-
电镀、化学镀等表面处理过程产生的废水中通常含有铬、锌、铜、镍等重金属及氰化物等污染物,必须对其进行严格处理[1]。铜是主要镀种之一,含铜废水主要来自镀件漂洗,其中含有大量铜和有机污染物[2]。电镀过程中广泛使用的络合剂(乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)、柠檬酸、酒石酸)会与铜形成稳定性高且形态复杂的络合铜[3],如EDTA-Cu稳定常数比Cu(OH)2高5个数量级[4]。络合态重金属多数具有很高的水溶性,且在广泛的pH范围内能够稳定存在,使得铜难以从废水中有效去除[5]。以碱沉淀法和硫化物沉淀法为代表的化学沉淀法是目前广泛使用且经济性较好的方法[6-9],但在铜浓度较低时效果不佳,且沉淀物在酸性条件下不稳定。吸附法[10-12]、电解法[13]、离子交换法[14-15]、高级氧化还原法[16-18]等其他方法也存在成本较高、再生困难等问题。因此,废水中络合铜的有效、经济去除是一个亟待解决的问题。
重金属捕集剂能与废水中的重金属或络合态重金属迅速发生螯合作用,产生难溶的螯合沉淀,具有反应速率快、沉淀物稳定、选择性好的优点,已成为重金属污染处理领域关注的热点,具有广泛的应用前景[19-22]。在重金属捕集剂中,二硫代氨基甲酸盐(DTC)类捕集剂使用广泛。谭聪等[23]用二硫化碳、碳酰肼为原料,合成了重金属捕集剂DT-SC,对Cu2+、Cd2+、Mn2+去除率均在90%以上。张翔等[24]采用二并哌嗪、二硫化碳等在碱性条件下合成重金属捕集剂TDDP,在最佳反应条件下对Cu2+和Pb2+去除率均超过96%,对Zn2+去除率也超过91%。二乙基二硫代氨基甲酸钠(DDTC)、SDDC[25]等小分子螯合剂及二硫代羧基化羟甲基聚丙烯酰胺(DTMPAM)[26]、聚-二硫代氨基甲酸铵(PADTC)[27]等高分子螯合剂,对Cu具有良好的去除性能。其中高分子螯合剂沉降性能较好,但其较大的空间位阻使得DTC基团利用率较低,且存在成本较高的问题[28]。同时,小分子螯合剂DTC基团利用率相对较高,但含有单个螯合基团的小分子螯合剂去除能力有限。分子质量大小适当并拥有多个DTC基团的螯合剂可提升捕集效率和去除性能。因此,采用三乙烯四胺等为原料合成多硫代氨基羧基基团的重金属捕集剂,一方面可提升二硫代羧基的数量,去除能力显著增强;另一方面具有适当分子链长,可降低空间位阻,使得基团利用效率进一步提升。综上所述,本文以三乙烯四胺等为原料,在操作简单、条件温和的条件下合成重金属捕集剂N,N-双(二硫代羧基)三乙烯四胺(TDTC),对EDTA-Cu等具有优异的去除效果,以期为含铜废水的高效处理提供参考。
-
本研究所用聚丙烯酰胺(PAM,MW 300万)购于天津市大茂化学试剂厂,氢氧化钠(NaOH)、乙二醇(C2H6O2)、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(C10H14N2O8Na2·2H2O)、硫酸铜(CuSO4·5H2O)、柠檬酸(C6H8O7·H2O)、酒石酸钾钠(C4H4O6KNa·4H2O)均购于广州化学试剂厂,三乙烯四胺(TETA)、二硫化碳(CS2)均购于上海阿拉丁公司,试剂均为分析纯。
-
1) TDTC的合成。向有冷凝和搅拌装置的250 mL三颈烧瓶中加入一定量的混合溶剂(V乙二醇/
VH2O =1∶1),加入TETA 0.1 mol(14.98 mL),冰水浴条件下中慢速滴加CS2 0.23 mol(13.86 mL),滴加完成后升至室温,恒温水浴条件下反应2 h,抽滤,用无水乙醇和去离子水洗涤产品2~3次,干燥至恒重,得到微溶于水的淡黄色粉末N,N-双(二硫代羧基)三乙烯四胺,即TDTC。重金属捕集剂TDTC制备反应如式(1)所示。
2)模拟废水的配制。按照络合剂与Cu摩尔比为1∶1称取适量的乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-2Na)、柠檬酸(C6H8O7·H2O,CA)与酒石酸钾钠(C4H4O6KNa·4H2O,TA)与五水硫酸铜(CuSO4·5H2O)配制乙二胺四乙酸二钠络合铜(EDTA-Cu)、柠檬酸络合铜(CA-Cu)、酒石酸络合铜(TA-Cu) 3种模拟废水。
3)络合Cu去除实验。在室温条件下,在150 mL烧杯中分别加入100 mL Cu质量浓度为50 mg·L−1的EDTA-Cu、CA-Cu、TA-Cu溶液,调节pH,添加一定量TDTC固体,置于搅拌器中快速(300 r·min−1)搅拌,然后液体投加1.0 mg·L−1 PAM,慢速(70 r·min−1)搅拌一定时间,静置 10 min,取液面下2 cm处上清液,上清液中残留的Cu浓度用原子吸收分光光度计测定,Cu去除率根据式(2)进行计算。
式中:
R 为去除率,%;C0为溶液中Cu的初始质量浓度,mg·L−1;C1为处理后溶液中Cu的剩余质量浓度,mg·L−1。 -
pH采用酸度计(雷磁pHS-25)测定;Cu浓度采用火焰原子吸收分光光度计(WFX-110B,检出限0.006 mg·L−1,北分瑞利)测定;TDTC及其沉淀表面形态观察使用扫描电子显微镜(Hitachi S4800,日本日立);TDTC捕集重金属前后红外光谱采用KBr压片法在傅立叶红外光谱仪(Nicolet 670,美国Thermo Fisher)上完成;XPS测试使用X射线光电子能谱仪(Thermo Scientific K-Alpha+,美国Thermo Fisher);捕集剂与螯合产物元素分析采用有机元素分析仪(Vario MACRO cube,德国Elementar)测定碳、氢、氮、硫含量。
-
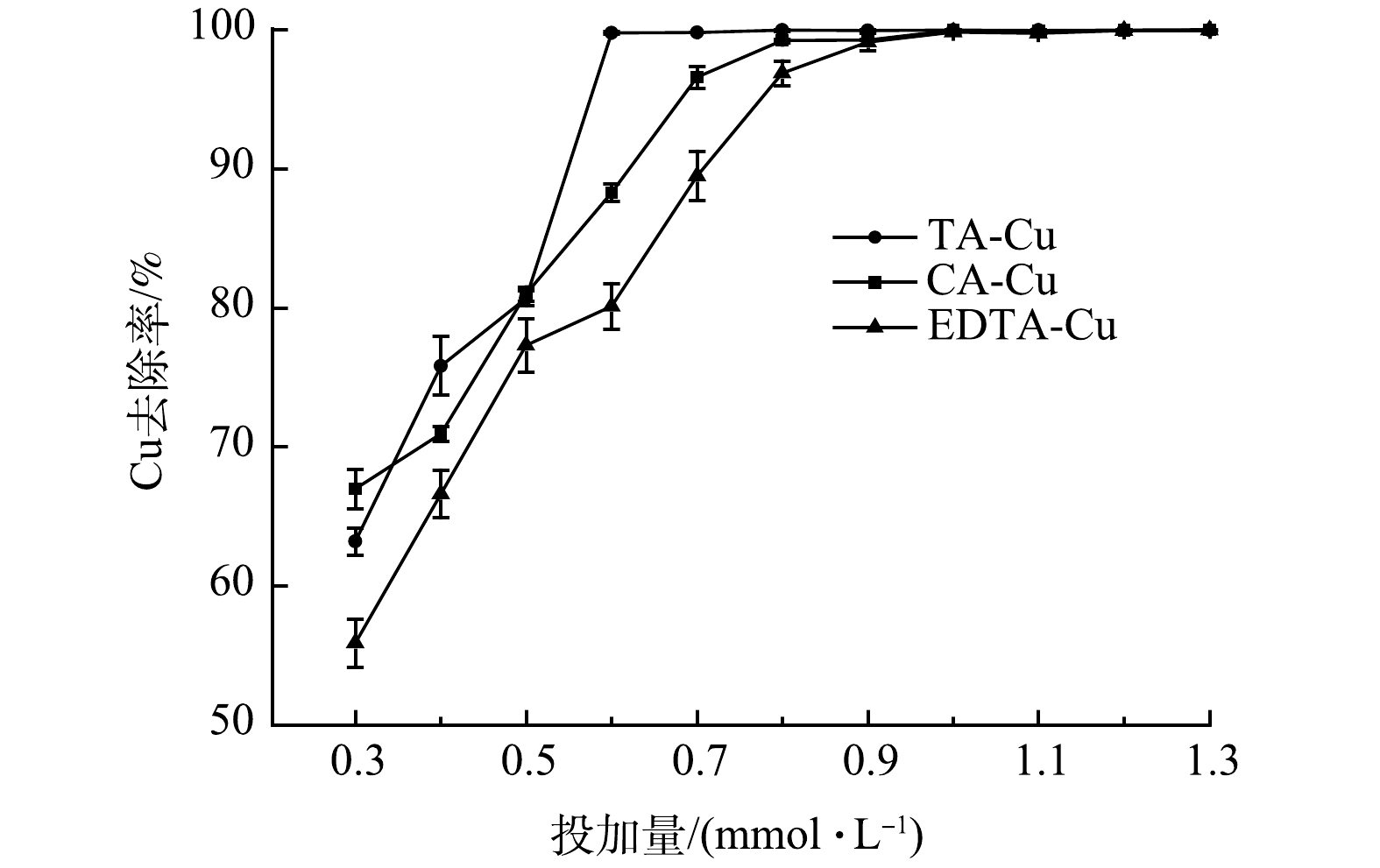
在PAM添加量为1.0 mg·L−1、反应时间5 min、静置10 min、溶液pH为4.0、 Cu质量浓度为50 mg·L−1的条件下,加入不同量的重金属捕集剂,络合Cu的去除率变化如图1所示。由图1可知,当TDTC投加量<1 mmol·L−1时,3种络合Cu的去除率随TDTC投加量增加而持续增加;当捕集剂达到1 mmol·L−1时,络合Cu去除率基本稳定,达到99.6%以上,此时反应体系中的Cu质量浓度均在0.2 mg·L−1以下。此外,TDTC对3种络合态Cu均有较好的去除效果,二硫代羧基对于Cu的络合能力强于TA、CA、EDTA。在TDTC投加量相同的情况下,Cu去除率由高到低为TA-Cu>CA-Cu>EDTA-Cu。这是因为3种络合剂与Cu形成络合物的稳定常数由低到高为TA-Cu<CA-Cu<EDTA-Cu[29],TDTC在与络合剂的配位竞争中络合剂的稳定常数越小,TDTC竞争越占优势,螯合沉淀效率越高,因此,同等投加量的TDTC对稳定常数小的络合Cu去除效果更好。继续增加投加量,去除率有一定上升,但幅度不大,投加量过高造成水中COD由170 mg·L−1增加到407.5 mg·L−1,同时会导致处理成本的上升,所以选定TDTC最佳投加量为1 mmol·L−1。
-
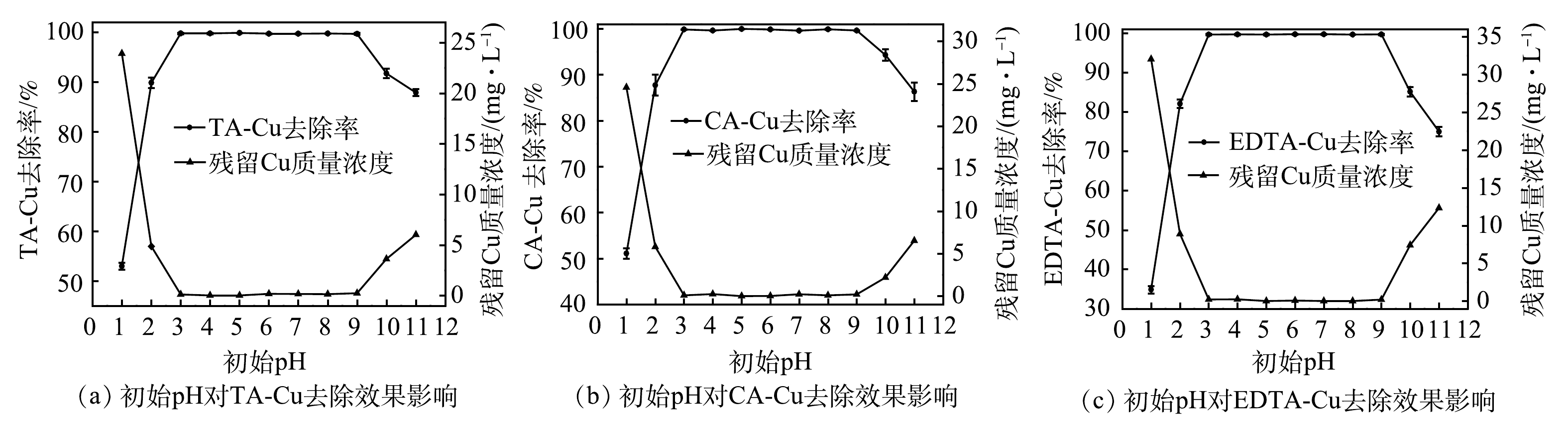
初始pH对TDTC捕集重金属离子效果影响较大。在PAM投加量为1.0 mg·L−1、TDTC投加量为1 mmol·L−1、反应时间5 min、静置10 min、 Cu质量浓度为50 mg·L−1的条件下,采用0.1 mol·L−1的HCl/NaOH调节体系初始pH,初始pH对络合Cu去除率影响结果如图2所示。投加捕集剂之前先分别调节反应体系pH为1.0~11.0,没有Cu(OH)2沉淀物的形成,表明TA-Cu、CA-Cu、EDTA-Cu在酸性和碱性条件下处于稳定状态,碱沉淀法不能处理含络合铜废水。由图2可知,当pH为3.0 ~ 9.0时,残留Cu质量浓度均在0.2 mg·L−1以下,达到排放标准要求;当pH<3.0或pH>9.0,即强酸或强碱情况下去除效果明显下降。初始pH会影响TDTC的电离平衡,当pH>11.0时,3种络合态Cu的去除率均有下降,处于在90%以下。这是因为pH的持续上升会使式(3)中的平衡向右移动,可使更多的二硫代羧基失去质子而呈离子化状态,更容易与Cu2+螯合,但在强碱情况下,络合剂与Cu2+的配合物稳定性更强,不利于捕集。
如柠檬酸在溶液中有C6H8O7、C6H7O7−、C6H6O72−、C6H5073− 4种形态,对应的电离常数分别为pk1=3.13、pk2=4.76、pk3=6.40。在碱性条件下,柠檬酸的酸效应减弱,与Cu2+形成的络合物更加稳定,导致去除效率下降;当pH<3.0时,式(3)中的电离平衡左移,产生的离子化二硫代羧基减少,不利于对Cu2+的捕集,且基团中的螯合位点相较于Cu2+更易与H+结合,带正电荷的—N+HR2与二硫代羧酸形成内盐,导致Cu2+去除率下降[30-31]。实际重金属废水多为酸性,TDTC处理含铜废水无需调节pH至中性或碱性,处理后的溶液也便于回用,适用范围广,比传统化学沉淀法具有明显优势。
-
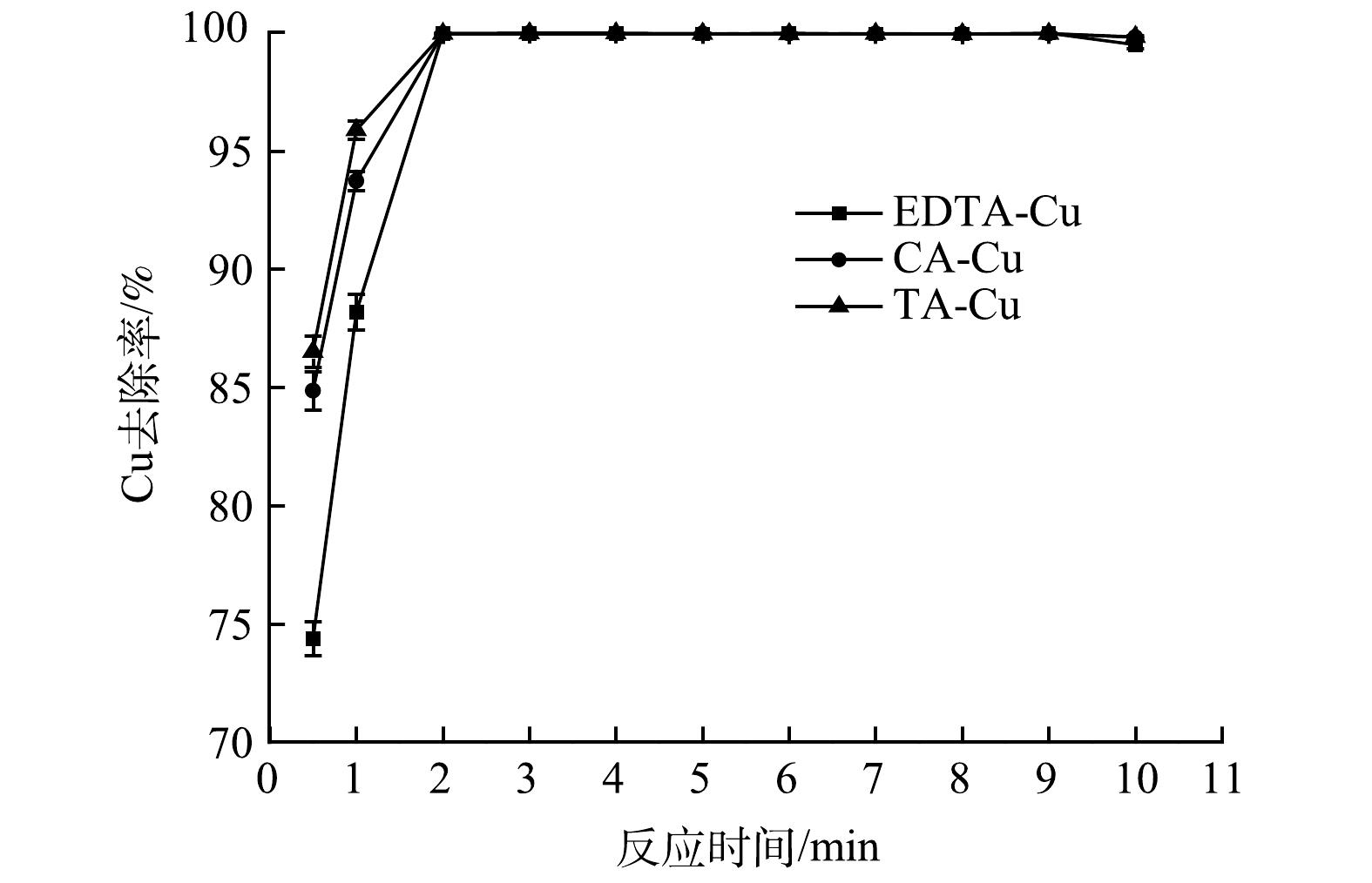
采用100 mL络合Cu质量浓度为50 mg· L−1的实验废水,TDTC投加量为1 mmol·L−1,调节pH=4.0,PAM添加量为1 mg·L−1,调节搅拌速度为慢搅(70 r·min−1),搅拌0~10 min,以探究反应时间对络合Cu去除效率的影响,结果见图3。由图3可知,前30 s时间段内络合Cu的去除率为70%~90%。这可能因为该阶段捕集剂与络合剂处于对Cu2+的螯合竞争,Cu2+从络合物中释放出来并立即形成螯合物。在前3 min,Cu去除率随反应时间的延长而提高,然后去除率逐渐趋于稳定,TDTC与络合Cu的反应基本完成,Cu去除率在99.8%以上;在反应时间大于10 min后,Cu去除率稍有下降,这可能是因为长时间搅拌会导致已形成的絮体破碎,从而影响出水水质。考虑到实际应用中的成本因素,选取反应时间为3 min。
-
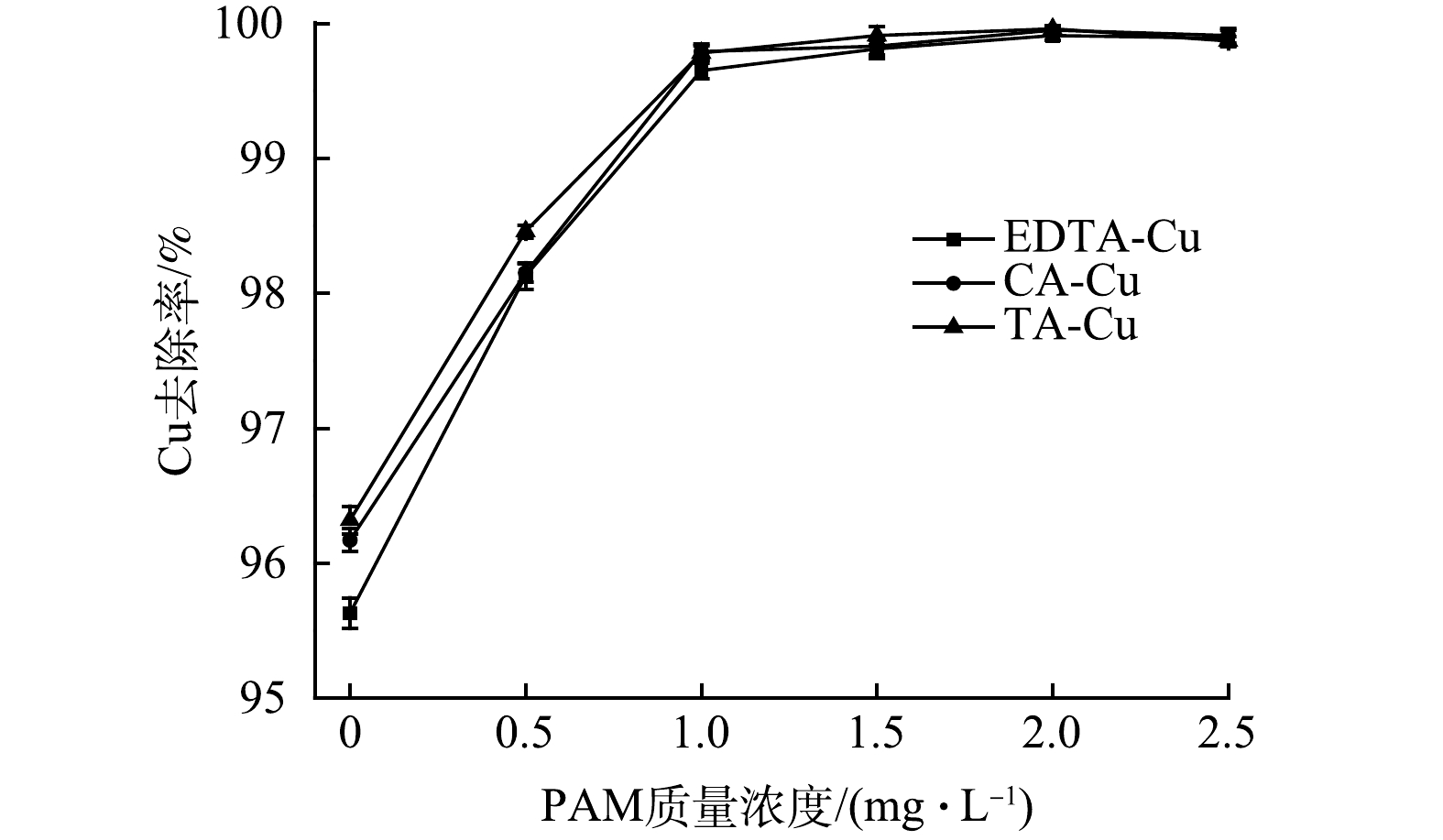
取100 mL、50 mg·L−1的3种络合Cu模拟废水,在pH为4.0,TDTC投加量为1 mmol·L−1,反应时间5 min,静置10 min的条件下,加入不同量的絮凝剂PAM,以探究絮凝剂PAM在对络合Cu去除的影响。由图4可知,在不添加絮凝剂PAM的情况下,EDTA-Cu、CA-Cu与TA-Cu的去除率分别为95.63%、96.17%和96.32%,沉降性能较没有添加絮凝剂PAM时弱。随着絮凝剂用量的增加,3种络合铜的去除率随之增大,这可能是部分捕集剂在将Cu从络合剂中捕集出来后,形成的细小微粒没有与絮体一同沉降去除,而PAM与细小悬浮颗粒物通过架桥作用连接形成大絮体从而使该部分得以去除。当PAM添加量为1 mg·L−1时,3种络合Cu的去除率均在99.6%以上,且趋于稳定。综合考虑经济成本,选用PAM最佳用量为1 mg·L−1。
-
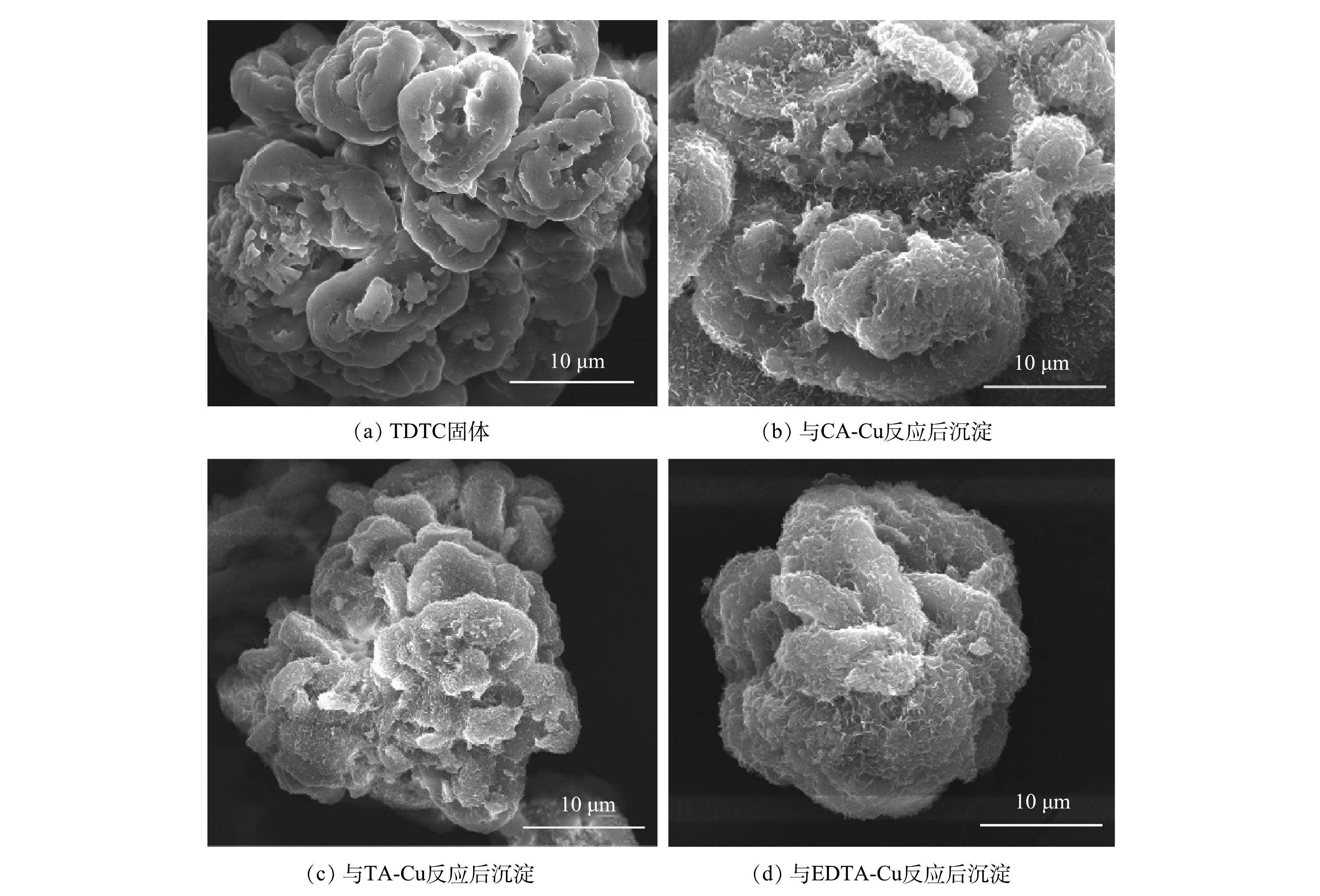
1) TDTC及其捕集产物的表面形态。通过扫描电镜观察TDTC及其捕集产物的表面形态。图5(a)为TDTC固体的SEM图,图5(b)、图5(c)和图5(d)为3种螯合沉淀的SEM图。由图5(a)可看出,捕集剂形态不规则,其表面光滑,比表面积大,结构紧密,层次堆积明显。由图5(b)、图5(c)与图5(d)可看出,相较于图5(a)中的TDTC,反应后生成的螯合沉淀形态不规则,表面变得相对粗糙,颗粒之间结合更加紧密。这是由TDTC将络合Cu中的Cu有效捕集出来所致。而3种沉淀形态的差异可能是由于TDTC在与不同络合Cu反应过程中,因不同络合剂络合能力大小不一,用于争夺Cu所用的TDTC量会有差异,导致形成沉淀的形态不同。
2) TDTC元素分析。由表1中数据计算可得,TDTC中C、H、N和S的摩尔比接近于4∶9∶2∶2的理论比值。结合上述分析结果,可以认为有效合成了TDTC,化合式为C4H9N2S2。产品中C、S超过理论值,说明产品不纯,还含有一定量杂质,推测其可能是CS2等反应物。
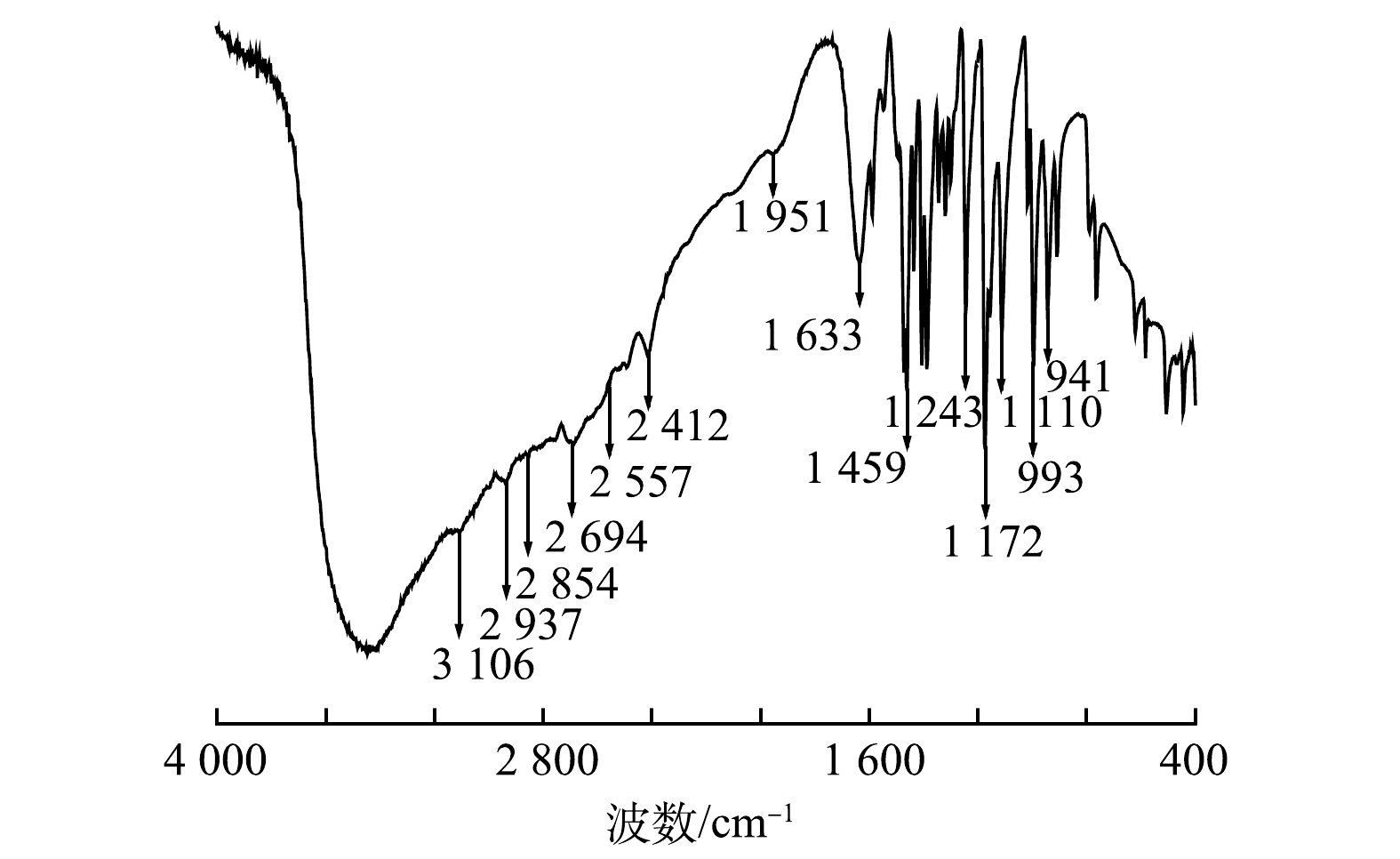
3)红外光谱分析。在400~4 000 cm−1对TDTC进行红外光谱扫描,结果如图6所示。2 937 cm−1处为C—H伸缩振动,低于3 000 cm−1,该吸收峰为C—H的饱和吸收峰[32];2 854 cm−1处为—CH2的对称伸缩振动峰[33];2 557 cm−1处为—SH的振动伸缩峰[34];1 633 cm−1处为N—H的变形振动峰[31];1 459 cm−1处为N—CS2的伸缩振动吸收峰,此峰介于C—N单键(1 300 cm−1)和C=N双键(1 600 cm−1)之间,具有部分双键性质[35];1 243 cm−1处有C=S特征吸收峰;在1 110、993、941 cm−1处有C—S的振动伸缩峰,低于C=S双键的特征吸收(1 501~1 200 cm−1),高于C—S单键的特征吸收(600~700 cm−1),且为强吸收峰,具有部分双键性质[36-37]。以上结果说明反应产物含有二硫代氨基羧基基团。
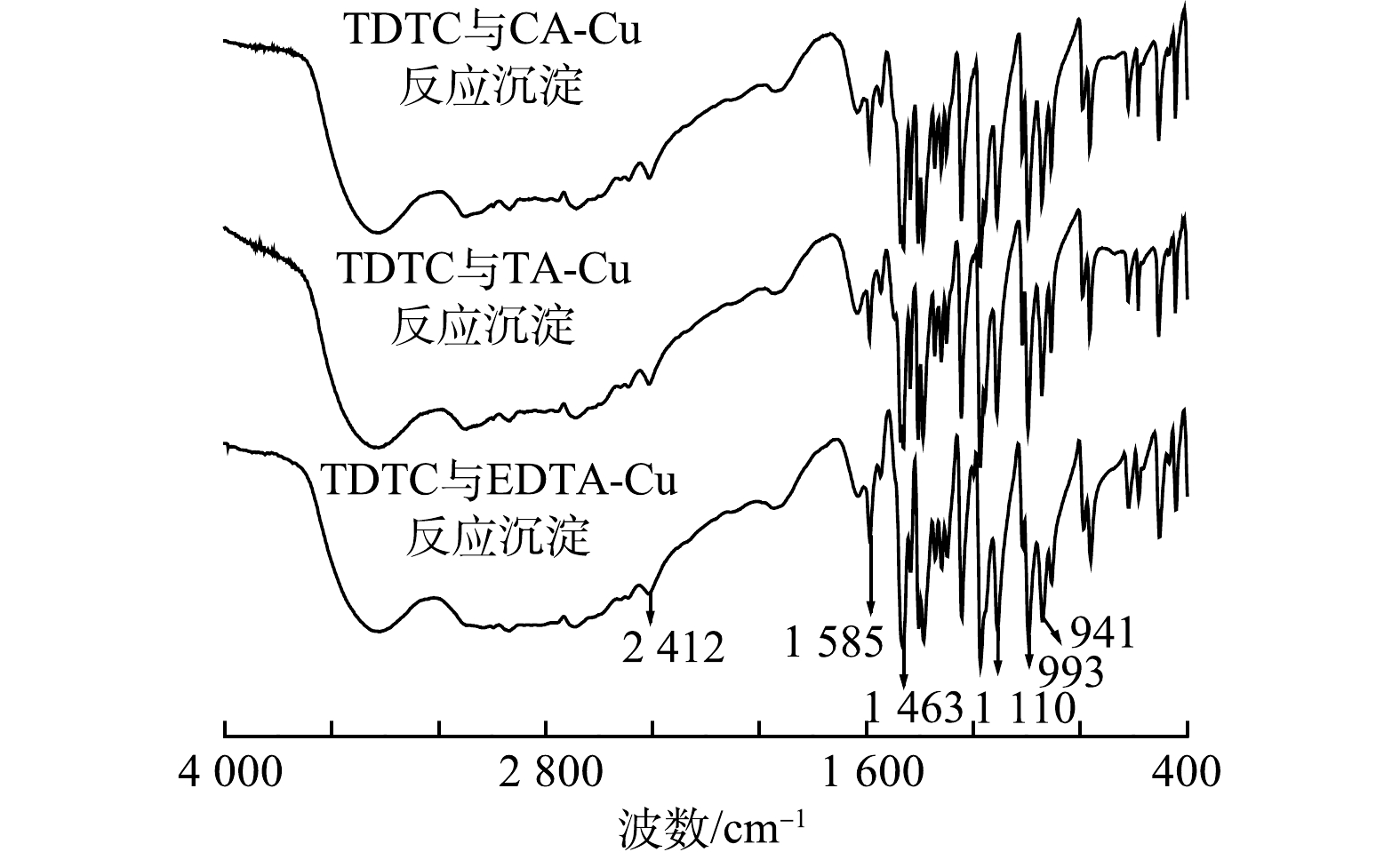
在上述最佳处理条件下,将捕集剂与3种模拟络合Cu废水反应得到棕红色沉淀,对其进行红外光谱表征,结果见图7。由图7可知,3种沉淀的红外谱图在强度及峰位上的表现差异不大,表明产生的3种沉淀在官能团类型大体上是一致的,而TA、CA、EDTA 3种络合剂官能团并不完全一致。由此可以推断,在螯合反应过程中产生的最终沉淀物不含各种络合剂,也可能是由于捕集剂和络合剂中部分官能团吸收峰重叠所致。
比较图6与图7结果可见,捕集剂在1 459 cm−1处的N—CS2的伸缩振动吸收峰发生位移至1 463 cm−1处且吸收峰强度减小,2 557 cm−1处的—SH特征吸收峰在与络合Cu反应之后消失,1 110、993、941 cm−1处的C—S振动伸缩峰与1 243 cm−1处的C=S特征吸收峰强度有所降低。以上峰变化的结果表明,反应的主要基团—CSS与络合剂上的Cu发生螯合反应,S的电负性减小,—CSS的共轭体系发生改变。同时,1 459 cm−1处的N—CS2的伸缩振动吸收峰的的位移与1 633 cm−1处的N—H峰强的变化可能是由于N与Cu形成配位键所致。
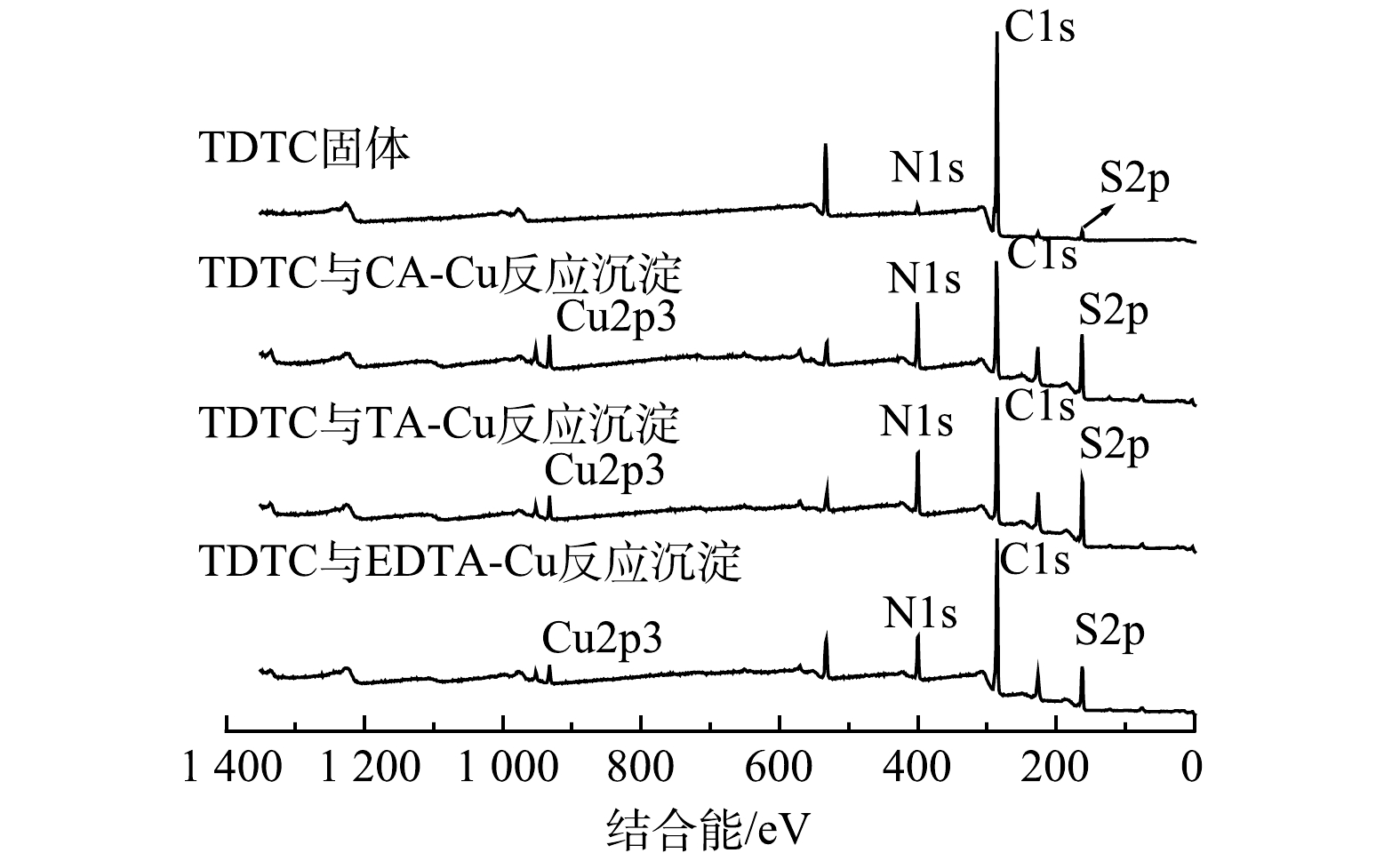
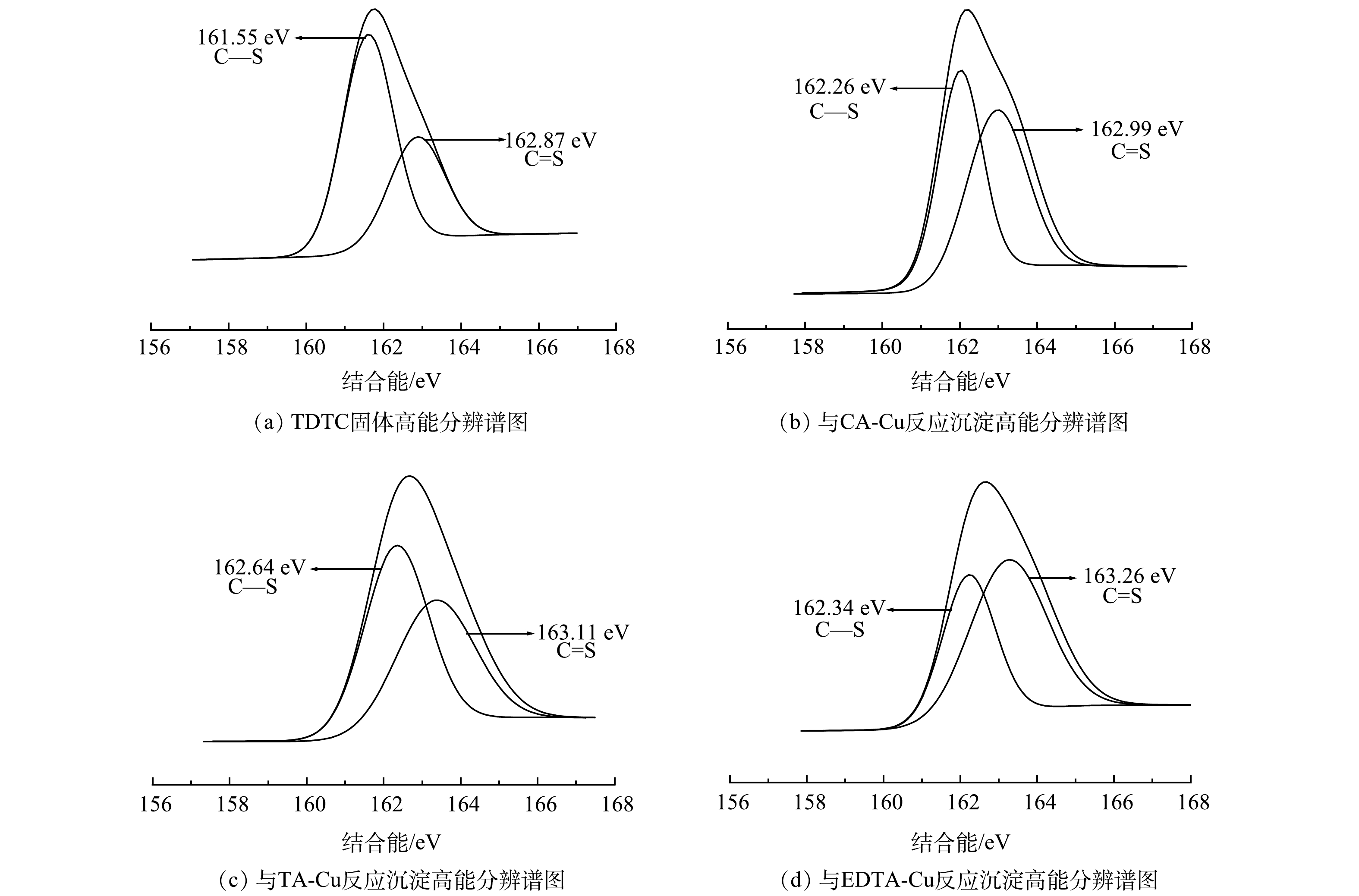
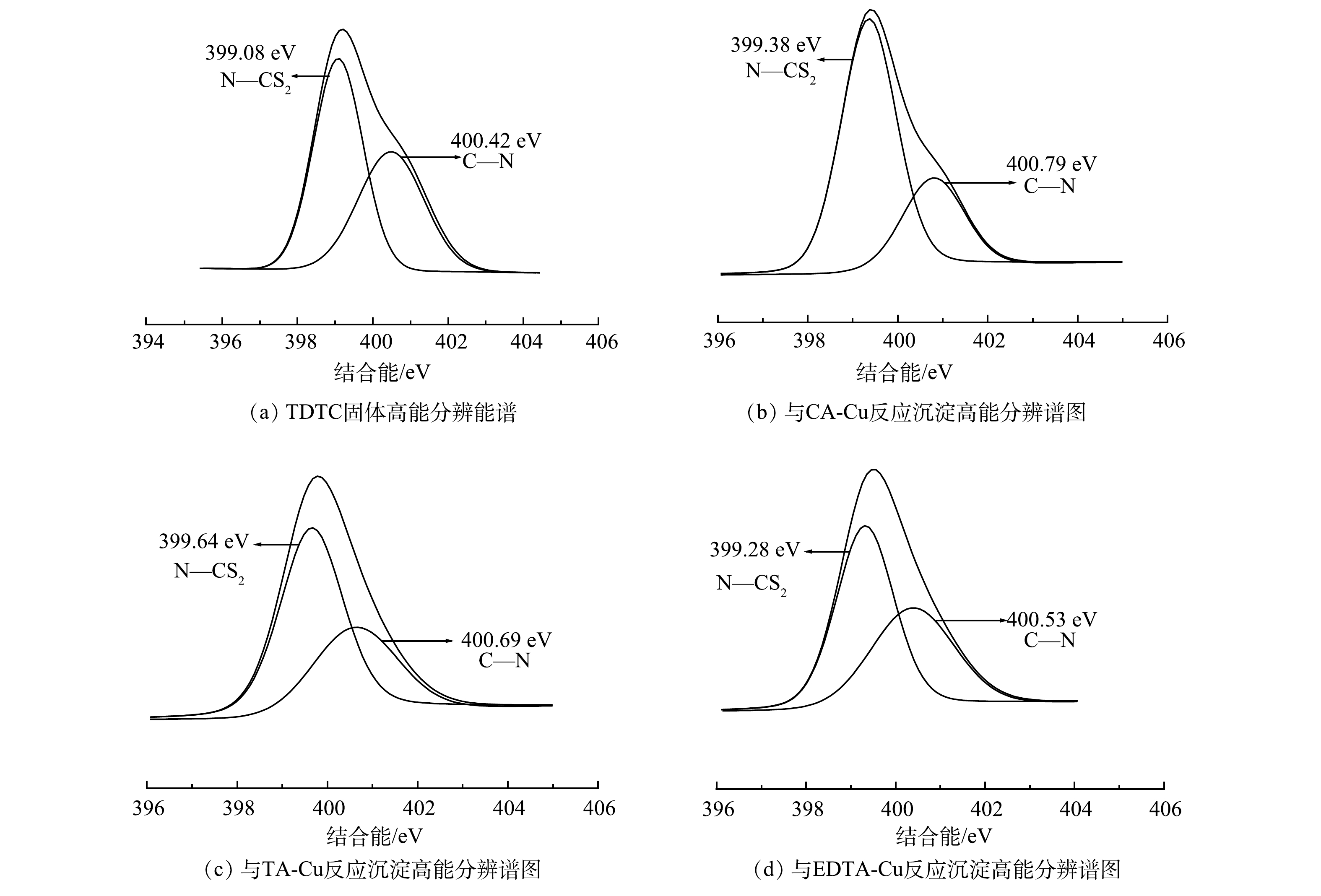
4) XPS分析。利用XPS来分析TDTC及其捕集3种不同络合Cu前后表面化学组成与结构变化及键合机理。图8为TDTC及3种螯合沉淀的XPS谱图,图9和图10为TDTC及3种螯合沉淀的S2p、N1s的XPS高分辨能谱图。由图8可知,在TDTC与CA-Cu、TA-Cu与EDTA-Cu反应形成沉淀的宽谱扫描能谱中均出现Cu2p3峰信号,而TDTC固体没有相应的峰,表明TDTC在与络合剂对Cu的竞争中成功将Cu螯合。由图9可知,TDTC与TDTC-Cu中二硫代羧基基团C—S键的S2p结合能分别为161.55 eV和162.64、162.26、162.34 eV,捕集后产生的3种沉淀S2p的结合能都大于前者。这是因为TDTC-Cu中二硫代氨基羧基中C—S的S原子螯合过程中向Cu贡献了电子,使反应后结合能升高[38]。TDTC和TDTC-Cu中二硫代羧基中C=S的S2p结合能分别为162.87 eV和163.11、162.99、163.26 eV,变化很小,说明DTC中C=S键也较微弱地参与了与Cu的螯合过程。图10中N1s高分辨率能谱图由N—CS2和C—N 2个峰组成,TDTC与TDTC-Cu中N—CS2键的结合能分别为399.08、399.64、399.38和399.28 eV,TDTC与TDTC-Cu中C—N键中N1s结合能分别为400.42、400.79、400.69与400.53 eV,后者结合能相较于前者稍有增加。这表明DTC基团中的N原子与Cu之间可能存在一定的配位作用,致使N原子上的电子向Cu移动。以上结果表示TDTC在与络合Cu反应过程中S、N与Cu存在配位作用,并主要通过二硫代羧基的螯合配位作用将Cu捕集,与红外光谱分析结果基本一致。
-
本研究中合成的TDTC与其他研究中的重金属捕集剂的比较见表2。由表2可见,虽然本研究中初始铜浓度较高,但捕集剂与铜的质量比较低,质量比也更能说明其捕集性能。TDTC表现出更突出的捕集性能,在较宽pH范围内TDTC对络合Cu的去除率达99.6%以上,而表中其他捕集剂均在90%以下。
二硫代羧酸盐与铜配位时,1个Cu2+需要2个二硫代羧基。DDTC与DTC-S属于小分子螯合剂,螯合基团数量为1。以DDTC为例,与铜形成C9H20N2S4Cu的类双环结构,其中C=S中的S也会微弱参与螯合,在质量比接近情况下,TDTC较DDTC二硫代羧基相对量增加,与Cu发生螯合作用的官能团变多,更利于Cu的去除。此外,拥有多个螯合官能团比只含有单个螯合团的捕集剂产生的絮体更大,提升了去除效率。DTMPAM为高分子螯合剂,聚合长链上有多个螯合基团,但在投加量大于TDTC情况下去除率只有70%左右。这可能是其部分螯合基团因空间位阻未能与金属螯合,没有充分反应,导致利用率不高。相比之下,1个TDTC分子可以提供2个二硫代羧基参与螯合成环,捕集性能得以提高。在TDTC与铜原子螯合时,推测其两端的二硫代羧基分别与2个Cu2+配位,这一点尚需进一步深入研究。
-
1)采用三乙烯四胺和CS2为原料,在混合溶剂中(V乙二醇/
VH2O =1∶1)合成重金属捕集剂TDTC,产物为淡黄色粉末固体。TDTC分子中含有多个二硫代氨基羧基基团,可有效提高重金属捕集效率。2)在pH为3.0~9.0、TDTC为1 mmol·L−1、PAM为1 mg·L−1、反应时间为3 min的条件下,3种初始质量浓度为50 mg·L−1的络合Cu溶液中,Cu去除率达到99.6%以上,络合态Cu可被TDTC有效去除,残留Cu质量浓度均小于0.2 mg·L−1,符合水污染物特别排放要求中关于Cu的排放限值要求。
3) TDTC捕集络合Cu主要通过与原有络合剂竞争及二硫代羧基与Cu螯合,将可溶性的络合Cu变为难溶的沉淀物而去除。
高效重金属捕集剂TDTC对络合铜的去除性能
The performance of highly-efficient dithiocarbamate-based heavy metal chelating agent on complex copper removal
-
摘要: 传统化学沉淀法存在对酸性及低浓度的络合态重金属去除率低的问题,为解决此问题,以三乙烯四胺、二硫化碳为原料合成了重金属捕集剂N, N-双(二硫代羧基)三乙烯四胺(TDTC),并采用红外光谱等分析方法对其结构和主要官能团进行了表征。以酒石酸铜、柠檬酸铜和EDTA铜3种络合铜为去除对象,研究了TDTC对络合铜的去除性能及去除机理。结果表明,在pH为3.0~9.0、TDTC投加量为1 mmol·L−1、Cu质量浓度为 50 mg·L−1、PAM投加量为1 mg·L−1条件下,Cu去除率可达到99.6%以上。进一步的沉淀表征分析结果表明,TDTC对络合Cu的去除过程存在螯合配位反应,具有与相应络合剂的竞争优势,能够把Cu从相应的络合剂中脱除并形成难溶的螯合沉淀,从而实现废水中Cu的有效去除。以上研究结果可为利用特异重金属捕集剂去除重金属的工程实践提供参考。Abstract: Wastewater containing complex heavy metal in acid and low-concentration is difficult to be treated effectively by traditional chemical precipitation. Triethylenetetramine and carbon disulfide were taken as raw materials to prepare a heavy metal chelating agent of N, N-bis(2-mercaptoethyl) triethylene-tetramine (TDTC) in a mixing solvent of ethylene glycol and deionized water. Fourier transform infrared spectra, scanning electron microscopy and elemental analysis were used to characterize the structure of TDTC. The removal performance and mechanism of TA-Cu(tartaric acid, TA), CA-Cu(citric acid, TA-Cu) and EDTA-Cu by TDTC were discussed. The experimental results show that at pH of 3.0 to 9.0, TDTC dosage of 1 mmol·L−1, reaction time of 3 min and PAM dosage of 1.0 mg·L−1, over 99.6% Cu could be removed from a simulated wastewater containing complex Cu with initial concentrations of 50 mg·L−1. IR, XPS and SEM analysis on the chelate precipitate showed that the chelating reaction occurred between TDTC and Cu. The competitive edge on Cu cheating by TDTC could withdrew Cu from other complexing agents and led to the occurrence of insoluble chelated precipitate. Thus, Cu could be efficiently removed from wastewater. This research can provide theoretical guidance for removing heavy metal by heavy metal chelation in engineering practice.
-
Key words:
- heavy metal chelating agent /
- complex copper /
- chelate /
- removal mechanism
-
挥发性有机物(VOCs)是导致城市雾霾与光化学污染等大气复合污染的重要前体物,对人类健康和生态环境产生重大影响,已经引起了政府和公众的广泛关注[1-3]。因此,打好蓝天保卫战,VOCs治理是关键。在众多VOCs末端控制技术中,催化氧化技术因其具有高效性和彻底性等优势引起了学界的极大关注[4-5]。催化氧化技术的核心问题是开发出高效稳定且具有低温活性的新型催化剂[4-6]。一般而言,能够催化降解VOCs的催化剂有贵金属和过渡金属2大类,其中,贵金属催化剂具有催化活性高、稳定性差等特点,此外,贵金属催化剂因其价格昂贵和易中毒失活使其在工业应用中受到了极大的限制[5]。因此,研究开发低温高效的过渡金属氧化物催化剂成为了目前研究的热点[4-5, 7]。
近年来,Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂因其具有良好的催化氧化性能受到了研究人员的极大关注[7-11]。Mn-Ce复合氧化物一方面具备CeO2优异的储氧/释氧能力[12-13],另一方面MnOx具有环保、廉价易得且存在多种价态等优点[14-17]。然而传统制备工艺合成的Mn-Ce催化剂存在颗粒易团聚和形貌不可控等问题,这一定程度上限制了该类催化剂的改进和应用。本研究通过简单的水热合成法制备了一系列Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂,有望解决上述提及的问题。
目前研究结果表明,纳米材料在催化过程中具有形貌效应[15-17],将其应用于催化氧化VOCs方面也取得了大量的研究成果[6-7, 12]。纳米材料的催化性能与其形貌特性密切相关,LIAO等[7]通过水热法制备的具有纳米棒形貌的Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂在反应温度225 ℃下即可实现甲苯的完全降解。YU等[11]采用溶胶凝胶法制备了一系列MnOx/TiO2和MnOx-CeO2/TiO2催化剂,考察了Ce添加量对催化降解性能的影响,结果表明MnOx-CeO2/TiO2(Ce/Ti=0.05)催化剂活性最高(T90=180 ℃),高度分散的无定型Mn及催化剂表面存在大量活性氧物种是其具有优异低温催化氧化甲苯性能的关键。郑宽等[18]通过共沉淀法制备不同Mn/Ce比的复合氧化物,发现对Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂的甲苯催化降解性能高于单一MnOx和CeO2。大多数报道的催化剂均未通过对催化剂形貌进行控制从而调控催化剂的反应活性[5, 18]。因此,本研究以表面为纳米针的氧化锰微球为基础,通过在水热前驱液中加入不同含量的Ce,原位合成出具有一定形貌的Mn-Ce复合氧化物,通过SEM、XRD、H2-TPR、O2-TPD、BET及拉曼光谱等手段对所合成的复合材料进行表征,并深入研究分析催化剂催化氧化甲苯的构效关系。
1. 实验材料和方法
1.1 催化剂的制备
将2.700 g MnSO4·H2O和13.185 g (NH4)2S2O8溶解于60 mL去离子水中,待完全溶解后,定容至80 mL,转移到100 mL的聚四氟乙烯的反应釜中,80 ℃反应4 h后,自然冷却至室温,将所得沉淀物用去离子水洗涤至中性,最后在80 ℃条件下干燥后保存备用,所制备的样品记为MnO2。
其他过程与氧化锰微球的制备过程相同,不同之处是,在加入MnSO4·H2O和(NH4)2S2O8的过程中同时加入不同含量的Ce(SO4)2·4H2O(Ce的摩尔分数为5%、10%、20%和40%)。所制备样品分别记为Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox、Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox、Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox和Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox。
1.2 催化剂活性评价
催化剂的甲苯催化氧化性能测定在连续流动的固定床反应器中进行[15-16]。催化反应器为自制的内径为8 mm 的U型石英管,固体催化剂床层由0.13 g(40~60目)催化剂和0.52 g的石英砂组成。采用质量流量器控制气体流量,以甲苯为目标反应物,浓度为550 ppm,空气总流量为200 mL·min−1,重时空速(GHSV)约为92 300 mL·(g·h)−1。由气质联用仪(7890B-GC,5977B-MSD,Agilent Technologies)对甲苯降解前后的尾气进行在线检测。其中甲苯利用MS(分析柱为TG-BOND Q:30 mm×0.32 mm×20 μm)进行检测。配备的FID与镍转化炉连接,用于CO和CO2的检测,其分析柱为5A分子筛(2 m×2 mm)、Porapak Q(1.83 m×1.2 mm)和Porapak Q(0.91 m×2 mm)。
1.3 材料表征
SEM结果采用S-3400N电子显微镜(日立,日本)对催化材料的形貌进行观察。
XRD采用D8 ADVANCE X射线衍射仪(Bruker,德国)进行测定(Cu Kα射线,扫描角度为5°~90°)。
N2吸附-脱附采用日本BEL公司的BELSORP-miniⅡanalyzer全自动比表面积及微孔孔隙分析仪测定催化剂的比表面积和孔结构参数。测试时取110 mg样品,在120 ℃下脱气4 h,脱气完毕后,以N2为吸附质,于−196 ℃下进行测定。采用BET方法计算样品的比表面积[15-16],而计算样品的孔容和孔径采用BJH法。
H2-TPR在FINESORB-3010(浙江泛泰仪器有限公司)全自动物理化学分析仪上进行。将100 mg催化剂置于U型管中,以高纯Ar为载气(30 mL·min−1),10 ℃·min−1升至120 ℃,维持30 min。然后降到50 ℃,将气路切换为10% H2/Ar,等基线稳定后,从50 ℃程序升温至600 ℃,升温的速率为10 ℃·min−1。在升温过程中,利用TCD检测器对耗氢量[15-16]进行检测。O2-TPD的测定也是在FINESORB-3010全自动物理化学分析仪上进行的。将100 mg催化剂置于U型管中,以高纯Ar (30 mL·min−1)为载气,10 ℃·min−1的升温速率升至120 ℃,加热30 min。降温至50 ℃,将气路切换为10% O2/Ar(30 mL·min−1),吸附60 min。然后再把气路切换为高纯Ar,基线稳定后,以10 ℃·min−1程序升温至700 ℃。升温过程中氧的脱附量利用TCD检测器[15-16]进行检测。
拉曼光谱分析(Raman)在法国HJY公司LabRAM Aramis拉曼光谱仪上进行,主要技术参数如下:532 nm激光波长,扫描范围为100~1 000 cm−1,样品每次扫描采集时间为60 s。
2. 实验结果与讨论
2.1 Mn-Ce复合氧化物的可控制备
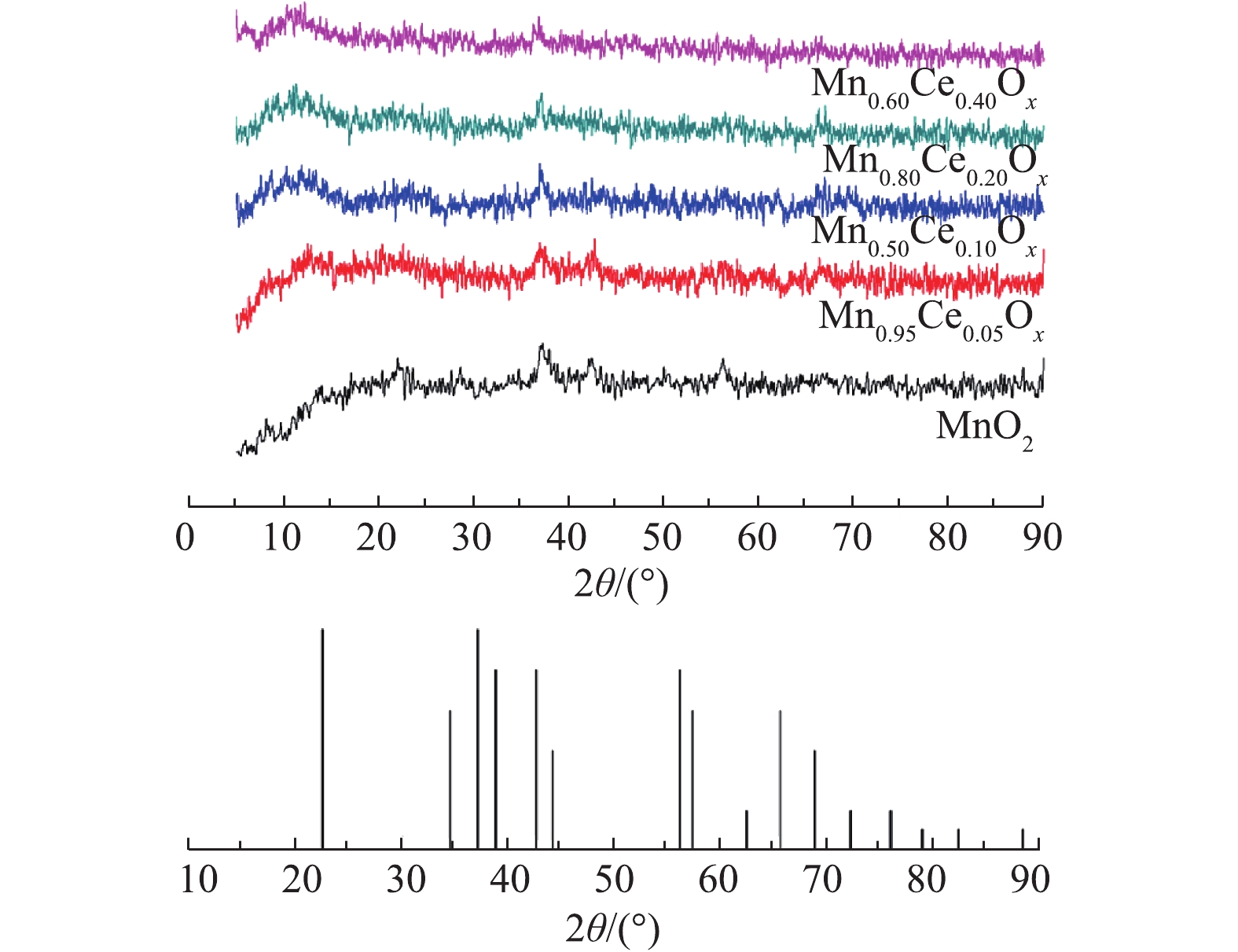
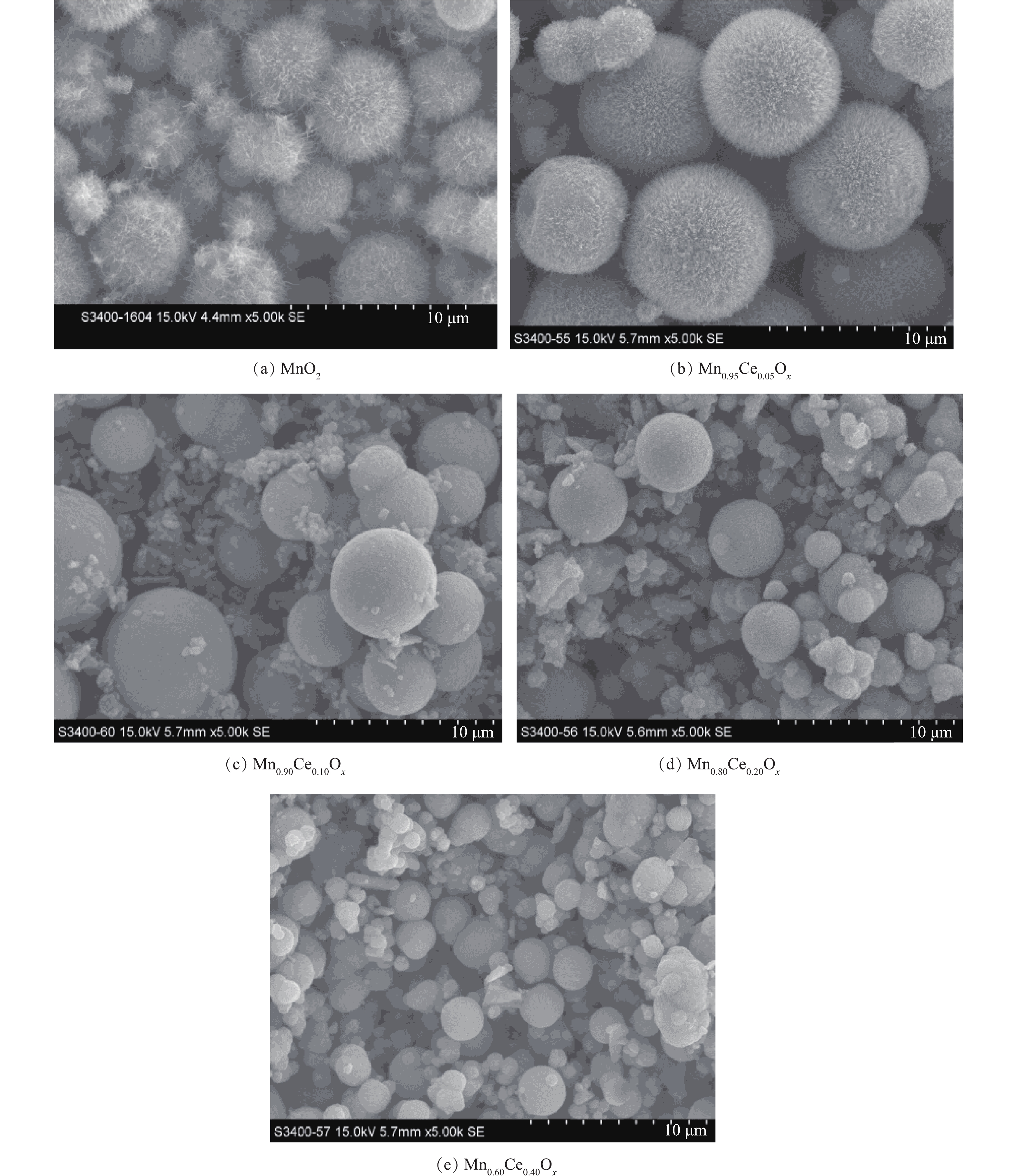
1)SEM分析。通过水热反应制备了一系列不同锰铈比例的氧化物催化剂,SEM结果如图1所示。以MnSO4·H2O为前驱体、(NH4)2S2O8为氧化剂条件下合成的MnO2呈现出表面为纳米针的海胆状微球结构,其直径为4.0~5.0 μm。而在海胆状MnO2微球制备的基础上,掺入一定比例的铈制备Mn-Ce复合氧化物,其SEM结果如图1(b)~图1(e)所示。当Ce掺杂量为5%时,形成的复合材料的形貌仍为海胆状微球结构,其微球颗粒粒径较纯的MnO2有所增加(7.0~8.5 μm)。但随着Ce掺杂量的增加,产物微球表面的针状结构逐渐消失,变为表面光滑的微球,其颗粒粒径呈现下降趋势,在10%时,微球直径为4.0~5.0 μm,且在微球的周围出现了较多无固定形态的物质(图1(c))。当含量增加到20%时,粒径进一步降低,约为3.59 μm(图1(d))。在含量为40%时,微球的粒径进一步降低至2.2 μm左右(图1(e))。但随着Ce含量的增加,微球的周围也生成了越来越多的表面碎片。同时,在水热反应过程中,通过对生成物产率的观察,发现随着Ce含量的增加,生成产物的量逐步减少,当不添加Mn时,利用Ce(SO4)2·4H2O与(NH4)2S2O8进行水热反应,在80 ℃反应4 h后,只有很少量淡黄色的物质生成,推测为CeO2,但产量极低,所以该方法不适合进行CeO2纳米材料的合成。
2)XRD分析。不同Mn-Ce复合氧化物的XRD谱图如图2所示。MnO2微球催化剂XRD谱图中在2θ=37.0°、42.0°,56.7°处出现的特征衍射峰归属于γ-MnO2(PDF#14-0644)[19]。但在所合成的含Ce微球催化剂XRD谱图中除37.0°处的峰没有变化外,其他对应的γ-MnO2特征峰均存在消失的现象。且没有观察到明显的CeO2的峰,这是因为在Ce的含量很低时(小于50%),在复合氧化物中仍以MnOx为主,因而无法探测到CeO2的衍射峰,这与之前研究报道的MnOx-CeO2催化剂所得出的结论[7]相似。
结合SEM结果可知,在加入Ce以后,在微球的周围出现了大量的颗粒物,说明Ce的加入会对催化剂的形貌产生较大的影响,但从XRD的结果可看出,这些小的颗粒物可能是一些无定型的Mn-Ce复合氧化物。随着Ce含量的增加,2θ=42.0°、56.7°处的衍射峰的强度降低,说明MnO2的结晶度随着Ce含量的增加而下降。
2.2 Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂催化氧化甲苯性能
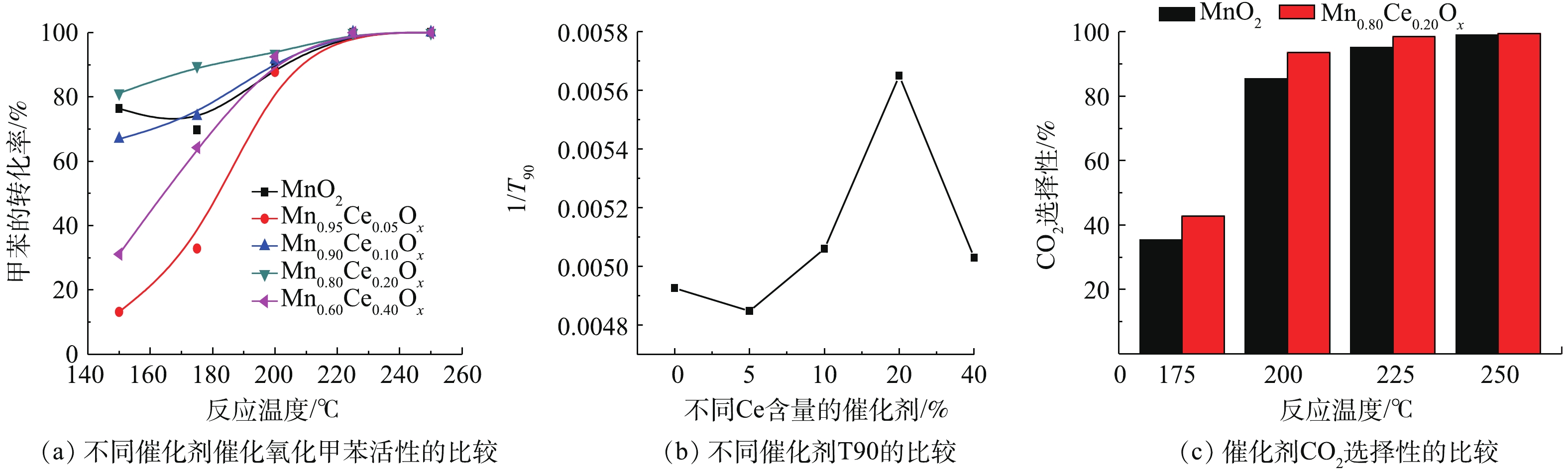
不同Mn-Ce比例的复合氧化物催化降解甲苯的性能如图3所示。由图3(a)可知,所制备的纯MnO2微球对甲苯的降解率随着反应温度上升呈现先降低后升高的趋势。在150 ℃降解率达到76.4%时,但当温度升高至175 ℃时却降低为65.3%,随后随着温度的进一步升高,降解率又开始增加,在200 ℃时,达到了89.8%,在225 ℃达到完全转化。这可能是由于MnO2催化剂在低温区间对甲苯主要为吸附作用,当吸附未达到饱和时,表现为甲苯的出口浓度在下降,因而甲苯的转化率偏高;当这个吸附作用达到饱和时,甲苯的出口浓度达到最低,随着反应温度的升高,吸附在催化剂表面的反应物逐渐脱附,甲苯的出口浓度增大,其降解率下降;当达到一定温度时,催化剂对甲苯的催化反应作用占主导地位,这种作用反应迅速,对甲苯的降解程度大,表现为甲苯的出口浓度迅速下降,因而甲苯的转化率急剧升高[7, 20]。LIAO等[7]和廖银念等[20]的研究也出现了类似的实验现象。
当加入不同含量的Ce后,所形成的Mn-Ce复合氧化物对甲苯的降解率都随着温度的升高而升高,达到完全转化时的温度均为225 ℃,但含Ce的催化剂在催化降解甲苯时未出现甲苯脱附现象。在较低的反应温度区域(<200 ℃),不同的Ce含量的催化剂对甲苯的降解性能具有明显差异,随催化剂中Ce含量的增加呈现先降低后升高再降低的趋势,活性顺序为Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox。大多文献报道用T90(甲苯转化90%所需的温度)来表示催化剂的活性[15-16, 20]。T90越低,表明催化剂的活性越高。为了更直观反映不同Mn-Ce比例的复合氧化物和催化活性的关系,本研究采用插值法估算了各催化剂降解甲苯转化率达90%时所需温度(T90),利用1/T90来表示催化剂的活性,结果如图3(b)所示。结果发现Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂T90值最低,表明该催化剂具有最佳的低温催化氧化甲苯活性。此外,纯MnO2和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂在催化氧化甲苯过程中对CO2的选择性存在一定的差异(图3(c)),Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂的CO2选择性略优于纯MnO2催化剂,且在反应温度200 ℃后,CO2生成率高于93.5%,由此说明,Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂实现完全甲苯催化氧化时,甲苯几乎都转化为CO2。
2.3 催化剂的表征
不同Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂的比表面积、孔容、孔径的结果见表1。由表1可知,单一MnO2和Mn-Ce复合氧化催化剂的比表面积随着Ce的含量的增加出现先减少后增加最后再减少的趋势。其中比表面积最大和最小的分别为Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox(162.29 m2·g−1)和Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox(68.07 m2·g−1)。催化剂的孔容最大和最小的分别为Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox(0.33 cm3·g−1)和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox(0.15 cm3·g−1);而催化剂的最大和最小的平均孔径分别为Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox(17.57 nm)和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox(5.48 nm)。由于甲苯催化氧化性能最优的为Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂,在所有合成的催化剂中,其具有最小的孔容和平均孔径,且具有适中的比表面积。这说明比表面积等物理性质并不是催化剂在低温催化氧化甲苯反应中起主导作用的影响因素。此外,由图3可知,Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂的低温催化氧化活性略优于MnO2催化剂,但具有少量Ce的Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox催化剂的活性却明显低于比表面积接近的MnO2催化剂,这可能是由于比表面积等物理性质并不是催化剂在低温催化氧化甲苯反应中起主导作用的因素,催化剂的低温催化氧化甲苯关键因素是催化剂的氧化还原性能和反应过程中的活性氧物种[15]。
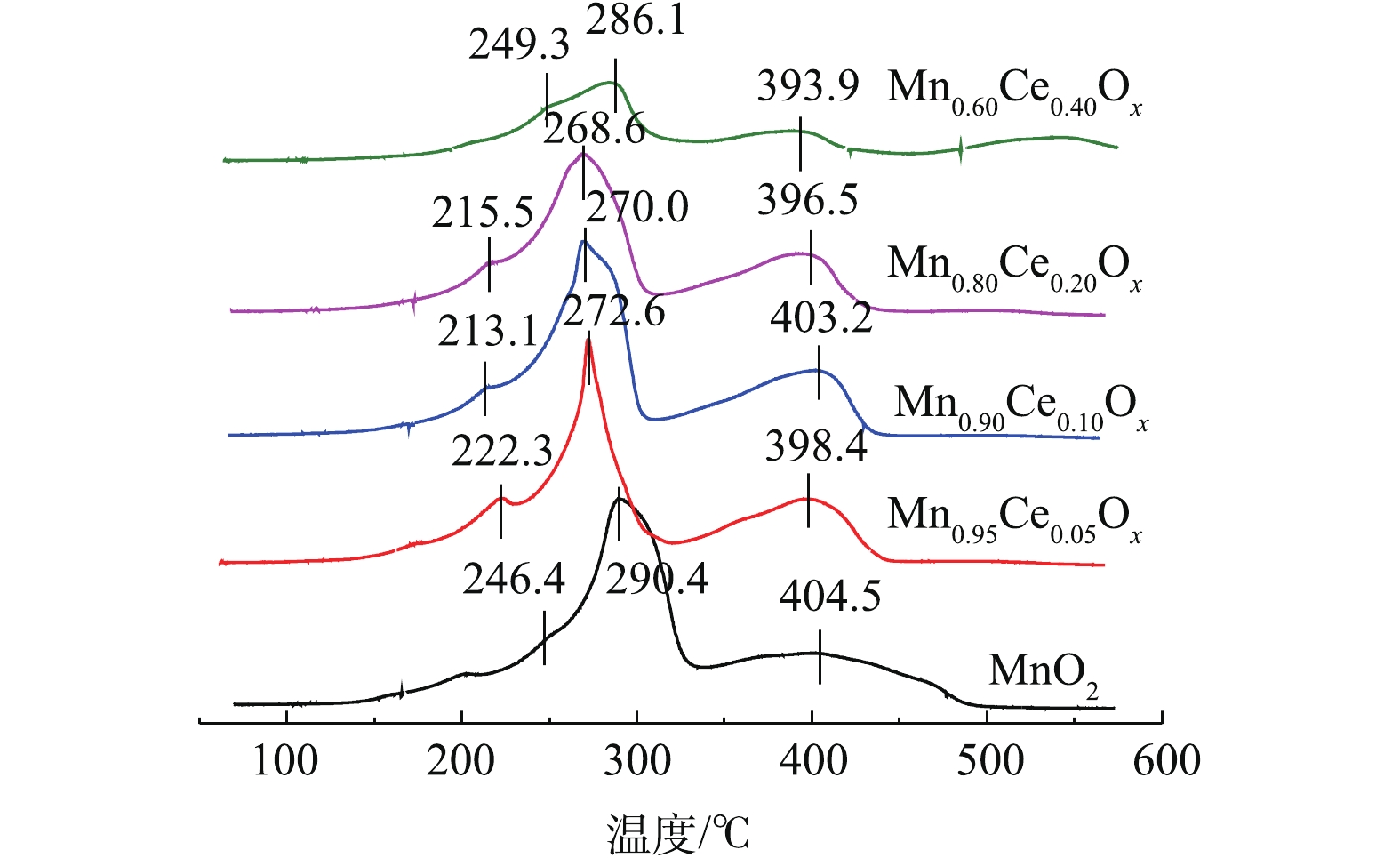
表 1 不同Mn-Ce复合氧化物微球催化剂的比表面积、孔容、孔径Table 1. BET surface areas, pore volumes, and pore diameters of different Mn-Ce composite oxide microspheres catalysts催化剂 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔容/(cm3·g−1) 平均孔径/nm MnO2 77.97 0.29 14.91 Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox 74.62 0.33 8.19 Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox 162.29 0.26 6.48 Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox 109.54 0.15 5.48 Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox 68.07 0.30 17.57 H2-TPR可以反映催化剂的氧化还原性能,其中氧物种伴随变价金属氧化还原循环与催化氧化反应密切相关[9, 15, 20]。不同比例的Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂的H2-TPR结果如图4所示。由此可以看出,纯的MnO2在246.4 ℃和290.4 ℃出现了2个还原峰,分别归属为MnO2→Mn2O3及Mn2O3→Mn3O4的还原,大约在400 ℃的还原峰归属为Mn3O4到MnO的还原峰[21-22]。据报道[7, 18],CeO2向Ce2O3的还原出现在380~450 ℃,而高于650 ℃才可能出现体相氧化铈的还原。深入分析Mn-Ce氧化物催化剂的TPR谱图可知,由于催化剂中Ce含量少,没有出现新的还原峰,说明在催化剂中Ce的还原峰面积比较小,极有可能被Mn2O3→Mn3O4的还原峰所掩盖,但随着Ce含量的增加,MnOx的还原温度向低温偏移。一般而言,催化剂还原峰中心所对应的温度越低,说明催化剂的氧化性越强[23-25],因此,催化剂的氧化性能依次为Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox>MnO2>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox。结合各催化剂催化氧化甲苯活性的结果,可以看出,催化剂的氧化还原性能与其在低温区间催化氧化甲苯的性能存在一定的相关性,也间接说明催化氧化还原能力是影响催化剂催化氧化甲苯性能的重要指标。
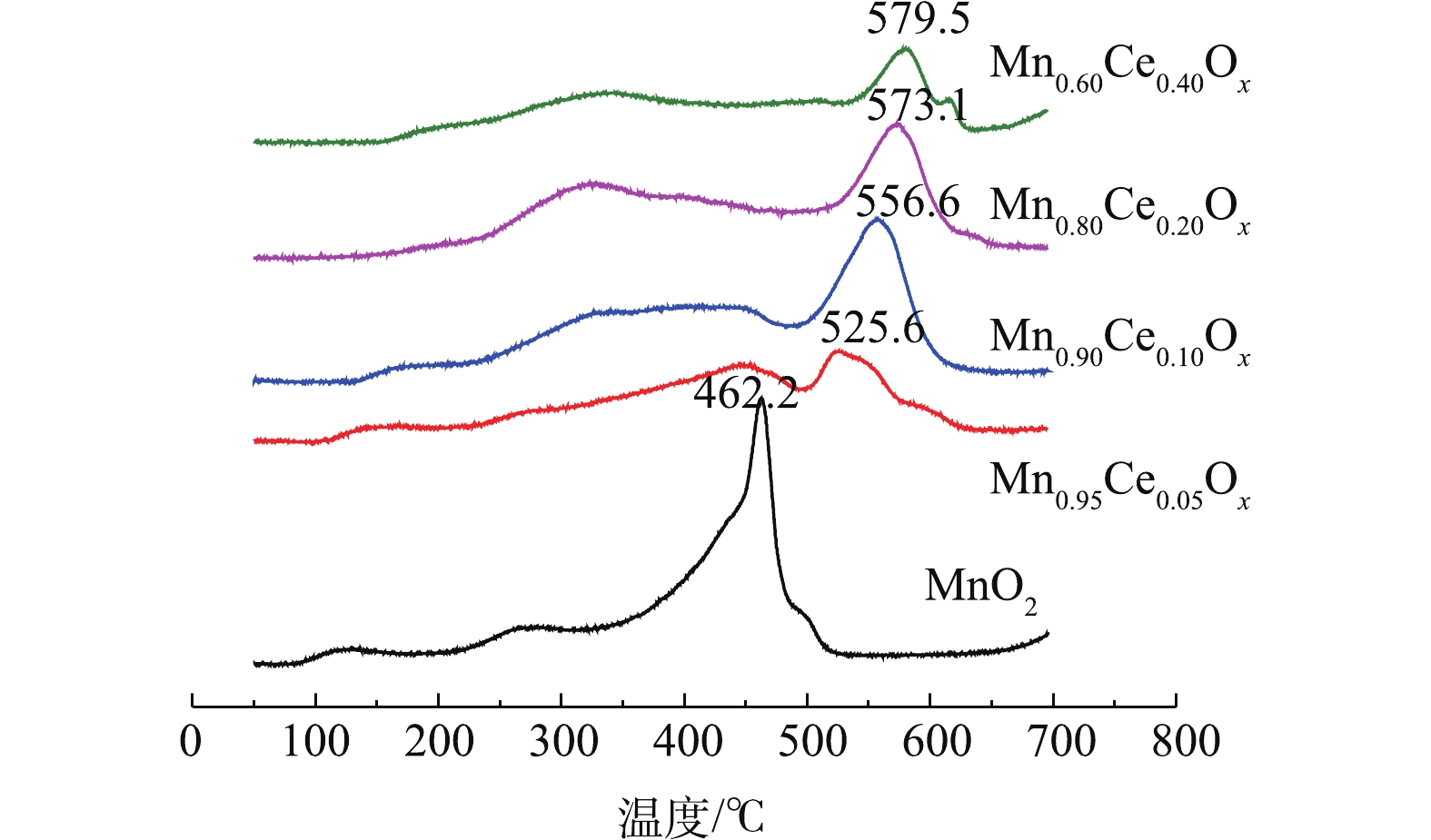
O2-TPD 可对催化剂表面的氧空位以及物种存在状况[6, 7, 15, 26]进行测定。不同Mn-Ce复合氧化物的O2-TPD的结果如图5所示。其中在80 ℃、300~400 ℃和大于500 ℃出现的氧脱附峰可分别归属于弱的分子吸附氧(
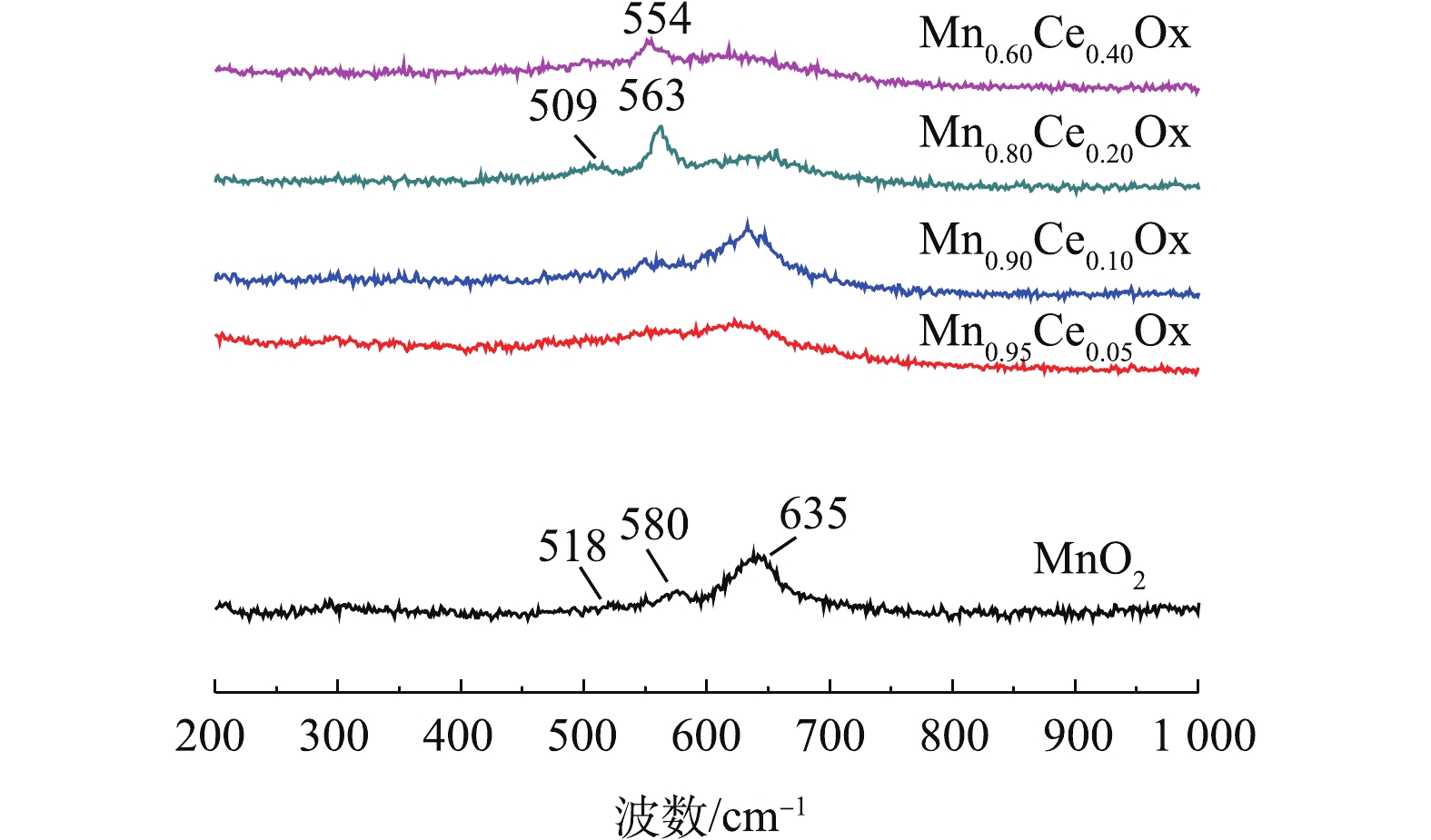
O−2 )、化学吸附氧(O−)和晶格氧O2−的脱附峰[6, 7, 15]。如图5所示,不同比例的Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂在300~400 ℃的氧脱附峰峰面积大小依次为Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>>Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox。这与催化氧化甲苯的活性评价结果一致,表明化学吸附氧的含量是低温催化氧化甲苯性能的重要因子。此外,在含Ce微球催化剂的低温催化氧化甲苯的活性存在差异的原因主要包括:1)催化剂还原峰中心所对应的温度越低,说明催化剂的氧化性越强,因此,催化剂的氧化性能依次为Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox>MnO2>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox。结合活性评价的结果,可以看出,催化剂的氧化还原性能与其在低温区间催化氧化甲苯的性能存在一定的相符性;2)催化剂的氧化还原性能接近(Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox),而低温区间催化氧化甲苯的性能存在差异,这是由于不同比例的Mn-Ce复合氧化物催化剂在300~400 ℃的氧脱附峰峰面积大小依次为:Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox>>Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox>Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox>Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox。这与催化氧化甲苯的活性评价结果一致,表明化学吸附氧的含量是低温催化氧化甲苯性能的重要因子,这些化学吸附氧物种对于完成催化氧化循环起着关键作用。图6是不同Mn-Ce复合氧化物微球催化剂的拉曼光谱图。其中纯MnO2和Mn-CeOx催化剂中都出现了500~700 cm−1的特征峰,该峰被认为是MnO2中[MnO6]八面体的伸缩振动,且纯MnO2所对应的特征峰正好与γ-MnO2的特征峰完全吻合[27],这一表征结果也更好地验证了前面的XRD结论。值得注意的是,与纯MnO2所对应的特征峰相比,Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂所对应的2个特征峰(509 cm−1和563 cm−1)及Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox催化剂所对应的1个特征峰(554 cm−1)都明显向低波数偏移,这表明Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox和Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂中都可能存在Mn-Ce固溶体,这与文献报道的结论[28]相符。而具有较低Ce含量的Mn0.90Ce0.10Ox和Mn0.95Ce0.05Ox所对应的特征峰并没有出现明显偏移现象,这说明当Ce掺杂量较低时,Mn-Ce催化剂中未形成固溶体。正由于Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂中形成了固溶体,使催化剂具有更优异的储氧能力,这与O2-TPD分析得出的该催化剂具有最高含量的化学吸附氧的结论相符。因此,Mn-Ce催化剂中存在固溶体也是其具有优异催化氧化甲苯性能的关键原因之一。值得一提的是,Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox催化剂中虽然也存在固溶体,但Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂具有比Mn0.60Ce0.40Ox催化剂更强的氧化还原性能和更高的化学吸附氧的含量,故Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂呈现更优异的低温催化氧化甲苯性能。
3. 结论
1)采用简单的水热法成功合成出了Mn-Ce氧化物微球,且铈摩尔含量占5%、10%和20%的产物结晶都比较完整,而铈摩尔含量为20%时,其形貌为较光滑的微球,结晶较完整,颗粒尺寸较小。MnO2微球催化剂中存在γ-MnO2的特征峰,而随着Ce的加入,催化剂的结晶度有所下降。
2)Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂呈现最佳的催化氧化甲苯性能,较强的氧化还原性能和较高的化学吸附氧的含量是其具有优异的低温催化氧化甲苯性能的重要原因。
3)Mn0.80Ce0.20Ox催化剂中存在Mn-Ce固溶体,这也是其具有最佳催化氧化甲苯性能的关键原因之一。
-
表 1 TDTC的元素分析
Table 1. Elementary analysis of TDTC
元素 比例/% 物质的量相对值 C 33.97 1.91 H 3.28 3.96 N 18.64 0.9 S 40.75 1.1 表 2 TDTC与其他重金属捕集剂去除效果对比
Table 2. Comparison of heavy metal removal effect between TDTC and other sulfur-containing heavy metal chelation agents
-
[1] NGAH W S W, HANAFIAH M. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: A review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99: 3935-3948. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.011 [2] 王蓬勃, 李金花, 周保学, 等. 电镀含铜废水的资源化回收利用[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(S2): 184-187. [3] 杨世迎, 薛艺超, 王满倩. 络合态重金属废水处理: 基于高级氧化技术的解络合机制[J]. 化学进展, 2019, 31(8): 1187-1198. [4] SHAN C, Xu Z, ZHANG X L, et al. Efficient removal of EDTA-complexed Cu(II) by a combined Fe(III)/UV/alkaline precipitation process: Performance and role of Fe(II)[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 193: 1235-1242. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.119 [5] 曹海峰. 络合态重金属废水处理技术研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2015, 35(11): 14-17. doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2015.35(11).014 [6] FU F L, WANG Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92: 407-418. [7] HU H M, LI X W, HUANG P W, et al. Efficient removal of copper from wastewater by using mechanically activated calcium carbonate[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 203: 1-7. [8] 刘金燕, 刘立华, 薛建荣, 等. 重金属废水吸附处理的研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(9): 2016-2024. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017110105 [9] LIU J, LUO X W, SUN Y Q, et al. Thallium pollution in China and removal technologies for waters: A review[J]. Environment International, 2019, 126: 771-790. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.076 [10] ABDOLALI A, NGO H H, GUO W S, et al. Application of a breakthrough biosorbent for removing heavy metals from synthetic and real wastewaters in a lab-scale continuous fixed-bed column[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 229: 78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.01.016 [11] 蒲生彦, 肖雨婷, 马慧, 等. CS-EGDE/Fe3O4凝胶微球对水中重金属离子的吸附性能及机理研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(7): 2172-2181. [12] LIU Q M, LI Y Y, CHEN H F, et al. Superior adsorption capacity of functionalised straw adsorbent for dyes and heavy-metal ions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 382: 121040. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121040 [13] KAZEMINEZHAD I, MOSIVAND S. Elimination of copper and nickel from wastewater by electrooxidation method[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2017, 422: 84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.08.049 [14] MA A, ABUSHAIKHA A, ALLEN S J, et al. Ion exchange homogeneous surface diffusion modelling by binary site resin for the removal of nickel ions from wastewater in fixed beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 358: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.135 [15] 杨海, 黄新, 林子增, 等. 离子交换法处理重金属废水的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2019, 48(7): 1675-1680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2019.07.038 [16] 王开峰, 彭娜, 李鑫, 等. UV/Fenton法处理EDTA-Cu-Ni络合废水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(11): 6524-6528. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201506160 [17] LI S L, WANG W, LIANG F P, et al. Heavy metal removal using nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Theory and application[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 322: 163-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.032 [18] NGUYEN M K, TRAN V S, PHAM T T, et al. Fenton/ozone-based oxidation and coagulation processes for removing metals (Cu, Ni)-EDTA from plating wastewater[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 39: 101836. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101836 [19] 王刚, 王志科, 常青, 等. 改性聚乙烯亚胺捕集和回收水中的Cu2+[J]. 环境科学研究, 2017, 30(6): 953-959. [20] DING X P, LI M, YANG W Z, et al. Experimental and theoretical studies of sodium acetyldithiocarbamate for the removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 579: 330-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.06.074 [21] POHL A. Removal of heavy metal ions from water and wastewaters by sulfur-containing precipitation agents[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 2020, 231: 503. doi: 10.1007/s11270-020-04863-w [22] LACHOWICZ J I, DEPIANO G R, ZANDA D, et al. Adsorption of Cu2+ and Zn2+ on SBA-15 mesoporous silica functionalized with triethylenetetramine chelating agent[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7: 103205. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103205 [23] 谭聪, 刘妮, 王双飞, 等. 重金属捕集剂DTC-SC处理含Cu2+、Cd2+和Mn2+废水研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2015, 41(9): 46-48. [24] 张翔, 冯修, 职红涛, 等. 重金属捕集剂TDDP的合成及性能研究[J]. 郑州大学学报(工学版), 2019, 40(3): 48-51. [25] KIM T K, KIM T, CHOE W S, et al. Removal of heavy metals in electroplating wastewater by powdered activated carbon (PAC) and sodium diethyldithiocarbamate-modified PAC[J]. Environmental Engineering Research, 2018, 23(3): 301-308. doi: 10.4491/eer.2017.208 [26] 袁海飞, 王刚, 徐敏, 等. 重金属絮凝剂DTMPAM去除水中Cu2+和EDTA-Cu的性能[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(12): 3985-3993. [27] CHEN H, ZHAO Y, YANG Q Y, et al. Preparation of poly-ammonium/sodium dithiocarbamate for the efficient removal of chelated heavy metal ions from aqueous environments[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2018, 6: 2344-2354. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.03.029 [28] 令玉林, 周建红, 李国斌, 等. 高效重金属螯合剂RDTC的研制及处理含铜废水性能[J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(8): 1390-1395. [29] 陈展灼, 王梓健. 电镀废水中常见铜镍络合物的紫外-可见光谱初步探讨[J]. 化工管理, 2018(30): 182-183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4800.2018.30.131 [30] TOKUYAMA H, HISAEDA J, NII S, et al. Removal of heavy metal ions and humic acid from aqueous solutions by co-adsorption onto thermosensitive polymers[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2010, 71: 83-88. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2009.11.005 [31] XIANG B, FAN W, YI X W, et al. Dithiocarbamate-modified starch derivatives with high heavy metal adsorption performance[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2016, 136: 30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.08.065 [32] SHA X S, XIANG Z J, BIN L, et al. Preparation and physical characteristics of resistant starch (type 4) in acetylated indica rice[J]. Food Chemistry, 2012, 134: 149-154. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.081 [33] 祁宗, 孙传尧. 脂肪酸作捕收剂白云石浮选规律及其机理研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2013, 42(3): 461-465. [34] 曾燕君, 周志军, 赵秋香. 蒙脱石-OR-SH复合体材料对土壤镉的钝化及机制[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(6): 2314-2319. [35] SHAABAN A F, FADEL D A, MAHMOUD A A, et al. Synthesis and characterization of dithiocarbamate chelating resin and its adsorption performance toward Hg(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) by batch and fixed-bed column methods[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2013, 1: 208-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2013.04.014 [36] GAO T T, YU J G, ZHOU Y, et al. The synthesis of graphene oxide functionalized with dithiocarbamate group and its prominent performance on adsorption of lead ions[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2017, 71: 426-432. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2016.11.033 [37] 刘立华, 吴俊, 李鑫, 等. 四乙烯五胺多(二硫代甲酸钠)的合成及其对重金属的去除性能[J]. 环境科学研究, 2011, 24(3): 332-339. [38] BAI L, HU H P, FU W, et al. Synthesis of a novel silica-supported dithiocarbamate adsorbent and its properties for the removal of heavy metal ions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 195: 261-275. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.038 [39] XIAO X, YAN P F, YE M Y, et al. Disodium N, N-bis-(dithiocarboxy)ethanediamine: Synthesis, performance, and mechanism of action toward trace ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid copper (II)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(19): 19696-19706. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7156-5 [40] FU H, LV X S, YANG Y P, et al. Removal of micro complex copper in aqueous solution with a dithiocarbamate compound[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2012, 39(1/2/3): 103-111. -






 下载:
下载: