-
过去40年,我国城市生活垃圾产量以5.82%的复合增长率持续增长[1]。填埋作为最主要的垃圾处理方式,消纳了近70%的生活垃圾[2],但也占用了累积达3.5×1010 m3的土地资源[3]。受地区气候条件和垃圾组成等因素影响,在不加人工调控的情况下,传统填埋场一般要在封场后30~50 a才能完全稳定。因此,垃圾填埋场不仅占地,且这种占地效应是长期的[4-6],这极大地制约了填埋场地及其周边区域的开发建设。近年来,随着城市化进程的加快,原本处于城市远郊区的填埋场逐渐进入城市近郊区甚至主城区范围,填埋场越发成为城市建设的“眼中钉”[6]。我国高度重视垃圾填埋/堆放场所的人工整治及土地再利用。国家环境保护“十二五”、“十三五”规划都强调要对垃圾简易处理或堆放设施和场所进行整治,对已封场的垃圾填埋场和旧垃圾场要进行生态修复、改造[6]。国务院《关于鼓励和引导民间投资健康发展的若干意见》国发〔2010〕13号中更指出,鼓励民间资本参与土地整治和矿产资源勘探开发。另外,《生活垃圾填埋场降解治理的监测与检测》《生活垃圾填埋场稳定化场地利用技术要求》等政策法规的相继颁布实施,也大大推动了填埋场的治理及土地开发利用工作。
国内外封场后的填埋场主要利用方向有休闲娱乐用地(如生态公园、高尔夫球场等)、林地、农业用地(如植物园、苗圃等)、硬化用地(如道路、停车场等)等[7-9]。如杭州天子岭填埋场、广州李坑填埋场封场后建成了生态公园;深圳玉龙坑填埋场内建起拥有60个标准杆位的高尔夫球场;武汉市金口垃圾填埋场修复后成为了第十届中国国际园林博览会主会场等[6, 10]。然而,这些封场填埋场工程往往是采取异地转运、原位封场、开挖筛分、好氧稳定化等技术,对整个填埋场进行污染整治与修复,涉及的工期长、投资高[6, 11-12]。相比之下,因局部占用填埋场土地,需采取的小范围整治工程则鲜见报道。
本文阐述科技路尾段二期道路局部穿越重庆市兴隆垃圾填埋场时,所采取的填埋场综合整治措施,并分析工程取得效果,以期为类似工程项目提供参考。
全文HTML
-
1)工程原始概况。重庆市九龙坡区兴隆垃圾场始建于1989年,占地面积33 000 m2,垃圾填埋总量(8~10)×105 t,垃圾层厚度20~30 m。该填埋场位于U形沟谷区,建设期未设置雨污分流及填埋气收集导排等系统。但垃圾场在2003年底实施规范封场时设置了雨水导排系统,将导排的雨水排入周边彩云湖。垃圾表面还覆盖了HDPE膜,以防止雨水入渗并阻隔气体。在渗滤液导排处理方面,考虑到场底以第四系黏土层为主,透水性差,故将其作为天然防渗层;场底存在自然坡度,堆体产生的渗滤液会自流至场地最低点(即下河谷口垃圾坝前),故在此处设置了渗滤液导排系统。鉴于检测到的渗滤液COD和氨氮分别小于200和30 mg·L−1,故收集的渗滤液直接排入周边污水处理项目中进行集中处理。此外,还单独设置了填埋气体收集竖井及水平收集管道,所抽气体集中到垃圾场北侧火炬燃烧处理。
2)前期整治情况。2005年和2009年,兴隆垃圾场东南侧及西侧分别进行了达飞彩云小区和渝高香洲小区的开发建设。在2个项目建设前,开发商都曾对其涉及的垃圾场边界进行整治,主要措施有场地清理换填、气体阻隔与导排及可燃气体报警等。由于这2个项目的开发建设,垃圾场顶部被建筑弃土覆盖,覆土厚度达7.6~19.0 m。
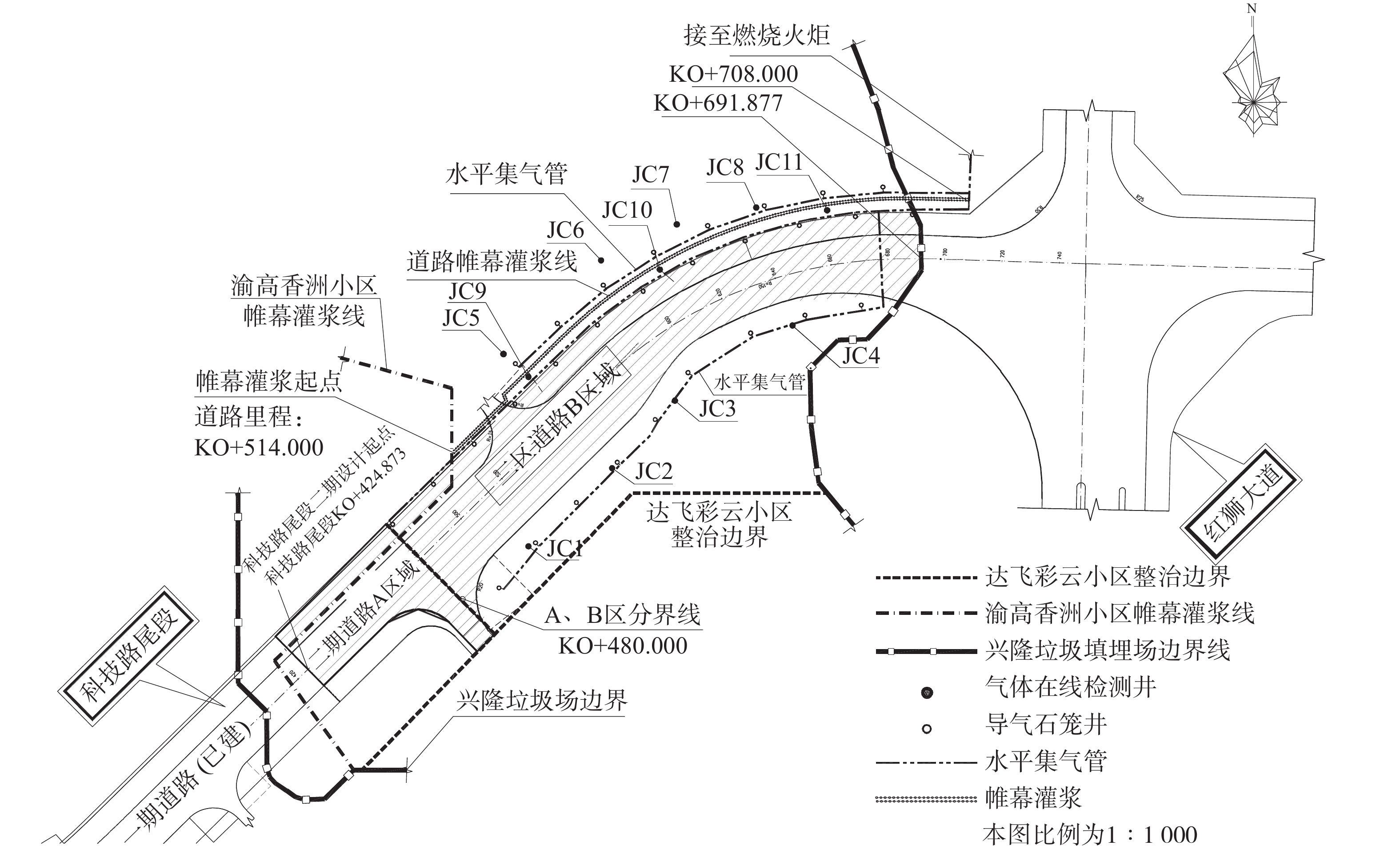
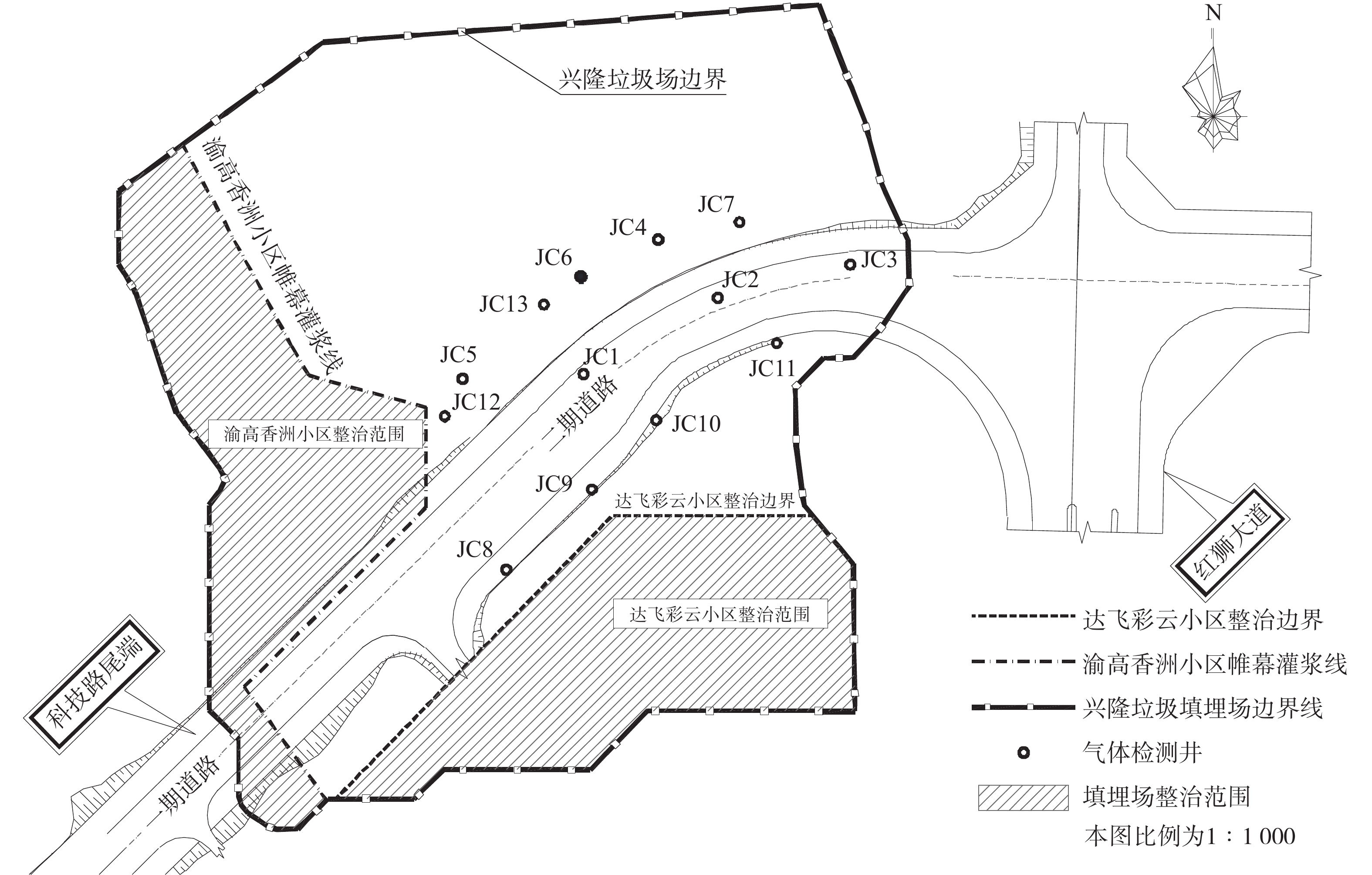
3)道路工程概况。科技路尾段道路为2016年规划的市政道路。道路位于重庆市高新区二郎科技新城,始于科技路中新区段,止于红狮大道。道路选址穿越了兴隆垃圾填埋场南侧场地,设计标高高于垃圾封场层10 m以上。地质勘探结果显示,拟建道路下部为建筑、生活垃圾形成的杂填土。地基承载力特征值160 kPa。道路沿线地形平坦,相对高差约3 m。涉及区域未见危岩崩塌、滑坡、泥石流、地下采空区、地下洞室等不良地质现象,仅存在填土不均匀沉降和湿陷性问题。另外,下伏基岩连续稳定,无断裂构造,拟建场地基本稳定。科技路尾段一期道路已于2016年修建完成,本项目涉及的二期道路计划工期为2018年。道路全长324.47 m,侵占填埋场土地9 910 m2。道路区位及与周边环境的关系见图1。
-
填埋场封场后开展土地利用应符合现行国家标准《生活垃圾填埋场稳定化场地利用技术要求》(GB/T 25179-2010)的规定。判定指标包括封场年限、填埋物有机质含量、地表水水质、填埋堆体中气体浓度等。此填埋场封场年限大于10 a;且道路穿越区为旱地,无地表水体,故着重对填埋场中垃圾的理化性质及产气情况进行了监测。
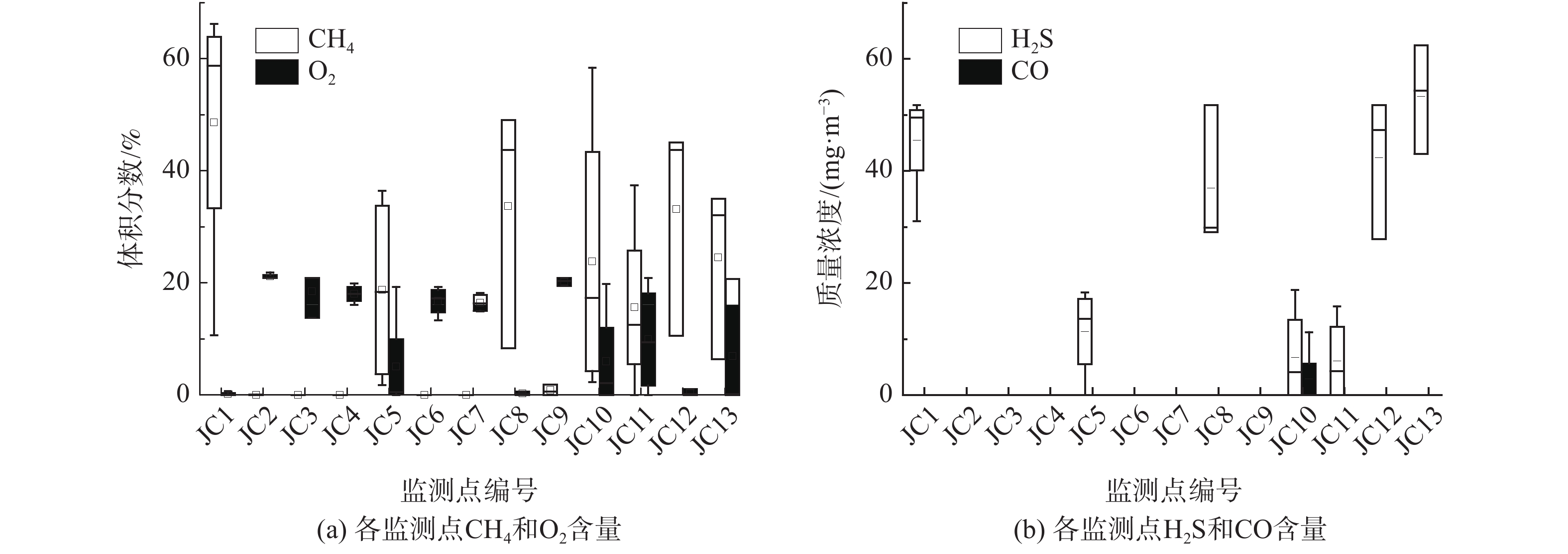
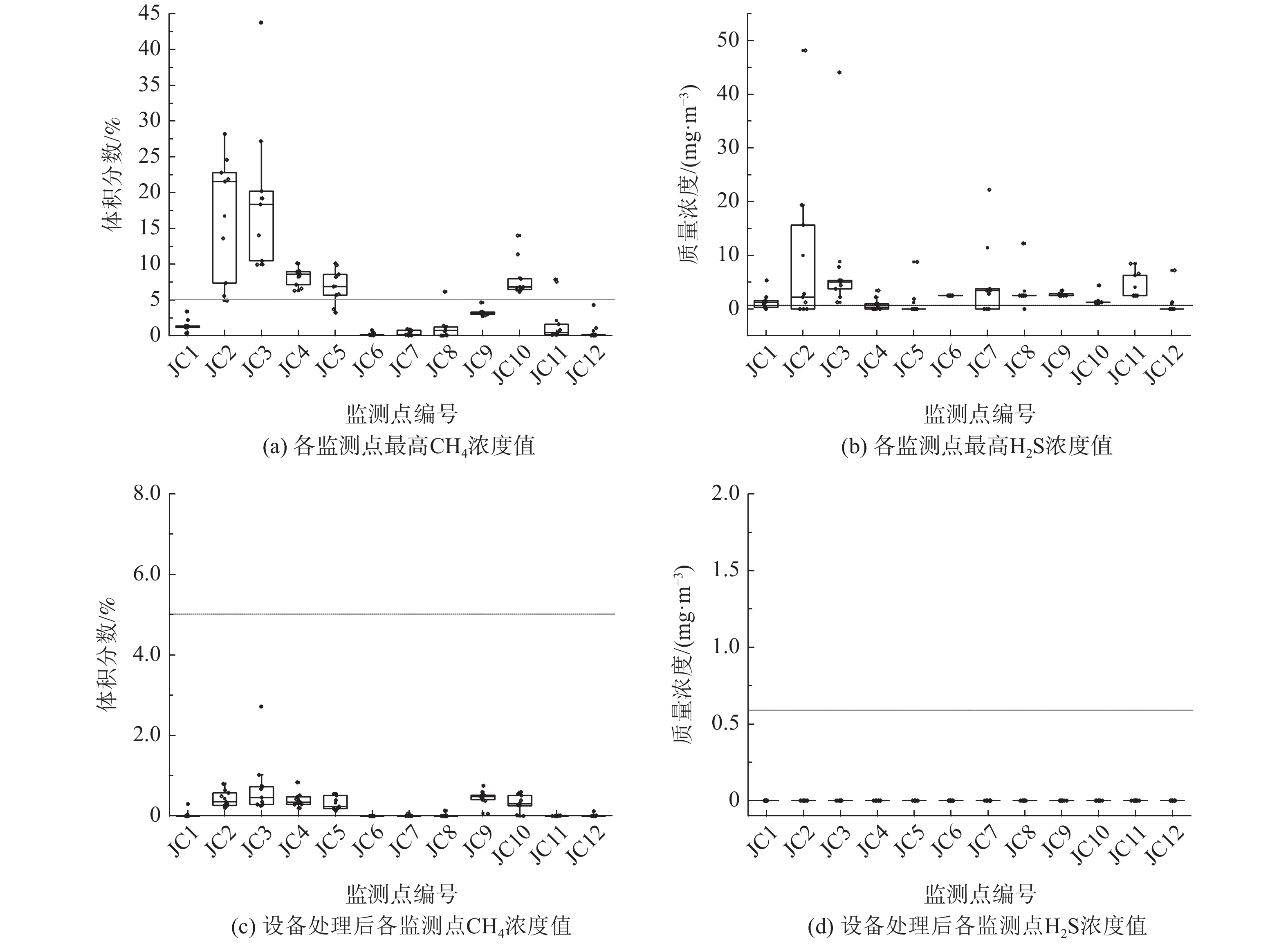
监测范围包括整治区域及其外扩20 m范围,共设置13个监测点进行填埋气(CO、H2S、CH4、O2)的监测(见图1)。对填埋场内的JC2、JC3、JC4、JC7这4个监测点进行钻孔取样,分析垃圾含水率、机质含量和生物可降解度(biologically degradable matter,BDM)。结果显示,监测区域内垃圾含水率为20%~30%,有机质含量约2%,BDM为11%~13%。我国湿垃圾含水率往往在45%~65%[13]。填埋过程中,随着垃圾的降解矿化,垃圾孔隙度增加,持水性能会变差,故含水率呈降低趋势[14]。本填埋场含水率与稳定度良好的填埋场垃圾含水率是可比的[14],且其有机质含量也已满足GB/T 25179-2010中的场地稳定化高度利用要求(<9%),表明产气已趋于衰竭。这与监测到的单孔产气量小于0.05 m3·d−1是一致的。而BDM高达10%以上则指示垃圾稳定度不足,这可能是部分区域检测到高浓度CH4和H2S的原因。从图2可知,13个监测井中,有7个点存在高浓度CH4和H2S。其中,CH4的体积分数最大可达66.2%,H2S的质量浓度最高可达62.2 mg·m−3。
有研究者指出,垃圾填埋场的BDM小于3%时,方可达到高度稳定状态[15]。大量简易填埋场在BDM低至5%时仍能在填埋气中检测到高浓度CH4[15-17],故本研究的监测结果是合理的。填埋气中的CH4源自于有机物的厌氧产沼,而H2S则可能是厌氧微生物(主要是硫酸盐还原菌)利用场内剩余BDM还原早期积累的硫酸盐而产生。杜耀等[18]曾指出这是老垃圾场H2S的主要来源,且很多填埋场都存在严重的H2S污染,如北京阿苏卫垃圾填埋场H2S质量浓度高达179.1 mg·m−3,国外有些填埋场的H2S质量浓度甚至超过5 000 mg·m−3。但也有部分区域未检测到CH4和H2S,而是存在高浓度O2,这可能是封场膜局部损坏,导致空气进入了堆体造成的。此外,堆体CO浓度基本都在1.25 mg·m−3以下,这与前期研究者指出的此类气体在填埋气中体积分数极低是一致的[19]。
综上所述,本填埋场垃圾填埋年限、有机质含量等指标已满足GB/T 25179-2010的中度甚至高度开发利用标准。拟建道路周边无地表水体,且设计标高远高于填埋场的渗滤液水位,不会与之相互干扰,因此,无渗滤液影响道路施工的风险。填埋场在规范封场时已整平,地基承载力良好,因此,也无堆体稳定性风险。但部分区域CH4浓度和恶臭气体浓度较高,存在燃烧爆炸及影响道路结构的风险,也易造成空气污染[20]。基于此,场地利用之前对填埋场进行适宜地整治是必须的。
1.1. 工程概况
1.2. 场地利用风险分析
-
本项目主要风险在于气体迁移可能引发爆炸、损坏道路结构,拟定采取阻隔、疏导和监测三者相结合的整治措施,确保道路建设及使用安全稳定。1)在道路左侧采取阻隔墙工艺阻隔填埋气向公路内侧迁移;2)设置气体导排系统,采取合适的抽气工艺保证场内的CH4气体被有效收集及处理;3)在两侧按国家标准布设CH4在线监测系统,实时监控气体浓度情况。此外,本次整治区域有部分与早年实施的渝高香洲小区及达飞彩云小区整治区域重叠。具体而言,道路K0+424.873~K0+480段北侧紧邻已实施的渝高香洲整治工程,南侧为已实施的达飞彩云小区整治工程。根据地质勘探报告,该段道路下方为素填土、粉质黏土、泥岩及砂岩组成,已无垃圾堆体。因此,本次整治工程以桩号K0+480为分界,K0+424.873~K0+480段为A区域,K0+480~K0+691.877段为B区域。整治分区图见图3。
-
B区道路左侧存在大量垃圾体。由于垃圾纵横向气体渗透系数差异明显,产生的填埋气会优先横向迁移[21]。为防止整治区域外的填埋气体向道路区域横向扩散迁移,本工程对道路K0+514~K0+708段左侧地下垃圾层采取帷幕灌浆阻隔处理,帷幕灌浆深入至基岩。帷幕灌浆本是广泛应用于水工建筑防渗工程和交通工程基础地基工程中的防渗技术,因具有工期短、见效快、设备简单、占地面积小、对环境影响小、易于控制等优点,近年来也被应用于城市生活垃圾填埋场处理工程。蒋良伟等[22]在重庆某已封场垃圾填埋场中采用帷幕灌浆技术进行气体防渗,就发现实施帷幕灌浆可有效阻断填埋场与周边建设工程间填埋气的横向逸出通道,从而确保填埋场场地上建设工程的安全性。
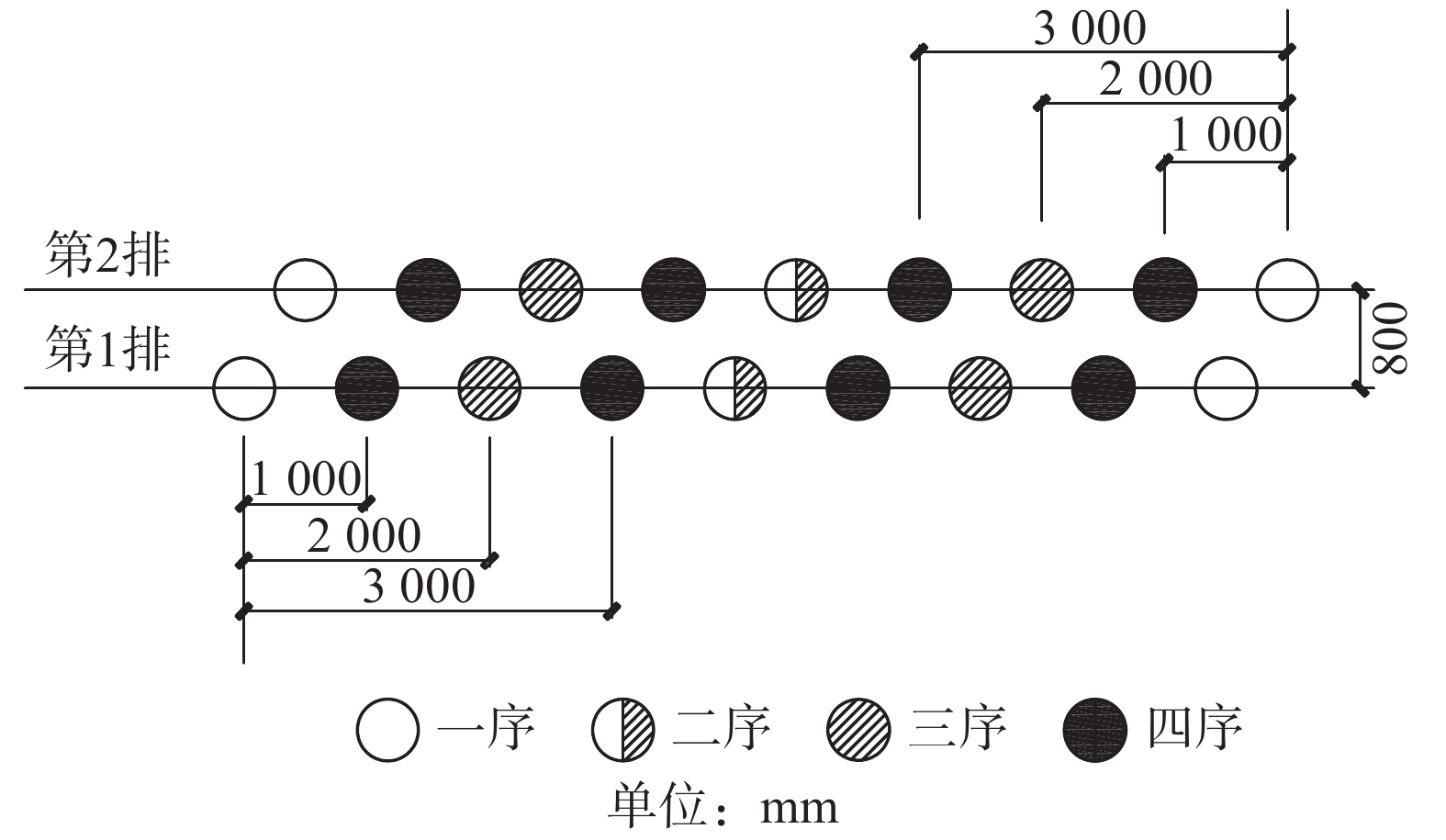
帷幕灌浆工程主要包括钻孔施工、水泥浆制备、灌浆施工、控制封孔4个环节[23]。作为帷幕灌浆的基础工程,钻孔的效果好坏直接影响该工程的效果好坏,并关系到整治工程的施工质量[24]。本工程采用取芯钻孔。帷幕灌浆孔在B区域道路左幅人行道边界外扩5 m处设置。处理平面长度约210 m,孔距1 m,设计分为2排,排距0.8 m,分四序施工,具体见图4。每孔灌浆自上而下分段进行,每段灌浆长度不大于5 m。上一段灌浆终凝之后才允许实施下一段灌浆,灌浆完成后用水泥砂浆封孔。灌浆压力根据垃圾的松散度不同,由现场试验确定。具体而言,考虑到垃圾层及填土层中空隙连通性较好,试验时灌浆采用无压灌浆,空隙连通较好时水灰比按1∶1、0.8∶1、0.5∶1由稀至浓试验,空隙连通性较差时水灰比按3∶1、2∶1、1∶1由稀至浓试验。试验完成后选择最优水灰比进行灌浆。灌浆材料采用42.5普通硅酸盐水泥浆液,如出现跑浆情况,采用间歇式灌浆或投入砂料增稠处理。结束灌浆标准为单位吸水量小于5 Lu。帷幕灌浆墙体渗透系数应小于1×10−5 cm·s−1。
-
B区道路下方及右侧也存在垃圾体。由于垃圾量少,该区域不设置帷幕灌浆。若该区域垃圾产生的气体出现局部聚集,也存在燃烧爆炸或损坏道路结构的风险,而填埋气导排是规避上述风险的重要措施,导排方式有主动导排和被动导排[25]。其中,被动导排系统主要依靠垃圾中设置的填埋气体流通管等,以自然导排的方式来排出垃圾中的气体。该系统受气候和气压变化等因素的影响较大,排气稳定性不高,只适用于对填埋气扩散要求不高的场景。主动导排系统是在填埋气导排管中加装抽气泵,可随时抽取或控制填埋场气体排放的大小,故能实现填埋气的快速收集及防止外漏[25]。本工程需严格控制填埋气的无序扩散,因此采用主动导排系统。
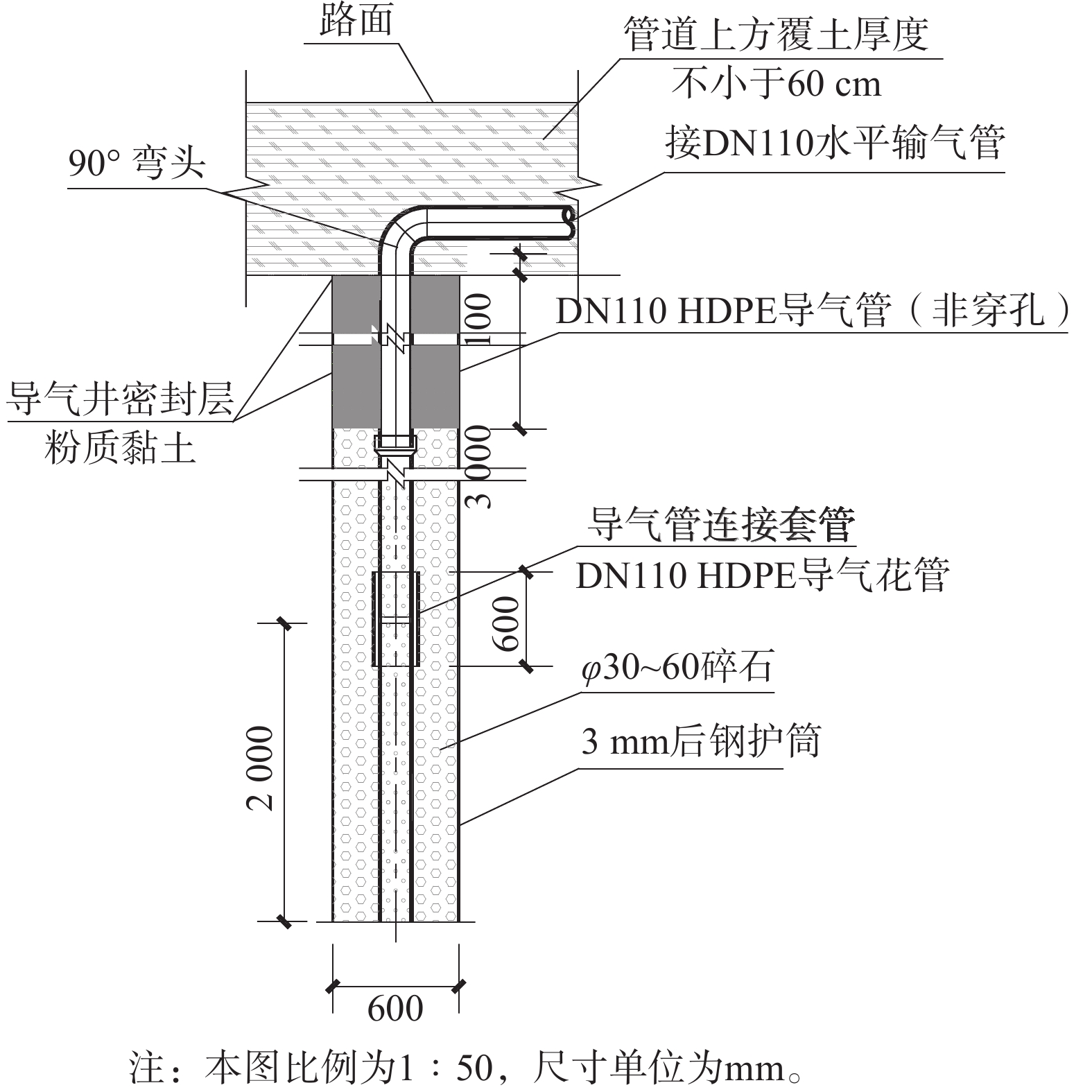
填埋气导排系统由主动抽气石笼井、水平集气管网和燃烧火炬3部分组成。《生活垃圾填埋场填埋气收集处理及利用工程技术规范》(CJJ 133-2009)中规定,垃圾堆体中部的主动导排井间距不应大于50 m,边缘布置的不宜大于25 m。然而,为提高填埋气收集效率,在工程中一般会将主动导排井的有效收集间距控制在15~25 m[19]。本研究中,主动导排石笼井按20 m间距加密布置在B区域道路两侧的人行道,以有效导排道路区域垃圾产生的填埋气体。同时,为进一步减缓整治区域外填埋气体向道路横向扩散,在帷幕灌浆墙北扩5 m处以同样间距加设一排主动导气石笼井。导气石笼井按成孔方式可分为钻孔法成孔和打桩法成孔。由于垃圾压实密度较低,用干钻法打井容易塌方,且空气易通过井孔进入井内,当钻头遇到石块产生火花则容易发生火灾或爆炸。相比之下,打桩法即管桩施工法,属挤土施工,其打入过程比较简单,施工过程中空气不与填埋气体接触。由打桩机将桩管送入设计深度即可,安全性较高[26],故本工程选用管桩法成孔。石笼井具体做法见图5。导气石笼井上部采用阀门井形式,阀门井内设置流量调节阀、流量计,便于根据实际情况调节各个石笼井的抽气流量。
上述导气石笼井通过水平集气管网连接。考虑到填埋气体的腐蚀性及在库区易发生不均匀沉降,水平集气管采用HDPE管。集气管网收集到的填埋气可采用高温焚烧进行无害化处理。因填埋气主要成分为CH4,具有较高的热值,很多填埋场也会选择将其收集进行热电联产、作为锅炉或工业炉窑燃料或提纯后作为清洁燃料使用[27-29]。一般进行资源化利用时,需要达到一定产气量。如美国华盛顿特区环保局指出的填埋场填埋气发电项目基本标准有:存量垃圾大于1×106 t;填埋场仍在运行或封场不久;填埋深度大于12 m[30]。而本整治区域垃圾存量低,且垃圾场已封场十余年,产气能力衰竭,故没有工程应用价值。考虑到填埋气中CH4具有极强温室效应,在本项目中选择集中燃烧排放作为其无害化处理手段。因此,收集到的填埋气被引至北侧燃烧火炬站燃烧排放。燃烧火炬由进气控制系统、引风机、火炬主体等组成。设计采用撬装站形式,即除火炬塔体外,其余设备均置于撬装房内。该形式具有构造简单、易于维护管理的特点。此外,填埋气导排系统还配备了2台罗茨风机(一用一备)抽气以实现填埋气的主动导排。风机的启停由2.3节的在线监测系统控制。
-
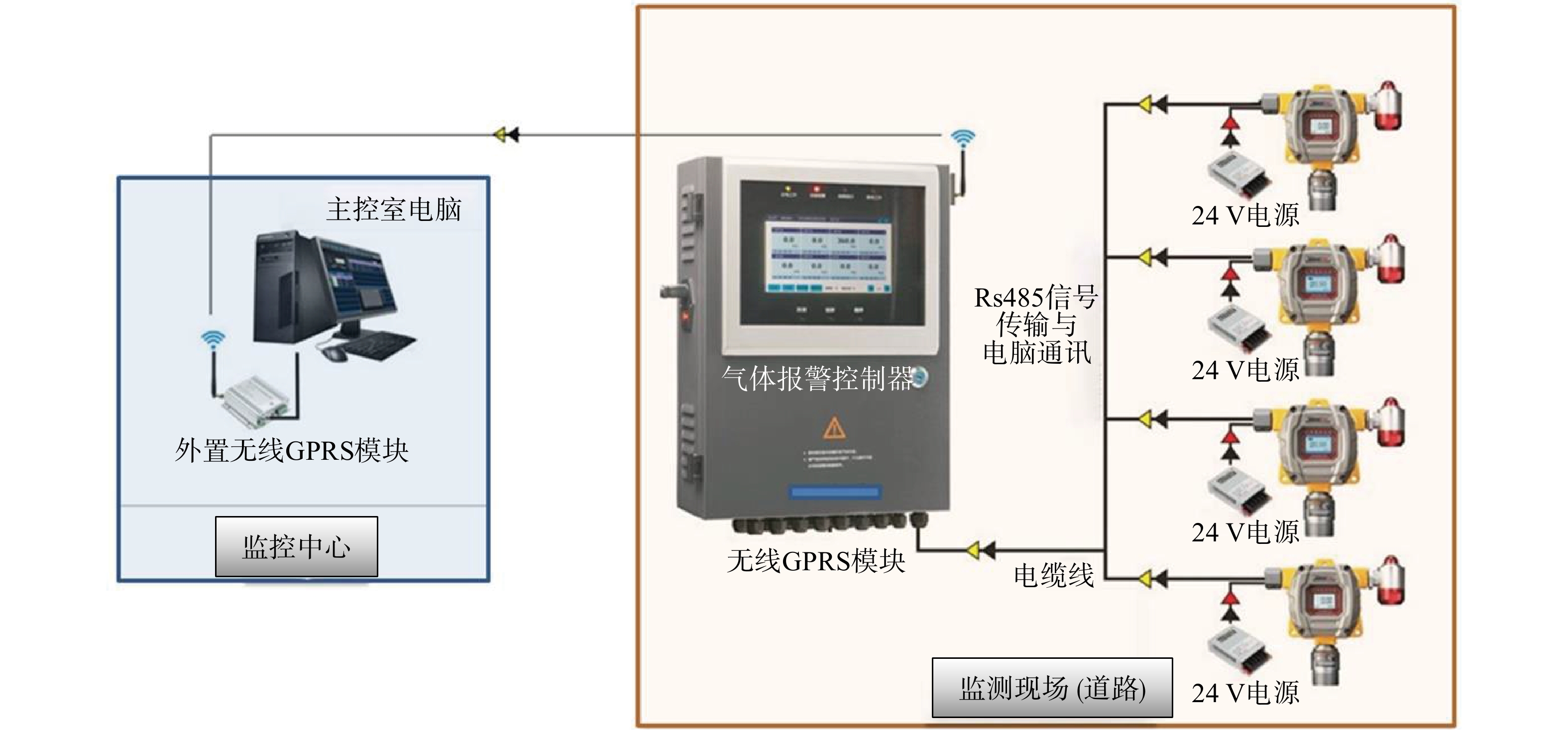
为便于后期对兴隆垃圾填埋场路段内填埋气体导排情况进行跟踪监测,在A、B区域布置了填埋气在线监测系统以实时监控可燃气体浓度。该系统由监测井、气体预处理系统、固定式CH4和H2S气体检测仪、无线网络服务器等组成(见图6)。
兴隆垃圾场原有8座稳定性监测井位于道路两侧人行道外。现沿用此8座监测井并在帷幕墙与道路边界之间加设3座,燃烧火炬处加设1座,共计12座监测井,进行填埋气体的在线监测(见图3)。监测井的布置方式与前述导气石笼井一致。监测井内气体收集管与地面气体检测仪器相接,并设仪器柜进行保护。检测仪器含固定式CH4、H2S气体检测仪,应用于现场CH4、H2S气体含量的24 h连续在线监测及温湿度的测量,可同时实现现场显示浓度和远程数据传输。此外,鉴于无线互联网监控服务(如GPRS)有助于促进环境监测和管理任务的进行[31],实现对环境应急事件的实时监控、指挥和管理,提高环保部门对环境突发事件的应急反应能力[32]。项目中还采用了无线网络服务器对数据进行传输和处理,将采集到的气体探头中的数据通过无线传输GPRS发射端进行实时上传,无线传输GPRS接收端把接收到的数据传送至电脑后进行处理。当监测系统监测到的气体浓度值达到预设限值时(CH4的体积分数>5%,H2S的质量浓度>0.6 mg·m−3),会发出告警并弹出告警信息(如告警位置、指标类别及其浓度值)。随后填埋气导排系统的抽气风机会启动,开始大风量抽气以使CH4的体积分数低于最低爆炸极限(1.25%)。即此系统不仅有跟踪检测整治效果的作用,还可以在出现异常时调控填埋气导排系统的运行。
2.1. 帷幕灌浆工程
2.2. 填埋气导排系统
2.3. 填埋气在线监控系统
-
从2018年11月整治系统建立完善并运行以来,通过固定式CH4、H2S气体检测仪对监测井中的CH4、H2S气体进行了连续在线监控。图7(a)和(b)分别展示了2019年1月—2020年3月期间各监测点的CH4及H2S浓度。由图可知,位于帷幕灌浆区域外垃圾侧的JC5~ JC8号监测井测得的气体浓度较低,表明帷幕灌浆措施很好的阻隔了填埋气向道路的横向迁移。而在未设帷幕灌浆的其余区域,受道路下方垃圾产气的影响,JC9~JC11号监测井部分数据达到了告警限值;而道路右侧的JC2~JC4号监测井,受道路下方及右侧垃圾的双重影响,气体浓度更持续超过警戒值。然而,启动主动气体导排系统,经过风机大风量抽气后,各监测井不论是CH4还是H2S,其含量都会急剧下降(见图7(c)和(d))。其中,CH4体积分数可降至1.5%以下甚至趋近于0,H2S降至报警值以下,可见对于这部分区域,主动填埋气导排措施很好控制了气体聚集及扩散的风险。
鉴于CO2不是GB/T25179-2010规定的填埋场中度利用必须的判定指标,在线监测系统中未对此指标进行监测。然而,老垃圾场往往含有高浓度CO2[33]。本研究离线检测了道路上CO2的质量浓度,发现尽管此道路通车车流量大(平均单向车流量为70辆·min−1),但CO2的质量浓度为(354.13±82.91)mg·m−3,远小于张雪报道的南京市机动车道路上大气CO2的质量浓度平均值(965.43±47.99) mg·m−3[34]。由此可见,填埋场并未加剧道路上大气中的CO2浓度,甚至由于开展整治工程可能对降低道路CO2含量产生积极影响。
综上所述,本工程采取的整治措施取得了良好气体阻隔及导排效果,对保证道路的安全建设及后期车辆的安全通行具有积极意义。
-
1) 对项目穿过的封场圾填埋场开展稳定性评估,发现垃圾堆体有机质含量低,产气趋于衰竭,但部分区域CH4体积分数为66.2%,H2S的质量浓度为62.2 mg·m−3,表明场内存在气体横向迁移引发燃烧爆炸或影响道路结构的风险,也存在空气污染风险。
2) 项目设置帷幕灌浆系统、填埋气主动导排及在线监测系统分别进行填埋气的阻隔、疏导和监测。实施帷幕灌浆后,可切断垃圾填埋场与道路间填埋气的横向通道。当监测系统监测到气体含量超过预设限值(CH4体积分数>5%,H2S的质量浓度>0.6 mg·m−3)时,启动主动抽气导排系统处理,处理后气体浓度可降至报警值以下。
3) 联合帷幕灌浆、填埋气主动导排及在线监测技术可实现对填埋气的有效阻隔与控制,可实现已封场垃圾填埋场场地的安全利用。



 下载:
下载: