-
多环麝香(Polycyclic musks,PCMs)作为重要的人工合成香料被广泛应用于日用品中,在土壤、水、沉积物和生物体等环境介质中均有检出[1]。其中,佳乐麝香(Galaxolide,HHCB)是土壤中检出率和检出浓度最高的典型PCMs之一,在长江三角洲、天津和东北三省土壤中已检测出,检出质量分数最高为7.22 μg·kg−1 [2]。HHCB被用于治疗心肌梗塞、调配香水香皂等,是一类低水溶性、高脂溶性的半挥发持久性有机污染物,在环境中难降解,容易在生物体内富集,具有内分泌干扰性和引起癌细胞增殖和胎畸[3]。由于对人体有雌激素作用与抗雌激素效应,该物质被欧盟列为“潜在人类致癌物”[3-4]。
目前,可用于原位修复半挥发性有机污染土壤方法主要有热脱附、气相抽提、电动修复和超临界流体修复等[5-7]。热脱附中的原位电阻加热技术(electrical resistance heating,ERH)在土壤中安装三相、六相电极后将土壤加热,其热量产生于土壤内部,相较于常规修复技术具有加热相对均匀、地质条件适应性强、对土壤扰动小、修复彻底和不引入外源性污染等优点[8-9]。ERH早期被应用于采油技术,随着应用的需要逐渐被引入到土壤和地下水污染修复中[10]。ERH是基于欧姆定律,将电能转化为热能,提升土壤温度,使部分挥发和半挥发性有机污染物与水溶液发生共沸,最终通过气相抽提将污染物转移并处置[11-12]。影响土壤ERH的因素包括土壤含水率、电场强度、土壤粒径以及加热时间等[12-15]。HAN等[13]和HAN等[16]发现,水分是ERH关键因素;没有足够的水分,即使电场强度在8 V·cm−1时,土壤也难以被加热到水沸点。田垚等[17]提出,在初始含水量充足的条件下,高电场强度使土壤快速升温,8 V·cm−1的电场强度能将15 g 土壤于5 min 内加热至水沸点,而2 V·cm−1电场无法使土壤加热,在8 V·cm−1电场强度下加6 mL0.1%NaCl,每30 min补水6 mL,苯并(a)芘去除率为51.56%。FU等[18]的研究表明,土壤中污染物脱附效率随粒径增加而增大,粒径为小于75 μm、75~125 μm、125~250 μm、250~425 μm土壤颗粒的多溴联苯醚脱附效率分别为49.53%、73.88%、83.56%和87.09%。李晓雅等[19]采用Design-Expert响应曲面法优化热强化土壤气相抽提技术的影响参数,考察通气速率、土量和水蒸气浓度单独变量和交互作用,发现单因素变量、通气速率与土量的交互项均对烃类污染物的去除速率有显著影响。目前,已发表的文献中仅对ERH处理PAHs污染土壤进行了初步探索,对性质相似的半挥发性有机污染物PCMs的研究鲜有报道,而且,ERH去除过程中的影响因素及脱附规律等尚未明晰。
因此,本研究使用自主研制的电阻加热装置,研究电场强度、含水率和土壤粒径对人工模拟HHCB污染土壤去除效果的影响,并采用Box-Behnken响应曲面法建立各因素与土壤HHCB去除率之间的回归模型,通过对响应曲面图和等高线图的分析,研究ERH修复HHCB污染土壤中各影响因素单独及交互作用,得到最优工艺参数,以期为电阻加热修复技术的工程应用提供理论和实践指导。
-
实验土壤采自北京市海淀区某未受污染表层土壤(0~25 cm),样品自然风干至恒重状态,研磨过筛后置于干燥阴凉处备用。供试土壤的基本性质如表1所示,为模拟均匀的浓度为1 mg·kg−1 的HHCB污染土壤,取200 mL 5 mg·L−1的HHCB溶液均匀洒入1 kg过筛的土壤中,边洒边充分搅拌,混合的样品经混匀机混匀24 h,老化14 d后备用。
-
1)实验试剂。佳乐麝香(C18H26O,分析纯)、正己烷(C6H14,色谱纯)、二氯甲烷(CH2Cl2,色谱纯)、丙酮(CH3COCH3,色谱纯)。
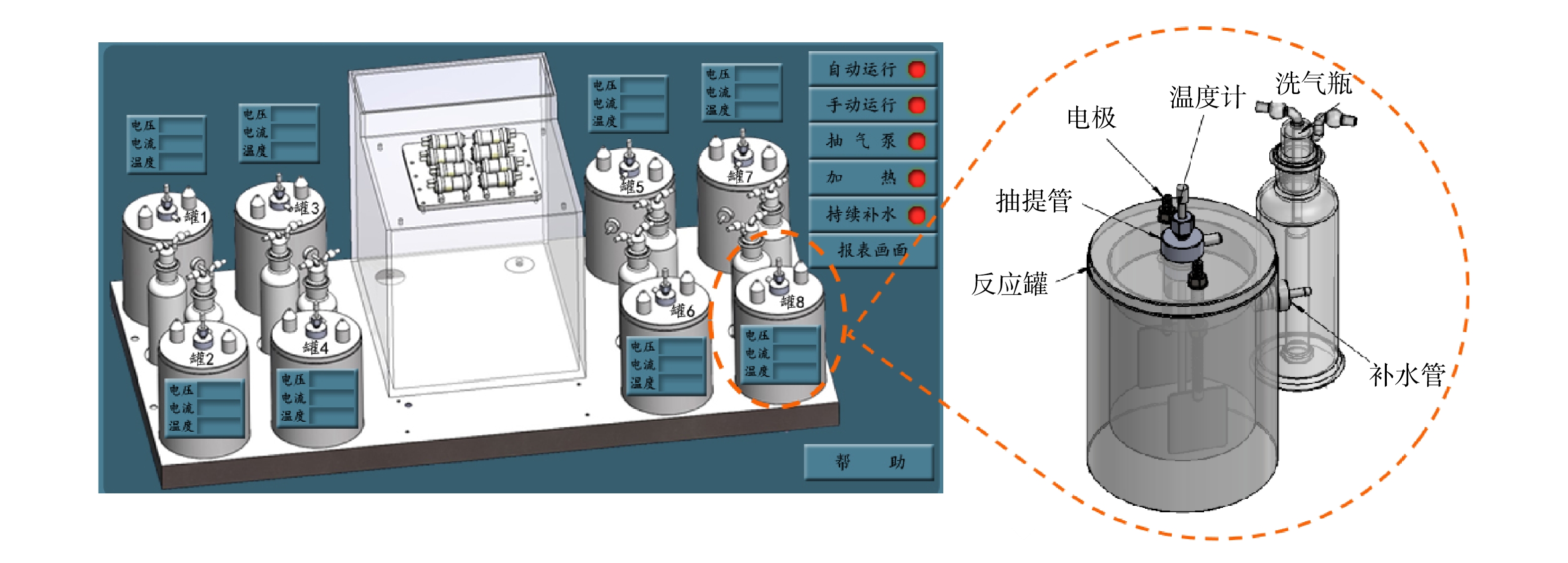
2)实验仪器。自主研制的电阻加热实验装置示意图如图1所示,主要由反应罐(内径10 cm、高8 cm)、交流电极、温度计、抽气泵、抽提管、注水泵、注水管和洗气瓶组成。气相色谱质谱联用仪(型号7890-7000B,美国安捷伦)、加速溶剂萃取仪(型号 350,赛默飞世尔)、混匀机(型号SCI-FS,美国赛洛捷克)。
-
1)单因素实验。选择电场强度、含水率和土壤粒径进行单因素实验,具体实验方案如表2所示。将800 g预先配置的污染土样置于反应罐中加入去离子水后搅拌均匀,打开交流电源设置电压开始进行加热去除,分别在不同时间间隔(30、60、120、180、240、300、360 min)取样,待土样冷却后装瓶,在4 ℃环境下保存待分析,进行3组平行实验。
2)响应曲面模拟优化。响应曲面法旨在考察各影响因素的单独变量作用及交互作用对土壤中HHCB去除率的影响。根据单因素的实验结果确定电场强度、含水率和土壤粒径为中心值,以最终去除率为参考因素,采用Box-Behnken模型对预先配制的污染土壤设计3因素3水平的实验,实验因素及水平见表3。
-
1)仪器分析。本研究采用加速溶剂萃取仪(ASE 350)提取土壤中的HHCB,采用气相色谱质谱联用仪(安捷伦7890-7000B)定量分析。配备 DB-5MS色谱柱 (30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm);色谱柱升温程序[20]为,初始温度120 ℃保持2 min,以15 ℃·min−1升至180 ℃,然后以2 ℃·min−1升至200 ℃,最后以30 ℃·min−1升至280 ℃并保持5 min;载气、辅助气为高纯氦气,载气流速为1 mL·min−1;进样方式不分流进样,不分流时间0.75 min;进样量,1 μL。质谱条件为,EI离子源,离子源温度为250 ℃,选择离子扫描模式,HHCB的保留时间为12.075 min,定量离子(m/z)为243.1。
2)数据分析。HHCB去除效率计算如式(1)所示。
式中:R为土壤中污染物的去除率,%;c0为污染物的初始质量分数,mg·kg−1;ct为电阻加热处置t时间后污染物的残留质量分数,mg·kg−1。
-
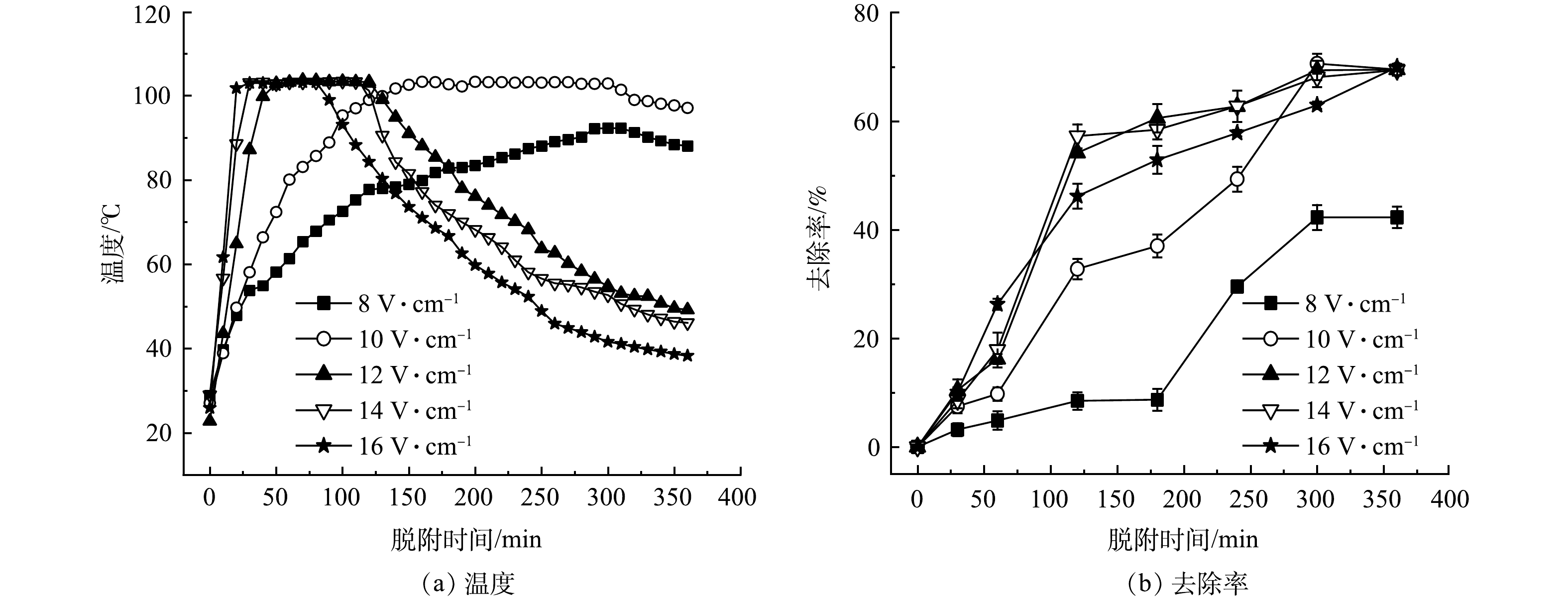
不同电场强度对土壤温度和HHCB去除率的影响如图2所示。由图2(a)可看出,电场强度为16 V·cm−1时,土壤升温速率为3.705 ℃·min−1,持温时间为70 min,电场强度10 V·cm−1时,升温速率为0.517 ℃·min−1,持温时间为190 min,电场强度8 V·cm−1时,即使加热360 min,温度也难以达到水的沸点。电场强度越大,土壤升温速率越快,温度保持水沸点时间(持温时间)越短,这表明电场强度是土壤电阻加热的重要因素[17]。电场主要通过2种机制使土壤升温:一是连通高压电,两电极之间形成电流回路,电能转化为热能;二是热传导,通电后两电极间土壤快速升温,电极间高温土壤将温度传导至电极周围的低温土壤[21]。施加的电场越大,两电极间电流越大,产生热量越多,升温速率越快。高电场强度持温时间短主要是因为随着土壤温度升高,含水量下降导致土壤导电性下降,加热效率降低。
由图2(b)可看出,反应前60 min,土壤HHCB去除率随电场强度增加而增加,电场强度为16 V·cm−1时去除效果最佳。电场强度为12、14 V·cm−1时,60~120 min高电场强度下由于水分的快速蒸发,温度下降,土壤HHCB去除速率最快。电场强度为10 V·cm−1时,180~300 min,土壤HHCB去除速率最快。反应360 min时,除8 V·cm−1外,温度和去除率受电场强度的影响变小。电场强度为10、12、14 V·cm−1时,土壤中HHCB在300 min趋于脱附平衡,最大脱附率为70.6%。土壤中HHCB的去除率随电场强度的增加呈现先增加后减小的趋势。其原因可能是,在反应前期,土壤水分充足,电场越大,自由电荷移动速率越快,电能向热能转化频率越高,水分蒸发速率越快,土壤HHCB被脱附去除越快。但随着反应进行,高电场强度加速土壤水分流失,减少离子传输通道,温度快速下降,土壤HHCB去除速率也随之下降[7, 21]。另外,电场强度太低时难以加热土壤至水沸点,污染物去除效果不理想[7]。因此,选择合适的电场维持加热温度和持温时间对去除土壤HHCB至关重要。
-
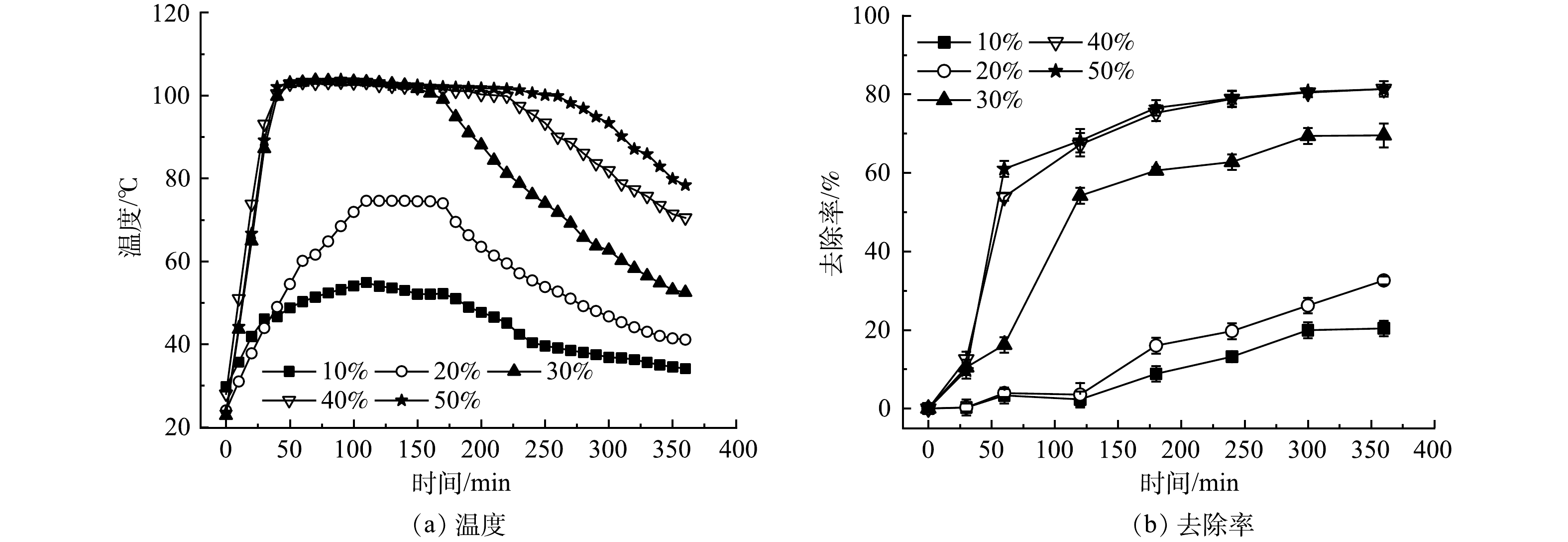
不同土壤含水率对土壤温度和HHCB去除率的影响如图3所示。由图3(a)可看出,电场强度为12 V·cm−1时,土壤初始含水率大于30%,持温时间大于90 min且仅需加热30 min,土壤就能达到水沸点温度;而土壤初始含水率低于20%时,加热110 min,土壤最高温度只能达到74.6 ℃。这说明,土壤初始含水率与土壤持温时间有正向关联。土壤含水量对土壤温度影响大是因为,在土壤通电时,充足的水分提供离子传输通道,电渗流通过离子流动促进孔隙中水换热,提高土壤的导热能力,因此有利于维持ERH温度[13]。当水分不断蒸发被抽提后,土壤含水率降低,土壤电阻增大,产生热量减少。这与葛松[21]和张辉[22]等对电阻加热水分研究的影响一致。
由图3(b)可看出,土壤初始含水率低于20%时,HHCB最大去除率为32.6%;土壤初始含水率高于40%时,反应120 min后,含水率的增加对土壤HHCB去除率影响不明显。这说明土壤HHCB去除率随土壤含水率的增加先增加后减少。在反应前160 min,土壤温度和HHCB去除率随脱附时间增加而增加,随着水分的减少,电解质载体不足导致温度下降,去除速率也随之减小。在本实验条件下,在反应前期,土壤含水量较大,强极性水分子占据了吸附在土壤表层的污染物分子HHCB的吸附点位,使得HHCB与水分子发生共沸而被脱附[23],进而提高了去除效率。有研究表明,污染物可以通过与水发生共沸而去除[24],此现象在ERH去除三氯乙烯等污染物的研究中也有类似的报道[5, 25]。孟宪荣等[26]提出,ERH修复土壤时,加热温度达到水沸点时,水蒸汽驱使锁定在土中的污染物离开土壤,蒸汽作为载气将污染物运输至抽提区域被抽提并处置。但是,如果含水率过高时,水分在土壤表层形成水膜可能会阻碍土壤颗粒深层包裹的HHCB组分向外扩散脱附,有机污染物从土壤向气相的转变过程会受到限制[27],且随着脱附时间的延长,对污染物脱附效率的影响越来越小。
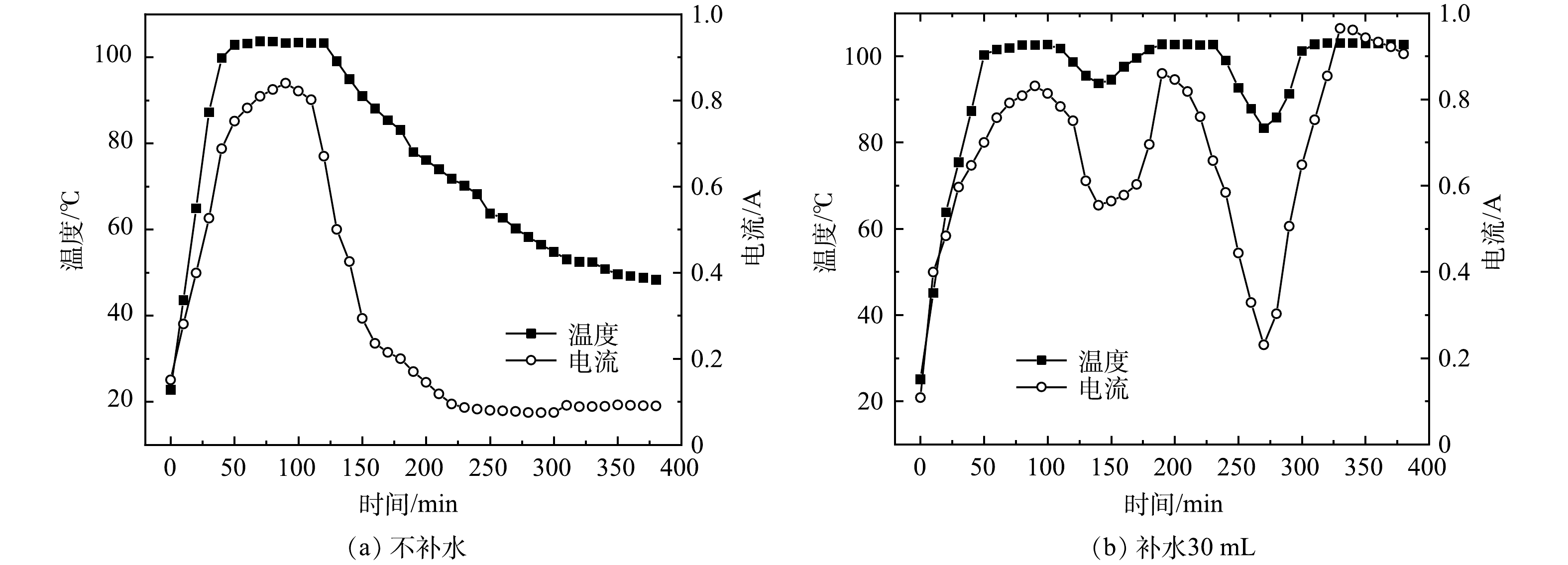
由图4(a)可看出,不补水的条件下,反应95 min后电流开始降低,随后温度也随之下降。由图(b)可看出,电流下降后,在100和200 min加入30 mL去离子水以增加电解质,保持温度,在该条件下初始升温速率较高,温度在100 ℃左右保持稳定,约50 min后大部分的水沸腾、挥发,电解质载体不足导致电流减小,温度也开始随之降低;补水后观察到,温度和电流明显上升。由此可知,水分是维持土壤电阻加热温度的关键因素。
-
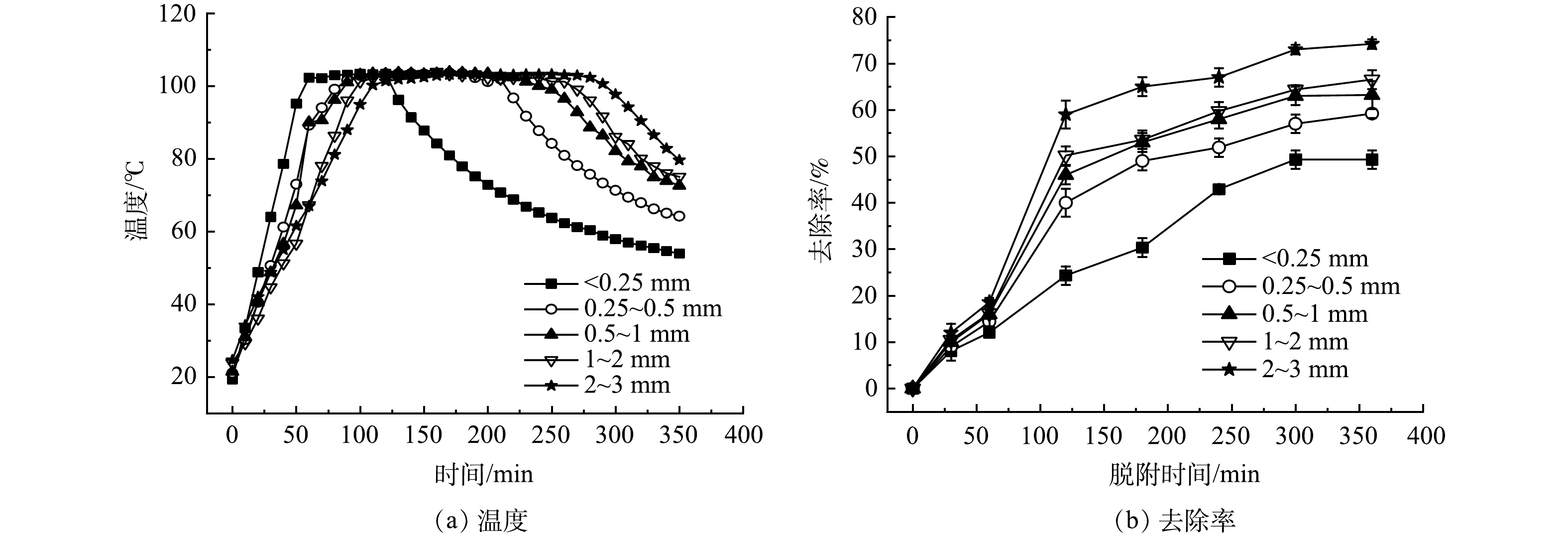
土壤粒径对土壤温度和HHCB去除率的影响如图5所示。由图5(a)可看出,土壤粒径越小,只需反应50 min土壤即被加热到100 ℃,土壤粒径越大加热到水沸点温度时间会延长。粒径小于0.25 mm,60 min时温度能达水沸点温度,持温时间为40 min。而土壤粒径为2~3 mm,110 min时才达到水沸点温度,持温时间为170 min。土壤粒径越小,升温速率越快,持温效果越差。这可能是因为,加热初期土壤颗粒间隙越小,透气性越差,保温效果越好,温度升高速率越快[28]。在高温(>100 ℃)保持一段时间后,随着土壤水分的快速蒸发,土壤电阻率增加,温度开始逐渐降低[21]。
由图5(b)可看出,土壤粒径小于0.25 mm时,土壤HHCB最大去除率为49.3%。土壤粒径为2~3 mm,土壤HHCB最大去除率为74.2%。土壤HHCB的去除率随土壤粒径的增大而增大,土壤粒径越小,其表面积越大,颗粒上吸附点位越多[29],HHCB易进入土壤微孔不易扩散释放出来,难以被脱附去除。GBADEBO等[30]的研究显示,粒径越小的土壤具有更多的吸附点位和更强的吸附力,从而降低了污染物的脱附。粗颗粒难以聚集,具有良好的导热性,土壤颗粒表面的HHCB大部分暴露于热介质中,可以完全接触热源,与水发生共沸分离,从而通过抽提而被转移处置。
-
1)响应面法分析。为优化HHCB电阻加热的工艺条件,选取3个因素(电场强度(X1)、含水率(X2)、土壤粒径(X3))进行3因素3水平的响应曲面优化实验,以+1、0、−1分别代表变量水平,以去除效率(Y1)作为响应值,得到二次回归模型,再计算出最优工艺参数。响应曲面实验工况如表4所示。
热脱附效率的低值和峰值分别为43.9%和86%。回归拟合方程如式(2)所示。
根据式(2),单因素的常数系数可表示此因素对Y1值的影响,而二阶常数系数可反应2种因素相互作用,如果系数为正则代表协同作用,为负则代表拮抗作用。由式(2)可知,电场强度、含水率和土壤粒径均对电阻加热去除效率有促进作用,电场强度和含水率、含水率和土壤粒径之间存在较强的协同作用,而电场强度和土壤粒径存在较弱的限制作用。回归模型的R2为0.991 6,这表明该模型拟合程度良好,即实验值与模拟预测值较为吻合。
2)响应面结果分析。响应面回归模型的方差分析如表5所示。从中可知,回归模型的F值为92.26,且Prob>F小于0.000 1,远小于0.05,即此模型有意义。本实验条件下,含水率和土壤粒径对此模型结果有较大影响,3种影响因素对热脱附效率的影响程度依次为,含水率>土壤粒径>电场强度。
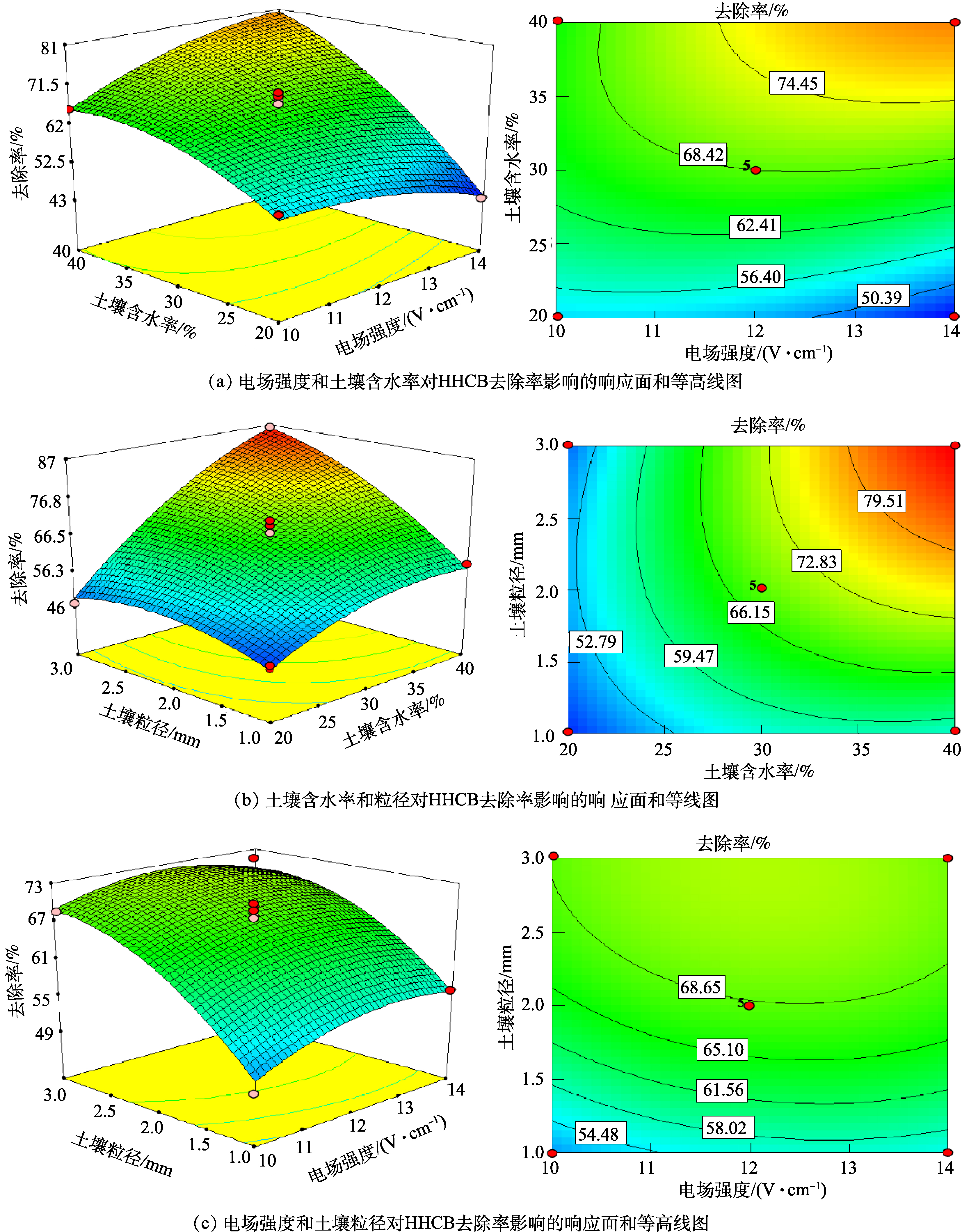
变量交互作用对HHCB去除率影响的响应面和等高线图如图6所示。响应曲面图和等高线图即表明了单个因子的影响,也反映出各因素交互作用的强弱[19]。由图6(a)可看出,电场强度与土壤含水率对HHCB去除率影响呈明显的坡面变化,电场强度的增加使得坡面变化较为缓慢。这说明电阻加热脱附效率的响应值受含水率的影响大于电场强度,2者的变化等高线呈现不明显椭圆状,交互作用不明显。出现此现象是因为,在本实验条件下,电场强度设置值已满足加热条件,土壤含水率变化显著影响脱附效率。这与ERH实际应用中,水分是维持 ERH 动态平衡的重要条件一致。土壤粒径和土壤含水率的响应面如图6(b)所示。随着含水率和土壤粒径的增加呈现明显的坡面变化,含水率对电阻加热去除率响应值的影响大于土壤粒径,2者的变化等高线呈现不明显椭圆状,交互作用不明显。相比之下,电场强度和土壤粒径的交互作用较明显。如图6(c)所示,随着电场强度和土壤粒径的增加,坡面变缓,等高线呈现椭圆状可知电场强度和土壤粒径有轻微的交互作用。出现该趋势的原因是,粒径增大影响土壤孔隙度和持水性[31],而电场强度增大导致水分快速蒸发随之温度降低,污染物解吸越来越弱[9],去除率减少。根据响应曲面预测的最优工艺参数条件是,含水率39.07%、粒径2.92 mm、电场强度12.64 V·cm−1。在工艺应用中,在电场强度、土壤含水率和土壤粒径3个因素给定的情况下,通过数学模型得出ERH对HHCB污染土壤去除效率,为工艺应用提供理论基础。
-
1)含水率、土壤粒径和电场强度对ERH去除土壤中HHCB具有重要影响。
2)土壤HHCB的去除主要通过影响ERH的升温速率和持温时间来间接实现。随着脱附时间的增加,电场强度和含水率越高,去除效率先增加后减少;土壤粒径越大,越易从吸附点位解吸从而被脱附去除。
3) 3个影响因素对HHCB去除率的影响依次为,含水率>土壤粒径>电场强度;而且,电场强度和含水率,含水率和土壤粒径之间存在较强的协同作用。ERH的最佳工艺参数条件为,含水率39.07%、粒径2.92 mm、电场强度12.64 V·cm−1,在此条件下,土壤HHCB的去除率为86.43%。
电阻加热修复佳乐麝香污染土壤的工艺优化
Optimization of Response Surface Process for Remediation of Galaxolide Contaminated Soil by Electric Resistance Heating
-
摘要: 佳乐麝香(Galaxolide,HHCB)是土壤中的一种新兴的半挥发性有机污染物,具有较高的毒性,需修复治理。电阻加热技术(electrical resistance heating,ERH)因加热均匀、效果好,逐渐被应用于有机污染土壤修复工程。采用自主研制的电阻加热装置,研究了加热过程中电场强度、土壤含水率和土壤粒径等因素对土壤HHCB去除效果的影响,并采用响应面法对工艺参数进行了优化。结果表明,土壤 HHCB去除率随电场强度和含水率的增大先增加后减小,随土壤粒径的增大而增大;在土壤含水率为40%、土壤粒径1~2 mm和电场强度12 V·cm−1的条件下,加热6 h,HHCB去除效果最好,去除率达到了81.35%。通过响应曲面模拟优化得到的最佳工艺参数条件为,含水率39.07%、土壤粒径2.92 mm、电场强度12.64 V·cm−1,在此条件下土壤HHCB的去除率为86.43%;在本实验条件下,3个因素对土壤HHCB去除率的影响为:含水率>土壤粒径>电场强度。本研究结果可为多环麝香污染土壤的修复提供参考。Abstract: Galaxolide(HHCB) is an emerging semi-volatile organic pollutant in soil, it has high toxicity and therefore needs remediation. Due to its high efficiency in achieving homogeneous soil heating, electrical resistance heating (ERH) technology has been more and more applied in organic polluted soil remediation. In this paper, the influence of electric field intensity, water content, and soil particle size on the ERH removal efficiency of HHCB was investigated using a self-made device, the operation parameters were optimized following the response surface methodology. The results showed that HHCB removal rate first increased and then decreased with the increment of electric field intensity and water content, and increased with the increase of soil particle size. Best removal rate 81.35% was achieved after ERH treatment for 6 h, under the conditions of soil water content 40%, soil particle size of 1~2 mm, and electric field intensity of 12 V·cm-1. The utilized parameters obtained by response surface simulation were as following: water content 39.07%, soil particle size 2.92 mm, and electric field intensity 12.64 V·cm-1, the estimated removal rate of HHCB was 86.43%. Under the experimental conditions, the effects of the three factors on the ERH removal rate of HHCB were as following: water content > soil particle size > electric field intensity. These results provide a new approach for polycyclic musk contaminated soil remediation.
-
多环麝香(Polycyclic musks,PCMs)作为重要的人工合成香料被广泛应用于日用品中,在土壤、水、沉积物和生物体等环境介质中均有检出[1]。其中,佳乐麝香(Galaxolide,HHCB)是土壤中检出率和检出浓度最高的典型PCMs之一,在长江三角洲、天津和东北三省土壤中已检测出,检出质量分数最高为7.22 μg·kg−1 [2]。HHCB被用于治疗心肌梗塞、调配香水香皂等,是一类低水溶性、高脂溶性的半挥发持久性有机污染物,在环境中难降解,容易在生物体内富集,具有内分泌干扰性和引起癌细胞增殖和胎畸[3]。由于对人体有雌激素作用与抗雌激素效应,该物质被欧盟列为“潜在人类致癌物”[3-4]。
目前,可用于原位修复半挥发性有机污染土壤方法主要有热脱附、气相抽提、电动修复和超临界流体修复等[5-7]。热脱附中的原位电阻加热技术(electrical resistance heating,ERH)在土壤中安装三相、六相电极后将土壤加热,其热量产生于土壤内部,相较于常规修复技术具有加热相对均匀、地质条件适应性强、对土壤扰动小、修复彻底和不引入外源性污染等优点[8-9]。ERH早期被应用于采油技术,随着应用的需要逐渐被引入到土壤和地下水污染修复中[10]。ERH是基于欧姆定律,将电能转化为热能,提升土壤温度,使部分挥发和半挥发性有机污染物与水溶液发生共沸,最终通过气相抽提将污染物转移并处置[11-12]。影响土壤ERH的因素包括土壤含水率、电场强度、土壤粒径以及加热时间等[12-15]。HAN等[13]和HAN等[16]发现,水分是ERH关键因素;没有足够的水分,即使电场强度在8 V·cm−1时,土壤也难以被加热到水沸点。田垚等[17]提出,在初始含水量充足的条件下,高电场强度使土壤快速升温,8 V·cm−1的电场强度能将15 g 土壤于5 min 内加热至水沸点,而2 V·cm−1电场无法使土壤加热,在8 V·cm−1电场强度下加6 mL0.1%NaCl,每30 min补水6 mL,苯并(a)芘去除率为51.56%。FU等[18]的研究表明,土壤中污染物脱附效率随粒径增加而增大,粒径为小于75 μm、75~125 μm、125~250 μm、250~425 μm土壤颗粒的多溴联苯醚脱附效率分别为49.53%、73.88%、83.56%和87.09%。李晓雅等[19]采用Design-Expert响应曲面法优化热强化土壤气相抽提技术的影响参数,考察通气速率、土量和水蒸气浓度单独变量和交互作用,发现单因素变量、通气速率与土量的交互项均对烃类污染物的去除速率有显著影响。目前,已发表的文献中仅对ERH处理PAHs污染土壤进行了初步探索,对性质相似的半挥发性有机污染物PCMs的研究鲜有报道,而且,ERH去除过程中的影响因素及脱附规律等尚未明晰。
因此,本研究使用自主研制的电阻加热装置,研究电场强度、含水率和土壤粒径对人工模拟HHCB污染土壤去除效果的影响,并采用Box-Behnken响应曲面法建立各因素与土壤HHCB去除率之间的回归模型,通过对响应曲面图和等高线图的分析,研究ERH修复HHCB污染土壤中各影响因素单独及交互作用,得到最优工艺参数,以期为电阻加热修复技术的工程应用提供理论和实践指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 土壤样品
实验土壤采自北京市海淀区某未受污染表层土壤(0~25 cm),样品自然风干至恒重状态,研磨过筛后置于干燥阴凉处备用。供试土壤的基本性质如表1所示,为模拟均匀的浓度为1 mg·kg−1 的HHCB污染土壤,取200 mL 5 mg·L−1的HHCB溶液均匀洒入1 kg过筛的土壤中,边洒边充分搅拌,混合的样品经混匀机混匀24 h,老化14 d后备用。
表 1 实验土壤基本理化性质Table 1. Basic properties of experimental soilpH TOC 有机质/% 总N/% 总P/% 总K/% 粒径分布 黏粒(<0.002 mm)/% 粉粒(0.002~0.02 mm)/% 砂粒(0.02~2 mm)/% 9.01 1.75 1.38 0.11 0.68 20.1 2.99 14.52 82.49 1.2 实验试剂与仪器
1)实验试剂。佳乐麝香(C18H26O,分析纯)、正己烷(C6H14,色谱纯)、二氯甲烷(CH2Cl2,色谱纯)、丙酮(CH3COCH3,色谱纯)。
2)实验仪器。自主研制的电阻加热实验装置示意图如图1所示,主要由反应罐(内径10 cm、高8 cm)、交流电极、温度计、抽气泵、抽提管、注水泵、注水管和洗气瓶组成。气相色谱质谱联用仪(型号7890-7000B,美国安捷伦)、加速溶剂萃取仪(型号 350,赛默飞世尔)、混匀机(型号SCI-FS,美国赛洛捷克)。
1.3 实验方法
1)单因素实验。选择电场强度、含水率和土壤粒径进行单因素实验,具体实验方案如表2所示。将800 g预先配置的污染土样置于反应罐中加入去离子水后搅拌均匀,打开交流电源设置电压开始进行加热去除,分别在不同时间间隔(30、60、120、180、240、300、360 min)取样,待土样冷却后装瓶,在4 ℃环境下保存待分析,进行3组平行实验。
表 2 单因素实验方案Table 2. Scheme of single factor experiment序号 电场强度/(V·cm−1) 含水率/% 土壤粒径/mm 1 8 30 1~2 2 10 30 1~2 3 12 30 1~2 4 14 30 1~2 5 16 30 1~2 6 12 10 1~2 7 12 20 1~2 8 12 30 1~2 9 12 40 1~2 10 12 50 1~2 11 12 30 <0.25 12 12 30 0.25~0.5 13 12 30 0.5~1 14 12 30 1~2 15 12 30 2~3 2)响应曲面模拟优化。响应曲面法旨在考察各影响因素的单独变量作用及交互作用对土壤中HHCB去除率的影响。根据单因素的实验结果确定电场强度、含水率和土壤粒径为中心值,以最终去除率为参考因素,采用Box-Behnken模型对预先配制的污染土壤设计3因素3水平的实验,实验因素及水平见表3。
表 3 响应曲面法的影响因子编码和水平Table 3. Level and code of experimental variables based on response surface methodology因素 编码 水平 −1 0 +1 电场强度 X1 10 v·cm−1 12 v·cm−1 14 v·cm−1 含水率 X2 20% 30% 40% 土壤粒径 X3 <1 mm 1~2 mm 2~3 mm 1.4 分析方法
1)仪器分析。本研究采用加速溶剂萃取仪(ASE 350)提取土壤中的HHCB,采用气相色谱质谱联用仪(安捷伦7890-7000B)定量分析。配备 DB-5MS色谱柱 (30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm);色谱柱升温程序[20]为,初始温度120 ℃保持2 min,以15 ℃·min−1升至180 ℃,然后以2 ℃·min−1升至200 ℃,最后以30 ℃·min−1升至280 ℃并保持5 min;载气、辅助气为高纯氦气,载气流速为1 mL·min−1;进样方式不分流进样,不分流时间0.75 min;进样量,1 μL。质谱条件为,EI离子源,离子源温度为250 ℃,选择离子扫描模式,HHCB的保留时间为12.075 min,定量离子(m/z)为243.1。
2)数据分析。HHCB去除效率计算如式(1)所示。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) 式中:R为土壤中污染物的去除率,%;c0为污染物的初始质量分数,mg·kg−1;ct为电阻加热处置t时间后污染物的残留质量分数,mg·kg−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 电场强度对土壤温度及HHCB去除率的影响
不同电场强度对土壤温度和HHCB去除率的影响如图2所示。由图2(a)可看出,电场强度为16 V·cm−1时,土壤升温速率为3.705 ℃·min−1,持温时间为70 min,电场强度10 V·cm−1时,升温速率为0.517 ℃·min−1,持温时间为190 min,电场强度8 V·cm−1时,即使加热360 min,温度也难以达到水的沸点。电场强度越大,土壤升温速率越快,温度保持水沸点时间(持温时间)越短,这表明电场强度是土壤电阻加热的重要因素[17]。电场主要通过2种机制使土壤升温:一是连通高压电,两电极之间形成电流回路,电能转化为热能;二是热传导,通电后两电极间土壤快速升温,电极间高温土壤将温度传导至电极周围的低温土壤[21]。施加的电场越大,两电极间电流越大,产生热量越多,升温速率越快。高电场强度持温时间短主要是因为随着土壤温度升高,含水量下降导致土壤导电性下降,加热效率降低。
由图2(b)可看出,反应前60 min,土壤HHCB去除率随电场强度增加而增加,电场强度为16 V·cm−1时去除效果最佳。电场强度为12、14 V·cm−1时,60~120 min高电场强度下由于水分的快速蒸发,温度下降,土壤HHCB去除速率最快。电场强度为10 V·cm−1时,180~300 min,土壤HHCB去除速率最快。反应360 min时,除8 V·cm−1外,温度和去除率受电场强度的影响变小。电场强度为10、12、14 V·cm−1时,土壤中HHCB在300 min趋于脱附平衡,最大脱附率为70.6%。土壤中HHCB的去除率随电场强度的增加呈现先增加后减小的趋势。其原因可能是,在反应前期,土壤水分充足,电场越大,自由电荷移动速率越快,电能向热能转化频率越高,水分蒸发速率越快,土壤HHCB被脱附去除越快。但随着反应进行,高电场强度加速土壤水分流失,减少离子传输通道,温度快速下降,土壤HHCB去除速率也随之下降[7, 21]。另外,电场强度太低时难以加热土壤至水沸点,污染物去除效果不理想[7]。因此,选择合适的电场维持加热温度和持温时间对去除土壤HHCB至关重要。
2.2 含水率对土壤温度及HHCB去除率的影响
不同土壤含水率对土壤温度和HHCB去除率的影响如图3所示。由图3(a)可看出,电场强度为12 V·cm−1时,土壤初始含水率大于30%,持温时间大于90 min且仅需加热30 min,土壤就能达到水沸点温度;而土壤初始含水率低于20%时,加热110 min,土壤最高温度只能达到74.6 ℃。这说明,土壤初始含水率与土壤持温时间有正向关联。土壤含水量对土壤温度影响大是因为,在土壤通电时,充足的水分提供离子传输通道,电渗流通过离子流动促进孔隙中水换热,提高土壤的导热能力,因此有利于维持ERH温度[13]。当水分不断蒸发被抽提后,土壤含水率降低,土壤电阻增大,产生热量减少。这与葛松[21]和张辉[22]等对电阻加热水分研究的影响一致。
由图3(b)可看出,土壤初始含水率低于20%时,HHCB最大去除率为32.6%;土壤初始含水率高于40%时,反应120 min后,含水率的增加对土壤HHCB去除率影响不明显。这说明土壤HHCB去除率随土壤含水率的增加先增加后减少。在反应前160 min,土壤温度和HHCB去除率随脱附时间增加而增加,随着水分的减少,电解质载体不足导致温度下降,去除速率也随之减小。在本实验条件下,在反应前期,土壤含水量较大,强极性水分子占据了吸附在土壤表层的污染物分子HHCB的吸附点位,使得HHCB与水分子发生共沸而被脱附[23],进而提高了去除效率。有研究表明,污染物可以通过与水发生共沸而去除[24],此现象在ERH去除三氯乙烯等污染物的研究中也有类似的报道[5, 25]。孟宪荣等[26]提出,ERH修复土壤时,加热温度达到水沸点时,水蒸汽驱使锁定在土中的污染物离开土壤,蒸汽作为载气将污染物运输至抽提区域被抽提并处置。但是,如果含水率过高时,水分在土壤表层形成水膜可能会阻碍土壤颗粒深层包裹的HHCB组分向外扩散脱附,有机污染物从土壤向气相的转变过程会受到限制[27],且随着脱附时间的延长,对污染物脱附效率的影响越来越小。
由图4(a)可看出,不补水的条件下,反应95 min后电流开始降低,随后温度也随之下降。由图(b)可看出,电流下降后,在100和200 min加入30 mL去离子水以增加电解质,保持温度,在该条件下初始升温速率较高,温度在100 ℃左右保持稳定,约50 min后大部分的水沸腾、挥发,电解质载体不足导致电流减小,温度也开始随之降低;补水后观察到,温度和电流明显上升。由此可知,水分是维持土壤电阻加热温度的关键因素。
2.3 土壤粒径对土壤温度及HHCB去除率的影响
土壤粒径对土壤温度和HHCB去除率的影响如图5所示。由图5(a)可看出,土壤粒径越小,只需反应50 min土壤即被加热到100 ℃,土壤粒径越大加热到水沸点温度时间会延长。粒径小于0.25 mm,60 min时温度能达水沸点温度,持温时间为40 min。而土壤粒径为2~3 mm,110 min时才达到水沸点温度,持温时间为170 min。土壤粒径越小,升温速率越快,持温效果越差。这可能是因为,加热初期土壤颗粒间隙越小,透气性越差,保温效果越好,温度升高速率越快[28]。在高温(>100 ℃)保持一段时间后,随着土壤水分的快速蒸发,土壤电阻率增加,温度开始逐渐降低[21]。
由图5(b)可看出,土壤粒径小于0.25 mm时,土壤HHCB最大去除率为49.3%。土壤粒径为2~3 mm,土壤HHCB最大去除率为74.2%。土壤HHCB的去除率随土壤粒径的增大而增大,土壤粒径越小,其表面积越大,颗粒上吸附点位越多[29],HHCB易进入土壤微孔不易扩散释放出来,难以被脱附去除。GBADEBO等[30]的研究显示,粒径越小的土壤具有更多的吸附点位和更强的吸附力,从而降低了污染物的脱附。粗颗粒难以聚集,具有良好的导热性,土壤颗粒表面的HHCB大部分暴露于热介质中,可以完全接触热源,与水发生共沸分离,从而通过抽提而被转移处置。
2.4 基于响应面法对电阻加热去除HHCB效率参数的优化
1)响应面法分析。为优化HHCB电阻加热的工艺条件,选取3个因素(电场强度(X1)、含水率(X2)、土壤粒径(X3))进行3因素3水平的响应曲面优化实验,以+1、0、−1分别代表变量水平,以去除效率(Y1)作为响应值,得到二次回归模型,再计算出最优工艺参数。响应曲面实验工况如表4所示。
表 4 响应曲面实验工况Table 4. Response surface experimental conditions序号 X1/ (V·cm−1) X2/% X3/mm Y1/% 1 14 40 2 78.9 2 10 20 2 55.0 3 14 30 3 71.5 4 12 30 2 66.9 5 12 20 3 47.7 6 12 30 2 69.5 7 14 30 1 56.0 8 12 20 1 46.3 9 10 30 1 49.2 10 12 40 1 58.4 11 12 40 3 86.0 12 12 30 2 68.0 13 12 30 2 68.7 14 14 20 2 43.9 15 10 40 2 66.1 16 12 30 2 69.0 17 10 30 3 68.5 热脱附效率的低值和峰值分别为43.9%和86%。回归拟合方程如式(2)所示。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) 根据式(2),单因素的常数系数可表示此因素对Y1值的影响,而二阶常数系数可反应2种因素相互作用,如果系数为正则代表协同作用,为负则代表拮抗作用。由式(2)可知,电场强度、含水率和土壤粒径均对电阻加热去除效率有促进作用,电场强度和含水率、含水率和土壤粒径之间存在较强的协同作用,而电场强度和土壤粒径存在较弱的限制作用。回归模型的R2为0.991 6,这表明该模型拟合程度良好,即实验值与模拟预测值较为吻合。
2)响应面结果分析。响应面回归模型的方差分析如表5所示。从中可知,回归模型的F值为92.26,且Prob>F小于0.000 1,远小于0.05,即此模型有意义。本实验条件下,含水率和土壤粒径对此模型结果有较大影响,3种影响因素对热脱附效率的影响程度依次为,含水率>土壤粒径>电场强度。
表 5 响应曲面二次模型方差分析Table 5. Response surface quadric model analysis of variance来源 平方和 自由度 均方和 F值 Prob>F 回归模型 2228.36 9 247.60 92.26 < 0.000 1** X1 16.53 1 16.53 6.16 0.042 1* X2 1164.03 1 1164.03 433.75 < 0.000 1** X3 508.80 1 508.80 189.59 < 0.000 1** X1 X2 142.80 1 142.80 53.21 0.000 2** X1 X3 3.61 1 3.61 1.35 0.284 1 X2 X3 171.61 1 171.61 63.95 < 0.000 1** X12 34.74 1 34.74 12.95 0.008 8** X22 88.03 1 88.03 32.80 0.000 7** X32 75.96 1 75.96 28.31 0.001 1** 残差 18.79 7 2.68 − − 失拟项 14.72 3 4.91 4.82 0.081 3 纯误差 4.07 4 1.02 − − 总离差 2247.14 16 − − − 注:“**”表示该项极显著(P<0.01);“*”表示该项显著(P<0.05);“−”表示此项无数值。 变量交互作用对HHCB去除率影响的响应面和等高线图如图6所示。响应曲面图和等高线图即表明了单个因子的影响,也反映出各因素交互作用的强弱[19]。由图6(a)可看出,电场强度与土壤含水率对HHCB去除率影响呈明显的坡面变化,电场强度的增加使得坡面变化较为缓慢。这说明电阻加热脱附效率的响应值受含水率的影响大于电场强度,2者的变化等高线呈现不明显椭圆状,交互作用不明显。出现此现象是因为,在本实验条件下,电场强度设置值已满足加热条件,土壤含水率变化显著影响脱附效率。这与ERH实际应用中,水分是维持 ERH 动态平衡的重要条件一致。土壤粒径和土壤含水率的响应面如图6(b)所示。随着含水率和土壤粒径的增加呈现明显的坡面变化,含水率对电阻加热去除率响应值的影响大于土壤粒径,2者的变化等高线呈现不明显椭圆状,交互作用不明显。相比之下,电场强度和土壤粒径的交互作用较明显。如图6(c)所示,随着电场强度和土壤粒径的增加,坡面变缓,等高线呈现椭圆状可知电场强度和土壤粒径有轻微的交互作用。出现该趋势的原因是,粒径增大影响土壤孔隙度和持水性[31],而电场强度增大导致水分快速蒸发随之温度降低,污染物解吸越来越弱[9],去除率减少。根据响应曲面预测的最优工艺参数条件是,含水率39.07%、粒径2.92 mm、电场强度12.64 V·cm−1。在工艺应用中,在电场强度、土壤含水率和土壤粒径3个因素给定的情况下,通过数学模型得出ERH对HHCB污染土壤去除效率,为工艺应用提供理论基础。
3. 结论
1)含水率、土壤粒径和电场强度对ERH去除土壤中HHCB具有重要影响。
2)土壤HHCB的去除主要通过影响ERH的升温速率和持温时间来间接实现。随着脱附时间的增加,电场强度和含水率越高,去除效率先增加后减少;土壤粒径越大,越易从吸附点位解吸从而被脱附去除。
3) 3个影响因素对HHCB去除率的影响依次为,含水率>土壤粒径>电场强度;而且,电场强度和含水率,含水率和土壤粒径之间存在较强的协同作用。ERH的最佳工艺参数条件为,含水率39.07%、粒径2.92 mm、电场强度12.64 V·cm−1,在此条件下,土壤HHCB的去除率为86.43%。
-
表 1 实验土壤基本理化性质
Table 1. Basic properties of experimental soil
pH TOC 有机质/% 总N/% 总P/% 总K/% 粒径分布 黏粒(<0.002 mm)/% 粉粒(0.002~0.02 mm)/% 砂粒(0.02~2 mm)/% 9.01 1.75 1.38 0.11 0.68 20.1 2.99 14.52 82.49 表 2 单因素实验方案
Table 2. Scheme of single factor experiment
序号 电场强度/(V·cm−1) 含水率/% 土壤粒径/mm 1 8 30 1~2 2 10 30 1~2 3 12 30 1~2 4 14 30 1~2 5 16 30 1~2 6 12 10 1~2 7 12 20 1~2 8 12 30 1~2 9 12 40 1~2 10 12 50 1~2 11 12 30 <0.25 12 12 30 0.25~0.5 13 12 30 0.5~1 14 12 30 1~2 15 12 30 2~3 表 3 响应曲面法的影响因子编码和水平
Table 3. Level and code of experimental variables based on response surface methodology
因素 编码 水平 −1 0 +1 电场强度 X1 10 v·cm−1 12 v·cm−1 14 v·cm−1 含水率 X2 20% 30% 40% 土壤粒径 X3 <1 mm 1~2 mm 2~3 mm 表 4 响应曲面实验工况
Table 4. Response surface experimental conditions
序号 X1/ (V·cm−1) X2/% X3/mm Y1/% 1 14 40 2 78.9 2 10 20 2 55.0 3 14 30 3 71.5 4 12 30 2 66.9 5 12 20 3 47.7 6 12 30 2 69.5 7 14 30 1 56.0 8 12 20 1 46.3 9 10 30 1 49.2 10 12 40 1 58.4 11 12 40 3 86.0 12 12 30 2 68.0 13 12 30 2 68.7 14 14 20 2 43.9 15 10 40 2 66.1 16 12 30 2 69.0 17 10 30 3 68.5 表 5 响应曲面二次模型方差分析
Table 5. Response surface quadric model analysis of variance
来源 平方和 自由度 均方和 F值 Prob>F 回归模型 2228.36 9 247.60 92.26 < 0.000 1** X1 16.53 1 16.53 6.16 0.042 1* X2 1164.03 1 1164.03 433.75 < 0.000 1** X3 508.80 1 508.80 189.59 < 0.000 1** X1 X2 142.80 1 142.80 53.21 0.000 2** X1 X3 3.61 1 3.61 1.35 0.284 1 X2 X3 171.61 1 171.61 63.95 < 0.000 1** X12 34.74 1 34.74 12.95 0.008 8** X22 88.03 1 88.03 32.80 0.000 7** X32 75.96 1 75.96 28.31 0.001 1** 残差 18.79 7 2.68 − − 失拟项 14.72 3 4.91 4.82 0.081 3 纯误差 4.07 4 1.02 − − 总离差 2247.14 16 − − − 注:“**”表示该项极显著(P<0.01);“*”表示该项显著(P<0.05);“−”表示此项无数值。 -
[1] LIU J V, ZHANG W Y, ZHOU Q X, et al. Polycyclic musks in the environment: A review of their concentrations and distribution, ecological effects and behavior, current concerns and future prospects[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science, 2020, 51(9): 1-55. [2] ZHENG M G, HU S Y, LIU X W, et al. Levels and distribution of synthetic musks in farmland soils from the Three Northeast Provinces of China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 172(5): 303-307. [3] WANG M E, PENG C, CHEN W P, et al. Ecological risks of polycyclic musk in soils irrigated with reclaimed municipal wastewater[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 97(11): 242-247. [4] EHIGUESE F O, RODGERS M L, ARAUJO C V M, et al. Galaxolide and tonalide modulate neuroendocrine activity in marine species from two taxonomic groups[J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 196: 110960. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110960 [5] HEGELE P R, MUMFORD K G. Gas production and transport during bench-scale electrical resistance heating of water and trichloroethene[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2014, 165: 24-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2014.07.002 [6] 焦文涛, 韩自玉, 吕正勇, 等. 土壤电阻加热技术原位修复有机污染土壤的关键问题与展望[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(9): 2027-2036. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201905138 [7] WEI Y M, WANG F, Liu X, et al. Thermal remediation of cyanide-contaminated soils: process optimization and mechanistic study[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 239: 124707. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124707 [8] 李书鹏, 焦文涛, 李鸿炫, 等. 燃气热脱附技术修复有机污染场地研究与应用进展[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(9): 2037-2048. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201905108 [9] ZHAO C, DONG Y, FENG Y, et al. Thermal desorption for remediation of contaminated soil: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 221: 841-855. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.079 [10] LI J J, WANG L, PENG L B, et al. A combo system consisting of simultaneous persulfate recirculation and alternating current electrical resistance heating for the implementation of heat activated persulfate ISCO[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 385: 123803. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123803 [11] WANG J G, ZHAN X H, ZHOU L X, et al. Biological indicators capable of assessing thermal treatment efficiency of hydrocarbon mixture-contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 80(8): 837-844. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.06.009 [12] KINGSTON J, DAHLEN P R, JOHNSON P C. 'Assessment of Ground Water Quality Improvements and Mass Discharge Reductions at Five In Situ Electrical Resistance Heating Remediation Sites'[J]. Ground Water Monitoring, 2014, 34(1): 27-29. doi: 10.1111/gwmr.12043 [13] HAN Z Y, JIAO W T, TIAN Y, et al. Lab-scale removal of PAHs in contaminated soil using electrical resistance heating: Removal efficiency and alteration of soil properties[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 239: 124496. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124496 [14] FALCIGLIA P P, SCANDURA P, VAGLIASINDI F G A. Modelling of in situ microwave heating of hydrocarbon-polluted soils: Influence of soil properties and operating conditions on electric field variation and temperature profiles[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 174: 91-99. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.06.005 [15] 谢炳坤, 姜祖明, 曾俊, 等. 多环芳烃类污染场地应用原位电热脱附技术的能效分析[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(8): 173-178+187. [16] HAN Z Y, LI S H, YUE Y, et al. Enhancing remediation of PAH-contaminated soil through coupling electrical resistance heating using Na2S2O8[J]. Environmental Research, 2020: 110457. [17] 田垚, 杨永刚, 韩自玉, 等. 电阻加热条件优化及其对污染土壤中苯并(a)芘的去除[J]. 环境工程学报, 2019, 13(10): 2336-2346. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201905176 [18] FU H, HUANG. Effects of soil particle size and organic matter content on thermal desorption of polybrominated diphenyl ether[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2013, 7(7): 2769-2774. [19] 李晓雅, 朱玲, 王春雨, 等. 响应曲面优化烃类污染土壤热强化SVE修复工艺[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(3): 914-922. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201708151 [20] TASSELLI S, GUZZELLA L. Polycyclic musk fragrances (PMFs) in wastewater and activated sludge: analytical protocol and application to a real case study[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(25): 30977-30986. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06767-7 [21] 葛松, 孟宪荣, 许伟, 等. 原位电阻热脱附土壤升温机制及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(8): 3822-3828. [22] 张辉, 陈太聪. NAPLs污染土壤电阻率影响因素研究[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2017, 43(2): 5-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2017.02.002 [23] 康绍果, 李书鹏, 范云. 污染地块原位加热处理技术研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(7): 2621-2631. [24] 冉雨灵, 罗启仕, 赵秀红, 等. 基于共沸共溶原理脱除污染土壤中1, 2-二氯乙烷[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(2): 639-644. [25] MUNHOLLAND J L, MUMFORD K G, KUEPER B H. Factors affecting gas migration and contaminant redistribution in heterogeneous porous media subject to electrical resistance heating[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2016, 184: 14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2015.10.011 [26] 孟宪荣, 葛松, 许伟, 等. 原位电阻热脱附修复氯代烃污染土壤[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(2): 669-676. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202009077 [27] 贺晓珍, 周友亚, 汪莉, 等. 土壤气相抽提法去除红壤中挥发性有机污染物的影响因素研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2008(5): 679-683. [28] NOUVEAU M, GRANDJEAN G, LEROY P, et al. Electrical and thermal behavior of unsaturated soils: experimental results[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2016, 128: 115-122. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2016.03.019 [29] 于天, 陈春红, 徐成华, 等. 基于碳数分段法的石油烃污染土壤异位热脱附工艺的优化[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(6): 1988-1999. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202011147 [30] ADEYINKA G C, MOODLEY B. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on partitioning of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) between aqueous solution and modeled individual soil particle grain sizes[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 76: 100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.04.003 [31] 桑义敏, 艾贤军, 马绍芳, 等. 基于超声波-微波耦合效应的石油烃类污染土壤的热脱附规律与参数优化[J]. ]环境工程学报, 2019, 13(10): 2311-2319. -






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: