-
随着我国工业化和城市化进程的不断加快,城市“退二进三”“退城进园”等调整规划的绿色推进,在京津冀等经济快速发展区相继涌现出大量的染料化工污染地块,一定程度上制约了区域社会经济与生态环境的协调发展[1]。氯苯类化合物(chlorobenzenes, CBs)是染料化工行业中广泛应用的原料和有机溶剂,是一类由氯原子取代苯环上的氢原子而形成的单环芳香族化合物,包括氯苯、二氯苯、三氯苯、四氯苯、五氯苯和六氯苯共6种(12个)同系物[2-3]。该类物质具有高毒性、持久性和生物蓄积性等特点,且具有“三致”作用[3-4]。我国已公布的优先控制污染物黑名单以及优先控制化学品名录等文件中已明确纳入氯苯、1,2-二氯苯、1,4-二氯苯、1,2,4-三氯苯、五氯苯和六氯苯[4]。在CBs的使用、生产、储存以及运输的过程中,因跑冒滴漏以及三废处置不当等因素,致使其进入企业用地及其周边的土壤环境中,进而迫害生态环境并危及人体健康[5-7]。
近年来,我国相继颁布的土壤污染防治法律法规逐步规范了污染地块环境管理流程[8],土壤污染状况调查是启动地块环境管理工作的开端,调查结果能否准确刻画污染物在地块的空间分布特征将直接影响后续风险评估及治理修复等环节,进而影响政府部门的管理决策。目前,国内外关于CBs在化工污染地块分布特征的研究众多[5-7,9-10],但选取的目标污染物普遍为某1种,或2~3种氯苯类化合物。孟宪荣等[6]研究了氯苯在某化工污染地块的水平和垂直分布特征,结果表明,生产功能分区和地块水文地质条件是影响氯苯分布的主要因素。余梅[9]以氯苯、二氯苯和三氯苯为例,研究了CBs在某化工污染地块的分布特征及迁移规律。SPIGARELLI等[10]研究了9个化工污染地块中六氯苯的分布特征,发现地块范围的空气、土壤和地下水中都存在不同程度的污染。而国内已开展的众多染料化工场地调查案例中,发现地块土壤环境中通常存在多种氯苯类化合物污染的情况。田亚静等[11]发现,二氯苯和三氯苯产品中混有少量的氯苯和其它多氯苯物质;酞菁系列染料生产过程中,三氯苯的使用通常会产生六氯苯。袁祎倩[12]研究了5个染料化工企业的印染废水,发现都存在三、四、五、六氯苯的普遍检出。因此,明确染料化工污染地块中不同氯苯类化合物的分布特征以及迁移转化规律,对后续风险评估、管控以及修复等地块管理环节至关重要。
本研究以北京某染料厂污染地块为研究对象,研究了地块包气带和饱和带中6种氯苯类化合物的分布特征。结合地块的历史生产功能区分布、地层结构以及污染物特性,进一步分析了不同氯苯类化合物的迁移转化规律,建立了地块内CBs迁移转化路径概念模型。
-
研究地块为北京地区某关停遗留的染料化工厂生产用地。该厂建于20世纪60年代,占地约80 000 m2,主要生产酞菁系列颜料,原料涉及二氯苯和三氯苯等。于2003年关停,2005年地块范围内的设备及构筑物全部拆除且平整,闲置至今。现场踏勘时,发现有刺鼻异味。
-
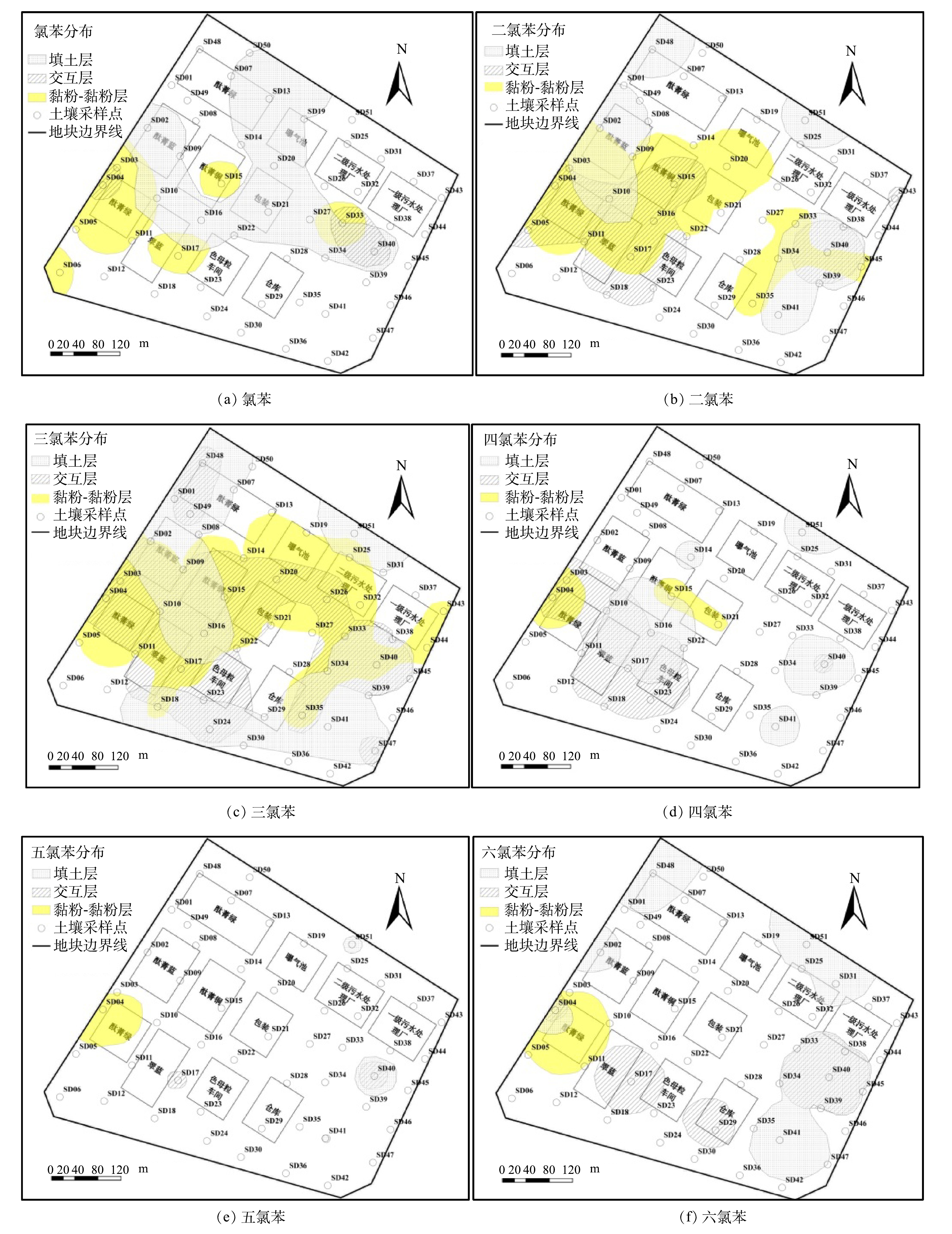
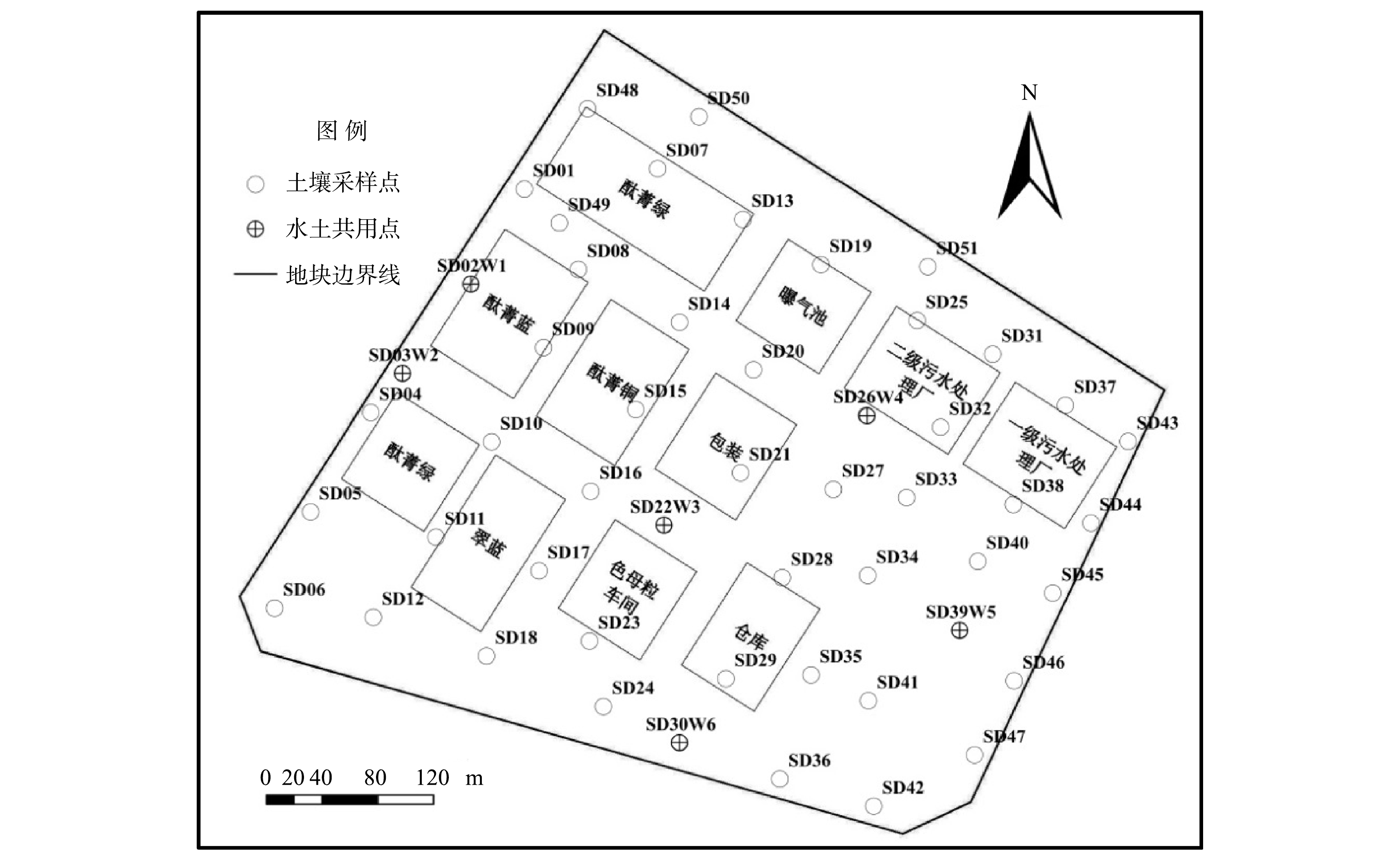
如图1所示,依据国家标准《建设用地土壤污染状况调查技术导则》(HJ25.1-2019)[13],结合生产功能区分布以及扰动情况,采用网格布点(40.0 m×40.0 m)与判断布点相结合的方式,现场共布设土壤采样点51个(SD01~SD51),钻孔深度7.0~24.0 m,采集土壤样品260个,并送至有检验检测资质的实验室,检测指标涵盖6种氯苯类化合物。土壤中氯苯、二氯苯和三氯苯采用《土壤和沉积物 挥发性有机物的测定 吹扫捕集/气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ605-2011)[14]测定,四氯苯、五氯苯采用《Semi-volatile organic compounds by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry》(EPA8270E-2018)[15]测定,六氯苯采用《土壤和沉积物 半挥发性有机物的测定 气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ834-2017)[16]测定。
选用系统布点方法,在地块潜水层布设地下水采样点(水土共用点)6个(W1~W6),采集并送检地下水样品6组。地下水中氯苯、二氯苯采用《水质 挥发性有机物的测定 吹扫捕集气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ639-2012)[17]测定,其余4种采用《水质 有机氯农药和氯苯类化合物的测定 气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ699-2014)[18]测定。本次研究的6种氯苯类化合物的基本理化性质具体见表1。
-
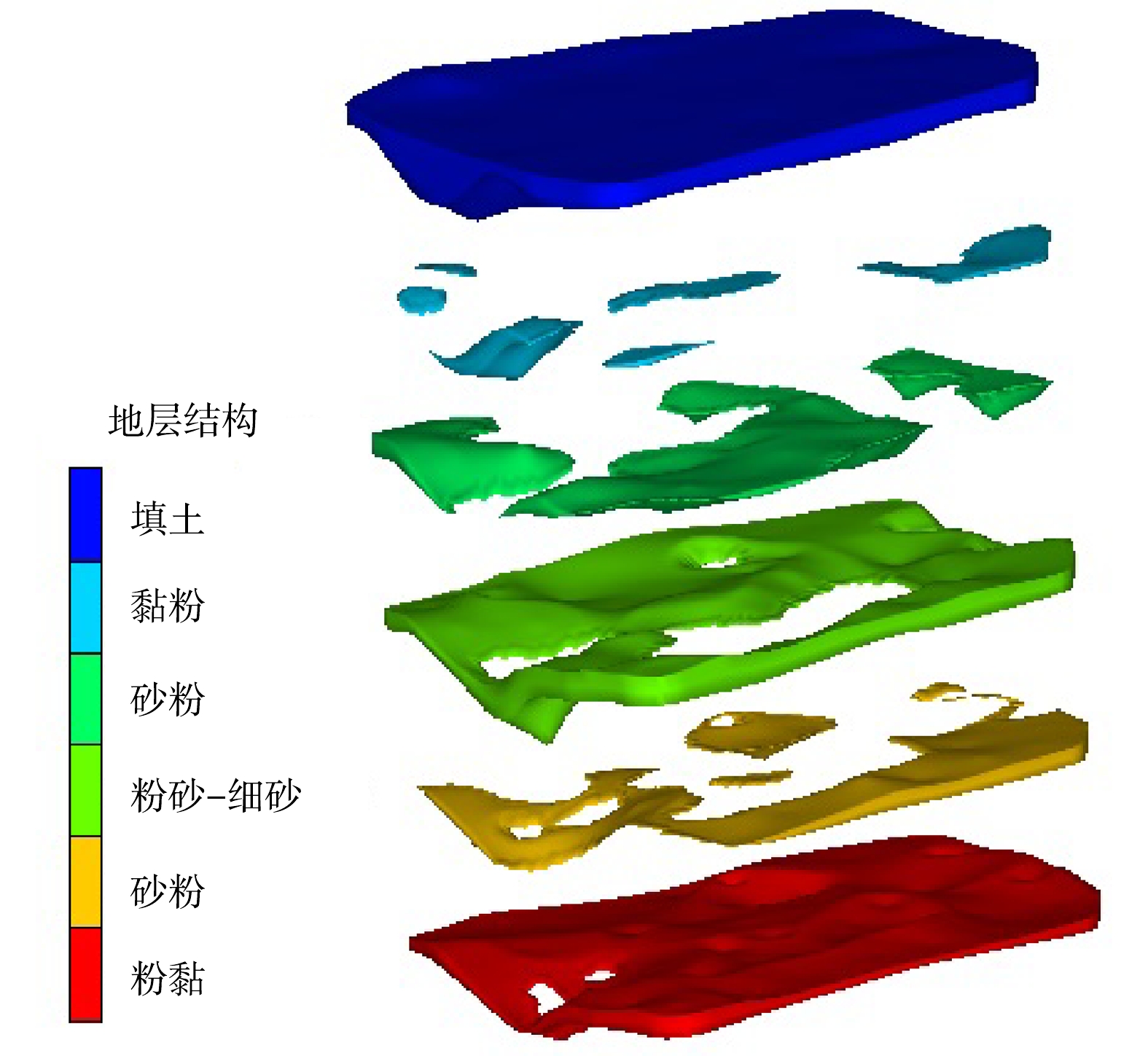
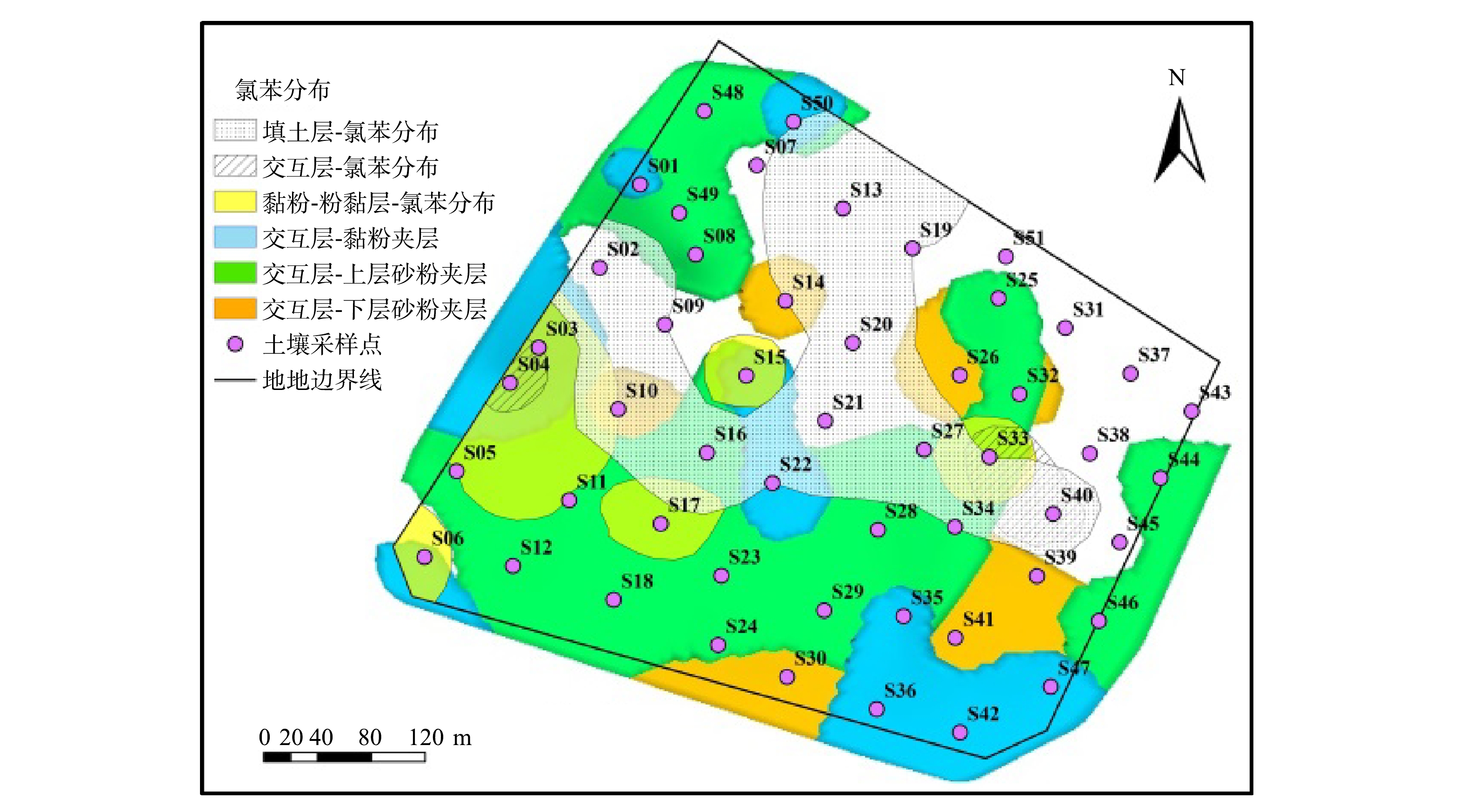
根据现场勘探情况,结合土质岩性、埋深分布等因素,地表以下约12.0 m深的包气带土壤分为3层(图2)。第1层为填土层(层底深度1.0~7.2 m),该层连续且完整。其中,酞菁蓝车间区域(SD02/SD09)填土已穿透包气带(约12.0 m)。第2层为以粉砂~细砂为主并伴有黏粉、砂粉的交互层(2.0~10.0 m),连续性较差。第3层为黏质粉土~粉质黏土层(6.0~13.7 m),较为连续。此外,地块北部区域(W4)存在滞水,埋深约9.0 m,厚度约1.0 m,受大气降水而波动。地表以下24.0 m以内的饱和带分2个土层。第1层为砂质土的含水层(埋深12.0~18.0 m);第2层为以黏性土为主的隔水底板层(16.0~24.0 m)。地下水水位埋深约12.0~13.7 m,厚度约4.0~6.0 m,流向主要为自北向南(图3)。
-
本研究使用SPSS 25.0和Excel 2010软件对数据进行统计分析;使用ArcGIS 10.2软件制作土壤CBs空间分布图,EVS-Pro 9.93制作地层结构分布图,Surfer 18.0制作地下水水位标高等值线图和CBs分布图,Origin 2018制作同一点位CBs随深度变化图。采用Kriging(ArcGIS 10.2)进行土壤CBs空间插值分析,边界阈值为其检出限值;采用Pearson相关系数法(SPSS 25.0)对填土层CBs进行迁移途径相关性分析。
-
35个土壤采样点(93个样品)都存在CBs不同程度的检出,点位检出率和样品检出率分别为68.63%和35.77%。地下水中CBs普遍检出。如表2所示,土壤CBs检测数值普遍呈正偏态(偏度>9)、高狭形态分布(峰度>90),低氯苯类化合物(一、二、三氯苯)检测数值的离散程度明显较高。地下水CBs检测数值的离散程度较大,但基本符合正态分布;水样中未检出高氯苯类化合物(四、五、六氯苯)。
如表3所示,包气带的3个土层CBs检测数值都呈正偏态、高狭形态分布,低氯苯类化合物的数值较为分散且最大检测数值明显比高氯苯类物质高出1~3个数量级。
-
由表2可知,土壤中CBs的点位检出率呈现三氯苯>二氯苯>氯苯>四氯苯≈六氯苯>五氯苯,基本都>20%。这说明CBs普遍存在于地块土壤中。填土层作为地块表层,是污染物进入土壤环境的“门户”。不同污染物的显著相关性分析能够反映它们来源途径的相似性程度[19]。填土层CBs的Pearson相关性分析结果显示(表4),5种氯苯类化合物(除氯苯)之间都呈显著的正相关。这表明,该5种物质进入土壤的途径较为相似。而氯苯与其它物质无相关。
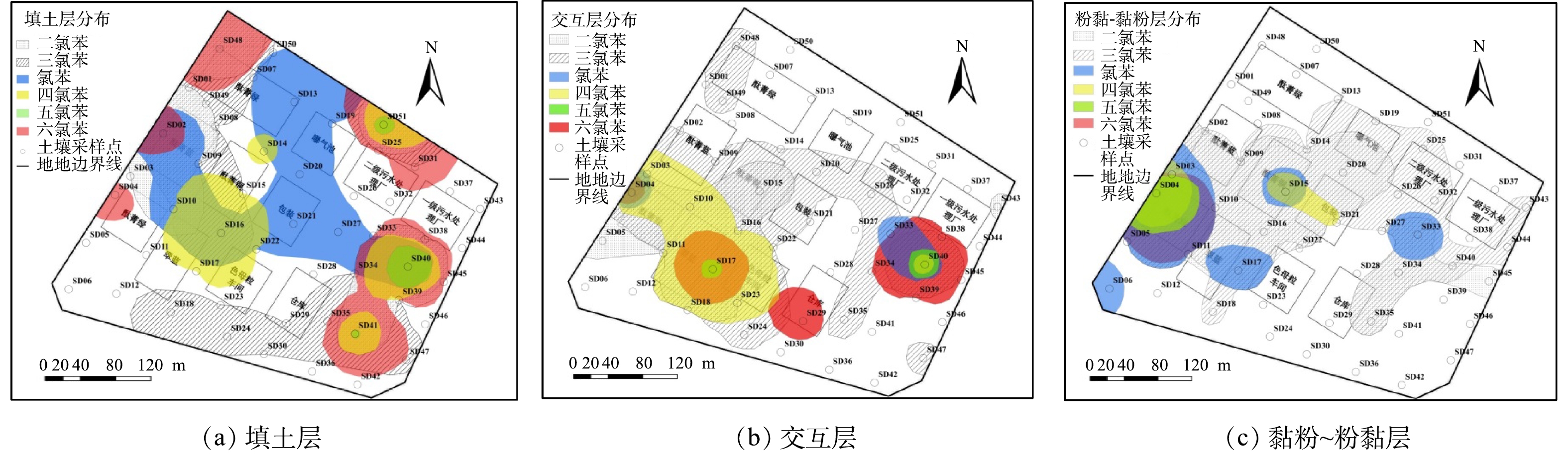
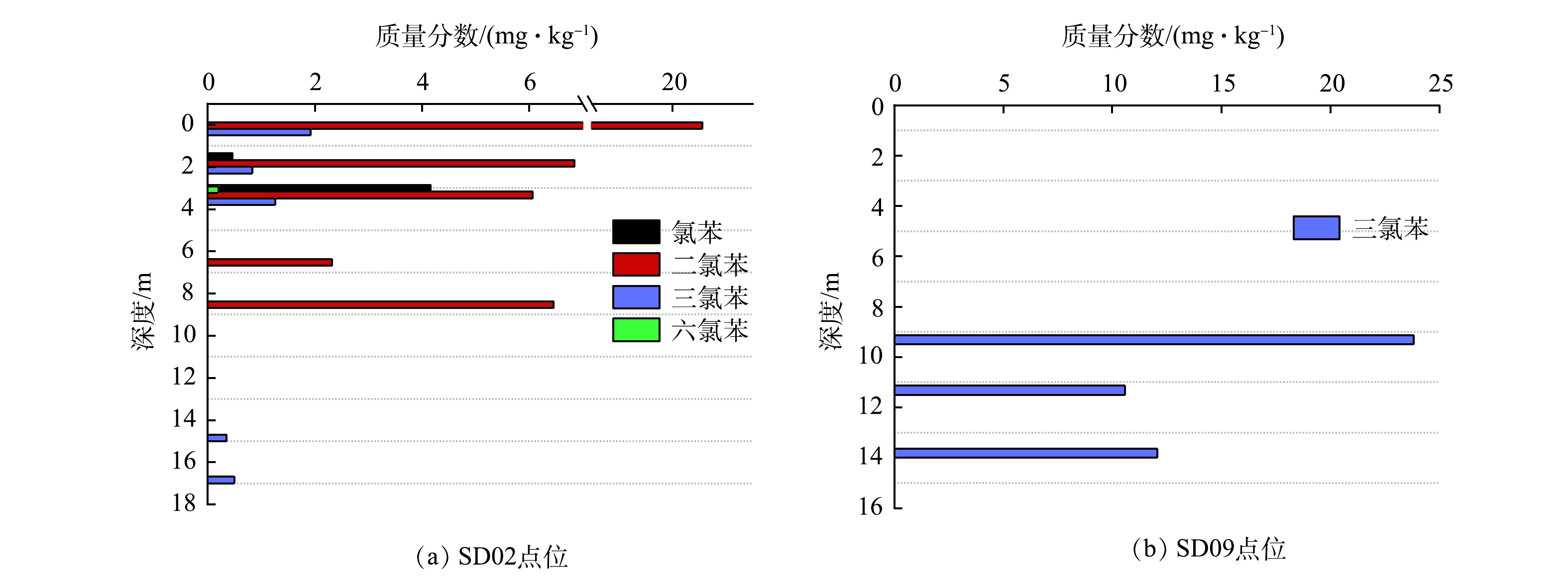
由图4可知,包气带中6种氯苯类化合物主要分布在生产车间、污水处理站周边等重污染区,各土层中CBs的水平分布之间有较为明显的相关性。二氯苯和三氯苯作为原料曾在地块内大量使用,都呈现水平分布广、含量高等特点;二者点位检出率分别为35.29%和50.00%,最大值为42 500.00和4 800.00 mg·kg−1(表2)。第1层土壤中三氯苯主要分布于酞菁绿车间西部(SD48/SD49)、酞菁蓝(SD02/SD09)、酞菁铜及其南侧(SD16)、一级污水处理厂南侧(SD40/SD41)、二级污水处理厂北侧(SD51)以及生产区南部(SD18/SD24);二氯苯分布于生产区(SD02/SD10/SD48)和污水处理区周边(SD40/D41/SD51)。原料污染物在第2层主要分布于生产区中南部的酞菁蓝、酞菁铜、酞菁绿、翠蓝、色母粒等车间,以及污水处理区南侧;第3层几乎遍布整个生产区和污水处理区。而高氯苯类化合物在各土层中的分布都明显嵌套于二氯苯和三氯苯的分布范围之内(图4),结合CBs之间的相关性分析结果(表4),推断其与原料污染物存在共同的“泄漏源”。
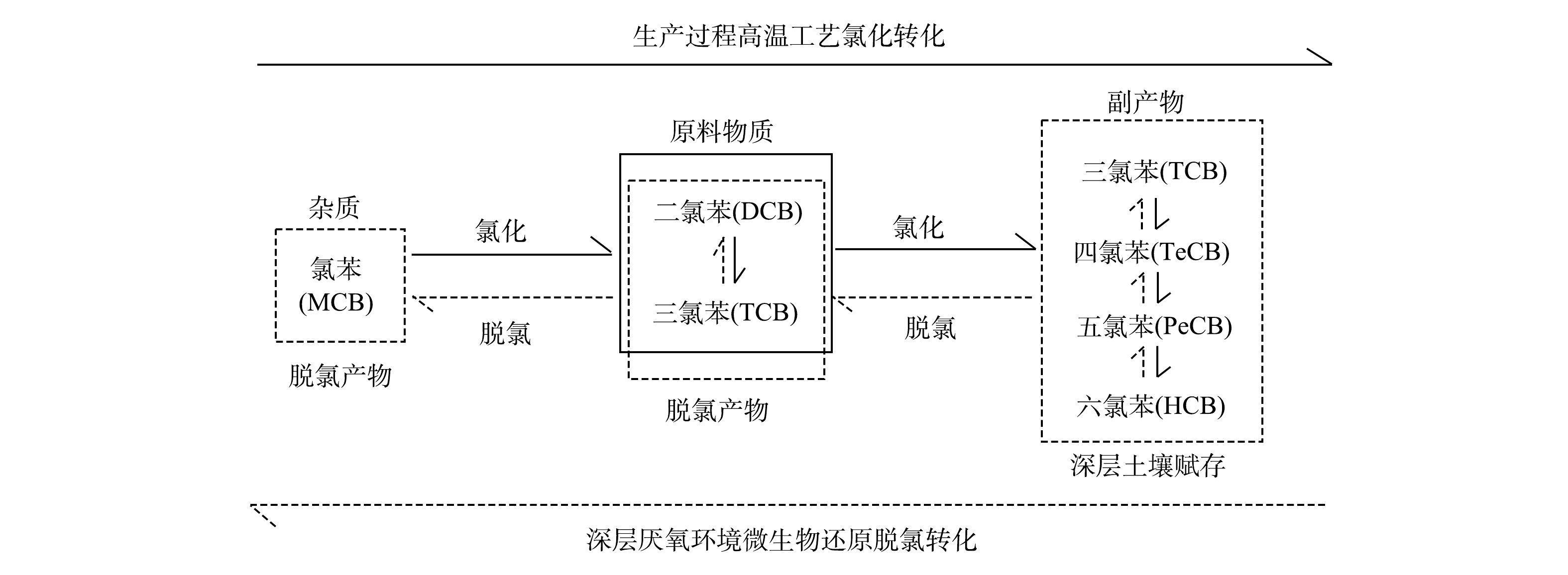
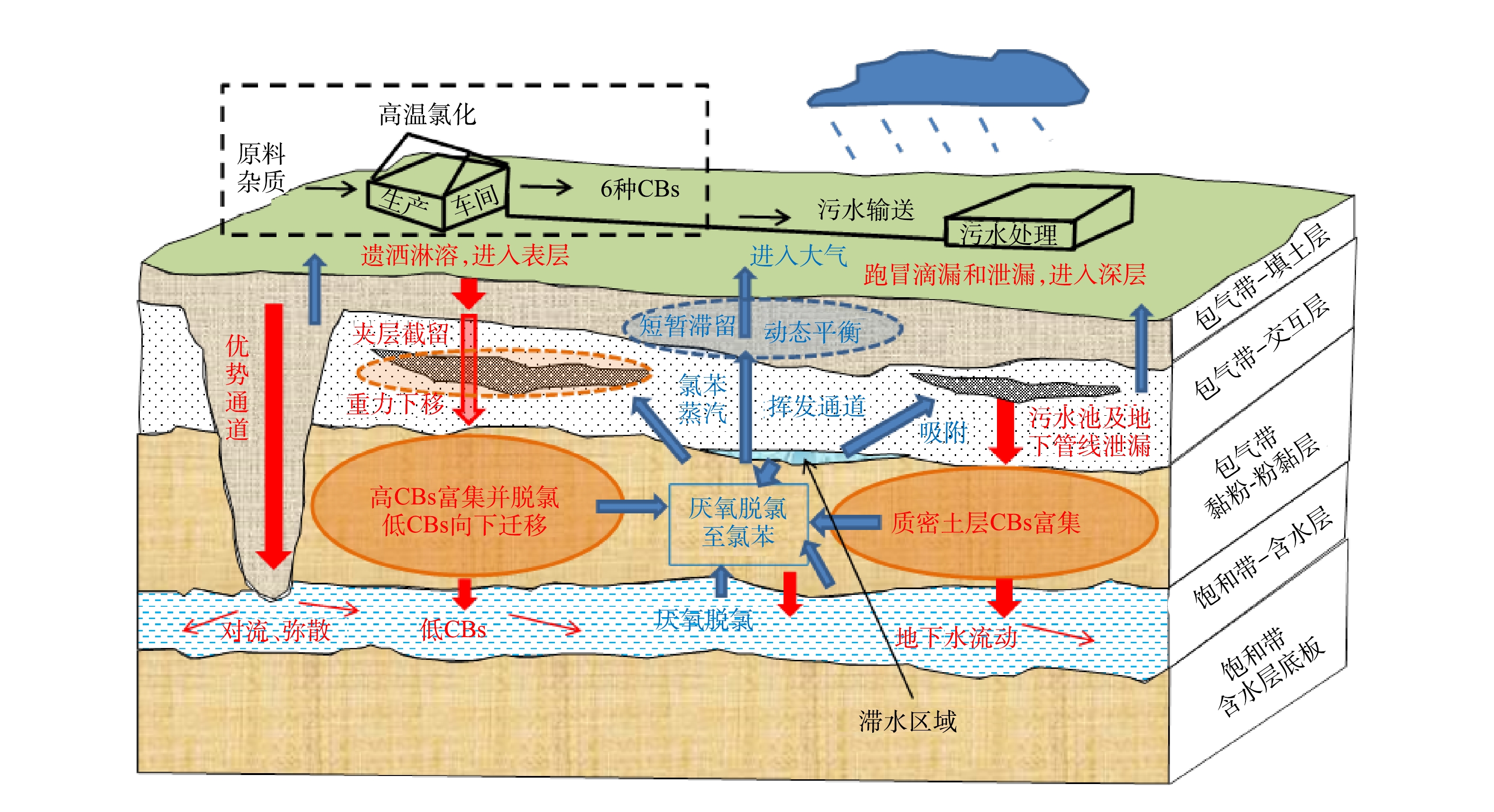
高氯苯类化合物的理化性质稳定且制备条件苛刻[20-22],进入土壤中的二氯苯和三氯苯几乎不可能通过化学反应转化为高氯苯类化合物。吴秀琪[20-21]发现,三氯苯经铁粉催化,在110~230 ℃条件下可制备五氯苯,该工艺往往造成设备严重腐蚀,并伴有大量的六氯苯副产物产生。吴志钦[22]发现,在105~110 ℃条件下,铁屑催化二氯苯、三氯苯的混合物发生氯化反应产生四、五、六氯苯。二氯苯和三氯苯的沸点为173~218.5 ℃(表1)。溶剂法生产酞菁铜的工艺中,需加热至175~200 ℃反应8h,而后高温蒸馏回收溶剂再循环使用(回收率约90%),该过程通常伴有高氯苯类化合物的产生[11]。此外,包气带土壤中CBs受微生物作用主要发生以下反应[23]:在表层好氧区发生好氧共代谢和异养氧化,均无氯苯类化合物副产物产生[24-25];在深层厌氧区主要发生还原脱氯,生成低氯代苯和Cl–[26-29]。综上,推断地块内的高氯苯类化合物主要是在生产过程中原料溶剂在高温等工艺条件下经氯化而成,随后伴随着二氯苯和三氯苯泄漏至土壤中(表4),迁移至深层土壤后再次还原脱氯转化为低氯代苯。因此,5种物质(除氯苯)在包气带中的水平分布呈明显相关性。此外,由于染料生产工艺中高温反应时间长、溶剂量大等因素,氯化反应充分,致使副产物中六氯苯的含量相对较高(图4(a)和图4 (b))。除此之外,原料杂质也是高氯苯类化合物的另一个来源[11,30-31],但含量相对较少。
氯苯在填土层的部分区域(SD13/SD20/SD21/SD27)呈连续分布,与其它5种物质的相关性较差(图4和表4)。氯苯可能来源于原料杂质[30-31],但其挥发性较强(蒸气压为1 670.0 Pa)(表1),少量氯苯泄漏至表土后主要通过挥发而消失[27,32-33],而地块拆除后已闲置近15年。因此,推断包气带中氯苯的来源主要为深层厌氧环境中CBs的还原脱氯产生。相关研究发现[27-29],厌氧条件下微生物能将二氯苯和三氯苯逐级脱氯至氯苯。滞水区域(W4/SD26)存在大量三氯苯(图4(c)),为微生物厌氧脱氯提供了良好条件。综上所述,建立地块内CBs转化路径概念模型(图5)。
-
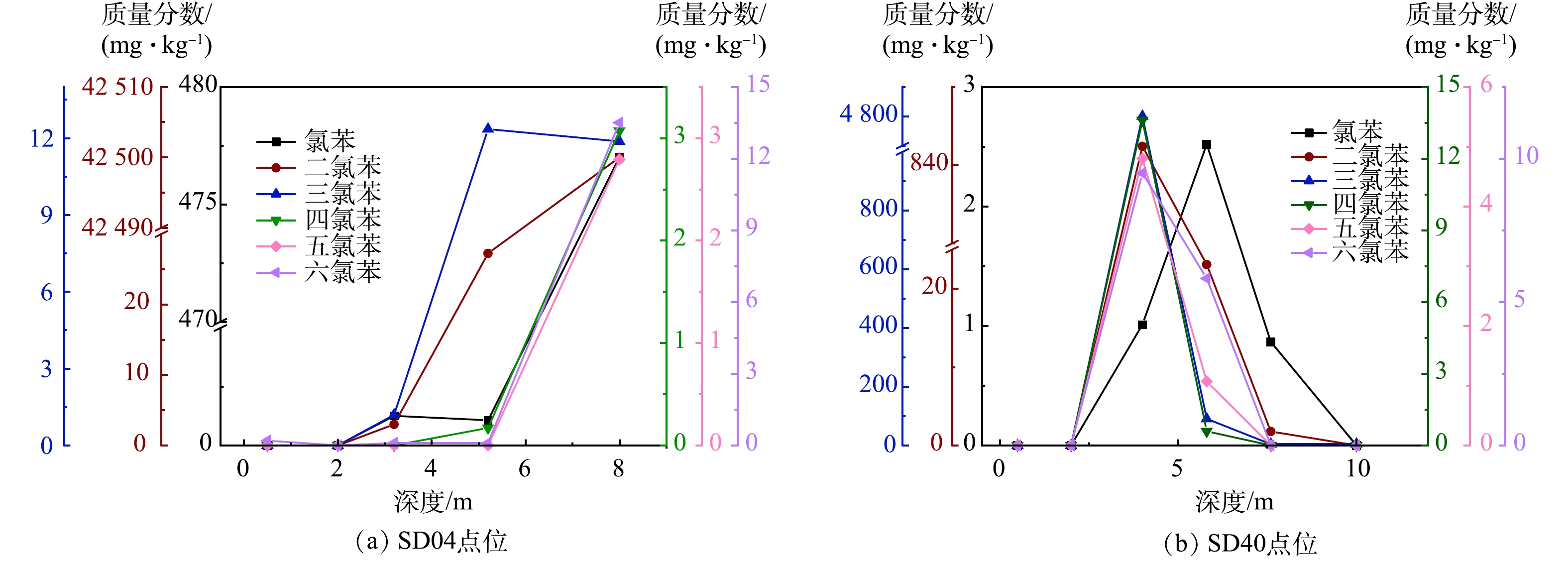
包气带的3个土层中6种氯苯类化合物的样品检出率与其点位检出率大小普遍呈正相关(表3)。这说明CBs进入土壤后发生了垂向迁移。如图6所示,3个土层CBs的分布在垂向上存在一定的连续性。酞菁绿车间西侧(SD04)和一级污水处理厂南侧(SD40)区域最为明显(图7)。相较于其它4种物质,二氯苯和三氯苯分布在垂向上的连续性更为明显(图6(b)和图6 (c))。
生产过程中的泄露等因素是CBs进入地块土壤的主要途径,分2种情况:一种是污染物直接泄漏至表层土中;另一种是通过地下管线、罐体以及污水池等泄漏至较深层的土壤中[6-7]。这可能是第1、2层中CBs垂向分布连续性较差的原因之一。进入土壤的CBs,在挥发、淋溶以及自身重力等作用下,在土壤颗粒、土壤水和土壤空气中进行分配并达到三相动态平衡,绝大部分的CBs吸附于土壤颗粒上[9,34]。受大气降水等外界因素影响,反复的淋溶作用促使CBs在吸附与解吸的动态平衡中不断向下迁移,并富集在有机质含量较高的黏粉~粉黏层[23,34]。以砂质土为主的第2层CBs检测数值明显低于第3层(表3)。随着氯原子数量的增加,CBs的溶解度和土壤吸附系数(Koc)不断升高且溶解度逐渐降低(表1),低氯苯类物质更容易向下迁移[9,35]。二氯苯和三氯苯的最大检出深度均为18.5 m,而六氯苯仅为8.0 m(表2)。包气带中二氯苯和三氯苯的检出率均呈现随着深度增加而升高的特点,而五、六氯苯与之相反(表3)。地块内CBs在重污染区进入包气带并垂向迁移,第2层和第3层的CBs分布在垂向上连续性较好,高氯苯类化合物主要分布于第1、2层(图6)。CBs垂向迁移的过程中,若遇到致密且连续的黏性土区域,可能会横向迁移[9,34]。第2层粉土夹层区以及第3层中CBs的横向迁移现象较为明显(图6)。地块南部区域(SD18/SD24)填土层仅有三氯苯检出(图4(a))。这可能是地块拆除活动造成的二次污染。
氯苯在污水处理区(SD33/SD40)的垂向分布存在一定的连续性,并在该区域的填土层中呈连续分布(图6(a))。受拆除扰动影响,该区域填土厚度约6.0 m,且交互层仅有砂土(图2和图8),便于雨水下渗并形成滞水。滞水区下层(第3层)的CBs经微生物脱氯至氯苯[27-29],因其具有较高的溶解度(293.0 mg·L−1)和蒸气压(1 670.0 Pa)(表1),在分配作用下扩散迁移,最终至空气和地下水中[23,33,35-39]。于海斌等[39]发现,排放至水体的氯苯达到环境系统平衡后,有将近95%的氯苯挥发进入大气中。由于该区域地层结构的特殊性,氯苯蒸汽穿过有机质含量极少的砂层,吸附于上层填土中。而其它区域的氯苯可能吸附截留于其上层(交互层)的粉土中(图8)。现场刺鼻异味主要源于氯苯的挥发[32,34]。
-
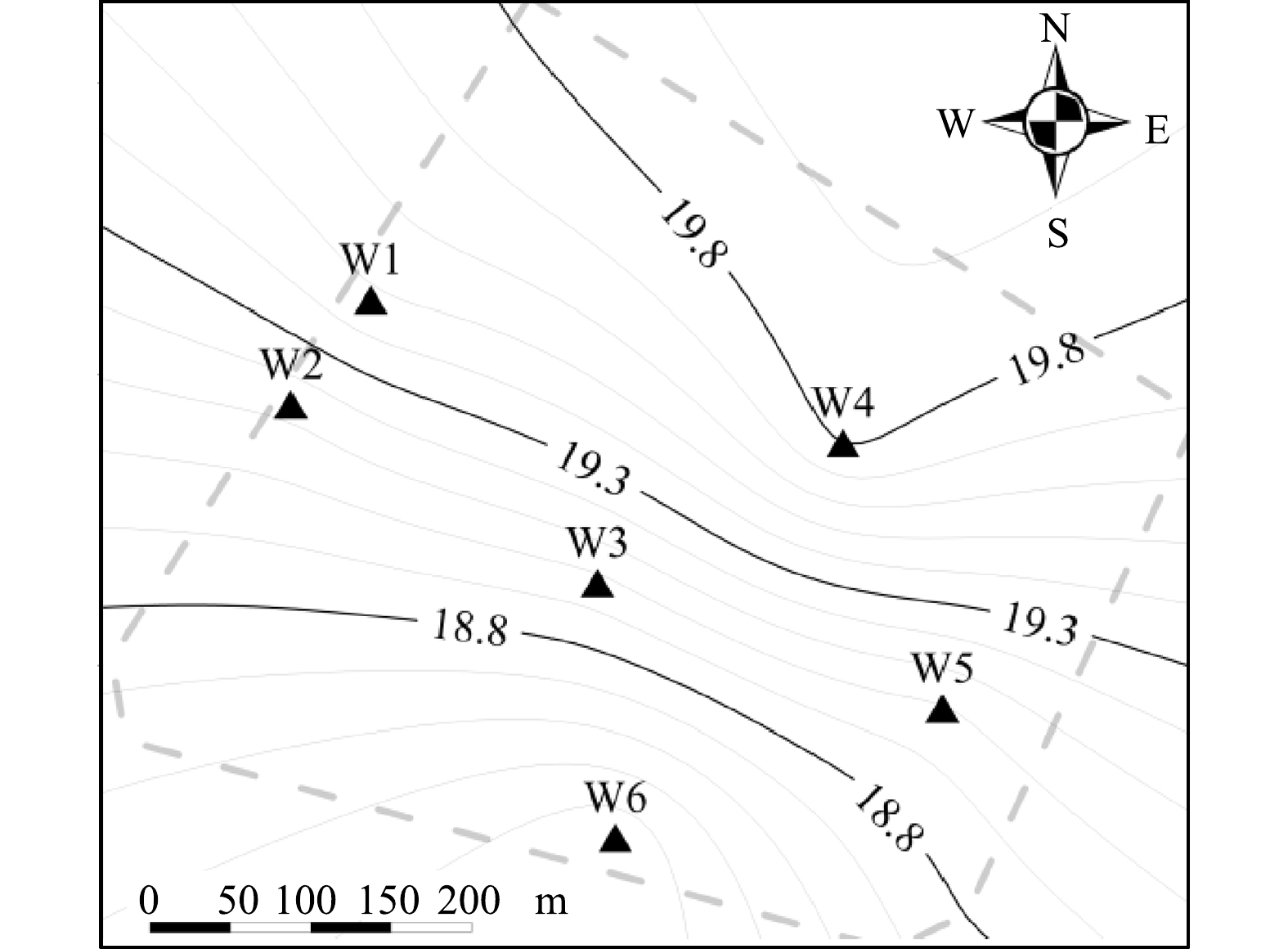
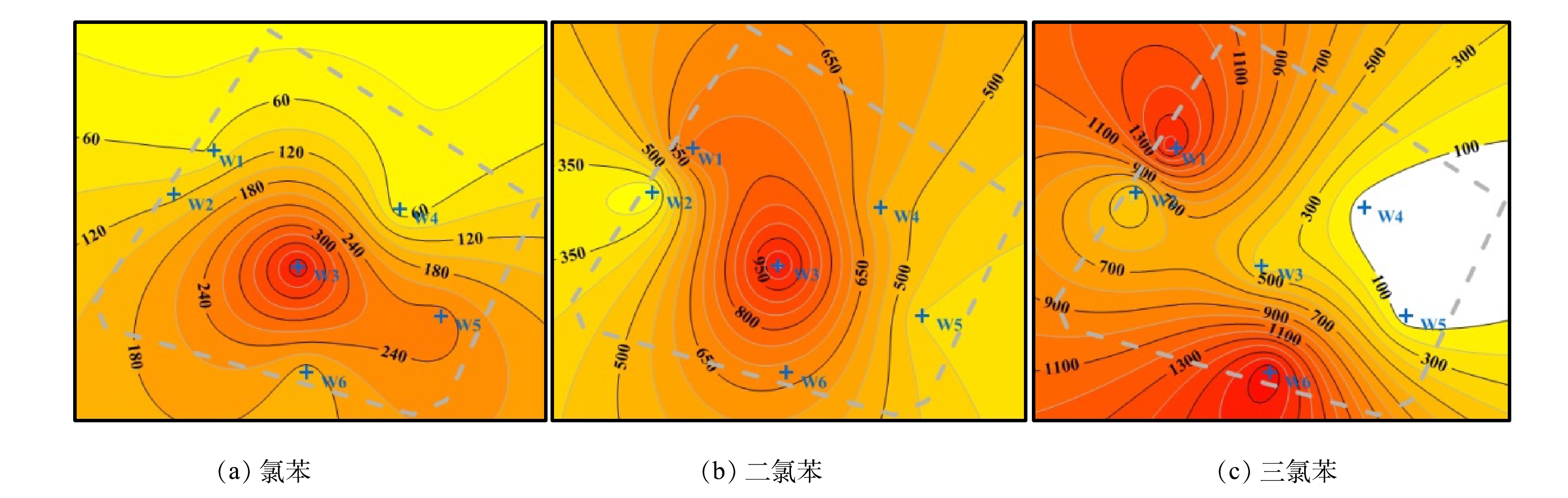
由表2、表5可知,饱和带主要为低氯苯类化合物污染,地下水中低氯苯类化合物检出率均为100%,CBs在土壤与地下水中分布的关联性较差。含水层隔水顶板(包气带第3层)中富集的CBs受重力作用向下迁移。而随着深度的增加,土壤含水率逐渐增加至饱和。土壤湿度增大时,CBs的吸附量逐渐减小;当土壤饱水时,其吸附容量降低两个数量级[36]。CBs向下迁移的过程中逐渐解吸并进入地下水中,在对流、弥散等物理作用下扩散至整个厂区[33,38]。低氯苯类化合物更易穿透包气带进入地下水[9],地下水中的二氯苯和三氯苯能够受微生物的作用而脱氯至氯苯[27-29]。水体中的氯苯主要分布于水相中(约98%),悬浮物和沉积物中的存量极少[39]。高氯苯类化合物因土壤吸附系数(Koc)高等特性(表1),其渗滤作用较弱且在土壤有机质上吸附牢固[9,32],而被隔水顶板(包气带第3层)截留。地下水中低氯苯类化合物的检测数值都呈现由北向南逐渐升高的特征(图9),与地下水流向基本相符(图2)。W3井位的氯苯和二氯苯检测数值最高,分别为449.00和1 068.00 µg·L−1(表2)。W6井位三氯苯的检测数值最高(1 806.00 µg·L−1) (表2),而该区域土壤中未有三氯苯垂向迁移现象(图6(c))。这说明,污染物是通过地下水流动迁移扩散至此。
饱和带土壤中CBs主要分布于SD02、SD03、SD09和SD22点位区域(表5),且仅SD03点位检出5种污染物(除六氯苯)。推断主要受填土优势通道(SD02/SD09)影响(图10),吸附有CBs的填土颗粒进入含水层,受地下水流动影响,通过砂层孔隙侧向迁移至下游区域(SD03/SD22)。
-
结合地块地层结构分布特征(图2和图3),通过分析地块包气带及饱和带中CBs的空间分布特征(2.2至2.4小节),推断了地块内CBs转化路径(图5),建立了地块土壤及地下水中CBs的迁移转化路径概念模型(图11)。氯苯主要由深层土壤及地下水中CBs经微生物脱氯产生,随后向上挥发扩散迁移,最终至大气中。其余5种物质主要源于生产原料及高温氯化反应,因跑冒滴漏乃至泄漏等因素而进入土壤,受淋溶以及重力作用向下迁移,富集于包气带第3层;二氯苯和三氯苯因水溶性较强、Koc较低等特性,更容易穿透包气带而进入地下水并迁移扩散。
-
1)该染料厂地块的土壤环境中存在6种氯苯类化合物不同程度的检出。CBs主要分布在在生产车间、污水处理区及废水管线等重污染区的包气带中,饱和带土壤中CBs分布较少,低氯苯类化合物遍布于整个厂区地下水中。
2)结合地层结构、CBs分布特征及其理化特性,推断四氯苯、五氯苯和六氯苯主要由生产原料(二氯苯和三氯苯)在高温等工艺条件下发生氯化反应转化而成,而氯苯是由深层厌氧环境中的CBs经微生物还原脱氯生成。
3)氯苯自地块深层厌氧区发生垂向迁移,部分向上扩散进入包气带再挥发至空气中;其它5种氯苯类化合物在重污染区进入包气带,主要受淋溶以及重力作用向下迁移,汇集于包气带的黏粉~粉黏层,其中二氯苯和三氯苯穿透包气带后进入地下水中,最终扩散至整个厂区。
北京某染料厂污染地块土壤和地下水6种氯苯类化合物的分布特征及迁移转化分析
Distribution, migration and transformation of six chlorobenzene compounds in soil and groundwater of a dye factory in Beijing
-
摘要: 针对染料化工企业用地存在多种氯苯类化合物污染的问题,以北京某染料厂污染地块为研究对象,采集并测定土壤样品260个、地下水样品6个,研究了地块包气带和饱和带中6种氯苯类化合物的分布特征,分析了6种物质的来源与迁移过程。结果表明,6种氯苯类化合物主要分布在生产区及污水处理区等重污染区的包气带中,低氯苯类化合物遍布地下水中。推断四氯苯、五氯苯和六氯苯主要由生产原料(二氯苯和三氯苯)在高温等工艺条件下发生氯化反应转化而成,而氯苯是由深层厌氧环境中的CBs经微生物还原脱氯生成。氯苯自深层厌氧区迁移扩散,部分向上扩散进入包气带再挥发至空气中;其它5种污染物在重污染区进入包气带,主要受淋溶以及重力作用向下迁移,汇集于包气带的黏粉~粉黏层,其中的二氯苯和三氯苯穿透包气带进入地下水并扩散至整个厂区。本研究结果可为染料化工污染地块的调查及修复工程提供参考。Abstract: Aiming at the pollution problem of a variety of chlorobenzene compounds in the land used by dye chemical enterprises, taking a dye contaminated site in Beijing as the research object. A total of 260 soil samples and 6 groundwater samples were collected and analyzed. The distribution of six chlorobenzene compounds in the vadose zone and saturation zone of the site were investigated, and the source and migration process of the six substances were analyzed. The results showed that six chlorobenzene compounds were mainly distributed in the vadose zone of the heavily polluted areas, such as the production area and the sewage treatment area. Additionally, the low chlorobenzene compounds were found all over the groundwater. It was inferred that tetrachlorobenzene, pentachlorobenzene and hexachlorobenzene were mainly produced by chlorination of raw materials (dichlorobenzene and trichlorobenzene) under high temperature and other process conditions, while chlorobenzene was generated by anaerobic microbial reduction dechlorination of CBs in deep anaerobic zone. Chlorobenzene migrates and diffuses from the deep anaerobic zone, and part of it diffuses upward into the vadose zone and then volatilizes into the air. The other five pollutants enter the vadose zone of the heavily polluted area, migrate downward mainly by leaching and gravity, and collect in the sticky powder ~ powder sticky layer of the vadose zone. Particularly, dichlorobenzene and trichlorobenzene penetrate the vadose zone and spread throughout in the groundwater of the site. The results of this study can provide a reference for the investigation and remediation of dye chemical contaminated sites.
-
Key words:
- chlorobenzene pollutants /
- vadose zone /
- saturation zone /
- distribution characteristics /
- migration /
- transformation
-
随着我国工业化和城市化进程的不断加快,城市“退二进三”“退城进园”等调整规划的绿色推进,在京津冀等经济快速发展区相继涌现出大量的染料化工污染地块,一定程度上制约了区域社会经济与生态环境的协调发展[1]。氯苯类化合物(chlorobenzenes, CBs)是染料化工行业中广泛应用的原料和有机溶剂,是一类由氯原子取代苯环上的氢原子而形成的单环芳香族化合物,包括氯苯、二氯苯、三氯苯、四氯苯、五氯苯和六氯苯共6种(12个)同系物[2-3]。该类物质具有高毒性、持久性和生物蓄积性等特点,且具有“三致”作用[3-4]。我国已公布的优先控制污染物黑名单以及优先控制化学品名录等文件中已明确纳入氯苯、1,2-二氯苯、1,4-二氯苯、1,2,4-三氯苯、五氯苯和六氯苯[4]。在CBs的使用、生产、储存以及运输的过程中,因跑冒滴漏以及三废处置不当等因素,致使其进入企业用地及其周边的土壤环境中,进而迫害生态环境并危及人体健康[5-7]。
近年来,我国相继颁布的土壤污染防治法律法规逐步规范了污染地块环境管理流程[8],土壤污染状况调查是启动地块环境管理工作的开端,调查结果能否准确刻画污染物在地块的空间分布特征将直接影响后续风险评估及治理修复等环节,进而影响政府部门的管理决策。目前,国内外关于CBs在化工污染地块分布特征的研究众多[5-7,9-10],但选取的目标污染物普遍为某1种,或2~3种氯苯类化合物。孟宪荣等[6]研究了氯苯在某化工污染地块的水平和垂直分布特征,结果表明,生产功能分区和地块水文地质条件是影响氯苯分布的主要因素。余梅[9]以氯苯、二氯苯和三氯苯为例,研究了CBs在某化工污染地块的分布特征及迁移规律。SPIGARELLI等[10]研究了9个化工污染地块中六氯苯的分布特征,发现地块范围的空气、土壤和地下水中都存在不同程度的污染。而国内已开展的众多染料化工场地调查案例中,发现地块土壤环境中通常存在多种氯苯类化合物污染的情况。田亚静等[11]发现,二氯苯和三氯苯产品中混有少量的氯苯和其它多氯苯物质;酞菁系列染料生产过程中,三氯苯的使用通常会产生六氯苯。袁祎倩[12]研究了5个染料化工企业的印染废水,发现都存在三、四、五、六氯苯的普遍检出。因此,明确染料化工污染地块中不同氯苯类化合物的分布特征以及迁移转化规律,对后续风险评估、管控以及修复等地块管理环节至关重要。
本研究以北京某染料厂污染地块为研究对象,研究了地块包气带和饱和带中6种氯苯类化合物的分布特征。结合地块的历史生产功能区分布、地层结构以及污染物特性,进一步分析了不同氯苯类化合物的迁移转化规律,建立了地块内CBs迁移转化路径概念模型。
1. 研究对象与分析方法
1.1 研究对象
研究地块为北京地区某关停遗留的染料化工厂生产用地。该厂建于20世纪60年代,占地约80 000 m2,主要生产酞菁系列颜料,原料涉及二氯苯和三氯苯等。于2003年关停,2005年地块范围内的设备及构筑物全部拆除且平整,闲置至今。现场踏勘时,发现有刺鼻异味。
1.2 样品采集与分析
如图1所示,依据国家标准《建设用地土壤污染状况调查技术导则》(HJ25.1-2019)[13],结合生产功能区分布以及扰动情况,采用网格布点(40.0 m×40.0 m)与判断布点相结合的方式,现场共布设土壤采样点51个(SD01~SD51),钻孔深度7.0~24.0 m,采集土壤样品260个,并送至有检验检测资质的实验室,检测指标涵盖6种氯苯类化合物。土壤中氯苯、二氯苯和三氯苯采用《土壤和沉积物 挥发性有机物的测定 吹扫捕集/气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ605-2011)[14]测定,四氯苯、五氯苯采用《Semi-volatile organic compounds by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry》(EPA8270E-2018)[15]测定,六氯苯采用《土壤和沉积物 半挥发性有机物的测定 气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ834-2017)[16]测定。
选用系统布点方法,在地块潜水层布设地下水采样点(水土共用点)6个(W1~W6),采集并送检地下水样品6组。地下水中氯苯、二氯苯采用《水质 挥发性有机物的测定 吹扫捕集气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ639-2012)[17]测定,其余4种采用《水质 有机氯农药和氯苯类化合物的测定 气相色谱-质谱法》(HJ699-2014)[18]测定。本次研究的6种氯苯类化合物的基本理化性质具体见表1。
表 1 氯苯类化合物的理化性质及其检出限Table 1. Physical and chemical properties, limit of detection of chlorobenzene compounds物质名称 简写 沸点/℃ 25℃水中溶解度/(mg·L−1) 25℃下的蒸汽压/Pa 土壤吸附系数/(Koc) 检出限/(mg·kg−1) 氯苯 MCB 132.0 293.0 1 670.0 466.0 0.006 二氯苯 DCB 173.0~180.5 30.9~123.0 90.0~269.0 987.0~1 470.0 0.019 三氯苯 TCB 208.0~218.5 3.99~45.3 17.3~45.3 2 670.0~3 680.0 0.019 四氯苯 TeCB 243.6~254.0 2.16~12.1 0.7~9.8 6 990.0~8 560.0 0.1 五氯苯 PeCB 277.0 0.83 - 28 700.0 0.1 六氯苯 HCB 323.0 0.01 0.3 317 000.0 0.1 1.3 地块地层结构
根据现场勘探情况,结合土质岩性、埋深分布等因素,地表以下约12.0 m深的包气带土壤分为3层(图2)。第1层为填土层(层底深度1.0~7.2 m),该层连续且完整。其中,酞菁蓝车间区域(SD02/SD09)填土已穿透包气带(约12.0 m)。第2层为以粉砂~细砂为主并伴有黏粉、砂粉的交互层(2.0~10.0 m),连续性较差。第3层为黏质粉土~粉质黏土层(6.0~13.7 m),较为连续。此外,地块北部区域(W4)存在滞水,埋深约9.0 m,厚度约1.0 m,受大气降水而波动。地表以下24.0 m以内的饱和带分2个土层。第1层为砂质土的含水层(埋深12.0~18.0 m);第2层为以黏性土为主的隔水底板层(16.0~24.0 m)。地下水水位埋深约12.0~13.7 m,厚度约4.0~6.0 m,流向主要为自北向南(图3)。
1.4 数据分析
本研究使用SPSS 25.0和Excel 2010软件对数据进行统计分析;使用ArcGIS 10.2软件制作土壤CBs空间分布图,EVS-Pro 9.93制作地层结构分布图,Surfer 18.0制作地下水水位标高等值线图和CBs分布图,Origin 2018制作同一点位CBs随深度变化图。采用Kriging(ArcGIS 10.2)进行土壤CBs空间插值分析,边界阈值为其检出限值;采用Pearson相关系数法(SPSS 25.0)对填土层CBs进行迁移途径相关性分析。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 数据统计
35个土壤采样点(93个样品)都存在CBs不同程度的检出,点位检出率和样品检出率分别为68.63%和35.77%。地下水中CBs普遍检出。如表2所示,土壤CBs检测数值普遍呈正偏态(偏度>9)、高狭形态分布(峰度>90),低氯苯类化合物(一、二、三氯苯)检测数值的离散程度明显较高。地下水CBs检测数值的离散程度较大,但基本符合正态分布;水样中未检出高氯苯类化合物(四、五、六氯苯)。
表 2 土壤和地下水中CBs检测数值统计Table 2. Statistics on the detection data of CBs in soil and groundwater介质 物质名称 点位检出率/% 样品检出率/% 最大值* 最小值* 平均值* 标准差 偏度 峰度 最大检出深度/m 土壤 氯苯 27.45 10.00 477.00 nd 3.77 36.02 11.23 133.64 13.6 二氯苯 35.29 15.00 42 500.00 nd 168.41 2 635.96 16.12 259.79 18.5 三氯苯 50.00 27.69 4 800.00 nd 33.95 307.53 14.61 225.21 18.5 四氯苯 23.53 6.54 61.20 nd 0.45 4.01 13.89 206.38 12.5 五氯苯 13.73 3.08 4.80 nd 0.10 0.42 9.45 92.65 12.5 六氯苯 21.57 6.92 13.50 nd 0.18 1.08 10.34 112.97 8.0 地下水# 氯苯 100.00 100.00 449.00 38.80 179.13 153.52 1.27 1.25 − 二氯苯 100.00 100.00 1 068.00 246.00 612.83 288.72 0.46 0.17 − 三氯苯 100.00 100.00 1 806.00 25.60 707.10 814.51 0.84 −1.81 − 注:“*”表示土壤单位为mg·kg−1,地下水单位为µg·L−1;“#”表示地下水样品中高氯苯类化合物都未检出;“nd”表示低于检出限。 如表3所示,包气带的3个土层CBs检测数值都呈正偏态、高狭形态分布,低氯苯类化合物的数值较为分散且最大检测数值明显比高氯苯类物质高出1~3个数量级。
表 3 包气带土壤中CBs检测数值统计Table 3. Statistics on the detection data of CBs in the vadose zone soil分层 物质 点位数/样品数 点位检出率/% 样品检出率/% 最大值/mg·kg−1 最小值/mg·kg−1 平均值/mg·kg−1 标准差 偏度 峰度 第1层 MCB 51/97 15.69 11.34 299.00 nd 4.85 33.81 7.84 64.21 DCB 11.76 10.31 842.40 nd 9.29 85.51 9.84 96.83 TCB 23.53 17.53 4 800.00 nd 50.97 487.30 9.84 96.93 TeCB 9.80 5.15 16.10 nd 0.37 2.12 6.92 47.26 PeCB 7.84 4.12 4.80 nd 0.14 0.62 6.96 47.95 HCB 15.69 10.31 9.49 nd 0.18 0.97 9.42 90.96 第2层 MCB 51/92 7.84 8.70 2.52 nd 0.09 0.41 5.07 26.41 DCB 17.65 14.13 111.70 nd 1.94 12.16 8.42 75.20 TCB 35.29 31.52 710.00 nd 20.27 90.89 6.04 40.28 TeCB 11.76 8.70 61.20 nd 0.75 6.37 9.58 91.86 PeCB 3.92 2.17 1.07 nd 0.07 0.12 7.81 63.76 HCB 7.84 6.52 5.82 nd 0.12 0.60 9.40 89.28 第3层 MCB 51/59 9.80 11.86 477.00 nd 8.39 62.07 7.68 58.95 DCB 19.61 23.73 42 500.00 nd 722.22 5 532.78 7.68 59.00 TCB 31.37 35.59 842.00 nd 32.32 123.96 5.47 32.98 TeCB 5.88 5.08 3.07 nd 0.15 0.50 5.34 27.94 PeCB 1.96 1.69 2.79 nd 0.10 0.36 7.68 59.00 HCB 3.92 3.39 13.50 nd 0.28 1.75 7.68 59.00 注:“nd”表示低于检出限。 2.2 包气带土壤中CBs的水平分布特征
由表2可知,土壤中CBs的点位检出率呈现三氯苯>二氯苯>氯苯>四氯苯≈六氯苯>五氯苯,基本都>20%。这说明CBs普遍存在于地块土壤中。填土层作为地块表层,是污染物进入土壤环境的“门户”。不同污染物的显著相关性分析能够反映它们来源途径的相似性程度[19]。填土层CBs的Pearson相关性分析结果显示(表4),5种氯苯类化合物(除氯苯)之间都呈显著的正相关。这表明,该5种物质进入土壤的途径较为相似。而氯苯与其它物质无相关。
表 4 填土层中CBs之间的相关系数Table 4. Correlation coefficient of CBs in fill layer物质 MCB DCB TCB TeCB PeCB HCB MCB 1 DCB -0.012 1 TCB -0.012 1.000** 1 TeCB -0.017 0.639** 0.640** 1 PeCB -0.019 0.773** 0.772** 0.515** 1 HCB -0.017 0.985** 0.986** 0.632** 0.854** 1 注:“**”表示在 0.01 水平(双侧)上显著相关。 由图4可知,包气带中6种氯苯类化合物主要分布在生产车间、污水处理站周边等重污染区,各土层中CBs的水平分布之间有较为明显的相关性。二氯苯和三氯苯作为原料曾在地块内大量使用,都呈现水平分布广、含量高等特点;二者点位检出率分别为35.29%和50.00%,最大值为42 500.00和4 800.00 mg·kg−1(表2)。第1层土壤中三氯苯主要分布于酞菁绿车间西部(SD48/SD49)、酞菁蓝(SD02/SD09)、酞菁铜及其南侧(SD16)、一级污水处理厂南侧(SD40/SD41)、二级污水处理厂北侧(SD51)以及生产区南部(SD18/SD24);二氯苯分布于生产区(SD02/SD10/SD48)和污水处理区周边(SD40/D41/SD51)。原料污染物在第2层主要分布于生产区中南部的酞菁蓝、酞菁铜、酞菁绿、翠蓝、色母粒等车间,以及污水处理区南侧;第3层几乎遍布整个生产区和污水处理区。而高氯苯类化合物在各土层中的分布都明显嵌套于二氯苯和三氯苯的分布范围之内(图4),结合CBs之间的相关性分析结果(表4),推断其与原料污染物存在共同的“泄漏源”。
高氯苯类化合物的理化性质稳定且制备条件苛刻[20-22],进入土壤中的二氯苯和三氯苯几乎不可能通过化学反应转化为高氯苯类化合物。吴秀琪[20-21]发现,三氯苯经铁粉催化,在110~230 ℃条件下可制备五氯苯,该工艺往往造成设备严重腐蚀,并伴有大量的六氯苯副产物产生。吴志钦[22]发现,在105~110 ℃条件下,铁屑催化二氯苯、三氯苯的混合物发生氯化反应产生四、五、六氯苯。二氯苯和三氯苯的沸点为173~218.5 ℃(表1)。溶剂法生产酞菁铜的工艺中,需加热至175~200 ℃反应8h,而后高温蒸馏回收溶剂再循环使用(回收率约90%),该过程通常伴有高氯苯类化合物的产生[11]。此外,包气带土壤中CBs受微生物作用主要发生以下反应[23]:在表层好氧区发生好氧共代谢和异养氧化,均无氯苯类化合物副产物产生[24-25];在深层厌氧区主要发生还原脱氯,生成低氯代苯和Cl–[26-29]。综上,推断地块内的高氯苯类化合物主要是在生产过程中原料溶剂在高温等工艺条件下经氯化而成,随后伴随着二氯苯和三氯苯泄漏至土壤中(表4),迁移至深层土壤后再次还原脱氯转化为低氯代苯。因此,5种物质(除氯苯)在包气带中的水平分布呈明显相关性。此外,由于染料生产工艺中高温反应时间长、溶剂量大等因素,氯化反应充分,致使副产物中六氯苯的含量相对较高(图4(a)和图4 (b))。除此之外,原料杂质也是高氯苯类化合物的另一个来源[11,30-31],但含量相对较少。
氯苯在填土层的部分区域(SD13/SD20/SD21/SD27)呈连续分布,与其它5种物质的相关性较差(图4和表4)。氯苯可能来源于原料杂质[30-31],但其挥发性较强(蒸气压为1 670.0 Pa)(表1),少量氯苯泄漏至表土后主要通过挥发而消失[27,32-33],而地块拆除后已闲置近15年。因此,推断包气带中氯苯的来源主要为深层厌氧环境中CBs的还原脱氯产生。相关研究发现[27-29],厌氧条件下微生物能将二氯苯和三氯苯逐级脱氯至氯苯。滞水区域(W4/SD26)存在大量三氯苯(图4(c)),为微生物厌氧脱氯提供了良好条件。综上所述,建立地块内CBs转化路径概念模型(图5)。
2.3 包气带土壤中CBs的垂向分布特征
包气带的3个土层中6种氯苯类化合物的样品检出率与其点位检出率大小普遍呈正相关(表3)。这说明CBs进入土壤后发生了垂向迁移。如图6所示,3个土层CBs的分布在垂向上存在一定的连续性。酞菁绿车间西侧(SD04)和一级污水处理厂南侧(SD40)区域最为明显(图7)。相较于其它4种物质,二氯苯和三氯苯分布在垂向上的连续性更为明显(图6(b)和图6 (c))。
生产过程中的泄露等因素是CBs进入地块土壤的主要途径,分2种情况:一种是污染物直接泄漏至表层土中;另一种是通过地下管线、罐体以及污水池等泄漏至较深层的土壤中[6-7]。这可能是第1、2层中CBs垂向分布连续性较差的原因之一。进入土壤的CBs,在挥发、淋溶以及自身重力等作用下,在土壤颗粒、土壤水和土壤空气中进行分配并达到三相动态平衡,绝大部分的CBs吸附于土壤颗粒上[9,34]。受大气降水等外界因素影响,反复的淋溶作用促使CBs在吸附与解吸的动态平衡中不断向下迁移,并富集在有机质含量较高的黏粉~粉黏层[23,34]。以砂质土为主的第2层CBs检测数值明显低于第3层(表3)。随着氯原子数量的增加,CBs的溶解度和土壤吸附系数(Koc)不断升高且溶解度逐渐降低(表1),低氯苯类物质更容易向下迁移[9,35]。二氯苯和三氯苯的最大检出深度均为18.5 m,而六氯苯仅为8.0 m(表2)。包气带中二氯苯和三氯苯的检出率均呈现随着深度增加而升高的特点,而五、六氯苯与之相反(表3)。地块内CBs在重污染区进入包气带并垂向迁移,第2层和第3层的CBs分布在垂向上连续性较好,高氯苯类化合物主要分布于第1、2层(图6)。CBs垂向迁移的过程中,若遇到致密且连续的黏性土区域,可能会横向迁移[9,34]。第2层粉土夹层区以及第3层中CBs的横向迁移现象较为明显(图6)。地块南部区域(SD18/SD24)填土层仅有三氯苯检出(图4(a))。这可能是地块拆除活动造成的二次污染。
氯苯在污水处理区(SD33/SD40)的垂向分布存在一定的连续性,并在该区域的填土层中呈连续分布(图6(a))。受拆除扰动影响,该区域填土厚度约6.0 m,且交互层仅有砂土(图2和图8),便于雨水下渗并形成滞水。滞水区下层(第3层)的CBs经微生物脱氯至氯苯[27-29],因其具有较高的溶解度(293.0 mg·L−1)和蒸气压(1 670.0 Pa)(表1),在分配作用下扩散迁移,最终至空气和地下水中[23,33,35-39]。于海斌等[39]发现,排放至水体的氯苯达到环境系统平衡后,有将近95%的氯苯挥发进入大气中。由于该区域地层结构的特殊性,氯苯蒸汽穿过有机质含量极少的砂层,吸附于上层填土中。而其它区域的氯苯可能吸附截留于其上层(交互层)的粉土中(图8)。现场刺鼻异味主要源于氯苯的挥发[32,34]。
2.4 饱和带土壤及地下水中CBs的分布特征
由表2、表5可知,饱和带主要为低氯苯类化合物污染,地下水中低氯苯类化合物检出率均为100%,CBs在土壤与地下水中分布的关联性较差。含水层隔水顶板(包气带第3层)中富集的CBs受重力作用向下迁移。而随着深度的增加,土壤含水率逐渐增加至饱和。土壤湿度增大时,CBs的吸附量逐渐减小;当土壤饱水时,其吸附容量降低两个数量级[36]。CBs向下迁移的过程中逐渐解吸并进入地下水中,在对流、弥散等物理作用下扩散至整个厂区[33,38]。低氯苯类化合物更易穿透包气带进入地下水[9],地下水中的二氯苯和三氯苯能够受微生物的作用而脱氯至氯苯[27-29]。水体中的氯苯主要分布于水相中(约98%),悬浮物和沉积物中的存量极少[39]。高氯苯类化合物因土壤吸附系数(Koc)高等特性(表1),其渗滤作用较弱且在土壤有机质上吸附牢固[9,32],而被隔水顶板(包气带第3层)截留。地下水中低氯苯类化合物的检测数值都呈现由北向南逐渐升高的特征(图9),与地下水流向基本相符(图2)。W3井位的氯苯和二氯苯检测数值最高,分别为449.00和1 068.00 µg·L−1(表2)。W6井位三氯苯的检测数值最高(1 806.00 µg·L−1) (表2),而该区域土壤中未有三氯苯垂向迁移现象(图6(c))。这说明,污染物是通过地下水流动迁移扩散至此。
表 5 饱和带土壤中CBs检测数值统计Table 5. Statistics of detection data of CBs in saturated soil物质名称 第1层 第2层 点位总数/检出数 样品总数/检出数 检出点位及其对应检测数值/(mg·kg−1) 点位总数/检出数 样品总数/检出数 检出点位及其对应检测值/(mg·kg−1) MCB 6/1 6/1 SD03(4.52) 6/0 6/0 — DCB 6/2 6/2 SD03/22(84.00/10.91) 6/1 6/1 SD03(6.41) TCB 6/4 6/4 SD02/03/09/22(0.35/56.3/12.06/57.60) 6/1 6/1 SD03(6.19) TeCB 6/1 6/1 SD03(2.94) 6/0 6/0 — PeCB 6/1 6/1 SD03(0.23) 6/0 6/0 — HCB 6/0 6/0 — 6/0 6/0 — 饱和带土壤中CBs主要分布于SD02、SD03、SD09和SD22点位区域(表5),且仅SD03点位检出5种污染物(除六氯苯)。推断主要受填土优势通道(SD02/SD09)影响(图10),吸附有CBs的填土颗粒进入含水层,受地下水流动影响,通过砂层孔隙侧向迁移至下游区域(SD03/SD22)。
2.5 地块土壤和地下水中CBs迁移转化分析
结合地块地层结构分布特征(图2和图3),通过分析地块包气带及饱和带中CBs的空间分布特征(2.2至2.4小节),推断了地块内CBs转化路径(图5),建立了地块土壤及地下水中CBs的迁移转化路径概念模型(图11)。氯苯主要由深层土壤及地下水中CBs经微生物脱氯产生,随后向上挥发扩散迁移,最终至大气中。其余5种物质主要源于生产原料及高温氯化反应,因跑冒滴漏乃至泄漏等因素而进入土壤,受淋溶以及重力作用向下迁移,富集于包气带第3层;二氯苯和三氯苯因水溶性较强、Koc较低等特性,更容易穿透包气带而进入地下水并迁移扩散。
3. 结论
1)该染料厂地块的土壤环境中存在6种氯苯类化合物不同程度的检出。CBs主要分布在在生产车间、污水处理区及废水管线等重污染区的包气带中,饱和带土壤中CBs分布较少,低氯苯类化合物遍布于整个厂区地下水中。
2)结合地层结构、CBs分布特征及其理化特性,推断四氯苯、五氯苯和六氯苯主要由生产原料(二氯苯和三氯苯)在高温等工艺条件下发生氯化反应转化而成,而氯苯是由深层厌氧环境中的CBs经微生物还原脱氯生成。
3)氯苯自地块深层厌氧区发生垂向迁移,部分向上扩散进入包气带再挥发至空气中;其它5种氯苯类化合物在重污染区进入包气带,主要受淋溶以及重力作用向下迁移,汇集于包气带的黏粉~粉黏层,其中二氯苯和三氯苯穿透包气带后进入地下水中,最终扩散至整个厂区。
-
表 1 氯苯类化合物的理化性质及其检出限
Table 1. Physical and chemical properties, limit of detection of chlorobenzene compounds
物质名称 简写 沸点/℃ 25℃水中溶解度/(mg·L−1) 25℃下的蒸汽压/Pa 土壤吸附系数/(Koc) 检出限/(mg·kg−1) 氯苯 MCB 132.0 293.0 1 670.0 466.0 0.006 二氯苯 DCB 173.0~180.5 30.9~123.0 90.0~269.0 987.0~1 470.0 0.019 三氯苯 TCB 208.0~218.5 3.99~45.3 17.3~45.3 2 670.0~3 680.0 0.019 四氯苯 TeCB 243.6~254.0 2.16~12.1 0.7~9.8 6 990.0~8 560.0 0.1 五氯苯 PeCB 277.0 0.83 - 28 700.0 0.1 六氯苯 HCB 323.0 0.01 0.3 317 000.0 0.1 表 2 土壤和地下水中CBs检测数值统计
Table 2. Statistics on the detection data of CBs in soil and groundwater
介质 物质名称 点位检出率/% 样品检出率/% 最大值* 最小值* 平均值* 标准差 偏度 峰度 最大检出深度/m 土壤 氯苯 27.45 10.00 477.00 nd 3.77 36.02 11.23 133.64 13.6 二氯苯 35.29 15.00 42 500.00 nd 168.41 2 635.96 16.12 259.79 18.5 三氯苯 50.00 27.69 4 800.00 nd 33.95 307.53 14.61 225.21 18.5 四氯苯 23.53 6.54 61.20 nd 0.45 4.01 13.89 206.38 12.5 五氯苯 13.73 3.08 4.80 nd 0.10 0.42 9.45 92.65 12.5 六氯苯 21.57 6.92 13.50 nd 0.18 1.08 10.34 112.97 8.0 地下水# 氯苯 100.00 100.00 449.00 38.80 179.13 153.52 1.27 1.25 − 二氯苯 100.00 100.00 1 068.00 246.00 612.83 288.72 0.46 0.17 − 三氯苯 100.00 100.00 1 806.00 25.60 707.10 814.51 0.84 −1.81 − 注:“*”表示土壤单位为mg·kg−1,地下水单位为µg·L−1;“#”表示地下水样品中高氯苯类化合物都未检出;“nd”表示低于检出限。 表 3 包气带土壤中CBs检测数值统计
Table 3. Statistics on the detection data of CBs in the vadose zone soil
分层 物质 点位数/样品数 点位检出率/% 样品检出率/% 最大值/mg·kg−1 最小值/mg·kg−1 平均值/mg·kg−1 标准差 偏度 峰度 第1层 MCB 51/97 15.69 11.34 299.00 nd 4.85 33.81 7.84 64.21 DCB 11.76 10.31 842.40 nd 9.29 85.51 9.84 96.83 TCB 23.53 17.53 4 800.00 nd 50.97 487.30 9.84 96.93 TeCB 9.80 5.15 16.10 nd 0.37 2.12 6.92 47.26 PeCB 7.84 4.12 4.80 nd 0.14 0.62 6.96 47.95 HCB 15.69 10.31 9.49 nd 0.18 0.97 9.42 90.96 第2层 MCB 51/92 7.84 8.70 2.52 nd 0.09 0.41 5.07 26.41 DCB 17.65 14.13 111.70 nd 1.94 12.16 8.42 75.20 TCB 35.29 31.52 710.00 nd 20.27 90.89 6.04 40.28 TeCB 11.76 8.70 61.20 nd 0.75 6.37 9.58 91.86 PeCB 3.92 2.17 1.07 nd 0.07 0.12 7.81 63.76 HCB 7.84 6.52 5.82 nd 0.12 0.60 9.40 89.28 第3层 MCB 51/59 9.80 11.86 477.00 nd 8.39 62.07 7.68 58.95 DCB 19.61 23.73 42 500.00 nd 722.22 5 532.78 7.68 59.00 TCB 31.37 35.59 842.00 nd 32.32 123.96 5.47 32.98 TeCB 5.88 5.08 3.07 nd 0.15 0.50 5.34 27.94 PeCB 1.96 1.69 2.79 nd 0.10 0.36 7.68 59.00 HCB 3.92 3.39 13.50 nd 0.28 1.75 7.68 59.00 注:“nd”表示低于检出限。 表 4 填土层中CBs之间的相关系数
Table 4. Correlation coefficient of CBs in fill layer
物质 MCB DCB TCB TeCB PeCB HCB MCB 1 DCB -0.012 1 TCB -0.012 1.000** 1 TeCB -0.017 0.639** 0.640** 1 PeCB -0.019 0.773** 0.772** 0.515** 1 HCB -0.017 0.985** 0.986** 0.632** 0.854** 1 注:“**”表示在 0.01 水平(双侧)上显著相关。 表 5 饱和带土壤中CBs检测数值统计
Table 5. Statistics of detection data of CBs in saturated soil
物质名称 第1层 第2层 点位总数/检出数 样品总数/检出数 检出点位及其对应检测数值/(mg·kg−1) 点位总数/检出数 样品总数/检出数 检出点位及其对应检测值/(mg·kg−1) MCB 6/1 6/1 SD03(4.52) 6/0 6/0 — DCB 6/2 6/2 SD03/22(84.00/10.91) 6/1 6/1 SD03(6.41) TCB 6/4 6/4 SD02/03/09/22(0.35/56.3/12.06/57.60) 6/1 6/1 SD03(6.19) TeCB 6/1 6/1 SD03(2.94) 6/0 6/0 — PeCB 6/1 6/1 SD03(0.23) 6/0 6/0 — HCB 6/0 6/0 — 6/0 6/0 — -
[1] 吴隽雅, 李昌儒. 城市“退二进三”调整规划及其社会生态影响分析[J]. 南京工业大学学报(社会科学版), 2020, 19(1): 69-79. [2] 黄雪琳, 杨丽, 李菊, 等. 氯苯类化合物及其检测方法研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(12Q): 236-239. [3] 宋艳辉, 曹先仲, 申松梅, 等. 氯代苯化合物的毒性分析[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2008, 33(9): 53-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2008.09.013 [4] 朱菲菲, 秦普丰, 张娟, 等. 我国地下水环境优先控制有机污染物的筛选[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2013, 3(5): 443-450. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-991X.2013.05.069 [5] YUAN Y Q, NING X A, ZHANG Y P, et al. Chlorobenzene levels, component distribution, and ambient severity in wastewater from five textile dyeing wastewater treatment plants[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020: 193. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110257 [6] 孟宪荣, 许伟, 张建荣. 化工污染场地氯苯分布特征[J]. 土壤, 2019, 51(6): 1144-1150. [7] 彭进进, 李琳, 郑川, 等. 某染料化工厂地块苯系物分布特征分析[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(4): 187-194. [8] 常春英, 吴俭, 邓一荣, 等. 中国土壤污染防治地方立法思路与探索——以广东省为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(11): 2170-2178. [9] 余梅. 氯苯类化合物在低渗透粘性土介质中的迁移规律研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2016. [10] SPIGARELLI J L, GOING J E, LI R. Hexachlorobenzene levels in multimedia environmental samples from selected chemical production plants[J]. IARC scientific publications, 1986(77): 155-160. [11] 田亚静, 余立风, 丁琼, 等. 无意产生的六氯苯污染场地产生机理分析[C]. //持久性有机污染物论坛2011暨第六届持久性有机污染物全国学术研讨会论文集. 2011: 233-234. [12] 袁祎倩. 印染废水中可吸附有机氯化物与氯苯类化合物的污染特征研究[D]. 广州: 广东工业大学, 2020. [13] 生态环境部. 建设用地土壤污染状况调查技术导则HJ25.1-2019[S]. 北京. 2019. [14] 环境保护部科技标准司. 土壤和沉积物 挥发性有机物的测定 吹扫捕集/气相色谱-质谱法(HJ605-2011)[S]. 北京. 中国环境科学出版社. 2011. [15] U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. Semi-volatile organic compounds by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry: EPA8270E[S]. Washton: U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, 2017. [16] 环境保护部科技标准司. 土壤和沉积物 半挥发性有机物的测定 气相色谱-质谱法(HJ834-2017)[S]. 北京. 中国环境科学出版社. 2017. [17] 环境保护部科技标准司. 水质 挥发性有机物的测定 吹扫捕集气相色谱-质谱法(HJ639-2012)[S]. 北京. 中国环境科学出版社. 2012. [18] 环境保护部科技标准司. 水质 有机氯农药和氯苯类化合物的测定 气相色谱-质谱法(HJ699-2014)[S]. 北京. 中国环境科学出版社. 2014. [19] 刘丽丽, 邓一荣, 廖高明, 等. 华南某污染场地土壤重金属污染健康风险评估与来源解析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2021, 43(7): 875-879. [20] 王秀琪. 五氯苯的合成[J]. 农药工业, 1979(1): 35-36. [21] 王秀琪. 国外五氯硝基苯合成工艺的进展[J]. 农药工业, 1979(2): 43-47. [22] 吴志钦. 以混合二氯苯为原料合成五氯硝基苯的研究[J]. 农药工业, 1980(1): 51-53. [23] 胡文庆, 邢志林, 赵天涛. 包气带中氯代烃运移特性及原位生物修复研究进展[J/OL]. 应用与环境生物学报: 1-13 [24] FRASCARI D, ZANAROLI G, DANKO A S. In situ aerobic cometabolism of chlorinated solvents: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 283: 382-399. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.09.041 [25] MATTES T E, ALESANDER A K, COLEMAN N V. Aerobic biodegradation of the chloroethenes: pathways, enzymes, ecology, and evolution[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2010, 34(4): 445-475. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00210.x [26] 刘翠英, 余贵芬, 蒋新, 等. 土壤和沉积物中多氯代有机化合物厌氧降解研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(8): 3482-3488. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.08.047 [27] 周妮, 乔文静, 叶淑君. 1, 2, 4-三氯苯厌氧还原脱氯过程及荧光增白剂PF对脱氯过程影响研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(10): 3954-3963. [28] JENNIFER M F, BRIAN P W, E ERIN M, et al. Reductive dehalogenation of dichlorobenzenes and monochlorobenzene to benzene in microcosms.[J]. Environmental science & technology, 2009, 43(7): 2302-2307. [29] 刘芷彤. 地下水1, 2, 4-三氯苯及其脱氯产物的厌氧微生物修复实验研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2020. [30] 林吉文, 蒋鹏举. 1, 4–二氯苯的优化合成[J]. 精细化工, 1988, 5(1): 38-42. [31] 王执中, 严兆明. 14C–三氯苯(均)的合成[J]. 有机化学, 1984(2): 157-158. [32] 胡枭, 胡永梅, 樊耀波, 等. 土壤中氯苯类化合物的迁移行为[J]. 环境科学, 2000(06): 32-36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2000.06.008 [33] MULLIGAN C N, YONG R N. Natural attenuation of contaminated soils[J]. Environment International, 2004, 30(4): 587-601. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2003.11.001 [34] 李佳斌, 王硕, 代小丽, 等. MIP系统在某挥发性氯代烃污染地块调查中的应用[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(2): 546-554. [35] LIU C Y, JIANG X, YANG X L, et al. Hexachlorobenzene dechlorination as affected by organic fertilizer and urea applications in two rice planted paddy soils in a pot experiment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(4): 958-964. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.031 [36] 叶旌, 周琪. 二氯苯在土壤中的迁移行为和生物降解[J]. 土壤与环境, 2002(4): 409-412. [37] FERDI B, FREDRICK O K, SONG Y, et al. Fate processes of chlorobenzenes in soil and potential remediation strategies: a review[J]. Pedosphere, 2017, 27(3): 407-420. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60338-2 [38] SALE T, NEWELL C, STROO H, et al Frequently asked questions regarding management of chlorinated solvents in soils and groundwater[J], Environmental Security Technology Certification Program, Arlington County, Virginia, USA. 2009. [39] 于海斌, 王业耀, 孟凡生. 松花江哨口江段氯苯的多介质迁移和归趋模拟[J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(3): 266-271. -




 下载:
下载: