-
厌氧氨氧化作为新型脱氮工艺,因其具有污泥产量少[1]、能耗低[2]以及不需要额外投加碳源[3]等优点,受到广泛关注。但厌氧氨氧化菌(anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria,AnAOB)生长缓慢,对环境因素的变化异常敏感[4]。温度下降(≤15 ℃)[5]、pH的变化[6]、COD值均会对其产生不利影响[7]。这些因素导致厌氧氨氧化污泥难以富集培养,限制了该技术的大规模应用[8]。如何快速有效地富集AnAOB是推动该工艺大规模应用的关键,而接种污泥的选择被认为是影响Anammox反应器启动的重要因素之一[9]。
目前Anammox反应器的启动多采用厌氧颗粒污泥[10]、厌氧消化污泥[11]以及反硝化污泥[12]作为接种污泥。有大量研究表明,AnAOB广泛存在于江河湖海的底泥中[13-15]。赵折红等[16]在三峡库区香溪河不同季节的沉积物中均发现了AnAOB的存在,且在0~10 cm内AnAOB丰度随着沉积物深度的增长呈现先增加后减少的趋势。秦红益[17]在富营养湖泊太湖的不同断面的沉积物中也都发现了AnAOB的存在,并发现0~5 cm处的沉积物是AnAOB集中分布的区域,且氮素水平会强烈影响沉积物中AnAOB的丰度和垂直分布。沈李东[18]在各种类型的淡水湿地的表层沉积物中均监测到AnAOB的存在,并说明Candidatus Brocadia和Candidatus Kuenenia属是淡水湿地系统中的优势AnAOB。虽然湿地系统广泛存在AnAOB,但截至目前,采用湿地底泥作为接种污泥启动Anammox工艺的研究鲜有报道。
基于上述研究结果,本研究采用UASB反应器,通过接种厌氧颗粒污泥、湿地底泥以及二者的混合物启动Anammox工艺,对各反应器在启动过程中的脱氮性能进行了监控,并利用高通量测序对污泥的微生物群落结构进行了分析,探讨了以湿地底泥为接种物启动Anammox反应器的可行性,以期为Anammox工艺的应用提供参考。
-
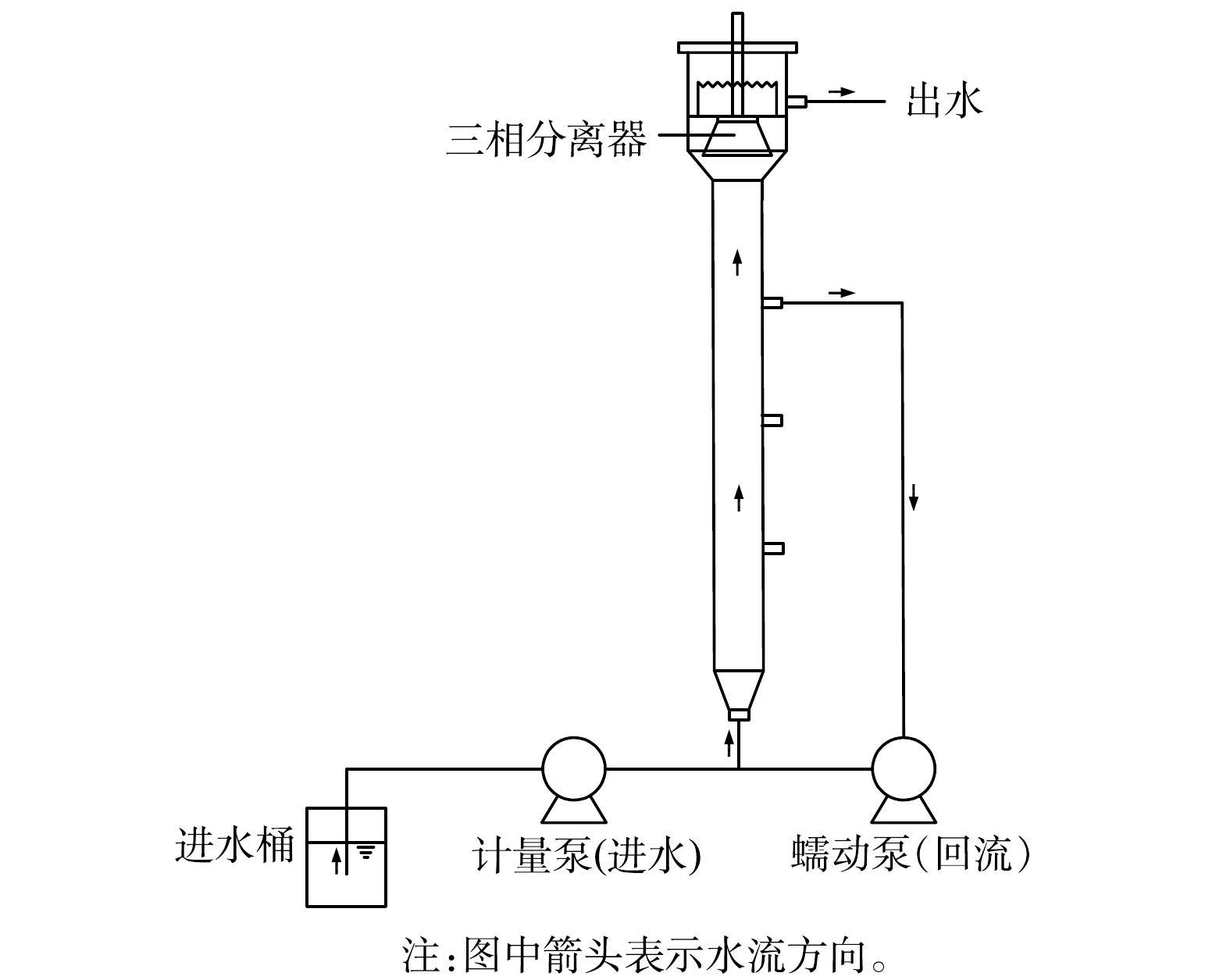
实验设备为有机玻璃制成的UASB反应器(共3台),反应器内径5 cm,高100 cm,有效容积约2 L,流量为0.083 L·h−1,装置外部包裹锡纸以避光,控制运行温度为32~35 ℃,实验装置如图1所示。由于仅靠低溶解氧难以抑制硝化菌的生长[19-20],故运行72 d后提高进水基质浓度;为改善水力条件,使微生物与底物充分接触[21-22],运行112 d后设置回流系统,具体运行策略见表1。
-
反应器进水采用人工配水,NH4Cl和NaNO2分别提供
NH+4 -N和NO−2 -N,其余成分为1 000 mg·L−1 NaHCO3、20 mg·L−1 KH2PO4、5 mg·L−1 CaCl2·2H2O、300 mg·L−1 MgSO4·7H2O、微量元素Ⅰ和微量元素Ⅱ各1 ml·L−1。微量元素Ⅰ组分为5 g·L−1 EDTA、5 g·L−1 FeSO4·7H2O。微量元素Ⅱ组分为15 g·L−1 EDTA、0.99 g·L−1 MnCl2·4H2O、0.25 g·L−1 CuSO4·5H2O、0.19 g·L−1 NiCl2·6H2O、0.24 g·L−1 CoCl2·6H2O、0.22 g·L−1 NaMoO4·2H2O、0.43 g·L−1 ZnSO4·7H2O、0.014 g·L−1 H3BO3、0.05 g·L−1 NaWO4·2H2O。采用氮吹,对配水进行脱氧(DO<0.1 mg·L−1)后进水。 -
接种的厌氧颗粒污泥取自处理酶制剂生产废水的厌氧反应器,MLSS为38.0 g·L−1,MLVSS为18.0 g·L−1。湿地底泥取自无锡市太湖边某湿地表层底泥,MLSS为192.6 g·L−1,MLVSS为13.8 g·L−1。R1反应器接种10 g·L−1厌氧颗粒污泥;R2反应器接种10 g·L−1 湿地底泥;R3反应器接种5 g·L−1厌氧颗粒污泥和5 g·L−1湿地底泥。
-
每2 d采集各反应器出水,水样经过0.45 μm滤膜过滤后根据《水和废水监测分析方法》测定各项水质指标,其中
NH+4 -N采用纳氏试剂分光光度法,NO−2 -N采用N-(1-萘基)-乙二胺分光光度法,NO−3 -N采用紫外分光光度法,TN采用碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法,COD采用快速消解分光光度法,MLSS和MLVSS采用重量法,pH采用在线式pH计(ST3100,奥豪斯),温度和DO则采用在线式溶解氧仪(WTW,Multi 3610 IDS)。总氮去除率(TRE)和总氮容积负荷(NLR)分别根据式(1)和式(2)进行计算。式中:ηTRE为总氮去除率,%;C(TN)inf为进水总氮质量浓度,mg·L−1;C(TN)eff为出水总氮质量浓度,mg·L−1;NV为总氮容积负荷,kg·(m3·d)−1;Qs为进水流量,m3·d−1;V为有效容积,m3。
-
采用16S rDNA高通量测序测定接种污泥和培养后污泥的微生物群落结构。污泥提取DNA后,选取通用引物338F(5'-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3')和806R(5'GGACTACCAGGGTATCTAAT-3')对V3~V4区进行PCR扩增。扩增程序为:95 ℃预变性3 min,27个循环(95 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延展45 s),最后72 ℃延展10 min。扩增产物利用Illumina公司Miseq PE300平台进行测序(上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司)测序数据采用FLASH和Trimmomatic软件进行优化,后采用UPARSE软件进行OTU聚类分析。
-
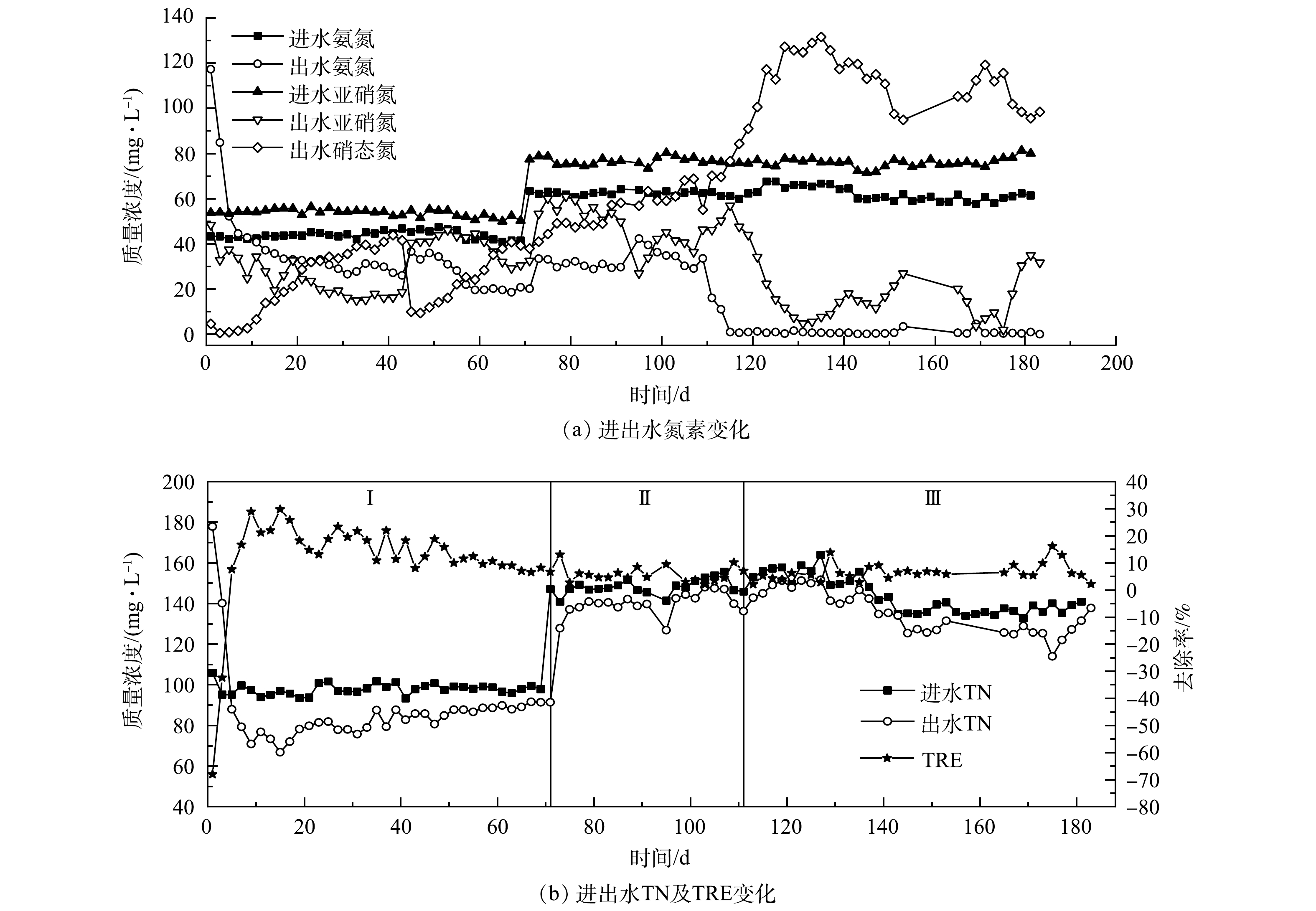
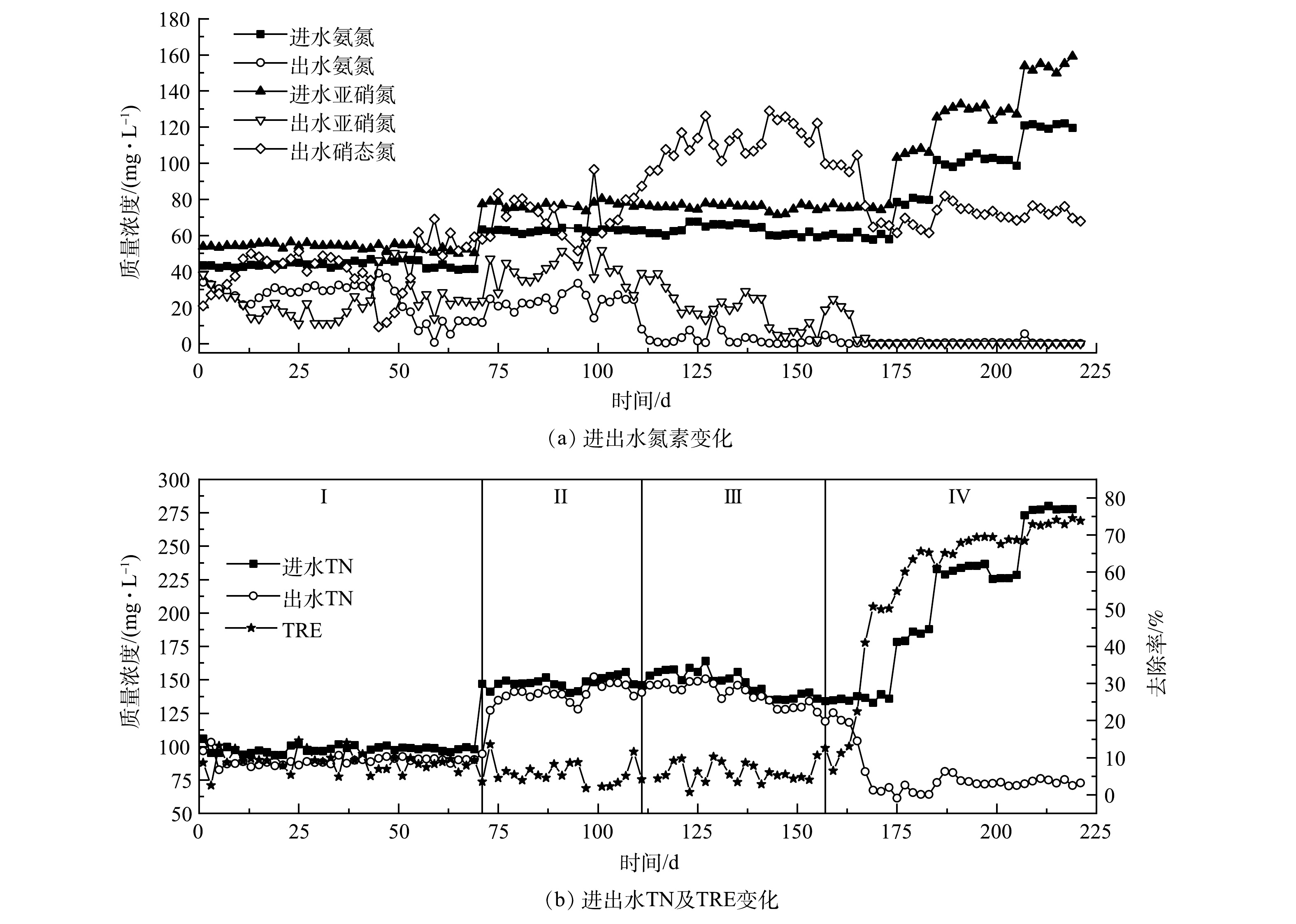
1)接种厌氧颗粒污泥的Anammox反应器启动。接种厌氧颗粒污泥的R1反应器运行期间进出水情况如图2所示。在反应器启动初期,出水氨氮及总氮质量浓度不降反升,高于进水。这是由于接种的厌氧颗粒污泥来自处理高浓度有机废水的反应器,其长期处于高COD废水环境中,存在大量异养菌,而进水中未添加有机碳源,异养菌因无法获得生长所需的足够底物而进行内源代谢,利用自身的贮藏物质,如酶等部分原生质的分解来获得营养物质,导致菌体自溶。在菌体自溶过程中,蛋白质等含氮有机物的分解导致了反应器中氨氮及总氮的升高。反应器运行至第13天,氨氮出水质量浓度开始低于进水,出水COD也由最初的425.55 mg·L−1降低至23.42 mg·L−1,标志着菌体自溶阶段结束。随着反应器继续运行,氨氮和亚硝氮去除率虽呈上升趋势,但在进水中残余溶解氧的影响下,氨氧化菌(AOB)和硝化菌(NOB)发挥了主要作用,大部分氮元素被转化为硝态氮,使出水硝态氮质量浓度不断增加。反应器中总氮去除率则呈现下降趋势,于第67天降低至6.51%。这主要是因为:随着菌体自溶现象减弱,水中COD下降,异养反硝化菌因缺少底物活性降低。
在第72天增加进水浓度后,出水硝态氮质量浓度依然上升明显,表明NOB活性抑制不明显,AnAOB在竞争过程中仍然处于劣势。在第112天增加回流后,出水氨氮质量浓度下降明显,基本保持在0.51 mg·L−1左右,出水亚硝氮质量浓度则先减后增,虽然出水硝态氮质量浓度呈现先增后减的趋势,但浓度依然较高,最高时达到131.56 mg·L−1;与此同时,总氮去除率也无明显上升,在2.20%~16.14%内波动。这些结果均表明,在R1中 AOB和NOB发挥主要作用,进水中几乎所有氮元素均在它们的共同作用下转化为硝态氮,反应器内无明显的厌氧氨氧化反应。
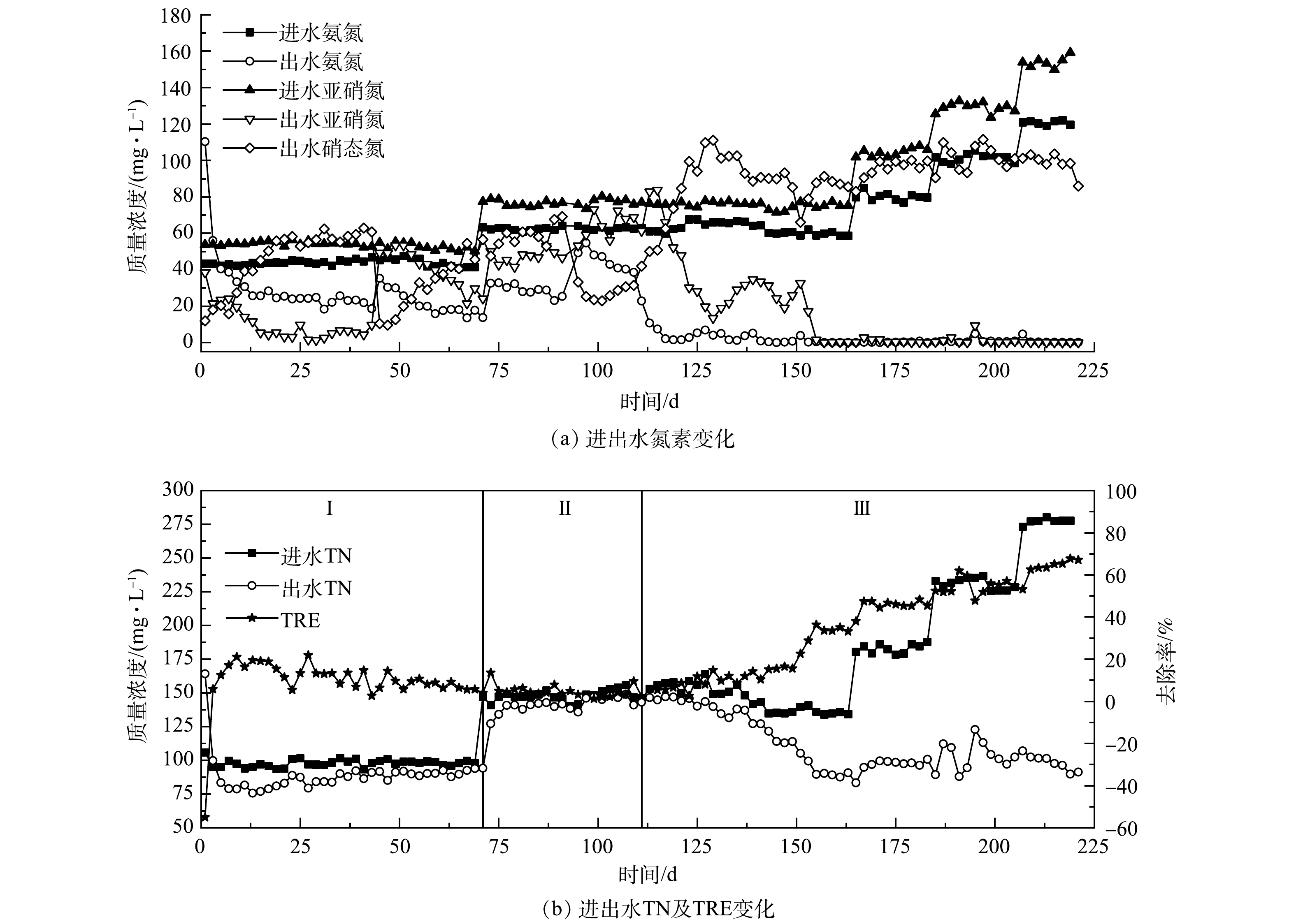
2)接种湿地底泥的Anammox反应器启动。接种湿地底泥的R2反应器运行期间进出水情况如图3所示。由于湿地水体中的COD和氮元素含量处于较低水平,底泥中的微生物能够较好地适应无机环境,故污泥接种进反应器后直接跳过了菌体自溶阶段而进入活性滞留阶段,总氮去除率维持在较低水平且无显著变化。在运行的前71 d,氨氮去除率逐步上升,出水亚硝氮质量浓度先减后增,出水硝态氮质量浓度持续增加,并于第63天达到最高值68.97 mg·L−1;而总氮去除率却无明显变化,一直维持在8.00%左右。可见,反应器内的氮元素大多通过AOB和NOB的作用转化为硝态氮,这与R1情况相似,
在第72天增加进水浓度后,氨氮和亚硝氮去除率均有所降低,出水硝态氮质量浓度也呈现下降趋势,AOB和NOB活性均受到了抑制。但从第95天开始,氨氮和亚硝态氮去除率升高,出水硝态氮质量浓度上升明显,而总氮去除率则无明显上升,表明AOB和NOB适应了环境的改变,受到的抑制效果减弱,AnAOB处于竞争劣势。设置回流系统后的前40 d内,出水氨氮和亚硝氮质量浓度逐渐降低,总氮去除率基本不变,在AOB和NOB的作用下出水硝态氮质量浓度增长迅速,最高时达到128.94 mg·L−1。运行至157 d开始,出水硝态氮质量浓度出现明显下降的趋势,并于第173天降低至65.48 mg·L−1,总氮去除率也迅速上升至50.19%,AnAOB开始展现活性且逐渐取代AOB和NOB成为R2内的优势菌种。由于从第167天起,出水中氨氮和亚硝态氮浓度较低,基本只含有硝态氮,故从第175天起逐步提高进水负荷。随着进水负荷的增加,氨氮和亚硝态氮去除率无明显降低,而出水硝态氮质量浓度却增长不明显,基本保持在70 mg·L−1左右。这是由于进水浓度的增加抑制了硝化菌的活性,同时刺激了AnAOB的增殖。随着负荷的提高,总氮去除率逐步上升,并于第219天开始在进水总氮质量浓度为275.55 mg·L−1,在氮负荷为0.275 kg·(m3·d)−1条件下,去除率稳定达到74.49%。
从R1和R2的启动结果来看,湿地底泥比处理高浓度有机废水的厌氧颗粒污泥更适合作为启动Anammox反应器的种泥。有研究[23]表明,长期较高负荷的有机物冲击会促进反硝化菌的生长,同时抑制AnAOB的生长。当COD>300 mg·L−1时,AnAOB将全部灭活,而酶制剂废水的COD值普遍高于300 mg·L−1,这也导致了接种的厌氧颗粒污泥中几乎不含AnAOB,从而致使反应器启动失败。而有大量研究[18,24]表明,湿地底泥中存在着AnAOB,且是湿地生态系统氮循环的重要组成部分,其产生的氮气可以占到湿地氮气产生总量的1.30%~42.70%,这也是采用湿地底泥为接种物成功启动Anammox反应器的重要原因。
3)接种混合污泥的Anammox反应器启动。接种混合污泥的R3反应器运行效果如图4所示。在反应器启动初期,由于微生物不能适应环境的改变而自溶,出水氨氮质量浓度高于进水;反应器运行至第7天时,出水氨氮质量浓度首次低于进水,出水COD由最初的307.12 mg·L−1降低至19.84 mg·L−1,表明反应器结束菌体自溶阶段。R3菌体自溶的时间要短于R1,这是因为反应器接种的是混合污泥,异养菌含量少于纯种厌氧颗粒污泥导致。与R1、R2运行初期情况相似,R3运行前71 d氨氮去除率逐步上升,出水亚硝氮质量浓度呈现先减后增的趋势,出水硝态氮质量浓度持续增加,最高时达到62.85 mg·L−1。由于反硝化菌逐渐被淘汰,总氮去除率下降明显,并于第71天下降至3.93%,这与R1的趋势相同。
在第72天增加进水浓度后,出水亚硝氮质量浓度缓慢上升,出水硝态氮质量浓度则呈现先增后减的趋势,但总氮去除率却无明显增长,最高也仅达到9.51%。这表明,虽然NOB的活性受到了一定的抑制,但AnAOB仍未展现明显活性。在第112天增加回流后,出水硝态氮质量浓度快速增加并于第129 天达到最高值后开始降低,总氮去除率则自第125天起呈现明显的上升趋势。这表明AnAOB开始展现活性,并逐渐成为优势菌种。由于从第155天开始,出水中几乎只有硝态氮,同时为了进一步提高反应器内的AnAOB丰度,自第165天起逐步提高进水负荷。提高进水负荷后,出水氨氮、亚硝态氮和硝态氮质量浓度均无明显变化,总氮去除率则上升明显,于第219天起在进水总氮质量浓度为275.55 mg·L−1,在氮负荷为0.275 kg·(m3·d)−1条件下,去除率稳定达到67.12%。
从以往学者的研究结果来看,接种混合污泥的启动时间均短于接种单一类型污泥。张泽文等[25]分别接种反硝化颗粒污泥和反硝化颗粒污泥与好氧硝化污泥的混合污泥启动Anammox反应器,结果显示,接种混合污泥的启动时间短于接种反硝化颗粒污泥。于德爽等[26]采用好氧硝化污泥和厌氧氨氧化污泥的混合物(比例2∶1)作为接种污泥,较采用好氧硝化污泥作为接种污泥的反应器的启动时间缩短约1/2。在本研究中,R3出现明显厌氧氨氧化反应特性的时间(125 d)要短于R2(155 d),表明混合污泥相较于单一的厌氧颗粒污泥或单一的湿地底泥更适合作为启动种泥,这与之前各学者研究的结果相类似。在本研究中出现这一结果的主要原因是,混合污泥中的厌氧颗粒污泥在启动过程中可以作为AnAOB依附的天然载体,又因其良好的沉降性能,使AnAOB不易流失,从而可缩短反应器的启动时间[27]。而对于混合污泥中2种污泥的最佳比例,还有待进一步研究。
-
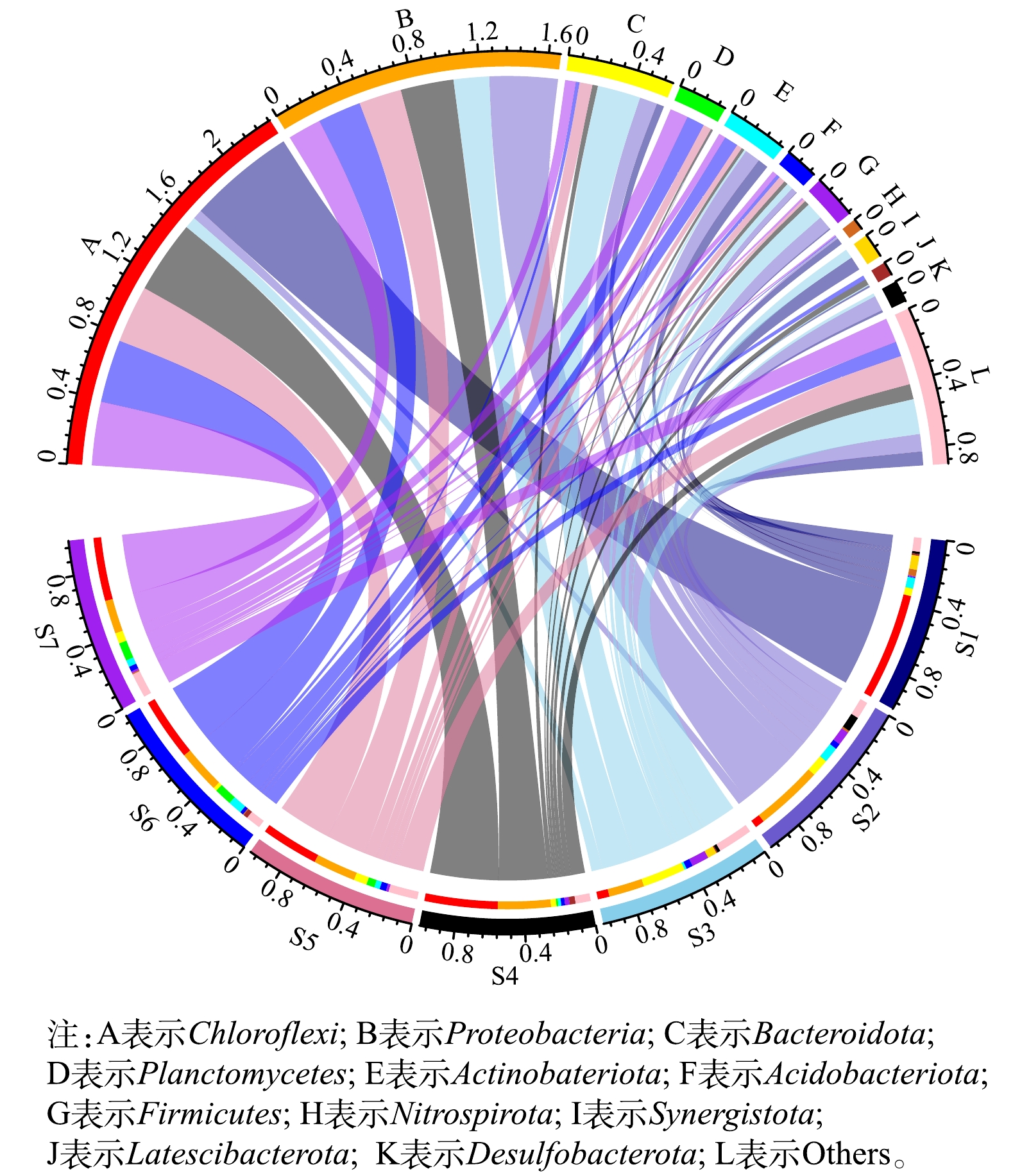
选取接种厌氧污泥(S1)、湿地底泥(S2)、R1183 d污泥(S3)、R2183 d污泥(S4)、R3183 d(S5)污泥、R2221 d污泥(S6)以及R3221 d污泥(S7)进行16S rDNA高通量测序检测微生物群落结构变化。各时期门分类水平上的微生物组成如图5所示。结果表明,S1中微生物所属的门主要为Chloroflexi(64.71%)、Actinobateriota(6.37%)、Synergistota(8.46%)、Bacteroidota(4.49%)、Nitrospirota(4.01%)等。S2中则是由Proteobacteria(41.05%)、Bacteroidota(10.66%)、Actinobateriota(9.44%)、Desulfobacterota(9.31%)、Firmicutes(8.49%)、Chloroflexi(5.75%)等组成,而AnAOB所属的Planctomycetes占比仅为0.07%。经过183 d的培养,S3中Chloroflexi门的丰度明显下降,由64.71%降低至7.12%,而Bacteroidota门和Proteobacteria门的丰度则分别上升至26.15% 和21.50%。有研究[28]表明,Proteobacteria门几乎涵盖了所有类型的AOB。这证实了AOB为R1中的优势菌种。NOB所属的Nitrospirota门在S3中的占比较S1中下降明显,但结合R1的运行状况可知,NOB依然发挥主要作用,氮元素在其和AOB的共同作用下转化为硝态氮。而在S3中未能检测出Planctomycetes门,这也说明R1中不存在厌氧氨氧化过程。S4和S6中Chloroflexi门的丰度相较于S2增长明显, Bacteroidota门的丰度则有一定程度降低,而二者在S4和S6中的丰度则无明显差异。据文献报道,Chloroflexi门常存在于Anammox系统中,其主要作用是作为AnAOB的骨架结构参与生物膜的形成[29],同时还能降解AnAOB死亡后残留下的有机物等物质[30];此外,Chloroflexi门和Bacteroidota门被认为在污泥颗粒化的过程中起着重要作用[31]。S6中Proteobacteria门的丰度相较于S4降低5.75%,而Planctomycetes门的丰度则从1.14%(S4)升高至10.80%(S6),在R3中也有相似的微生物结构变化,S7中Proteobacteria门的丰度相较于S5也下降了5.64%, Planctomycetes门的丰度则从4.99%(S5)升高至11.00%(S7)。这些数据表明,随着反应器的运行,硝化菌逐渐被淘汰,AnAOB成为R2和R3中的优势菌种。
各时期属水平上的微生物组成如图6所示。结果显示,norank_f__norank_o__SBR1031在S1中处于显著地位,其丰度达到53.30%,据报道,该菌种属于厌氧微生物具有碳水化合物发酵的能力[32]。由于湿地底泥处于自然环境中,而厌氧颗粒污泥长期处于特定人工环境中,故S2中的微生物种类明显多于S1,其优势菌种为Dechloromonas。值得指出的是,在S1和S2中都未能检测出AnAOB相关菌属,表明AnAOB在接种污泥中的含量低于万分之一,甚至可能不存在AnAOB。S3中norank_f__norank_o__SBR1031的丰度下降至0.31%,这是由于进水中不含有机物,微生物缺少底物而被淘汰。经过183 d的培养,S3中未能检测出AnAOB相关菌属,优势菌种为norank_f__Bacteroidetes_vadinHA17和Limnobacter,其丰度分别达到7.45%和6.00%。其中,前者的主要作用是参与水解酸化[33],而后者属于厌氧菌,据报道,该菌属可与AnAOB共存,可保护AnAOB免受外界干扰[34]。在S4-S7中,也都检测出一定丰度的Limnobacter。
有研究[35]表明,Candidatus Brocadia作为AnAOB的一种菌属经常出现在Anammox反应器中。如图5所示,S4~S7样品中均检测到了Candidatus Brocadia,且其丰度随着反应器的运行时间延长而增加,在R2中S6的丰度比S4增加了9.28%,达到了9.82%;而其在R3中的丰度也由5.07%(S5)增加至10.70%(S7)。这也进一步证明了反应器内的氮元素主要通过AnAOB的作用去除。
R2和R3中的Nitrosomonas的丰度随着反应器的运行逐渐减少,其在S4中的丰度为3.97%,而在S6中丰度仅为0.64%,在S7中更是未检测出该菌属。有研究[36]表明,该菌属为AOB细菌,这说明随着反应器的运行,AOB逐渐被淘汰。反应器内还存在着具有硝化作用的Nitrospira,虽然其丰度随着反应器的运行而增加,但仍处于较低水平。在S4~S7中,Nitrospira在S7中的丰度最高,但也仅为0.77%,这也从生物学角度解释了为何R3出水的硝态氮浓度要高于R2。在R2和R3启动的不同时期均检测到了硝化细菌,这可能是由反应器进水中残留的溶解氧造成的。以往学者也均在研究中发现了这一现象。例如,王晓曈等[37]在采用上流式生物滤池启动Anammox反应器的过程中发现反应器中微生物结构分层明显,底层污泥中主要以硝化菌和异养菌为主;吴珊等[38]在Anammox反应器运行过程中也发现体系中存在硝化细菌。与此同时,S4~S7中也均检测到了具有反硝化作用的Denitratisoma[39],且随着反应器的运行呈现出增加的趋势,其丰度在S6和S7中分别达到0.94%和3.04%。这可能是由AOB等微生物死亡后残留的有机物所导致。总的来说,随着反应器的运行,AnAOB逐渐在R2和R3中富集,而不能适应环境的菌种逐渐被淘汰。
根据不同时期的微生物群落结构并结合3台反应器的启动过程,可以看出,进水溶解氧对Anammox反应器的启动有着较大影响。由于AOB和NOB均为自养菌,且两者均能在低溶解氧条件下发挥作用[21],这就导致即使进水中溶解氧浓度处于较低水平,氨氮和亚硝氮仍能在二者的作用下被转化为硝态氮,使得AnAOB缺少营养基质而难以生长,进而加长启动时间。对此,可通过适当提高进水基质浓度来抑制硝化菌的活性,故高基质暴露水平培养方式下更有利于AnAOB的快速富集培养[40]。而在高基质暴露水平下,AOB和NOB活性在较高的FA和低溶解氧的双重作用下受到抑制[19,41],减少二者与AnAOB对基质的竞争,从而缩短启动时间。
-
1)采用UASB反应器接种湿地底泥和混合污泥(厌氧颗粒污泥与湿地底泥的污泥浓度比值为1:1)成功启动了Anammox反应器,但采用厌氧颗粒污泥启动Anammox反应器则失败;接种混合污泥的反应器开始展现厌氧氨氧化反应特性的时间(125 d)明显短于接种湿地底泥的反应器(155 d);反应器启动成功后逐步提高进水负荷,最终在进水NLR为0.275 kg·(m3·d)−1条件下,接种湿地底泥和混合污泥的Anammox反应器中的TN去除率分别达到74.49%和67.12%。
2)湿地底泥中的原生AnAOB含量高于处理高浓度有机废水的厌氧颗粒污泥;在接种混合污泥的反应器中,厌氧颗粒污泥可作为AnAOB的载体,又因其良好的沉降性能,故能够减少AnAOB流失,从而缩短Anammox反应器启动时间。
3)培养前后反应器内微生物群落结构发生了较大变化。接种湿地底泥和混合污泥的Anammox反应器中Planctomycetes门的丰度增长明显,Bacteroidota门的丰度则呈现下降趋势,反应器内的AnAOB为Candidatus_Brocadia,其丰度于第221天分别达到9.82%和10.70%。
接种湿地底泥的Anammox反应器启动特性
Start up characteristics of Anammox reactor inoculated with wetland sediment
-
摘要: 在3台UASB反应器中分别以厌氧颗粒污泥、湿地底泥以及二者的混合物(污泥浓度比为1∶1)为接种污泥启动厌氧氨氧化(Anaerobic ammonium oxidation,Anammox)反应器,考察了以湿地底泥为接种物启动Anammox反应器的可行性。结果表明,接种厌氧颗粒污泥的反应器经过183 d启动运行,仍未出现明显厌氧氨氧化反应特性,接种混合污泥的反应器于第125天开始出现明显厌氧氨氧化反应特性,短于接种湿地底泥的155 d。Anammox反应器启动并稳定运行后,在进水总氮质量浓度为275 mg·L−1、负荷为0.275 kg·(m3·d)−1条件下,出水总氮质量浓度可降至90 mg·L−1以下,其中接种湿地底泥和混合污泥的Anammox反应器的TN去除率分别达到74.49%和67.12%。高通量结果表明,在接种湿地底泥和混合污泥的反应器中的厌氧氨氧化菌属为Candidatus Brocadia,其丰度分别达到9.82%和10.70%。Abstract: Anaerobic granular sludge, wetland sediment and their mixture (SS ratio of 1∶1) were used as inoculated sludge to start the Anammox reactor in three UASB tanks, and the feasibility of starting Anammox reactor with wetland sediment as inoculum was investigated. The results showed that the USAB inoculated with anaerobic granular sludge didn’t present the obvious Anammox reaction characteristics after 183 days of start-up operation. The USAB inoculated with mixed sludge began to show obvious Anammox reaction characteristics on day 125, which was shorter than USAB inoculated with wetland sediment on day 155. After the start-up and stable operation of the Anammox reactor, the total nitrogen concentration in the effluent could be reduced to less than 90 mg·L−1 under the conditions of the total nitrogen concentration in the influent of 275 mg·L−1 and the load of 0.275 kg·(m3·d)−1. The TN removal rates of the Anammox reactor inoculated with wetland sediments and mixed sludge reached 74.49% and 67.12%, respectively. The high-throughput results showed that the Anammox bacteria in the two reactors were Candidatus Brocadia, and their abundances reached 9.82% and 10.70%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- Anammox /
- wetland sediment /
- start process /
- microbial community
-
白洋淀为华北平原最大的半封闭式浅水湖泊,淀区物种丰富,多数水域大型水生植物覆盖度为60%左右。经调查,白洋淀共有水生植物39种,隶属于19科30属,其中分布面积较广的优势群落有芦苇群落、狭叶香蒲群落、金鱼藻群落等[1]。水生植物构成了白洋淀湿地独特的环境生态,然而由于收割不及时、管护不到位,湿地水生植被残体在水体中大量堆积、腐烂,导致水体溶解氧降低、透明度减少[2],水体恶臭,氮、磷等有机物浓度升高,并释放多种硫化物(硫醇、甲硫醚、二甲基二硫醚等),引发生态灾害[3]。沈爱春等[4]在太湖进行的原位实验发现,蓝藻的集聚死亡会导致水体的溶解氧降低,水体营养盐含量迅速增加,TN和
NH+4 NH+4 好氧堆肥是固体废弃物资源化处理的有效技术之一,已在沉水植物“减量化、无害化”处理方面有诸多应用[7]。沉水植物与非沉水植物相比,具有氮、磷、钾等营养元素丰富、含水量高、C/N低等特点。程花等[8]通过分析马来眼子菜、金鱼藻等6种沉水植物的理化性质,证实了沉水植物堆肥的可行性。王亚等[9]以麦秸和树叶为辅料,提高了沉水植物堆肥的腐熟度。陆伟东等[10]利用水葫芦与猪粪混合堆肥,王丽芬等[11]利用水葫芦与污泥混合堆肥,均取得了满意的堆肥效果。王亚梅[12]的研究结果表明,生物炭的添加可显著提高猪粪堆肥的腐熟度。有研究表明,在有机废弃物堆肥中添加生物质炭可提高堆体温度,延长堆肥高温持续的时间,减少氮素损失[13]。卢妙[14]证实了秸秆-污泥基生物炭的添加有利于污泥堆肥,同时在制备生物炭的过程中消耗了大量污泥,可更大程度的使脱水污泥减量化及无害化。NIGUSSIE等[15]通过荟萃分析发现,微生物菌剂对堆肥总氮(+30%)、总磷(+46%)、C/N(−31%)、腐殖化指数(+60%)和种子发芽指数(+28%)等堆肥腐熟指标均有明显的积极作用。张秧等[16]的研究表明,在小麦秸秆中添加微生物菌剂对腐殖质的形成有一定的促进作用。以上研究已证实,好氧堆肥是沉水植物利用的有效途径,生物炭、湿地底泥和微生物菌剂作为调理剂均可促进堆肥进程、提高堆肥品质,但以上调理剂对沉水植物堆肥腐熟的影响有待进一步研究。
本研究以白洋淀湿地大型沉水植物(金鱼藻和马来眼子菜)为研究对象,以生物炭、湿地底泥和微生物菌剂为调理剂,通过对比不同调理剂处理下好氧堆肥各处理组的理化及生物学指标,探明不同调理剂对堆肥腐熟效果的影响,提出沉水植物堆肥腐熟的科学调控方法,以期为改善白洋淀水体环境和沉水植物的资源化利用方式提供新思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
本实验沉水植物(金鱼藻和马来眼子菜)和湿地底泥在白洋淀打捞获取;干鸡粪和尿素用来调节堆肥碳氮比(C/N);生物炭为SC-101型秸秆生物炭;发芽实验选择紫穗槐种子;复合微生物菌剂含有乳酸菌、酵母菌等微生物菌群,EM菌种含有双岐菌、乳酸菌、芽孢杆菌等微生物菌群。
本实验自制微生物菌剂的培养方法为:将500 g红糖溶于含有9 L蒸馏水的塑料桶中,取2.5 g EM菌种加入塑料桶,并混合均匀,将塑料桶密封好后置于32 ℃的气候箱中培养7 d,即可得到菌剂原液,将原液与蒸馏水按1∶10稀释后即可得到所需菌剂。堆肥原料性质见表1。
表 1 堆肥原料特征参数Table 1. Characteristic parameters of composting raw material% 供试材料 总有机质 全氮 半纤维素 纤维素 木质素 沉水植物 84.62 1.33 15.8 29.2 8.9 干鸡粪 63.11 3.62 — — — 堆肥物料 76.36 2.69 7.62 15.9 4.88 注:堆肥物料为沉水植物(金鱼藻∶马来眼子菜=1∶1)与干鸡粪按一定比例混合。 1.2 实验设计和取样
本研究实验于2021年2月23日至3月30日在雄安生态环境研究院实验室进行。将沉水植物风干粉碎成1 cm左右的小段,置于120 ℃、1.5 kPa的高温灭菌锅中灭菌20 min,用干鸡粪和尿素调节沉水植物的C/N为28~30,湿地底泥和生物炭的添加量分别为物料总干重的10%和2%,保持堆体水分含量为65%左右。将原料置于32 cm×22 cm×16 cm的发酵盒中,并排列在温度50 ℃、湿度为65%的气候箱中进行高温发酵[17-18]。实验容器为耐高温的PP环保发酵盒,覆盖带孔的塑料薄膜,以降低水分蒸发速率。同时,根据堆体温度、水分的变化情况,在堆肥开始后每6 d翻堆1次并补充菌剂。在起堆的第0、6、12、18、24、30、36 d采用“五点取样法”取样,即分别在堆体的前、后、左、右及中心采集样品200 g,并均匀混合,一部分做风干处理用于理化指标测定,一部分常温存放用于测定种子发芽指数。
本实验共设计8个处理组,实验周期为36 d,各处理组设计见表2。
表 2 实验因素水平表Table 2. Standard table of experimental处理组别 湿地底泥/% 生物炭/% 菌剂类型 CK-C 0 0 复合微生物菌剂 S-C 10 0 复合微生物菌剂 B-C 0 2 复合微生物菌剂 SB-C 10 2 复合微生物菌剂 CK-H 0 0 自制微生物菌剂 S-H 10 0 自制微生物菌剂 B-H 0 2 自制微生物菌剂 SB-H 10 2 自制微生物菌剂 注:CK为对照组,S代表湿地底泥,B代表生物炭,SB代表湿地底泥+生物炭,C代表复合微生物菌剂,H代表自制微生物菌剂。 1.3 测定指标与方法
每天在固定时间测定堆肥上、中、下的温度,并取均值作为该堆体的温度;采用外加热法测定有机质;采用凯氏定氮法测定全氮;用pH/EC仪测定pH和EC值[19];半纤维素、纤维素、木质素的测定采用Van Soest洗涤法[20];富里酸和胡敏酸的测定参考NY/T 1971-2010《水溶肥料腐植酸含量的测定》[21];将鲜样与蒸馏水按1∶10(g∶mL)混合震荡2 h,浸提后在25 ℃的恒温箱内培养紫穗槐种子,48 h后记录发芽个数及根长,计算种子发芽指数。
2. 结果与讨论
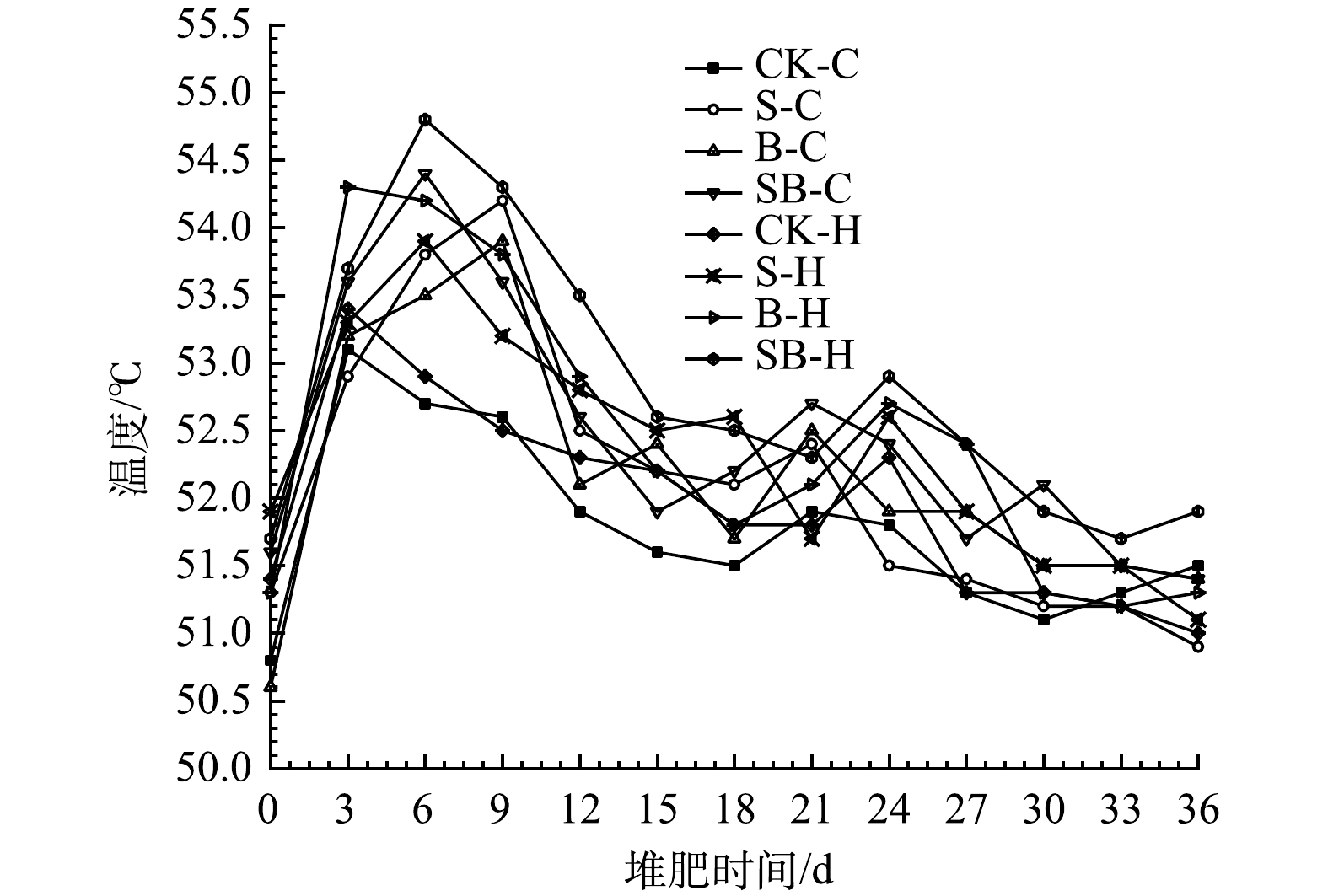
2.1 不同处理堆肥的温度变化
温度是堆肥工艺比较常用的物理评价指标之一,在堆肥过程中温度是影响微生物活动和堆肥工艺过程的关键因素。从图1可以看出,本实验8个处理组的温度变化趋势大致相同,主要可分为升温期、高温期、降温腐熟期[22-23]。在起堆的3~9 d,温度迅速升高且均达到最大值。这说明堆体具有良好的碳氮比、孔隙度等发酵条件,嗜热微生物分解有机物产生大量热量和气体并迅速繁殖,使得堆体迅速达到高温期。随后,温度总体呈现波动下降,并逐渐稳定。堆体最高温度为53.1~54.8 ℃,其可能的原因是,高温堆肥前期有机酸、无机酸含量升高较快,部分嗜温微生物活性受阻,数量减少,嗜热微生物成为整个堆肥过程中的优势菌种[24]。C组和H组堆肥平均温度的组间排序分别为:SB-H>S-H>B-H>CK-H、SB-C>B-C>S-C>CK-C。自制微生物菌剂较复合微生物菌剂含有更多、更有效的活性微生物,这导致喷洒自制微生物菌剂处理组的平均温度均高于其他处理组。没有添加生物炭和湿地底泥的对照组均为组内最低温度,由此说明,添加湿地底泥和生物炭的处理组也对促进堆体升温有一定的效果。在堆肥24 d左右,部分处理组堆体温度有小幅度的升高。其可能的原因为:翻堆和微生物菌剂补充的作用,高温好氧微生物再次繁殖,剩余的难分解纤维素类大分子物质开始被缓慢消耗,堆体内未分解完全的物质进行二次反应发酵。随后,堆体温度逐渐降低并趋于稳定,预示着堆肥过程结束。
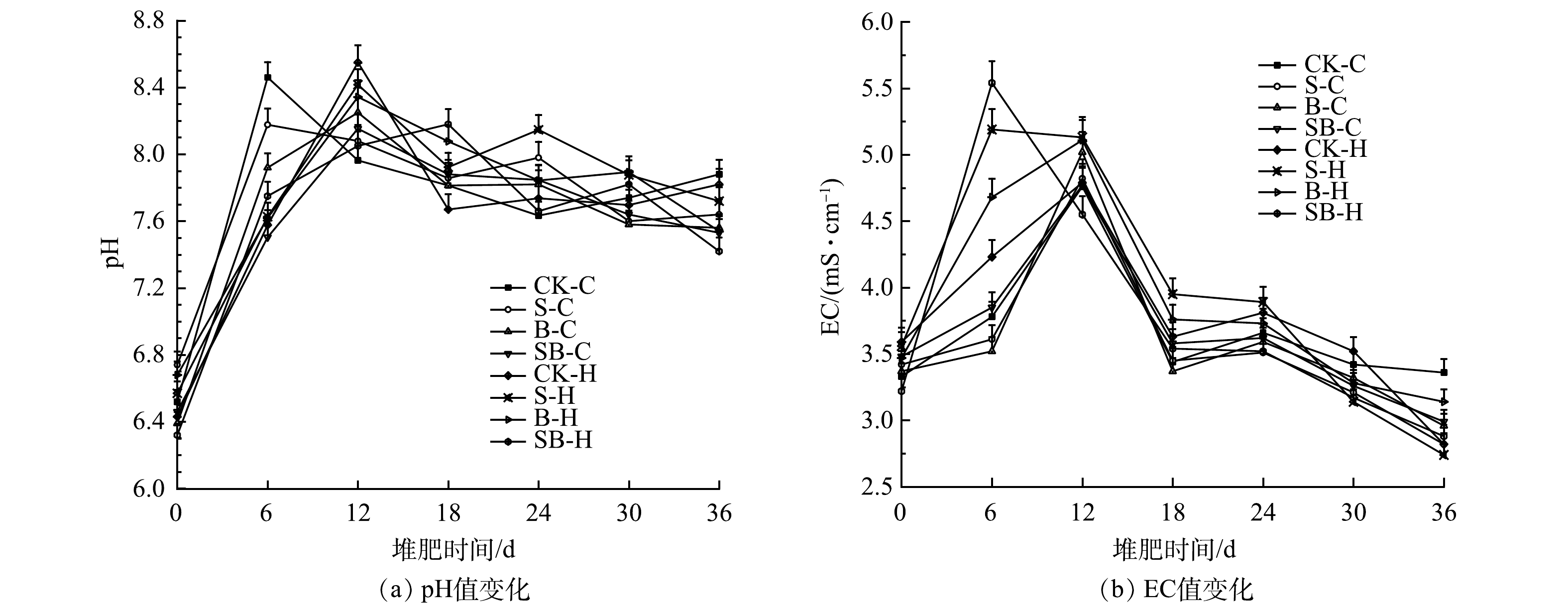
2.2 不同处理对堆肥pH、EC的影响
图2(a)表明,不同处理堆肥的pH均呈现出先升高后降低的趋势,堆肥结束时,pH均在7.55~7.81,这符合高温堆肥产品腐熟的pH标准[25]。在0~6 d的反应过程中,微生物降解含氮有机物发生氨化作用,产生大量的
NH+4 NH+4 NH+4 电导率(EC)主要反映堆体中存在的可溶性盐的浓度,可作为判定堆肥是否限制作物生长的指标。当EC值小于9.0 mS·cm−1时,可认为对种子发芽没有抑制作用;当EC值小于4.0 mS·cm−1时,才能施用于土壤中,并且不会对植物产生抑制作用[28]。如图2(b)所示,不同处理的EC值在堆肥的初始阶段都有增加。造成这种趋势的原因是:部分有机物质在堆肥初期被降解成具有可溶性的小分子物质,如铵盐、磷酸盐、小分子有机酸和其他溶解的有机物等,随着堆肥反应的进行,由于有机酸的降解、腐殖质的形成以及NH3、CO2的排放等因素,不同处理的EC值均略有下降并趋于稳定。堆肥结束时,各处理的EC值为2.74(S-H)~3.36(CK-C)。这说明S-H处理组的堆肥产品对植物的毒害作用最小,CK-C处理组可能会对植物种子产生渗透压胁迫,对植物生长起到一定的抑制作用。综上所述,本实验的所有处理均可排除盐害的影响。
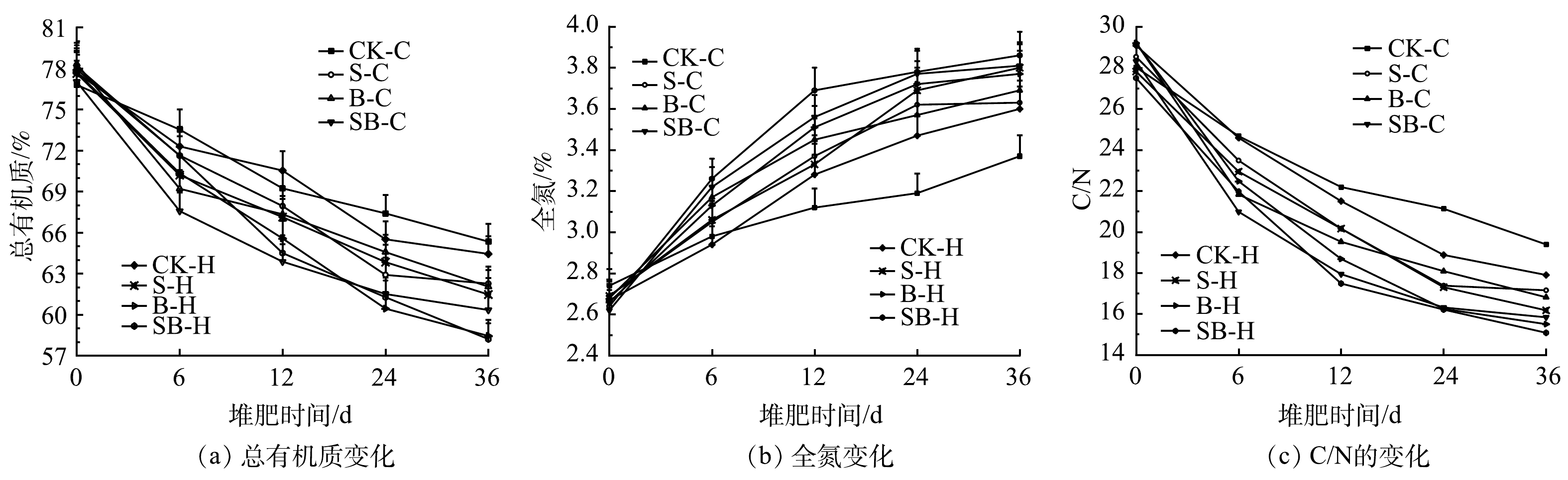
2.3 不同处理对堆肥碳、氮含量的影响
图3(a)和图3(b)为堆肥过程中总有机质(TOM)和全氮(TN)的质量分数变化情况。TOM是堆肥过程中主要损失的物质,是堆肥进程中微生物进行生物化学反应的有效底物[29],在堆肥过程中呈现出逐渐降低的趋势。固体有机物通过微生物的代谢活动形成更容易被微生物利用的溶解性有机物(DOM),随着堆肥反应的进行,小分子有机物重组形成具有稳定结构的腐殖质[30]。在0~12 d的反应过程中,TOM质量分数降低明显。其可能的原因是:堆肥初期微生物活动旺盛,TOM以CO2、CH4、热量等形式快速损耗降解。不同处理由于物料有机碳组分的不同造成有机质降解率差异显著。第36天时, SB-H和SB-C处理组的TOM降解率分别为25.51%和21.68%,均大于添加相同菌剂的其他处理,这说明湿地底泥和生物炭的协同作用更有利于TOM的分解利用。对比B-H处理组与S-H处理组、B-C处理组与S-C处理组的TOM含量可知,生物炭对促进堆体TOM损耗转化的作用大于湿地底泥。堆肥结束时,TOM质量分数均在45%以上,符合有机肥料标准[20]。在堆肥进程中一直伴随着氮素的损失[31],氮素在发酵过程中会不断进行氨化作用、硝化作用、反硝化作用和固氮作用等,随着堆肥时间的推移、堆体体积的减小TN质量分数总体呈现上升的趋势。堆肥前期,TN质量分数明显上升。其可能的原因是:前期缩堆现象明显,湿地底泥的添加为反应提供了部分氮源,生物炭的作用减少了氮素的损失。当堆肥结束时,各处理的TN质量分数增加了22.99%~41.73%。堆体碳氮比是判断堆体是否腐熟的重要指标,当堆体C/N<20时,可认为堆肥已腐熟[32]。如图3(c)所示,本实验中,所有处理在堆肥结束时C/N均在15.08~19.39,都已达到腐熟条件。
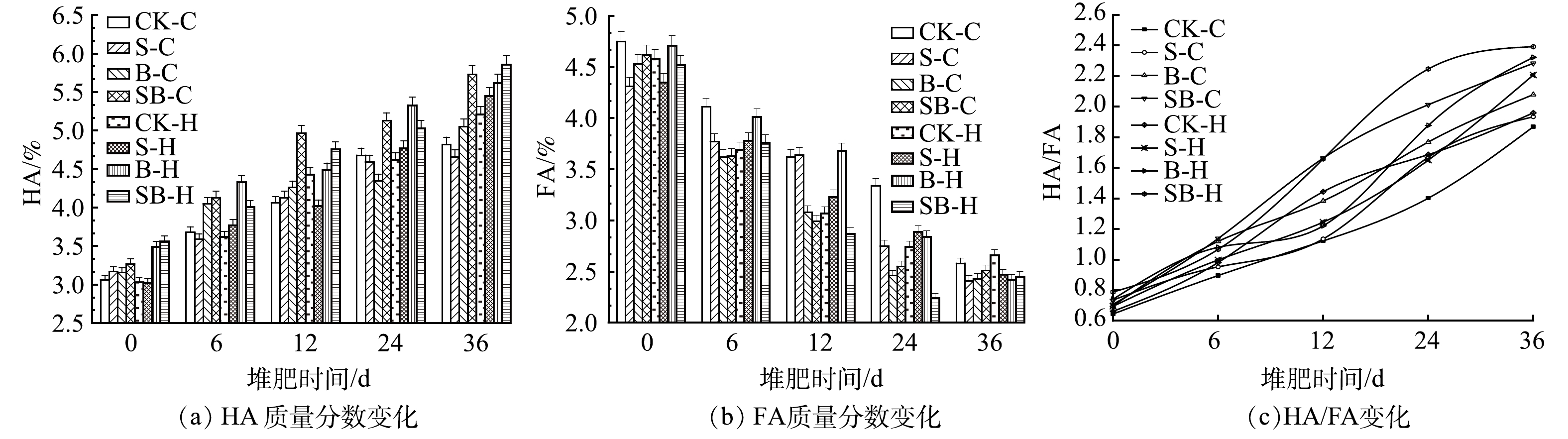
2.4 不同处理对堆肥HA、FA和HA/FA的影响
腐殖质(HS)主要由胡敏酸(HA)和富里酸(FA)组成,它不仅是堆肥的重要产物,也是评价堆肥质量的重要指标[33]。HA是指能够溶于碱溶液而不能够在酸溶液中被溶解的腐殖质物质,在土壤养分的保持以及土壤团粒结构的形成过程中发挥着重要作用[34]。从图4(a)中可以看出,HA的质量分数整体呈波动上升趋势。堆肥结束时,各处理堆肥HA的质量分数总体上差别不大,基本稳定在4.82%~5.86%。其中,SB-C处理组的HA质量分数由初始的3.16%到堆肥结束时的5.73%,增长率最高达75.23%,除S-C处理组(47.00%)外的HA增长率均在50%以上。图4(b)为FA的质量分数变化情况。从图4(b)可以看出,FA因其较小的相对分子质量、较简单的结构特点,随着堆体中微生物的大量繁殖,原料中的FA被微生物大量分解,堆体在微生物作用下分解合成FA的速率与其矿化或聚合成HA的速率的动态变化影响着FA含量的动态变化。堆肥结束时,各处理的FA含量为2.41%~2.66%,与初始质量分数相比减少幅度表现为:SB-H>S-C>B-H>S-H>B-C>SB-C>CK-H>CK-H。
HA/FA是用来评价最终堆肥成熟度的指标之一,该指数越高表示产品越稳定。一般认为,HA/FA大于1.9时,可视为堆肥已完全腐熟,因此,分析腐殖化指数对确定堆肥成熟度至关重要[35]。HA和FA在堆肥过程中可以相互转化,在微生物的作用下,大量新的稳定的HA分子逐渐被合成,而分子量小、结构简单、不稳定的FA则逐渐被分解。因此,如图4(c)所示,随着堆肥化过程的推进,各处理HA/FA呈上升趋势。这一趋势与REN等[36]的研究结果一致。本堆肥实验结束时,HA/FA的值为1.23~1.54,腐殖化最高的4个处理组是SB-H、B-H、SB-C、S-H。这表明,在堆体中添加湿地底泥、生物炭和微生物菌剂,均能够促进沉水植物堆肥的腐殖化和聚合化,生物炭的微孔结构为微生物提供了更多的生长繁殖空间[37],湿地底泥能显著增加堆体的微生物多样性及丰度,自制微生物菌剂的添加有效促进了难降解化合物的降解,添加剂间的协同作用能够有效促进HA的形成和FA的降解,逐渐产生复杂的HS,进而提高堆体的腐殖化程度[38]。
2.5 不同处理堆肥对种子发芽指数的影响
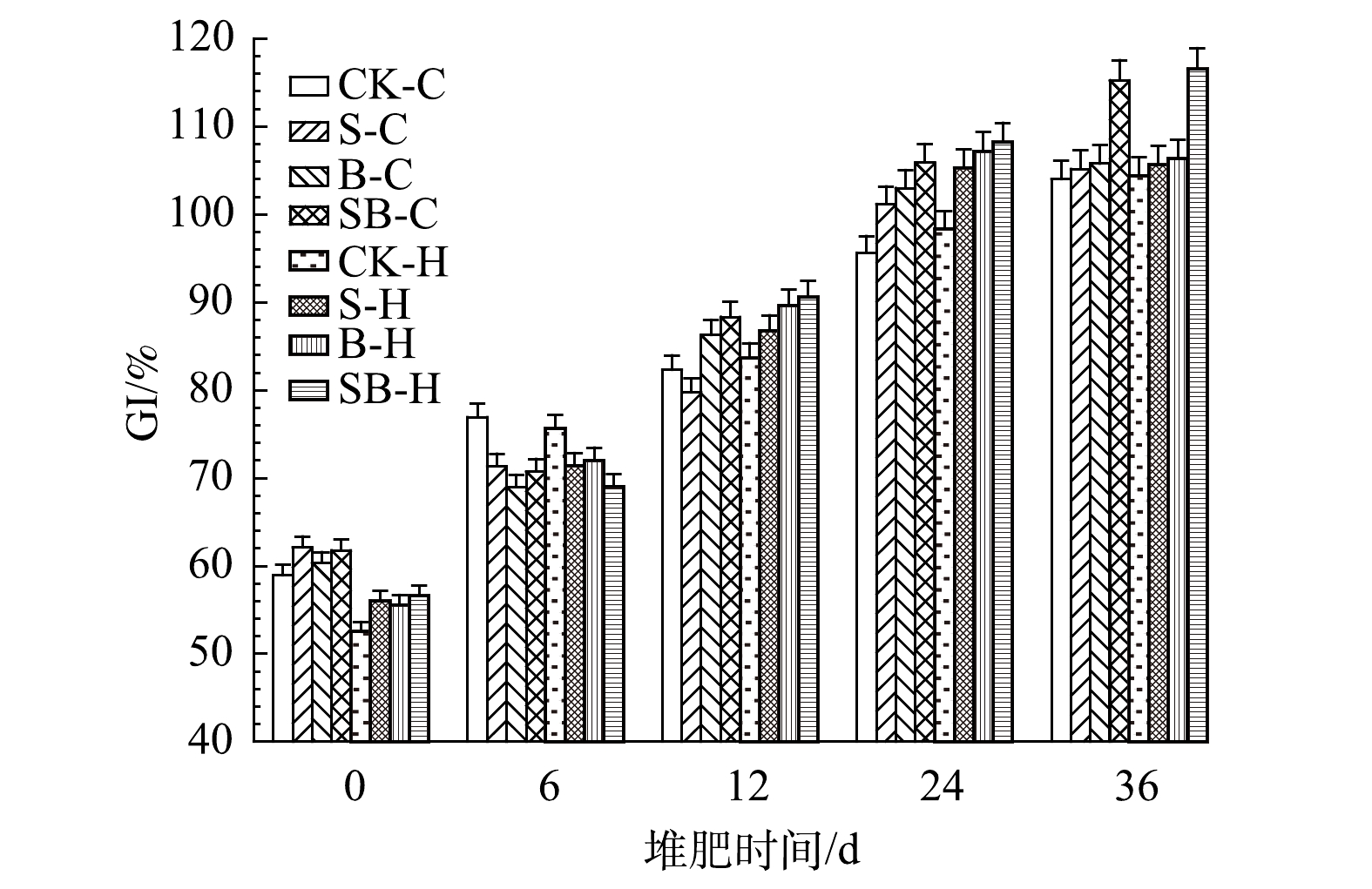
发芽指数(GI)是堆肥腐熟度评价生物学指标之一,该指数既考虑了种子的发芽率,也考虑了毒性物质对种子生根的影响。当GI大于80%时,证明堆肥已基本达到腐熟状态;当GI大于100%时,可认为堆肥产物对种子生长发挥了积极作用[39]。如图5所示,堆肥初期由于产生了大量的有毒物质,铵态氮浓度过高会抑制种子萌发,不同处理的种子发芽指数在60%左右。经过36 d的堆肥腐熟,所有处理的发芽指数均有较大幅度的提升,发芽指数为104.00%~116.57%,各组的排序为:SB-H>SB-C>B-H>B-C>S-H>S-C>CK-H>CK-H。对比相同添加剂下不同微生物菌剂的作用可知,自制微生物菌剂的堆肥处理较之复合微生物菌剂更能促进种子发芽和根系生长;添加生物炭及其联用实验组发芽指数更具优势,湿地底泥和生物炭协同作用下的堆肥处理种子发芽指数最高,同时生物炭的积极作用大于湿地底泥。
2.6 不同处理对堆肥木质纤维素含量的影响
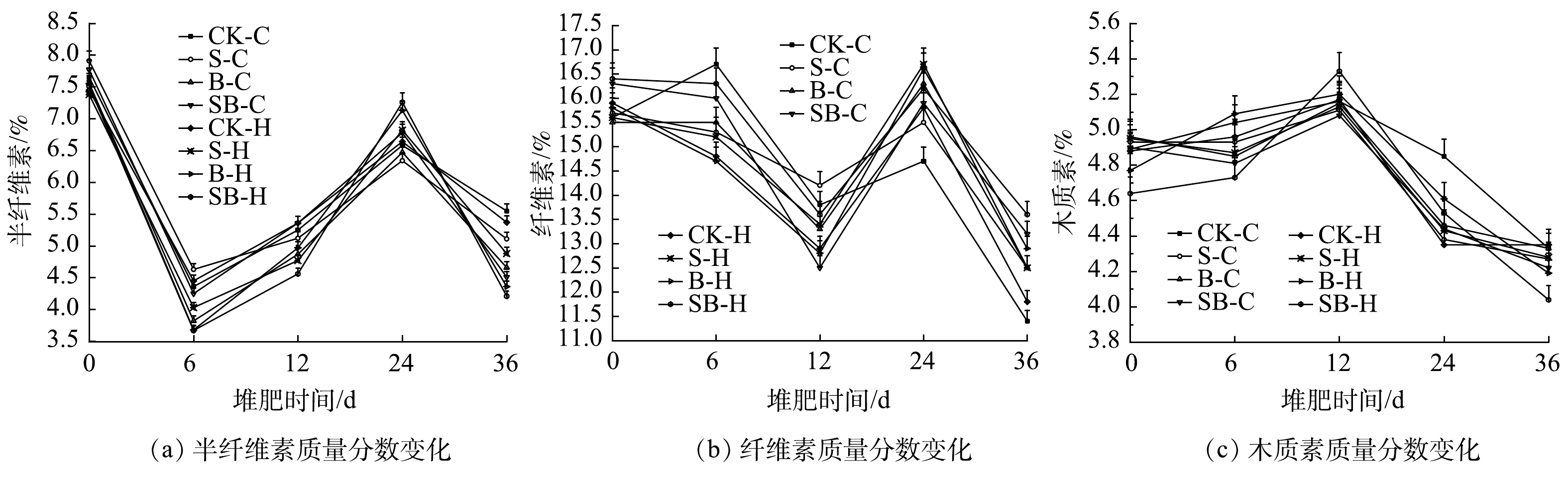
木质纤维素是构成植物的主体部分,其结构复杂较难降解,通常大量存在于生活垃圾和农业废物中。纤维素的降解直接影响着堆肥的腐殖化过程,也是限制堆肥周期的关键因素[40]。木质纤维素中的半纤维素是最易被降解的。如图6(a)所示,半纤维素质量分数总体呈现出波动下降的趋势。在堆肥初期,半纤维素作为易被降解的有机物优先成为碳源。在6 d的反应过程中,部分半纤维素的降解率均达到50%左右。在6~24 d反应过程中,半纤维素质量分数增加。其可能的原因是半纤维素的消耗速率降低,其他有机质被消耗降解,堆体总质量减小。在24~36 d反应过程中,由于微生物菌剂的补充,微生物活动旺盛,堆体中的半纤维素再次加速消耗,使得堆肥后期半纤维质量分数有小幅度的下降。堆肥结束时,各处理的半纤维素降解率为27.45%~43.94%,各处理的排序为:SB-H>B-H>SB-C>B-C>S-C>S-H>CK-H>CK-H。添加湿地底泥和生物炭的处理均对半纤维素有较高的降解率,在添加相同微生物菌剂的处理组中,添加生物炭处理的半纤维素降解率均高于添加湿地底泥的处理,且都高于对照组。
如图6(b)所示,纤维素质量分数的变化趋势与半纤维素相似。经过36 d的堆肥,各处理纤维素的降解率基本稳定在17.07%~26.92%。纤维素是植物残体中最丰富的部分,相比于半纤维素较难降解[41]。堆肥结束时,各处理纤维素的降解率为17.07%~26.92%,各处理的排序为:CK-H>CK-H>S-C>S-H>B-C>SB-C>B-H>SB-H。该降解率趋势与半纤维的降解率相反。可能的原因为:1)有效微生物通过合成纤维素酶来降解堆体中的纤维素,微生物菌剂与湿地底泥和生物炭的协同作用并不能起到促进纤维素酶合成的作用,湿地底泥和生物炭对堆体纤维素的降解没有明显的积极作用,导致处理组较对照组对纤维素的降解较差;2)由于堆肥反应的复杂性,不同处理堆体总质量的不均匀减小导致纤维素的绝对含量呈现此趋势。
如图6(c)所示,木质素的质量分数呈现出先增加后降低的趋势。堆肥前期木质素的质量分数变大,可能的原因是,木质素不含有易水解而重复的单元,是微生物最难降解的部分[42]。在堆肥反应中,微生物优先分解消耗结构相对简单、易分解的有机物,与纤维素的降解相比,木质素的降解主要集中在堆肥腐熟阶段;堆肥结束时,各处理木质素的降解率为10.86%~13.54%。SB-C处理组木质素降解率(13.54%)显著高于对照组CK-C(11.45%),这说明生物炭和湿地底泥在沉水植物腐熟过程中对木质素的降解有促进作用。对比B-H与S-H处理组、B-C与S-C处理组的木质素含量可知,湿地底泥对堆肥过程中木质素降解的促进作用大于生物炭。其可能的原因是,生物炭虽然为微生物的生长繁殖营造了一个相对适宜的环境,但湿地底泥具有更丰富的微生物群落及数量,微生物活动更加旺盛,产生更多益于木质素分解的酶。
3. 结论
1)在沉水植物堆肥时,将生物炭和湿地底泥作为调理剂可使堆体迅速升温并延长高温持续时间,从而促进沉水植物堆肥中碳、氮转化循环过程,提高腐殖质含量。
2)生物炭较湿地底泥更能促进堆肥C/N下降,提高种子发芽指数;生物炭和湿地底泥的协同作用可显著提高沉水植物好氧堆肥进程、优化堆肥的理化性质。
3)自制微生物菌剂为堆体提供了更有效的微生物种群,可促进木质纤维素降解酶的合成,提高木质纤维素的生物降解率,加速腐殖质的形成,从而易形成更稳定、更高效的堆肥产品。
-
表 1 反应器运行策略
Table 1. Operation strategy in the reactors
反应器名称 运行阶段 时间/d 进水NH4+-N/(mg·L−1) 进水NO2−-N/(mg·L−1) HRT/h 有无回流 R1 Ⅰ 1~71 40 50 24 无 Ⅱ 72~111 60 80 24 无 Ⅲ 112~183 60 80 24 有 R2 Ⅰ 1~71 40 50 24 无 Ⅱ 72~111 60 80 24 无 Ⅲ 112~157 60 80 24 有 Ⅳ 158~221 80~120 100~150 24 有 R3 Ⅰ 1~71 40 50 24 无 Ⅱ 72~111 60 80 24 无 Ⅲ 112~221 80~120 100~150 24 有 -
[1] KARTAL B, KUENEN J G, LOOSDRECHT M C M V. Sewage treatment with anammox[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5979): 702-703. doi: 10.1126/science.1185941 [2] LI B J, WANG Y, WANG W H, et al. High-rate nitrogen removal in a continuous biofilter anammox reactor for treating low-concentration nitrogen wastewater at moderate temperature[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 337: 125496. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125496 [3] LIU Y X, LIU W, LI Y Y, et al. Layered inoculation of anaerobic digestion and anammox granular sludges for fast start-up of an anammox reactor[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 339: 125573. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125573 [4] KANG D, LI Y Y, XU D D, et al. Deciphering correlation between chromaticity and activity of anammox sludge[J]. Water Research, 2020, 185: 116184. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116184 [5] KWAK W, ROUT P R, LEE E, et al. Influence of hydraulic retention time and temperature on the performance of an anaerobic ammonium oxidation fluidized bed membrane bioreactor for low-strength ammonia wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 386: 123992. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123992 [6] MARIUSZ T, GRZEGORZ C, ALEKSANDRA Z B. Influence of temperature and pH on the anammox process: A review and meta-analysis[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 182: 203-214. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.003 [7] 汪瑶琪. 有机物对厌氧氨氧化反应的影响及其微生物研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州科技大学, 2018. [8] MA W J, LI G F, HUANG B C, et al. Advances and challenges of mainstream nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater with anammox-based processes[J]. Water Environment Research, 2020, 92(11): 1899-1909. doi: 10.1002/wer.1342 [9] 陈文静, 陈圣东, 梁佳茵, 等. Anammox脱氮工艺启动研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(11): 130-140. [10] 程荟瑜. Anammox-EGSB反应器启动及回流比对脱氮性能影响研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020. [11] 朱晓桐, 于冰洁, 林久淑, 等. Anammox-UASB反应器启动特性[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(12): 143-150. [12] 唐崇俭, 郑平, 陈建伟, 等. 不同接种物启动Anammox反应器的性能研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2008, 28(8): 683-688. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2008.08.003 [13] 姜晓芬. 河口近岸厌氧氨氧化菌群结构、丰度及活性对盐度变化的响应[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2017. [14] ZHENG Y L, HOU L J, LIU M, et al. Dynamics and environmental importance of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) bacteria in urban river networks[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254(PtA): 112998. [15] FU L L, CHEN Y Y, LI S Q, et al. Shifts in the anammox bacterial community structure and abundance in sediments from the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacentarea[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 2019, 42(3): 383-396. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2018.12.008 [16] 赵折红, 李月秋, 皮海廷, 等. 三峡库区香溪河沉积物厌氧氨氧化菌的时空分布[J]. 生物学杂志, 2021, 38(2): 70-74. [17] 秦红益. 太湖沉积物厌氧氨氧化细菌分布、多样性及其活性研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2017. [18] 沈李东. 湿地亚硝酸盐型厌氧氨氧化和厌氧甲烷氧化微生物生态学研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014. [19] ANTHONISEN A C, LOEHR R C, PRAKASAM T B S, et al. Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid[J]. Journal - Water Pollution Control Federation, 1976, 48(5): 835-852. [20] LIU G Q, WANG J M. Long-term low DO enriches and shifts nitrifier community in activated sludge[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(10): 5109-5117. [21] 李祥, 黄勇, 周呈, 等. 增设回流提高厌氧氨氧化反应器脱氮效能[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(9): 178-183. [22] 付昆明, 苏雪莹, 王会芳, 等. 内回流对厌氧氨氧化UASB反应器脱氮性能的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(12): 3560-3566. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.12.005 [23] CHAMCHOI N, NITISORAVUTS S, SCHMIDT J E. Inactivation of anammox communities under concurrent operation of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) and denitrification[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(9): 3331-3336. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.029 [24] ZHU G B, WANG S Y, WANG W, et al. Hotspots of anaerobic ammonium oxidation at land-freshwater interfaces[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(2): 103-107. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1683 [25] 张泽文, 李冬, 张杰, 等. 接种单一/混合污泥对厌氧氨氧化反应器快速启动的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(12): 5215-5221. [26] 于德爽, 赵丹, 李津, 等. 接种不同污泥源条件下厌氧氨氧化菌的特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(11): 4339-4345. [27] 明大成. Anammox反应器的快速启动及有机物影响脱氮性能的研究[D]. 湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2018. [28] 郑林雪, 李军, 胡家玮, 等. 同步硝化反硝化系统中反硝化细菌多样性研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(1): 116-121. [29] SPEIRS LACHLAN B M, RICE DANIEL T F, PETROVSKI S, et al. The phylogeny, biodiversity, and ecology of the chloroflexi in activated sludge[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 2015. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02015 [30] TOMONORI K, SHOTA Y, NORIATSU O, et al. Ecophysiological role and function of uncultured chloroflexi in an anammox reactor[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2012, 66(12): 2256-2561. [31] BEATRIZ F G, MICHAEL R, MARGARETE S, et al. Ecology of marine bacteroidetes: A comparative genomics approach[J]. The ISME Journal, 2013, 7(5): 1026-1037. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.169 [32] SUN H M, ZHOU Q, ZHAO L, et al. Enhanced simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate using novel solid carbon source/zero-valent iron composite[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 289: 125757. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125757 [33] CHEN C, GUO W S, NGO H H, et al. Evaluation of a sponge assisted-granular anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SG-AnMBR) for municipal wastewater treatment[J]. Renewable Energy, 2017, 111: 620-627. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2017.04.055 [34] WANG C, LIU S, XU X, et al. Achieving mainstream nitrogen removal through simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification process in an integrated fixed film activated sludge reactor[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 203: 457-466. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.016 [35] DU R, CAO S B, LI B K, et al. Performance and microbial community analysis of a novel DEAMOX based on partial-denitrification and anammox treating ammonia and nitrate wastewaters[J]. Water Research, 2017, 108: 46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.10.051 [36] ZHAO L, FU G P, WU J F, et al. Bioaugmented constructed wetlands for efficient saline wastewater treatment with multiple denitrification pathways[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 335: 125236. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125236 [37] 王晓曈, 杨宏, 苏杨, 等. 生物滤池快速启动ANAMMOX运行策略及菌群特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(7): 3345-3355. [38] 吴珊, 王淑雅, 王芬, 等. 温度对ANAMMOX生物膜工艺的脱氮影响与菌群结构分析[J/OL]. 环境科学, 2021: 1-11[2021-09-01]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202105280. [39] ZHANG X J, ZHANG N, CHEN C, et al. Long-term impact of sulfate on an autotrophic nitrogen removal system integrated partial nitrification, anammox and endogenous denitrification (PAED)[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 235: 336-343. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.175 [40] 陈方敏, 高佳琦, 黄勇, 等. 基质暴露水平对ANAMMOX微生物活性及生物量的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(11): 5066-5072. [41] 汪倩, 宋家俊, 郭之晗, 等. 低基质浓度下生物膜亚硝化工艺的快速启动及其运行效能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(7): 2512-2521. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202102098 -






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: