-
氮元素过多会导致的水体富营养化问题,高效的氮素去除技术是当前研究热点[1-2] 。然而,生物法在处理污水时常会遇到系统不稳定和性能恶化等问题。生物强化技术成为改善污水生物处理系统运行效能有效方法[3],亦是研究重点[4]。TANG等[5]发现,向pH为6.5的系统中加入6% (质量分数) 的硝化菌后,可显著提高系统脱氮效率,NH4+-N去除速率由0.21 mg·(g·h)−1增加至mg·(g·h)−1; PATUREAU等[6]在除磷活性污泥系统中接种好氧反硝化菌,以实现系统在好氧阶段同时实现硝酸盐还原和磷去除;还有研究者在UASB反应器中接种Thiopseudomonas denitrificans X2后发现强化系统可同时去除有机物和含氮化合物[7]。生物强化技术在实际应用中存在引入功能菌失效的潜在风险,亦可能对生物系统产生负面影响。如何使强化菌株成功定殖并高效降解污染物是亟需解决的问题,群体感应 (quorum sensing,QS) 的发现为生物强化技术提供了新方向,可促进引入功能菌适应环境条件并改善与其他微生物的相互作用[3, 8]。酰化高丝氨酸内酯类(Acyl-homoserine lactones,AHLs)化合物是革兰氏阴性菌群体感应系统中最重要的一类信号分子,并调控许多生理特性的表达[9]。细菌可通过分泌和释放AHLs信号分子,来调控微生物功能并促进生物脱氮等过程[10-11]。
外源投加信号分子和群感菌是利用微生物群体感应现象强化污水生物脱氮的主要方法[12]。LI等[13]通过外源性添加AHLs以加速自养硝化污泥系统中硝化颗粒的形成。在众多类型的AHLs中,C6-HSL (N-己酰基-L-高丝氨酸内酯) 和C8-HSL (N-辛酰基-L高丝氨酸内酯) 在活性污泥工艺中占主导地位[14-17]。外源C6-HSL和C8-HSL明显提高了氮的去除效率,亦可调节EPS生成和微生物群落结构[13, 18-21]。冯惠[22]发现C6-HSL和C8-HSL可提升氨氮去除效能;同时长链AHLs如C12-HSL (N-十二烷酰-L-高丝氨酸内酯) 和C14-HSL (N-十四烷酰-L-高丝氨酸内酯) 等具有更强的疏水性、耐水解性和生物质黏附性,对于受基因调控的反硝化还原酶的活性也有显著影响[23],从而对生物脱氮有较好的促进效果[24-26]。因此,外源投加群体感应信号分子协同功能菌是解决单一功能菌效果不佳的有效方法。
以反硝化菌FX-4为研究对象,选取信号分子C6-HSL和C12-HSL,研究信号分子对反硝化菌FX-4NO3−-N去除性能的影响,以及两者协同作用下SBR系统脱氮性能。通过对菌株单独投加和混合投加,考察菌株的生长和作用效果,筛选出最优投加方式和浓度,随即将筛选出信号分子投入活性污泥系统,以未加信号分子组为空白对照,研究其脱氮性能的影响、实验前后信号分子浓度,并分析微生物群落优势菌群变化,以得出信号分子对生物脱氮的影响,从而为投加信号分子强化脱氮提供参考。
-
1) LB培养基。蛋白胨10.0 g∙L−1,酵母膏5.0 g∙L−1,NaCl 5.0 g∙L−1,pH 7.0,121 ℃灭菌20 min。驯化培养基:醋酸钠 3.6 g∙L−1,硝酸钾 1.44 g∙L−1,硫酸镁 g∙L−1,磷酸氢二钾 1 g∙L−1,微量元素 1mL∙L−1,氯化钠 2.5 g∙L−1,pH 7.0,121 ℃灭菌20 min。
2) 反硝化复筛培养基:乙酸钠1.8 g∙L−1,氯化钠2.5 g∙L−1,硝酸钾0.8 g∙L−1,磷酸氢二钾1 g∙L−1,硫酸镁0.1 g∙L−1,微量元素液1 mL∙L−1,pH 7.0,121 ℃灭菌20 min。
3) 微量元素液:EDTA 50 g∙L−1,硫酸锌2.2 g∙L−1,氯化钙5.5 g∙L−1,四水氯化锰5.06 g∙L−1,七水硫酸亚铁5 g∙L−1,四水钼酸铵1.1 g∙L−1,无水硫酸铜1.5 g∙L−1,六水氯化钴1.61 g∙L−1。
-
实验中选取的2种N-酰化高丝氨酸内酯类化合物(AHLs) 信号分子C6-HSL (己酰L-高丝氨酸内酯) 和C12-HSL (N-十二烷酰-L-高丝氨酸内酯) 均购自 Sigma-aldrich。AHLs有较好的水溶性。用纯水将其配制成0.1 g∙L−1的标准液,加入0.1% (体积分数) 的甲酸防止AHLs自身降解,于−20°C下保存备用[31]。
-
实验所用反硝化菌FX-4为假单胞菌属的Pseudomonas stutzeri,其具有良好的反硝化能力,由本课题组分离筛选。筛选过程:采用驯化培养基进行初筛,随后在反硝化复筛培养基中进行复筛,培养条件为30 ℃、150r·min−1、接种量为5%;对其进行生长特性、理化性质、信号分子及底物利用速率等生理生化性能的比较,选择生长代谢速率高、能大量消耗NO3-N的菌株参与本研究。该过程详见参考文献[32]。
-
本研究使用的接种污泥来自兰州城市污水处理厂的回流污泥。对其进行3 d的闷曝,期间定期加入适当营养盐,使其微生物生长达到最优水平,以有效适应合成污水进行后续实验。
-
1) 通过投加反硝化菌和信号分子影响活性污泥脱氮性能。实验初期,接种到反应器的污泥MLSS约为 3 210 mg∙L−1,将0.4 L污泥接种到1.6 L的SBR反应器中,按9 h一个循环周期 (依次是进水15 min、厌氧1.5 h、曝气5 h、缺氧1 h、沉降1 h和出水15 min) 在室温下运行。反应器进水采用的人工配水:乙酸钠0.5 g∙L−1,葡萄糖0.1 g∙L−1,氯化铵0.2 g∙L−1,磷酸二氢钾0.025 g∙L−1,硝酸钾0.15 g∙L−1,硫酸镁0.025 g∙L−1,氯化钠0.5 g∙L−1,微量元素液1 mL∙L−1。
2) 信号分子对反硝化菌FX-4反硝化性能影响。将反硝化菌FX-4菌悬液按5% (质量分数) 的接种量接种到LB培养基中,同时投加适量的信号分子 (C6-HSL、C12-HSL和C6-HSL+C12-HSL) 于LB培养基中。设置4组培养组:R0 (空白对照组) 、R1 (投加C6-HSL) 、R2 (投加C12-HSL) 、R3 (投加C6-HSL+C12-HSL) 。将LB培养基置于30 ℃、150 r∙min−1恒温振荡培养箱内培养3 d制成种子液。将种子液按5% (质量分数) 的接种量接种到含有100 mL反硝化复筛培养基的250 mL锥形瓶中,置于30 ℃、150 r∙min−1恒温振荡培养箱中培养5 d,每隔24 h无菌取样,在波长600 nm下测定菌体密度OD600,绘制反硝化菌FX-4的生长曲线,采用紫外分光光度法测定NO3−-N质量浓度并计算去除率,筛选出效果最佳的信号分子种类。在筛选出效果最佳的信号分子后,将反硝化菌FX-4菌悬液按5% (质量分数) 的接种量接种到LB培养基中,同时投加不同浓度的信号分子于LB培养基中,设置6组培养组其信号分子投加量分别为0、5 nmol∙L−1、50 nmol∙L−1、200 nmol∙L−1、500 nmol∙L−1和1 000 nmol∙L−1。将LB培养基置于30 ℃、150 r∙min−1恒温振荡培养箱内培养3 d制成种子液。将种子液按5% (质量分数) 的接种量接种到含有100 mL反硝化复筛培养基的250 mL锥形瓶中,重复上述操作。测定菌体密度OD600及NO3−-N质量浓度并计算去除率,筛选出效果最佳的信号分子浓度。以上每组实验设置3个平行实验。
3) C12-HSL信号分子对活性污泥系统脱氮影响。向7组有效体积1.6 L的SBR反应器内分别接入400 mL污泥和1200 mL污水,实验中反应器采用曝气泵头进行曝气。7组反应器分别为:R0 (空白对照组,未投加菌剂和信号分子) 、R1 (FX-4反硝化菌+0 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R2 (FX-4反硝化菌+5 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R3 (FX-4反硝化菌+50 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R4 (FX-4反硝化菌+100 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R5 (FX-4反硝化菌+200 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R6 (FX-4反硝化菌+500 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 。实验初期为投菌期,将反硝化菌FX-4接入反应器R1~R6中,每2 d投加一次种子液,驯化培养12 d,之后向反应器R1~R6投加0 nmol∙L−1、5 nmol∙L−1、50 nmol∙L−1、200 nmol∙L−1、500 nmol∙L−1、1000 nmol∙L−1的AHLs信号分子,前12 d每隔2 d投加一次信号分子,后10 d不投加,实验运行34 d,每天检测 TN、[NH4+-N]、[NO2−-N]、[NO3−-N]并计算各指标的去除率。
-
1) 常规指标的测定。实验中需要测定的常规指标有TN 、[NH4+-N]、[NO2−-N]、[NO3−-N]。[NH4+-N]采用纳氏试剂光度法测定,TN采用过硫酸钾氧化紫外分光光度法测定,[NO3−-N]采用紫外分光光度法测定,[NO2−-N]采用N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺光度法[33]测定。
2) 信号分子的检测。活性污泥中信号分子的检测采用高效液相串联质谱法检测。活性污泥样品在4 ℃下9 000 r∙min−1离心30 min,取上清液用0.45 μm微孔滤膜过滤,然后用等量含有0.5% (质量分数) 甲酸的乙酸乙酯进行萃取3次,将收集得到的上层有机相用氮吹仪吹干后,用100 μL甲醇定容[34]。预处理过后的水样采用HPLC-MS /MS进行检测。色谱条件如下:反相C18色谱柱 (50 mm×2.1 mm,3.5 μm; Waters Sunfire) ;流动相流速0.3 mL∙min−1;进样量10 μL,分析时间为10 min。质谱条件:采用电喷雾离子源正离子模式 (ESI+) ,多反应离子检测 (MRM模式) ,毛细管电压3.0 kV;锥孔电压30 V;载气高纯氮气 (99.999%) ;载气流速180 L∙h−1; 载气温度300 ℃;碰撞气高纯氮气 (99.999%) [34-35]。
3) 群落结构分析。微生物群落结构测定采用16SrRNA基因高通量测序进行检测[35]。污泥样品DNA的提取及PCR扩增采用PLFA法[36]。以上检测及分析均由广州美格生物科技有限公司完成。
-
将反硝化菌FX-4种子液和不同种类的信号分子投加在含100 mL反硝化复筛培养基的锥形瓶中,随着菌株生长,反硝化菌FX-4对NO3−-N的去除效果如图1所示。
在30 ℃、150 r∙min−1的恒温振荡培养下,投加信号分子12 h后,R1、R2和R3组的NO3−-N去除率明显提高且远高于R0,最大NO3−-N去除率约为94%左右。YAN等[37]也证明投加信号分子与生物脱氮过程密切相关,并且可以有效促进脱氮过程;R2和R3对NO3−-N的去除效果几乎一致,均在36 h后达到最佳去除效果且效果持续稳定,在84 h后开始出现下降;R1在60 h去除率才达到最大值,且对NO3−-N的去除效果相对于R2稍差。但LI[13]等观察到,与其他类型的AHLs相比,添加C6-HSL的反应器显示出最高的氨降解速率,这说明C6-HSL对脱氮效果的主要影响不是体现在NO3-N的去除上。以上结果表明投加信号分子可优化反硝化菌FX-4,使其消耗NO3−-N的性能大大提高;R2和R3对NO3−-N去除情况相似,并且都比R1优先达到NO3−-N去除率最大值。这说明C12-HSL比C6-HSL起作用时间更迅速,作用效果更稳定,去除效果更好。因此,可确定C12-HSL能较大程度提升菌株FX-4去除NO3−-N能力。
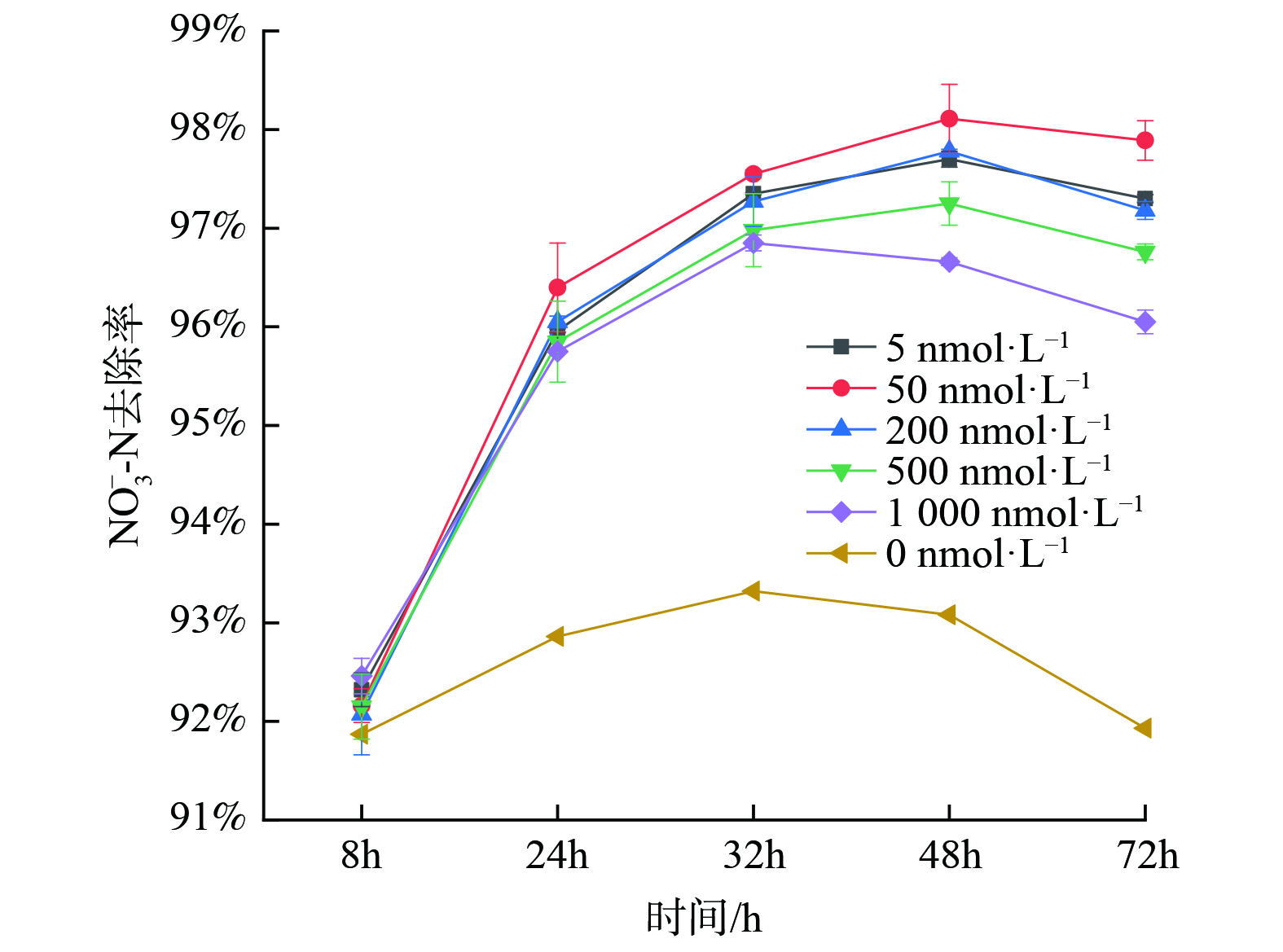
随后对不同C12-HSL浓度梯度下的去除效果进行了分析,结果如图2所示。不同浓度梯度的C12-HSL对反硝化菌FX-4的NO3−-N去除效果均有促进作用。相比于空白对照组,NO3−-N的去除率明显提高且均大于95%。其中,信号分子浓度在50 nmol∙L−1对菌株的强化效果最好,去除率高达98%;5 nmol∙L−1和200 nmol∙L−1的去除效果较为相近;而投加浓度更高的2组去除效果反而没有较低投加量的效果显著。胡惠秩[31]也发现在AHLs添加浓度较低时,系统的处理效率更高,而AHLs添加浓度较高时,系统处理效果略微受到抑制。
-
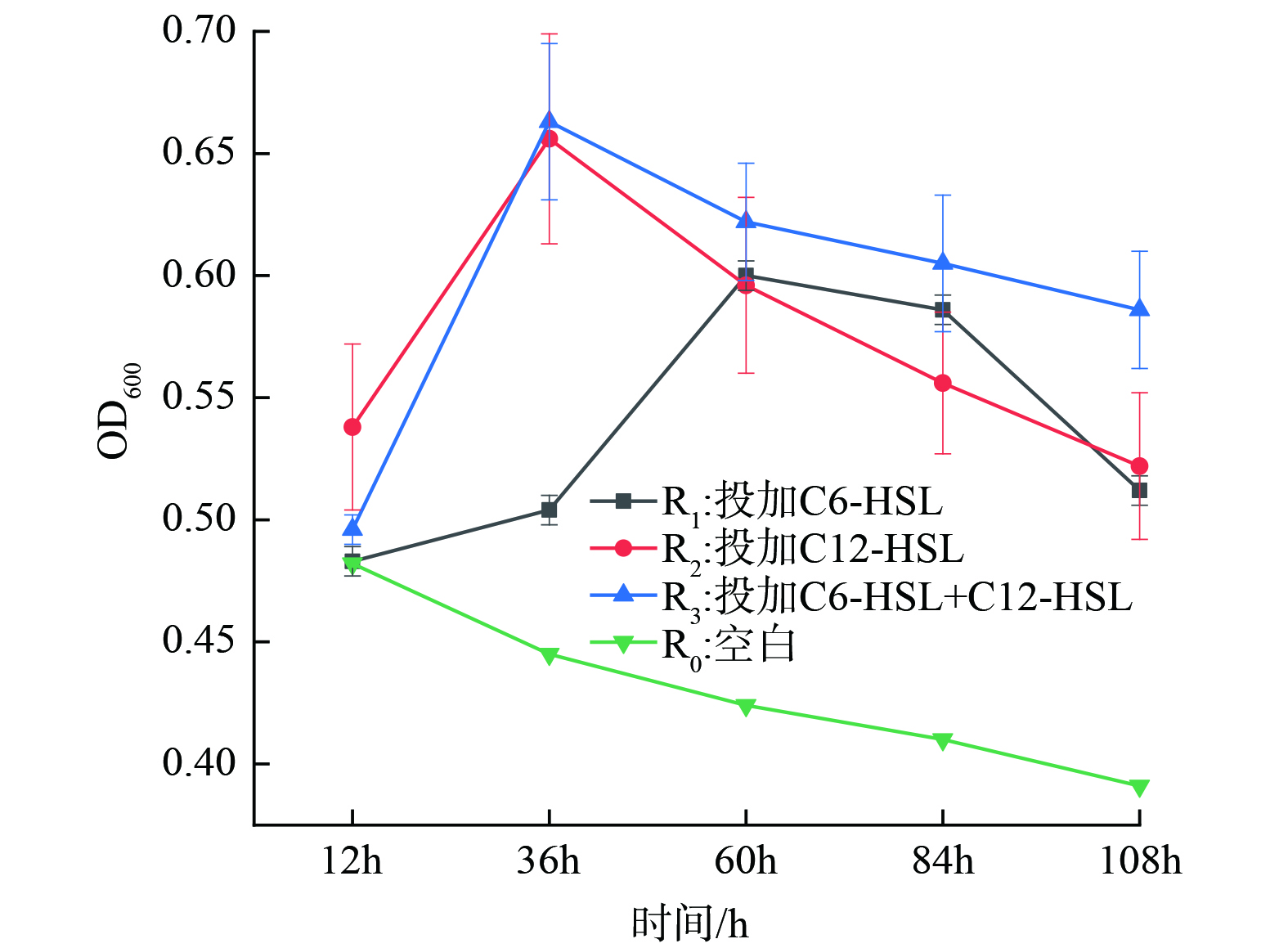
将反硝化菌种子液按5% (质量分数) 接种量接种至100 mL反硝化复筛培养基中,在投加不同种类的信号分子后,菌株的生长情况及NO3−-N去除效果如图3所示。微生物生长在12 h后,信号分子开始发挥作用,R1、R2和R3组反硝化菌生长情况明显优于R0组。外源添加AHLs不仅可增加生物量密度,还可提高反硝化细菌的生物活性[21],而本研究结果更验证了这一结论。在36 h时,R2和 R3的菌群密度达到最大值,OD600分别达到0.656和0.663,并且进入平稳生长阶段。随后在生长60 h后,菌群密度逐渐降低。这是由于培养基中营养物质被消耗完全,菌群生长进入衰老期;R1组在60 h菌群生长密度达到最大值。结果还表明,投加信号分子使反硝化菌FX-4微生物量显著上升,在R1组中,C6-HSL起作用的时间较长,几乎是R2和R3组2倍。同时,在R2和R3组对比下,二者反硝化菌生长情况及NO3−-N消耗情况几乎一致,于是经分析得出结果是C12-HSL对反硝化菌FX-4生长代谢情况影响更显著。
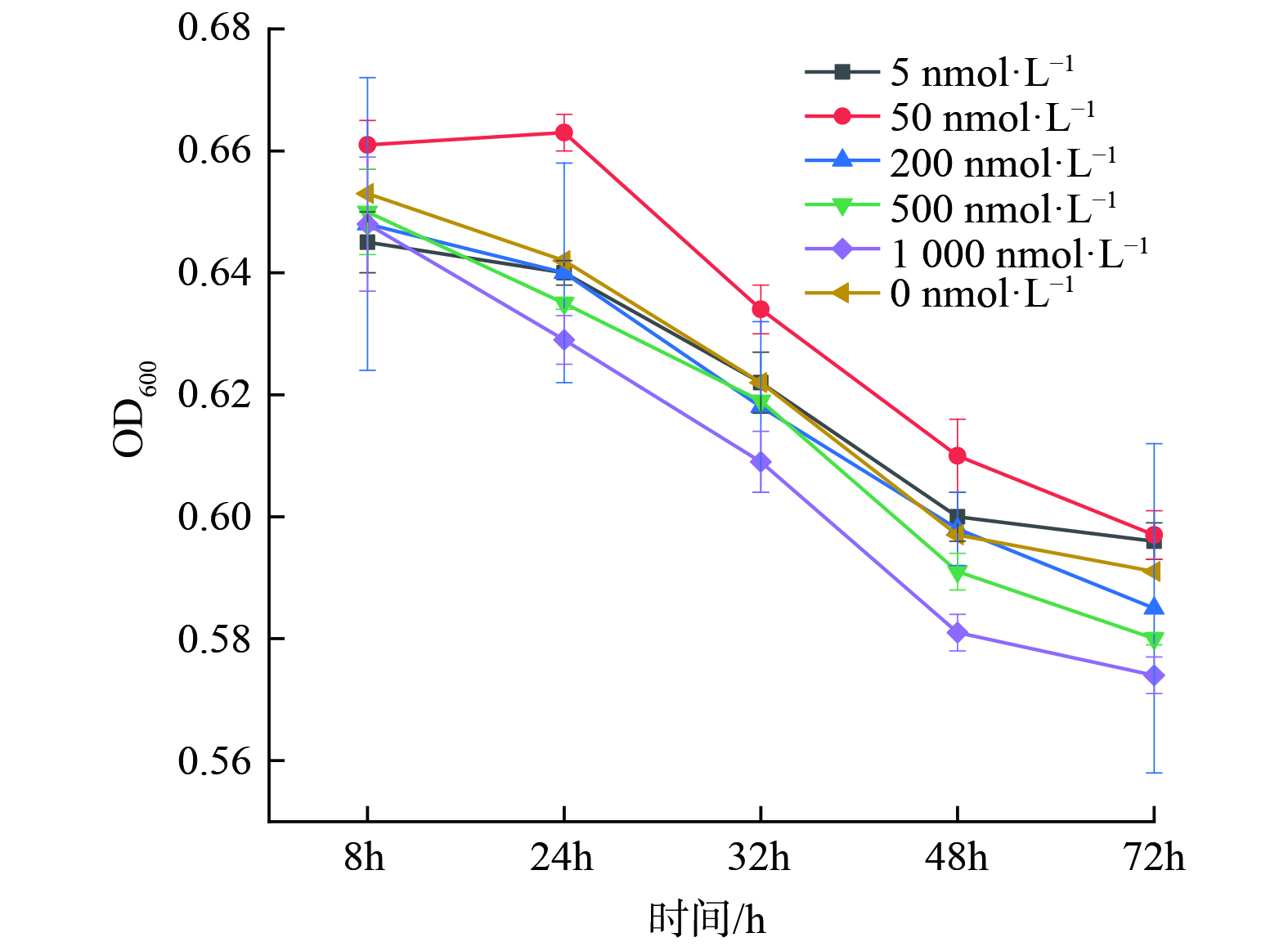
随后展开投加不同浓度C12-HSL后反硝化菌处理效果的实验,结果如图4所示。当信号分子浓度为50 nmol∙L−1时,反硝化菌生长情况最好且菌群密度明显高于未投加信号分子组。同时,当投加较高浓度 (200 nmol∙L−1、500 nmol∙L−1、1000 nmol∙L−1) 的组生长情况弱于不投加组,这说明投加信号分子最合适的投加浓度为50 nmol∙L−1,且信号分子浓度过高会对反硝化菌生长有抑制作用。胡惠秩[31]也发现外源性AHLs浓度对系统的影响不是一种简单的线性关系,低浓度AHLs促进微生物的增长,而高浓度AHLs会抑制微生物生长。针对该现象,TAIT等[38]的解释是细菌群落附近如果存在大量外来AHLs信号分子持续时间过长会限制细菌群落对环境变化的响应能力。
-
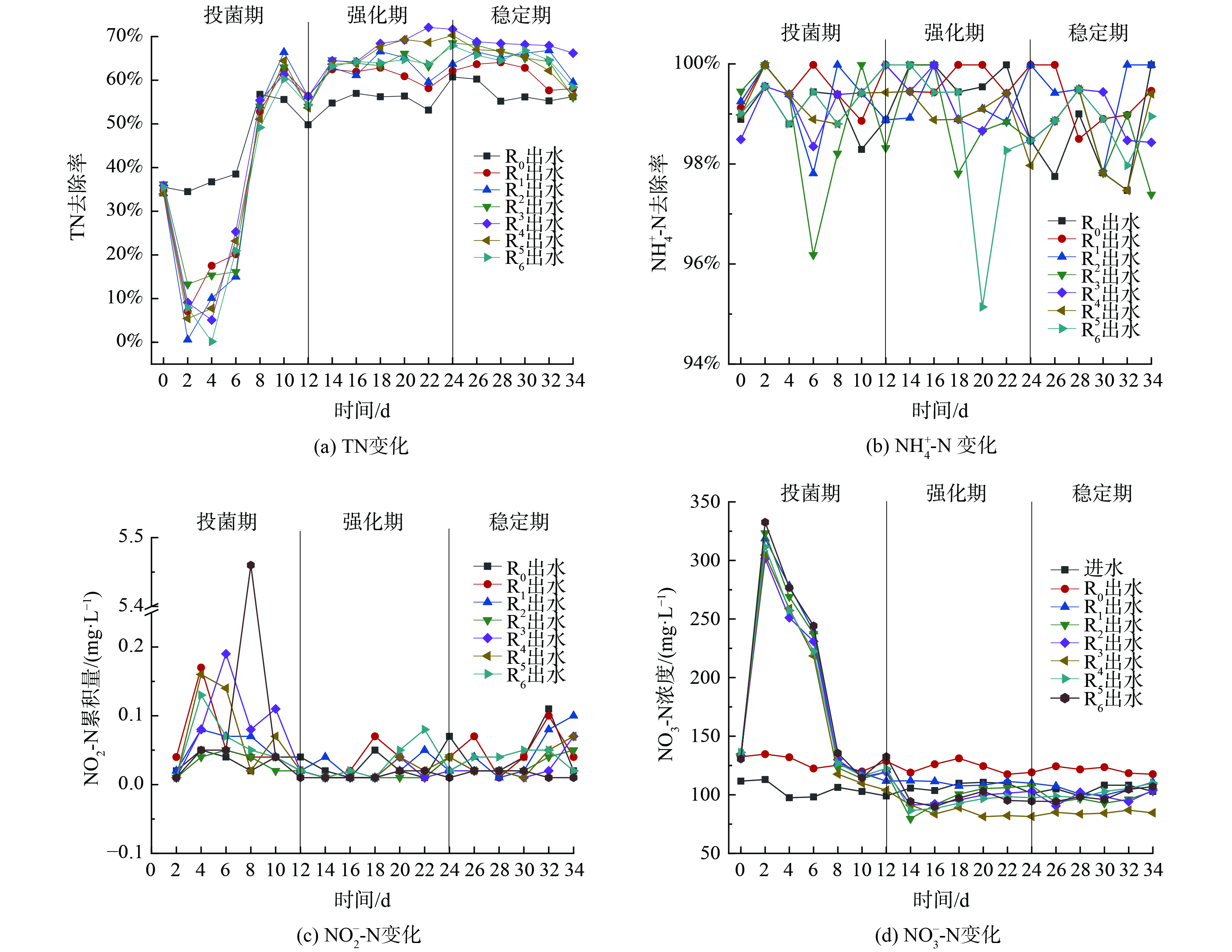
取兰州市城市污水处理厂剩余污泥闷曝3 d,其间定期投加一定营养,结束后分别添加到反应器中。在反应器启动运行后,为研究反硝化菌FX-4协同信号分子对SBR反应器脱氮效果的影响,将实验初的0~12 d为投菌期。每2 d在反应器R1~R6中投加1次反硝化菌FX-4种子液,共驯化培养12 d。之后,将12~24 d定为信号分子强化阶段,每隔2 d向反应器R1~R6投加1次不同浓度梯度的AHLs信号分子 (C12-HSL) 。将24~34 d设为稳定期,此期间系统持续稳定运行。系统的运行效果如图5所示。
在投菌期 (1~12 d) ,R1~R6的TN去除效果较差并低于未投加菌株的R0。R1~R6反应器中[NO3−-N]大幅增加。这可能是由于外源菌的加入,系统竞争激烈,同时种子液也含有菌种未代谢完的含氮有机物,增加了系统氮负荷,故表现出脱氮不佳现象。在强化阶段 (11~24 d) ,向反应器R1~R6中投加不同浓度信号分子,以调控污泥中的微生物从而提升反应器脱氮性能。在投加信号分子阶段,R1~R6组的[NO3−-N]并没有大幅变化,而当反应器R4中投加浓度100 nmol∙L−1的信号分子后,NO3−-N去除效果优势较明显;而R1~R6反应器的TN 去除率均显著提高,这说明投加C12-HSL可有效提升系统的脱氮性能。其原因是外源投加AHLs可有效提高系统生物量同时刺激微生物自身AHLs的生成。衣隆强等[23]也发现添加外源AHLs可提前达到能刺激QS机制的胞外AHLs浓度,从而强化QS的控制功能,与本研究结果一致。在稳定运行阶段 (24~34 d) ,R1~R6的TN去除情况趋于稳定,去除率为60%~70%,但相对于强化阶段效果略有降低。[NO3−-N]几乎不累积的原因可能是外源信号分子反应完毕,故导致反硝化过程进行有所缓慢。整个运行过程中,随着外源添加菌株和不同浓度信号分子,[NO3−-N]不断变化,R1~R6呈现不同的TN去除效果。尽管R0~R6反应器对TN的去除呈现相似的变化趋势,但R0的平均TN去除率65.53%与R1组的66.00%对比说明,R1的处理效果更好。这表明投加反硝化菌FX-4后NO3−-N被大量消耗,累积量减少,从而促进了TN去除。同时,当投加信号分子浓度为100 nmol∙L−1时,R4在运行20 d后呈现较好的脱氮能力,TN去除率达72.08%比对照组R0组和R1组高出8.93%。而信号分子投加浓度偏高的R5和R6组脱氮效果略差于R0组,这表明添加合适浓度的信号分子可增强活性污泥的脱氮效果,但过高的信号分子浓度投加会使系统脱氮效果受到抑制。
图5 (b) 和 (c) 表明R0~R6反应器各阶段的NH4-N平均去除率均大于95%,且NO2−-N几乎不存在积累。在整个运行过程中,尽管反应器中外源投加了菌株和信号分子,但都没有影响反应器对NH4+-N的良好去除,并且NO2−-N累积量极少。这说明外源投加反硝化菌FX-4和信号分子不会对系统其他污染物的去除产生不利影响。
-
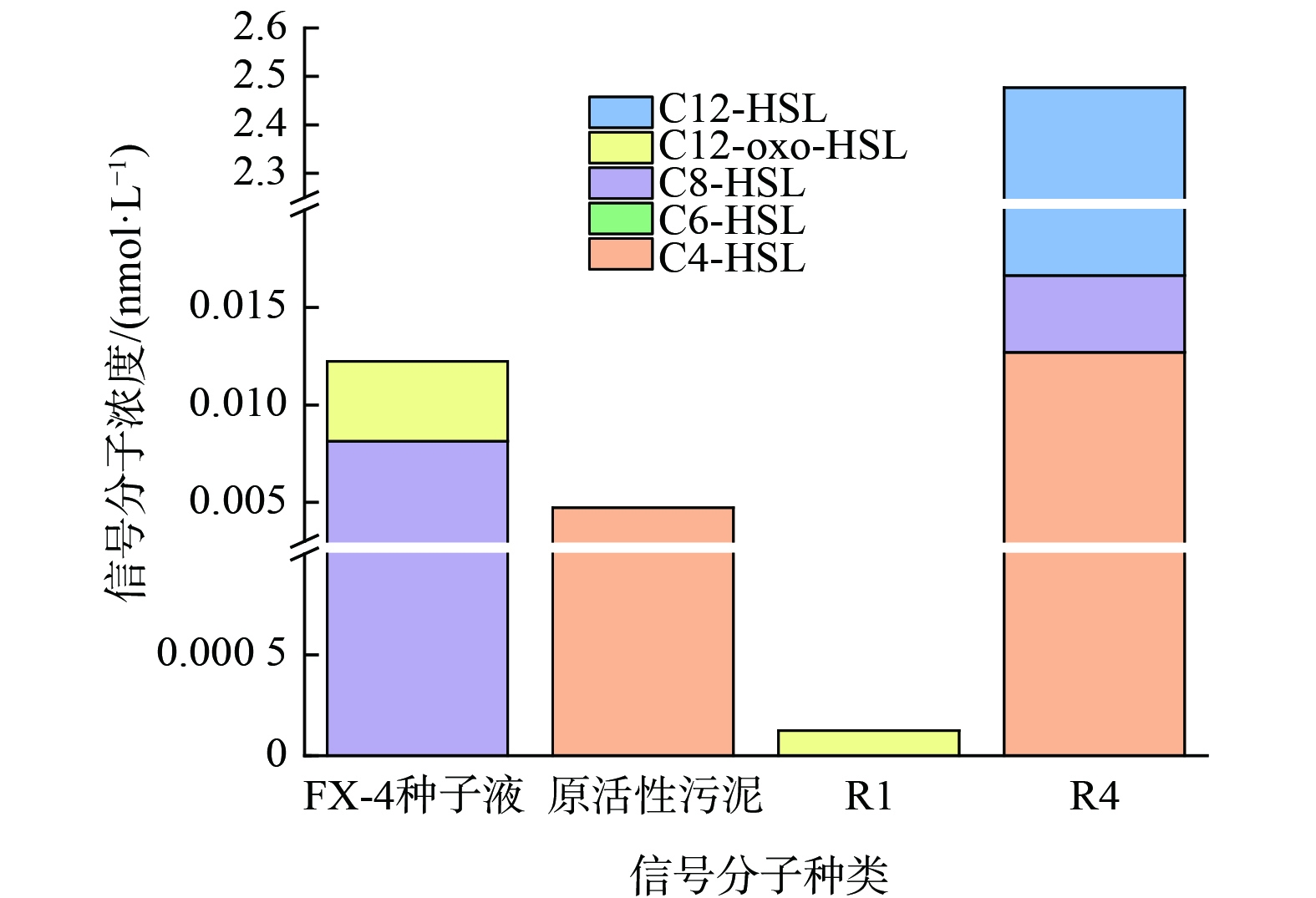
分别对反硝化菌FX-4种子液、实验开始时期原活性污泥、投菌定殖之后的R1及投加过信号分子脱氮效果良好的R4进行取样,并对其信号分子种类和浓度进行监测,反应器内信号分子的变化结果如图6所示。
反硝化菌FX-4自身分泌的信号分子有C8-HSL和C12-oxo-HSL。在原活性污泥中,信号分子浓度较小,只检测到C4-HSL。在投菌阶段,反硝化菌FX-4种子液投加到活性污泥中,活性污泥中的信号分子浓度降低,在R1中只检测到少量C12-oxo-HSL,C4-HSL和C8-HSL消失。分析其原因可能是反硝化菌FX-4与活性污泥中的土著菌群存在竞争关系导致其定殖未完成,此阶段信号分子种类及浓度下降。在强化阶段,反硝化菌FX-4定殖后的污泥中继续投加信号分子C12-HSL,R4组信号分子总量显著升高,特别是C12-HSL浓度大量增加,C8-HSL和C4-HSL又重新出现,且C4-HSL浓度明显较原活性污泥和R1组高。分析其原因是在外源投加了C12-HSL的同时,促进了系统内部微生物自身分泌,从而产生了大量信号分子。这说明反硝化菌FX-4定殖完成后,活性污泥系统重新达到平衡,当信号分子C12-HSL达到一定浓度后,激发活性污泥中微生物自身分泌信号分子表达,诱发了群体感应现象。结合此前实验中R4组较好的脱氮效果,微生物群落感受到系统分泌产生的AHLs后,促进不同功能菌群响应,从而提高脱氮效果。因此,信号分子C12-HSL不仅与脱氮效能密切相关,且投加C12-HSL还可促进反应器活性污泥内部微生物分泌大量内源信号分子。特别是C4-HSL和C8-HSL,推测这两种信号分子与系统脱氮性能的提高也存在一定关联。
-
为研究外源添加信号分子C12-HSL对SBR反应器活性污泥中微生物群落结构的影响,分别对原活性污泥的R0组、投加反硝化菌FX-4后的R1组及外源投加信号分子C12-HSL的R4组进行高通量测序并对其微生物群落变化进行分析。
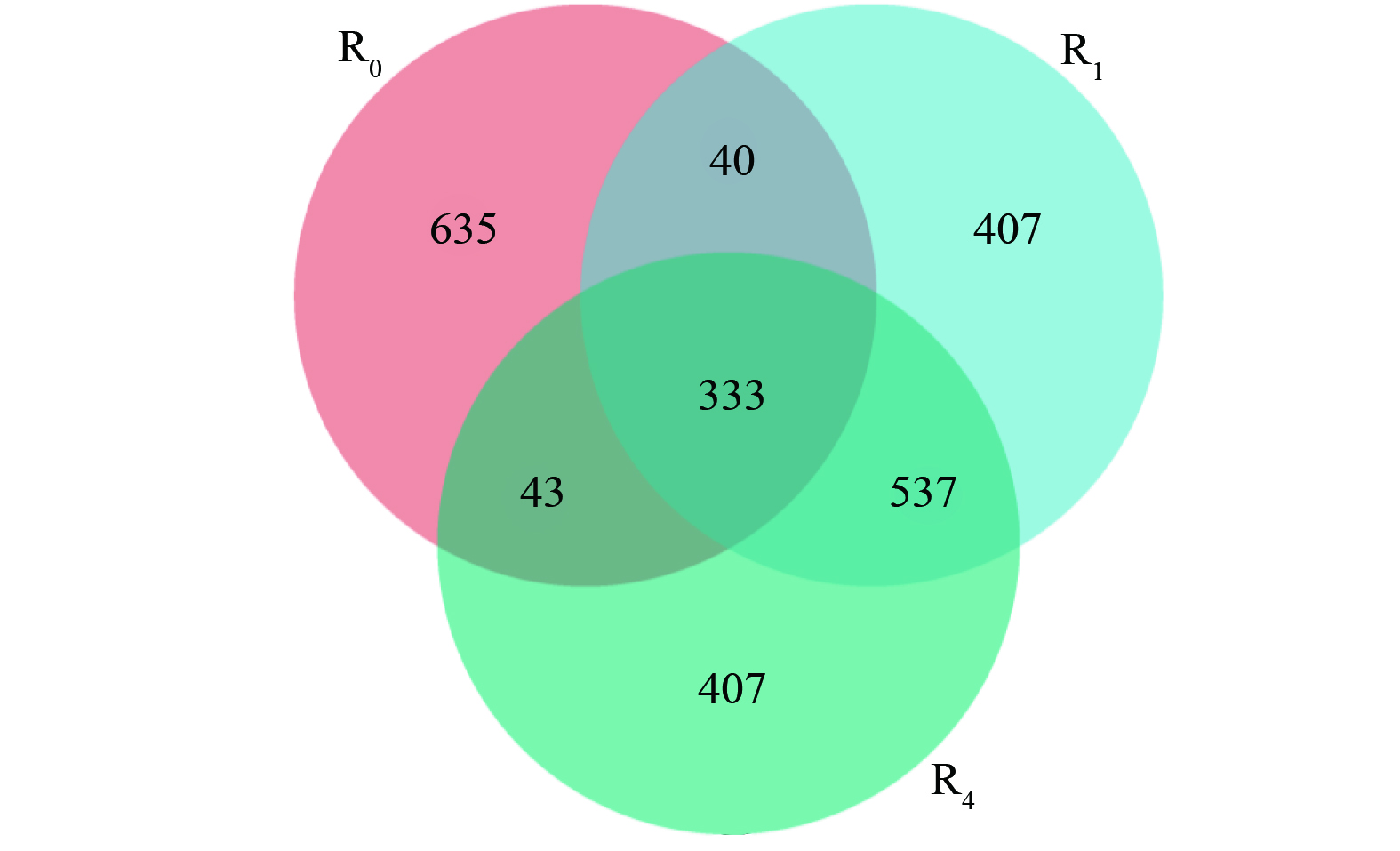
具有共享和唯一OTU的维恩图如图7所示。333个OTU中的大多数在3个样本中共享,分别占31.68% (R0) 、25.28% (R1) 和25.23% (R4) 。这说明活性污泥中微生物种群的物种丰富度和多样性在通过投菌和外源投加信号分子之后都得到了显著提高。YAN等[37]通过研究外源投加AHLs对SBR反应器运行的影响也发现,微生物群落丰富度指数会随着AHLs剂量的增加而增加。
反应器R0、R1和R4的Alpha多样性如表1所示。Alpha多样性可反映样本内微生物群落的丰富度和多样性。Observed_species和Chao1指数体现物种丰度即物种数量的多少,Shannon和Simpson指数体现物种多样性。在相同物种丰度的情况下,群落中各物种具有越大的均匀度,则认为群落具有越大的多样性;Shannon指数和Simpson指数值越大,则说明物种多样性越高。
表1数据表明,投加反硝化菌FX-4和C12-HSL后,反应器R1和R4相对于对照组R0 Observed_species和Chao1指数显著提高,反应器R1和R4中物种丰度增加了300多,即外源投加菌株和C12-HSL使得活性污泥系统内部生物量增加。推测这是由于反硝化菌FX-4与污泥内微生物发生协同作用,增加了生物丰富度。经过投加反硝化菌FX-4,R1的Shannon指数和Simpson指数是降低的,即生物多样性是降低的。这说明在加菌定殖后污泥内形成了新的稳定生物群落结构,多样性较空白组反应器R1低。继续外源投加C12-HSL后,R1和R4的Shannon指数和Simpson指数无显著差异。这亦说明活性污泥系统中微生物多样性及均匀度无显著变化。
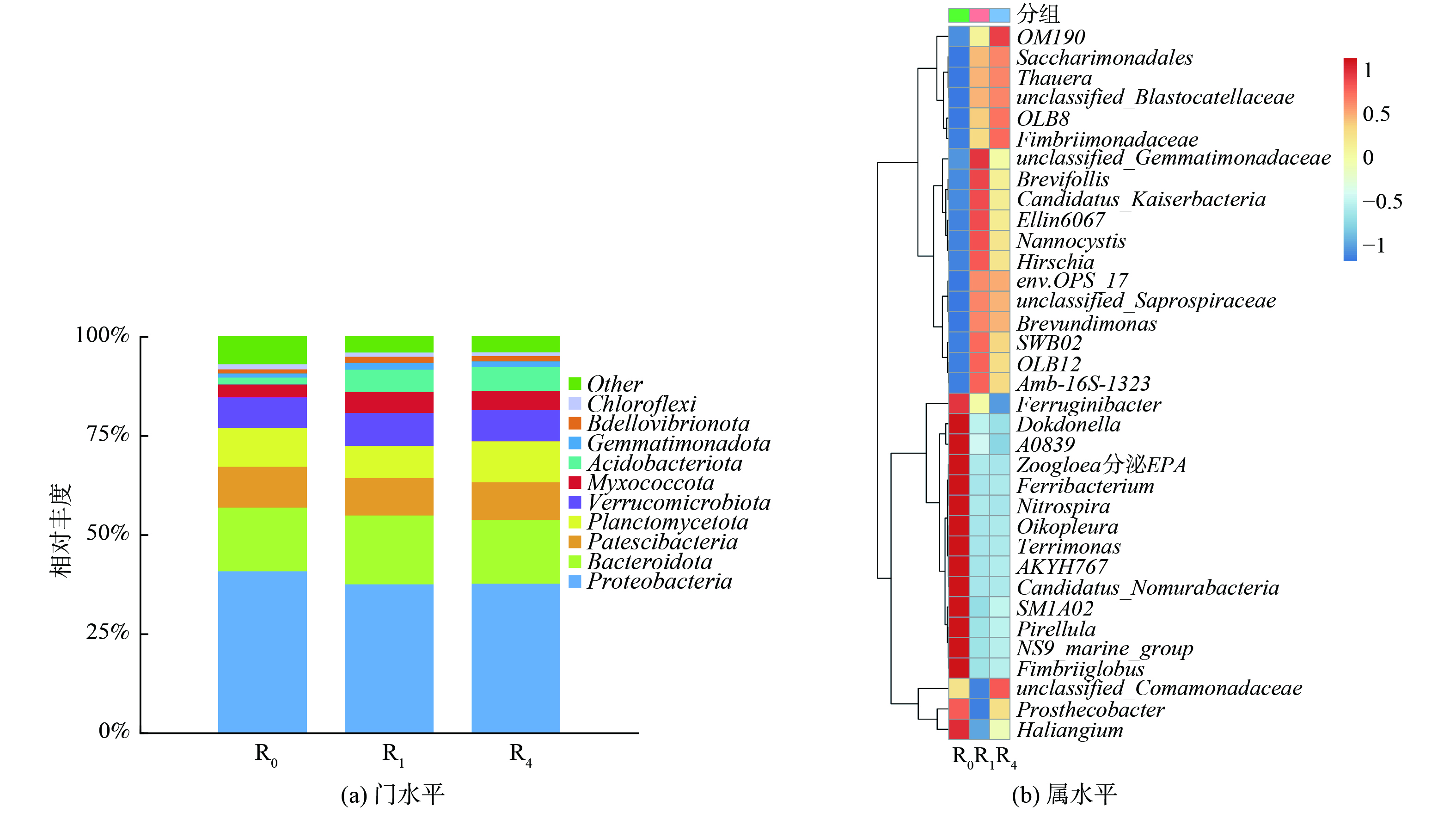
在微生物群落中优势门和属的比较如图8所示,此图揭示了添加信号分子后细菌组成特征的更具体信息。
在门水平上,活性污泥中的主要优势菌为变形菌门 (Proteobactera) 、拟杆菌门 (Bacteroidota) 、浮霉菌门 (Planctomycetota) 和Platescibacteria等。其中,变形菌门 (37.65%) 和拟杆菌门 (16.02%) 是去除NH4-N的主要菌门[39]。在浮霉菌门中存在大量厌氧氨氧化菌,故在此前实验过程中体现了良好的NH4-N去除效果且较少的NO2−-N累积。Gemmatimonadota中大多数是好氧菌和兼性厌氧菌,可利用硝酸盐而起到良好的反硝化作用。投加反硝化菌FX-4的反应器R1相对于对照组R0变形菌门、浮霉菌门和Platescibacteria相对丰度略有降低,而拟杆菌门、Verrucomicrobiota、Myxococcota和Acidobacteriota相对丰度均有增加。体现在实验中,即反应器保持了良好的去污效果,同时Gemmatimonadota的相对丰度上升证明反硝化菌FX-4在SBR系统定殖效果比较好,可较好提升反硝化性能。外源投加信号分子C12-HSL后,将反应器R4和R1进行对比,各优势菌门变化波动较小,但结合前面脱氮效能,投加C12-HSL维持了系统有效运行且对脱氮有正向影响。
图8 (b) 显示了属水平上优势菌群投加反硝化菌FX-4和外源投加信号分子C12-HSL后相对丰度的变化情况。与R0相对比,反应器R1在投加反硝化菌FX-4 之后多个菌种如Thauera、Brevifollis、OLB12、Saccharimonadales、Candidatus-Kaiserbacteria、Nannocystis等的丰度明显提高,而Fimbriiglobus、Nitrospira、NS9-marine-group、AKYH767、Zoogloea、Ferribacterium、Candidatus-Nomurabacteria等菌株丰度会有不同程度的降低。在外源投加信号分子C12-HSL之后,反应器R4相对于对照组R0,优势菌属为OM190、Saccharimonadales、OLB12、 Thauera、unclassified_Blastocatellaceae、OLB8,其丰度分别为4.52%、4.99%、4.97%、18.11%、 2.84%和1.59%。
索氏菌属 (Thauera) 是变形菌门下的一类革兰氏阴性菌,是一种具有硝化反硝化作用军属,同时与反应器内的群体感应密切相关。短波单胞菌度属 (Brevundimonas) 是好氧或兼性厌氧菌,可少量还原硝酸盐。同时,Zoogloea属、Thauera属、Flavobacterium属等都是常见的可产生EPS的菌属,且大多具有硝酸盐氮还原能力。亚硝酸菌属 (Nitrosomonas) 能将NH4+-N转化为NO2−-N。在反应器R1中投加反硝化菌FX-4定殖之后,Thauera、Brevundimonas等菌属与R0较低质量分数的情况相比微生物含量提高了10.8%和4.29%,并且在定殖后的R2反应器中外源投加C12-HSL后质量分数又进一步增加。这说明外源投加菌株和C12-HSL有利于硝化反硝化相关菌属生长,使其成为活性污泥系统中新的优势菌属。然而,Zoogloea属、Flavobacterium属、Nitrospira属和NS9-marine-group等菌属在R1和R2菌株含量都相对于R0相对丰度显著下降了8.21%、3.56%、1.45%和2.10%,这说明投加的菌株会与原微生物群落形成竞争,会抑制某些微生物群落生长。检测分析结果说明,外源投加反硝化菌和C12-HSL对系统反硝化效能具有显著影响,同时改变活性污泥系统中的微生物群落结构,促进微生物种群演替。
-
1) 投加50 nmol∙L−1的C12-HSL信号分子可强化反硝化菌去除NO3−-N的能力,但较高的投加浓度会对菌株生长起抑制作用,强化效果偏弱。2) C12-HSL信号分子协同反硝化菌FX-4可优化系统对氮的去除效能,投加100 nmol∙L−1 C12-HSL的反应器活性污泥系统中TN去除效果提升更显著,且外源投加信号分子对反应器的NH4+-N去除率、NO2−-N积累量、对NO3−-N积累量没有明显影响。3) 活性污泥系统中信号分子种类及含量会影响反应器的脱氮效能,同时外源投加信号分子可刺激系统内部信号分子C4-HSL和C8-HSL的产生,从而进一步促进脱氮过程。4) 外源投加反硝化菌FX-4和外源投加信号分子C12-HSL可显著影响活性污泥中微生物群落结构,提高Thauera、Brevundimonas等脱氮相关菌属的占比。
外源C12-HSL信号分子协同反硝化菌FX-4对活性污泥系统脱氮效果的影响
Effect of exogenous C12-HSL signal molecule in coordination with denitrifying bacteria FX-4 on nitrogen removal in activated sludge system
-
摘要: 为探究外源信号分子的群体感应效应对反硝化菌FX-4及活性污泥系统脱氮的影响,将外源AHLs (酰基高丝氨酸内酯类) 的C6-HSL和C12-HSL信号分子投加至反硝化复筛培养基中,探究AHLs对反硝化菌FX-4去除NO3−-N的影响。结果发现,外源投加C6-HSL和C12-HSL均可有效地提高反硝化菌FX-4的NO3−-N去除性能,增加反硝化菌FX-4的生物量,且C12-HSL协同反硝化菌FX-4的NO3−-N去除效果最佳;不同浓度的C12-HSL对反硝化菌FX-4的NO3−-N去除效果均有提升,且50 nmol∙L−1的C12-HSL可较大提升菌株FX-4的NO3−-N去除效果。将浓度为0、5 nmol∙L−1、50 nmol∙L−1、200 nmol∙L−1、500 nmol∙L−1和1 000 nmol∙L−1的C12-HSL和反硝化菌FX-4同时投加至SBR活性污泥系统中,考察两者协同下系统脱氮性能、信号分子浓度和微生物群落结构的变化。结果表明,两者协同作用可对NO3−-N去除性能产生明显影响,投加信号分子的实验组R1~R6相对于空白对照组R0的NO3−-N积累量减少20~50 mg∙L−1,且C12-HSL投加量为100 nmol∙L−1的反应器R3的NO3−-N消耗量最多,NO3−-N出水质量浓度较R0降低约45 mg∙L−1;此外C12-HSL信号分子对TN去除产生正影响显著,且C12-HSL投加量为100 nmol∙L−1的反应器能更有效地提升活性污泥系统TN去除效能。信号分子浓度变化检测结果显示,外源投加C12-HSL可以刺激系统其他AHLs分泌,特别是促进系统C4-HSL的分泌。微生物群落结构分析结果显示,外源投加反硝化菌FX-4和信号分子C12-HSL可显著影响活性污泥中微生物群落组成,加快活性污泥中微生物种群演替,使Thauera、Brevundimonas等脱氮相关菌属占比升高。以上结果可为信号分子作为应急手段强化活性污泥系统生物脱氮性能提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 反硝化菌FX-4 /
- N-十二烷酰-L-高丝氨酸内酯 /
- 群体感应 /
- 脱氮
Abstract: In order to explore the influence of quorum sensing effect of exogenous signal molecules on denitrifying bacteria FX-4 and denitrification of activated sludge system, C6-HSL and C12-HSL signal molecules of exogenous AHLs (acyl homoserine lactones) were added into denitrifying resieve medium to explore the effect of AHLs on denitrifying bacteria FX-4's removal of NO3−-N. The experimental results showed that both C6-HSL and C12-HSL could effectively improve the NO3−-N removal performance of denitrifying bacterium FX-4 and increase the biomass of denitrifying bacterium FX-4, and C12-HSL synergic denitrifying bacterium FX-4 had the best NO3−-N removal efficiency. The NO3−-N removal efficiency of denitrifying bacterium FX-4 was improved by different concentrations of C12-HSL, and C12-HSL of 50 nmol∙L−1 significantly improved the NO3−-N removal efficiency of strain FX-4. C12-HSL at concentrations of 0, 5 nmol∙L−1, 50 nmol∙L−1, 200 nmol∙L−1, 500 nmol∙L−1, and 1 000 nmol∙L−1 were simultaneously added to the SBR activated sludge system, as well as the denitrification bacterium FX-4. The nitrogen removal performance, signal molecule concentration and microbial community structure of the system were investigated.The results showed that the synergistic effects of the two could significantly affect theNO3−-N removal performance of the reactor. The accumulation of NO3−-N in R1-R6 treated with signal molecules decreased by 20 mg∙L−1 to 50 mg∙L−1 compared with the control group R0. The consumption of NO3−-N in R3 was the highest in the reactor with 100 nmol∙L−1 C12-HSL, and the NO3−-N concentration in effluent was about 45 mg∙L−1 lower than that of R0. In addition, C12-HSL signal molecules had a significant positive effect on TN removal, and the TN removal efficiency of activated sludge system was improved more effectively with 100 nmol∙L−1 C12-HSL dosage. Signal molecule concentration change detection results showed that exogenous addition of C12-HSL could stimulate the secretion of other AHLs in the system, especially the secretion of C4-HSL in the system. The results of microbial community structure analysis showed that exogenous addition of denitrifiers FX-4 and signal molecule C12-HSL could significantly affect microbial community composition in activated sludge, accelerate microbial population succession in activated sludge, and increase the relative abundance of denitrification bacteria such as Thauera and Brevundimonas. This study can provide technical parameter reference for signal molecules as emergency methods to enhance biological nitrogen removal performance of activated sludge system. -
氮元素过多会导致的水体富营养化问题,高效的氮素去除技术是当前研究热点[1-2] 。然而,生物法在处理污水时常会遇到系统不稳定和性能恶化等问题。生物强化技术成为改善污水生物处理系统运行效能有效方法[3],亦是研究重点[4]。TANG等[5]发现,向pH为6.5的系统中加入6% (质量分数) 的硝化菌后,可显著提高系统脱氮效率,NH4+-N去除速率由0.21 mg·(g·h)−1增加至mg·(g·h)−1; PATUREAU等[6]在除磷活性污泥系统中接种好氧反硝化菌,以实现系统在好氧阶段同时实现硝酸盐还原和磷去除;还有研究者在UASB反应器中接种Thiopseudomonas denitrificans X2后发现强化系统可同时去除有机物和含氮化合物[7]。生物强化技术在实际应用中存在引入功能菌失效的潜在风险,亦可能对生物系统产生负面影响。如何使强化菌株成功定殖并高效降解污染物是亟需解决的问题,群体感应 (quorum sensing,QS) 的发现为生物强化技术提供了新方向,可促进引入功能菌适应环境条件并改善与其他微生物的相互作用[3, 8]。酰化高丝氨酸内酯类(Acyl-homoserine lactones,AHLs)化合物是革兰氏阴性菌群体感应系统中最重要的一类信号分子,并调控许多生理特性的表达[9]。细菌可通过分泌和释放AHLs信号分子,来调控微生物功能并促进生物脱氮等过程[10-11]。
外源投加信号分子和群感菌是利用微生物群体感应现象强化污水生物脱氮的主要方法[12]。LI等[13]通过外源性添加AHLs以加速自养硝化污泥系统中硝化颗粒的形成。在众多类型的AHLs中,C6-HSL (N-己酰基-L-高丝氨酸内酯) 和C8-HSL (N-辛酰基-L高丝氨酸内酯) 在活性污泥工艺中占主导地位[14-17]。外源C6-HSL和C8-HSL明显提高了氮的去除效率,亦可调节EPS生成和微生物群落结构[13, 18-21]。冯惠[22]发现C6-HSL和C8-HSL可提升氨氮去除效能;同时长链AHLs如C12-HSL (N-十二烷酰-L-高丝氨酸内酯) 和C14-HSL (N-十四烷酰-L-高丝氨酸内酯) 等具有更强的疏水性、耐水解性和生物质黏附性,对于受基因调控的反硝化还原酶的活性也有显著影响[23],从而对生物脱氮有较好的促进效果[24-26]。因此,外源投加群体感应信号分子协同功能菌是解决单一功能菌效果不佳的有效方法。
以反硝化菌FX-4为研究对象,选取信号分子C6-HSL和C12-HSL,研究信号分子对反硝化菌FX-4NO3−-N去除性能的影响,以及两者协同作用下SBR系统脱氮性能。通过对菌株单独投加和混合投加,考察菌株的生长和作用效果,筛选出最优投加方式和浓度,随即将筛选出信号分子投入活性污泥系统,以未加信号分子组为空白对照,研究其脱氮性能的影响、实验前后信号分子浓度,并分析微生物群落优势菌群变化,以得出信号分子对生物脱氮的影响,从而为投加信号分子强化脱氮提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 培养基
1) LB培养基。蛋白胨10.0 g∙L−1,酵母膏5.0 g∙L−1,NaCl 5.0 g∙L−1,pH 7.0,121 ℃灭菌20 min。驯化培养基:醋酸钠 3.6 g∙L−1,硝酸钾 1.44 g∙L−1,硫酸镁 g∙L−1,磷酸氢二钾 1 g∙L−1,微量元素 1mL∙L−1,氯化钠 2.5 g∙L−1,pH 7.0,121 ℃灭菌20 min。
2) 反硝化复筛培养基:乙酸钠1.8 g∙L−1,氯化钠2.5 g∙L−1,硝酸钾0.8 g∙L−1,磷酸氢二钾1 g∙L−1,硫酸镁0.1 g∙L−1,微量元素液1 mL∙L−1,pH 7.0,121 ℃灭菌20 min。
3) 微量元素液:EDTA 50 g∙L−1,硫酸锌2.2 g∙L−1,氯化钙5.5 g∙L−1,四水氯化锰5.06 g∙L−1,七水硫酸亚铁5 g∙L−1,四水钼酸铵1.1 g∙L−1,无水硫酸铜1.5 g∙L−1,六水氯化钴1.61 g∙L−1。
1.2 实验试剂
实验中选取的2种N-酰化高丝氨酸内酯类化合物(AHLs) 信号分子C6-HSL (己酰L-高丝氨酸内酯) 和C12-HSL (N-十二烷酰-L-高丝氨酸内酯) 均购自 Sigma-aldrich。AHLs有较好的水溶性。用纯水将其配制成0.1 g∙L−1的标准液,加入0.1% (体积分数) 的甲酸防止AHLs自身降解,于−20°C下保存备用[31]。
1.3 菌株来源
实验所用反硝化菌FX-4为假单胞菌属的Pseudomonas stutzeri,其具有良好的反硝化能力,由本课题组分离筛选。筛选过程:采用驯化培养基进行初筛,随后在反硝化复筛培养基中进行复筛,培养条件为30 ℃、150r·min−1、接种量为5%;对其进行生长特性、理化性质、信号分子及底物利用速率等生理生化性能的比较,选择生长代谢速率高、能大量消耗NO3-N的菌株参与本研究。该过程详见参考文献[32]。
1.4 接种污泥
本研究使用的接种污泥来自兰州城市污水处理厂的回流污泥。对其进行3 d的闷曝,期间定期加入适当营养盐,使其微生物生长达到最优水平,以有效适应合成污水进行后续实验。
1.5 实验方法
1) 通过投加反硝化菌和信号分子影响活性污泥脱氮性能。实验初期,接种到反应器的污泥MLSS约为 3 210 mg∙L−1,将0.4 L污泥接种到1.6 L的SBR反应器中,按9 h一个循环周期 (依次是进水15 min、厌氧1.5 h、曝气5 h、缺氧1 h、沉降1 h和出水15 min) 在室温下运行。反应器进水采用的人工配水:乙酸钠0.5 g∙L−1,葡萄糖0.1 g∙L−1,氯化铵0.2 g∙L−1,磷酸二氢钾0.025 g∙L−1,硝酸钾0.15 g∙L−1,硫酸镁0.025 g∙L−1,氯化钠0.5 g∙L−1,微量元素液1 mL∙L−1。
2) 信号分子对反硝化菌FX-4反硝化性能影响。将反硝化菌FX-4菌悬液按5% (质量分数) 的接种量接种到LB培养基中,同时投加适量的信号分子 (C6-HSL、C12-HSL和C6-HSL+C12-HSL) 于LB培养基中。设置4组培养组:R0 (空白对照组) 、R1 (投加C6-HSL) 、R2 (投加C12-HSL) 、R3 (投加C6-HSL+C12-HSL) 。将LB培养基置于30 ℃、150 r∙min−1恒温振荡培养箱内培养3 d制成种子液。将种子液按5% (质量分数) 的接种量接种到含有100 mL反硝化复筛培养基的250 mL锥形瓶中,置于30 ℃、150 r∙min−1恒温振荡培养箱中培养5 d,每隔24 h无菌取样,在波长600 nm下测定菌体密度OD600,绘制反硝化菌FX-4的生长曲线,采用紫外分光光度法测定NO3−-N质量浓度并计算去除率,筛选出效果最佳的信号分子种类。在筛选出效果最佳的信号分子后,将反硝化菌FX-4菌悬液按5% (质量分数) 的接种量接种到LB培养基中,同时投加不同浓度的信号分子于LB培养基中,设置6组培养组其信号分子投加量分别为0、5 nmol∙L−1、50 nmol∙L−1、200 nmol∙L−1、500 nmol∙L−1和1 000 nmol∙L−1。将LB培养基置于30 ℃、150 r∙min−1恒温振荡培养箱内培养3 d制成种子液。将种子液按5% (质量分数) 的接种量接种到含有100 mL反硝化复筛培养基的250 mL锥形瓶中,重复上述操作。测定菌体密度OD600及NO3−-N质量浓度并计算去除率,筛选出效果最佳的信号分子浓度。以上每组实验设置3个平行实验。
3) C12-HSL信号分子对活性污泥系统脱氮影响。向7组有效体积1.6 L的SBR反应器内分别接入400 mL污泥和1200 mL污水,实验中反应器采用曝气泵头进行曝气。7组反应器分别为:R0 (空白对照组,未投加菌剂和信号分子) 、R1 (FX-4反硝化菌+0 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R2 (FX-4反硝化菌+5 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R3 (FX-4反硝化菌+50 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R4 (FX-4反硝化菌+100 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R5 (FX-4反硝化菌+200 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 、R6 (FX-4反硝化菌+500 nmol∙L−1C12-HSL) 。实验初期为投菌期,将反硝化菌FX-4接入反应器R1~R6中,每2 d投加一次种子液,驯化培养12 d,之后向反应器R1~R6投加0 nmol∙L−1、5 nmol∙L−1、50 nmol∙L−1、200 nmol∙L−1、500 nmol∙L−1、1000 nmol∙L−1的AHLs信号分子,前12 d每隔2 d投加一次信号分子,后10 d不投加,实验运行34 d,每天检测 TN、[NH4+-N]、[NO2−-N]、[NO3−-N]并计算各指标的去除率。
1.6 检测方法
1) 常规指标的测定。实验中需要测定的常规指标有TN 、[NH4+-N]、[NO2−-N]、[NO3−-N]。[NH4+-N]采用纳氏试剂光度法测定,TN采用过硫酸钾氧化紫外分光光度法测定,[NO3−-N]采用紫外分光光度法测定,[NO2−-N]采用N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺光度法[33]测定。
2) 信号分子的检测。活性污泥中信号分子的检测采用高效液相串联质谱法检测。活性污泥样品在4 ℃下9 000 r∙min−1离心30 min,取上清液用0.45 μm微孔滤膜过滤,然后用等量含有0.5% (质量分数) 甲酸的乙酸乙酯进行萃取3次,将收集得到的上层有机相用氮吹仪吹干后,用100 μL甲醇定容[34]。预处理过后的水样采用HPLC-MS /MS进行检测。色谱条件如下:反相C18色谱柱 (50 mm×2.1 mm,3.5 μm; Waters Sunfire) ;流动相流速0.3 mL∙min−1;进样量10 μL,分析时间为10 min。质谱条件:采用电喷雾离子源正离子模式 (ESI+) ,多反应离子检测 (MRM模式) ,毛细管电压3.0 kV;锥孔电压30 V;载气高纯氮气 (99.999%) ;载气流速180 L∙h−1; 载气温度300 ℃;碰撞气高纯氮气 (99.999%) [34-35]。
3) 群落结构分析。微生物群落结构测定采用16SrRNA基因高通量测序进行检测[35]。污泥样品DNA的提取及PCR扩增采用PLFA法[36]。以上检测及分析均由广州美格生物科技有限公司完成。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 外源信号分子对菌株FX-4去除NO3-N的影响
将反硝化菌FX-4种子液和不同种类的信号分子投加在含100 mL反硝化复筛培养基的锥形瓶中,随着菌株生长,反硝化菌FX-4对NO3−-N的去除效果如图1所示。
在30 ℃、150 r∙min−1的恒温振荡培养下,投加信号分子12 h后,R1、R2和R3组的NO3−-N去除率明显提高且远高于R0,最大NO3−-N去除率约为94%左右。YAN等[37]也证明投加信号分子与生物脱氮过程密切相关,并且可以有效促进脱氮过程;R2和R3对NO3−-N的去除效果几乎一致,均在36 h后达到最佳去除效果且效果持续稳定,在84 h后开始出现下降;R1在60 h去除率才达到最大值,且对NO3−-N的去除效果相对于R2稍差。但LI[13]等观察到,与其他类型的AHLs相比,添加C6-HSL的反应器显示出最高的氨降解速率,这说明C6-HSL对脱氮效果的主要影响不是体现在NO3-N的去除上。以上结果表明投加信号分子可优化反硝化菌FX-4,使其消耗NO3−-N的性能大大提高;R2和R3对NO3−-N去除情况相似,并且都比R1优先达到NO3−-N去除率最大值。这说明C12-HSL比C6-HSL起作用时间更迅速,作用效果更稳定,去除效果更好。因此,可确定C12-HSL能较大程度提升菌株FX-4去除NO3−-N能力。
随后对不同C12-HSL浓度梯度下的去除效果进行了分析,结果如图2所示。不同浓度梯度的C12-HSL对反硝化菌FX-4的NO3−-N去除效果均有促进作用。相比于空白对照组,NO3−-N的去除率明显提高且均大于95%。其中,信号分子浓度在50 nmol∙L−1对菌株的强化效果最好,去除率高达98%;5 nmol∙L−1和200 nmol∙L−1的去除效果较为相近;而投加浓度更高的2组去除效果反而没有较低投加量的效果显著。胡惠秩[31]也发现在AHLs添加浓度较低时,系统的处理效率更高,而AHLs添加浓度较高时,系统处理效果略微受到抑制。
2.2 外源信号分子对FX-4菌株生长曲线的影响
将反硝化菌种子液按5% (质量分数) 接种量接种至100 mL反硝化复筛培养基中,在投加不同种类的信号分子后,菌株的生长情况及NO3−-N去除效果如图3所示。微生物生长在12 h后,信号分子开始发挥作用,R1、R2和R3组反硝化菌生长情况明显优于R0组。外源添加AHLs不仅可增加生物量密度,还可提高反硝化细菌的生物活性[21],而本研究结果更验证了这一结论。在36 h时,R2和 R3的菌群密度达到最大值,OD600分别达到0.656和0.663,并且进入平稳生长阶段。随后在生长60 h后,菌群密度逐渐降低。这是由于培养基中营养物质被消耗完全,菌群生长进入衰老期;R1组在60 h菌群生长密度达到最大值。结果还表明,投加信号分子使反硝化菌FX-4微生物量显著上升,在R1组中,C6-HSL起作用的时间较长,几乎是R2和R3组2倍。同时,在R2和R3组对比下,二者反硝化菌生长情况及NO3−-N消耗情况几乎一致,于是经分析得出结果是C12-HSL对反硝化菌FX-4生长代谢情况影响更显著。
随后展开投加不同浓度C12-HSL后反硝化菌处理效果的实验,结果如图4所示。当信号分子浓度为50 nmol∙L−1时,反硝化菌生长情况最好且菌群密度明显高于未投加信号分子组。同时,当投加较高浓度 (200 nmol∙L−1、500 nmol∙L−1、1000 nmol∙L−1) 的组生长情况弱于不投加组,这说明投加信号分子最合适的投加浓度为50 nmol∙L−1,且信号分子浓度过高会对反硝化菌生长有抑制作用。胡惠秩[31]也发现外源性AHLs浓度对系统的影响不是一种简单的线性关系,低浓度AHLs促进微生物的增长,而高浓度AHLs会抑制微生物生长。针对该现象,TAIT等[38]的解释是细菌群落附近如果存在大量外来AHLs信号分子持续时间过长会限制细菌群落对环境变化的响应能力。
2.3 外源C12-HSL强化SBR脱氮的影响
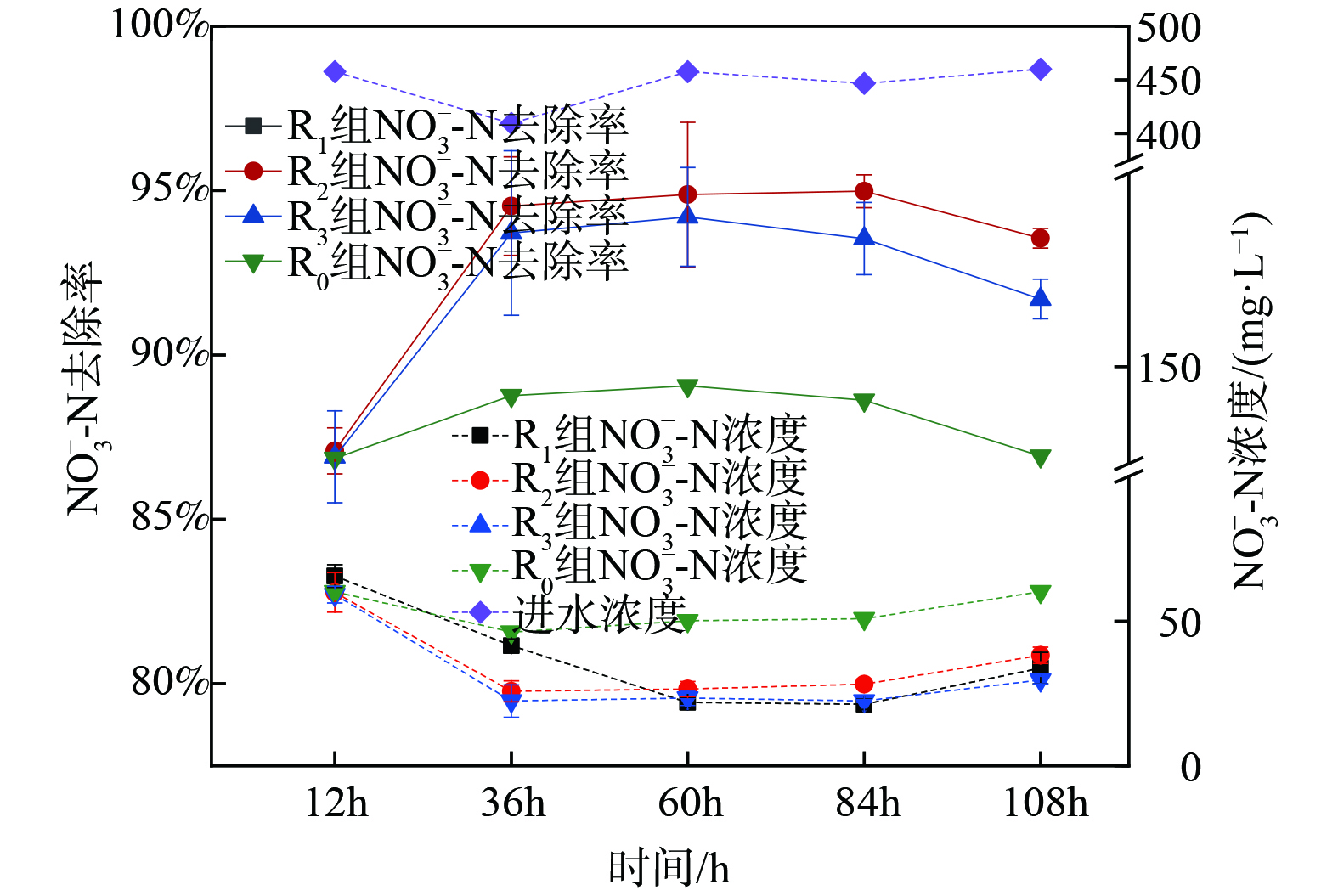
取兰州市城市污水处理厂剩余污泥闷曝3 d,其间定期投加一定营养,结束后分别添加到反应器中。在反应器启动运行后,为研究反硝化菌FX-4协同信号分子对SBR反应器脱氮效果的影响,将实验初的0~12 d为投菌期。每2 d在反应器R1~R6中投加1次反硝化菌FX-4种子液,共驯化培养12 d。之后,将12~24 d定为信号分子强化阶段,每隔2 d向反应器R1~R6投加1次不同浓度梯度的AHLs信号分子 (C12-HSL) 。将24~34 d设为稳定期,此期间系统持续稳定运行。系统的运行效果如图5所示。
在投菌期 (1~12 d) ,R1~R6的TN去除效果较差并低于未投加菌株的R0。R1~R6反应器中[NO3−-N]大幅增加。这可能是由于外源菌的加入,系统竞争激烈,同时种子液也含有菌种未代谢完的含氮有机物,增加了系统氮负荷,故表现出脱氮不佳现象。在强化阶段 (11~24 d) ,向反应器R1~R6中投加不同浓度信号分子,以调控污泥中的微生物从而提升反应器脱氮性能。在投加信号分子阶段,R1~R6组的[NO3−-N]并没有大幅变化,而当反应器R4中投加浓度100 nmol∙L−1的信号分子后,NO3−-N去除效果优势较明显;而R1~R6反应器的TN 去除率均显著提高,这说明投加C12-HSL可有效提升系统的脱氮性能。其原因是外源投加AHLs可有效提高系统生物量同时刺激微生物自身AHLs的生成。衣隆强等[23]也发现添加外源AHLs可提前达到能刺激QS机制的胞外AHLs浓度,从而强化QS的控制功能,与本研究结果一致。在稳定运行阶段 (24~34 d) ,R1~R6的TN去除情况趋于稳定,去除率为60%~70%,但相对于强化阶段效果略有降低。[NO3−-N]几乎不累积的原因可能是外源信号分子反应完毕,故导致反硝化过程进行有所缓慢。整个运行过程中,随着外源添加菌株和不同浓度信号分子,[NO3−-N]不断变化,R1~R6呈现不同的TN去除效果。尽管R0~R6反应器对TN的去除呈现相似的变化趋势,但R0的平均TN去除率65.53%与R1组的66.00%对比说明,R1的处理效果更好。这表明投加反硝化菌FX-4后NO3−-N被大量消耗,累积量减少,从而促进了TN去除。同时,当投加信号分子浓度为100 nmol∙L−1时,R4在运行20 d后呈现较好的脱氮能力,TN去除率达72.08%比对照组R0组和R1组高出8.93%。而信号分子投加浓度偏高的R5和R6组脱氮效果略差于R0组,这表明添加合适浓度的信号分子可增强活性污泥的脱氮效果,但过高的信号分子浓度投加会使系统脱氮效果受到抑制。
图5 (b) 和 (c) 表明R0~R6反应器各阶段的NH4-N平均去除率均大于95%,且NO2−-N几乎不存在积累。在整个运行过程中,尽管反应器中外源投加了菌株和信号分子,但都没有影响反应器对NH4+-N的良好去除,并且NO2−-N累积量极少。这说明外源投加反硝化菌FX-4和信号分子不会对系统其他污染物的去除产生不利影响。
2.4 外源C12-HSL对系统内信号分子组成影响
分别对反硝化菌FX-4种子液、实验开始时期原活性污泥、投菌定殖之后的R1及投加过信号分子脱氮效果良好的R4进行取样,并对其信号分子种类和浓度进行监测,反应器内信号分子的变化结果如图6所示。
反硝化菌FX-4自身分泌的信号分子有C8-HSL和C12-oxo-HSL。在原活性污泥中,信号分子浓度较小,只检测到C4-HSL。在投菌阶段,反硝化菌FX-4种子液投加到活性污泥中,活性污泥中的信号分子浓度降低,在R1中只检测到少量C12-oxo-HSL,C4-HSL和C8-HSL消失。分析其原因可能是反硝化菌FX-4与活性污泥中的土著菌群存在竞争关系导致其定殖未完成,此阶段信号分子种类及浓度下降。在强化阶段,反硝化菌FX-4定殖后的污泥中继续投加信号分子C12-HSL,R4组信号分子总量显著升高,特别是C12-HSL浓度大量增加,C8-HSL和C4-HSL又重新出现,且C4-HSL浓度明显较原活性污泥和R1组高。分析其原因是在外源投加了C12-HSL的同时,促进了系统内部微生物自身分泌,从而产生了大量信号分子。这说明反硝化菌FX-4定殖完成后,活性污泥系统重新达到平衡,当信号分子C12-HSL达到一定浓度后,激发活性污泥中微生物自身分泌信号分子表达,诱发了群体感应现象。结合此前实验中R4组较好的脱氮效果,微生物群落感受到系统分泌产生的AHLs后,促进不同功能菌群响应,从而提高脱氮效果。因此,信号分子C12-HSL不仅与脱氮效能密切相关,且投加C12-HSL还可促进反应器活性污泥内部微生物分泌大量内源信号分子。特别是C4-HSL和C8-HSL,推测这两种信号分子与系统脱氮性能的提高也存在一定关联。
2.5 外源C12-HSL对系统微生物群落结构的影响
为研究外源添加信号分子C12-HSL对SBR反应器活性污泥中微生物群落结构的影响,分别对原活性污泥的R0组、投加反硝化菌FX-4后的R1组及外源投加信号分子C12-HSL的R4组进行高通量测序并对其微生物群落变化进行分析。
具有共享和唯一OTU的维恩图如图7所示。333个OTU中的大多数在3个样本中共享,分别占31.68% (R0) 、25.28% (R1) 和25.23% (R4) 。这说明活性污泥中微生物种群的物种丰富度和多样性在通过投菌和外源投加信号分子之后都得到了显著提高。YAN等[37]通过研究外源投加AHLs对SBR反应器运行的影响也发现,微生物群落丰富度指数会随着AHLs剂量的增加而增加。
反应器R0、R1和R4的Alpha多样性如表1所示。Alpha多样性可反映样本内微生物群落的丰富度和多样性。Observed_species和Chao1指数体现物种丰度即物种数量的多少,Shannon和Simpson指数体现物种多样性。在相同物种丰度的情况下,群落中各物种具有越大的均匀度,则认为群落具有越大的多样性;Shannon指数和Simpson指数值越大,则说明物种多样性越高。
表 1 各反应器微生物群落alpha多样性Table 1. Alpha diversity of microbial community in each reactorSample Observed_species Shannon Simpson Pielou Chao 1 PD_whole_tree R0 1 051 5.723 2 0.987 5 0.822 6 1 052.52 37.149 4 R1 1 317 5.212 7 0.973 4 0.725 7 1 317.51 42.890 8 R4 1 320 5.273 2 0.974 9 0.733 9 1 320.96 43.996 9 表1数据表明,投加反硝化菌FX-4和C12-HSL后,反应器R1和R4相对于对照组R0 Observed_species和Chao1指数显著提高,反应器R1和R4中物种丰度增加了300多,即外源投加菌株和C12-HSL使得活性污泥系统内部生物量增加。推测这是由于反硝化菌FX-4与污泥内微生物发生协同作用,增加了生物丰富度。经过投加反硝化菌FX-4,R1的Shannon指数和Simpson指数是降低的,即生物多样性是降低的。这说明在加菌定殖后污泥内形成了新的稳定生物群落结构,多样性较空白组反应器R1低。继续外源投加C12-HSL后,R1和R4的Shannon指数和Simpson指数无显著差异。这亦说明活性污泥系统中微生物多样性及均匀度无显著变化。
在微生物群落中优势门和属的比较如图8所示,此图揭示了添加信号分子后细菌组成特征的更具体信息。
在门水平上,活性污泥中的主要优势菌为变形菌门 (Proteobactera) 、拟杆菌门 (Bacteroidota) 、浮霉菌门 (Planctomycetota) 和Platescibacteria等。其中,变形菌门 (37.65%) 和拟杆菌门 (16.02%) 是去除NH4-N的主要菌门[39]。在浮霉菌门中存在大量厌氧氨氧化菌,故在此前实验过程中体现了良好的NH4-N去除效果且较少的NO2−-N累积。Gemmatimonadota中大多数是好氧菌和兼性厌氧菌,可利用硝酸盐而起到良好的反硝化作用。投加反硝化菌FX-4的反应器R1相对于对照组R0变形菌门、浮霉菌门和Platescibacteria相对丰度略有降低,而拟杆菌门、Verrucomicrobiota、Myxococcota和Acidobacteriota相对丰度均有增加。体现在实验中,即反应器保持了良好的去污效果,同时Gemmatimonadota的相对丰度上升证明反硝化菌FX-4在SBR系统定殖效果比较好,可较好提升反硝化性能。外源投加信号分子C12-HSL后,将反应器R4和R1进行对比,各优势菌门变化波动较小,但结合前面脱氮效能,投加C12-HSL维持了系统有效运行且对脱氮有正向影响。
图8 (b) 显示了属水平上优势菌群投加反硝化菌FX-4和外源投加信号分子C12-HSL后相对丰度的变化情况。与R0相对比,反应器R1在投加反硝化菌FX-4 之后多个菌种如Thauera、Brevifollis、OLB12、Saccharimonadales、Candidatus-Kaiserbacteria、Nannocystis等的丰度明显提高,而Fimbriiglobus、Nitrospira、NS9-marine-group、AKYH767、Zoogloea、Ferribacterium、Candidatus-Nomurabacteria等菌株丰度会有不同程度的降低。在外源投加信号分子C12-HSL之后,反应器R4相对于对照组R0,优势菌属为OM190、Saccharimonadales、OLB12、 Thauera、unclassified_Blastocatellaceae、OLB8,其丰度分别为4.52%、4.99%、4.97%、18.11%、 2.84%和1.59%。
索氏菌属 (Thauera) 是变形菌门下的一类革兰氏阴性菌,是一种具有硝化反硝化作用军属,同时与反应器内的群体感应密切相关。短波单胞菌度属 (Brevundimonas) 是好氧或兼性厌氧菌,可少量还原硝酸盐。同时,Zoogloea属、Thauera属、Flavobacterium属等都是常见的可产生EPS的菌属,且大多具有硝酸盐氮还原能力。亚硝酸菌属 (Nitrosomonas) 能将NH4+-N转化为NO2−-N。在反应器R1中投加反硝化菌FX-4定殖之后,Thauera、Brevundimonas等菌属与R0较低质量分数的情况相比微生物含量提高了10.8%和4.29%,并且在定殖后的R2反应器中外源投加C12-HSL后质量分数又进一步增加。这说明外源投加菌株和C12-HSL有利于硝化反硝化相关菌属生长,使其成为活性污泥系统中新的优势菌属。然而,Zoogloea属、Flavobacterium属、Nitrospira属和NS9-marine-group等菌属在R1和R2菌株含量都相对于R0相对丰度显著下降了8.21%、3.56%、1.45%和2.10%,这说明投加的菌株会与原微生物群落形成竞争,会抑制某些微生物群落生长。检测分析结果说明,外源投加反硝化菌和C12-HSL对系统反硝化效能具有显著影响,同时改变活性污泥系统中的微生物群落结构,促进微生物种群演替。
3. 结论
1) 投加50 nmol∙L−1的C12-HSL信号分子可强化反硝化菌去除NO3−-N的能力,但较高的投加浓度会对菌株生长起抑制作用,强化效果偏弱。2) C12-HSL信号分子协同反硝化菌FX-4可优化系统对氮的去除效能,投加100 nmol∙L−1 C12-HSL的反应器活性污泥系统中TN去除效果提升更显著,且外源投加信号分子对反应器的NH4+-N去除率、NO2−-N积累量、对NO3−-N积累量没有明显影响。3) 活性污泥系统中信号分子种类及含量会影响反应器的脱氮效能,同时外源投加信号分子可刺激系统内部信号分子C4-HSL和C8-HSL的产生,从而进一步促进脱氮过程。4) 外源投加反硝化菌FX-4和外源投加信号分子C12-HSL可显著影响活性污泥中微生物群落结构,提高Thauera、Brevundimonas等脱氮相关菌属的占比。
-
表 1 各反应器微生物群落alpha多样性
Table 1. Alpha diversity of microbial community in each reactor
Sample Observed_species Shannon Simpson Pielou Chao 1 PD_whole_tree R0 1 051 5.723 2 0.987 5 0.822 6 1 052.52 37.149 4 R1 1 317 5.212 7 0.973 4 0.725 7 1 317.51 42.890 8 R4 1 320 5.273 2 0.974 9 0.733 9 1 320.96 43.996 9 -
[1] 李娜, 刘来胜, 张泽中. 2株好氧反硝化菌株的分离鉴定与脱氮特性研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(6): 98-102. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2021.06.013 [2] 侯保连, 李安婕, 孙趣. AHLs群体感应信号分子对硝化污泥附着生长及硝化效果的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(9): 2773-2779. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2014.1060 [3] 王亚军, 司运美, 李彦娟. 群体感应在生物强化功能菌定殖及其降解能力增强中的作用研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(10): 2871-2880. [4] 滕弢. 好氧-厌氧下AHLs类群体感应信号分子对厌氧氨氧化系统影响的研究 [D]. 汕头: 汕头大学, 2021. [5] TANG H L, CHEN H. Nitrification at full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants: Evaluation of inhibition and bioaugmentation of nitrifiers[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 190: 76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.04.063 [6] PATUREAU D, HELLOIN E, RUSTRIAN E, et al. Combined phosphate and nitrogen removal in a sequencing batch reactor using the aerobic denitrifier, Microvirgula aerodenitrificans[J]. Water research, 2001, 35(1): 189-197. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00244-X [7] ZHOU X L, LI J B, ZHANG J, et al. Bioaugmentation mechanism on humic acid formation during composting of food waste[J]. The Science of the total environment, 2022, 830: 154783-154783. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154783 [8] 陈瑞, 王大力, 林志芬, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌的群体感应信号系统及其在环境领域的应用前景[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2012, 12(6): 5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2012.06.002 [9] HU H Z, HE J G, LIU J, et al. Biofilm activity and sludge characteristics affected by exogenous N-acyl homoserine lactones in biofilm reactors[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 211: 399-347. [10] MA H J, WANG X Z, ZHANG Y, et al. The diversity, distribution and function of N -acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) in industrial anaerobic granular sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.043 [11] 于多. 群体感应(QS)对MBR膜污染影响分析 [D]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学, 2016. [12] 李金璞, 唐珠, 杨新萍. 纳米银对SBRs脱氮效率的影响及外源AHLs的调控作用[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(9): 2942-2951. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202104088 [13] LI A J, HOU B L, LI M X. Cell adhesion, ammonia removal and granulation of autotrophic nitrifying sludge facilitated by N-acyl-homoserine lactones[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 196: 550-558. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.022 [14] SUN Y, MEN M Q, XU B S, et al. Assessing key microbial communities determining nitrogen transformation in composting of cow manure using illumina high-throughput sequencing[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 92: 59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.05.007 [15] SUN Y P, HE K, YIN Q D, et al. Determination of quorum-sensing signal substances in water and solid phases of activated sludge systems using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 69: 85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2017.04.017 [16] SUN Y P, GUAN Y T, ZENG D F, et al. Metagenomics-based interpretation of AHLs-mediated quorum sensing in Anammox biofilm reactors for low-strength wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 344: 42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.047 [17] SUN Y P, GUAN Y T, WANG D, et al. Potential roles of acyl homoserine lactone based quorum sensing in sequencing batch nitrifying biofilm reactors with or without the addition of organic carbon[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 259: 136-145. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.025 [18] ZHANG Z W, HAN Y X, XU CY, et al. Effect of low-intensity direct current electric field on microbial nitrate removal in coal pyrolysis wastewater with low COD to nitrogen ratio[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 287: 121456. [19] ZHANG P, FENG B, CHEN Y P, et al. In situ characterizations for EPS-involved microprocesses in biological wastewater treatment systems[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 49(11): 917-946. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2018.1477416 [20] ZHANG J, LI J, ZHAO B H, et al. Long-term effects of N-acyl-homoserine lactone-based quorum sensing on the characteristics of ANAMMOX granules in high-loaded reactors[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 218: 632-642. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.170 [21] LV L Y, LI W G, ZHENG Z J, et al. Exogenous acyl-homoserine lactones adjust community structures of bacteria and methanogens to ameliorate the performance of anaerobic granular sludge[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 354: 72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.075 [22] 冯惠. 基于AHL的群体感应强化受微污染水中微生物去除氨氮及机制研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017. [23] 衣隆强, 吴英海, 刘长远, 等. 外源酰基高丝氨酸内酯强化生物膜脱氮性能的研究进展 [J/OL]. 大连海洋大学学报. https://doi.org/10.16535/j.cnki.dlhyxb.2022-044 [24] CHEN H, LI A, CUI C W, et al. AHL-mediated quorum sensing regulates the variations of microbial community and sludge properties of aerobic granular sludge under low organic loading[J]. Environment International, 2019, 130: 104946. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.104946 [25] BUETON E O READ H W PELLITTERI M C et al. Identification of acyl-homoserine lactone signal molecules produced by Nitrosomonas europaea strain Schmidt[J]. Applied and environmental microbiology, 2005, 71(8): 4906-4909. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.8.4906-4909.2005 [26] BATCHELOR S E COOPER M CHHABRA S R et al. Cell density-regulated recovery of starved biofilm populations of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria[J]. Applied and environmental microbiology, 1997, 63(6): 2281-2286. doi: 10.1128/aem.63.6.2281-2286.1997 [27] 郭少鹏, 江兴龙, 王泽旭, 等. 高效硝化与反硝化功能菌株的分离筛选及其性能研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2020, 51(6): 1520-1529. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20200400106 [28] 汤默然, 李茹莹. 异养硝化-好氧反硝化菌株的分离筛选及复配菌剂对河水的净化效果[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(7): 2657-2663. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0481 [29] 惠昊, 李娟娟, 李宏, 等. 天然橡胶加工废水中异养硝化好氧反硝化菌株的筛选及其脱氮特性 [J/OL]. 生物学杂志. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1081.Q.20220610.1037.002.html. [30] 李海红, 佟欣宇, 宦臣臣, 等. 高效异养硝化-好氧反硝化菌株TS-1筛选及降解特性[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2020, 26(4): 791-799. doi: 10.19675/j.cnki.1006-687x.2019.10016 [31] 胡惠秩. 常/低温下AHLs类群体感应信号分子对SBBR系统影响的研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017. [32] 蔡文娟. 强化生物处理生活污水的高效混合菌群筛选及降解特性实验研究 [D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2021. [33] 王兆阳, 陈国耀, 姜珂, 等. 1株耐冷兼性嗜碱好氧反硝化菌的分离鉴定及反硝化特性[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(6): 2341-2348. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.06.042 [34] 罗梦, 易皓, 陈静, 等. 高效液相串联质谱法检定活性污泥中N-高丝氨酸内酯[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(2): 281-286. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2018030704 [35] 朱颖楠, 王旭, 王瑾丰, 等. 外源群体感应-好氧反硝化菌强化生物膜脱氮研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(10): 3225-3237. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0283 [36] 周莉娜, 苏润华, 马思佳, 等. 基于PLFA法分析亚硝氮、硝氮和氨氮对厌氧微生物细菌群落的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(2): 499-505. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2015.0567 [37] YAN X, ZHENG S K, HUO Z M, et al. Effects of exogenous N-acyl-homoserine lactones on nutrient removal, sludge properties and microbial community structures during activated sludge process[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 255: 126945. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126945 [38] KAREN T, LAN J, MAVIS D, et al. Disruption of quorum sensing in seawater abolishes attraction of zoospores of the green alga Ulva to bacterial biofilms[J]. Environmental microbiology, 2005, 7(2): 229-240. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2004.00706.x [39] 曾秋宇. 基于垂直折流式生物膜反应器的反硝化工艺 [D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2020. -




 下载:
下载: