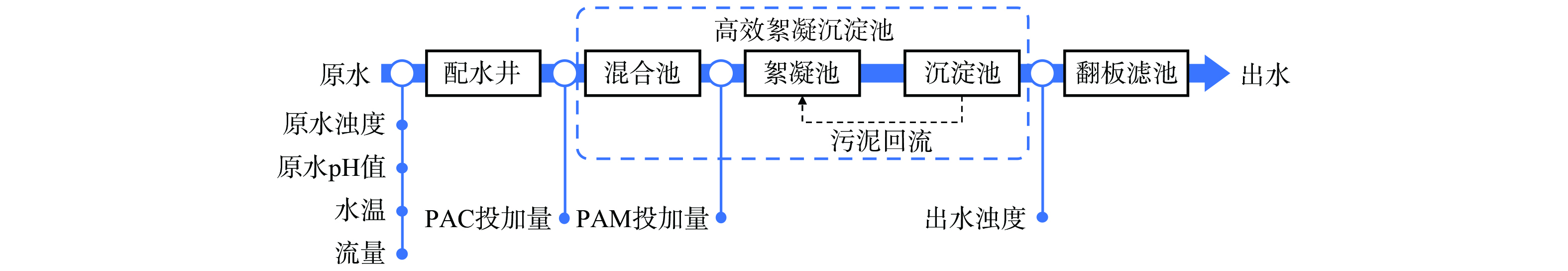
本研究所采用数据来源于银川市某给水厂,水源为黄河宁夏段,经水库调蓄后的出水作为水厂原水。水厂采用高效絮凝沉淀池和翻板滤池的组合净水工艺,采集了2021年12月—2022年12月的水质日检测数据,水厂工艺流程和数据采集点如图1所示。选取PAC投加量为预测目标,原水浊度、原水pH值、水温、流量、出水浊度和PAM投加量6个指标为影响变量。
-
由于数据采集过程中存在人为检测误差和药剂投加系统故障等特殊情况,因此原始数据集中存在异常值和缺测值,需进行预处理以便后续构建模型。预处理主要包括以下内容:1) 采用3σ准则[16]剔除各变量中的异常值;2) 对于数据缺值,利用各变量缺值前后各3日数据的平均值进行替代;3) 采用最大最小值归一化法[5]对各变量进行归一化处理,消除量纲的影响。经预处理后,得到有效数据共1 095组。
-
PAC投加量预测模型的构建是基于预处理后的数据集开展的,主要包括数据集划分和集成学习2个步骤,具体流程如图2所示。
1) 数据集划分。为了使模型在训练阶段能够掌握更全面的加药量规律,对预处理后的数据先进行水质分类,再进行样本划分。K-Means聚类是一种常用于无标签数据分类问题的无监督学习算法,能够通过不断迭代调整聚类中心,使得损失函数最小,最终将数据划分为K类。具有时间效率高、可解释性强、可指定聚类类别数等特点。首先,采用K-Means聚类根据原水浊度与水温2个特征对水质分类,类别数根据肘部法则[17]确定;其次,采用分层抽样方法按照80%∶20%的比例将预处理后的数据划分为训练集和测试集,具体方法为从各类水质数据中各抽取80%组成训练集,其余20%组成测试集。在小样本数据中,相比于传统的随机抽取划分方式,先分类后分层抽样的方法可以指定将包含不同规律的水质数据均匀划分,使模型在有限的样本中获得更全面的训练效果。
2) 集成学习。集成学习是一种将多个学习器组合得到一个性能更好的学习器的方法,常见的集成学习可以分为Bagging、Boosting和Stacking[13]。其中,Bagging方法的原理是利用自助抽样法抽取若干数据子集,在各子集上分别训练学习器,取各学习器的预测均值作为最终预测结果。Bagging方法能够实现各学习器间的优势互补,有效降低测试误差[18]。学习器类型的选择是也影响集成学习效果的重要因素,选择准确度高且差异性大的学习器具有更好的集成预测效果[19]。
采用自助抽样法有放回地从训练集中抽取7个数据子集。选择支持向量机 (Super Vector Machine, SVM)、随机森林 (Random Forest, RF)、Adaboost、GBDT、Catboost、XGBoost和LightGBM共7种学习器进行集成。SVM在解决小样本、非线性和高维模式识别问题中有良好的效果[20]。RF、Adaboost、GBDT等其他6种学习器均为树类集成学习算法,对缺失值和噪声具有鲁棒性,同时对稀疏矩阵也具有良好的处理能力[21-23]。取7种学习器的预测平均值作为KM-Bagging模型对PAC投加量的最终预测结果。
-
选取R2、均方根误差 (RMSE) 和平均相对误差 (MAPE) 3种误差指标评价对PAC投加量的预测效果。R2越接近1,RMSE越接近0,MAPE越接近0,预测效果越好。3种指标的计算见式(1)~式(3)。
式中:yi为预测值;fi为实际值;
$ {\bar f_i} $ 为实际值的均值。 -
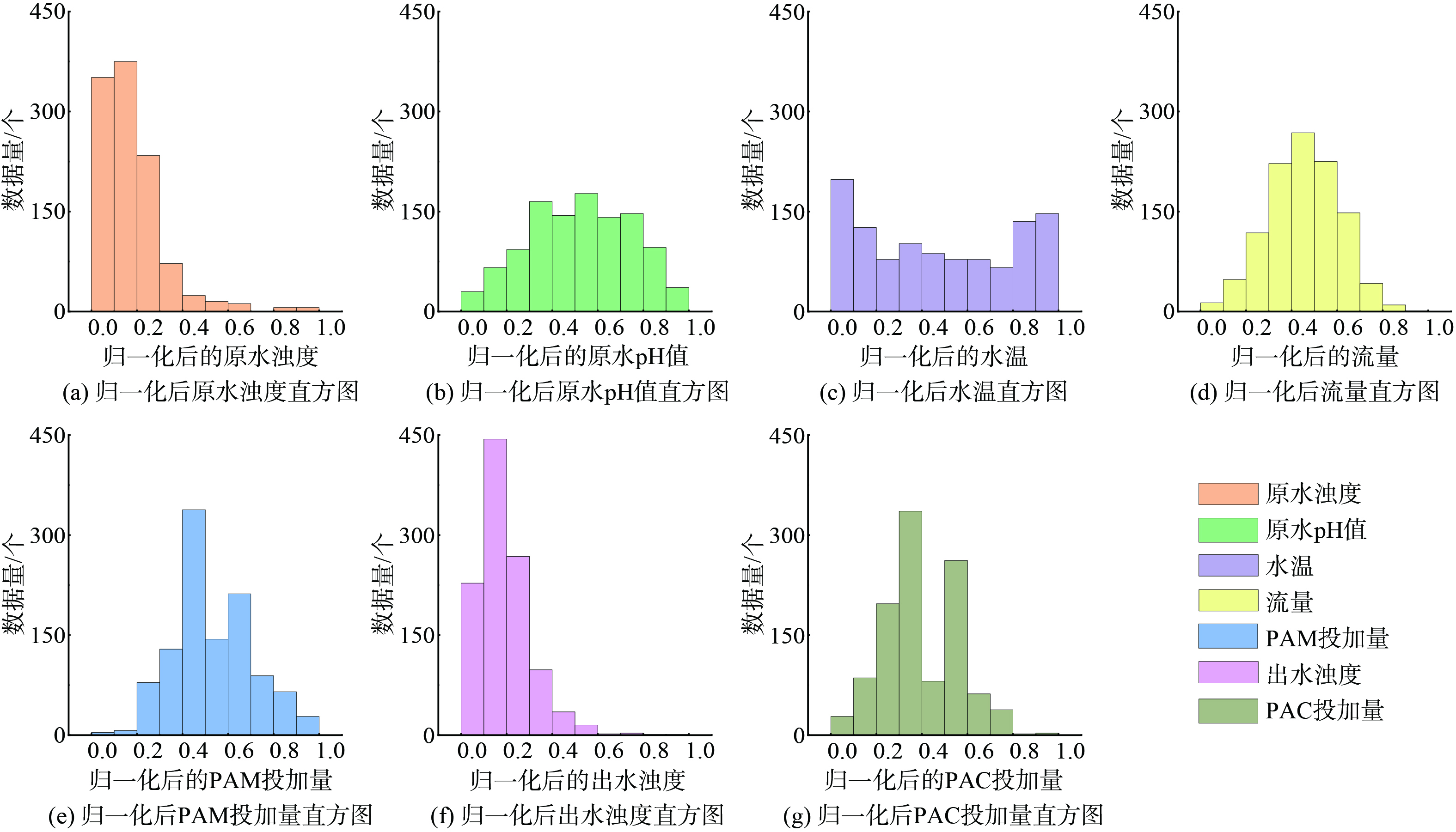
本研究共采集混凝过程的原始数据1 095组,其中原水pH值数据缺失率为5%,其他变量数据均完整。经数据预处理后各变量的变化范围如表1所示。流量和其他变量的数据量级相差较大,因此将所有变量值归一化至[0, 1]内。归一化后各变量的分布情况如图3所示,其中原水pH值和流量近似为正态分布。原水pH值围绕8.34变化,属于弱碱性水质。进水流量主要稳定在2 005 m3左右,机组启闭过程是小流量数据的主要来源,水库上水和黄河汛期是导致流量增加的主要原因。原水浊度和出水浊度的分布具有一致性,均为正偏态分布,整体以低浊度为主。原水水温与其他变量均不同,具有鲜明的高温和低温特征,原水冬季最低温接近0 ℃,全年超过30%以上的水温数据大于20 ℃。PAC与PAM投加量的分布也具有较高的相似性。常规情况下,PAC和PAM的投加量分别在2.4和0.1 mg·L−1左右。冬季低温和夏季浊度升高时水处理难度增加,PAC和PAM的投加量分别提高至2.7和0.12 mg·L−1左右。
-
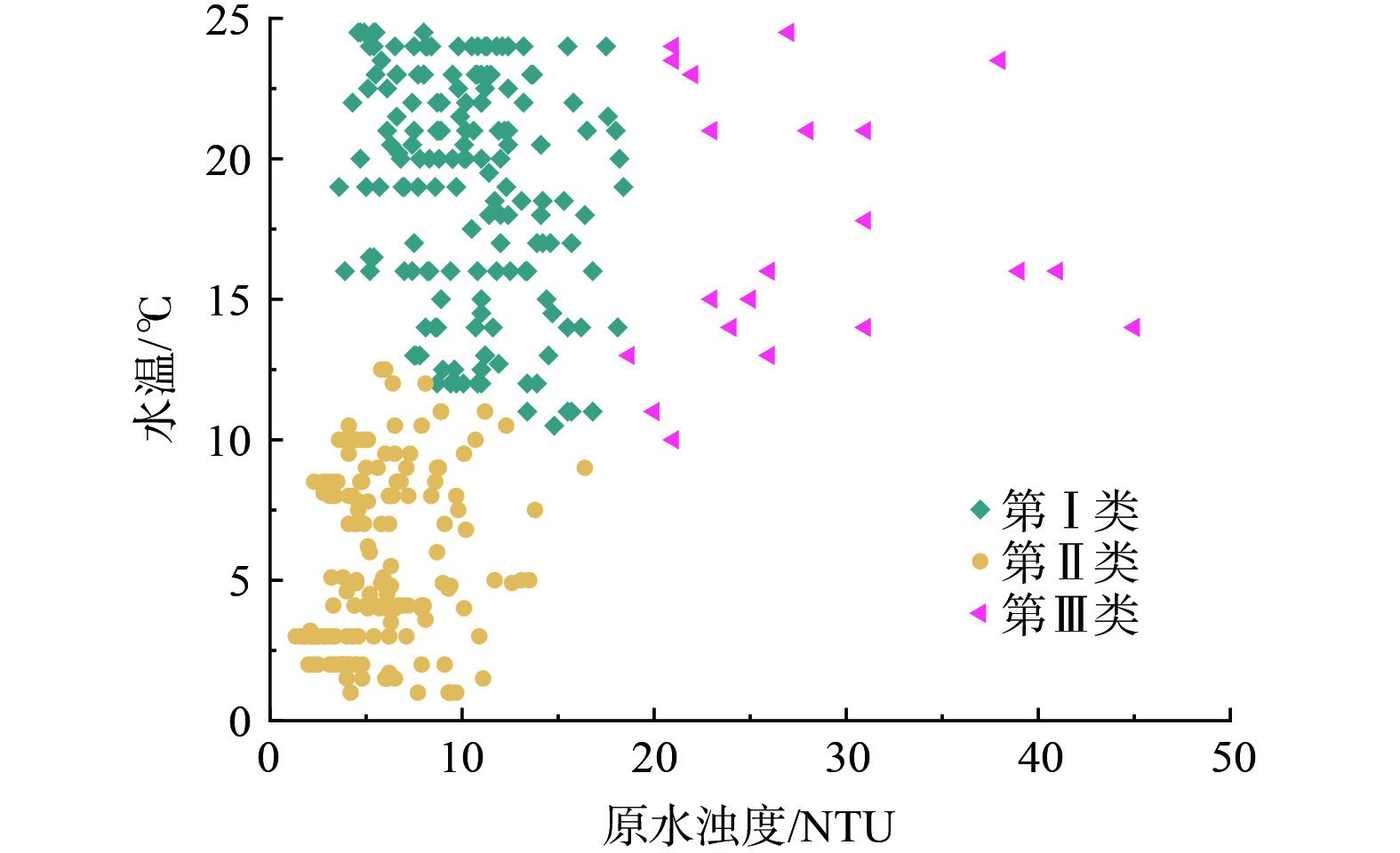
根据肘部法确定将水质划分为3类,聚类结果如图4所示。第Ⅰ类水质占比为45.5%,特点为高温 ( (17.5±7.0) ℃) 低浊度 ( (11.0±7.4) NTU) ,产生原因为夏秋季温度升高;第Ⅱ类水质占比为48.5%,特点为低温 ( (6.8±5.8) ℃) 低浊度 ( (8.9±7.5) NTU) ,主要分布在冬季和春季融冰期;第Ⅲ类水质占比为6.0%,特点为高温 ( (17.3±7.3) ℃) 高浊度 ( (31.9±13.2) NTU) ,主要是由黄河汛期以及水库上水导致的水量增加和浊度上升造成的。
预处理后的数据共1 095组,根据水质分类结果分层抽取训练集和测试集,具体结果如表2所示。训练集共876组数据,其中包含第Ⅰ类398组、第Ⅱ类425组、第Ⅲ类53组。测试集共219组数据,其中包含第Ⅰ类100组、第Ⅱ类106组、第Ⅲ类13组。
-
KM-Bagging模型及其内部各学习器对PAC投加量的预测结果如表3所示。可以发现KM-Bagging模型的预测精度优于其他学习器,预测R2超过0.8。7种学习器的训练集预测R2均超过0.9、MAPE均小于2%,表明各学习器在训练过程中充分拟合了PAC投加量与其影响变量间的关系。但测试集的预测误差均有较明显增加,这说明训练过程中各学习器对加药量规律均存在过度拟合问题,即将部分数据对应的局部规律当做通用规律进行学习和保存,导致测试集数据无法完全匹配。KM-Bagging模型通过取均值的方式弱化了学习器各自训练的局部规律,提高了对测试集数据的适应性。相比其他7种学习器,KM-Bagging模型的预测R2平均提高了10%、MAPE平均降低9%、RMSE平均降低14%。此外,除SVM外的6种学习器均为由若干决策树组成的集成算法,其测试集预测精度均未超过KM-Bagging模型。这是因为KM-Bagging模型集成了不同类型的学习器,相比由单一决策树组成的集成模型更能发挥各学习器的优点,更全面地学习加药量规律。
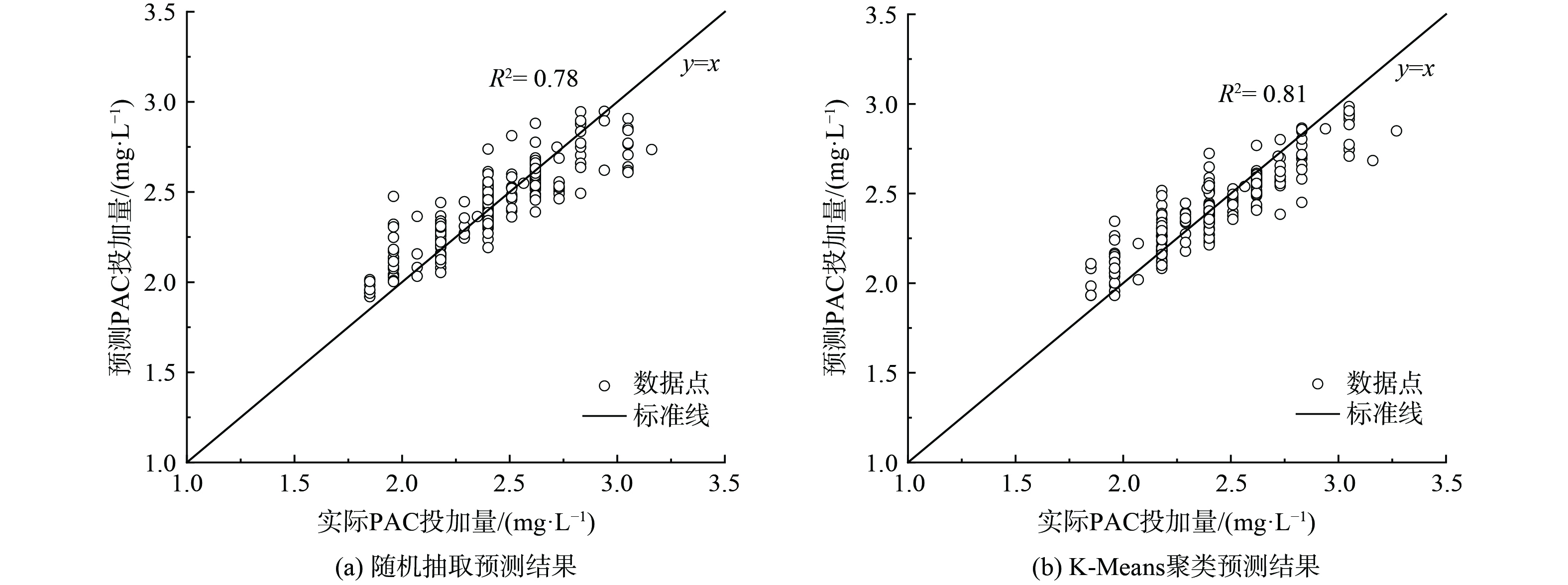
为了探究水质分类对与提高PAC投加量预测精度的影响,比较了采用K-Means聚类和随机抽取2种数据集划分方式的PAC投加量预测结果。如图5所示,随机抽取划分方式的PAC投加量预测效果较好,R2为0.78。经过K-Means聚类重新划分数据集后,预测精度进一步提高。相比于随机抽取划分方式,聚类后的测试集R2提高了5%,MAPE降低了3%,RMSE降低了5%。由图5还可以发现,当PAC投加量为2.5~3.0 mg·L−1时,随机抽取情况下的预测PAC投加量高于实际值,而K-Means聚类情况下二者则较为接近。这是由于该部分PAC投加量数据与聚类后的第Ⅲ类水质相对应,随机抽取划分方式未考虑到第Ⅲ类水质数据占比小的特点,将其过多或过少地分配给训练集。当第Ⅲ类水质数据过多地分配给训练集时,模型在测试集上可能表现为过拟合。相反地,过少地分配给训练集时则表现为学习能力不足即欠拟合。K-Means聚类能够将3类水质按照各自占比分配给训练集和测试集,平衡训练和测试误差,防止过拟合和欠拟合问题的出现。
整体而言,KM-Bagging方法对PAC投加量预测精度较高,能够满足工程应用要求。其中,K-Means聚类能够有效提取样本数据的水质特征并分类,通过重新划分数据集的方式提高模型对加药量规律的训练拟合效果。
-
在实际数据采集过程中,由于设备、检测条件等客观因素的限制,可获取的数据量有限。有研究表明,样本的数据量与模型预测精度呈正相关[21],数据量稀疏是导致模型预测精度低的主要原因之一[24]。因此,为了探究KM-Bagging模型在不同长度样本数据下的预测效果,对100% (1 095组) 、75% (821组) 、50% (548组) 和25% (274组) 共4种不同长度数据集的PAC投药量进行预测,并与BP神经网络、RBF神经网络、RF及SVM等4种常用模型进对比,预测结果如表4和图6所示。
由表4可以发现,在4种不同数据集长度下,预测精度排序由高到低依次为KM-Bagging模型>RF>SVM>RBF神经网络>BP神经网络。相比其他模型,KM-Bagging模型的预测R2平均提高25%,MAPE平均降低18%,RMSE平均降低12%,说明KM-Bagging模型对不同规模数据集的PAC投加量均具有良好的预测效果。通过与阎有运等[25]、庹婧艺等[26]及伊学农等[27]的研究结果对比,在相同规模数据集下,KM-Bagging模型对于混凝投药量的预测精度高于自适应神经模糊推理系统(ANFIS)、GA-BP及单一神经网络等模型。KM-Bagging模型在所有长度数据集下的预测R2均大于0.5,MAPE均小于10%,RMSE均小于0.2。随着数据集长度的减小,预测精度也随之降低。由图6可以看出,在不同数据集长度下,当实际PAC投加量小于2.5 mg·L−1时,KM-Bagging模型的大部分预测值高于实际值;当实际PAC投加量大于2.5 mg·L−1时则相反,且该现象随着数据集的减小更加明显。这是因为KM-Bagging模型在小样本数据上更容易学习局部规律,而随着数据量及其所包含信息量的增加,PAC投加量与水质变量间的完整规律才逐渐被模型掌握。
100%长度的数据集为水厂运行1年的实际产生数据,75%、50%和25%长度的数据集则分别对应9个月、6个月和3个月的实际产生数据量。对KM-Bagging模型在不同长度数据集的预测效果分析可以发现,当使用25%长度数据集时,PAC投加量的预测R2为0.52,无法反映加药量变化规律;当使用50%和75%长度数据集时,预测R2均大于0.6,MAPE均小于6%,能够较准确预测PAC投加量变化趋势。当使用100%长度数据集时,预测R2均大于0.8,MAPE小于5%,能够完整地反映不同水质条件下的PAC投加量变化规律。因此,采用6个月和9个月对应的日监测数据预测PAC投加量,适合数据监测时间短、精度要求不高的情况,预测结果可为原水水质发生突变时的PAC投加量调整提供参考。采用1年的日监测数据预测PAC投加量,能够满足工程应用的精度要求,可作为辅助参考为水厂日常运行的PAC投加提供指导。
-
1) 选取原水浊度、原水pH值、水温、流量、出水浊度和PAM投加量6个指标作为PAC投加量的影响变量,采用K-Means聚类和集成学习方法构建了基于KM-Bagging的PAC投加量预测模型。分析结果表明,KM-Bagging模型在小样本数据上具有良好的预测精度,预测R2超过0.8,MAPE小于5%,RMSE小于0.15。
2) KM-Bagging方法在不同长度的样本数据集上均具有良好的预测效果。采用6个月和9个月对应的日监测数据预测PAC投加量,适合数据监测时间短、精度要求不高的情况,预测结果可为原水水质发生突变时的PAC投加量调整提供参考。采用1年的日监测数据预测PAC投加量,预测结果能够满足工程应用的精度要求,可为水厂实际PAC投加提供辅助指导。
小样本数据下基于K-Means聚类和集成学习的混凝投药预测
Research on coagulation dosing prediction based on K-Means clustering and ensemble learning under small sample data
-
摘要: 为了解决混凝投药预测过程中的小样本问题,提出基于K-Means聚类和集成学习的PAC投加量预测方法。首先,根据原水浊度和水温2个特征采用K-Means聚类将水质分为3类,利用分层抽样从3类水质数据中抽取训练集和测试集;其次,基于Bagging集成学习算法,构建由支持向量机、随机森林、Adaboost、GBDT、Catboost、XGBoost和LightGBM共7种学习器组成的PAC投加量集成预测模型(KM-Bagging);最后,以银川市某给水厂2021—2022年的运行数据为例进行验证。结果表明,KM-Bagging模型对小样本的PAC投加量具有较高预测精度,R2超过0.8,MAPE小于5%。采用6个月和9个月的日监测数据预测PAC投加量,适合数据监测时间短、精度要求不高的情况,预测结果可为原水水质发生突变时的PAC投加量调整提供参考。采用1年的日监测数据预测PAC投加量,预测精度能够满足工程应用的要求,可为水厂实际PAC投加提供辅助指导。研究结果对小样本数据下的混凝药剂投加建模与预测具有参考价值。
-
关键词:
- 混凝投药量预测 /
- 小样本数据 /
- Bagging集成学习 /
- K-Means聚类
Abstract: A PAC dosage prediction method was proposed to address small sample size issues in coagulant dosage prediction. The method was based on K-Means clustering and ensemble learning. Firstly, Water quality was divided into three categories using K-Means clustering based on raw water turbidity and water temperature. The training and test sets were then extracted from the data using stratified sampling. Secondly, a PAC dosage ensemble prediction model (KM-Bagging) was constructed based on the Bagging ensemble learning algorithm. The model consisted of seven learners: Support Vector Machine, Random Forest, Adaboost, Gradient Boosting Decision Tree, Catboost, XGBoost, and LightGBM. The method was validated using operational data from a water supply plant in Yinchuan City from 2021 to 2022. The results showed that the KM-Bagging model had high prediction accuracy for small sample sizes, with an R2 exceeding 0.8 and MAPE less than 5%. When 6- and 9-month daily monitoring data were used to predict PAC dosing, the model was suitable for cases where monitoring time was short and high accuracy was not required. The predicted results can be used as a reference for adjusting the PAC dosage when there was a sudden change in raw water quality. When one year of daily monitoring data was used to predict PAC dosing, the prediction accuracy met the requirements for engineering applications and provided auxiliary guidance for actual PAC dosage in water treatment plants. The results of study can provide reference value for modeling coagulant dosage prediction with small sample data. -

-
表 1 预处理后各变量的变化范围
Table 1. The range of changes in each variable after preprocessing
原水浊度/NTU 原水pH值 水温/ ℃ 流量/m3 PAM投加量
/(mg·L−1)出水浊度/NTU PAC投加量/(mg·L−1) 23.2±21.8 8.34±0.28 12.8±11.8 2 005±1 205 0.10±0.06 1.7±1.5 2.62±0.88 表 2 数据集划分结果
Table 2. Results of data set partitioning
水质类别 数据量占比/% 训练集数据量/组 测试集数据量/组 Ⅰ 45.5 398 100 Ⅱ 48.5 425 106 Ⅲ 6.0 53 13 表 3 PAC投加量的预测结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of the prediction results of PAC dosage
模型 训练集 测试集 R2 MAPE RMSE R2 MAPE RMSE SVM 0.94 1.56 0.067 0.70 5.07 0.164 RF 0.95 1.86 0.060 0.70 5.14 0.169 adaboost 1.00 0.01 0.002 0.74 4.04 0.156 GBDT 0.99 0.27 0.008 0.77 4.35 0.145 Catboost 0.97 1.54 0.049 0.76 4.79 0.151 XGBoost 0.99 0.30 0.011 0.76 4.42 0.147 LightGBM 0.97 1.35 0.032 0.74 4.79 0.153 Bagging — — — 0.78 4.36 0.141 KM-Bagging — — — 0.81 4.23 0.134 表 4 不同长度数据集下的PAC投加量预测结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of PAC dosing prediction results under different length data sets
数据集长度 模型 R2 MAPE RMSE 100% KM-Bagging 0.81 4.23 0.134 BP 0.42 16.70 0.226 RBF 0.50 5.84 0.183 SVM 0.71 4.49 0.147 RF 0.77 4.18 0.135 75% KM-Bagging 0.69 5.07 0.156 BP 0.54 6.37 0.192 RBF 0.51 6.33 0.185 SVM 0.63 5.33 0.169 RF 0.65 5.24 0.156 50% KM-Bagging 0.64 5.73 0.168 BP 0.41 6.73 0.189 RBF 0.40 6.52 0.198 SVM 0.58 6.32 0.166 RF 0.60 6.01 0.168 25% KM-Bagging 0.52 6.48 0.198 BP 0.41 7.21 0.234 RBF 0.42 6.89 0.217 SVM 0.47 6.58 0.213 RF 0.47 6.56 0.208 -
[1] 程方, 秦涛, 赵现勇, 等. 加药量和水力搅拌速度对雨水混凝效果的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2012, 6(11): 3905-3909. [2] 何嘉莉, 袁耀芬, 周沛良, 等. 自来水厂混凝剂自动精准投加系统建设与运行[J]. 中国给水排水, 2021, 37(18): 139-143. [3] 王涛, 吴福雨, 程紫微, 等. 基于5参数GA-BP模型的出水水质预测——以宁夏某水厂为例[J/OL]. 环境保护科学: 1-10. [4] 张凯. 集成学习框架下的水厂混凝剂智慧投加预测模型构建 [J/OL]. 工业水处理, 1-11[2024-01-17] https://doi.org/10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2023-0257. [5] LIN S B, KIM J, HUA C, et al. Coagulant dosage determination using deep learning-based graph attention multivariate time series forecasting model[J]. Water Research, 2023, 232: 119665. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.119665 [6] 刘洪波, 黄剑虹, 张国荣, 等. 给水厂混凝剂智能投加模型构建与应用[J]. 上海理工大学学报, 2022, 44(4): 351-356+387. [7] MAIER H R, MORGAN N, CHOW C W K. Use of artificial neural networks for predicting optimal alum doses and treated water quality parameters[J]. Environmental Modelling and Software, 2004, 19(5): 485-494. doi: 10.1016/S1364-8152(03)00163-4 [8] VINITHA E V, AHAMMED M, GADEKAR M R. Chemical coagulation of greywater: modelling using artificial neural networks[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2018, 2017(3): 869-877. doi: 10.2166/wst.2018.263 [9] 余峰, 王珂佳, 张文龙, 等. 基于遗传算法优化BP神经网络的水生态修复原位控浊混凝投药预测[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41(4): 154-163. [10] 王涛, 张俊, 王坪, 等. 基于高效絮凝沉淀池与翻板滤池组合工艺的工程案例[J]. 环境工程学报, 2023, 17(3): 1043-1050. [11] DAYARATHNE H N P, ANGOVE M J, JEONG S, et al. Effect of temperature on turbidity removal by coagulation: Sludge recirculation for rapid settling[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 46: 102559. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102559 [12] ZHANG P, CAI Y, WANG J. A simulation-based real-time control system for reducing urban runoff pollution through a stormwater storage tank[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 183: 641-652. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.130 [13] 王增帅. 基于集成学习的不平衡数据分类问题研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2022. [14] 王雪晴, 刘小军, 刘艳, 等. 采用最优集成学习的小样本电磁脉冲信号分类[J]. 振动与冲击, 2023, 42(11): 193-198. [15] YU S W, WEI Y M, FAN J L, et al. Exploring the regional characteristics of inter-provincial CO2 emissions in China: An improved fuzzy clustering analysis based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 92: 552-562. [16] 徐琛辉, 马明辉. 基于拉依达准则的交通数据粗大误差处理优化方法[J]. 上海工程技术大学学报, 2018, 32(1): 4. [17] 梁曦文, 肖峰, 闵昊凌, 等. 基于ESMD-LSSVM模型的径流式水电站出力预测研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2023(9): 224-229+235. [18] LU C, DEVOS A, SUYKENS J, et al. Bagging linear sparse Bayesian learning models for variable selection in cancer diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 2001, 11(3): 338-347. [19] 陈俊彦, 卢贤涛, 黄雪锋, 等. 基于Double-Bagging特征降维异质集成入侵检测[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2023, 45(6): 1011-1019. [20] 丁世飞, 齐丙娟, 谭红艳. 支持向量机理论与算法研究综述[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2011, 40(1): 2-10. [21] CHEN K Y, CHEN H X, ZHOU C L, et al. Comparative analysis of surface water quality prediction performance and identification of key water parameters using different machine learning models based on big data[J]. Water Research, 2020, 171: 115454. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115454 [22] 鲁淑霞, 张振莲, 翟俊海. 代价敏感惩罚AdaBoost算法的非平衡数据分类[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 55(2): 339-346. [23] 徐玲, 景向楠, 杨英, 等. 基于SMOTE-GA-CatBoost算法的全国地表水水质分类评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(7): 3848-3856. [24] WEI S, CHEN Z, ARUMUGASAMY S K, et al. Data augmentation and machine learning techniques for control strategy development in bio-polymerization process[J]. Environment Science and Ecotechnology, 2022, 11: 100172. doi: 10.1016/j.ese.2022.100172 [25] 阎有运, 常波, 刘建国, 等. ANFIS在混凝投药前馈控制器中应用的仿真研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2010, 4(6): 1357-1362. [26] 庹婧艺, 徐冰峰, 徐悦, 等. 优化RBF神经网络控制水厂混凝剂投加的研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2021(8): 212-215+220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2021.08.036 [27] 伊学农, 韦秋梅, 何通, 等. 基于GA-BP网络混凝投药系统预测模型的研究[J]. 化工自动化及仪表, 2009, 36(2): 75-78. -



 下载:
下载: