-
除草剂在农业生产中必不可少,其中阿特拉津(C8H14ClN5,atrazine,ATZ)就是使用最广泛的氯类除草剂之一[1]。阿特拉津非常稳定,会污染土壤和水环境[2],从而影响生态系统并对人类构成健康风险。欧盟在2003年就禁止了阿特拉津,但在中国、巴西和伊朗等发展中国家仍广泛使用[3]。目前,我国在河流、湖泊和水库中陆续检出到阿特拉津,并表现出逐年增加的趋势[4]。由于阿特拉津及其代谢产物毒性大,传统的处理技术如吸附和生化处理难以将其有效去除[1,4]。以臭氧催化氧化法和Fenton/类Fenton氧化法为代表的高级氧化法虽然能有效地氧化ATZ,但臭氧产生成本高,实际利用率低,Fenton/类Fenton氧化法pH范围小,反应过程中产生大量污泥[1,5]。因此,迫切需要研究更高效的处理方法。
近年来,由于SO4·−具有极高的氧化-还原电位(2.50~3.10 eV,HO·为1.89~2.72 eV)、相对较长的半衰期(30~40 μs,HO·为20 ns)和广泛的pH适用范围(2~8)[6-8],基于SO4·−的催化氧化技术已成为极富希望的处理方法[9-10]。由于过一硫酸盐(peroxymonosulfate, PMS)非均相催化剂主要以过渡金属氧化物为主,其中以氧化钴的催化效率最高[11-12],但不够稳定,浸出的钴离子可能对环境有害[13]。为克服这一问题,最有效的方法之一是制备钙钛矿结构的钴基催化剂[14-15]。具有ABO3结构的钙钛矿复合金属氧化物用作PMS催化剂受到了广泛的关注[16],A位点一般为稀土金属,与氧形成密集的立方堆积,对其结构的稳定起着主要作用;B位点一般为过渡金属,占据八面体中心,影响电子转移能力和氧空位的数量,从而影响催化活性[17]。A位金属通常为金属镧,有利于B位金属的暴露而不影响催化活性[18-19]。在LaBO3中,Co被认为是最活跃的金属,因为Co(Ⅱ)/Co(Ⅲ)氧化还原对能催化PMS产生更多的ROS(reactive oxygen species)[20]。LaCoO3已被证明可有效活化PMS以降解萘普生[21]、四环素[22]、卡马西平[23]和2-苯基-5-磺基苯并咪唑[24]。然而,有关LaCoO3活化PMS降解ATZ性能和降解机理,以及ATZ与LaCoO3表面吸附态PMS之间是否存在直接电子传递作用,并导致其对ATZ降解,尚缺乏相关报道。
阴离子对PMS催化体系具有重要影响[25],共存阴离子在实际废水中经常出现,研究阴离子对PMS催化体系的影响具有重要意义。阴离子一方面可能改变催化剂的稳定性,另一方面可能通过干扰自由基的产生和后续反应[26],在负载型Co3O4活化PMS降解罗丹明B体系中,Cl−有轻微的促进作用[27];而HCO3−、CO32−和Cl−会明显抑制钴酸锰活化PMS降解有机染料[28]。有研究表明,实际废水与模拟废水的处理效果存在较大差异,可能是实际废水中无机阴离子产生了干扰[29]。关于阴离子对PMS催化体系性能的研究还不太充分。为此,本研究系统地探究了常见无机阴离子和腐植酸(HA)对催化体系的影响。
本文采用溶胶-凝胶法制备了钙钛矿催化剂,并将其用于活化PMS降解ATZ,评价了催化剂类型、PMS投加量、催化剂投加量、ATZ质量浓度、pH和实验用水等因素的影响,讨论了Cl−、NO3−、HCO3−、H2PO4− 和SO42−及HA的影响,阐明了PMS的催化机理。
-
硝酸镧(La(NO3)3·6H2O)、硝酸钴(Co(NO3)2·6H2O)、无水柠檬酸(C6H8O7)、叔丁醇(TBA)、L-组氨酸(C6H9N3O2)、硫酸(H2SO4)、对苯醌(p-BQ)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、乙腈(色谱纯)、5,5-二甲基-1-吡咯啉-N-氧化物(DMPO),2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶(TEMP)和过一硫酸盐(PMS,KHSO5·0.5KHSO4·0.5K2SO4)购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。阿特拉津(ATZ,≥97%)和甲醇(CH3OH)购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。此外,实验中使用的化学药品和溶剂除单独注明外均为分析纯。
-
采用溶胶-凝胶法制备钙钛矿催化剂[30]。将一定比例的金属硝酸盐溶解在50 mL去离子水中,完全溶解后,添加柠檬酸(添加物质的量等于总金属物质的量)作为配体,随后将金属硝酸盐和柠檬酸的混合物搅拌2.00 h,然后继续搅拌并在80.00 ℃水浴加热直至凝胶状物质出现。所得到的凝胶随后在105.00 ℃下烘干6.00 h得到海绵状材料,冷却后将其研磨成细粉,随后在马弗炉中煅烧4.00 h(800.00 ℃,5.00 ℃·min−1)。冷却后将样品用无水乙醇和纯水洗净数次并烘干保存待用。
-
将0.01 g阿特拉津溶于1.00 L(10.00 mg·L−1)去离子水中,搅拌24.00 h待用。将15.00 mg催化剂和4 mL PMS溶液(0.1 mmol·L−1)加入到100.00 mL ATZ溶液中,以300.00 r·min−1的转速搅拌,实验温度为室温(25±1.00) ℃。取样时在取样管中预先加入1.00 mL的甲醇(1.00 mol·L−1),用注射器取出反应液1.00 mL,过0.45 μm水系膜后待测。
催化降解实验:分别设置不同的ATZ初始质量浓度(1.00、2.50、5.00、7.50和10.00 mg·L−1)、PMS初始质量浓度(0.064、0.128、0.256、0.320、0.384和0.512 g·L−1)、催化剂投加量(0.05、0.10、0.15、0.20和0.25 g·L−1)和模拟废水初始pH(3.00、4.00、5.42、7.00、9.00和11.00)。
无机阴离子影响实验:分别设置Cl−、NO3−、HCO3−、H2PO4−和SO42−(1.00、5.00、10.00和20.00 mmol·L−1)、腐殖酸(10、20、50和100 mg·L−1)和不同实验用水(纯净水、自来水和地表水)。其中纯净水由分析型超纯水机(WP-UP-WF-30,沃特浦,中国)制得,电导率约为1~10 μS·cm−1(25 ℃),自来水为广州大学城管道自来水,地表水取自珠江广州大学城河段南亭村断面)。
-
利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,蔡司-Sigma300,牛津能谱,德国)观测LaCoO3表面形貌;利用能谱仪(EDS,蔡司-Sigma300,牛津能谱,德国)测定元素组成;利用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Bruker D8 Advance,德国)检测LaCoO3的结构;利用X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,ThermoFisher Nexsa,美国)分析LaCoO3表面元素和价态;利用电化学工作站(CHI760E,辰华,中国)测定计时电流;利用电子顺磁共振(EPR,Bruker-EMXplus-10/12,德国)检测体系中的ROS。
采用高效液相色谱(HPLC,Waters-e2695,USA)检测样品中ATZ的质量浓度[31]。色谱柱为C-18(Waters,5 μm,4.6 mm×250 mm),检测器为紫外检测器(2998 PDA Detector),流动相由乙腈和0.10%乙酸溶液组成,其体积比为60%:40%,流速1.00 mL·min−1,柱温40 ℃,检测波长221.00 nm,注射体积20.00 μL。采用电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS,Agilent 7700/7800,美国)检测镧元素和钴元素的浸出质量浓度。pH由pH-3c仪(Rex,上海雷磁,中国)测定。
-
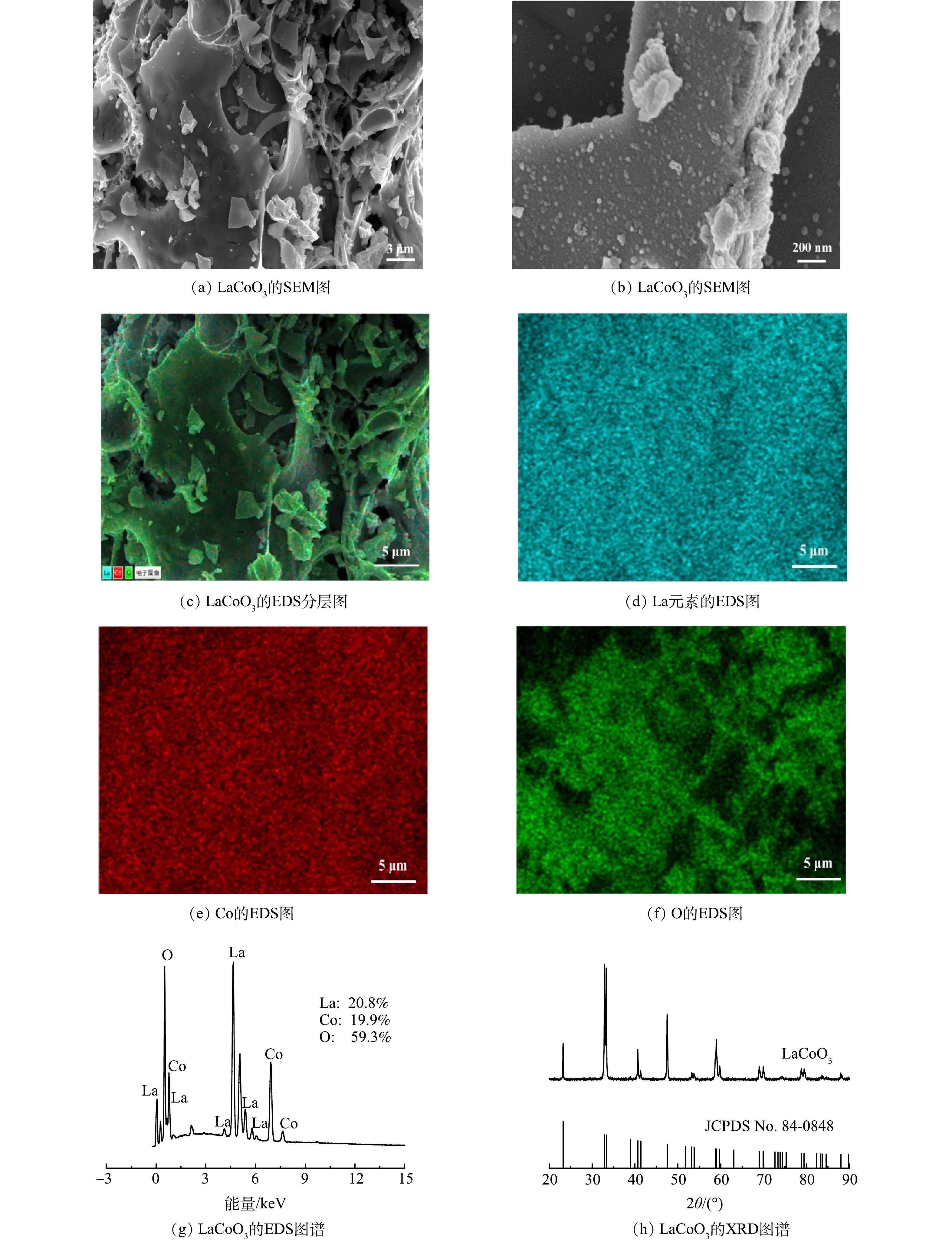
1) SEM、EDS和XRD分析。如图1(a)~(b)所示,LaCoO3具有立体块状结构,表面存在许多细颗粒,这有利于催化。为了进一步确认LaCoO3表面元素,还对其进行了元素映射分析。如图1(c)~(f)所示,La、Co和O在所选区域均匀分布,La和Co的密度低于O元素。EDS成像进一步揭示了LaCoO3表面元素由La、Co和O元素组成。如图1(g)所示,La、Co和O元素比近似为1∶1∶3,这与化学式基本一致。为了确认LaCoO3的晶体结构,进行了XRD测试。由图1(h)可以看出,样品在2θ为23.20°,32.80°,33.30°和47.50°的特征衍射峰与LaCoO3(JCPDS 84-0848)匹配。这说明催化剂具有结构良好的钙钛矿结构,除LaCoO3相外,没有形成Co3O4和La2O3等常见的氧化物杂质。
2) XPS分析。利用XPS对LaCoO3的元素和化学状态进行了研究。图2(a)为LaCoO3的全尺寸XPS能谱。此外,还利用C1s(284.80 eV)对各元素能谱进行了标定。由图2(b)可见,位于830.00~840.00 eV和847.00~857.00 eV分别对应于La3d5/2和La3d3/2。833.60、837.70、850.50和854.60 eV的峰可以归因于La(Ⅲ)[32]。钙钛矿中B位元素的价态尤为重要。如图2(c)所示,Co2p能谱由4个峰组成。Co2p3/2峰(780.6 eV)和Co2p1/2峰(795.6 eV)可归因于Co(Ⅲ),Co2p3/2峰(782.00 eV)和Co2p1/2峰(796.60 eV)则由Co(Ⅱ)产生[8]。由图2(c)中Co2p3/2的峰强度计算可知,使用前催化剂中Co(Ⅱ)和Co(Ⅲ)的含量分别为46%和54%;使用后则为40%和60%,由Co2p1/2的数据也得到相同的结果。多次使用后的催化剂的催化性能有所降低,这说明低价态Co(Ⅱ)含量与催化性能密切相关。O1s能谱的XPS能谱如图2(d)所示。钙钛矿中以528.40、529.60、530.80和532.30 eV为中心的峰分别对应晶格氧(OL)、表面氧(Os)、氧空位(Ov)和吸附的分子水[33]。本研究制备的LaCoO3使用前含有大量的OL和Ov,使用后OL和Ov的相对比例分别由19.50%和39.80%降至0.00%和27.30%。这可能是由于其参与到了Co(Ⅲ)/Co(Ⅱ)的氧化还原反应中[34],关于氧的各种形态分布与催化性能之间的关系还需要进一步深入研究。
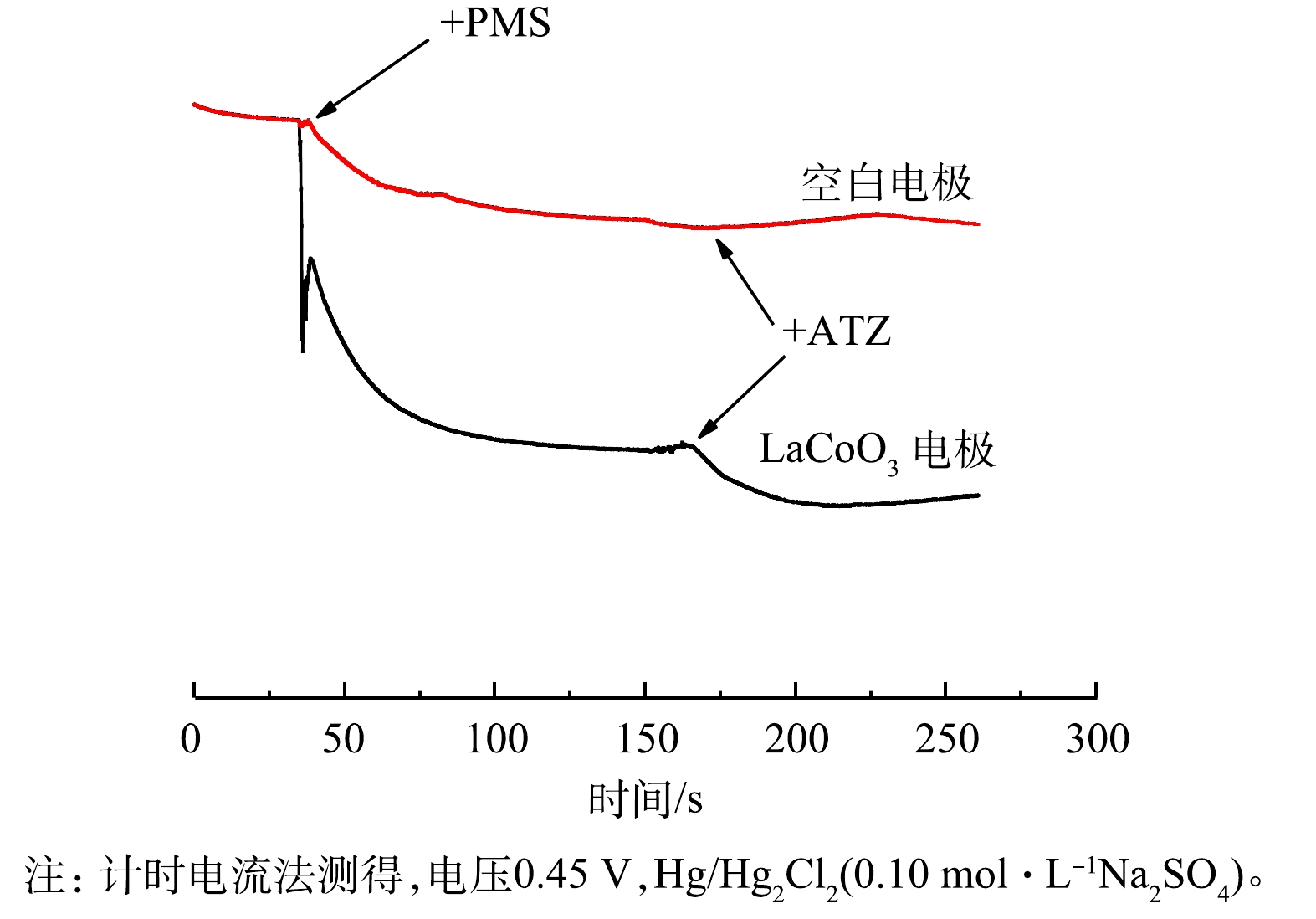
3)计时电流测定。如图3所示,添加PMS对电流输出有明显影响。这表明PMS和LaCoO3表面之间确实发生了电子转移[35]。随着ATZ的加入,电流也发生了变化,预示着LaCoO3可以有效地介导电子从ATZ转移到PMS[36-38]。相比之下,空白电极在添加PMS和ATZ后表面电流的变化很小。
-
1)材料筛选实验。不同催化体系下ATZ的去除结果如图4(a)所示。单独的PMS几乎不能氧化ATZ。所有体系对ATZ的吸附不显著,去除率均小于5.00%。几种钙钛矿活化PMS催化氧化ATZ的效率为LaCoO3>LaCuO3>LaMnO3>LaFeO3,在10 min内,LaFeO3、LaMnO3和LaCuO3对ATZ的去除率分别为7.00%、17.00%和73.00%,而LaCoO3活化PMS后对ATZ的去除率几乎为100.00%,相应的速率常数分别为0.005、0.011、0.070和0.129 min−1。显然,B位元素对LaBO3的催化性能有重大影响。此外,考虑到使用过程中钴元素会浸出,还制备了2种核壳结构催化剂。但初步研究结果(图4(a))表明,在使用2种核壳结构催化剂的情况下,反应速率常数由LaCoO3的0.129 min−1降到0.037 min−1和0.041 min−1。这表明外围的壳抑制了核的催化性能,还需要深入研究。本文后续研究选择LaCoO3作为催化剂。
2) ATZ初始质量浓度对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解效果的影响。如图4(b)所示,所有选定质量浓度均在10 min内有效降解,在前2 min内快速衰减,当ATZ初始质量浓度由2.50 mg·L−1增加到10.00 mg·L−1时,相应的降解速率常数由1.210 min−1降至0.728 min−1。原因可能是在相同条件下,固定的催化剂用量和PMS质量浓度所产生的自由基总量是恒定的,无法在特定时间内将高质量浓度的ATZ完全降解。结果表明,ATZ的降解速率常数发生了变化。分析可能的原因为:ROS与ATZ及其中间产物之间均可能发生反应,在活性氧总量一致的情况下,ATZ质量浓度越高,催化剂表面新生成的中间产物质量浓度也越高,阻碍了ATZ向催化剂表面的传质,催化剂表面ATZ质量浓度下降,表观速率常数降低。因此,选择10.00 mg·L−1为后续实验初始质量浓度。
3) PMS投加量对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图4(c)所示,随着PMS浓度的增加,ATZ的降解速率迅速增加。因为PMS质量浓度越高,可以增强与催化剂的接触,从而产生更多的活性氧。当PMS质量浓度由0.320 g·L−1增加到0.512 g·L−1时,速率常数反而略有降低。这可能是因为过量的SO4·−会发生自淬灭[39]。综合考虑后续研究选择0.256 g·L−1作为PMS的质量浓度。
4)催化剂用量对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图4(d)所示,在不添加催化剂的情况下,10 min内PMS降解ATZ的速率常数仅为0.004 min−1;催化剂用量为0.05 g·L−1时,速率常数提高到0.088 min−1,说明LaCoO3能有效催化PMS降解ATZ;催化剂用量为0.15 g·L−1时,速率常数增加到0.129 min−1。主要原因是随着催化剂用量的增加,催化剂表面的活性位点增多,催化PMS的能力增强,从而产生更多的ROS以降解污染物[40]。因此,后续研究中选择0.15 g·L−1作为催化剂用量。
5) pH对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。由图4(e)可见,当pH为3.00~5.42时,去除率随初始pH的增加而增加。当pH升高到11.00时,速率常数由0.129 min−1下降到0.003 min−1,pH=5.42为最佳条件。PMS的形式主要取决于溶液的pH及其pKa2(pKa2=9.40)。在酸性和中性条件下,主要存在形式为HSO5−[12],SO4·−或HSO5−与OH−/H2O反应生成HO·,SO4·−和HO·的存在可获得较高的ATZ去除率。PMS在酸性条件下比中性或碱性条件下更稳定,导致活化相对较慢。此外,H+还消耗了一定量的SO4·−和HO·,导致这2种自由基的不必要消耗[27]。以上原因共同导致了ATZ降解率的下降。当pH>9.00时,PMS的主要存在形式转化为SO52−[10]。此外,SO52−的催化活性低于HSO5−,在pH>10.00时,催化剂表面会形成氢氧化钴,限制了ATZ的降解,降低了催化剂的催化活性[41]。
6)催化剂的稳定性。如图4(f)所示,在前2次重复实验中,ATZ的去除率变化不明显;经第3次使用后,性能稍有下降,10.00 min后速率常数由0.129 min−1降到0.100 min−1,第5次后降至0.087 min−1。这可能是由于LaCoO3使用过程中表面结构和活性中心发生了变化。采用ICP-MS检测从LaCoO3/PMS中浸出La和Co元素质量浓度,反应60 min后La元素浸出质量浓度为5.72 mg·L−1,Co元素浸出质量浓度为0.85 mg·L−1,催化剂具有一定的稳定性。
-
1) NO3−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图5(a)所示,NO3−轻微抑制ATZ的降解。这是因为NO3−不会引起溶液pH的变化,对氧化剂的稳定性没有影响;其次,NO3−对催化剂的催化活性也没有影响[42]。但NO3−可以与HO·和SO4·−反应形成氧化能力较弱的硝酸根自由基(NO3·−),如式(1)和式(2)所示[42-43]。
2) SO42−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。SO42−对ATZ的降解比NO3−表现出更为轻微抑制作用。这是因为与NO3−一样,SO42−不会改变溶液的pH,对催化剂的催化活性也没有影响。其次SO42−是惰性离子,不会与HO·和SO4·−反应[44]。
3) Cl−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图5(c)所示,当Cl−浓度从1.00 mmol·L−1增加到20.00 mmol·L−1时,对ATZ的降解呈现出先抑制后促进的现象,低浓度的Cl−(<10.00 mmol·L−1)抑制降解,而高浓度的Cl−(>10.00 mmol·L−1)可促进降解。这可能是由于较低浓度的Cl−会优先与SO4·−反应,而产生活性更小的Cl·,从而减弱了ATZ的降解;当Cl−浓度进一步增大,Cl−通过双电子转移直接与PMS反应产生活性氯(即Cl·、Cl2·−和Cl2,
E0Cl· =2.40 V;E0cl2·− =2.40 V;E0Cl2 =1.40 V),与ATZ的反应路径与SO4·−相似[45]。除上述原因外,大量的活性氯可以催化反应产生更多的SO4·−,从而提高降解效率[46]。4) HCO3−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图5(d)所示,HCO3−浓度从1.00 mmol·L−1增加到20.00 mmol·L−1时,速率常数从0.015 min−1降至0.005 min−1。这是因为HCO3−可以改变溶液的pH,会影响PMS的稳定性。此外,pH的变化也会影响催化剂的表面电荷,从而影响其催化性能。最后,HCO3−还会与SO4·−和HO·反应生成氧化能力较弱的活性物种(式(3)~式(4))[47-49]。
5) H2PO4−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图5(e)所示,添加1 mmol·L−1 H2PO4−后,ATZ的降解速率常数由0.129 min−1降至0.047 min−1。H2PO4−浓度由1.00 mmol·L−1增加到20.00 mmol·L−1时,速率常数由0.047 min−1降至0.034 min−1。这是由于H2PO4−可以改变溶液的pH,这会进一步影响PMS的稳定性和催化剂的催化活性。此外,H2PO4−与催化剂表面的活性位点具有较强的络合能力。有研究表明,H2PO4−可以在零价铁表面[50]、氧化铈纳米颗粒表面形成络合从而影响催化剂的催化活性[51]。此外,H2PO4−可以淬灭HO·和SO4·−(式(5)~式(6))[42,49]。
-
天然有机物(NOM)在地表水中普遍存在,含有丰富的官能团(羧基、酚羟基和醇基等),这些基团可与催化剂上的活性中心和有机污染物相互作用,从而影响ATZ的去除[52]。本研究以腐植酸(HA)作为典型的NOM,考察了反应体系对ATZ去除的影响,结果图6(a)所示。微量的HA的抑制作用较弱,当HA投加量为100 mg·L−1时,ATZ的速率常数降低到0.092 min−1。这是因为带负电荷的HA在水中会与催化剂表面的金属活性中心螯合,阻碍活性中心的暴露,抑制催化。事实上,天然水体中的HA含量相对较低,微量的HA对反应体系影响较小。此外,ATZ溶液配制用水也会对催化效果产生极大影响。如图6(b)所示,在自来水和地表水中,LaCoO3/PMS对ATZ的去除速率常数分别降至0.082 min−1和0.005 min−1。这说明LaCoO3/PMS体系受实验用水中共存离子和其他成分的影响较大。
-
通过淬灭实验,测定了LaCoO3/PMS体系中产生或存在的自由基。甲醇(MeOH)是有效的SO4·−和HO·淬灭剂(
kso4⋅− =2.50×107 L·(mol·s)−1,kHO⋅ =9.70×108 L·(mol·s)−1),而叔丁醇(TBA)可有效淬灭HO·(kHO⋅ =(3.80~7.60)×108 L·(mol·s)−1),与SO4·−反应速率较低(kso4⋅− =(4.00~9.10)×105 L·(mol·s)−1)[53]。由图7(a)中可以看出,TBA对ATZ降解的抑制作用小于MeOH,说明HO·和SO4·−均有显著作用,但SO4·−起着更重要的作用。本研究中使用L-组氨酸淬灭单线态氧(1O2,0.15 V)。结果表明,加入1 mmol·L−1的L-组氨酸便终止了反应的进行。这是由于L-组氨酸会可以快速消除PMS[54]。为了排除PMS质量浓度降低对ATZ去除的影响,通过一系列实验验证1O2是否为主要活性物质。如图4(c)所示,当PMS质量浓度进一步增加到0.384 g·L−1时,ATZ的去除速率常数没有显着变化。这表明过量的PMS不能被有限的LaCoO3催化剂完全活化。因此,通过在反应体系中加入1 mmol·L−1L-组氨酸来测试0.384 g·L−1 PMS的消耗,发现消耗了44%PMS,这表明系统中仍然存在56% PMS。然而,在本研究中,L-组氨酸的抑制作用仍然显著(Kobs下降到0.022 min−1),并且体系中残留的PMS超过0.124 g·L−1。这表明LaCoO3活化剩余的PMS产生的1O2被淬灭,从而削弱了降解效果,因此,1O2是LaCoO3/PMS 系统中的主要活性物质。
对苯醌(p-BQ)常用来淬灭O2·−(
ko2⋅− =2.90×109 L·(mol·s)−1)[55-56]。在本研究中,10 mmol·L−1 p-BQ显示出与TBA相似的抑制效果,因此,推测系统中可能存在极少的O2·−,因为在中性pH下,p-BQ也可清除HO·(kHO· =1.20×109 L·(mol·s)−1)[57]。为了进一步验证上述推论,对LaCoO3/PMS系统中可能生成的ROS进行电子顺磁共振(EPR)测试分析。如图8所示,在捕获剂/PMS系统中无法识别出明显的自由基信号。说明PMS自身不能产生ROS。如图8(a)所示,加入LaCoO3后,分别在系统中观察到DMPO-HO·和DMPO-SO4·−加合物的特征峰。这表明生成了SO4·−和HO·。此外,信号比为1:1:1的TEMP-1O2加合物的三重特征峰也被清晰地观察到,表明1O2参与了催化过程。然而,随着LaCoO3的引入,并没有观察到DMPO-O2·−加合物信号,这意味着在LaCoO3/PMS系统中O2·−可以忽略不计。综上所述,推测LaCoO3/PMS体系中存在SO4·−、HO·和1O2,且SO4·−和1O2优先于HO·与ATZ反应。
基于以上结果,LaCoO3/PMS体系中存在自由基氧化和非自由基氧化过程。在自由基氧化过程中,通常Co(Ⅱ)是PMS催化产生SO4·−和HO·的主要活性位点[58](式(7)~式(9))。另外,LaCoO3中的晶格氧(OL)可提供电子生成SO4·−[58](式(10))。在非自由基反应过程中,Co(Ⅱ)作为主要吸附位点,可与SO5·−反应生成1O2(式(11)),OL也可随着Co(Ⅱ)和Co(Ⅲ)的还原而转化为1O2(式(12))[59-60]。另外,SO5·−由于反应速率高而催化能低,易发生自反应,导致1O2的产生(式(13)~式(14))[61]。LaCoO3上丰富的氧空位更容易吸附PMS从而自分解,促进1O2的析出[62](式(15)~式(16))。此外,氧空位的存在也为B位金属阳离子的氧化还原循环的实现提供了连接,从而提高了催化稳定性[20,58]。综上所述,LaCoO3优异的催化性能主要是由于氧空位、表面Co(Ⅱ)位点和晶格氧的存在,产生了大量的ROS (式(17))所致。
-
1)在最佳条件下(ATZ=10.00 mg·L−1,LaCoO3= 0.15 g·L−1,PMS=0.256 g·L−1,初始pH=5.42),ATZ可在10.00 min内快速被完全降解。经过5次循环实验,ATZ的去除率在可接受范围内,反应60 min后Co元素浸出质量浓度为0.85 mg·L−1。
2) SO42−和NO3−轻微抑制LaCoO3活化PMS降解ATZ,高浓度的Cl−促进了降解,H2PO4−、HCO3−和低浓度的Cl−及天然有机物HA抑制了降解。
3) LaCoO3具有立体的块状组织结构,表面存在许多细颗粒原点;LaCoO3含有大量的氧空位,表面Co(Ⅱ)位点、氧空位和晶格氧在反应中起到了重要作用;在LaCoO3/PMS体系存在电子转移过程。
4) LaCoO3/PMS体系中存在SO4·−、HO·和1O2,且SO4·−和1O2优先于HO·与ATZ反应。
LaCoO3催化过一硫酸盐高效降解阿特拉津的性能及机理
Performance and mechanism of LaCoO3 catalyzed permonosulfate on efficient degradation of atrazine
-
摘要: 钙钛矿类活化过一硫酸盐(PMS)催化氧化技术已成为一种有效处理难降解有机物的方法。然而,关于其活化PMS降解阿特拉津的性能、机理和无机阴离子及天然有机物对催化的影响并不清晰。为此,制备了钙钛矿催化剂,系统地研究了LaCoO3催化PMS降解阿特拉津(ATZ)的性能和机理,并探究了常见无机阴离子和腐植酸(HA)对降解性能的影响。结果表明,在中性pH下具有良好的降解效果;SO42−和NO3−轻微抑制降解,高浓度Cl−则具有明显的促进作用,其他无机阴离子(低浓度的Cl−、H2PO4−、HCO3−)和HA抑制降解。自由基淬灭实验和EPR测试证明体系中1O2和SO4·−起着重要作用,HO·对降解过程也有贡献。XPS测试表明LaCoO3表面的Co(Ⅱ)位点、晶格氧和氧空位在催化中发挥了重要作用;计时电流测定表明LaCoO3/PMS体系存在电子转移过程。LaCoO3表现出较好的稳定性,连续使用5次后ATZ去除率略有下降。最后提出了LaCoO3活化PMS降解ATZ的可能机理。以上研究结果可为LaCoO3活化PMS去除ATZ的应用提供参考。Abstract: Perovskite-based activated peroxymonosulfate(PMS) catalytic oxidation technology has become an effective method for the treatment of refractory organics. However, its performance and mechanism, as well as the effects of inorganic anions and natural organics on atrazine degradation are not clear. Thus, perovskite catalysts were prepared, the performance and mechanism of LaCoO3 catalyzing PMS to degrade of atrazine (ATZ) were systematically studied, and the effects of common inorganic anions and humic acid (HA) on the degradation performance were explored. The results showed that a good degradation effect occurred at neutral pH; SO42− and NO3− slightly inhibited the degradation, high concentration of Cl− had a significant promoting effect, and other inorganic anions (low concentration Cl−, H2PO4−, HCO3−) and HA inhibited degradation. Radical quenching experiments and EPR tests showed that 1O2 and SO4·− played an important role in the system, and HO· also contributed to the degradation process. XPS test showed that Co(Ⅱ) sites, lattice oxygen and oxygen vacancies on the surface of LaCoO3 played an important role in the catalysis; Chronoamperometry showed that there was an electron transfer process in the LaCoO3/PMS system. LaCoO3 showed a good stability, and the removal rate of ATZ decreased slightly after 5 consecutive usages of LaCoO3. Finally, the possible mechanism of LaCoO3-activated PMS to degrade ATZ was proposed. The above research results can provide a reference for the application of LaCoO3-activated PMS to remove ATZ.
-
Key words:
- LaCoO3 /
- atrazine /
- peroxymonosulfate /
- inorganic anion /
- catalytic
-
除草剂在农业生产中必不可少,其中阿特拉津(C8H14ClN5,atrazine,ATZ)就是使用最广泛的氯类除草剂之一[1]。阿特拉津非常稳定,会污染土壤和水环境[2],从而影响生态系统并对人类构成健康风险。欧盟在2003年就禁止了阿特拉津,但在中国、巴西和伊朗等发展中国家仍广泛使用[3]。目前,我国在河流、湖泊和水库中陆续检出到阿特拉津,并表现出逐年增加的趋势[4]。由于阿特拉津及其代谢产物毒性大,传统的处理技术如吸附和生化处理难以将其有效去除[1,4]。以臭氧催化氧化法和Fenton/类Fenton氧化法为代表的高级氧化法虽然能有效地氧化ATZ,但臭氧产生成本高,实际利用率低,Fenton/类Fenton氧化法pH范围小,反应过程中产生大量污泥[1,5]。因此,迫切需要研究更高效的处理方法。
近年来,由于SO4·−具有极高的氧化-还原电位(2.50~3.10 eV,HO·为1.89~2.72 eV)、相对较长的半衰期(30~40 μs,HO·为20 ns)和广泛的pH适用范围(2~8)[6-8],基于SO4·−的催化氧化技术已成为极富希望的处理方法[9-10]。由于过一硫酸盐(peroxymonosulfate, PMS)非均相催化剂主要以过渡金属氧化物为主,其中以氧化钴的催化效率最高[11-12],但不够稳定,浸出的钴离子可能对环境有害[13]。为克服这一问题,最有效的方法之一是制备钙钛矿结构的钴基催化剂[14-15]。具有ABO3结构的钙钛矿复合金属氧化物用作PMS催化剂受到了广泛的关注[16],A位点一般为稀土金属,与氧形成密集的立方堆积,对其结构的稳定起着主要作用;B位点一般为过渡金属,占据八面体中心,影响电子转移能力和氧空位的数量,从而影响催化活性[17]。A位金属通常为金属镧,有利于B位金属的暴露而不影响催化活性[18-19]。在LaBO3中,Co被认为是最活跃的金属,因为Co(Ⅱ)/Co(Ⅲ)氧化还原对能催化PMS产生更多的ROS(reactive oxygen species)[20]。LaCoO3已被证明可有效活化PMS以降解萘普生[21]、四环素[22]、卡马西平[23]和2-苯基-5-磺基苯并咪唑[24]。然而,有关LaCoO3活化PMS降解ATZ性能和降解机理,以及ATZ与LaCoO3表面吸附态PMS之间是否存在直接电子传递作用,并导致其对ATZ降解,尚缺乏相关报道。
阴离子对PMS催化体系具有重要影响[25],共存阴离子在实际废水中经常出现,研究阴离子对PMS催化体系的影响具有重要意义。阴离子一方面可能改变催化剂的稳定性,另一方面可能通过干扰自由基的产生和后续反应[26],在负载型Co3O4活化PMS降解罗丹明B体系中,Cl−有轻微的促进作用[27];而HCO3−、CO32−和Cl−会明显抑制钴酸锰活化PMS降解有机染料[28]。有研究表明,实际废水与模拟废水的处理效果存在较大差异,可能是实际废水中无机阴离子产生了干扰[29]。关于阴离子对PMS催化体系性能的研究还不太充分。为此,本研究系统地探究了常见无机阴离子和腐植酸(HA)对催化体系的影响。
本文采用溶胶-凝胶法制备了钙钛矿催化剂,并将其用于活化PMS降解ATZ,评价了催化剂类型、PMS投加量、催化剂投加量、ATZ质量浓度、pH和实验用水等因素的影响,讨论了Cl−、NO3−、HCO3−、H2PO4− 和SO42−及HA的影响,阐明了PMS的催化机理。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验试剂
硝酸镧(La(NO3)3·6H2O)、硝酸钴(Co(NO3)2·6H2O)、无水柠檬酸(C6H8O7)、叔丁醇(TBA)、L-组氨酸(C6H9N3O2)、硫酸(H2SO4)、对苯醌(p-BQ)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、乙腈(色谱纯)、5,5-二甲基-1-吡咯啉-N-氧化物(DMPO),2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶(TEMP)和过一硫酸盐(PMS,KHSO5·0.5KHSO4·0.5K2SO4)购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。阿特拉津(ATZ,≥97%)和甲醇(CH3OH)购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。此外,实验中使用的化学药品和溶剂除单独注明外均为分析纯。
1.2 钙钛矿催化剂制备方法
采用溶胶-凝胶法制备钙钛矿催化剂[30]。将一定比例的金属硝酸盐溶解在50 mL去离子水中,完全溶解后,添加柠檬酸(添加物质的量等于总金属物质的量)作为配体,随后将金属硝酸盐和柠檬酸的混合物搅拌2.00 h,然后继续搅拌并在80.00 ℃水浴加热直至凝胶状物质出现。所得到的凝胶随后在105.00 ℃下烘干6.00 h得到海绵状材料,冷却后将其研磨成细粉,随后在马弗炉中煅烧4.00 h(800.00 ℃,5.00 ℃·min−1)。冷却后将样品用无水乙醇和纯水洗净数次并烘干保存待用。
1.3 实验方法
将0.01 g阿特拉津溶于1.00 L(10.00 mg·L−1)去离子水中,搅拌24.00 h待用。将15.00 mg催化剂和4 mL PMS溶液(0.1 mmol·L−1)加入到100.00 mL ATZ溶液中,以300.00 r·min−1的转速搅拌,实验温度为室温(25±1.00) ℃。取样时在取样管中预先加入1.00 mL的甲醇(1.00 mol·L−1),用注射器取出反应液1.00 mL,过0.45 μm水系膜后待测。
催化降解实验:分别设置不同的ATZ初始质量浓度(1.00、2.50、5.00、7.50和10.00 mg·L−1)、PMS初始质量浓度(0.064、0.128、0.256、0.320、0.384和0.512 g·L−1)、催化剂投加量(0.05、0.10、0.15、0.20和0.25 g·L−1)和模拟废水初始pH(3.00、4.00、5.42、7.00、9.00和11.00)。
无机阴离子影响实验:分别设置Cl−、NO3−、HCO3−、H2PO4−和SO42−(1.00、5.00、10.00和20.00 mmol·L−1)、腐殖酸(10、20、50和100 mg·L−1)和不同实验用水(纯净水、自来水和地表水)。其中纯净水由分析型超纯水机(WP-UP-WF-30,沃特浦,中国)制得,电导率约为1~10 μS·cm−1(25 ℃),自来水为广州大学城管道自来水,地表水取自珠江广州大学城河段南亭村断面)。
1.4 分析方法
利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,蔡司-Sigma300,牛津能谱,德国)观测LaCoO3表面形貌;利用能谱仪(EDS,蔡司-Sigma300,牛津能谱,德国)测定元素组成;利用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Bruker D8 Advance,德国)检测LaCoO3的结构;利用X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS,ThermoFisher Nexsa,美国)分析LaCoO3表面元素和价态;利用电化学工作站(CHI760E,辰华,中国)测定计时电流;利用电子顺磁共振(EPR,Bruker-EMXplus-10/12,德国)检测体系中的ROS。
采用高效液相色谱(HPLC,Waters-e2695,USA)检测样品中ATZ的质量浓度[31]。色谱柱为C-18(Waters,5 μm,4.6 mm×250 mm),检测器为紫外检测器(2998 PDA Detector),流动相由乙腈和0.10%乙酸溶液组成,其体积比为60%:40%,流速1.00 mL·min−1,柱温40 ℃,检测波长221.00 nm,注射体积20.00 μL。采用电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS,Agilent 7700/7800,美国)检测镧元素和钴元素的浸出质量浓度。pH由pH-3c仪(Rex,上海雷磁,中国)测定。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 催化剂表征
1) SEM、EDS和XRD分析。如图1(a)~(b)所示,LaCoO3具有立体块状结构,表面存在许多细颗粒,这有利于催化。为了进一步确认LaCoO3表面元素,还对其进行了元素映射分析。如图1(c)~(f)所示,La、Co和O在所选区域均匀分布,La和Co的密度低于O元素。EDS成像进一步揭示了LaCoO3表面元素由La、Co和O元素组成。如图1(g)所示,La、Co和O元素比近似为1∶1∶3,这与化学式基本一致。为了确认LaCoO3的晶体结构,进行了XRD测试。由图1(h)可以看出,样品在2θ为23.20°,32.80°,33.30°和47.50°的特征衍射峰与LaCoO3(JCPDS 84-0848)匹配。这说明催化剂具有结构良好的钙钛矿结构,除LaCoO3相外,没有形成Co3O4和La2O3等常见的氧化物杂质。
2) XPS分析。利用XPS对LaCoO3的元素和化学状态进行了研究。图2(a)为LaCoO3的全尺寸XPS能谱。此外,还利用C1s(284.80 eV)对各元素能谱进行了标定。由图2(b)可见,位于830.00~840.00 eV和847.00~857.00 eV分别对应于La3d5/2和La3d3/2。833.60、837.70、850.50和854.60 eV的峰可以归因于La(Ⅲ)[32]。钙钛矿中B位元素的价态尤为重要。如图2(c)所示,Co2p能谱由4个峰组成。Co2p3/2峰(780.6 eV)和Co2p1/2峰(795.6 eV)可归因于Co(Ⅲ),Co2p3/2峰(782.00 eV)和Co2p1/2峰(796.60 eV)则由Co(Ⅱ)产生[8]。由图2(c)中Co2p3/2的峰强度计算可知,使用前催化剂中Co(Ⅱ)和Co(Ⅲ)的含量分别为46%和54%;使用后则为40%和60%,由Co2p1/2的数据也得到相同的结果。多次使用后的催化剂的催化性能有所降低,这说明低价态Co(Ⅱ)含量与催化性能密切相关。O1s能谱的XPS能谱如图2(d)所示。钙钛矿中以528.40、529.60、530.80和532.30 eV为中心的峰分别对应晶格氧(OL)、表面氧(Os)、氧空位(Ov)和吸附的分子水[33]。本研究制备的LaCoO3使用前含有大量的OL和Ov,使用后OL和Ov的相对比例分别由19.50%和39.80%降至0.00%和27.30%。这可能是由于其参与到了Co(Ⅲ)/Co(Ⅱ)的氧化还原反应中[34],关于氧的各种形态分布与催化性能之间的关系还需要进一步深入研究。
3)计时电流测定。如图3所示,添加PMS对电流输出有明显影响。这表明PMS和LaCoO3表面之间确实发生了电子转移[35]。随着ATZ的加入,电流也发生了变化,预示着LaCoO3可以有效地介导电子从ATZ转移到PMS[36-38]。相比之下,空白电极在添加PMS和ATZ后表面电流的变化很小。
2.2 不同因素对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响
1)材料筛选实验。不同催化体系下ATZ的去除结果如图4(a)所示。单独的PMS几乎不能氧化ATZ。所有体系对ATZ的吸附不显著,去除率均小于5.00%。几种钙钛矿活化PMS催化氧化ATZ的效率为LaCoO3>LaCuO3>LaMnO3>LaFeO3,在10 min内,LaFeO3、LaMnO3和LaCuO3对ATZ的去除率分别为7.00%、17.00%和73.00%,而LaCoO3活化PMS后对ATZ的去除率几乎为100.00%,相应的速率常数分别为0.005、0.011、0.070和0.129 min−1。显然,B位元素对LaBO3的催化性能有重大影响。此外,考虑到使用过程中钴元素会浸出,还制备了2种核壳结构催化剂。但初步研究结果(图4(a))表明,在使用2种核壳结构催化剂的情况下,反应速率常数由LaCoO3的0.129 min−1降到0.037 min−1和0.041 min−1。这表明外围的壳抑制了核的催化性能,还需要深入研究。本文后续研究选择LaCoO3作为催化剂。
2) ATZ初始质量浓度对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解效果的影响。如图4(b)所示,所有选定质量浓度均在10 min内有效降解,在前2 min内快速衰减,当ATZ初始质量浓度由2.50 mg·L−1增加到10.00 mg·L−1时,相应的降解速率常数由1.210 min−1降至0.728 min−1。原因可能是在相同条件下,固定的催化剂用量和PMS质量浓度所产生的自由基总量是恒定的,无法在特定时间内将高质量浓度的ATZ完全降解。结果表明,ATZ的降解速率常数发生了变化。分析可能的原因为:ROS与ATZ及其中间产物之间均可能发生反应,在活性氧总量一致的情况下,ATZ质量浓度越高,催化剂表面新生成的中间产物质量浓度也越高,阻碍了ATZ向催化剂表面的传质,催化剂表面ATZ质量浓度下降,表观速率常数降低。因此,选择10.00 mg·L−1为后续实验初始质量浓度。
3) PMS投加量对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图4(c)所示,随着PMS浓度的增加,ATZ的降解速率迅速增加。因为PMS质量浓度越高,可以增强与催化剂的接触,从而产生更多的活性氧。当PMS质量浓度由0.320 g·L−1增加到0.512 g·L−1时,速率常数反而略有降低。这可能是因为过量的SO4·−会发生自淬灭[39]。综合考虑后续研究选择0.256 g·L−1作为PMS的质量浓度。
4)催化剂用量对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图4(d)所示,在不添加催化剂的情况下,10 min内PMS降解ATZ的速率常数仅为0.004 min−1;催化剂用量为0.05 g·L−1时,速率常数提高到0.088 min−1,说明LaCoO3能有效催化PMS降解ATZ;催化剂用量为0.15 g·L−1时,速率常数增加到0.129 min−1。主要原因是随着催化剂用量的增加,催化剂表面的活性位点增多,催化PMS的能力增强,从而产生更多的ROS以降解污染物[40]。因此,后续研究中选择0.15 g·L−1作为催化剂用量。
5) pH对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。由图4(e)可见,当pH为3.00~5.42时,去除率随初始pH的增加而增加。当pH升高到11.00时,速率常数由0.129 min−1下降到0.003 min−1,pH=5.42为最佳条件。PMS的形式主要取决于溶液的pH及其pKa2(pKa2=9.40)。在酸性和中性条件下,主要存在形式为HSO5−[12],SO4·−或HSO5−与OH−/H2O反应生成HO·,SO4·−和HO·的存在可获得较高的ATZ去除率。PMS在酸性条件下比中性或碱性条件下更稳定,导致活化相对较慢。此外,H+还消耗了一定量的SO4·−和HO·,导致这2种自由基的不必要消耗[27]。以上原因共同导致了ATZ降解率的下降。当pH>9.00时,PMS的主要存在形式转化为SO52−[10]。此外,SO52−的催化活性低于HSO5−,在pH>10.00时,催化剂表面会形成氢氧化钴,限制了ATZ的降解,降低了催化剂的催化活性[41]。
6)催化剂的稳定性。如图4(f)所示,在前2次重复实验中,ATZ的去除率变化不明显;经第3次使用后,性能稍有下降,10.00 min后速率常数由0.129 min−1降到0.100 min−1,第5次后降至0.087 min−1。这可能是由于LaCoO3使用过程中表面结构和活性中心发生了变化。采用ICP-MS检测从LaCoO3/PMS中浸出La和Co元素质量浓度,反应60 min后La元素浸出质量浓度为5.72 mg·L−1,Co元素浸出质量浓度为0.85 mg·L−1,催化剂具有一定的稳定性。
2.3 共存阴离子对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响
1) NO3−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图5(a)所示,NO3−轻微抑制ATZ的降解。这是因为NO3−不会引起溶液pH的变化,对氧化剂的稳定性没有影响;其次,NO3−对催化剂的催化活性也没有影响[42]。但NO3−可以与HO·和SO4·−反应形成氧化能力较弱的硝酸根自由基(NO3·−),如式(1)和式(2)所示[42-43]。
NO−3+SO4⋅−↔SO2−4+NO3⋅−k=2.10×102L⋅(mol⋅s)−1 (1) NO−3+HO⋅↔OH−+NO3⋅−k<5.00×105L⋅(mol⋅s)−1 (2) 2) SO42−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。SO42−对ATZ的降解比NO3−表现出更为轻微抑制作用。这是因为与NO3−一样,SO42−不会改变溶液的pH,对催化剂的催化活性也没有影响。其次SO42−是惰性离子,不会与HO·和SO4·−反应[44]。
3) Cl−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图5(c)所示,当Cl−浓度从1.00 mmol·L−1增加到20.00 mmol·L−1时,对ATZ的降解呈现出先抑制后促进的现象,低浓度的Cl−(<10.00 mmol·L−1)抑制降解,而高浓度的Cl−(>10.00 mmol·L−1)可促进降解。这可能是由于较低浓度的Cl−会优先与SO4·−反应,而产生活性更小的Cl·,从而减弱了ATZ的降解;当Cl−浓度进一步增大,Cl−通过双电子转移直接与PMS反应产生活性氯(即Cl·、Cl2·−和Cl2,
E0Cl· E0cl2·− E0Cl2 4) HCO3−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图5(d)所示,HCO3−浓度从1.00 mmol·L−1增加到20.00 mmol·L−1时,速率常数从0.015 min−1降至0.005 min−1。这是因为HCO3−可以改变溶液的pH,会影响PMS的稳定性。此外,pH的变化也会影响催化剂的表面电荷,从而影响其催化性能。最后,HCO3−还会与SO4·−和HO·反应生成氧化能力较弱的活性物种(式(3)~式(4))[47-49]。
HCO−3+SO4⋅−↔SO2−4+HCO3⋅−k=9.1×106L⋅(mol⋅s)−1 (3) HCO−3+HO⋅↔OH−+HCO3⋅−k=8.5×106L⋅(mol⋅s)−1 (4) 5) H2PO4−对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响。如图5(e)所示,添加1 mmol·L−1 H2PO4−后,ATZ的降解速率常数由0.129 min−1降至0.047 min−1。H2PO4−浓度由1.00 mmol·L−1增加到20.00 mmol·L−1时,速率常数由0.047 min−1降至0.034 min−1。这是由于H2PO4−可以改变溶液的pH,这会进一步影响PMS的稳定性和催化剂的催化活性。此外,H2PO4−与催化剂表面的活性位点具有较强的络合能力。有研究表明,H2PO4−可以在零价铁表面[50]、氧化铈纳米颗粒表面形成络合从而影响催化剂的催化活性[51]。此外,H2PO4−可以淬灭HO·和SO4·−(式(5)~式(6))[42,49]。
H2PO−4+SO4⋅−↔SO2−4+H2PO4⋅−k=7×106L⋅(mol⋅s)−1 (5) H2PO−4+HO⋅↔OH−+H2PO4⋅−k=8×105L⋅(mol⋅s)−1 (6) 2.4 天然有机物和实验用水对LaCoO3/PMS体系降解ATZ的影响
天然有机物(NOM)在地表水中普遍存在,含有丰富的官能团(羧基、酚羟基和醇基等),这些基团可与催化剂上的活性中心和有机污染物相互作用,从而影响ATZ的去除[52]。本研究以腐植酸(HA)作为典型的NOM,考察了反应体系对ATZ去除的影响,结果图6(a)所示。微量的HA的抑制作用较弱,当HA投加量为100 mg·L−1时,ATZ的速率常数降低到0.092 min−1。这是因为带负电荷的HA在水中会与催化剂表面的金属活性中心螯合,阻碍活性中心的暴露,抑制催化。事实上,天然水体中的HA含量相对较低,微量的HA对反应体系影响较小。此外,ATZ溶液配制用水也会对催化效果产生极大影响。如图6(b)所示,在自来水和地表水中,LaCoO3/PMS对ATZ的去除速率常数分别降至0.082 min−1和0.005 min−1。这说明LaCoO3/PMS体系受实验用水中共存离子和其他成分的影响较大。
2.5 反应机理
通过淬灭实验,测定了LaCoO3/PMS体系中产生或存在的自由基。甲醇(MeOH)是有效的SO4·−和HO·淬灭剂(
kso4⋅− kHO⋅ kHO⋅ kso4⋅− 本研究中使用L-组氨酸淬灭单线态氧(1O2,0.15 V)。结果表明,加入1 mmol·L−1的L-组氨酸便终止了反应的进行。这是由于L-组氨酸会可以快速消除PMS[54]。为了排除PMS质量浓度降低对ATZ去除的影响,通过一系列实验验证1O2是否为主要活性物质。如图4(c)所示,当PMS质量浓度进一步增加到0.384 g·L−1时,ATZ的去除速率常数没有显着变化。这表明过量的PMS不能被有限的LaCoO3催化剂完全活化。因此,通过在反应体系中加入1 mmol·L−1L-组氨酸来测试0.384 g·L−1 PMS的消耗,发现消耗了44%PMS,这表明系统中仍然存在56% PMS。然而,在本研究中,L-组氨酸的抑制作用仍然显著(Kobs下降到0.022 min−1),并且体系中残留的PMS超过0.124 g·L−1。这表明LaCoO3活化剩余的PMS产生的1O2被淬灭,从而削弱了降解效果,因此,1O2是LaCoO3/PMS 系统中的主要活性物质。
对苯醌(p-BQ)常用来淬灭O2·−(
ko2⋅− kHO· 为了进一步验证上述推论,对LaCoO3/PMS系统中可能生成的ROS进行电子顺磁共振(EPR)测试分析。如图8所示,在捕获剂/PMS系统中无法识别出明显的自由基信号。说明PMS自身不能产生ROS。如图8(a)所示,加入LaCoO3后,分别在系统中观察到DMPO-HO·和DMPO-SO4·−加合物的特征峰。这表明生成了SO4·−和HO·。此外,信号比为1:1:1的TEMP-1O2加合物的三重特征峰也被清晰地观察到,表明1O2参与了催化过程。然而,随着LaCoO3的引入,并没有观察到DMPO-O2·−加合物信号,这意味着在LaCoO3/PMS系统中O2·−可以忽略不计。综上所述,推测LaCoO3/PMS体系中存在SO4·−、HO·和1O2,且SO4·−和1O2优先于HO·与ATZ反应。
基于以上结果,LaCoO3/PMS体系中存在自由基氧化和非自由基氧化过程。在自由基氧化过程中,通常Co(Ⅱ)是PMS催化产生SO4·−和HO·的主要活性位点[58](式(7)~式(9))。另外,LaCoO3中的晶格氧(OL)可提供电子生成SO4·−[58](式(10))。在非自由基反应过程中,Co(Ⅱ)作为主要吸附位点,可与SO5·−反应生成1O2(式(11)),OL也可随着Co(Ⅱ)和Co(Ⅲ)的还原而转化为1O2(式(12))[59-60]。另外,SO5·−由于反应速率高而催化能低,易发生自反应,导致1O2的产生(式(13)~式(14))[61]。LaCoO3上丰富的氧空位更容易吸附PMS从而自分解,促进1O2的析出[62](式(15)~式(16))。此外,氧空位的存在也为B位金属阳离子的氧化还原循环的实现提供了连接,从而提高了催化稳定性[20,58]。综上所述,LaCoO3优异的催化性能主要是由于氧空位、表面Co(Ⅱ)位点和晶格氧的存在,产生了大量的ROS (式(17))所致。
Co(Ⅱ)+HSO−5↔Co(Ⅲ)+SO4⋅−+OH− (7) Co(Ⅲ)+HSO−5↔SO5⋅−+Co(Ⅱ)+H+ (8) SO4⋅−+H2O↔SO2−4+H++HO⋅ (9) SO5⋅−+OL↔SO4⋅−+O2 (10) Co(Ⅱ)+SO5⋅−↔Co(Ⅲ)+1O2+SO2−4 (11) Co(Ⅲ)+2O2−L↔Co(Ⅱ)+1O2+3e− (12) HSO−5↔SO5⋅−+H++e− (13) 2SO5⋅−↔1O2+S2O2−8 (14) HSO−5+HSO−5↔OV↔HSO−6+HSO−4 (15) HSO−6↔HSO−4+1O2 (16) SO4⋅−,1O2,HO⋅+ATZ↔中间体↔CO2+H2O+SO2−4 (17) 3. 结论
1)在最佳条件下(ATZ=10.00 mg·L−1,LaCoO3= 0.15 g·L−1,PMS=0.256 g·L−1,初始pH=5.42),ATZ可在10.00 min内快速被完全降解。经过5次循环实验,ATZ的去除率在可接受范围内,反应60 min后Co元素浸出质量浓度为0.85 mg·L−1。
2) SO42−和NO3−轻微抑制LaCoO3活化PMS降解ATZ,高浓度的Cl−促进了降解,H2PO4−、HCO3−和低浓度的Cl−及天然有机物HA抑制了降解。
3) LaCoO3具有立体的块状组织结构,表面存在许多细颗粒原点;LaCoO3含有大量的氧空位,表面Co(Ⅱ)位点、氧空位和晶格氧在反应中起到了重要作用;在LaCoO3/PMS体系存在电子转移过程。
4) LaCoO3/PMS体系中存在SO4·−、HO·和1O2,且SO4·−和1O2优先于HO·与ATZ反应。
-
-
[1] ROSTAMI S, JAFARI S, MOEINI Z, et al. Current methods and technologies for degradation of atrazine in contaminated soil and water: A review[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 24: 102019. [2] 陈建军, 何月秋, 祖艳群, 等. 除草剂阿特拉津的生态风险与植物修复研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(S1): 289-293. [3] SHIRMARDI M, ALAVI N, LIMA E C, et al. Removal of atrazine as an organic micro-pollutant from aqueous solutions: A comparative study[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2016, 103: 23-35. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2016.06.014 [4] 董静, 夏龙超, 平永青, 等. 水环境中阿特拉津污染及修复研究现状[J]. 应用化工, 2022, 51(1): 144-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2022.01.032 [5] 钱玉亭, 黄红, 陈际雨, 等. 水中阿特拉津的高级氧化工艺去除研究进展[J]. 山东化工, 2020, 49(10): 69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2020.10.024 [6] BUXTON G V, GREENSTOCK C L, HELMAN W P, et al. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (·OH/·O− in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1988, 17(2): 513-886. doi: 10.1063/1.555805 [7] OLMEZ-HANCI T, ARSLAN-ALATON I. Comparison of sulfate and hydroxyl radical based advanced oxidation of phenol[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 224: 10-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.007 [8] ZHANG L, ZHANG L, SUN Y, et al. Porous ZrO2 encapsulated perovskite composite oxide for organic pollutants removal: Enhanced catalytic efficiency and suppressed metal leaching[J]. Journal Colloid And Interface Science, 2021, 596: 455-467. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.03.171 [9] HODGES B C, CATES E L, KIM J H. Challenges and prospects of advanced oxidation water treatment processes using catalytic nanomaterials[J]. Nature Nanotechnolgy, 2018, 13(8): 642-650. doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0216-x [10] OH W-D, DONG Z, LIM T-T. Generation of sulfate radical through heterogeneous catalysis for organic contaminants removal: Current development, challenges and prospects[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 194: 169-201. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.003 [11] DONG X, DUAN X, SUN Z, et al. Natural illite-based ultrafine cobalt oxide with abundant oxygen-vacancies for highly efficient Fenton-like catalysis[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2020, 261: 118214. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118214 [12] HU P, LONG M. Cobalt-catalyzed sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation: A review on heterogeneous catalysts and applications[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2016, 181: 103-117. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.024 [13] SHUKLA P, WANG S, SINGH K, et al. Cobalt exchanged zeolites for heterogeneous catalytic oxidation of phenol in the presence of peroxymonosulphate[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2010, 99(1-2): 163-169. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.06.013 [14] MIAO J, DUAN X, LI J, et al. Boosting performance of lanthanide magnetism perovskite for advanced oxidation through lattice doping with catalytically inert element[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 355: 721-730. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.192 [15] YAO Y, CAI Y, WU G, et al. Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by cobalt manganese oxides (CoxMn3-xO4) for Fenton-Like reaction in water[J]. Journal Hazardous Materials, 2015, 296: 128-137. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.04.014 [16] ZHU J, LI H, ZHONG L, et al. Perovskite oxides: Preparation, characterizations, and applications in heterogeneous catalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2014, 4(9): 2917-2940. doi: 10.1021/cs500606g [17] Rojas-Cervantes M, Castillejos E. Perovskites as Catalysts in Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment[J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9(3): 230. doi: 10.3390/catal9030230 [18] MUELLER D N, MACHALA M L, BLUHM H, et al. Redox activity of surface oxygen anions in oxygen-deficient perovskite oxides during electrochemical reactions[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6097. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7097 [19] GONG S, XIE Z, LI W, et al. Highly active and humidity resistive perovskite LaFeO3 based catalysts for efficient ozone decomposition[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 241: 578-587. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.041 [20] LIANG P, MENG D, LIANG Y, et al. Cation deficiency tuned LaCoO3−δ perovskite for peroxymonosulfate activation towards bisphenol A degradation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 409: 128196. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.128196 [21] 王柯晴, 徐劼, 沈芷璇, 等. LaCoO3钙钛矿活化过一硫酸盐降解萘普生[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 1326-1334. [22] YANG X, WU P, CHU W, et al. Peroxymonosulfate/LaCoO3 system for tetracycline degradation: Performance and effects of co-existing inorganic anions and natural organic matter[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 43: 102231. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102231 [23] GUO H, ZHOU X, ZHANG Y, et al. Carbamazepine degradation by heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate with lanthanum cobaltite perovskite: Performance, mechanism and toxicity[J]. Journal Environ mental Scienses, 2020, 91: 10-21. [24] PANG X, GUO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. LaCoO3 perovskite oxide activation of peroxymonosulfate for aqueous 2-phenyl-5-sulfobenzimidazole degradation: Effect of synthetic method and the reaction mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 304: 897-907. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.027 [25] WANG S, WANG J. Radiation-induced degradation of sulfamethoxazole in the presence of various inorganic anions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 351: 688-696. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.137 [26] GHANBARI F, MORADI M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 310: 41-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.064 [27] 王渊源, 阎鑫, 艾涛, 等. 碳化泡沫负载Co3O4活化过硫酸盐降解罗丹明B[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(04): 2039-2046. [28] DUNG N T, THU T V, VAN NGUYEN T, et al. Catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate with manganese cobaltite nanoparticles for the degradation of organic dyes[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(7): 3775-3788. doi: 10.1039/C9RA10169A [29] 杨贤, 梁嘉林, 曾刘婷, 等. 负载磁性废茶生物炭活化过一硫酸盐高效降解水中腐殖酸和富里酸[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(8): 3185-3199. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0043 [30] SOTELO J L, OVEJERO G, MARTÍNEZ F, et al. Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenolic solutions over a LaTi1−xCuxO3 perovskite catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2004, 47(4): 281-294. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.09.007 [31] 叶国杰. 钴镍双金属有机框架高效催化臭氧去除难生物降解污染物[J]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2020: 21-22. [32] PHOKHA S, PINITSOONTORN S, MAENSIRI S, et al. Structure, optical and magnetic properties of LaFeO3 nanoparticles prepared by polymerized complex method[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2014, 71(2): 333-341. doi: 10.1007/s10971-014-3383-8 [33] GAO P, TIAN X, FU W, et al. Copper in LaMnO3 to promote peroxymonosulfate activation by regulating the reactive oxygen species in sulfamethoxazole degradation[J]. Journal Hazardous Materials, 2021, 411: 125163. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125163 [34] 徐劼, 陈家斌, 卢建, 等. LaCo0.5Cu0.5O3型钙钛矿活化过一硫酸盐降解AO7[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(3): 1123-1131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.03.023 [35] WANG H, GUO W, LIU B, et al. Edge-nitrogenated biochar for efficient peroxydisulfate activation: An electron transfer mechanism[J]. Water Research, 2019, 160: 405-414. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.059 [36] LI J, ZHU K, LI R, et al. The removal of azo dye from aqueous solution by oxidation with peroxydisulfate in the presence of granular activated carbon: Performance, mechanism and reusability[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 259: 127400. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127400 [37] LONG Y, HUANG Y, WU H, et al. Peroxymonosulfate activation for pollutants degradation by Fe-N-codoped carbonaceous catalyst: Structure-dependent performance and mechanism insight[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 369: 542-552. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.097 [38] LONG Y, BU S, HUANG Y, et al. N-doped hierarchically porous carbon for highly efficient metal-free catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate in water: A non-radical mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 216: 545-555. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.175 [39] HU L, YANG F, LU W, et al. Heterogeneous activation of oxone with CoMg/SBA-15 for the degradation of dye Rhodamine B in aqueous solution[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 134-135: 7-18. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.12.028 [40] LU S, WANG G, CHEN S, et al. Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by LaCo1-xCuxO3 perovskites for degradation of organic pollutants[J]. Journal Hazardous Materials, 2018, 353: 401-409. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.021 [41] SU S, GUO W, LENG Y, et al. Heterogeneous activation of Oxone by CoxFe(3-x)O4 nanocatalysts for degradation of rhodamine B[J]. Journal Hazardous Materials, 2013, 244-245: 736-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.11.005 [42] MA J, YANG Y, JIANG X, et al. Impacts of inorganic anions and natural organic matter on thermally activated persulfate oxidation of BTEX in water[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 190: 296-306. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.148 [43] YU X, JIN X, LI M, et al. Degradation mechanism of tetracycline using sulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron driven peroxymonosulfate and metabolomic insights into environmental risk of intermediates products[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430(Pt 4): 133141. [44] YUAN R, JIANG M, GAO S, et al. 3D mesoporous α-Co(OH)2 nanosheets electrodeposited on nickel foam: A new generation of macroscopic cobalt-based hybrid for peroxymonosulfate activation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 380: 122447. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122447 [45] PENG J, LU X, JIANG X, et al. Degradation of atrazine by persulfate activation with copper sulfide (CuS): Kinetics study, degradation pathways and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 354: 740-752. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.038 [46] XU Y, LIN H, LI Y, et al. The mechanism and efficiency of MnO2 activated persulfate process coupled with electrolysis[J]. Science of Total Environmental, 2017, 609: 644-654. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.151 [47] 赖树锋, 梁锦芝, 肖开棒, 等. Ag改性石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)可见光辅助活化过一硫酸盐降解罗丹明B[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(5): 1847-1858. [48] CAO J, LAI L, LAI B, et al. Degradation of tetracycline by peroxymonosulfate activated with zero-valent iron: Performance, intermediates, toxicity and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 364: 45-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.113 [49] WANG J, WANG S. Effect of inorganic anions on the performance of advanced oxidation processes for degradation of organic contaminants[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 411: 128392. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.128392 [50] NAGOYA S, NAKAMICHI S, Kawase Y. Mechanisms of phosphate removal from aqueous solution by zero-valent iron: A novel kinetic model for electrostatic adsorption, surface complexation and precipitation of phosphate under oxic conditions[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 218: 120-129. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.02.042 [51] SINGH S, DOSANI T, KARAKOTI A S, et al. A phosphate-dependent shift in redox state of cerium oxide nanoparticles and its effects on catalytic properties[J]. Biomaterials, 2011, 32(28): 6745-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.05.073 [52] ZHU S, XIAO P, WANG X, et al. Efficient peroxymonosulfate (PMS) activation by visible-light-driven formation of polymorphic amorphous manganese oxides[J]. Journal Hazardous Materials, 2022, 427: 127938. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127938 [53] WANG Y, CHEN S. Droplets impact on textured surfaces: Mesoscopic simulation of spreading dynamics[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 327: 159-167. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.11.148 [54] SUN J, WANG L, WANG Y, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by MgCoAl layered double hydroxide: Potential enhancement effects of catalyst morphology and coexisting anions[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 286(Pt 1): 131640. [55] DUAN P, QI Y, FENG S, PENG X, WANG W, YUE Y, et al. Enhanced degradation of clothianidin in peroxymonosulfate/catalyst system via core-shell FeMn @ N-C and phosphate surrounding[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2020, 267: 118717. [56] FAN X, LIN Q, ZHENG J, FU H, XU K, LIU Y, et al. Peroxydisulfate activation by nano zero-valent iron graphitized carbon materials for ciprofloxacin removal: Effects and mechanism[J]. Journal Hazardous Materials. 2022, 437: 129392. [57] WANG Y, CHEN L, CAO H, et al. Role of oxygen vacancies and Mn sites in hierarchical Mn2O3/LaMnO3-δ perovskite composites for aqueous organic pollutants decontamination[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 245: 546-554. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.025 [58] LIU B, GUO W, WANG H, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by cobalt-impregnated biochar for atrazine degradation: The pivotal roles of persistent free radicals and ecotoxicity assessment[J]. Journal Hazardous Materials, 2020, 398: 122768. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122768 [59] ALI M B, BARRAS A, ADDAD A, et al. Co2SnO4 nanoparticles as a high performance catalyst for oxidative degradation of rhodamine B dye and pentachlorophenol by activation of peroxymonosulfate[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 19(9): 6569-6578. doi: 10.1039/C6CP08576H [60] LIU Y, GUO H, ZHANG Y, et al. Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by sillenite Bi25FeO40: Singlet oxygen generation and degradation for aquatic levofloxacin[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 343: 128-137. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.125 [61] LIANG P, ZHANG C, DUAN X, et al. An insight into metal organic framework derived N-doped graphene for the oxidative degradation of persistent contaminants: formation mechanism and generation of singlet oxygen from peroxymonosulfate[J]. Environmental Science-Nano, 2017, 4(2): 315-324. doi: 10.1039/C6EN00633G [62] GAO P, TIAN X, NIE Y, et al. Promoted peroxymonosulfate activation into singlet oxygen over perovskite for ofloxacin degradation by controlling the oxygen defect concentration[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 359: 828-839. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.184 -






 下载:
下载: