-
近年来我国的养猪行业逐渐规模化、企业化,猪的出栏量以达世界最多[1]。养猪行业每年可产生大量的粪便,但其有效资源化利用率却不足50%[2]。我国每年产生大量的猪粪水,其中包括了粪便、尿液以及洗涤废水[3-4]。猪场废水在经过处理之前大多需要经过沼气池厌氧发酵过程,而将猪场沼液直接排放到江河中会引起水体富营养化等一系列环境问题[5-6]。因此,亟待研发出一种高效且低能耗的猪场沼液处理优化工艺[7]。目前常用的生化处理工艺有SBR工艺[8]、生物过滤器[9]、厌氧氨氧化技术[10]和缺氧/好氧工艺A/O工艺[11]等。A/O工艺前置缺氧池,可补充硝化池所需碱度,同时使反硝化池未完全处理的有机物得到进一步去除,降低运行费用[12-13];此外,A/O工艺因其运行成本低,故结合其他技术可以起到良好的处理效果,因而被广泛应用。陈锦良[14]基于A/O工艺的微电解耦合反硝化污泥深度处理猪场沼液,出水水质中COD、
NH+4 -N、NO−3 -N平均质量浓度分别为42.5、2.4、9.8 mg·L−1。LIU等[15]采用两级缺氧/好氧复合膜生物反应器A/O-A/O-MBR对垃圾填埋场产生的渗滤液进行了81 d的处理,对总氮以及氨氮的去除率达80.7%和99.3%。孙亚平等[16]利用两级A/O工艺以及人工湿地等工艺组合深度处理猪场废水,对NH+4 -N的去除率为76.40%~98.41%,TP的去除率维持在83.92%~99.84%,COD的去除率则为89.26%~98.62%。有研究结果[17]表明,沉水植物对水体中营养物质的吸收要大于漂浮植物和挺水植物。金树权等[18]通过研究发现,水体生物修复中的微生物与植物修复效果之间存在密切联系,虽然沉水植物直接吸收氮磷比例占水质中氮磷比例不高,但通过促进植物体吸附、改善环境提高水体微生物转化等增效作用较为明显。狐尾藻是沉水植物中常见的一种,其对水体中氮磷等营养物质具有较强的吸收能力[19],植物根系对有机碳的释放有助于提高低C/N污水的总氮去除效率,收割后的狐尾藻还可作为湿地景观观赏以及作为饲料使用[20-21]。吴晓梅等[22]利用狐尾藻处理猪场沼液,结果表明,当水力停留时间为40 d 时对沼液的处理效果最好,沼液中COD以及
NH+4 -N去除率分别为65.99%和59.54%。近年来人们提出了运用填料与A/O工艺相结合的污水处理方法[23]。晁雷等[24]运用3种不同填料对比了强化A/O工艺处理炼化废水,结果表明,弹性填料对炼化废水中COD、NH+4 -N和TN的去除效果相对较好,去除率分别为80.6%、95%、75%。弹性填料因其结构具备弹性可保持稳定性,可使填料表层吸附微生物并进行正常的新陈代谢,在好氧池中可减少对微生物的冲击作用,因此,弹性填料的加入有助于微生物更好生长繁殖[25],在一定程度上可强化A/O工艺。本研究中采用对A/O工艺进行方法的优化,在池中加挂弹性填料仿生水草的同时在表面种植狐尾藻,监测了其水质指标变化并调整了运行参数,同时设置对照组观察,对比探讨了A/O工艺和改良A/O工艺对猪场沼液常规污染物质去除能力的优化效果,以期为强化A/O工艺处理猪场沼液提供参考。
全文HTML
-
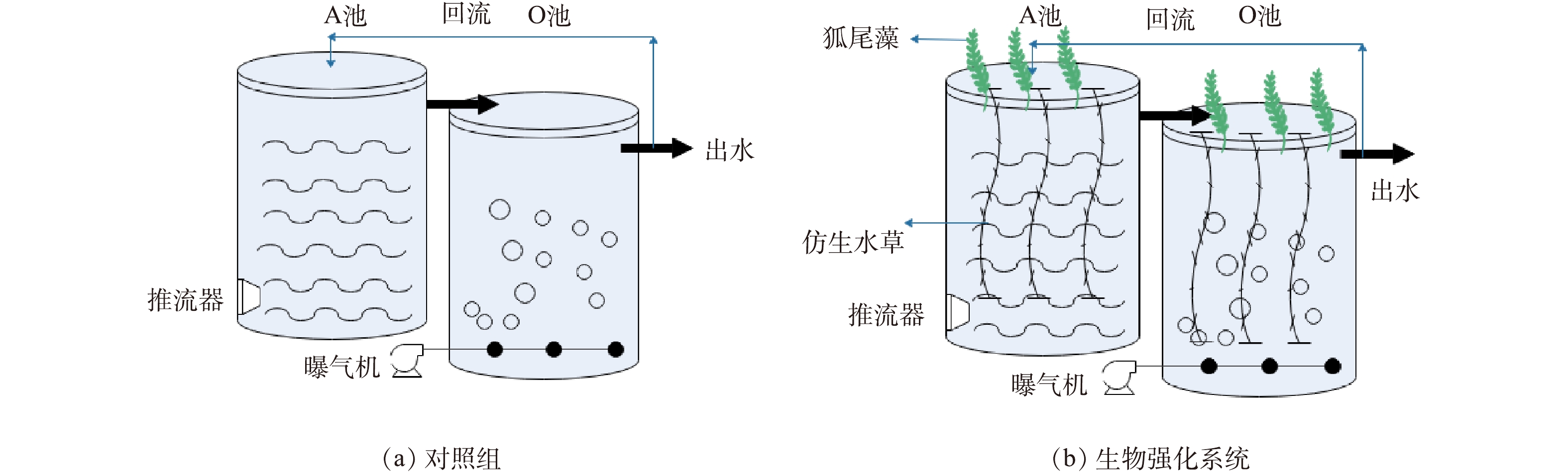
实验装置如图1所示。2套实验装置均由反硝化池、硝化池组成,池与池之间由PVC管连接,装置均由单个容积200 L的塑料桶制成。运行过程中添加的沼液均为实际废水,通过水泵的作用将沼液抬升自流到反硝化池和硝化池;外接曝气装置,同时在反硝化池内安装推流器,并控制进水量、曝气量以及回流量;好氧池中溶解氧控制在2.0~4.0 mg·L−1,外回流比控制为50%,硝化液回流比为1∶1,污泥龄控制为20 d。通过添加弹性填料仿生水草强化微生物处理技术,种植狐尾藻增强对水体中污染物质的去除能力,提升植物微生物共生系统的处理效果;在硝化池与反硝化池中均悬挂弹性填料仿生水草并在池表面种植狐尾藻,仿生水草在池内的填充量为50%,狐尾藻种植面积覆盖池表面的75%;同时,设置空白组作为水质排放指标的对照。
本实验在广东省惠州市某猪场内进行,系统运行前期通过接种猪场废水处理厂中的沉淀污泥启动反应器,将沼液曝气培养驯化微生物,进水沼液各项指标参见表1。
-
A/O工艺系统运行前期进行15 d污泥驯化,每日早晚各进实际废水沼液1 h,通过添加碳酸氢钠调节池中pH。水力停留时间测试分为3个时间阶段:第1~70天水力停留时间20 d,每日计划进水20 L;第70~130天水力停留时间13 d,每日计划进水30 L;第130~190天水力停留时间10 d,每日计划进水40 L。每7 d测1次水样,分别测定进水沼液、反硝化池和硝化池出水中
NH+4 -N、NO−3 -N、NO−2 -N、COD、TN、SS、MLSS、DO等水质指标,通过对比A/O工艺以及改良A/O工艺中NH+4 -N、NO−3 -N、COD、TN的去除率以及出水的质量浓度,以此来对比两者去除效果的差异。实验结束后保留植物样本,称量狐尾藻的湿重和干重以此计算植物含水量;同时,测试植物中N、P的积累量,观察植物吸收猪场沼液中氮磷的情况。 -
水质测定方法:COD采用重铬酸钾消解法;总氮(TN)采用碱性过硫酸钾消解-紫外分光光度法;铵态氮(
NH+4 -N)采用纳氏试剂分光光度法;硝态氮(NO−3 -N)采用酚二磺酸分光光度法;亚硝酸盐氮(NO−2 -N)采用N-(1-奈基)-乙二胺光度法;污泥质量浓度(MLSS)和挥发性污泥质量浓度(MLVSS)使用标准称量法测定;溶解氧(DO)使用便携式溶解氧仪测定;pH使用雷诺pH计测定。植物指标的测定方法:植物含水量采用烘箱法;植物中全氮(TN)采用TN-H2SO4-H2O2消煮-奈氏比色法;植物中全磷(TP)采用TP-H2SO4-H2O2消煮-钼睇抗比色法。
1.1. 实验装置及进水
1.2. 实验方法
1.3. 分析方法
-
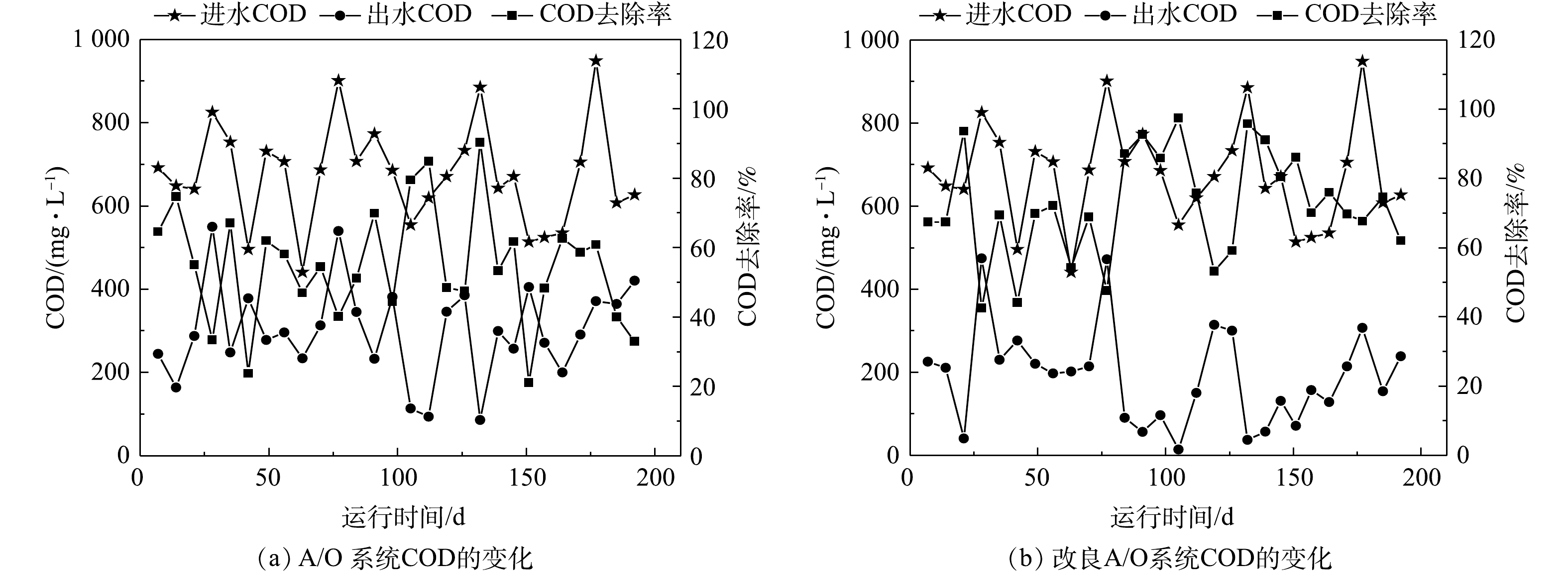
如图2所示,猪场沼液进水COD值为441~948 mg·L−1,A/O工艺对COD的去除率为32.9%~90.3%,改良A/O工艺对COD的去除率为42.5%~97.4%,改良A/O工艺COD平均去除率较A/O工艺提升17%。A/O工艺耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)出水质量浓度为86~571 mg·L−1,改良A/O工艺出水质量浓度为37~475 mg·L−1。改良A/O工艺中耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)出水浓度明显低于A/O工艺出水浓度,但由于沼液进水COD值波动较大,从而导致出水浓度以及去除率的变化较大,故当沼液进水耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)浓度过高时,改良A/O工艺未能充分将耗氧有机物分解,出水浓度未能完全满足排放标准。因此,后续应用中可设置多级改良A/O工艺,从而实现进一步对耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)的去除[16]。A/O工艺水力停留时间过长并不利于对猪场沼液中耗氧有机污染物的去除,而且还会增加运行成本,因此,A/O工艺加挂弹性填料种植狐尾藻在水力停留时间为10 d时最符合实际运行的情况,耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)的平均去除率和出水质量浓度分别为75.3%和162 mg·L−1。
-
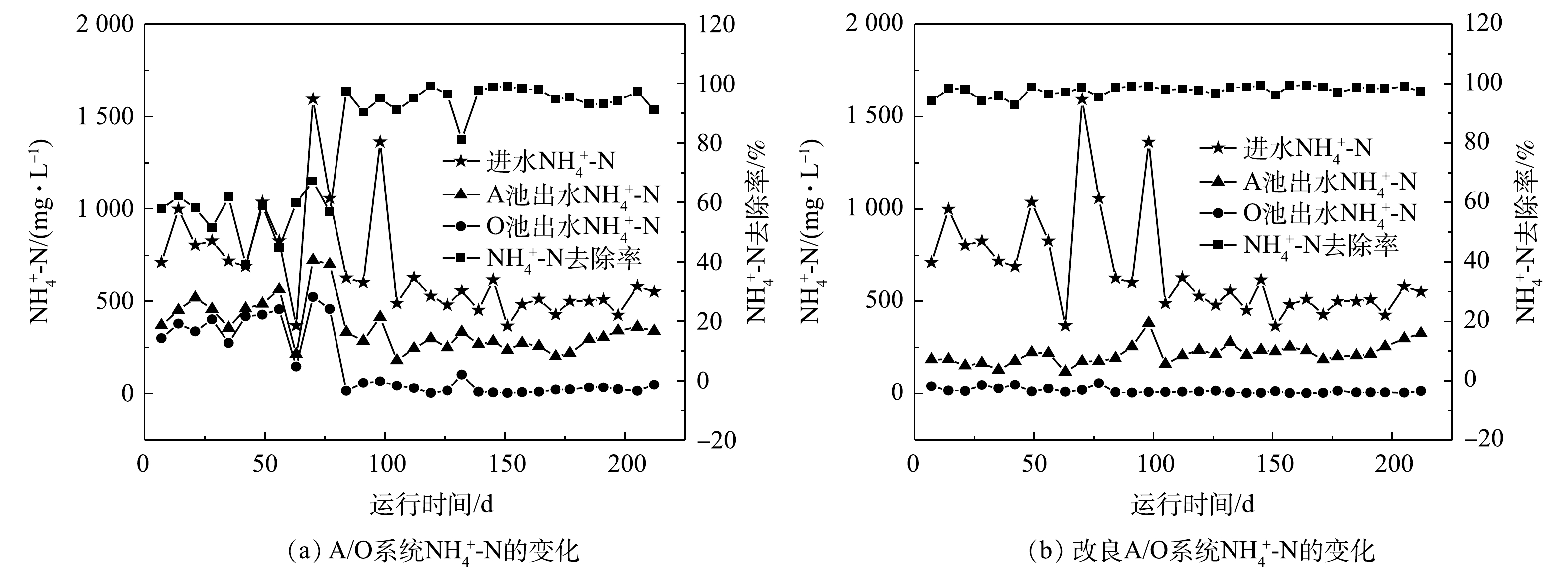
如图3所示,猪场沼液
NH+4 -N的进水质量浓度为369~1 594 mg·L−1,波动范围较大。A/O工艺对NH+4 -N的去除率为39.2%~99.2%,改良A/O工艺对NH+4 -N的去除率为94.2%~99.4%,平均去除率提升至97.2%。A/O工艺和改良A/O工艺NH+4 -N的出水质量浓度分别为4~523 mg·L−1和2~49 mg·L−1,改良A/O工艺NH+4 -N的出水质量浓度均小于50 mg·L−1,满足国家排放标准。改良A/O工艺中因悬挂仿生水草,因而强化了微生物对NH+4 -N的去除效果[24],仿生水草表面的生物膜能够提高系统硝化菌的数量;狐尾藻对一定浓度的沼液中NH+4 -N具有较强的吸收作用,同时,植物结合微生物对NH+4 -N去除能力具有增强效果[18]。综上所述,改良A/O工艺对沼液中NH+4 -N去除能力显著。改良A/O工艺在水力停留时间20 d时对NH+4 -N的去除效果较差,平均去除率和出水质量浓度分别为94.6%和48 mg·L−1;在水力停留时间为10 d时,平均去除率和出水质量浓度分别为98.4%和7 mg·L−1,去除效果较优于水力停留时间13 d的98.3%和10 mg·L−1。当水力停留时间为20 d时,O池对NH+4 -N的去除能力大大减弱,水力停留时间过长导致A池和O池的NH+4 -N出水浓度均有所增加,对O池中硝化作用去除NH+4 -N能力的削弱尤为明显。由于水力停留时间过长,导致负荷过小,仅为0.3 m3·(m2·d)−1,远低于傅金祥等[26]在A/O工艺运用中的最佳负荷1 m3·(m2·d)−1,而污泥自身发生氧化导致污泥越来越少从而降低硝化反硝化途径处理效果,进而削弱了好氧硝化细菌将NH+4 -N转化为NO−3 -N和NO−2 -N的能力。综上可知,改良A/O工艺对NH+4 -N的去除效果更优,并随着水力停留时间的减少,对NH+4 -N去除能力不断增强,且在水力停留时间为10 d时去除效果达到最佳。这与李海华等[27]的研究结果相近。如图4所示,当进水沼液
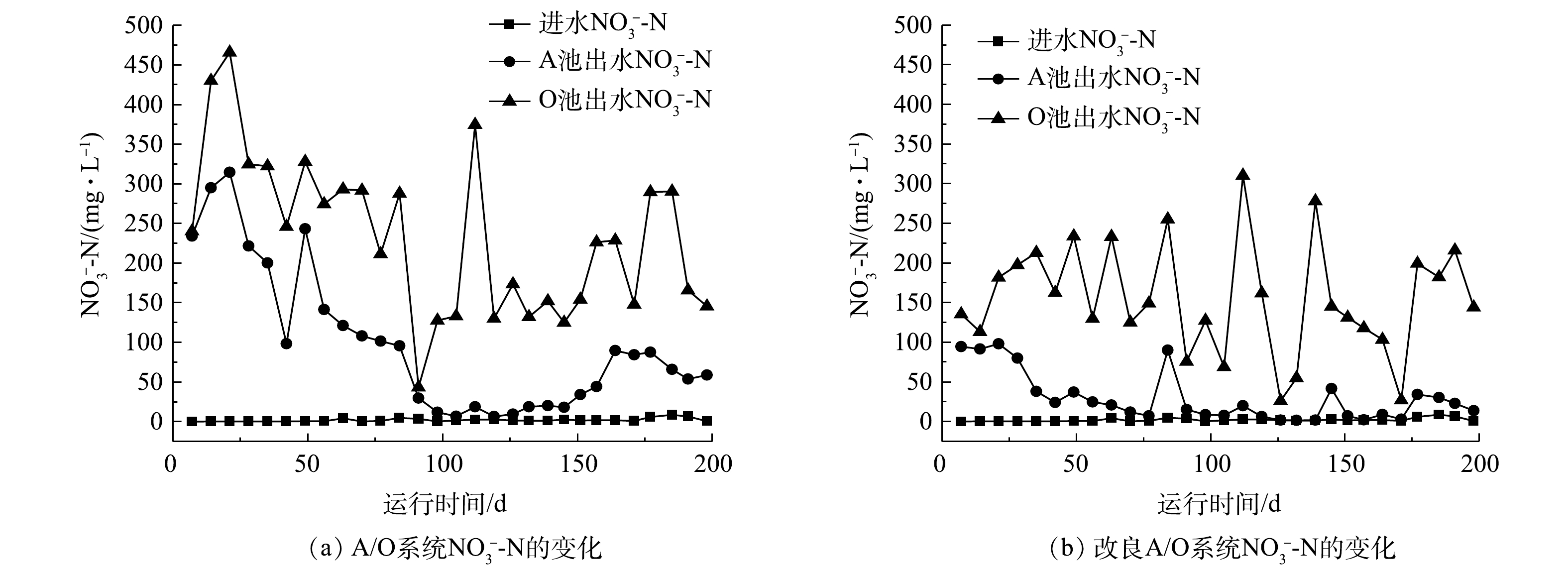
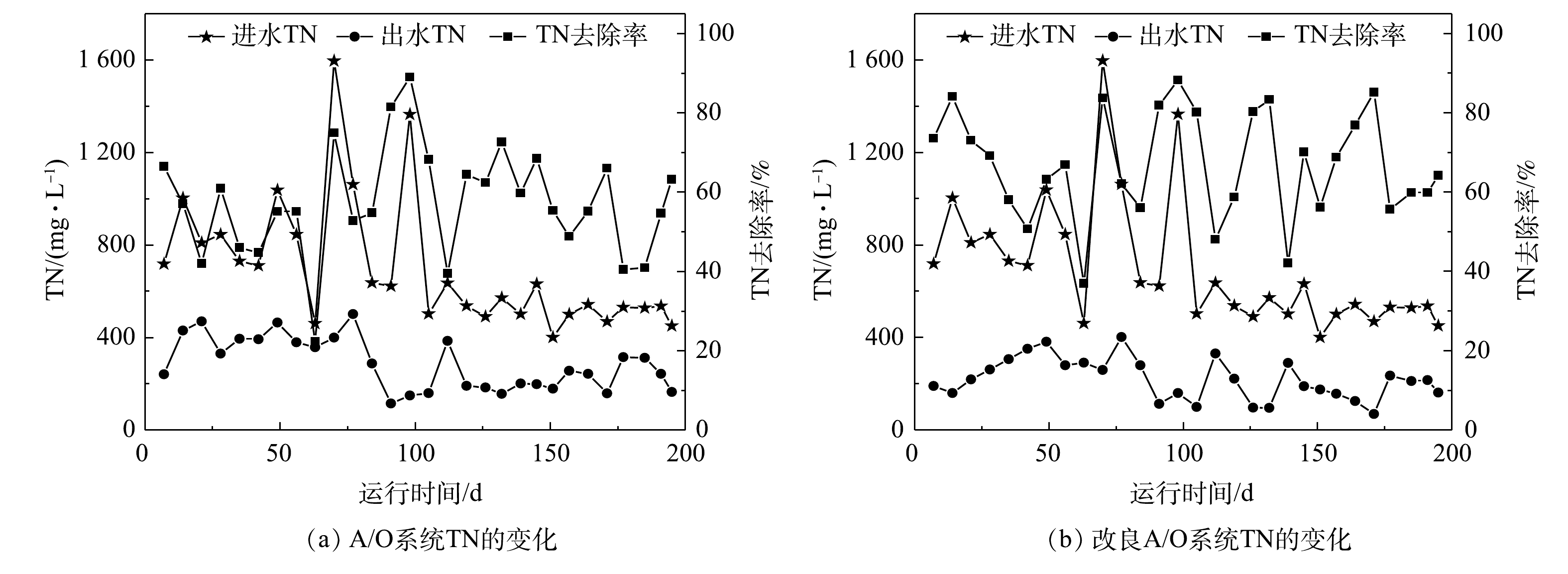
NO−3 -N质量浓度为0.1~9 mg·L−1时,改良A/O工艺A池NO−3 -N出水质量浓度在1~98 mg·L−1,O池出水的NO−3 -N质量浓度为27~310 mg·L−1。可见,改良A/O工艺平均出水质量浓度比A/O工艺平均出水质量浓度低78 mg·L−1,有明显改善。O池出水质量浓度波动较大的原因是,由于进水沼液污染物浓度波动较大,当进水沼液NH+4 -N质量浓度过高时,NH+4 -N在O池中硝化菌作用下转化为NO−3 -N的质量浓度也随之升高。在水力停留时间20 d时A池和O池中NO−3 -N浓度过高,水力停留时间过长导致营养物质缺乏不利于硝化池和反硝化池中微生物的生长,降低反硝化菌将NO−3 -N转化为N2的效率。此外,低C/N比废水也会降低脱氮的效率,导致A池中NO−3 -N浓度过高,进而影响O池中的NO−3 -N出水浓度。当减少水力停留时间时,A池与O池中NO−3 -N浓度均有不同程度的下降,改良A/O工艺在水力停留时间为13 d时,排放质量浓度均值最低,达到135 mg·L−1。如图5所示,沼液进水TN质量浓度为401~1 597 mg·L−1,波动范围较大。A/O工艺TN的出水质量浓度为115~502 mg·L−1,TN的去除率为22.3%~88.3%;改良A/O工艺TN的质量浓度为70~402 mg·L−1,TN的去除率为36.9%~89.0%,TN平均去除率提升至67.1%,去除效果具有明显改善。受进水沼液中TN浓度的影响,导致改良A/O工艺出水的TN的质量浓度和去除率波动较为明显,后续可通过多级改良A/O工艺结合组合工艺进一步降低TN的出水浓度。改良A/O工艺TN的出水质量浓度在水力停留时间20、13和10 d时的均值分别为281、175和183 mg·L−1。可见,水力停留时间过长同样不利于TN的去除,
NH+4 -N和NO−3 -N出水质量浓度的增加影响TN的变化,负荷过小不利于植物微生物结合的共生系统对污染物质的去除。当水力停留时间在13 d时,改良A/O工艺TN的出水质量浓度达到最低值,为95~330 mg·L−1,同时TN去除率达到最高值,为72.2%。 -
改良A/O工艺中测得狐尾藻各项指标结果见表2。一般而言,改良A/O工艺中种植狐尾藻的含水量要略低于常规富营养化水体中生长狐尾藻的含水量[28]。本实验中,A池和O池种植狐尾藻TN的含量远高于常规富营养化水体环境下种植狐尾藻10.5~20.7 g·kg−1的TN含量,TP含量则略高于常规富营养化水体中1.7~3.4 g·kg−1的TP含量[29]。有研究表明,沉水植物净化增效作用大于本身直接吸收作用[30],在一定浓度范围内, 水生植物的净化率随水体中氮、磷等物质的含量增加而加大[31],这说明狐尾藻在改良A/O工艺中能够更好的吸收水体中的含氮物质。此外,A池中狐尾藻的湿质量和干质量都远大于O池,且A池中狐尾藻的TN、TP和含水量含量也高于O池中的含量。由此可知,A池中的狐尾藻要比O池中的狐尾藻生长更加旺盛,更有利于对猪场沼液中污染物的去除,这可能是由于A池中的共生环境更利于狐尾藻的生长。以上结果均表明,在一定条件下改良A/O工艺种植狐尾藻能够大量生长且能充分吸收其中的含氮物质。
2.1. 改良A/O工艺对猪场沼液中耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)的去除效果
2.2. 改良A/O工艺对猪场沼液中氮素的去除效果
2.3. 改良A/O工艺中狐尾藻植物中的含水量以及氮、磷积累量
-
1)在A/O工艺中加挂弹性填料以及种植狐尾藻均对猪场沼液中COD和氮素均有明显的去除效果。其中,COD的去除率为42.5%~97.4%,较对照组中COD平均去除率提升了17%;
NH+4 -N的去除率为97.2%,较对照组平均去除率提升了16%,满足排放标准;A池中NO−3 -N出水质量浓度为1~98 mg·L−1,O池出水的NO−3 -N质量浓度为27~310 mg·L−1;改良A/O工艺中TN的去除率为36.9%~89.0%,较A/O工艺具有明显改善。后续可通过多级改良A/O工艺结合组合工艺进一步优化出水水质。2)当改良A/O工艺水力停留时间为10 d时,出水水质最符合实际排放要求。其中,耗氧有机污染物(以COD计)的排放质量浓度为57~307 mg·L−1,去除率可达75.3%;
NH+4 -N排放质量浓度为2~15 mg·L−1,去除率为96.2%~99.5%,平均去除率可高达98.4%;TN的排放质量浓度为70~296 mg·L−1,平均去除率可达70%以上。3)狐尾藻植物含水率为88.8%~89.1%,在A池中狐尾藻TN和TP含量分别为53.8 g·kg−1和5.2 g·kg−1,O池中TN和TP含量分别为51.4 g·kg−1和3.4 g·kg−1。改良A/O工艺狐尾藻TN的含量要远高于常规富营养化水体中狐尾藻TN的含量,且狐尾藻净化增效作用大于本身直接吸收作用。因此,狐尾藻在改良A/O工艺中能够更好的吸收去除污染水体中的含氮物质。











 下载:
下载: