-
四环素(tetracycline,TC)是最常见的广谱抗生素之一,在医疗、畜牧业和水产养殖中大量用于治疗各种细菌流行病和致病性微生物导致的疾病[1-2]。据统计[3],70%以上的抗生素由于任意排放和过度使用被排入土壤、天然水甚至饮用水中,其中这些抗生素大部分为具有耐药性、毒性以及难降解特性的四环素类抗生素,对人类健康构成了巨大威胁。此外,四环素类抗生素在各种水环境中的持续积累,给生态系统也带来许多不利后果[4-5]。因此,迫切需要从废水中去除四环素类抗生素,以降低其毒性和危害。此外,超过85%的可用淡水被归为硬水,水的硬度主要是由Ca2+和Mg2+离子引起的,这些水硬度离子的存在降低水的清洁效率,导致出现水垢和热交换器故障等问题[6-7]。长期饮用硬水还会增加人体泌尿系统结石的得病率,因此,硬水的软化处理引起人们的高度关注。然而,现有的硬水处理技术如化学沉淀法、离子交换、膜过滤等,需要过度使用化学物质、复杂的基础设施、昂贵的维护费用且能源消耗高。自然水体中,TC和水硬度离子(如Ca2+和Mg2+)的共存是一种广泛的污染现象[8]。然而,由于实际水系统中有机污染物和无机金属离子的复杂性,处理复杂水体污染需要结合多种方式,导致工序繁琐且成本高。因此,开发高效简洁的综合技术,同时消除废水中的四环素和水硬度离子具有重要的实际意义[9]。
与传统的吸附、沉淀和离子交换等技术相比,电容去离子技术 (capacitive deionization, CDI)作为一种新型的水处理技术,可同时去除水中阴离子和阳离子,由于其操作方便、环境友好、能耗低、循环寿命长等优点,已被应用于海水淡化、硬水软化和重金属污染物去除等领域[10]。四环素在水体中通常以离子形式存在,且容易与水硬度离子络合。天然水的pH通常约为6.5~8.5,TC分子的三羰基体系和酚二酮部分倾向于失去质子,以TCH−或TC2-的形式存在,在水中呈电负性[11],因此,可以采用CDI技术同步去除带电荷的四环素和硬度离子。CDI新型水处理技术在有害离子选择性去除方面具有独特的优势和广阔的应用前景,但在四环素等有机化合物去除和硬水软化领域鲜有报道。
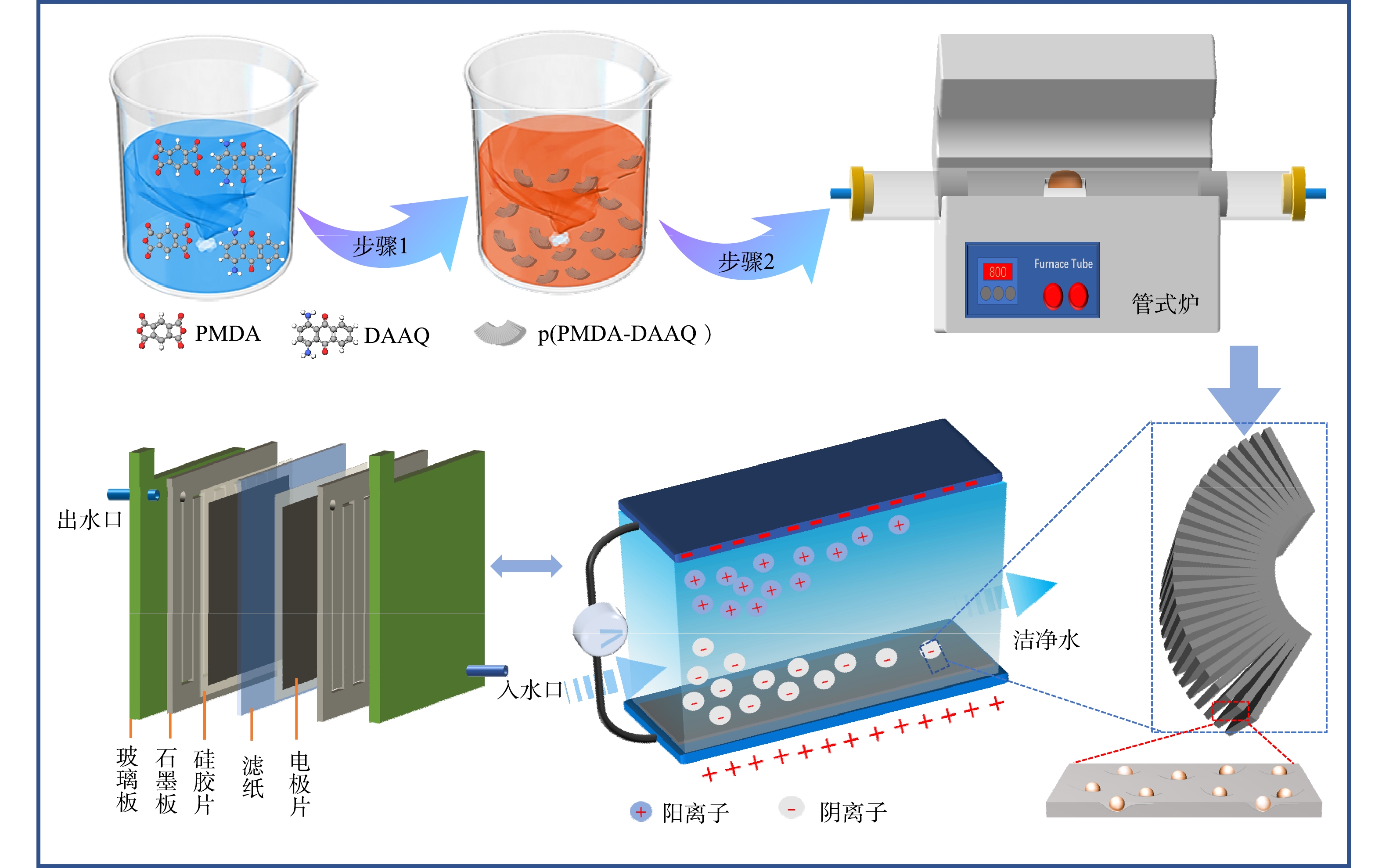
本研究基于芳香族富氮聚合物固碳碳化和自掺杂特性,通过分散聚合法将富氮单体合成为风琴状碳前驱体,进一步热处理制备得到氮掺杂(氮质量分数6.72%)的手风琴状分级多孔碳(NPC),探究基于NPC电极的CDI技术电吸附TC和硬度离子的效率;通过系统研究NPC对TC的吸附等温线、动力学、共存硬度离子、水体环境的影响和循环稳定性等,分析NPC电吸附机理,旨在为同步去除复杂水体中多种离子型污染物提供参考。
-
无水乙醇、NaOH、HCl、CaCl2、MgCl2、NaCl、KCl均为分析纯,购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司;均苯四甲酸二酐(pyromellitic dianhydride,PMDA)、2, 6-二氨基蒽醌(2, 6-diaminoanthraquinone, DAAQ)、聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(polyvinylpyrrolidone, PVP)和四环素等均为化学纯,购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;实验用水为自制超纯水。
-
小型高温管式炉(OTF-1200X-S,合肥科晶材料技术有限公司)、数显电导率仪(S230,瑞士梅特勒-托利多)、数显pH计(S210,瑞士梅特勒-托利多)、电子分析天平(赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司)、高速离心机(VL-200B,湖南迈克尔实验仪器有限公司)、超纯水机(四川优普超纯科技有限公司)。
-
以PMDA和DAAQ为二酐和二胺单体,聚乙烯吡咯烷酮为分散剂,乙二醇作为反应溶剂,通过分散聚合法制备多孔碳前体p(PMDA-DAAQ)型聚酰亚胺。典型制备工艺为:将1.00 g聚乙烯吡咯烷酮加入到含有50 mL乙二醇溶液的三口烧瓶中搅拌溶解,然后加入1.00 g的DAAQ,继续搅拌1 h。待DAAQ充分溶解后,将PMDA按照二胺∶二酐=1∶1.02的摩尔比称取,小量分批次的加入,加完二酐后继续反应4 h,得到二胺和二酐的单体盐分散液。最后,将单体盐分散液升温至180 ℃亚胺化反应4 h,自然冷却到室温后得到NPC的前驱体聚酰亚胺分散液。过滤、离心、干燥后,得到p(PMDA-DAAQ)型聚酰亚胺粉末。将聚酰亚胺粉末放入高温管式炉中,在氮气氛围中以10 ℃·min−1的速度升至800 ℃,保持2 h,得到最终产物p(PMDA-DAAQ)衍生的手风琴状分级多孔碳。
-
采用紫外分光光度计(UV -2600 日本岛津)测定TC浓度。采用傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR) (Thermo Scientific Nicolet 6700,美国)确定样品的表面官能团,波数为4 000~400 cm−1,扫描32次,分辨率为4 cm−1。采用扫描电镜(SEM) (TESCAN MIRA LMS,捷克)观测样品的微观形貌。使用 XPS (Thermo Scientific K-Alpha,美国)确定样品表面的C、N、O等元素的化学形态,并进行半定量分析。使用有机元素分析仪(Vario EL cube,Elementar,Germany) 测定样品的 C、H、N、S含量,利用差减法计算O的含量。采用全自动比表面及孔隙度分析仪(Quantachrome Autosorb IQ,美国)进行比表面积、孔径和微孔孔容分析。采用电感耦合等离子体技术ICP-OES (PerkinElmer 8300)测定溶液中的Ca、Mg和 Na等元素的浓度。
-
采用紫外可见分光光度计测定TC浓度,所有实验数据均为3个平行样本的平均值。由 Lambert-beer 定律可知,溶液质量浓度与紫外吸光度在一定范围内存在线性关系,超出这个范围后线性关系将受到影响。此外,盐分的加入也会影响紫外吸光度,且受金属阳离子电荷半径的影响较大[12]。为避免误差,提高拟合的准确度和可信度,预先测定了盐分含量(氯化钠、氯化钙、氯化钾、氯化镁)对TC吸光度的干扰情况,验证并确定盐分区间0.001%~0.004%,此时TC的紫外吸光度变化微小[12-13]。因此,在实际测试时,用去离子水将不同浓度母液(待测液)稀释到盐分质量分数为0.005%~0.003%后,再进行紫外光谱的检测。对于不同水体中待测液,均进行适当稀释后再测试紫外光谱吸光度。
测量TC质量浓度为10~200 mg·L−1的溶液在 358 nm 处的吸光度,将TC溶液质量浓度与吸光度进行拟合,得到标准曲线方程(式 (1))。
式中:Y为吸光度;X为所测溶液中的质量浓度,mg·L−1。
在NPC自吸附TC实验过程中,取质量浓度为200 mg·L−1 的TC储备液置于50 mL容量瓶中,定容,转移至100 mL 具塞锥形瓶,用 0.5 mg·L−1 H2SO4 或 NaOH 调节 pH ,加入一定量NPC,密封后,放入(25±1) ℃恒温摇床中,振荡24 h。吸附完毕后取样,过 0.22 μm 滤膜,在波长为 358 nm处测定 TC的吸光度。所有实验重复3次,取平均值。
NPC电极片由80% 的活性物质 (约0.12 g的NPC)、10%的导电剂(Super P)和10%的黏结剂 (PTFE)组成。将上述3种材料在乙醇溶液中均匀混合成浆料,擀成厚度约0.1 mm、面积为4.0 cm×4.0 cm、质量约40 mg的薄片后,压制在石墨纸上,于120 ℃烘箱中干燥24 h,即得到 用于CDI器件的NPC电极片。
在进行NPC电吸附四环素实验过程中,首先,在CDI装置上进行四环素吸附性能测试。该装置由玻璃板 (10 cm×10 cm)、硅胶片 (厚度为2.0 mm)、NPC电极片和石墨板等组装而成,然后,采用直流电源驱动1.2 V的CDI,蠕动泵以20 mL·min−1的恒定流速将处理液注入CDI装置。所有实验均在总体积为100 mL 的溶液中进行,温度约为298 K,在 波长为358 nm处测定实验后溶液的吸光度。
在相同的实验条件下,考察共存金属离子 (Na+、Ca2+和Mg2+)对NPC电吸附 TC的影响。采用吸附和解吸(短路或反向电压)的方式对电极进行循环稳定性实验。
-
为方便描述,NPC自吸附TC的吸附容量和基于CDI技术的电吸附容量以及再生性能的循环吸附-解吸效率相应的计算方法[10-14]见式 (2)和式 (3)。
式中:qt为NPC自吸附TC的吸附容量和基于CDI技术的电吸附容量;η为再生性能的循环吸附-解吸效率;
C0 和Ct 分别为初始浓度、t时刻TC的质量浓度,mg·L−1;V 为反应液体积,mL;m 为NPC的添加量,g;初始的TC质量浓度为C0,经过吸附-解吸附后的TC质量浓度为Ct,如经过1次吸附-解吸附后的TC质量浓度为C1,经过5次吸附-解吸附后的TC质量浓度为C5,以此类推。在实际水体中的吸附四环素实验过程中,2022年5月10日,采集水体样品,样品分别取自衡阳市松木污水处理厂二沉池出水 (SW) 和衡阳市洪卫水库湖水 (LW) 的实际水,相应的水质参数见表1。
-
NPC的制备过程路线和CDI电吸附原理见图1。首先,将单体二胺和二酐在乙二醇溶液中进行混合,在室温条件下,生成单体盐;然后,在原位升温条件下进行分散聚合、亚胺化,得到风琴状聚酰亚胺;最后,在简单热处理后,得到自掺杂的风琴状分级多孔碳材料。将多孔碳制成电极片,组装到CDI器件中,一般来说,CDI是基于双电层电容原理实现离子快速吸附的。典型的 CDI 电吸附过程:当电极两端施加一定电压时,水体中的离子被吸附到电极上,形成双电层;当移出电压或者反接电路时,被吸附的离子从电极上释放出来,电极得到再生[15]。
-
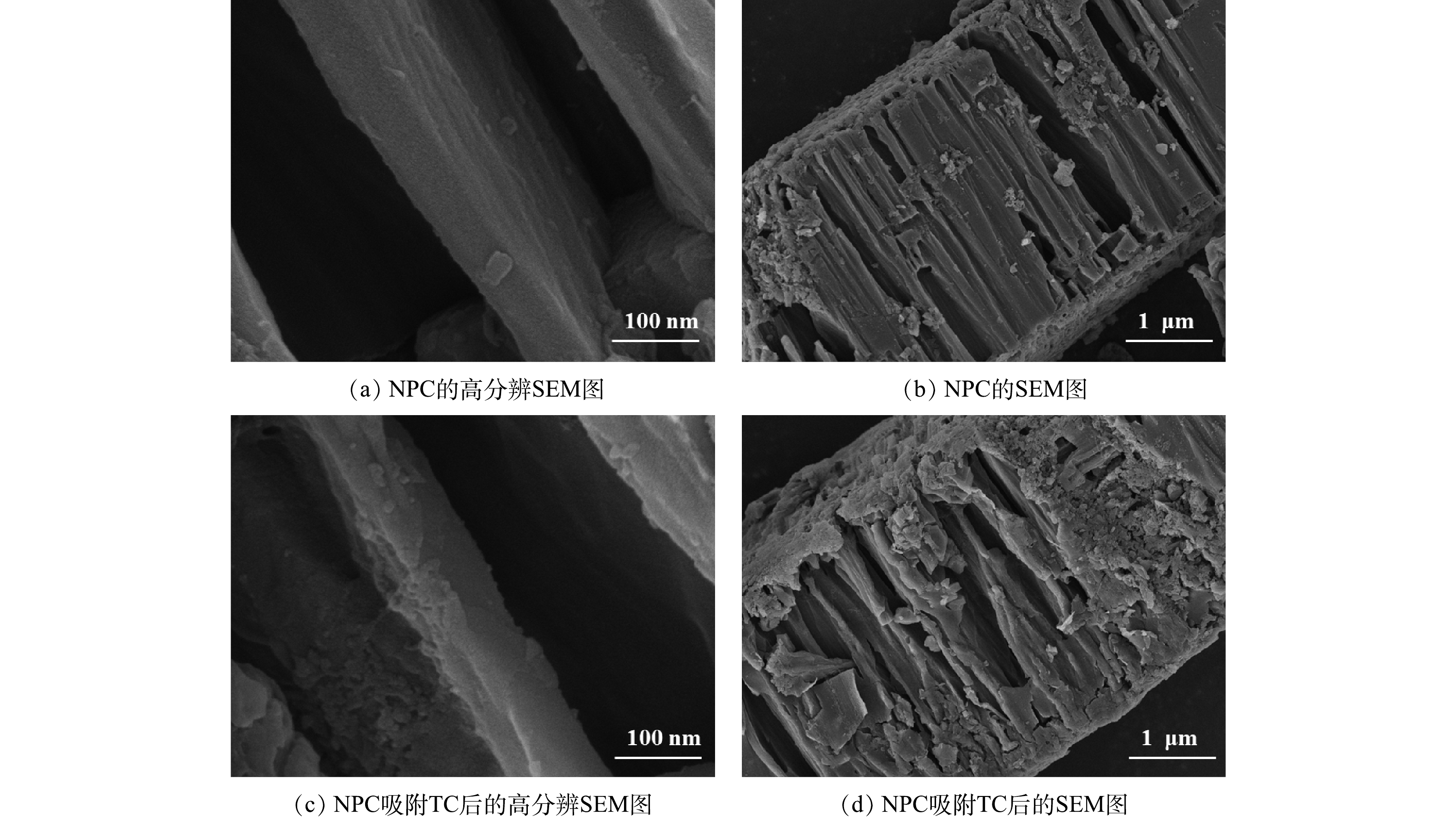
由图2(a)和图2(b)可以看出,合成的NPC呈规则的手风琴状结构,内部的碳纳米片厚度约为50 nm,表面较平整。吸附TC后的NPC如图2(c)和图2(d)所示。可以看出,原本光滑的纳米片表面出现了许多附着物,整个材料表面也被吸附物质包覆起来。样品吸附实验后进行了简单过滤,附着物依然牢牢黏附,说明NPC对水体污染物有较强的吸附能力。
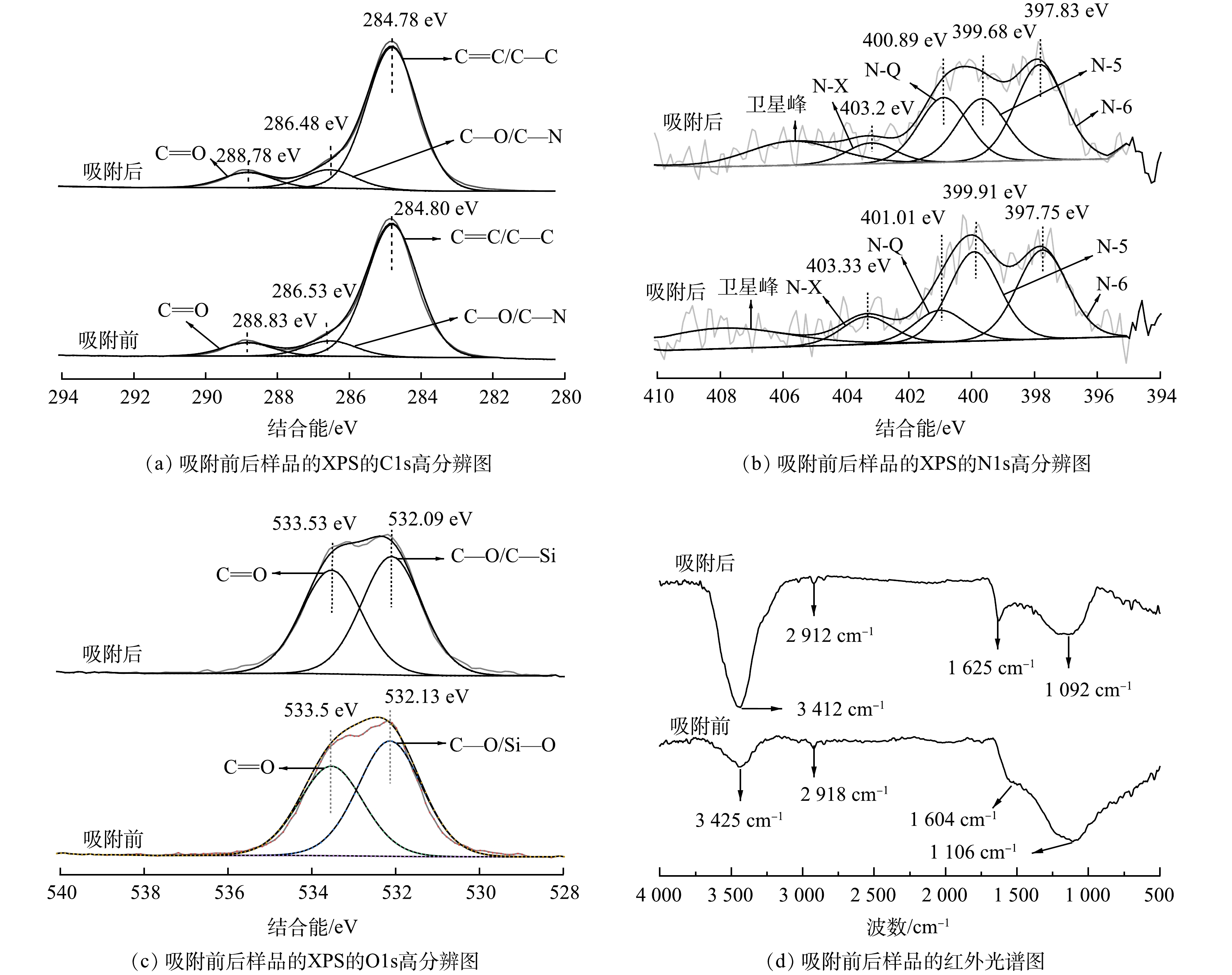
元素分析结果表明,NPC主要由82.16%的C原子、6.72%的N原子和11.12%的O原子组成。对XPS高分辨图谱的分峰拟合,由图3(a)~图3(c)可以看出,吸附前 NPC 中 C1s 结合能为 284.80、286.53 和 288.83 eV的峰分别对应C=C/C—C、C—O/C—N和—C=O [16]。O1s 结合能为 532.13 和 533.50 eV 的峰[17]对应 C—O 和 C=O; N1s 结合能为 397.75 、399.91 、401.01 和403.33 eV 的峰对应吡啶氮(N-6)、吡咯氮(N-5)、石墨氮(N-Q)和含氧吡啶氮(N-X)[18],其中吡啶氮和吡咯氮在各种氮构型中的总氮占比为87.56%。碳网络中的吡啶氮和吡咯氮被认为是活性氮,它们具有强亲和力和结合力,能高效捕捉溶液的离子,增强电吸附性能[19]。由吸附前后的结合能对比结果可以看出,NPC吸附TC后,吡啶氮和吡咯氮的含量降低了13%,且C=C/C—C、C—O/C—N、C—O、吡咯氮和吡啶氮等的结合能位置及相对含量均发生变化,说明这些含氧和含氮官能团参与了NPC对 TC 的吸附过程。
由图3(d)的红外光谱分析图也可以看出,NPC表面基团主要有—OH (3 425 cm−1和1 106 cm−1)、C—H (2 918 cm−1),—COOH和C=O (1 604 cm−1)等。吸附后,—OH的吸收峰偏移至3 412 cm−1和1 092 cm−1处,且峰形变宽,这可能是NPC的—OH与TC分子中带有孤对电子的O、N发生氢键作用所致[20]。—COOH和C=O吸收峰则向高频区发生了明显的移动,说明NPC表面对四环素发生明显的吸附,与XPS分析结果一致。
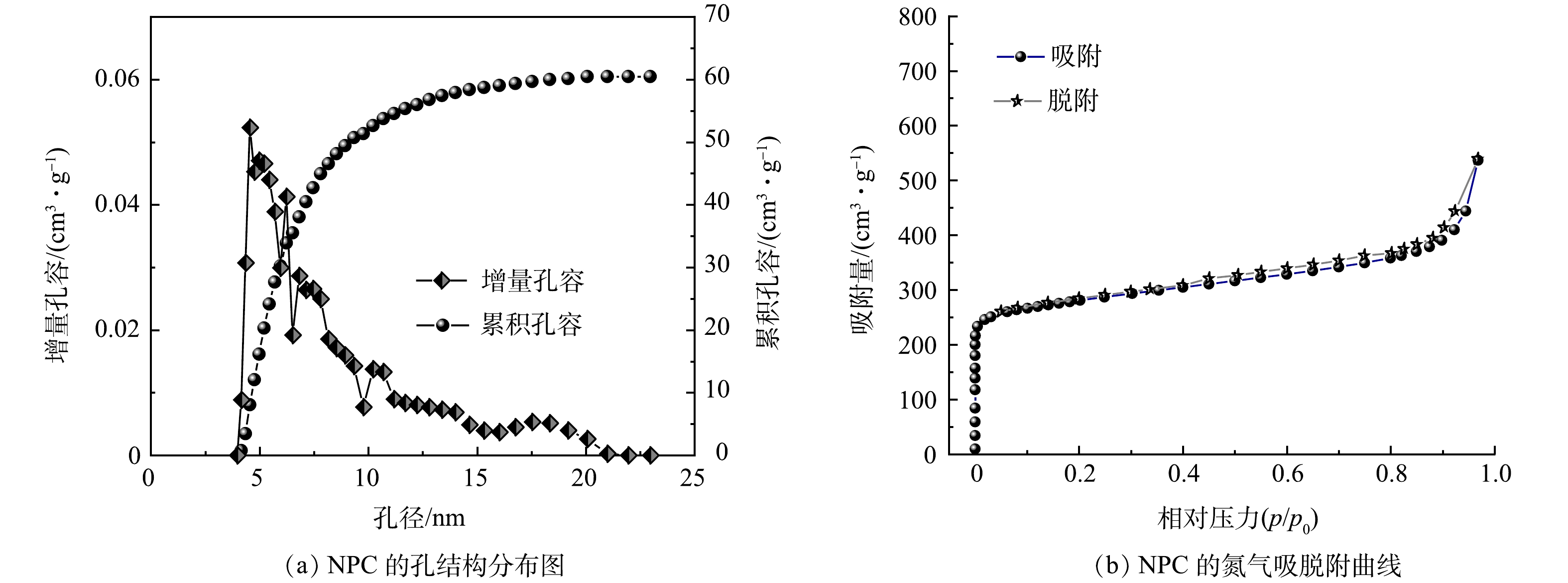
图4为NPC的氮气吸附解吸曲线和孔径分布曲线。由图4(a)可知,NPC的曲线呈Ⅰ/Ⅳ型,即高压处存在回滞环。由图4(b)可以看出,NPC存在丰富的介孔和微孔结构。基于BET模型计算的比表面积SBET为678.88 m2·g−1,总孔容VT为 0.58 m3·g−1,平均孔径Dav为 4.68 nm。由此可知,NPC拥有发达的介孔和微孔,可为污染物的去除提供丰富的吸附位点。
-
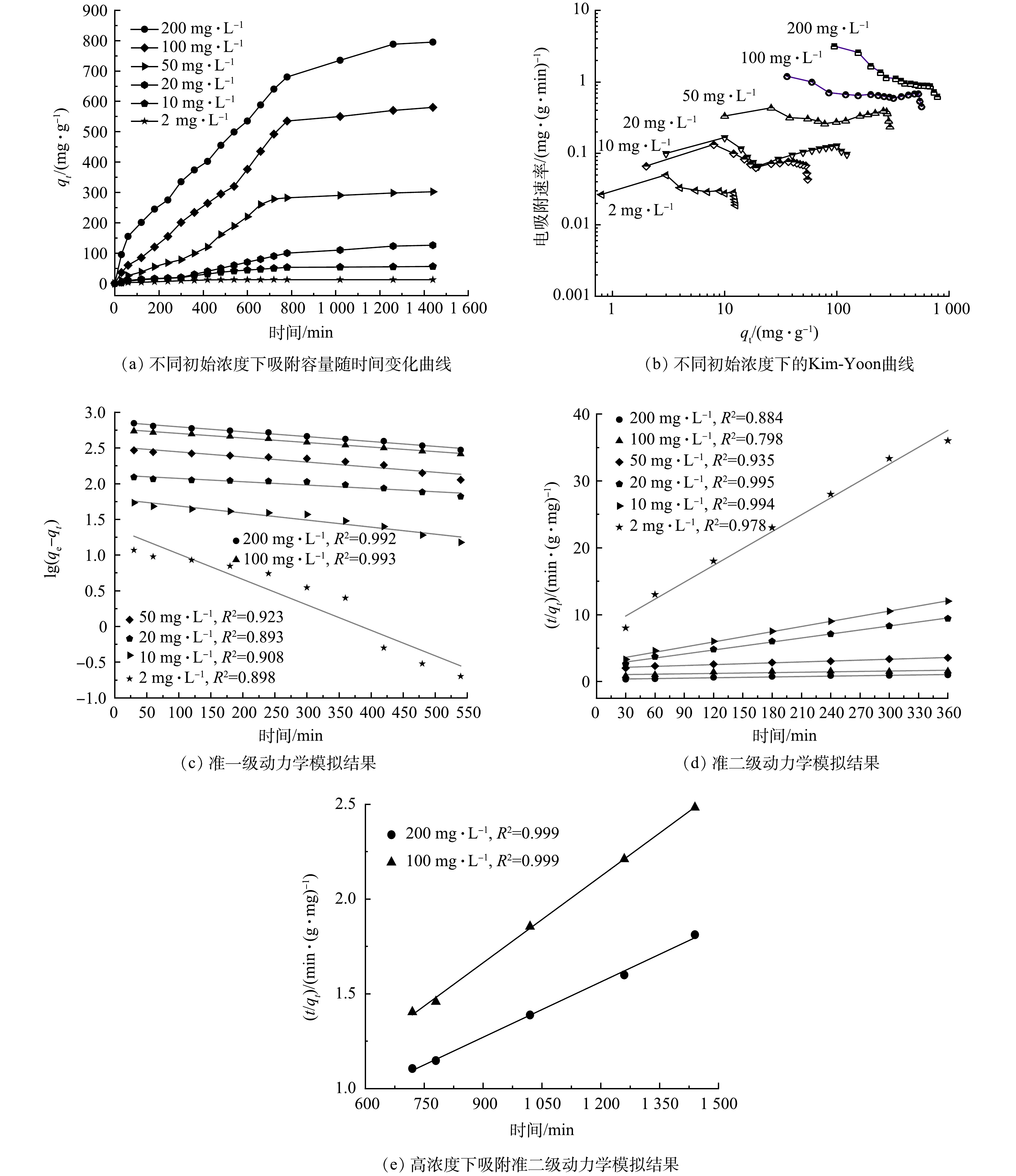
动力学参数对于阐明电吸附限速步骤的吸附机理至关重要。为了获得动力学参数,以20 mL·min−1在100 mL体积、298 K恒温环境下测试了NPC电极对TC的吸附量。在不同TC质量浓度下,NPC电吸附容量随时间的变化如图5(a)所示。吸附初期,尽管TC的质量浓度不同,但是电吸附容量在吸附初始阶段的增长均非常迅速,说明TC被NPC电极表面的活性位点快速捕获并牢牢吸附。随着电吸附时间的增加,TC已经占据了电极的大部分吸附活性位点,电吸附速率缓慢降低直到平衡。吸附饱和的时间因TC溶液的浓度不同而不同,在初始质量浓度为2 mg·L−1和100 mg·L−1时,NPC电极分别需要40 min和720 min达到吸附饱和,电吸附容量为分别为11.8 mg·g−1和596.7 mg·g−1。由图5(b)可以看出,随着TC初始质量浓度的增加,NPC电极的电吸附容量和电吸附速率(SER)向增大的方向移动,表明NPC具有优越的电吸附TC性能。值得一提的是:NPC在200 mg·L−1的TC溶液中自吸附24 h后的吸附量为350.6 mg·g−1;而使用CDI技术后,同等条件下NPC电极吸附TC量可达到854.3 mg·g−1,是传统自吸附的2.4倍。这表明CDI技术极大地提高了NPC电极对TC的吸附效率。
此外,利用动力学模型对TC在NPC电极上电吸附的主要影响因素进行了分析。如图5(c)和5(d)所示,在低TC初始质量浓度(2 mg·L−1和10 mg·L−1)时,NPC电极的吸附行为更符合准二级(PSO)模型的吸附动力学。但在高TC初始质量浓度(100 mg· L−1和200 mg·L−1)时,NPC电极的吸附行为可分为2个阶段:初始电吸附阶段(0~500 min),TC的吸附动力学符合准一级(PFO)模型;第2吸附阶段(600~1 680 min),由于电吸附后期TC质量浓度较低,TC的吸附动力学符合PSO模型(图5(e))。总体而言,TC的电吸附行为在高浓度时符合PFO动力学,而在低浓度时则转变为PSO动力学,这可能是CDI技术电吸附有机污染物的一种独特现象。
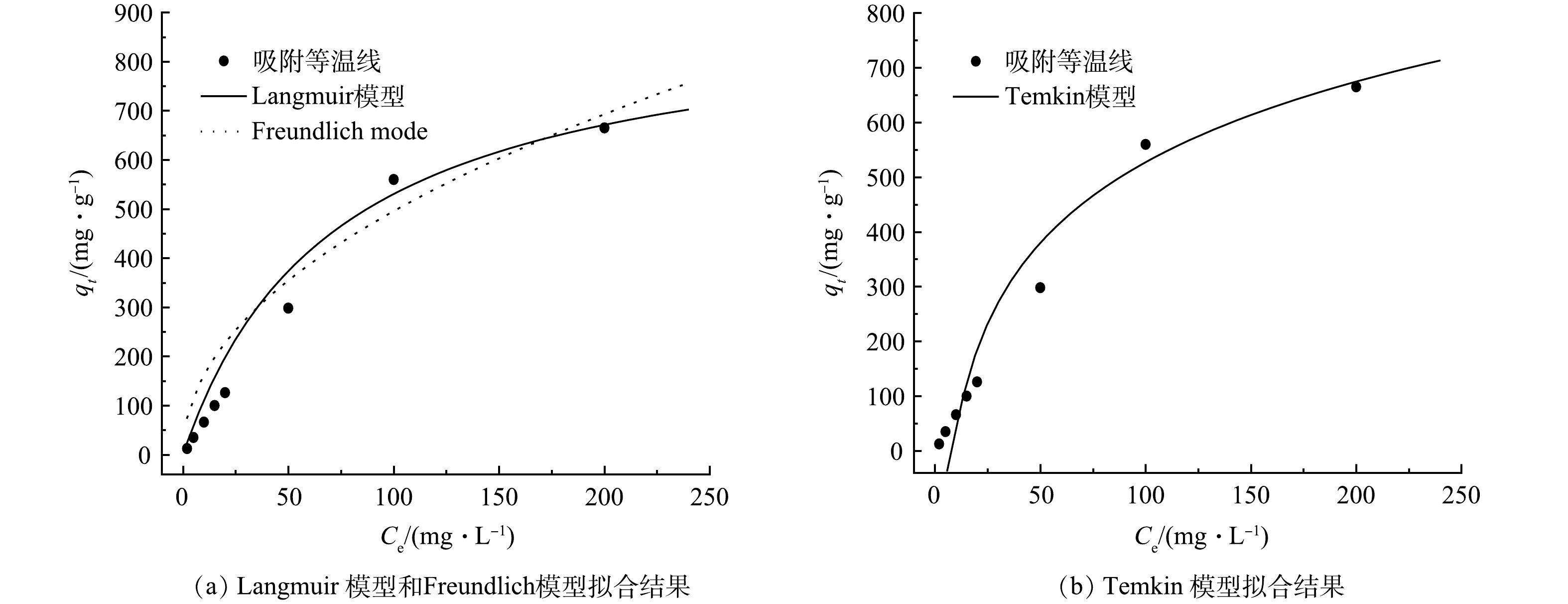
采用Langmuir,Freundlich和Temkin模型对NPC样品在不同平衡质量浓度下TC的吸附等温线进行非线性拟合。由图6(a)可知,Langmuir 模型(RL = 0.999)和 Freundlich 模型(RF = 0.995)均能较好地拟合四环素在NPC上的等温吸附线。这表明,NPC对TC的电吸附机理较复杂,主要归因于NPC优异的表面性质及表面官能团的作用。Freundlich模型的1/n值小于1,表明 NPC对四环素的吸附过程为优惠吸附[21-22]。Langmuir 模型模拟的最大吸附容量远远高于先前报道的相同类型的碳基吸附剂[3]。这表明基于CDI技术的NPC电吸附在实际应用中具有更大的优势。此外,由图6(b)可知,Temkin 模型(RT = 0.998)拟合效果较好,表明吸附过程存在强静电作用或离子交换作用[23]。
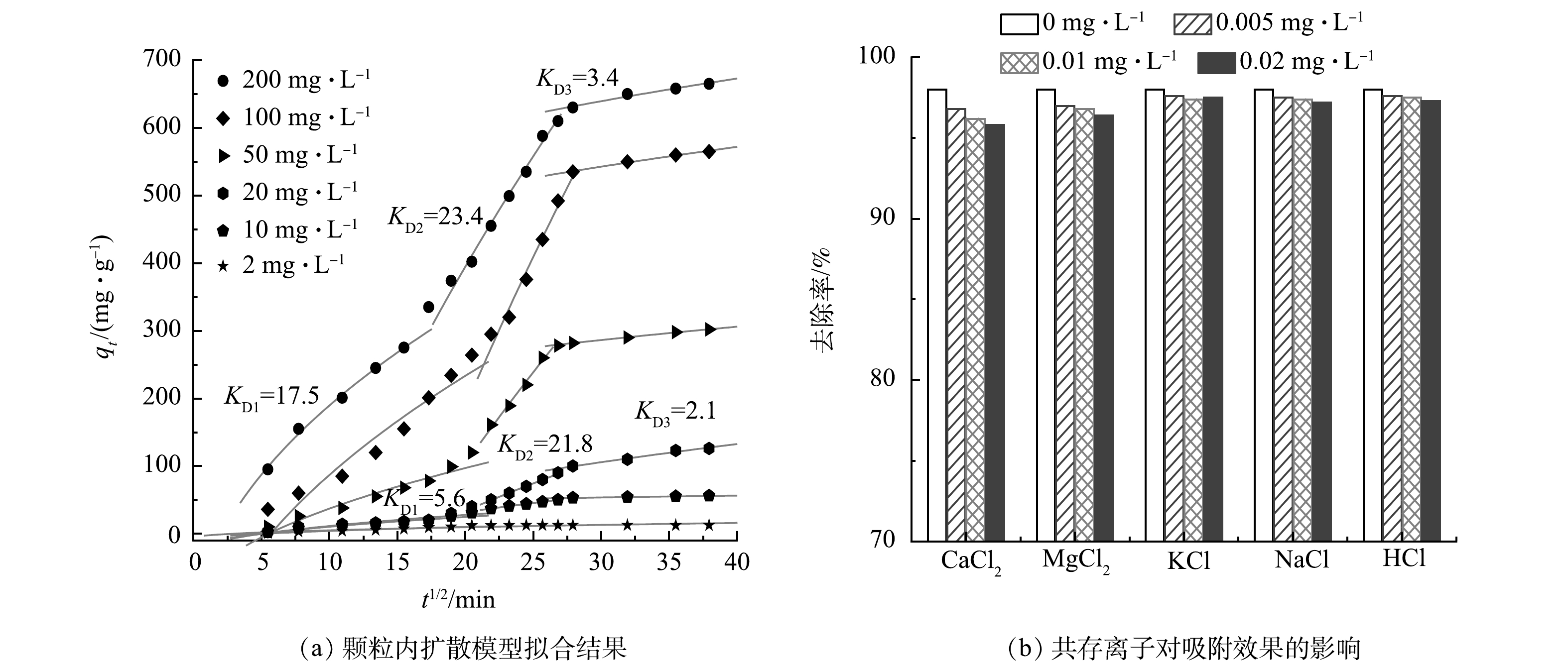
颗粒内扩散模型拟合结果如图7(a)所示,可以看出,不同TC初始质量浓度下,NPC对TC的吸附均可分为3个阶段。由于NPC在不同初始TC质量浓度下的颗粒内扩散模型模拟结果相似,故图7(a)中仅列出200 mg·L−1和10 mg·L−1的拟合数据。第1阶段为膜扩散过程,KD1较大,表明在电场作用与浓差驱动力协同作用下四环素快速扩散到NPC碳边界层;第2阶段为颗粒内大孔扩散过程,KD2明显增大,且与传统吸附模式相比要大很多,可能是因为近表面处碳网络的高导电作用和活性位点的高吸附效率,进一步增强了电极的吸附效率;第3阶段为颗粒内中孔和微孔扩散过程,传质阻力增大,导致吸附速率下降,且 KD3最小,表明此过程为控速步骤。但第2阶段和第3阶段拟合曲线均不通过坐标原点,表明颗粒内扩散不是唯一的控速步骤,吸附过程较为复杂[24]。NPC吸附四环素的速率可能由表面吸附、膜扩散和颗粒内扩散共同控制。
为进一步验证吸附过程的静电吸附作用,针对实际水体中有机污染物和无机金属离子的复杂性,研究了不同离子,尤其是硬度离子(0.005 、0.01 、0.02 mg·L−1的氯化钙、氯化镁、氯化钠和氯化钾溶液)与100 mg·L−1的TC共存时,NPC电极的电吸附容量。在CDI充放电循环步骤,即吸附和解吸过程中,在电位诱导过程中电负性TC或Cl−和正电性金属离子(Ca2+、Mg2+、Na+、K+)将分别储存在相对的带电电极侧,从而去除水中的离子污染物,达到净水的目的;当去除电压时,吸附的离子可以释放到溶液中,实现CDI电极的再生。如图7(b)所示,在不同离子共存的水体中,NPC对TC的去除率均略有下降,可能是共存离子Cl−在阳极上与TC的竞争吸附所致,共存的离子可通过屏蔽效应改变吸附质-吸附剂之间的静电作用,从而影响TC的吸附。
-
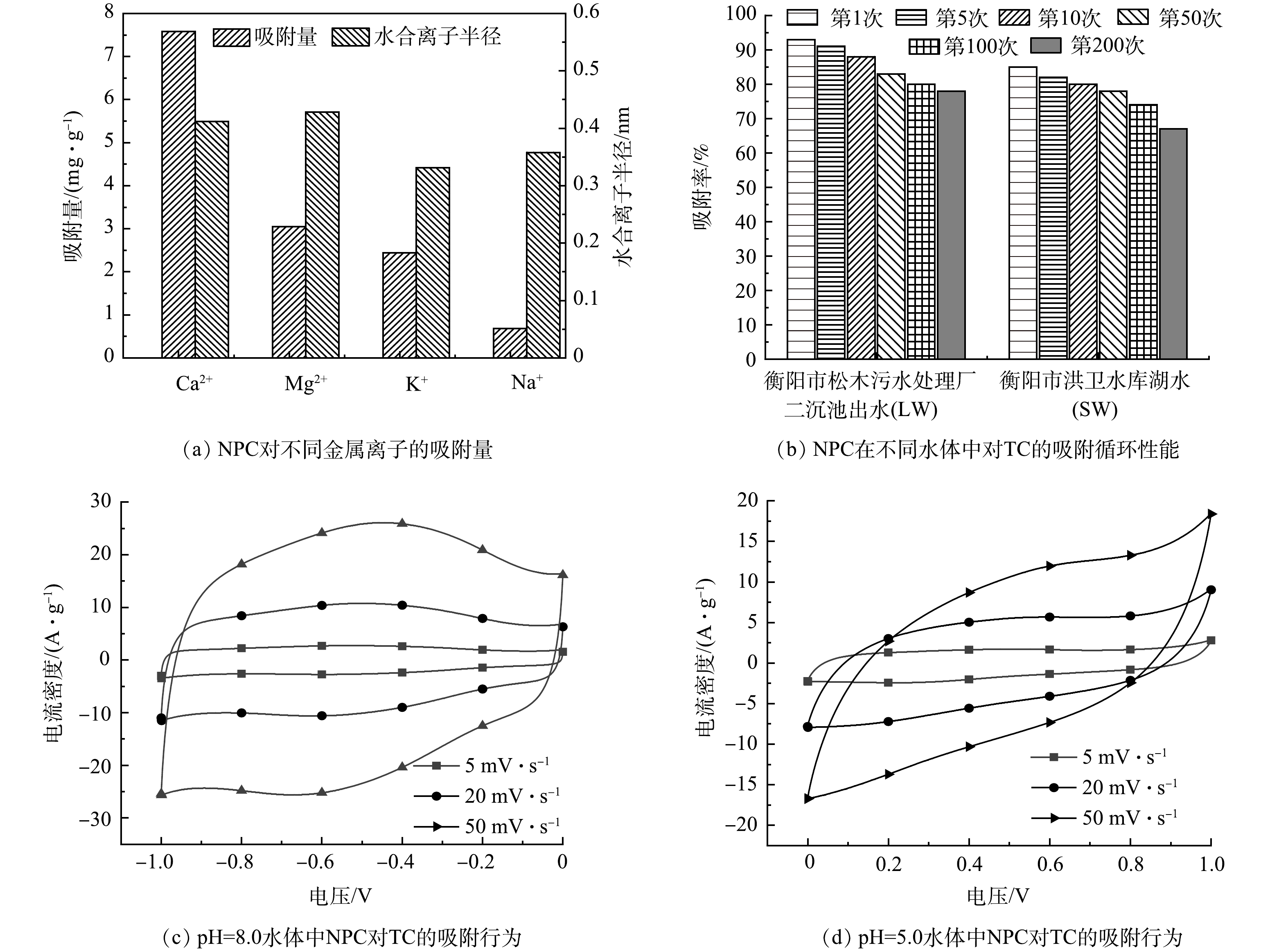
长期摄入自然水体中最常见的几种离子,包括Ca2+、Mg2+、Na+、K+等,会损害人体健康,尤其是Ca2+、Mg2+硬度离子会增加肾脏或肝胆疾病的发病率。因此,去除水中多余的有害离子是至关重要的。使用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP)测定处理液中残留金属离子的浓度,发现采用CDI技术电吸附水体中四环素的同时,可以在对电极同步去除这些阳离子[25-26]。图8(a)展示了4种离子的吸附容量和离子半径,金属离子共存时的优先离子吸附顺序为Ca2+ >Mg2+ >K+ >Na+,且Ca2+的电吸附容量(7.58 mg·g−1)高于Mg2+离子的电吸附容量(3.08 mg·g−1)。HOU等[27] 认为,对于价态相同的离子,较大的水合半径将导致较高的双电极层重叠,导致离子在电极的介孔结构中的扩散受到强烈限制。因此,较小的Ca2+离子在电吸附过程中表现出比Mg2+更好的亲和力。在不同电荷的Na+(单价阳离子)和Ca2+(多价阳离子)之间的比较发现,NPC电极更优先吸附高价阳离子Ca2+。这是因为高电荷离子会与带电表面产生强烈的库仑相互吸引作用,并有利于电极材料选择性地吸附高价离子[28]。上述结果证明,由于电吸附过程中的静电力比自吸附的静电力更强,高价和较小水合半径的离子更容易被吸收,而且离子价态对电吸附的影响远大于水合半径的影响。
为研究NPC在2种水体中(LW和SW)对TC的吸附性能,在TC初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1的条件下,探索NCP电极对TC的吸附-解吸循环再生性能,吸附效果如图8(b)所示。可以看出,第1次电吸附后,TC的吸附率分别为92.8%和87.6%。这表明NPC能够有效去除实际水体中TC的残留。在SW水体中的吸附率低于LW。这可能是污水中部分溶解性有机物吸附在NPC表面,与TC分子之间竞争碳表面的吸附位点导致的。在第200次的吸附-解吸循环再生后,吸附率略有下降,但仍能达到78.2%和67.5%,表明基于CDI技术的NPC电极具有良好的再生性能。
为研究不同酸碱值水体环境中TC的电吸附过程,在TC初始质量浓度为10 mg·L−1时,探索不同pH条件下NPC电极对TC的去除率。由图8(c)循环伏安曲线(CV)可以看出,在pH=8时,电极的CV曲线呈准矩形,且有明显的氧化还原峰,表明此过程既存在双电层吸附(物理吸附)也存在化学吸附。这可能是因为,pH>7.7时,在去质子化反应中,TC分子中的三羰基体系和酚二酮部分倾向于失去质子,导致形成TCH−或TC2-[29],使TC分子呈现电负性,可与CDI电极上的NPC产生强烈的吸附作用。图8(d)为pH=5时的水体CV曲线。可以看出,酸性环境下的CV曲线积分面积小于碱性环境下的,且无明显的氧化还原峰。原因可能是,pH为3.3~7.7时,TC分子以TCH2± 2种离子形式存在,较难被表面带正电荷的NPC活性位点吸附,吸附过程以双电层吸附(物理吸附)为主。天然水的pH通常为6.5~8.5,TC分子在水中呈电负性[11],因此,基于电容去离子技术,NPC对 TC分子可进行物理吸附和化学吸附协同作用,吸附效率高。
-
1) 基于绿色、简便法制备的手风琴状聚酰亚胺基多孔碳NPC,具有高活性氮含量和发达的介微孔结构,这些结构特点有助于提升NPC电吸附四环素的性能,并同步去除水体中的硬度离子。
2) 将NPC电极组装成CDI器件进行电吸附TC实验,结果表明,NPC电吸附TC的吸附容量高达854.3 mg·g−1,是传统自吸附的2.4倍(350.6 mg·g−1)。
3) 稳定的层次结构与高导电碳网络结构,协同增强了NPC电极的吸附稳定性、再生性和循环稳定性,使其在自然水体中200次吸-脱附后,吸附容量仍可保持78%以上。
4) 表征分析与模拟计算结果表明,NPC的电吸附过程包含物理吸附和化学吸附,在孔隙扩散、化学吸附与双电层吸附多种机制协同作用下,实现了对TC和硬度离子的高效去除。
5) NPC在不同水体中均表现出高效的TC吸附性能和同步去除水体中硬度离子的能力,在处理复杂水体污染领域具有广泛的应用前景。
氮掺杂多孔碳电极CDI技术对水中四环素和硬度离子的高效去除
Highly effective removal of tetracycline and water hardness ions by the CDI technology with nitrogen-doped porous carbon electrode
-
摘要: 为解决水体中过剩四环素 (tetracycline, TC)与水硬度离子(Ca2+和Mg2+)等共存带来的复杂环境污染问题,采用分散聚合法将含氮单体聚合成手风琴状碳前驱体并将其碳化后,制备得到氮掺杂多孔碳材料 (nitrogen-doped porous carbon, NPC),采用电容去离子技术考察了NPC电极同步去除不同水体、pH、初始浓度中TC和水硬度离子的能力。结果表明:Langmuir,Freundlich和Temkin模型对NPC样品电吸附TC的吸附等温线分别进行拟合,发现电吸附过程包含了化学吸附、强静电吸附和物理吸附等机制,吸附过程较为复杂;NPC独特的手风琴状层次结构,使得TC的电吸附容量高达854.3 mg·g−1,是传统自吸附的2.4倍 (350.6 mg·g−1);稳定的层次结构与高导电碳网络结构,协同增强了NPC电极的吸附稳定性、再生性和循环稳定性,使其在自然水体中经过200次吸-脱附后吸附容量仍可保持在78%以上。由此可知,基于CDI技术的氮掺杂多孔碳电极能够有效地同步去除水体中的四环素和硬度离子。该研究结果可为复杂水体污染处理提供参考。Abstract: To solve the complex environmental pollution problem caused by the coexistence of excess tetracycline (TC) and water hardness ions (Ca2+ and Mg2+) in water bodies, nitrogen-containing monomers were polymerized into accordion-like carbon precursors by the dispersion polymerization method, and then they were carbonized and nitrogen-doped porous carbon (NPC) was prepared accordingly. The ability of NPC electrode to remove TC and water hardness ions simultaneously under different water bodies, pHs and initial concentrations was investigated by capacitive deionization technique. The results showed that the Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin models were used to fit the adsorption isotherms for the electroadsorption of TC on NPC samples, respectively, and it was found that the electroadsorption process contained the mechanisms of chemisorption, strong electrostatic adsorption and physical adsorption, and the adsorption process was complex; the unique accordion-like hierarchical structure of NPC resulted in the electroadsorption capacity of NPC to TC as high as 854.3 mg·L−1, which is 2.4 times higher than that of conventional self-adsorption (350.6 mg·L−1). The stable hierarchical structure and high conductive carbon network structure synergistically enhanced the adsorption stability, regeneration and cycling stability of NPC electrode, so that its adsorption capacity could still be maintained at higher than 78% after 200 times of adsorption-desorption in natural water bodies. In conclusion, the nitrogen-doped porous carbon electrode based on CDI technology can effectively and simultaneously remove tetracycline and hardness ions from water bodies. The results of this study can provide an important reference for the treatment of complex water pollution.
-
Key words:
- tetracycline /
- water hardness ions /
- N-doped /
- accordion-like /
- hierarchically porous carbon
-
我国是跨国界河流最多的国家之一,其中的绝大部分为出境河流。2020年5月31日,国务院办公厅印发了《生态环境领域中央与地方财政事权和支出责任划分改革方案》(国办发﹝2020﹞13号),将跨国界水体污染防治确认为中央财政事权,由中央承担支出责任。鉴于跨国界河流的极端敏感性和新形势下日益突出的水环境风险问题[1],为确保跨国界河流的水环境安全,维护我国与邻国边境地区稳定,推动我国“一带一路”倡议的顺利实施,开展跨国界河流水环境风险防控及环境应急能力建设工作已迫在眉睫[2]。目前,国内学术界有关跨国界河流水环境风险防控及环境应急能力建设的研究尚未见报道。
1. 跨国界河流突发环境事件概况
我国跨国界河流主要分布于东北、西北和西南3大片区(见表1),“一带一路”陆上丝绸之路经济带基本位于跨国界河流流域。其中,东北片区跨国界河流有黑龙江、乌苏里江、额尔古纳河、鸭绿江、图们江、绥芬河;西北片区有额尔齐斯河—鄂毕河、伊犁河、塔里木河等;西南片区有伊洛瓦底江、怒江—萨尔温江、澜沧江—湄公河、雅鲁藏布江—布拉马普特拉河、巴吉拉提河(恒河)、森格藏布河(印度河)、元江—红河等[3]。2005年以来,由生态环境部调度的跨国界河流突发环境事件共8起。如2005年松花江污染事件[4],2016年新疆额尔齐斯河汞污染事件,2016年新疆伊犁河柴油泄漏事件,2020年黑龙江伊春鹿鸣矿业尾矿库泄漏事件[5]等。这些突发环境事件动辄影响数百甚至上千千米河段,对出境断面水质造成严重威胁,引起国内外的广泛关注。
表 1 我国主要跨境河流情况表Table 1. Table of major cross- border rivers in China序号 河流名称 境内河流长度/km 流域 省份 涉境外国家(相邻) 1 额尔古纳河 1 305 松花江流域 内蒙古自治区 蒙古国、俄罗斯 2 黑龙江 1 938 松花江流域 黑龙江省 俄罗斯 3 松花江 2 305 松花江流域 内蒙古自治区、吉林省、黑龙江省 俄罗斯 4 第二松花江 900 松花江流域 吉林省 俄罗斯 5 乌苏里江 516 松花江流域 黑龙江省 俄罗斯 6 绥芬河 276 松花江流域 吉林省、黑龙江省 俄罗斯 7 图们江 552 松花江流域 吉林省 朝鲜 8 鸭绿江 847 辽河流域 吉林省、辽宁省 朝鲜 9 红河 695 西南诸河流域 云南省 越南 10 李仙江 487 西南诸河流域 云南省 越南 11 勐拉河 179 西南诸河流域 云南省 越南 12 澜沧江 2 213 西南诸河流域 云南省 老挝 13 怒江 2 132 西南诸河流域 云南省 缅甸 14 独龙江 184 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区、云南省 缅甸 15 大盈江 197 西南诸河流域 云南省 缅甸 16 瑞丽江 387 西南诸河流域 云南省 缅甸 17 雅鲁藏布江 2 341 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区 印度 18 康布麻曲 95 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区 不丹 19 洛扎雄曲 131 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区 不丹 20 娘江曲 133 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区 不丹 21 西巴霞曲 431 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区 印度 22 察隅河 306 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区 印度 23 朋曲 418 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区 尼泊尔 24 森格藏布(狮泉河) 524 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区 印度 25 朗钦蔵布 404 西南诸河流域 西藏自治区 印度 26 额敏河 266 西北诸河流域 新疆维吾尔自治区 哈萨克斯坦 27 伊犁河 555 西北诸河流域 新疆维吾尔自治区 哈萨克斯坦 28 额尔齐斯河 665 西北诸河流域 新疆维吾尔自治区 哈萨克斯坦 跨国界河流突发环境事件时有发生且极端敏感,主要原因有如下3点。1)我国是世界上跨界河流最多的国家之一。2)我国边疆地区整体经济落后,大部分地区还是以粗放型经济增长方式为主。如东北片区产业主要为石油化工、煤化工、制药等行业,西北片区主要为采矿、制药、煤化工等行业,西南片区主要为采矿、冶炼等行业,流域突发环境风险高。3)生态环境问题已成为国际履约中的敏感议题,跨国界河流水资源、水污染等关系到国计民生,成为国际与公众普遍关注的问题。因此,跨国界河流一旦发生突发环境事件,如处置不力,势必影响到我国的“一带一路”倡议相关部署,在国际社会造成严重负面影响。
2. 跨国界河流突发环境事件处理中的问题与短板
1)跨国界河流流域水环境风险底数不清。跨国界河流大多地处经济发展相对落后地区,生态环境保护底子薄弱,流域水文、水生态环境、产业结构与布局等基础信息不足,流域水环境风险底数不清。同时,突发环境事件大多由生产安全事故、危化品运输事故等衍生,诱因呈现复杂化、多元化态势,其发展难以精确预测,更增加了流域水环境风险摸清家底的难度[6]。
2)跨国界河流流域水环境风险防控与应急体系尚未建立。与非跨界河流相比,跨界河流突发环境事件发生后,污染强度大、跨度广,污染团迁移速度快,应急处置措施需在较短时间内实施。同时,大多数跨国界河流无闸坝或水库等水工构筑物,无法采用水利调度方法稀释污染团,这对流域水环境风险防控工程提出更高要求。目前,我国跨国界河流流域总体尚未建立水环境风险防控工程并形成相关机制[7]。流域性突发环境污染事件发生时,往往只能采取临时决策应对、临时建设处置设施等办法,但采取临时方法耗时长、难度大,且极易贻误时机,从而造成大量人力、物力、财力损失。
3)跨国界河流流域水环境监控预警及应急监测能力薄弱。由于经济发展与地理位置限制,跨国界河流所处地区应急监测能力总体较弱,应急监测设备、车辆少,现有应急监测设备存在普遍老化,难以满足应急监测等问题。同时,环境应急机构和人员配备不足,且缺乏环境应急指挥调度信息化平台,相关机构和人员的环境应急专业能力亦亟待提高。在监控预警能力方面,现有自动站监测指标仅有常规五参数,不含重金属等流域重要风险源特征污染物指标,无法实现流域特征污染物指标的监控预警[8]。
4)跨国界河流流域环境应急物资保障体系薄弱。环境应急物资保障是环境应急管理体系中至关重要的一环。除西北片区部分跨国界河流建设有环境应急物资库外,其他片区尚无专属物资库。跨国界河流长,区域物资运输半径大,若未针对流域风险源特征及分布建立相应的应急物资储备库和物资调度机制,一旦发生突发环境事件,需长距离紧急调运应急物资,成本极高,亦很难及时保障。同时,因相应地方财政资金短缺,已建成的跨国界河流物资库无法保障长期稳定运行。
3. 建议
1)全面开展跨国界河流突发性环境风险评估。针对出境跨国界河流,应探明流域重点工业企业、工业园区、尾矿库等固定环境风险源,危化品道路及管道运输等移动环境风险源及敏感目标的种类以及分布,绘制流域“突发环境风险一张图”[9]。针对入境跨国界河流,应开展流域突发环境风险预警工作,通过卫星遥感、水质在线监测等手段,预警预报可能影响入境河流水质的情况。
2)建立“一河一策一图”水环境风险防控工程体系。建议由生态环境部统筹,推动跨国界河流地区践行“以空间换时间”的“南阳实践”的经验做法[10],在流域风险评估基础上,探明环境风险源下游可用于截流、引流、导流、贮存污染物的场地,以及可用于应急处置的桥梁、闸、坝等环境应急基础设施;在此基础上,编制有针对性的跨国界河流流域环境应急预案,建设风险防控工程,形成“一河一策一图”电子化成果,实现应急处置从“被动应对”到“主动防控”的重大转变。
3)提升跨国界河流水环境风险防控与环境应急能力。建议由生态环境部牵头,编制跨国界河流水环境风险防控与环境应急能力建设规划。应推动跨国界流域环境应急队伍、机构建设;按“老旧更新、补齐备足”、“适当超前”的原则,加强应急监测、流域监控预警等方面的基础能力建设;应建设国家跨国界河流水环境应急信息化平台,全面提升跨国界河流水环境风险防控与环境应急能力[11]。
4)建立跨国界河流水环境应急物资储备管理体系。建议由生态环境部统筹,根据跨国界河流流域水环境风险特征,推动地方优化环境应急物资类别及配置,并开展物资储备库建设[12-13]。应按照事权划分,在流域内重点风险区域加强应急物资储备、区域布局和调度保障,由国家、地方政府和企业协同实施。此外,还应完善全国环境应急物资信息库建设与管理,借鉴并依托现代物流模式或企业,建立高效的应急物资储备及调度体系。
-
表 1 2种实际水体的水质参数
Table 1. Water quality parameter of two water samples
样品 COD/(mg·L−1) TP/(mg·L−1) NH4+−N/(mg·L−1) NO3−−N/(mg·L−1) NO2−−N/(mg·L−1) 色度/度 pH 衡阳市松木污水处理厂二沉池出水(SW) 29.28 0.587 2.457 4.988 0.102 9 7.35 衡阳市洪卫水库湖水(LW) 10.32 0.294 0.047 0.54 0.258 6 7.05 -
[1] DANNER M C, ROBERTSON A, BEHRENDS V, et al. Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 664: 793-804. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.406 [2] 蒋海燕, 段毅, 刘宇琪, 等. 煅烧高岭土活化过一硫酸盐去除废水中的四环素[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(9): 2494-2505. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202003163 [3] SUN N, ZHOU H, ZHANG H, et al. Synchronous removal of tetracycline and water hardness ions by capacitive deionization[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 316: 128251. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128251 [4] HU F, LUO W, LIU C, et al. Fabrication of graphitic carbon nitride functionalized P-CoFe2O4 for the removal of tetracycline under visible light: Optimization, degradation pathways and mechanism evaluation[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 274: 129783. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129783 [5] 韩歆宇, 刘志, 王琪, 等. 共价三嗪多孔聚合材料对水中四环素的吸附行为及其机理[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(9): 2995-3002. [6] AHN M K, CHILAKALA R, HAN C, et al. Removal of hardness from water samples by a carbonation process with a closed pressure reactor[J]. Water, 2018, 10(54): w10010054. [7] LIU Y, NIU Q, ZHU J, et al. Efficient and green water softening by integrating electrochemically accelerated precipitation and microfiltration with membrane cleaning by periodically anodic polarization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 449: 137832. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.137832 [8] GABRIELLI C, MAURIN G, FRANCY-CHAUSSON H, et al. Electrochemical water softening: Principle and application[J]. Desalination, 2006, 201(1): 150-163. [9] WERNER J J, ARNOLD W A, MCNEILL K. Water hardness as a photochemical parameter: Tetracycline photolysis as a function of calcium concentration, magnesium concentration, and pH[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(23): 7236-7241. [10] LIU T, SERRANO J, ELLIOTT J, et al. Exceptional capacitive deionization rate and capacity by block copolymer-based porous carbon fibers[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(16): eaaz0906. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz0906 [11] JIN J, YANG Z, XIONG W, et al. Cu and Co nanoparticles co-doped MIL-101 as a novel adsorbent for efficient removal of tetracycline from aqueous solutions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 650: 408-418. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.434 [12] 刘子龙, 侯晓楠, 郭丰志, 等. 金属盐对阴离子表面活性剂紫外吸收特性的影响[J]. 应用化工, 2022, 51(5): 1330-1334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2022.05.022 [13] 刘总堂, 邵江, 李艳, 等. 碱改性小麦秸秆生物炭对水中四环素的吸附性能[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(8): 3736-3743. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.08.031 [14] JIN J, SUN K, WANG Z, et al. Effects of chemical oxidation on phenanthrene sorption by grass- and manure-derived biochars[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 598: 789-796. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.160 [15] 王刚, 车小平, 汪仕勇, 等. 水溶性带电聚合物黏结剂修饰炭电极用于增强电容去离子性能[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1763-1771. [16] XIAO J, HU R, CHEN G. Micro-nano-engineered nitrogenous bone biochar developed with a ball-milling technique for high-efficiency removal of aquatic Cd(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 387: 121980. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121980 [17] LIN T, CHEN I W, LIU F, et al. Nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon of extraordinary capacitance for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Science, 2015, 350(6267): 1508-1513. doi: 10.1126/science.aab3798 [18] YANG M, ZHOU Z. Recent breakthroughs in supercapacitors boosted by nitrogen-rich porous carbon materials[J]. Advanced Science, 2017, 4(8): 1600408. doi: 10.1002/advs.201600408 [19] YANG H B, MIAO J, HUNG S F, et al. Identification of catalytic sites for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution in N-doped graphene materials: Development of highly efficient metal-free bifunctional electrocatalyst[J]. Science Advances, 2016, 2(4): e1501122. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1501122 [20] 魏红, 史刘敏, 钮金芬, 等. 荞麦皮生物炭对奥硝唑的吸附研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(11): 12-24. [21] WANG T, XUE L, LIU Y, et al. N self-doped hierarchically porous carbon derived from biomass as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of tetracycline antibiotics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 822: 153567. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153567 [22] 智丹, 王建兵, 周云惠, 等. 钛基锡锑阳极电化学氧化去除水中的四环素[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(1): 57-64. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201705098 [23] 占鹏, 胡锋平, 朱建华, 等. Fe-Cu/N共掺杂的ZIFs衍生材料活化过硫酸盐降解四环素[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(3): 187-196. [24] ALTUN T, ECEVIT H, KAR Y, et al. Adsorption of Cr(VI) onto cross-linked chitosan-almond shell biochars: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies[J]. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 2021, 12(1): 38. doi: 10.1186/s40543-021-00288-0 [25] NIE P, HU B, SHANG X, et al. Highly efficient water softening by mordenite modified cathode in asymmetric capacitive deionization[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 250: 117240. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117240 [26] ZHI S L, ZHANG K Q. Hardness removal by a novel electrochemical method[J]. Desalination, 2016, 381: 8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2015.12.002 [27] HOU C H, HUANG C Y. A comparative study of electrosorption selectivity of ions by activated carbon electrodes in capacitive deionization[J]. Desalination, 2013, 314: 124-129. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2012.12.029 [28] HOU C H, TABOADA-SERRANO P, YIACOUMI S, et al. Electrosorption selectivity of ions from mixtures of electrolytes inside nanopores[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2008, 129(22): 224703. doi: 10.1063/1.3033562 [29] MARTINS A C, PEZOTI O, CAZETTA A L, et al. Removal of tetracycline by NaOH-activated carbon produced from macadamia nut shells: Kinetic and equilibrium studies[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 260: 291-299. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.017 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: