-
挥发性有机物 (volatile organic compounds, VOCs) 是光化学烟雾和二次有机气溶胶 (SOAs) 的重要前体物[1],易引发大气污染如臭氧污染及PM2.5[2]。VOCs会导致人体内肿瘤的形成[3]。2020年,我国工业源VOCs的排放量约为217.1×104 t,占总排放量的35.6%。其中,石油、煤炭及其他燃料加工业为52.79×104 t,化学原料和化学制品制造业为42.77×104 t,橡胶和塑料制品业为13.46×104 t,其他行业为108.12×104 t[4]。为进一步改善环境空气质量,应全面加强重点行业VOCs的综合治理。
吸附技术具有能耗低、操作简单、运行成本低等优点,广泛应用于低浓度含VOCs废气的净化中[5]。活性炭是最为常用的吸附剂,具有良好的物理化学性质,但在温度较高时易自燃存在安全隐患[6]。分子筛不易燃,其煅烧再生性能优异,在干燥条件下对VOCs吸附性能良好而成为替代活性炭的吸附材料[7]。在实际工业过程中,VOCs中往往含有水分,将与VOCs发生竞争吸附,从而导致吸附剂的吸附容量下降,尤其在高湿度环境下,吸附容量将急剧下降[8-10]。YIN等[11]采用高温水热法对NaY分子筛疏水改性,未改性的NaY分子筛在干燥条件下对甲苯的吸附量为178.6 mg·g−1,在相对湿度 (relative humidity,RH) 为50%时对甲苯的吸附量为11.26 mg·g−1,对水的吸附量为237.24 mg·g−1。LI等[12]在不同湿度下,研究了10种商业吸附剂在碱改性前后对VOCs的吸附解吸特性,发现在加入湿度后的体系中,大部分分子筛对二甲苯的吸附能力几乎下降到零。因此,提高水分存在条件下分子筛吸附剂的吸附性能是吸附工艺实际应用面临的关键问题。
分子筛的亲疏水性程度与SiO2/AlO3和表面极性羟基有关,故分子筛疏水改性的方法通常包括脱铝和覆硅改性[13-14]。常用的脱铝方法有水热脱铝、酸处理、EDTA处理,但其对材料的晶体结构有影响,会降低材料结晶度[15]。覆硅法有接枝法、共缩合法、有序介孔有机硅法,其中接枝法和共缩合法这2种方法研究较多[16-17]。LU等[18]通过苯基硅烷的架桥作用合成了具有高疏水性和热稳定性的Y@St-DVB复合材料,在RH为60%和90%条件下分别是Y沸石的1.97和1.96倍,对甲苯的吸附量分别为131.9 mg·g−1和118.3 mg·g−1。李承龙等[19]利用正辛基三乙氧基硅烷改性,成功地将—Si(CH2)7CH3基团接枝到ZSM-5分子筛表面,改性后的分子筛水接触角增大到152°,静态水吸附量下降了26.4%,实现了超疏水性,但由于改性后分子筛的孔容减小,对正己烷静态吸附量由8.60%降至7.45%。张媛媛等[20]采用3种不同硅烷试剂对NaY分子筛进行改性,改性后的样品在RH为80%条件下甲苯的吸附量都得到了增加,其中三甲基氯硅烷 (TMCS) 增加量最大为78%,由12.2 mg·g−1增至21.1 mg·g−1。
汽车涂装行业废气湿度高、成分复杂,亟需根据涂装行业环境条件,研究相关污染物的排放特征及吸附过程特点,并开展相应的分子筛疏水改性研究。然而,相关成果尚未见报道。本研究以汽车涂装行业VOCs污染物为对象,选取甲苯、二甲苯、乙酸丁酯为代表污染物,对NaY分子筛进行覆硅改性研究,结合分子筛结构表征和疏水测定,获取有效的疏水改性方法,制备用于汽车涂装高湿度环境的疏水性强且吸附性能佳的改性NaY分子筛,以期为涂装行业分子筛转轮VOCs吸附的工业应用提供参考。
-
NaY、13X、5A、10A分子筛购置于南开催化剂,其参数见表1。甲苯、二甲苯、乙酸丁酯购置于阿拉丁生化科技有限公司均为分析纯,动力学直径和沸点见表2。正硅酸乙酯、正己烷、无水乙醇购置于科密欧化学试剂有限公司均为分析纯。盐酸购置于国药集团化学试剂有限公司均为分析纯。氨水、三甲基氯硅烷购置于阿拉丁生化科技有限公司均为分析纯。
-
分子筛在实验前置于马弗炉中500 ℃下活化5 h。首先,对NaY分子筛进行预处理,将正硅酸乙酯 (tetraethyl orthosilicate,TEOS) 、无水乙醇、水混合,并用1 mol·L−1的盐酸调节pH到2~3,促进TEOS水解;在6 h后,缓慢加入质量分数为5%氨水调节pH至7配制好老化液,将10 g分子筛加入老化液中,在室温下静置12 h;加入50 mL正己烷及不同体积 (0、2.5、5、7.5、10、12.5 mL) 的三甲基氯硅烷 (trimethylchlorosilane,TMCS) 静置24 h,正己烷淋洗3遍后,于60 ℃下干燥12 h,再在200 ℃下干燥12 h,得到不同TMCS/正己烷比例的材料,并分别记为NaY-1 (无TMCS)、NaY-2 (1∶20)、NaY-3 (1∶10)、NaY-4 (1∶7)、NaY-5 (1∶5)、NaY-6 (1∶4)。
-
采用比表面积测试仪 (V-Sorb 2800P) 对分子筛比表面积孔径分布进行表征;X射线衍射仪 (UItima Ⅳ) 对分子筛晶体结构进行表征;傅里叶红外光谱仪 (Vertex 70) 对分子筛表面官能团进行表征;采用能量色散光谱 (JEOL Corp) 对分子筛中的所有元素种类和含量进行测定;NH3-TPD (ChemiSorb 2720) 对分子筛表面Lewis酸位点和Brønsted酸位点进行表征;水接触角测试仪 (JYC-8) 对分子筛亲疏水性进行表征。
-
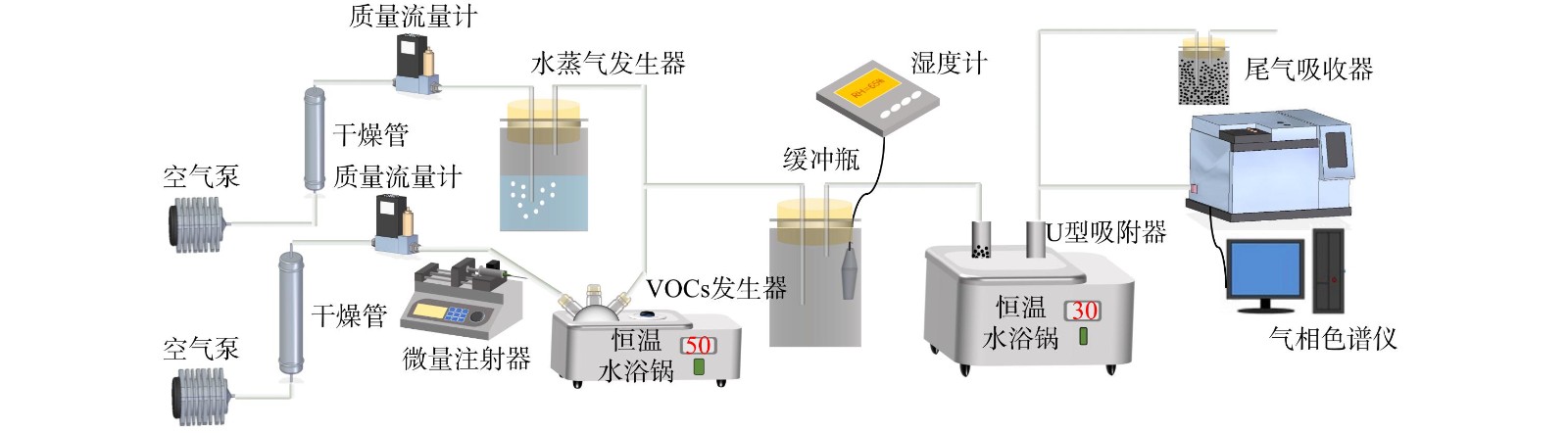
吸附实验在常温常压下进行,实验系统如图1所示。由注射泵 (LSP02-D) 将VOCs液体精准注入置于恒温水浴锅 (50 ℃) 中的烧瓶内,由质量流量计 (北京七星CS-200D,10 L) 控制经硅胶除湿后的总空气流量为3 L·min−1。一路空气进入水浴锅内三颈烧瓶,另一路空气进入水蒸气发生器,通过鼓泡法控制湿度,两路气体共同进入缓冲瓶内,浓度、湿度稳定的VOCs模拟废气经分子筛吸附后排出。吸附器内径为10 mm,长度120 mm,分子筛装填量3.20 g。吸附器置于恒温水浴锅 (温度为30 ℃) 中。在吸附器进、出口使用气相色谱仪 (福立GC9700Ⅱ) 测定VOCs质量浓度,得到穿透曲线。当吸附反应器VOCs出口浓度为进口浓度的95%时认为吸附达到饱和,即可结束实验。尾气经净化后排出。
以吸附时间 (t) 为横坐标,以i分钟时进出口VOCs质量浓度之比 (Ci/C0) 为纵坐标,得到VOCs的吸附穿透曲线。通过式 (1) 对吸附穿透曲线进行积分计算,得到VOCs的平衡吸附容量。
式中:Q为平衡吸附容量,mg·g−1;F为气流速度,mL·min−1;C0为进口VOCs质量浓度,mg·m−3;Ci为i分钟时吸附器出口VOCs质量浓度,mg·m−3;W为吸附剂装填量,g;ti为吸附平衡时间,min。
-
分子筛静态水吸附实验按照国标GB/T 6287-2021《分子筛静态水吸附测定方法》测定计算。具体操作步骤为:试料550 ℃焙烧1 h,取出瓷坩埚,放入真空干燥器内,冷却至室温;取出瓷坩埚,将样品倒入质量为m1的称量瓶内;随后立即在分析天平上称重m2;将装有试样的称量瓶置于盛有饱和氯化钠溶液的干燥器中;将干燥器放在鼓风干燥箱内,开启鼓风机,箱温控制在 (35±1) ℃,恒温吸附24 h;取出称量瓶称重m3。再按式 (2) 计算静态水吸附量。
式中:m3为称量瓶加吸水后材料的质量,g;m2为称量瓶加焙烧后材料的质量,g;m1为称量瓶的质量,g。
-
将筛选出的疏水性最佳的分子筛进行重复吸脱附实验,以二甲苯、甲苯、乙酸丁酯为吸附质,在相对湿度RH为0%和65%的条件下,采用热脱附的方式在250 ℃下脱附2 h,对脱附后的样品进行动态吸附测试。
-
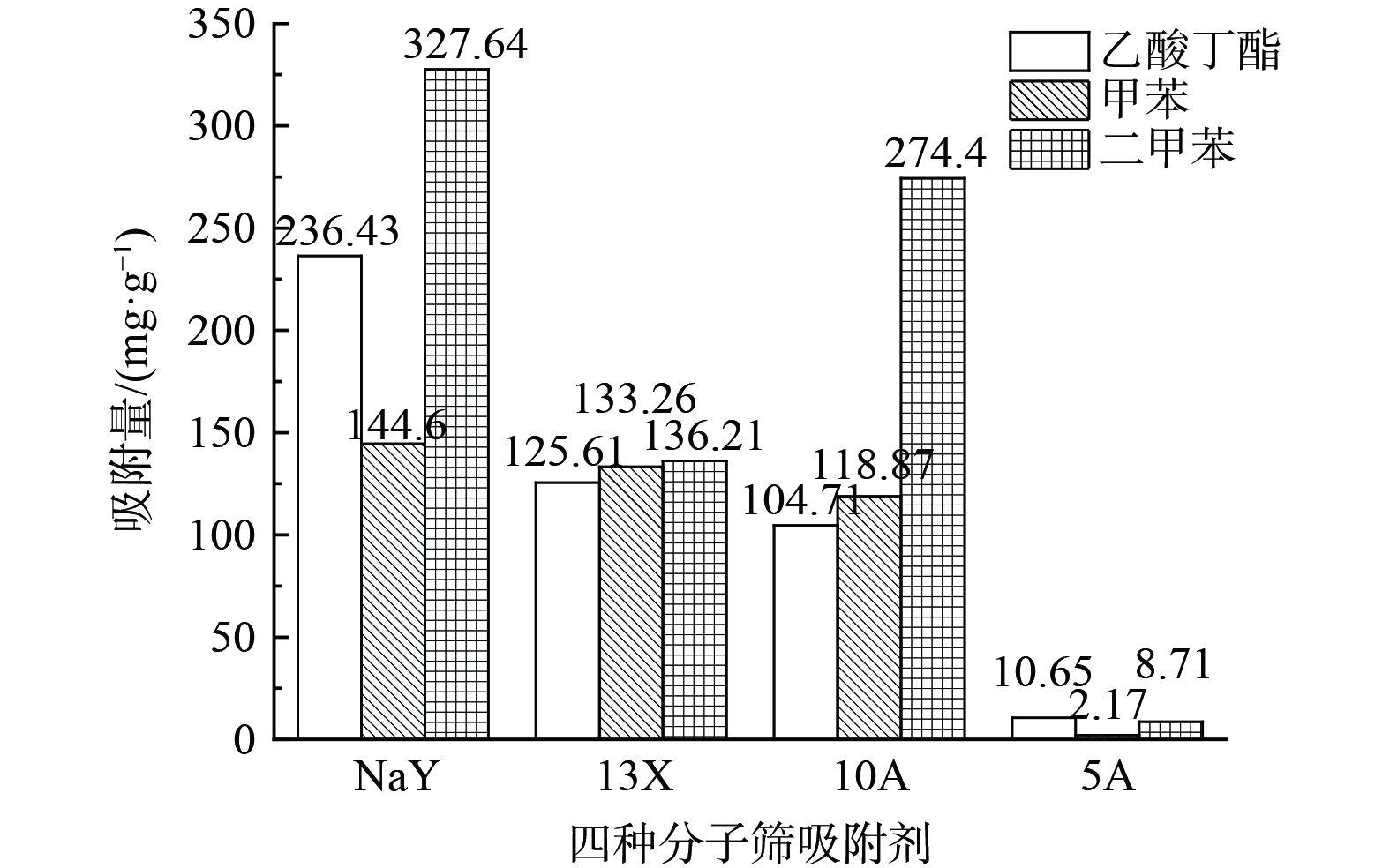
在温度为30 ℃、RH为0%、进气量为3 L·min−1的条件下,测定3种VOCs在NaY、13X、10A、5A这4种分子筛上的饱和吸附量,结果如图2所示。乙酸丁酯、甲苯、二甲苯在NaY分子筛上的平衡吸附量分别为236.43、144.6、327.64 mg·g−1,均大于其他3种分子筛,而乙酸丁酯、甲苯、二甲苯在5A分子筛上吸附量最小。分析原因为NaY分子筛的比表面积、孔容、孔径均大于其他3种,可为VOCs的吸附提供更多吸附位点,而乙酸丁酯、甲苯、二甲苯的动力学直径均大于5A分子筛的有效孔径 (0.5 nm) 。因此,5A分子筛的吸附量最小,故选用NaY分子筛进行后续研究。
-
在保证两路气流的总体积流速为3L·min−1的前提下,通过质量流量计控制气流速度从而控制鼓泡速率来调节湿度。NaY分子筛在温度为30 ℃,RH分别为0%、25%、45%、65%、85%这5个不同湿度条件下的乙酸丁酯、甲苯,以及二甲苯,3种污染物的吸附穿透曲线如图3所示。
图3 (a) 和 (b) 表明,H2O-二甲苯、H2O-甲苯在NaY分子筛上的二元吸附过程存在竞争吸附行为。在吸附开始时,H2O和污染物均能被吸附在NaY上,在吸附器的出口污染物浓度为零。随着吸附的进行,污染物的Ci/C0从零逐渐增加,当NaY表面吸附位点被吸附物占据时,H2O的进一步吸附会取代已被吸附的污染物,导致出口污染物的浓度大于初始质量浓度。如在H2O-二甲苯体系中,二甲苯被取代,在H2O-甲苯体系中,甲苯被取代,被取代组分穿透曲线出现驼峰 (Ci/C0≥1) 。导致这一现象的原因是NaY表面存在亲水性Si—OH键,水分子因具有—OH键比甲苯和二甲苯更易吸附。VOCs吸附以物理吸附为主,与吸附剂的比表面积密切相关[21]。与VOCs在吸附剂上的吸附机制不同,水分子首先在较低的相对压力下通过H键牢牢地吸附在含氧基团上,然后再进一步吸附在之前吸附的水分子上形成水簇,最终在较高相对压力下被填充到孔隙中[22-23]。随着吸附的进行,污染物质量浓度最终趋于稳定,达到吸附平衡,Ci/C0接近1。图3 (c) 表明,H2O-乙酸丁酯在NaY分子筛上的二元吸附过程与前2种不太相同。随着吸附的进行,穿透曲线上并未出现H2O取代已经被吸附的乙酸丁酯的驼峰。分析其原因,是由于乙酸丁酯因具有酯基故具有极性,水分子也是极性的,因此H2O-乙酸丁酯在极性NaY分子筛上的吸附并未表现出竞争取代现象。
图3还表明,随着湿度增加,乙酸丁酯、甲苯和二甲苯的穿透曲线均向左移动,穿透时间急剧缩短,如RH由0%增至85%时,NaY分子筛对二甲苯的穿透时间由485 min缩短至12 min,对甲苯的穿透时间由410 min缩短至11 min,对乙酸丁酯的穿透时间由350 min缩短至35 min。由图3 (a) 、 (b) 还发现,随着湿度的增加,Ci/C0的最大值不断增加,这说明水分对VOCs在NaY分子筛上的取代作用增强。
-
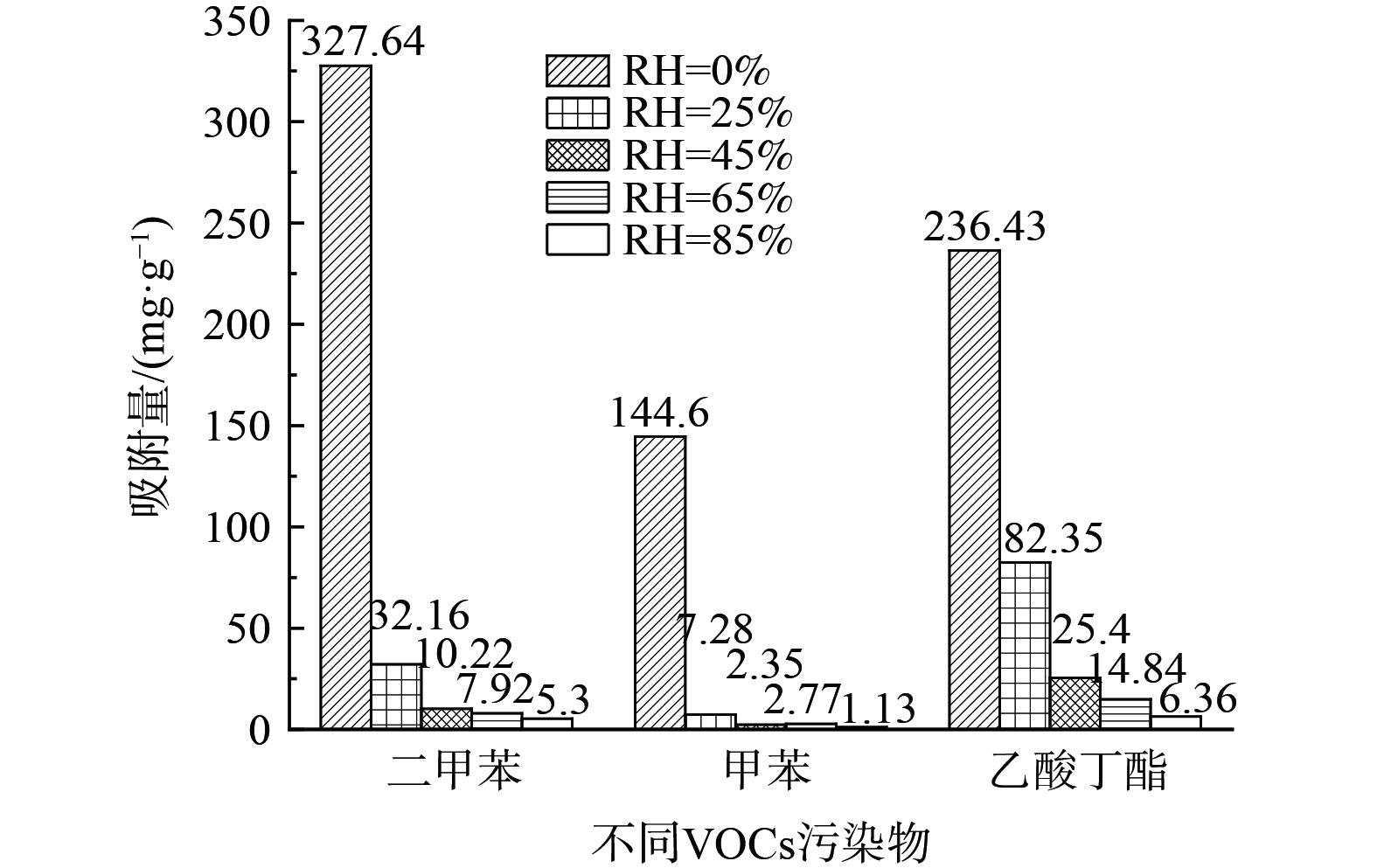
图4表明,对于H2O-VOCs在NaY分子筛的二元吸附体系,湿度对吸附过程影响显著。随着湿度的增加,NaY分子筛对污染物的饱和吸附量急剧降低。相对湿度由0%增至85%时,NaY分子筛对二甲苯的吸附量由327.64 mg·g−1降至5.3 mg·g−1 (下降98.38%) ,对甲苯的吸附量由144.6 mg·g−1降至1.13 mg·g−1 (下降99.22%) ,对乙酸丁酯的吸附量由236.43 mg·g−1降至6.36 mg·g−1 (下降97.31%) 。乙酸丁酯相对于其他2种污染物来说减低幅度相对较小,分析原因为水和乙酸丁酯均为极性吸附质,吸附表现为共吸附,取代作用不显著,该结果与图3 (c) 的穿透曲线一致。二甲苯、甲苯这2种污染物都是随着湿度的增加而减小,该结果与图3 (a) 和 (b) 的穿透曲线结果一致,且随着湿度的增加取代作用增强,驼峰越来越高,即Ci/C0的最大值随着湿度的增加愈来愈大。因此,当吸附系统存在水分时,随着湿度的增加会显著降低吸附剂对VOCs的饱和吸附量。
-
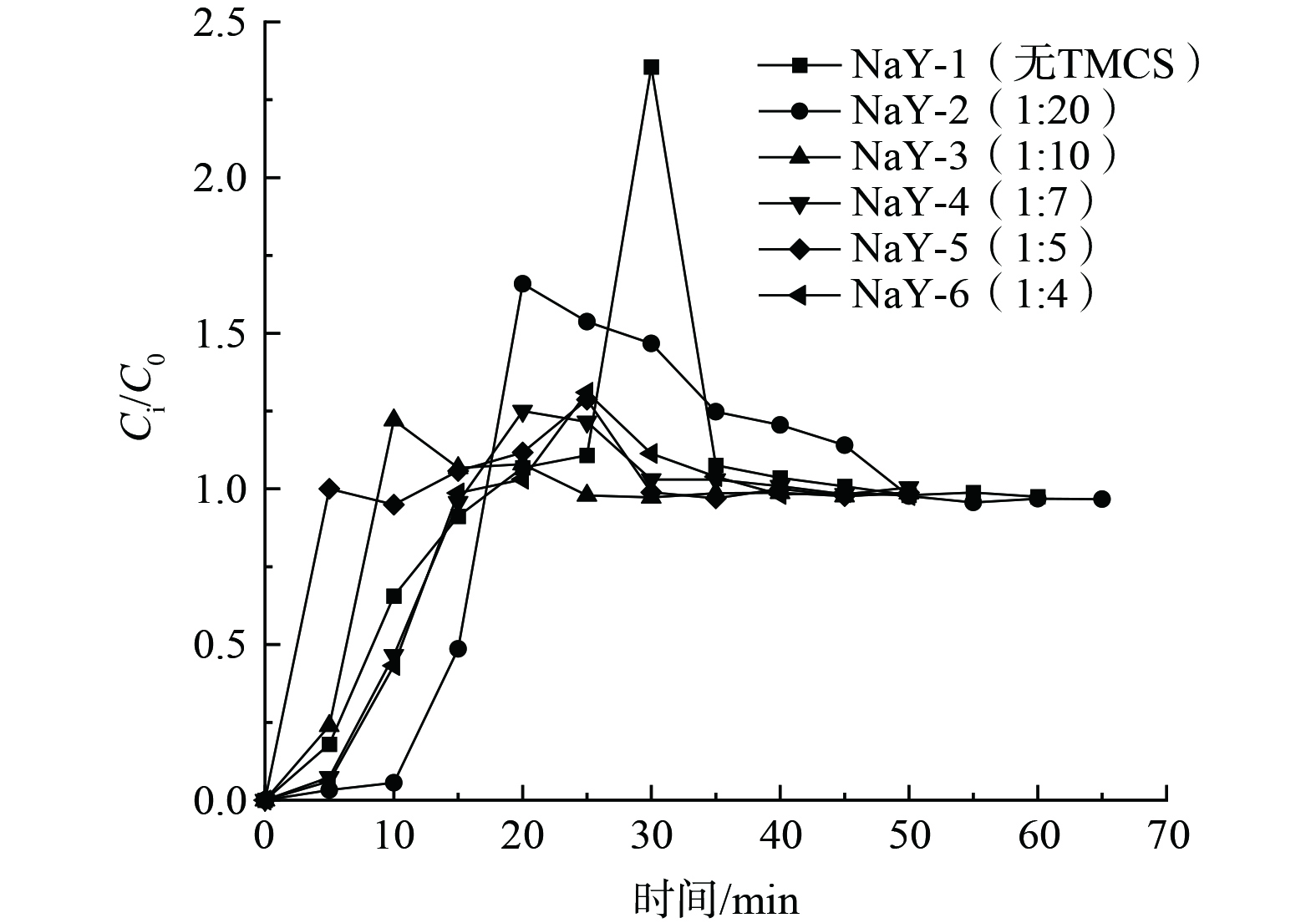
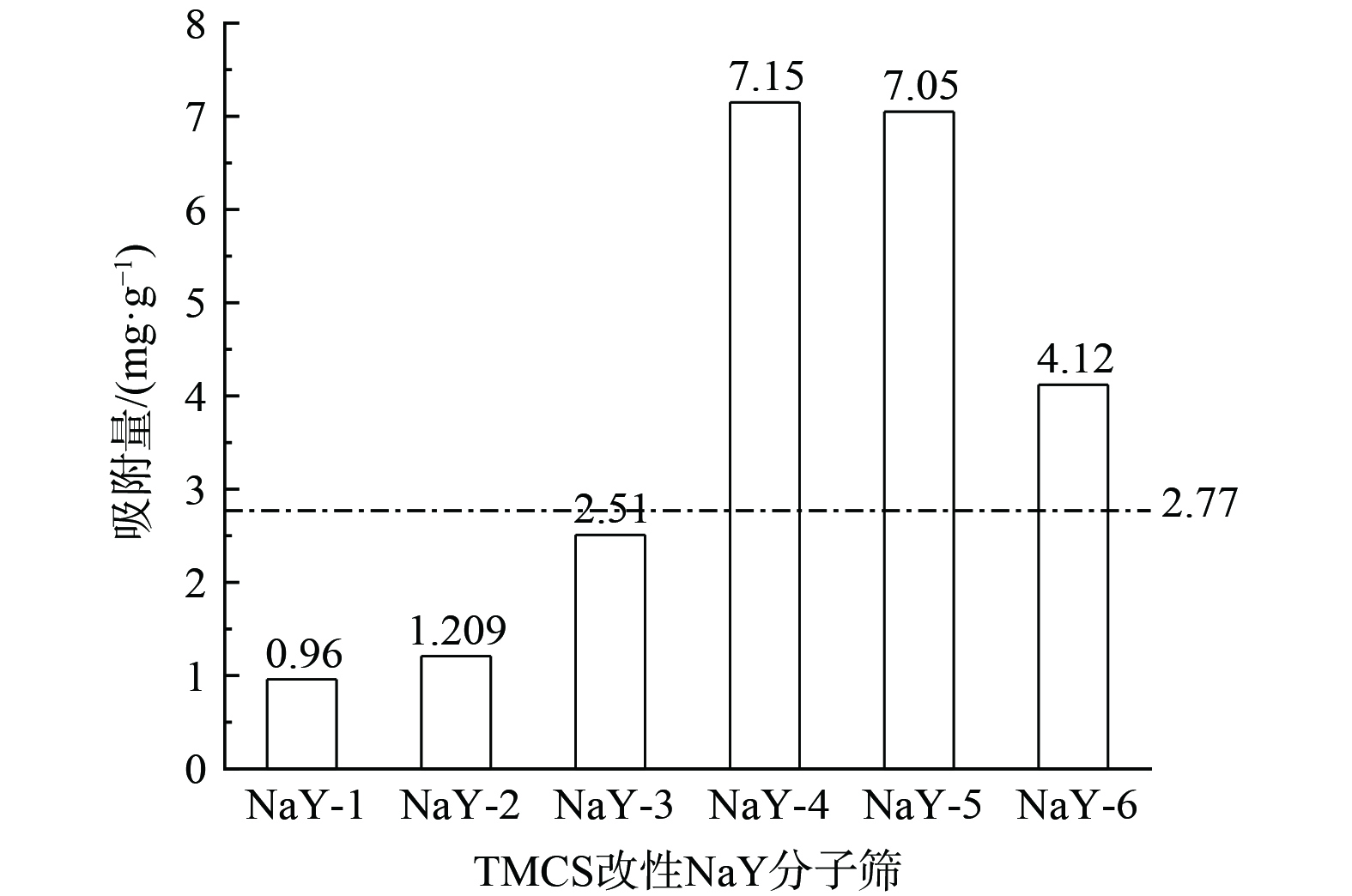
因汽车涂装车间要求维持相对湿度在 (65±5) %,制备不同TMCS投加量的改性分子筛,即不同TMCS/正己烷比例的NaY-1、NaY-2、NaY-3、NaY-4、NaY-5、NaY-6,研究在温度为30 ℃、RH为65%的湿度条件吸附剂对甲苯的吸附性能,以确定适宜的TMCS投加量,结果如图5及图6所示。
图6表明,在H2O-甲苯的二元体系中,随着浸渍分子筛的TMCS/正己烷比例的增加,改性分子筛对甲苯的吸附量呈现先增加后减小的趋势。在TMCS/正己烷比例为1∶7时,即NaY-4对甲苯的吸附量最大,为7.15 mg·g−1,是原始NaY分子筛的吸附量 (2.77 mg·g−1) 的1.95倍。这说明通过正硅酸乙酯、无水乙醇、水混合老化液预处理后再经不同比例的TMCS/正己烷对NaY分子筛进行疏水改性是可行的,其中最佳的TMCS/正己烷体积比为1∶7。
-
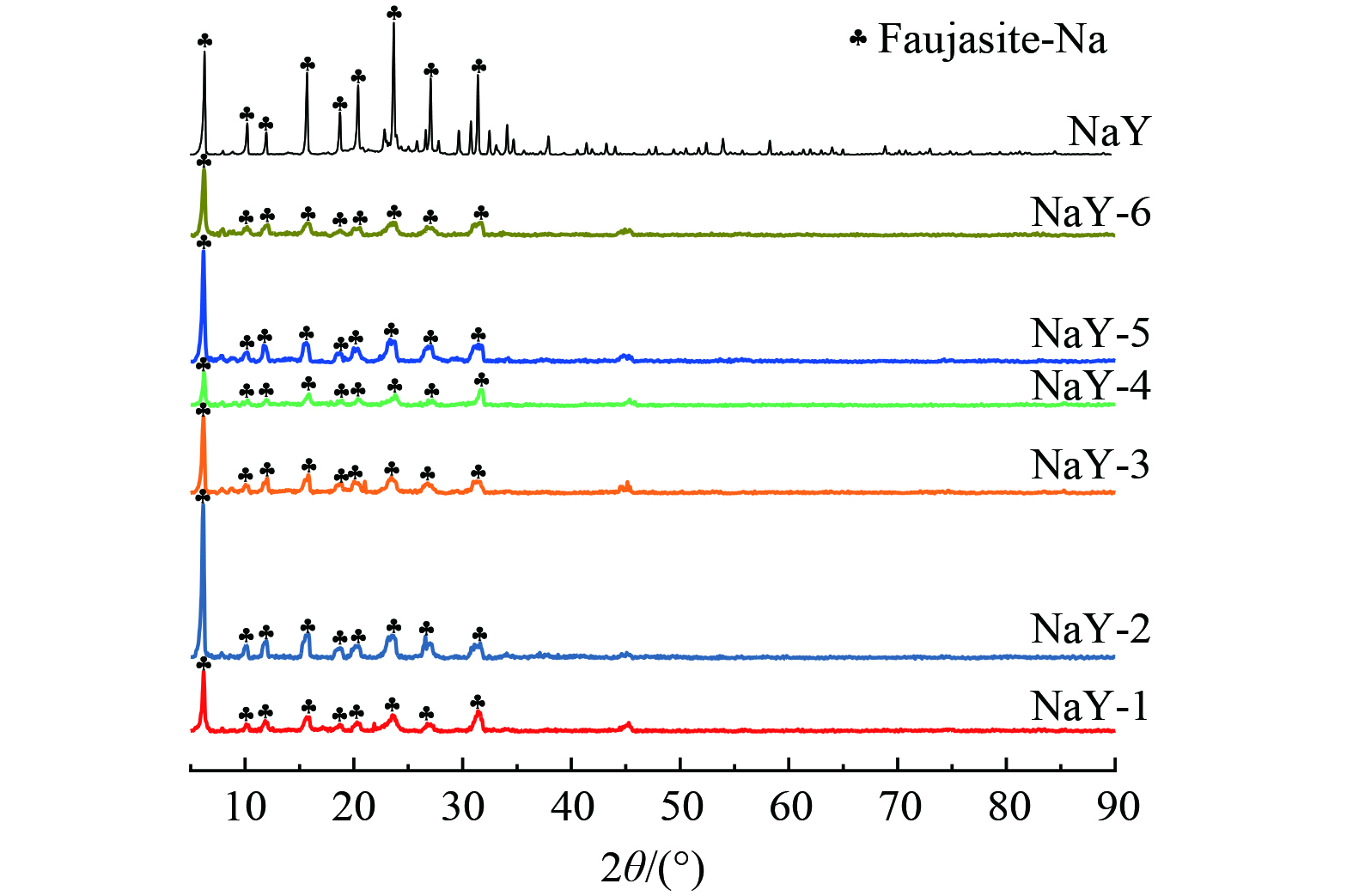
改性前后样品的XRD谱图如图7所示。所有改性后样品的谱图均与NaY分子筛的谱图极为相似,峰的位置及衍射角几乎相同,没有其他杂质峰,改性后的分子筛保留了NaY分子筛的衍射峰特征,这表明TMCS疏水改性并未破坏分子筛的结构。与此同时,衍射峰的强度虽有所下降,但并未出现其他杂质峰,则说明其结构并未受到很大影响。因此,经预处理的样品及预处理后再经不同比例TMCS/正己烷改性的方法,能在不损坏分子筛结构的前提下对其完成改性。
-
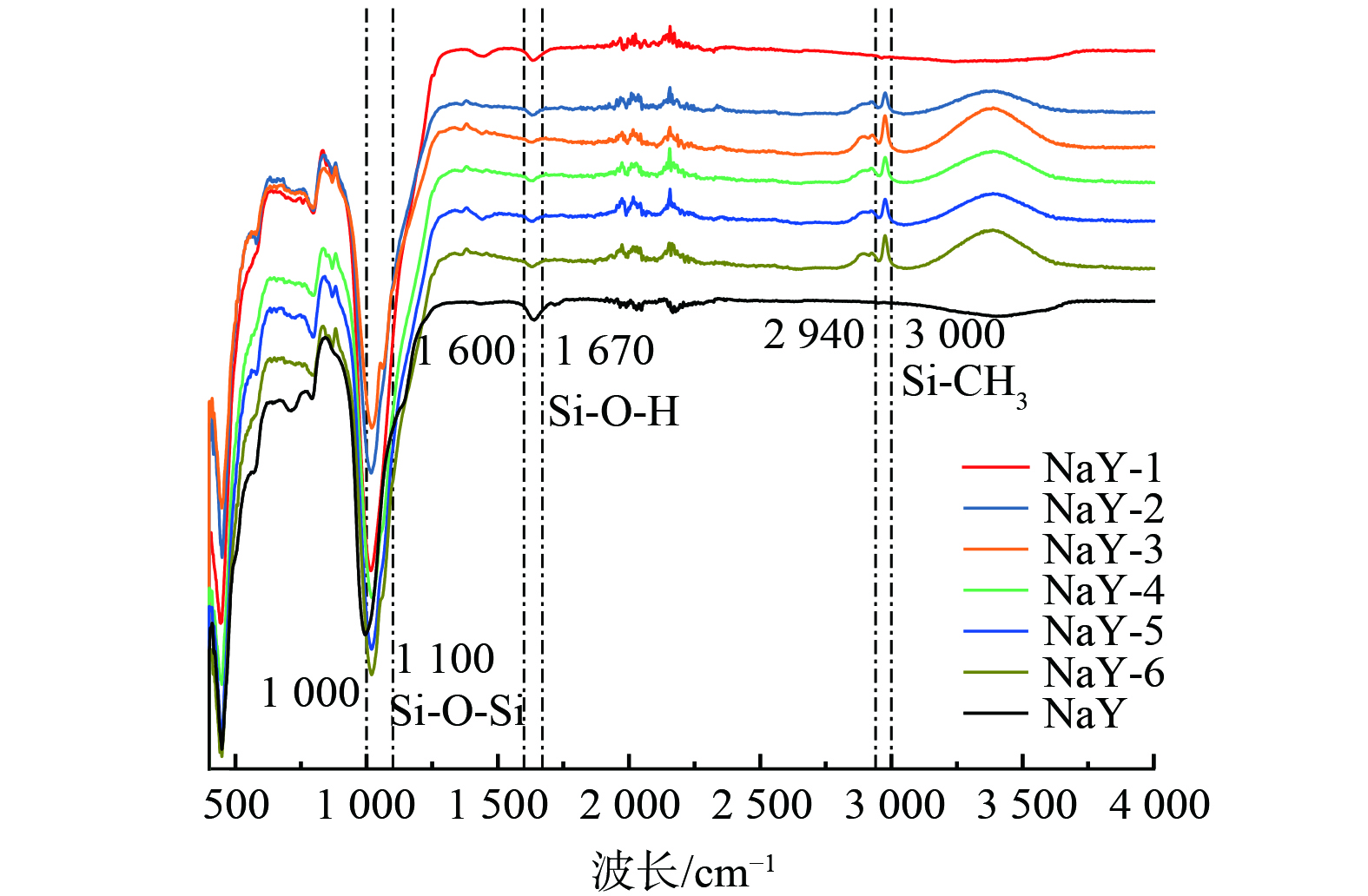
改性前后样品的FTIR谱图如图8所示。1 000~1 100 cm−1附近的吸收峰代表为Si—O—Si,1 600~1 670 cm−1附近的吸收峰代表为Si—OH,2 940~3 000 cm−1附近的吸收峰代表为Si—CH3[24-25]。对比NaY分子筛和改性后样品的谱图发现,NaY-1 (老化液预处理但无TMCS添加) 样品Si—OH振动峰强度增强,峰形变窄。这可能是由于预处理的老化液生成的SiO2气凝胶会在分子筛表面形成羟基 (—OH) ;再经不同比例TMCS/正己烷改性后样品,Si—CH3、Si—O—Si振动峰强度增强,峰形变窄。这可能是由于TMCS的—Si(CH3)3将NaY-1分子筛表面的 (—OH) 取代。疏水性的Si—CH3及Si—O—Si官能团的增多,使得改性后的材料具有良好的疏水性。这也解释了在同一湿度下NaY-1对甲苯的吸附量减少,与原始NaY分子筛相比NaY-1表面亲水的Si—OH官能团增多,H2O会占据甲苯吸附位点。随着TMCS的引入,表面的疏水官能团的引入,对甲苯的吸附也逐渐增多。
-
表3为改性前后样品的比表面积、孔容、孔径以及静态水吸附量。再结合表1的内容,改性后样品的比表面积、孔容、孔径均较原始NaY分子筛有所减小;NaY-1的静态水吸附量较NaY的25.74%增加到35.93%,但随着TMCS的引入,样品的静态水吸附量逐渐减小,由35.93%减小到0.53%。分析原因为,预处理的老化液生成的SiO2气凝胶会在分子筛表面形成沉积堵塞孔道使得分子筛的比表面积、孔容、孔径均有所减小,NaY-1分子筛表面亲水的羟基使得其静态水吸附量增大;而经不同比例TMCS/正己烷处理是在预处理后形成的羟基上接枝—Si(CH3)3会使得比表面积等减小,但疏水的Si—O—Si以及Si—CH3增加,使得其静态水吸附量减小。
-
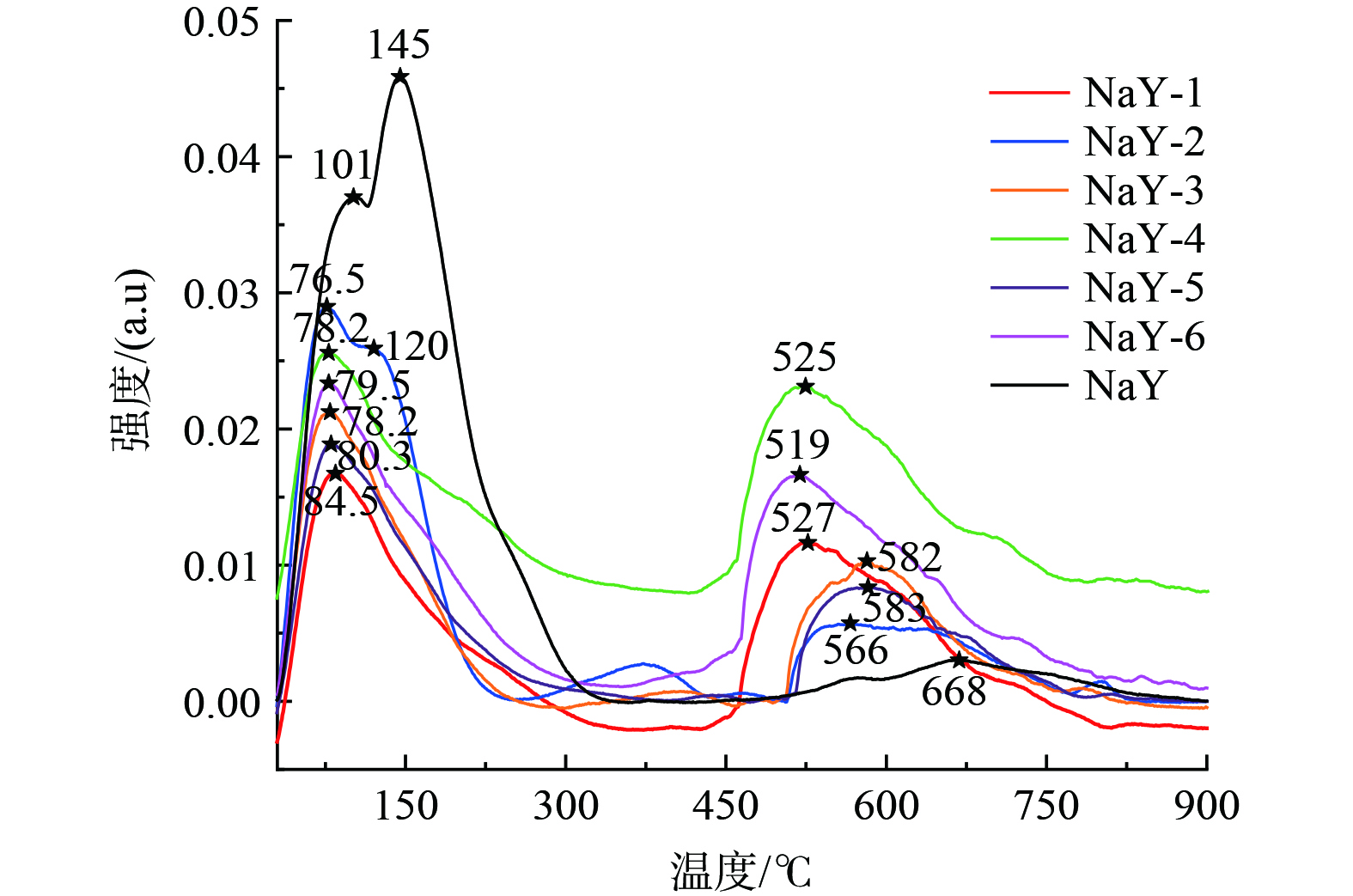
改性前后样品的NH3-TPD谱图如图9所示,主要用于了解分子筛表面酸度。样品分别在100 ℃以下和500 ℃以上有2个NH3的解吸峰,100 ℃以下的为弱酸位点,500 ℃以上的为强酸位点。经过预处理及预处理后再经不同体积比的TMCS/正己烷改性的分子筛在500 ℃以上的NH3解吸峰峰面积和峰值都得到增强,峰的强度由原来的0.003增至0.023,峰面积由原来的3.19增至3.76。研究表明,VOCs污染物会优先吸附在酸性更强的位置,且在环境温度下很难从强酸位点脱附,故随着TMCS的引入,在相同湿度下与未改性的分子筛相比吸附甲苯的Ci/C0的最大值减小 (图5) [26]。
-
改性前后样品的EDS谱图以及改性后各样品的Si/Al计算结果如图10所示,主要用于了解分子筛中Si和Al的含量。未改性分子筛的Si/Al为5.2 (图10 (a) ) ,NaY-1的Si/Al为6.3 (图10 (b) ),NaY-1的Si/Al相对稍有增加。这是由于预处理的老化液会在分子筛表面生成SiO2气凝胶,但其形成的Si—OH官能团是亲水的,故Si/Al的增加并不能增强其疏水性;预处理后再利用TMCS/正己烷改性。随着TMCS投加量的增加—Si(CH3)3引入,使Si元素的峰增强,导致Si/Al逐渐增大。这说明TMCS的投加会使得NaY分子筛表面Si元素增加,增大的Si/Al使得分子筛具有良好的疏水性。由表3可知,Si/Al虽是影响分子筛亲疏水性的主要因素,但Si/Al的增加会导致比表面积、孔容、孔径的减小,VOCs在吸附剂上的吸附以物理吸附为主,比表面积等的减小会降低对VOCs的吸附量。
-
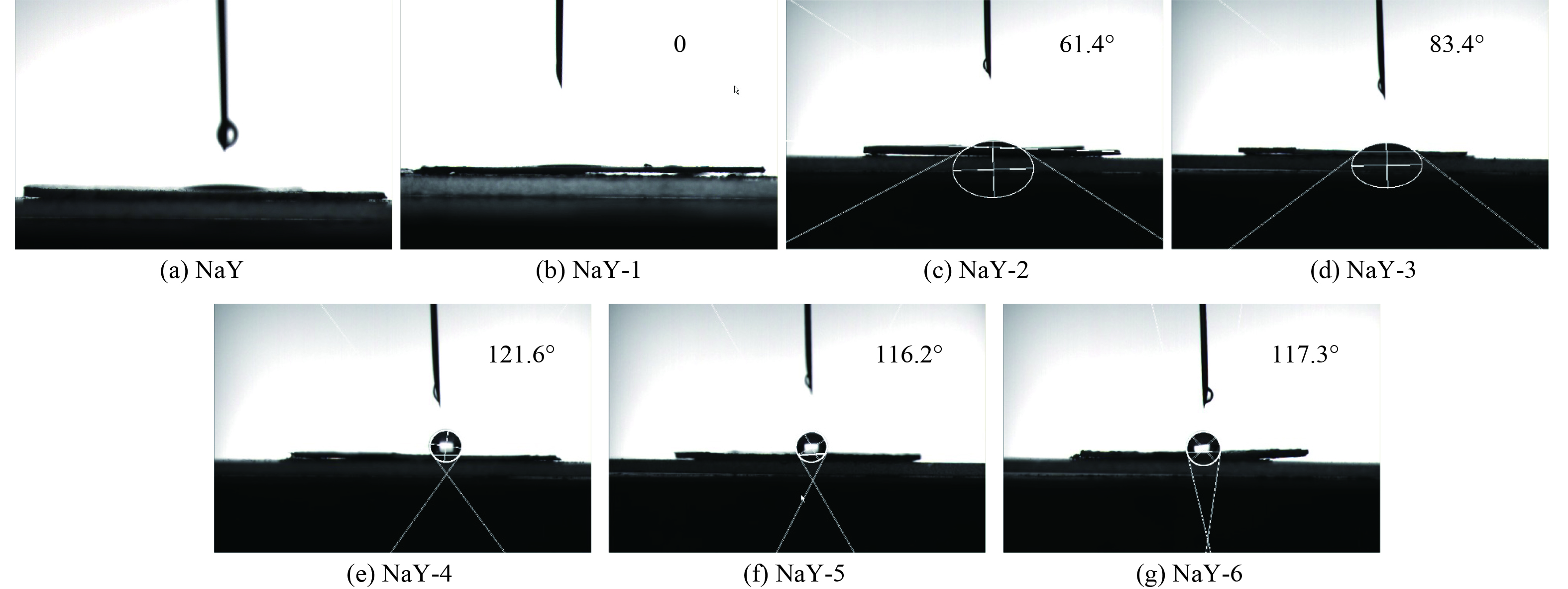
改性前后样品的水接触角如图11所示,用于判断改性前后吸附剂的疏水性的变化。通常对于水接触角>90°的样品被认为是疏水性的,对于水接触角˂90°的样品被认为是亲水性的[27]。经预处理后的分子筛的水接触角由原来的13.2°降至0°,亲水性增强,这是因为表面接枝了亲水的Si—OH官能团所致;但再经TMCS改性的分子筛的水接触角由原来的13.2°增至121.6°,疏水性增强,这是由于表面接枝了疏水的—Si(CH3)3官能团所致。同时,TMCS接枝在分子筛上后,使得分子筛的比表面积、孔径等减小,增加水分子进入分子筛的困难度,故分子筛的疏水性增强。但随着TMCS/正己烷的体积比的继续增大,分子筛的水接触角稍有下降,但变化不大。故NaY-4,即TMCS/正己烷的体积比为1∶7的改性分子筛效果最佳。
-
对改性后的NaY-4分子筛进行重复吸脱附实验,以二甲苯、甲苯、乙酸丁酯为吸附质,在RH为65%的条件下吸附VOCs,采用热脱附的方式在250 ℃下脱附2 h,后对样品进行动态吸附脱附循环实验,以吸附量和循环使用率 (循环使用后的VOCs吸附量与首次使用的吸附量的比值) 表征吸附剂的吸附脱附性能,结果如图12所示。
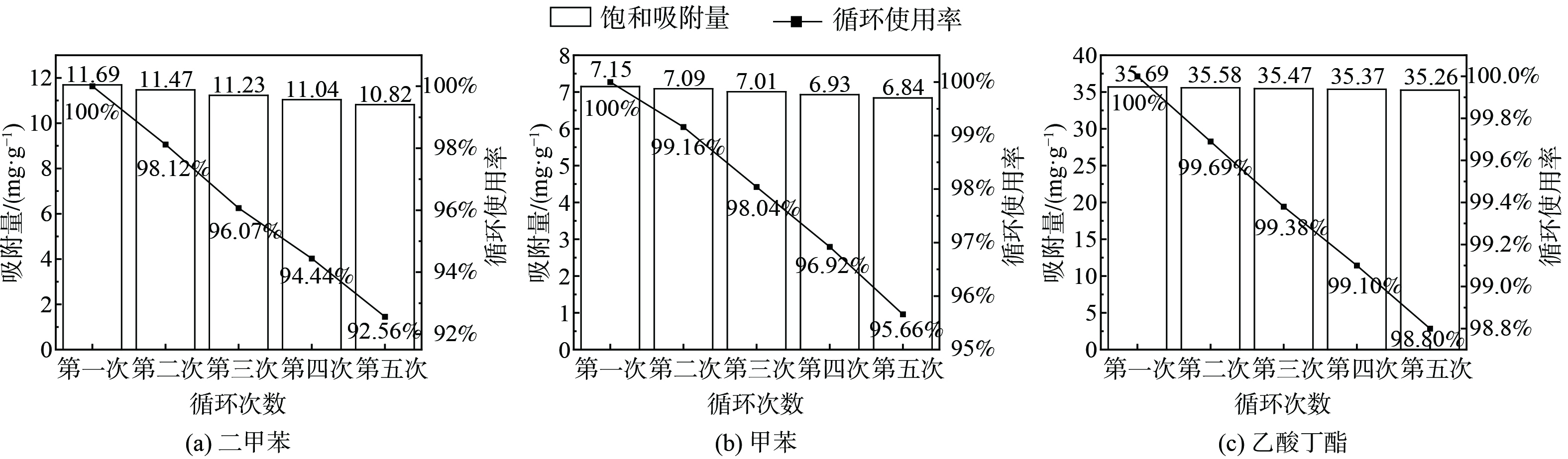
在RH为65%的条件下,NaY-4分子筛经5次吸附脱附循环实验后吸附容量稍有下降。其中,二甲苯由11.69 mg·g−1降至10.82 mg·g−1,降低了7.44%;甲苯由7.15 mg·g−1降至6.84 mg·g−1,降低了4.34%;乙酸丁酯由35.69 mg·g−1降至35.26 mg·g−1,降低了1.20%;但下降幅度较小,约为1.20%~7.44%。这表明NaY-4分子筛在高湿度条件下 (RH为65%) 吸附性能较为稳定。同时,经5次吸附脱附循环实验后循环使用率仍保持在92.56%以上,这表明改性的NaY-4分子筛再生性能良好。
-
1) TMCS/正己烷比例为1∶7是NaY分子筛疏水改性的最佳比例,在RH为65%时对甲苯的吸附量为7.15 mg·g-1,是未改性分子筛的2.58倍。2) BET、XRD、NH3-TPD、EDS、水接触角等表征结果表明,改性并未对分子筛的晶型结构造成影响。随着TMCS/正己烷比例的增加,NaY分子筛的比表面积减小,只经预处理的样品会在分子筛表面形成羟基(—OH);而再经不同比例TMCS/正己烷改性后样品羟基会被—Si(CH3)3取代。疏水的Si—CH3及Si—O—Si官能团的增多,使得改性后的材料具备良好疏水性。3) 对NaY-4分子筛进行5次连续吸附脱附,改性后分子筛吸附脱附性能较为稳定,在RH为65%时对VOCs的吸附量仍可保持在92.56%以上。
NaY分子筛疏水改性及其对汽车涂装VOCs废气的吸附
Hydrophobic modification of NaY molecular sieve and its adsorption on VOCs exhaust gas from automobile painting
-
摘要: 针对水分存在条件下分子筛吸附VOCs吸附容量急剧下降的问题,以汽车涂装过程产生的二甲苯、甲苯、乙酸丁酯为VOCs代表,采用三甲基氯硅烷 (TMCS) /正己烷对NaY分子筛进行疏水改性,以提高高湿度条件下分子筛对VOCs的吸附性能。结果表明,最佳的TMCS/正己烷体积比为1:7 (NaY-4) ,在RH=65%条件下,NaY-4对甲苯的吸附量为7.15 mg·g−1,是未改性NaY分子筛吸附量的2.58倍,且经5次吸附脱附循环实验,吸附容量仍保持在92.56%以上。BET、XRD、FTIR及接触角等表征结果表明,改性并未对分子筛的晶型结构造成影响,但会减小其比表面积;改性后Si—CH3和Si—O—Si疏水官能团增多,接触角由13.2°增加到121.6°,疏水性增强。该研究结果可为分子筛转轮VOCs吸附技术的工业应用提供参考。Abstract: In view of the sharp decline of VOCs adsorption capacity in the presence of moisture, the NaY molecular sieve was modified by trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS)/hexane to improve the adsorption performance of molecular sieve for VOCs under high humidity, using xylene, toluene and butyl acetate in automotive painting process as VOCs representatives. The results showed that the optimal volume ratio of TMCS/hexane was 1:7 (NaY-4), and the adsorption capacity of NaY-4 for toluene was 7.15 mg·g−1 at RH=65%, which was 2.58 times as much as the adsorption capacity of unmodified NaY molecular sieve, and the adsorption capacities remained above 92.56% after five adsorption and desorption cycles. The characterization results of BET, XRD, FTIR and contact angle showed that the modification did not affect the crystalline structure of molecular sieve, but reduced its specific surface area. After modification, hydrophobic functional groups of Si—CH3 and Si—O—Si increased, the contact angle increased from 13.2° up to 121.6°, and the hydrophobicity was enhanced. The research results can provide references for the industrial application of the molecular sieve runner VOCs adsorption technology.
-
Key words:
- VOCs adsorption /
- molecular sieve /
- coating industry /
- hydrophobic modification
-
挥发性有机物 (volatile organic compounds, VOCs) 是光化学烟雾和二次有机气溶胶 (SOAs) 的重要前体物[1],易引发大气污染如臭氧污染及PM2.5[2]。VOCs会导致人体内肿瘤的形成[3]。2020年,我国工业源VOCs的排放量约为217.1×104 t,占总排放量的35.6%。其中,石油、煤炭及其他燃料加工业为52.79×104 t,化学原料和化学制品制造业为42.77×104 t,橡胶和塑料制品业为13.46×104 t,其他行业为108.12×104 t[4]。为进一步改善环境空气质量,应全面加强重点行业VOCs的综合治理。
吸附技术具有能耗低、操作简单、运行成本低等优点,广泛应用于低浓度含VOCs废气的净化中[5]。活性炭是最为常用的吸附剂,具有良好的物理化学性质,但在温度较高时易自燃存在安全隐患[6]。分子筛不易燃,其煅烧再生性能优异,在干燥条件下对VOCs吸附性能良好而成为替代活性炭的吸附材料[7]。在实际工业过程中,VOCs中往往含有水分,将与VOCs发生竞争吸附,从而导致吸附剂的吸附容量下降,尤其在高湿度环境下,吸附容量将急剧下降[8-10]。YIN等[11]采用高温水热法对NaY分子筛疏水改性,未改性的NaY分子筛在干燥条件下对甲苯的吸附量为178.6 mg·g−1,在相对湿度 (relative humidity,RH) 为50%时对甲苯的吸附量为11.26 mg·g−1,对水的吸附量为237.24 mg·g−1。LI等[12]在不同湿度下,研究了10种商业吸附剂在碱改性前后对VOCs的吸附解吸特性,发现在加入湿度后的体系中,大部分分子筛对二甲苯的吸附能力几乎下降到零。因此,提高水分存在条件下分子筛吸附剂的吸附性能是吸附工艺实际应用面临的关键问题。
分子筛的亲疏水性程度与SiO2/AlO3和表面极性羟基有关,故分子筛疏水改性的方法通常包括脱铝和覆硅改性[13-14]。常用的脱铝方法有水热脱铝、酸处理、EDTA处理,但其对材料的晶体结构有影响,会降低材料结晶度[15]。覆硅法有接枝法、共缩合法、有序介孔有机硅法,其中接枝法和共缩合法这2种方法研究较多[16-17]。LU等[18]通过苯基硅烷的架桥作用合成了具有高疏水性和热稳定性的Y@St-DVB复合材料,在RH为60%和90%条件下分别是Y沸石的1.97和1.96倍,对甲苯的吸附量分别为131.9 mg·g−1和118.3 mg·g−1。李承龙等[19]利用正辛基三乙氧基硅烷改性,成功地将—Si(CH2)7CH3基团接枝到ZSM-5分子筛表面,改性后的分子筛水接触角增大到152°,静态水吸附量下降了26.4%,实现了超疏水性,但由于改性后分子筛的孔容减小,对正己烷静态吸附量由8.60%降至7.45%。张媛媛等[20]采用3种不同硅烷试剂对NaY分子筛进行改性,改性后的样品在RH为80%条件下甲苯的吸附量都得到了增加,其中三甲基氯硅烷 (TMCS) 增加量最大为78%,由12.2 mg·g−1增至21.1 mg·g−1。
汽车涂装行业废气湿度高、成分复杂,亟需根据涂装行业环境条件,研究相关污染物的排放特征及吸附过程特点,并开展相应的分子筛疏水改性研究。然而,相关成果尚未见报道。本研究以汽车涂装行业VOCs污染物为对象,选取甲苯、二甲苯、乙酸丁酯为代表污染物,对NaY分子筛进行覆硅改性研究,结合分子筛结构表征和疏水测定,获取有效的疏水改性方法,制备用于汽车涂装高湿度环境的疏水性强且吸附性能佳的改性NaY分子筛,以期为涂装行业分子筛转轮VOCs吸附的工业应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
NaY、13X、5A、10A分子筛购置于南开催化剂,其参数见表1。甲苯、二甲苯、乙酸丁酯购置于阿拉丁生化科技有限公司均为分析纯,动力学直径和沸点见表2。正硅酸乙酯、正己烷、无水乙醇购置于科密欧化学试剂有限公司均为分析纯。盐酸购置于国药集团化学试剂有限公司均为分析纯。氨水、三甲基氯硅烷购置于阿拉丁生化科技有限公司均为分析纯。
表 1 分子筛参数Table 1. Parameters of molecular sieve分子筛 BET比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔容/(cm3·g−1) 孔径/nm 静态水吸附量 Si/Al NaY 390.233 0.947 9.706 25.74% 5.2 13X 297.347 0.444 7.976 21.42% 4.8 5A 203.873 0.277 5.429 18.46% 3 10A 289.237 0.642 8.878 21.85% 2.5 表 2 VOCs的物性参数Table 2. Physical parameters of VOCsVOCs 分子式 分子量/(g·mol−1) 沸点/ ℃ 动力学直径/nm 甲苯 C7H8 92.14 110.6 0.67 二甲苯 C8H10 106.17 138.5 0.70 乙酸丁酯 C6H12O2 116.16 126.6 1.20 1.2 实验材料制备
分子筛在实验前置于马弗炉中500 ℃下活化5 h。首先,对NaY分子筛进行预处理,将正硅酸乙酯 (tetraethyl orthosilicate,TEOS) 、无水乙醇、水混合,并用1 mol·L−1的盐酸调节pH到2~3,促进TEOS水解;在6 h后,缓慢加入质量分数为5%氨水调节pH至7配制好老化液,将10 g分子筛加入老化液中,在室温下静置12 h;加入50 mL正己烷及不同体积 (0、2.5、5、7.5、10、12.5 mL) 的三甲基氯硅烷 (trimethylchlorosilane,TMCS) 静置24 h,正己烷淋洗3遍后,于60 ℃下干燥12 h,再在200 ℃下干燥12 h,得到不同TMCS/正己烷比例的材料,并分别记为NaY-1 (无TMCS)、NaY-2 (1∶20)、NaY-3 (1∶10)、NaY-4 (1∶7)、NaY-5 (1∶5)、NaY-6 (1∶4)。
1.3 吸附剂表征
采用比表面积测试仪 (V-Sorb 2800P) 对分子筛比表面积孔径分布进行表征;X射线衍射仪 (UItima Ⅳ) 对分子筛晶体结构进行表征;傅里叶红外光谱仪 (Vertex 70) 对分子筛表面官能团进行表征;采用能量色散光谱 (JEOL Corp) 对分子筛中的所有元素种类和含量进行测定;NH3-TPD (ChemiSorb 2720) 对分子筛表面Lewis酸位点和Brønsted酸位点进行表征;水接触角测试仪 (JYC-8) 对分子筛亲疏水性进行表征。
1.4 吸附实验
吸附实验在常温常压下进行,实验系统如图1所示。由注射泵 (LSP02-D) 将VOCs液体精准注入置于恒温水浴锅 (50 ℃) 中的烧瓶内,由质量流量计 (北京七星CS-200D,10 L) 控制经硅胶除湿后的总空气流量为3 L·min−1。一路空气进入水浴锅内三颈烧瓶,另一路空气进入水蒸气发生器,通过鼓泡法控制湿度,两路气体共同进入缓冲瓶内,浓度、湿度稳定的VOCs模拟废气经分子筛吸附后排出。吸附器内径为10 mm,长度120 mm,分子筛装填量3.20 g。吸附器置于恒温水浴锅 (温度为30 ℃) 中。在吸附器进、出口使用气相色谱仪 (福立GC9700Ⅱ) 测定VOCs质量浓度,得到穿透曲线。当吸附反应器VOCs出口浓度为进口浓度的95%时认为吸附达到饱和,即可结束实验。尾气经净化后排出。
以吸附时间 (t) 为横坐标,以i分钟时进出口VOCs质量浓度之比 (Ci/C0) 为纵坐标,得到VOCs的吸附穿透曲线。通过式 (1) 对吸附穿透曲线进行积分计算,得到VOCs的平衡吸附容量。
Q=F×C0×10−6W×(ti−∫ti0CiC0dt) (1) 式中:Q为平衡吸附容量,mg·g−1;F为气流速度,mL·min−1;C0为进口VOCs质量浓度,mg·m−3;Ci为i分钟时吸附器出口VOCs质量浓度,mg·m−3;W为吸附剂装填量,g;ti为吸附平衡时间,min。
1.5 静态水吸附实验
分子筛静态水吸附实验按照国标GB/T 6287-2021《分子筛静态水吸附测定方法》测定计算。具体操作步骤为:试料550 ℃焙烧1 h,取出瓷坩埚,放入真空干燥器内,冷却至室温;取出瓷坩埚,将样品倒入质量为m1的称量瓶内;随后立即在分析天平上称重m2;将装有试样的称量瓶置于盛有饱和氯化钠溶液的干燥器中;将干燥器放在鼓风干燥箱内,开启鼓风机,箱温控制在 (35±1) ℃,恒温吸附24 h;取出称量瓶称重m3。再按式 (2) 计算静态水吸附量。
X=m3−m2m2−m1×100% (2) 式中:m3为称量瓶加吸水后材料的质量,g;m2为称量瓶加焙烧后材料的质量,g;m1为称量瓶的质量,g。
1.6 吸附剂多次吸附脱附实验
将筛选出的疏水性最佳的分子筛进行重复吸脱附实验,以二甲苯、甲苯、乙酸丁酯为吸附质,在相对湿度RH为0%和65%的条件下,采用热脱附的方式在250 ℃下脱附2 h,对脱附后的样品进行动态吸附测试。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 分子筛比选
在温度为30 ℃、RH为0%、进气量为3 L·min−1的条件下,测定3种VOCs在NaY、13X、10A、5A这4种分子筛上的饱和吸附量,结果如图2所示。乙酸丁酯、甲苯、二甲苯在NaY分子筛上的平衡吸附量分别为236.43、144.6、327.64 mg·g−1,均大于其他3种分子筛,而乙酸丁酯、甲苯、二甲苯在5A分子筛上吸附量最小。分析原因为NaY分子筛的比表面积、孔容、孔径均大于其他3种,可为VOCs的吸附提供更多吸附位点,而乙酸丁酯、甲苯、二甲苯的动力学直径均大于5A分子筛的有效孔径 (0.5 nm) 。因此,5A分子筛的吸附量最小,故选用NaY分子筛进行后续研究。
2.2 不同湿度下NaY分子筛对VOCs的吸附
2.2.1 不同湿度下VOCs的二元吸附穿透曲线
在保证两路气流的总体积流速为3L·min−1的前提下,通过质量流量计控制气流速度从而控制鼓泡速率来调节湿度。NaY分子筛在温度为30 ℃,RH分别为0%、25%、45%、65%、85%这5个不同湿度条件下的乙酸丁酯、甲苯,以及二甲苯,3种污染物的吸附穿透曲线如图3所示。
图3 (a) 和 (b) 表明,H2O-二甲苯、H2O-甲苯在NaY分子筛上的二元吸附过程存在竞争吸附行为。在吸附开始时,H2O和污染物均能被吸附在NaY上,在吸附器的出口污染物浓度为零。随着吸附的进行,污染物的Ci/C0从零逐渐增加,当NaY表面吸附位点被吸附物占据时,H2O的进一步吸附会取代已被吸附的污染物,导致出口污染物的浓度大于初始质量浓度。如在H2O-二甲苯体系中,二甲苯被取代,在H2O-甲苯体系中,甲苯被取代,被取代组分穿透曲线出现驼峰 (Ci/C0≥1) 。导致这一现象的原因是NaY表面存在亲水性Si—OH键,水分子因具有—OH键比甲苯和二甲苯更易吸附。VOCs吸附以物理吸附为主,与吸附剂的比表面积密切相关[21]。与VOCs在吸附剂上的吸附机制不同,水分子首先在较低的相对压力下通过H键牢牢地吸附在含氧基团上,然后再进一步吸附在之前吸附的水分子上形成水簇,最终在较高相对压力下被填充到孔隙中[22-23]。随着吸附的进行,污染物质量浓度最终趋于稳定,达到吸附平衡,Ci/C0接近1。图3 (c) 表明,H2O-乙酸丁酯在NaY分子筛上的二元吸附过程与前2种不太相同。随着吸附的进行,穿透曲线上并未出现H2O取代已经被吸附的乙酸丁酯的驼峰。分析其原因,是由于乙酸丁酯因具有酯基故具有极性,水分子也是极性的,因此H2O-乙酸丁酯在极性NaY分子筛上的吸附并未表现出竞争取代现象。
图3还表明,随着湿度增加,乙酸丁酯、甲苯和二甲苯的穿透曲线均向左移动,穿透时间急剧缩短,如RH由0%增至85%时,NaY分子筛对二甲苯的穿透时间由485 min缩短至12 min,对甲苯的穿透时间由410 min缩短至11 min,对乙酸丁酯的穿透时间由350 min缩短至35 min。由图3 (a) 、 (b) 还发现,随着湿度的增加,Ci/C0的最大值不断增加,这说明水分对VOCs在NaY分子筛上的取代作用增强。
2.2.2 湿度对VOCs吸附量的影响
图4表明,对于H2O-VOCs在NaY分子筛的二元吸附体系,湿度对吸附过程影响显著。随着湿度的增加,NaY分子筛对污染物的饱和吸附量急剧降低。相对湿度由0%增至85%时,NaY分子筛对二甲苯的吸附量由327.64 mg·g−1降至5.3 mg·g−1 (下降98.38%) ,对甲苯的吸附量由144.6 mg·g−1降至1.13 mg·g−1 (下降99.22%) ,对乙酸丁酯的吸附量由236.43 mg·g−1降至6.36 mg·g−1 (下降97.31%) 。乙酸丁酯相对于其他2种污染物来说减低幅度相对较小,分析原因为水和乙酸丁酯均为极性吸附质,吸附表现为共吸附,取代作用不显著,该结果与图3 (c) 的穿透曲线一致。二甲苯、甲苯这2种污染物都是随着湿度的增加而减小,该结果与图3 (a) 和 (b) 的穿透曲线结果一致,且随着湿度的增加取代作用增强,驼峰越来越高,即Ci/C0的最大值随着湿度的增加愈来愈大。因此,当吸附系统存在水分时,随着湿度的增加会显著降低吸附剂对VOCs的饱和吸附量。
2.3 改性分子筛对VOCs的吸附及改性机理分析
2.3.1 不同TMCS投加量疏水改性吸附甲苯
因汽车涂装车间要求维持相对湿度在 (65±5) %,制备不同TMCS投加量的改性分子筛,即不同TMCS/正己烷比例的NaY-1、NaY-2、NaY-3、NaY-4、NaY-5、NaY-6,研究在温度为30 ℃、RH为65%的湿度条件吸附剂对甲苯的吸附性能,以确定适宜的TMCS投加量,结果如图5及图6所示。
图6表明,在H2O-甲苯的二元体系中,随着浸渍分子筛的TMCS/正己烷比例的增加,改性分子筛对甲苯的吸附量呈现先增加后减小的趋势。在TMCS/正己烷比例为1∶7时,即NaY-4对甲苯的吸附量最大,为7.15 mg·g−1,是原始NaY分子筛的吸附量 (2.77 mg·g−1) 的1.95倍。这说明通过正硅酸乙酯、无水乙醇、水混合老化液预处理后再经不同比例的TMCS/正己烷对NaY分子筛进行疏水改性是可行的,其中最佳的TMCS/正己烷体积比为1∶7。
2.3.2 XRD谱图分析
改性前后样品的XRD谱图如图7所示。所有改性后样品的谱图均与NaY分子筛的谱图极为相似,峰的位置及衍射角几乎相同,没有其他杂质峰,改性后的分子筛保留了NaY分子筛的衍射峰特征,这表明TMCS疏水改性并未破坏分子筛的结构。与此同时,衍射峰的强度虽有所下降,但并未出现其他杂质峰,则说明其结构并未受到很大影响。因此,经预处理的样品及预处理后再经不同比例TMCS/正己烷改性的方法,能在不损坏分子筛结构的前提下对其完成改性。
2.3.3 FTIR谱图分析
改性前后样品的FTIR谱图如图8所示。1 000~1 100 cm−1附近的吸收峰代表为Si—O—Si,1 600~1 670 cm−1附近的吸收峰代表为Si—OH,2 940~3 000 cm−1附近的吸收峰代表为Si—CH3[24-25]。对比NaY分子筛和改性后样品的谱图发现,NaY-1 (老化液预处理但无TMCS添加) 样品Si—OH振动峰强度增强,峰形变窄。这可能是由于预处理的老化液生成的SiO2气凝胶会在分子筛表面形成羟基 (—OH) ;再经不同比例TMCS/正己烷改性后样品,Si—CH3、Si—O—Si振动峰强度增强,峰形变窄。这可能是由于TMCS的—Si(CH3)3将NaY-1分子筛表面的 (—OH) 取代。疏水性的Si—CH3及Si—O—Si官能团的增多,使得改性后的材料具有良好的疏水性。这也解释了在同一湿度下NaY-1对甲苯的吸附量减少,与原始NaY分子筛相比NaY-1表面亲水的Si—OH官能团增多,H2O会占据甲苯吸附位点。随着TMCS的引入,表面的疏水官能团的引入,对甲苯的吸附也逐渐增多。
2.3.4 BET及静态水吸附量
表3为改性前后样品的比表面积、孔容、孔径以及静态水吸附量。再结合表1的内容,改性后样品的比表面积、孔容、孔径均较原始NaY分子筛有所减小;NaY-1的静态水吸附量较NaY的25.74%增加到35.93%,但随着TMCS的引入,样品的静态水吸附量逐渐减小,由35.93%减小到0.53%。分析原因为,预处理的老化液生成的SiO2气凝胶会在分子筛表面形成沉积堵塞孔道使得分子筛的比表面积、孔容、孔径均有所减小,NaY-1分子筛表面亲水的羟基使得其静态水吸附量增大;而经不同比例TMCS/正己烷处理是在预处理后形成的羟基上接枝—Si(CH3)3会使得比表面积等减小,但疏水的Si—O—Si以及Si—CH3增加,使得其静态水吸附量减小。
表 3 不同比例TMCS/正己烷改性分子筛的比表面积、孔结构及静态水吸附量Table 3. Specific surface area, pore structure and static water adsorption of molecular sieves modified with different ratios of TMCS/hexane分子筛 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔容/(cm3·g−1) 孔径/nm 静态水吸附量 NaY-1 310.53 0.536 9.034 35.93% NaY-2 270.393 0.3403 8.793 3.86% NaY-3 172.425 0.3143 8.039 2.18% NaY-4 167.609 0.281 7.672 1.36% NaY-5 153.188 0.258 7.302 0.95% NaY-6 149.166 0.236 7.046 0.53% 2.3.5 NH3-TPD
改性前后样品的NH3-TPD谱图如图9所示,主要用于了解分子筛表面酸度。样品分别在100 ℃以下和500 ℃以上有2个NH3的解吸峰,100 ℃以下的为弱酸位点,500 ℃以上的为强酸位点。经过预处理及预处理后再经不同体积比的TMCS/正己烷改性的分子筛在500 ℃以上的NH3解吸峰峰面积和峰值都得到增强,峰的强度由原来的0.003增至0.023,峰面积由原来的3.19增至3.76。研究表明,VOCs污染物会优先吸附在酸性更强的位置,且在环境温度下很难从强酸位点脱附,故随着TMCS的引入,在相同湿度下与未改性的分子筛相比吸附甲苯的Ci/C0的最大值减小 (图5) [26]。
2.3.6 EDS谱图分析
改性前后样品的EDS谱图以及改性后各样品的Si/Al计算结果如图10所示,主要用于了解分子筛中Si和Al的含量。未改性分子筛的Si/Al为5.2 (图10 (a) ) ,NaY-1的Si/Al为6.3 (图10 (b) ),NaY-1的Si/Al相对稍有增加。这是由于预处理的老化液会在分子筛表面生成SiO2气凝胶,但其形成的Si—OH官能团是亲水的,故Si/Al的增加并不能增强其疏水性;预处理后再利用TMCS/正己烷改性。随着TMCS投加量的增加—Si(CH3)3引入,使Si元素的峰增强,导致Si/Al逐渐增大。这说明TMCS的投加会使得NaY分子筛表面Si元素增加,增大的Si/Al使得分子筛具有良好的疏水性。由表3可知,Si/Al虽是影响分子筛亲疏水性的主要因素,但Si/Al的增加会导致比表面积、孔容、孔径的减小,VOCs在吸附剂上的吸附以物理吸附为主,比表面积等的减小会降低对VOCs的吸附量。
2.3.7 水接触角图分析
改性前后样品的水接触角如图11所示,用于判断改性前后吸附剂的疏水性的变化。通常对于水接触角>90°的样品被认为是疏水性的,对于水接触角˂90°的样品被认为是亲水性的[27]。经预处理后的分子筛的水接触角由原来的13.2°降至0°,亲水性增强,这是因为表面接枝了亲水的Si—OH官能团所致;但再经TMCS改性的分子筛的水接触角由原来的13.2°增至121.6°,疏水性增强,这是由于表面接枝了疏水的—Si(CH3)3官能团所致。同时,TMCS接枝在分子筛上后,使得分子筛的比表面积、孔径等减小,增加水分子进入分子筛的困难度,故分子筛的疏水性增强。但随着TMCS/正己烷的体积比的继续增大,分子筛的水接触角稍有下降,但变化不大。故NaY-4,即TMCS/正己烷的体积比为1∶7的改性分子筛效果最佳。
2.4 吸附脱附循环性能
对改性后的NaY-4分子筛进行重复吸脱附实验,以二甲苯、甲苯、乙酸丁酯为吸附质,在RH为65%的条件下吸附VOCs,采用热脱附的方式在250 ℃下脱附2 h,后对样品进行动态吸附脱附循环实验,以吸附量和循环使用率 (循环使用后的VOCs吸附量与首次使用的吸附量的比值) 表征吸附剂的吸附脱附性能,结果如图12所示。
在RH为65%的条件下,NaY-4分子筛经5次吸附脱附循环实验后吸附容量稍有下降。其中,二甲苯由11.69 mg·g−1降至10.82 mg·g−1,降低了7.44%;甲苯由7.15 mg·g−1降至6.84 mg·g−1,降低了4.34%;乙酸丁酯由35.69 mg·g−1降至35.26 mg·g−1,降低了1.20%;但下降幅度较小,约为1.20%~7.44%。这表明NaY-4分子筛在高湿度条件下 (RH为65%) 吸附性能较为稳定。同时,经5次吸附脱附循环实验后循环使用率仍保持在92.56%以上,这表明改性的NaY-4分子筛再生性能良好。
3. 结论
1) TMCS/正己烷比例为1∶7是NaY分子筛疏水改性的最佳比例,在RH为65%时对甲苯的吸附量为7.15 mg·g-1,是未改性分子筛的2.58倍。2) BET、XRD、NH3-TPD、EDS、水接触角等表征结果表明,改性并未对分子筛的晶型结构造成影响。随着TMCS/正己烷比例的增加,NaY分子筛的比表面积减小,只经预处理的样品会在分子筛表面形成羟基(—OH);而再经不同比例TMCS/正己烷改性后样品羟基会被—Si(CH3)3取代。疏水的Si—CH3及Si—O—Si官能团的增多,使得改性后的材料具备良好疏水性。3) 对NaY-4分子筛进行5次连续吸附脱附,改性后分子筛吸附脱附性能较为稳定,在RH为65%时对VOCs的吸附量仍可保持在92.56%以上。
-
表 1 分子筛参数
Table 1. Parameters of molecular sieve
分子筛 BET比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔容/(cm3·g−1) 孔径/nm 静态水吸附量 Si/Al NaY 390.233 0.947 9.706 25.74% 5.2 13X 297.347 0.444 7.976 21.42% 4.8 5A 203.873 0.277 5.429 18.46% 3 10A 289.237 0.642 8.878 21.85% 2.5 表 2 VOCs的物性参数
Table 2. Physical parameters of VOCs
VOCs 分子式 分子量/(g·mol−1) 沸点/ ℃ 动力学直径/nm 甲苯 C7H8 92.14 110.6 0.67 二甲苯 C8H10 106.17 138.5 0.70 乙酸丁酯 C6H12O2 116.16 126.6 1.20 表 3 不同比例TMCS/正己烷改性分子筛的比表面积、孔结构及静态水吸附量
Table 3. Specific surface area, pore structure and static water adsorption of molecular sieves modified with different ratios of TMCS/hexane
分子筛 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔容/(cm3·g−1) 孔径/nm 静态水吸附量 NaY-1 310.53 0.536 9.034 35.93% NaY-2 270.393 0.3403 8.793 3.86% NaY-3 172.425 0.3143 8.039 2.18% NaY-4 167.609 0.281 7.672 1.36% NaY-5 153.188 0.258 7.302 0.95% NaY-6 149.166 0.236 7.046 0.53% -
[1] ZHANG K, LI L, HUANG L, et al. The impact of volatile organic compounds on ozone formation in the suburban area of Shanghai[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2020, 232: 11751. [2] ZHENG Y F, FU K X, YU Z H, et al. Oxygen vacancies in a catalyst for VOCs oxidation: synthesis, characterization, and catalytic effects[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(27): 14171-14186. doi: 10.1039/D2TA03180A [3] TSAI W T. An overview of health hazards of volatile organic compounds regulated as indoor air pollutants[J]. Reviews on Environmental Health, 2019, 34(1): 81-89. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2018-0046 [4] 吴季友, 田成川, 刘廷良. 中国生态环境统计年报2020[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2022. [5] YANG C T, MIAO G, PI Y H, et al. Abatement of various types of VOCs by adsorption/catalytic oxidation: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 370: 1128-1153. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.232 [6] LI X Q, ZHANG L, YANG Z Q, et al. Adsorption materials for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and the key factors for VOCs adsorption process: A review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 235: 116213. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116213 [7] ZHANG L, PENG Y X, ZHANG J, et al. Adsorptive and catalytic properties in the removal of volatile organic compounds over zeolite-based materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(6): 800-809. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(15)61073-7 [8] PUI W K, YUSOFF R, AROUA M K. A review on activated carbon adsorption for volatile organic compounds (VOCs)[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2019, 35(5): 649-668. doi: 10.1515/revce-2017-0057 [9] GUO X C, LI X Y, GAN G Q, et al. Functionalized activated carbon for competing adsorption of volatile organic compounds and water[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(47): 56510-56518. [10] KEAUS M, TROMMLER U, HOLZER F, et al. Competing adsorption of toluene and water on various zeolites[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 351: 356-363. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.128 [11] YIN T, MENG X, JIN L, et al. Prepared hydrophobic Y zeolite for adsorbing toluene in humid environment[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 305: 110327. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110327 [12] LI X F, WANG J, GUO Y Y, et al. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of hydrophobic hierarchical zeolites for the removal of volatile organic compounds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 411: 128558. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128558 [13] 刘星园, 张永锋, 肖凯, 等. 分子筛材料在VOCs吸附中的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(5): 2504-2510. [14] 黄海凤, 戎文娟, 顾勇义, 等. ZSM-5沸石分子筛吸附-脱附VOCs的性能研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(12): 3144-3151. [15] WANG C, GUO H D, LENG S Z, et al. Regulation of hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of aluminosilicate zeolites: a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences, 2021, 46(4): 330-348. doi: 10.1080/10408436.2020.1819198 [16] 庄瑞杰, 于庆君, 唐晓龙, 等. 介孔硅基分子筛吸附去除挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(15): 15013-15020. [17] FRANK H, MAXIMILIAN C, JÜRGEN M, et al. Silica-based mesoporous organic-inorganic hybrid materials[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(20): 3216-3251. doi: 10.1002/anie.200503075 [18] LU S C, LIU Q L, HAN R, et al. Core-shell structured Y zeolite/hydrophobic organic polymer with improved toluene adsorption capacity under dry and wet conditions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 409: 128194. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.128194 [19] 李承龙, 刘才林, 杨海君, 等. ZSM-5高硅分子筛硅烷化疏水改性的研究[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2013, 25(2): 236-239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2013.02.019 [20] 张媛媛, 王笠力, 何丽, 等. 分子筛改性及其在高湿条件下对甲苯的吸附[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(10): 5509-5514. [21] 党小庆, 王琪, 曹利, 等. 吸附法净化工业VOCs的研究进展[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(11): 3479-3492. [22] LU S C, LIU Q L, HAN R, et al. Potential applications of porous organic polymers as adsorbent for the adsorption of volatile organic compounds[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 105(7): 184-203. [23] BRENNAN J K, BANDOSZ T J, THOMSON K T, et al. Water in porous carbons[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2001, 187: 539-268. [24] 马越, 程妍. 热处理对粉煤灰酸渣基二氧化硅气凝胶结构和疏水性的影响[J]. 无机盐工业, 2022, 54(3): 109-112. [25] 刘媛. 改性分子筛对二氯甲烷废气吸附性能研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. [26] WANG J L, SHI Y J, KONG F Z, et al. Low-temperature VOCs oxidation performance of Pt/zeolites catalysts with hierarchical pore structure[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2023, 124: 505-512. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2021.11.016 [27] 祝振鑫. 膜材料的亲水性、膜表面对水的湿润性和水接触角的关系[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2014, 34(2): 1-4. -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: