-
随着土地资源的日益紧张,垃圾焚烧已经成为我国城市生活垃圾无害化处理的主要方式。根据国家统计局发布的2021中国统计年鉴[1],我国城市生活垃圾焚烧处理量达到567 804 t·d−1,占总生活垃圾日清运量的59%。生活垃圾进行焚烧前通常需要堆酵3~7 d,此过程中垃圾自有水分、发酵产生水分和雨水等环境因素共同作用下将产生大量渗滤液[2-3]。垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液的水质特点主要为有机污染物浓度高、氨氮含量高、有毒物质和无机盐含量高,如果收集和处理不当,将会对周边环境造成严重污染[4]。本课题组在前期研究中采用厌氧膜生物反应器(anaerobic membrane bioreactor,AnMBR)有效去除了垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液中的有机污染物,然而由于厌氧消化过程中含氮有机物进一步分解产生氨氮[5-6],导致出水中仍存在大量氨氮。当前,垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液脱氨工艺多采用多级硝化反硝化工艺,但由于AnMBR出水氨氮质量浓度高达2 000 mg·L−1以上,处理难度较大;此外,出水C/N严重不均衡,需要投加大量碳源,从而导致占地面积大、能耗高和处理成本高等问题[7-9]。因此寻找合适的工艺对AnMBR出水中的氨氮进一步处理十分必要。
目前应用最为广泛的物化脱氨法为吹脱法。此法通常作为垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液处理的预处理,以减少废水中的氨氮尤其是游离氨对厌氧消化的影响[10-12]。其缺点在于:处理过程中对废水的pH有较高要求,需要投加大量碱以维持废水碱度,导致药剂成本较高;另外,吹脱法所用空气量大,导致动力消耗大,运行成本高等[13]。负压原位碱度脱氨法是一种新型高氨氮废水处理方法,在不需要投加碱及真空负压的条件下,废水中的游离氨不断进入气相继而被抽走,从而实现氨氮去除。相对常规脱氨法,负压原位碱度脱氨节约药剂和能耗,成本更低[14]。陈晗[15]采用负压脱氨法去除模拟高氨氮废水,在真空度为−0.015~−0.2 MPa,初始pH为11,停留时间为1.5~2 h时,获得最大脱氨率为46.63%。垃圾渗滤液厌氧消化液是一类特殊的高氨氮废水,由于其本身含有较高的碱度,在吹脱或者负压条件下重碳酸盐可以分解为二氧化碳,释放OH−,从而提高废水的pH。废水中离子铵结合OH−不断转化为分子氨,进一步进入气相,在吹脱或者负压作用下被分离出来,从而达到脱氨的目的[16]。
目前采用负压原位碱度脱氨工艺的报道较少。赵贤广等[17]采用“负压蒸发-吹脱”组合工艺在不调整初始pH条件下处理垃圾渗滤液厌氧消化液,当负压蒸发温度为67 ℃、真空度为−0.08 MPa、吹脱气液比为1 000∶1时,NH4+-N质量浓度由2 621.6 mg·L−1降至500 mg·L−1左右,去除率为80.3%。LEVERENZ等[18]采用负压吹脱工艺处理厌氧沼液,分为加碱处理组和不加碱处理组,发现在温度达到92 ℃时两组具有相似的氨氮去除性能。可见负压原位碱度脱氨法处理高氨氮厌氧消化液废水具有一定可行性,然而,目前的研究主要侧重于单因素影响和去除效果分析,而对多因素参数优化选择鲜有报道。响应面分析法是一种结合数学和统计学的渐近似优化方法,可以对受多个因素影响的响应问题进行建模分析并优化响应值,从而得出最优化工艺条件[12]。
本研究采用Box-Behnken实验设计,建立各影响因素与负压原位碱度脱氨处理垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水中氨氮去除率的多元二次模型,用响应面分析法分析各因素之间交互作用的程度,寻求最佳去除条件,以期为利用负压原位碱度脱氨法处理垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水中氨氮的工业化应用提供参考。
-
垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液原液取自江苏省无锡市某垃圾焚烧发电厂,经AnMBR处理后收集,4 ℃下保存。AnMBR出水水质指标如下:COD为2 270~2 317 mg·L−1,NH4+-N质量浓度为1 860~2 040 mg·L−1,TN质量浓度为1 960~2 050 mg·L−1,碳酸盐碱度为6 200~6 300 mg·L−1,重碳酸盐碱度为1 750~1 850 mg·L−1,pH值为8.46~8.53。可见,该废水的C/N较低,其中氮源主要以NH4+-N形式存在。
-
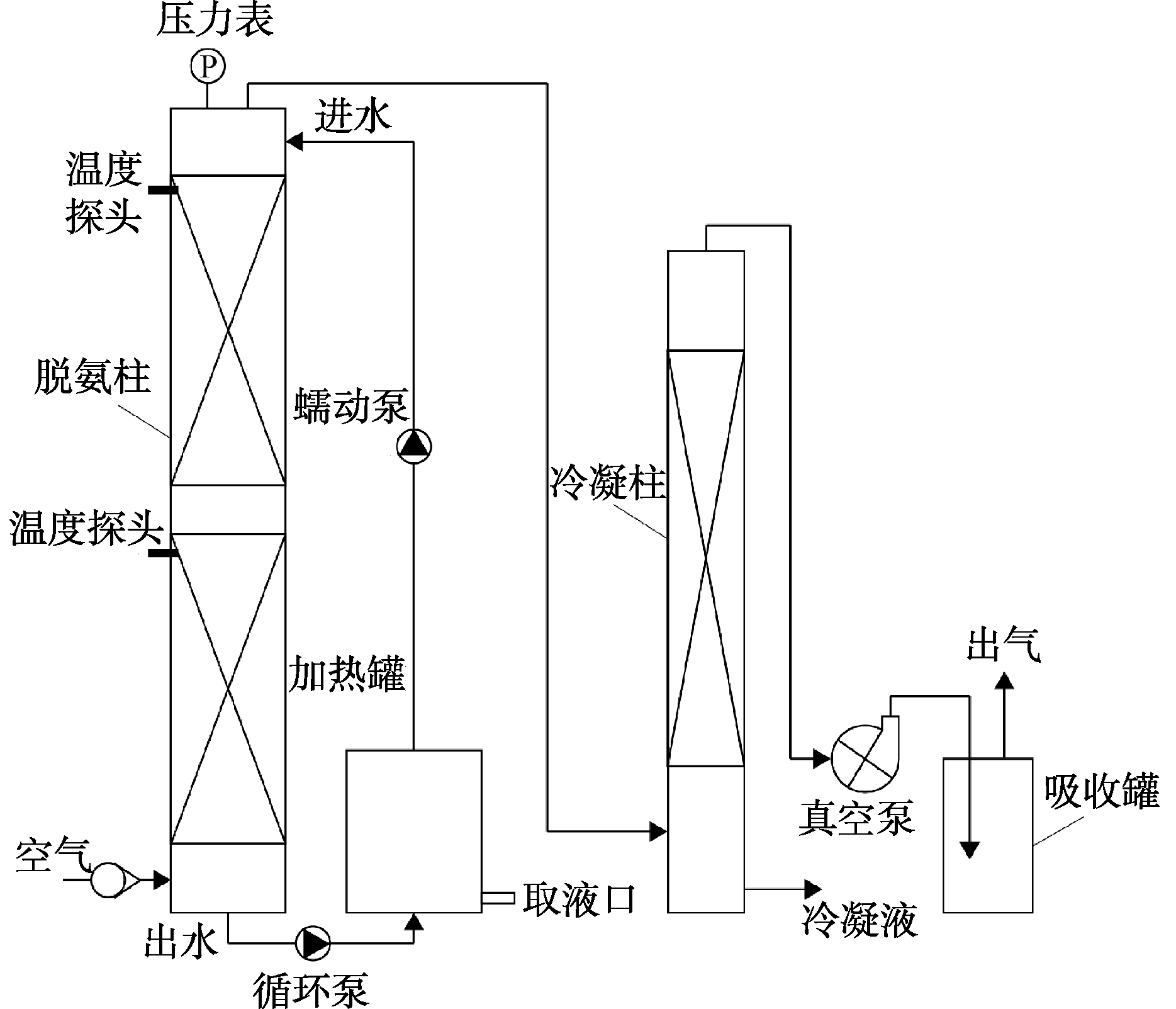
研究采用的原位碱度脱氨装置如图1所示。该装置由脱氨柱、冷凝柱和吸收罐组成。脱氨柱为有机玻璃填料塔,其直径为20 cm,有效高度为1 m。为减少壁流效应,将填料区设置为双层,中间设多孔塔板将进水再分布。填料塔底部设有进气口,通过气体流量计控制进气流量为1 m3·h−1。每批实验开始前,将5 L垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水加入加热罐中,预热到实验所需温度后通过进水泵进入脱氨柱。在单次实验预设时间中,废水通过循环泵在脱氨柱中不断回流循环,实验结束后从脱氨柱底部排出。在实验过程中,通过调节真空泵控制装置内部真空度,通过温度探头和温控装置控制脱氨柱温度。含氨蒸汽从脱氨柱顶部吸出,进入冷凝柱将水蒸汽冷凝,最后进入吸收罐将气体中氨气吸收后排放。
-
1)单因素实验。为探索负压原位碱度脱氨工艺处理垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水优化条件,分别设置温度、真空度、时间3个单因素影响实验。在实验过程中,改变其中某一变量(A)而使其他2个变量(B和C)保持恒定,考察单因素对负压原位碱度脱氨效果的影响。每次间隔30 min取样,测定NH4+-N质量浓度变化。根据实验中NH4+-N去除率来衡量负压原位碱度脱氨效果。
2)多因素复合实验。本实验根据单因素影响实验确定响应面分析(response surface methodology,RSM)中单个影响因子的适宜范围。以NH4+-N去除率为响应值,构建Box-Behnken模型,应用RSM对负压原位脱氨过程中温度、真空度、时间等可能的影响因素进行3因素3水平的实验设计,并进行理论优化与实验验证,最终确定最优运行条件,为后续实验提供理论依据,具体条件见表1。
-
pH采用玻璃电极法测定;碱度(ALK)采用电位滴定法测定,以CaCO3计;氨氮采用纳氏试剂法进行测定;响应面实验采用Design-Expert 12.0进行设计和分析。
-
在负压原位碱度脱氨过程中,废水中氨氮的脱除原理见式(1)和式(2)。垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液厌氧消化液是一类特殊的高氨氮废水,由于其本身含有较高的HCO3−,在负压高温的条件下,HCO3−可以分解为CO2,释放OH−(式(1)),从而提高废水的pH。废水中离子铵结合OH−不断转化为分子氨,进一步进入气相,从而达到脱氨的目的(式(2))。
已有研究[19]表明,氨氮脱除主要取决于2种平衡:气液两相的氨平衡以及液相中氨的解离平衡。气液两相的氨平衡与亨利定律有关,在温度一定的条件下,溶液中游离氨的摩尔分数与该气体在气相中的平衡分压成正比。当废水上方空气出现负压时,气相中的氨氮不断被抽离,氨气分压降低,促进废水中的NH4+不断转化为NH3,故真空度是影响气液两相氨平衡的重要因素。液相中氨的解离平衡主要受pH和温度影响,游离氨质量浓度按照式(3)进行计算。
式中:c(NH3)为游离氨质量浓度;c(NH3+NH4+)为总氨氮质量浓度;c(H+)为氢离子质量浓度;Ka为氨氮的酸电离常数;T为反应温度。由式(3)可知,温度和pH越高,游离氨含量越高。在不加碱条件下,控制温度成为游离氨质量浓度变化的主要外部影响因素,进而影响脱氨效率。而体系中的pH主要受HCO3−的水解平衡影响,真空度和温度均影响着HCO3−的水解平衡,从而影响着体系的pH,进一步影响了氨氮脱除。此外,反应时间同样是影响脱氨的又一重要因素,若溶液中反应已达到平衡,进一步延长时间毫无意义。故选取温度、真空度、时间3个因素进行单因素实验,考察并分析各因素对负压原位碱度脱氨的影响。
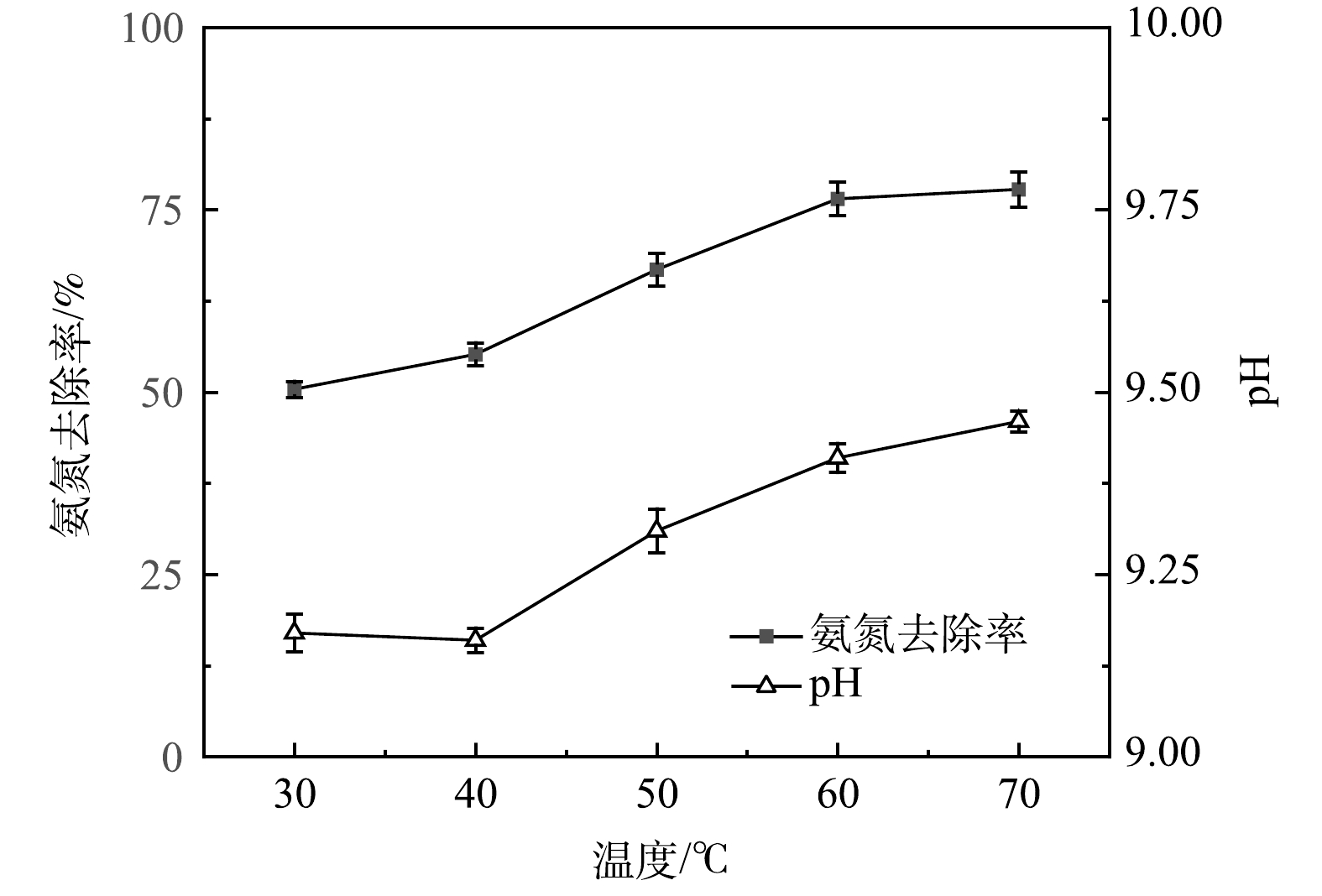
1)温度对负压原位碱度脱氨的影响。本实验在真空度为-0.07 MPa、反应时间为3 h、初始氨氮质量浓度为2 000 mg·L−1以及循环流量为20 L·h−1的条件下,考察进水温度对负压原位碱度脱氨过程氨氮去除率和废水pH变化的影响。如图2所示,NH4+-N去除率与温度呈正相关,随着温度的提高,氨氮去除率逐渐提高。在温度为30 ℃时,NH4+-N去除率偏低,仅为50.4%,说明在接近常温状态下废水中的离子铵难以转化为分子氨;在温度为40~60 ℃时,NH4+-N去除率呈现明显上升趋势,氨氮去除率从55.2%上升至76.5%;随着温度继续上升至70 ℃,此条件下废水在负压条件下达到沸点,出现明显沸腾导致液泛现象,对反应器运行不利,NH4+-N去除率为77.8%,去除率仅增加了1.3%。不同温度条件下的pH变化结果表明,温度越高,实验终点的pH越高。说明在负压原位碱度脱氨过程中,提高温度可促进HCO3−的分解,从而提高了废水pH。根据式(2)和式(3),pH的改变在提高游离氨质量浓度的同时使得氨氮平衡向右移动,促进了氨氮的脱除。考虑到温度太高势必会增大能耗,使运行成本上升,从而失去应用价值,而温度过低则性能不足。因此,综合考虑后,确定温度因素响应区间为40~60 ℃。
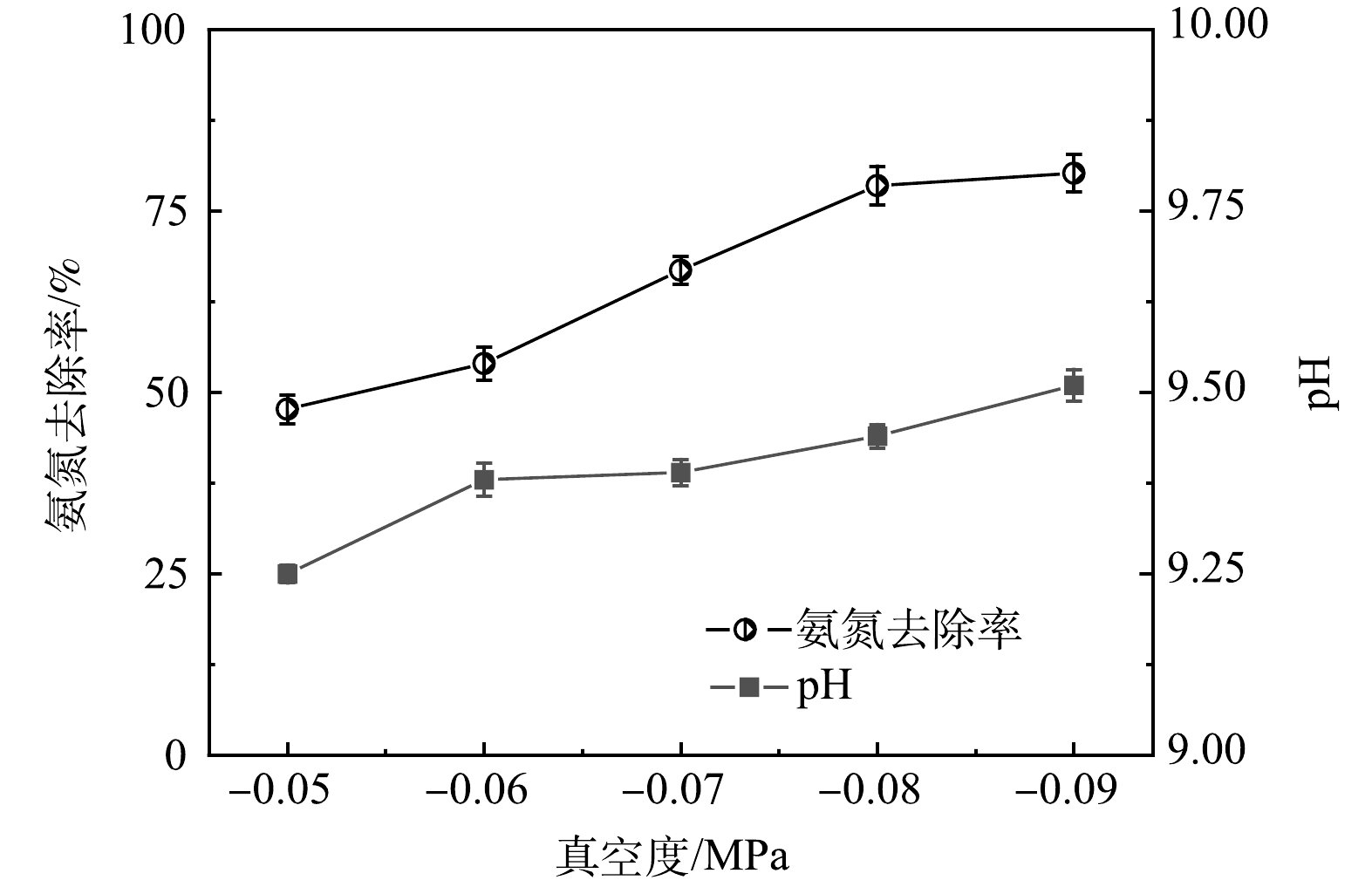
2)真空度对负压原位碱度脱氨的影响。在负压原位碱度脱氨过程中,垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水在脱氨柱内与与对流空气充分接触。根据气液两相氨平衡理论,真空度的变化主要影响游离氨的气液传质过程,液体中的分子氨在负压驱动作用下不断逸出至气相,同时由于负压抽吸作用,含氨气体迅速排出,气相氨分压的降低促进废水中游离氨的释放,从而促进氨氮的脱除。为探究真空度对垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水负压原位碱度脱氨的影响,控制温度为50 ℃、反应时间为3 h、初始质量浓度为2 000 mg·L−1以及循环流量为20 L·h−1,实验结果如图3所示。氨氮去除率随着真空度的提高呈整体上升趋势,在真空度为−0.06~−0.08 MPa时,氨氮去除率有明显变化,分别为54.0%、66.8%和78.5%。随着真空度的提高,实验结束时废水的pH也逐渐上升,在真空度为−0.06~−0.09 MPa时,pH上升了0.13,这说明真空度也可以通过改变体系内的pH促进氨氮脱除。当真空度为−0.09 MPa时,氨氮去除率为80.2%,仅升高1.7%。这可能是由于随着氨氮去除率的升高,废水中的氨氮逐渐减少,真空度对氨氮去除率的促进作用进一步下降,程兵[16]对真空度与氨氮去除率的关系进行模型拟合,发现两者呈指数关系,这与本文实验结果一致。而真空度为−0.05 MPa时氨氮去除率<50%,去除率过低。综合考虑后,确定真空度因素响应区间为−0.06~−0.08 MPa。
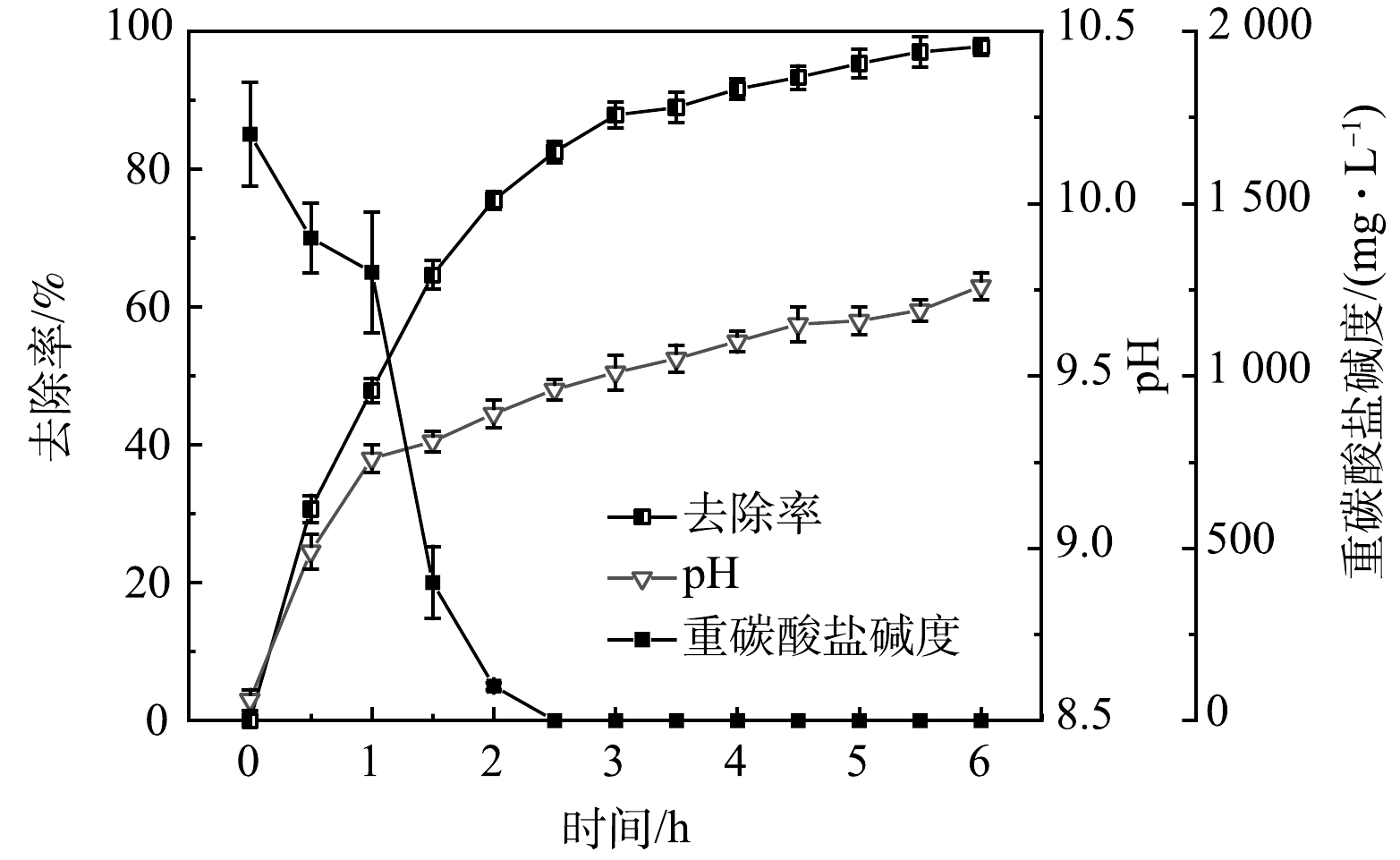
3)时间对负压原位碱度脱氨的影响。在温度为60 ℃,真空度为−0.08 MPa,初始质量浓度为2 000 mg·L−1以及循环流量为20 L·h−1的条件下,考察时间对负压原位碱度脱氨处工艺理垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水的影响。为分析在负压原位碱度脱氨过程中厌氧出水的pH变化以及自有碱度对pH的影响,还对负压原位碱度脱氨过程中pH和重碳酸盐碱度的变化规律进行跟踪测定,实验过程中废水中氨氮去除率、pH和碱度随反应时间的变化情况如图4所示。在整个过程中,氨氮去除率与反应时间呈正相关,且去除速率呈先快后慢的趋势。在脱氨的前2 h,氨氮去除率达到75.5%,在2~4 h,去除率进一步升高到91.6%,4 h后,氨氮去除率增加缓慢。脱氨时间在6 h时,NH4+-N去除率达到97.8%,出水氨氮质量浓度为41.6 mg·L−1,此时的出水C/N比良好,适宜后续处理。厌氧出水的初始pH为8.50,在脱氨的前1 h,废水pH明显上升至9.26,随后pH上升趋势较缓,在第6小时实验结束,pH上升到9.76。然而负压原位碱度脱氨过程中重碳酸盐碱度呈明显下降趋势。厌氧出水中的重碳酸盐碱度来源于厌氧消化过程中有机物厌氧消化过程产生的二氧化碳,二氧化碳溶于水后生成碳酸氢盐。在温度为60 ℃条件下,碳酸氢根不稳定,水解平衡不断右移,进一步生成碳酸根和氢氧根,从而导致pH的升高(式(1))。TIAN等[20]采用负压脱氨工艺处理高碱度废水,也在6 h的停留时间内观察到碱度的迅速下降和氨氮去除率的不断上升。已有研究[21-22]表明,投加碱在提高pH的同时也可以显著提高脱氨效率。在本研究中,利用AnMBR出水中存在的自有碱度,在不加碱的前提下对废水pH进行调控,显著降低处理成本的同时可取得较高的氨氮去除率,具有较好的应用价值。脱氨时间可以根据工艺对氨氮去除率的要求灵活调整,但在此实验中,反应时间<2 h时,氨氮去除率过低;而反应时间过长,必然增加运行成本,因此综合考虑本实验中确定时间因素响应区间为2~4 h。
-
1)Box-Behnken设计组合与结果。以氨氮去除率为响应值,选取脱氨时间(A)、真空度(B)、温度(C)3因素3水平进行实验设计,采用响应面法优化脱氨工艺,使用软件Design Expert 12.0进行Box-Behnken设计组合,实验结果见表2。
2)模型选择和方差分析。对表2中氨氮去除率(Y)及3个影响因素进行二次回归模型拟合,得到多元回归模型(式(4))。
由式(4)可以看出,3个因素对氨氮去除率的影响是交互的,而不是简单的线性关系。方差分析结果见表3。由模型分析可以看出,F=791.38,P<0.000 1,表明拟合的二次模型极其显著[23]。失拟项P=0.143 9,P>0.05说明失拟项不显著,方程拟合度较好,可以进行数据分析。由F值可知,3个因素对垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水中氨氮去除率的影响大小依次为温度>真空度>时间。3个影响因子的一次项、二次项A2、C2的P<0.001,说明这些因子对氨氮去除率的影响极为显著;交互项AB、AC的P<0.01,说明时间和真空度2个交互项及时间与温度2个交互项对氨氮去除率的影响高度显著;交互项BC的P<0.05,说明温度和真空度两交互项对氨氮去除率的影响呈现差异性。回归模型的决定系数R2=0.999 1,表明模型中99.91%的响应值来源于实验选取的因素。校正决定系数R2adj=0.998 0,与R2的数值接近,表明实验值与预测值吻合度较好,在此模型下实验的预测值具有较高的可信度。
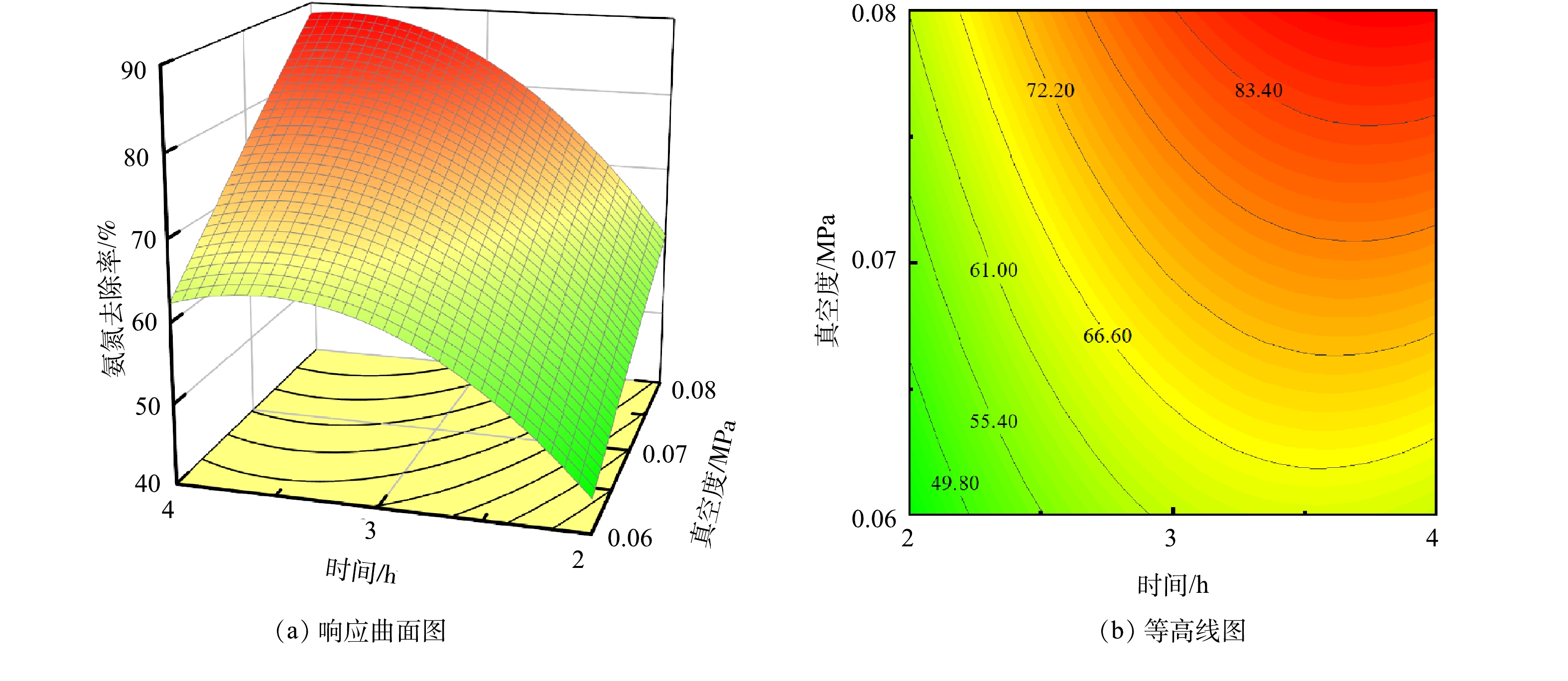
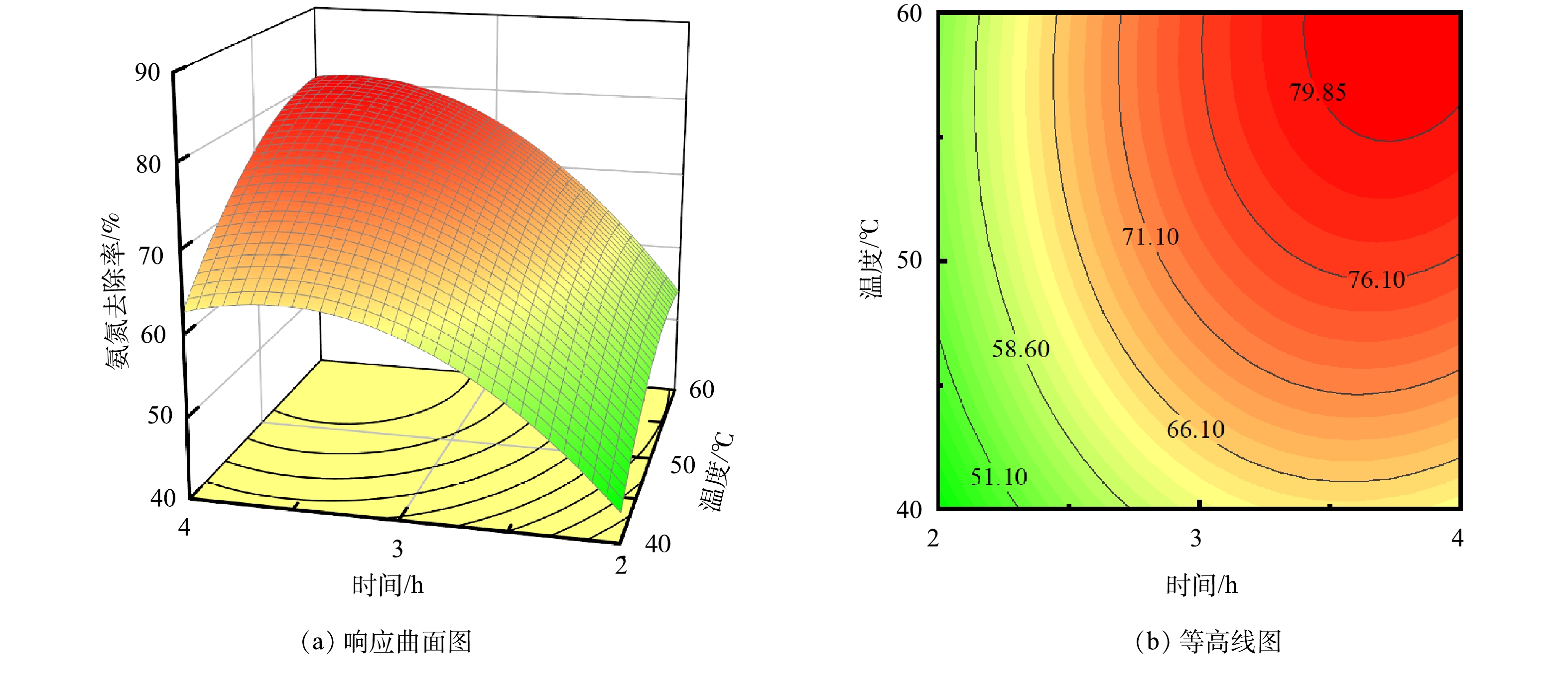
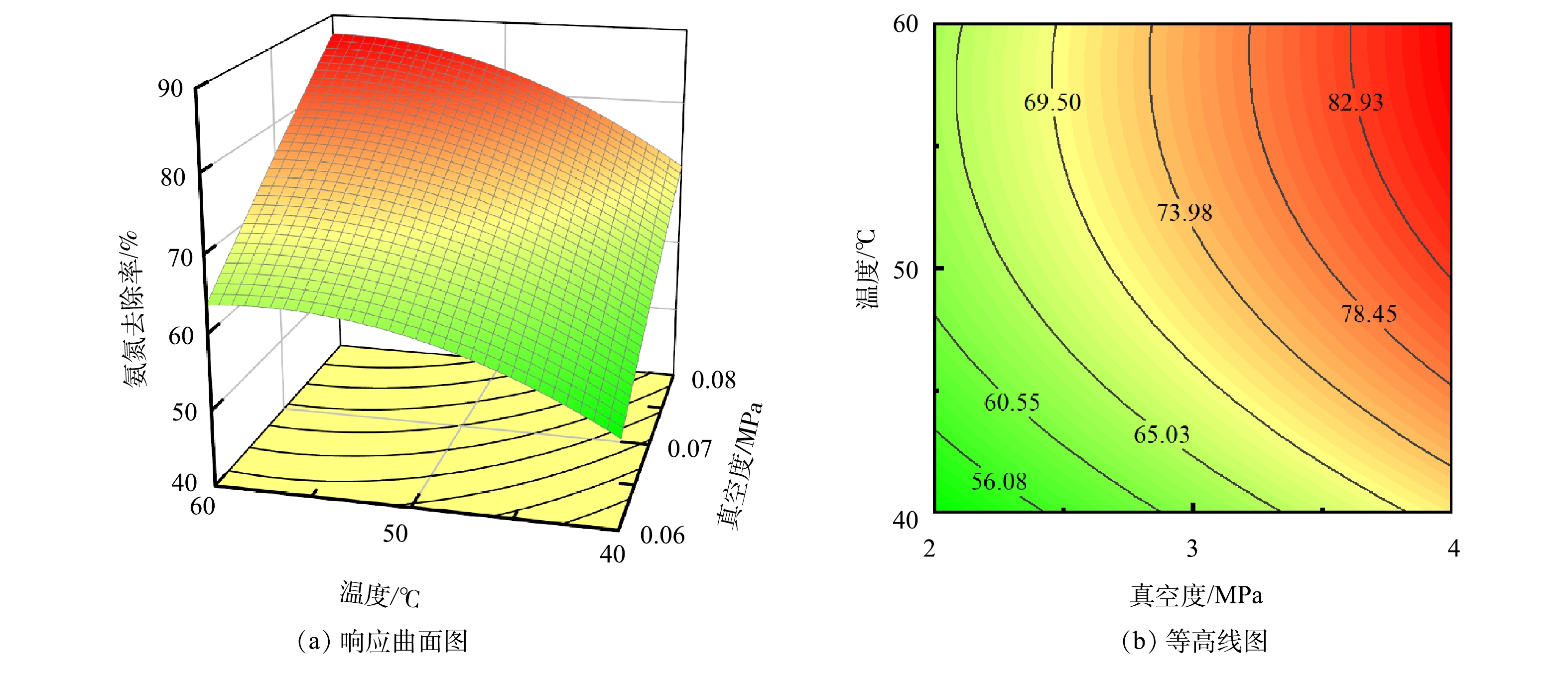
3)响应面和等高线分析。时间、真空度、温度3组变量的交互作用对氨氮去除率的影响可以用响应面表示。图5~图7为负压原位脱氨过程中各因素交互的响应曲面和等高线图,通常响应曲面图越陡,说明2个因素对响应值的交互作用越明显。等高线形状能反映交互作用的显著性,等高线中心呈椭圆形表示2个因素之间的交互作用显著,圆形则表示不显著[24-26]。由图5(a)可知,当温度为中间值(50 ℃),脱氨时间和真空度对氨氮去除率影响呈现明显的坡面变化,且两者对氨氮去除率的促进作用基本相同。等高线图(图5(b))呈现明显的椭圆形,说明时间和真空度2个因素的交互作用显著。而当脱氨时间为中间值(3 h),温度和真空度对氨氮去除率响应曲面图(图6(a))坡面较为平缓,真空度对氨氮去除率的影响高于温度,且等高线图(图6(b))呈不明显的椭圆形,说明温度和真空度2个因素的交互作用相对不显著。这可能是由于2个因素对负压原位碱度脱氨过程中的影响机理不同,温度主要影响氨氮的分子化过程,而真空度主要影响氨氮的气液两相平衡。当真空度为中间值(−0.07 MPa),脱氨时间和温度2个因素对氨氮去除率的响应曲面图(图7(a))影响呈现明显的坡度变化,脱氨时间对氨氮去除率的影响高于温度,且等高线图呈明显的椭圆形(图7(b)),说明两者对响应值的交互作用显著。
4)响应面结果预测和验证。通过响应曲面法分析,利用Design Expert 12.0软件中的预测功能可以对处理组的操作条件进行模拟。以获得最高氨氮去除率为响应值,设置温度、真空度和脱氨时间分别在响应范围内,可模拟出大量不同的处理条件。随机选择的5组处理组如表4所示。为验证其结果,选择第3处理组,并对处理组给出的对应条件下氨氮去除率进行实验验证。在脱氨时间为3.50 h、真空度为−0.078 MPa、温度59.00 ℃的条件下,再次进行3组重复实验,对应氨氮去除率均在92.0%左右。实验结果与预测值比较接近,说明通过响应面预测出的模型具有较好的可信度。
-
1)本实验以某垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水为处理对象,采用负压原位碱度脱氨工艺脱除氨氮,在脱氨过程中,垃圾渗滤液中的碳酸氢盐分解,CO2逸出,pH由8.5提高至9.7,工艺无需加碱,可以显著减少处理成本。
2)采用单因素实验,分别考察了温度、真空度、脱氨时间对垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水氨氮去除率的影响,并进行显著性研究,得出其影响显著性顺序,由大到小依次为温度>真空度>脱氨时间。
3)在单因素实验基础上,利用响应面分析,建立了3组因素对垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水中氨氮去除率的二次多项数学模型,并探讨其交互作用。采用Box-Behnken实验设计对实验数据进一步优化,分析确定氨氮去除的最佳工艺:吹脱时间为3.5 h,真空度为−0.078 MPa,温度为59 ℃,对应去除率92%。实验验证结果表明,RSM的预测值与实验值吻合较好。
响应面法优化负压原位碱度脱氨处理垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水
Optimization of vacuum in-situ alkalinity ammonia removal from the effluent of AnMBR treating the incineration leachate by response surface methodology
-
摘要: 针对垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液厌氧膜生物反应器(anaerobic membrane bioreactor, AnMBR)出水中仍含有高浓度氨氮,无法满足现行排放标准的问题,采用负压原位碱度脱氨工艺对AnMBR出水进行进一步处理;考察了温度、真空度和脱氨时间3个因素对负压原位碱度脱氨工艺氨氮去除率的单独作用,分析了不加碱前提下脱氨过程中体系pH的变化,并利用响应面学的方法对3因素的交互作用进行了探讨和分析。单因素实验结果表明:各因素在响应范围内对氨氮的去除有显著性影响,在温度为60 ℃、真空度为−0.08 MPa、脱氨时间为2 h时,氨氮去除率达到75.5%;在负压原位碱度脱氨过程中,AnMBR出水中自有碱度对pH具有显著调控作用,碳酸氢根水解致使反应体系pH上升进而促进氨氮脱除;利用响应面法探讨了各因素对氨氮去除率的影响,其对于氨氮去除率的贡献排序为温度>真空度>脱氨时间;确定负压原位碱度脱氨的最佳时间为3.5 h,温度为59 ℃,真空度为−0.079 MPa,该条件下氨氮去除率为92%以上,并对该模型进行了实验验证;响应面法的预测值与实验值吻合较好。由此可知,通过负压原位碱度脱氨可以去除垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水中大部分氨氮,并大幅提高C/N比,为后续与适当的生化处理工艺组合处理奠定了良好基础。该研究结果可为负压原位碱度脱氨法处理垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液AnMBR出水中氨氮的工业化应用提供参考。Abstract: Generally, the quality of anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR) effluent from incineration leachate cannot meet the discharge standard due to the high concentration of ammonia nitrogen. In this study, vacuum in-situ alkalinity ammonia removal process was used to conduct the advanced treatment of AnMBR effluent. The respective effect of temperature, vacuum degree or time on ammonia nitrogen removal rate was investigated. Then the change in pH in the system without adding alkalinity was analyzed during the ammonia removal process. Furthermore, the interaction of three factors was discussed and analyzed by response surface methodology (RSM). The results of single factor experiment showed that each factor presented a significant effect on ammonia nitrogen removal rate. At 60 ℃, the vacuum degree of −0.08 MPa, and the deamination time of 2 h, the ammonia nitrogen removal rate reached 75.5%. The own alkalinity in AnMBR effluent had a significant regulation effect on pH during the vacuum in-situ alkalinity ammonia removal process. Bicarbonate in the AnMBR effluent hydrolyzed under the conditions of vacuum and heating, and the produced carbon dioxide volatilized from the system. This process could lead to a pH increase and promote ammonia nitrogen removal. In addition, the effects of temperature, vacuum degree and time on ammonia nitrogen removal rate were investigated by RSM. The order of contribution of three factors to ammonia nitrogen removal rate was as follows: temperature > vacuum degree > time. Under the optimum conditions as follows: time of 3.5 h, temperature of 59 ℃ and vacuum degree of −0.079 MPa, the ammonia nitrogen removal rate was over 92%. Then the model was further verified by experiments. The results showed that the predicted values were in agreement with the experimental values. Therefore, most of ammonia nitrogen in AnMBR effluent could be removed by vacuum in-situ alkalinity ammonia removal process, and the C/N ratio of the incineration leachate increased substantially. The results of this study can provide a reference for the industrial application of vacuum in-situ alkalinity ammonia removal process treating the AnMBR effluent from incineration leachate.
-
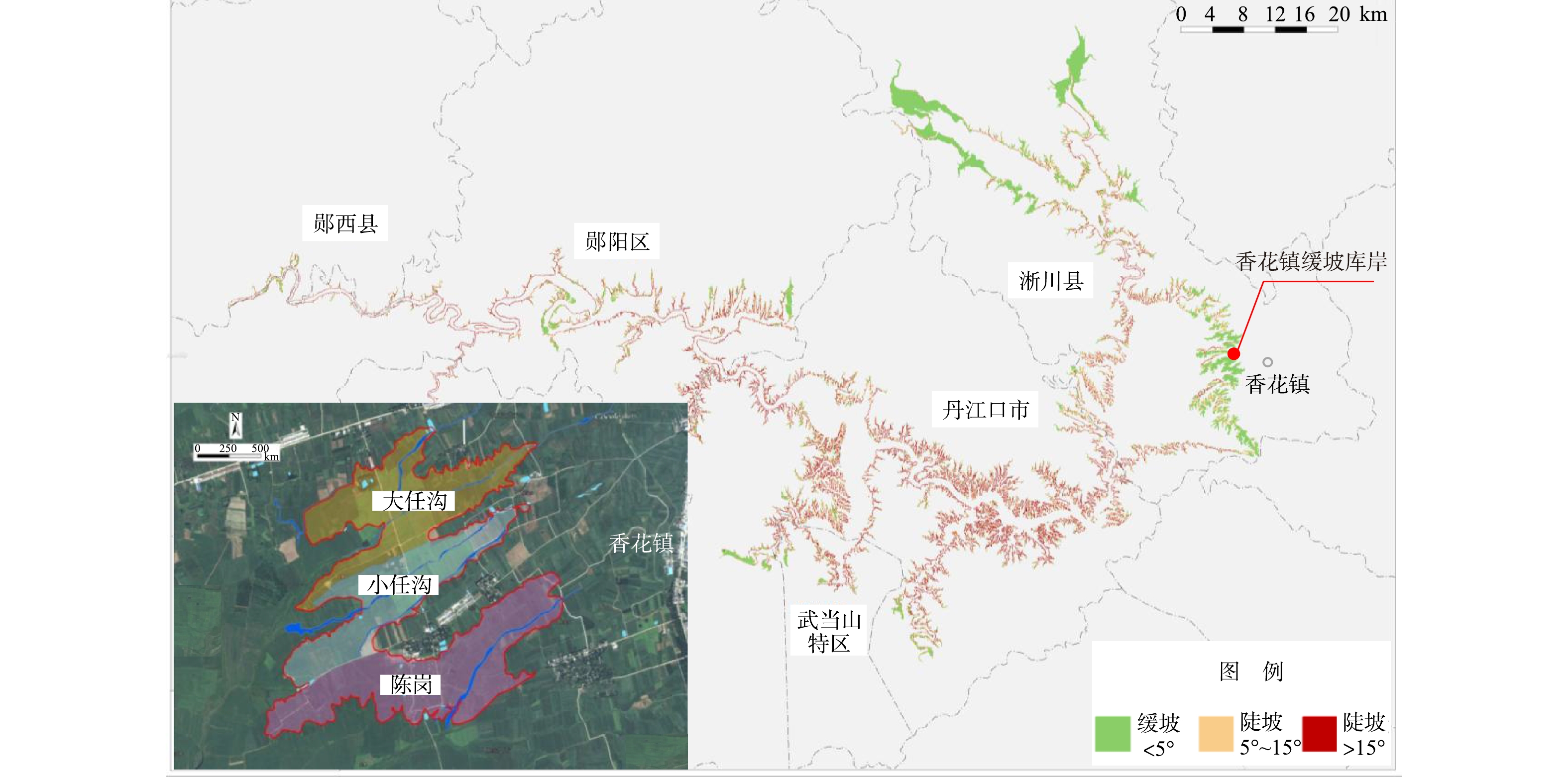
丹江口水库是南水北调中线工程水源地,水质保护十分重要。随着库区点源逐步得到治理,面源污染对丹江口水库水质的影响越来越大[1]。缓坡型库岸是丹江口水库重要的库岸类型,大坝加高前一直都是库周群众重要的土地资源[2]。由于农业生产强度较大,植被覆盖度低,缓坡型库岸面源输出强度较高。已有研究显示,丹江口库区面源污染产生的TN和TP负荷分别达到3.7×104 t和1.9×103 t,其中以缓坡型库岸面积最大的河南淅川县污染强度最高[3]。2013年,丹江口大坝加高工程完工,坝顶高程从162 m加高至176.6 m,丹江口水库水位抬升后,大量农田耕地将被淹没。然而,近年来水库水位始终没有达到170 m的水位目标,消落区无序耕种现象依然时有发生[4],加剧了库周面源污染输入。此外,新淹没区域土壤的氮磷释放[5]、库周土壤侵蚀[6]、以及周边农村生活[7]等面源污染都成为威胁库区水质的重要因素。
开展库岸生态屏障建设,恢复植被系统和污染阻控能力,是控制库周面源污染的有效途径。在国外,河湖岸边带生态修复和保护技术推广应用较为普及[8-9];我国从20世纪90年代开始开展岸边带保护与修复技术的研究与应用[10-11],探索出设置植被缓冲带、调整土地利用、优化种植结构等有效措施[12-15]。丹江口水库缓坡型库岸农业生产强度大,土地资源利用和水质保护存在矛盾;同时新形成的消落区因水文情势改变将进入新一轮植被演替过程[16-17],若不加以人工干预,植被恢复过程漫长且生态效益有限[18-19]。针对上述特点,国内外尚没有成熟的治理模式可供参考。本研究基于丹江口水库缓坡型库岸特殊的水文条件及其土地资源价值,选择典型区域探索生态屏障构建的技术方案,以期为南水北调中线水源地保护提供依据,亦为我国其他湖库岸带生态建设提供借鉴和参考。
1. 区域概况
丹江口水库横跨河南、湖北两省,由汉江库段(汉库)和丹江库段(丹库)2部分组成。丹江口水利枢纽分初期工程和大坝加高工程两期建设,初期工程于1973年底竣工,水库正常蓄水位157 m;大坝加高工程于2013年建成,正常蓄水位为170 m,最低水位为160 m。大坝加高后,160~170 m水位线区间成为新的消落区。根据水库运行调节方式,每年5月初至6月21日,水库水位逐渐降低到夏季汛限水位160 m;8月21—31日逐渐抬高到秋季汛限水位163.5 m;10月1日以后,逐渐充蓄到正常蓄水位170 m。
从地形条件看,汉库库岸以陡坡型为主,库岸曲折、立地陡峭,多为石质坡面,土地类型多为林地;丹库库岸以缓坡型为主,库岸地势平缓,消落区宽度从数百米到几公里,大坝加高前土地类型多为自然荒草漫滩和农耕用地。缓坡型库岸土壤肥沃、水分充足,农业耕种比较普遍。根据各库周各区县统计资料,大坝加高前160~170 m高程范围耕种面积25.67 km2,占消落区总面积的10.52%,主要分布在淅川、丹江口、郧阳3区县,其中淅川县14.4 km2,丹江口市5.00 km2,郧阳区6.27 km2(见图1)。根据国务院南水北调办2010年5月批准的《南水北调中线一期工程丹江口水库初步设计阶段建设征地移民安置规划设计报告》,丹江口水库淹没涉及的区域应全部实施征地移民。2013年,水库移民征地工作全部完成,并完成了库底清理工作,为水库蓄水奠定了良好基础。然而,由于近年来上游来水量不足,最高水位仅达到167 m左右。由于消落区管理办法尚不完善,加上库周土地资源紧张,消落区无序耕种的现象依然存在。
2. 总体思路和技术框架
2.1 总体思路
缓坡型库岸受水文情势变化的影响,消落区植被系统退化,拦滤吸收和阻滞净化能力丧失或下降。库岸土地无序耕种造成土壤侵蚀和化肥流失,形成的面源污染对库区水质也会造成威胁。生态屏障构建的关键在于恢复消落区植被系统,强化库岸面源阻控能力,在此基础上形成消落区土地资源的可持续利用模式,协调水质保护和库周群众生存发展的关系(见图2)。
1)构建消落区植被系统。水库调度造成的水文条件变化阻断了消落区植被的自然演替过程,可能造成植被群落退化消亡。通过植物群落的合理搭配和布局,能够引导库岸植被适应水文变化规律,促进群落的稳定化和生态环境效益的充分发挥。植被带布局以水库调度方式为依据,按照淹水时间的长短,在不同高程布设具有不同耐淹能力的植物群落,对草本、灌丛、乔木等不同植物群落类型进行合理搭配和种植。植被群落的优选配置过程中,应选择污染物吸收效率高、径流拦截能力强、根系固土能力强,并适应于库岸带地形地质条件的群落类型。
2)充分利用微地形条件构建库周生态水系统。针对库岸带面源负荷高,坑塘沟道阻控能力差的问题,对自然的汇水沟道和坑塘湿地系统进行适当人工改造,形成基于生态塘/生态沟道/近自然湿地的生态水系统,增强库岸污染阻滞能力。生态水系统构建过程中,要结合消落区地形特征,合理搭配生态塘、生态沟道、近自然湿地等措施。针对水库水位变幅较大的特点,要基于不同措施的功能特点,合理安排水体系统的空间布局,保证在不同水位条件下都能够实现污染阻滞效果。
3)建立消落区土地保护利用模式。根据国务院颁布的《全国大中型水利水电工程建设征地补偿和移民安置条例》,大中型水利水电工程建成后形成的水面和水库消落区土地属于国家所有,这些土地可以在服从水库统一调度和保证工程安全、符合水土保持和水质保护要求的前提下,通过当地县级人民政府优先安排给当地农村移民使用。当前,丹江口水库消落区尚存在无序耕种的问题,要建立合理的保护利用模式,有效引导库周群众积极参与,保障库岸生态屏障建设的可持续开展。
2.2 技术框架
植被恢复过程中,将消落区划分为拦滤净化带、固岸缓冲带、保土持水带和适度利用带。拦滤净化带位于160~163.5 m高程范围内,淹水时间最长,主要种植生长速度快、养分吸收能力强的草本植物。此区域可拦截上游来水中夹带的枯枝落叶以及碎屑颗粒物,同时通过根系作用吸收净化水体中的营养物质。固岸缓冲带位于163.5~165 m范围内,淹水时间减少,植物群落以乔草群落为主。此区域位于拦滤净化带和保土持水带之间,具有较强的缓冲作用;同时乔木的发达根系能够抵抗风浪,对库岸能够起到良好的固定作用。保土持水带位于165~167 m高程范围内,淹水时间较短,植物群落为乔灌草群落。乔灌草群落层次分明,对降水缓冲作用明显,能够减少降雨对土壤的侵蚀,起到保土持水的作用。适度利用带位于167~170 m高程范围,淹水时间最短,植物群落以经济苗木为主,能够实现一定的经济效益。该区带严格实施管护制度,禁止使用化肥农药及其他可能污染土壤和水体的行为。
生态水系统由生态塘、近自然湿地、生态透水坝和生态沟道等组成。生态塘是对天然塘堰加以人工修整,强化植物措施,径流在塘内滞留沉降,有机物通过植物和微生物降解[20]。近自然湿地是对低洼沼泽地进行微地形改造,强化已有植被条件,提升水力停留时间,形成径流净化系统[21]。生态透水坝利用砾石或碎石在河道中适当位置人工垒筑坝体,通过调节坝体的过流量,减缓径流流速,强化拦滤和沉降过程,控制面源污染[22]。生态沟道是对现有汇水沟道进行适当改造,增加水力停留和植物吸收,实现面源径流净化[23]。
植被功能带是库岸生态屏障的主要部分,生态水系统是重要补充。二者构通过拦截过滤、沉降吸收等作用对消落区土壤本身的存量污染和库周汇入径流污染起到深度净化作用,保证入库径流水质良好。植被功能带的建设能够杜绝消落区无序耕种的行为,减少了新的污染源输入,而适度利用带的设置缓解了土地利用和水质保护的矛盾。上述保护利用模式应由县级人民政府统一规划,乡政府和村委会具体实施,通过引入企业投资、建立合作社等模式[24],实现大面积推广。
3. 香花镇库岸典型案例
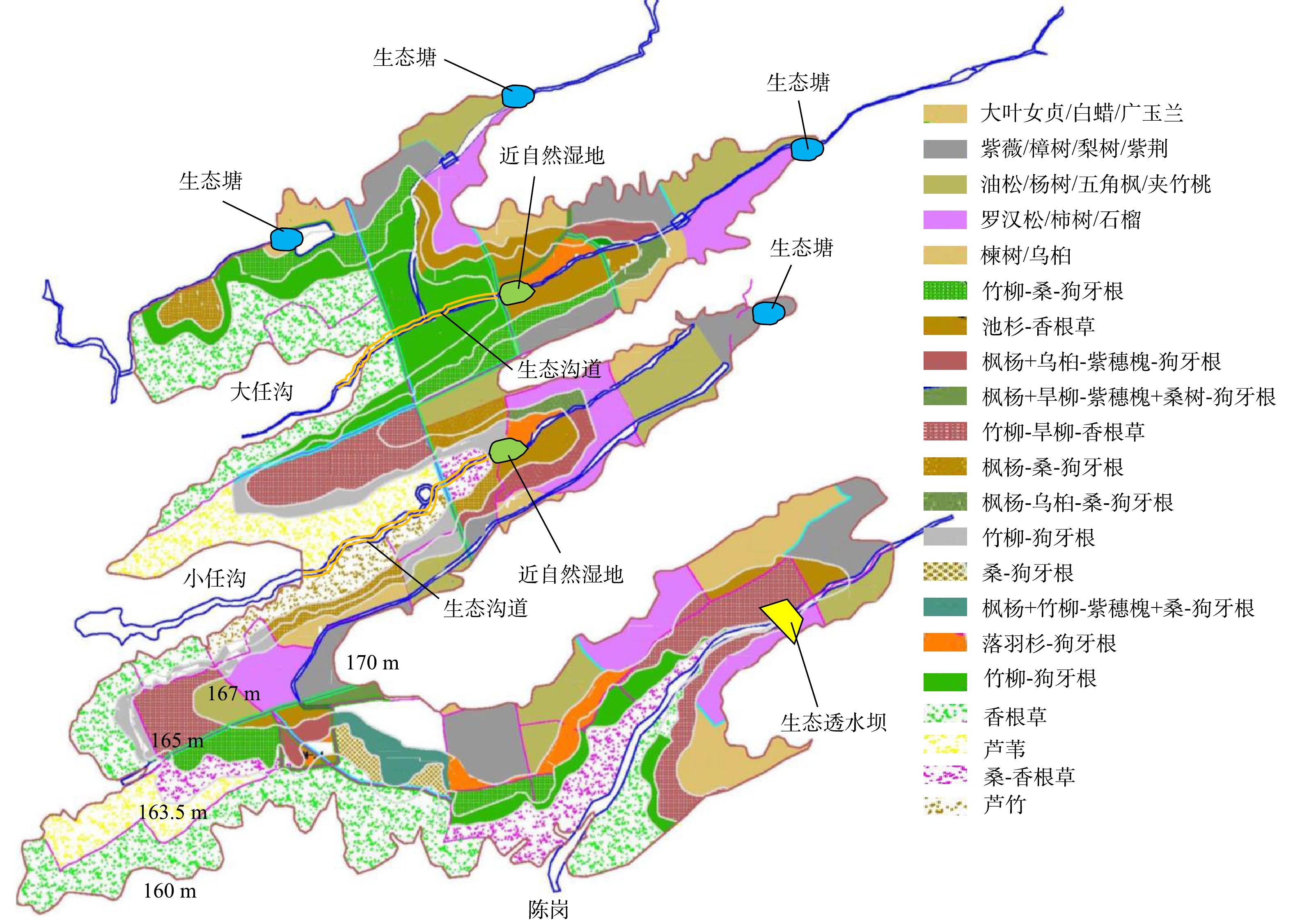
香花镇库岸位于河南省淅川县,紧邻丹江口水库,同时紧靠南水北调中线工程陶岔取水口;地理坐标为北纬32°44′30″~33°45′50″,东经110°39′40″~110°41′15″,高程为160~170 m,面积为2.16 km2。项目区由3个小流域组成,分别为大任沟流域,小任沟流域和陈岗流域(见图1)。区内主要土地利用类型为农耕用地,伴随着少量的林地、村庄和自然坑塘斑块,是缓坡型库岸带的典型代表。
3.1 消落区植被恢复设计
根据课题组对丹江口水库消落区恢复适宜物种的筛选成果[18],结合区域主要经济苗木类型,确定消落区的植被恢复物种。选择乔木物种16种,分别为落羽杉、池杉、竹柳、旱柳、枫杨、乌桕、大叶女贞、梨树、五角枫、油松、广玉兰、楝树、柿树、白蜡、罗汉松、樟树、杨树;选择灌木物种6种,分别为桑树、紫穗槐、石榴、紫薇、紫荆、夹竹桃;选择草本物种4种,分别为狗牙根、香根草、芦苇、芦竹。
各植被功能带的植物群落模式有:拦滤净化带以香根草、芦苇、芦竹为主要种植物种,分别布置在不同的库湾,既可以满足生态截污及净化作用,又便于对3种耐水湿草本植物的水体净化效果进行对比研究;固岸缓冲带以竹柳、旱柳、落羽杉、池杉、桑树、狗牙根、香根草作为主要建群物种,分别营造以竹柳-香根草、竹柳-狗牙根、旱柳-香根草、旱柳-狗牙根、落羽杉-香根草、落羽杉-狗牙根、池杉-香根草、池杉-狗牙根、桑树-香根草、桑树-狗牙根为主的10种不同群落类型;保土持水带以落羽杉、池杉、竹柳、旱柳、枫杨、乌桕、桑树、紫穗槐、香根草、狗牙根作为主要建群物种,主要营造竹柳-桑树-香根草、竹柳-桑树-狗牙根、旱柳-桑树-香根草、旱柳-桑树-狗牙根、竹柳+旱柳-香根草、竹柳+旱柳-狗牙根、枫杨-桑树-狗牙根、枫杨+乌桕-紫穗槐-狗牙根+美人蕉+黄菖蒲、旱柳+乌桕-紫穗槐+桑树-狗牙根+黄菖蒲、枫杨+旱柳-紫穗槐+桑树-狗牙根、枫杨+旱柳+乌桕-桑树+紫穗槐-狗牙根、枫杨+竹柳-紫穗槐+桑树-狗牙根等群落配置模式;适度利用带植物以罗汉松、油松、樟树、大叶女贞、梨树、五角枫、广玉兰、楝树、柿树、白蜡、杨树、石榴、紫薇、紫荆、夹竹桃作为主要选育物种,同时结合场地现状条件,部分图斑搭配种植枫杨、乌桕、旱柳、桑树、紫穗槐等营造示范区特色景观林。
植被恢复共涉及113个图斑,32种群落配置模式(见图3)。其中160~163.5 m淹没区图斑17个,总面积约71.80 hm2;163.5~165 m淹没区图斑32个,总面积约29.92 hm2;165~167 m淹没区图斑30个,总面积约43.46 hm2;167~170 m淹没区图斑34个总面积约72.34 hm2。
3.2 生态水系统设计
结合项目区水系汇流情况及坑塘分布现状带,对流域内已有的沟渠、坑塘进行简单人工修整改造,形成“塘-湿地”水系统,共布设9处水系统措施(见图3)。
大任沟布设生态塘3处(位于170 m高程),近自然湿地1处(位于164 m高程),生态沟道1处(位于160~163.5 m高程);小任沟布设生态塘1处(位于170 m高程),近自然湿地1处(位于164 m高程),生态沟道1处(位于160~163.5 m高程);陈岗小流域地形起伏较大,仅在坡降最大处(位于165 m高程)布设生态透水坝1处。构建的生态水系统能够在不同水文情景下满足面源阻控需求。正常蓄水位170 m条件下,生态塘来对上游沟道来水发挥阻控作用。秋季汛限水位163.5 m条件下,“生态塘-近自然湿地-生态透水坝”系统共同发挥生态阻控作用。夏季汛限水位160 m条件下,生态沟道可在“生态塘-近自然湿地”系统的基础上,进一步发挥阻控作用,确保入库径流水质优良。
生态塘主要是对原有坑塘进行生态化改造[25],改造内容包括:对排水沟进行疏浚清理,连通生态塘与主沟道;修整进水沟渠,保证周边农田径流能够进入生态塘;对边坡进行平整,水面以上部分种植美人蕉,形成缓冲区;生态塘内种植香蒲。近自然湿地主要是对原有低洼沼泽湿地进行修整[26],内容包括:中间修建土埂,用于导流,延长水力停留时间;导流土埂之间种植水生植物,土埂上植草;湿地浅水区种植挺水植物,深水区种植沉水植物;对排水沟进行疏浚清理,保证上游沟道和周边径流能够汇入湿地系统。生态透水坝位于田间废弃河道,坝体分为控制层、溢流层、稳定层和过滤层,分别由不同粒径碎石和砾石构成[27]。生态沟道针对项目区溪沟泥沙淤积,边坡坍塌等问题,开展清淤及加固防护,并在沟道种植芦苇、香蒲等湿生植物,控制沟道侵蚀、减少水土流失和面源污染。
3.3 污染阻控效果评估
利用输出系数法[28]估算项目区3条沟道流域范围的面源污染负荷产生量。基于项目区1∶2 000地形图,统计得到170 m高程以上各地类面积;170 m高程以下消落区全部按林地计算。降雨量取南阳地区多年平均降雨量800.5 mm。根据丹江口水库调度规程,170、163.5和160 m水位大致对应冬春季、秋季和夏季,结合淅川县降雨季节分布特征[29],3种水位对应的降雨量占比约为10%、30%、60%。按照该比例分配年均降雨量,计算3种水位的面源负荷产生量,结果见表1。面源负荷主要集中在163.5 m和160 m 2个水位时期,170 m水位时负荷量较少。
表 1 香花镇缓坡型库岸生态屏障面源负荷阻控效果评估Table 1. Evaluation of load resistance control effect of non-point source of ecological barriers in the gentle slope bank of Xianghua Town小流域 季节 水位/m 面源负荷产生量/(t·a−1) 阻控措施和污染物去除率 面源负荷削减量/(t·a−1) TSS TN TP TSS TN TP 大任沟 冬春季 170 12.78 0.17 0.02 生态塘 5.42 0.06 0.01 秋季 163.5 53.61 0.72 0.04 生态塘+植被功能带+近自然湿地 51.97 0.67 0.04 夏季 160 62.68 0.84 0.05 生态塘+植被功能带+近自然湿地+生态沟道 62.30 0.81 0.05 全年 129.07 1.73 0.11 — 119.69 1.54 0.1 小任沟 冬春季 170 5.12 0.08 0.01 生态塘 2.17 0.03 0.00 秋季 163.5 45.94 0.62 0.03 生态塘+植被功能带+近自然湿地 44.54 0.58 0.03 夏季 160 55.02 0.74 0.04 生态塘+植被功能带+近自然湿地+生态沟道 54.68 0.72 0.04 全年 106.08 1.44 0.08 — 101.39 1.33 0.07 陈岗 冬春季 170 11.67 0.16 0.02 — 0.00 0.00 0.00 秋季 163.5 52.49 0.71 0.04 植被功能带 41.99 0.50 0.03 夏季 160 61.56 0.83 0.05 植被功能带+生态透水坝 52.71 0.58 0.04 全年 125.72 1.7 0.11 — 94.7 1.08 0.07 合计 冬春季 170 29.57 0.41 0.04 污染物去除率:TSS 26%,TN 21%,TP 21% 7.59 0.09 0.01 秋季 163.5 152.04 2.05 0.12 污染物去除率:TSS 91%,TN 85%,TP 80% 138.51 1.74 0.10 夏季 160 179.26 2.41 0.14 污染物去除率:TSS 95%,TN 87%,TP 88% 169.69 2.11 0.12 全年 360.87 4.87 0.30 污染物去除率:TSS 88%,TN 81%,TP 77% 315.79 3.94 0.23 研究表明,生态塘对TN、TP、TSS去除率分别为34.7%、34.8%[30]和42.4%[31];近自然湿地对TN、TP、TSS去除率分别为62.9%、54.7%、73.5%[32];生态透水坝对对TP、TSS去除率分别为19.0%、28.1%[33];植被功能带对TN、TP、TSS去除率分别约为70%、64%、80%[34];生态沟道对TN、TP、TSS去除率分别53.2%、71.8%、80.2%[35]。各项措施按照串联关系逐级累积,计算得到不同水文情境下的污染负荷去除量,结果如表1所示。项目区全年对TN、TP、TSS的削减量分别为3.94、0.23、315.79 t·a−1,各污染物去除率在77%~88%;夏季(160 m水位)项目区对TN、TP、TSS的削减量分别为2.11、0.12、169.69 t·a−1,各污染物去除率在85%以上。虽然冬春季(170 m水位)污染物去除能力相对较弱,但由于面源产生量较少,对面源负荷削减需求较低,所以不会造成面源负荷大量输入。
4. 结论
1)丹江口水库缓坡型库岸生态屏障建设的关键在于消落区植被恢复和库岸生态水系统构建。植被恢复将消落区划分为拦滤净化带、固岸缓冲带、保土持水带和适度利用带,适度利用带能够解决消落区土地土地无序耕种的问题。生态水系统通过坑塘沟道的微地形生态化改造,形成生态塘、近自然湿地、生态透水坝和生态沟道等,能够对库周面源径流起到阻控作用。
2)香花镇缓坡型库岸的生态屏障构建选择16种乔木、6种灌木、4种草本植物进行消落区植被恢复,布设生态塘4处、近自然湿地2处、生态透水坝1处、生态沟道2处形成生态水系统。
-
表 1 Box-Behnken实验因子编码及水平
Table 1. Variables and levels chosen for Box-Behnken
变量 因素 时间(A)/h 真空度(B)/MPa 温度(C)/℃ −1 2 0.06 40 0 3 0.07 50 1 4 0.08 60 表 2 响应面实验设计方案及数据
Table 2. Experiment design and data of RSM
编号 时间(A)/h 真空度(B)/MPa 温度(C)/℃ 氨氮去除率/% 1 3 0.08 40 70.55 2 3 0.07 50 72.84 3 2 0.08 50 60.89 4 2 0.06 50 44.12 5 3 0.07 50 73.2 6 4 0.07 60 80.09 7 4 0.06 50 62.46 8 3 0.07 50 72.75 9 3 0.07 50 73.54 10 2 0.07 60 53.61 11 3 0.06 40 51.15 12 3 0.07 50 72.36 13 3 0.08 60 87.85 14 2 0.07 40 44.24 15 3 0.06 60 64.13 16 4 0.07 40 63.04 17 4 0.08 50 88.7 表 3 响应面方差分析结果
Table 3. Variance analysis of response surface experiments results
项目 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 模型 2 817.08 9 313.01 791.38 <0.000 1*** A 401.86 1 401.86 1 016.03 <0.000 1*** B 927.30 1 927.30 2 344.49 <0.000 1*** C 1 044.93 1 1 044.93 2 641.90 <0.000 1*** AB 22.42 1 22.42 56.69 0.000 1** AC 14.75 1 14.75 37.28 0.000 5** BC 4.67 1 4.67 11.80 0.010 9* A2 306.74 1 306.74 775.53 <0.000 1*** B2 0.546 4 1 0.546 4 1.38 0.278 3 C2 72.79 1 72.79 184.03 <0.000 1*** 残差 2.77 7 0.395 5 失拟项 1.96 3 0.652 9 3.22 0.143 9 纯误差 0.81 4 0.202 5 模型+残差 2 819.85 16 注:***表示差异极其显著(P<0.001),**表示差异高度显著(P<0.01),*表示差异显著(P<0.05);回归模型的决定系数R2=0.9991,校正决定系数R2adj=0.9980。 表 4 响应面预测处理组条件
Table 4. The conditions for response surface prediction
编号 时间(A)/h 真空度(B)/MPa 温度(C)/℃ 氨氮去除率/% 1 3.28 −0.080 57.25 90.3 2 3.50 −0.080 50.72 88.8 3 3.50 −0.078 59.00 92.0 4 3.85 −0.080 58.90 94.3 5 3.66 −0.076 59.55 89.3 -
[1] 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021. [2] 严显超, 叶杰旭, 穆永杰. 生活垃圾焚烧厂沥滤液处理技术研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2012, 35(6): 134-139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2012.06.029 [3] BOLYARD S C, REINHART D R. Evaluation of leachate dissolved organic nitrogen discharge effect on wastewater effluent quality[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 65: 47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.03.025 [4] ABUABDOU S M A, AHMAD W, AUN N C, et al. A review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors (AnMBR) for the treatment of highly contaminated landfill leachate and biogas production: Effectiveness, limitations and future perspectives[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 255: 120215. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120215 [5] XIE Z, WANG Z, WANG Q, et al. An anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactor (AnDMBR) for landfill leachate treatment: Performance and microbial community identification[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014, 161: 29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.014 [6] 闫林涛, 黄振兴, 肖小兰, 等. 厌氧膜生物反应器处理高浓度有机废水的中试研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2015, 34(12): 1248-1255. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2015.12.003 [7] 杨静, 黄丹. 垃圾发电厂渗沥液处理中存在的问题剖析[J]. 水处理技术, 2020, 46(3): 135-137. [8] 余崑. 垃圾渗滤液处理技术的方法及成本分析[J]. 中国设备工程, 2020(16): 198-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2020.16.102 [9] 朱卫兵, 李月中, 龚方红. MBR工艺在垃圾焚烧发电厂渗滤液处理中的应用[J]. 江苏工业学院学报, 2008, 20(2): 17-19. [10] CIRIK K, GOCER S. Performance of anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating landfill leachate[J]. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 2020, 18(2): 383-393. doi: 10.1007/s40201-019-00376-9 [11] LEITE V D, PAREDES J M R, SOUSA T A T, et al. Ammoniacal nitrogen stripping from landfill leachate at open horizontal flow reactors[J]. Water Environment Research, 2018, 90(5): 387-394. doi: 10.2175/106143017X15131012152942 [12] 曾晓岚, 李作鑫, 丁文川, 等. 响应面法优化吹脱处理垃圾渗滤液[J]. 水处理技术, 2011, 37(3): 61-64. [13] 林志国, 郜洪文. 高浓度氨氮废水处理技术及研究进展[J]. 山东化工, 2015, 44(6): 57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2015.06.020 [14] UKWUANI A T, TAO W. Developing a vacuum thermal stripping - acid absorption process for ammonia recovery from anaerobic digester effluent[J]. Water Research, 2016, 106: 108-115. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.09.054 [15] 陈晗. 负压吹脱法除氨氮的试验研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2008. [16] 程兵. 负压脱氮法去除锰渣渗滤液中氨氮的工艺研究及应用[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2016. [17] 赵贤广, 杨世慧, 邱明建, 等. 负压蒸发-吹脱组合新技术处理垃圾沥滤液高浓度氨氮实验研究[J]. 现代化工, 2020, 40(2): 187-190. doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2020.02.039 [18] LEVERENZ H, ADAMS R, HAZARD J, et al. Continuous thermal stripping process for ammonium removal from digestate and centrate[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(4): 2185. doi: 10.3390/su13042185 [19] BONMATI A, FLOTATS X. Air stripping of ammonia from pig slurry: Characterisation and feasibility as a pre- or post-treatment to mesophilic anaerobic digestion[J]. Waste Management, 2003, 23(3): 261-272. doi: 10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00144-7 [20] TIAN X, GAO Z, FENG H, et al. Efficient nutrient recovery/removal from real source-separated urine by coupling vacuum thermal stripping with activated sludge processes[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 220: 965-973. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.181 [21] 傅金祥, 张荣新, 范旭, 等. 吹脱法去除垃圾渗滤液中氨氮[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 27(4): 741-745. [22] 戴兰华. 城市生活垃圾焚烧厂渗滤液资源化利用技术及展望[J]. 中国给水排水, 2016, 32(7): 112-116. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2016.07.028 [23] 马宏林, 贺涛, 洪雷, 等. 响应面分析法优化给水污泥吸附除磷工艺[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(2): 546-552. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20150208 [24] 王波, 池勇志, 田秉晖, 等. 水洗法处理酮连氮法制水合肼副产废盐的工艺优化[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(6): 2054-2062. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202101108 [25] 林伟雄, 顾海奇, 武纯, 等. 响应面法优化化学沉淀螯合生物絮凝处理含镍废水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(2): 493-500. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202005139 [26] 谢亚平, 陈爱侠, 陈贝, 等. 响应曲面法对污泥热解剩余半焦吸附水中刚果红的优化[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(3): 622-631. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201904180 -




 下载:
下载: