-
目前,我国众多城市仍保留了大面积的截流式合流制排水系统。在降雨条件下,超出管网截流倍数的雨污混合水通过溢流井或泵站直接排放到受纳水体而造成的污染,称为合流制溢流(combined sewer overflow, CSO)污染[1]。CSO污染具有水质和水量波动大、非连续性的特点,是导致城市黑臭水体、地表水污染的主要原因之一。近年来,随着城市的快速扩张与持续更新,不透水面大幅增加,暴雨突发性污染事件频发,致使CSO流量大、频次多,严重制约了城市面源污染控制。在黑臭水体整治和海绵城市建设的背景下,CSO污染控制成为当前不可回避且亟待解决的重要问题[2]。CSO污染控制措施主要分为源头减量、管道截流、调蓄储存和末端控制[3]。其中,CSO末端控制技术主要采用物理性处理,例如水力旋流分离器[4-5]、混凝沉淀池[6]、高效沉淀池[7]、溶气气浮[8]等,这些技术的优势是能够应对CSO污水的水量大、非连续性的特点,但是对COD指标去除非常有限,难以消除CSO溢流引起的水体污染问题。CSO末端控制也可采用人工湿地[9]、生物滤池[10]等生态、生物处理方法,但在城市区域存在场地受限、投资成本高、无雨期维护困难等难题。
CSO污染中含有较高水平的悬浮物(SS)、总磷(TP)和耗氧有机物(以COD计),混凝气浮是去除污水中SS、TP的有效方法,但对COD去除非常有限。臭氧在水处理领域应用广泛,具有氧化效率高、稳定性强、易现场制取、无二次污染等优点,是降解有机污染物的有力技术手段。现有研究表明,臭氧氧化与混凝气浮存在协同作用,可显著增强污水净化效果。臭氧通过促进混凝剂水解,攻击难凝聚有机物的不饱和结构,强化混凝效果;金属盐混凝剂及其水解产物能够催化臭氧产生氧化性更强的活性氧中间物质,进一步提升有机污染物降解效果[11]。目前,臭氧气浮工艺用于市政污水二级出水处理,以及印染废水、油田采出水等工业废水处理[12-13],均表现出良好的净化效果,但用于CSO污水处理还未见相关报道。
臭氧气浮工艺具有占地面积小、抗冲击负荷、处理效率高等优点,基于此,本文拟对臭氧气浮工艺处理CSO污染进行深入研究,通过实验室小试,探明影响规律和最适反应条件,考察该工艺对CSO典型污染物的去除效果和机制。此外,进一步设计制造臭氧气浮处理CSO的集成化撬装式设备,以武汉市某溢流污水为工程实验对象,考察臭氧气浮设备出水水质和运行稳定性,以期为合流制溢流污染治理提供理论指导和技术依据。
-
1)模拟污水。考虑到CSO水质复杂多变、保存时间短,参考实际CSO污水和国内外溢流污染水质情况[14-15]配制模拟污水。采用邻苯二甲酸氢钾、高岭土、磷酸二氢钾、氯化钠和硫酸钠分别配制COD为150 mg·L−1,SS为150 mg·L−1,TP为3 mg·L−1,Cl−和SO42-均为50 mg·L−1的模拟污水,仅用于实验室小试。
2)实际CSO污水。取自武汉市某调蓄池,该池进水主要来自合流制排水管道,收集服务区内的生活污水、工业废水和降雨径流,小试用水采样后在4 ℃下储存备用,工程实验在取水现场进行,实验期间CSO实际污水水质见表1。
-
1)混凝小试实验。取500 mL水样在搅拌器上进行混凝烧杯实验,用1 mol·L−1 NaOH或H2SO4调节溶液pH,混凝剂选用聚合氯化铝(PAC),助凝剂选用聚丙烯酰胺(PAM),混凝程序为:加入PAC快搅2 min,转速为200 r·min−1;再加入PAM慢搅10 min,转速为50 r·min−1;静置沉淀20 min后取样测定相关指标。
2)臭氧小试实验。采用内径40 mm、高500 mm的有机玻璃反应器,底部设微孔钛曝气头,水样体积为500 mL。将氧气通入氧气源臭氧发生器(3S-X10,北京同林科技有限公司,中国),调节电流产生特定浓度的臭氧;由臭氧在线浓度检测仪(3S-J5000,北京同林科技有限公司,中国)测试进气浓度;调节三通阀和转子流量计(LZB-3WB,常州双环热工仪表有限公司,中国)控制进气流量为0.5 L·min−1;未反应的臭氧经KI溶液吸收。小试实验均设置3组平行。
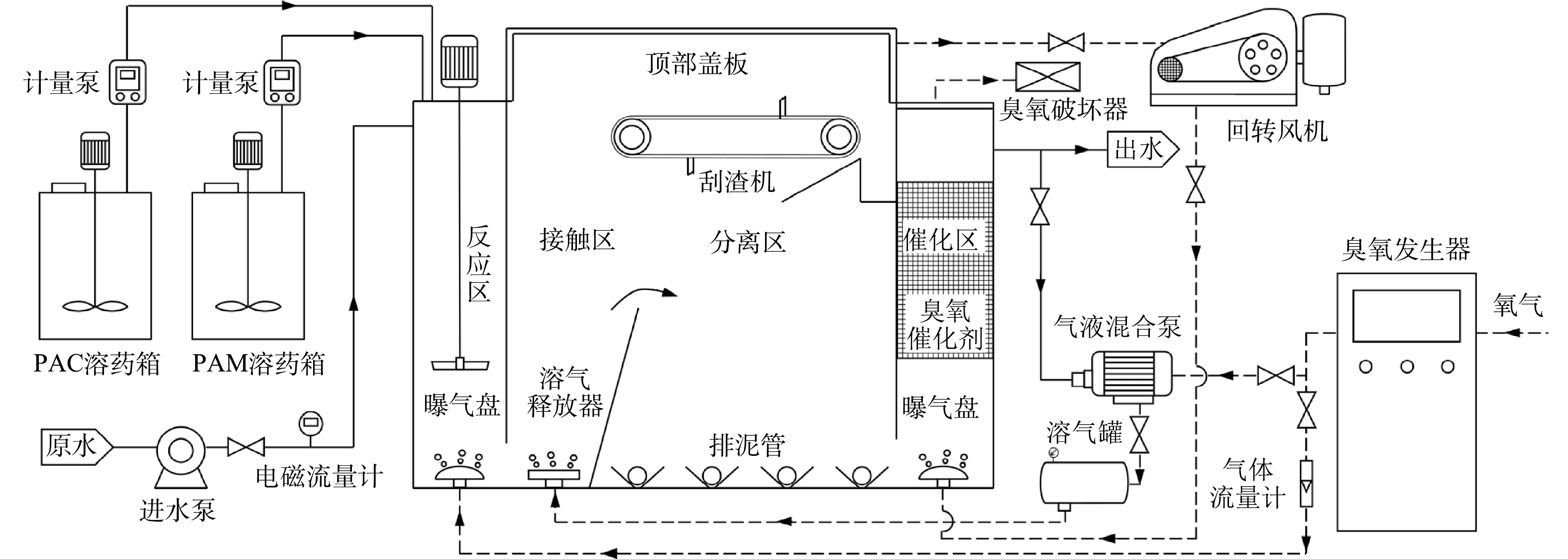
3)臭氧气浮工程实验。新型一体化撬装式臭氧气浮设备如图1,实验处理水量为1 m3·h−1,集装箱外形尺寸为6 m×2.4 m×3 m,内部池体为3 m×1.8 m×2.5 m,有效水深为2 m。成套设备包括主反应单元、药剂投加单元、臭氧发生单元、残余臭氧处理单元和浮渣处理单元。采用氧气源臭氧发生器(MB-S-F100,南京盟博环保科技有限公司,中国)配置制氧机,臭氧产量为100 g·h−1,臭氧浓度为90~135 mg·L−1,PAC、PAM采用小试最佳投加量。主反应单元包括反应区、接触区、分离区和催化区,其中反应区、接触区和分离区顶部设密封不锈钢盖板。工艺流程为:污水经提升泵进入反应区,与PAC、PAM接触絮凝,并与臭氧反应;随后进入接触区,在气液混合泵释放的臭氧微气泡作用下进入分离区;固液分离后上清液进入催化区,在少量催化填料(氧化铝基负载型,丰泽环保材料有限公司,中国)作用下进一步去除有机物,反应后出水一部分回流至前端气液混合泵,其余直接排放。臭氧一部分通入反应区,实现臭氧混凝同步反应;另一部分在气液混合泵作用下加压溶于回流水,气液比为1:9,溶气水经释放器进入接触区。为提高臭氧利用率并强化有机物去除效果,将残余臭氧通入催化区二次利用,末端尾气经臭氧破坏器处理后排放。设备在降雨期间运行,采样间隔为1 h,每次采样设置3个平行样。
-
SS采用便携式水质分析仪(DR900,哈希公司,美国)测定;TP采用过硫酸钾消解-钼酸铵分光光度法测定;COD采用快速消解分光光度法测定;紫外-可见光谱采用紫外分光光度计(UV5900PC,上海元析仪器有限公司,中国),扫描波长为200~500 nm,间距为1 nm。三维荧光采用荧光光谱仪(FS-5,爱丁堡仪器公司,英国),水样经0.45 μm滤膜过滤后上机测试,超纯水做空白校正以消除拉曼散射。激发波长Ex和发射波长Em的扫描区间分为220~450 nm和280~550 nm,扫描间隔分别为5 nm和2 nm,狭缝宽度均为5 nm,利用荧光区域积分法(FRI)进行荧光强度定量分析[16]。
-
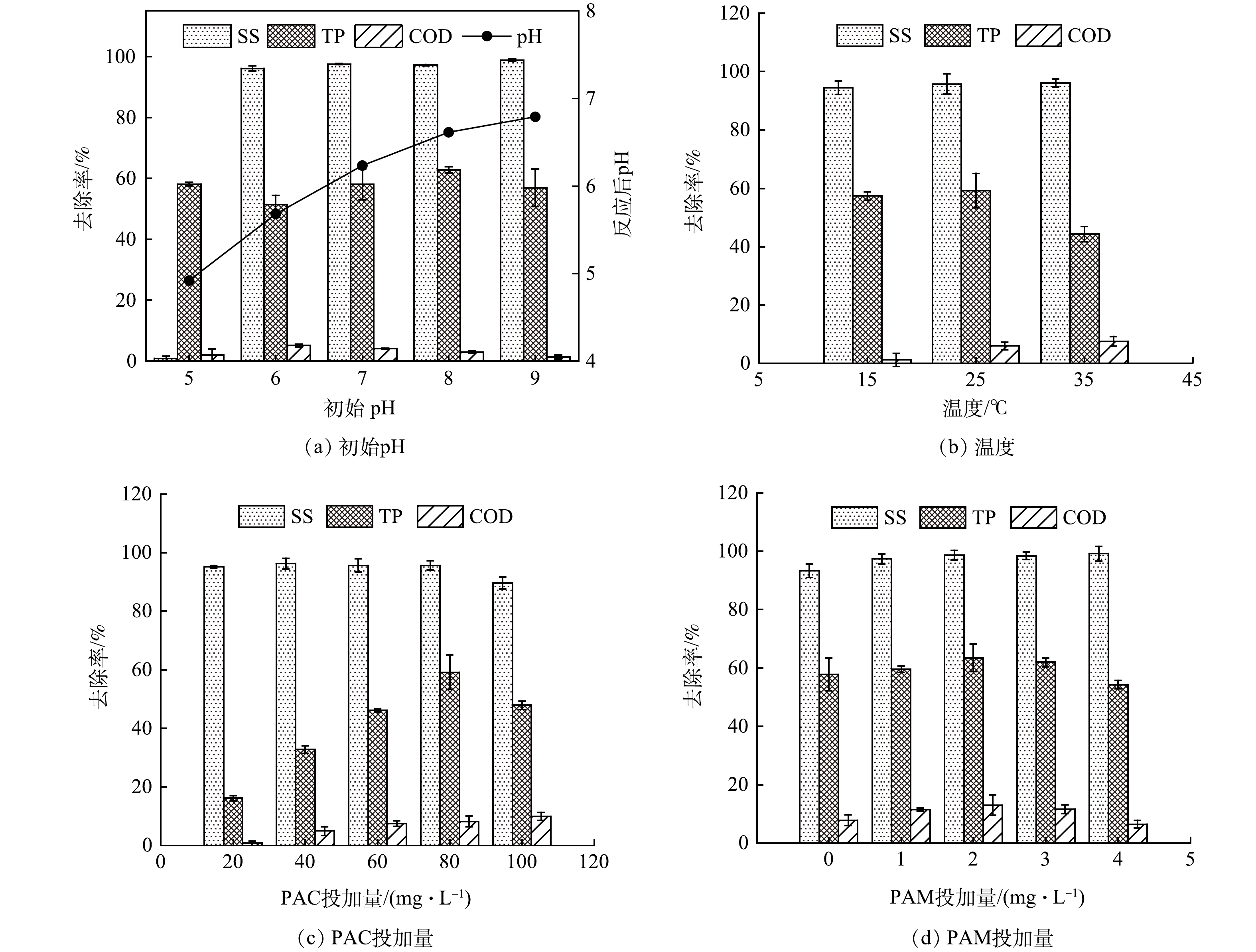
首先探究了反应条件对混凝效果的影响规律,其中初始pH的影响结果如图2(a)所示。将溶液pH分别调至5~9,实验过程中观察到pH=5时几乎未形成絮体矾花,在pH较低时絮体颗粒细小且绵密,而pH较高时絮体颗粒粗大而密实,且反应后pH均有所下降。pH过低对SS处理效果不佳,pH在6~9对污染物去除影响不显著。由于pH在7左右时保持较高去除率,且实际污水pH一般在7.3~7.6,考虑到经济适用性,后续混凝实验均调至pH=7。
环境温度(15、25、35 ℃)对混凝效果的影响如图2(b)所示。温度对SS去除率影响不大,均保持在90%以上,COD去除率在低温下仅有1.2%,在常温和高温下均在6%~8%,TP在25 ℃时去除效果优于15 ℃和35 ℃。这是因为低温导致分子热运动减缓,水的黏度增加且PAC水解速率下降,絮团较为松散,反应迟缓且效果变差。虽然温度较高时絮凝剂水解速率加快、水的黏度降低,但絮凝剂在高温下易分解,因此温度过高也不利于混凝,故混凝过程适宜在25 ℃下进行。
PAC投加量对混凝效果的影响如图2(c)所示。实验设置PAC投加量分别为20、40、60、80、100 mg·L−1,在此条件下,SS去除率均达90%,COD去除率均在10%以下。TP去除效果受PAC投加量的影响显著,随PAC投加量增加,矾花增多且絮体颗粒更密实,TP去除率呈现先升高后降低的趋势,在PAC投加量为80 mg·L−1时达到59.2%。混凝剂投加量较小时,系统处于凝聚阶段,絮体小且数量少,絮凝不充分,难以实现吸附架桥。但PAC投加量过大时,凝聚效果反而下降,这与EL SAMRANI等[17]得到的结果一致。这是由于吸附过量的异号离子使得电荷变号、斥力变大,胶粒重新稳定。无机絮凝剂含有金属盐离子,胶粒表面被带正电的聚合物包覆而相互排斥、难以聚集,反而削弱了混凝效果,故PAC最适投加量取80 mg·L−1。
采用PAM为助凝剂,强化吸附架桥作用,可加速絮体的形成和团聚,从而进一步提高出水水质。如图2(d)所示,随着PAM增加,各指标去除率上升趋势不显著,但絮体团聚增大,沉降速度明显加快,混凝速率得以提升,一定程度上提高了污染物的去除效果,然而投加过量PAM又会使出水黏度升高,投加量为2 mg·L−1时SS、TP、COD的去除率分别为98.6%、63.5%、12.9%,故取2 mg·L−1作为PAM最适投加量。
-
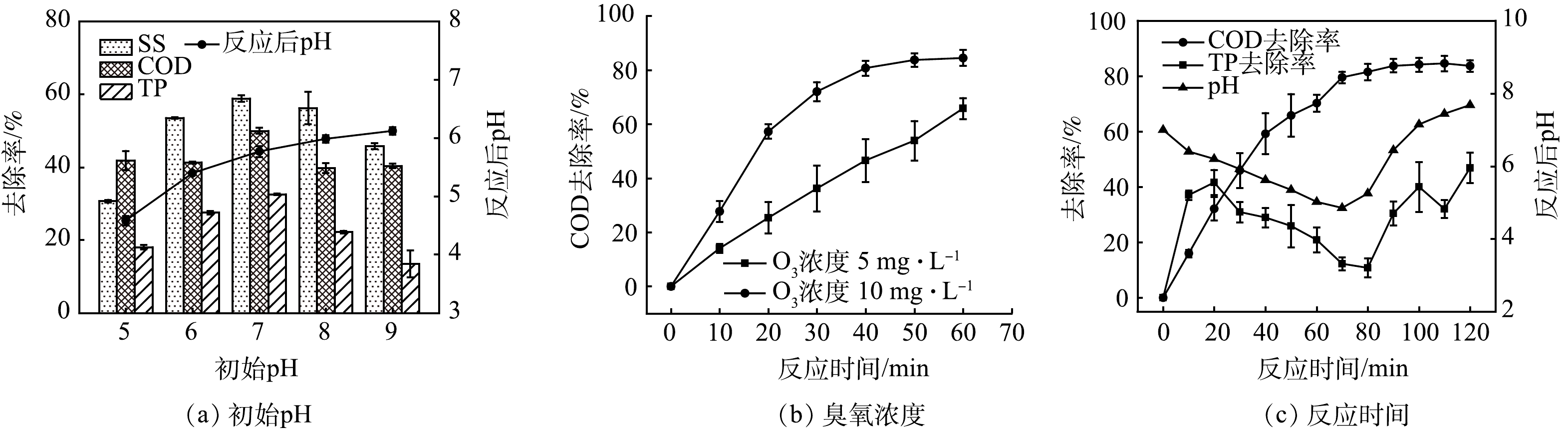
初始pH对混凝同步O3氧化CSO模拟污水的处理效果影响情况如图3(a)所示。已有研究表明,O3对溶液pH具有很强依赖性[18],故在pH为5~9内开展实验。在酸性条件下,主要依靠臭氧的选择性直接氧化作用,故COD去除率较低。随着pH升高,在碱性条件下反应体系内OH−引发链式反应生成强氧化性的·OH,COD去除率明显提高。再进一步提高溶液pH至8~9,由于短时间内生成大量自由基并相互淬灭[19],COD去除率反而下降。CSO实际污水pH一般呈中性,故pH不作调整。
臭氧浓度对COD去除效果的影响如图3(b)所示。控制进气量为0.5 L·min−1,臭氧浓度分别为5 mg·L−1和10 mg·L−1(即臭氧投加速率为2.5 mg·min−1和5 mg·min−1)。在低浓度(5 mg·L−1)条件下,COD去除率基本呈线性增长,60 min时达到63.8%;在高浓度(10 mg·L−1)条件下,COD去除率先升高后趋于平缓,60 min时达到84.5%。臭氧浓度为5 mg·L−1条件下COD、TP、pH随反应时间的变化情况如图3(c)所示。可见,反应初期COD去除率随时间的增加不断升高,此时体系内臭氧浓度是去除COD的限制因素,在70 min内COD去除率升至79.5%,但随O3投加量的提高该制约逐渐减弱,COD去除率差异不显著,最终在120 min稳定至83.7%,说明此时底物浓度是主要限制因素,这与罗新浩等[18]的研究结果一致。在反应过程中,体系pH先降低后升高,TP去除率也呈现相同趋势。这是因为O3很难将有机物直接矿化,而是将其降解为小分子有机酸等中间产物,并随反应时间不断累积,使得体系pH下降。若继续投加O3,中间产物被进一步降解为CO2和H2O等,体系pH回升,而TP去除效果因受pH影响也随之变化。考虑到处理效果和运行费用,臭氧利用率会随时间降低,反应30 min内平均每去除1 mg COD需要消耗2.18 mg O3,此时COD去除率为45.9%,故取反应时间为30 min。综上所述,臭氧混凝耦合工艺的最适实验参数为pH=7,常温,臭氧浓度为5 mg·L−1,反应时间30 min,PAC和PAM投加量分别为80 mg·L−1和2 mg·L−1。
-
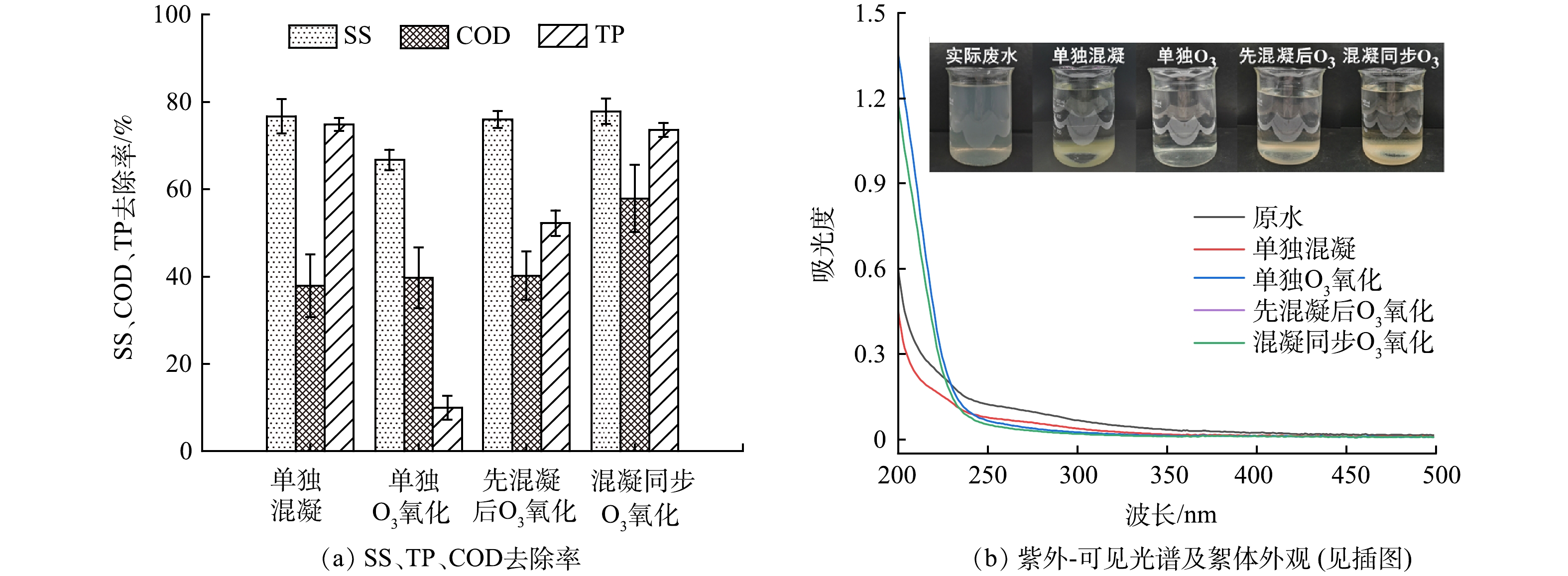
基于以上结果,在最适条件下考察混凝-O3氧化同步处理CSO实际污水的效果,分别采用“单独混凝”、“单独O3氧化”、“先混凝后O3氧化”和“混凝同步O3氧化”4种处理方式,实验结果如图4所示。可以看出单独混凝后上清液清澈,底部沉积大量絮体;单独O3氧化后,溶液较澄澈,O3将不溶性颗粒物直接氧化,使得SS有所下降;先混凝后O3氧化后,溶液内悬浮大量松散絮体,混凝后产生的絮体被通入的O3吹散,不易上浮也不易沉降;混凝同步O3氧化处理后絮体较前者密度更大且易于沉淀,上清液也较澄清。
如图4(a),单独O3氧化对SS去除效果最差,其余三种处理方式得益于絮凝剂的投加,SS去除率均75~78%之间。对于总磷的去除,单独混凝的去除率为74.8%,先混凝后O3氧化后的TP去除率为52.2%,低于混凝同步O3氧化处理的73.6%,这是因为污水中的部分磷是通过絮凝的吸附架桥作用去除的,而臭氧的投加导致混凝后的部分絮体稳态结构被破坏,致使TP去除效果被削弱。对于有机物的去除,单独混凝对COD去除率为37.9%,实际污水中的非溶解态有机物吸附在悬浮颗粒表面,随混凝的卷扫和网捕作用一并去除。单独O3氧化通过直接和间接氧化降解有机物,对COD去除率为39.7%。先混凝后O3氧化的COD去除率为40.2%,但低于混凝同步O3氧化的57.9%。“混凝同步O3氧化”耦合工艺对COD去除效果相较于单独混凝和臭氧氧化分别提高了20%和18.2%,说明臭氧与混凝之间存在协同增效的作用,PAC及其水解产物催化O3分解产生更多活性氧物质,有机物去除效果明显提高。总体而言,混凝与O3氧化耦合同步处理对CSO实际污水典型污染物的去除效果良好,耦合工艺有效提升了有机物去除效果,从而达到高效、快速处理CSO污水并直接排放的目的。
不同工艺处理后的紫外-可见光谱如图4(b)所示。可见,经单独混凝处理后,各波段吸光度有所下降,其中代表不饱和有机物含量的UV254去除率为40.9%。经O3氧化后240~350 nm波段内吸光度降低明显,单独O3氧化和先混凝后O3氧化UV254去除率分别为52.5%和52%,而混凝同步O3氧化对UV254去除率为63.8%,有机物净化效果更为显著,这与侯瑞等[20]的研究结果一致,O3的亲电性使有机化合物不饱和键开环断链、芳香性降低,紫外吸光度也随之降低。
通过三维荧光光谱分析反应前后荧光性有机物的转化规律,图5为原水和不同工艺处理后的荧光光谱,Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ区分别对应酪氨酸类、色氨酸类、富里酸类、溶解性微生物代谢产物和腐殖酸类物质。原水显示3个明显的荧光峰,峰A(Ex/Em=245 nm/444 nm)、峰B(Ex/Em=280 nm/352 nm) 和峰C(Ex/Em=340 nm /436 nm)分别属于Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ荧光区。由此可见,CSO污染废水中主要以腐殖酸、富里酸类腐殖质和溶解性微生物为主。经混凝工艺处理后,峰A、峰B和峰C范围均缩小且荧光强度下降,但去除率不高。单独O3氧化后荧光强度显著削弱,无明显的特征峰,说明臭氧能够有效去除腐殖质类物质。由图5(c)和图5(d)对比发现,混凝与臭氧耦合工艺比单独臭氧处理的荧光强度削减更明显,说明在溶解性有机物的去除方面混凝与臭氧耦合也存在协同效果。荧光光谱各区域经FRI荧光区域积分法[21]计算结果见图5(e)和图5(f),耦合工艺对全部区域荧光强度去除率为95.6%,相较于单独混凝的和单独臭氧氧化分别提高了43.9%和4.5%。由此可见,混凝对溶解性有机物去除效果有限,而臭氧氧化是耦合工艺去除溶解性有机物的关键。
-
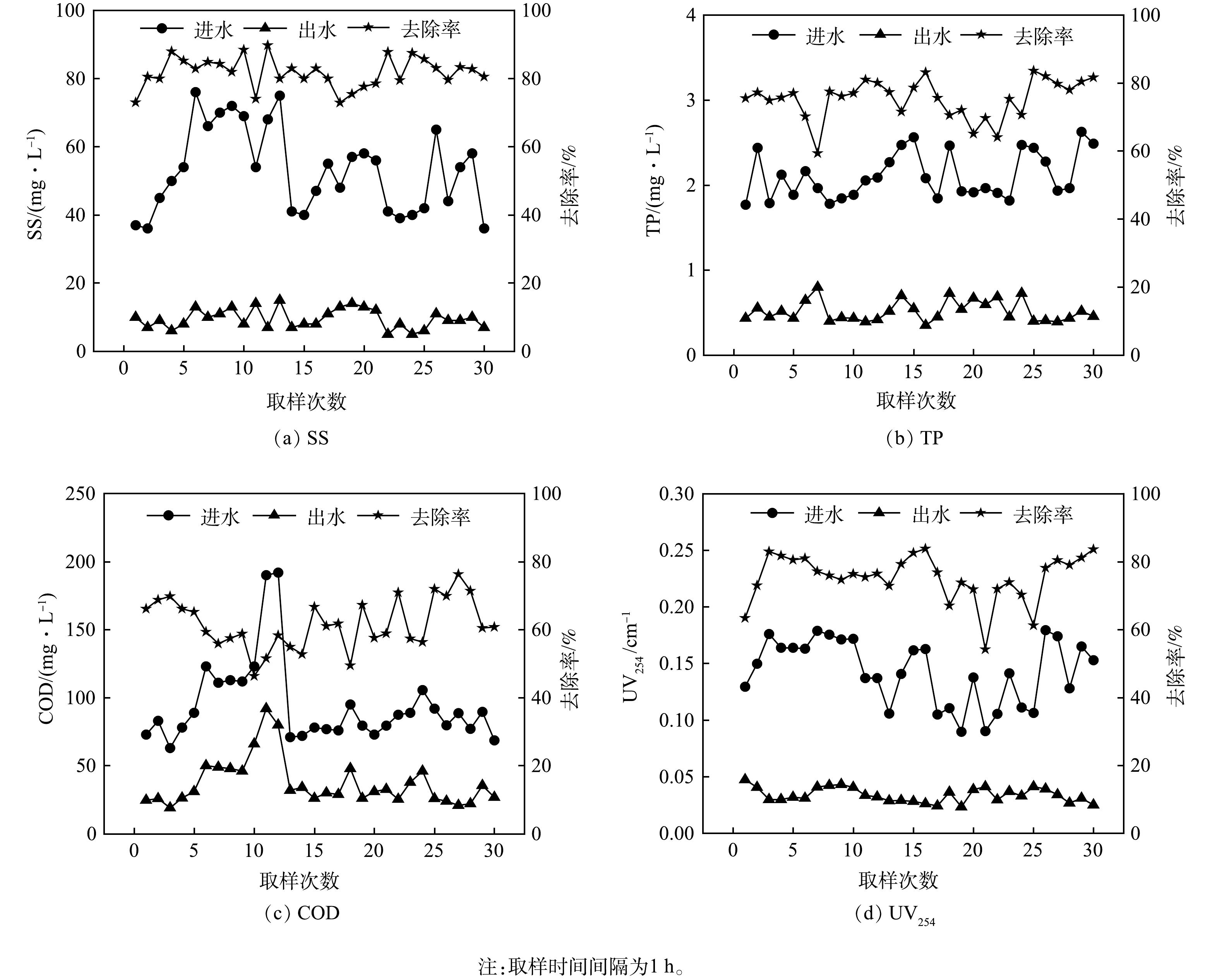
针对CSO实际污水水质特点,结合前期小试结果并借鉴平流式气浮池的特点,自主研发一体化撬装式的臭氧气浮设备。为突破传统气浮设备气量输出有限的问题,布设2处微气泡曝气,分别为反应区曝气和接触区气液混合泵加压溶气,以此提高臭氧气的输入量。在主反应单元加设整体不锈钢顶盖,通过回转风机将前端残余臭氧通入催化区,二次利用残余臭氧,进一步氧化难降解有机物,既避免臭氧逸散造成污染、提高臭氧利用率,又能提高设备的处理效能。臭氧气浮设备现场工程实验对CSO污染去除效果见图6。可见,原水水质波动范围较大,SS、TP、COD和UV254的平均去除率分别为81.8%、75.4%、61.7%和75.4%,出水平均浓度为9.57、0.52、37.05 mg·L−1和0.034 cm−1。以上结果说明臭氧气浮工艺对CSO实际污水处理效果优良。基于相同的混凝剂和臭氧投加比例,工程实验处理效果略优于小试,原因是加压溶气和残余臭氧再利用的设计使得臭氧利用率提高,处理效果有所提升。
臭氧气浮设备运行成本主要由药剂费和设备电耗组成,药剂包括PAC和PAM,折算吨水药剂费为0.2元·t−1;主要用电来自臭氧发生系统,电耗为3 kWh·t−1,电费以0.5元·(kWh)−1计,可得吨水处理成本为1.7元·t−1,略低于国外报道的CSO“过滤-消毒”处理方法[15,22]。目前,国内城市主要采用混凝沉淀池处理CSO污水,其运行成本约为0.3元·t−1[23],但这一方法去除COD能力有限。臭氧气浮作为一种高级氧化方法,在COD去除方面具有显著优势。在实际应用中,可以通过调整混凝剂投加量、臭氧用量和污水停留时间等工艺参数以降低运行成本。
-
1)在pH=7、25 ℃、PAC、PAM投加量分别为80 mg·L−1和2 mg·L−1、臭氧浓度为5 mg·L−1、反应时间为30 min条件下,混凝-臭氧同步处理对实际CSO污水中SS、TP、COD和UV254去除率分别为77.8%、73.6%、57.9%和63.8%,COD去除效果相较于单独混凝的和单独臭氧氧化分别提高了20%和18.2%,克服了单一工艺的局限性,实现多水质目标的协同控制。
2)混凝-臭氧同步处理工艺对CSO实际污水的荧光强度削减率为95.6%,相较于单独混凝和单独臭氧氧化分别提高了43.9%和4.5%,混凝和臭氧氧化在溶解性有机物的降解中存在协同作用,其中臭氧氧化是去除溶解性有机物的关键。
3)采用撬装式臭氧气浮设备处理CSO污水,SS、TP、COD和UV254平均去除率分别为81.8%、75.4%、61.7%和75.4%。该耦合工艺具有处理效果好、抗冲击负荷、便于移动调度、运行管理灵活、适用性优良等优势,具有良好的工程应用前景,可为合流制溢流污染有效治理提供参考。
臭氧气浮工艺处理城市合流制溢流污染
Treatment of urban combined sewer overflow pollution by ozone flotation process
-
摘要: 合流制溢流(CSO)污水具有水质水量波动大、非连续产生的特点,采用臭氧气浮技术对CSO污水进行处理,研究该技术对化学需氧量(COD)、总磷(TP)、悬浮固体(SS)等污染指标的控制效果。实验室小试结果表明,在最适工艺条件下,混凝-臭氧同步处理对CSO实际污水SS、TP、COD去除率分别为77.8%、73.6%和57.9%,显著削弱了腐殖质类有机物荧光强度,混凝与臭氧氧化之间表现出良好的协同作用,能够实现CSO污染的有效控制。进一步设计了臭氧气浮撬装式设备,并在武汉市开展了CSO处理现场实验研究,运行结果表明,臭氧气浮工艺系统对SS、TP、COD的平均去除率分别为81.8%、75.4%和61.7%,净化效果良好,实现了对CSO典型污染物的协同治理。通过实验室研究和工程实验结果,证实了臭氧气浮工艺用于CSO污水治理的工程可行性,上述研究结果可为CSO污水的多水质目标协同控制提供理论指导和技术参考。Abstract: Combined sewer overflow (CSO) sewage has the characteristics of large fluctuations of water quality and quantity along with discontinuous generation. Ozone air flotation technology was used to treat CSO wastewater, and its effect on the control of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total phosphorus (TP), suspended solids (SS) and other pollution indicators is studied. Laboratory tests reveal that under the optimal process conditions, the coagulation-ozone simultaneous treatment could remove 77.8% of SS, 73.6% of TP, and 57.9% of COD in actual CSO sewage, respectively, as well as significantly decreased the fluorescence intensity of humus organic matter. A strong synergy effect occurred between coagulation and ozonation in this process and could achieve an effective control of CSO pollution. Furthermore, the skid-mounted ozone flotation equipment was designed, and a field test was conducted for CSO treatment in Wuhan City. The operation results demonstrate that the ozone air flotation process system showed the average removal rates of 81.8%, 75.4% and 61.7% for SS, TP, and COD, respectively, indicating effective purification effects. Through laboratory research and engineering trials, the engineering feasibility of ozone air flotation process for CSO sewage treatment was proved. This study provides both theoretical guidance and technical support for the collaborative control of CSO sewage with diverse water quality targets.
-
表 1 合流制溢流实际污水水质特征
Table 1. Water quality of combined sewer overflows sewage
检测结果 pH SS/(mg·L−1) TP/(mg·L−1) COD/(mg·L−1) UV254/(cm−1) Cl−/(mg·L−1) SO42-/(mg·L−1) 范围 7.32~7.55 36~76 1.77~2.63 63~192 0.0897~0.1796 28.10~51.81 36.77~50.13 平均值 7.44 56 2.2 127.5 0.1347 39.96 43.45 -
[1] 徐祖信, 王卫刚, 李怀正, 等. 合流制排水系统溢流污水处理技术[J]. 环境工程, 2010, 28(S1): 153-156. [2] 程熙, 车伍, 唐磊, 等. 美国合流制溢流控制规划及其发展历程剖析[J]. 中国给水排水, 2017, 33(6): 7-12. [3] 李思远. 合流制管网污水溢流污染特征及其控制技术研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2015. [4] 黄勇强, 刘荣平. 合流制排水系统的集成优化处理[J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(12): 57-61. [5] LEE D H, MIN K S, KANG J H. Performance evaluation and a sizing method for hydrodynamic separators treating urban stormwater runoff[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2014, 69(10): 2122-2131. doi: 10.2166/wst.2014.125 [6] 张善发, 马鲁铭, 高廷耀. 合流制溢流污水的一级化学强化处理[J]. 中国给水排水, 2005, 21(11): 6-9. [7] 史昊然. 合流制溢流调蓄处理工艺效果评估及优化对策[J]. 中国给水排水, 2021, 37(5): 106-110. [8] MAENG M, KIM H, LEE K, et al. Effect of DAF configuration on the removal of phosphorus and organic matter by a pilot plant treating combined sewer overflows[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 124: 17-25. [9] MASI F, RIZZO A, BRESCIANI R, et al. Constructed wetlands for combined sewer overflow treatment: Ecosystem services at Gorla Maggiore, Italy[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2017, 98: 427-438. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.03.043 [10] 马晶伟, 林潇, 施周, 等. 生物滤池/生物滞留池组合设施控制CSO污染的效果[J]. 中国给水排水, 2021, 37(19): 131-138. [11] JIN X, JIN P, HOU R, et al. Enhanced WWTP effluent organic matter removal in hybrid ozonation-coagulation (HOC) process catalyzed by Al-based coagulant[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 327: 216-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.12.043 [12] 刘雨果, 金鑫, 许建军, 等. 电凝聚臭氧化耦合工艺的二级出水处理特性与机理研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(11): 3877-3884. [13] 邱壮, 金鹏康, 王丹, 等. 多级臭氧气浮装置深度处理印染生化出水中试研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2017, 37(8): 53-56. doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2017.37(8).053 [14] YU D, DIAN L, HAI Y, et al. Effect of rainfall characteristics on the sewer sediment, hydrograph, and pollutant discharge of combined sewer overflow[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 303: 114268. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114268 [15] VENDITTO T, MANOLI K, RAY A K, et al. Combined sewer overflow treatment: Assessing chemical pre-treatment and microsieve-based filtration in enhancing the performance of UV disinfection[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 807: 150725. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150725 [16] CHEN W, WESTERHOFF P, LEENHEER J A, et al. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(24): 5701-5710. [17] EL SAMRANI A G, LARTIGES B S, VILLIÉRAS F. Chemical coagulation of combined sewer overflow: Heavy metal removal and treatment optimization[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(4/5): 951-960. [18] 罗新浩, 胡勇有, 陈元彩, 等. 臭氧氧化印染工业园废水的效能与机理研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(12): 12-21. [19] 杨晓斌. 混凝-臭氧-电渗析工艺处理印染废水效能与机理研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2020. [20] 侯瑞, 金鑫, 金鹏康, 等. 污水厂二级出水中难凝聚有机物的臭氧化特性[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(2): 844-851. [21] HE X, XI B, WEI Z, et al. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy with regional integration analysis for characterizing composition and transformation of dissolved organic matter in landfill leachates[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 190(1/2/3): 293-299. [22] IGLESIAS R, ORTEGA E, BATANERO G, et al. Water reuse in Spain: Data overview and costs estimation of suitable treatment trains[J]. Desalination, 2010, 263(1/2/3): 1-10. [23] 孙巍, 赵红兵. 武汉市黄孝河合流制溢流强化处理设施工艺设计[J]. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(10): 101-105. -






 下载:
下载: