-
好氧颗粒污泥是微生物在一定条件下自凝聚形成的一种颗粒状活性污泥,具有沉降性能优良、微生物种类多样、生物量高、单级同步脱氮除磷等优点[1-2]。因此,好氧颗粒污泥在污水处理领域的应用日益成为研究热点。但是,储存过程中的好氧颗粒污泥易出现的颗粒解体和微生物失活等问题。可见,储存后的好氧颗粒污泥活性能否快速恢复到储存前水平是解决其技术发展的关键。
相关研究[3-4]表明,储存后的好氧颗粒污泥活性恢复时间受储存基质、储存时间、反应器运行条件以及储存前颗粒污泥特性等诸多因素影响。邹金特等[5]耗时11 d将在常温下使用清水储存60 d后的好氧颗粒污泥活性完全恢复。当好氧颗粒污泥储存在清水中并在−18 ℃环境下存放260 d,需要30 d才可恢复其高效的污染物降解能力[6]。GAO等[7]在室温下将好氧颗粒污泥储存在蒸馏水和400 mg·L−1葡萄糖溶液中8个月,储存后的好氧颗粒污泥经过10 d的活性恢复就可达到储存前的颗粒污泥特性。高景峰等[8]研究发现,在−20 ℃下将好氧颗粒污泥储存在蔗糖和海藻糖溶液中35 d,经过4 d的颗粒污泥再恢复即可达到储存前水平。好氧颗粒污泥储存在有毒溶液中,可使好氧颗粒污泥内部微生物处于存活但不可培养状态,从而有效维持其结构稳定性。然而,有关对有毒溶液储存后的好氧颗粒污泥活性恢复的研究鲜有报道。
因此,本研究在室温下,将储存于60 mg·L−1苯酚溶液中150 d 的好氧颗粒污泥接种至序批式反应器(sequencing batch reactor, SBR)中,采用增加进水有机物(以COD计)浓度、曝气量,通过减少污泥沉淀时间对储存后的好氧颗粒污泥进行活性恢复研究,考察了其理化特性及其对进水污染物的去除效果影响情况,以期为探索快速恢复好氧颗粒污泥活性方法提供参考。
-
接种污泥为室温下在60 mg·L−1苯酚溶液中储存150 d后的好氧颗粒污泥,其为淡黄色颗粒状,污泥浓度(MLSS)和混合液挥发性固体质量浓度(MLVSS)分别为13 047 mg·L−1和8 220 mg·L−1,MLVSS/MLSS为0.63,污泥容积指数(SVI30)为39.6 mL·g−1,污泥脱氢酶活性(DHA)为34.02 μg·(g·h)−1。
实验用水为人工配制的模拟废水,以葡萄糖为碳源,氯化铵为氮源,磷酸二氢钾为磷源,并向进水添加1 mL·L−1的微量元素溶液,用NaHCO3调节进水pH 为7~8。COD为600~1 500 mg·L−1,总氮(TN)为60~150 mg·L−1,总磷(TP)为6~15 mg·L−1。
-
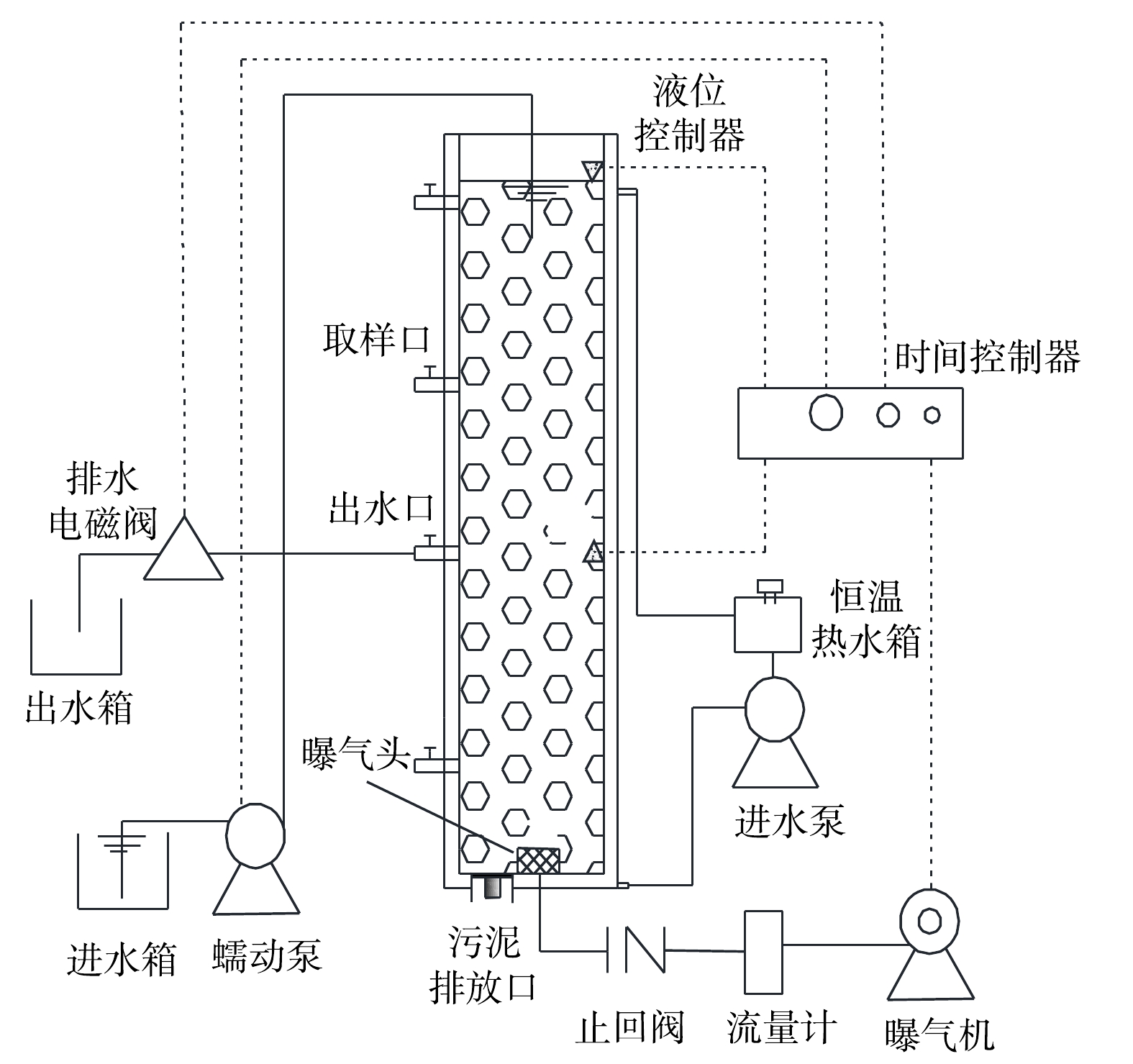
1)实验装置。在SBR中对储存后的好氧颗粒污泥活性进行恢复,反应器主体为有机玻璃制成的圆柱体,其内径为9.8 cm,总高度为100 cm,有效高度为98 cm,有效高径比为10,反应器有效容积为 7.39 L。装置如图1所示。
2)运行方式。在好氧污泥颗粒化过程中,SBR运行过程包括进水、曝气、沉淀、排水和闲置5个阶段,运行周期为6 h,包括进水4 min、曝气339~350 min、沉淀3~14 min、排水1 min、闲置2 min。曝气量为1.5~9.7 L·min−1,各阶段进水碳、氮和磷的质量浓度比控制在100∶10∶1,容积交换率为50%,通过水浴加热使SBR温度维持在25 ℃。采用调控COD、曝气量和污泥沉降时间等参数以恢复好氧颗粒污泥。SBR运行的具体参数见表1。
-
好氧颗粒污泥形态变化和微观结构分别采用数码相机、FIB-SEM双束电镜(LYRA 3 XMU)进行拍摄、记录和观察。MLSS、MLVSS、SVI、TN、TP、硝酸盐(
NO−3 -N)、亚硝酸盐(NO−2 -N)和氨氮(NH+4 -N)均采用国家标准方法[9]测定。粒径分布采用湿式筛分法[10]确定。DHA采用2,3,5-氯化三苯基四氮唑还原法[11]测定。采用热提取法[12]提取好氧颗粒污泥的胞外聚合物(EPS)。采用荧光光谱仪(FluoroMax-4, HORIBA Jobin Yvon)对EPS进行分析。激发波长(Ex)和发射波长(Em)分别为240~400 nm和290~500 nm,增量均为 5 nm,激发和发射狭缝宽度为3.6 nm,扫描速度为1 200 nm·min−1,响应时间为0.1 s。使用origin 8.0软件进行数据处理和EPS的三维荧光光谱(3D-EEM)绘制。
-
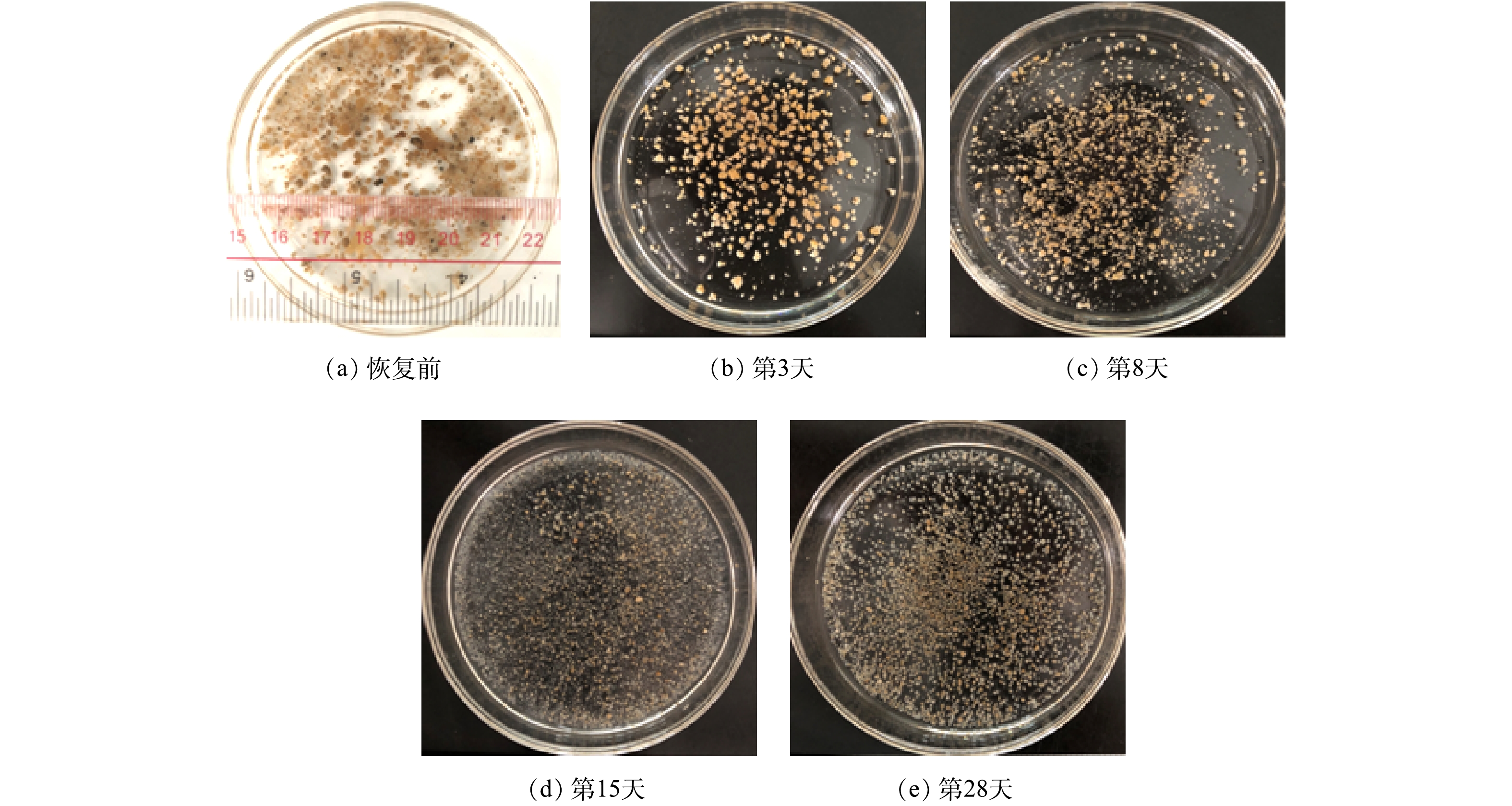
好氧颗粒污泥在活性恢复过程的形态变化如图2所示。图2(a)为室温下在60 mg·L−1苯酚溶液中储存150 d后的好氧颗粒污泥(恢复前)形态。其颗粒状的立体结构保持良好,粒径维持在2.26~3.62 mm,大部分好氧颗粒污泥为淡黄色,极少数转化为灰褐色。 储存后的好氧颗粒污泥在活性恢复过程中经历了从破碎到重塑的变化过程。在第3天时,好氧颗粒污泥为橙黄色,灰褐色颗粒消失,但形状并不规则且有少量破碎的颗粒污泥碎片出现(图2(b))。恢复到第8天时,由于长期储存后的好氧颗粒污泥结构强度下降,颗粒表层松散,因此,在SBR曝气量增大的情况下,好氧颗粒污泥所受的水利剪切增大,导致SBR中的碎片和絮状颗粒污泥比例明显增加,颗粒污泥粒径主要集中在1.0~2.0 mm(图2(c))。SBR运行到第15天时,大量乳白色小颗粒污泥出现,同时还伴随着少量黄褐色、形状较为规则的好氧颗粒污泥形成(图2(d))。随着SBR不断运行,小颗粒污泥逐渐生长。第28天时,好氧颗粒污泥活性恢复成功,恢复后的好氧颗粒污泥为黄褐色,呈现规则的球状或椭球状立体结构,大多数颗粒粒径分布在1.43~2.26 mm(图2(e))。
-
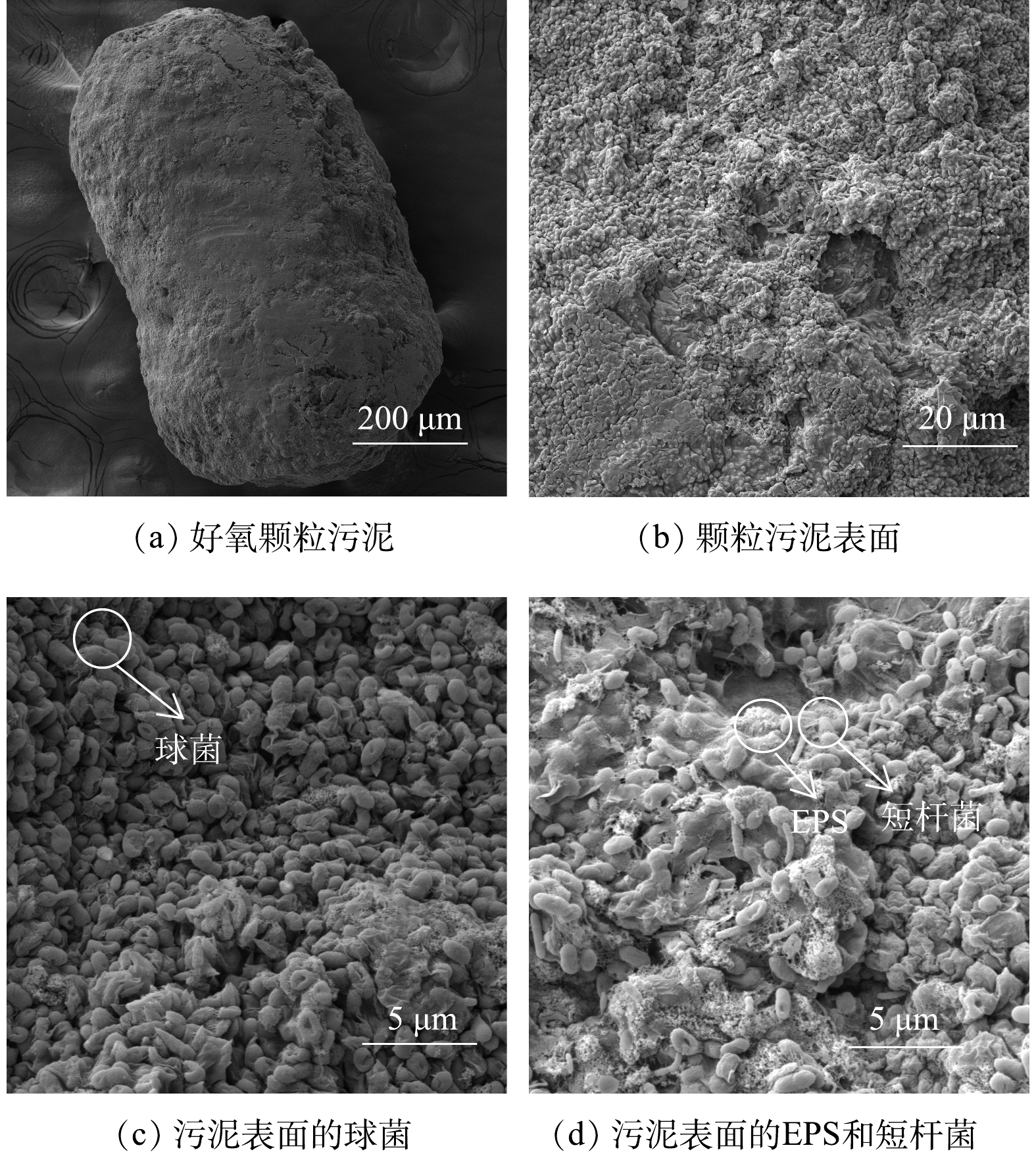
图3为好氧颗粒污泥恢复后的扫描电镜(SEM)图像。如图3(a)所示,恢复后的好氧颗粒污泥为形状规则的颗粒状立体结构,结构较为密实。图3(b)~(d)分别为好氧颗粒污泥表面放大4 000、20 000和20 000倍的SEM图像。由图3(b)可看出,好氧颗粒污泥表面存在一定的褶皱和微小空隙;由图3(c)和图3(d)可看出,好氧颗粒污泥表面生长着大量的球状微生物,还有少量的短杆状和丝状微生物。此外,好氧颗粒污泥表面附着一种透明色物质,推测该物质为微生物分泌的EPS,是微生物细胞菌胶团的主要组分。有研究[13-15]表明,EPS可增强微生物细胞间的凝聚力,促进好氧颗粒污泥的形成并维持其颗粒状立体结构,故其对好氧颗粒污泥的形成具有重要作用。
-
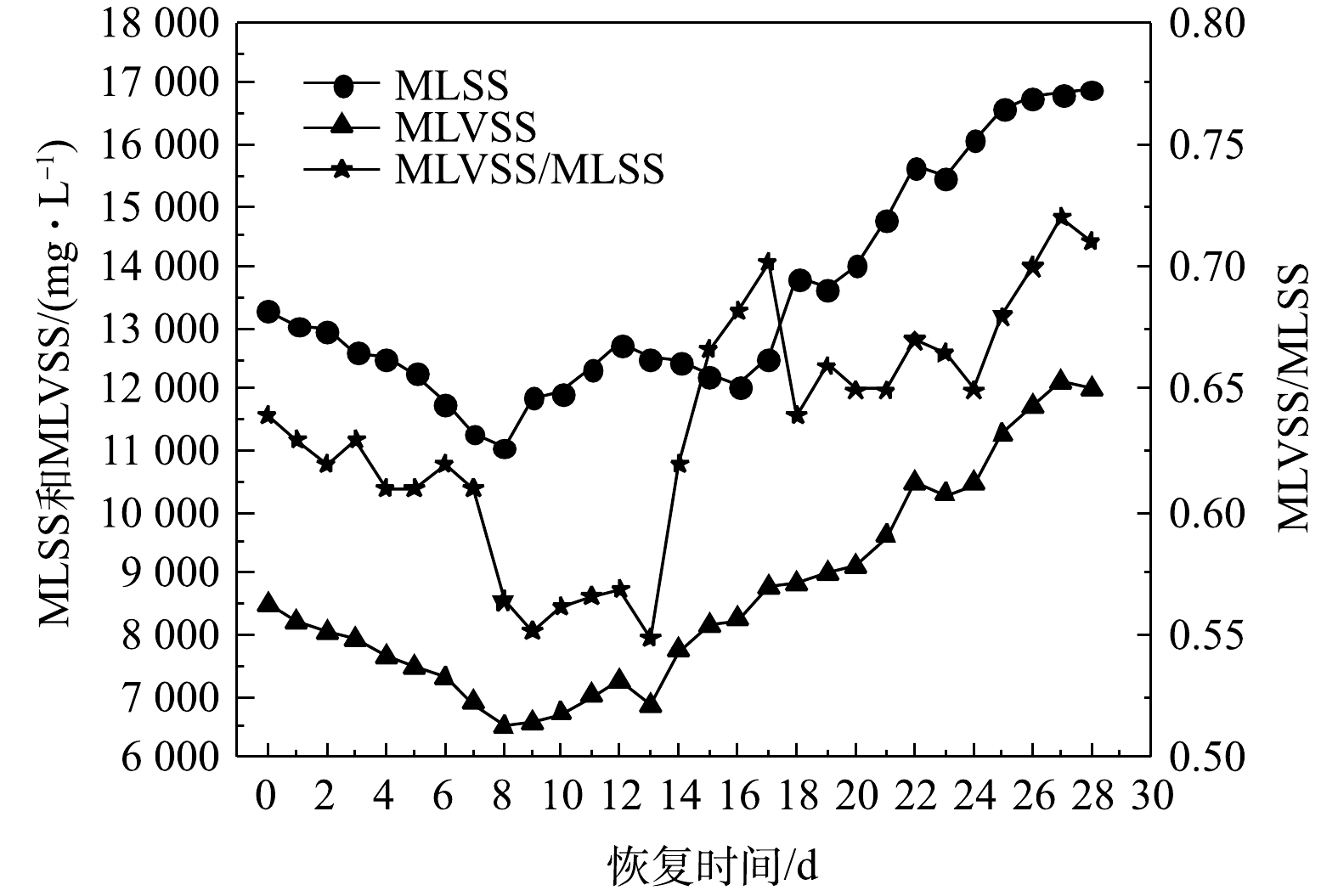
好氧颗粒污泥活性恢复过程中MLSS、MLVSS和MLVSS/MLSS的变化情况如图4所示。储存前,好氧颗粒污泥的MLSS、MLVSS和MLVSS/MLSS分别为17 400 mg·L−1、12 528 mg·L−1、0.72。由于储存期间的好氧颗粒污泥处于缺氧、营养物质匮乏状态,微生物内源呼吸导致MLSS和MLVSS下降[16]。因此,与储存前相比,储存后(恢复前)的MLSS、MLVSS和MLVSS/MLSS (分别为13 047 mg·L−1、8 220 mg·L−1、0.63)均有所降低。MLSS和MLVSS在恢复实验的前8 d内均逐渐减少。这主要是因为污泥沉淀时间减少(由10 min减少至8 min)导致大量沉降性能较差的颗粒污泥被排出SBR。第8天时的MLSS和MLVSS最低,分别为11 064 mg·L−1和6 518 mg·L−1。在恢复的第9~12天,一方面因为污泥沉淀时间增加至14 min;另一方面因为颗粒污泥中的微生物适应SBR运行环境后,活性得到一定程度的恢复,微生物开始生长繁殖,微生物量增加,所以MLSS和MLVSS处于增加趋势。在第18天时,MLSS为13 832 mg·L−1,高于恢复前的水平;此时的MLVSS为8 852 mg·L−1。随后的19~28 d,污泥沉淀时间由7 min减少到3 min,但MLSS和MLVSS增加显著,表明新的好氧颗粒污泥不断生成,沉降性能良好的好氧颗粒污泥被截留在SBR中且占绝对优势。第28天时的MLSS和MLVSS分别达到16 903 mg·L−1和12 001 mg·L−1,结合图2(e)中的污泥形貌可判断,储存后的好氧颗粒污泥得到恢复。
MLVSS/MLSS在恢复期间整体呈现先减小后增大的趋势。在第8天时降低到最小值,为0.56。随后因为污泥沉淀时间减少,MLSS增大,而此时微生物适应SBR运行条件后数量增加导致MLVSS增大,所以MLVSS/MLSS急剧增大。随着好氧颗粒污泥不断得到恢复,在第28天时,MLVSS/MLSS为0.71。
-
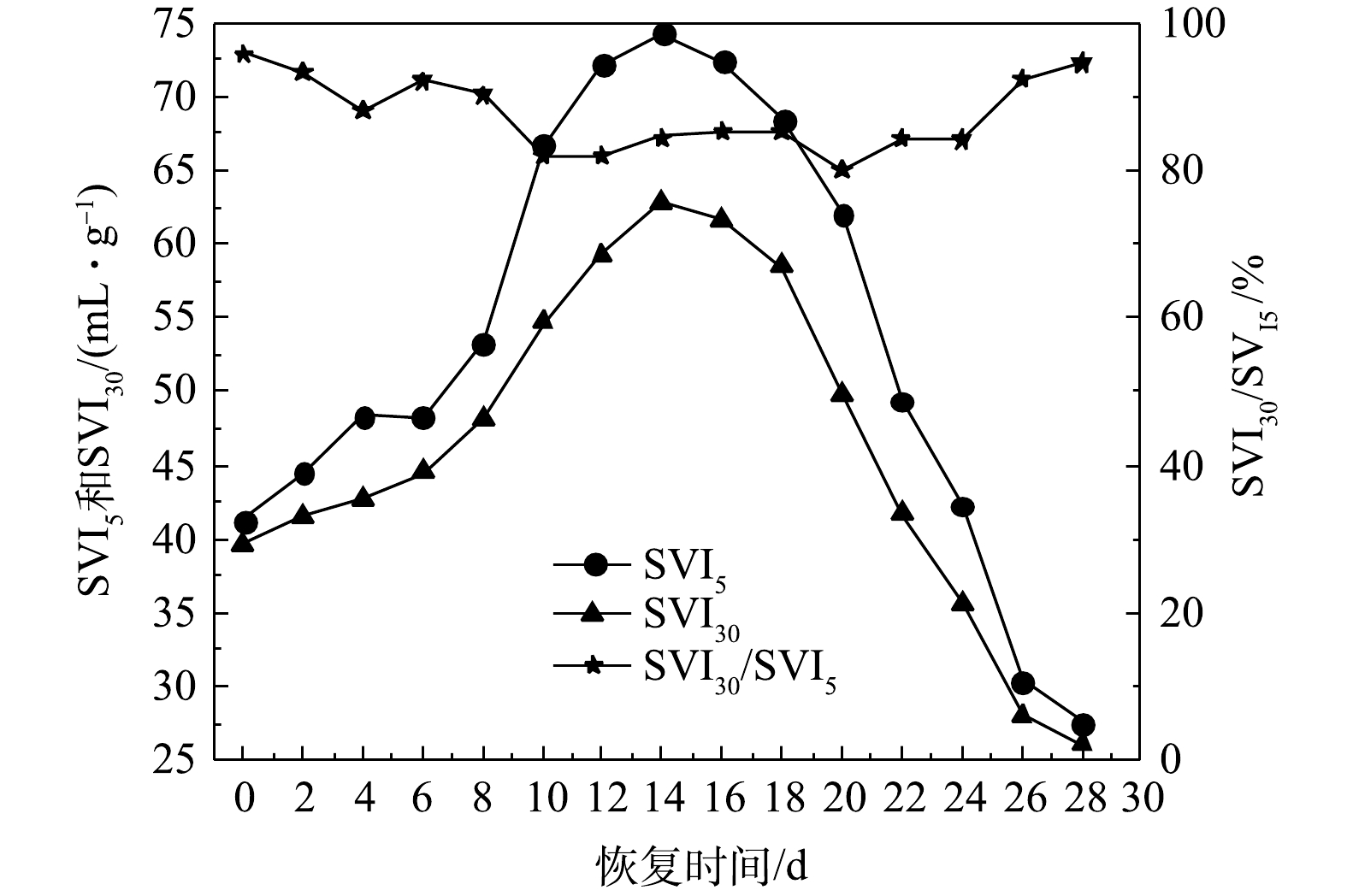
好氧颗粒污泥在活性恢复过程中的沉降性能变化如图5所示。恢复前,好氧颗粒污泥的SVI30和SVI5分别为39.6 mL·g−1和41.3 mL·g−1,SVI30/SVI5为95.88%。SBR运行的0~14 d,好氧颗粒污泥处于破碎阶段,即储存后的好氧颗粒污泥因曝气量的增大(由1.5 L·min−1增加到6.0 L·min−1)而发生解体,导致反应器中的细小颗粒污泥和絮状污泥增多,污泥沉降性能变差。所以,该阶段的SVI30和SVI5值均呈现增大的趋势,且SVI30和SVI5在第14天时达到最大值,分别为62.8 mL·g−1和74.3 mL·g−1,SVI30/SVI5下降到84.52%。随着反应的进行,絮状污泥以破碎的颗粒污泥微粒为载体开始向新的好氧颗粒污泥转化,重塑的好氧颗粒污泥在SBR中逐渐占主体。因此,从第16天起,SVI30和SVI5开始急剧下降,在第28 d时,SVI30和SVI5分别为26.1 mL·g−1和27.6 mL·g−1,均低于恢复前水平,而SVI30/SVI5由85.22%(第16天)增大到94.57%(第28天),表明恢复后的好氧颗粒污泥具有良好的沉降性能。
-
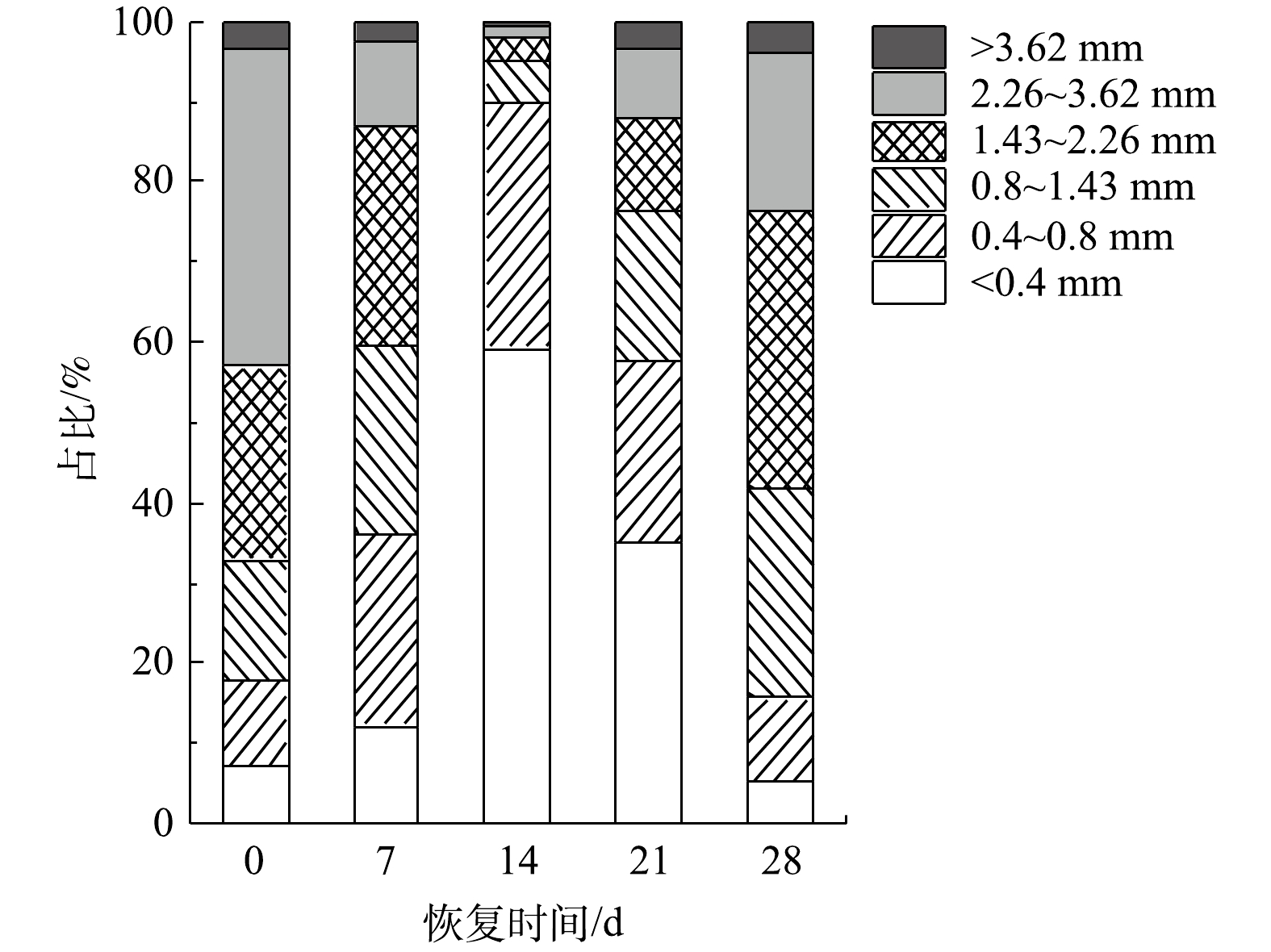
好氧颗粒污泥恢复过程中的粒径分布变化如图6所示。恢复前的好氧颗粒污泥主要以粒径为2.26~3.62 mm的颗粒为主。SBR运行到第7天时,颗粒污泥粒径主要分布在1.43~2.26 mm,占总体的27.6%,部分粒径较大的好氧颗粒污泥破碎,小颗粒污泥数量增多;粒径<1.43 mm的颗粒污泥由恢复前的32.9%增加到59.4%;而粒径为2.26~3.62 mm的颗粒污泥由39.5%减少到10.3%。第15天时,粒径<0.4 mm的颗粒污泥在反应器中占主体,占比达到59.3%;而粒径为0.4~0.8 mm的颗粒污泥占比为30.5%。随后,大粒径(>1.43 mm)的颗粒污泥占比由4.9%(第15天)增加到23.7%(第21天)。恢复后的好氧颗粒污泥粒径主要集中在1.43~2.26 mm,粒径在0.8~3.62 mm的颗粒污泥占比为80.5%。
-
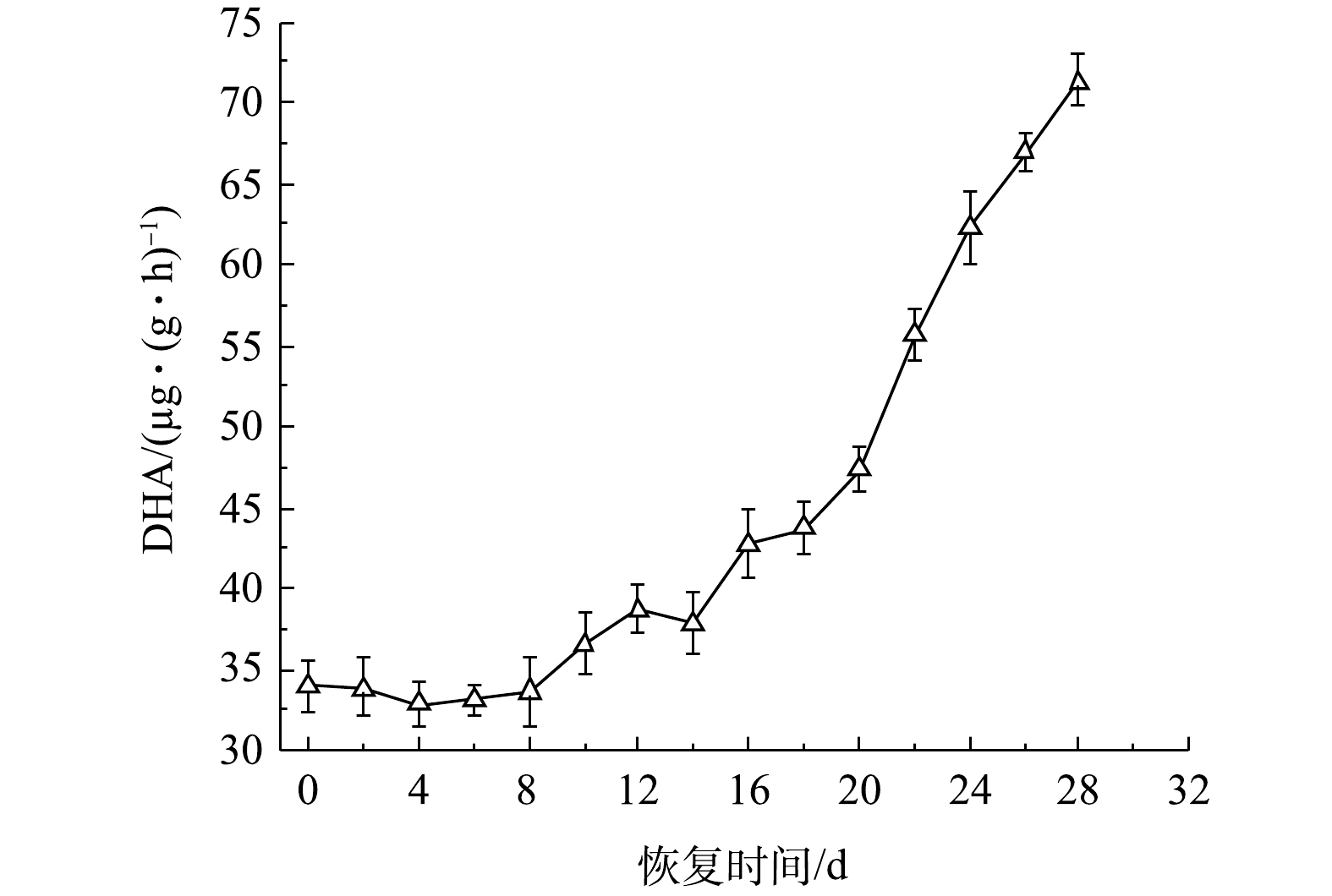
以脱氢酶活性(dehydrogenase activity, DHA)为表征恢复过程中的好氧颗粒污泥微生物活性[17]。图7为活性恢复过程中DHA变化情况。恢复前的DHA为34.02 μg·(g·h)−1,仅为储存前的41.16%。这主要是因为:一是好氧颗粒污泥储存在无溶解氧和营养物的环境中,微生物生理活动能力下降;二是由于苯酚毒性进一步抑制微生物活性,所以储存后DHA降低。在SBR运行的第0~6天,由于好氧颗粒污泥受到因曝气所产生的水力剪切力,导致部分颗粒污泥解体,微生物细胞受到损害,所以DHA下降缓慢。随后,因为颗粒污泥中的微生物对环境条件的逐渐适应,微生物活性逐渐得到改善,所以DHA呈现缓慢增加的趋势。第10天时DHA增加到36.58 μg·(g·h)−1,超过恢复前的活性。第20天时,由于微生物大量生长,MLSS增加,好氧颗粒污泥形成,所以DHA显著增加。第28天时的DHA为71.36 μg·(g·h)−1,约是恢复前活性的2.1倍,储存前的DHA为82.65 μg·(g·h)−1,几乎和储存前的颗粒污泥活性相当,表明好氧颗粒污泥在苯酚溶液储存150 d后,经过28 d的再培养即可完全恢复其微生物活性。
-
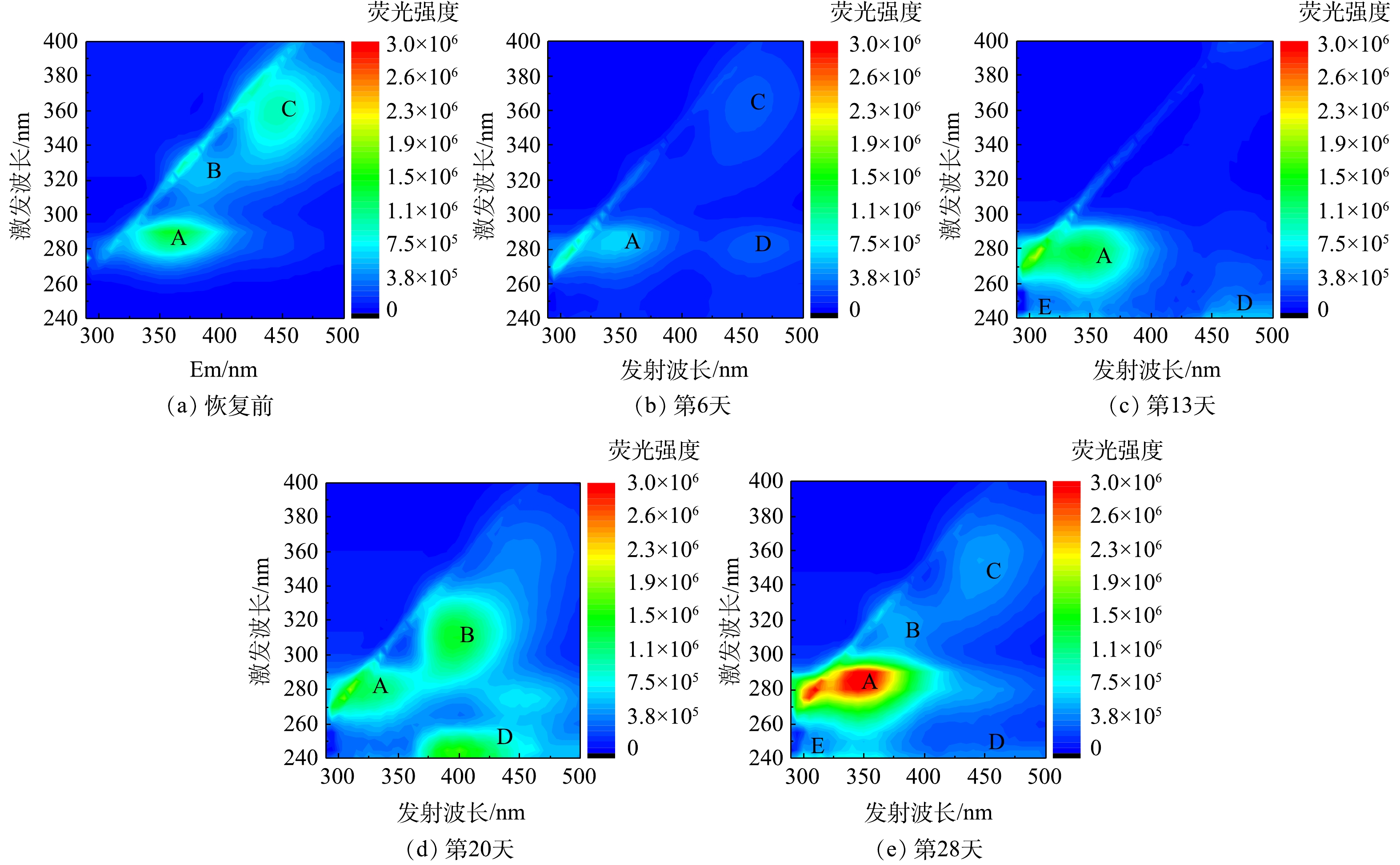
采用3D-EEM技术鉴定好氧颗粒污泥在恢复过程中其EPS的荧光物质的组分,结果如图8所示。由图8可知,EPS中可能具体存在5个荧光区域,其中荧光峰A(Ex/Em=280~295 nm/340~380 nm)为酪氨酸/色氨酸类蛋白;荧光峰B(Ex/Em=315~330 nm/360~390 nm)为多糖类物质[18-19];荧光峰C(Ex/Em=340~380 nm /420~470 nm)为腐殖酸类物质;荧光峰D(Ex/Em=240~280 nm /380~470 nm)为富里酸类物质;荧光峰E(Ex/Em=240~250 nm /290~330 nm)为芳香族蛋白类物质。
由图8可知,与恢复前(图8(a))相比,恢复到第6天时(图8(b))的EPS荧光峰A和C的荧光强度减弱,荧光峰B甚至消失,但富里酸类物质(荧光峰D)形成。第13天时,代表酪氨酸/色氨酸类蛋白的荧光峰A的荧光强度增强,代表芳香族蛋白类物质的荧光峰E出现,这可能是因为,此时颗粒污泥中的微生物适应环境条件后伴随着活性的恢复,微生物细胞开始分泌EPS。有研究[20]表明,色氨酸类蛋白与微生物细胞内蛋白质的新陈代谢相关,具有促进絮状污泥颗粒化的作用。第20天时,代表多糖类物质的荧光峰B出现。这可能是因为荧光峰A所代表的部分物质红移(荧光峰向长波方向移动)的结果,说明EPS基团中的羟基、羧基和烃基增加[21]。代表富里酸类物质的荧光峰D的荧光强度增加且发生蓝移(荧光峰向短波方向移动),说明部分大分子在微生物的作用下转化为小分子[22]。郝晓地等[23]指出,EPS中多糖类物质可为絮状污泥转化为颗粒状污泥提供骨架结构,而富里酸类物质可促进胞内的酶促反应,提高微生物活性。第28天时,代表蛋白质的荧光峰A和E的荧光强度增强且明显高于恢复前对应的荧光强度(图8(a)),而代表多糖类物质的荧光峰B的荧光强度和恢复前的相似。综合以上结果可知:在好氧颗粒污泥恢复过程中,EPS组分不断发生改变;相比于腐殖酸类物质,酪氨酸/色氨酸类蛋白和芳香族蛋白类物质对微生物细胞聚集体的形成以及颗粒污泥的活性恢复具有更重要的作用。
-
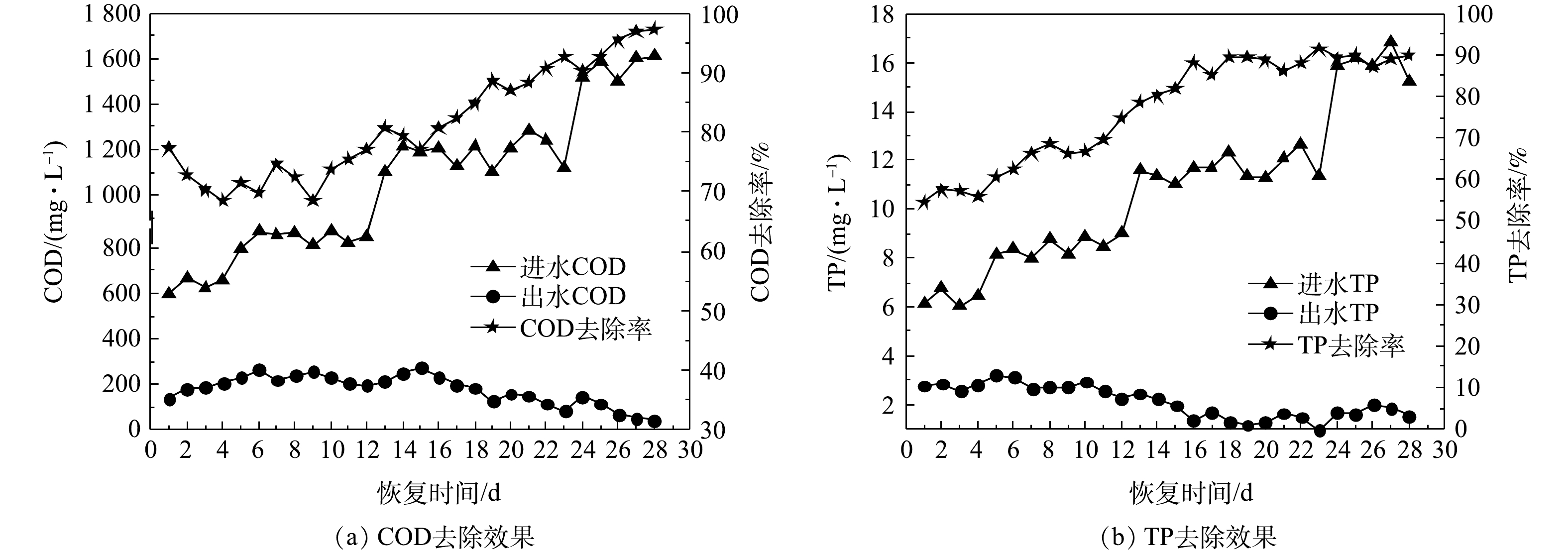
1) COD和TP去除效果。好氧颗粒污泥活性恢复过程中COD和TP去除效果的变化如图9所示。由图9(a)可知,活性恢复初期(第1~10天),进水COD由600.46 mg·L−1增加到873.91 mg·L−1,由于污泥中的微生物在该恢复阶段内正处于环境适应期,微生物活性尚未完全恢复且部分颗粒污泥发生解体,因此,COD去除率降低(由77.33%下降到73.85%),出水COD由136.15 mg·L−1增大到228.53 mg·L−1。随着微生物对SBR运行环境的适应,微生物数量和活性开始增加,破碎的颗粒污泥碎片和絮状污泥逐渐被新生成的好氧颗粒污泥取代,所以从第11天开始,COD去除率不断增大,出水COD不断减小。第28天时,进水COD为1 610.34 mg·L−1,出水COD为42.84 mg·L−1,COD去除率达到97.34%,该COD去除率高于与储存前的COD去除率(95%),说明经过28 d的活性恢复,好氧颗粒污泥降解耗氧有机物(以COD计)的能力即可达到储存前水平。
好氧颗粒污泥活性恢复过程中TP去除效果的变化如图9(b)所示。恢复第1天时的进水TP为6.14 mg·L−1,出水TP为2.78 mg·L−1,TP去除率为54.72%。在第2~18天,TP去除率由57.64%增加到89.41%。这主要是因为,在曝气条件下,污泥中的聚磷菌具有摄取磷酸盐的功能,当污泥沉淀时间减少(由14 min减少到8 min)时,大量絮状含磷污泥被排出反应器,所以TP去除率增加。由图2(d)可知,恢复第15天时好氧颗粒污泥已经生成,反应器中的好氧颗粒污泥数量逐渐增加。第19天以后,在进水TP增加的情况下,TP去除率没有发生明显变化,基本维持在88.81%~91.62%,因此,可推测颗粒污泥对TP去除效果与恢复初期的絮状或破碎污泥的活化有关,而恢复后期的好氧颗粒污泥生长对TP去除效果没有较大影响。当好氧颗粒污泥完全恢复(第28天)时,TP去除率为89.88%,出水TP为1.54 mg·L−1。
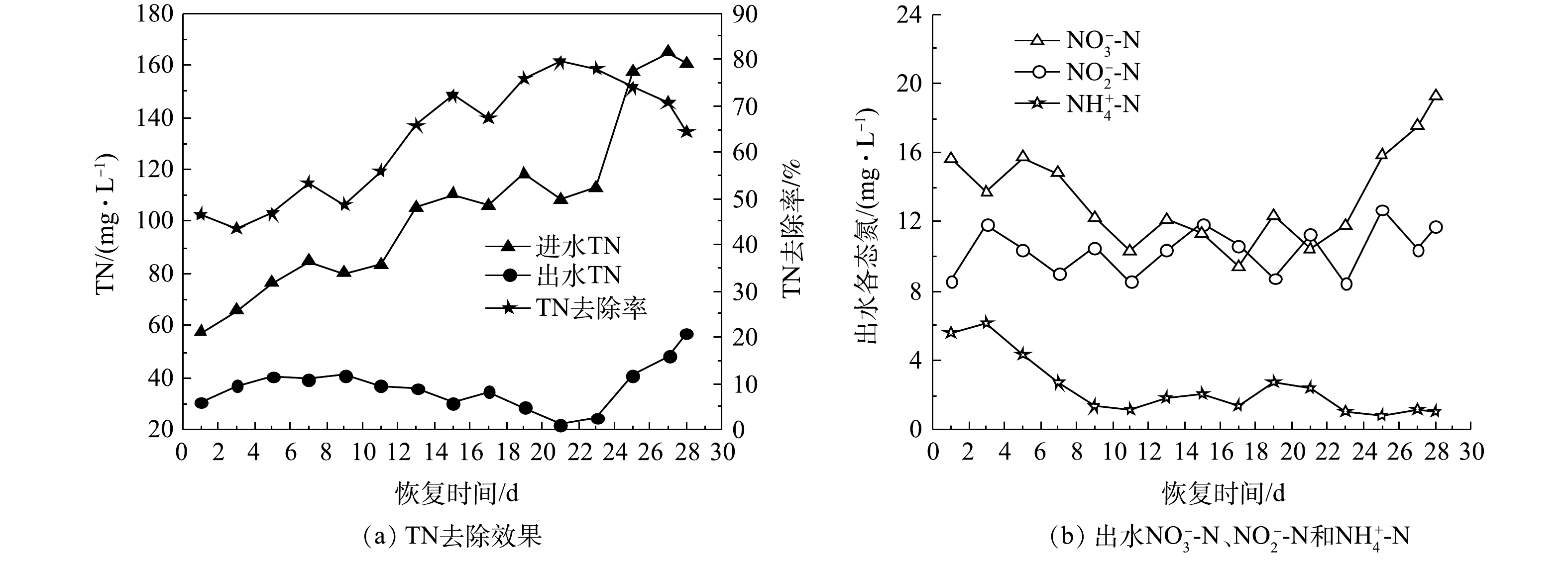
2)脱氮效果。图10为好氧颗粒污泥活性恢复期间脱氮效果的变化。如图10(a)所示,在1~21 d,进水TN由57.48 mg·L−1逐渐增加到118.60 mg·L−1,随着微生物活性和数量的增加和,TN去除率呈增大趋势,由46.50%增大到79.53%。在恢复的第21天前,出水
NO−3 -N和NH+4 -N均呈缓慢下降趋势(图10(b)),第21天时的出水NO−3 -N和NH+4 -N分别为10.42 mg·L−1和2.40 mg·L−1。随后,TN去除率随进水TN增加而下降,出水TN开始增加(图10(a))。由图10((b))可知,出水NO−3 -N从第23天开始出现积累,第28天时的出水NO−3 -N达到19.27 mg·L−1,出水NH+4 -N在第23~28天维持在0.83~1.21 mg·L−1。而在整个颗粒污泥恢复过程中,出水NO−2 -N波动在8.45~12.73 mg·L−1,未发生积累现象。以上脱氮效果表明,在恢复的前23 d,颗粒污泥中的微生物大量增殖引起同化效应增强,脱氮效果明显。随着好氧颗粒污泥的不断生长、恢复,硝化细菌逐渐富集,SBR内主要是以同步硝化和反硝化为主要脱氮途径。这可能是由于缺乏反硝化碳源,反硝化作用减弱,因此,活性恢复后期的脱氮效果下降。在第28天时,出水TN为57.19 mg·L−1,TN去除率下降到64.37%。 -
1)好氧颗粒污泥在活性恢复过程中经历了破碎到重塑的演变过程。经过28 d的再培养,好氧颗粒污泥完全恢复其结构完整性和微生物活性。恢复后的好氧颗粒污泥为黄褐色,大多数颗粒粒径集中在1.43~2.26 mm。颗粒污泥表面生长着大量的钟虫、球菌和短杆菌且有EPS分布在其表面。
2)第28天时,好氧颗粒污泥MLSS和MLVSS分别为16 903 mg·L−1和12 001 mg·L−1,MLVSS/MLSS为0.71,表明恢复后的好氧颗粒污泥浓度高且微生物量大。SVI30和SVI5分别为26.1 mL·g−1和27.6 mL·g−1,DHA为71.36 μg·(g·h)−1。好氧颗粒污泥的EPS组分在恢复期间不断发生改变,相比于腐殖酸类物质,酪氨酸/色氨酸类蛋白和芳香族蛋白类物质对好氧颗粒污泥的活性恢复具有更重要的作用。
3)恢复后的好氧颗粒污泥对COD和TP的去除率分别为97.34%和89.88%;但脱氮效果不佳,出水
NO−3 -N、NO−2 -N和NH+4 -N分别为19.27、11.72、1.05 mg·L−1,对TN的去除率为64.37%。
存储于苯酚溶液后的好氧颗粒污泥的活性恢复效果
Activity recovery effect of aerobic granular sludge stored in phenol solution
-
摘要: 通过调控SBR的进水COD、曝气量和污泥沉淀时间,对储存于苯酚溶液后的好氧颗粒污泥进行了活性恢复研究,为好氧颗粒污泥活性恢复方法的选择提供参考。结果表明,室温下在60 mg·L−1苯酚溶液中储存150 d的好氧颗粒污泥,经过28 d的培养即可恢复其结构完整性和微生物活性。在活性恢复期间中,好氧颗粒污泥经历了破碎到重塑的演变过程。恢复后的好氧颗粒污泥具有良好的沉降性能,微生物量较大且活性较高,SVI30和SVI5分别为26.1 mL·g−1和27.6 mL·g−1,MLSS和MLVSS分别为16 903 mg·L−1和12 001 mg·L−1,MLVSS/MLSS为0.71,DHA为71.36 μg·(g·h)−1。好氧颗粒污泥的EPS组分在恢复期间不断发生改变,代表酪氨酸/色氨酸类蛋白和芳香族蛋白类物质的荧光强度随颗粒污泥的活性恢复逐渐增强。恢复后的好氧颗粒污泥对COD、TP和TN的去除率分别为97.34%、89.88%和64.37%。Abstract: In this study, the activity recovery of the stored aerobic granular sludge was conducted by regulating the influent COD, aeration and sludge settling time of the SBR, which will provide a reference for the selection of aerobic granular sludge activity recovery methods. The results showed that aerobic granular sludge stored in 60 mg·L−1 phenol solution for 150 d at room temperature could regain its structural integrity and microbial activity after 28 d of incubation. Aerobic granular sludge underwent an evolutionary process from fragmentation to reconstruction during activity recovery. The recovered aerobic granular sludge had a good settleability, high microbial load and activity, SVI30 and SVI5 were 26.1 mL·g−1 and 27.6 mL·g−1, respectively, MLSS and MLVSS were 16 903 and 12 001 mg·L−1, respectively, and MLVSS/MLSS was 0.71, and DHA was 71.36 μg·(g·h)−1. The EPS fraction of aerobic granular sludge changed continuously during the recovery period, representing a gradual increase in fluorescence intensity of tyrosine/tryptophan-like proteins and aromatic protein-like substances with the recovery of granular sludge activity. The recovered aerobic granular sludge showed 97.34%, 89.88% and 64.37% removal of COD, TP and TN, respectively.
-
Key words:
- aerobic granular sludge /
- activation recovery /
- storage /
- decontamination effect /
- phenol
-
表 1 SBR运行参数
Table 1. Operating parameters of SBR
恢复时间/d 各阶段时间/min 曝气量/(L·min−1) 总氮、总磷及COD/(mg·L−1) 进水 曝气 沉淀 排水 闲置 COD TN TP 1~4 4 343 10 1 2 1.5~2 600 60 6 5~8 4 345 8 1 2 3.5~4.0 800 80 8 9~12 4 339 14 1 2 4.5~5.5 800 80 8 13~18 4 342 11 1 2 6.0~7.0 1 100 110 11 19~23 4 346 7 1 2 7.5~8.6 1 100 110 11 24~28 4 350 3 1 2 9.0~9.7 1 500 150 15 -
[1] ZHANG Q G, HU J J, LEE D J. Aerobic granular processes: Current research trends[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 210: 74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.098 [2] ZOU J T, TAO Y Q, LI J, et al. Cultivating aerobic granular sludge in a developed continuous-flow reactor with two-zone sedimentation tank treating real and low-strength wastewater[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 247: 776-783. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.088 [3] 赵珏, 宣鑫鹏, 程媛媛, 等. 好氧颗粒污泥的储存稳定性研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2018, 38(2): 1-5. doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2018.38(2).001 [4] 袁京群, 康达, 毛伟华, 等. 温度和储存基质对储存后厌氧颗粒污泥特性的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(7): 2622-2631. [5] 邹金特, 何航天, 潘继阳, 等. 低碳源废水培养的好氧颗粒污泥常温储存后活性恢复研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(12): 4530-4536. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.12.017 [6] 王维红, 康增彦, 董星辽, 等. 番茄酱加工废水的好氧颗粒污泥活性恢复研究[J]. 应用化工, 2020, 49(11): 2743-2747. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.11.015 [7] GAO D W, YUAN X J, LIANG H. Reactivation performance of aerobic granules under different storage strategies[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(10): 3315-3322. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.045 [8] 高景峰, 苏凯, 陈冉妮, 等. 不同储存方法对好氧颗粒污泥恢复的影响[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2011, 19(3): 408-415. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0930.2011.03.007 [9] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [10] LAGUNG A, OUATTARA A, GONZALEZ R O, et al. A simple and low cost technique for determining the granulometry of up flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor sludge[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1999, 40(8): 1-8. doi: 10.2166/wst.1999.0371 [11] 陈琳琳, 闪金华, 吕弈成, 等. 电镀废水物化处理工艺对各阶段出水水质及污泥脱氢酶活性的影响[J]. 净水技术, 2020, 39(5): 134-139. [12] 张云霞, 季民, 李超, 等. 好氧颗粒污泥胞外聚合物(EPS)的生化性研究[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(11): 3124-3127. [13] LIN Y M, DE KREUK M, VAN LOOSDRECHT M C M, et al. Characterization of alginate-like exopolysaccharides isolated from aerobic granular sludge in pilot-plant[J]. Water Research, 2010, 44(11): 3355-3364. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.03.019 [14] JIANG B, LIU Y. Roles of ATP-dependent N-acylhomoserine lactones (AHLs) and extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) in aerobic granulation[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 88(9): 1058-1064. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.04.059 [15] OLIVEIRA A S, AMORIM C L, RAMOS M A, et al. Variability in the composition of extracellular polymeric substances from a full-scale aerobic granular sludge reactor treating urban wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 104-156. [16] WANG Y Y, ZHOU S, WANG H, et al. Comparison of endogenous metabolism during long-term anaerobic starvation of nitrite/nitrate cultivated denitrifying phosphorus removal sludges[J]. Water Research, 2015, 68(1): 374-386. [17] ZHANG Y, ZHAO X H. The effects of powdered activated carbon or ferric chloride on sludge characteristics and microorganisms in a membrane bioreactor[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2014, 52(37/38/39): 6868-6877. [18] 朱大伟, 武道吉, 孙翠珍, 等. 三维荧光光谱(3D-EEM)技术在溶解性有机质(DOM)分析中的应用[J]. 净水技术, 2015, 34(1): 14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0177.2015.01.003 [19] 支丽玲, 马鑫欣, 刘奇欣, 等. 好氧颗粒污泥形成过程中群感效应的作用研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(5): 2148-2156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.05.035 [20] 邵尤炼. 胞外多聚物在厌氧污泥颗粒化及应用过程中的作用研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2014. [21] ZHU L, QI H Y, LV M L, et al. Component analysis of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) during aerobic sludge granulation using FTIR and 3D-EEM technologies[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 124: 455-459. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.08.059 [22] SWIETLIK J, DABROWSKA A, RACZYKSTANISAWIAK U, et al. Reactivity of natural organic matter fractions with chlorine dioxide and ozone[J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(3): 547-558. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2003.10.034 [23] 郝晓地, 周鹏, 曹亚莉. 污水处理中腐殖质的来源及其演变过程[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(1): 1-11. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201606072 -






 下载:
下载: