-
沙河水库位于北京市昌平区,上接南沙河、北沙河、东沙河,下连温榆河,是北运河上游干流的关键节点[1]。近年来,周边的生产生活使沙河库区水体污染严重,水库水质仅为《我国地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838-2002)劣Ⅴ类水体。库区水生植物群落遭到严重破坏,水体自净能力减弱,水生态系统逐渐恶化[2]。因此,亟需开展沙河水库水质提升和水生态修复工作。
水生植物是水生态系统的重要组成部分,参与调控系统的物质循环和能量传递[3],对水生态修复起到关键作用。其中,沉水植物是水生植物群落的重要组成部分,对水体和底泥中的氮、磷等污染物的去除效果良好,同时还能承载水体中的有益微生物[4]。因此,恢复沉水植物群落是水生态系统恢复的关键环节。已有研究表明,沉水植物群落的恢复受温度、pH、营养盐浓度、藻类、风浪等诸多因素影响,其中水体透明度是最关键因素之一[5]。若水体透明度很低,水下光场无法满足沉水植物的生长,植物光合作用受阻而不能成活[6]。现阶段沙河水库水体透明度较低,仅为30~40 cm。因此,提升水体透明度是恢复沙河水库沉水植物群落、修复水库生态系统的先决条件。
投加化学药剂可快速提高水体透明度,但对库区水体内的鱼虾贝壳等水生动物的生长存在风险[7]。近年来,通过投放枝角类等浮游动物的生物操纵手段受到普遍关注[8]。常见的枝角类浮游动物,如大型溞、长肢秀体溞、多刺裸腹溞等,会直接摄食藻类。其分泌物还会促进悬浮颗粒态污染物的沉降,可在短期内提高水体透明度,进而为沉水植物的恢复提供条件[9]。其中,大型溞的应用最为广泛。任文彬[10]在武汉市东湖植物园的研究发现,大型溞在短期内可使湖内水体透明度由50 cm提高至138 cm,效果明显;霍元子等[11]的研究结果表明,大型溞在5 d内便可将上海滴水湖的水体透明度提高至150 cm。上述2个研究中,利用大型溞提高水体透明度的特性,可成功为沉水植物的重建创造条件,从而间接净化水质。而在实际工程应用中,也不乏大型溞提高污染水体透明度的成功案例。如管卫兵等[12]在太湖水域围隔修复区内投放大型溞,利用其对藻类的控制效应,提高了太湖水域的透明度,为后期移栽沉水植物解决太湖水体富营养化问题创造了良好条件。南京市月牙湖通过投放大型溞,后期建立“大型溞-沉水植物”共生生态系统,促进了湖泊生态环境的修复和平衡,使其水质稳定在地表Ⅳ类[13]。
然而,以往通过大型溞提升湖库水体透明度的实际工程中,尚无对大型溞的投放密度开展研究。本研究基于沙河水库的水质改善情况,对大型溞的投放密度参数进行优化,探讨不同投放密度下,大型溞对藻类的摄食及自身的生长情况,并对投溞后沙河水库水体及底泥主要污染物的变化展开研究,以期为后续沉水植物的恢复奠定基础,并为类似湖库的生态修复提供参考。
全文HTML
-
本实验所用的大型溞购于湖南怀化,为孤雌生殖的纯种大型溞。实验前将其置于沙河水库原水中进行驯化。驯化5 d后,取存活的大型溞进行研究。实验在5月份开展,实验用水和底泥取自北京沙河水库,其COD、TN、NH3-N、
NO−3 -N和TP分别为(26.4±1.2) mg·L−1、(5.79±0.21) mg·L−1、(0.254±0.013) mg·L−1、(0.82±0.16) mg·L−1、(0.144±0.003) mg·L−1,浊度为(19.7±1.2) NTU,透明度(40±4.1) cm。底泥主要污染物包括有机质,TN和TP,其质量浓度分别为(7.4±0.8) g·kg−1、(0.56±0.04) g·kg−1、(0.63±0.08) g·kg−1。 -
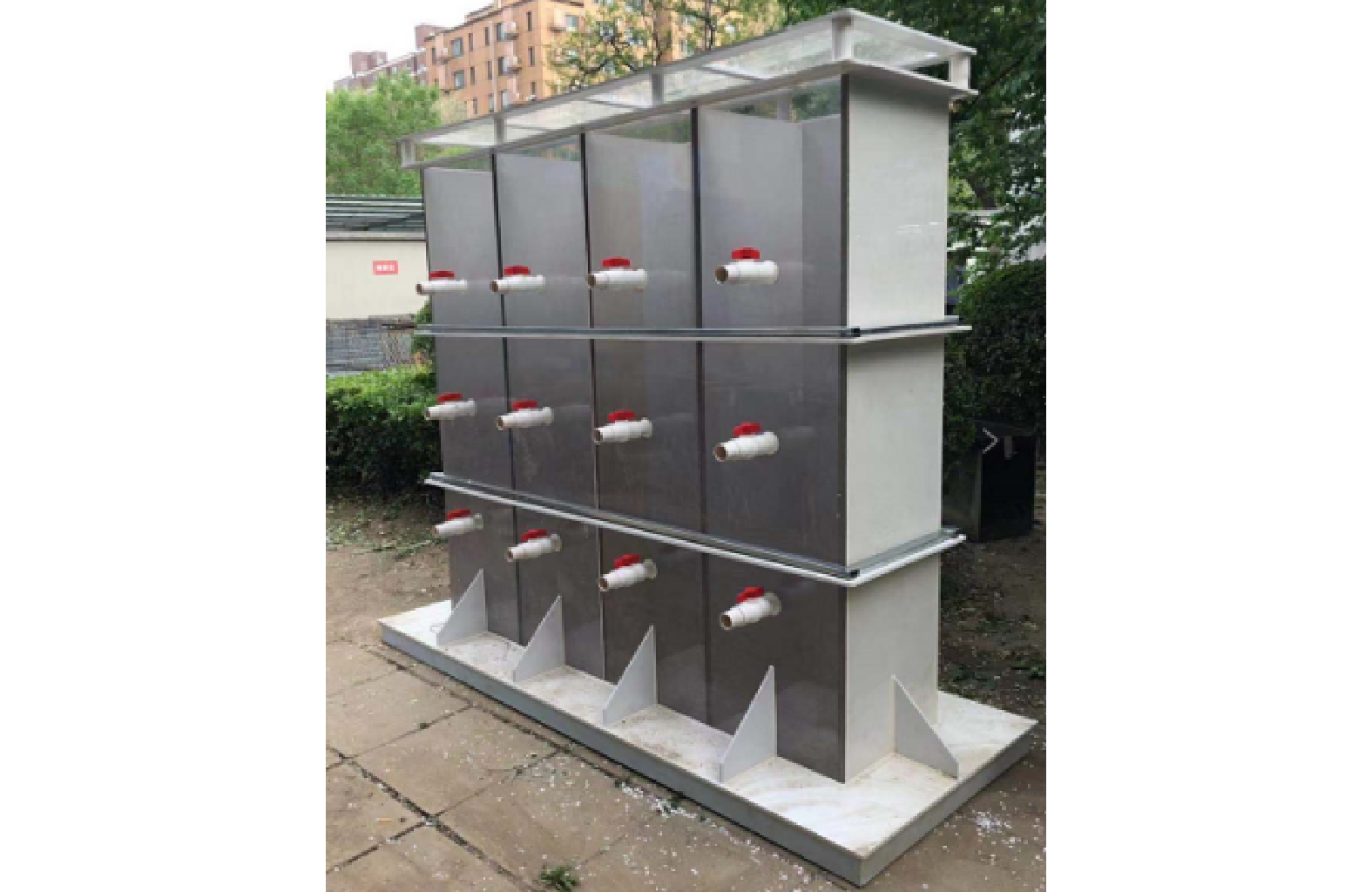
装置置于北京林业大学校园内,实物图见图1。装置是长×宽×高为200 cm×50 cm×200 cm的UPVC水箱,水箱侧面为厚度12 mm的UPVC板,正面为厚度为12 mm的有机玻璃板,便于观察投溞后水体透明度的变化。水箱内部分成4个不相互连通的小水箱。小水箱的长×宽×高分别为50 cm×50 cm×200 cm。水箱底部设置泥槽,泥槽的长×宽×高分别为50 cm×50 cm×20 cm。槽底放置沙河水库实际底泥。
-
将沙河水库底泥混合均匀后铺入各水箱底部泥槽,铺设厚度为5 cm。为保证底泥不受注水过程的剧烈扰动,将取自沙河水库的原水由蠕动泵缓慢抽入4个独立水箱。各水箱注水量为250 L,水深为1 m。2 h后,向水箱内投放不同密度大型溞,投放密度分别为0、5、15和35 ind·L−1。其中,投加密度0为对照组。实验期共35 d,每2 d取各水箱表层水样500 mL,监测主要水质指标有COD、TN、NH3-N、
NO−3 -N、TP、浊度、透明度;每2 d测定各水箱大型溞密度的变化;每5 d测定各水箱水样中藻类密度的变化。考虑到水体蒸发和每次取样的水体损失,每2 d补充库区原水1次,使各装置水体保持在250 L。实验投溞前和实验结束时检测各水箱泥槽内底泥中的有机质、TN和TP。 -
水样COD采用重铬酸钾消解法(GB 11914-1989)、TN采用碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法(HJ 636-2012)、NH3-N采用纳氏试剂分光光度法(HJ 535-2009)、
NO−3 -N采用盐酸-氨基磺酸光度法(HJ 346-2007)、TP采用钼锑抗比色法(GB 11893-1989)进行测定。透明度采用塞氏盘测定,浊度采用WGZ-500B浊度测定仪进行测定。藻类数量测定采用镜检直接计数藻细胞数量。在测定大型溞密度时,先轻微搅动装置内水体,使大型溞均匀分布于装置水体中。装置在不同高度设置了3个取样口。每个取样口均用1 L量筒取样5次,取样后对大型溞进行逐一计数,取平均值记为大型溞密度。底泥中有机质采用重铬酸钾-硫酸消解法(NYT 1121.6-2006)、TN采用凯氏法(HJ 717-2014)、TP采用碱熔-钼锑抗分光光度法(HJ 632-2011)进行测定。
1.1. 实验原料
1.2. 实验装置
1.3. 实验方法
1.4. 分析方法
-
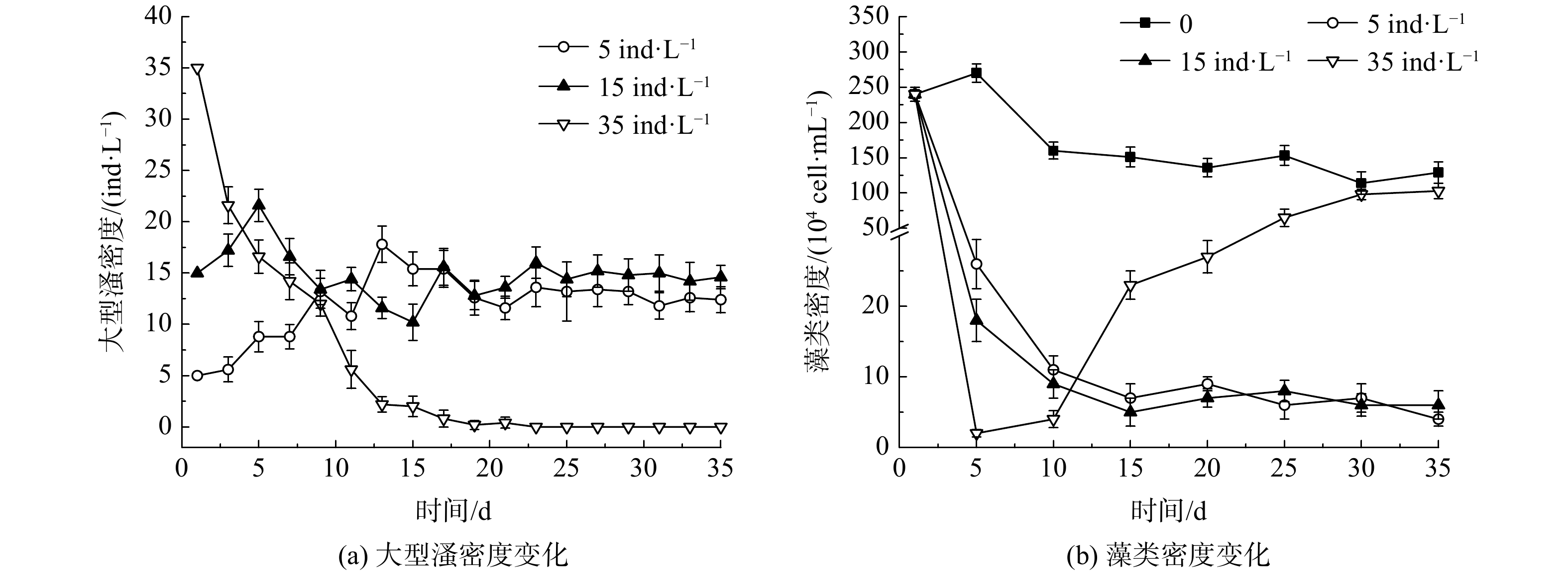
不同投放密度下大型溞的繁殖情况如图2(a)所示。在初始投放密度为5和15 ind·L−1的实验组,大型溞的密度在实验初期上升至18~20 ind·L−1,随后降低,并在实验末期达到相对稳定的状态,密度为14~15 ind·L−1。但当初始投放密度为35 ind·L−1时,一开始水体中大型溞密度会持续下降;投放至10 d时,由起始的35 ind·L−1下降至(5.6±0.3)ind·L−1,15 d后水体中已无法检测到大型溞存在。
藻类是大型溞的主要摄食对象,其数量变化与大型溞的密度变化有密切关系[14]。在不同大型溞投放密度下,水体中藻类的变化如图2(b)所示。投放大型溞后,水体中藻类密度迅速降低,且呈现出大型溞投放密度越大、藻密度下降越快的趋势。当大型溞投放密度为5和15 ind·L−1时,水体中藻密度逐渐下降,并在最终维持在(4~6)×104 cell·mL−1。在此阶段,大型溞生长情况良好,大型溞与藻类之间捕食关系达到动态平衡。而当大型溞投放密度为35 ind·L−1,水体中藻类密度会在第5天骤减至(6±0.2)×104 cell·mL−1,并在5~10 d内维持较低水平;15 d后藻密度逐渐上升,并在实验末期与对照组藻类密度相近。这与大型溞投加密度的变化相关:当大型溞投放密度过大时,短时间将可摄食的藻类捕食殆尽,两者的捕食平衡遭到破坏;之后大型溞由于得不到充足的食物供应而数量急剧下降,甚至死亡;随后,藻类又由于没有了大型溞的捕食,繁殖环境宽松,密度又逐渐上升。
上述结果表明,在适宜的投放密度下,大型溞在沙河水库水样中生长良好,密度维持在14~15 ind·L−1。若初始投放密度过大,大型溞密度会出现不可逆的迅速降低。一方面是由于高密度的大型溞导致种间竞争加剧,大型溞无法得到满足其生长繁殖的食物供应,导致其密度迅速下降[15];另一方面,大型溞种群密度越高,其释放的代谢产物越多,代谢产物的增多会对大型溞的摄食率产生明显的抑制作用,进而影响到大型溞的生长繁殖,促使其失去生命活性产生休眠卵[16]。
-
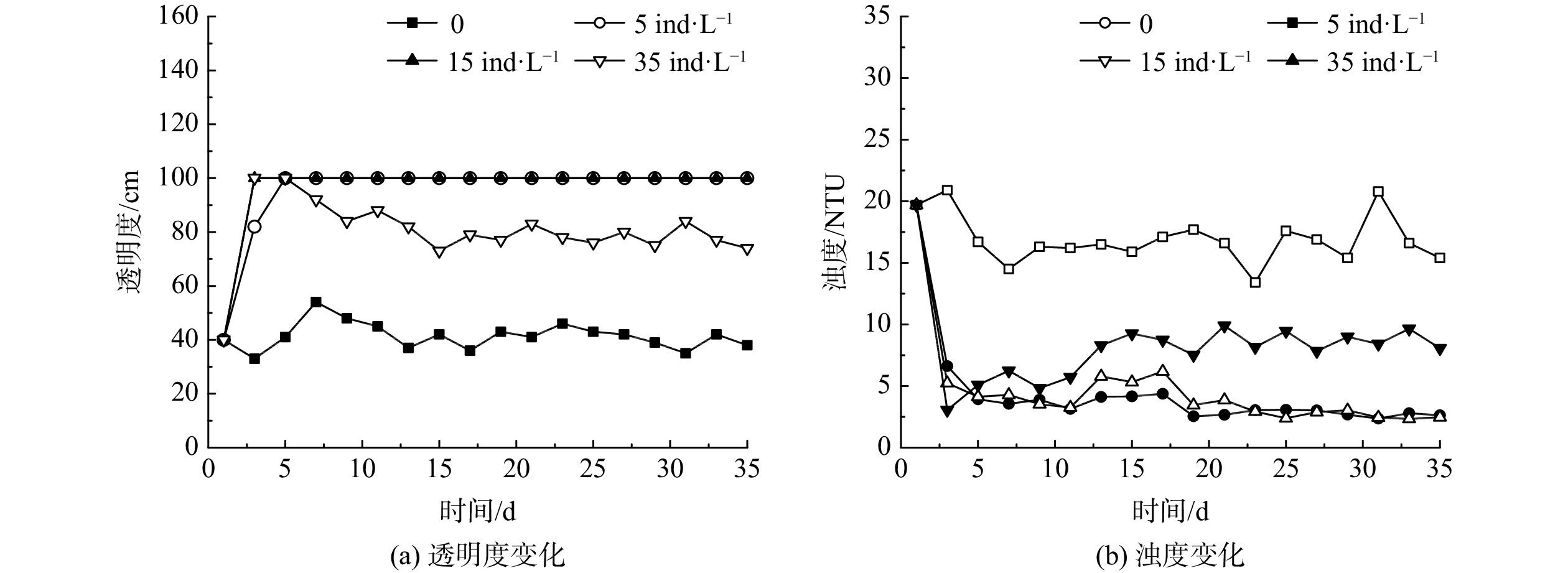
不同大型溞投放密度下水体透明度和浊度的变化如图3所示。对照组水体透明度基本保持不变,为(41.4±4.8)cm,浊度小幅下降后维持在(16.4±1.6)NTU。在大型溞投放密度为5和15 ind·L−1的实验组,水体透明度在投溞后3~5 d内迅速由40 cm升高至100 cm,为对照组的2.5倍;浊度由初始的19.7 NTU下降至(3.4±0.9) NTU。值得注意的是,当投放密度达到35 ind·L−1时,虽然水体透明度在5 d内由40 cm升高至100 cm,浊度也从19.7 NTU下降至5.1 NTU;但在之后的5~15 d,水体透明度由100 cm逐渐下降至73 cm,浊度升高至9.3 NTU;投溞15 d后水体透明度维持在(78.3±3.1) cm,浊度维持在(8.7±0.8) NTU。当初始投放密度达到35 ind·L−1时,由于大型溞在实验后期不断死亡,水体透明度在上升至100 cm后出现了下降;而当投放密度为5和15 ind·L−1时,实验期内大型溞密度稳定,水体透明度可一直维持在100 cm。
上述结果表明,选取适宜的投放密度,投溞可短时间内提高沙河水库水体透明度,降低浊度,并且效果稳定。一方面是由于大型溞会摄食粒径为0.5~40 μm的颗粒物,包括藻类、细菌和碎屑等[17];另一方面,水中悬浮颗粒物可在大型溞排泄物的絮凝作用下成团块状得以沉降,进而从水中得以分离去除[18]。根据实验结果,确定沙河水库大型溞的适宜投放密度为5~15 ind·L−1。
-
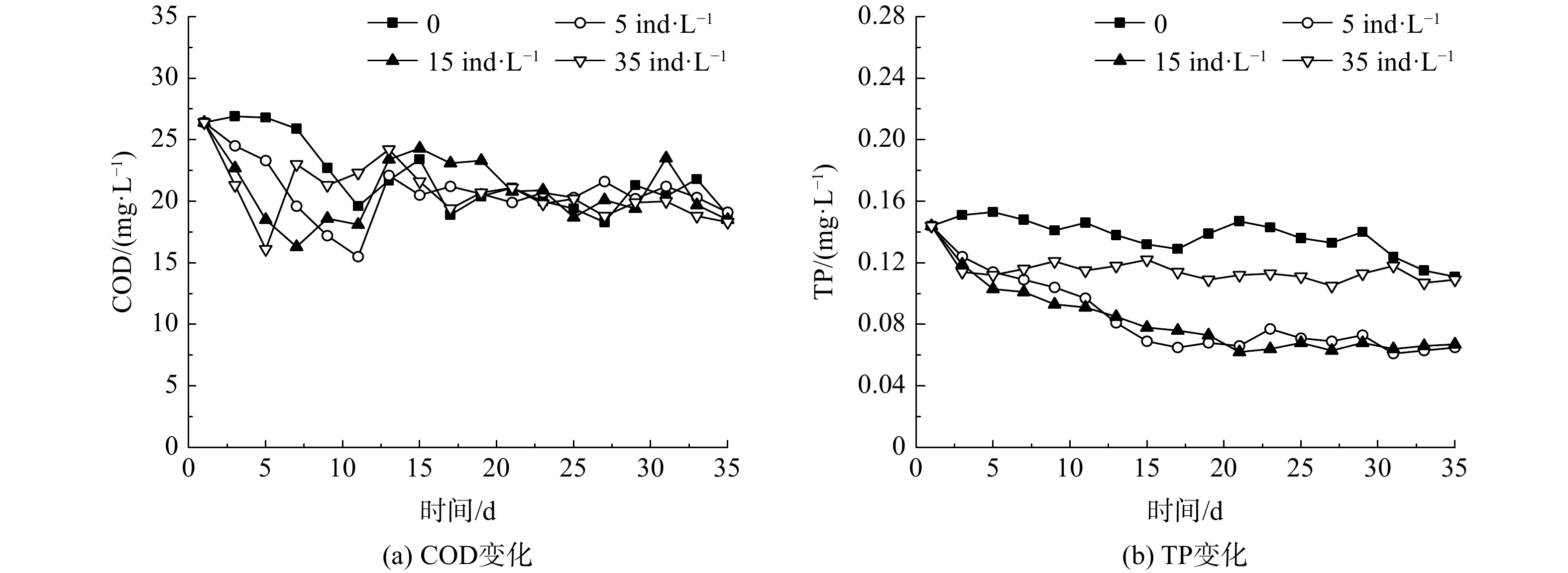
在不同大型溞投放密度下,水体COD和TP的变化如图4所示。由于水体中颗粒态有机物在实验期内发生自然沉降而略有下降,所以对照组的COD也随之下降。各实验组水样的COD在初期均出现了下降,但在5~10 d后,又出现了上升,并在实验后期与对照组相近。COD总体呈现出类似从波动到稳定的趋势,表明大型溞的投放并未引起水体COD的明显变化。
投溞后初期的COD出现下降,是由于大型溞分泌物的絮凝作用使水体中悬浮颗粒态有机物发生沉降。大型溞投放密度为5和15 ind·L−1的水样在之后出现COD上升的现象,可能是因为大型溞在生长过程中的排泄物被微生物分解。当大型溞密度趋于稳定后,COD也相对稳定,只在一定范围内呈现出波动。投放密度为35 ind·L−1的实验组水样中COD出现上升,可能是由于大型溞大量死亡后,其尸体导致水体中COD上升。
在不同的大型溞投放密度下,水体中TP的变化如图4(b)所示。对照组TP较为稳定,保持在(0.137±0.011) mg·L−1。当投放密度为5和15 ind·L−1时,实验过程中TP持续降低,15 d后基本保持稳定;实验结束时,TP由0.144 mg·L−1分别降至0.065 mg·L−1和0.067 mg·L−1,去除率分别为54.9%和53.5%;当投放密度为35 ind·L−1时,TP仅在实验初期1~5 d从0.144 mg·L−1降至0.112 mg·L−1;当大型溞死亡后,水体TP保持稳定,为0.113 mg·L−1。
大型溞不仅可以吸收同化水体中的可溶性磷为自身营养物质[19],其分泌物还可促进水体中悬浮性颗粒态磷的沉降[18]。石岩等[20]在长春南湖投放大型溞,使南湖水体的TP明显下降,去除率达到了89.7%;韩士群等[21]投放长肢秀体溞对水体中TP去除效果明显,去除率为53%。因此,在适宜的投放密度下,大型溞的投放对库区水体TP有较好的去除效果。
-
在不同大型溞投放密度下,3种形态氮素(NH3-N、
NO−3 -N和TN)的变化如图5所示。由图5(a)可知,大型溞的投放会使水体中NH3-N升高。当投放密度为5和15 ind·L−1时,水体NH3-N浓度从初始的0.254 mg·L−1分别升高至0.317 mg·L−1和0.336 mg·L−1,较原水提高24.8%和32.2%。而投放密度为35 ind·L−1的实验组仅在实验初期大型溞存活阶段出现了上升,后期随着大型溞数量的逐渐降低,NH3-N逐渐下降至对照组水平。大型溞投放后,水中藻类被抑制,导致藻类对水体中NH3-N吸收减少,水体中NH3-N上升。有研究表明,藻类可吸收水中营养物质,将无机态氮转化为藻细胞内有机态氮[22],且藻类一般优先利用NH3-N,当其被耗尽时才利用NO−3 -N[23]。本课题组对沙河水库浮游植物调研结果表明,蓝藻与硅藻是优势种群,这2种藻类对NH3-N的吸收优于其他类型无机氮[24]。因此,当向水体中投放大型溞后,其迅速摄食藻类,导致藻类数量的迅速降低,而使其对NH3-N的吸收减弱,水体中NH3-N小幅升高。如图5(b)所示,投溞后水体
NO−3 -N逐渐下降。实验结束时,不同投放密度的实验组NO−3 -N浓度分别从0.82 mg·L−1降至0.23、0.25和0.4 mg·L−1,去除率分别达到71.9%、69.5%和51.2%。水体中NO−3 -N的降低主要是由于大型溞表面和其肠道内部附着了大量可参与反硝化反应的微生物种群,包括β-变形菌纲(β-proteobacteria)、γ-变形菌纲(γ-proteobacteria)以及拟杆菌纲(Bacteroidetes)和芽孢杆菌纲(Bacilli)等[25]。不同投放密度下,水体TN变化如图5(c)所示。3个实验组中TN从5.79 mg·L−1分别降至1.725、1.883和3.094 mg·L−1,去除率分别达到了70.2%、68.3%和46.5%。投入大型溞会降低水体中TN的浓度已有诸多报道,但不同研究的结果差异较大。张喜勤等[26]研究表明,大型溞对富营养化水体中TN的去除率可高达96.6%;而董旭峰[27]用大型溞净化猪场废水时,TN去除率仅为41.76%。造成差异的原因包括温度、外界干扰条件、水质等多方面的影响。
本研究结果表明,大型溞可通过附着菌群的反硝化作用促进
NO−3 -N降低外,对库区水体中NH3-N并未呈现出良好的去除效果,反而会引起水体中NH3-N浓度增加。由此可推测,在沙河水库水体中,大型溞的投放对水体中溶解态氮的去除能力十分有限,对TN的去除是由于大型溞对藻类的摄食以及分泌物的絮凝作用,促使水体中颗粒态氮发生沉降,进而导致水体中TN降低。 -
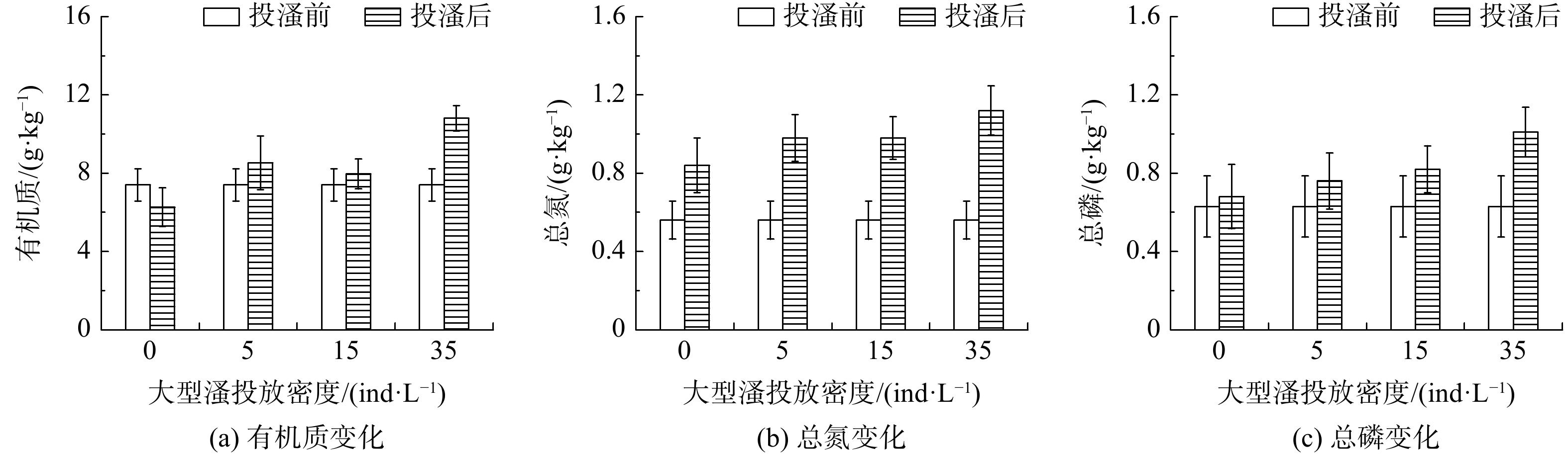
在不同投放密度下,大型溞对沙河水库底泥有机质、TN、TP的影响如图6所示。大型溞投放后,各实验组的有机质均高于对照组,投放密度为5、15和35 ind·L−1的实验组底泥中有机质含量从初始的7.4 g·kg−1分别升高至8.53、7.96和10.81 g·kg−1,分别增加了15.3%、7.7%和46.1%。在不同投放密度下,底泥TN变化如图6(b)所示。对照组总氮由0.56 g·kg−1升高至0.84 g·kg−1,增加了50%,主要是由于水体静止后加速了颗粒态氮的沉降。而投加大型溞的实验组促进了水体中氮素向底泥的沉降作用,实验结束时,底泥总氮的含量分别为0.98、0.98和1.12 g·kg−1,增加率分别为75%、75%和100%。与总氮变化规律一致,底泥中的TP也呈现出不断升高的趋势,不同投放密度实验组的底泥总磷含量分别增加了20.6%、28.5%和60.3%。
由前述分析可知,大型溞分泌的排泄物具有絮凝作用,可使水中的悬浮物沉降,进而引起底泥有机质、TN及TP的增加。投放密度为5和15 ind·L−1的实验组底泥各指标增幅相近,而投放密度为35 ind·L−1的实验组底泥各指标的增幅要远高于前2个实验组。这是由于,在实验中后期大型溞不断死亡,其尸体以及产生的休眠卵发生沉降进入底泥中,故该实验组底泥各指标上幅较大。
2.1. 不同投放密度下大型溞的繁殖情况
2.2. 大型溞投放对沙河水库水质的影响
2.2.1. 投放密度对水体透明度及浊度的影响
2.2.2. 投放密度对水体COD及TP的影响
2.2.3. 投放密度对水体不同形态氮的影响
2.3. 大型溞投放对库区底泥的影响
-
1)大型溞在沙河水库水样中可正常生长繁殖。在一定的初始投放密度范围内(5~15 ind·L−1),大型溞保持稳定的生存状态,最终密度为13~14 ind·L−1。经过大型溞的摄食作用,藻类密度最终控制在4×104~6×104 cell·mL−1。
2)投放大型溞利用其摄食藻类、分泌物促进悬浮颗粒态污染物沉降等特性,可在短期内将透明度从40 cm提升至100 cm,并使浊度由最初的19.7 NTU下降至(3.4 ± 0.9) NTU,可为种植水生植物提供良好的先决条件。
3)投溞后,水体中COD并未发生明显改变。由于大型溞促进悬浮颗粒态氮、磷的沉降,TN和TP的去除率分别可达70.2%和54.9%。大型溞投放使实验水体中NH3-N浓度升高32.2%,对水体
NO−3 -N亦有较好的去除效果,去除率可达到71.9%。由于大型溞促进水体悬浮性颗粒态污染物的沉降,投溞的实验组底泥中有机质、TN、TP均高于未投溞的对照组。







 下载:
下载: