-
随着我国城市化进程的加速,产生的城镇污水逐渐增加,导致污水处理之后产生的污泥量也大幅提升。据统计,至2 020年底,我国城镇污泥的排放量达到了5 130×104 t (以含水率80%计) [1],预计到2025年底,全国污泥的产量大约在9 000×104 t左右 (以含水率80%计) [2]。这些污泥不仅量多,而且含水率高,还含有较高浓度的有机物。若不对污泥进行处理而排入环境中,会对环境产生二次污染,危害人体健康,且国内关于污泥的最终处理处置的方式要求污泥的含水率小于60%[3],然而由于污泥EPS中蛋白多糖通过氢键等作用力使得部分水分与EPS结合,导致传统的污泥脱水技术只能将含水率降到80%左右[4-5],因此对污泥调理降低其含水率是污泥减量化以及处置的必不可少的一环。
絮凝剂调理由于其价格低廉和调理效果好在污泥调理领域使用较为广泛[6]。目前使用最多的絮凝剂是无机高分子絮凝剂和有机高分子絮凝剂。最常见的无机高分子絮凝剂是聚合氯化铝 (PAC),CAO等[7]合成了不同种类PAC,并将其调理污泥之后认为,Alb (中等聚合态铝) 和Alc (高度聚合态铝) 比Ala (单体铝或低聚合态铝) 更稳定且带的正电荷更多,其形成的絮体强度更高,污泥调理效果更好。有机高分子絮凝剂主要是聚丙烯酰胺 (PAM) ,邹鹏等[8]比较了壳聚糖和阳离子型聚丙烯酰胺 (CPAM) 对污泥脱水性能的影响,结果表明CPAM对污泥的絮凝效果比壳聚糖好。微生物絮凝剂和复合絮凝剂也逐渐加入了污泥调理,LEE等[9]从秋葵中提取出了一种生物絮凝剂,发现当其用量为商业絮凝剂的2倍时,2者脱水性能相当;WEI[10]等将3-氯-2-羟丙基三甲基铵氯化物 (CTA) 接枝到淀粉上获得了6种不同聚合度的淀粉基絮凝剂,调理污泥后发现电荷密度越高的絮凝剂电中和及吸附架桥能力越强,脱水效果更好。
然而,不同的絮凝剂也有着各自的缺点。无机絮凝剂虽然价格便宜,但是会导致污泥量增加,泥饼和滤液中铁铝等金属含量增加且脱水性能受pH影响较大;有机絮凝剂价格比无机絮凝剂高,生物毒性未知[11- 12]。聚合硅酸铝絮凝剂作为一种复合絮凝剂,同时结合了铝盐的电中和能力和聚硅酸的吸附架桥功能,受pH影响小、价格低廉、且研究证明聚硅酸用于污水混凝处理时效果好,在污水处理方面具有良好的前景[13-14]。但是,有关将其改性作为絮凝剂用于污泥脱水方面的研究却不多见。
本研究以硅酸钠和十八水硫酸铝为原材料,通过共聚反应制得了PASS。以某市市政厌氧污水厂剩余污泥为研究对象,探讨了不同PASS投量对污泥脱水性能的影响,包括SRF和CST;同时,研究了不同投量下污泥EPS中蛋白多糖的变化,结合污泥的脱水效果,深入分析了影响污泥脱水的因素。
-
偏硅酸钠九水化合物 (Na2SiO3·9H2O) 和PAC均为实验纯;考马斯亮蓝G250、葡萄糖 (C6H12O6)、苯酚 (C6H6O) 和十八水硫酸铝 (Al2(SO4)3·18H2O) 均为分析纯;牛白蛋白为生化试剂;硫酸 (H2SO4) 为优级纯。
-
实验中的活性污泥取自某市污水处理厂厌氧消化池污泥。污泥由污水处理厂取回后,测得含水率及各项指标,剩余污泥于4 oC低温保存,并在7 d内用完。初始污泥的各项指标如表1。
-
1) PASS的制备。PASS根据MA等[15]的方法制备。首先在磁力搅拌下,通过注射泵将47 mL的 0.5 mol·L−1硅酸钠溶液以0.2 mL·min−1的速率注射进20%的硫酸溶液中,使混合溶液pH达到3.5,将所得的混合溶液室温下活化9 h得到聚硅酸溶液。继续在磁力搅拌条件下,再用注射泵以0.2 mL·min−1的速率将0.5 mol·L−1的十八水硫酸铝溶液以硅铝比为1∶1和1∶2的量缓慢注射入活化的聚硅酸溶液中,混合后的溶液室温下活化24 h,然后放入烘箱中65 oC烘至恒重,将得到的固体研磨成粉末以备后续检测。
2) 污泥调理试验方法。取200 mL污泥于300 mL烧杯中,置于电动搅拌器 (HD2004W,上海司乐) 上,向污泥中投入一定量浓度为300 g·mL−1的PASS以及PAC溶液,在250 r·min−1下快速搅拌3 min,使絮凝剂充分混匀,然后再80 r·min−1下慢搅30 min,发生絮凝反应。絮凝结束后取污泥样品进行后续指标测定。
-
1) PASS的结构表征。采用傅里叶红外 (FTIR,Spectrum Two,PerkinElmer, 美国) 表征PASS的分子结构,红外光谱波数扫描范围为2 000~400 cm−1,扫描速度为4 cm−1,扫描3次样品,取均值。
2) 污泥比阻测定。SRF采用CAO等[7]所描述的方法。取50 mL污泥于超滤杯 (Amicon8400,Millipore,美国) 中在0.2 MPa外加气压下过滤,并使用电子天平 (AX523ZH,OHAUS,美国) 每隔10 s记录过滤时滤液的重量,直至污泥表面开裂。SRF通过式 (1) 计算。
式中:P为过滤压强,Pa;A为过滤面积,m2;b为过滤时t/V和V作图时直线的斜率,其中t为过滤时间,s,V为对应时间下过滤的体积,mL;μ为滤液的粘度,Pa·S;ω为过滤介质上单位体积的干污泥质量,kg·m−3。
3) 污泥CST检测。CST采用污泥CST测定仪 (304M,Triton,英国) 测量。
4) 污泥泥饼含水率的检测。采用超滤杯 (Millipore,美国) 将污泥预压为泥饼后,采用活塞装置模拟的板框压滤机 (天津津冠) 对污泥进行脱水,将所得泥饼放入105 ℃烘箱 (PH-030A,上海一恒) 烘至恒重,通过烘干前后泥饼的重量测量泥饼含水率。
5) 污泥表面形貌检测。调理后的污泥冷冻干燥后,通过扫描电子显微镜 (JSM7401F,JEDL,日本) 观察污泥表面的形貌。
6) 污泥EPS提取。污泥EPS提取参考ZHANG等的方法[16]。取50 mL调理污泥于离心管中,使用离心机在3 000 r·min−1下离心10 min,所得上清液为SEPS;向离心管中加入0.05% NaCl溶液定容到50 mL,采用漩涡振荡器 (Vortex-Genie 2,Scientific industries,美国) 混匀样品,用超声于20 kHz下超声10 min,随后置于摇床150 rpm摇匀10 min,再超声3 min,最后于5 000 g下离心10 min,提取上清液为LBEPS;继续向离心管中加入0.05% NaCl溶液定容到50 mL,使用漩涡振荡器 (Vortex-Genie 2,Scientific industries,美国) 混匀样品,先于20 kHz下超声3 min,然后放入水浴机中于60 ℃水浴30 min,随即再5 000 g下离心10 min,上清液即TBEPS。提取后的EPS采用0.45 μm滤膜过滤后以备后续检测。
7) 污泥EPS检测。通过分光光度法测量提取后EPS的多糖与蛋白含量。以牛血清蛋白为标样,采用考马斯亮蓝G-250法测得[17];以葡萄糖为标样,通过硫酸-苯酚法测出多糖含量[18]。
-
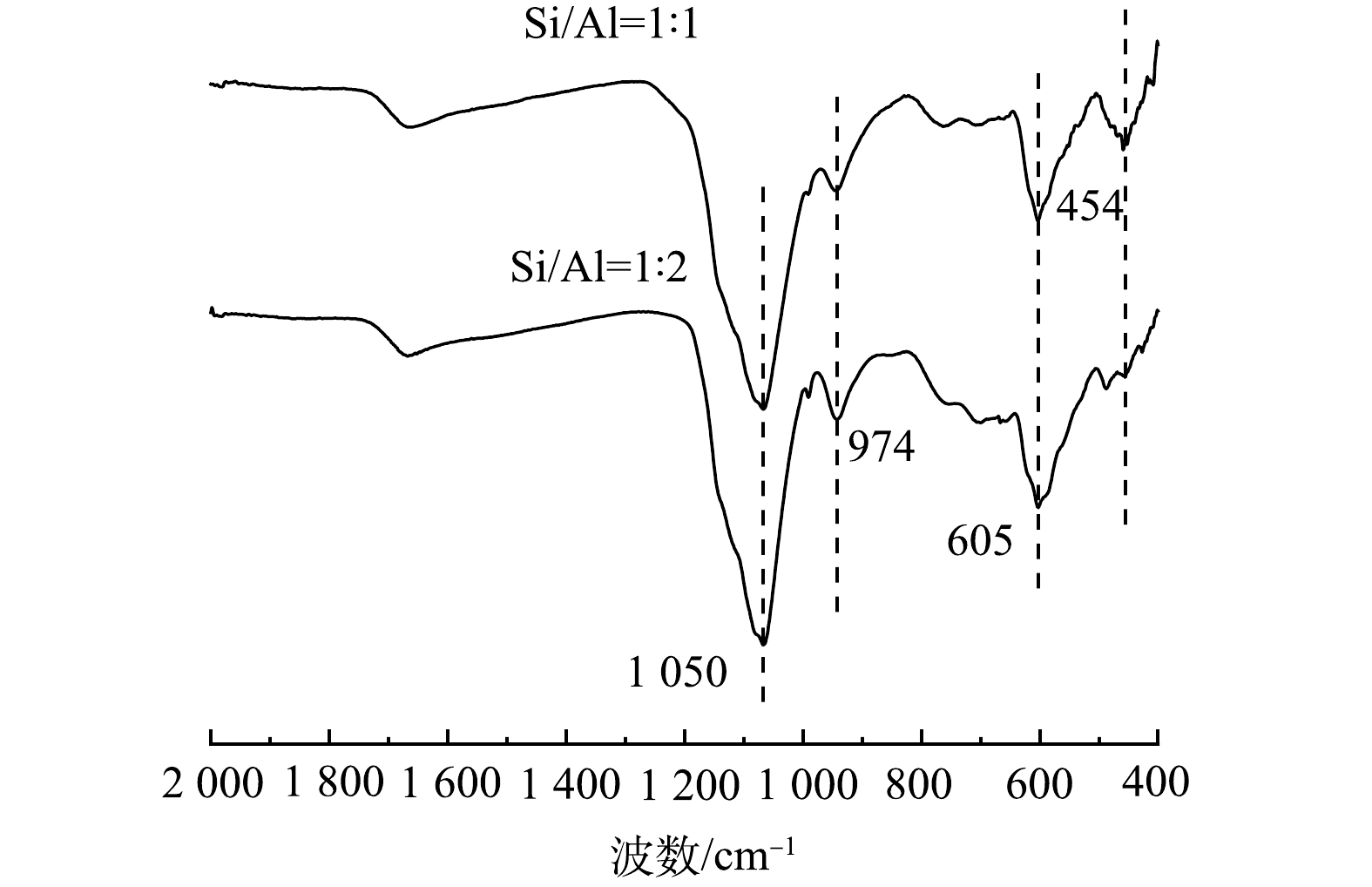
图1为PASS的FTIR谱图,1 050 cm−1处的特征峰符合Al-O-Si键的伸缩振动[19],表示聚硅酸和Al3+发生了络合反应;974 cm−1处的吸收峰表示的是Al-OH-Al不对称的拉伸振动[20],605 cm−1处的吸收峰表示的式Al-OH的伸缩振动[21];454 cm−1处的吸收峰代表Si-O,H-O键的弯曲振动[22]。Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS在605、454 cm−1处的红外吸收峰高于1∶2时,说明此时PASS中产生较多的Si-O,H-O以及Al-OH基团,其吸附架桥效果可能较好;而在974 cm−1处时Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS红外吸收峰低于Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2的PASS,说明Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2的PASS具有更多的Al-OH-Al键,此时电中和作用可能较强。
-
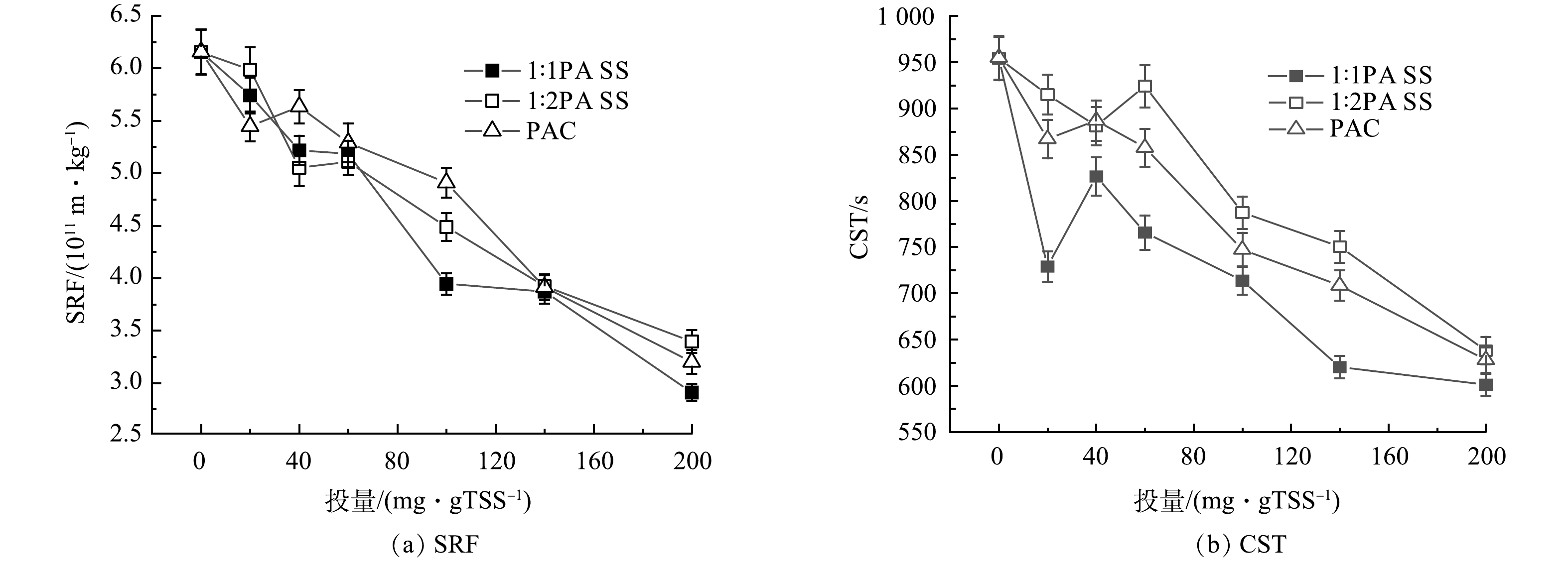
图2是不同投加量下SRF和CST随PASS及PAC投加量的变化情况。3种材料调理后污泥的SRF和CST都随着投加量的增加逐渐减小。这是因为,污泥表面带有负电荷,当带有正电荷的絮凝剂投入污泥中时,会与污泥发生电中和反应,使得污泥脱稳聚集,释放污泥中的束缚水[23];同时PASS的长链结构会进一步架桥脱稳的污泥从而形成更大的絮体,提高污泥的过滤性能,降低污泥的SRF与CST。当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,PASS调理后污泥的SRF由6.15×1011 m·kg−1下降到了2.91×1011 m·kg−1,CST由954.1 s下降到了601.1 s;PAC调理后污泥的SRF由6.15×1011 m·kg−1下降到了3.39×1011 m·kg−1,CST由954.1 s下降到了638 s,高于前者。这说明,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时的PASS的调理效果高于PAC。改变Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时,PASS调理后污泥的SRF与CST都比摩尔比为1∶1时高,这是因为当Si/Al摩尔比较低时,由于Al3+的增加导致共聚的Al越多,电中和能力较强,吸附架桥能力较弱[24]。也可能是因为当Si/Al摩尔比较低时,PASS的中等聚合态Alb较少,而当Si/Al摩尔比适中时,中等聚合态Alb为PASS的主要部分[25]。
-
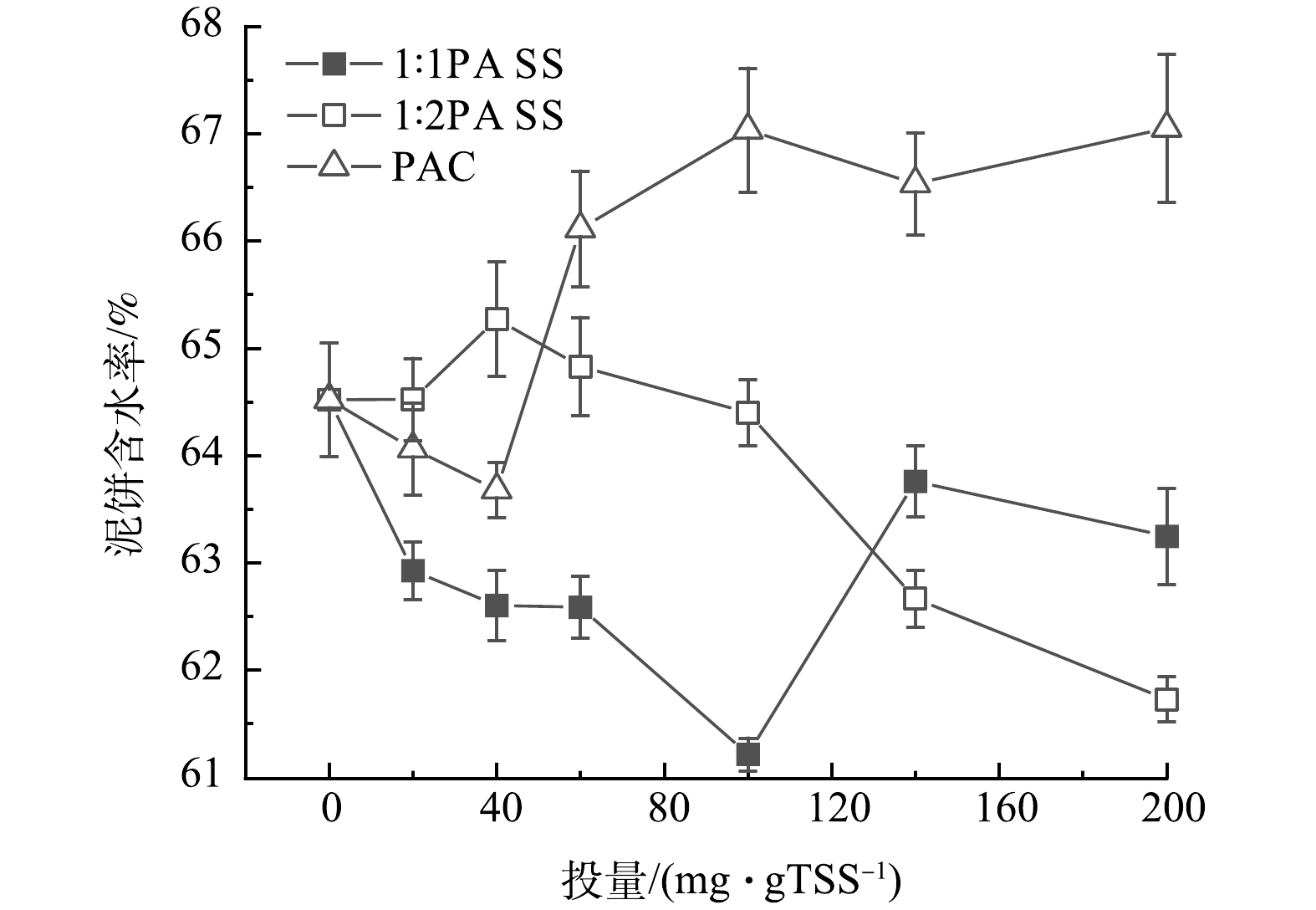
图3为泥饼含水率随着PAC和不同Si/Al摩尔比PASS投量的变化。当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,PASS和PAC调理后的泥饼含水率都是随着投量的增加先减小后增大。当PASS的投量为100 mg·g−1 TSS时,泥饼含水率达到最小,为61.21%,PAC在40 mg·g−1 TSS时达到最小值63.68%,且所有投量下PAC的泥饼含水率都高于Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时PASS,说明Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,PASS对污泥水分的去除效果更好,这是因为PASS不仅有电中和作用,还有吸附架桥作用,而PAC以电中和作用为主[26]。而当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时,PASS在200 mg·g−1 TSS时含水率最低,为61.72%,且当投量较低时,其泥饼含水率高于Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时PASS调理的污泥。当絮凝剂投加过量时,污泥颗粒被絮凝剂完全包裹,此时污泥絮体表面开始带正电荷,污泥絮体之间出现排斥力,污泥重新到达稳定状态,污泥脱水效果变差[27]。
-
EPS作为污泥重要的一部分,占总有机质的50%~90%,且EPS中大部分有机物为亲水性的蛋白多糖,这些亲水物质与水分紧密结合从而影响了污泥的脱水性能[28]。图4为不同Si/Al摩尔比的PASS及PAC调理后污泥EPS蛋白多糖的变化规律。当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,随着PASS投加量的增加,SEPS蛋白和多糖浓度先上升后下降,LBEPS蛋白和多糖浓度逐渐下降,而TBEPS则是先上升后下降,这是因为PASS压缩了污泥的EPS,使得LBEPS部分蛋白和多糖向TBEPS转移[29]。SEPS蛋白多糖先上升的原因可能是初始时絮凝剂加入污泥中时先与污泥LBEPS的蛋白多糖反应,压缩LBEPS的结构,导致一部分蛋白转移到SEPS,同时释放LBEPS里的结合水,这与WANG等的研究一致[30]。随着投量继续增加,LBEPS结构被絮凝剂压缩破坏,絮凝剂开始压缩TBEPS的蛋白多糖。Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时的PASS与PAC调理后污泥SEPS和LBEPS蛋白多糖的变化与Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时相似,但是Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时TBEPS蛋白浓度先下降后上升, PAC调理后的污泥TBEPS蛋白浓度逐渐减小。这可能是因为,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时的PASS及PAC中低聚合态Ala占主体,此时絮凝剂的电中和能力强于吸附架桥能力,对EPS的压缩能力更强。
-
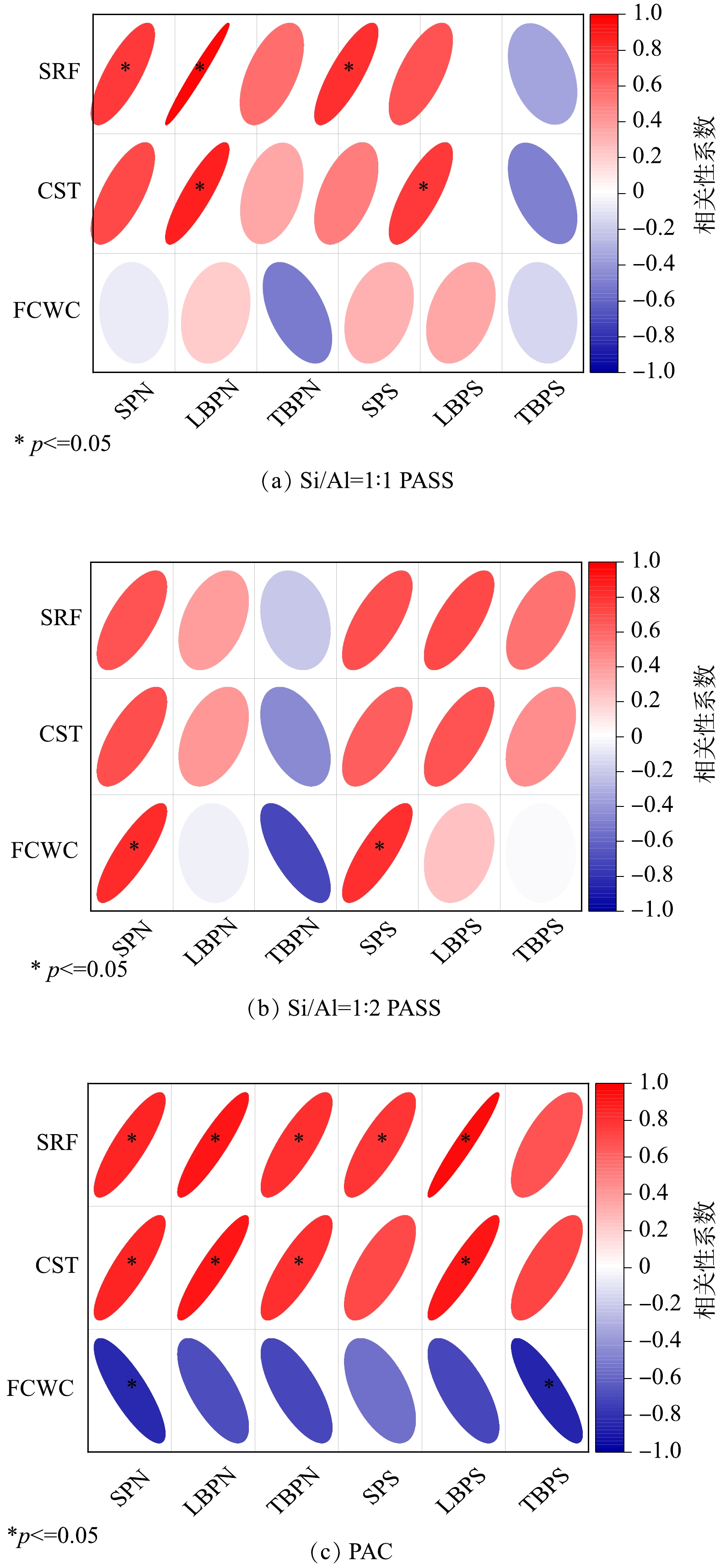
图5为不同絮凝剂调理后污泥EPS的蛋白多糖含量与污泥脱水指标SRF、CST和泥饼含水率之间的相关性。经过3种絮凝剂调理后,SRF和CST均与SEPS和LBEPS蛋白多糖含量呈现正相关性,且SRF和CST与LBEPS蛋白多糖有较强的相关性,这可能是因为污泥EPS中的蛋白多糖为亲水性物质,EPS中蛋白多糖的降低意味着污泥的亲水性和粘性降低,提高了污泥的脱水性能[31, 32]。然而三种材料调理后污泥TBEPS蛋白多糖与三种脱水指标的相关性却不同。当PASS的Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,TBEPS多糖与SRF和CST表现为负相关,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时PASS和PAC调理后TBEPS多糖与SRF、CST以及泥饼含水率却为正相关关系;当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时,TBEPS蛋白与SRF、CST和泥饼含水率呈负相关,PAC调理后TBEPS蛋白与SRF和CST呈现正相关性,原因可能是相较于PAC,PASS有较强的吸附架桥能力,且Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时PASS的电中和作用强于Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1。
-
图6为不同絮凝剂调理后的污泥SEM图。原泥具有松散结构,表面较为平滑,孔隙较少,导致脱水困难。而经过PASS和PAC调理之后的污泥表面变得粗糙且多孔,形成了致密结构,这有助于机械压缩时自由水的去除[32]。当投药量为40 mg·g−1 TSS时,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS所调理的污泥表面的孔隙以及大孔径的孔隙所占的比例多,且孔径也大,而PAC调理后的污泥表面的孔隙率较少,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时的PASS调理的污泥表面孔隙多但大孔径少,说明Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS调理后的污泥脱水通道多,导致其脱水效果最好。而当絮凝剂投量上升到100 mg·g−1 TSS时,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS以及PAC调理的污泥表面的孔隙率减少,孔径也下降,污泥表面脱水通道减少,使得其含水率上升,而Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时PASS调理的污泥表面孔径增大,孔隙率基本不变,污泥脱水通道扩大,导致泥饼含水率下降。这与泥饼含水率的变化一致。
-
表2为制备PASS所需的工业级药剂以及工业级PAC的价格。通过表3计算可算得,在不包括机械和电力消耗的前提下,不同Si/Al摩尔比PASS的价格核算。合成1 t Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS大约需要1 988元,而1 t Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2的PASS的合成价格在1 814元左右,而工业级PAC的价格为2 400元∙t−1,高于2种Si/Al摩尔比的PASS,其脱水性能比Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS差,这说明所制材料在污泥脱水方面具有实际意义。
-
1) 通过FTIR证实成功制作了聚硅酸硫酸铝絮凝剂并用于污泥脱水领域,发现其具有压缩双电层和吸附架桥的功能。将所制PASS与PAC比较后发现,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,PASS调理后污泥的SRF与CST比PAC低,脱水性能比PAC好。
2) 测定污泥泥饼含水率后发现与PAC相比,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时PASS调理效果较好。且在低投加量的情况下,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时PASS的调理效果也比1∶2时好。
3) 通过相关性分析发现,PASS和PAC调理后LBEPS和SEPS蛋白多糖的浓度与SRF和CST均表现为正相关,且LBEPS蛋白多糖与脱水指标相关性更强,而调理后TBEPS与SRF和CST的相关性均不同。
4) 通过观察调理后污泥的SEM发现,经过PASS及PAC调理后,污泥絮体表面从光滑变成了粗糙多孔。当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1且絮凝剂投量较低时,污泥絮体表面大孔径的孔隙和孔隙率均最多。对所制PASS的价格核算以及与PAC的工程价格比较发现,不包括动力和设备损耗的前提下,所制2种Si/Al摩尔比PASS的造价比PAC少,在工程应用上具有实际意义。
聚硅酸硫酸铝强化污水厂污泥脱水效能
Effectiveness and feasibility of enhanced sludge dewatering in wastewater plants with PASS
-
摘要: 以硅酸盐和铝盐为原料,通过共聚反应制备了2种Si/Al摩尔比的聚硅酸硫酸铝 (PASS) 絮凝剂。以某市政污水厂污泥为研究对象,比较了PAC和PASS调理后污泥比阻 (SRF) 、毛细吸水时间 (CST) 和泥饼含水率,并分析了胞外聚合物 (EPS) 的蛋白和多糖变化规律分析。结果表明,PASS能够有效的降低SRF、CST和泥饼含水率,且PASS的Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,脱水效果最好。经过PASS以及PAC调理后,溶解性EPS (SEPS) 和松散附着EPS (LBEPS) 的蛋白多糖的含量均有下降,而PAC调理后紧密附着层EPS (TBEPS) 下降,PASS调理后却存在上升阶段。通过污泥扫描电子显微镜 (SEM) 发现,污泥絮体表面由光滑、均匀分布变成了粗糙多孔,且Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时孔隙率及孔径最大。SEPS和LBEPS蛋白多糖与CST和SRF具有正相关性。所制PASS的不计动力和设备损耗的工程成本比PAC要低。本研究结果可为PASS用于污泥脱水提供参考。Abstract: Two Si/Al molar ratios PASS flocculants were prepared by copolymerization reaction with silicate and aluminium salts. The sludge specific resistance (SRF), capillary suction time (CST) and moisture content of sludge cake after flocculating with PAC and PASS were compared, and the changes of protein and polysaccharide of extracellular polymers (EPS) was analyzed. The results showed that PASS could effectively reduce SRF, CST and moisture content of sludge cake, and the best dewatering effect was achieved when the Si/Al molar ratio was 1:1. The contents of protein and polysaccharide in soluble EPS (SEPS) and loosely bound layer EPS (LBEPS) reduced after PASS and PAC flocculation. The contents in tightly bound EPS (TBEPS) also decreased after PAC conditioning, but after PASS conditioning, the contents exerted an increasing trend. The sludge scanning electron microscope (SEM) image revealed that the sludge floc changed from smooth and uniform distribution to rough and porous, and the porosity and pore size reached the maximum at Si/Al molar ratio of 1:1. Additionally, correlation analysis concluded that protein and polysaccharide in SEPS and LBEPS were positively correlated with CST and SRF. Finally, as to economic evaluation, it is found that the cost of PASS without power and equipment considerations was lower than that of PAC, which laid the engineering significance for the application of PASS for sludge dewatering.
-
Key words:
- PASS /
- EPS /
- sludge dewatering /
- dewatering performance /
- correlation analysis
-
随着我国城市化进程的加速,产生的城镇污水逐渐增加,导致污水处理之后产生的污泥量也大幅提升。据统计,至2 020年底,我国城镇污泥的排放量达到了5 130×104 t (以含水率80%计) [1],预计到2025年底,全国污泥的产量大约在9 000×104 t左右 (以含水率80%计) [2]。这些污泥不仅量多,而且含水率高,还含有较高浓度的有机物。若不对污泥进行处理而排入环境中,会对环境产生二次污染,危害人体健康,且国内关于污泥的最终处理处置的方式要求污泥的含水率小于60%[3],然而由于污泥EPS中蛋白多糖通过氢键等作用力使得部分水分与EPS结合,导致传统的污泥脱水技术只能将含水率降到80%左右[4-5],因此对污泥调理降低其含水率是污泥减量化以及处置的必不可少的一环。
絮凝剂调理由于其价格低廉和调理效果好在污泥调理领域使用较为广泛[6]。目前使用最多的絮凝剂是无机高分子絮凝剂和有机高分子絮凝剂。最常见的无机高分子絮凝剂是聚合氯化铝 (PAC),CAO等[7]合成了不同种类PAC,并将其调理污泥之后认为,Alb (中等聚合态铝) 和Alc (高度聚合态铝) 比Ala (单体铝或低聚合态铝) 更稳定且带的正电荷更多,其形成的絮体强度更高,污泥调理效果更好。有机高分子絮凝剂主要是聚丙烯酰胺 (PAM) ,邹鹏等[8]比较了壳聚糖和阳离子型聚丙烯酰胺 (CPAM) 对污泥脱水性能的影响,结果表明CPAM对污泥的絮凝效果比壳聚糖好。微生物絮凝剂和复合絮凝剂也逐渐加入了污泥调理,LEE等[9]从秋葵中提取出了一种生物絮凝剂,发现当其用量为商业絮凝剂的2倍时,2者脱水性能相当;WEI[10]等将3-氯-2-羟丙基三甲基铵氯化物 (CTA) 接枝到淀粉上获得了6种不同聚合度的淀粉基絮凝剂,调理污泥后发现电荷密度越高的絮凝剂电中和及吸附架桥能力越强,脱水效果更好。
然而,不同的絮凝剂也有着各自的缺点。无机絮凝剂虽然价格便宜,但是会导致污泥量增加,泥饼和滤液中铁铝等金属含量增加且脱水性能受pH影响较大;有机絮凝剂价格比无机絮凝剂高,生物毒性未知[11- 12]。聚合硅酸铝絮凝剂作为一种复合絮凝剂,同时结合了铝盐的电中和能力和聚硅酸的吸附架桥功能,受pH影响小、价格低廉、且研究证明聚硅酸用于污水混凝处理时效果好,在污水处理方面具有良好的前景[13-14]。但是,有关将其改性作为絮凝剂用于污泥脱水方面的研究却不多见。
本研究以硅酸钠和十八水硫酸铝为原材料,通过共聚反应制得了PASS。以某市市政厌氧污水厂剩余污泥为研究对象,探讨了不同PASS投量对污泥脱水性能的影响,包括SRF和CST;同时,研究了不同投量下污泥EPS中蛋白多糖的变化,结合污泥的脱水效果,深入分析了影响污泥脱水的因素。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料
偏硅酸钠九水化合物 (Na2SiO3·9H2O) 和PAC均为实验纯;考马斯亮蓝G250、葡萄糖 (C6H12O6)、苯酚 (C6H6O) 和十八水硫酸铝 (Al2(SO4)3·18H2O) 均为分析纯;牛白蛋白为生化试剂;硫酸 (H2SO4) 为优级纯。
1.2 污泥来源及性质
实验中的活性污泥取自某市污水处理厂厌氧消化池污泥。污泥由污水处理厂取回后,测得含水率及各项指标,剩余污泥于4 oC低温保存,并在7 d内用完。初始污泥的各项指标如表1。
表 1 原始污泥的性质Table 1. Properties of raw sludge含水率/% SRF/(×1012 m·kg−1) pH TSS/(g·L−1) CST/s TOC/(mg·L−1) 94.31±0.025 0.958±0.06 7.71±0.02 56.95±0.25 954±9.3 2 336±14 1.3 实验方法
1) PASS的制备。PASS根据MA等[15]的方法制备。首先在磁力搅拌下,通过注射泵将47 mL的 0.5 mol·L−1硅酸钠溶液以0.2 mL·min−1的速率注射进20%的硫酸溶液中,使混合溶液pH达到3.5,将所得的混合溶液室温下活化9 h得到聚硅酸溶液。继续在磁力搅拌条件下,再用注射泵以0.2 mL·min−1的速率将0.5 mol·L−1的十八水硫酸铝溶液以硅铝比为1∶1和1∶2的量缓慢注射入活化的聚硅酸溶液中,混合后的溶液室温下活化24 h,然后放入烘箱中65 oC烘至恒重,将得到的固体研磨成粉末以备后续检测。
2) 污泥调理试验方法。取200 mL污泥于300 mL烧杯中,置于电动搅拌器 (HD2004W,上海司乐) 上,向污泥中投入一定量浓度为300 g·mL−1的PASS以及PAC溶液,在250 r·min−1下快速搅拌3 min,使絮凝剂充分混匀,然后再80 r·min−1下慢搅30 min,发生絮凝反应。絮凝结束后取污泥样品进行后续指标测定。
1.4 分析方法
1) PASS的结构表征。采用傅里叶红外 (FTIR,Spectrum Two,PerkinElmer, 美国) 表征PASS的分子结构,红外光谱波数扫描范围为2 000~400 cm−1,扫描速度为4 cm−1,扫描3次样品,取均值。
2) 污泥比阻测定。SRF采用CAO等[7]所描述的方法。取50 mL污泥于超滤杯 (Amicon8400,Millipore,美国) 中在0.2 MPa外加气压下过滤,并使用电子天平 (AX523ZH,OHAUS,美国) 每隔10 s记录过滤时滤液的重量,直至污泥表面开裂。SRF通过式 (1) 计算。
SRF=2PA2bμω (1) 式中:P为过滤压强,Pa;A为过滤面积,m2;b为过滤时t/V和V作图时直线的斜率,其中t为过滤时间,s,V为对应时间下过滤的体积,mL;μ为滤液的粘度,Pa·S;ω为过滤介质上单位体积的干污泥质量,kg·m−3。
3) 污泥CST检测。CST采用污泥CST测定仪 (304M,Triton,英国) 测量。
4) 污泥泥饼含水率的检测。采用超滤杯 (Millipore,美国) 将污泥预压为泥饼后,采用活塞装置模拟的板框压滤机 (天津津冠) 对污泥进行脱水,将所得泥饼放入105 ℃烘箱 (PH-030A,上海一恒) 烘至恒重,通过烘干前后泥饼的重量测量泥饼含水率。
5) 污泥表面形貌检测。调理后的污泥冷冻干燥后,通过扫描电子显微镜 (JSM7401F,JEDL,日本) 观察污泥表面的形貌。
6) 污泥EPS提取。污泥EPS提取参考ZHANG等的方法[16]。取50 mL调理污泥于离心管中,使用离心机在3 000 r·min−1下离心10 min,所得上清液为SEPS;向离心管中加入0.05% NaCl溶液定容到50 mL,采用漩涡振荡器 (Vortex-Genie 2,Scientific industries,美国) 混匀样品,用超声于20 kHz下超声10 min,随后置于摇床150 rpm摇匀10 min,再超声3 min,最后于5 000 g下离心10 min,提取上清液为LBEPS;继续向离心管中加入0.05% NaCl溶液定容到50 mL,使用漩涡振荡器 (Vortex-Genie 2,Scientific industries,美国) 混匀样品,先于20 kHz下超声3 min,然后放入水浴机中于60 ℃水浴30 min,随即再5 000 g下离心10 min,上清液即TBEPS。提取后的EPS采用0.45 μm滤膜过滤后以备后续检测。
7) 污泥EPS检测。通过分光光度法测量提取后EPS的多糖与蛋白含量。以牛血清蛋白为标样,采用考马斯亮蓝G-250法测得[17];以葡萄糖为标样,通过硫酸-苯酚法测出多糖含量[18]。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 PASS的结构表征
图1为PASS的FTIR谱图,1 050 cm−1处的特征峰符合Al-O-Si键的伸缩振动[19],表示聚硅酸和Al3+发生了络合反应;974 cm−1处的吸收峰表示的是Al-OH-Al不对称的拉伸振动[20],605 cm−1处的吸收峰表示的式Al-OH的伸缩振动[21];454 cm−1处的吸收峰代表Si-O,H-O键的弯曲振动[22]。Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS在605、454 cm−1处的红外吸收峰高于1∶2时,说明此时PASS中产生较多的Si-O,H-O以及Al-OH基团,其吸附架桥效果可能较好;而在974 cm−1处时Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS红外吸收峰低于Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2的PASS,说明Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2的PASS具有更多的Al-OH-Al键,此时电中和作用可能较强。
2.2 PASS的脱水性能
图2是不同投加量下SRF和CST随PASS及PAC投加量的变化情况。3种材料调理后污泥的SRF和CST都随着投加量的增加逐渐减小。这是因为,污泥表面带有负电荷,当带有正电荷的絮凝剂投入污泥中时,会与污泥发生电中和反应,使得污泥脱稳聚集,释放污泥中的束缚水[23];同时PASS的长链结构会进一步架桥脱稳的污泥从而形成更大的絮体,提高污泥的过滤性能,降低污泥的SRF与CST。当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,PASS调理后污泥的SRF由6.15×1011 m·kg−1下降到了2.91×1011 m·kg−1,CST由954.1 s下降到了601.1 s;PAC调理后污泥的SRF由6.15×1011 m·kg−1下降到了3.39×1011 m·kg−1,CST由954.1 s下降到了638 s,高于前者。这说明,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时的PASS的调理效果高于PAC。改变Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时,PASS调理后污泥的SRF与CST都比摩尔比为1∶1时高,这是因为当Si/Al摩尔比较低时,由于Al3+的增加导致共聚的Al越多,电中和能力较强,吸附架桥能力较弱[24]。也可能是因为当Si/Al摩尔比较低时,PASS的中等聚合态Alb较少,而当Si/Al摩尔比适中时,中等聚合态Alb为PASS的主要部分[25]。
2.3 PASS对泥饼含水率的影响
图3为泥饼含水率随着PAC和不同Si/Al摩尔比PASS投量的变化。当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,PASS和PAC调理后的泥饼含水率都是随着投量的增加先减小后增大。当PASS的投量为100 mg·g−1 TSS时,泥饼含水率达到最小,为61.21%,PAC在40 mg·g−1 TSS时达到最小值63.68%,且所有投量下PAC的泥饼含水率都高于Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时PASS,说明Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,PASS对污泥水分的去除效果更好,这是因为PASS不仅有电中和作用,还有吸附架桥作用,而PAC以电中和作用为主[26]。而当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时,PASS在200 mg·g−1 TSS时含水率最低,为61.72%,且当投量较低时,其泥饼含水率高于Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时PASS调理的污泥。当絮凝剂投加过量时,污泥颗粒被絮凝剂完全包裹,此时污泥絮体表面开始带正电荷,污泥絮体之间出现排斥力,污泥重新到达稳定状态,污泥脱水效果变差[27]。
2.4 PASS对EPS蛋白多糖的影响
EPS作为污泥重要的一部分,占总有机质的50%~90%,且EPS中大部分有机物为亲水性的蛋白多糖,这些亲水物质与水分紧密结合从而影响了污泥的脱水性能[28]。图4为不同Si/Al摩尔比的PASS及PAC调理后污泥EPS蛋白多糖的变化规律。当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,随着PASS投加量的增加,SEPS蛋白和多糖浓度先上升后下降,LBEPS蛋白和多糖浓度逐渐下降,而TBEPS则是先上升后下降,这是因为PASS压缩了污泥的EPS,使得LBEPS部分蛋白和多糖向TBEPS转移[29]。SEPS蛋白多糖先上升的原因可能是初始时絮凝剂加入污泥中时先与污泥LBEPS的蛋白多糖反应,压缩LBEPS的结构,导致一部分蛋白转移到SEPS,同时释放LBEPS里的结合水,这与WANG等的研究一致[30]。随着投量继续增加,LBEPS结构被絮凝剂压缩破坏,絮凝剂开始压缩TBEPS的蛋白多糖。Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时的PASS与PAC调理后污泥SEPS和LBEPS蛋白多糖的变化与Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时相似,但是Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时TBEPS蛋白浓度先下降后上升, PAC调理后的污泥TBEPS蛋白浓度逐渐减小。这可能是因为,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时的PASS及PAC中低聚合态Ala占主体,此时絮凝剂的电中和能力强于吸附架桥能力,对EPS的压缩能力更强。
2.5 EPS蛋白多糖与脱水性能相关性分析
图5为不同絮凝剂调理后污泥EPS的蛋白多糖含量与污泥脱水指标SRF、CST和泥饼含水率之间的相关性。经过3种絮凝剂调理后,SRF和CST均与SEPS和LBEPS蛋白多糖含量呈现正相关性,且SRF和CST与LBEPS蛋白多糖有较强的相关性,这可能是因为污泥EPS中的蛋白多糖为亲水性物质,EPS中蛋白多糖的降低意味着污泥的亲水性和粘性降低,提高了污泥的脱水性能[31, 32]。然而三种材料调理后污泥TBEPS蛋白多糖与三种脱水指标的相关性却不同。当PASS的Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,TBEPS多糖与SRF和CST表现为负相关,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时PASS和PAC调理后TBEPS多糖与SRF、CST以及泥饼含水率却为正相关关系;当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时,TBEPS蛋白与SRF、CST和泥饼含水率呈负相关,PAC调理后TBEPS蛋白与SRF和CST呈现正相关性,原因可能是相较于PAC,PASS有较强的吸附架桥能力,且Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时PASS的电中和作用强于Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1。
2.6 污泥絮体结构
图6为不同絮凝剂调理后的污泥SEM图。原泥具有松散结构,表面较为平滑,孔隙较少,导致脱水困难。而经过PASS和PAC调理之后的污泥表面变得粗糙且多孔,形成了致密结构,这有助于机械压缩时自由水的去除[32]。当投药量为40 mg·g−1 TSS时,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS所调理的污泥表面的孔隙以及大孔径的孔隙所占的比例多,且孔径也大,而PAC调理后的污泥表面的孔隙率较少,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时的PASS调理的污泥表面孔隙多但大孔径少,说明Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS调理后的污泥脱水通道多,导致其脱水效果最好。而当絮凝剂投量上升到100 mg·g−1 TSS时,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS以及PAC调理的污泥表面的孔隙率减少,孔径也下降,污泥表面脱水通道减少,使得其含水率上升,而Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2时PASS调理的污泥表面孔径增大,孔隙率基本不变,污泥脱水通道扩大,导致泥饼含水率下降。这与泥饼含水率的变化一致。
2.7 经济核算
表2为制备PASS所需的工业级药剂以及工业级PAC的价格。通过表3计算可算得,在不包括机械和电力消耗的前提下,不同Si/Al摩尔比PASS的价格核算。合成1 t Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS大约需要1 988元,而1 t Si/Al摩尔比为1∶2的PASS的合成价格在1 814元左右,而工业级PAC的价格为2 400元∙t−1,高于2种Si/Al摩尔比的PASS,其脱水性能比Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1的PASS差,这说明所制材料在污泥脱水方面具有实际意义。
表 2 制备PASS所需的工业级药剂的单价Table 2. The unit price of the industrial-grade agent required to prepare PASS药剂 价格/ (元∙t-1) 硫酸 1 200 九水硅酸钠 2 000 十八水硫酸铝 800 聚合氯化铝 2 400 表 3 不同Si/Al摩尔比的PASS的价格核算Table 3. Price calculation of PASS with different Si/Al molar ratio元∙t−1 (以制备1 t PASS计) 絮凝剂 硫酸 九水硅酸钠 十八水硫酸铝 1∶1 PASS 133 1 262 593 1∶2 PASS 93 888 833 注:未包括机械和电力损耗。 3. 结论
1) 通过FTIR证实成功制作了聚硅酸硫酸铝絮凝剂并用于污泥脱水领域,发现其具有压缩双电层和吸附架桥的功能。将所制PASS与PAC比较后发现,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时,PASS调理后污泥的SRF与CST比PAC低,脱水性能比PAC好。
2) 测定污泥泥饼含水率后发现与PAC相比,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时PASS调理效果较好。且在低投加量的情况下,Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1时PASS的调理效果也比1∶2时好。
3) 通过相关性分析发现,PASS和PAC调理后LBEPS和SEPS蛋白多糖的浓度与SRF和CST均表现为正相关,且LBEPS蛋白多糖与脱水指标相关性更强,而调理后TBEPS与SRF和CST的相关性均不同。
4) 通过观察调理后污泥的SEM发现,经过PASS及PAC调理后,污泥絮体表面从光滑变成了粗糙多孔。当Si/Al摩尔比为1∶1且絮凝剂投量较低时,污泥絮体表面大孔径的孔隙和孔隙率均最多。对所制PASS的价格核算以及与PAC的工程价格比较发现,不包括动力和设备损耗的前提下,所制2种Si/Al摩尔比PASS的造价比PAC少,在工程应用上具有实际意义。
-
表 1 原始污泥的性质
Table 1. Properties of raw sludge
含水率/% SRF/(×1012 m·kg−1) pH TSS/(g·L−1) CST/s TOC/(mg·L−1) 94.31±0.025 0.958±0.06 7.71±0.02 56.95±0.25 954±9.3 2 336±14 表 2 制备PASS所需的工业级药剂的单价
Table 2. The unit price of the industrial-grade agent required to prepare PASS
药剂 价格/ (元∙t-1) 硫酸 1 200 九水硅酸钠 2 000 十八水硫酸铝 800 聚合氯化铝 2 400 表 3 不同Si/Al摩尔比的PASS的价格核算
Table 3. Price calculation of PASS with different Si/Al molar ratio
元∙t−1 (以制备1 t PASS计) 絮凝剂 硫酸 九水硅酸钠 十八水硫酸铝 1∶1 PASS 133 1 262 593 1∶2 PASS 93 888 833 注:未包括机械和电力损耗。 -
[1] 肖琼, 赵喜亮, 傅涛. 中国污泥处理处置行业市场分析报告[R]. 中国水网/中国固废网研究, 2020. [2] 戴晓虎. 我国污泥处理处置现状及发展趋势[J]. 科学, 2020, 72(6): 30-34. [3] 郑志坤. 城市污泥处置方法的研究及建议[C]//以供给侧结构性改革引领能源转型与创新—第十三届长三角能源论坛论文集. 中国浙江杭州: 2016: 168-172. [4] 董立文, 张鹤清, 汪诚文, 等. 造纸污泥的电渗透脱水效果[J]. 环境工程学报. 2012, 6(11): 4185-4190. [5] 王杰, 陈钰, 赵玉婷, 等. 芬顿氧化钙体系联合DDBAC对污泥脱水性能的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(4): 1424-1431. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202009033 [6] WEI H, GAO B Q, REN J, et al. Coagulation/flocculation in dewatering of sludge: A review[J]. Water Research, 2018, 143: 608-631. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.07.029 [7] CAO B D, ZHANG W J, Wang Q D, et al. Wastewater sludge dewaterability enhancement using hydroxyl aluminum conditioning: Role of aluminum speciation[J]. Water Research, 2016, 105: 615-624. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.09.016 [8] 邹鹏, 宋碧玉, 王琼. 壳聚糖絮凝剂的投加量对污泥脱水性能的影响[J]. 工业水处理, 2005, 25(5): 35-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2005.05.010 [9] LEE C S, CHONG M F, ROBINSON J, et al. Optimisation of extraction and sludge dewatering efficiencies of bio-flocculants extracted from Abelmoschus esculentus (okra)[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2015, 157: 320-325. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.04.028 [10] WEI H, REN J, LI A M, et al. Sludge dewaterability of a starch-based flocculant and its combined usage with ferric chloride[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal[J], 2018, 349: 737-747. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.151 [11] 王鑫, 易龙生, 王浩. 污泥脱水絮凝剂研究与发展趋势[J]. 给水排水, 2012, 48(S1): 155-159. doi: 10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2012.s1.047 [12] 田玲, 何芳. 无 机高分子絮凝剂的研究进展[J]. 化工设计通讯, 2016, 42(5): 143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2016.05.112 [13] 江露英, 刘红, 朱小丽, 等. 聚硅酸金属盐复合絮凝剂形貌结构及性能研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2013, 36(6): 128-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2013.06.025 [14] 李剑锋, 刘信源, 孙慧芳, 等. 聚硅酸盐类絮凝剂改性及在水处理中的应用研究进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2016, 42(7): 12-16. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2016.07.003 [15] MA J, WANG R N, WANG X Y, et al. Drinking water treatment by stepwise flocculation using polysilicate aluminum magnesium and cationic polyacrylamide[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7(3): 103049. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103049 [16] ZHANG W J, CAO B D, WANG D S, et al. Influence of wastewater sludge treatment using combined peroxyacetic acid oxidation and inorganic coagulants re-flocculation on characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)[J]. Water Research, 2016, 88: 728-739. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.049 [17] BRADFORD M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1976, 72(1): 248-254. [18] FROLUND B, PALMGREN R, KEIDING K, et al. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin[J]. Water Research, 1996, 30(8): 1749-1758. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(95)00323-1 [19] 熊丽丽, 高丽, 秦冬玲, 等. 聚硅酸铝、聚硅酸铁和聚硅酸铝铁的制备及离子残留分析[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 39(4): 150-156. [20] YANG S, LI W, ZHANG H J, et al. Treatment of paper mill wastewater using a composite inorganic coagulant prepared from steel mill waste pickling liquor[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 209: 238-245. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.07.049 [21] LI J F, LIU X Y, CHENG F Q. Bio-refractory organics removal and floc characteristics of poly-silicic-cation coagulants in tertiary-treatment of coking wastewater[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 324: 10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.142 [22] 高丽, 熊丽丽, 朱超, 等. 硅溶胶-聚硅酸铝锌复合絮凝剂的制备及应用[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 40(2): 65-70. [23] HU P, ZHUNG S H, SHEN S H, et al. Dewaterability of sewage sludge conditioned with a graft cationic starch-based flocculant: Role of structural characteristics of flocculant[J]. Water Research, 2021, 189: 116578. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116578 [24] SUN T, SUN C H, ZHU G L, et al. Preparation and coagulation performance of poly-ferric-aluminum-silicate-sulfate from fly ash[J]. Desalination, 2011, 268(1-3): 270-275. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.023 [25] 高宝玉, 刘总纲, 岳钦艳. 聚合硅酸硫酸铝溶液中铝的形态分布及转化规律[J]. 环境化学, 2004(2): 208-212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-6108.2004.02.017 [26] LI L X, PENG C, DENG L H, et al. Understanding the synergistic mechanism of PAM-FeCl3 for improved sludge dewaterability[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 301: 113926. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113926 [27] LIN Q T, PENG H L, ZHONG S X, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and secondary sludge dewatering performance of a novel combined silicon-aluminum-iron-starch flocculant[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 285: 199-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.005 [28] 周俊, 周立祥, 黄焕忠. 污泥胞外聚合物的提取方法及其对污泥脱水性能的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(7): 2752-2757. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.07.056 [29] YANG P, LI D D, ZHANG W J, et al. Flocculation-dewatering behavior of waste activated sludge particles under chemical conditioning with inorganic polymer flocculant: Effects of typical sludge properties[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 218: 930-940. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.169 [30] WANG H F, HU H, WANG H J, et al. Impact of dosing order of the coagulant and flocculant on sludge dewatering performance during the conditioning process[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 643: 1065-1073. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.161 [31] QIAN X, WANG Y L, ZHENG H L. Migration and distribution of water and organic matter for activated sludge during coupling magnetic conditioning-horizontal electro-dewatering (CM-HED)[J]. Water Research, 2016, 88: 93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.001 [32] PENG H L, ZHONG S X, XIANG J X, et al. Characterization and secondary sludge dewatering performance of a novel combined aluminum-ferrous-starch flocculant (CAFS)[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 173: 335-345. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2017.08.005 -






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: