-
我国污水厂进水普遍具有低C/N的水质特征,限制了污水厂的脱氮除磷效率[1-2]。为满足出水氮磷的达标排放,通常选择在污水处理流程中投加有机碳源[3-4]。虽然提升了氮磷脱除效果,但存在碳源药剂费用高昂、污泥产量增加、后续处理处置费用高、大部分有机物转化为CO2 (不符合碳达峰、碳中和的时代发展需求)[5]等诸多问题。因此,急需找寻新的方法或策略以摆脱低C/N污水处理对外加碳源的依赖。
污水处理工艺中好氧区会消耗大量有机物,造成碳源的浪费,控制溶解氧能够节约碳源,提高碳源在缺氧段的脱氮利用率。近几年,较多研究提出通过控制污水处理工艺中好氧区溶解氧(DO)可实现低C/N污水的高效脱氮除磷,无需外加碳源的同时可节省曝气能耗。JIN等在低C/N进水条件下,通过2步控制DO<0.5 mg·L−1,实现87.9%的TN去除率[6]。赵智超等在AAO反应器中通过间歇曝气降低好氧区DO浓度,在无硝化液内回流条件下实现了同步硝化反硝化脱氮除磷,出水TN和TP分别为5.8 mg·L−1和0.3 mg·L−1[7]。此外,低DO控制过程中微生物群落与功能基因的变化,也是实现低C/N进水条件下各工艺高效脱氮除磷的关键原因之一[8-9]。池玉蕾等[10]的研究表明,对于低C/N污水而言,好氧区DO的降低能显著提高系统内反硝化菌和聚磷菌的丰度,从而提高污水处理系统的脱氮除磷效率。
然而,在低C/N进水条件和低DO控制策略下污水处理效能及微生物群落结构的研究大多停留在小试及中试阶段,缺乏针对实际工程的应用研究。对于城镇污水处理厂而言,DO的变化会对整个工艺系统产生较大影响,其准确调控至关重要。因此,有必要针对实际工程研究低DO调控策略下污水处理系统的综合效能。本研究选择山东某城镇污水处理厂(低C/N进水)进行实验,比较在无外加碳源并调控好氧区DO措施实施前后污水厂脱氮除磷效能及微生物种群结构的变化,并综合分析低DO控制策略产生的经济效益。面对碳达峰、碳中和的时代发展目标,本研究通过低DO调控,保障低C/N进水污水厂出水达标的同时,实现药耗(无需外加碳源)和能耗(降低曝气)的同步节省,不仅大大节约了运行费用,也为同类型实际工程的调控及改造提供参考。
-
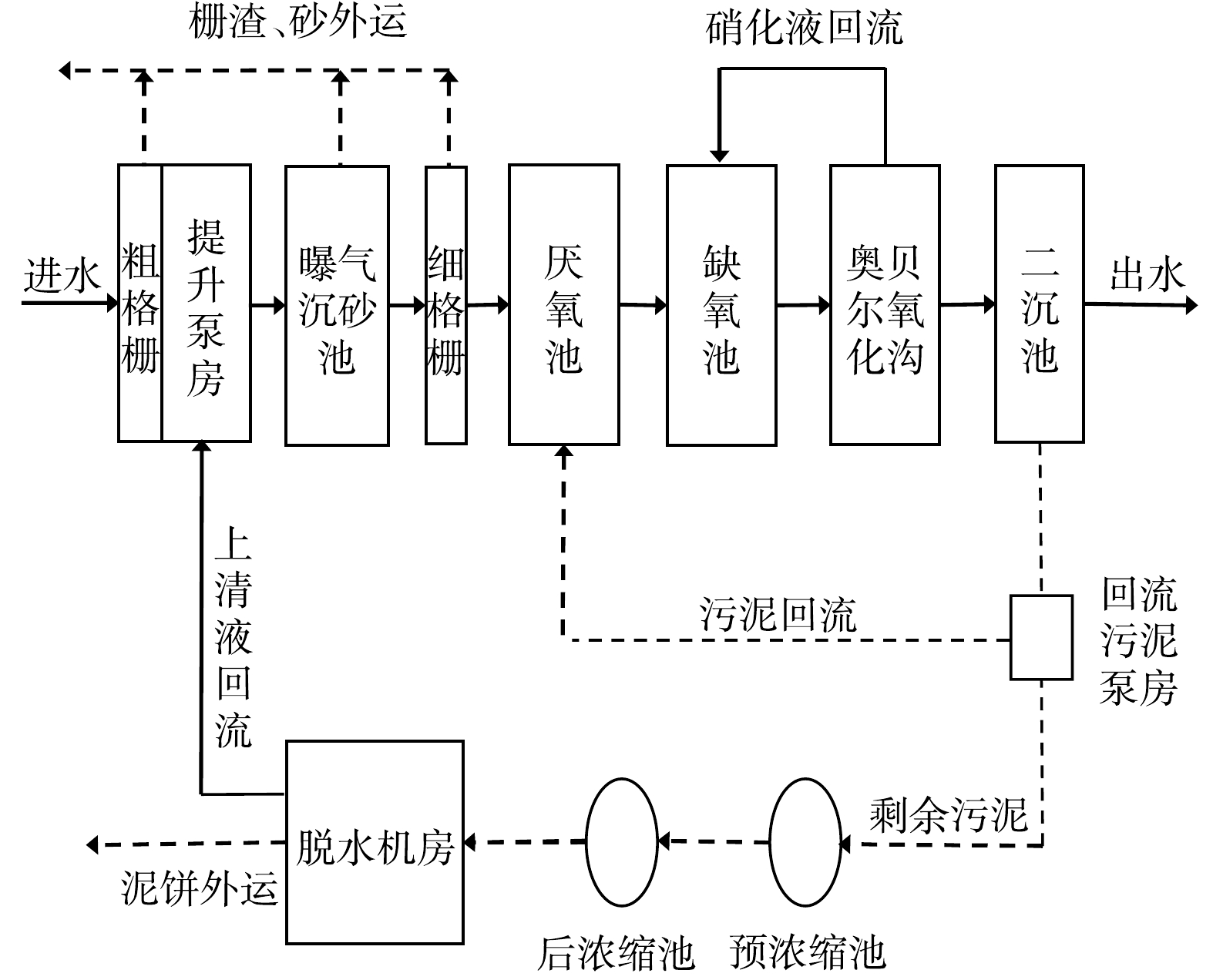
本研究依托于山东省某城镇污水处理厂,该厂设计处理规模为8×104 t·d−1,实际运行规模8×104 t·d−1,采用A2O工艺。进水C/N平均值为4.2:1,属典型低C/N进水水质,常年大量投加有机碳源,出水水质执行《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。主要工艺流程见图1,主要构筑物参数见表1。
-
本研究的运行周期分为2个阶段,第1阶段(P1)为2020-01-01—2020-12-31,共365 d,每天根据出水TN浓度投加碳源(乙酸钠);第2阶段(P2)为2021-01-01—2021-05-22,共143 d。其中P2阶段开始逐渐减少碳源投加量,在416 d后停止投加碳源。同时,P2阶段硝化液回流比分4个阶段下调:366~399 d维持在370%;400~425 d逐渐下调至280%;426~455 d逐渐下调至180%;456~484 d逐渐下调至90%,之后不再改变。2个阶段运行参数见表2。
-
1)水质指标测定与分析。水样COD、NH4+-N、NO3−-N、NO2−-N、TN、TP、MLSS等指标均根据国家标准方法测定[11]。水样DO浓度通过便捷式溶解氧仪(YSI-pro20)测量。
2)微生物样品采集与保存。基于表观实验数据,分别于P1(第140天)和P2(第499天)2个阶段从污水厂采集2组活性污泥样品。采样位置为奥贝尔氧化沟好氧区的前段、中段和后段,每段于液面下1、3和5 m处采集3个样品,将9个样品混合形成1组微生物样品。采集后样品保存于−20 oC,用于后续微生物测序。
3)宏基因测序与分析。利用E.Z.N.A.® Soil DNA Kit(Omega Bio-tek,美国)试剂盒对活性污泥微生物样品进行DNA抽提;使用NEXTflexTM Rapid DNA-Seq(Bioo Scientific,美国)建库;使用Illumina NovaSeq测序平台进行宏基因组测序;使用上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司云平台进行数据分析。
-
好氧区硝化比例、好氧区亚硝化比例、好氧区同步脱氮比例按式(1)、式(2)、式(3)计算。
式中:R1为好氧区硝化比例,%;R2为好氧区亚硝化比例,%;R3为好氧区同步脱氮比例,%;
CNH+4−N,in ,CNH+4−N,ef 分别为好氧区进出水NH4+-N质量浓度,mg·L−1;CNO−3−N,in ,CNO−3−N,ef 分别为好氧区进出水NO3−-N质量浓度,mg·L−1;CNO−2−N,in ,CNO−2−N,ef 分别为好氧区进水NO2−-N质量浓度,mg·L−1。 -
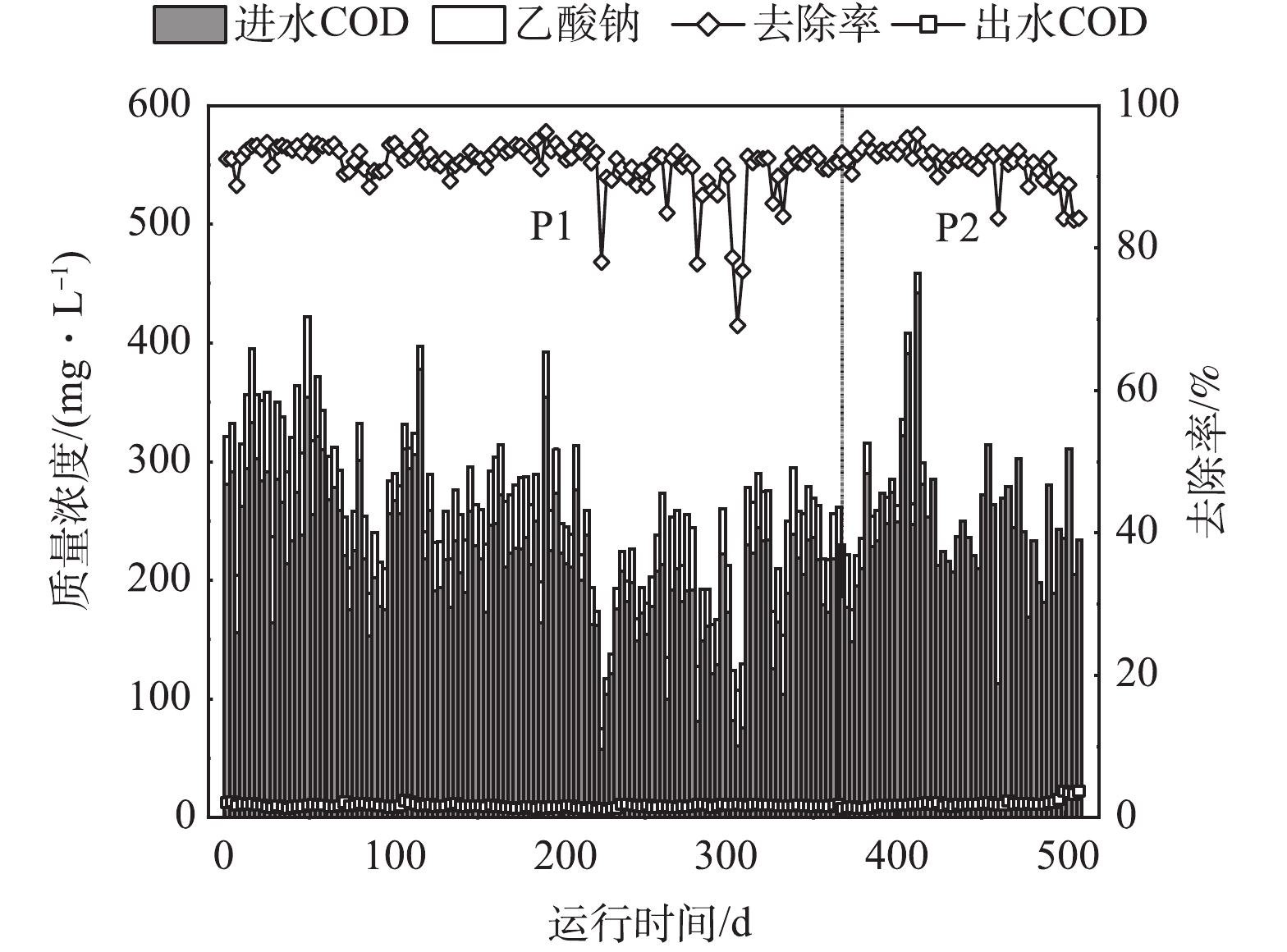
针对P1、P2 2个阶段,考察系统在调控DO前后对有机物、氮、磷等污染物的转化去除效果。实验过程中污水厂进出水COD变化情况见图2。P1和P2阶段污水厂出水COD值无显著差异。P1阶段实际进水COD平均值为215 mg·L−1(C/N=4.4∶1),外加碳源COD当量平均值为41 mg·L−1(总C/N=5.2∶1);P2阶段实际进水COD平均值为244 mg·L−1(C/N=4.2∶1)。在P2阶段降低好氧池DO浓度后,污水厂出水COD值基本维持在25 mg·L−1以下,490 d后出水COD略有上升,但仍然满足排放要求。COD平均去除率由P1阶段的91.5%变为P2阶段的92.5%,变化不明显,可见DO的降低对有机物的去除几乎无影响。
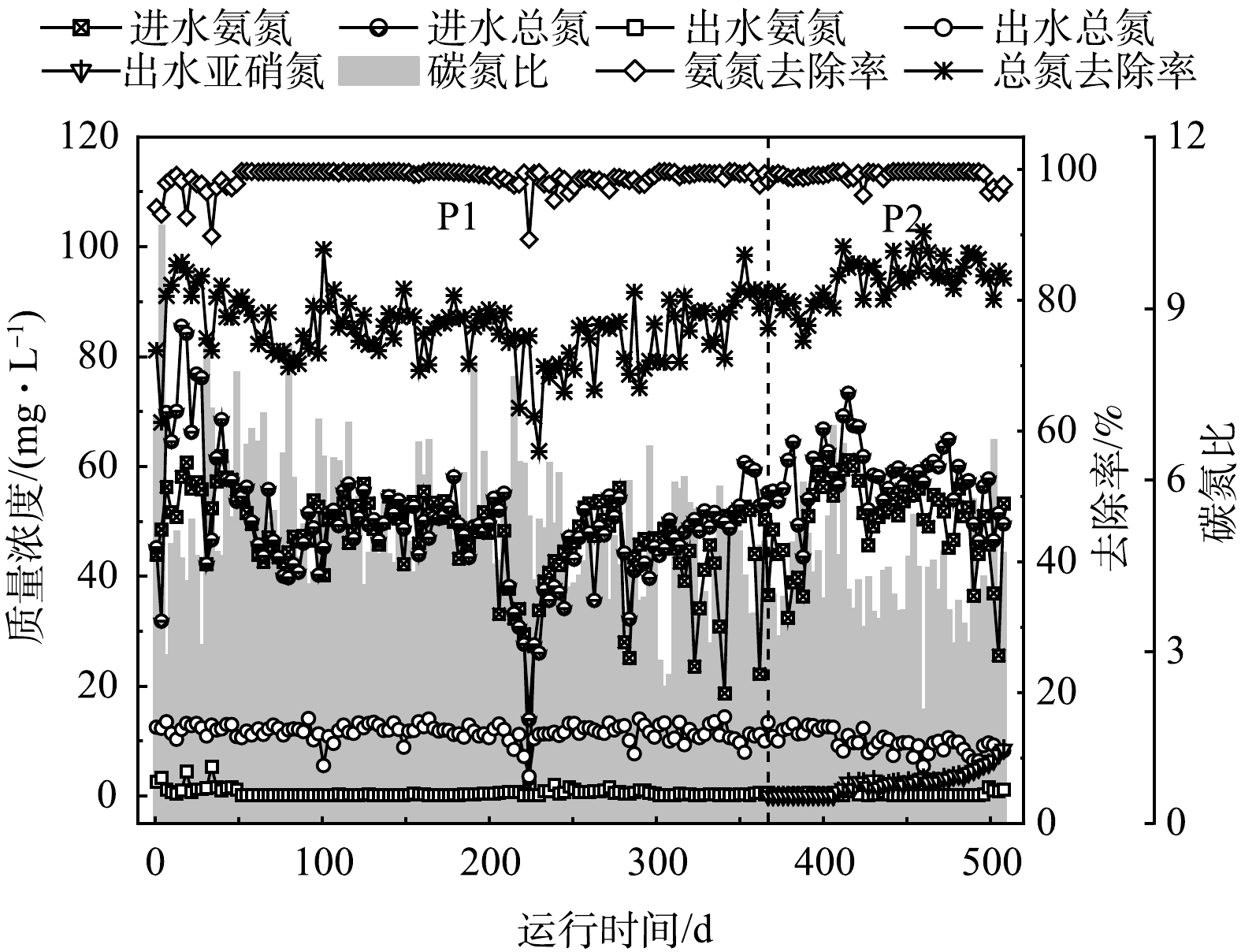
2个阶段的NH4+-N、TN去除及NO2−-N积累情况见图3。P1和P2阶段对NH4+-N的去除效果无显著差异。2个阶段污水厂进水NH4+-N平均质量浓度分别为46.6 mg·L−1和49.6 mg·L−1,降低好氧区DO浓度后,P1和P2阶段污水厂出水NH4+-N质量浓度基本都维持在1 mg·L−1以下,平均去除率在97%以上。可见DO浓度的降低对NH4+-N的去除效果无显著影响。
P2阶段污水厂对总氮的去除效果明显好于P1阶段。P1阶段污水厂进水和出水TN平均质量浓度分别为48.9 mg·L−1和 11.6 mg·L−1,平均去除率为76.3%;P2阶段污水厂进出水TN平均质量浓度分别为57.9 mg·L−1和 9.9 mg·L−1,平均去除率升高至82.9%。P2阶段,本研究在控制DO浓度、降低外加碳源的同时,硝化液回流比从P1阶段的370%逐渐下调,最终调整为P2阶段的90%,再加上100%的污泥回流比,TN的理论去除率应从82.5%降至65.5%。P1阶段的TN平均去除率低于理论去除率;然而,P2阶段的TN去除率却明显高于理论去除率。控制溶解氧浓度及减少碳源投加控制策略下,污水处理厂的脱氮能力非但没有降低,反而显著提升。
P2阶段开始对污水厂出水NO2−-N浓度进行跟踪检测,结果如图3所示。长期低DO运行条件下,出水TN逐渐以NO2−-N为主。第367~406天,出水NO2−-N质量浓度几乎为0,之后逐渐升高,在508 d时达到最高值8.5 mg·L−1,有明显的NO2−-N积累。这与姚丽婷等在小试实验中的研究结果一致。在低DO条件下,会出现显著的NO2−-N积累现象,主要原因为亚硝酸盐氧化菌(NOB)受到抑制,氨氧化菌(AOB)逐渐成为优势菌,最终实现短程硝化[12]。P2阶段开始逐渐停止外加碳源,C/N从5.2∶1(含外加碳源)降至4.2∶1,而TN去除效果却明显有提升。其原因之一可能是降低DO后,好氧区发生短程硝化,而反硝化去除NO2−-N所需电子供体仅为NO3−-N的60%,大大降低了污水厂脱氮对碳源的需求[13],也是保障低碳源条件下脱氮效能的关键因素之一。
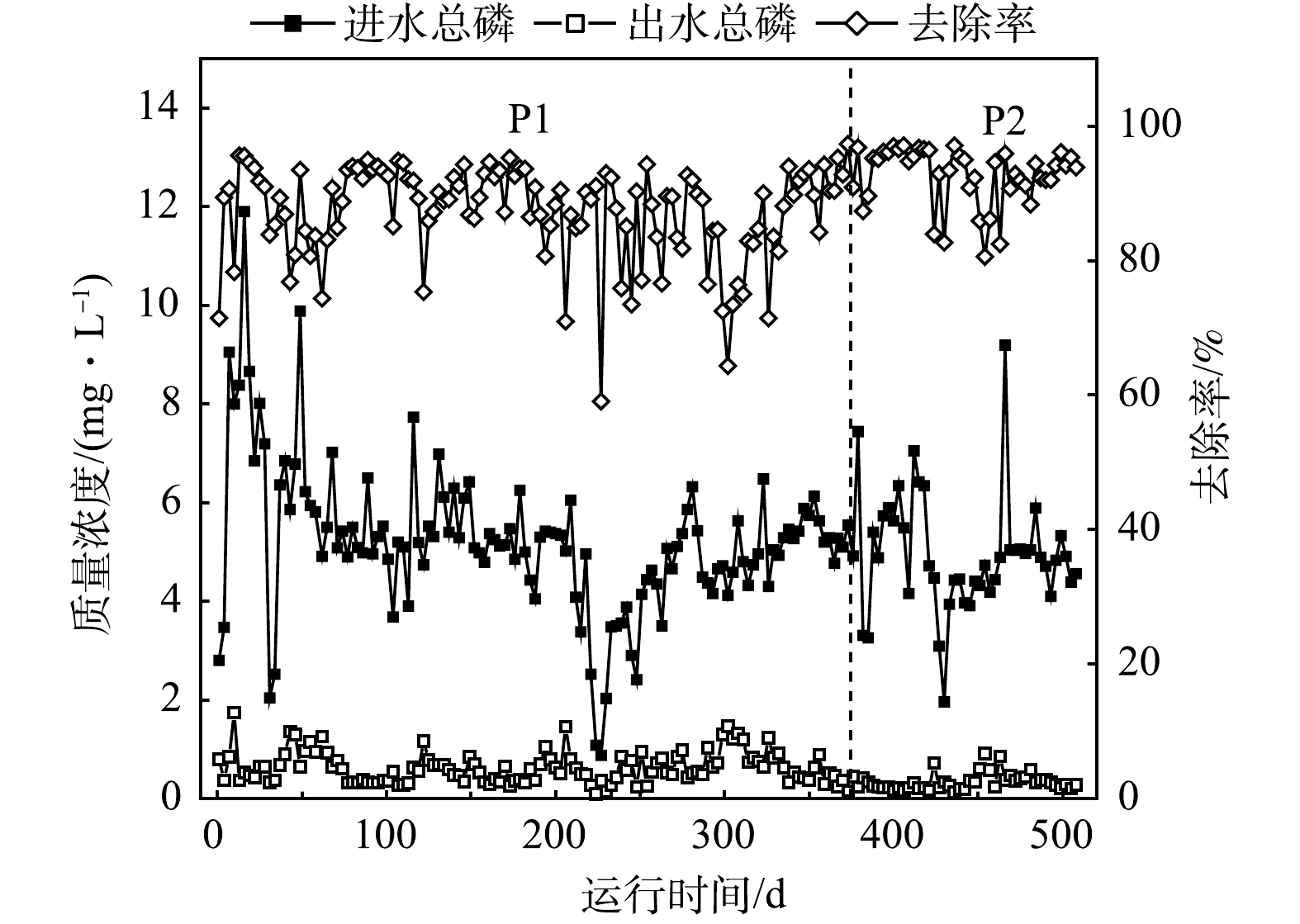
污水厂2个阶段TP去除效果见图4。P2阶段污水厂对TP的去除效果优于P1阶段。降低好氧区DO浓度后,TP的去除效果有明显提升,沉淀池出水平均质量浓度从0.64 mg·L−1降至0.34 mg·L−1,去除率由87.0%上升至92.7%,说明DO浓度的降低提升了污水处理系统的除磷效果。池玉蕾等在小试实验研究中得出同样的结果,认为低DO条件促进了系统中除磷功能微生物的生长,从而表现出更好的除磷效能[10]。
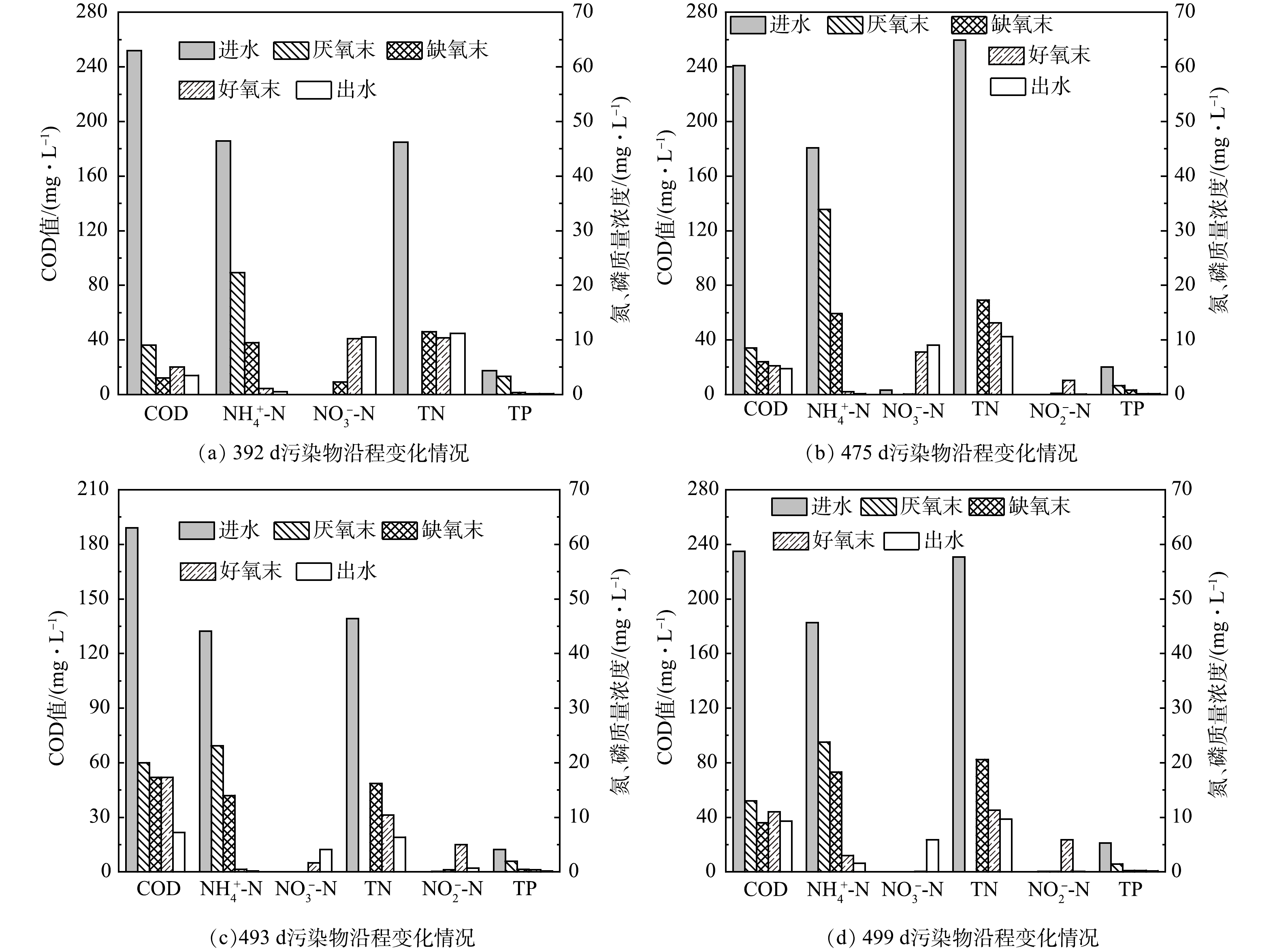
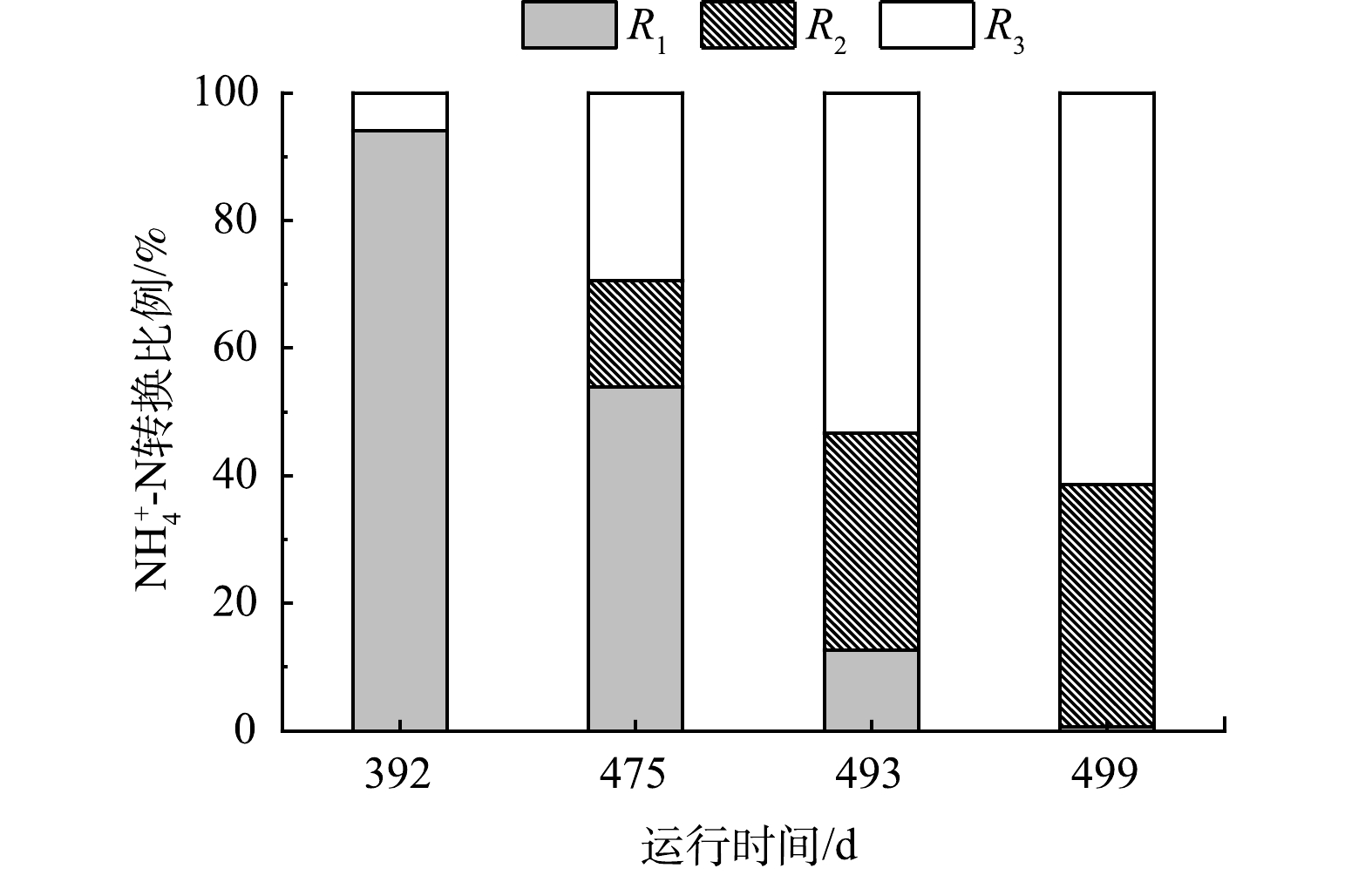
为探究低DO条件下污水厂脱氮能力提升的原因,分别于P2阶段的第392、475、493、499天监测各生化单元的出水水质情况,结果如图5所示。COD、NH4+-N与TP在各池体单元的去除规律无显著变化。其中,在厌氧池中的COD显著下降。分析主要原因为非溶解性有机物在厌氧池被活性污泥快速吸附及污泥回流(100%)的稀释作用[14-15]。
P2阶段降低DO后,短程硝化作用逐渐显现。第392、475、493、499天,NH4+-N在好氧池的转化量基本无差异;然而,随着时间的增加,好氧池末端出水NO3−-N质量浓度逐渐降低,分别为11.1、7.8、1.7和0.1 mg·L−1;好氧池末端出水NO2−-N质量浓度逐渐升高,分别为0、2.6、5.0、5.9 mg·L−1。长期低DO运行条件下,好氧池对NH4+-N的转化逐渐从全程硝化变为短程硝化。此外,第475、493、499天,好氧池出现了明显的TN脱除现象。
P2阶段低DO运行条件下,针对好氧区的氮转化平衡问题进行分析,结果如图6所示。P2阶段好氧区全程硝化逐渐转化为短程硝化,且表现出明显的脱氮效果。392 d时,好氧区主要发生全程硝化,之后好氧区全程硝化比例不断下降,由392 d的94.1%降至499 d的0.7%,而短程硝化的比例从0增加到38.0%。然而,值得注意的是,在长期低DO运行条件下,除了全程硝化和短程硝化外,仍有部分NH4+-N既未转化为NO3−-N也未转化为NO2−-N。该部分NH4+-N的比例由392 d的0逐渐上升至499 d的61.3%。基于好氧区的低DO及NO2−-N持续积累状态,推测本研究在好氧区发生了同步脱氮作用,可能为同步硝化(也可能短程硝化)反硝化或者厌氧氨氧化作用。
-
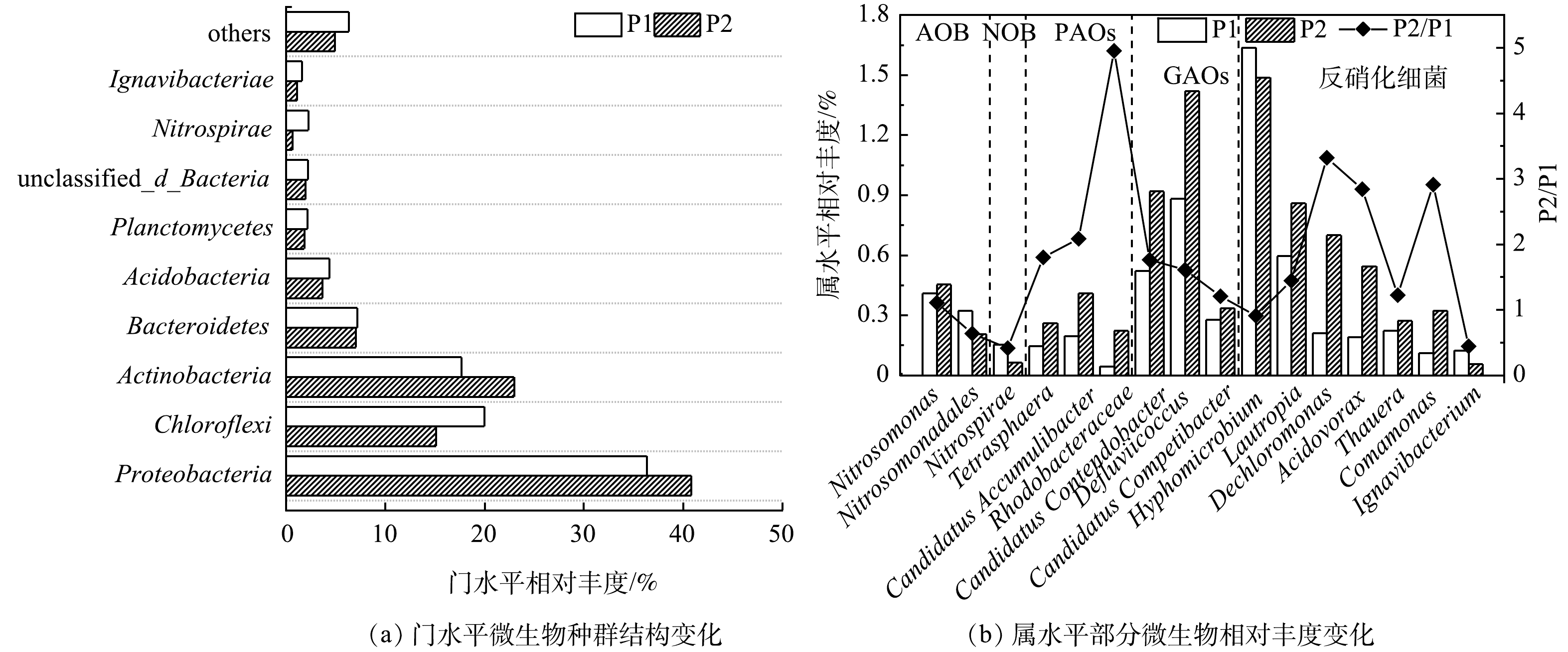
为进一步探索P1和P2阶段污水厂表观差异的内部机制,对2个阶段污水厂好氧区的微生物进行宏基因组学测序并对比分析。微生物在门水平的群落结构如图7(a)所示。长期低DO运行条件造成污水处理系统内微生物在门水平上差异性显著。P1阶段系统内的优势菌为Proteobacteria(36.3%),其次为Chloroflexi(20.0%)与Actinobacteria(17.7%);P2阶段系统中丰度最高的仍为Proteobacteria(40.8%),而Chloroflexi(15.1%)明显下降Actinobacteria(23.0%)显著升高。此外,值得注意的是,Nitrospirae(亚硝酸盐氧化相关菌门)的丰度由P1阶段的2.2%下降至P2阶段的0.6%。
微生物在属水平的丰度如图7(b)所示。P1和P2阶段系统内脱氮除磷主要功能微生物在属水平的差异性同样显著。硝化作用相关功能微生物变化为:氨氧化菌(AOB)Nitrosomonas和Nitrosomonadales的丰度分别由P1阶段的0.41%、0.32%变化至P2阶段的0.45%、0.21%,总丰度略有下降;而亚硝酸盐氧化菌(NOB)Nitrospirae的丰度却从P1阶段的0.15%大幅下降至P2阶段的0.06%[16]。由此可见,低DO运行条件对NOB的明显抑制作用,可能是造成好氧区NO2−-N积累的主要因素。
长期低DO运行条件下,P2阶段系统内反硝化功能微生物Hyphomicrobium、Lautropia、Dechloromonas、Acidovorax、Thauera、Comamonas、Ignavibacterium总体较P1阶段有所增加[17-19],相对丰度为原来的1.4倍。此外,P2阶段系统中除磷菌(PAOs)Candidatus Accumulibacter、Rhodobacteraceae和聚糖菌(GAOs)Defluviicoccus、Candidatus Competibacter均较P1阶段有显著提升,总的相对丰度为P1阶段的1.7倍。有研究表明,这4种功能菌能够利用厌氧期储存的内碳源进行反硝化脱氮[20-21]。由此可见,低DO条件下系统内各反硝化功能微生物的增加同样是保障低碳源脱氮的关键。
长期低DO运行条件下,好氧区氮平衡的分析结果表明,好氧区有明显的氨氮(总氮)缺失,推测其原因可能为好氧区发生同步硝化反硝化或者厌氧氨氧化。ZHANG等的研究表明,在低DO条件下部分GAOs、PAOs在厌氧段储存的内碳源未被完全消耗,微氧条件下仍然能够进行反硝化脱氮[22]。而对于微生物的分析中,未发现有厌氧氨氧化相关的功能微生物,认为未发生厌氧氨氧化作用。因此,本研究认为长期低DO运行条件促使具备反硝化功能的PAOs与GAOs丰度升高,在好氧区形成了基于内碳源的同步反硝化(包括亚硝氮反硝化)作用,从而在无外加碳源及降低内回流的条件下提高了污水厂对低碳源污水的脱氮效能。
此外,上节研究结果表明在长期低DO运行条件下,系统除磷效果有明显提升。基于此,对系统内除磷相关功能微生物进行分析。结果表明,低DO运行条件下,除具备反硝化除磷功能的Candidatus Accumulibacter、Rhodobacteraceae(能利用DO或NO3−作为电子受体的PAOs)外,系统内另外一种除磷菌Tetrasphaera(仅能利用DO作为电子受体的PAOs)的丰度也有显著提升,P2阶段3种菌属在系统中的总丰度为P1阶段的2.3倍。分析其原因可能为,低DO运行条件下,提高了有机物作为内碳源用于生物除磷的利用率,促进了除磷相关功能微生物的生长,从而提升了系统的除磷效能[10]。
基于功能微生物数据,对P1、P2 2个阶段污水处理系统内氮代谢相关功能基因进行分析,结果如图8所示。2个阶段微生物脱氮相关的主要功能基因丰度有显著性差异。P2阶段降低DO后,氨氧化相关功能基因AmoCAB总丰度几乎未变,亚硝酸盐氧化还原酶功能基因NxrAB和硝酸盐还原酶功能基因NarGHI/NapAB总丰度分别下降了6.7%和4.2%,亚硝酸盐还原酶功能基因NirKS总丰度升高了13.5%[23-24]。结合表观效能及功能微生物丰度数据,推测系统中存在的一个内部机制为:长期低DO运行条件可抑制NOB,导致Nxr基因相对丰度下降,造成NO3−-N生成量减少、NO2−-N积累;而长期低NO3−-N、高NO2−-N条件下,Nar/Nap基因相对丰度降低,Nir基因相对丰度升高,也是保障无外加碳源条件下低C/N进水城镇污水厂脱氮效能的关键因素之一。
-
长期低DO运行条件下,为污水厂带来的经济效益主要体现在3个方面:1)节省外加碳源,药剂费用大大降低;2)曝气量降低,电耗费用减少;3)低DO、低/无外加碳源条件下,污泥产量降低,污泥处理处置成本降低。污水采用低DO运行策略所带来的主要经济效益计算见表3,其中乙酸钠(含量20%)750 元·t−1,电费0.52 元·(kWh)−1,污泥处理费(80%含水率)270 元·t−1,P2阶段的污水厂运行费用比P1阶段降低2.44 万元·d−1,吨水处理费用减少0.3元。
-
1)长期低DO运行策略下,低C/N进水城镇污水厂(A2O工艺)逐渐停止外加碳源,在硝化液回流比由370%降低到90%的过程中,TN去除效果不降反升,平均去除率由76.3%提升至82.9%。这主要由于好氧区短程硝化和同步反硝化作用比例的升高所致。
2)短程硝化作用的内在原因为长期低DO条件对AOB抑制作用小,对NOB抑制作用明显,NOB的丰度从0.15%下降至0.06%,亚硝酸盐氧化还原酶功能基因NxrAB丰度显著下降,造成NO2−-N积累。
3)好氧区同步反硝化作用的内在原因为低DO条件下具备反硝化功能的PAOs与GAOs比例升高,总丰度从2.06%提升至3.57%,好氧区低DO条件下利用厌氧期储存的内碳源完成反硝化脱氮;而内碳源利用率的提升又促进了PAOs的生长,提升了除磷效能。
4)低DO运行策略下,污水厂外加碳源、曝气电耗、污泥处理等费用大大降低,吨水处理费用节省0.3元。
低C/N进水城镇污水厂低溶解氧运行效能及微生物变化
The efficiency and microbial community change of urban sewage plant with low C/N influent based on low DO strategy
-
摘要: 低C/N进水污水厂通常需要外加碳源以保障脱氮除磷效能,运行费用高。本研究以摆脱低C/N污水处理对外碳源依赖及降低运营成本为目的,依托山东省某城镇污水厂(A2O工艺)开展基于低DO调控策略的污水厂综合效能研究。结果表明,在长期低DO运行策略下,污水厂逐渐停止外加碳源,在硝化液回流比由370%逐渐降至90%的过程中,TN平均去除率由76.3%提升至82.9%,且除磷效率有所提升。对好氧区氮平衡进行分析发现,在低DO运行条件下,好氧区NH4+-N的转化逐渐以短程硝化和同步反硝化作用为主。微生物宏基因组学结果表明,在低DO条件下,NOB丰度由0.15%下降至0.06%,而具备反硝化功能的PAOs与GAOs的总体丰度由2.06%升高至3.57%。长期低DO、无外加碳源运行条件下,脱氮效能的显著提升主要由于好氧区短程硝化和同步反硝化作用的比例升高所致。低DO对AOB抑制作用小,对NOB抑制作用显著,导致NO2−-N的积累,保障了脱氮效能;PAOs与GAOs利用厌氧期储存的内碳源在好氧区反硝化脱氮,提升了脱氮效能;而内碳源利用率的提升又促进了PAOs的生长,提升了除磷效能。此外,污水厂低DO运行策略下,节省了运营成本,吨水处理费用降低了0.3元。Abstract: Low C/N influent wastewater plants usually need additional carbon source to ensure nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency, leading to the high operation cost. In order to get rid of external carbon sources for low C/N wastewater treatment and reduce operation cost, a comprehensive efficiency study was carried out in an urban wastewater treatment plant with A2O process in Shandong Province based on low DO regulation strategy. The results showed that under the long-term low DO operation strategy, when the wastewater plant gradually stopped additional carbon sources and decreased the reflux ratio of nitrification liquid from 370% to 90%, TN average removal rate increased from 76.3% to 82.9%, and phosphorus removal effect also increased. The analysis of nitrogen balance in aerobic zone showed that the transformation of NH4+-N in aerobic zone was gradually dominated by partial nitrification and simultaneous denitrification under low DO condition. Microbial metagomenomics results showed that under low DO condition, the abundance of NOB decreased from 0.15% to 0.06%, while the total abundance of PAOs and GAOs with denitrifying function increased from 2.06% to 3.57%. The significant improvement of nitrogen removal efficiency under long-term low DO and no external carbon source was mainly due to the increased proportion of partial nitrification and simultaneous denitrification in aerobic zone. Low DO had slight inhibitory effect on AOB, while inhibited NOB significantly, resulting in NO2−-N accumulation and ensuring TN removal efficiency. PAOs and GAOs used the internal carbon source stored in the anaerobic stage for denitrification in the aerobic zone, which improved the denitrification efficiency. The improvement of internal carbon source utilization rate promoted the growth of PAOs and raised phosphorus removal efficiency. In addition, under the low DO operation strategy of the sewage plant, the operating cost was saved and the wastewater treatment cost was reduced by 0.3 yuan per ton wastewater.
-
我国是抗生素生产大国,每年产生的抗生素菌渣量达到1.3×106 t以上[1]。菌渣在自然环境下易腐败变质,任意堆放极易造成环境污染。此外,菌渣不合理处置会导致其中的残留抗生素在环境介质中扩散和传播,从而对人群健康和生态环境造成巨大威胁。而另一方面,菌渣中含有大量的微生物菌丝体及未代谢利用完的有机物,营养物质含量丰富,可对其进行资源化利用。因此,如何将抗生素菌渣无害化处理及资源化利用已成为当今急需解决的难题。
好氧堆肥被广泛应用于固体有机废物处理,研究表明畜禽粪便或抗生素菌渣中的残留抗生素可以通过好氧堆肥降解[2-3]。菌渣经好氧堆肥后可被制成有机肥料,其不仅可提高土壤肥力,还保证了农产品品质安全[4]。堆肥中的微生物除了参与有机物料的分解外,其也对抗生素降解有重要作用。赵军超[5]发现,红霉素菌渣经好氧堆肥处理后降解率可达99%以上。这表明,好氧堆肥可实现抗生素菌渣无害化处理。
由于传统好氧堆肥温度不够高,限制了其对抗生素的降解[6]。因此,目前关于应用好氧堆肥法处理抗生素菌渣的研究都是在外源添加物的条件下进行的。一般外源添加物主要分为生物炭、氯化铁、天然沸石和生物菌剂等,而在好氧堆肥处理中添加生物菌剂效果显著[7]。研究发现,在堆肥中添加微生物菌剂,可提高堆肥温度,增加堆肥中微生物的种类和活性,延长高温分解周期,加快堆肥腐殖化进程,提高其中抗生素去除率,降低其环境风险,使堆肥成品达到无害化要求[8-12]。
本研究选取土霉素菌渣为研究对象,探究添加复合菌剂后土霉素菌渣和玉米秸秆混合堆肥的基本理化参数、堆肥中土霉素降解和微生物群落结构变化情况,并优化好氧堆肥对土霉素菌渣中残留土霉素的处理,为抗生素菌渣的无害化处理和资源化利用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 堆肥原料
土霉素菌渣取自石家庄市某制药厂。玉米秸秆取自石家庄周边农户农田中,将其在105 ℃条件下烘干处理后破碎,长度约为1~2 cm。堆肥原料初始基本理化性质如表1所示。
表 1 堆肥原料基本理化性质Table 1. Basic physical and chemical property of compost raw materials供试样品 含水率/% pH 电导率EC/(mS·cm−1) C/N 玉米秸秆 9.89 5.32 2.67 50.89 土霉素菌渣 78.04 4.47 — 5.73 1.2 实验装置和设计
堆肥试验在河北科技大学堆肥实验场进行。堆肥容器容积70 L,底部连接曝气泵以调节气量,并装有气体流量计。装置中连有3个温度探头,对其上、中、下温度进行实时监控。本实验设计分为2组,一组添加自制菌剂A(制备方法见专利:申请号CN 202111337864.9,编号C);另一组不添加菌剂(编号CK)作为对照组。C组为15 kg菌渣+15 kg玉米秸秆+菌剂A(0.3%);CK组为15 kg菌渣+15 kg玉米秸秆。
通过调节气体流量计,控制曝气速度为7 L·min−1。采样天数设定为第0、4、8、15、22、28、34、38 d,每次取样前进行翻堆,每次取样在罐体的上、中、下3个平面取样,遵循5点取样原则。每次取200 g样品,分为2份保存,一份用真空冷冻干燥机(FD-1A 50,博医康(北京)仪器有限公司)冷冻干燥,然后在20 ℃下保存,用于土霉素质量浓度的测定,另一份在4 ℃下保存用于理化性质分析。
1.3 实验测定指标及分析方法
堆肥温度采用自制堆肥装置内PT100温度探头对温度进行实时监测,每天选取0、4、8、12、16、20 h进行数据记录;含水率的测定运用失重法,参照GB/T 1931-2009中检测方法[13];堆肥样品中pH采用雷磁ZD-2自动电位滴定仪测定(PHS-2F,上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司);EC采用多参数在线测定仪(哈纳HI993302,上海耀壮检测仪器设备有限公司);全碳、全氮、全磷和全钾含量采用流动分析仪测定(AA3,英国希尔公司)。
种子发芽指数(GI)测定:首先取10 g样品与蒸馏水按比例1∶10放入250 mL锥形瓶中,然后置于150 r·min−1摇床振荡30 min;再取其上清液过滤后吸取5 mL滤液于铺有滤纸的培养皿中,在其中放置20颗白菜种子,置于25 ℃下避光培养48 h后;最后,测定种子的根长,同时用去离子水做空白对照。
细菌群落结构通过宏全基因组法进行测定。残留土霉素采用高效液相色谱法测定(岛津LCM S8050,色谱柱为C18,1.9 μm×2.1 mm×50 mm;初始流动相为20%乙腈:80%甲酸水),土霉素降解率(D)如式(1)。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) 式中:D为土霉素降解率;C0为第0 d堆肥中土霉素质量分数,mg·g−1;Cn为第n 天堆肥中土霉素质量分数,mg·g−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 堆肥过程的理化性质
图1为堆肥过程中理化性质变化。含水率是堆肥过程中重要影响因素之一,其变化如图1(a)。C组和CK组的初始含水率分别为66.42%和64.05%。在堆肥初期,2组反应的含水率均小幅上升,然后开始下降。这可能是因为,微生物大量繁殖生长,产生了水分,后由于微生物分解有机质并散发较多热量,使堆体保持较长时间的高温,水分随热量挥发,故经翻堆后堆体含水率明显下降。堆肥结束后C组和CK组的含水率分别下降至41.08%和43.04%,由此表明,添加菌剂有利于堆体水分挥发。
由图1(b)可看出,2组堆体pH变化趋势相似。投加菌剂对堆体pH的影响不大,均出现先上升,再降低,翻堆后又升高的趋势。pH上升可能是由于堆肥前期大量排放的氨气的累积。随后氨气的产生速率小于其随曝气带出堆肥体系中的速率,pH开始下降[14]。堆肥第21 d后进入降温期,堆肥过程中的营养消耗减少,大量N元素以NH3的形式释放,并且在该阶段硝化细菌增多,其进行硝化反应产生大量H+,从而导致堆体的pH有轻微下降[15]。
堆体中铵态氮(NH4+-N)的转化过程如图1(c)所示。C组和CK组在堆肥第2 d后NH4+-N均呈上升状态,第21 d分别达到284.14和347.68 mg·kg−1。这可能是因为,堆体的C/N较低,物料中有机氮源被微生物矿化分解,使硝化反应在高温环境下受阻,导致NH4+-N大量积累[16-17]。此趋势与红霉素和青霉素菌渣堆肥研究中NH4+-N的转化过程相似[5,18]。NH4+-N的浓度达到峰值后开始下降,且C组下降速率大于CK组,最终C组NH4+-N质量浓度略低于CK组。这表明,添加菌剂有利于保留堆体中的氮源。
EC是反映堆肥中的可溶性盐含量的指标。一般情况下,堆体的EC>4 mS·cm−1,对植物种子发芽有强烈的抑制作用。因此,对堆肥过程中EC的变化过程进行了研究,结果如图1(d)所示。堆体的EC变化趋势为先上升后下降,可能是前期随着物料的消耗,释放出矿物盐和铵根离子而上升。高温期后,有机质降解速率下降,由于CO2和NH3的挥发,导致EC下降,这与以往的研究结果相似[19]。2组堆肥中的EC峰值达到3.0和2.85 mS·cm−1,均未超过其应用限值,故不会对植物种子发芽产生较强的抑制。C组初始EC值高于CK组,但最终EC值分别为2.57和2.21 ms·cm−1,低于CK组,处于安全水平。这表明,添加菌剂有利于降低堆肥中的可溶性盐的含量。
2.2 堆肥毒性
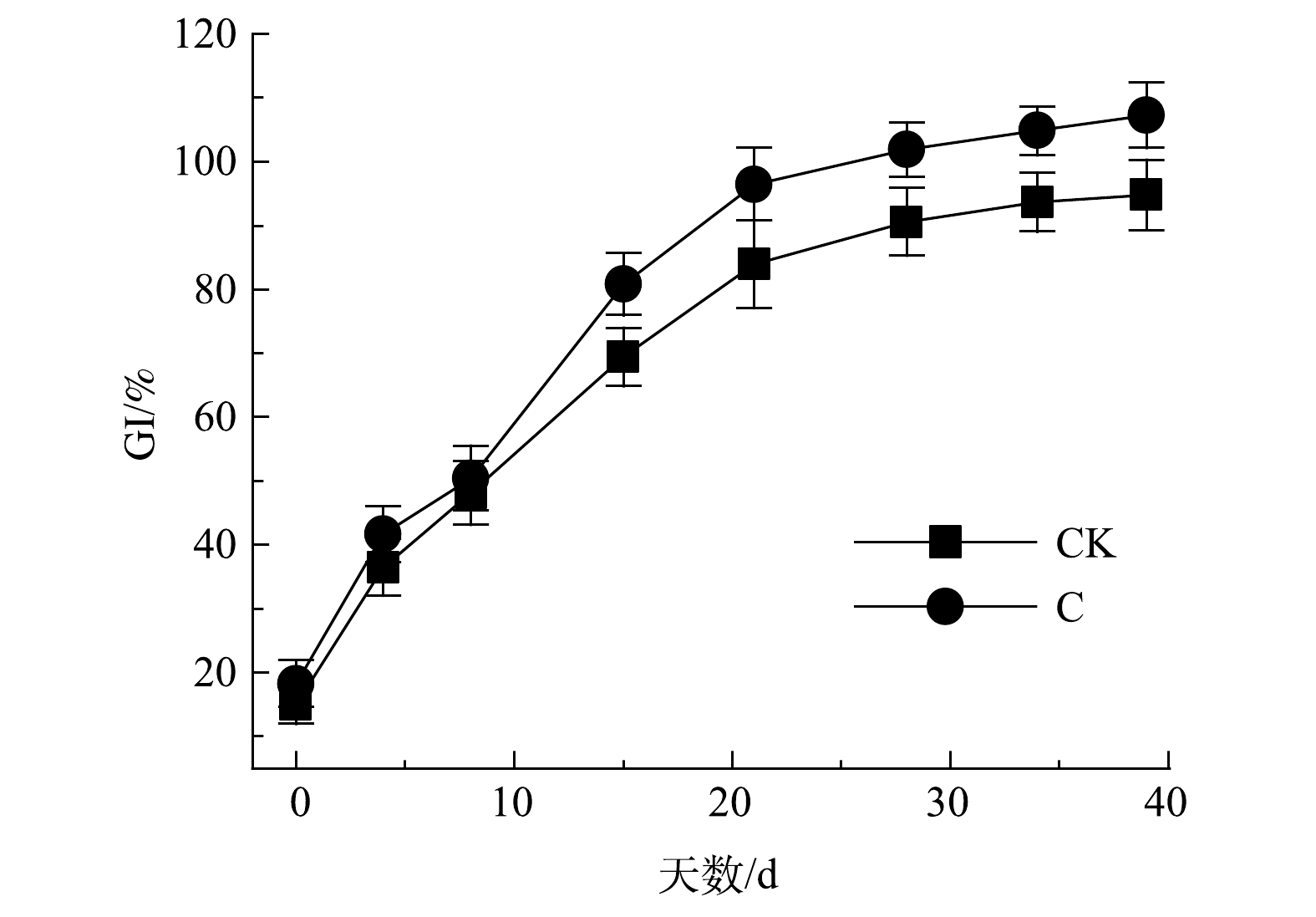
堆肥过程中种子发芽率指数(GI)可在一定程度上代表堆肥产品对植物毒性的强弱。其变化如图2所示,2组堆肥初期GI均低于20%。这表明,土霉素菌渣有较强的植物毒性,在农田应用中可能会存在较大的环境风险[20]。由于堆肥初期物料中的有机酸和铵根离子浓度较高,故导致了堆体初期的GI偏低。随着堆肥的进行,在微生物的作用下,物料GI逐渐升高,逐步实现脱毒。当GI>80%时,认定堆肥产品对植物基本无毒,2组堆肥产品均达到安全水平。添加菌剂使C组比CK组处理时间提前了7 d。这表明,复合菌剂在一定程度上加强了堆肥对植物毒性的削减。最终产品的GI分别为94.8%和107.3%。添加菌剂后,在提高微生物的种类和活性的作用下,缩减了堆肥周期,加快了堆肥物料的脱毒。马骏[21]研究表明,牛粪堆肥产品的GI高达124%,远高于本研究结果。由此可推测,土霉素残留不仅对GI有抑制作用,且质量浓度越高其抑制效应越强。
2.3 堆肥肥效
随着堆肥的进行,微生物的生长发育消耗了一定的碳源,导致有机质质量分数下降。堆肥结束后C组中有机物质的降解率为14.80%,而CK组仅为9.24%。因此,投加复合菌剂可增加堆体中微生物的数量和活性,加快了对碳源的消耗,提高了堆肥过程的最高温度,可间接增强对有机质的降解。
对堆肥成品进行检测,检测指标参照《有机肥料标准》(NY/T525-2021)[22]中对肥料的要求,将检测结果同标准中要求值进行对比,其结果见表2。堆肥成品指标除水分的质量分数偏高外,其余指标均满足《有机肥料标准》(NY/T 525-2021)[22]中标准,在后续晾干过程中可降低其水分的质量分数。本研究结果可为抗生素菌渣及其衍生物的工程化好氧堆肥资源化利用提供数据支持和技术参考。
表 2 堆肥成品指标Table 2. Composting product index对照指标 本实验检测值 NY/T 525-2021指标值[22] 有机质的质量分数(以烘干基计) 57.3%~58.1% ≥30% 总养分(N+P2O5+K2O)的质量分数(以烘干基计) 5.7%~6.7% ≥4.0% 水分(鲜样)的质量分数 41.08%~43.04% ≤30% 种子发芽率指数(GI) 99.8%~107.3% ≥70% 机械杂质的质量分数 <0.3% ≤0.5% 2.4 菌剂对堆肥中土霉素降解及微生物群落结构变化影响
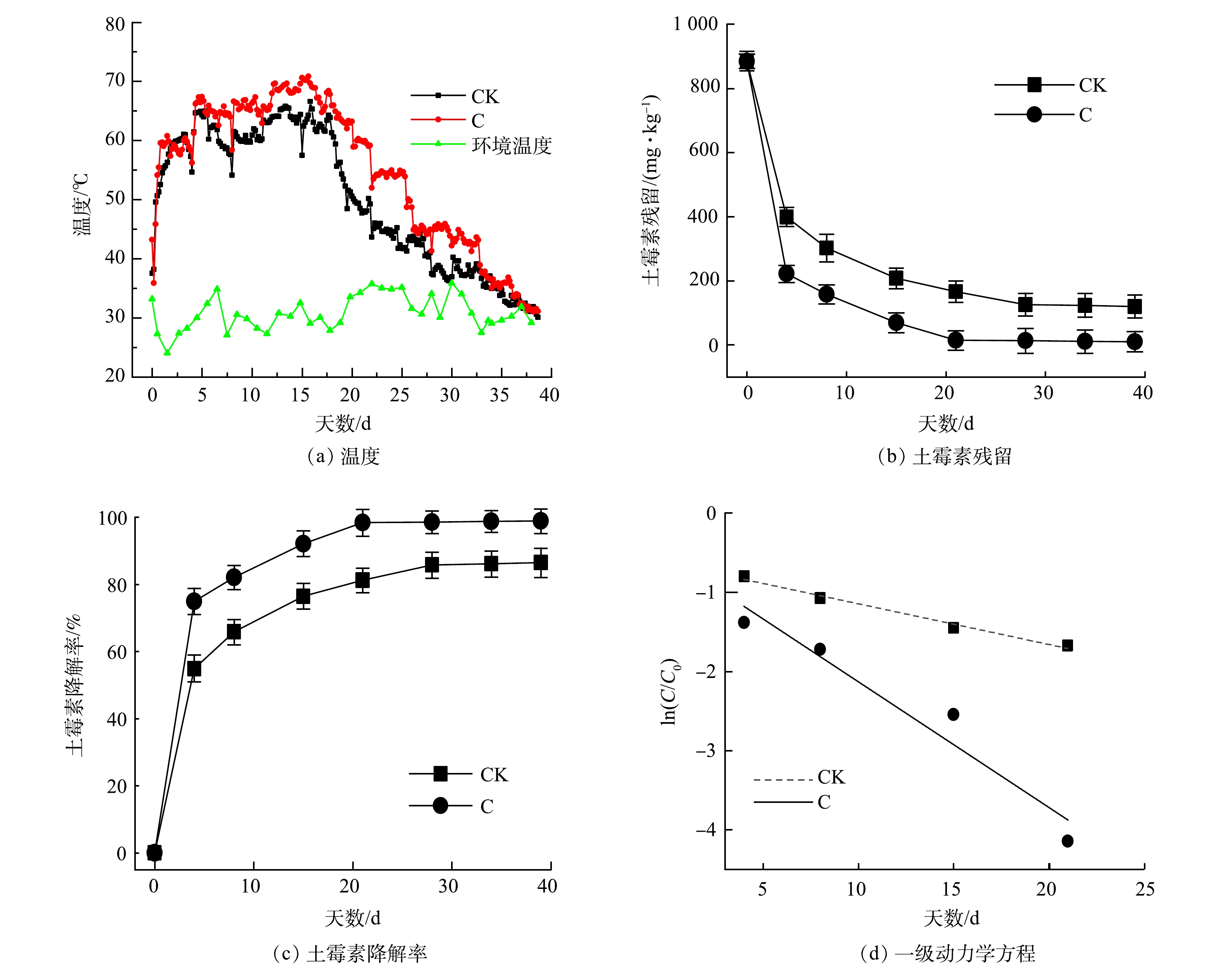
1)菌剂对堆肥中土霉素降解影响。堆体温度是堆肥过程中最重要的参数之一,与有机物降解程度和堆肥产物的腐熟程度密切相关。堆肥温度变化和土霉素降解变化间的关系如图3所示。堆肥期间,温度变化经历了升温期、高温期和降温腐熟期3个阶段。在堆肥第2天,2组温度分别达到54.56和52.66 ℃。其中,C组比CK组提前1 d达到最高温度,最高温度分别为70.55和66.57 ℃,且高温期延长了5 d。这可能是因为,堆肥初期CK组含有的土著微生物较少,微生物活性较差,难以迅速降解堆体中的有机物。堆肥38 d时,堆体温度与环境温度接近,堆肥发酵结束,有机质降解完全,实现了土霉素菌渣的无害化和资源化。马骏[21]研究发现,菌剂能提高堆肥温度,使最高温度达到80 ℃以上,高于本次堆肥温度。这可能是因为,制药菌渣中高浓度的重金属对高温期优势微生物菌群的抑制作用。ZHANG等[23]在泰乐菌素菌渣与污泥堆肥的研究中也表明,高浓度Cu能致使高温期温度不高,与本研究结果一致。
由图3(b)可知,土霉素降解趋势为先迅速下降,最后趋于稳定。CK组在堆肥21 d降解率为81.23%。这表明,堆肥处理可以降低土霉素残留。堆肥结束时,CK组土霉素质量分数为119.67 mg·kg−1,降解率达86.47%;C组土霉素质量分数为10 mg·kg−1,降解率高达98.87%(图3(c))。C组优于CK组,这与REN等[24]、ZHU等[25]、EZZARIAI等[26]、SARDAR等[27]和SARDAR等[28]的研究结果结果相似。土霉素降解主要发生在升温期及高温期。这一方面可能是,升温中键能较弱的四环素类分子中的C—N易断裂,导致羧基及哌嗪环断裂并脱去;另一方面可能是,温度升高增强了嗜温菌和嗜热菌的生物活性,进而提高了土霉素的降解。因此,高温是抗生素降解的重要影响因素,有利于将抗生素菌渣无害化和资源化[29]。
图3(d)是对2组降解曲线的一级动力学模拟图,CK组和C组R2分别为0.986和0.941。表3列出了堆肥过程中几种抗生素的半衰期,C组和CK组的半衰期分别为13.59和4.38。对比发现,CK组的半衰期最大。这表明,土霉素为难降解抗生素[30-31]。但是,C组的半衰期小于CK组。这说明,复合菌剂的添加有利于土霉素的降解。
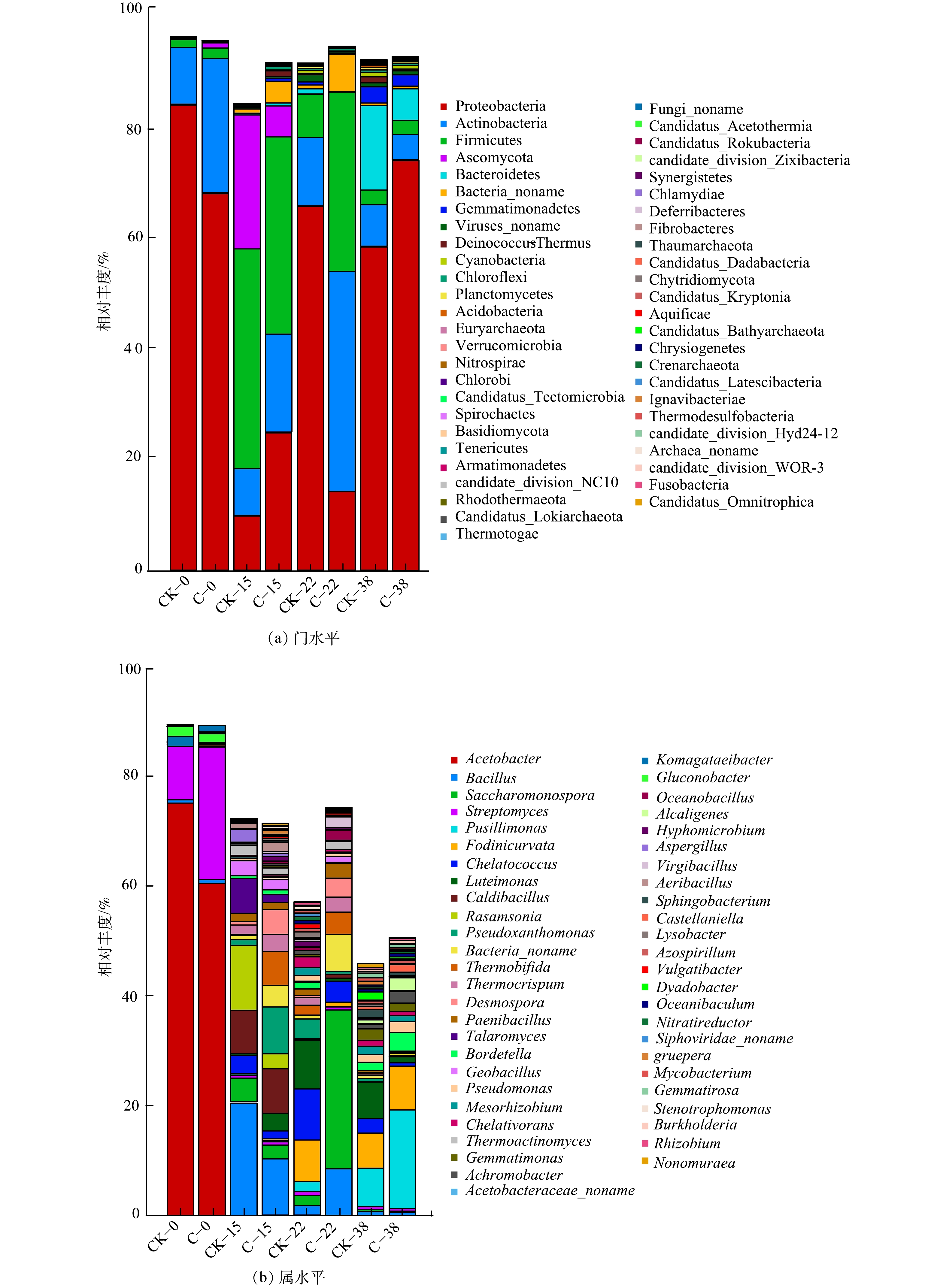
表 3 土霉素降解的线性拟合方程、半衰期和R2Table 3. Linear fitting equation for oxytetracycline degradation, half-life, and R2组别 方程 斜率 R2 半衰期 数据来源 CK ln(C/C0)=−0.051x−0.632 −0.051 0.986 13.59 本研究 C ln(C/C0)=−0.158x−0.544 −0.158 0.941 4.38 本研究 红霉素 ln(C/C0)=−0.500x−0.604 −0.500 0.801 1.40 [26] 多环西素 ln(C/C0)=−0.183x−0.638 −0.183 0.765 3.80 [26] 诺氟沙星 ln(C/C0)=−0.328x−0.689 −0.328 0.894 2.10 [26] 青霉素 ln(C/C0)=−0.798x−0.697 −0.798 0.962 1.72 [30] 庆大霉素 ln(C/C0)=−0.116x−0.087 −0.116 0.985 6.70 [31] 2)菌剂对堆肥中微生物群落结构影响。2组堆肥处理中细菌群落组成在门水平和属水平的相对丰度见图4。C组堆肥样品细菌、真菌和病毒所占的比例分别为94.86%、0.21%和0.97%。细菌主要由放线菌门Actinobacteria、变形菌门Proteobacteria、厚壁菌门Firmicutes和拟杆菌门Bacteroidetes组成。细菌群落在高温期变化较大,而土霉素降解也主要发生在高温期。这表明,土霉素降解可能与其微生物群落变化有密切关系。在堆肥初期,C组中Firmicutes增加到40.03%,Proteobacteria从68.45%降低到9.55%。此时优势菌群为Firmicutes和Actinobacteria,其耐受力强,释放热量促使堆体升温。在升温期,C组中Firmicutes和Bacteroidetes相对丰度分别增加了10.1%和2.5%,Actinobacteria减少了15%。在高温期后,Firmicutes和Bacteroidetes相对丰度分别增加了12.27%和5.7%。堆肥结束时,细菌中Actinobacteria数量下降到4.49%,真菌数量下降到0.16%,病毒降低到0.72%。这说明,土霉素菌渣对细菌、放线菌和真菌生长均有不同程度的抑制。此外,在堆肥过程中,子囊菌门Ascomycota只出现在高温期,随堆肥的进行其相对丰度降低,Ascomycota可能为致病菌,故堆肥有利于致病菌的去除。此结果与PENG等[32]的研究结果相似。
从属水平上分析细菌相对丰度,堆肥升温期,以Acetobacter为代表的1类好氧或兼性厌氧的杆状菌群能够分解堆料,提高堆体温度。在堆肥第22 d,堆体中优势菌群以Saccharomonospora和Bacillus为代表,Saccharomonospora具有较强的蛋白酶、淀粉酶和脂肪酶活性,有较强的有机质分解能力;Bacillus为木质纤维素降解菌。因此,C组堆肥产物中纤维素和半纤维素含量的下降可能与Bacillus菌群数量的增加有关。堆肥高温期,C组的优势菌属无论在功能还是数量上都比CK组能更好的加速堆肥进程。而且,CK组中反硝化细菌存在较多,降低了堆体中氮的含量,导致氮元素缺少,不利于菌渣堆肥产品向有机肥方向发展。在堆肥第38 d,由于复合菌剂中存在Geobacillusthermodenitrificans,因此堆体中优势菌群以Geobacillus为代表,其可分解菌渣中的蛋白质,进而提高抗生素降解率。
3)环境因子和细菌群落之间的相关性分析。环境因素(pH、残留土霉素、温度、C/N)与细菌群落(基于门的丰度)的RDA分析结果如图5所示。RDA1和RDA2分别解释了细菌群落和环境因子总变异的72.85%和42.09%。这表明,残留土霉素的变化主要受细菌群落变化的影响。随着堆肥的进行,Firmicutes减少,而其他菌群在升温期和高温期增加,促进了土霉素的降解。这表明,Firmicutes和Actinobacteria是降解土霉素的优势菌群。在堆肥初期,残留土霉素和C/N是影响堆肥进程的主要因素。然而,在高温和降温阶段,pH和温度成为影响堆肥效果的主要因素。且RAMASWAMY等[33]和BAO等[34]的研究也表明,pH、温度以及微生物的活性在降解抗生素过程中起重要作用。因此,在堆肥过程中,土霉素残留的变化和温度、微生物群落的变化有着密不可分的关系。堆肥结束时,C组土霉素质量浓度小于CK组。这表明,添加菌剂可提高微生物种类和活性以及堆体温度,促进了土霉素的降解。
综上所述,细菌群落的演替和环境因素的变化都会影响土霉素的降解。因温度变化而引起的不同细菌丰度在不同堆肥阶段的差异,可能是残留抗生素随堆肥过程变化的内在机制。接种菌剂既改变了堆肥土著细菌群落的互作模式,降低了细菌群落的复杂度,又为优化建立新的和更健康的堆肥细菌群落奠定了基础。
3. 结论
1) C组的NH4+-N浓度比CK组提前7 d降至腐熟堆肥的安全浓度范围内。堆肥后的成品基本可以满足《有机肥料标准》(NY/T525-2021),复合菌剂在促进堆肥腐熟和氮磷保留中具有良好的效果。
2)复合菌剂增加了堆体中微生物活性,延长了高温期5 d;C组的土霉素降解率高达98.41%,比CK组高12.39 %。这表明,菌剂堆肥化处理在提高堆体温度的同时提高了土霉素降解率。
3)在堆肥中,优势门为Firmicutes和Actinobacteria,土霉素残留的变化与其密切相关。因温度变化而造成的不同细菌丰度在不同堆肥阶段的差异可能是引起残留抗生素随堆肥过程变化的原因。
-
表 1 工艺构筑物参数
Table 1. Parameters of process structures
构筑物 HRT/h 池体数/个 容积/m3 水深/m 厌氧区 3.6 1 12 000 4.3 缺氧区 2.5 2 8 332 6.0 好氧区 5.0 2 16 664 6.0 二沉池 6.0 4 20 400 4.5 表 2 污水厂2个阶段运行参数
Table 2. Operating parameters of sewage treatment plant in two phases
阶段 乙酸钠投加量/(mg·L−1) DO/(mg·L−1) 硝化液回流比/% 污泥回流比/% P1 73~575 2~4 370 100 P2 0~284 0.5~1.4 370~90 100 表 3 污水厂经济效益表
Table 3. The economic benefit calculation of sewage treatment plant
项目 乙酸钠用量/( t·d−1) 曝气电耗/(kWh·d−1) 污泥产量/( t·d−1) 费用/(万元·d−1) P1阶段 20 9 600 76 4.05 P2阶段 0 3 960 52 1.61 -
[1] 郑俊田, 郑俊, 程洛闻, 等. 混合液回流比对多点进水新型A/O/A/A/O泥膜耦合工艺脱氮除磷的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15: 1744-52. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202011119 [2] ZHANG M, WANG Y, FAN Y, et al. Bioaugmentation of low C/N ratio wastewater: effect of acetate and propionate on nutrient removal, substrate transformation, and microbial community behavior[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 306: 122465. [3] 朱启荣, 操家顺, 张腾, 等. 污水厂反硝化传统及可供替代碳源研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50: 1600-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.06.033 [4] 尹亚云, 蒲文鹏, 陈永娟, 等. 污水处理厂外加碳源模拟优化研究[J]. 给水排水, 2021, 57: 156-9. doi: 10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2021.S1.032 [5] 张岳, 葛铜岗, 孙永利, 等. 基于城镇污水处理全流程环节的碳排放模型研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2021, 37: 65-74. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2021.09.011 [6] JIN P, CHEN Y, XU T, et al. Efficient nitrogen removal by simultaneous heterotrophic nitrifying-aerobic denitrifying bacterium in a purification tank bioreactor amended with two-stage dissolved oxygen control[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 281: 392-400. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.119 [7] 赵智超, 黄剑明, 李健, 等. 间歇曝气连续流反应器同步硝化反硝化除磷[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40: 799-807. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201807093 [8] LIU X, HU S, SUN R, et al. Dissolved oxygen disturbs nitrate transformation by modifying microbial community, co-occurrence networks, and functional genes during aerobic-anoxic transition[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021: 790. [9] XU G, ZHANG Z, GAO F. Effect of COD/N ratios and DO concentrations on the NOB suppression in a multi-cycle SBR[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(4). [10] 池玉蕾, 石烜, 任童, 等. 溶解氧对低碳源城市污水处理系统脱氮性能与微生物群落的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42: 4374-82. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202012261 [11] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法 第4版 [M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [12] 姚丽婷, 梁瑜海, 陈漫霞, 等. 高溶解氧条件下不同曝气量对短程硝化性能及微生物特征的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41: 3258-67. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0188 [13] 陈思宇, 张绍青, 陈鹏, 等. 基于短程反硝化的生物脱氮技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39: 38-44. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202105006 [14] 王东, 王小东, 朱引, 等. 生物吸附-多级A/O-活性焦组合工艺对污水中氮磷及有机污染物的去除[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12: 1907-16. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201712110 [15] 朱明璇, 李梅, 王洪波, 等. 污泥对有机物的去除效果及荧光特性研究[J]. 应用化工, 2020, 49: 1457-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.06.029 [16] WANG J, RONG H, ZHANG C. Evaluation of the impact of dissolved oxygen concentration on biofilm microbial community in sequencing batch biofilm reactor[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2018, 125(5): 532-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2017.11.007 [17] XIN X, QIN J. Rapid start-up of partial nitritation in aerobic granular sludge bioreactor and the analysis of bacterial community dynamics[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2019, 42(12): 1973-81. doi: 10.1007/s00449-019-02190-x [18] YANG N, ZHAN G, LI D, et al. Performance and microbial community of a novel non-aeration-based up-flow bioelectrochemical filter (UBEF) treating real domestic wastewater[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 348: 271-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.200 [19] 徐翩翩, 孟佳, 汪聪, 等. 限氧废水处理系统的再启动与ANAMMOX功能恢复[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2019, 51: 32-8. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.03676234.201801014 [20] OEHMEN A, CARVALHO G, LOPEZ-VAZQUEZ C M, et al. Incorporating microbial ecology into the metabolic modelling of polyphosphate accumulating organisms and glycogen accumulating organisms[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(17): 4992-5004. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.071 [21] CHU G, YU D, WANG X, et al. Comparison of nitrite accumulation performance and microbial community structure in endogenous partial denitrification process with acetate and glucose served as carbon source[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 320(Pt B): 124405. [22] ZHANG F, PENG Y, LIU Z, et al. Development of a novel partial nitrification, fermentation-based double denitrification bioprocess (PN-F-Double/DN) to simultaneous treatment of mature landfill leachate and waste activated sludge[J]. Water Research, 2021, 203: 117540. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117540 [23] 王朱珺, 王尚, 刘洋荧, 等. 宏基因组技术在氮循环功能微生物分子检测研究中的应用[J]. 生物技术通报, 2018, 34: 1-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5464.2018.02.001 [24] ASAMOTO C K, REMPFERT K R, LUU V H, et al. Enzyme-specific coupling of oxygen and nitrogen isotope fractionation of the nap and nar nitrate reductases[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(8): 5537-46. -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: