-
随着我国城市化和工业化的迅速发展,大量的含磷废水未经有效处理排入水环境中,导致河道和湖泊的水质急剧恶化,出现水体黑臭现象[1]。过量的磷是引起水体富营养化的主要原因[2],水体富营养化会导致藻类过度生长,降低水质,严重危害水生态系统及人类健康[3]。因此,开发经济高效的除磷技术成为研究的重点。目前,污水除磷技术主要包括化学沉淀法、生物处理法、膜处理法、吸附法等。与其他方法相比,吸附法具有操作简单,经济效益好,灵活性高等优点,使其在水处理中得到广泛研究和应用[4]。
近年来,层状双金属氢氧化物(layered double hydroxides, LDH)作为一种新兴材料得到研究人员的广泛关注,其特殊的层状结构相比其他常规吸附剂具有更好的阴离子交换能力及更高的吸附容量,同时其具有制备简单、成本廉价的优点[5]。但在以前的报道中,所制备LDH大多为
CO2−3 -LDH,而对于Cl−-LDH吸附磷的研究较少。由于CO2−3 的离子交换性能要强于H2PO−4 [6],CO2−3 不易与磷酸根进行离子交换,限制了其对磷的吸附性能。例如,EDAÑOL等[7]采用共沉淀法合成Mg-Al-CO2−3 LDH,其对磷的吸附量仅为23.792 mg·L−1。由于Mg、Al元素在地壳中丰度高,采用Mg、Al作为原料可减少成本,相对其他金属,对环境也更友好[8]。因此,本研究以Cl-作为层间阴离子以及Mg、Al为金属前体,通过成核/晶化隔离法制备了Mg-Al-Cl− LDH,通过表征手段对吸附剂吸附前后的结构形貌进行分析,且考察了其对磷的吸附性能,探究了可能的吸附机理,以期为Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附除磷提供参考。
-
主要试剂:抗坏血酸、酒石酸锑钾、磷酸二氢钾、钼酸铵、盐酸、氢氧化钠、六水合氯化镁、六水合氯化铝,均为分析纯,均购置于西陇化工集团有限公司。
主要仪器:Bruke D8X 射线衍射仪、Nicolet 6700傅里叶变换红外光谱仪、Zeiss Gemini 300扫描电子显微镜、UV-1801紫外可见分光光度计、SHA-B恒温振荡器(上海力辰邦西仪器科技有限公司)。
-
采用成核/晶化隔离法制备,即成核和晶化分开,以去离子水为溶剂。首先,按照Mg:Al摩尔比为2∶1称取一定量的MgCl2·6H2O与AlCl3·6H2O溶于100 mL去离子水中,超声处理15 min使其充分溶解混合,标记为溶液A。同时,配置一定量的3 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液作为沉淀剂,标记为溶液B。在60 ℃下同时将A、B 2种溶液滴入盛有50 mL去离子水的烧杯中并伴随高转速搅拌,整个体系pH维持在10左右。随后,将浆液置入聚四氟乙烯内衬反应釜中,在150 ℃下晶化12 h,将晶化产物离心,再洗涤至上清液pH为中性,将所得白色膏体置于鼓风干燥箱中以80 ℃恒温干燥至恒重后研磨过100目筛,得到白色粉末即为Mg-Al-Cl− LDH。
-
通过静态吸附实验研究Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附,考察溶液pH、吸附剂投加量、共存离子等因素对磷的吸附效果影响。取50 mL已知浓度的KH2PO4溶液于50 mL具塞三角瓶中,用0.1 mol·L−1的NaOH和HCl调节至所需pH,投加一定量的Mg-Al-Cl− LDH,置于25 ℃、180 r·min−1恒温水浴振荡箱中振荡一定时间后取上清液经0.45 μm滤膜过滤,根据(GB 11893-1989)钼酸铵分光光度法测定滤液中的剩余磷质量浓度。按照式(1)和式(2)计算磷吸附量和去除率。
式中:qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;ƞ为磷去除率,%;C0为吸附前溶液中磷的初始质量浓度,mg·L−1;Ce为吸附后溶液中的剩余磷质量浓度,mg·L−1;V为溶液体积,L;m为吸附剂投加量,g。
1)吸附动力学实验。分别在1、3、5、10、15、30、45、60、75、90、120、150 min取样测定磷质量浓度,计算吸附量,pH为5,磷的初始质量浓度为50 mg·L−1,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH投加量为1 g·L−1。采用准一级(式(3))、准二级(式(4))和颗粒内扩散(式(5))动力学模型对数据进行拟合。
式中:qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;qt为时间为t时的吸附量,mg·g−1;t为吸附时间,min;k1为准一级动力学方程常数,min−1;k2为准一级动力学方程常数,g·(mg·min)−1;ki为
颗粒内扩散速率常数,g·(mg·min0.5)−1;C为与边界层厚度有关的参数。 2)吸附等温线实验。分别在磷质量浓度为20、30、50、100、150、200、250 mg·L−1的条件下测定吸附后的剩余磷质量浓度,计算吸附量,pH为5,磷的初始质量浓度为50 mg·L−1,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH投加量为1 g·L−1,吸附时间为150 min。采用Langmuir(式(6))、Freundlich(式(7))和Sips(式(8))吸附等温模型对数据进行拟合。
式中:qe、qm分别为平衡吸附量、吸附剂的最大吸附量,mg·g−1;KL为Langmuir 吸附常数,L·mg−1;Ce为溶液剩余磷质量浓度,mg·L−1;KF为Freundlich 等温吸附常数,(mg·g−1)·(mg·L−1)−n;n为吸附常数;Ks为Sips吸附参数,L·mg−1;N为非均一系数。
3) pH对吸附的影响。调节溶液pH为3~11,Mg-Al-Cl- LDH投加量为1 g·L−1,磷的初始质量浓度为50 mg·L−1,吸附时间为150 min,吸附后测定剩余磷质量浓度,计算吸附量。
4)吸附剂投加量对吸附的影响。改变Mg-Al-Cl− LDH投加量,使其投加量分别为0.4、0.8、1、1.2、1.6、2 g·L−1,pH为5,磷的初始质量浓度为50 mg·L−1,吸附时间为150 min,吸附后测定剩余磷质量浓度,计算吸附量。
5)共存离子对吸附的影响。向溶液中分别加入质量浓度为50 mg·L−1的
CO2−3 、SO2−4 、NO−3 、Cl−,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH投加量为1 g·L−1,磷的初始质量浓度为50 mg·L−1,吸附时间为150 min,吸附后测定剩余磷质量浓度,计算吸附量。 -
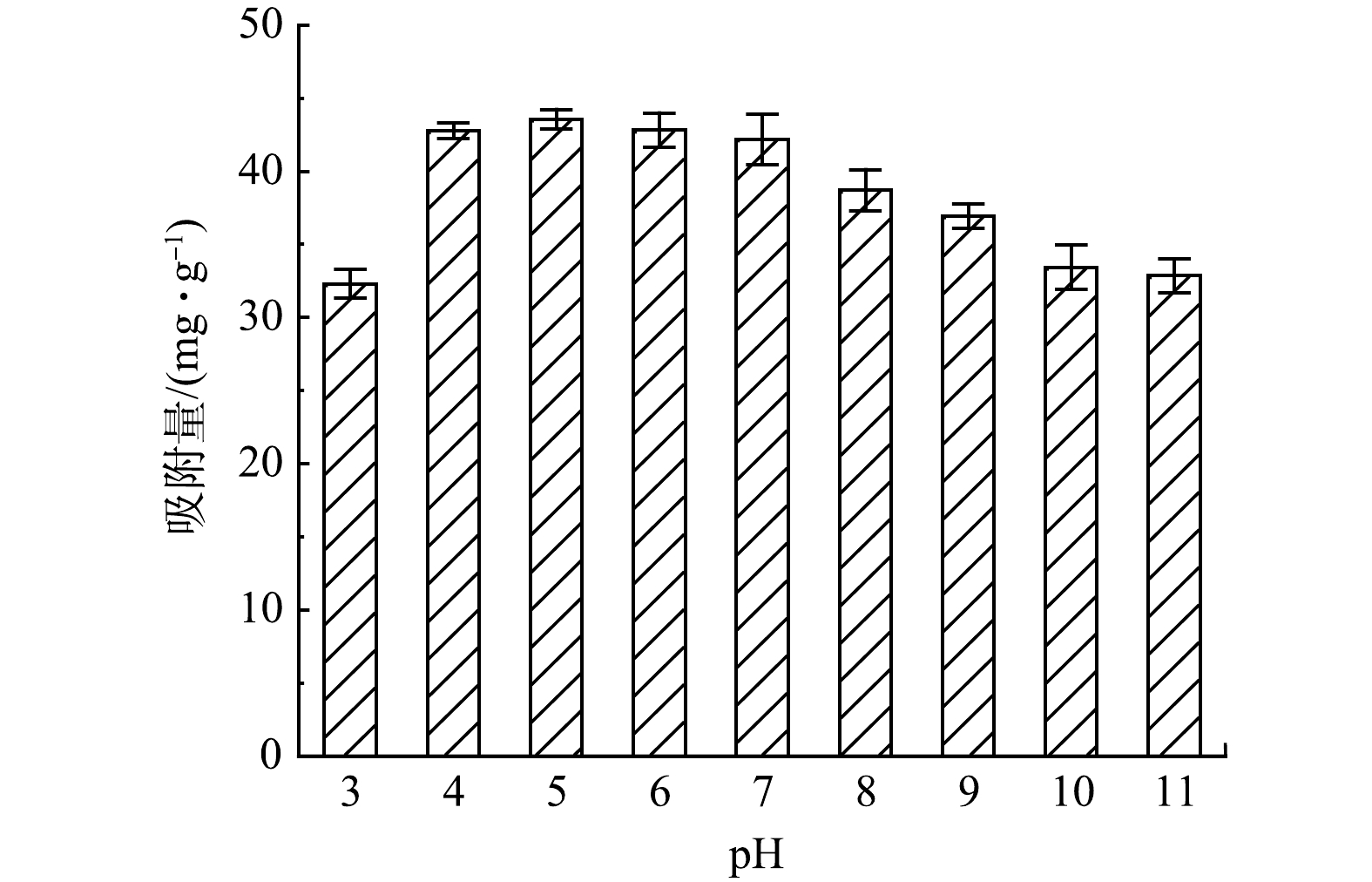
1) pH对吸附性能的影响。不同pH下,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附效果如图1所示。当体系pH在3~10时,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附量表现为先升高后降低,在pH为4~7的条件下的吸附效果最佳。由于LDH的等电点普遍较高,因此,根据吸附材料的零点电荷性质,在较低pH范围内,pH<pHpzc,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH层板上的M—OH发生质子化得到带正电荷的M—OH+,可通过静电引力吸附
H2PO−4 与HPO2−4 。磷在不同pH中的存在形式也不同(式(9))[9]。式中:pK1=2.12,pK2=7.21,pK3=12.67。
当pH为3~11时,磷酸盐主要以
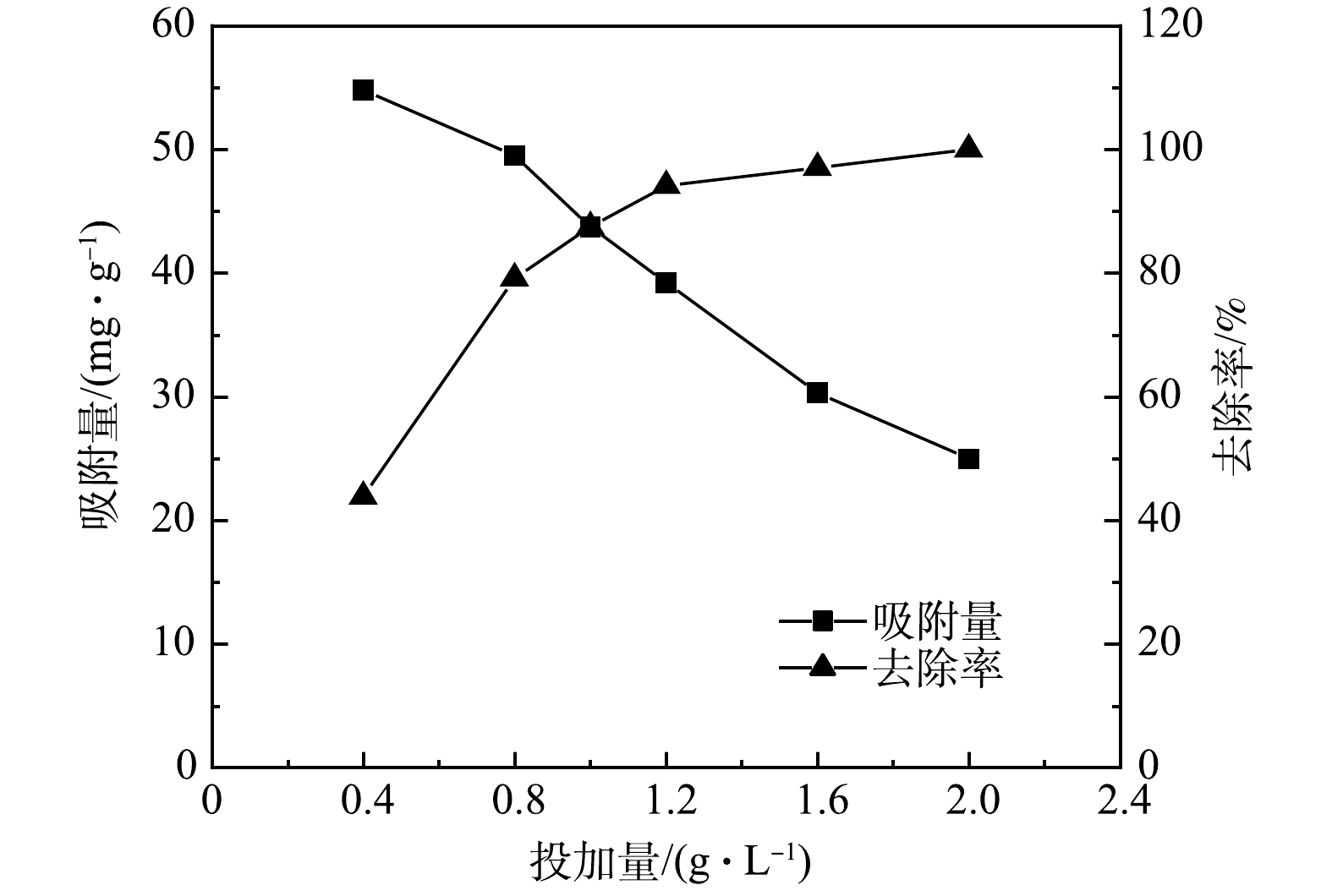
H2PO−4 和HPO2−4 的形式存在;随着pH的逐渐增加,H2PO−4 所占比例先升高后降低,随后逐渐转化为HPO2−4 。由于H2PO−4 的吸附自由能低于HPO2−4 ,H2PO−4 比HPO2−4 更容易被吸附[10],且HPO2−4 与LDH形成络合相比H2PO−4 需要占据更多的吸附位点,形成的络合物覆盖了吸附位点也可能导致吸附效率的降低[11]。因此,当pH>7之后,H2PO−4 逐渐转化为HPO2−4 ,吸附量开始下降。随着pH的继续增大,当pH>pHpzc后,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH表面呈现电负性,静电斥力导致磷酸盐离子难以吸附到其表面,同时溶液中的OH−含量也逐渐增加,会与磷酸盐竞争吸附位点,因此吸附量持续下降。然而,在碱性条件下,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH依旧拥有一定的吸附量,说明静电吸附作用只是其一,吸附过程还存在其他相互作用。在pH为3时吸附量下降,可能是由于Mg-Al-Cl− LDH在较酸性的条件下溶解导致结构坍塌[11]。2)吸附剂投加量对吸附性能的影响。Mg-Al-Cl− LDH投加量对吸附效果的影响如图2所示。当投加量由0.4 g·L−1增加到1.2 g·L−1时,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的去除率由43.84%增加到94.14%;增加到2 g·L−1时,去除率到达了100%。这说明Mg-Al-Cl− LDH是一种优良的磷吸附剂。然而,当吸附剂投加量增加到2 g·L−1时,吸附量由54.79 mg·L−1下降到了25 mg·L−1。这是由于:当水中磷质量浓度一定时,投加量的增加相应所提供的吸附位点越多,去除率也越高,但同时也会导致吸附能力过剩,吸附剂并未达到饱和吸附,吸附位点的利用率降低;此外,过高的投加量也会导致吸附剂的浪费,增加不必要的成本。另外,随着Mg-Al-Cl− LDH的投加量由1.2 g·L−1增加到2 g·L−1,磷的去除率的上升趋势并不明显,但磷的吸附量却持续下降。因此,为了同时获得合适磷的吸附量及去除率,后续实验的Mg-Al-Cl− LDH投加量采用1 g·L−1。
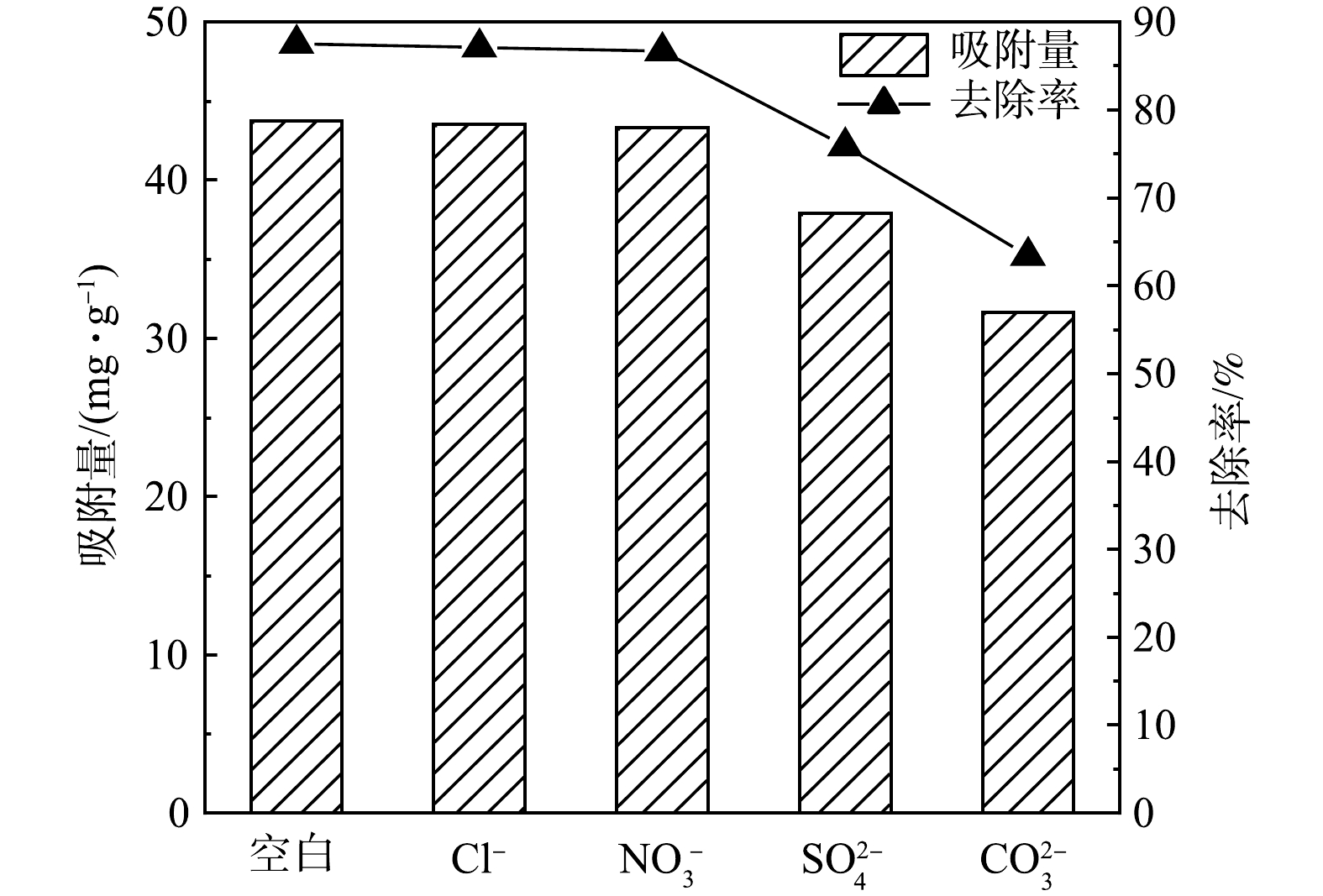
3)共存离子对吸附性能的影响。在实际废水中一般会存在多种阴离子,这些共存阴离子可能会与磷酸盐离子形成竞争吸附,从而影响吸附剂的吸附效果。图3显示了几种常见阴离子存在的情况下,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附量及去除率变化情况。可以看出,共存离子干扰强弱的顺序为
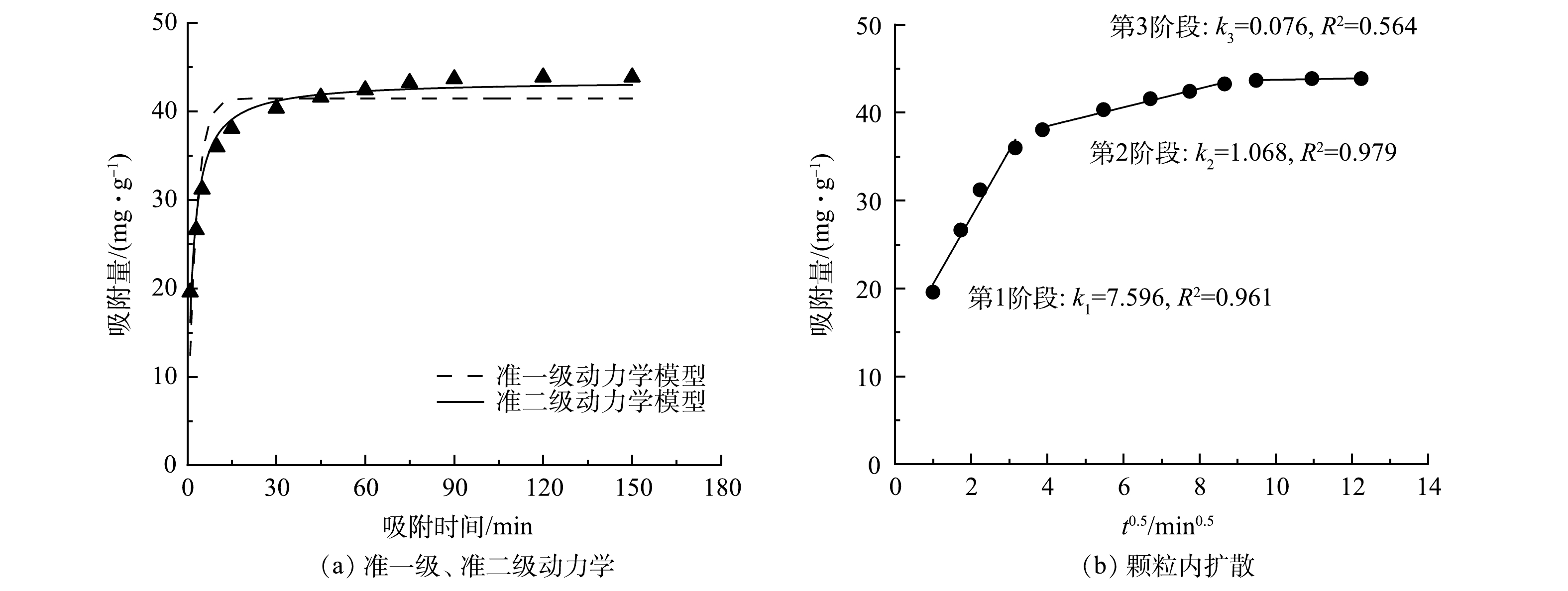
CO2−3 >SO2−4 >NO−3 >Cl−。Cl−和NO−3 对吸附几乎没有影响。SO2−4 和CO2−3 对吸附有较大影响,主要是由于SO2−4 和CO2−3 具有更高的负价态,更容易通过离子交换进入层间[12],且SO2−4 和CO2−3 会通过静电吸附和络合作用在Mg-Al-Cl− LDH表面竞争吸附位点[13]。此外,CO2−3 的存在也会使溶液pH升高,从而导致吸附量下降。在CO2−3 的影响下,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的去除率为63%,说明其对磷酸盐具有一定的选择性。4)吸附动力学分析。本实验使用准一级动力学、准二级动力学和颗粒内扩散模型动力学对数据进行了拟合,结果如图4所示,动力学相关参数见表1。由图4(a)可知,吸附反应在前15 min非常迅速,这是因为在反应初始阶段吸附剂含有大量的吸附位点。随着时间推移,吸附剂上可提供的吸附位点逐渐较少,吸附速率逐渐平缓,在90 min左右基本达到平衡,此时饱和吸附容量为43.85 mg·L−1。由表1可知,准二级动力学模型的拟合度(R2>0.966)高于准一级动力学模型的拟合度(R2>0.819),说明Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附过程更符合准二级动力学模型,且准二级动力学拟合所得吸附容量与实验所得值接近。由此可推断Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附主要由化学吸附所控制[14]。
颗粒内扩散模型拟合见图4(b)。由表1可知,颗粒内扩散相关参数k1>k2>k3,说明吸附的过程有3个限制步骤。其中k1较大,说明第1阶段反应速率快,在Mg-Al-Cl− LDH表面上扩散的速率限制是由静电吸引引起的[15];第2阶段为磷酸盐离子通过孔隙扩散进入Mg-Al-Cl− LDH内表面,速率缓慢,受颗粒内扩散限制;第3阶段为吸附平衡阶段,吸附位点饱和,基本达到吸附平衡。直线并未经过原点,说明颗粒内扩散并不是唯一控制吸附反应速率的因素[16]。
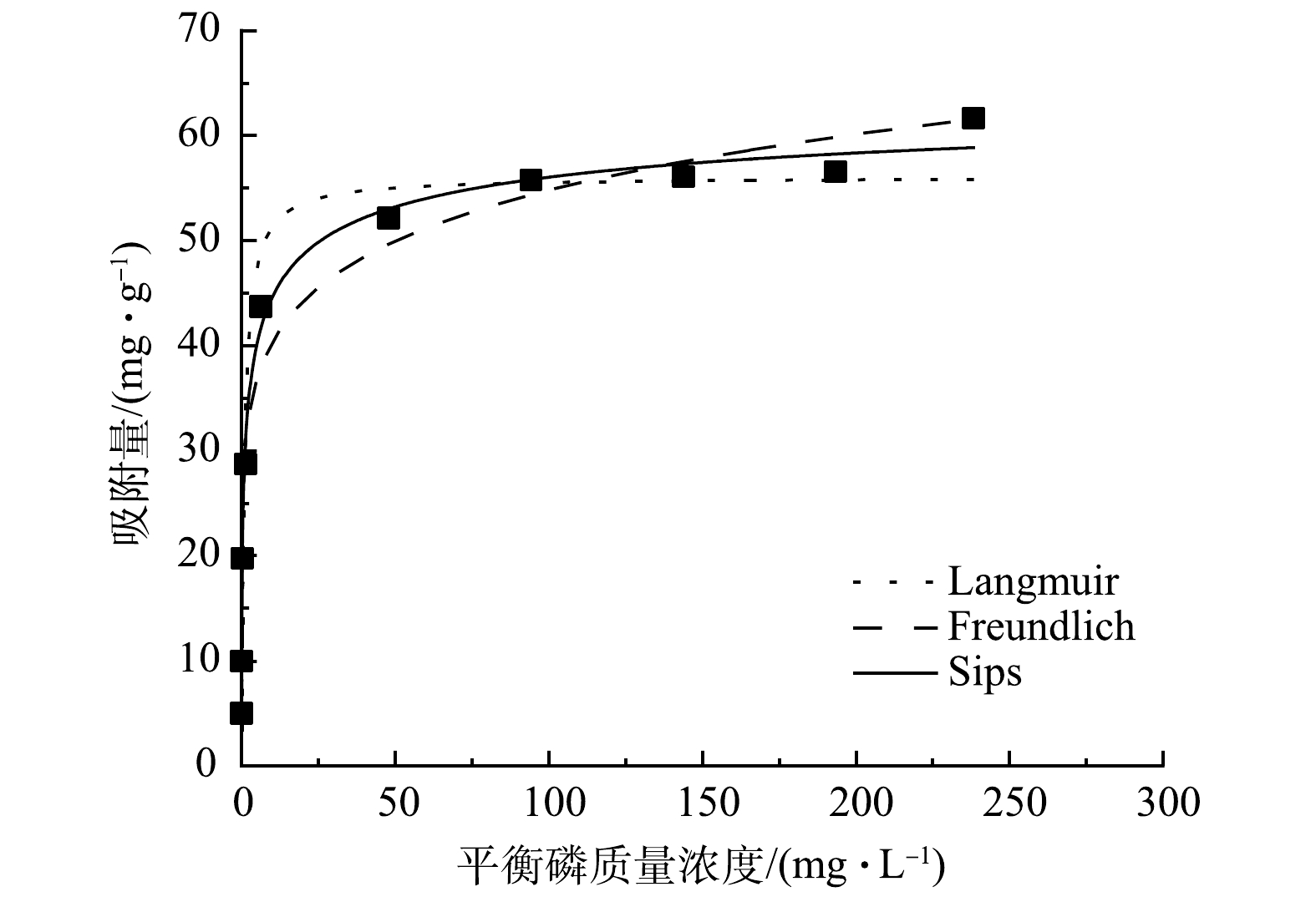
5)吸附等温线。图5为Mg-Al-Cl− LDH的吸附等温线拟合曲线,拟合参数见表2。随着溶液中磷质量浓度增加,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附量也随之增加。这是因为:当溶液中磷酸盐质量浓度增加时,浓度梯度具有更强的驱动力来克服固液之间的传质阻力,使磷酸盐与Mg-Al-Cl− LDH之间的碰撞概率增加。当Mg-Al-Cl− LDH的吸附位点逐渐被占据达到饱和后,吸附量不再变化,达到吸附平衡。由表2可知,吸附等温线的拟合程度为Sips>Freundlich>Langmuir。这说明Sips模型能更好的描述Mg-Al-Cl− LDH的等温吸附行为,即该体系的吸附过程在磷质量浓度低时为Freundlich模型的非均匀多分子层吸附,在磷质量浓度高时为Langmuir模型的单层吸附[17]。同时,Langmuir模型拟合的最大吸附量也与实验所得吸附量接近。Freundlich模型中1/n在0.1~0.5,表明Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附易于进行[18]。表3列举了不同吸附剂对磷的最大吸附量。可以看出,本研究的Mg-Al-Cl− LDH具有相对较高的吸附容量,作为磷吸附剂有很强的竞争力。
-
Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷前后的SEM-EDS图如图6所示。图6(a)为Mg-Al-Cl− LDH的SEM图。可以看出,通过成核/晶化隔离法制备的Mg-Al-Cl− LDH为规则的六边形层片结构,晶体大小均一,表面光滑,结晶度较好,而LAFI等[24]单纯通过共沉淀法制备的Mg-Al-Cl− LDH没有达到此效果。图6(b)为Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷后的SEM图。由图6(b)可知,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷后依旧保持层片结构但表面光滑度降低。这可能是因磷被吸附在Mg-Al-Cl− LDH表面所造成的。图6(c)和图6(d)分别为Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷前后的EDS图。由图6(c)和图6(d)可知,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷后,图谱中出现磷元素,可见磷被成功吸附在Mg-Al-Cl− LDH上,且吸附后Cl的峰强度降低,Cl含量减少,说明氯离子通过离子交换被磷酸盐离子交换出层间。
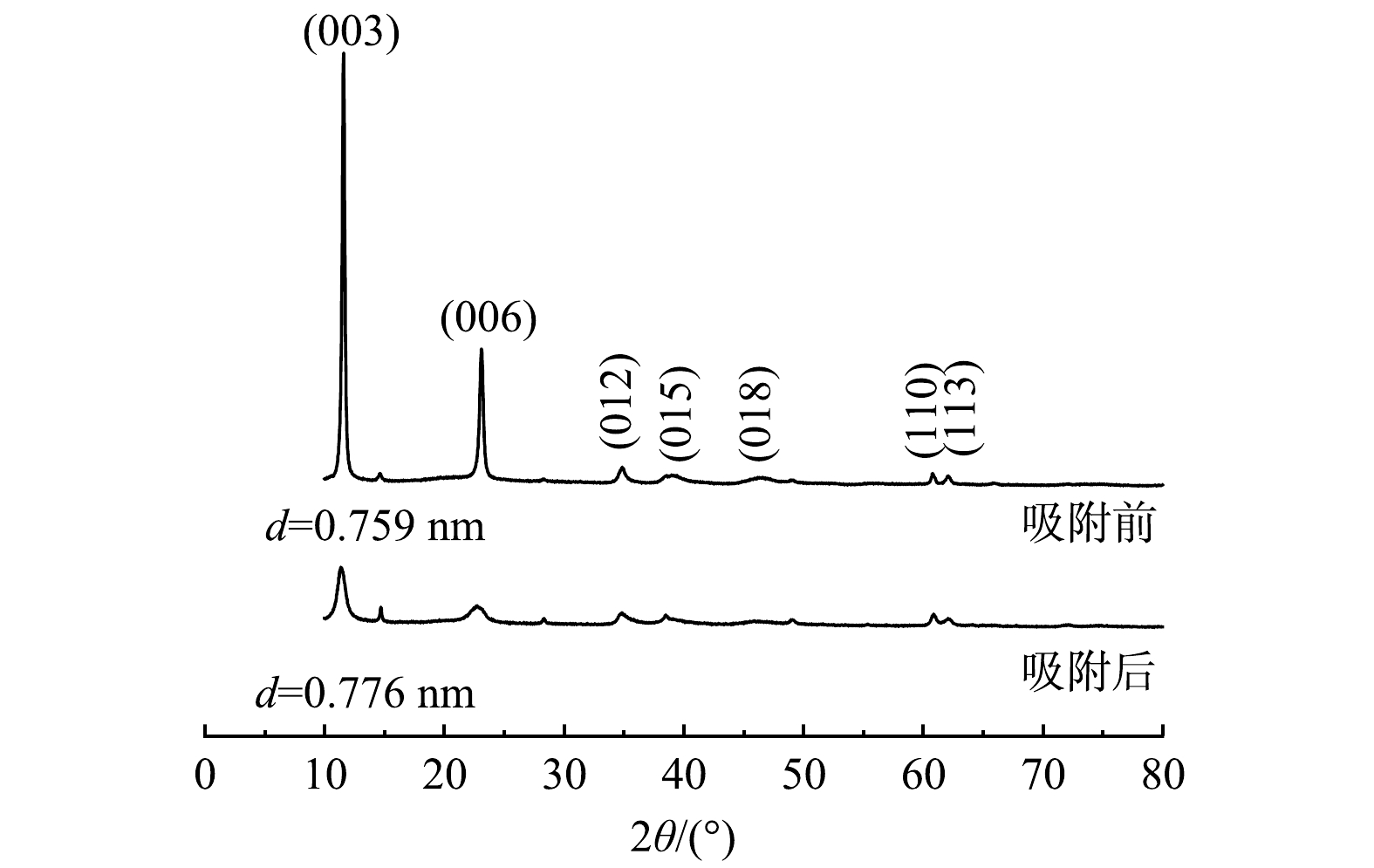
图7为Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷前后的XRD图。在衍射角2θ值约为11.3°、22.8°、34.7°、39.1°、46.3°、60.5°、61.8°处分别对应的衍射晶面(003)、(006)、(012)、(015)、(018)、(110)、(113),表现出典型的LDH结构特征,且衍射峰强而尖锐,没有出现其他杂相峰,说明其纯度和结晶度较高[25]。在Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷后,结晶度降低,但各个特征衍射峰依然存在,说明其依旧保持层状结构。通过Jade 6.0软件分析得到,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷后的层间距发生变化,由0.759 nm增加到0.776 nm,说明层间发生了离子交换,磷酸盐离子的插入扩大了层间距。d为0.776 nm也与磷酸盐作为层间阴离子所制备的LDH层间距接近[26]。
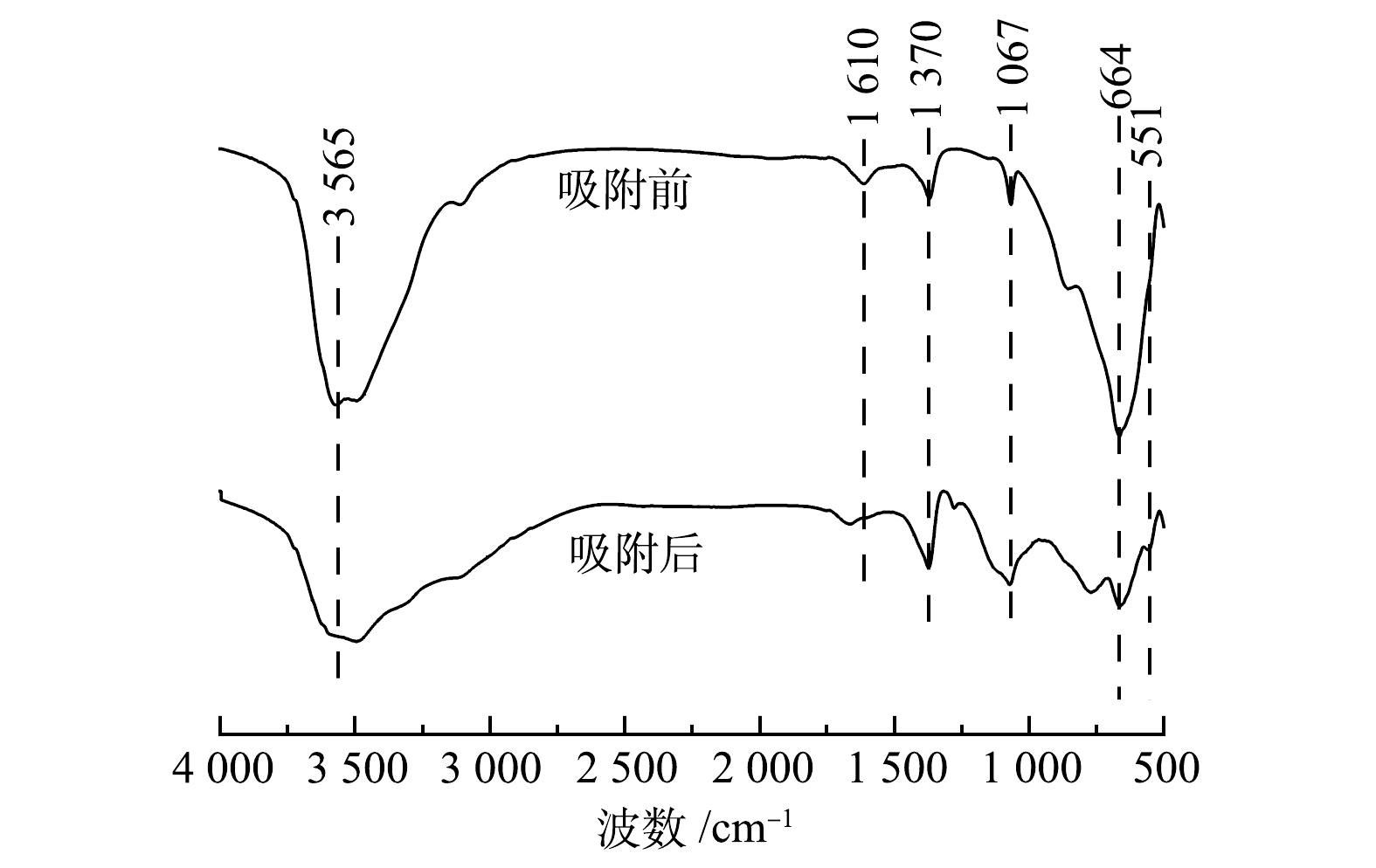
Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷前后的FT-IR如图8所示。图8中3 565 cm−1处较大的吸收峰是金属氢氧化物层板上—OH基团的伸缩振动,1 610 cm−1处的吸收峰为—OH的弯曲振动,表明层间结晶水的存在[27]。1 370 cm−1处为
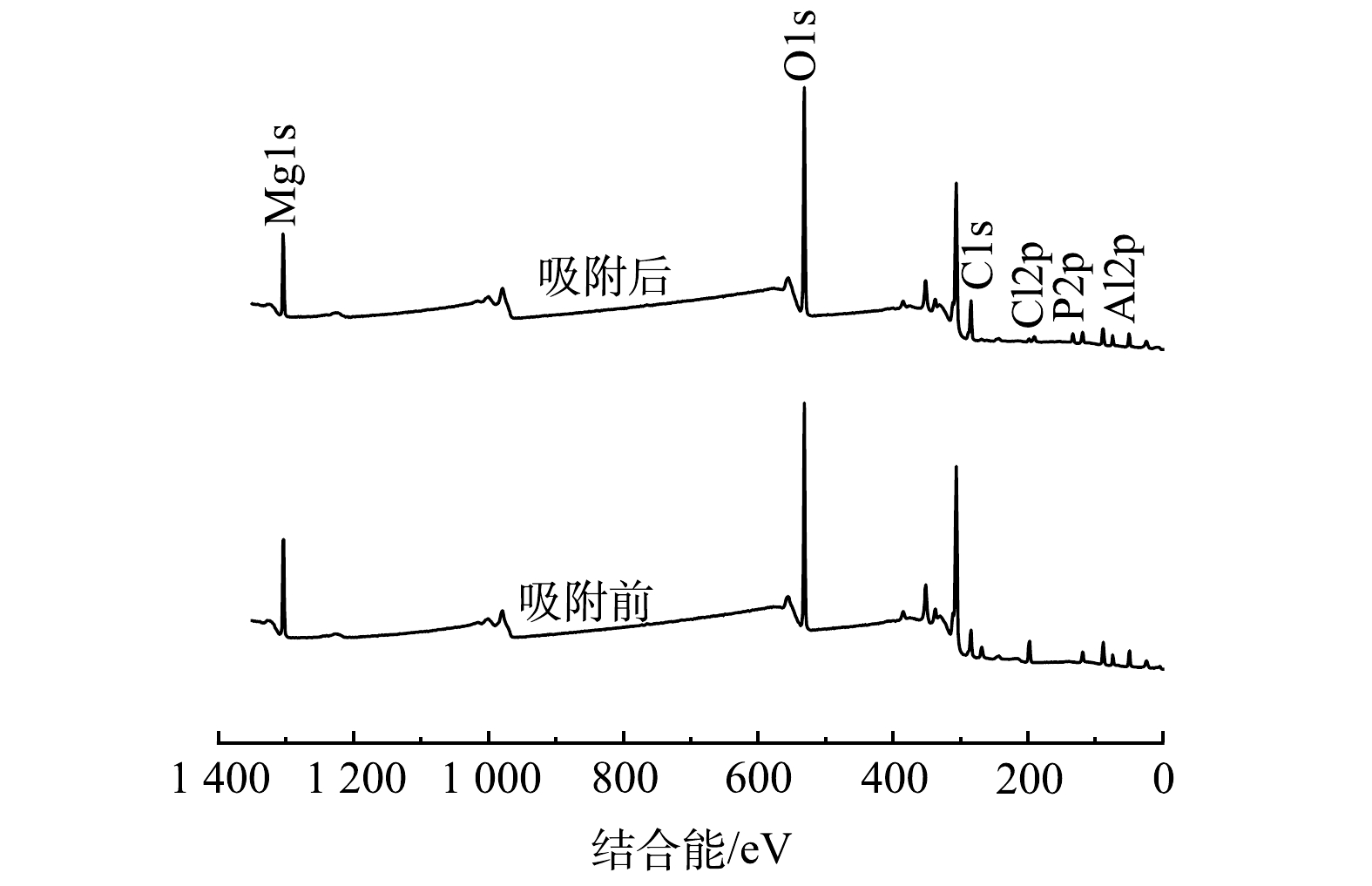
CO2−3 中C—O的不对称伸缩振动峰,可能来自制备过程中去离子水或空气中的CO2。1 067 cm−1处属于P—O键的不对称振动峰[28],说明磷吸附在了Mg-Al-Cl− LDH上。664 cm−1处为M—O(M为Mg,Al)的拉伸振动峰[29],并且在吸附过后峰强度降低,说明M—O参与了吸附反应。此外,—OH基团对应的吸收峰发生了偏移,551 cm−1处的振动带归因于O—P—O的弯曲振动[30]。这进一步说明了磷酸盐与Mg-Al-Cl− LDH层板上的—OH通过配体交换形成了络合物。图9为Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷前后的XPS全谱图。由图9可以看出,在Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷后,出现了一个新的P2p峰,同时Cl2p峰在吸附后几乎消失,因而进一步证实了磷酸盐离子与氯离子之间的离子交换行为。
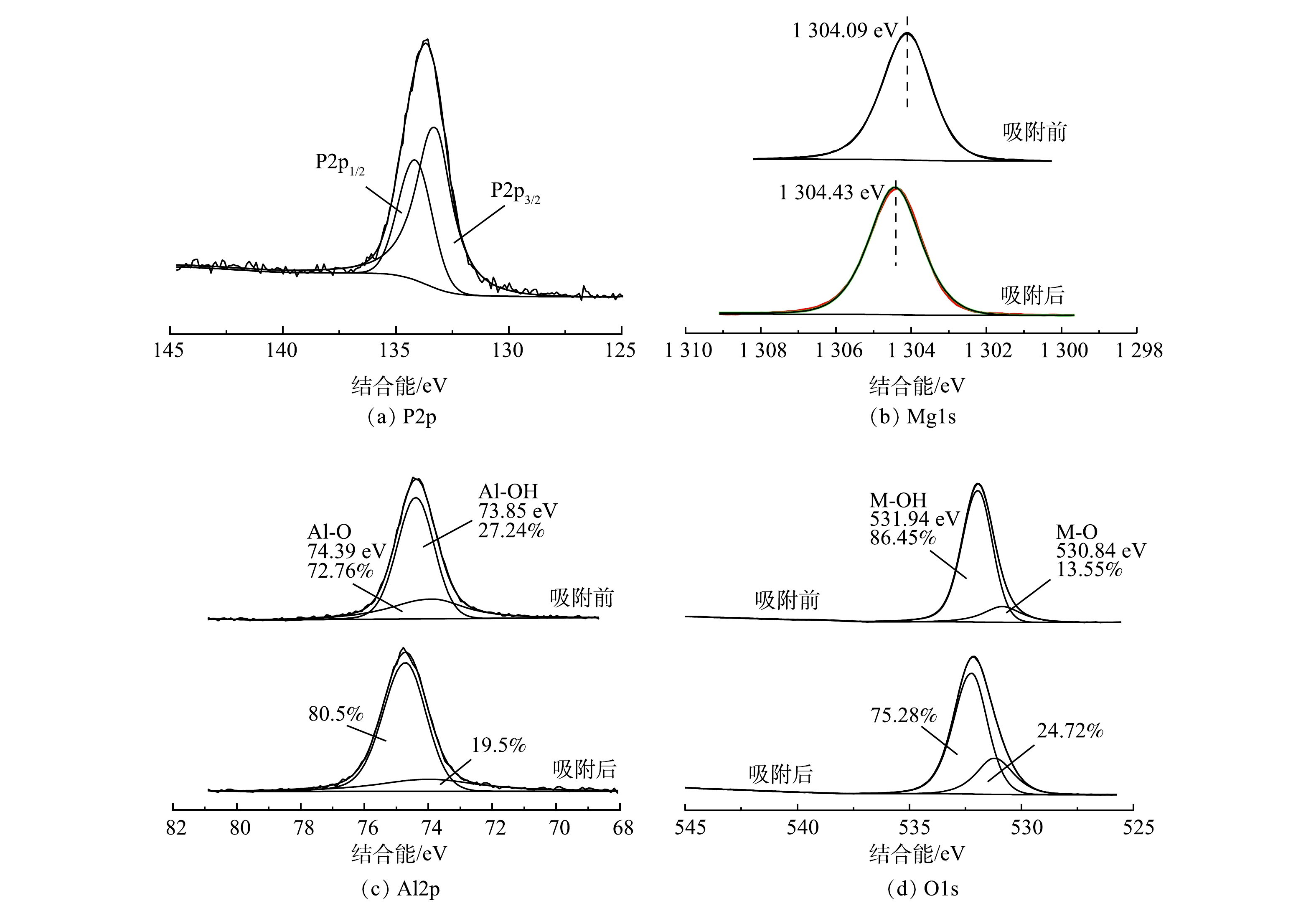
图10显示了O1s、P2p、Al2p、Mg1s的XPS谱图。图10(a)为P2p图,P2p解卷成2个重叠的峰,分别归因于磷酸盐的P2p1/2和P2p3/2,对应以
H2PO−4 与HPO2−4 形式存在的磷酸盐。图10(b)为Mg1s图,在吸附后Mg1s由1 304.09 eV向较高能级偏移了0.34 eV。图10(c)为Al2p图,Al2p1/2和Al2p3/2的峰面积比发生了明显的变化,结合能为73.85 eV对应的Al—OH峰面积比由27.24%降至19.5%,说明Mg-Al-Cl− LDH表面的羟基官能团通过配体交换形成Mg(Al)—O—P络合[31]。此外,图10(d)中O1s在结合能531.94 eV处对应的M—OH(M为Mg,Al)峰在吸附后峰面积比由86.45%降至75.28%,M—O的比例由13.55%升高至24.72%,也表明了Mg-Al-Cl− LDH上的含氧官能团对磷酸盐具有很强的亲和力[32],其表面的—OH参与了磷酸盐的吸附过程形成了M—O—P络合[33]。以上对吸附剂的表征分析结果表明,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH吸附磷酸盐的机理为层间阴离子交换(式(10))、配体交换形成单齿或双齿络合(式(11)和式(12))以及在pH较低时(pH<pHpzc)存在静电吸附(式(13))。
-
1) Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附效果优于前人所研究的Mg-Al-
CO2−3 LDH。pH会影响Mg-Al-Cl− LDH的吸附性能,在pH为4~7时吸附效果最佳;随着pH增大,吸附量会下降。在50 mg·L−1磷的质量浓度下,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的去除率随投加量增加持续上升,当其投加量为2 g·L−1时,水中磷可全部去除。在质量浓度为50 mg·L−1的CO2−3 的影响下,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的去除率在60%以上,表现出一定的选择性。2) Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附在前15 min反应迅速,在90 min时可达到吸附平衡,符合准二级动力学模型,吸附过程主要为化学吸附,颗粒内扩散并不是唯一控制吸附反应速率的因素。Sips模型能更好的描述吸附过程,对磷的理论最大吸附量可达62.46 mg·g−1。
3)通过表征分析发现,成核/晶化隔离法制备的Mg-Al-Cl- LDH拥有规整的六边形层片结构,具备典型的LDH结构,且晶体大小均一,结晶度较好,在吸附磷后依旧保持层状结构。Mg-Al-Cl- LDH对磷酸盐的吸附机理主要为静电吸引、离子交换、配体交换过程。
Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附性能及其机理
Adsorption performance and mechanism of Mg-Al-Cl− LDH on phosphate
-
摘要: 通过成核/晶化隔离法制备了氯离子型镁铝层状双金属氢氧化物(Mg-Al-Cl− LDH),并用于磷酸盐的吸附;借助扫描电镜(SEM)、X射线衍射仪(XRD)、傅里叶红外光谱仪(FT-IR)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)进行了表征,并探究其吸附磷酸盐的机理。结果表明:当pH为4~7时,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附效果较好,而在碱性条件下吸附量会下降;磷质量浓度为50 mg·L−1,当pH为5时,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH投加量为2 g·L−1时,磷去除率可达到100%;共存离子
CO2−3 会对吸附产生一定影响,当CO2−3 质量浓度为50 mg·L−1时,磷去除率由87%降低到63%。Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附过程在前15 min迅速,90 min时达到平衡,符合准二级动力学和Sips吸附等温模型,说明主要吸附过程以化学吸附为主,理论最大吸附量为62.46 mg·g−1。表征结果表明,Mg-Al-Cl− LDH为典型的六边形层片结构,吸附后依旧保持该结构。Mg-Al-Cl− LDH对磷的吸附机理主要为静电吸引、层间阴离子交换、配体交换过程。Abstract: The chloride ion type magnesium aluminum layered double hydroxide (Mg-Al-Cl− LDH) was prepared by nucleation and crystallization isolation method, and used to absorb phosphate. Scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffractometer (XRD), Fourier Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) were employed to characterize the fresh and P absorbed Mg-Al-Cl− LDH and identify the corresponding adsorption mechanism. The results show that Mg-Al-Cl− LDH had a good adsorption performance towards phosphate at pH 4~7, whereas the adsorption capacity decreased under alkaline conditions. At the initial phosphate concentration of 50 mg·L−1, pH 5 and Mg-Al-Cl− LDH dosage of 2 g·L−1, the phosphate removal rate could reach 100%. The coexisting anion ofCO2−3 had a certain influence on the adsorption, at its concentration of 50 mg·L−1, the phosphate removal rate decreased from 87% to 63%. The phosphate adsorption process on Mg-Al-Cl− LDH was rapid in the first 15 min, then reached equilibrium in 90 min, which conformed to the pesudo-second-order kinetics and the Sips adsorption isotherm model. This indicated that the adsorption process was dominated by chemical adsorption with the maximum theoretical adsorption capacity of 62.46 mg·g−1. The characterization results showed that Mg-Al-Cl− LDH was a typical hexagonal layered structure and still maintained it after adsorption. The phosphate adsorption mechanism on Mg-Al-Cl−LDH was mainly electrostatic attraction, interlayer anion exchange and ligand exchange.-
Key words:
- layered double hydroxide /
- phosphate /
- adsorption /
- influencing factors /
- adsorption mechanism
-
表 1 吸附动力学拟合参数
Table 1. Adsorption kinetics fitting parameters
准一级动力学 准二级动力学 颗粒内扩散 qe(cal)/(mg·g−1) k1/min−1 R2 qe(cal)/(mg·g−1) k2/(g·(mg·min)−1) R2 k1/(g·(mg·min0.5)−1) R12 k2/(g·(mg·min0.5)−1) R22 k3/(g·mg·min0.5)−1) R32 41.476 0.357 0.819 43.460 0.014 0.966 7.596 0.961 1.068 0.979 0.076 0.564 表 2 吸附等温线拟合参数
Table 2. Adsorption isotherm fitting parameters
温度/K Langmuir Freundlich Sips qm /(mg·g−1) KL /(L·mg−1) R2 1/n KF R2 qm /(mg·g−1) Ks /(L·mg−1) N R2 298 54.524 1.194 0.890 0.134 29.563 0.929 62.460 0.876 0.470 0.989 -
[1] 赵鹏, 苏子龙, 何剑伟, 等. DSB+CPB复合改性膨润土对磷酸盐的吸附[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(4): 906-916. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201909035 [2] 王乐阳, 许骐, 周琴, 等. 镧铝/壳聚糖复合小球对水中磷的吸附及机理[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(9): 2490-2501. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201803229 [3] NAKARMI A, BOURDO S E, RUHL L, et al. Benign zinc oxide betaine-modified biochar nanocomposites for phosphate removal from aqueous solutions[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 272: 111048. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111048 [4] JUNG K, LEE S Y, CHOI J, et al. Synthesis of Mg-Al layered double hydroxides-functionalized hydrochar composite via an in situ one-pot hydrothermal method for arsenate and phosphate removal: Structural characterization and adsorption performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 129775. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129775 [5] SHARMA R, ARIZAGA G G C, SAINI A K, et al. Layered double hydroxide as multifunctional materials for environmental remediation: From chemical pollutants to microorganisms[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2021, 29: e319. [6] 吕维扬, 孙继安, 姚玉元, 等. 层状双金属氢氧化物的控制合成及其在水处理中的应用[J]. 化学进展, 2020, 32(12): 2049-2063. [7] EDAÑOL Y D G, POBLADOR J A O, TALUSAN T J E, et al. Co-precipitation synthesis of Mg-Al-CO3 layered double hydroxides and its adsorption kinetics with phosphate(V) ions[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 33: 1809-1813. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.059 [8] AHMED S, ASHIQ M N, LI D, et al. Recent progress on adsorption materials for phosphate removal[J]. Recent Patents on Nanotechnology, 2019, 13(1): 3-16. doi: 10.2174/1872210513666190306155245 [9] 张倩. 层状双金属氢氧化物除磷材料及氨基酸插层改性性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018. [10] TANG Q, SHI C, SHI W, et al. Preferable phosphate removal by nano-La(Ⅲ) hydroxides modified mesoporous rice husk biochars: Role of the host pore structure and point of zero charge[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 662: 511-520. [11] ZHOU H, TAN Y, YANG Y, et al. Application of FeMgMn layered double hydroxides for phosphate anions adsorptive removal from water[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2020, 200: 105903. [12] MIYATA S. Anion-exchange properties of hydrotalcite-like compounds[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1983, 31(4): 305-311. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.1983.0310409 [13] SAADAT S, RA EI E, TALEBBEYDOKHTI N. Enhanced removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions using a modified sludge derived biochar: Comparative study of various modifying cations and RSM based optimization of pyrolysis parameters[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 225: 75-83. [14] LEE S Y, CHOI J, SONG K G, et al. Adsorption and mechanistic study for phosphate removal by rice husk-derived biochar functionalized with Mg/Al-calcined layered double hydroxides via co-pyrolysis[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2019, 176: 107209. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107209 [15] 张兴枝. 类花状水滑石材料的制备及其对水体中磷的吸附再利用性能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2020. [16] ZHU N, YAN T, QIAO J, et al. Adsorption of arsenic, phosphorus and chromium by bismuth impregnated biochar: Adsorption mechanism and depleted adsorbent utilization[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 164: 32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.036 [17] 刘泽珺. 壳聚糖基半互穿网络水凝胶的制备及其对水中腐殖酸的吸附性能[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018. [18] ZHANG Z, YAN L, YU H, et al. Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution by vegetable biochar/layered double oxides: Fast removal and mechanistic studies[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 284: 65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.113 [19] LI X D, KUANG Y, CHEN J B, et al. Competitive adsorption of phosphate and dissolved organic carbon on lanthanum modified zeolite[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 574: 197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.04.050 [20] 万骏. 基于功能设计的水凝胶对水中磷酸盐去除研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2018. [21] 郑力. 氧化镁/果胶复合除磷剂的制备及其除磷机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017. [22] WANG Y, XIE X, CHEN X, et al. Biochar-loaded Ce3+-enriched ultra-fine ceria nanoparticles for phosphate adsorption[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 396: 122626. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122626 [23] ZOU Y, ZHANG R, WANG L, et al. Strong adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution by zirconium-loaded Ca-montmorillonite[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2020, 192: 105638. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105638 [24] LAFI R, CHARRADI K, DJEBBI M A, et al. Adsorption study of congo red dye from aqueous solution to Mg-Al-ayered double hydroxide[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2016, 27(1): 232-237. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2015.12.004 [25] LEE S Y, CHOI J W, SONG K G, et al. Adsorption and mechanistic study for phosphate removal by rice husk-derived biochar functionalized with Mg/Al-calcined layered double hydroxides via co-pyrolysis[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2019, 176: 107209.1-107209.15. [26] HE H, KANG H, MA S, et al. High adsorption selectivity of ZnAl layered double hydroxides and the calcined materials toward phosphate[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 343(1): 225-231. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2009.11.004 [27] 何天旭. 铁改性镁铝水滑石吸附剂制备及其对水中磷的吸附研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019. [28] JIA Z, ZENG W, XU H, et al. Adsorption removal and reuse of phosphate from wastewater using a novel adsorbent of lanthanum-modified platanus biochar[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 140: 221-232. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.05.017 [29] 程福龙, 李超, 陈娟, 等. Zr4+掺杂对Mg/Al水滑石磷酸根吸附行为的影响[J]. 精细化工, 2019, 36(10): 2122-2127. [30] LING Z, QI Z, JIANYONG L, et al. Phosphate adsorption on lanthanum hydroxide-doped activated carbon fiber[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 185-186: 160-167. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.066 [31] BUI T H, HONG S P, YOON J. Development of nanoscale zirconium molybdate embedded anion exchange resin for selective removal of phosphate[J]. Water Research, 2018, 134: 22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.061 [32] YANG F, ZHANG S S, SUN Y Q, et al. Assembling biochar with various layered double hydroxides for enhancement of phosphorus recovery[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 365: 665-673. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.11.047 [33] 刘晨, 张美一, 潘纲. 超薄水滑石纳米片除磷效果与机理[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(9): 2446-2456. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201803195 -







 下载:
下载: